- Product overview
- All features
- App integrations

CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana Intelligence
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Marketing strategic planning
- Request tracking
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- View all uses arrow-right icon
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- What's new Learn about the latest and greatest from Asana
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Support Need help? Contact the Asana support team
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- Business strategy |
- What is strategic planning? A 5-step gu ...
What is strategic planning? A 5-step guide

Strategic planning is a process through which business leaders map out their vision for their organization’s growth and how they’re going to get there. In this article, we'll guide you through the strategic planning process, including why it's important, the benefits and best practices, and five steps to get you from beginning to end.
Strategic planning is a process through which business leaders map out their vision for their organization’s growth and how they’re going to get there. The strategic planning process informs your organization’s decisions, growth, and goals.
Strategic planning helps you clearly define your company’s long-term objectives—and maps how your short-term goals and work will help you achieve them. This, in turn, gives you a clear sense of where your organization is going and allows you to ensure your teams are working on projects that make the most impact. Think of it this way—if your goals and objectives are your destination on a map, your strategic plan is your navigation system.
In this article, we walk you through the 5-step strategic planning process and show you how to get started developing your own strategic plan.
How to build an organizational strategy
Get our free ebook and learn how to bridge the gap between mission, strategic goals, and work at your organization.
What is strategic planning?
Strategic planning is a business process that helps you define and share the direction your company will take in the next three to five years. During the strategic planning process, stakeholders review and define the organization’s mission and goals, conduct competitive assessments, and identify company goals and objectives. The product of the planning cycle is a strategic plan, which is shared throughout the company.
What is a strategic plan?
![strategy business plan meaning [inline illustration] Strategic plan elements (infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/7d1f14e4-b008-4ea6-9579-5af6236ce367/inline-business-strategy-strategic-planning-1-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
A strategic plan is the end result of the strategic planning process. At its most basic, it’s a tool used to define your organization’s goals and what actions you’ll take to achieve them.
Typically, your strategic plan should include:
Your company’s mission statement
Your organizational goals, including your long-term goals and short-term, yearly objectives
Any plan of action, tactics, or approaches you plan to take to meet those goals
What are the benefits of strategic planning?
Strategic planning can help with goal setting and decision-making by allowing you to map out how your company will move toward your organization’s vision and mission statements in the next three to five years. Let’s circle back to our map metaphor. If you think of your company trajectory as a line on a map, a strategic plan can help you better quantify how you’ll get from point A (where you are now) to point B (where you want to be in a few years).
When you create and share a clear strategic plan with your team, you can:
Build a strong organizational culture by clearly defining and aligning on your organization’s mission, vision, and goals.
Align everyone around a shared purpose and ensure all departments and teams are working toward a common objective.
Proactively set objectives to help you get where you want to go and achieve desired outcomes.
Promote a long-term vision for your company rather than focusing primarily on short-term gains.
Ensure resources are allocated around the most high-impact priorities.
Define long-term goals and set shorter-term goals to support them.
Assess your current situation and identify any opportunities—or threats—allowing your organization to mitigate potential risks.
Create a proactive business culture that enables your organization to respond more swiftly to emerging market changes and opportunities.
What are the 5 steps in strategic planning?
The strategic planning process involves a structured methodology that guides the organization from vision to implementation. The strategic planning process starts with assembling a small, dedicated team of key strategic planners—typically five to 10 members—who will form the strategic planning, or management, committee. This team is responsible for gathering crucial information, guiding the development of the plan, and overseeing strategy execution.
Once you’ve established your management committee, you can get to work on the planning process.
Step 1: Assess your current business strategy and business environment
Before you can define where you’re going, you first need to define where you are. Understanding the external environment, including market trends and competitive landscape, is crucial in the initial assessment phase of strategic planning.
To do this, your management committee should collect a variety of information from additional stakeholders, like employees and customers. In particular, plan to gather:
Relevant industry and market data to inform any market opportunities, as well as any potential upcoming threats in the near future.
Customer insights to understand what your customers want from your company—like product improvements or additional services.
Employee feedback that needs to be addressed—whether about the product, business practices, or the day-to-day company culture.
Consider different types of strategic planning tools and analytical techniques to gather this information, such as:
A balanced scorecard to help you evaluate four major elements of a business: learning and growth, business processes, customer satisfaction, and financial performance.
A SWOT analysis to help you assess both current and future potential for the business (you’ll return to this analysis periodically during the strategic planning process).
To fill out each letter in the SWOT acronym, your management committee will answer a series of questions:
What does your organization currently do well?
What separates you from your competitors?
What are your most valuable internal resources?
What tangible assets do you have?
What is your biggest strength?
Weaknesses:
What does your organization do poorly?
What do you currently lack (whether that’s a product, resource, or process)?
What do your competitors do better than you?
What, if any, limitations are holding your organization back?
What processes or products need improvement?
Opportunities:
What opportunities does your organization have?
How can you leverage your unique company strengths?
Are there any trends that you can take advantage of?
How can you capitalize on marketing or press opportunities?
Is there an emerging need for your product or service?
What emerging competitors should you keep an eye on?
Are there any weaknesses that expose your organization to risk?
Have you or could you experience negative press that could reduce market share?
Is there a chance of changing customer attitudes towards your company?
Step 2: Identify your company’s goals and objectives
To begin strategy development, take into account your current position, which is where you are now. Then, draw inspiration from your vision, mission, and current position to identify and define your goals—these are your final destination.
To develop your strategy, you’re essentially pulling out your compass and asking, “Where are we going next?” “What’s the ideal future state of this company?” This can help you figure out which path you need to take to get there.
During this phase of the planning process, take inspiration from important company documents, such as:
Your mission statement, to understand how you can continue moving towards your organization’s core purpose.
Your vision statement, to clarify how your strategic plan fits into your long-term vision.
Your company values, to guide you towards what matters most towards your company.
Your competitive advantages, to understand what unique benefit you offer to the market.
Your long-term goals, to track where you want to be in five or 10 years.
Your financial forecast and projection, to understand where you expect your financials to be in the next three years, what your expected cash flow is, and what new opportunities you will likely be able to invest in.
Step 3: Develop your strategic plan and determine performance metrics
Now that you understand where you are and where you want to go, it’s time to put pen to paper. Take your current business position and strategy into account, as well as your organization’s goals and objectives, and build out a strategic plan for the next three to five years. Keep in mind that even though you’re creating a long-term plan, parts of your plan should be created or revisited as the quarters and years go on.
As you build your strategic plan, you should define:
Company priorities for the next three to five years, based on your SWOT analysis and strategy.
Yearly objectives for the first year. You don’t need to define your objectives for every year of the strategic plan. As the years go on, create new yearly objectives that connect back to your overall strategic goals .
Related key results and KPIs. Some of these should be set by the management committee, and some should be set by specific teams that are closer to the work. Make sure your key results and KPIs are measurable and actionable. These KPIs will help you track progress and ensure you’re moving in the right direction.
Budget for the next year or few years. This should be based on your financial forecast as well as your direction. Do you need to spend aggressively to develop your product? Build your team? Make a dent with marketing? Clarify your most important initiatives and how you’ll budget for those.
A high-level project roadmap . A project roadmap is a tool in project management that helps you visualize the timeline of a complex initiative, but you can also create a very high-level project roadmap for your strategic plan. Outline what you expect to be working on in certain quarters or years to make the plan more actionable and understandable.
Step 4: Implement and share your plan
Now it’s time to put your plan into action. Strategy implementation involves clear communication across your entire organization to make sure everyone knows their responsibilities and how to measure the plan’s success.
Make sure your team (especially senior leadership) has access to the strategic plan, so they can understand how their work contributes to company priorities and the overall strategy map. We recommend sharing your plan in the same tool you use to manage and track work, so you can more easily connect high-level objectives to daily work. If you don’t already, consider using a work management platform .
A few tips to make sure your plan will be executed without a hitch:
Communicate clearly to your entire organization throughout the implementation process, to ensure all team members understand the strategic plan and how to implement it effectively.
Define what “success” looks like by mapping your strategic plan to key performance indicators.
Ensure that the actions outlined in the strategic plan are integrated into the daily operations of the organization, so that every team member's daily activities are aligned with the broader strategic objectives.
Utilize tools and software—like a work management platform—that can aid in implementing and tracking the progress of your plan.
Regularly monitor and share the progress of the strategic plan with the entire organization, to keep everyone informed and reinforce the importance of the plan.
Establish regular check-ins to monitor the progress of your strategic plan and make adjustments as needed.
Step 5: Revise and restructure as needed
Once you’ve created and implemented your new strategic framework, the final step of the planning process is to monitor and manage your plan.
Remember, your strategic plan isn’t set in stone. You’ll need to revisit and update the plan if your company changes directions or makes new investments. As new market opportunities and threats come up, you’ll likely want to tweak your strategic plan. Make sure to review your plan regularly—meaning quarterly and annually—to ensure it’s still aligned with your organization’s vision and goals.
Keep in mind that your plan won’t last forever, even if you do update it frequently. A successful strategic plan evolves with your company’s long-term goals. When you’ve achieved most of your strategic goals, or if your strategy has evolved significantly since you first made your plan, it might be time to create a new one.
Build a smarter strategic plan with a work management platform
To turn your company strategy into a plan—and ultimately, impact—make sure you’re proactively connecting company objectives to daily work. When you can clarify this connection, you’re giving your team members the context they need to get their best work done.
A work management platform plays a pivotal role in this process. It acts as a central hub for your strategic plan, ensuring that every task and project is directly tied to your broader company goals. This alignment is crucial for visibility and coordination, allowing team members to see how their individual efforts contribute to the company’s success.
By leveraging such a platform, you not only streamline workflow and enhance team productivity but also align every action with your strategic objectives—allowing teams to drive greater impact and helping your company move toward goals more effectively.
Strategic planning FAQs
Still have questions about strategic planning? We have answers.
Why do I need a strategic plan?
A strategic plan is one of many tools you can use to plan and hit your goals. It helps map out strategic objectives and growth metrics that will help your company be successful.
When should I create a strategic plan?
You should aim to create a strategic plan every three to five years, depending on your organization’s growth speed.
Since the point of a strategic plan is to map out your long-term goals and how you’ll get there, you should create a strategic plan when you’ve met most or all of them. You should also create a strategic plan any time you’re going to make a large pivot in your organization’s mission or enter new markets.
What is a strategic planning template?
A strategic planning template is a tool organizations can use to map out their strategic plan and track progress. Typically, a strategic planning template houses all the components needed to build out a strategic plan, including your company’s vision and mission statements, information from any competitive analyses or SWOT assessments, and relevant KPIs.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. business plan?
A business plan can help you document your strategy as you’re getting started so every team member is on the same page about your core business priorities and goals. This tool can help you document and share your strategy with key investors or stakeholders as you get your business up and running.
You should create a business plan when you’re:
Just starting your business
Significantly restructuring your business
If your business is already established, you should create a strategic plan instead of a business plan. Even if you’re working at a relatively young company, your strategic plan can build on your business plan to help you move in the right direction. During the strategic planning process, you’ll draw from a lot of the fundamental business elements you built early on to establish your strategy for the next three to five years.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. mission and vision statements?
Your strategic plan, mission statement, and vision statements are all closely connected. In fact, during the strategic planning process, you will take inspiration from your mission and vision statements in order to build out your strategic plan.
Simply put:
A mission statement summarizes your company’s purpose.
A vision statement broadly explains how you’ll reach your company’s purpose.
A strategic plan pulls in inspiration from your mission and vision statements and outlines what actions you’re going to take to move in the right direction.
For example, if your company produces pet safety equipment, here’s how your mission statement, vision statement, and strategic plan might shake out:
Mission statement: “To ensure the safety of the world’s animals.”
Vision statement: “To create pet safety and tracking products that are effortless to use.”
Your strategic plan would outline the steps you’re going to take in the next few years to bring your company closer to your mission and vision. For example, you develop a new pet tracking smart collar or improve the microchipping experience for pet owners.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. company objectives?
Company objectives are broad goals. You should set these on a yearly or quarterly basis (if your organization moves quickly). These objectives give your team a clear sense of what you intend to accomplish for a set period of time.
Your strategic plan is more forward-thinking than your company goals, and it should cover more than one year of work. Think of it this way: your company objectives will move the needle towards your overall strategy—but your strategic plan should be bigger than company objectives because it spans multiple years.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. a business case?
A business case is a document to help you pitch a significant investment or initiative for your company. When you create a business case, you’re outlining why this investment is a good idea, and how this large-scale project will positively impact the business.
You might end up building business cases for things on your strategic plan’s roadmap—but your strategic plan should be bigger than that. This tool should encompass multiple years of your roadmap, across your entire company—not just one initiative.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. a project plan?
A strategic plan is a company-wide, multi-year plan of what you want to accomplish in the next three to five years and how you plan to accomplish that. A project plan, on the other hand, outlines how you’re going to accomplish a specific project. This project could be one of many initiatives that contribute to a specific company objective which, in turn, is one of many objectives that contribute to your strategic plan.
What’s the difference between strategic management vs. strategic planning?
A strategic plan is a tool to define where your organization wants to go and what actions you need to take to achieve those goals. Strategic planning is the process of creating a plan in order to hit your strategic objectives.
Strategic management includes the strategic planning process, but also goes beyond it. In addition to planning how you will achieve your big-picture goals, strategic management also helps you organize your resources and figure out the best action plans for success.
Related resources

Write better AI prompts: A 4-sentence framework

How to find alignment on AI

What is content marketing? A complete guide
Grant management: A nonprofit’s guide
More Like this
What is the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan.
It is not uncommon that the terms ‘strategic plan’ and ‘business plan’ get confused in the business world. While a strategic plan is a type of business plan, there are several important distinctions between the two types that are worth noting. Before beginning your strategic planning process or strategy implementation, look at the article below to learn the key difference between a business vs strategic plan and how each are important to your organization.
Definition of a business plan vs. a strategic plan
A strategic plan is essential for already established organizations looking for a way to manage and implement their strategic direction and future growth. Strategic planning is future-focused and serves as a roadmap to outline where the organization is going over the next 3-5 years (or more) and the steps it will take to get there.
Get the Free Guide for Setting OKRs that Work (with 100 examples!)
A strategic plan serves 6 functions for an organization that is striving to reach the next level of their growth:.
- Defines the purpose of the organization.
- Builds on an organization’s competitive advantages.
- Communicates the strategy to the staff.
- Prioritizes the financial needs of the organization.
- Directs the team to move from plan to action.
- Creates long-term sustainability and growth impact
Alternatively, a business plan is used by new businesses or organizations trying to get off the ground. The fundamentals of a business plan focus on setting the foundation for the business or organization. While it looks towards the future, the focus is set more on the immediate future (>1 year). Some of the functions of a business plan may overlap with a strategic plan. However, the focus and intentions diverge in a few key areas.
A business plan for new businesses, projects, or organizations serves these 5 functions:
- Simplifies or explains the objectives and goals of your organization.
- Coordinates human resource management and determines operational requirements.
- Secures funding for your organization.
- Evaluates potential business prospects.
- Creates a framework for conceptualizing ideas.
In other words, a strategic plan is utilized to direct the momentum and growth of an established company or organization. In contrast, a business plan is meant to set the foundation of a newly (or not quite) developed company by setting up its operational teams, strategizing ways to enter a new market, and obtaining funding.
A strategic plan focuses on long-term growth and the organization’s impact on the market and its customers. Meanwhile, a business plan must focus more on the short-term, day-to-day operational functions. Often, new businesses don’t have the capacity or resources to create a strategic plan, though developing a business plan with strategy elements is never a bad idea.
Business and strategic plans ultimately differ in several key areas–timeframe, target audience, focus, resource allocation, nature, and scalability.
While both a strategic and business plan is forward-facing and focused on future success, a business plan is focused on the more immediate future. A business plan normally looks ahead no further than one year. A business plan is set up to measure success within a 3- to 12-month timeframe and determines what steps a business owner needs to take now to succeed.
A strategic plan generally covers the organizational plan over 3 to 5+ years. It is set with future expansion and development in mind and sets up roadmaps for how the organization will reach its desired future state.
Pro Tip: While a vision statement could benefit a business plan, it is essential to a strategic plan.
Target Audience
A strategic plan is for established companies, businesses, organizations, and owners serious about growing their organizations. A strategic plan communicates the organization’s direction to the staff and stakeholders. The strategic plan is communicated to the essential change makers in the organization who will have a hand in making the progress happen.
A business plan could be for new businesses and entrepreneurs who are start-ups. The target audience for the business plan could also be stakeholders, partners, or investors. However, a business plan generally presents the entrepreneur’s ideas to a bank. It is meant to get the necessary people onboard to obtain the funding needed for the project.
A strategic plan provides focus, direction, and action to move the organization from where they are now to where they want to go. A strategic plan may consist of several months of studies, analyses, and other processes to gauge an organization’s current state. The strategy officers may conduct an internal and external analysis, determine competitive advantages, and create a strategy roadmap. They may take the time to redefine their mission, vision, and values statements.
Alternatively, a business plan provides a structure for ideas to define the business initially. It maps out the more tactical beginning stages of the plan.
Pro Tip: A mission statement is useful for business and strategic plans as it helps further define the enterprise’s value and purpose. If an organization never set its mission statement at the beginning stages of its business plan, it can create one for its strategic plan.
A strategic plan is critical to prioritizing resources (time, money, and people) to grow the revenue and increase the return on investment. The strategic plan may start with reallocating current financial resources already being utilized more strategically.
A business plan will focus on the resources the business still needs to obtain, such as vendors, investors, staff, and funding. A business plan is critical if new companies seek funding from banks or investors. It will add accountability and transparency for the organization and tell the funding channels how they plan to grow their business operations and ROI in the first year of the business.
The scalability of a business plan vs. strategic plan
Another way to grasp the difference is by understanding the difference in ‘scale’ between strategic and business plans. Larger organizations with multiple business units and a wide variety of products frequently start their annual planning process with a corporate-driven strategic plan. It is often followed by departmental and marketing plans that work from the Strategic Plan.
Smaller and start-up companies typically use only a business plan to develop all aspects of operations of the business on paper, obtain funding and then start the business.
Why understanding the differences between a business plan vs a strategic plan matters
It is important to know the key differences between the two terms, despite often being used interchangeably. But here’s a simple final explanation:
A business plan explains how a new business will get off the ground. A strategic plan answers where an established organization is going in the future and how they intend to reach that future state.
A strategic plan also focuses on building a sustainable competitive advantage and is futuristic. A business plan is used to assess the viability of a business opportunity and is more tactical.
10 Comments
I agree with your analysis about small companies, but they should do a strategic plan. Just check out how many of the INC 500 companies have an active strategic planning process and they started small. Its about 78%,
Strategic management is a key role of any organization even if belong to small business. it help in growth and also to steam line your values. im agree with kristin.
I agree with what you said, without strategic planning no organization can survive whether it is big or small. Without a clear strategic plan, it is like walking in the darkness.. Best Regards..
Vision, Mission in Business Plan VS Strategic Plan ?
you made a good analysis on strategic plan and Business plan the difference is quite clear now. But on the other hand, it seems that strategic plan and strategic management are similar which I think not correct. Please can you tell us the difference between these two?. Thanks
Thank you. I get points to work on it
super answer Thanking you
Hi. I went through all the discussions, comments and replies. Thanks! I got a very preliminary idea about functions and necessity of Strategic Planning in Business. But currently I am looking for a brief nice, flowery, juicy definition of “Business Strategic Planning” as a whole, which will give anyone a fun and interesting way to understand. Can anyone help me out please? Awaiting replies…… 🙂
that was easy to understand,
Developing a strategic plan either big or small company or organization mostly can’t achieve its goal. A strategic plan or formulation is the first stage of the strategic management plan, therefore, we should be encouraged to develop a strategic management plan. We can develop the best strategic plan but without a clear plan of implementation and evaluation, it will be difficult to achieve goals.
Comments Cancel
Join 60,000 other leaders engaged in transforming their organizations., subscribe to get the latest agile strategy best practices, free guides, case studies, and videos in your inbox every week..

Leading strategy? Join our FREE community.
Become a member of the chief strategy officer collaborative..
Free monthly sessions and exclusive content.
Do you want to 2x your impact.
Essential Guide to the Strategic Planning Process
By Joe Weller | April 3, 2019 (updated March 26, 2024)
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
In this article, you’ll learn the basics of the strategic planning process and how a strategic plan guides you to achieving your organizational goals. Plus, find expert insight on getting the most out of your strategic planning.
Included on this page, you'll discover the importance of strategic planning , the steps of the strategic planning process , and the basic sections to include in your strategic plan .
What Is Strategic Planning?
Strategic planning is an organizational activity that aims to achieve a group’s goals. The process helps define a company’s objectives and investigates both internal and external happenings that might influence the organizational path. Strategic planning also helps identify adjustments that you might need to make to reach your goal. Strategic planning became popular in the 1960s because it helped companies set priorities and goals, strengthen operations, and establish agreement among managers about outcomes and results.
Strategic planning can occur over multiple years, and the process can vary in length, as can the final plan itself. Ideally, strategic planning should result in a document, a presentation, or a report that sets out a blueprint for the company’s progress.
By setting priorities, companies help ensure employees are working toward common and defined goals. It also aids in defining the direction an enterprise is heading, efficiently using resources to achieve the organization’s goals and objectives. Based on the plan, managers can make decisions or allocate the resources necessary to pursue the strategy and minimize risks.
Strategic planning strengthens operations by getting input from people with differing opinions and building a consensus about the company’s direction. Along with focusing energy and resources, the strategic planning process allows people to develop a sense of ownership in the product they create.

“Strategic planning is not really one thing. It is really a set of concepts, procedures, tools, techniques, and practices that have to be adapted to specific contexts and purposes,” says Professor John M. Bryson, McKnight Presidential Professor of Planning and Public Affairs at the Hubert H. Humphrey School of Public Affairs, University of Minnesota and author of Strategic Planning for Public and Nonprofit Organizations: A Guide to Strengthening and Sustaining Organizational Achievement . “Strategic planning is a prompt to foster strategic thinking, acting, and learning, and they all matter and they are all connected.”
What Strategic Planning Is Not
Strategic planning is not a to-do list for the short or long term — it is the basis of a business, its direction, and how it will get there.
“You have to think very strategically about strategic planning. It is more than just following steps,” Bryson explains. “You have to understand strategic planning is not some kind of magic solution to fixing issues. Don’t have unrealistic expectations.”
Strategic planning is also different from a business plan that focuses on a specific product, service, or program and short-term goals. Rather, strategic planning means looking at the big picture.
While they are related, it is important not to confuse strategic planning with strategic thinking, which is more about imagining and innovating in a way that helps a company. In contrast, strategic planning supports those thoughts and helps you figure out how to make them a reality.
Another part of strategic planning is tactical planning , which involves looking at short-term efforts to achieve longer-term goals.
Lastly, marketing plans are not the same as strategic plans. A marketing plan is more about introducing and delivering a service or product to the public instead of how to grow a business. For more about marketing plans and processes, read this article .
Strategic plans include information about finances, but they are different from financial planning , which involves different processes and people. Financial planning templates can help with that process.
Why Is Strategic Planning Important?
In today’s technological age, strategic plans provide businesses with a path forward. Strategic plans help companies thrive, not just survive — they provide a clear focus, which makes an organization more efficient and effective, thereby increasing productivity.

“You are not going to go very far if you don’t have a strategic plan. You need to be able to show where you are going,” says Stefan Hofmeyer, an experienced strategist and co-founder of Global PMI Partners . He lives in the startup-rich environment of northern California and says he often sees startups fail to get seed money because they do not have a strong plan for what they want to do and how they want to do it.
Getting team members on the same page (in both creating a strategic plan and executing the plan itself) can be beneficial for a company. Planners can find satisfaction in the process and unite around a common vision. In addition, you can build strong teams and bridge gaps between staff and management.
“You have to reach agreement about good ideas,” Bryson says. “A really good strategy has to meet a lot of criteria. It has to be technically workable, administratively feasible, politically acceptable, and legally, morally, and ethically defensible, and that is a pretty tough list.”
By discussing a company’s issues during the planning process, individuals can voice their opinions and provide information necessary to move the organization ahead — a form of problem solving as a group.
Strategic plans also provide a mechanism to measure success and progress toward goals, which keeps employees on the same page and helps them focus on the tasks at hand.
When Is the Time to Do Strategic Planning?
There is no perfect time to perform strategic planning. It depends entirely on the organization and the external environment that surrounds it. However, here are some suggestions about when to plan:
If your industry is changing rapidly
When an organization is launching
At the start of a new year or funding period
In preparation for a major new initiative
If regulations and laws in your industry are or will be changing
“It’s not like you do all of the thinking and planning, and then implement,” Bryson says. “A mistake people make is [believing] the thinking has to precede the acting and the learning.”
Even if you do not re-create the entire planning process often, it is important to periodically check your plan and make sure it is still working. If not, update it.
What Is the Strategic Planning Process?
Strategic planning is a process, and not an easy one. A key is to make sure you allow enough time to complete the process without rushing, but not take so much time that you lose momentum and focus. The process itself can be more important than the final document due to the information that comes out of the discussions with management, as well as lower-level workers.

“There is not one favorite or perfect planning process,” says Jim Stockmal, president of the Association for Strategic Planning (ASP). He explains that new techniques come out constantly, and consultants and experienced planners have their favorites. In an effort to standardize the practice and terms used in strategic planning, ASP has created two certification programs .
Level 1 is the Strategic Planning Professional (SPP) certification. It is designed for early- or mid-career planners who work in strategic planning. Level 2, the Strategic Management Professional (SMP) certification, is geared toward seasoned professionals or those who train others. Stockmal explains that ASP designed the certification programs to add structure to the otherwise amorphous profession.
The strategic planning process varies by the size of the organization and can be formal or informal, but there are constraints. For example, teams of all sizes and goals should build in many points along the way for feedback from key leaders — this helps the process stay on track.
Some elements of the process might have specific start and end points, while others are continuous. For example, there might not be one “aha” moment that suddenly makes things clear. Instead, a series of small moves could slowly shift the organization in the right direction.
“Don’t make it overly complex. Bring all of the stakeholders together for input and feedback,” Stockmal advises. “Always be doing a continuous environmental scan, and don’t be afraid to engage with stakeholders.”
Additionally, knowing your company culture is important. “You need to make it work for your organization,” he says.
There are many different ways to approach the strategic planning process. Below are three popular approaches:
Goals-Based Planning: This approach begins by looking at an organization’s mission and goals. From there, you work toward that mission, implement strategies necessary to achieve those goals, and assign roles and deadlines for reaching certain milestones.
Issues-Based Planning: In this approach, start by looking at issues the company is facing, then decide how to address them and what actions to take.
Organic Planning: This approach is more fluid and begins with defining mission and values, then outlining plans to achieve that vision while sticking to the values.
“The approach to strategic planning needs to be contingent upon the organization, its history, what it’s capable of doing, etc.,” Bryson explains. “There’s such a mistake to think there’s one approach.”
For more information on strategic planning, read about how to write a strategic plan and the different types of models you can use.
Who Participates in the Strategic Planning Process?
For work as crucial as strategic planning, it is necessary to get the right team together and include them from the beginning of the process. Try to include as many stakeholders as you can.
Below are suggestions on who to include:
Senior leadership
Strategic planners
Strategists
People who will be responsible for implementing the plan
People to identify gaps in the plan
Members of the board of directors
“There can be magic to strategic planning, but it’s not in any specific framework or anybody’s 10-step process,” Bryson explains. “The magic is getting key people together, getting them to focus on what’s important, and [getting] them to do something about it. That’s where the magic is.”
Hofmeyer recommends finding people within an organization who are not necessarily current leaders, but may be in the future. “Sometimes they just become obvious. Usually they show themselves to you, you don’t need to look for them. They’re motivated to participate,” he says. These future leaders are the ones who speak up at meetings or on other occasions, who put themselves out there even though it is not part of their job description.
At the beginning of the process, establish guidelines about who will be involved and what will be expected of them. Everyone involved must be willing to cooperate and collaborate. If there is a question about whether or not to include anyone, it is usually better to bring on extra people than to leave someone out, only to discover later they should have been a part of the process all along. Not everyone will be involved the entire time; people will come and go during different phases.
Often, an outside facilitator or consultant can be an asset to a strategic planning committee. It is sometimes difficult for managers and other employees to sit back and discuss what they need to accomplish as a company and how they need to do it without considering other factors. As objective observers, outside help can often offer insight that may escape insiders.
Hofmeyer says sometimes bosses have blinders on that keep them from seeing what is happening around them, which allows them to ignore potential conflicts. “People often have their own agendas of where they want to go, and if they are not aligned, it is difficult to build a strategic plan. An outsider perspective can really take you out of your bubble and tell you things you don’t necessarily want to hear [but should]. We get into a rhythm, and it’s really hard to step out of that, so bringing in outside people can help bring in new views and aspects of your business.”
An outside consultant can also help naysayers take the process more seriously because they know the company is investing money in the efforts, Hofmeyer adds.
No matter who is involved in the planning process, make sure at least one person serves as an administrator and documents all planning committee actions.
What Is in a Strategic Plan?
A strategic plan communicates goals and what it takes to achieve them. The plan sometimes begins with a high-level view, then becomes more specific. Since strategic plans are more guidebooks than rulebooks, they don’t have to be bureaucratic and rigid. There is no perfect plan; however, it needs to be realistic.
There are many sections in a strategic plan, and the length of the final document or presentation will vary. The names people use for the sections differ, but the general ideas behind them are similar: Simply make sure you and your team agree on the terms you will use and what each means.
One-Page Strategic Planning Template
“I’m a big fan of getting a strategy onto one sheet of paper. It’s a strategic plan in a nutshell, and it provides a clear line of sight,” Stockmal advises.
You can use the template below to consolidate all your strategic ideas into a succinct, one-page strategic plan. Doing so provides you with a high-level overview of your strategic initiatives that you can place on your website, distribute to stakeholders, and refer to internally. More extensive details about implementation, capacity, and other concerns can go into an expanded document.
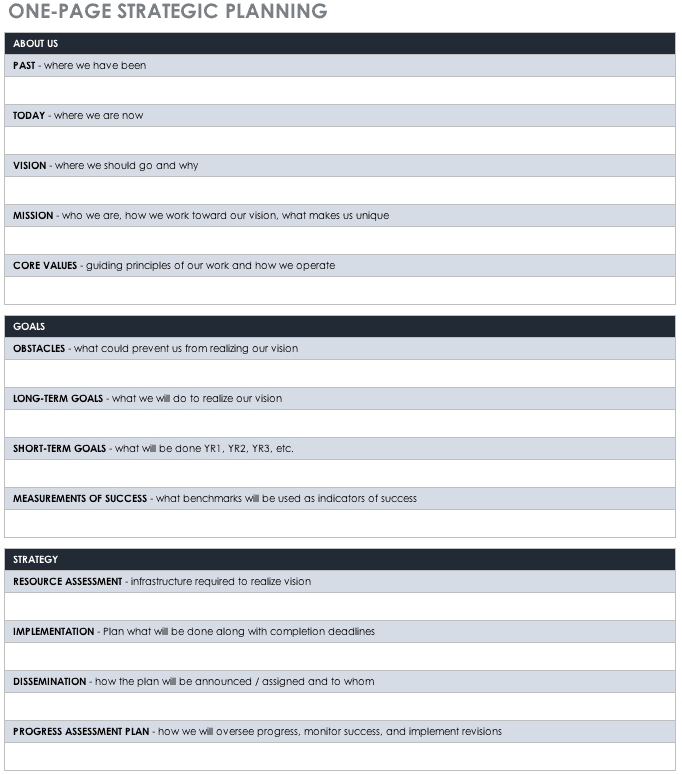
Download One-Page Strategic Planning Template Excel | Word | Smartsheet
The most important part of the strategic plan is the executive summary, which contains the highlights of the plan. Although it appears at the beginning of the plan, it should be written last, after you have done all your research.
Of writing the executive summary, Stockmal says, “I find it much easier to extract and cut and edit than to do it first.”
For help with creating executive summaries, see these templates .
Other parts of a strategic plan can include the following:
Description: A description of the company or organization.
Vision Statement: A bold or inspirational statement about where you want your company to be in the future.
Mission Statement: In this section, describe what you do today, your audience, and your approach as you work toward your vision.
Core Values: In this section, list the beliefs and behaviors that will enable you to achieve your mission and, eventually, your vision.
Goals: Provide a few statements of how you will achieve your vision over the long term.
Objectives: Each long-term goal should have a few one-year objectives that advance the plan. Make objectives SMART (specific, measurable, achievable, and time-based) to get the most out of them.
Budget and Operating Plans: Highlight resources you will need and how you will implement them.
Monitoring and Evaluation: In this section, describe how you will check your progress and determine when you achieve your goals.
One of the first steps in creating a strategic plan is to perform both an internal and external analysis of the company’s environment. Internally, look at your company’s strengths and weaknesses, as well as the personal values of those who will implement your plan (managers, executives, board members). Externally, examine threats and opportunities within the industry and any broad societal expectations that might exist.
You can perform a SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) analysis to sum up where you are currently and what you should focus on to help you achieve your future goals. Strengths shows you what you do well, weaknesses point out obstacles that could keep you from achieving your objectives, opportunities highlight where you can grow, and threats pinpoint external factors that could be obstacles in your way.
You can find more information about performing a SWOT analysis and free templates in this article . Another analysis technique, STEEPLE (social, technological, economic, environmental, political, legal, and ethical), often accompanies a SWOT analysis.
Basics of Strategic Planning
How you navigate the strategic planning process will vary. Several tools and techniques are available, and your choice depends on your company’s leadership, culture, environment, and size, as well as the expertise of the planners.
All include similar sections in the final plan, but the ways of driving those results differ. Some tools are goals-based, while others are issues- or scenario-based. Some rely on a more organic or rigid process.
Hofmeyer summarizes what goes into strategic planning:
Understand the stakeholders and involve them from the beginning.
Agree on a vision.
Hold successful meetings and sessions.
Summarize and present the plan to stakeholders.
Identify and check metrics.
Make periodic adjustments.
Items That Go into Strategic Planning
Strategic planning contains inputs, activities, outputs, and outcomes. Inputs and activities are elements that are internal to the company, while outputs and outcomes are external.
Remember, there are many different names for the sections of strategic plans. The key is to agree what terms you will use and define them for everyone involved.
Inputs are important because it is impossible to know where you are going until you know what is around you where you are now.
Companies need to gather data from a variety of sources to get a clear look at the competitive environment and the opportunities and risks within that environment. You can think of it like a competitive intelligence program.
Data should come from the following sources:
Interviews with executives
A review of documents about the competition or market that are publicly available
Primary research by visiting or observing competitors
Studies of your industry
The values of key stakeholders
This information often goes into writing an organization’s vision and mission statements.
Activities are the meetings and other communications that need to happen during the strategic planning process to help everyone understand the competition that surrounds the organization.
It is important both to understand the competitive environment and your company’s response to it. This is where everyone looks at and responds to the data gathered from the inputs.
The strategic planning process produces outputs. Outputs can be as basic as the strategic planning document itself. The documentation and communications that describe your organization’s strategy, as well as financial statements and budgets, can also be outputs.
The implementation of the strategic plan produces outcomes (distinct from outputs). The outcomes determine the success or failure of the strategic plan by measuring how close they are to the goals and vision you outline in your plan.
It is important to understand there will be unplanned and unintended outcomes, too. How you learn from and adapt to these changes influence the success of the strategic plan.
During the planning process, decide how you will measure both the successes and failures of different parts of the strategic plan.
Sharing, Evaluating, and Monitoring the Progress of a Strategic Plan
After companies go through a lengthy strategic planning process, it is important that the plan does not sit and collect dust. Share, evaluate, and monitor the plan to assess how you are doing and make any necessary updates.
“[Some] leaders think that once they have their strategy, it’s up to someone else to execute it. That’s a mistake I see,” Stockmal says.
The process begins with distributing and communicating the plan. Decide who will get a copy of the plan and how those people will tell others about it. Will you have a meeting to kick off the implementation? How will you specify who will do what and when? Clearly communicate the roles people will have.
“Before you communicate the plan [to everyone], you need to have the commitment of stakeholders,” Hofmeyer recommends. Have the stakeholders be a part of announcing the plan to everyone — this keeps them accountable because workers will associate them with the strategy. “That applies pressure to the stakeholders to actually do the work.”
Once the team begins implementation, it’s necessary to have benchmarks to help measure your successes against the plan’s objectives. Sometimes, having smaller action plans within the larger plan can help keep the work on track.
During the planning process, you should have decided how you will measure success. Now, figure out how and when you will document progress. Keep an eye out for gaps between the vision and its implementation — a big gap could be a sign that you are deviating from the plan.
Tools are available to assist with tracking performance of strategic plans, including several types of software. “For some organizations, a spreadsheet is enough, but you are going to manually enter the data, so someone needs to be responsible for that,” Stockmal recommends.
Remember: strategic plans are not written in stone. Some deviation will be necessary, and when it happens, it’s important to understand why it occurred and how the change might impact the company's vision and goals.
Deviation from the plan does not mean failure, reminds Hofmeyer. Instead, understanding what transpired is the key. “Things happen, [and] you should always be on the lookout for that. I’m a firm believer in continuous improvement,” he says. Explain to stakeholders why a change is taking place. “There’s always a sense of re-evaluation, but do it methodically.”
Build in a schedule to review and amend the plan as necessary; this can help keep companies on track.
What Is Strategic Management?
Strategic planning is part of strategic management, and it involves the activities that make the strategic plan a reality. Essentially, strategic management is getting from the starting point to the goal effectively and efficiently using the ongoing activities and processes that a company takes on in order to keep in line with its mission, vision, and strategic plan.
“[Strategic management] closes the gap between the plan and executing the strategy,” Stockmal of ASP says. Strategic management is part of a larger planning process that includes budgeting, forecasting, capital allocation, and more.
There is no right or wrong way to do strategic management — only guidelines. The basic phases are preparing for strategic planning, creating the strategic plan, and implementing that plan.
No matter how you manage your plan, it’s key to allow the strategic plan to evolve and grow as necessary, due to both the internal and external factors.
“We get caught up in all of the day-to-day issues,” Stockmal explains, adding that people do not often leave enough time for implementing the plan and making progress. That’s what strategic management implores: doing things that are in the plan and not letting the plan sit on a shelf.
Improve Strategic Planning with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
The 5 steps of the strategic planning process
.jpg)
Starting a project without a strategy is like trying to bake a cake without a recipe — you might have all the ingredients you need, but without a plan for how to combine them, or a vision for what the finished product will look like, you’re likely to end up with a mess. This is especially true when working with a team — it’s crucial to have a shared plan that can serve as a map on the pathway to success.
Creating a strategic plan not only provides a useful document for the future, but also helps you define what you have right now, and think through and outline all of the steps and considerations you’ll need to succeed.
What is strategic planning?
While there is no single approach to creating a strategic plan, most approaches can be boiled down to five overarching steps:
- Define your vision
- Assess where you are
- Determine your priorities and objectives
- Define responsibilities
- Measure and evaluate results
Each step requires close collaboration as you build a shared vision, strategy for implementation, and system for understanding performance.
Related: Learn how to hold an effective strategic planning meeting
Why do I need a strategic plan?
Building a strategic plan is the best way to ensure that your whole team is on the same page, from the initial vision and the metrics for success to evaluating outcomes and adjusting (if necessary) for the future. Even if you’re an expert baker, working with a team to bake a cake means having a collaborative approach and clearly defined steps so that the result reflects the strategic goals you laid out at the beginning.
The benefits of strategic planning also permeate into the general efficiency and productivity of your organization as a whole. They include:
- Greater attention to potential biases or flaws, improving decision-making
- Clear direction and focus, motivating and engaging employees
- Better resource management, improving project outcomes
- Improved employee performance, increasing profitability
- Enhanced communication and collaboration, fostering team efficiency
Next, let’s dive into how to build and structure your strategic plan, complete with templates and assets to help you along the way.
Before you begin: Pick a brainstorming method
There are many brainstorming methods you can use to come up with, outline, and rank your priorities. When it comes to strategy planning, it’s important to get everyone’s thoughts and ideas out before committing to any one strategy. With the right facilitation , brainstorming helps make this process fair and transparent for everyone involved.
First, decide if you want to run a real-time rapid ideation session or a structured brainstorming . In a rapid ideation session, you encourage sharing half-baked or silly ideas, typically within a set time frame. The key is to just get out all your ideas quickly and then edit the best ones. Examples of rapid ideation methods include round robin , brainwriting , mind mapping , and crazy eights .
In a structured brainstorming session, you allow for more time to prepare and edit your thoughts before getting together to share and discuss those more polished ideas. This might involve brainstorming methods that entail unconventional ways of thinking, such as reverse brainstorming or rolestorming .
Using a platform like Mural, you can easily capture and organize your team’s ideas through sticky notes, diagrams, text, or even images and videos. These features allow you to build actionable next steps immediately (and in the same place) through color coding and tagging.
Whichever method you choose, the ideal outcome is that you avoid groupthink by giving everyone a voice and a say. Once you’ve reached a consensus on your top priorities, add specific objectives tied to each of those priorities.
Related: Brainstorming and ideation template
1. Define your vision
Whether it’s for your business as a whole, or a specific initiative, successful strategic planning involves alignment with a vision for success. You can think of it as a project-specific mission statement or a north star to guide employees toward fulfilling organizational goals.
To create a vision statement that explicitly states the ideal results of your project or company transformation, follow these four key steps:
- Engage and involve the entire team . Inclusivity like this helps bring diverse perspectives to the table.
- Align the vision with your core values and purpose . This will make it familiar and easy to follow through.
- Stay grounded . The vision should be ambitious enough to motivate and inspire yet grounded enough to be achievable and relevant.
- Think long-term flexibility . Consider future trends and how your vision can be flexible in the face of challenges or opportunities.
For example, say your vision is to revolutionize customer success by streamlining and optimizing your process for handling support tickets. It’s important to have a strategy map that allows stakeholders (like the support team, marketing team, and engineering team) to know the overall objective and understand the roles they will play in realizing the goals.
This can be done in real time or asynchronously , whether in person, hybrid, or remote. By leveraging a shared digital space , everyone has a voice in the process and room to add their thoughts, comments, and feedback.
Related: Vision board template
2. Assess where you are
The next step in creating a strategic plan is to conduct an assessment of where you stand in terms of your own initiatives, as well as the greater marketplace. Start by conducting a resource assessment. Figure out which financial, human, and/or technological resources you have available and if there are any limitations. You can do this using a SWOT analysis.
What is SWOT analysis?
SWOT analysis is an exercise where you define:
- Strengths: What are your unique strengths for this initiative or this product? In what ways are you a leader?
- Weaknesses: What weaknesses can you identify in your offering? How does your product compare to others in the marketplace?
- Opportunities: Are there areas for improvement that'd help differentiate your business?
- Threats: Beyond weaknesses, are there existing potential threats to your idea that could limit or prevent its success? How can those be anticipated?
For example, say you have an eco-friendly tech company and your vision is to launch a new service in the next year. Here’s what the SWOT analysis might look like:
- Strengths : Strong brand reputation, loyal customer base, and a talented team focused on innovation
- Weaknesses : Limited bandwidth to work on new projects, which might impact the scope of its strategy formulation
- Opportunities : How to leverage and experiment with existing customers when goal-setting
- Threats : Factors in the external environment out of its control, like the state of the economy and supply chain shortages
This SWOT analysis will guide the company in setting strategic objectives and formulating a robust plan to navigate the challenges it might face.
Related: SWOT analysis template
3. Determine your priorities and objectives
Once you've identified your organization’s mission and current standing, start a preliminary plan document that outlines your priorities and their corresponding objectives. Priorities and objectives should be set based on what is achievable with your available resources. The SMART framework is a great way to ensure you set effective goals . It looks like this:
- Specific: Set clear objectives, leaving no room for ambiguity about the desired outcomes.
- Measurable : Choose quantifiable criteria to make it easier to track progress.
- Achievable : Ensure it is realistic and attainable within the constraints of your resources and environment.
- Relevant : Develop objectives that are relevant to the direction your organization seeks to move.
- Time-bound : Set a clear timeline for achieving each objective to maintain a sense of urgency and focus.
For instance, going back to the eco-friendly tech company, the SMART goals might be:
- Specific : Target residential customers and small businesses to increase the sales of its solar-powered device line by 25%.
- Measurable : Track monthly sales and monitor customer feedback and reviews.
- Achievable : Allocate more resources to the marketing, sales, and customer service departments.
- Relevant : Supports the company's growth goals in a growing market of eco-conscious consumers.
- Time-bound : Conduct quarterly reviews and achieve this 25% increase in sales over the next 12 months.
With strategic objectives like this, you’ll be ready to put the work into action.
Related: Project kickoff template
4. Define tactics and responsibilities
In this stage, individuals or units within your team can get granular about how to achieve your goals and who'll be accountable for each step. For example, the senior leadership team might be in charge of assigning specific tasks to their team members, while human resources works on recruiting new talent.
It’s important to note that everyone’s responsibilities may shift over time as you launch and gather initial data about your project. For this reason, it’s key to define responsibilities with clear short-term metrics for success. This way, you can make sure that your plan is adaptable to changing circumstances.
One of the more common ways to define tactics and metrics is to use the OKR (Objectives and Key Results) method. By outlining your OKRs, you’ll know exactly what key performance indicators (KPIs) to track and have a framework for analyzing the results once you begin to accumulate relevant data.
For instance, if our eco-friendly tech company has a goal of increasing sales, one objective might be to expand market reach for its solar-powered products. The sales team lead would be in charge of developing an outreach strategy. The key result would be to successfully launch its products in two new regions by Q2. The KPI would be a 60% conversation rate in those targeted markets.
Related: OKR planning template
5. Manage, measure, and evaluate
Once your plan is set into motion, it’s important to actively manage (and measure) progress. Before launching your plan, settle on a management process that allows you to measure success or failure. In this way, everyone is aligned on progress and can come together to evaluate your strategy execution at regular intervals.
Determine the milestones at which you’ll come together and go over results — this can take place weekly, monthly, or quarterly, depending on the nature of the project.
One of the best ways to evaluate progress is through agile retrospectives (or retros) , which can be done in real time or asynchronously. During this process, gather and organize feedback about the key elements that played a role in your strategy.
Related: Retrospective radar template
Retrospectives are typically divided into three parts:
- What went well.
- What didn’t go well.
- New opportunities for improvement.
This structure is also sometimes called the “ rose, thorn, bud ” framework. By using this approach, team members can collectively brainstorm and categorize their feedback, making the next steps clear and actionable. Creating an action plan during a post-mortem meeting is a crucial step in ensuring that lessons learned from past projects or events are effectively translated into tangible improvements.
Another method for reviewing progress is the quarterly business review (QBR). Like the agile retrospective, it allows you to collect feedback and adjust accordingly. In the case of QBRs, however, we recommend dividing your feedback into four categories:
- Start (what new items should be launched?).
- Stop (what items need to be paused?).
- Continue (what is going well?).
- Change (what could be modified to perform better?).
Strategic planners know that planning activities continue even after a project is complete. There’s always room for improvement and an action plan waiting to be implemented. Using the above approaches, your team can make room for new ideas within the existing strategic framework in order to track better to your long-term goals.
Related: Quarterly business review template
Conclusions
The beauty of the strategic plan is that it can be applied from the campaign level all the way up to organizational vision. Using the strategic planning framework, you build buy-in , trust, and transparency by collaboratively creating a vision for success, and mapping out the steps together on the road to your goals.
Also, in so doing, you build in an ability to adapt effectively on the fly in response to data through measurement and evaluation, making your plan both flexible and resilient.
Related: 5 Tips for Holding Effective Post-mortems
Why Mural for strategic planning
Mural unlocks collaborative strategic planning through a shared digital space with an intuitive interface, a library of pre-fab templates, and methodologies based on design thinking principles.
Outline goals, identify key metrics, and track progress with a platform built for any enterprise.
Learn more about strategic planning with Mural.
About the authors

Bryan Kitch
Tagged Topics
Related blog posts
%20(2).jpg)
How to hold effective strategic planning meetings
%20(2).jpg)
Tactical vs. strategic planning: Why you need both
%20(2).jpg)
5 effective strategic planning models for your business
Related blog posts.
%20(3).jpg)
A guide to the Agile development lifecycle

Team collaboration software: A buyer’s guide

How to plan and organize a workshop
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading Change and Organizational Renewal
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
Why Is Strategic Planning Important?

- 06 Oct 2020
Do you know what your organization’s strategy is? How much time do you dedicate to developing that strategy each month?
If your answers are on the low side, you’re not alone. According to research from Bridges Business Consultancy , 48 percent of leaders spend less than one day per month discussing strategy.
It’s no wonder, then, that 48 percent of all organizations fail to meet at least half of their strategic targets. Before an organization can reap the rewards of its business strategy, planning must take place to ensure its strategy remains agile and executable .
Here’s a look at what strategic planning is and how it can benefit your organization.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is Strategic Planning?
Strategic planning is the ongoing organizational process of using available knowledge to document a business's intended direction. This process is used to prioritize efforts, effectively allocate resources, align shareholders and employees on the organization’s goals, and ensure those goals are backed by data and sound reasoning.
It’s important to highlight that strategic planning is an ongoing process—not a one-time meeting. In the online course Disruptive Strategy , Harvard Business School Professor Clayton Christensen notes that in a study of HBS graduates who started businesses, 93 percent of those with successful strategies evolved and pivoted away from their original strategic plans.
“Most people think of strategy as an event, but that’s not the way the world works,” Christensen says. “When we run into unanticipated opportunities and threats, we have to respond. Sometimes we respond successfully; sometimes we don’t. But most strategies develop through this process. More often than not, the strategy that leads to success emerges through a process that’s at work 24/7 in almost every industry.”
Strategic planning requires time, effort, and continual reassessment. Given the proper attention, it can set your business on the right track. Here are three benefits of strategic planning.
Related: 4 Ways to Develop Your Strategic Thinking Skills
Benefits of Strategic Planning
1. create one, forward-focused vision.
Strategy touches every employee and serves as an actionable way to reach your company’s goals.
One significant benefit of strategic planning is that it creates a single, forward-focused vision that can align your company and its shareholders. By making everyone aware of your company’s goals, how and why those goals were chosen, and what they can do to help reach them, you can create an increased sense of responsibility throughout your organization.
This can also have trickle-down effects. For instance, if a manager isn’t clear on your organization’s strategy or the reasoning used to craft it, they could make decisions on a team level that counteract its efforts. With one vision to unite around, everyone at your organization can act with a broader strategy in mind.
2. Draw Attention to Biases and Flaws in Reasoning
The decisions you make come with inherent bias. Taking part in the strategic planning process forces you to examine and explain why you’re making each decision and back it up with data, projections, or case studies, thus combatting your cognitive biases.
A few examples of cognitive biases are:
- The recency effect: The tendency to select the option presented most recently because it’s fresh in your mind
- Occam’s razor bias: The tendency to assume the most obvious decision to be the best decision
- Inertia bias: The tendency to select options that allow you to think, feel, and act in familiar ways
One cognitive bias that may be more difficult to catch in the act is confirmation bias . When seeking to validate a particular viewpoint, it's the tendency to only pay attention to information that supports that viewpoint.
If you’re crafting a strategic plan for your organization and know which strategy you prefer, enlist others with differing views and opinions to help look for information that either proves or disproves the idea.
Combating biases in strategic decision-making requires effort and dedication from your entire team, and it can make your organization’s strategy that much stronger.
Related: 3 Group Decision-Making Techniques for Success
3. Track Progress Based on Strategic Goals
Having a strategic plan in place can enable you to track progress toward goals. When each department and team understands your company’s larger strategy, their progress can directly impact its success, creating a top-down approach to tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) .
By planning your company’s strategy and defining its goals, KPIs can be determined at the organizational level. These goals can then be extended to business units, departments, teams, and individuals. This ensures that every level of your organization is aligned and can positively impact your business’s KPIs and performance.
It’s important to remember that even though your strategy might be far-reaching and structured, it must remain agile. As Christensen asserts in Disruptive Strategy , a business’s strategy needs to evolve with the challenges and opportunities it encounters. Be prepared to pivot your KPIs as goals shift and communicate the reasons for change to your organization.

Improve Your Strategic Planning Skills
Strategic planning can benefit your organization’s vision, execution, and progress toward goals. If strategic planning is a skill you’d like to improve, online courses can provide the knowledge and techniques needed to lead your team and organization.
Strategy courses can range from primers on key concepts (such as Economics for Managers ), to deep-dives on strategy frameworks (such as Disruptive Strategy ), to coursework designed to help you strategize for a specific organizational goal (such as Sustainable Business Strategy ).
Learning how to craft an effective, compelling strategic plan can enable you to not only invest in your career but provide lasting value to your organization.
Do you want to formulate winning strategies for your organization? Explore our portfolio of online strategy courses and download the free flowchart to determine which is the best fit for you and your goals.

About the Author
What is a Business Plan? Definition, Tips, and Templates
Published: June 07, 2023
In an era where more than 20% of small enterprises fail in their first year, having a clear, defined, and well-thought-out business plan is a crucial first step for setting up a business for long-term success.

Business plans are a required tool for all entrepreneurs, business owners, business acquirers, and even business school students. But … what exactly is a business plan?

In this post, we'll explain what a business plan is, the reasons why you'd need one, identify different types of business plans, and what you should include in yours.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a documented strategy for a business that highlights its goals and its plans for achieving them. It outlines a company's go-to-market plan, financial projections, market research, business purpose, and mission statement. Key staff who are responsible for achieving the goals may also be included in the business plan along with a timeline.
The business plan is an undeniably critical component to getting any company off the ground. It's key to securing financing, documenting your business model, outlining your financial projections, and turning that nugget of a business idea into a reality.
What is a business plan used for?
The purpose of a business plan is three-fold: It summarizes the organization’s strategy in order to execute it long term, secures financing from investors, and helps forecast future business demands.
Business Plan Template [ Download Now ]

Working on your business plan? Try using our Business Plan Template . Pre-filled with the sections a great business plan needs, the template will give aspiring entrepreneurs a feel for what a business plan is, what should be in it, and how it can be used to establish and grow a business from the ground up.
Purposes of a Business Plan
Chances are, someone drafting a business plan will be doing so for one or more of the following reasons:
1. Securing financing from investors.
Since its contents revolve around how businesses succeed, break even, and turn a profit, a business plan is used as a tool for sourcing capital. This document is an entrepreneur's way of showing potential investors or lenders how their capital will be put to work and how it will help the business thrive.
All banks, investors, and venture capital firms will want to see a business plan before handing over their money, and investors typically expect a 10% ROI or more from the capital they invest in a business.
Therefore, these investors need to know if — and when — they'll be making their money back (and then some). Additionally, they'll want to read about the process and strategy for how the business will reach those financial goals, which is where the context provided by sales, marketing, and operations plans come into play.
2. Documenting a company's strategy and goals.
A business plan should leave no stone unturned.
Business plans can span dozens or even hundreds of pages, affording their drafters the opportunity to explain what a business' goals are and how the business will achieve them.
To show potential investors that they've addressed every question and thought through every possible scenario, entrepreneurs should thoroughly explain their marketing, sales, and operations strategies — from acquiring a physical location for the business to explaining a tactical approach for marketing penetration.
These explanations should ultimately lead to a business' break-even point supported by a sales forecast and financial projections, with the business plan writer being able to speak to the why behind anything outlined in the plan.
.webp)
Free Business Plan Template
The essential document for starting a business -- custom built for your needs.
- Outline your idea.
- Pitch to investors.
- Secure funding.
- Get to work!
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Free Business Plan [Template]
Fill out the form to access your free business plan., 3. legitimizing a business idea..
Everyone's got a great idea for a company — until they put pen to paper and realize that it's not exactly feasible.
A business plan is an aspiring entrepreneur's way to prove that a business idea is actually worth pursuing.
As entrepreneurs document their go-to-market process, capital needs, and expected return on investment, entrepreneurs likely come across a few hiccups that will make them second guess their strategies and metrics — and that's exactly what the business plan is for.
It ensures an entrepreneur's ducks are in a row before bringing their business idea to the world and reassures the readers that whoever wrote the plan is serious about the idea, having put hours into thinking of the business idea, fleshing out growth tactics, and calculating financial projections.
4. Getting an A in your business class.
Speaking from personal experience, there's a chance you're here to get business plan ideas for your Business 101 class project.
If that's the case, might we suggest checking out this post on How to Write a Business Plan — providing a section-by-section guide on creating your plan?
What does a business plan need to include?
- Business Plan Subtitle
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- The Business Opportunity
- Competitive Analysis
- Target Market
- Marketing Plan
- Financial Summary
- Funding Requirements
1. Business Plan Subtitle
Every great business plan starts with a captivating title and subtitle. You’ll want to make it clear that the document is, in fact, a business plan, but the subtitle can help tell the story of your business in just a short sentence.
2. Executive Summary
Although this is the last part of the business plan that you’ll write, it’s the first section (and maybe the only section) that stakeholders will read. The executive summary of a business plan sets the stage for the rest of the document. It includes your company’s mission or vision statement, value proposition, and long-term goals.

3. Company Description
This brief part of your business plan will detail your business name, years in operation, key offerings, and positioning statement. You might even add core values or a short history of the company. The company description’s role in a business plan is to introduce your business to the reader in a compelling and concise way.
4. The Business Opportunity
The business opportunity should convince investors that your organization meets the needs of the market in a way that no other company can. This section explains the specific problem your business solves within the marketplace and how it solves them. It will include your value proposition as well as some high-level information about your target market.

5. Competitive Analysis
Just about every industry has more than one player in the market. Even if your business owns the majority of the market share in your industry or your business concept is the first of its kind, you still have competition. In the competitive analysis section, you’ll take an objective look at the industry landscape to determine where your business fits. A SWOT analysis is an organized way to format this section.
6. Target Market
Who are the core customers of your business and why? The target market portion of your business plan outlines this in detail. The target market should explain the demographics, psychographics, behavioristics, and geographics of the ideal customer.
7. Marketing Plan
Marketing is expansive, and it’ll be tempting to cover every type of marketing possible, but a brief overview of how you’ll market your unique value proposition to your target audience, followed by a tactical plan will suffice.
Think broadly and narrow down from there: Will you focus on a slow-and-steady play where you make an upfront investment in organic customer acquisition? Or will you generate lots of quick customers using a pay-to-play advertising strategy? This kind of information should guide the marketing plan section of your business plan.
8. Financial Summary
Money doesn’t grow on trees and even the most digital, sustainable businesses have expenses. Outlining a financial summary of where your business is currently and where you’d like it to be in the future will substantiate this section. Consider including any monetary information that will give potential investors a glimpse into the financial health of your business. Assets, liabilities, expenses, debt, investments, revenue, and more are all useful adds here.
So, you’ve outlined some great goals, the business opportunity is valid, and the industry is ready for what you have to offer. Who’s responsible for turning all this high-level talk into results? The "team" section of your business plan answers that question by providing an overview of the roles responsible for each goal. Don’t worry if you don’t have every team member on board yet, knowing what roles to hire for is helpful as you seek funding from investors.
10. Funding Requirements
Remember that one of the goals of a business plan is to secure funding from investors, so you’ll need to include funding requirements you’d like them to fulfill. The amount your business needs, for what reasons, and for how long will meet the requirement for this section.
Types of Business Plans
- Startup Business Plan
- Feasibility Business Plan
- Internal Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Business Acquisition Plan
- Business Repositioning Plan
- Expansion or Growth Business Plan
There’s no one size fits all business plan as there are several types of businesses in the market today. From startups with just one founder to historic household names that need to stay competitive, every type of business needs a business plan that’s tailored to its needs. Below are a few of the most common types of business plans.
For even more examples, check out these sample business plans to help you write your own .
1. Startup Business Plan

As one of the most common types of business plans, a startup business plan is for new business ideas. This plan lays the foundation for the eventual success of a business.
The biggest challenge with the startup business plan is that it’s written completely from scratch. Startup business plans often reference existing industry data. They also explain unique business strategies and go-to-market plans.
Because startup business plans expand on an original idea, the contents will vary by the top priority goals.
For example, say a startup is looking for funding. If capital is a priority, this business plan might focus more on financial projections than marketing or company culture.
2. Feasibility Business Plan
This type of business plan focuses on a single essential aspect of the business — the product or service. It may be part of a startup business plan or a standalone plan for an existing organization. This comprehensive plan may include:
- A detailed product description
- Market analysis
- Technology needs
- Production needs
- Financial sources
- Production operations
According to CBInsights research, 35% of startups fail because of a lack of market need. Another 10% fail because of mistimed products.
Some businesses will complete a feasibility study to explore ideas and narrow product plans to the best choice. They conduct these studies before completing the feasibility business plan. Then the feasibility plan centers on that one product or service.
3. Internal Business Plan

Internal business plans help leaders communicate company goals, strategy, and performance. This helps the business align and work toward objectives more effectively.
Besides the typical elements in a startup business plan, an internal business plan may also include:
- Department-specific budgets
- Target demographic analysis
- Market size and share of voice analysis
- Action plans
- Sustainability plans
Most external-facing business plans focus on raising capital and support for a business. But an internal business plan helps keep the business mission consistent in the face of change.
4. Strategic Business Plan

Strategic business plans focus on long-term objectives for your business. They usually cover the first three to five years of operations. This is different from the typical startup business plan which focuses on the first one to three years. The audience for this plan is also primarily internal stakeholders.
These types of business plans may include:
- Relevant data and analysis
- Assessments of company resources
- Vision and mission statements
It's important to remember that, while many businesses create a strategic plan before launching, some business owners just jump in. So, this business plan can add value by outlining how your business plans to reach specific goals. This type of planning can also help a business anticipate future challenges.
5. Business Acquisition Plan

Investors use business plans to acquire existing businesses, too — not just new businesses.
A business acquisition plan may include costs, schedules, or management requirements. This data will come from an acquisition strategy.
A business plan for an existing company will explain:
- How an acquisition will change its operating model
- What will stay the same under new ownership
- Why things will change or stay the same
- Acquisition planning documentation
- Timelines for acquisition
Additionally, the business plan should speak to the current state of the business and why it's up for sale.
For example, if someone is purchasing a failing business, the business plan should explain why the business is being purchased. It should also include:
- What the new owner will do to turn the business around
- Historic business metrics
- Sales projections after the acquisition
- Justification for those projections
6. Business Repositioning Plan
.webp?width=650&height=450&name=businessplan_6%20(1).webp)
When a business wants to avoid acquisition, reposition its brand, or try something new, CEOs or owners will develop a business repositioning plan.
This plan will:
- Acknowledge the current state of the company.
- State a vision for the future of the company.
- Explain why the business needs to reposition itself.
- Outline a process for how the company will adjust.
Companies planning for a business reposition often do so — proactively or retroactively — due to a shift in market trends and customer needs.
For example, shoe brand AllBirds plans to refocus its brand on core customers and shift its go-to-market strategy. These decisions are a reaction to lackluster sales following product changes and other missteps.
7. Expansion or Growth Business Plan
When your business is ready to expand, a growth business plan creates a useful structure for reaching specific targets.
For example, a successful business expanding into another location can use a growth business plan. This is because it may also mean the business needs to focus on a new target market or generate more capital.
This type of plan usually covers the next year or two of growth. It often references current sales, revenue, and successes. It may also include:
- SWOT analysis
- Growth opportunity studies
- Financial goals and plans
- Marketing plans
- Capability planning
These types of business plans will vary by business, but they can help businesses quickly rally around new priorities to drive growth.
Getting Started With Your Business Plan
At the end of the day, a business plan is simply an explanation of a business idea and why it will be successful. The more detail and thought you put into it, the more successful your plan — and the business it outlines — will be.
When writing your business plan, you’ll benefit from extensive research, feedback from your team or board of directors, and a solid template to organize your thoughts. If you need one of these, download HubSpot's Free Business Plan Template below to get started.
Editor's note: This post was originally published in August 2020 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

24 of My Favorite Sample Business Plans & Examples For Your Inspiration
![strategy business plan meaning How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/executive-summary-example_5.webp)
How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]

Maximizing Your Social Media Strategy: The Top Aggregator Tools to Use

The Content Aggregator Guide for 2023
![strategy business plan meaning 7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/gantt-chart-example.jpg)
7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]
![strategy business plan meaning The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/flowchart%20templates.jpg)
The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]

16 Best Screen Recorders to Use for Collaboration

The 25 Best Google Chrome Extensions for SEO

Professional Invoice Design: 28 Samples & Templates to Inspire You
Customers’ Top HubSpot Integrations to Streamline Your Business in 2022
2 Essential Templates For Starting Your Business
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans for May 2024 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How To Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
What is a Business Strategy and How to Create One

13 min. read
Updated April 19, 2024
There is so much you could do to grow your business . You could develop new business partnerships, build new features for your product, or add new products and services. It’s an ever-growing list of seemingly good ideas.
But you can only do so much with the time and resources available, and chasing the wrong thing can be incredibly costly. How are you supposed to know what’s worth pursuing?
By developing a business strategy.
- What is a business strategy?
A business strategy outlines what makes your business unique and how you’ll solve a specific problem for your customers. It helps you focus on creating value to solidify a competitive advantage in the market and reach your goals.
Creating a business strategy gives you a guide for making decisions that prioritize growth . A few use cases for your strategy include:
- Entering a new market
- Launching a product
- Repositioning your business
- Allocating resources
- Addressing business challenges
- Why is a business strategy important?
A good business strategy helps you:
Maintain focus
With a business strategy in place, you’ll be better prepared to avoid chasing every new opportunity. It helps channel your efforts toward opportunities that align with your objectives.
Avoid wasting resources
Without a well-thought-out strategy, there’s a higher risk of wasting time and money, possibly leading to business failure.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
Keep your team aligned
A clear strategy keeps you and your team on the same page. It guides your collective focus towards specific business goals and ensures everyone moves in the right direction.
Attract investment
Investors need to see how you solve a problem in a way that differs from the competition. Your strategy explains that and shows how you’ll execute on your idea.
Stay competitive
Your business strategy doesn’t just take your customers into account—it also forces you to understand your competitors. You’ll understand how you compare and what it will take to grow beyond them.
- How to create a business strategy
When developing a strategy, keep it simple. Focus on the needs of your customers and the value of your business. Here’s how:
Tip: Download our free one-page business plan template . It provides a simple but effective format to document your business strategy.
1. Know your customers
You shouldn’t take action without understanding your customers’ needs . Read reviews, conduct surveys, dig into forums, and—most importantly—talk to your customers.
Whatever you do, collect real-world data and develop an understanding of your target market .
Now, you need to document your results. Add enough information for you, and anyone else, to easily understand:
- Who your target customers are
- How many potential customers there are
- Specific preferences like buying habits, cultural affinities, etc.
Don’t go into too much detail here. Just have enough information to paint a picture of your ideal customer.
What if you’re an up-and-running business?
If you have created a business plan , you should already have a profile of your target market. For this step, revisit your information and determine if it is still relevant and accurate.
Tip: You may find it valuable to craft a customer persona —a faux customer profile based on your market research . It’s a helpful tool to visualize your customers and keep them top of mind.
2. Define your value proposition
The crux of your strategy is the distinct value your business provides. The research and information you’ve documented will make defining that value much easier. By the end of this step, you will have brief descriptions of:
- The problem you solve
- Your solution
- Your value proposition
These will be brief but powerful statements for your business. It’s where you define what you do, why, and how you do it better. They’ll drive your strategy and help turn your customers’ needs into memorable statements that you, your employees, and even potential investors will focus on.
Tip: If you’ve written a business plan , you don’t have to start this process from scratch. You likely already have the components or even entirely written statements in your Products and Services and Sales and Marketing sections to use.
Describing the problem
In a sentence or two, outline the critical problem your target customers face.
Example: “Most local consumers lack access to fresh, organic bakery options that support health and community sustainability.”
Explaining your solution
Briefly describe how your product or service addresses the problem identified.
Example: “Our bakery offers daily-baked, organic bread and pastries using locally sourced ingredients, providing a healthy and community-supportive alternative to mass-produced baked goods.”
Creating your value proposition
Your value proposition is a clear, concise statement explaining:
- The unique benefits your products or services provide
- Who you provide them to
- How they are different or better than similar offerings in the market
You can use your descriptions of the problem and solution to help define the key product/service benefits in your value proposition.
List what factors set you apart from the competition. Hone in on a theme for both that resonates with your customer’s needs and preferences. Then, combine these ideas into a single sentence.
Example: For a local organic bakery focused on quality and healthy eating, your value proposition might look like:
“Enjoy fresh, organic goods baked daily with locally sourced ingredients to support your health and community sustainability.”
Read More: When your strategy needs a story
3. Analyze your competitors
Understanding your competition is crucial for carving out your unique space in the market. Here’s what to look for:
- List your competitors: Identify the main players in your market.
- Evaluate their offerings: Examine their products or services. Try to spot differences in product features, pricing, customer service, or brand perception.
- Assess their value proposition: Understand how they position themselves, the unique value they claim to offer, and how they communicate this to customers.
- Understand what customers think: Look at customer reviews, testimonials, and social media feedback to gauge customer satisfaction and common pain points.
Like your customer research, you don’t need to be overly detailed here. You want a simple summary of the competition and why you’re different or better than them. That should provide enough information to help with the final step.
Example: After checking out the competition, you realize that your bakery offers far more gluten-free and vegan options (and they taste far better). You’re also planning to offer delivery services, which current bakeries in the area lack.
But what if your business provides a solution that isn’t drastically different from competitors? It’s a fairly common situation, and you may struggle to immediately identify how to set your business apart.
If this sounds like you, then you’ll need to focus your differentiation efforts on:
- Where the product/service is sold
- Messaging and marketing channels
- How your business makes money
All of which we’ll cover over the next three steps.
4. List your sales channels
The sales channels you choose and prioritize should be based on the needs of your target customers .
- Where do they expect products/services like yours to be?
- Where do your competitors sell theirs?
- Are there untapped sales opportunities that would better serve your customers?
Focus on that last question if you’re trying to differentiate through your sales efforts. The biggest opportunity may simply be to better serve the purchasing habits of customers instead of offering a fully unique solution.
Example:
Let’s revisit our bakery and assume you plan to open a physical storefront. That’s one sales channel—customers make purchases in person. Your competitors also do that, but maybe the location you choose is more convenient and accessible to people on their morning commute.
As previously mentioned, you also plan to offer your baked goods through 3rd party delivery apps—another sales channel.
Sticking with that idea, you realize that online ordering is a very attractive benefit to your customers and that most competitors don’t have an up-to-date website. So, you decide to offer online ordering directly through your website.
Other sales options you consider include distribution through local grocery stores and bulk catering contracts. For the purposes of your strategy document, you’d list off these sales channels based on how you’ll prioritize them and end up with something like this:
Sales channels
- 3rd party delivery
- Catering contracts
- Retailer distribution
5. Explain your marketing activities
How will you spread the word about your business?
Will you take out traditional ads in newspapers and on billboards? Focus on paid advertising through Google search or Facebook? Maybe branch out and partner with influencers?
Whatever you choose, focus on marketing activities that get you in front of your customers. There’s no reason to invest money in places where your customers aren’t spending their time. If you do, you’ll struggle to see any real return on marketing efforts.
Now, that doesn’t mean you just replicate what your competitors are doing and do the same marketing activities. They may not be the most effective or targeted efforts. In fact, by taking a different approach, you could differentiate your business through the channels and messaging you choose.
You notice that most of your competitors’ marketing consists of billboards, flyers, and similar out-of-home awareness efforts. They don’t market much online or try to directly connect with customers.
You believe that your target customers appreciate a more personal approach. So, you split your efforts and try to build a connection through complimentary digital and traditional marketing efforts.
You send direct mailers providing regular incentives that also feature your Instagram. Then you create regular posts showing how your baked goods are made and previewing upcoming treats—which can be repurposed for online ads.
This approach, compared to your competitors, is far more interconnected. Each effort promotes and bolsters the rest—potentially leading to more consistent messaging and cost-effective creation.
Read More: How to Create a Zero-Waste Business Strategy
6. Describe your business model
Your business model describes how your business will make money—covering where revenue comes from and your expenses.
But, did you know that your strategy can be focused on innovating with your business model?
You don’t need to invent a fully new business model either. Instead, focus on identifying ways to optimize:
- The creation of your product/service
- How you sell your product/service
- How and what your customers pay
You’re not trying to break the mold with how you make money through your bakery. However, you have identified a few ways to make your business model more profitable.
First, you found local suppliers who can provide high-quality ingredients but are far less expensive to acquire due to a lack of shipping costs. Your expanded sales channels also provide far more options for customers to engage and purchase however they want.
And since your products are of a higher quality, you’re positioning them as a premium option. However, due to your cost-saving efforts, you’ve been able to keep prices relatively close to competitors and even have the flexibility to go lower if needed.
If you’re just putting your strategy together, don’t focus on going too in-depth with your number crunching. Instead, describe your business model by simply listing your revenue streams and key expenses.
Once you have a business model that you believe will work (and have ideally tested it with customers ) then create detailed forecasts to make it usable.
Tip: Check out the financial plan step in our business planning guide for in-depth guidance on creating financial forecasts.
Dig deeper:
3 questions to help you build a long-term strategy
Clarify your value, target the right buyers, and understand how to reach them meaningfully by asking three simple questions.
11 tips for creating a long-term strategic plan
Try implementing these tips to turn your strategy into an effective management tool for your business.
- How to execute your business strategy
The process above helps you create your business-level strategy. However, there are ways to make your strategy more actionable.
Define your tactics
Transitioning your business strategy into functional tactics is essential to achieve your business goals. While your strategy sets the direction—tactics detail the operational steps and day-to-day activities necessary for execution.
Example: One of your differentiation strategies is to provide greater customer service than your competitors. You need to enhance customer satisfaction, which may translate into tactics like implementing a feedback system or training staff in customer service.
Successfully implementing your tactics requires setting clear deadlines, identifying and addressing potential bottlenecks, and adjusting processes. Remember, you want every tactic to contribute to your long-term goals. If you find that work isn’t aligning with your strategy, it likely isn’t worth prioritizing.
Why strategy is useless without execution
Tactics and specific details make your strategy actionable. You’ll struggle to achieve consistent growth if you fail to understand how these three things work together.
7 steps for successful project planning
Similar to your strategy, the most effective projects are thoroughly planned before starting. It may take more time up front, but it will save you time and money in the long run.
Measure performance
The entire point of developing a strategy is to ensure you are making progress toward the growth of your business. Even if you’ve worked through all of the steps we’ve outlined here, you will struggle to make any real progress without tracking and evaluating your performance.
The metrics or key performance indicators (KPIs) you focus on measuring fully depend on your strategy. You should at least track revenue growth and cash flow. These will provide you with the basics for understanding the health of your business. The rest is up to you.
Are you focusing on bringing in customers? Track your customer acquisition costs and retention rate.
Looking to improve brand visibility? Retention rate, market share, and Net Promoter Score may be useful options.
In any case, know what you need to track and set up a way to do so as early as possible. Regularly reviewing these metrics provides insights into whether your strategy is working. The longer you go without knowing what demonstrates success, the longer it will take to execute your strategy.
5 signs you need to pivot your business
If you’re losing customers, bleeding cash, or underutilizing your team it may be time to rethink your strategy.
Bring in your team
Engaging key stakeholders early provides unique insights that can lead to a more well-rounded strategy. It also helps foster a sense of ownership and trust between you and your employees.
You don’t need to share it with everyone in this early stage—but collaborating with the right people can streamline your efforts. You’ll avoid misalignment between individuals, teams, and the business. Plus, it can lead to discussions and ideas for applying the strategy to smaller projects and goals.
How to create business management standards
Before you get your team involved in developing your strategy, it may be wise to establish set guidelines for everyone to follow and reference.
- What makes a successful business strategy?
Your strategy won’t be perfect. Even if you follow these steps to the letter, unforeseen circumstances, changes in the market, or any number of things will force you to adjust.
The key to a successful strategy is to pay attention to your performance and change course when necessary. Your strategy cannot be static and isolated. If it is, you’ll struggle to grow as things change.
If you’re looking for a tool to help you document and review your strategy—the one-page business plan is a simple but effective option.
Kody Wirth is a content writer and SEO specialist for Palo Alto Software—the creator's of Bplans and LivePlan. He has 3+ years experience covering small business topics and runs a part-time content writing service in his spare time.

Table of Contents
Related Articles

7 Min. Read
How to Turn First Time Customers Into Repeat Customers

11 Tips for Creating a Long-Term Strategic Plan

11 Min. Read
10 Tips to Increase Your Restaurant Sales

8 Min. Read
10 Ways to Grow Your SaaS Startup Faster
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

- Certifications
- Associate Business Strategy Professional
- Senior Business Strategy Professional
- Examination
- Partnership
- For Academic Affiliation
- For Training Companies
- For Corporates
- Help Center
- Associate Business Strategy Professional (ABSP™)
- Senior Business Strategy Professional (SBSP™)
- Certification Process
- TSI Certification Examination
- Get your Institution TSI Affiliated
- Become a Corporate Education Partner
- Become a Strategy Educator
- Frequently Asked Questions
What is Business Strategy? Definition, Importance, Levels, and Examples

Business strategy is the battle plan for a better future. - Patrick Dixon
Scaling up a business without a clear strategy is like captaining a ship without a rudder. The success of any business depends on the strategy that one follows. The business strategy establishes the needs of the business. Business strategy plays an important role for businesses of all sizes and entrepreneurs. It sets the direction of the organization and helps to create goals to aim towards.
What is Business Strategy?
Business strategy is defined as the course of action or set of decisions that support entrepreneurs in achieving certain business goals. It is a master plan that outlines the direction the organization intends to make, the actions it will undertake, and the resources it will give to attain certain competitive benefits and drive sustainable growth. It involves a combination of decisions, actions, and resource allocation that positions an organization in its industry or market.
Why is a Business Strategy important?
Business Strategy plays a crucial role in guiding a firm’s growth, competitiveness, and success. It offers a roadmap for decision-making, resource providing, and adaptation to transforming circumstances, ensuring that the firm stays agile, focused, and well-prepared to achieve its goals successfully. It is carefully planned and flexibly designed with the purpose of:
- Achieving effectiveness
- Perceiving and utilizing opportunities
- Mobilizing resources
- Securing an advantageous position
- Meeting the challenges and threats
- Directing efforts, behavior and
- Gaining command over the situation
What is the Difference between Business Strategy & Business Plan & Business Model
Business Strategy, Business Plan, and Business Model are three distinct elements that offer various purposes in the world of business. They are vital for the success and sustainability of a business, and they are interconnected, with slight changes which are often confused by several aspiring business strategists , especially during their interviews. Here's a breakdown of the important differences between these:
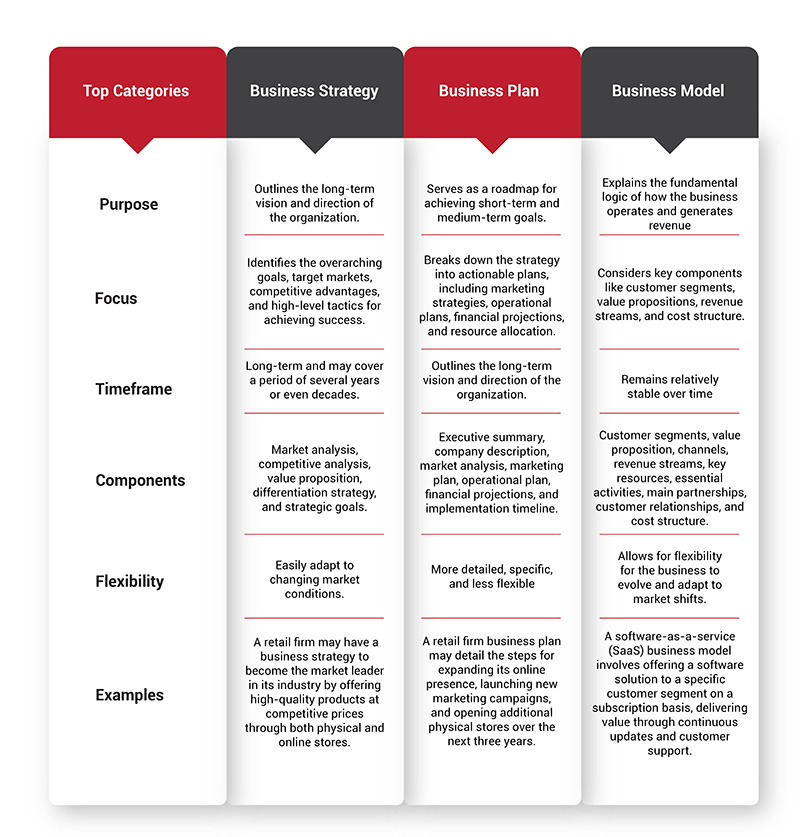
Levels of Business Strategy
Effective strategic management consists of coordination and alignment across various levels of strategy to achieve the organization's long-term goals and competitive advantage. Business strategy can be categorized into different levels depending on its scope, focus, and the organizational hierarchy at which it functions.
The three primary levels of business strategy are:
- Corporate level strategy Corporate level strategy is a long-range, action-oriented, integrated, and comprehensive plan, which is formulated by the top management of a company. It is very helpful to ascertain business lines, expansion, growth, takeovers and mergers, diversification , integration, and the latest fields for investment.
- Business level strategy The strategies that relate to a specific business are known as business-level strategies. It is developed by the general managers, who convert mission and vision into concrete, clear, and result-driven strategies. It acts like a blueprint for the total business.
- Functional level strategy Developed by the first-line managers or supervisors, the functional level strategy involves decision-making at the operational level concerning functional areas such as marketing, production, human resources, research and development, finance, and so on.
How to Implement a Successful Business Strategy?
A business strategist feels that it is tough to ideate any plan in a few hours. It requires a step-by-step procedure to be associated with completing a SWOT analysis . Here are the top steps that can be considered to build the best business strategies and execute them with precision:
- Understand the targets One of the clearest challenges for growth is poor targeting. Clear target markets offer an organization the ability to create an integrated sales and marketing approach, where marketing enables sales productivity. Sales and marketing business plan gets executed more efficiently if the targets are fixed in a proper way.
- Outline the tactics A successful business strategy is made up of several various tactics, including both online and offline options. The goals, target audience, and industry factor into this decision. For instance, if the target audience is young, focusing on social media is more beneficial as this is primarily where this group consumes content. If the industry is product-based (for instance, jewelry designing), then using a more visual platform would better showcase the products. To be most effective, one must choose which methods are right for the business. Once the selection of tactics is done, list them in the plan and determine how they’ll help to reach the goals.
- Think long term In the scope of constant change, planning the horizons is usually shorter than it can be. However, only thinking quarter to quarter is a trap that may rob organizations of their ability to see around the bend. Best-in-class organizations create processes designed for a series of financial and non-financial metrics to treat strategy as an annual cycle rather than a one-time, static event.
- Create a timeline Time is precious mainly when it is about the business. Based on the goals and objectives one can set for the business. Creating a timeline that will define what tasks can be completed and when they can be completed. It is highly advisable to allocate extra time for unexpected events that may delay some of the goals.
- Focus on growth A thriving organization is a growing organization. It is only through growth that the firms can afford to invest in aspects such as technology, the best staff, and the latest tools. The business strategy should identify the segments where an organization will grow and in what proportion.
- Have a budget plan Creating a budget for the business strategy can inform the efforts by determining what can be done and cannot be. Choosing the most cost-effective options for the business ensures the success of the overall business strategy. This doesn’t have to limit the options. Paid advertising on social media and search engines gives access to manage budgets well.
- Make fact-based decisions Several executives often complain about a lack of fruitful data, but they consistently find information that is useful in the formation of business strategy. The business has a set of values that guides it. Making fact-based decisions will outline the values and ensure that the people who interact with the business are aware of them. It will also ease the message that reflects on the brand honestly so it can actively demonstrate the values outlined in the mission statement through the interactions with clients.
- Invest in pre-work Always allocate time to do proper pre-work so that one can be up to date. It is better to conduct proper end-to-end research and prepare relevant information in advance of the business strategy meetings. The goals and needs will change over time. Ideally, it is important to revisit the business plan every annum to make adjustments as needed. Follow industry news and trends that can add to the existing strategy.
- Execute well and measure results Measuring the effectiveness of the business strategy will inform the current plan and future efforts. Always be sure to track and measure the business so these measurements are effective. Set up a corporate calendar to enhance the productive meetings, and also to form a performance management cycle. One should write the marketing plan with this growth in mind so they can measure it. The execution of strategic planning needs discipline, and it must be taken care of by the senior executives to promote processes that keep the team focused.
Examples of Business Strategy
Hubspot developed and executed a perfect business strategy where it created a market that didn’t even exist – inbound marketing. It created an online resource guide explaining the limitations of interruption marketing and informing about the advantages of inbound marketing. The organizations even offered free courses to help the target audience understand its offering better.
Apple Inc. differentiated its Smartphone operating system iOS by making it simple as compared to Android. This differentiated it and built its followership. The organization has been following a similar business strategy for its other products as well.
Wrapping up
Establishing the business strategy keeps the business goals organized and focused, saving valuable time and money. With the increase in the competition, the demand for business strategy is becoming apparent and there is a tremendous increase in the types of business strategies used by the businesses.

Recent Posts

How Data Analytics Can Revolutionize Your Business - A Strategist's Guide
Download this Strategist's Guide to empower yourself with resourceful insights:
- Roadblocks to Data Usage
- Advantages that Data Analytics offer for businesses
- Elements of a Data Analytics Strategy
- Top reasons why businesses must adopt a Data Analytics Strategy
- Case studies, Scenarios, and more

CredBadge™ is a proprietary, secure, digital badging platform that provides for seamless authentication and verification of credentials across digital media worldwide.
CredBadge™ powered credentials ensure that professionals can showcase and verify their qualifications and credentials across all digital platforms, and at any time, across the planet.

Verify A Credential
Please enter the License Number/Unique Credential Code of the certificant. Results will be displayed if the person holds an active credential from TSI.
Stay Informed!
Keep yourself informed on the latest updates and information about business strategy by subscribing to our newsletter.
Start Your Journey with The Strategy Institute by Creating Your myTSI Account Today.
- Manage your professional profile conveniently.
- Manage your credentials anytime.
- Share your experiences and ideas with The Strategy Institute.
Account Login
- Remember Password
- Forgot Password?
Forgot Password
Mobile Menu Overlay
The White House 1600 Pennsylvania Ave NW Washington, DC 20500
FACT SHEET: President Biden Takes Action to Protect American Workers and Businesses from China’s Unfair Trade Practices
President Biden’s economic plan is supporting investments and creating good jobs in key sectors that are vital for America’s economic future and national security. China’s unfair trade practices concerning technology transfer, intellectual property, and innovation are threatening American businesses and workers. China is also flooding global markets with artificially low-priced exports. In response to China’s unfair trade practices and to counteract the resulting harms, today, President Biden is directing his Trade Representative to increase tariffs under Section 301 of the Trade Act of 1974 on $18 billion of imports from China to protect American workers and businesses. The Biden-Harris Administration’s Investing in America agenda has already catalyzed more than $860 billion in business investments through smart, public incentives in industries of the future like electric vehicles (EVs), clean energy, and semiconductors. With support from the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, CHIPS and Science Act, and Inflation Reduction Act, these investments are creating new American jobs in manufacturing and clean energy and helping communities that have been left behind make a comeback. As President Biden says, American workers and businesses can outcompete anyone—as long as they have fair competition. But for too long, China’s government has used unfair, non-market practices. China’s forced technology transfers and intellectual property theft have contributed to its control of 70, 80, and even 90 percent of global production for the critical inputs necessary for our technologies, infrastructure, energy, and health care—creating unacceptable risks to America’s supply chains and economic security. Furthermore, these same non-market policies and practices contribute to China’s growing overcapacity and export surges that threaten to significantly harm American workers, businesses, and communities. Today’s actions to counter China’s unfair trade practices are carefully targeted at strategic sectors—the same sectors where the United States is making historic investments under President Biden to create and sustain good-paying jobs—unlike recent proposals by Congressional Republicans that would threaten jobs and raise costs across the board. The previous administration’s trade deal with China failed to increase American exports or boost American manufacturing as it had promised. Under President Biden’s Investing in America agenda, nearly 800,000 manufacturing jobs have been created and new factory construction has doubled after both fell under the previous administration, and the trade deficit with China is the lowest in a decade—lower than any year under the last administration. We will continue to work with our partners around the world to strengthen cooperation to address shared concerns about China’s unfair practices—rather than undermining our alliances or applying indiscriminate 10 percent tariffs that raise prices on all imports from all countries, regardless whether they are engaged in unfair trade. The Biden-Harris Administration recognizes the benefits for our workers and businesses from strong alliances and a rules-based international trade system based on fair competition. Following an in-depth review by the United States Trade Representative, President Biden is taking action to protect American workers and American companies from China’s unfair trade practices. To encourage China to eliminate its unfair trade practices regarding technology transfer, intellectual property, and innovation, the President is directing increases in tariffs across strategic sectors such as steel and aluminum, semiconductors, electric vehicles, batteries, critical minerals, solar cells, ship-to-shore cranes, and medical products. Steel and Aluminum The tariff rate on certain steel and aluminum products under Section 301 will increase from 0–7.5% to 25% in 2024. Steel is a vital sector for the American economy, and American companies are leading the future of clean steel. Recently, the Biden-Harris Administration announced $6 billion for 33 clean manufacturing projects including for steel and aluminum, including the first new primary aluminum smelter in four decades, made possible by the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law and the Inflation Reduction Act. These investments will make the United States one of the first nations in the world to convert clean hydrogen into clean steel, bolstering the U.S. steel industry’s competitiveness as the world’s cleanest major steel producer. American workers continue to face unfair competition from China’s non-market overcapacity in steel and aluminum, which are among the world’s most carbon intensive. China’s policies and subsidies for their domestic steel and aluminum industries mean high-quality, low-emissions U.S. products are undercut by artificially low-priced Chinese alternatives produced with higher emissions. Today’s actions will shield the U.S. steel and aluminum industries from China’s unfair trade practices. Semiconductors The tariff rate on semiconductors will increase from 25% to 50% by 2025. China’s policies in the legacy semiconductor sector have led to growing market share and rapid capacity expansion that risks driving out investment by market-driven firms. Over the next three to five years, China is expected to account for almost half of all new capacity coming online to manufacture certain legacy semiconductor wafers. During the pandemic, disruptions to the supply chain, including legacy chips, led to price spikes in a wide variety of products, including automobiles, consumer appliances, and medical devices, underscoring the risks of overreliance on a few markets. Through the CHIPS and Science Act, President Biden is making a nearly $53 billion investment in American semiconductor manufacturing capacity, research, innovation, and workforce. This will help counteract decades of disinvestment and offshoring that has reduced the United States’ capacity to manufacture semiconductors domestically. The CHIPS and Science Act includes $39 billion in direct incentives to build, modernize, and expand semiconductor manufacturing fabrication facilities as well as a 25% investment tax credit for semiconductor companies. Raising the tariff rate on semiconductors is an important initial step to promote the sustainability of these investments. Electric Vehicles (EVs) The tariff rate on electric vehicles under Section 301 will increase from 25% to 100% in 2024. With extensive subsidies and non-market practices leading to substantial risks of overcapacity, China’s exports of EVs grew by 70% from 2022 to 2023—jeopardizing productive investments elsewhere. A 100% tariff rate on EVs will protect American manufacturers from China’s unfair trade practices. This action advances President Biden’s vision of ensuring the future of the auto industry will be made in America by American workers. As part of the President’s Investing in America agenda, the Administration is incentivizing the development of a robust EV market through business tax credits for manufacturing of batteries and production of critical minerals, consumer tax credits for EV adoption, smart standards, federal investments in EV charging infrastructure, and grants to supply EV and battery manufacturing. The increase in the tariff rate on electric vehicles will protect these investments and jobs from unfairly priced Chinese imports. Batteries, Battery Components and Parts, and Critical Minerals The tariff rate on lithium-ion EV batteries will increase from 7.5%% to 25% in 2024, while the tariff rate on lithium-ion non-EV batteries will increase from 7.5% to 25% in 2026. The tariff rate on battery parts will increase from 7.5% to 25% in 2024. The tariff rate on natural graphite and permanent magnets will increase from zero to 25% in 2026. The tariff rate for certain other critical minerals will increase from zero to 25% in 2024. Despite rapid and recent progress in U.S. onshoring, China currently controls over 80 percent of certain segments of the EV battery supply chain, particularly upstream nodes such as critical minerals mining, processing, and refining. Concentration of critical minerals mining and refining capacity in China leaves our supply chains vulnerable and our national security and clean energy goals at risk. In order to improve U.S. and global resiliency in these supply chains, President Biden has invested across the U.S. battery supply chain to build a sufficient domestic industrial base. Through the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, the Defense Production Act, and the Inflation Reduction Act, the Biden-Harris Administration has invested nearly $20 billion in grants and loans to expand domestic production capacity of advanced batteries and battery materials. The Inflation Reduction Act also contains manufacturing tax credits to incentivize investment in battery and battery material production in the United States. The President has also established the American Battery Materials Initiative, which will mobilize an all-of-government approach to secure a dependable, robust supply chain for batteries and their inputs. Solar Cells The tariff rate on solar cells (whether or not assembled into modules) will increase from 25% to 50% in 2024. The tariff increase will protect against China’s policy-driven overcapacity that depresses prices and inhibits the development of solar capacity outside of China. China has used unfair practices to dominate upwards of 80 to 90% of certain parts of the global solar supply chain, and is trying to maintain that status quo. Chinese policies and nonmarket practices are flooding global markets with artificially cheap solar modules and panels, undermining investment in solar manufacturing outside of China. The Biden-Harris Administration has made historic investments in the U.S. solar supply chain, building on early U.S. government-enabled research and development that helped create solar cell technologies. The Inflation Reduction Act provides supply-side tax incentives for solar components, including polysilicon, wafers, cells, modules, and backsheet material, as well as tax credits and grant and loan programs supporting deployment of utility-scale and residential solar energy projects. As a result of President Biden’s Investing in America agenda, solar manufacturers have already announced nearly $17 billion in planned investment under his Administration—an 8-fold increase in U.S. manufacturing capacity, enough to supply panels for millions of homes each year by 2030. Ship-to-Shore Cranes The tariff rate on ship-to-shore cranes will increase from 0% to 25% in 2024. The Administration continues to deliver for the American people by rebuilding the United States’ industrial capacity to produce port cranes with trusted partners. A 25% tariff rate on ship-to-shore cranes will help protect U.S. manufacturers from China’s unfair trade practices that have led to excessive concentration in the market. Port cranes are essential pieces of infrastructure that enable the continuous movement and flow of critical goods to, from, and within the United States, and the Administration is taking action to mitigate risks that could disrupt American supply chains. This action also builds off of ongoing work to invest in U.S. port infrastructure through the President’s Investing in America Agenda. This port security initiative includes bringing port crane manufacturing capabilities back to the United States to support U.S. supply chain security and encourages ports across the country and around the world to use trusted vendors when sourcing cranes or other heavy equipment. Medical Products The tariff rates on syringes and needles will increase from 0% to 50% in 2024. For certain personal protective equipment (PPE), including certain respirators and face masks, the tariff rates will increase from 0–7.5% to 25% in 2024. Tariffs on rubber medical and surgical gloves will increase from 7.5% to 25% in 2026. These tariff rate increases will help support and sustain a strong domestic industrial base for medical supplies that were essential to the COVID-19 pandemic response, and continue to be used daily in every hospital across the country to deliver essential care. The federal government and the private sector have made substantial investments to build domestic manufacturing for these and other medical products to ensure American health care workers and patients have access to critical medical products when they need them. American businesses are now struggling to compete with underpriced Chinese-made supplies dumped on the market, sometimes of such poor quality that they may raise safety concerns for health care workers and patients. Today’s announcement reflects President Biden’s commitment to always have the back of American workers. When faced with anticompetitive, unfair practices from abroad, the President will deploy any and all tools necessary to protect American workers and industry.
Stay Connected
We'll be in touch with the latest information on how President Biden and his administration are working for the American people, as well as ways you can get involved and help our country build back better.
Opt in to send and receive text messages from President Biden.
Difference Between Fully-Insured vs. Self-Funded Health Plans

Businesses typically choose between fully insured and self-insured (self-funded) plans when evaluating health benefit options. Understanding the difference between self-funded and fully insured plans is crucial for effective health insurance strategy planning.
Overview of Fully-Insured vs Self-Funded Health Plans
What is a fully insured health plan.
In a fully insured plan, the company pays fixed premiums to an insurance carrier, which handles all healthcare claims. The premiums are determined based on employee count, projected healthcare costs, and benefit levels. This model offers predictable costs and minimal management duties, making it attractive to smaller businesses that favor stability and a hands-off approach.
In 2019, 61% of U.S. workers with employer-sponsored health insurance were enrolled in a self-funded plan , indicating a significant shift towards self-insurance among American companies.
Self-Funded vs Fully Insured Insurance
In contrast, self-insured plans involve employers setting aside funds to pay for employee medical claims directly, offering potential cost savings by avoiding insurer profit margins. This model also allows for greater benefits customization to meet specific needs and goals, providing more control over the plan.
Fully Funded vs Self-Funded Insurance
Deciding between fully funded and self-funded insurance hinges on a company’s financial stability, risk tolerance, and administrative capabilities. While fully insured plans are less risky and simpler to manage, self-insured plans can offer significant cost savings and flexibility but come with greater financial variability and management complexity.
More information about small business health insurance plans:
Health insurance for small business
Guide to small business health insurance
What Are Fully-Insured Health Plans?
Fully insured health plans are a traditional model where businesses pay fixed premiums to an insurance provider, assuming all risks and responsibilities for employee healthcare claims. This model is favored by small to medium-sized businesses seeking financial predictability and ease of benefits management. In a fully insured plan, the employer signs a contract with an insurer that agrees to cover all eligible healthcare claims for a set premium. These premiums are calculated monthly based on the number of employees, their risk profiles, and desired coverage levels. Insurers use actuarial data to estimate expected claims and adjust premiums to cover these costs plus a profit margin.
Pros and Cons of Fully-Insured Plans
- Predictability of Costs: Employers can know exactly what they will owe each month, regardless of their employees' actual health care costs. This makes budgeting easier and reduces financial uncertainty.
- Ease of Administration: Because the insurance company handles all claims processing and benefits administration, the employer's administrative burden is significantly reduced.
- Reduced Risk: The insurance company assumes all risks related to health care claims, protecting employers from the financial impact of high or unexpected claims.
- Higher Cost in the Long Term: Premiums include the insurance company's overhead and profit margins, making fully insured plans more expensive over time compared to self-funded plans, where employers might save money in years of lower-than-expected claims.
- Less Flexibility: Employers cannot customize plan options and benefits, as they must choose from the plans the insurance company offers.
- Potential for Premium Increases: Premiums can increase at renewal each year based on overall claim trends within the insured pool, age demographics, and other factors, leading to potential unpredictability in long-term healthcare budgeting.
Understanding Self-Funded Health Plans
As of 2020, 80% of covered workers in larger companies (over 5000 employees) were enrolled in self-funded health plans , demonstrating the scalability and appeal of self-insurance in substantial enterprises.
Self-insured health plans offer an alternative approach where employers assume the financial risk for providing employee health benefits, often favored by larger organizations seeking greater control over plan design and costs.
In this model, rather than paying fixed premiums to an insurance company, employers allocate a pool of funds to cover employee health claims directly. They commonly work with a third-party administrator (TPA) to manage claims processing and benefits administration. This setup allows employers to pay for claims as they occur, potentially yielding significant cost savings when claims are lower than anticipated.
Pros and Cons of Self-Funded Plans
- Cost Savings: If the health claims are lower than expected, the employer can save significant money, as they are not paying a premium that includes margins for an insurance company’s overhead and profit.
- Flexibility and Customization: Employers can design and adjust the plan according to their needs and preferences. This includes choosing which benefits to offer and structuring copays, deductibles, and other plan features.
- Improved Cash Flow: Since premiums are not paid upfront to an insurance company, employers can retain more cash in the business until it is needed to pay claims. This can improve overall cash flow management.
- Financial Risk: The major downside of self-insuring is the potential for high costs from unexpected claims. If claims are higher than anticipated, the employer must cover these costs, which can be financially challenging.
- Administrative Burden: Although third-party administrators can help, employers still face an increased administrative burden in managing the health plan, negotiating with providers, and ensuring compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
- Stop-Loss Insurance Needed: Most self-insured plans purchase stop-loss insurance, which can be a significant expense. This insurance reimburses the employer for claims that exceed a certain dollar threshold to mitigate the risk of very high claims.
While self-funded plans offer greater flexibility and potential cost savings, with average monthly premiums reported at $697 for individuals and $2,004 for families in 2020, they require robust risk management strategies, as evidenced by 79% of private sector establishments with such plans having a stop-loss policy.
Comparing Fully-Insured and Self-Insured Plans
The decision between fully insured and self-insured health plans significantly affects a company's finances, risk management, and benefits design. Understanding the difference between self-funded and fully insured plans is vital to align with a company’s goals.
Cost Implications and Savings Potential
Fully insured plans involve fixed premiums, which may result in higher long-term costs due to the inclusion of the insurer's overhead and profit. Conversely, self-insured plans allow companies to reduce costs by eliminating these overheads, although savings depend on actual claim costs, which can be unpredictable.
Risk Management and Liability
In fully insured plans, the insurer manages all claim risks, offering predictability at the cost of higher premiums. In self-insured plans, the employer bears the claims risk, which might lead to substantial financial exposure but can be mitigated by purchasing stop-loss insurance to cover catastrophic claims.
Flexibility and Customization Options
Self-insured plans offer greater flexibility, allowing employers to customize benefits to meet specific workforce needs, including tailored deductibles and copays. Fully insured plans provide less customization, as employers must select from preset options offered by insurers.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
Navigating health insurance regulations is essential for maintaining compliant and effective health plans. Understanding the impact of these regulations on different types of plans helps employers make informed decisions.
ERISA and State Regulations
The Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA) sets federal standards for most private industry health plans, applying to both fully insured and self-insured plans. Fully insured plans must also adhere to state insurance laws, which vary by state and influence claims processing and mandated benefits. Conversely, self-insured plans are generally exempt from state insurance regulations under ERISA, offering greater flexibility but requiring strict compliance with federal standards.
Compliance Requirements for Self-Insured Plans
Self-insured plans must comply with several federal regulations, including specific provisions of the Affordable Care Act (ACA), HIPAA privacy rules, and the Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act. These plans must avoid health-based discrimination, provide adequate coverage, and fulfill reporting and disclosure requirements. Effective management of these requirements typically requires either an adept in-house legal team or a partnership with a knowledgeable third-party administrator (TPA).
Important Considerations For Managing Plans
When choosing between self-funded and fully insured health plans, it's crucial to understand the management responsibilities each entails. Self-funded plans offer the flexibility to design and manage health benefits tailored to specific business and employee needs, but this comes with ensuring efficient operation and compliance. Most self-funded plans utilize a Third-Party Administrator (TPA) to handle administrative tasks like claims processing and regulatory compliance, which reduces the administrative load but may limit customization and control over plan operations.
In contrast, fully insured plans provide less flexibility but increase ease of management as the insurance carrier handles most administrative tasks and assumes risk. This arrangement suits businesses looking for simplicity and less direct involvement in plan management.
It may be worth noting that, in 2020, 39% of firms with multiple locations opted for at least one self-funded plan , compared to 28% of single-location firms. This highlights the administrative considerations and the need for experienced third-party administrators (TPAs) to manage these plans effectively.
Making the Decision: Which Is Right For Your Business?
Choosing between fully insured and self-insured health plans is a critical decision that affects your business's finances, risk management, and employee satisfaction. Understanding the difference between self-funded and fully insured plans is essential for informed decision-making.
Key Factors to Consider:
- Financial Stability and Cash Flow: Self-insured plans may offer cost savings but require a stable cash flow to manage high-cost claims, whereas fully insured plans provide a predictable cost model with fixed premiums, with the insurer bearing the risk of high claims.
- Employee Demographics and Healthcare Needs: Younger, healthier employee groups may see more economic benefits from self-funded plans due to fewer health claims, while a diverse or older workforce may find the risk-sharing and stability of fully insured plans more beneficial.
- Administrative Capacity: Self-insured plans demand significant management for compliance, claims processing, and overall plan administration. Fully insured plans reduce this burden by offloading management to the insurer.
- Risk Tolerance: Fully insured plans offer peace of mind with fixed premiums but may come at a higher cost. Conversely, self-insured plans pose more financial risk due to the potential for unexpectedly high claims.
- Regulatory Considerations: Self-funded plans are predominantly governed by federal laws like ERISA, whereas fully insured plans are subject to state regulations, which can vary and include additional mandates.
Balancing these considerations with each plan type's potential benefits and challenges is crucial. The right choice depends on your company's specific circumstances, including financial health, employee needs, and long-term business strategies. Evaluating these factors will help determine your business's most suitable health insurance option.
Let's talk through your HRA questions

Susanne is a copywriter specializing in the health and wellness industry. Before starting her own business, she spent nearly a decade at a marketing agency doing all of the things – advisor, copywriter, SEO strategist, social media specialist, and project manager. That experience gives her a unique understanding of how the consumer-focused content she writes flows into each marketing piece. Susanne lives in Oklahoma City with her husband and two daughters. She loves being outdoors, exercising and reading.

We’re on a mission to create a consumer-centric healthcare system.
(214) 866-7757
©2024 Take Command. All Rights Reserved.
Take Command Health is not a bank. Banking services are provided by Blue Ridge Bank, N.A, Member FDIC. Deposits are FDIC-insured through Blue Ridge Bank, N.A., Member FDIC. The Take Command Health Visa Debit Card is issued by Blue Ridge Bank, N.A., Member FDIC, pursuant to a license from Visa USA Inc. Your funds are FDIC insured up to $250,000 through Blue Ridge Bank; Member FDIC.
Privacy Policy Terms of Use Licensing Sitemap Secured with SSL
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.
- For business
- For advisors
- For brokers
- For vendors
- For bookkeepers
Agricultural Transition Plan
Page written by AI. Reviewed internally on May 17, 2024.
The Agricultural Transition Plan (ATP) outlines the government’s strategy for improving agricultural policy following the country’s departure from the European Union.
What is the Agricultural Transition Plan?
This transition plan is a significant shift in how farmers are supported and how agricultural land is managed. The purpose of the Agricultural Transition Plan is to support farmers in increasing productivity, improving resilience to climate change, and promoting biodiversity while ensuring fair economic returns.
One of the key features of the ATP is its focus on environmental responsibility. The plan includes measures to encourage farmers to adopt sustainable farming practices, such as agroforestry, organic farming, and soil conservation. Funding will be allocated for projects that improve water quality, improve biodiversity, and reduce climate change.
The ATP encourages the adoption of innovative technologies and practices to improve productivity and efficiency in agriculture. This includes support for research and development , investment in agricultural infrastructure, and the promotion of precision farming techniques.
Knowing the challenges that farmers may face during this transition period, the ATP includes provisions for financial assistance, training, and advisory services. Farming communities will be supported in adapting to the changes and getting new opportunities from the shift in agricultural policy.
The development of the ATP involves consultation with stakeholders, including farmers, environmental organisations, and industry representatives. Collaboration between the government and these stakeholders is important to make sure the transition plan reflects the diverse interests and priorities of the agricultural sector .

Pub mortgage

How to find investors for your business

How to find angel investors

R&D: Why it pays to work with Swoop
Clever finance tips and the latest news
delivered to your inbox, every week
Join the 70,000+ businesses just like yours getting the Swoop newsletter.
Free. No spam. Opt out whenever you like.
By subscribing, I accept the privacy-policy and I give my consent to receive Swoop Funding e-mails about the latest updates and offers.

We work with world class partners to help us support businesses with finance
18 Soho Square, W1D 3QH, London, UK
Suite 42, 4th Floor, Oriel Chambers, 14 Water Street, Liverpool, L2 8TD
Kingfisher Way, Silverlink Business Park, Newcastle upon Tyne, NE28 9NX, UK
Suite 105A, Airivo, 18 Bennetts Hill, Birmingham, B2 5QJ
Aberystwyth
Aberystwyth Innovation and Enterprise Campus Gogerddan Campus Aberystwyth University Ceredigion SY23 3EE
Dogpatch Labs, The CHQ Building, Custom House Quay, Dublin, Ireland
Suite 801, Level 8, 84 Pitt Street, Sydney, NSW 2000, Australia
180 John St, Toronto, ON M5T 1X5, Canada
43 W 23rd St, New York, NY 10010, United States
21 Dreyer Street, Cape Town, South Africa, 7708
Join the 70,000+ businesses just like yours getting the Swoop newsletter. Free. No spam. Opt out whenever you like.
Choose the platform

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
1. Helps formulate better strategies using a logical, systematic approach. This is often the most important benefit. Some studies show that the strategic planning process itself makes a significant contribution to improving a company's overall performance, regardless of the success of a specific strategy. 2.
Step 1: Assess your current business strategy and business environment. Before you can define where you're going, you first need to define where you are. Understanding the external environment, including market trends and competitive landscape, is crucial in the initial assessment phase of strategic planning.
Business strategy is the strategic initiatives a company pursues to create value for the organization and its stakeholders and gain a competitive advantage in the market. This strategy is crucial to a company's success and is needed before any goods or services are produced or delivered. According to Harvard Business School Online's Business ...
A good strategic plan evolves and shifts as opportunities and threats arise. "Most people think of strategy as an event, but that's not the way the world works," says Harvard Business School Professor Clayton Christensen in the online course Disruptive Strategy. "When we run into unanticipated opportunities and threats, we have to respond.
A strategic plan is more than just a business tool, it also plays a key role in defining operational, cultural, and workplace ethics. Here are some of the key aspects of the importance of strategic planning: 1. Provides a unified goal . A strategic plan is like a unified action plan for the whole company in order to achieve common outcomes.
A strategic plan answers where an established organization is going in the future and how they intend to reach that future state. A strategic plan also focuses on building a sustainable competitive advantage and is futuristic. A business plan is used to assess the viability of a business opportunity and is more tactical.
Putting your strategic plan into practice (our final step) is the key to making it all work during the strategy implementation plan, and getting these details 80% right in a timely fashion is much more important than getting them 100% right in a year. 3. Putting your strategic plan into practice.
Strategic plans bridge the gap from overall direction to specific projects and day-to-day actions that ultimately execute the strategy. Job No. 1 is to know the difference between strategy and strategic plans — and why it matters. Strategy defines the long-term direction of the enterprise. It articulates what the enterprise will do to compete ...
Strategic planning is an organizational activity that aims to achieve a group's goals. The process helps define a company's objectives and investigates both internal and external happenings that might influence the organizational path. Strategic planning also helps identify adjustments that you might need to make to reach your goal.
Determine your priorities and objectives. Define responsibilities. Measure and evaluate results. Each step requires close collaboration as you build a shared vision, strategy for implementation, and system for understanding performance. Related: Learn how to hold an effective strategic planning meeting.
Strategic planning is the ongoing organizational process of using available knowledge to document a business's intended direction. This process is used to prioritize efforts, effectively allocate resources, align shareholders and employees on the organization's goals, and ensure those goals are backed by data and sound reasoning. It's ...
4. Strategic Business Plan. Strategic business plans focus on long-term objectives for your business. They usually cover the first three to five years of operations. This is different from the typical startup business plan which focuses on the first one to three years. The audience for this plan is also primarily internal stakeholders.
Strategic planning is a process in which organizational leaders determine their vision for the future as well as identify their goals and objectives for the organization. The process also includes establishing the sequence in which those goals should fall so that the organization is enabled to reach its stated vision .
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
Focus on the needs of your customers and the value of your business. Here's how: Tip: Download our free one-page business plan template. It provides a simple but effective format to document your business strategy. 1. Know your customers. You shouldn't take action without understanding your customers' needs.
Overcoming Challenges and Pitfalls. Challenge of consensus over clarity. Challenge of who provides input versus who decides. Preparing a long, ambitious, 5 year plan that sits on a shelf. Finding a balance between process and a final product. Communicating and executing the plan. Lack of alignment between mission, action, and finances.
Strategic planning is an organization 's process of defining its strategy or direction, and making decisions on allocating its resources to attain strategic goals. Furthermore, it may also extend to control mechanisms for guiding the implementation of the strategy. Strategic planning became prominent in corporations during the 1960s and remains ...
Strategic planning is a must for every business, big and small. It's a process to figure out where your company is going and how to get there—but it's also so much more. A strategic plan defines who you are as a business and lists concrete actions to achieve your goals. When the unexpected occurs, a strategic plan helps your business ...
Corporate level strategy is a long-range, action-oriented, integrated, and comprehensive plan, which is formulated by the top management of a company. It is very helpful to ascertain business lines, expansion, growth, takeovers and mergers, diversification, integration, and the latest fields for investment.
Strategic planning is a helpful organizational process that, if executed effectively, can increase the likelihood that a company will successfully meet its goals. Additional benefits of strategic planning include: Building consensus and engagement of all stakeholders. Establishing systems of accountability.
An annual strategic business plan should include 8 key sections. Follow these steps to write an effective annual strategic business plan: State information that defines the company. Perform a SWOT analysis. Identify business goals. Identify key performance indicators. Perform and summarize market research. Outline the business marketing plan.
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
Traditional business plans use some combination of these nine sections. Executive summary. Briefly tell your reader what your company is and why it will be successful. Include your mission statement, your product or service, and basic information about your company's leadership team, employees, and location.
Crafting a strategic plan is a fundamental process for any business aiming to navigate the complexities of the market and achieve long-term success. The journey begins with a thorough assessment ...
The strategic framework template simplifies the process by allowing you to define precise objectives and track the progress of three key results associated with each objective. Using this strategic plan template, you can streamline goal management and enhance productivity. 6. General Strategic Plan Template.
President Biden's economic plan is supporting investments and creating good jobs in key sectors that are vital for America's economic future and national security. China's unfair trade ...
Balancing these considerations with each plan type's potential benefits and challenges is crucial. The right choice depends on your company's specific circumstances, including financial health, employee needs, and long-term business strategies. Evaluating these factors will help determine your business's most suitable health insurance option.
Definition. The Agricultural Transition Plan (ATP) outlines the government's strategy for improving agricultural policy following the country's departure from the European Union. What is the Agricultural Transition Plan? This transition plan is a significant shift in how farmers are supported and how agricultural land is managed.