Enterprise Planning: 6 Steps to Creating a Security Plan that Works

Significant events spark change.
Just as the invention of the computer revolutionized technology in the workplace, the COVID-19 virus and its related complications were no exception to this pattern, pushing thousands of companies to embrace remote work. A recent report by Global Workplace Analytics shares that while only 3% of the U.S. workforce worked remotely (at least half the time) before pandemic-related changes, an estimated 25-30% will work from home multiple days a week by the end of 2021.
This overnight evolution brought new security concerns to enterprise organizations. Dispersed teams require increased reliance on technology and mobile IP. Consumers turned to e-commerce and home deliveries over shopping in-store, and those who did unintentionally posed increased security risks as mask mandates made it challenging to identify shoppers and prevent potential theft.
No matter what industry or niche your enterprise services, having a workable security plan in place helps protect your data, products, and team better. Here’s a practical, six-step process to help you ideate, create, and implement the security plan you need to help your senior security officer sleep at night.

1. Analyze Your Security Needs
You can’t protect what you don’t know needs guarding. Before you can start developing, implementing, and measuring the effectiveness of your security plan, you need to understand your business, and the information that needs to be secured, and the associated risks that come from not protecting it.
Know your business
The first step in creating an effective security plan is to understand what products’ or information must be secured. Determining what needs to be protected requires a deep understanding of your enterprise. Where it has been, where it’s going, and where it will be in the future all come into play during the security planning phase as you consider revenue sources, client information, leadership goals, existing IP, expansion plans, and more. Questions like “do you have remote employees who need a secure network connection?“, and ”do your high-value products need better in-person support to keep them safe?“ help identify areas of need.
Assess existing risk
Once you know what your corporate security policy will protect, understanding risk early in the planning process helps establish benchmark metrics for success and set a foundation for additional or expanded goals down the road. A thorough risk assessment gauges how much damage an incident or other unforeseen force could do if and when it occurs. Thinking through these worst-case scenarios helps create a realistic security plan, so you’ll be better equipped to respond when the real threat comes.
2. Make a Security Plan
Once you have an understanding of the data that needs protecting and your current risk, you’re ready to create the policies and procedures that form a well-rounded security plan. The risk assessments conducted during the planning phase are invaluable as you determine the specific areas of risk each policy should address. From remote access and password sharing to in-person fraud prevention, each aspect of your security plays a vital role in either protecting the others or leaving them open to vulnerabilities.
If just one security policy or procedure leaves room for error, you leave your enterprise vulnerable to an overall break or larger incident. No company is too small to be targeted , and according to Forbes, every company likely will be at some point. Some points to consider as you make your security plan:
- Research how other companies in your industry successfully handle sensitive data or inventory.
- Ask questions and get feedback throughout the planning process to prevent unintentional blind spots.
- Work within relevant standards (HIPAA, GLBA, etc.) to ensure compliance.
- Set clear standards for handling sensitive data, IP, brick-and-mortar security, etc.
- Have a security officer designated to support and enforce the policy and conduct audits and corrective action when needed.
- Be open: your security policy will need regular updates as your team grows and compliance changes.
After you’ve developed solid policies to make up your security plan, get it in writing and have all employees sign it after they have completed training. This gives employees a clear point of reference by outlining proper security protocols and provides supporting evidence for correction if a policy is violated.
3. Get People on Board
While your team is your greatest asset and the driving force behind continued success, they can also be your biggest security vulnerability if they don’t understand your security plan and how to follow it. Developing a security-first culture—especially in a fully-remote or hybrid workplace —means focusing less on the tech and infrastructure and more on how you can reinforce team members’ behaviors and habits to best protect your data. Employees often unintentionally place your products or information at risk, from falling for phishing scams and compromising passwords to using employee discounts for too many family members and friends.
These types of accidental violations can be thoroughly mitigated through security awareness training . Learning to create a strong password and set boundaries with purchasing are two great examples. As your policies change or expand, continued education helps keep your security plan optimized by making sure your team is properly trained at all times. Once they’re equipped to handle data safely, they’ll also be more ready to help minimize larger incidents when they inevitably happen.
4. Define and Address Incident Response
Incident response should be a collaborative process—not a defensive, last-resort action like many companies think. Outlining how your enterprise and teams define, assess, and respond to an incident or breach is perhaps the most powerful tool in your security plan arsenal.
Your incident response should answer several important questions:
- How can we best prepare for potential incidents?
- What should breach or incident reporting and assessment look like?
- Who will handle incidents when they happen?
- How can we learn from breaches to prevent future incidents?
Asking—and answering—these questions before an incident occurs not only helps you be more prepared when a breach occurs but can actually lessen the chances of a potential breach or incident occurring.
5. Implement Your Security Plan
You’re ready to put your security plan into action—but even the best security policy will fail without full team support and stellar incident response protocols. The easiest way to help your team follow your security policy? Keep it simple , and make it specific. Clear communication, regular security training, and dedicated security professionals empower your team to keep your data safe.
As you implement your new security policy, keep in mind that new regulations are rarely perfectly enforced—especially at first. No one is perfect, and accidental errors are inevitable. Give your team a grace period and offer warnings and corrections instead of penalties as you learn safer security practices together. Encouraging your team members and thanking them for their efforts to support and enforce your policy are the final steps in making your security plan work.
6. Don’t Go It Alone
You’ve developed, created, and implemented your security plan. But that doesn’t mean your work is done. Partnering with a risk management company to augment and support your IT and security team protects your products, systems, and information today and tomorrow. As your team scales and needs evolve, laying the groundwork for adequate continued security gives you the confidence you need to move forward safely and securely.
At Resolver, our sophisticated, easy-to-use solutions are designed to help your growing enterprise reach new heights. Whether you need improved corporate security, best-in-class risk and compliance, or experienced IT management, Resolver’s technology and data-driven reporting help you drive your business forward. Contact us today to request your demo and see how our solutions can work for you.
Discover Resolver's Software
Incident management software.
Protect your organization and prove your security team’s value with Resolver’s Incident Management application. Improve data capture, increase operational efficiency, and generate actionable insights, so you can stop chasing incidents and start getting ahead of them.
Enterprise Risk Management Software
Provide your organization’s board and senior leaders a top-down, strategic perspective of risks on the horizon. Manage risk holistically and proactively to increase the likelihood your business will achieve its core objectives.
Regulatory Compliance
Save time by monitoring all regulatory compliance activities, providing insights into key risk areas, and then focusing resources on addressing regulatory concerns.
Request a Demo
- I'd like to learn more about
- Enterprise Risk Management
- Incident Management
- IT Compliance
- Investigations Management
- Security Operations Management
- Security Audit
- Loss Prevention
- Brand Protection
- Internal Audit
- Internal Control (SOX)
- Third Party Risk Management
- Threat Assessment
I agree to receive promotional email messages from Resolver Inc about its products and services. I understand I can unsubscribe at any time. By submitting this form you agree to Resolver's Terms Of Service and Privacy Policy.

We value your privacy
Privacy overview.

Researched by Consultants from Top-Tier Management Companies

Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
Top 5 Security Plan Templates with Samples and Examples
Mohammed Sameer
"An ounce of prevention is better than a pound of cure" - Benjamin Franklin
Have you ever thought about how fragile a porcelain vase is? One small jolt and it will shatter into a million pieces, never to be put back together. Like a porcelain vase, a business can be equally delicate and vulnerable to threats if it doesn't have a solid security plan.
Did you know that 60% of small businesses that experience a cyber attack go out of business within six months? That's a staggering statistic, yet many businesses still operate without a comprehensive security plan in place.
To safeguard your business and protect it from potential threats, it's imperative to have a well-thought-out security plan. This is where our Security Plan PPT Templates come into play. The 100% customizable nature of the templates provides you with the desired flexibility to edit your presentations. The content-ready slides give you the much-needed structure.
Our templates are designed to help you develop a comprehensive and effective security plan that takes all the essential elements into account. Download our Security Plan PPT Templates today and protect your business from potential threats.
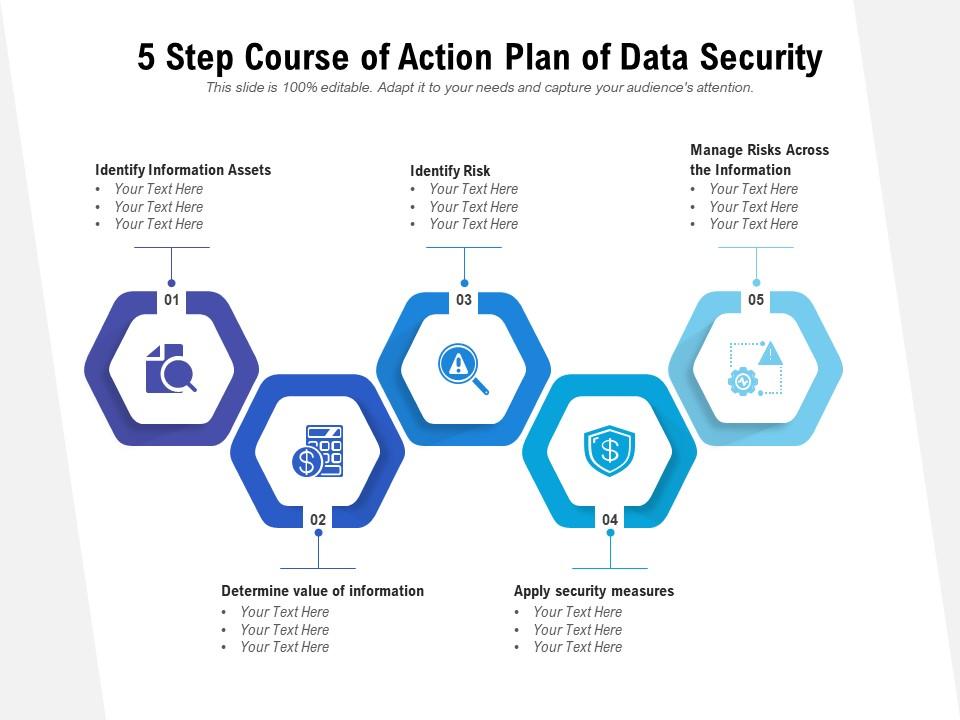
Template 1: 5-Step Course of Action Plan for Data Security PPT Template
Protect your valuable information assets with our PPT Template. In today's digital world, data security is more important than ever. This easy-to-use template breaks down the steps to secure your information into five simple, actionable steps: Identify Information Assets, Determine the Value of Information, Identify Risk, Apply Security Measures, and Manage Risks across the Information. Perfect for businesses and individuals who want to take their data security to the next level, download this slide now and safeguard your information assets!
Download this template
Template 2: Effective Security Monitoring Plan to Eliminate Cyber Threats and Data Breaches Complete Deck
Shield your business from the perils of cyber threats with our comprehensive PPT Layout. Don't let your guard down against ever-evolving cyber threats with our easy-to-use template that outlines the essential components of a security monitoring plan, including key performance indicators (KPIs), elements, challenges, and best practices. Whether you're a small business owner, a government agency, or an individual, our template will help you stay one step ahead of cybercriminals. Say goodbye to worries of data breaches and hello to a secure future with our PPT Preset. Download now!

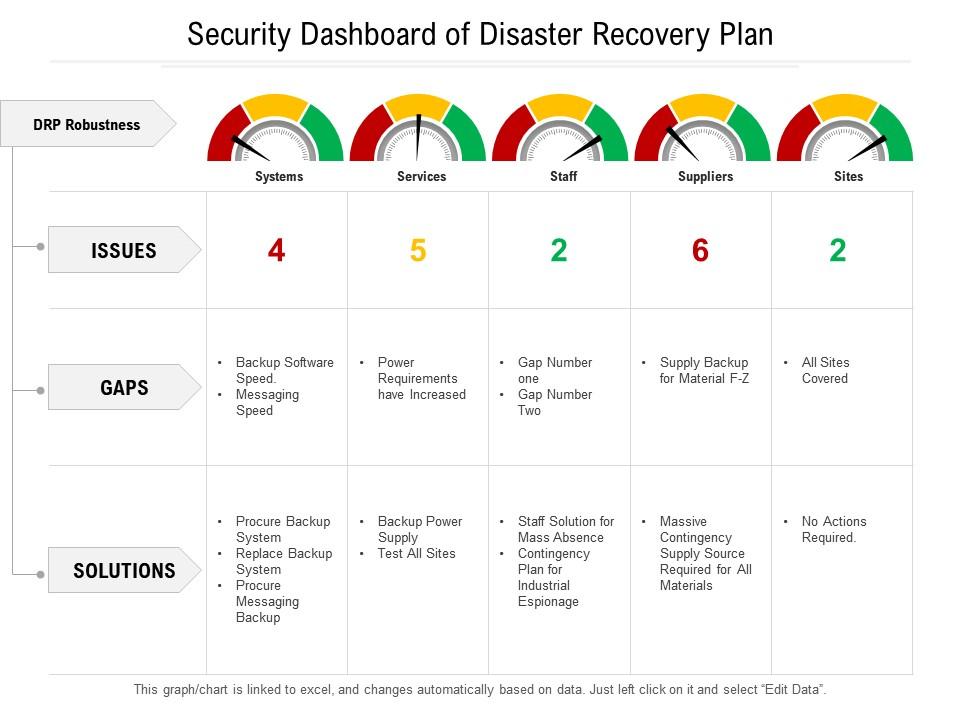
Template 3: Security Dashboard of Disaster Recovery Plan PPT Template
Be prepared for the unexpected with our Security Dashboard PPT Slide. Disasters can strike at any time, leaving behind chaos and destruction. But, with our template, you'll be ready for anything life throws your way. Our comprehensive dashboard highlights the key issues, gaps, and solutions surrounding systems, services, staff, suppliers, and sites to ensure your business stays up and running in the face of adversity. No matter how big your business, our template is the perfect tool to help you be ready for anything. Download now and take control of your disaster recovery plan!
Get this template
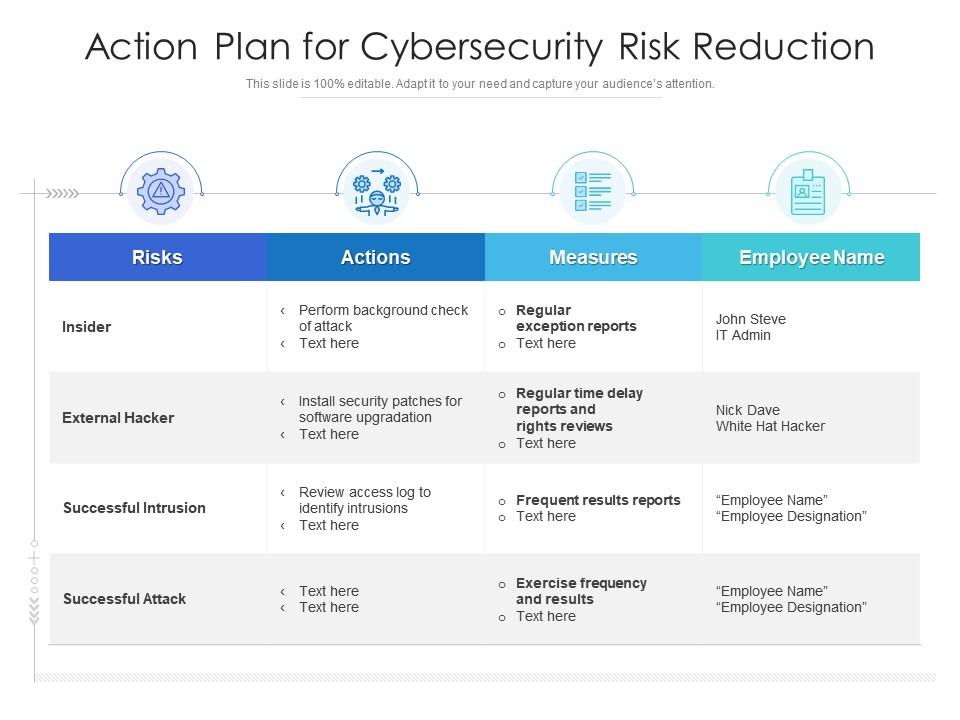
Template 4: Action Plan for Cybersecurity Risk Reduction
Stay protected in the ever-changing digital world with our Action Plan PPT Template. It outlines the major risks, the actions and measures that can be taken against them, and the person responsible for monitoring each risk. Our template is the perfect tool to help reduce your cybersecurity risks and stay protected. Don't wait until it's too late. Download our Risk Reduction PPT Theme now and secure your future!
Template 5: Implementing Security Management Plan to Reduce Threats and Protect Sensitive Company Data PPT Deck
Keep your company's sensitive information safe with our Security Management Plan PPT Template. Data breaches and cyber threats are a major concern for businesses of all sizes. Our comprehensive template outlines the critical success factors of security management, the elements of a successful security management plan, the challenges you may face and ways to overcome them, and a detailed security risk management process and checklist. Download now and take control of your security management plan!

Bonus Security Plan PPT Templates
Template 6: cyber security risk management plan ppt framework.
Unleash the power of unbeatable cyber protection with our Risk Management Plan PPT Template! Are you ready to take your security to the next level and keep your business protected from threats and data breaches? This comprehensive PPT template is your key to building a robust security framework that identifies business environment threats, implements threat awareness training, detects anomalies and incidents, and plans mitigation and recovery strategies. Whether you're a small business owner or a security professional, this template is the perfect tool to help you stay ahead of the game and protect what matters most. Download now and start securing your business today!
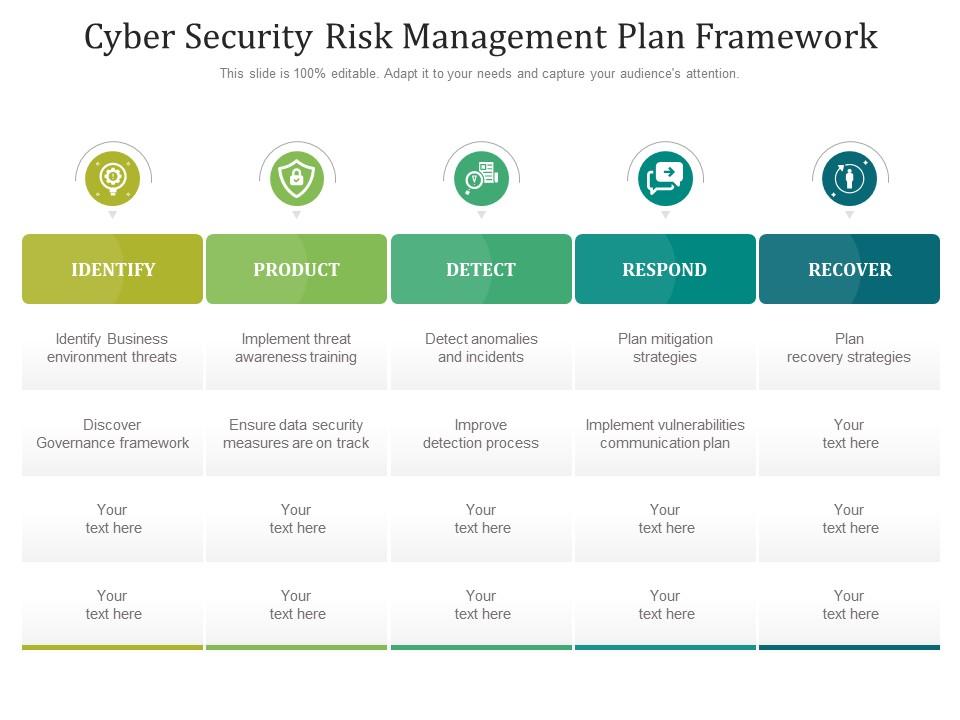
Grab this template
Template 7: Building Organizational Security Strategy Plan PPT Template
Unlock the power of digital protection with our Security Strategy Plan PPT Template! In today's rapidly evolving digital landscape, it's crucial to have a security strategy in place to safeguard your organization from potential threats. Our template provides a comprehensive framework to implement security management, incident management, and corporate governance, develop security centers, and reinforce brand protection, threat protection, and overall security. Don't wait, download now and take control of your organization's security with ease!

Protected and Prosperous: The Key to a Successful Security Plan
A robust security plan protects sensitive information, assets, and individuals. It is a comprehensive and multi-faceted approach that requires a combination of technology, process, and people to be effective. Organizations can significantly reduce the risk of a security breach and the resulting consequences by taking the time to assess the risks, implement the necessary controls, and regularly review and update the plan.
By prioritizing security and making it a core component of your operations, you can maintain the trust of your customers, employees, and stakeholders. Employing our security plan templates is an investment in the future success of your organization.
FAQs on Security Plan Templates
How do you write a security plan.
A security plan is a comprehensive document that outlines the measures an organization will take to protect its assets, information, and individuals. To write a security plan, follow these steps:
- Conduct a risk assessment: Evaluate the organization's vulnerabilities and assess the likelihood and impact of potential threats. It will help determine which areas of the business need the most protection.
- Define objectives and scope: Determine the specific goals of the security plan and the areas it will cover.
- Identify assets : List all the assets that need protection, including physical assets, information, and personnel.
- Develop security controls: Based on the risk assessment results, determine what security controls need to be implemented to protect the assets. These may include access controls, encryption, firewalls, and incident response procedures.
- Write the plan: Put the security plan in writing, including a description of the security controls, who is responsible for implementing them, and how they will be monitored and updated.
- Train personnel: Ensure that all employees are trained on the security plan and understand their role in maintaining the organization's security.
- Test and update: Regularly test and update the security plan to ensure it remains effective and relevant in light of changes to the business or the threat landscape.
What are the five pillars of security?
The five pillars of security refer to the key components that make up a comprehensive security program. These pillars are:
- Access control: This involves managing and controlling who has access to information and assets and how they access them. It includes both physical and logical access controls.
- Network security: This includes measures to protect a network and its components from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction.
- Incident response: This involves having a plan to respond to security incidents, including identifying and containing threats and restoring normal operations.
- Data protection: This involves protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. It includes data encryption, backups, and disaster recovery.
- Identity and access management: This involves managing user identities, granting access to systems and information, and controlling the actions the users can perform within those systems.
What are the five phases of the security life cycle?
The five phases of the security life cycle are a systematic approach to managing and improving an organization's security. The phases are:
- Planning: This involves defining the scope and objectives of the security program, conducting a risk assessment, and developing a security plan.
- Implementation: This involves implementing the security plan, including deploying security controls and training personnel.
- Operations: This involves maintaining and monitoring the security program on an ongoing basis, including reviewing and updating the security plan as needed.
- Assessment: This involves regularly evaluating the effectiveness of the security program and identifying areas for improvement. It may include internal audits, vulnerability assessments, and penetration testing.
- Continuous improvement: This involves making changes to the security program based on the results of the assessments and the evolving threat landscape. It includes updating security controls, processes, and personnel training.
Related posts:
- [Updated 2023] Top 25 Cybersecurity PowerPoint Templates To Safeguard Technology
- Top 20 Cybersecurity Templates to Raise Your Guard Against Online Attacks
- Top 10 Templates to Devise a Data Governance Framework for Your Company
- Top 10 PPT Templates on Data Security to Ace That Presentation
Liked this blog? Please recommend us

Top 10 Cybersecurity Dashboard Templates With Samples and Examples

Must-Have Security Report Templates with Samples and Examples
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA - the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

Digital revolution powerpoint presentation slides

Sales funnel results presentation layouts
3d men joinning circular jigsaw puzzles ppt graphics icons

Business Strategic Planning Template For Organizations Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Future plan powerpoint template slide

Project Management Team Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Brand marketing powerpoint presentation slides

Launching a new service powerpoint presentation with slides go to market

Agenda powerpoint slide show

Four key metrics donut chart with percentage

Engineering and technology ppt inspiration example introduction continuous process improvement

Meet our team representing in circular format


- Why Riot Glass?
- Riot Glass®
- ArmorPlast®
- ArmorPlast® Gen II Series
- ArmorPlast® Gen I Series
- ArmorPlast® IGU Series
Blast Mitigation
- BULLET RESISTANT GLASS
Energy Efficiency
- Forced Entry Resistant Doors & Windows
- HURRICANE WINDOWS & STORM WINDOWS
Sound Attenuation
Commercial buildings, hospitality, religious facilities, retail storefronts.
- Data Sheets
- Rating Charts
- Test Results
AP100-BR-LV2
Ballistic Glazing - UL 752 Level 2
AP125BR-LV6
Ballistic Glazing - UL 752 Level 6
AR Polycarbonate Sheets
Containment and Safety Glazing
Ballistic Glazing - HPW Level A
Ballistic Glazing - UL 752 Level 1
ArmorPlast® Gen I Series
Armorplast® gen ii series, armorplast® igu series.
Ballistic & Forced Entry Grade Sub-framing
Ballistic Glazing UL 752 Level 2
Ballistic Glazing - UL 752 Level 3
Ballistic Glazing - UL 752 Level 4
Ballistic Glazing - UL 752 Level 5
Ballistic Glazing - UL 752 Level 7
Riot Glass® retrofit systems consist of custom-made security glass and framing designs that provide maximum protection against forced entry and ballistic threats.
Forced Entry
Virtually unbreakable retrofit solutions
Bulletproof Protection
Ideal protection against active threats
Hurricane & Windstorm
Great protection against storm damage
Sustainable, reliable and affordable Low-E solutions
Security window film to a complete retrofit
Window glazing ideal for blocking external noise
Riot Glass® can be used to secure any building. Virtually invisible yet nearly indestructible, it blends seamlessly in almost any existing window, door, or storefront.
Converting Commercial Glass Entryway Doors into Unbreakable Glass Security Doors
Exterior security door retrofit options and their benefits, bulletproof glass windows for business protection, does ballistic window film exist, what are the best types of security glass for commercial buildings, a guide to improving security for glass doors in commercial buildings, retailer security: create a safety plan for your small business or retail store.
Written By: Brad Campbell | April 7, 2020
One of the biggest concerns for retailers of all sizes is security. No matter what types of products a retail store sells, it’s vital to have a physical business security plan to prevent theft and keep employees safe.
In 2018, retail stores made a record profit of $6 trillion.
By 2023, due to increased growth, this sector is projected to hit $30 trillion.
Given the importance that retail stores represent for the country’s economy, it only stands to reason that the assets of each one should be well protected.
Check out these stats from the FBI Uniform Crime Reporting Statistics:
- There are around 6.5 million burglaries per year, with 34% of them happening in businesses. That is 2.21 million break-ins!
- The amount of these burglaries resolved by the police?: Only 13%.
- Burglary rates are higher in the summer.
- The most common tools used by intruders are pliers, screwdrivers, pry bars, and little hammers.
- Most of these break-ins are done by amateurs who, out of desperation, will bring about as much destruction as possible. This is actually dangerous.
When a retail store becomes the target of a crime, whether it be shoplifting, armed robbery, or a violent attack, the physical security measures the store has in place make all the difference in how the scenario plays out.
A burglar will avoid a place that is difficult to break in or too risky.
Let’s take a look at some of the best ways you can put a robust security plan for your business to protect your merchandise and employees.
1. Conduct a Threat Assessment
To effectively create a physical security plan for your small business, you have to consider the material risks your business faces.
For example:
Are you most worried about shoplifting?
Burglary?
Armed robbery?
After you’ve decided what your main security concerns are, look at all the areas of your store and any security measures you already have in place to determine how vulnerable your store is to these threats.
2. Have a Working Security System For Your Business

All retail stores should have the security system basics, including surveillance cameras and an alarm system, up and running at all times.
Make sure that cameras are visible to discourage shoplifting and burglary and place decals in shop windows to advertise the fact that the premises are video-monitored and have an active alarm system.
Remember to always set the alarm system when the store is closed so that if someone does try to break in after hours the authorities will be notified.
3. Hire Security Guards to Prevent Retailer Security Breach

If you deal in expensive merchandise or handle large amounts of cash in-store, there should be at least one dedicated security staff member in your business security plan.
Security guards are specifically trained on how to patrol retail stores, monitor customers for suspicious behavior, and react in the event of a retailer security breach.
If you run an ample retail space, it makes sense to employ multiple security personnel to monitor different areas of the store, such as every exit, as well as have a guard monitoring the surveillance footage.
4. Enact Loss Prevention Security Measures

Retail loss prevention refers to a variety of strategies and tactics designed to combat shoplifting. One such measure is to tag items with sensors that go off whenever someone tries to leave the store with an item before paying and getting the sensor tag removed by a cashier.
Another loss prevention tactic is to place the most high-end, expensive items near the cash register or in plain sight of employees.
5. Install Riot Glass Laminated Security Glass

One of the absolute best ways to increase retailer security is to upgrade existing window and door glass with laminated security glass.
Riot Glass is a type of laminated glass that is 5x stronger and 100x stiffer than standard security glass.
Unlike shatter-resistant (but breakable) tempered safety glass, which is commonly used in retail stores, Riot Glass is specifically designed to withstand deliberate forced entry attempts and even ballistic impacts.
Riot Glass can be retrofitted onto almost any existing window, glass storefront, or door glass to fortify the glass against burglary, armed robbery, and active threat scenarios.
Depending on the perceived threats to your retail business, you can choose security glass with different grades of resistance to mitigate your security concerns.
From containment-grade panels that will withstand repeated impacts from burglary tools like hammers and crowbars, to ballistic-grade shields that can resist bullets from high-caliber handguns, there’s a Riot Glass product for every retail security need.
6. Train Employees on Security Procedures
Employees are the ones on the floor responsible for retailer security, so it’s important to ensure that all of your staff members are trained on how to react in different retailer security breach scenarios.
For example, create a plan for how employees should react if they catch someone shoplifting, if there is an armed robbery, or if an active threat scenario is underway. Make sure that everyone knows important information like how to lock down or evacuate the building in an emergency properly.
7. Identify Sensitive Areas in Your Security Plan and Control Access To These Areas
Make a checklist of what those sensitive areas are:
Usually, someone trying to break in to your business will not go for the files. However, the intruder does not know that and will still try to break in. This can cause damage to the critical documents in the file rooms.
Supply Cabinets
Depending on the types of goods you sell, burglars are very likely to target supply cabinets.
Tool Storage
The instruments that you need to complete the work at your business may also be a target of robbers.
Server Rooms
If your business has a server room, you know how critical it is to keep that sensitive area away from potential intruders.
The following are some simple steps you can take to protect these areas better:
- Lock doors to sensitive back-of-building areas like offices and storerooms and control access to them with pass cards, pin codes, or keys.
- Give access only to the employees that need to be in these areas.
- These areas can also be used as hiding places for employees if there is a violent individual on the loose in the store, so they can lock themselves in and wait for help if they are unable to get out of the store.
8. Upgrade Window Locks
Though your windows probably already have some type of window locks, their security can be greatly enhanced by installing new aftermarket locks. For example, pin locks, keyed locks, hinged wedge locks, and sash locks can all make your windows more secure against forced entry.
When used in tandem with security glass, aftermarket window locks will decrease the vulnerability of your windows and deter burglars or other intruders.
9. Light Things Up

In your business security plan, budget for using indoor lights to illuminate hard-to-see areas of your store and leaving some lights on inside at night.
Also, light up the outside of your store and parking areas or garages with light fixtures that turn on at night or install motion-sensing lights. Well-illuminated premises will discourage criminals and make it easier to spot suspicious activity.

Retail businesses have to confront a variety of security threats on a daily basis and are especially popular targets for theft. This is why it’s so essential to improve retailer security by implementing a comprehensive physical security plan for your small or large business.
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to physical retail security, but when you employ some of the methods listed above, you can feel more confident about the safety of your merchandise and employees.
Contact us today to find out more about how you can improve the physical security of your retail business with Riot Glass.

Related Articles
Riot glass® solutions for smash and grab crime, armorplast retrofit ballistic solutions, protecting a herculite® frameless glass door, which level ballistic glass do you need.
HOW CAN WE HELP YOU?
17941 Brookshire Lane Huntington Beach, CA 92647 (800) 580-2303 [email protected]
1661 Glenlake Ave, Itasca, IL 60143
Interested in becoming a dealer? Email us: [email protected]

- Case Studies
- Koorsen Companies
- Koorsen Training Center
- Kasey Program
- Fire Protection
- Communications
- Mobile Equipment Solutions
- Additional Products + Services
- Restaurants
- Property Management
- Hospitality
- Construction
- Koorsen Blog
- Koorsen In The News
- Kasey the Dog Blog
How to Create a Security Plan for Your Business

Businesses in the United States, particularly the small and medium scale, are vital to the economy's growth. As of today, over 56 million jobs in the United States come from these businesses.
Unfortunately, the scale of these businesses makes them a target for theft, vandalism, and other related criminal activities. When these crimes occur, they result in grave losses that could be worth millions of dollars.
To avoid these losses, business owners must develop their security plans to identify their vulnerabilities and make out strategies to keep their companies safe and secure.
This article discusses how you can create a security protection plan to secure all assets in your business.

The Process of Creating a Master Security Plan
A master security plan is a detailed, long-term strategy that entails all the aspects of security operations in an organization. For such programs to be successful, they must be based on two core principles.
First, it must be in line with your business's strategic plans while combining the best principles for protection and support.
For example, if one of your critical business goals is to value customer relationships, your security plan should include customer safety. As such, you would be looking to protect customer records and information both online and offline.
Second, your business security plan will only work well when it inputs all your business's critical stakeholders. All these people will come together to evaluate security risks and develop a documented plan that they would test, implement and maintain over time.
How Do You Evaluate Existing Security Risks?
To evaluate existing security risks, the management has to go through a series of information gathering. Risk evaluation allows you to plan for any risks using the already existing business security layout.
You will need to work with different leaders in your firm, starting with those at the C-suite and then with the HR manager and other key leaders in your organization. You might also have to do an on-site assessment to see the issues on the ground correctly.
You will be looking for records of theft, corruption, hazards, extortions, and any other security challenges. As you explore these challenges, you should also consider their impacts financially and the impacts on people's safety in your environment. You should also consider how much these risks affect your production schedules, delivery, and your company's overall reputation.
To get the most out of the evaluation exercise, you must ask as many questions as possible to get all the needed information.
Addressing the Risks with Security System Tools and Equipment
Understanding the risks alone would not do you any good. Your master security plan must also address the needed tools to combat the security risks you evaluated. The following are some helpful tools.
Video Surveillance
Video surveillance cameras are security tools that allow you to record and collect video footage of activities on your business's premises. In many cases, the police would require the footage from these devices as evidence for prosecution. The footage can also help expedite your claims from insurance companies.
Alarm Systems
Monitored alarm systems are essential tools for the safety of your business. They can be security alarm systems and fire alarm systems , and their job is to notify you and the authorities in cases of emergencies and crimes.
Access Control
Access control refers to pass cards, keys, pin codes, or other security technologies that you can use to secure sensitive areas of your business. Using access control tools, you can limit the number of people who have access to certain areas on your premises.
Staff Training / Monitoring
Training your staff can help reduce the occurrences of crime. The training will cover how they can recognize security threats and deal with them without causing issues for your customers.
Training alone is not enough. You also need to monitor your staff after you have trained them. Aside from the fact that monitoring boosts productivity, it will also reduce the risk of your employees committing crimes.
Contact Koorsen for Your Security Needs!
To learn more about Business Security Plans and how Koorsen Fire & Security can help address security risks, contact your local branch today. At Koorsen Fire & Security, our security experts can help evaluate your business's potential security risks and provide a customized solution to reduce security and safety issues.

Topics: Monitoring , Commercial Security , Small Business Security , Video Surveillance
Contact Us Now!
Disclaimer: The information in this article is for informational purposes only. It is believed to be reliable, but Koorsen Fire & Security assumes no responsibility or liability for any errors or omissions in the content of this article. It does not constitute professional advice. The user of this article or the product(s) is responsible for verifying the information's accuracy from all available sources, including the product manufacturer. The authority having jurisdiction should be contacted for code interpretations.
Related posts

SEARCH OUR BLOG
- There are no suggestions because the search field is empty.
Subscribe to Our Blog
Recent posts.
- Fire Protection (110)
- Commercial Security (105)
- Fire Safety & Security (72)
- Koorsen News (72)
- Fire Extinguisher (59)
- Fire Safety (59)
- Fire Sprinkler Systems (59)
- Fire Alarm Systems (56)
- Inspection/Testing (43)
- Access Control Systems (40)
- Fire Suppression (39)
- Small Business Security (39)
- Kitchen Fire Suppression (35)
- Restaurant Industry (25)
- Video Surveillance (25)
- Fire Training (24)
- Emergency/Exit Lighting (20)
- Education Industry (18)
- Commercial Kitchen (17)
- Monitoring (15)
- Training & Education (15)
- Healthcare Industry (12)
- Property Management Industry (10)
- General (9)
- Nurse Call System (9)
- Kasey Program (8)
- Restaurant (8)
- Education (7)
- Property Management (7)
- Construction Industry (6)
- Emergency Notification (6)
- Fire Pumps (6)
- Koorsen Family Foundation (6)
- Retail Industry (6)
- Mobile Equipment (4)
- Vehicle Fire Suppression (4)
- Engineering (3)
- Hospitality Industry (3)
- Long Term Care (3)
- Podcast (3)
- Bi-Directional Amplifier (2)
- Dry Chem Suppression (2)
- Industrial (2)
- Infographics (2)
- KnoxBox (2)
- Backflow Preventer (1)
- Construction (1)
- Distributed Antenna Systems (1)
- Flame Detection (1)
- Government (1)
- Home Security (1)
- The Joint Commission (1)
- Underground Services (1)
ALL PRODUCTS AND SERVICES
- Fire Extinguishers
- General Fire Products
- Emergency/Exit Lighting
- Fire Alarm Systems
- Fire Sprinkler Systems
- Kitchen Fire Suppression
- Fire Suppression Systems
- Commercial Security
- Emergency Notification
- Home Security
- Nurse Call Systems
OTHER COMPANIES
- KOORSEN ENVIRONMENTAL
- KOORSEN FACILITIES MANAGEMENT
CONTACT KOORSEN
866-311-7753
- KOORSEN CAREERS
- MEDIA RELATIONS
- TRANSPARENCY IN COVERAGE
© 2024 Koorsen Fire & Security | PRIVACY POLICY

Cyber Security Plan Template

What is a Cyber Security Plan?
A cyber security plan is a structured approach to protecting an organization's data, systems, and networks from malicious cyber threats. It outlines the processes, procedures, and technologies in place to protect the organization's digital assets from unauthorized access, theft, and malicious damage. It also outlines the steps to take in the event of a security breach.
What's included in this Cyber Security Plan template?
- 3 focus areas
- 6 objectives
Each focus area has its own objectives, projects, and KPIs to ensure that the strategy is comprehensive and effective.
Who is the Cyber Security Plan template for?
The Cyber Security Plan template is designed to help IT security teams in organizations of all sizes and industries create a cyber security plan company-wide. It provides a comprehensive structure to define objectives, set measurable targets (KPIs), and implement related projects to achieve those objectives.
1. Define clear examples of your focus areas
A focus area is a broad topic that you want to address in your security plan. Examples of focus areas include increasing cyber security, reducing data loss, and strengthening authentication.
2. Think about the objectives that could fall under that focus area
Objectives are the goals that you want to achieve within each focus area. They should be well-defined and measurable to ensure that the security plan is effective and trackable. Examples of some objectives for the focus area of Increase Cyber Security could be: Develop organizational cyber security plan, and Implement security protocols.
3. Set measurable targets (KPIs) to tackle the objective
Key performance indicators (KPIs) are the metrics that you will use to measure progress towards objectives. They should be relevant, measurable, and achievable in order to ensure successful completion of objectives. An example of a KPI for the focus area of Increase Cyber Security could be: Increase security assessment score from 65/100 to 90/100.
4. Implement related projects to achieve the KPIs
Projects (actions) are the steps that need to be taken to achieve objectives. Each project should have a defined timeline and a designated person responsible for its completion. An example of a project related to Increase Cyber Security could be: Conduct security assessment.
5. Utilize Cascade Strategy Execution Platform to see faster results from your strategy
Cascade is a strategy execution platform that helps organizations stay on track with their strategic plans. It helps teams visualize goals, track progress, and identify areas of improvement to increase efficiency and effectiveness.
Creating a comprehensive cyber security plan template for small businesses: A step-by-step guide for protecting your business from cyber attacks

A cyber attack is disastrous for businesses. This is even more true for small businesses without the proper security strategies in place.
Luckily, you can protect your business from unwanted threats with a cyber security plan template for small business success.
Keep reading to learn about the importance of strong cyber security practices and find out how you can create your own plan.
What is a cyber security plan template for small business?
A cyber security plan template for small business outlines everything you need to protect your business from cyber security threats.
Our research indicates that any effective cyber security plan includes both preventative and reactionary measures for cyber-attacks and breaches.
What is the purpose of the cyber security plan template for small business?
There are many reasons behind a cyber security plan template for small businesses. As per our expertise, preparing against security threats is crucial to reduce risk as your company grows.
In general, a cyber security plan takes three factors into account.
- Technologies: Downloading protection software for your devices.
- Processes: Educating your team and enforcing security policies.
- Access controls: Segmenting your business information, and giving access to only those who need it.
Focusing on these three factors, a cyber security template clarifies the different kinds of security risks you need in order to protect your company.
Why you need a cyber security plan
Every day, your team relies on business data to keep operations moving. This includes:
- Customer information.
- Financial data.
- Sales history.
If you lose this data to a cyber security breach, you risk losing your business.
Unfortunately, no business is immune to cyber security threats! Our findings show that even organizations at the forefront of their industry have fallen victim to this.
But it’s a lesser known fact that small and medium businesses are the prime targets for cyber attacks.
“43% of cyber attacks target small businesses.” – Cybint , 2022.
A cyber security strategy is your first line of defense against these attacks. A complete security plan prevents cyber attacks, and provides quick solutions when required.
Based on our firsthand experience, the more secure your organization, the more trust customers have in your product or service. And more trust leads to more sales .
For example, companies with log-in websites often implement two-factor authentication for their users. This adds an additional level of security, as it requires more than just a password for access to your system.
Without proper security procedures, both your physical computers and online accounts are at risk of security breaches. And through our practical knowledge, if you don’t take advantage of antivirus resources, for example, entire operating systems can crash on you.
Usually, companies that thrive in cybersecurity have systems in place that prevent and solve security issues. And drawing from our experience, you can achieve both with an incident response plan.
Planning for the worst saves you time and stress. More importantly, it clarifies exactly what actions you need to take in the event of an emergency.
The more concise your plan, the better your business will be at handling cybersecurity responsibilities.
Local network security devices like firewalls are key in filtering the connection between your private network and the public Internet.
Encryption of sensitive files on your computer, or within applications, is another key factor to consider. Any file or program that contains customer data is important to protect.
Let’s take a look at the cyber threats that can affect your business below.
Common cyber threats for small businesses
Of course, one of the requirements for creating a cyber security plan template for small business protection is to understand your business’ risk.
To identify your possible vulnerabilities, you need to know what threats are out there. Our research indicates that these are the most common cyber security threats for small businesses.
Malware attacks
Malware is the biggest cyber threat for small businesses today.
The term itself is broad and refers to all categories of malicious software meant to harm devices or networks.
Three common types of malware attacks include:
- Ransomware.
Let’s dive deeper into each one.
In short, a virus is a piece of computer code meant to harm your technological equipment. Computer viruses affect your devices in many ways, including:
- Corrupting or deleting files.
- Damaging computer programs.
- Slowing down device performance.
- Causing excessive pop-up windows.
In your cyber security plan template for small business, there are several benefits to highlighting the signs when a device has become infected with a virus.
What’s more is that there are several ways that your devices can catch a virus, such as:
- File sharing.
- Downloading harmful software.
- Infected emails.
Viruses used to be the only cyber threat that businesses worried about, but cyber security has evolved and now includes other attack strategies.
Ransomware attacks
Ransomware is malware where hackers access your data and hold it for ransom by encrypting it. You then pay them to decrypt your data and regain access.
So, if your business experiences a ransomware attack, your products or services provided will likely come to a screeching halt.
A surprising statistic:
“Ransomware is the third most popular type of malware used in data breaches.” – Verizon , 2020.
Our findings show that this will do more than just affect your numbers. Depending on the information that the hacker gathers, a ransomware attack can be tragic for your small business. It could cost you everything to pay off the hacker.
Unfortunately, even if you comply with the hacker, there’s a chance that they won’t keep up their end of the deal. They may ask for additional payments, or cut communications once they have what they want.
Spyware is a type of malware that collects information from your device without your knowledge. Based on our observations, it’s difficult to detect, and many people never know that they’ve been subject to a spyware attack!
With spyware, cyber criminals can not only oversee your business operations. Data privacy and data security become a pipe dream as well.
Since it’s invisible, once spyware has been downloaded to a device, there is little you can do to restore your network security.
One of the most common ways spyware hackers install spyware is through phishing emails.
Phishing scams
Unlike the other attacks on this list, phishing isn’t software. Phishing is a technique used to gather sensitive information through deception.
The act of convincing someone to disclose information to a hacker is called social engineering.
The most common case of phishing involves sending emails with links that lead to a website infected with malware. These scams can affect consumers and businesses alike.
A common social engineering strategy is to trick recipients to reply to emails with personal information by pretending to be a credible source, such as a colleague.
Our findings show that cyber criminals often claim to have management roles in the businesses they target. A similar strategy involves impersonating a company that has a strong reputation.
As per our expertise, it’s important to include strategies to prevent phishing attacks in your cyber security plan template, most of which surrounds employee education (more on this later).
The state of your cybersecurity hinges on making a plan. Let’s jump into how to create a cyber security plan for small business.
How to create your business cyber security plan
Creating a security plan requires you to look at your current business processes to figure out your vulnerabilities.
From there, you can put together a plan to eliminate those vulnerabilities and reduce your risk.
You might think as a relatively unknown “small biz” that you’re safe against cyberattacks. In reality, it’s small business cybersecurity that cybercriminals target most. This is because a small organization tends to have much weaker cyber security than a larger enterprise.
It’s a good idea to use a cyber security plan template for small business through this process. Through our practical knowledge, templates for your business’ cybersecurity plan are useful tools as they eliminate internal confusion over protocols and best practices.
To guide you, here are 5 key steps to creating your plan.
1. Identify your biggest threats
Of course, drawing from our experience, protecting your company from cyber threats requires more than just filling out a planner.
Creating a cyber security plan is similar to setting your sales goals . For example, both involve taking every aspect of your business into account.
You can’t create a line of defense if you don’t know what you need defending from.
This is why the first step in creating a cyber security plan for small business is to understand your business risk.
The most common threats for small businesses include:
- Ransomware.
- Weak passwords.
Our research indicates that identifying your risks helps you find ways to prevent these risks from happening. This includes solutions, such as:
- Antivirus software.
- Newer devices with updated security features (i.e., fingerprint scanning).
- Password parameters.
If you have an IT team, this is a job for them. If not, consult an IT professional to identify your exposure and create a plan.
2. Prioritize your assets
Cyber security asset assessment involves identifying your IT assets and potential security risks. Your assets include traditional devices as well as digital assets.
Here are some examples of common business assets to consider:
- PCs and mobile devices.
- Networks and servers.
- Cloud-based data.
In reality, any part of your IT infrastructure is at risk of cyber security threats, so be sure to create a comprehensive list.
From there, decide which assets are the most important. That way you can determine the most vulnerable ones to begin creating your security plan.
3. Set your goals
The goal of your security plan is to protect your small business. However, several smaller goals play into this larger objective.
In a perfect world, creating a plan to prevent cyber attacks, and including a network security device like a firewall, would be enough. However, solely relying on prevention is unrealistic.
As much as you try to prevent cyber security attacks, there’s always a risk of cyber attackers getting through your defense. So, as per our expertise, your goals should also include optimal readiness to respond to threats.
If you’ve already made the plans to handle unauthorized users in your system, then you’ll greatly reduce the amount of damage they can do.
Of course, malware detection is the first step once your cybersecurity is breached. So planning the ways to detect threats is as important as planning how to deal with them.
Better yet, our research indicates that you should have a goal for your recovery time to minimize your exposure and damage to your assets.
4. Document your plan
Once you’ve determined your current cyber security risks and created a business plan to improve your response readiness, it’s time to document your plan.
Based on our firsthand experience, documenting is easy if you use a cyber security plan template for small business, as you just have to fill in the sections in the template.
There are several reasons why documenting cybersecurity plans is important.
For starters, you don’t want anything to slip through cracks when it comes to a cyber security plan for small business. It only takes one small slip-up for a hacker to access your information.
Thoroughly documenting your plan minimizes the risk of overlooking an aspect of your business, and removes the possibility for any intrusion into it.
Sometimes, you’ll have conversations with your customers that are difficult . But nothing’s harder than explaining that your cyber security has been compromised. A well-documented plan softens the blow and reduces a breach’s impact.
What’s more, employee training plays a huge part in your cyber security strategy. So, document your plan in a way that’s easy to understand.
5. Do a test run
Once you have the proper cyber security infrastructure in place that your employees are trained on, test your plan.
Don’t forget to test your employees’ ability to recognize threats by sending test phishing emails. You can also simulate a ransomware attack through encryption of your own files.
It’s important to note that cyber security is always evolving. Once you confirm that your new plan works, set up a schedule to conduct regular tests to ensure up to date strategies.
Now that you know how to create your plan, let’s explore what to include in your template.
What to include in your cyber security plan template for small business
Making a cyber security strategy is no small task. There are two points to remember about your plan:
- It’s a document your team regularly references.
- The security of your business depends on it.
Organizations that acknowledge these points always have the most robust security strategy, making them the most cyber secure. To address these two factors, you want to ensure that you include as much detail in your plan as possible.
Using a cyber security plan template for small business simplifies the process and ensures that your plan captures every aspect of your business.
Since this plan will be included in the core employee resources of your organization, a template ensures that you’ve covered all your bases in a way that’s still easy to follow.
Here’s what to include in your template.
Your objectives
To kick things off, your cyber security plan for small business protection should open with your goals.
Your goals guide your plan, so clearly stating them at the start gives context to your proposed strategies.
As a result, the reader sees the bigger picture and better understands the importance of cyber security strategies.
Common threats
To fully understand your cyber security strategies, you need to outline your business’ security threats.
Make sure that your plan describes each threat to your business. This means associating each common threat with an asset.
For example, one common threat to small business security is password hacking, and one of the assets at risk is your company’s data. Knowing this, you can strengthen your employee passwords to prevent data breach.
Identifying threats specific to your business is a crucial step in protecting your staff and your customers from cyber attacks.
Security policies
Cyber security policies serve as the framework of your plan.
Policies outline how you expect your team to protect your business assets. Some basic security practices include:
- Limiting who accesses information.
- Restricting internet browsing on your network.
- Implementing a plan of action for suspicious emails.
There are also companies that offer products or services, like antivirus software to ward off security threats.
Your security policies are mainly preventative, so you should consider how to react to security breaches.
Breach response plan
Prevention is the best tool to protect your business, but it shouldn’t be your only tool. If your business does become the victim of a cyber attack, you should have a plan of how you’ll react.
When unauthorized users infiltrate your business systems, panic sets in. It becomes difficult to think clearly and act accordingly.
Without an established breach response plan, you’ll lack the tools to quickly restore your business.
A breach response process allows you to identify an attack and shut it down as soon as possible. This reduces damage to your business data and ensures that you’re back up and running in no time.
Your breach response plan should include clear steps and a timeline of how long you have to shut down an attack before your business is at risk.
Employee education plan
You can have the tightest cyber security policies in place, but if your employees don’t know them, your business is still exposed.
So, it’s important to implement a system that educates your employees. A cyber security plan for small business isn’t complete without employee training.
To be successful, your employees need to be up to speed on your business’ cyber risks and security policies. Design a cyber security training program to walk your employees through these.
A complete employee education plan results in your employees:
- Creating strong passwords.
- Recognizing phishing emails.
- Resisting other social engineering techniques.
- Knowing what to do if they accidentally disclose information.
Highlight your training plan in your cyber security plan template for small business.
For best results, conduct a cyber security training at least once a year and test employees’ knowledge monthly.
Wrap up: Cyber security plan template for small business success
The truth is that if you don’t have a solid cyber security plan for small business, you risk losing your business completely.
With this in mind, it’s important to prioritize cyber security policies and implement them into your business process. The applications of this plan will guarantee longevity for your business.
The key content of a complete plan includes:
- Clear goals.
- Potential threats.
- Security policies.
- A breach response plan.
- Employee training.
The health of your cyber security depends on these five factors for a number of reasons. Establishing each of these now means that you can quickly shut down unauthorized user or activities within your business down the road.
The quality of your product or service means nothing if your cyber system is unsecure.
With the support of a template, your cybersecurity plan is clear, concise, and comprehensive. It allows you to draft and organize all the content that your plan requires.
Free cyber security plan template for small businesses
Protect your business from cyber attacks by drafting a robust cyber security plan.
If you don’t see the download form, download template here .
Brush up on other technology trends for your small business in this blog !
Cyber security plan template for small business FAQs
How do i implement a cyber security plan for small business.
To implement a cyber security plan for your small business, the most important step is educating your employees. Once your plan has been created, the hard part is done.
Make your cyber security plan customary and accessible so that your employees know about your business’ strategies in the event of a cyber threat.
If you’re unfortunate enough to experience a cyber threat, remind your staff of your plan– then follow each step closely.
How do I choose the right cyber security products for my small business?
To choose the right cyber security products for your small business, first identify all your company’s potential cyber threats. Once those are established, there are many security products to choose from.
There is not a one-size-fits all solution to cyber security. You can choose which products suit your needs, but it’s important to note that you can never be too secure.
Many cyber security companies offer free trials, so consider experimenting with different products to find the perfect fit for your business.
Where can I find a cyber security plan template for small business?
For a comprehensive cyber security plan template for small businesses plus more, simply:
- Follow this link .
- Fill out your business’ basic information.
- Click download.
Keep your data more secure with a free trial of Method:CRM.
Image credit: cottonbro via Pexels .
About The Author
Shana Cesaire
Related posts.

3 ways you win with QuickBooks mobile access

Conference Travel Tips to Get You There Energized
Streamline your business with method.
Start your free trial — no credit card, no contract.
Business growth
Business tips
9 cybersecurity tips to protect your business
An easy-to-implement plan for small business owners and employees to protect against cyberattacks.

When launching my business, I certainly didn't pay much attention to security. It wasn't because I didn't care about it—I just wasn't aware of how common and devastating cyberattacks could be. But now that I'm part of the small business community, I see it happening everywhere. It's not uncommon for me to see comments on Facebook groups from people who've recently started a blog for their business saying they got hacked.
Cyberattacks cost your business time and money, and if sensitive information about your customers gets out, it could also ruin your reputation.
One of the simplest ways to avoid cyberattacks is to make sure each individual at the business is taking steps to help—especially if the majority of employees are working remotely .
The tips here are mostly to protect your computer and software. If your business runs on WordPress, here are some free WordPress security plugins to help protect your website.
Common types of cyberattacks
Before I show you what I do to secure my infrastructure, I want to quickly go over some of the most common attacks small businesses face.
Phishing . These are emails pretending to be from your bank, internet service provider, or other places that aren't who they say they are. They typically want you to click a link so they can gather some type of personal information from you.
RAT. A Remote Access Trojan allows attackers to access your computer's camera and microphone, and install other types of malware.
Keylogger. This one records everything you type on your keyboard (terrifying enough for you?), and it's often used to steal passwords and credit card details.
Shoulder surfing. This is when attackers gather personal or private information by simply looking at your screen.
Malware attack. Malware is any kind of malicious software meant to harm or exploit a device, service, or network. It's an umbrella term, and it includes things like viruses, Trojans, worms, ransomware, and more.
Man-in-the-Middle attack. A MitM attack intercepts the communication between you and the server. For example, if you wanted to log in to your bank account, the attacker would receive your login information and then send it to the bank, the bank would then send the response to the attacker, and the attacker would send it back to you. This is very common when connecting to public Wi-Fi.
What each team member can do to secure small business infrastructure
Each business will need different security measures , but there are a few things employees can do on their own to help. Send this list to the rest of your team, add it to your standard operating procedures , and make sure that everyone on the team is following these best practices.
1. Don't leave your computer unattended
One of the coffee shops I frequent the most to do my work doesn't have a restroom inside. So in order to answer nature's call, I have to leave the coffee shop, walk over to the building next to it, and go up to the third floor.
This means that anyone wanting to take a peek at my computer, install malware, or simply steal it, would have plenty of time to do it. To prevent any of these things from happening, I just put my laptop inside a sleeve and take it with me.
Since it's a small coffee shop, it's pretty easy to lose my spot, so I typically leave my backpack on top of my chair and my headphones on the table. Obviously, I don't keep anything of value inside the backpack (it's often empty) in case someone decides to take it.
I know that not leaving your belongings unattended might sound obvious, but I see it happening almost every time I go to the coffee shop. Even if it's just for a minute or two, that's enough time for someone to download malware or steal your laptop. Just take your stuff with you—it's not worth the risk.
2. Use a VPN when connecting to public Wi-Fi
A few years ago, I used to travel a lot for work, which meant I had to connect to many unsecured Wi-Fi networks in airports and hotels. The issue with these types of networks is that hackers can position themselves between you and the connection point—Man-in-the-Middle attacks.
So instead of your data going directly to the hotspot, it goes to the hacker, who then sends it to the hotspot. This gives them access to anything you send over the internet, which could be emails, bank statements, credit card information, your website's login information, the list goes on. Basically, they can access your systems as if they were you.
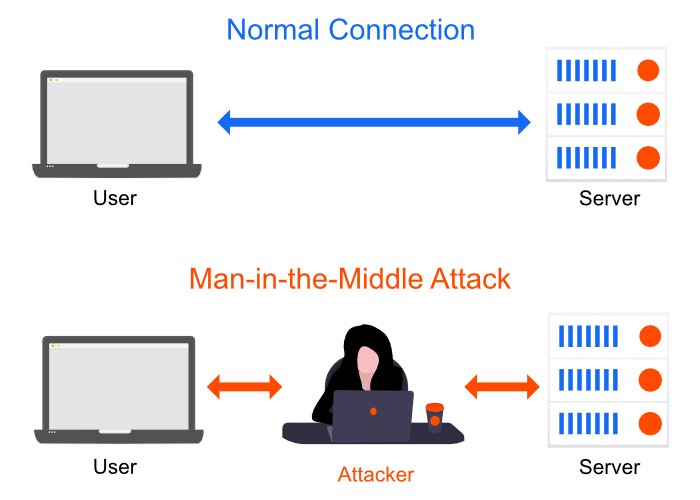
Other common things hackers do with these types of unsecured connections are distributing malware and creating fake connecting points to connect to.
To protect myself from these attacks when connecting to public Wi-Fi, I use a virtual private network (VPN) called CyberGhost. One of the things a VPN does is encrypt your data traffic, so that even if an attacker gets their hands on it, they won't be able to decipher it because it'll show as a bunch of gibberish to them. Since hackers typically go for easy targets, once they see that you have a VPN set up, they'll simply skip you and go on to the next victim who isn't protecting their data.
3. Use a privacy screen
One thing I saw a lot when traveling was people opening up their laptops in the airplane rows in front of me and working on what was obviously sensitive information. If I'd been interested in learning more about their jobs or stealing their information, I could have easily done it.
If I could see other people's screens, that meant they could see mine. So to prevent people from shoulder surfing me, I use a privacy screen. It's essentially a piece of plastic you put on your laptop screen that allows only someone directly in front of the computer to see what's going on. Anyone looking from the sides will see a completely black screen.
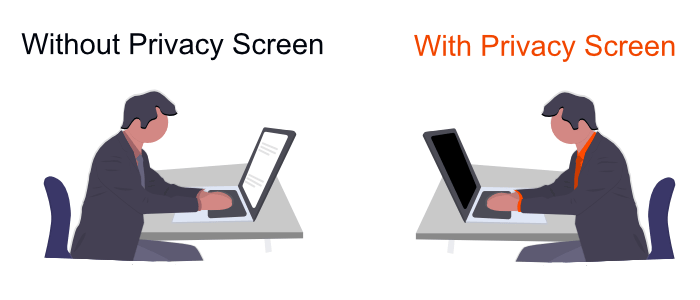
There are plenty of privacy screen brands you can get online, but the brands I've liked the most are SightPro and Akamai. I've tried super cheap ones as well, but they always ended up deteriorating fairly quickly. I guess it's true what they say: "Buy nice or buy twice."
4. Don't click on unknown links
I'm also very wary of clicking on links in emails. A lot of people think that as long as they don't download anything, they'll be safe. But even clicking a bad link can cause your computer to get infected. And while sometimes they're easy to spot, spammers are getting pretty good at disguising their links to make you think they're legitimate.
Here's an example of an email I received pretending to be from Norton AntiVirus, but it was actually redirecting me to a different website:
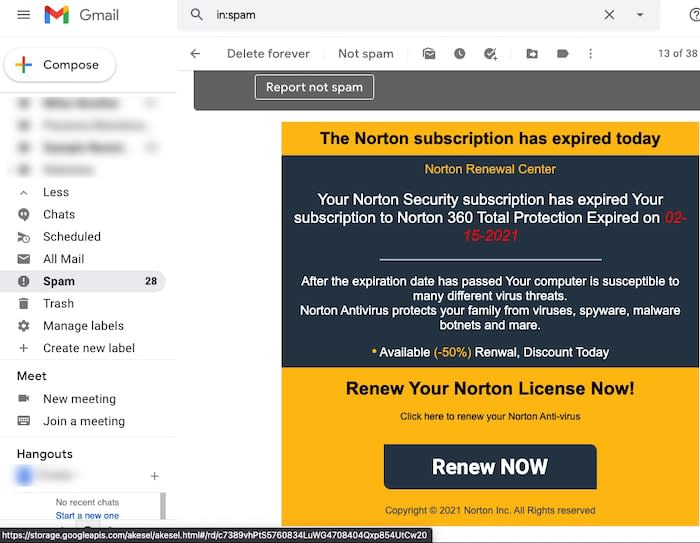
Sure, it's not the best ripoff of Norton branding, but if I were doing a quick email cleanup, I might not notice. So, before clicking a link, no matter who it's from, I always hover over it to see where it actually goes. The real website is typically shown at the bottom-left corner of the browser screen, as you can see in the image above.
I also get the occasional spam comment with weird links on my website. Clicking any one of those unknown links could deploy various types of malware, such as RAT, keylogger, and botnets. If you're bombarded with spam comments, you can block them using a plugin like Akismet. Another option (and the one I use) is to copy this list of common strings used by spammers to automatically send those comments to the trash.
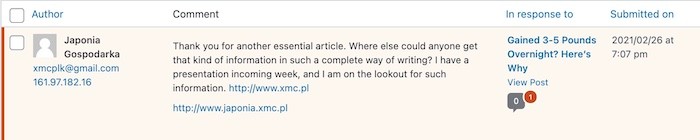
Simply copy all the strings on that list, and then go to your WordPress dashboard > Settings > Discussion > Disallowed Comments Keys > paste the strings > Save Changes.
5. Keep everything up-to-date
Apps seem to require updates all the time, which can seem annoying. But those updates contain important fixes to known vulnerabilities that hackers can exploit to install malware, steal your data, or do any other type of harm to your system.
You can automate the process of keeping things up-to-date. Here's how to enable automatic updates on the two most popular operating systems:
How to enable automatic updates on macOS
Open the App Store > Click App Store on the top menu > Preferences > tick the Automatic Updates box.
How to enable automatic updates on Windows
Open the Microsoft Store > click the three dots on the upper-right corner > Settings > App updates > turn on Update apps automatically.
While you're at it, it's worth doing the same on your phone.
6. Use full-disk encryption
As a small business owner, I have lots of private information on my computer, including banking information, business plans, account numbers, taxes, client data, and more. Having someone access some of this information, especially my clients' data, could seriously damage my business and reputation—not to mention the harm it would do to the client.
If your business stores things like personal health information (PHI) from your clients, and this information gets revealed, you could face huge fines and even jail time for allowing the breach. The HIPAA and FINRA regulations are justifiably strict.
Without full-disk encryption, if someone steals your laptop, they can access the data on your drive, even if you have a password protecting your login: they can simply remove the drive and install it on another computer. With full-disk encryption, they won't be able to see anything that's inside the drive since it'll all be encrypted.
Both macOS and Windows come with free full-disk encryption, which should be enabled by default. However, if yours isn't enabled, you can follow these steps.
How to enable full-disk encryption on macOS
If you're using macOS, then FileVault is the program you want to activate. To do this, click the Apple logo on the top-left corner > System Preferences… > Security & Privacy.
Then, click the FileVault tab > Click on the lock icon at the bottom-left of the window > enter your password > Click Turn On FileVault.
How to enable full-disk encryption on Windows
If you're using Windows, click on the Start button > Settings > Update & Security > Device encryption > click on Turn on.
7. Create regular backups
Creating regular backups is a good way of preventing ransomware, a type of malware that holds your data hostage by encrypting it and demands a payment to release the data back to you. If you make regular backups of your data, you can simply wipe your computer, reset it to factory settings, and restore your data from the backup.
I like keeping my backups in an external hard drive instead of the cloud . While it's not as convenient as simply connecting to the cloud and uploading your files, it keeps everything in a secure off-site location.
I typically create backups every month, but if you're constantly creating important information, you can do them weekly or daily. My favorite brand for external hard drives is Western Digital (WD), but Samsung also makes good options.
How to create backups on macOS
To create backups, I like using macOS' built-in backup tool called Time Machine. The cool thing about it is that, once I plug in my hard drive, it works automatically in the background. It continuously saves copies of all my files, apps, and any other important information and excludes useless files in the trash, cache files, and logs.
To use Time Machine, plug in your external drive > go to System Preferences > Time Machine > toggle the switch to On > Select Disk… > select the drive you want to use.
In order to use the drive, it needs to be formatted as macOS Extended (journaled). If yours isn't, Time Machine will ask if you want to reformat it, which will erase all the existing files on it.
How to create backups on Windows
Windows' built-in backup tool is called File History. To start backing up data on Windows, connect your external drive > click Start > Settings > Update & Security > Backup > Add a drive > select the external drive where you want to store the backups.
8. Use strong passwords
Growing up, I used to use the same password for everything. To be honest, I still use it, but only for accounts that don't really matter—like the email account I use to sign up for random newsletters to get coupons and discounts from stores.
When it comes to things like my website, laptop, bank accounts, email, and other products that require me to add more personal information, I go ahead and create longer and more difficult passwords that include mixed characters like numbers and symbols.
But now I've reached a point where I have too many accounts, so keeping track of all of the passwords is a nightmare. To create and store complex passwords, I use the free version of a password management tool called LastPass (you can compare it to the other popular option, 1Password, using Zapier's password manager showdown ). It has an autofill option that automatically fills usernames and passwords when visiting websites, so you don't have to copy/paste them.
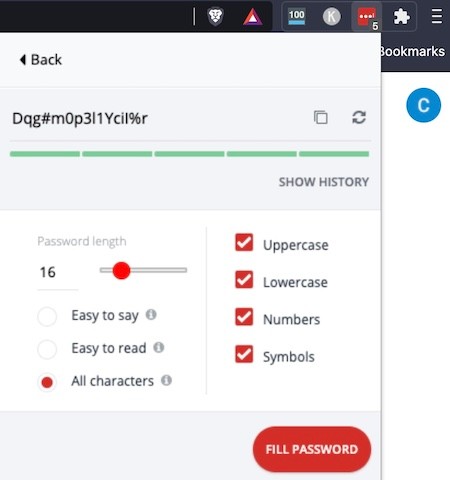
Besides keeping everything secure on LastPass, I also like keeping a hard copy of my passwords in a safe place at home, just in case something happens to LastPass or I don't have access to it. If you do write your passwords on a sheet of paper, make sure that you place them in a secure place—i.e., not behind your computer monitor or under the desk.
If you don't want to install the LastPass extension but want to create strong passwords , you can just use the free password generator tool on their website.
9. Use two-factor authentication (2FA)
Two-factor authentication (2FA) means you need to verify your identity in two unique ways before you can access a website or app.
For example, if you enable 2FA for your email account, once you enter your username and password, you'll be asked to enter a unique one-time access code sent to your phone via text or an authenticator app like Microsoft Authenticator, which is the one I use.
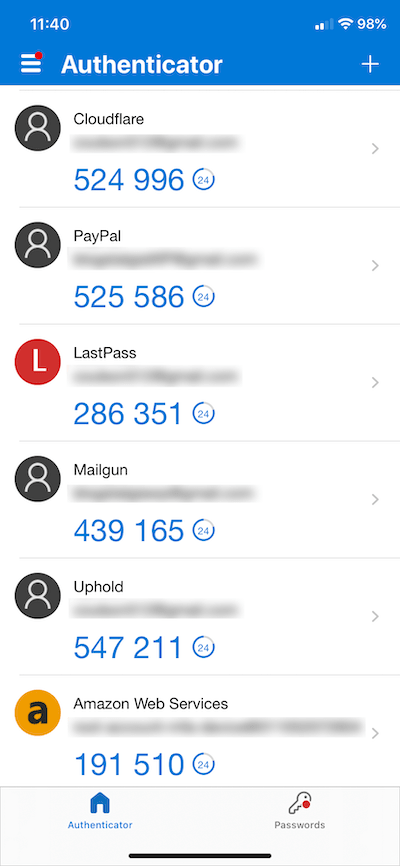
So, even if someone knows your email and password, they won't be able to access the system without your phone.
If I'm completely honest, I dislike using two-factor authentication. My issue with it is that I have so many accounts it becomes a little annoying having to go to my phone and verify my identity every time I want to log in.
Still, I'd rather be safe than sorry, so I enable it for important accounts, such as my bank accounts, emails, and websites. If you have online accounts with important information that support two-factor authentication, I recommend enabling it.
If everyone on your team follows these relatively simple steps, it'll add a massive layer of protection against cybercriminals. After all, cyberattackers (usually) want easy targets, so simply by not being one, you're decreasing your risk.
Get productivity tips delivered straight to your inbox
We’ll email you 1-3 times per week—and never share your information.
Christian Coulson
Christian is an industrial engineer with a background in programming who's used his knowledge and experience to grow 7Sigma Physiques—his fitness coaching business and blog with thousands of monthly readers. He now teaches other entrepreneurs how to scale their business at blogstalgia.com.
- Small business
Related articles

11 management styles, plus tips for applying each type
11 management styles, plus tips for applying...
Keep your company adaptable with automation
How to enrich lead data for personalized outreach
How to enrich lead data for personalized...
What is a proof of concept? And how to write one (with template)
What is a proof of concept? And how to write...
Improve your productivity automatically. Use Zapier to get your apps working together.

- Security Agreement
- Security Analyst
- Security Architect
- Security Brochure
- Security Company
- Security Consultant
- Security Guard
- Security Guard Service
- Security ID Card
- Security Letter
- Security Letterhead
- Security Management
- Security Management Plan
- Security Manager
Security Plan Templates
Every Business Organization Should Have Risk Management and Contingency Planning in Case of Sudden Unexpected Events. Improve the Security Position of Your Company or Organization with Help from Template.net’s Free Security Plan Templates. Download Professionally Written Strategic and Operational Security Plan Samples for Your IT Network, Buildings, Events, Schools, and More. All Templates Are Available for Immediate Use After Downloading.
Get Access to All Plan Templates
- Security Manager Cover Letter
- Security Manager Resume
- Security Officer
- Security Officer Cover Letter
- Security Officer Resume
- Security Plan
- Security Policy
- Security Report
- Security Resume
- Security Roadmap
- Security Service
- Security Supervisor
- Security White Paper
A security plan is essential to any establishment. Be it a building, school, construction, church, business, office, airport, warehouse, or hospital, this will make sure that everything is secured and in place. If you need to make a security plan then good news for you as Template.net offers templates that will help you in making one without any hassle.
We have a wide variety of Security Plan Templates to choose from. These templates will serve as your outline in making your own security plan. They are already complete with a well-crafted layout and suggestive content so all you have to do is choose the best template that suits your preference. Edit it right away as our templates are highly editable to give you the freedom in customizing them. You can use our built-in editor tool and take advantage of using the design elements to match your purpose fittingly. After making the necessary changes, save them and download them in any available format that you want. An added edge of our templates is they are accessible and can be edited using the device of your choice. That’s how convenient our templates are!
So stop thinking twice about using our templates because these are written and designed by our team of industry professionals! With our editable and printable templates, you will surely have your security plan finished in no time. Save a considerable amount of time and get these templates today! Check out our other products that you can use alongside security plans such as healthcare plans , incident plans , and property plans . Subscribe to our templates now!

Cyber Security Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky

Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 500 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans to start and grow their cyber security companies.
If you’re unfamiliar with creating a cyber security business plan, you may think creating one will be a time-consuming and frustrating process. For most entrepreneurs it is, but for you, it won’t be since we’re here to help. We have the experience, resources, and knowledge to help you create a great business plan.
In this article, you will learn some background information on why business planning is important. Then, you will learn how to write a cyber security business plan step-by-step so you can create your plan today.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here >
What is a Cyber Security Business Plan?
A business plan provides a snapshot of your cyber security business as it stands today, and lays out your growth plan for the next five years. It explains your business goals and your strategies for reaching them. It also includes market research to support your plans.
Why You Need a Business Plan for a Cyber Security Company
If you’re looking to start a cyber security business or grow your existing cyber security company, you need a business plan. A business plan will help you raise funding, if needed, and plan out the growth of your cyber security business to improve your chances of success. Your cyber security business plan is a living document that should be updated annually as your company grows and changes.
Sources of Funding for cyber security Businesses
With regard to funding, the main sources of funding for a cyber security business are personal savings, credit cards, bank loans, and angel investors. When it comes to bank loans, banks will want to review your business plan and gain confidence that you will be able to repay your loan and interest. To acquire this confidence, the loan officer will not only want to ensure that your financials are reasonable, but they will also want to see a professional plan. Such a plan will give them the confidence that you can successfully and professionally operate a business. Personal savings and bank loans are the most common funding paths for cyber security companies.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
How to write a business plan for a cyber security business.
If you want to start a cyber security business or expand your current one, you need a business plan. The guide below details the necessary information for how to write each essential component of your cyber security business plan.
Executive Summary
Your executive summary provides an introduction to your business plan, but it is normally the last section you write because it provides a summary of each key section of your plan.
The goal of your executive summary is to quickly engage the reader. Explain to them the kind of cyber security business you are running and the status. For example, are you a startup, do you have a cyber security business that you would like to grow, or are you operating a chain of cyber security businesses?
Next, provide an overview of each of the subsequent sections of your plan.
- Give a brief overview of the cyber security industry.
- Discuss the type of cyber security business you are operating.
- Detail your direct competitors. Give an overview of your target customers.
- Provide a snapshot of your marketing strategy. Identify the key members of your team.
- Offer an overview of your financial plan.
Company Overview
In your company overview, you will detail the type of cyber security business you are operating.
For example, you might specialize in one of the following types of cyber security businesses:
- Remote security center services : This type of cyber security is focused on providing comprehensive security for networks and devices remotely from a main control center.
- Cloud security services . As more businesses turn to storage in cloud platforms, this type of service protects the data of clients from being utilized by others in that platform.
- Vulnerability scan & management: This service screens client devices and network systems remotely on a monthly maintenance basis.
- Endpoint security services: This service is dedicated to the mobile and end user devices in corporate offices; protection for computers is not included.
In addition to explaining the type of cyber security business you will operate, the company overview needs to provide background on the business.
Include answers to questions such as:
- When and why did you start the business?
- What milestones have you achieved to date? Milestones could include the number of security breaches determined, the amount of revenue earned, or reaching X number of clients served, etc.
- Your legal business Are you incorporated as an S-Corp? An LLC? A sole proprietorship? Explain your legal structure here.
Industry Analysis
In your industry or market analysis, you need to provide an overview of the cyber security industry.
While this may seem unnecessary, it serves multiple purposes.
First, researching the cyber security industry educates you. It helps you understand the market in which you are operating.
Secondly, market research can improve your marketing strategy, particularly if your analysis identifies market trends.
The third reason is to prove to readers that you are an expert in your industry. By conducting the research and presenting it in your plan, you achieve just that.
The following questions should be answered in the industry analysis section of your cyber security business plan:
- How big is the cyber security industry (in dollars)?
- Is the market declining or increasing?
- Who are the key competitors in the market?
- Who are the key suppliers in the market?
- What trends are affecting the industry?
- What is the industry’s growth forecast over the next 5 – 10 years?
- What is the relevant market size? That is, how big is the potential target market for your cyber security business? You can extrapolate such a figure by assessing the size of the market in the entire country and then applying that figure to your local population.
Customer Analysis
The customer analysis section of your cyber security business plan must detail the customers you serve and/or expect to serve.
The following are examples of customer segments: government contractors, for-profit corporations, securities businesses, private security services, and individuals.
As you can imagine, the customer segment(s) you choose will have a great impact on the type of cyber security business you operate. Clearly, government contractors would respond to different marketing promotions than individuals, for example.
Try to break out your target customers in terms of their demographic and psychographic profiles. With regards to demographics, including a discussion of the ages, genders, locations, and income levels of the potential customers you seek to serve.
Psychographic profiles explain the wants and needs of your target customers. The more you can recognize and define these needs, the better you will do in attracting and retaining your customers.
Finish Your Cyber Security Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Competitive Analysis
Your competitive analysis should identify the indirect and direct competitors your business faces and then focus on the latter.
Direct competitors are other cyber security businesses.
Indirect competitors are other options that customers have to purchase from that aren’t directly competing with your product or service. Software companies, home or office hardware, and remote alarm services may be examples of indirect competitors. You will want to mention any direct competition, as well.
For each direct competitor, provide an overview of their business and document their strengths and weaknesses. Unless you once worked at your competitors’ businesses, it will be impossible to know everything about them. But you should be able to find out key things about them such as
- What types of customers do they serve?
- What type of cyber security business are they?
- What is their pricing (premium, low, etc.)?
- What are they good at?
- What are their weaknesses?
With regard to the last two questions, think about your answers from the customers’ perspective. And, don’t be afraid to ask your competitors’ customers what they like most and least about them.
The final part of your competitive analysis section is to document your areas of competitive advantage. For example:
- Will you provide discounts for major government contractors?
- Will you offer scan protection and management that your competition doesn’t?
- Will you provide better customer service?
- Will you offer better pricing?
Think about ways you will outperform your competition and document them in this section of your plan.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
Marketing plan.
Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P’s: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For a cyber security business plan, your marketing strategy should include the following:
Product : In the product section, you should reiterate the type of cyber security company that you documented in your company overview. Then, detail the specific products or services you will be offering. For example, will you provide in-person and remote cyber security services for major corporations or will you offer compliance solutions for select clients?
Price : Document the prices you will offer and how they compare to your competitors. Essentially in the product and price sub-sections of your plan, you are presenting the products and/or services you offer and their prices.
Place : Place refers to the site of your cyber security company. Document where your company is situated and mention how the site will impact your success. For example, is your cyber security business located in a professional business district, a quiet corporate area, a standalone building or a remote, unnamed location? Discuss how your site might be the ideal location for your customers.
Promotions : The final part of your cyber security marketing plan is where you will document how you will drive potential customers to your location(s). The following are some promotional methods you might consider:
- Advertise in trade magazines
- Reach out to websites
- Engage in email marketing
- Advertise on social media platforms
- Improve the SEO (search engine optimization) on your website for targeted keywords
Operations Plan
While the earlier sections of your business plan explained your goals, your operations plan describes how you will meet them. Your operations plan should have two distinct sections as follows.
Everyday short-term processes include all of the tasks involved in running your cyber security business, including answering calls, planning and providing scan management, responding to emergency situations, billing clients and assisting with computer equipment, etc.
Long-term goals are the milestones you hope to achieve. These could include the dates when you expect to book your Xth client, or when you hope to reach $X in revenue. It could also be when you expect to expand your cyber security business to a new city.
Management Team
To demonstrate your cyber security business’ potential to succeed, a strong management team is essential. Highlight your key players’ backgrounds, emphasizing those skills and experiences that prove their ability to grow a company.
Ideally, you and/or your team members have direct experience in managing cyber security businesses. If so, highlight this experience and expertise. But also highlight any experience that you think will help your business succeed.
If your team is lacking, consider assembling an advisory board. An advisory board would include 2 to 8 individuals who would act as mentors to your business. They would help answer questions and provide strategic guidance. If needed, look for advisory board members with experience in managing a cyber security business or successfully running a data management business.
Financial Plan
Your financial plan should include your 5-year financial statement broken out both monthly or quarterly for the first year and then annually. Your financial statements include your income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statements.
Income Statement
An income statement is more commonly called a Profit and Loss statement or P&L. It shows your revenue and then subtracts your costs to show whether you turned a profit or not.
In developing your income statement, you need to devise assumptions. For example, will you increase customer retention by 20% quarterly, offer reduced pricing for hardware maintenance contracts, or offer discounted packaged pricing for multiple services? And will sales grow by 2% or 10% per year? As you can imagine, your choice of assumptions will greatly impact the financial forecasts for your business. As much as possible, conduct research to try to root your assumptions in reality.

Balance Sheets
Balance sheets show your assets and liabilities. While balance sheets can include much information, try to simplify them to the key items you need to know about. For instance, if you spend $50,000 on building out your cyber security business, this will not give you immediate profits. Rather it is an asset that will hopefully help you generate profits for years to come. Likewise, if a lender writes you a check for $50,000, you don’t need to pay it back immediately. Rather, that is a liability you will pay back over time.
Cash Flow Statement
Your cash flow statement will help determine how much money you need to start or grow your business, and ensure you never run out of money. What most entrepreneurs and business owners don’t realize is that you can turn a profit but run out of money and go bankrupt.
When creating your Income Statement and Balance Sheets be sure to include several of the key costs needed in starting or growing a cyber security business:
- Cost of computer and software equipment
- Payroll or salaries paid to staff
- Business insurance
- Other start-up expenses (if you’re a new business) like legal expenses, permits, furnishings and travel expenses
Attach your full financial projections in the appendix of your plan along with any supporting documents that make your plan more compelling. For example, you might include the cyber security credentials of the CEO and COO or a list of client contracts.
Writing a business plan for your cyber security business is a worthwhile endeavor. If you follow the template above, by the time you are done, you will truly be an expert. You will understand the cyber security industry, your competition, and your customers. You will develop a marketing strategy and will understand what it takes to launch and grow a successful cyber security business.
Cyber Security Business Plan FAQs
What is the easiest way to complete my cyber security business plan.
Growthink's Ultimate Business Plan Template allows you to quickly and easily write your cyber security company business plan.
How Do You Start a Cyber Security Business?
Starting a Cyber Security business is easy with these 14 steps:
- Choose the Name for Your Cyber Security Business
- Create Your Cyber Security Business Plan
- Choose the Legal Structure for Your Cyber Security Business
- Secure Startup Funding for Your Cyber Security Business (If Needed)
- Secure a Location for Your Business
- Register Your Cyber Security Business with the IRS
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Get the Required Business Licenses and Permits
- Get Business Insurance for Your Cyber Security Business
- Buy or Lease the Right Cyber Security Business Equipment
- Develop Your Cyber Security Business Marketing Materials
- Purchase and Setup the Software Needed to Run Your Cyber Security Business
- Open for Business
Where Can I Download a Free Business Plan Template PDF?
Click here to download the pdf version of our basic business plan template.
Our free business plan template pdf allows you to see the key sections to complete in your plan and the key questions that each must answer. The business plan pdf will definitely get you started in the right direction.
We do offer a premium version of our business plan template. Click here to learn more about it. The premium version includes numerous features allowing you to quickly and easily create a professional business plan. Its most touted feature is its financial projections template which allows you to simply enter your estimated sales and growth rates, and it automatically calculates your complete five-year financial projections including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. Here’s the link to our Ultimate Business Plan Template.
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your Cyber Security business plan?
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success.
Click here to see how a Growthink business planning consultant can create your business plan for you.
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates

Upmetrics AI Assistant: Simplifying Business Planning through AI-Powered Insights. Learn How
Entrepreneurs & Small Business
Accelerators & Incubators
Business Consultants & Advisors
Educators & Business Schools
Students & Scholars
AI Business Plan Generator
Financial Forecasting
AI Assistance
Ai Pitch Deck Generator
Strategic Planning
See How Upmetrics Works →
- Sample Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Customer Success Stories
Business Plan Course
Small Business Tools
Strategic Planning Templates
E-books, Guides & More
- Sample Business Plans
Security Agency Business Plan
If you are planning to start a new security agency business, the first thing you will need is a business plan. Use our sample security company business plan created using upmetrics business plan software to start writing your business plan in no time.
Before you start writing your business plan for your new security company, spend as much time as you can reading through some examples of services-related business plans .
Reading sample business plans will give you a good idea of what you’re aiming for and also it will show you the different sections that different entrepreneurs include and the language they use to write about themselves and their business plans.
We have created this sample Security Company Business Plan for you to get a good idea about how perfect a security agency business plan should look and what details you will need to include in your stunning business plan.
Security Agency Business Plan Outline
This is the standard security agency business plan outline which will cover all important sections that you should include in your business plan.
- Business Overview
- Vision & Mission Statement
- Business Objectives
- Corporate Philosophy
- Business Model
- Our Core Values
- 3 Year profit forecast
- Company Resources
- Demography Analysis Of Los Angels, California
- Risks And Risk Mitigation Process
- Company Ownership
- Legal Status
- Our services
- Industry Overview
- System Insights
- End-Use Insights
- Service Insights
- Regional Insights
- Industry Keynote: The Business Side: Policies, Costs, And Compliance
- The Threat Of New Entry
- Competitive Rivalry
- Buyer Power
- Supplier Power
- Threat Of Substitution
- Opportunities
- Our Competitive Advantages
- Marketing Plan
- Marketing & Communication Execution Recommendations
- Marketing Objectives
- Growth Strategy
- Expansion Strategy
- Contingency Plan
- Future Goals
- Average Salary of Employees
- Important Assumptions
- Brake-even Analysis
- Profit Yearly
- Gross Margin Yearly
- Projected Cash Flow
- Projected Balance Sheet
- Business Ratios
Say goodbye to boring templates
Build your business plan faster and easier with AI
Plans starting from $7/month

After getting started with Upmetrics , you can copy this sample business plan into your business plan and modify the required information and download your security agency business plan pdf and doc file. It’s the fastest and easiest way to start writing your business plan.
Download a sample security agency business plan
Need help writing your business plan from scratch? Here you go; download our free security agency business plan pdf to start.
It’s a modern business plan template specifically designed for your security agency business. Use the example business plan as a guide for writing your own.
Related Posts
Cyber Security Business Plan
Law Firm Business Plan
Crafting Business Plan Presentation
10 Best Business Plan Software
About the Author
Upmetrics Team
Upmetrics is the #1 business planning software that helps entrepreneurs and business owners create investment-ready business plans using AI. We regularly share business planning insights on our blog. Check out the Upmetrics blog for such interesting reads. Read more
Plan your business in the shortest time possible
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Popular Templates

Create a great Business Plan with great price.
- 400+ Business plan templates & examples
- AI Assistance & step by step guidance
- 4.8 Star rating on Trustpilot
Streamline your business planning process with Upmetrics .

Security Company Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Security Company Business Plan
You’ve come to the right place to create your Security Company business plan.
We have helped over 5,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans and many have used them to start or grow their Security Companies.
Below is a template to help you create each section of your Security Company business plan.
Executive Summary
Business overview.
KB Security is a new security company located in San Antonio, Texas. KB Security provides security professionals to local establishments that need protection for their business or assets. We train our professionals for numerous situations so they are prepared for any security job. This includes anything from theft prevention to handling crisis situations. Whatever our clients’ concerns are, they can rest assured that they have hired the best security professionals in the San Antonio area.
KB Security is founded by Keith Baldwin, who has been a security professional for ten years. He has worked both as a professional security guard and as a certified trainer. In addition to his experience, he also holds an MBA. Keith’s combination of experience and education have given him the knowledge and skills to run a successful security company.
Product Offering
KB Security provides security professionals that can help businesses with all their security and surveillance needs. These can include but are not limited to:
- Protecting individuals
- Guarding property
- Preventing theft
- Helping with crisis situations
Businesses can sign up with one of our flexible contract programs when hiring our security services. We also offer a discounted trial period for those who are considering a long-term contract and want to test out our services before signing.
Customer Focus
KB Security will target local businesses, government organizations, and individuals located in San Antonio who need to hire security professionals. We expect most of our clients to be retail establishments who need help with theft prevention and guarding property and assets.
Management Team
KB Security is founded by Keith Baldwin, who has been a security professional for ten years. He has worked both as a professional security guard and as a certified trainer and received an MBA from the University of Texas. Keith’s education and experience has given him all the essential skills to run his dream security company. However, he will also hire other administrative staff to help him with the essential day-to-day functions.
Success Factors
KB Security will be able to achieve success by offering the following competitive advantages:
- Expert Security Professionals: KB Security only hires the best security professionals that have extensive training in security protocols.
- Location: KB Security is in a prime location, giving us quick and easy access to prime commercial districts. This is ideal especially when hired to handle crisis situations or alarm response.
- Affordable Pricing: The services offered by KB Security are similar in quality to its most premium-positioned competitors but are offered at a more affordable price.
- Management: Our management team has years of security and business experience that allows us to market to and serve customers in a much more sophisticated manner than our competitors.
Financial Highlights
KB Security is seeking a total funding of $300,000 of debt capital to open its office. The funding will be dedicated towards securing the office space and the office build-out. Funding will also be dedicated towards three months of overhead costs to include payroll of the staff, rent, and working capital. The breakout of the funding is below:
- Office design/build: $100,000
- Three months of overhead expenses (payroll, rent, utilities): $100,000
- Marketing & advertising: $50,000
- Working capital: $50,000
The following graph below outlines the pro forma financial projections for KB Security.
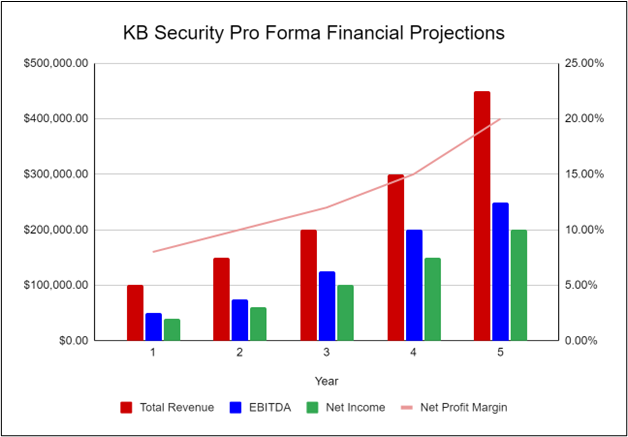
Company Overview
Who is kb security.
KB Security is founded by Keith Baldwin, who has been a security professional for ten years. He has worked both as a professional security guard and as a certified trainer. In addition to his experience, he also holds an MBA. Keith’s combination of experience and education have given him the knowledge and skills to run a successful security company.
KB Security’s History
After surveying the local customer base, and finding a potential office location, Keith Baldwin incorporated KB Security as an S-Corporation on May 1st, 2023.
Currently, the business is being run out of Keith’s home office, but once the lease on KB Security’s location is finalized, all operations will be run from there.
Since incorporation, KB Security has achieved the following milestones:
- Found a commercial space and signed a Letter of Intent to lease it
- Developed the company’s name, logo, social media accounts, and website
- Began networking with some of the area’s largest companies to understand their security needs
- Began recruiting key employees
KB Security’s Services
Businesses can sign up with one of our flexible contract programs when hiring our security services. We also offer a discounted trial period for those who are considering a long-term contract and want to test out our services before signing.
Industry Analysis
With increasing illegal events, terrorism, and fraudulent activities happening all around the world, the demand for professional security is greater than ever. Every establishment needs some form of security, whether it be in the form of security professionals or in the form of cybersecurity. As the world continues to navigate its violent challenges, security professionals will be needed to protect important assets and respond to crisis situations.
The security industry has transformed substantially to meet this demand. In addition to hiring security professionals, many businesses also invest in security tech such as cameras, motion sensors, and software. Security companies that offer a mix of security personnel and technology can provide their clients extensive and tight-knit security options that puts their clients’ minds at ease.
According to research, the security industry is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 8% over the next 10 years. This is substantial growth, which shows just how essential the industry will be in the coming decade. Businesses like KB Security will continue to be in high demand and very profitable.
Customer Analysis
Demographic profile of target market.
The demographics for San Antonio, Texas are as follows:
Customer Segmentation
We will primarily target the following customer segments:
- Individuals
- Local businesses
- Government organizations
Competitive Analysis
Direct and indirect competitors.
KB Security will face competition from other companies with similar business profiles. A description of each competitor company is below.
Sky High Security
Sky High Security is a security company that was established in 2002. It provides a large team of security professionals specifically trained to protect high-value assets, such as museum collections and expensive jewelry. Their services include providing in-person officers as well as high-tech surveillance equipment.
Prime Security
Founded in 2003, Prime Security is the best security company in town for those looking for guard and patrol services. Prime Security aims to protect establishments and offer patrols to deter any unwanted visitors. The company has been highly successful and is the largest security company in the region.
First Responders Security
First Responders Security is the most popular security company for those who have more complex security concerns. They offer a wide range of services, including alarm response, theft prevention, and patrolling. Instead of hiring several companies to do several jobs, companies can depend on First Responders Security to manage all of their security concerns.
Competitive Advantage
KB Security will be able to offer the following advantages over their competition:
Marketing Plan
Brand & value proposition.
KB Security will offer the unique value proposition to its clientele:
- Professional security services
- Flexible contracts and a trial period
- Great security services at moderate rates
- Excellent customer service
Promotions Strategy
The promotions strategy for KB Security is as follows:
KB Security understands that the best promotion comes from satisfied customers. The company will encourage its clients to refer other businesses by providing economic or financial incentives for every new client produced. This strategy will increase in effectiveness after the business has already been established.
Social Media
KB Security will invest heavily in a social media advertising campaign. The brand manager will create the company’s social media accounts and invest in ads on all social media platforms. It will use targeted marketing to appeal to the target demographics.
Website/SEO
KB Security will invest heavily in developing a professional website that displays all of the features and benefits of KB Security. It will also invest heavily in SEO so that the brand’s website will appear at the top of search engine results.
Direct Mail
KB Security will blanket businesses with direct mail pieces. These pieces will provide general information on KB Security, offer discounts, and/or provide other incentives for companies to use our services.
KB Security’s pricing will be on par with competitors so clients feel they receive great value when hiring our security services.
Operations Plan
The following will be the operations plan for KB Security.
Operation Functions:
- KB Security will be owned and operated by Keith Baldwin. Keith will oversee the general operations of the company.
- Keith is joined by Jeffrey Liebowitz, who will oversee all financial and accounting aspects of the business, such as accounts payable and receivable, payroll, budgeting, forecasting, and cash flow analysis. Jeffrey will also manage all tax obligations and licensing for KB Security.
- Keith is also joined by Felicia Monroe, who will oversee all marketing and communications for the business. She will handle all in-client calls, appointments, networking, and follow-up. She will manage all advertising aspects with flyers, emails, social media, and the SEO process.
- Keith will hire an Administrative Assistant to help him with general administrative and operations tasks.
- Keith will also hire an extensive staff of security professionals that will help his clients with their security needs. He will also provide these professionals with training as necessary.
Milestones:
KB Security will have the following milestones completed in the next six months.
- 8/1/202X – Finalize contract to lease office space.
- 9/1/202X – Begin build-out and design of staffing agency office.
- 10/1/202X – Begin social media and website advertising campaign.
- 11/1/202X – Attend large industry networking events.
- 12/1/202X – Hire key employees.
- 1/1/202X – Grand opening of KB Security.
Financial Plan
Key revenue & costs.
KB Security’s revenues will come primarily from charging clients for its security services. Depending on the contract in place, KB Security may charge an hourly fee per professional working for the client or a flat fee per month.
The office lease, equipment, supplies, and labor expenses will be the key cost drivers of KB Security. Ongoing marketing expenditures are also notable cost drivers for KB Security, especially in the first few years as the company establishes itself in the market.
Funding Requirements and Use of Funds
Key assumptions.
The following outlines the key assumptions required in order to achieve the revenue and cost numbers in the financials and pay off the startup business loan.
- Year 5: 110
- Office Lease per Year: $100,000
Financial Projections
Income statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement, security company business plan faqs, what is a security company business plan.
A security company business plan is a plan to start and/or grow your security company business. Among other things, it outlines your business concept, identifies your target customers, presents your marketing plan and details your financial projections.
You can easily complete your Security Company business plan using our Security Company Business Plan Template here .
What are the Main Types of Security Company Businesses?
There are a number of different kinds of security company businesses , some examples include: Crisis management, Security guards, Surveillance company, and Security patrol.
How Do You Get Funding for Your Security Company Business Plan?
Security Companies are often funded through small business loans. Personal savings, credit card financing and angel investors are also popular forms of funding.
What are the Steps To Start a Security Company Business?
Starting a security company business can be an exciting endeavor. Having a clear roadmap of the steps to start a business will help you stay focused on your goals and get started faster.
1. Develop A Security Company Business Plan - The first step in starting a business is to create a detailed security company business plan that outlines all aspects of the venture. This should include potential market size and target customers, the services or products you will offer, pricing strategies and a detailed financial forecast.
2. Choose Your Legal Structure - It's important to select an appropriate legal entity for your security company business. This could be a limited liability company (LLC), corporation, partnership, or sole proprietorship. Each type has its own benefits and drawbacks so it’s important to do research and choose wisely so that your security company business is in compliance with local laws.
3. Register Your Security Company Business - Once you have chosen a legal structure, the next step is to register your security company business with the government or state where you’re operating from. This includes obtaining licenses and permits as required by federal, state, and local laws.
4. Identify Financing Options - It’s likely that you’ll need some capital to start your security company business, so take some time to identify what financing options are available such as bank loans, investor funding, grants, or crowdfunding platforms.
5. Choose a Location - Whether you plan on operating out of a physical location or not, you should always have an idea of where you’ll be based should it become necessary in the future as well as what kind of space would be suitable for your operations.
6. Hire Employees - There are several ways to find qualified employees including job boards like LinkedIn or Indeed as well as hiring agencies if needed – depending on what type of employees you need it might also be more effective to reach out directly through networking events.
7. Acquire Necessary Security Company Equipment & Supplies - In order to start your security company business, you'll need to purchase all of the necessary equipment and supplies to run a successful operation.
8. Market & Promote Your Business - Once you have all the necessary pieces in place, it’s time to start promoting and marketing your security company business. This includes creating a website, utilizing social media platforms like Facebook or Twitter, and having an effective Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategy. You should also consider traditional marketing techniques such as radio or print advertising.
Learn more about how to start a successful security company :
- How to Start a Security Company
BreachSight
Vendor risk, trust exchange, product features, vendor risk assessments, security questionnaires.
- Security Ratings
Data Leaks Detection
- Integrations
AI Autofill
- Financial Services
eBooks, Reports, & more
Third-party risk management policy template (free).

Leah Sadoian
Organizations commonly rely on third parties such as vendors , suppliers, and other business partners to handle critical operations. While third-party relationships can provide many benefits, they also introduce a range of risks that can threaten data security , compliance, and business continuity. Therefore, it's crucial to recognize and manage these risks with a robust Third-Party Risk Management policy .
A third-party risk management policy is a set of guidelines that helps organizations manage risks associated with third-party sources such as vendors, suppliers, contractors, and service providers. This policy provides a clear structure for an organization’s TPRM program , including guidelines for different vendor situations throughout the entire third-party lifecycle.
This blog explains TPRM policies, their key components, and why your organization should implement one. Included is a free TPRM policy template that provides a structured approach to document and address the risks associated with third-party relationships , which your organization can customize to its specific TPRM goals.
Check out how UpGuard makes third-party risk management a breeze >
What is a third-party risk management policy?
A third-party risk management policy is a set of guidelines and procedures an organization adopts to manage its third-party risk management program . This program includes identifying, evaluating, and mitigating any risks associated with third parties such as vendors , suppliers, contractors, and service providers.
This policy safeguards the organization from potential adverse impacts that may arise from these third-party relationships, such as data breaches , compliance violations, operational failures, and harm to the organization's reputation.
While third-party risk management involves various risks, it is primarily a term used in relation to third-party cybersecurity risk management. This type of risk management involves assessing the vendor's security controls, monitoring their activities, and implementing measures to reduce the risk of a security breach or data loss. Effective third-party risk management is critical for businesses to ensure the security and integrity of their systems and data and to maintain the trust of their customers and stakeholders.
Key components of TPRM policies
A third-party risk management policy includes several key components that help organizations structure their TPRM program, establishing controls and processes for managing any security risks introduced by third parties. These components include:
- Risk identification
- Due diligence and assessment
- Risk evaluation
- Contract management
- Continuous monitoring
- Incident management
- Termination procedures
These components work best together in a TPRM policy, which provides organizations with structure and established processes for managing their third-party relationships while minimizing risks.
Why organizations need a TPRM policy
Third-party risk management policies provide organizations with various benefits, all aimed at protecting an organization from third-party risks , especially cybersecurity risks . Other benefits of establishing a TPRM policy include:
- Risk reduction
- Regulatory compliance
- Data security
- Financial stability
- Reputational protection
- Operational continuity
- Strategic alignment
- Efficient resource allocation
Third-party risks can cause serious security incidents for organizations, so having a robust TPRM policy is vital for organizational stability and business continuity.
Third-party risk management policy template
Below is a free TPRM policy template that covers key sections like risk assessment , vendor onboarding , ongoing monitoring, and organizational roles and responsibilities. Use this template as a starting point to develop a comprehensive TPRM framework that enhances your organization’s security and compliance posture.
Remember to customize this template to fit your organization's needs by incorporating your business objectives, contexts, and regulatory requirements.
[Organization Name] engages with external entities such as vendors , suppliers, contractors, partners, software providers, and open-source projects to support business operations. Recognizing the risks these third-party relationships introduce, [Organization Name] is committed to managing and mitigating potential disruptions that could impact its operational capabilities and business objectives.
This policy establishes a Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) program designed to assess, respond to, monitor, and manage the risks associated with [Organization Name]’s third-party relationships. The TPRM program will be aligned with enterprise-wide standards and tailored to meet the specific requirements and risks posed by third-party interactions . Through effective implementation of this program, [Organization Name] aims to protect its data, assets, and mission-critical functions from third-party risks, ensuring sustained business operations and achievement of strategic goals.
2. Organizational roles and responsibilities
The success of this TPRM policy relies on the clear definition and delegation of roles and responsibilities to ensure effective oversight and execution of third-party risk management processes. The following roles are crucial for the administration and enforcement of the TPRM policy.
2.1 Chief Information Security Officer (CISO)
The CISO provides overall leadership and strategic direction for implementing the TPRM policy. They ensure alignment of the TPRM strategy with [Organization Name]’s overall security posture and business objectives, approve third-party risk management frameworks and major risk decisions, and report on third-party risk exposures to the executive management and board of directors. This role may operate under different titles including Chief Information Officer (CIO), Chief Technology Officer (CTO), VP of Security, etc.
2.2 TPRM Team
The TPRM Team develops, maintains, and updates the TPRM policy and associated procedures. This office oversees risk identification, evaluation, and mitigation tasks related to third parties, conducting regular audits and compliance checks on third-party vendors to ensure adherence to the TPRM policy. Additionally, the TPRM Team serves as the central point of communication for issues related to third-party risks. This team may include outsourced Third-Party Risk Analysts .
2.3 TPRM Lead
TPRM Leads each manages different day-to-day operations of third-party risk assessments and monitoring, including leading the due diligence and ongoing monitoring processes for third-party vendors . TPRM Leads ensure that personnel document, communicate, and resolve risk assessment findings in accordance with this policy. TPRM Leads also train the TPRM team on risk assessment techniques and policy enforcement.
2.5 Department Heads
Department heads ensure that their respective departments comply with the TPRM policy during all stages of third-party engagements, including informing the TPRM team about any planned changes in third-party relationships that may affect the organization's risk posture . Department heads work with TPRM leads to address any specific risks related to their department's third-party engagements.
3. Oversight and coordination
[Organization Name] shall establish the following coordination mechanisms to facilitate effective implementation and ongoing management of third-party risks :
3.1 TPRM Committee
This cross-departmental committee, led by the CISO and composed of the TPRM Lead and key Department Heads, meets quarterly to review third-party risk exposures, discuss significant changes in the risk landscape , and adjust the TPRM strategy as necessary.
3.2 Regular reporting
The TPRM Security Office will provide monthly reports on third-party risk status to the CISO, TPRM Committee, and relevant stakeholders, ensuring timely information dissemination and decision-making.
4. Risk tolerance minimum security requirements
[Organization Name]’s Third-Party Risk Management policy sets forth clear guidelines regarding the acceptable level of risk tolerance and the minimum security requirements that third-party vendors must meet to maintain a business relationship with our company. This section outlines these standards and the mechanisms used to enforce them.
4.1 Risk tolerance minimum
[Organization Name] determines its level of risk acceptance by considering the importance of the services offered by third-party vendors and the potential effects on our business operations, reputation, and compliance responsibilities. The TPRM Committee reviews this tolerance level on a yearly basis and modifies it as required based on changes in the business environment and regulatory framework.
4.2 Minimum security requirements
The following outline minimum security requirements all third parties must adhere to when working with [Organization Name]:
- 4.2.1 Security ratings : Third-party vendors must maintain a minimum security rating that reflects [Organization Name]’s risk tolerance. Ratings are assessed based on security practices, data protection, incident response, access control , and compliance. The minimum acceptable rating is defined by the TPRM Security Office and approved by the CISO using standardized tools.
- 4.2.2 Continuous monitoring : [Organization Name] continuously scans third-party vendors ' systems and networks to detect vulnerabilities , misconfigurations, and non-compliance with minimum security requirements. The monitoring frequency and scope depend on the third-party service's criticality and potential risk to the organization.
- 4.2.3 Compliance and enforcement : The TPRM team reviews vendors with failing security ratings . Remedial actions include rectification measures, enhanced monitoring, or contract termination if a vendor does not meet contract requirements within the proposed timeframe.
- 4.2.4 Reporting and documentation : All findings from continuous monitoring and security assessments are documented and reported to the TPRM Committee. Reports include details of the vendor’s compliance status with the minimum security requirements and any corrective actions taken or recommended.
- 4.2.5 Stakeholder communication : The TPRM Security Office is responsible for communicating with stakeholders about any changes to vendor risk statuses and ensuring all concerned parties understand potential impacts and planned responses.
5. Vendor risk management tools
To effectively manage third-party risks , it is important to have a comprehensive set of tools to help identify, assess, and monitor risks associated with external vendors . This section outlines the various tools that our organization uses as part of our VRM program to ensure that all third-party vendors meet our security and compliance standards.
5.1 Security rating services
[Organization Name] uses security ratings to pre-screen potential vendors and continuously monitor existing ones, ensuring they meet the minimum security standards this policy sets. These ratings evaluate a vendor’s security posture through a quantifiable score based on public and propriety data.
5.2 Risk assessment tools
[Organization Name] uses vendor risk assessment tools to perform initial and periodic risk assessments on each vendor, evaluating cybersecurity practices, compliance with relevant regulations , and operational resilience. These tools automate the risk assessment process by collecting and analyzing data on vendor risk exposures.
5.3 Security questionnaires
[Organization Name] sends risk-mapped customizable questionnaires to vendors as part of the onboarding process and at regular intervals throughout the vendor lifecycle or when significant changes occur within the vendor’s organization or the services they provide. These questionnaires gather detailed information directly from vendors regarding their security policies , practices, and data management procedures .
5.4 Penetration testing
If the third party is a critical vendor, your organization must require them to perform penetration tests . Penetration testing must be conducted annually or bi-annually, depending on the criticality of the vendor’s services. Security personnel use these results to identify vulnerabilities and enforce corrective measures. This type of testing evaluates the security of vendors’ systems by simulating cyber-attacks .
5.5 Compliance tracking tools
Compliance tracking tools track and verify a vendor's compliance status with specific regulatory requirements relevant to the services they provide. These tools ensure ongoing compliance with standards such as GDPR , HIPAA , SOC 2 , etc., and document compliance for audit purposes.
5.6 Contract management systems
Contract management systems manage and monitor the contractual aspects of third-party engagements, including compliance with risk-related clauses and conditions. [Organization Name] uses these tools to enforce and track adherence to security and risk management requirements specified in contracts with third parties.
5.7 Vendor portals
Vendor portals streamline communication and information sharing with vendors regarding risk management practices and requirements. Portals are a central hub for submitting and reviewing security documentation, risk assessments , and compliance certificates, facilitating transparency and efficiency in vendor interactions.
5.8 Automated alerting systems
Automated alerting systems provide real-time alerts when a vendor’s risk status or security posture changes. This system is integrated with other VRM tools to trigger notifications based on predefined risk thresholds, ensuring that any risk exceeding the organization’s tolerance is quickly identified and addressed.
5.9 Continuous monitoring software
This software continuously monitors and evaluates the security and operational status of third-party vendors , providing ongoing visibility into vendor activities, alerting the organization to new risks or changes in risk levels, and enabling proactive management of potential issues.
6. Vendor onboarding process
This section outlines the procurement process and criteria for the due diligence and evaluation of prospective third-party vendors to ensure they align with the organization’s VRM objectives and risk thresholds.
6.1 Due diligence process
- 6.1.1 Initial screening : Prospective vendors must undergo an initial screening process, which collects and reviews basic information about the vendor's business, financial stability, and market reputation. This preliminary step helps determine whether a prospective vendor meets the organization's basic criteria and standards.
- 6.1.2 Comprehensive due diligence : Following initial approval, a more detailed due diligence process begins. This includes security assessments , compliance reviews, operational resilience evaluations, and reference checks.
- 6.1.3 Criticality rating assignment : A potential vendor is assessed for criticality during due diligence based on factors like the nature of data accessed, the vendor's role in operations, and the difficulty of replacing them. The vendor's criticality is then categorized as high-risk, medium-risk, or low-risk.
- 6.1.4 Risk assessment : A risk assessment is conducted to evaluate the identified risks against [Organization Name]’s predefined risk threshold. This assessment considers the criticality rating, the results of the security and compliance reviews, and any other relevant risk factors.
- 6.1.5 Approval and risk mitigation : If the vendor meets or exceeds the [Organization Name]’s VRM objectives and falls within acceptable risk thresholds, they proceed to final approval. If any risks exceed acceptable levels are identified, they must be mitigated through additional controls, revised contract terms, or specific vendor commitments before proceeding.
- 6.1.6 Contract finalization : Upon successful completion of the due diligence and risk assessment processes, and once all risk mitigation strategies are in place, a contract can be finalized. This contract will include all necessary clauses related to compliance, data security , risk management responsibilities, and penalties for non-compliance.
- 6.1.7 Vendor onboarding : The vendor is formally onboarded and integrated into [Organization Name]’s systems and processes. This includes providing access to necessary resources, conducting training on compliance and security requirements, and establishing lines of communication for ongoing management and reporting.
6.2 Failed due diligence outcomes
- 6.2.1 Rejection of vendor: If a prospective vendor fails the due diligence process by not meeting the necessary security, compliance, or operational requirements or poses a risk beyond the [Organization Name]’s defined tolerance, the pending partnership may be revoked.
- 6.2.2 Communication and feedback: The decision and the reasons for rejection are communicated to the prospective vendor, who has an option for feedback to understand the decision-making process, ensuring transparency and fairness in vendor selection.
7. Vendor criticality
This section outlines the methodology used to assess the criticality of vendors , which informs [Organization Name]’s management and monitoring strategies based on the potential impact a vendor could have on our organization’s operations, security, and compliance.
7.1 Determination of vendor criticality
Vendor criticality can be categorized into three main levels: High, Medium, and Low. Each level reflects the potential impact on [Organization Name]’s operational integrity, business continuity, data security , and compliance status. The criticality assessment is based on a combination of quantitative and qualitative evaluations conducted using various tools and metrics.
- 7.1.1 High criticality : This category includes vendors whose failure or breach could significantly disrupt critical business operations or lead to substantial non-compliance or security issues. Examples include vendors handling sensitive or regulated data , providing essential infrastructure services , or being integral to the supply chain .
- 7.2.2 Medium criticality : These vendors are necessary for business operations, but their failure would not result in immediate or catastrophic disruption. Examples of such vendors include those who provide non-critical but important services that have indirect impacts on [Organization Name], or those whose services or products are more easily replaceable.
- 7.3.3 Low criticality : These vendors are necessary for business operations, but their failure would not result in immediate or catastrophic disruption. Examples of such vendors include those who provide non-critical but important services that have indirect impacts on [Organization Name], or those whose services or products are more easily replaceable.
7.2 Tools used to determine criticality
- 7.2.1 Security ratings : These ratings are utilized to gain a real-time, objective measure of a vendor's security posture. Higher security risks usually contribute to a higher criticality rating, particularly if those risks directly impact [Organization Name]’s business operations or data security .
- 7.2.2 Risk assessments : These assessments are comprehensive evaluations that analyze the operational and security risks a vendor may pose. This process includes reviewing the potential impacts of a vendor’s failure, the nature of data accessed, and the vendor's compliance with relevant regulations .
- 7.3.3 Questionnaires : These questionnaires are tailored to help gather specific information directly from the vendor about their business practices, security measures, data handling practices, and compliance with standards. The responses are critical in assessing how integral the vendor is to [Organization Name]’s business operations and what risks they might carry.
7.3 Criticality review process
- 7.3.1 Initial assessment : When a vendor is first considered for engagement, the TPRM team conducts an initial criticality assessment using the tools mentioned above. This initial rating is provisional and subject to confirmation.
- 7.3.2 Ongoing re-assessment : Vendor criticality is not static and is reviewed regularly or when significant changes occur in the vendor’s services, our business needs, or the regulatory environment. This process ensures that the criticality rating remains current and reflective of the actual risk.
- 7.3.2 Documentation and reporting : All criticality assessments and subsequent updates are thoroughly documented. Reports are maintained within the TPRM system and are accessible for audit purposes and routine reviews.
8. Ongoing vendor monitoring
Ongoing monitoring ensures that all third-party vendors continuously adhere to the agreed-upon standards and regulations throughout the duration of their engagement with [Organization Name]. This section outlines the continuous monitoring processes that are implemented after the initial due diligence phase.
8.1 Objectives of ongoing monitoring
- 8.1.1 Ensure compliance : Continuous oversight to ensure that vendors meet the compliance requirements of all relevant laws , regulations, and standards that impact their services to our organization
- 8.1.2 Maintain security standards : Regular assessments to verify that vendors maintain high levels of security as per their contractual obligations and [Organization Name]’s security requirements
- 8.1.3 Detect and address changes : Identify any changes in the vendor’s service delivery, business stability, or security posture that might affect their risk level or performance.
8.2 Monitoring methods
- 8.2.1 Automated security scanning : Automated tools are used to scan vendors' systems and services for vulnerabilities on a regular basis. This process includes utilizing security rating services to continuously monitor the vendor's security posture . Depending on the vendor's criticality, these scans can be conducted monthly, quarterly, or bi-annually.
- 8.2.2 Regulatory compliance audits : Scheduled and ad hoc audits are conducted to ensure that vendors continue to comply with relevant regulatory requirements , including vendors handling sensitive data or operating in heavily regulated industries. Documentation of compliance status and any audit findings are reviewed and addressed promptly.
- 8.2.3 Performance reviews : Regular performance reviews are conducted to assess the quality and reliability of the vendor's services. Reviews are based on performance metrics agreed upon at the start of the contract and monitored through key performance indicators (KPIs).
- 8.2.4 Regular risk assessments : Periodic risk assessments are conducted annually to identify any new or evolving risks associated with the vendor. These assessments consider changes in the vendor’s business, the external environment, or within [Organization Name]. More frequent assessments may occur if significant changes are implemented.
- 8.2.5 Stakeholder feedback : Feedback is gathered from internal stakeholders of the vendor’s services to gain insights into the vendor’s performance and any issues that may not be evident through automated systems or formal audits.
- 8.2.6 Contract compliance monitoring : The vendor’s adherence to contractual terms, particularly those related to security and compliance obligations, is reviewed on an ongoing basis. Contract management tools alert the TPRM team about upcoming renewals, terminations, or breaches of contract.
8.3 Response procedures
- 8.3.1 Escalation process : [Organization Name] has established clear guidelines for escalating issues found during monitoring, including who is responsible for taking action and the timelines for response.
- 8.3.2 Remediation and incident response plans : Vendors are provided with procedures for addressing any non-compliance, security issues, or other concerns identified during monitoring. This process involves [Organization Name] and vendor working together to develop and implement corrective action plans.
- 8.3.3 Contractual adjustments : If ongoing issues are identified, adjustments to the vendor contract may be necessary to better protect the organization and enforce compliance.
8.4 Reporting and documentation
- 8.4.1 Regular reporting : Management will receive monthly or quarterly reports detailing vendor performance, compliance status, and any issues or risks identified.
- 8.4.2 Documentation : For auditing and review purposes, comprehensive records are maintained of all monitoring activities, findings, and communications with the vendor.
9. Vendor contract termination
This section outlines the procedures and consequences associated with the termination of vendor contracts due to violations of the TPRM policy , including failure to meet required standards, compliance issues, or breaches of contract terms.
9.1 Grounds for termination
- 9.1.1 Non-compliance with TPRM policy : A vendor fails to adhere to specific security measures, operational requirements, or regulatory compliance as stipulated in the TPRM policy and the contractual agreement. Examples include inadequate data protection , unauthorized data access, and failure to maintain the agreed-upon security certifications or standards.
- 9.1.2 Breach of contract : A vendor violates any contractual obligations that relate to performance standards, confidentiality, data security , and compliance with laws and regulations. This contract breach includes failure to correct deficiencies or address issues highlighted during regular audits , assessments, or as notified by [Organization Name].
- 9.1.3 Operational failures : A vendor continuously underperforms or cannot meet service level agreements (SLAs), which critically impacts our operations. Significant disruptions caused by the vendor affect [Organization Name]’s business continuity or operational integrity.
9.2 Termination procedures
- 9.2.1 Notification : The vendor will receive a formal notification outlining the reasons for potential contract termination. This notice will specify the nature of the violation, the supporting evidence, and any prior warnings issued. Vendors will typically be given an opportunity to respond to the allegations, rectify breaches, or appeal the decision within a specified timeframe, usually 30 days.
- 9.2.2 Rectification period : If applicable, a rectification period may be offered, allowing the vendor to correct the breach and comply with the policy requirements. The length and terms of this period depend on the severity and nature of the breach. Failure to rectify the cited issues within the given timeframe will result in immediate contract termination.
- 9.2.3 Formal termination : If [Organization Name] pursues termination post-notification and rectification period (if provided), the contract will be formally terminated in accordance with the terms specified within the agreement. Access to all organizational resources, data, and systems will be revoked, and the vendor must comply with all contract exit requirements, including the return or destruction of confidential information .
- 9.2.4 Legal and financial considerations : The termination process will consider any legal implications or financial liabilities incurred by either party. This includes penalties for breach of contract, any outstanding payments, and damages. Legal counsel should review all termination actions to ensure compliance with contractual terms and applicable laws.
9.3 Documentation and record keeping
All proceedings related to contract termination due to policy violations must be thoroughly documented, including the initial notice, communications, corrective actions taken by the vendor, and final termination notices. These records are essential for legal protection and for auditing purposes.
UpGuard can help you maintain an efficient TPRM program
UpGuard Vendor Risk is the premier cybersecurity software platform to help you maintain a robust and efficient third-party risk management program. From always-on vendor risk management to risk remediation workflows and reporting , Vendor Risk is the complete toolkit for data-conscious companies.
UpGuard features include:
- Third-party attack surface monitoring : Reduce your attack surface by discovering exploitable vulnerabilities and permutations of your domains at risk of typosquatting.
- Managed Vendor Assessments: Partner with an UpGuard analyst and put your vendor assessments on autopilot.
- Security questionnaire automation: Accelerate your assessment process using UpGuard’s powerful and flexible in-built questionnaires.
- Risk remediation workflows: Streamline your cybersecurity risk remediation requests to third-party vendors. Use our real-time data for context, track progress with our workflows, and get notified when issues are resolved.
- Regulatory compliance tracking: Our compliance reporting feature enables customers to view their own or their vendor’s risk details (including web risks) mapped against recognized security standards or compliance frameworks like NIST CSF or ISO 27001.
- Vendor security posture tracking: Utilize UpGuard’s data-driven security ratings to gain insight and dynamic measurement of an organization’s security posture.
- Cybersecurity reporting workflows: UpGuard's Reports Library provides customized reports for different stakeholders in one centralized location. This allows you to effectively report on your third-party risk management program to the Board, C-Suite, and other interested parties.
Reviewed by

Kaushik Sen
Ready to see upguard in action, ready to save time and streamline your trust management process, scale your tprm.

Join 27,000+ cybersecurity newsletter subscribers
Related posts
What are security ratings cyber performance scoring explained.

How to Manage Third-Party Risk in a World of Breaches
What is third-party risk management (tprm) 2024 guide, introducing upguard's new sig lite questionnaire.

Scaling Third-Party Risk Management Despite the Odds
9 ways to prevent third-party data breaches in 2024.
- UpGuard Vendor Risk
- UpGuard BreachSight
- Product Video
- Release notes
- SecurityScorecard
- All comparisons
- Security Reports
- Instant Security Score
- Third-Party Risk Management
- Attack Surface Management
- Cybersecurity

Partner Overview
Join Us for Growth, Innovation and Cybersecurity Excellence.
Become a Channel Partner
Be a Valued Partner and Embark on a Journey of Profitability.
Partner Portal
Unified Security Platform
Latest Content and Resources
Threat Report 2023
NRGi Holding Case Study
[Free & Downloadable] Incident Management Policy Template – 2024
Last updated on May 10, 2024
The Incident Management Policy template serves as an essential tool for organizations aiming to fortify their defenses against digital threats.
This document provides a structured approach to establishing and maintaining robust information security measures, tailored to meet the specific needs of each organization while complying with relevant legal and federal guidelines.
You cand find the templates in three different formats: PDF, Word, Google Docs.
Download the templates
Incident management policy template – pdf, incident management policy template – word, incident management policy template – google docs, template highlights.
The Incident Management Policy template encompasses several key areas crucial for effective information security management:
- Sets the minimum standards for information security, allowing for customization based on unique business requirements.
- Defines the governance of the policy, applicable across all systems and types of information managed by the organization.
- Details the roles and responsibilities related to risk management functions and security oversight.
- Outlines the duties of executive and IT management, as well as the Chief Information Security Officer (CISO), in ensuring the implementation and adherence to security policies.
- Emphasizes the importance of ongoing risk assessments, IT asset management, and the establishment of a secure development lifecycle.
- Provides a framework for the detection, reporting, and management of security incidents.
- Specifies standards for account management, authentication, and access privileges.
- Describes procedures for conducting vulnerability scans, penetration testing, and addressing identified risks.
- Mandates adherence to established policies and standards, with provisions for seeking exceptions through a formal process.
Target audience
Who is the Incident Management Policy template for?
- Executives: To integrate information security into business strategy.
- IT and Security Professionals: For implementing and managing security protocols.
- Risk Management Teams: To align security risk management with organizational goals.
- All employees: To understand their role in upholding security measures.
Significance
This free and downloadable Incident Management Policy Template is vital for organizations seeking to protect against data breaches, ensure regulatory compliance, and maintain the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their information assets.
It offers a proactive approach to information security, emphasizing the importance of preparedness and continuous improvement.
In addition to the Incident Management Policy Template, we offer a suite of other essential templates, including Patch Management Policy Templates , Risk Assessment and Management Templates , Threat & Vulnerability Management Templates , and many more.
Each template is designed to streamline the implementation of critical information security practices and ensure a comprehensive, cohesive approach to safeguarding your organization’s digital assets.
For further insights and resources, feel free to follow us on LinkedIn , YouTube , Facebook , and Twitter .
Our channels provide a wealth of informative content, industry updates, and best practices in information security management. Join our community to stay informed and equipped with the tools necessary for a secure, resilient digital environment.
Gabriella Antal
SMM & Corporate Communications Officer
Gabriella is the Social Media Manager and Cybersecurity Communications Officer at Heimdal®, where she orchestrates the strategy and content creation for the company's social media channels. Her contributions amplify the brand's voice and foster a strong, engaging online community. Outside work, you can find her exploring the outdoors with her dog.
Related Articles
Leave a Reply (Cancel Reply)
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
CHECK OUR SUITE OF 11 CYBERSECURITY SOLUTIONS
- Cyber Resources And Beginners
- Cyber Security Glossary
- The Daily Security Tip
- Cyber Security For Small Business Owners
- Cybersecurity Webinars
- About Heimdal®
- Press Center
- Partner with us
- Affiliate Program
© 2024 Heimdal ®
Vat No. 35802495, Vester Farimagsgade 1, 2 Sal, 1606 København V
- +1 (800) 826-0777
- VIRTUAL TOUR
- Mass Notification
- Threat Intelligence
- Employee Safety Monitoring
- Travel Risk Management
- Emergency Preparedness
- Remote Workforce
- Location and Asset Protection
- Business Continuity
- Why AlertMedia
- Who We Serve
- Customer Spotlights
- Resource Library
- Downloads & Guides

Minimizing Downtime With a Comprehensive Disaster Recovery Plan Checklist
Preparing for recovery starts long before a disaster occurs. Use this checklist to help plan ahead to minimize disruptions and downtime from any business disaster.

- Checklist Infographic
13-Step Disaster Recovery Plan Checklist
When a disaster strikes—whether it’s a crippling ransomware event or a destructive natural disaster—a smooth recovery process is critical to getting back on your feet. But that recovery doesn’t simply unfold as soon as the storm recedes. Rapid operational recovery starts with planning long before the disaster even occurs.
Before Hurricane Michael hit Panama City in 2018, Coca-Cola Bottling Company UNITED, Inc., thought they were thoroughly prepared for the storm and recovery. “We have a really extensive hurricane preparedness plan across all of our coastal locations,” explains Gianetta Jones, Vice President & Chief People Officer. But the Category 5 storm caused severe damage to cell phone infrastructure that the Coca-Cola team was not ready for. Gianetta told us on The Employee Safety Podcast , “We had to pivot and purchased several very expensive satellite phones for our operators that were local to be able to communicate with us at the corporate office.”
Flexibility is necessary in disaster recovery, as disasters hardly follow a predictable plan. But the right preparation can make it possible to adapt and maximize your time and resources through recovery. A comprehensive disaster recovery plan is not just a “good-to-have” safety net; it serves as a roadmap for resuming operations efficiently and effectively, minimizing the impact on your business and clients. And a great way to get started on your disaster recovery planning process (or to review and reassess your standing plan) is with a disaster recovery plan checklist.
Whether you’re facing natural calamities, cyberattacks, or technological failures, this checklist will guide you through establishing robust protocols to protect your assets, data, and your operational continuity.
Download Our Business Continuity Checklist

1. Assess the risks and impacts
Conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify potential disasters and emergencies and look for vulnerabilities. Then, perform a detailed business impact analysis to understand the potential impact of disasters on your business operations. These assessments will help you determine what disasters you must prepare for and what recovery might be necessary.
2. Coordinate with departments and identify stakeholders
Engage all internal departments to gather input and ensure comprehensive coverage. In particular, you’ll want to work with teams involved in emergency preparedness, IT, business continuity, security, and any other function that may be impacted by the event. Additionally, determine any stakeholders, internal and external, crucial to the recovery processes.
3. Review past emergencies
Analyze any previous incidents your organization has been through to learn from past emergencies and refine your current planning efforts. You can also look at organizations similar in size and industry to understand how they have experienced disasters.
4. Assemble the leadership team
The disaster recovery team members will be dedicated to managing the disaster recovery process, though not necessarily executing the entire disaster recovery plan themselves. They will serve as important leaders and decision-makers throughout the process.
5. Document systems and processes
Thoroughly record all critical business systems and processes. This might include software applications, physical items in your facility, digital systems, on-site and off-site resources, or processes vital to your operations. If it is something that a disaster might impact, it should be considered in this step.
Once you have your list, do the following for each item:
For example, when building an IT disaster recovery plan, you’ll want to document all your IT systems, identify the most critical pieces of IT infrastructure, and arrange for data backups, secondary data centers, and other data protection for any critical data that may be impacted.
6. Analyze your recovery needs
Perform a detailed recovery analysis for each type of disaster that could impact the business. Include the following steps in this analysis:
7. Set up your recovery plan templates
If you are using a disaster recovery plan template, you’ll want to make copies of the template pages to fill out. You want a tailored recovery plan for each type of disaster, so multiple versions of the template are a must.
8. Assign personnel
Identify and document all personnel who will be involved in each recovery and response plan. Write down their roles and responsibilities within the recovery efforts and contact information.
9. Establish the activation criteria
Set clear criteria for when to activate the disaster recovery plan. Clarify the turning point between disaster response procedures and disaster recovery, so you don’t hesitate in the event of a disaster.
10. Write the recovery plan
The previous disaster recovery checklist stages prepare you to document your plan. Detail the specific steps and strategies to recover from each disaster you may face.
11. List resources and related documents
Document all the resources required for the recovery plan and their locations. Include links or references to any related plans and supportive documentation. This might include your business continuity plan , risk assessments from earlier in the process, or documentation for a specific recovery strategy.
12. Develop a communication plan
Communication is critical to recovery, so ensure your plan includes a clear process for reaching your employees, stakeholders, and external resources. Design a comprehensive emergency communication plan detailing:
13. Evaluate your response
Don’t make the mistake of building out your disaster recovery plan and assuming it can stay the same year after year. Not only are the disaster scenarios you face likely to change, but your organization will also grow and change; what worked for recovery at one point won’t necessarily work weeks, months, or years later. Regularly test, evaluate, and update the disaster recovery plan to ensure it still meets your business needs over time.
Planning for Resilience Through Operational Failback
With the right plan in place, recovery doesn’t have to feel like a disaster in and of itself. Develop a comprehensive disaster recovery plan with this checklist to keep your whole team on the same page and align their efforts.
Unlike an IT system failback, to recover your business operations, you often need to build them back up one by one. Following all 13 steps, you can ensure you don’t miss a critical system in your DR plan, and you minimize the effort it takes to quickly and confidently return to normal operations.
More Articles You May Be Interested In

Business Continuity Checklist
Please complete the form below to receive this resource.
Check Your Inbox!
The document you requested has been sent to your provided email address.
Cookies are required to play this video.
Click the blue shield icon on the bottom left of your screen to edit your cookie preferences.


- Your Project
- MoSCoW Method
What is the MoSCoW Method?
The MoSCoW Method is a prioritization tool that helps professionals in managing their time and effort .
To do so, it proposes to classify the importance of the different characteristics of a product (or a Project) according to their importance .
Its name is an acronym of the 4 Prioritization Categories proposed (adding two “o”):
- M ust Have .
- S hould Have .
- C ould Have .
- W on’t Have .
Four Prioritization Categories
Must Have : Essential Requirements that the product or project must have.
- Critical Features without replacement.
Should Have : Important desired Requirements for the product or project.
- They can be substituted if necessary.
Could Have : Improvements to the product or project.
- There are different alternatives.
Won’t have : Characteristics agreed not to be adopted .
- No one will waste time implementing them.
Let’s see the first example:
MoSCoW Method example

Imagine that you have been hired to create a Website for a Law firm.
They want a professional Site where people can Register and, once inside, track their court cases .
Since you want to deliver the best possible Site on time, you decide to follow the MoSCoW method .
How does it look like?
Must Have :
- Solid programming without any bugs.
- A Solid Register System.
- A Safe and Reliable personal directory.
Should Have :
- A Fast Site.
- An outstanding Design.
- Notifications sent by e-mail.
Could Have :
- Custom menus.
- Suggestions.
- A Blog section with latest news.
Won’t Have :
- Paid content.
- A Public Members section.
As we usually say, this Method may seem obvious.
Then… Why is it important?
Why is the MoSCoW Method important?
Many of professionals end up wasting time , effort and resources on useless task s that are ultimately not essential at all.
Surely you have experienced this situation working in a Team:
- Everyone spends hours modifying a minor feature and, ultimately, the important thing is missing .
That is why this Method is so important:
- Because it concentrates your efforts and forces you to think about what is really important .
As you can imagine, this Tool can be employed in practically all kinds of situations.
But when do we especially recommend it?
When should you use the MoSCoW Method?
We highly recommend to use the MoSCoW Method:
- To put order and prioritization.
- To avoid wasting time with non-essential touch-ups.
- In order to meet the Essential Requirements.
- When the product can have very different characteristics.
Now, let’s see more examples:
MoSCoW Method examples
We have chosen different real examples where the MoSCoW Method can be of great help for the development of certain products.
Let’s begin:
A Wallet - MoSCoW Method example

Let’s imagine that you are developing a wallet .
As you know, wallets are very modular products.
They can have:
- Several or few departments for cards.
- Coin purse… or not.
- 1 or 2 bill slots.
There is not a canonical wallet (one that is the benchmark for all the others).
- That is why you decided to use the MoSCoW Method to develop it.
After some thoughts, you decide that your wallet:
- 2 bill slots.
- 8 compartments for credit cards.
- High resistance materials and sewing.
- Leather as its main material.
- A translucid Credit card compartment.
- A transverse horizontal compartment.
- A striking color on the inside of the bill slots.
- Completely black exterior color.
- One translucid compartment for small photos.
- A Coin purse.
- A Passport compartment.
Making a Cake - MoSCoW Method example

In this example, we’ll imagine that you are preparing a wedding Cake .
- You have a very rigid deadline (the wedding day, of course).
In addition, as you also know, Cakes can have lots of variations.
- We could say they are very modular .
That is why you decide to use the MoSCoW Method.
How does it look?
Well, your Cake:
- White coating.
- Two sugar figurines on top.
- 6 layers of sponge cake inside.
- Belgian chocolate between the layers.
- Decorations on the edges
- Sugar flowers.
- Chocolate balls.
- Scattered sugar pearls.
- Multicolor layers.
- An excessive amount of decoration.
- Fruit flavor.
Designing a Poster - MoSCoW Method example

You are now an artist hired to Design a poster for a Rock concert.
Obviously, this is a Design job with infinite variations possible.
- Also, you have a close deadline to finish it.
No need to mention that you will use the MoSCoW Method.
Finally, the Poster:
- The name of the Main rock band, very prominent.
- Images and colors that best suit their style.
- A typeface that best suits the musical style.
- An illustration related to Rock in the middle.
- The name of the rest of the bands that will play.
- Where and when it will take place.
- Where you can buy the tickets.
- Nearby metro and bus stations.
- The name of the city.
- The maximum capacity of the stadium
- At what time each band will play.
Summarizing
The MoSCoW Method is a prioritization tool that helps professionals in managing their time and effort.
It proposes to classify the importance of the different characteristics of a product in 4 Categories :
- M ust Have.
- S hould Have.
- C ould Have.
- W on’t Have.
Although this Method can be used in all kinds of situations, we highly recommend to use it:
- When working in a team .
- In Design tasks .
- When there is a close deadline .
- With modular products or projects .
- Economies of Scale
- Business Plan for Beginners
- Business Plan Basics
- How to write a Business Plan
- Cash Flow Calculation
- Raising Funds for a Business
- 4 C’s of Credit
- Business Plan Templates
- Customer Insight
- Customer Experience
- Customer Pain Points
- 4C Marketing Model
- RATER Model
- Augmented Product
- Product Mix
- Unique Selling Proposition
- DAGMAR Model
- Marketing Storytelling
- Content Marketing
- Psychographics
- Barnum Effect
- Market Segmentation
- Market Research & Big Data
- Marketing to Generation Z
- 4P Marketing Mix
- 7P Marketing Mix
- Sales Funnel
- Loyalty Ladder
- RACE Planning
- Push and Pull Marketing
- Marketing Strategy
- Marketing Templates
- Starting your own business
- From Startup to a Business
- Entrepreneur FAQs
- Start your Business Idea
- Entrepreneur Golden Rules
- Innovate or Imitate?
- Design Thinking
- SCAMPER Model
- AAR Process
- Work From Home
- Growth strategies for Startups
- VMOST Analysis
- 3P Framework
- SOAR Analysis
- TELOS Analysis
- 5 C’s of Entrepreneurship
- Crowdfunding
- BATNA & ZOPA Negotiation
- Entrepreneur with no Money
- Entrepreneurship Templates
- Strategy vs Tactics
- Mission and Vision
- Business Values
- Value Chain
- Scenario Planning
- Porter 6 Forces
- Bowman’s Strategy Clock
- GE-McKinsey Matrix
- Delta Model
- PEST Analysis
- PESTEL Analysis
- SWOT Analysis
- VRIO Framework
- Strategy Canvas
- Competitive Advantages
- Porter’s Four Corners
- 5 Ps of Strategy
- Porter’s Generic Strategies
- Porter’s Diamond Model
- Wardley Map
- Core Competencies
- Resource Based View
- Bridges Transition Model
- CAGE Distance Framework
- McKinsey’s 3 Horizons
- Vertical Integration
- Horizontal Integration
- Blue Ocean Strategy
- Red Ocean Strategy
- Porter 5 Forces
- Ansoff Matrix
- McKinsey 7S Framework
- CATWOE Analysis
- Strategy Pyramid
- Bain’s RAPID Framework
- Balanced Scorecard
- Resources and Capabilities
- Strategy of Apple
- Strategy of Amazon
- Strategy of Starbucks
- Strategy Templates
- Communicate Effectively
- COIN Conversation Model
- SCARF Model
- SBI Feedback Model
- CEDAR Feedback Model
- How to behave at a meeting
- Gibbs’ Reflective Cycle
- Bloom’s Taxonomy
- 5E Learning Model
- 9-Box Performance Grid
- SEEDS Bias Model
- Halo Effect
- Pygmalion Rosenthal Effect
- Dunning-Kruger Effect
- How to be an Entrepreneur
- How to be a Leader
- Mintzberg Managerial Roles
- Cog’s Ladder
- The Peter Principle
- How to Negotiate
- Teamwork Skills and Profiles
- Gantt Chart
- RACI Matrix
- Eisenhower Matrix
- FMEA Process
- Problem Solving
- Ishikawa Fishbone diagram
- 5 Whys Method
- 8 Disciplines Method
- ADDIE Model
- ORAPAPA Method
- Cynefin Framework
- Just In Time
- SMART Goals
- KISS Principle
- Birkinshaw’s 4 Dimensions
- Parkinson’s Law
- OGSM Framework
- OKR Methodology
- APQP Framework
- Theory of Constraints
- Success through Organization
- ADKAR Model
- Lewin’s Change Model
- Kotter’s 8-Step Model
- The Greiner Curve
- GAP Analysis
- Planning Templates
- Mean, Median and Mode
- Define your Data
- Pareto Principle 80/20 Rule
- Decision Matrix
- Decision Tree
- TARA Framework
- Root Cause Analysis
- Simplex Process
- Forecasting Methods
- Product Life Cycle
- How to use Google Trends
- Correlation vs Causation
© 2024 - Consuunt .
We're not around right now. But you can send us an email and we'll get back to you, asap.
Log in with your credentials
Forgot your details.

The MoSCoW prioritization method to manage priorities & drive alignment

This post is also available in: German
In projects with a fixed timeframe, it’s vital to understand the relevance of individual tasks to work at maximum efficiently and meet deadlines. The MoSCoW prioritization or MoSCoW method is a popular visual roadmap used to help identify and manage competing priorities. Because of the collaborative design of the template, cross-functional teams can use the simple method to ensure priorities are captured from a range of perspectives. This also makes it a great tool for release planning .
MoSCoW stands for the four different quadrants of the method:
- M ust-haves
- S hould-haves
- C ould-haves
- W ill not have at this time
Let’s take a look at exactly how the MoSCoW method works.
When should the MoSCoW Prioritization Method be used?
For best results, the method should be seen as a collaborative effort with individuals across departments. This will allow the session to be more wide-ranging and include priorities from various angles, not just the tech or development team. To ensure the collaborative session runs smoothly, use Conceptboard’s ready-to-use template, and everyone in the session can add ideas, comments and thoughts in real-time for everyone to see.
Because Conceptboard is a cloud-based application, the template will be saved automatically, so it can be restored to changes down the track to be updated or reviewed.
How to use our MoSCoW prioritization method template
If you’re ready to get started, simply open our free template below. You can then invite team members to collaborate by sharing a link to the board- it’s that simple.
According to the MoSCoW Method, you will need to allocate tasks into the following four categories:
Use template
Must-have initiatives
The first step is identifying the must-haves for your product. These are the essential components that must be included in the release to ensure it functions. For example, an online store might list an online checkout facility as a must-have.
To help you separate the must-haves, ask yourself these three questions:
- Will the product work without this?
- Is there a simpler way to accomplish this?
Should-have initiatives
These are the elements that are just below the above category in terms of importance. They are very important to the value and purpose of the product, but it can still function without it. So they would most likely be included in the second release, once the basic functionality has been proven.
Could-have initiatives
Things that would be nice, but certainly not essential, belong In this category. They are the extra elements that don’t directly affect the functionality of the product, but may improve customer satisfaction, reliability or increase the options. Often, the things that are big projects with small impact belong in the category.
Will not have (this time)
This final section is one of the key differentiators with the MoSCoW method compared to others, as it asks teams to list features that will NOT be included. This is important as it can help avoid the feeling of overwhelm, and can help the team to accurately predict workload and manage delivery expectations.
While some of the items on this list may be looked at further down the line, perhaps in the next round of updates, some may simply not be worth the time, effort or cost and thus will never happen.
The online whiteboard built for agile teams
Make sure you explore our vast library of ready-to-use templates for all your Agile ceremonies, design thinking or brainstorming sessions .
Prioritise with the MoSCoW-Methode
Use the free template with your team & customize as you go!
Use Template
More interesting articles for you

Unwrap the Joy: Elevate Your Team’s Holiday Spirit with Our Exclusive Christmas Game Template!
The holiday season is upon us, and at Conceptboard, we’re thrilled to unwrap the gift of festive cheer with our special Christmas Game Template!
Wireframe Template – A structure to build something great | Free Template
By using Wireframe Templates, you can streamline your workflow and ensure a more efficient and effective design process.
How do we handle the onboarding of new employees at Conceptboard? With Conceptboard!
Here at Conceptboard, our tool has become an indispensable part of our everyday work. We are constantly discovering new use cases and finding new, better processes. Find out what we achieved in the field of HR.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Post Comment
Experience the power of visual collaboration
Experience how Conceptboard boosts your team’s hybrid collaboration and communication.
No credit card
No commitments
Start right now

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The purpose of this document is to describe the Company's Security Management System. The Company is committed to the safety and security of our employees, the customers we serve, and the general public. We urge all employees to help us implement this plan and to continuously improve our security efforts. 1.2 Background
Give your team a grace period and offer warnings and corrections instead of penalties as you learn safer security practices together. Encouraging your team members and thanking them for their efforts to support and enforce your policy are the final steps in making your security plan work. 6. Don't Go It Alone.
Template 4: Action Plan for Cybersecurity Risk Reduction. Stay protected in the ever-changing digital world with our Action Plan PPT Template. It outlines the major risks, the actions and measures that can be taken against them, and the person responsible for monitoring each risk.
This IT security plan template is designed for IT leaders, managers, and teams of all sizes and industries who need to create a comprehensive plan to manage their IT security. This template provides a comprehensive framework for developing an IT security plan that addresses the organization's specific needs and goals. 1.
When used in tandem with security glass, aftermarket window locks will decrease the vulnerability of your windows and deter burglars or other intruders. 9. Light Things Up. In your business security plan, budget for using indoor lights to illuminate hard-to-see areas of your store and leaving some lights on inside at night.
The Information Security Plan template is designed for IT teams to develop a plan to protect their organization's data and systems. This template provides the framework to create a comprehensive plan that meets the needs of the organization, while complying with any applicable regulations or industry standards. 1.
A master security plan is a detailed, long-term strategy that entails all the aspects of security operations in an organization. For such programs to be successful, they must be based on two core principles. First, it must be in line with your business's strategic plans while combining the best principles for protection and support.
The Cyber Security Plan template is designed to help IT security teams in organizations of all sizes and industries create a cyber security plan company-wide. It provides a comprehensive structure to define objectives, set measurable targets (KPIs), and implement related projects to achieve those objectives. 1.
Make the security plan, or at least the relevant parts, available in the language of the users. If translation is not feasible, consider alternative ways to disseminate the information in the security plan. Explain the security plan to all levels of staff, including those who are less involved in the organization such as cleaners and watchmen.
Security Company Marketing Plan Template. Details. File Format. Google Docs; Word; Pages; Size: A4 & US Download Now. While designing a secure marketing plan for the company you need to make a proper research study of the market. It can help you in designing an effective marketing plan for your organization.
3. Set your goals. The goal of your security plan is to protect your small business. However, several smaller goals play into this larger objective. In a perfect world, creating a plan to prevent cyber attacks, and including a network security device like a firewall, would be enough.
How to create backups on Windows. Windows' built-in backup tool is called File History. To start backing up data on Windows, connect your external drive > click Start > Settings > Update & Security > Backup > Add a drive > select the external drive where you want to store the backups. 8. Use strong passwords.
Every Business Organization Should Have Risk Management and Contingency Planning in Case of Sudden Unexpected Events. Improve the Security Position of Your Company or Organization with Help from Template.net's Free Security Plan Templates.
Security Company Business Plan. Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 500 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans to start and grow their security companies. If you're unfamiliar with creating a security company business plan, you may think creating one will be a time-consuming and frustrating process.
A successful security strategy cannot be developed in isolation. Security and risk management leaders must recognize a range of factors when developing their strategies and position them accordingly. Use this template as a starting point to ask the right questions and position your plans.
• Chapter 3 takes the reader through the steps of system security plan development. • Appendix A provides a system security plan template. • Appendix B provides a glossary of terms and definitions. • Appendix C includes references that support this publication. 1.4 Systems Inventory and Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS 199)
Adapt existing security policies to maintain policy structure and format, and incorporate relevant components to address information security. Establish a project plan to develop and approve the policy. Create a team to develop the policy. Schedule management briefings during the writing cycle to ensure relevant issues are addressed.
Published: 30 May 2016 Summary. Use this template to communicate Information Security's strategic plan to stakeholders in the business, IT function, security function, and other peer risk management functions, explain investment decisions and acquire stakeholder buy-in for investment and risk management trade-off decisions, and provide status updates regarding key risks, controls, and major ...
Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P's: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For a cyber security business plan, your marketing strategy should include the following: Product: In the product section, you should reiterate the type of cyber security company that you documented in your company overview.
Here you go; download our free security agency business plan pdf to start. It's a modern business plan template specifically designed for your security agency business. Use the example business plan as a guide for writing your own. Upmetrics is the #1 business planning software that helps entrepreneurs and business owners create investment ...
The breakout of the funding is below: Office design/build: $100,000. Three months of overhead expenses (payroll, rent, utilities): $100,000. Marketing & advertising: $50,000. Working capital: $50,000. Easily complete your Security Company business plan! Download the Security Company business plan template (including a customizable financial ...
A third-party risk management policy includes several key components that help organizations structure their TPRM program, establishing controls and processes for managing any security risks introduced by third parties. These components include: Risk identification. Due diligence and assessment. Risk evaluation.
Significance. This free and downloadable Incident Management Policy Template is vital for organizations seeking to protect against data breaches, ensure regulatory compliance, and maintain the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their information assets. It offers a proactive approach to information security, emphasizing the ...
13-Step Disaster Recovery Plan Checklist. 1. Assess the risks and impacts. Conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify potential disasters and emergencies and look for vulnerabilities. Then, perform a detailed business impact analysis to understand the potential impact of disasters on your business operations.
The MoSCoW Method is a prioritization tool that helps professionals in managing their time and effort.. To do so, it proposes to classify the importance of the different characteristics of a product (or a Project) according to their importance. Its name is an acronym of the 4 Prioritization Categories proposed (adding two "o"):. M ust Have.; S hould Have.; C ould Have.
The MoSCoW prioritization or MoSCoW method is a popular visual roadmap used to help identify and manage competing priorities. Because of the collaborative design of the template, cross-functional teams can use the simple method to ensure priorities are captured from a range of perspectives. This also makes it a great tool for release planning .