

12 Best Practices for Successful Task Assignment and Tracking
.jpg)
Build with Retainr
Sell your products and services, manage clients, orders, payments, automate your client onboarding and management with your own branded web application.
1. What are the top 12 practices for successful task assignment and tracking?
Key practices for effective task assignment.
The assignment of tasks should always be done strategically to ensure successful completion. Here are six key practices for successful task assignment:
- Clear and concise instructions: Always provide clear steps on how to accomplish the task. Vague instructions may lead to misunderstandings and poor results.
- Assign tasks based on skills and experience: Certain tasks require special skills. Assign tasks to those who have the skills and experience needed to perform them efficiently.
- Establish realistic deadlines: Set achievable deadlines to prevent unnecessary pressure and poor quality of work.
- Communicate the task's importance: Explain why the task is necessary and how it contributes to the overall project.
- Availability check: Make sure that the person assigned to the task has the capacity to do it.
- Empower them: Give them the freedom to do the work in their own way, as long as they meet the project’s quality standards.
Efficient Task Tracking Methods
Task tracking not only ensures timely completion but also guarantees that the quality of work is not compromised. Here are six efficient task tracking methods:
- Use of tracking tools: Implementing task tracking tools like Trello or Asana can automate the tracking process.
- Regular follow-ups: Frequent check-ins allow early detection of issues and timely resolution.
- Setting Milestones: Break down the tasks into manageable chunks or stages with set deadlines.
- Encourage self-reporting: Ask team members to provide status updates on assigned tasks. This makes tracking easier and instills a sense of responsibility.
- Document progress: Keep a record of task progression to easily identify bottlenecks and delays.
- Feedback session: Constructive feedback sessions aimed at learning can be helpful for future tasks.
Comparison Table for Task Assignment and Task Tracking
2. how can i effectively use these best practices in my daily work management, utilizing best practices in daily work management.
Deploying the best practices in your daily work management is all about integration and consistency. Whether you are leading a small team or managing a large project, the successful task assignment and tracking methods will boost productivity and keep everyone on the same page. Here's how you can effectively use these practices:
- Clear Communication: Always communicate task details clearly. Specify the project description, important deadlines, and the expected deliverables. Make use of tools like Slack or Microsoft Teams for smooth communication.
- Team Collaboration: Encourage teamwork, brainstorming sessions and ensure everyone contributes their ideas. Collaborative tools like Google Workspace or Monday.com can assist in shared work.
- Prioritization & Scheduling: Prioritize tasks based on their urgency and importance. Use scheduling tools, like Asana or Trello, to arrange tasks for all team members, ensuring they are aware of their responsibilities.
Implementing Task Assignment Practices
Assigning tasks effectively involves understanding each team member's strengths and weaknesses. The following steps are recommended:
Successful Task Tracking
Tracking tasks helps in maintaining the project's accuracy ensuring that everything is running smoothly. Adopting effective tracking practices can lead to a drop in missed deadlines, an increase in productivity, and a more efficient workflow. Here are some tracking methods:
- Use a Project Management System that offers real-time tracking.
- Conduct regular progress meetings.
- Encourage team members to provide progress reports.
3. Can these best practices for task assignment and tracking be applied to any industry?
Applicability of best practices across industries.
The best practices for task assignment and tracking are versatile, adaptable and can be beneficial to most, if not all industries. This includes but is not limited to the IT, healthcare, construction, education, and manufacturing industries. The principles of clarity, efficiency, and productivity that underscore these best practices are universal needs across business operations.
List of Industries
- Information Technology
- Construction
- Manufacturing
Each of these industries can make use of the best practices in their own unique way. For instance, in the IT industry, these best practices can be utilized to assign and track different coding or debugging tasks. In healthcare, these practices can be used to efficiently assign patient care tasks to different members of a healthcare team. In education, teachers can assign tasks to students and track their progress more effectively. In short, these practices foster a culture of accountability and efficiency.
Tabular Representation of Application in Different Industries
In conclusion, these best practices provide a standard system that is convenient, effective and that can be customized to any industry’s specifics. The consistent theme across all industries is to enhance productivity and optimize resources.
4. What is the first step one should take to apply these practices effectively?
Understanding the task.
The first step towards effectively applying the practices for successful task assignment and tracking is gaining a thorough understanding of the task at hand. To successfully delegate assignments and oversee their completion, you must grasp the task's specifics, objectives, and requirements. The following goals can guide you:
- Determine the nature and scope of the task: Exactly what does this task entail? What are its dimensions and boundaries?
- Identify the expected outcome: What should the ideal result look like once the task is completed?
- Analyze potential problems: What kind of issues may arise during the execution of the task? How can they be addressed proactively?
Establishing Clear Objective and Goals
Once you've comprehended the task, the next step involves establishing clear objectives and goals. These goals should ideally be SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound). A well-defined goal gives a clear direction to the entire task assignment process. Consider the following points when mapping out your goals:
Identifying the Right People for the Task
Once each task has been clearly defined and its goals set, the next step is to assign the right people to the task. This requires analyzing your team's strengths, weaknesses, preferences, and workload. Here are some factors to consider:
- Skills and capabilities: Does the person possess the necessary skills and abilities to perform the task effectively?
- Workload: Does the person have the necessary time and bandwidth to take on the task?
- Preference: Does the person show an interest in the task? Are they excited about the work they're assigned?
5. Are there specific tools that help facilitate these best practices for task assignment and tracking?
Top tools for task assignment and tracking.
There are numerous tools designed specifically to facilitate task assignment and tracking. They range from simple to-do list apps to complex project management systems. Here are a few popular options:
- Asana: This tool is designed for both individuals and teams. It allows for task assignment, due dates, priorities, comments, file attachments, and progress tracking.
- JIRA: Popular among software development teams, JIRA provides a detailed view of ongoing tasks, project timelines, and allows for personalized workflows.
- Trello: Trello operates on a board-and-card system, allowing for easy visualization of tasks and assignments. It also supports collaboration and progress tracking.
- Basecamp: This is a project management tool that integrates discussions, tasks, files, and timelines in one place. It offers a clear view of who’s working on what.
Choosing the Right Tool for Your Needs
To choose the right tool for task assignment and tracking, you need to consider the size of your team, the complexity of the tasks, and the specific features you need. Equally important is the user-friendliness and cost of the tool. Here's a simple comparison:
Consistent Use of Tools
Regardless of which tool you choose, consistent use is essential. All team members should be trained on how to use the tool effectively. Regular updates and reviews are also crucial to keep everyone aligned and ensure smooth progression of tasks. Remember, a tool is only as good as how you use it.
6. How does clear communication help in successful task assignment and tracking?
Benefits of clear communication.
Successfully assigning and tracking tasks in any business or organization often hinge on clear and effective communication. With effective communication, team members can understand their responsibilities, tasks can be properly tracked, and project deadlines can be met. There are several benefits that clear communication provides:
- Boosts Team Morale: When everyone understands their role in a project, they feel valued, which increases motivation and productivity.
- Prevents Confusion: Clear instructions prevent misunderstandings, ensuring tasks are done correctly the first time.
- Increases Efficiency: When goals and objectives are clear, teams can work more efficiently, saving time and resources.
How to Communicate Clearly
Implementing the right communication strategies can be crucial for successful task assignment and tracking. Here are a few methods to foster better communication:
Elements of Clear Communication
To ensure your communication is clear and effective, consider the following elements:
- Clarity: Ensure the message is simple, direct and that technical jargon is minimized where possible.
- Conciseness: Too much information can confuse. State only necessary details.
- Feedback: Encourage feedback - it helps affirm the message was understood correctly.
7. Why is it important to define expected outcomes when assigning tasks?
Importance of defining expected outcomes.
Defining expected outcomes is a vital step in task assignment and tracking because it sets the direction and provides a clear vision of what needs to be achieved. It helps in setting the standards, improving performance, and ensuring better accountability. The following points will further elucidate its significance:
- Clarity and direction: defining the expected outcome provides clear instructions to the task performer about what exactly needs to be achieved. It gives them a sense of direction and purpose.
- Performance measurement: With a defined outcome, it becomes easier to measure performance. The actual results can easily be compared against the expected results, simplifying performance appraisal.
- Increased Accountability: If expected outcomes are well-defined, it can help increase accountability. Task performers are more likely to take ownership and responsibility of their work, ensuring that they deliver the expected results.
Best Practices When Defining Expected Outcomes
While defining expected outcomes is important, it is equally crucial to ensure they are well drafted. Following are some best practices to consider when defining the expected outcomes:
Defining expected outcomes when assigning tasks is a fundamental step to ensure smooth progress and successful task completion. It not only provides a clear vision of what needs to be achieved but also facilitates performance measurement, leading to improved productivity and increased accountability. Employing the best practices while defining these outcomes can greatly enhance their effectiveness.
8. How can these best practices improve overall team productivity?
Enhancing team productivity through best practices.
Implementing best practices in task assignment and tracking can significantly improve overall team productivity. Effective task assignment ensures that the right tasks are allocated to the right people based on their skills, capabilities, and availability. This eliminates confusion, reduces the chances of mistakes, and improves efficiency. When tasks are tracked effectively, it's easier to identify bottlenecks, improve workload distribution, and ensure timely completion of tasks.
Key benefits include:
- Better task distribution: When tasks are assigned judiciously taking into consideration individual skills and capabilities, it ensures a better distribution of workload. This leads to improved efficiency and higher productivity.
- Proactive problem-solving: Effective task tracking allows for early detection of problems or issues that might arise during the execution of tasks. This allows for proactive problem-solving, ensuring the smooth continuation of work.
- Effective communication: These practices foster better communication within the team as tasks and responsibilities are clear. This reduces chances of misunderstanding or confusion, promoting a more harmonious and productive work environment.
Illustrating Productivity Improvement Through a Table
Here's a simple table illustrating the difference in overall team productivity before and after implementing these best practices:
9. What are some challenges one might face when implementing these best practices and how can they be overcome?
Challenges faced in implementing best practices.
When initiating the best practices for successful task assignment and tracking, several challenges might pop up which could hinder the effective execution of the process. Firstly, resistance to change is a common obstacle that organizations face. Employees might resist the new strategies brought about by these best practices, partly due to their unfamiliarity or because they feel comfortable with the old systems. Secondly, lack of adequate resources such as software and tools for task assignment and tracking can also pose a significant challenge. Lastly, the lack of appropriate training to equip the workforce with the necessary skills can impede the implementation of these practices.
Overcoming the Challenges
The good news is, these challenges aren't insurmountable. Here are a few solutions:
- Resistance to Change: This can be overcome by fostering a culture of open communication where the benefits of the new practices are clearly articulated. Regular feedback forums where employees' concerns can be addressed can also help ease the transition.
- Lack of Resources: For businesses facing this issue, it could be worth investing in project management software or tools which have proven to enhance task assignment and tracking. There are many budget-friendly options available.
- Inadequate Training: Conduct regular training sessions and workshops. Such initiatives would enhance employees' skills, thus boosting their confidence in using new systems.
Considerations for Successful Implementation
10. can these practices be adjusted for small teams or individuals, or are they only relevant for large organizations, adapting practices for different team sizes.
The beauty of best practices for task assignment and tracking is that they can be adapted to suit any team size, from large organizations to small teams and even individuals. Indeed, achieving productivity and efficiency is not merely the preserve of the big players. A small team or self-employed individual can efficiently manage their tasks by adjusting these practices to their unique needs.
- Small teams: Best practices can be refined to a simpler format for smaller teams. For instance, daily huddles could replace full-blown weekly meetings for status updates. Task tracking might also involve a more shared responsibility, with every team member being able to monitor and update their progress. Prioritization is still key, but it takes on a more immediate, flexible form.
- Individuals: For solo entrepreneurs or self-employed professionals, these practices can be tailored to personal task management. Clear objectives and deadlines are just as crucial and can be self-imposed. Tools such as personal to-do lists, digital diaries, or task management software can replace team boards and project management platforms.
Best Practices Table
To sum up, while these best practices were developed with larger organizations in mind, they are certainly not restricted to them. With some adjustments, they can offer immense benefits to the efficiency and productivity of smaller teams and individuals too. Therefore, it is important to experiment with, and adapt these practices to fit the specific dynamics and requirements of your working arrangement.
Best Practices for Successful Task Assignment and Tracking
Successful task assignment and tracking is often the difference between successful and unsuccessful projects. The following are the 12 best practices that can streamline your working process and ensure successful task tracking:
- Clarity: Make certain that instructions are clear and comprehensible.
- Define Objectives: Clearly state the purpose and outcome of each task.
- Relevant Skills: Assign tasks based on individual competencies.
- Priority Tasks: Highlight priority tasks.
- Transparent Communication: Maintain an open communication line to deal with problems quickly.
- Empowerment: Empower your team members in task management.
- Use of Technology: Utilize technology to track and manage tasks efficiently.
- Time tracking: Employ a software to track time spent on each task.
- Regular Updates: Showcase constant updates to keep the team on track.
- Project progress visualization: Represent the progression of the project visually for better understanding.
- Deadlines: Set realistic and flexible deadlines.
- Feedback: Regularly give feedback to promote constant improvement.
In light of the above-mentioned practices, the role of technology in task assignment and tracking cannot be overstressed. Several softwares are available in the market to help you streamline your task assignment and tracking processes but none are more efficient and user-friendly than Retainr.io .
Improve Your Business Operations with Retainr.io
Retainr.io is a whitelabel software that unifies all your task management needs. It enables you to sell, manage clients, orders, & payments with your own branded app, ensuring that all information is kept in one place, thus, making accessibility and tracking easier.
With its vast array of features, it empowers your team members by making task assignment and tracking seamless and efficient. It simplifies project management and enhances transparency in communication. The software's use of visual aids for project progress ensures that all team members have a clear view of where the project stands and what needs to be done.
So, harness the power of Retainr.io to ensure a well-coordinated, proficient, and successful execution of your projects. Start your journey towards efficient task management with Retainr.io today.
Fuel Your Agency's Growth with Retainr Accelerator
Uncover secrets, strategies, and exclusive blueprints to supercharge your startup's growth - from marketing insights to effective presentations and working with technology..

SOPs, Cheatsheets & Blueprints
Leverage 50+ SOPs (valued over $10K) offering practical guides, scripts, tools, hacks, templates, and cheat sheets to fast-track your startup's growth.
Connect with fellow entrepreneurs, share experiences, and get expert insights within our exclusive Facebook community.
.jpg)
Join a thriving community of growth hackers. Network, collaborate, and learn from like-minded entrepreneurs on a lifelong journey to success.

Gain expertise with recorded Courses, Live Bootcamps and interactive Workshops on topics like growth hacking, copywriting, no-code funnel building, performance marketing and more, taught by seasoned coaches & industry experts.
See why thousands of influencers & entrepreneurs love Retainr.
"After fifteen years in the industry I thought the way I handled my clients was very efficient. And I did...That is until I ran into Retainr"
@retainr.io You heard that right—Retainr helps you sell your services, collect payments, manage clients in one powerful web app. Looking for more insights to help you tap into the power of Retainr? Check out our latest collab with @ari_travels #retainr #digitalnomad #travellife #freelancertips #entrepreneur #makemoneyonline2023 ♬ original sound - Retainr
@retainr.io Exciting news! 🌟 We're thrilled to announce our collaboration with @jarennsilverfox , a dedicated gym enthusiast and health coach! Thanks to Retainr, he can seamlessly offer his services online anytime, anywhere. 💪🏋️♂️ Say goodbye to the 9-to-5 grind in a dull office! Embark on your freelance journey with Retainr.io and unlock the secrets to transforming your business into a thriving online venture. Ready to make the leap? Click the link in our bio to start your new freelance era today! 🚀 #retainr #workremote #freelancelife #startyouragency ♬ original sound - Retainr
@retainr.io We're all about making remote work easier for people. That's why we've teamed up with @nyyahrose to show you the magic behind Retainr. ✨ #retainr #workremote #entrepreneur #freelancertips #digitalnomad #collab ♬ original sound - Retainr
.jpeg)
Business owner

Productise your Agency with AI & Tech
Sell More with Retainr
From your own branded app to streamlined client management, Retainr.io empowers you at every step.
Join the league of agencies experiencing unparalleled growth, transparency, and efficiency.
Related Blogs

10 Reasons How Niche Targeting Can Benefit Your Small Agency
15 examples of small agencies excelling in niche targeting, top 5 industry-specific services every freelancer needs, 6 key steps to penetrate niche markets successfully, 7 inspiring examples of freelancers with exceptional industry-focused brands, how to develop a unique selling proposition for your small agency, 9 steps to choose the right industry specialization as a freelancer, how do industry-specific services impact freelancers' success, 13 must-have tools for freelancers to boost industry expertise.
How to Give Assignments to Team Members
Table of Contents
The project has been divided into milestones, goals and objectives broken into tasks, and now it’s time to assign them. But as you open the project management platform, you’re faced with the unflattering process of wording the tasks, and choosing whom to assign them to.
Well, in this article, we offer advice on how to make that jumbled first moment a little clearer. There are actionable tips, learning the difference between allocating and delegating tasks, and suggested criteria on how to choose the best person for the job.
For a more precise overview, here’s a table of contents:
How do you assign employees tasks?
We normally think that assigning tasks is a time-consuming process that focuses on clearing out task lists to keep the project going. However, task assignment should actually be a more employee-oriented process that requires additional dedication and effort, which yields incredible results. But what do we mean by that?
Properly assigned tasks push your employees, projects, and the overall company forward. Here’s how.
- They strengthen accountability and trust between managers and employees;
- They help teach new skills and perfect old ones;
- They allow employees to get familiar with other teams and avenues of work;
- It becomes easier to make project estimates;
- Makes for great bases for performance reviews, etc.
The list could go on, but we’ll stop there for now.
Of course, such long-term benefits don’t come without some proverbial blood and sweat in the planning stage. Let’s take a look at the general ideas on assigning employee tasks, and specific steps you can take.
Motivation comes from knowing the bigger picture
When we talk about the bigger picture in project management, we talk about each team member’s task affecting their peer’s down the line. Since all tasks are usually small pieces of the puzzle, it helps to remind employees how their work contributes. For example:
- A high-quality draft can make a great foundation for the final version, and it can be completed more quickly.
- A well-prepared presentation can shave time off unnecessary questions and additional email inquiries.
It comes as no surprise that people work better and are more productive, when they know that their work has an impact on the company level.
And so, when you assign tasks, try to emphasize how they fit in the bigger picture. Simply saying: “ You doing X will help with Y and Z ” and how it reflects on the project as a whole will let an employee know that the task they were assigned is important.
Get your employees excited to commit
Telling people about the bigger picture and showing them what’s possible can only get them so far. It’s enough to ignite the initial spark, but for them to fully commit to the task, you need to define what that task entails.
They should be able to picture how to go about the work, what skills to use, and how to reach the desired result. The clearer the instructions, the more motivated they will be to work.
Simply put, give directions on how the task should be done, and make sure they understand. You can’t read each other’s minds, so it’s important everyone is on the same page.
Ask for task transparency
One of the best practices a company can employ is transparency among coworkers.
This is achieved by having everyone input their tasks for the day in a timesheet. The purpose of timesheets is to get an accurate idea of what everyone is working on at any given time.
When people know who works on what tasks, it’s easier for them to know if a person is available or busy, how far along they are with a task, etc.
So, when you give assignments to employees, label them with deadlines. Alternatively, you can ask for employees’ assessments on how long the work would take them, and use those timeframes.
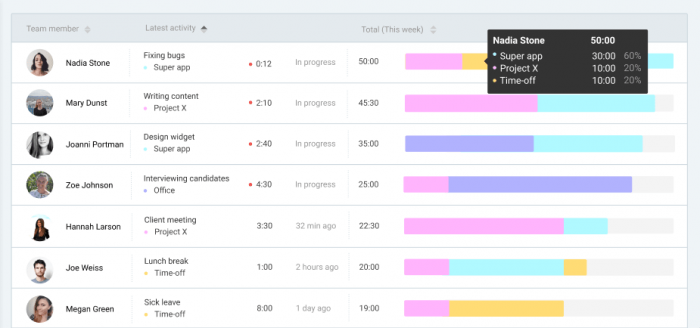
Source: Clockify team timesheet
Timesheets are a great way to keep an eye on tasks and the people doing them. You get to:
- see who struggles with what (helps assess people’s skill sets);
- who burns through their workload and is available for additional tasks;
- whether your time estimates need correction;
- identify any wasted time.
💡 If your employees are insecure about keeping public records of their tasks, here are a few resources that can help:
- How to create order in your daily work tasks
- How to be more efficient with your tasks
Keep a crystal clear timeframe
While we’re discussing timesheets and deadline transparency, it’s important to mention that the times you set for task completions need to be clear-cut.
As we’ve mentioned, the safest way to assign deadlines is to consult the employees. They are better at assessing how long it will take them due to the tasks’ difficulty, overall deadlines, the standards that need to be met, and the skill required to complete it.
When they get a say in how long they should be doing an assignment, people tend to feel more accountable for the whole process. They will do their best to finish in time, since they actively participated in setting the deadline.
Set very clear expectations
Assigning a task should always include your (the supervisor’s) expectations pointed out. For example:
- Does a logo pitch need as many drafts as possible, or just a few finished pieces?
If you ask a designer to make some drafts for a logo pitch, you must specify the kind of quality you’re looking for. Explain whether you are looking for some sketches and drafts for a brainstorming meeting, or if you want clean, presentable pieces to show.
Additionally:
- How many pieces should the designer do?
- Is there a specific color palette they need to follow?
- How important is the task? Is this the day they finally decide on a logo, or is it still in the brainstorming stage? (decides on the quality of the work itself)
Assigning the task using the above questions, you help the designer understand how much effort precisely they need to invest. They become more motivated with clear instructions, as they know what is expected of them. There’s no fear of having their work criticized for something that wasn’t communicated in the beginning. And on your end, it prevents breached deadlines or subpar results.
Avoid creating dependency by being less involved
It’s not unusual for employees to ask their supervisors for their opinion on a certain task, or their performance.
The problem arises when a supervisor makes themselves too involved with the process. When they feel like the project might fall apart if they don’t have their eyes on every moving part all of the time. And when you have, say, 20 people waiting for that person’s approval, advice, or consultation, the workflow runs into a gridlock.
And wait time is wasted time.
Plus, people lose motivation, patience, and grow frustrated, as they could be doing other things.
So, learn not to jump in every time people call for your aid. Assign reliable people who can address smaller issues, while you handle the big picture. Learn how to expend your own energy where it is needed more.
For example – making a pitch presentation for potential investors keeps getting put off because one person needs you to check a client email they want to send, another wants your signature on a form, and the third wants to ask something about employee feedback that’s coming up.
In order to not be stretched thin, and have your time wasted on menial tasks, here’s where you can start:
How to mitigate the risk of being over-involved when assigning
- Remember that you match tasks to people
Which means that, by matching the right people with the right tasks, your involvement will be minimal. Take time to carefully choose who gets to do what. What is the point of assigning tasks if they can’t be done without you?
- Have a 10-point scale to judge the importance of items
How important are certain aspects of your leadership role? Are you absolutely necessary in every meeting, or during every call? Which tasks need your approval, and which ones can be approved by someone under you?
Rank these items on a scale of 0 to 10, based on their importance to you and the project. Top priority tasks should get your undivided attention. And what can be delegated, should be.
- Analyze your schedule
Your energy and time are needed on a much broader scale. The best way to spot if you’re wasting time being too involved is to look at your schedule. Identify how much time you’ve spent on low-priority items, and assess which issues could’ve been solved without you.
- Take into account priorities and deadlines
Step in only when absolutely necessary. You are in charge of things getting done on time, by people most qualified for assigned tasks. Determine what your priorities are for each project, and concern yourself only with those issues, unless there is a risk of breaching a deadline.
- Formulate a list of dependable people
If you know your employees (or team members) well enough, then you should be able to single out those who are more dependable and ready to take on a little more responsibilities. Write out the reasons how they could help by getting involved on low-priority items instead of you. When the time comes, rally them and present them with the idea, keeping in mind that this solution helps push the project forward. When authority is delegated to several people, there’s fewer chances of a hold-up in the workflow.
This also falls into the realm of task delegation , which we’ll get into later.
How do you decide what tasks to assign to which employees?
1. assign based on priority.
Naturally, some tasks will be more important than others. When you break down a project into tasks , spend some time assessing their priority level.
High-priority tasks should be the first on your list to allocate. Whether it’s because they’re time-sensitive, or require more effort and dedication.
Low priority tasks can be allocated as fillers to the first available person.
2. Assign based on employee availability
Another factor to consider when assigning tasks is who is available at the moment.
As the project moves along, new tasks will be added. You will have to allocate new work, but odds are you won’t always be able to pick who you want. Especially if a deadline is approaching, the person with the smallest workload should be your first choice.
Overloading an already busy individual just because they’re more skilled or you have faith in them the most puts an unnecessary strain on them. It’s cause for frustration, poorer results, and decreased productivity.
And as we’ve mentioned, if you have a timesheet with an overview of all the tasks and employees working on them, it’ll be much easier to spot who is free and who isn’t.
3. Assign based on employee skill level
High-priority tasks should go to employees with more experience in a given field or skill. However, you should occasionally give such tasks to other employees as well, to help them grow and become just as dependable. Giving people challenging tasks that can boost their experience is essential to productivity and morale.
Not to mention you get to have multiple high-skilled employees.
Low-priority tasks can be assigned to anyone, despite their experience level. They’re a good opportunity to practice, pick up new skills, or get smaller tasks out of the way to make room for more important ones.
4. Assign based on preference
Last, but not the least, preference can also play a big part in how you assign tasks.
It’s a given that some employees will prefer certain tasks over others. So it could be good to assign tasks at a meeting with the team. As you discuss priorities, deadlines, and availability, ask them which tasks they would like to work on.
If someone shows interest in a specific type of work, they should (with some consideration), be allowed to take it. After all, people are more productive when they’re assigned to something they find new or exciting.
Note: Apply this rule with caution. Letting people do only the tasks they want can stunt their career growth. Getting out of our comfort zones and occasionally doing tasks that we don’t like is how we develop and learn. So, don’t forget to document assignments as you hand them out, to spot these potential issues early on.
Allocating vs delegating tasks
While semantically similar words, delegation and allocation in terms of tasks are two different things.
When you allocate tasks , you are assigning tasks without giving the employees much authority, challenge, or room to grow. It includes you keeping all of the responsibility – writing out the tasks, making deadlines, providing resources, tools, etc. These are usually recurring tasks that can become repetitive.
When you delegate tasks , you allow for some of that responsibility to fizzle out from your fingers. All you think about are the objectives, while letting the employees figure out the details and means to get there.
However, that doesn’t mean delegation is right and the allocation is wrong.
Task allocation has its own place. It is just as important, as a lot of tasks come down to repeated processes that are still vital to the project progress. Task delegation is just a good opportunity for employees to learn, challenge themselves, and assess their skills and performance.
When should you allocate tasks?
Management and BizDev consultant Artem Albul shared his concept on task assignment, which he dubbed an “algorithm”. He emphasized how these criteria are useful only and only when you wish that employees perform the tasks based on your guidelines and instructions (aka allocation).
Here is how Albul broke down the algorithm:
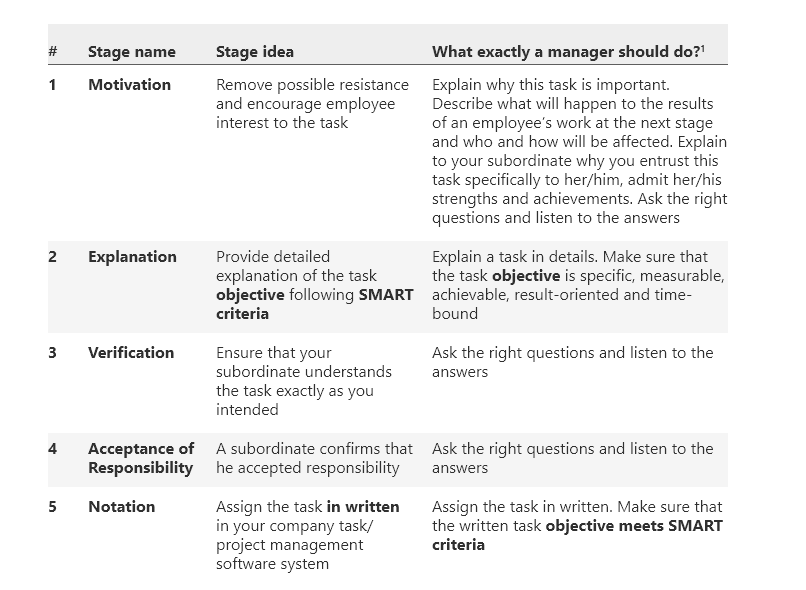
Source: Artem Albul, TWA Consulting
As we can see, task allocation, while the more “controlling” of the two, also gives in-depth instructions and asks for confirmation on task clarity. A lot of it comes down to everyone being on the same page, leaving little to no room for misinterpretation (but also creative freedom).
How should you allocate tasks?
With all that we’ve mentioned in the previous section, here’s how your task allotment could look like, step by step.
- Break down your project
Detail out the goals, objectives, and some individual tasks (not all, be careful not to start micromanaging). Place the most important deadlines.
- Prioritize tasks and sort them
It’s important to know what tasks need to be done faster/better, to properly allocate your resources and manpower from the start.
- Make a list of teams and team members
Assign team leaders (if you don’t have them), and alternatively, ask for their input on individual employees skills, for a more informed decision on who gets what.
- Schedule a meeting
Make a meeting with the team leads and go through the points above. Assign tasks according to each team’s availability, interest, and skill required to successfully push the project forward.
- As team leads – assign tasks further down the pipeline
- Track task completion and make necessary changes along the way
Whether it’s pushing deadlines, reassigning tasks, or shifting around resources. This is perfectly fine and expected, so long as it doesn’t happen on every task you’ve assigned. Then, it is an indicator of poor pre-planning.
- Offer feedback and write performances
Don’t forget to track the progress and make notes of important details that might help the next task allocation/delegation process. It’s also a useful piece of information for the employees on what they need to improve on.
Allocating tasks is somewhat more complicated than we want it to be. But, this kind of thorough research and preparation will make projects run more smoothly. Employees will also be more satisfied with their work, and there will be less hurdles as deadlines approach.
When should you delegate tasks?
Delegation is a great practice in trust for both the employer/supervisor and the employee. The employer learns how to give away some of their control over the process, while the employee learns how to take more accountability for their work.
This lets you focus on big-picture aspects of your job, since you deal less with assignments that are low-priority for you. You save time and energy, while helping others move up in their careers.
How do you effectively delegate tasks as a leader?
As we’ve mentioned, delegating includes more employee independence. There are some additional components which make this type of task assignment more appealing than allocation, with great opportunities for growth.
Focus on delegating objectives instead of actual tasks
When you delegate, you focus on the objective that needs to be done. You shouldn’t give employees a “color by numbers” instruction on how to complete a task.
Communicate clearly what the end result should be and what expectations you (or the higher-ups) have. Leave the means for reaching that end goal to the employees themselves. Because how you solve a task may be completely different to how they will. And that is perfectly fine, so long as the result is the one you are looking for.
Keep the objectives challenging
When the objectives you’re delegating are too easy, chances are the person will either procrastinate, or feel like you don’t trust them enough. And if they’re too difficult, they get frustrated, anxious, and begin to panic.
It’s a good idea to be aware of an employee’s skill level, so you can gauge how much challenge and responsibility they can take on. For them to be the most productive and achieve great results, they need to enter “the state of Flow”.
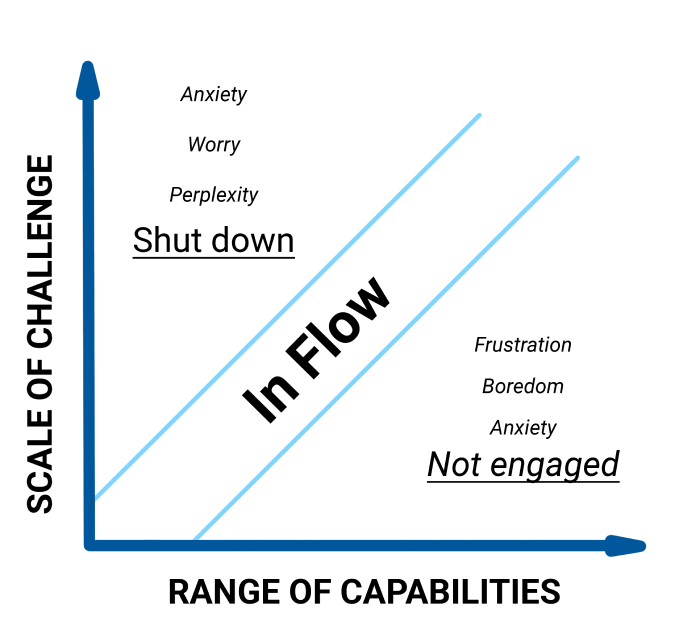
Source: Optimal Experience , M. Csikszentmihalyi
💡 We’ve discussed the state of Flow in more detail in an article on time organization.
Encourage discussion and feedback
Let employees voice their opinions on the topic.
They should ask anything about the task, the goals, or the overall impact their work will have on the later stages or others’ workflow. It means they are interested in the task, and getting involved.
And if they aren’t asking questions themselves, you can always nudge them into proactivity.
- Is there something you’d like me to clarify?
- Do you already have any ideas on how to go about the task?
- Is the time we agreed upon enough for you?
- Will you need other resources, tools, or support?
- Do you see any problems or risks?
Questions like these help them feel valued, their efforts acknowledged, and let them know you care about the task and how well they perform. Just be careful not to overdo it, or you’ll start to look like a micromanager.
Give employees free rein, but offer support
Speaking of micromanaging, delegation means you let people problem-solve their way out on their own. There should be no reason for a manager to step in and control or supervise any step of the process, unless absolutely necessary.
However, what you should do is let them know you’re available for any advice should they feel stuck. Just because employees get authority on a certain task, and are left to their own devices, doesn’t mean the project has to suffer until they pull themselves up.
From time to time, ask them if they need anything from you, and make sure they know you’re there for any kind of support, consultation, or mediation. ANother good practice is to also give them additional learning opportunities – such as training, conferences, courses, etc.
Delegate objectives that move people forward
Choose assignments that boost the skills and employ all of their experiences, instead of something that simply needs to be done. For example:
- Tasks that require they brush up on their team communication skills;
- Learning how to allocate smaller tasks;
- Supervising others’ work and doing quality control;
- Learning to work with a new tool;
- Holding a meeting (or more), etc.
Find out which skills your employees may want or need to develop, and then plan your delegations accordingly. You want them to complete the task while having learned something new at the same time.
How to choose who to delegate to
Paul Beesley, senior director and consultant at Beyond Theory proposed a nifty checklist for when you’re choosing an employee to delegate to. It’s meant to simplify and speed up the process.
To successfully complete the delegated task, your chosen employee needs:
S – the skill to perform and complete a task
T – the time to complete the task, and if needed, learn the required skill
A – the authority to handle everything concerning the task
R – the necessary level of responsibility
R – the recognition for successfully completing the task
This list is a set of important criteria that should be covered when you consider who to assign to a specific task. However, depending on your niche, type of service, company size and the project at hand, the criteria are likely to change. And it should accommodate your needs, not the other way around.
Common task delegation mistakes to avoid
With all being said, there are some common mistakes managers and employers make, sometimes without even realizing it.
- Being too vague concerning deadlines (using: as soon as possible, when you get to it, I need it by yesterday). It creates unnecessary pressure.
- Being unavailable for questions and concerns. While you shouldn’t micromanage, you should still be present for support if an employee feels stuck. Ignoring them or handing them over to someone else could cause distrust. However, if you are usually swamped with work, set consultation hours each day or week.
- Having unclear directions. Specifying the allotted time for task completion and expectations should be the bare minimum when delegating tasks.
- Not providing feedback. No feedback is worse than bad feedback. Employees need to be aware when they’re doing good work, as well. In one company I worked for, the mantra was: “If no one is complaining about your work, that means you’re doing good”. And while it sounds like sound logic, it actually caused a lot of frustration. We were left directionless, and simply “floating” from task to task, never knowing if any of them had a positive impact on our performance.
- Not listening to employees. Take into account how they feel about a task or the objective. Let them give you feedback and if there are potential problems from the get-go.
- Assigning other people to the same task. If you notice a person struggling, the first instinct should be to ask them how they’re faring, and if they need any help. Some managers tend to assign other employees to help them without consultation, which leaves a sore taste. The employee will feel even more incompetent and will be less likely to take on a similar task in the future.
- Assuming people will know what you mean. This is one of the biggest problems. When you’re formulating a task, be as clear as possible about the goals and expectations. Oftentimes managers think that these things are implied, but the truth is – no one is a mind reader. To avoid having information misconstrued or misunderstood, communicate clearly and directly.
There could be more mistakes, especially for every different field and industry. If at all possible, identify the most common ones, made either by you or your peers. Note down all the instances where certain tasks weren’t up to par, and see what you could have changed in your assignment process to fix it. Maybe there wasn’t enough time or resources, you were unclear, or the employee wasn’t ready for such responsibility. Use the same procedure in all future task delegations. It’s the only way to learn and make the process quicker.
Use Clockify to assign tasks with ease
Now you’re a master of task delegation — congrats!
But there’s more to it than meets the eye.
In fact, what if you used a digital tool like Clockify to increase the likelihood that each job would be completed on time and on point?
In Clockify, you can easily create highly descriptive assignments that contain information like:
- Start time,
- Billability status,
- Name of the employee,
- Period for getting the assignment done,
- Hours per day to spend on the assignment, and more.
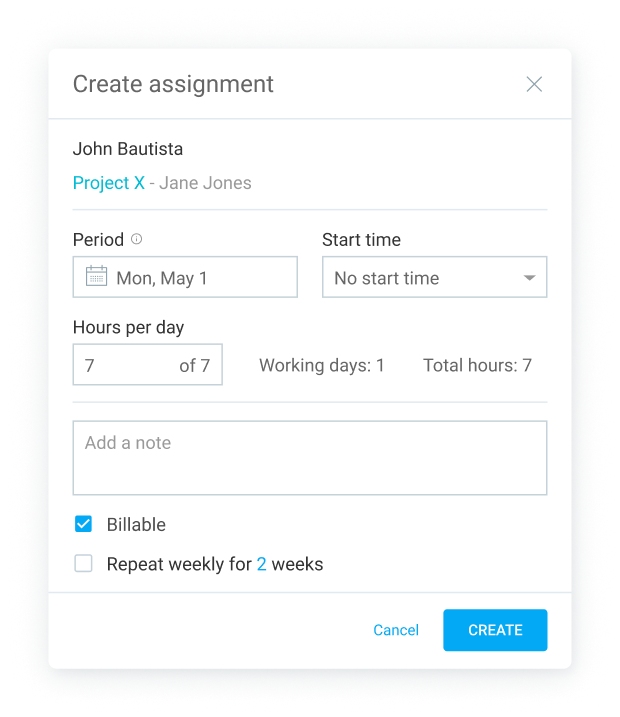
That way, you can plan who works on what, how long, and when.
Similarly, Clockify allows you to create project milestones to achieve results faster.
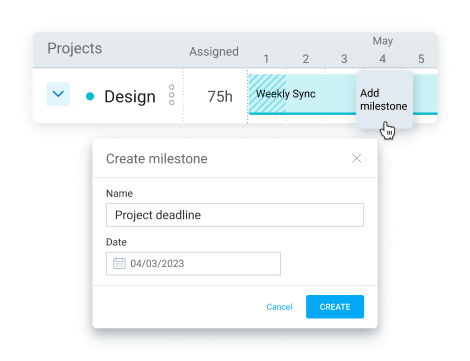
With the Milestones option, you can select dates for deadlines, allowing you to pin down important events in your projects.
For example, if your client expects you to keep them in the loop about developments, you can inform them promptly on whether your team has reached the agreed-upon milestones.
Refocus on your company’s big picture with a project and time tracking tool.

Marijana Stojanovic is a writer and researcher who specializes in the topics of productivity and time management.
Where does the time go?
START TRACKING TIME
with Clockify
How to create a PTO policy
Everything you need to know about creating a PTO policy — from the basics of PTO to choosing a PTO tracking system that suits your workflow.
Working Overtime Without Pay – Know Your Rights and Options
Discover the legal and financial aspects of working overtime without pay. Learn your rights and how to handle common concerns regarding off-clock work.
PTO vs. Vacation: What Is the Difference?
Learn the difference between PTO and vacation and find out the answers to the most frequently asked questions regarding paid leave!
Best methods for tracking team productivity
Find out the most useful methods of tracking team productivity, followed by actual examples of how different teams measure their effectiveness.
Difference between a freelancer, a contractor, and an employee
Learn which work category you fall into, to better protect your rights as a worker and avoid worker exploitation.
10+ Life-changing tips to increase office productivity in 2023
Workplace distractions, stress, and poor performance are everywhere. Read this guide with life-changing tips to increase office productivity now!
FREE FOREVER • UNLIMITED USERS
Free time tracker
Time tracking software used by millions. Clockify is a time tracker and timesheet app that lets you track work hours across projects.
- Sign in / Join

Task assignment in project management

Task assignment in project management is an essential aspect of project management. It involves assigning specific tasks or activities to team members to ensure the smooth functioning and completion of a project.
A well-structured task assignment process helps in breaking down the project into manageable parts, and delegates responsibilities to individuals who have the necessary skills and experience to carry out the work efficiently. In this article , we will discuss the importance of task assignment in project management, the steps involved in the process, and some tips for effective task assignment.
Importance of Task Assignment in Project Management
Task assignment is crucial for the success of a project for several reasons:
- Effective Utilization of Resources: Task assignment helps in identifying the right team members who have the necessary skills and experience to carry out specific tasks. This ensures the effective utilization of resources, avoiding overloading of individuals, and improving productivity.
- Improved Time Management: Task assignment helps in determining the estimated time required to complete each task. This enables project managers to schedule tasks and set realistic deadlines, thereby improving time management and reducing the risk of delays.
- Better Coordination: Task assignment promotes better coordination among team members, as each person knows their specific responsibilities and the tasks they need to complete. This leads to fewer misunderstandings and improves communication between team members.
- Enhanced Accountability: Task assignment enhances accountability, as team members know they are responsible for specific tasks and are expected to complete them within the specified time frame.
Steps Involved in Task Assignment Process
The task assignment process typically involves the following steps:
- Define the project scope and objectives : The first step in task assignment is to clearly define the project scope and objectives. This helps in identifying the tasks that need to be completed to achieve the project goals.
- Identify tasks: The next step is to identify the tasks required to complete the project. This involves breaking down the project into smaller, manageable tasks and activities.
- Assess team members’ skills and availability: Once the tasks have been identified, the next step is to assess the skills and availability of team members. This helps in determining who is best suited for specific tasks and who has the necessary experience and expertise.
- Allocate tasks: Based on the assessment of team members’ skills and availability, tasks are allocated to individuals. It is important to consider individual strengths and preferences when assigning tasks.
- Set deadlines: Once the tasks have been assigned, the next step is to set deadlines for each task. This helps in ensuring that work is completed within the specified time frame.
- Monitor progress: Regular monitoring of task progress is essential to ensure that tasks are being completed on time and to the required standard. Project managers should also address any issues or challenges that arise during the task completion process.
Tips for Effective Task Assignment
- Clearly Define Tasks: It is essential to clearly define tasks to ensure that team members understand their responsibilities and the work they need to complete.
- Consider Individual Strengths and Weaknesses: When assigning tasks, it is important to consider individual strengths and weaknesses. This helps in ensuring that tasks are assigned to individuals who are best suited to carry out the work.
- Set Realistic Deadlines: Deadlines should be set realistically to ensure that tasks are completed on time and to the required standard.
- Regular Communication: Regular communication is important to ensure that team members are aware of any changes or updates to tasks and that any issues or challenges are addressed in a timely manner.
- Project management
- Software Developer Roles and Responsibilities
- Project lead roles and responsibilities in software development
- Roles and Responsibilities of Risk Champion
- Project management tools
- Types of project management consultants
- Does Project Management Require Coding?
- Why project leader is higher than project manager
10 benefits of task assignment
What are the benefits of task assignment? Task assignment can bring a variety of benefits to the workplace, which can have a positive impact on both the organization and its employees.
- Improved productivity: By assigning tasks to the right people, organizations can ensure that the right skills are being used to complete tasks efficiently and effectively. This leads to higher levels of productivity and helps organizations meet their goals.
- Better time management: Task assignment enables individuals and teams to prioritize their workload, manage their time more effectively, and meet deadlines. This helps organizations operate in a more efficient and organized manner.
- Enhanced accountability: Task assignment makes individuals and teams more accountable for their work. This leads to higher levels of performance, as people are more likely to take ownership of their tasks and work to the best of their ability.
- Better delegation: Task assignment allows managers to delegate tasks effectively, freeing up their own time to focus on other important tasks. This helps organizations run more smoothly and improves the overall workflow.
- Improved communication: Task assignment can help improve communication within an organization. When tasks are assigned, individuals and teams are able to discuss their responsibilities, share information, and collaborate effectively.
- Better team collaboration: Task assignment can also help teams work together more effectively. When tasks are assigned to teams, individuals are able to work together to achieve common goals, improving the overall performance of the team.
- Increased motivation: Task assignment can also help increase motivation in the workplace. When individuals and teams are given meaningful tasks that are aligned with their skills and interests, they are more likely to feel engaged and motivated to complete their work.
- Better decision-making: Task assignment helps organizations make better decisions. By assigning tasks to individuals and teams with the relevant expertise, organizations can ensure that the right people are making the right decisions.
- Improved quality: Task assignment can also help improve the quality of work. When tasks are assigned to individuals and teams who have the relevant skills and expertise, the end result is likely to be of higher quality.
- Better resource utilization: Task assignment can help organizations utilize their resources more effectively. By assigning tasks to the right individuals and teams, organizations can ensure that their resources are being used in the most efficient and effective way possible.
In conclusion, task assignment is an essential aspect of project management that plays a critical role in ensuring the success of a project. By breaking down the
Similar Content
- Risk Owner in Project Management
- Calculate Risk Probability and Impact Matrix
- Risk Probability and Impact Matrix
- The 5 levels of risk
- Difference Between Consequence and Risk
- Five Ways to Manage Risk
- Project Risk Management
- What Is Involved In Risk Matrix?
- 3 Types Of Project Risk
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
Best Project Management Institute in Nigeria
Universities offering Project Management in Nigeria
Advantages and disadvantages of project planning

POPULAR CATEGORY
- Education 93
- Business 81
- Government 1
Definition of 'assignment'

assignment in British English
Assignment in american english, examples of 'assignment' in a sentence assignment, cobuild collocations assignment, trends of assignment.
View usage for: All Years Last 10 years Last 50 years Last 100 years Last 300 years
Browse alphabetically assignment
- assigned randomly
- assigned risk
- assimilability
- assimilable
- All ENGLISH words that begin with 'A'
Related terms of assignment
- seat assignment
- tough assignment
- writing assignment
- challenging assignment
- difficult assignment
- View more related words
Quick word challenge
Quiz Review
Score: 0 / 5

Wordle Helper

Scrabble Tools

- Dictionaries home
- American English
- Collocations
- German-English
- Grammar home
- Practical English Usage
- Learn & Practise Grammar (Beta)
- Word Lists home
- My Word Lists
- Recent additions
- Resources home
- Text Checker
Definition of assignment noun from the Oxford Advanced American Dictionary
Take your English to the next level
The Oxford Learner’s Thesaurus explains the difference between groups of similar words. Try it for free as part of the Oxford Advanced Learner’s Dictionary app
While the word “task” might bring about feelings of despair related to chores or undesirable actions, this is usually related more so to the way you have to manage your time than the task itself.
In this article, we’ll do a deep dive into tasks, show you the best ways to break down larger projects into them, while covering efficient approaches to manage and distribute tasks.
Try monday.com
What is a task in a project?
In project management, a task is a work item or activity with a specific purpose related to the larger goal. It’s a necessary step on the road towards project completion.
For example, it could be something as complex as a mobile app bug fix.

Or it could be something as simple as photocopying the latest brochure for distribution.
Single tasks are typically assigned to a single person or team, while the larger project could be a company-wide endeavor.
The task may or may not include a start and end date or a series of subtasks—this all depends on the complexity of the project at hand, which could be related to industry.
How do you break down a project into smaller tasks?
Even long term Scrum projects that last 11.6 weeks on average make use of task management to get their work done efficiently and effectively.
Part of task management includes creating manageable workloads, considering task dependencies, and of course, communicating across teams to avoid double work or roadblocks.
To avoid these issues, you need some way to break down the high-level project deliverables and goals into tangible tasks.
In the next section, we’ll show you two of the most popular methodologies, Waterfall, and Scrum.
Work Breakdown Structure
The work breakdown structure (WBS) is the official method of breaking down projects in the PMI Guidebook.
To figure out how to break the entire project into tasks, you first need to divide it into the actual deliverables required to hand over the final product or result to the client.
For example, if you’re planning to make a mountain bike, you can break that down into the frame, handlebars, pedals, wheels, chains, and so on.

( Image Source )
You also need to work out the dependencies of the project (aka which deliverables require another one for completion).
If we were to simplify the WBS, the section on manufacturing the bike frame might look something like this.

Of course, each item contains multiple tasks such as sourcing vendors, reviewing designs, picking materials, and more.
But if you assign these tasks to teams who have the necessary skills to complete all of them, that’s what the top-level plan might look like.
If you use an Agile framework, like Scrum, you won’t bother breaking down the entire project into detailed tasks at an early stage. Avoiding this large-scale exercise in prediction is one of the primary principles of Agile.
Instead, you’ll focus on planning out a deliverable increment of your product in Scrum sprints . These are 2–4 week periods of focused work dedicated to delivering a working product version of the final deliverable.
The basis for planning out these iterations is a backlog of features or user stories (functionality from the user’s perspective). You may also have a product roadmap to outline the long-term product direction as well.

The product backlog is continually pruned and optimized before, during, and after sprints. Even if you’re not planning software projects, you can often single out elements that you can deliver in increments.
Before each Sprint, you meet with your team and stakeholders (invested parties) to discuss which user stories are the most important. You select a few items and create a dedicated sprint backlog.
Each user story is then further divided into tasks, and team members take ownership of the specific tasks they can handle.
It’s not ideal for all organizations or projects, but it’s an antidote against micromanagement in complex projects.
What size should a project task be?
So how granular should you get? What should the scope and length of the task in your project be?
It depends on the size of your project and your PM framework, but here are some rules of thumb.
The 8/80 rule for WBS
In traditional project management, a rule of thumb is that no task should be shorter than 8 hours or longer than 80 hours in the WBS.
That’s why the PMI recommends keeping tasks between 20–80 hours in the WBS.
Your individual teams can then have more granular task boards to manage their own to-do lists and/or break 2-week tasks down into daily sub-tasks.
Task length in Scrum
While user stories generally have no specified length, they’re often broken down into manageable chunks, usually one workday or less.
The official Scrum Guide doesn’t use the word tasks, but instead uses the term work unit:
“ Work planned for the first days of the Sprint by the Development Team is decomposed by the end of this meeting, often to units of one day or less. ”
On a Scrum board , you can use story points (at monday.com, we equate 1 SP to a workday) to estimate the length of the task.

Tasks shouldn’t require more than one resource
When you break down deliverables into individual tasks, time isn’t the only consideration. The best approach is to make sure the person (or resource) who’s assigned the task can complete it from start to finish.
For example, a graphic designer could create a wireframe for an app, but wouldn’t be able to create a working prototype.
So you should split the larger deliverable of a working feature prototype into wireframe/design and development (at the very least).
For larger companies, a resource could be an entire team that includes designers, developers, and software testers. In which case, you don’t have to get as granular when planning and assigning tasks.
Accurately estimating task durations
The best way to predict the duration of tasks is to involve the actual resources who will handle the task in the planning process.
You don’t need to switch to Agile or Scrum to make this happen. You just need to involve the actual project implementers in the planning process, not just management.
Not only can they help with task durations, but they can also help with dependencies and expecting potential bottlenecks.
What is the best way to organize project tasks?
There are hundreds of different frameworks and methods for managing projects and breaking them down into tasks.
A few stand out because of their efficiency and ease of adoption and have become popular as a result.

Let’s take a closer look at these industry-leading options.
Waterfall refers to the traditional “predictive” project management approach. It’s called predictive because you plan every phase of the project from start to finish before even getting started.
The reason it’s called waterfall is that the projects are planned to follow a sequential order.

First, you start out by figuring out the requirements of the project. What deliverables do you need to deliver a finished product?
Then you move on to designing and creating (implementing) it. Finally, you verify that the product works as intended, and launch it. The last stage includes the long-term maintenance of the product.
While berating waterfall is a popular pastime among younger management professionals, it has its place.
For physical products with a lot of dependencies and high costs associated with actual production time, mapping out the entire project in detail can be the best approach.
Instead of a specific methodology, Agile outlines a core set of values and principles to apply to your projects. As a result, Agile is an umbrella term that covers many different methodologies and frameworks .
The most famous principle is to deliver working iterations of your project frequently. That’s in contrast to planning out an entire product from start to finish like with waterfall.
Lean, like Agile, is not a specific framework that details a project management approach. Instead, it refers to a management philosophy with a core set of principles.
The focus of Lean is eliminating waste in processes throughout each stage of production. The execution is what controls the outcome, after all.
Fixing bottlenecks between departments to speed up the final assembly is a good example.
Not to be confused with Agile, which is more about high-level concepts and principles, Scrum is an actual framework for project management.
It outlines clear rules, meetings (ceremonies), and deliverables (artifacts), not just values.

For example, Scrum teams should only include a maximum of 9 regular team members. Daily Scrum meetings should only last 15 minutes.
The entire process of designing and completing a sprint is laid out in detail. That’s what makes the Scrum framework so useful for teams that want to implement more Agile principles into practice.
How to use a project management platform for effective task management
Instead of slowing down your managers and teams with an inefficient process, take advantage of the latest task management software .
monday.com is a digital workspace with all the functionality a project manager could ever want, wrapped in a package that’s actually easy to learn and use.
Pick the framework or methodology you want to work with
If you want to reach a completely new target level of productivity, basic task management won’t cut it. You need to introduce a project management framework that goes beyond daily tasks.
Luckily, monday.com makes it easy to make the switch. We offer dedicated templates for everything from WBS to Scrum.
Develop the high-level project roadmap

For consistent results, you should develop a high-level project roadmap. It will help guide all decisions and priorities as the project progresses.
Get more granular with a WBS and other task boards
This is where you break the larger goals into smaller deliverables and start to establish the workload for each team or department that’s involved.
It should outline the overall process but may not specify every activity or task, depending on the scale of the project.

But it’s not the best for planning individual tasks within the involved teams or departments.
Which is why monday.com also offers more basic task boards that these teams can use to manage the day-to-day.

You can easily divide larger items into smaller subtasks and assign them as well.
Use integrations and automations to automate menial tasks
If you want to perfect your workflow , it’s not enough to create some new task boards. You also need to eliminate repetitive menial tasks.
For example, with our smart integrations, you can automatically update a card or create a new task when you receive an email or message.

It’s a useful feature for a wide variety of teams and use-cases. For example, your software team could get a new task with every bug report.
By automating menial tasks, you give your managers and team the time and space to focus on crucial high-level decisions.
Keep managers up to speed with dashboards and reports
Want to see at a glance if tasks are being completed on schedule, or which people (or teams) are available for last-minute work?
You can easily create and customize a dashboard that will give your managers instant access to all the information they need.

Master your tasks
Breaking down a project into tasks and assigning them effectively requires a bit of balance.
Finding the framework that works best for your industry and internal workflows and pairing them with the tips above can help you find the happy medium of management and autonomy that will allow your teams to thrive.
Whichever you choose, monday.com has the right templates and tools to help your projects succeed.
- Jump to menu
- Student Home
- Accept your offer
- How to enrol
- Student ID card
- Set up your IT
- Orientation Week
- Fees & payment
- Academic calendar
- Special consideration
- Transcripts
- The Nucleus: Student Hub
- Referencing
- Essay writing
- Learning abroad & exchange
- Professional development & UNSW Advantage
- Employability
- Financial assistance
- International students
- Equitable learning
- Postgraduate research
- Health Service
- Events & activities
- Emergencies
- Volunteering
- Clubs and societies
- Accommodation
- Health services
- Sport and gym
- Arc student organisation
- Security on campus
- Maps of campus
- Careers portal
- Change password
Glossary of Task Words
Understanding the meaning of words, especially task words, helps you to know exactly what is being asked of you. It takes you halfway towards narrowing down your material and selecting your answer.
Task words direct you and tell you how to go about answering a question. Here is a list of such words and others that you are most likely to come across frequently in your course.
Maddox, H 1967, How to Study , 2nd ed, Pan Books, London.
Marshall, L., & Rowland, F 1998, A guide to learning independently , Addison Wesley Longman, Melbourne.
Northedge, A 1997, The good study guide , Open University, Milton Keynes, UK.
Essay and assignment writing guide
- Essay writing basics
- Essay and assignment planning
- Complex assignment questions
- Glossary of task words
- Editing checklist
- Writing a critical review
- Annotated bibliography
- Reflective writing
- ^ More support
Scholarly Resources 4 Students | scite.ai 21 May 2024
Discover your Library: Main Library 21 May 2024

Understanding Assignments
What this handout is about.
The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms and practices into meaningful clues to the type of writing your instructor expects. See our short video for more tips.
Basic beginnings
Regardless of the assignment, department, or instructor, adopting these two habits will serve you well :
- Read the assignment carefully as soon as you receive it. Do not put this task off—reading the assignment at the beginning will save you time, stress, and problems later. An assignment can look pretty straightforward at first, particularly if the instructor has provided lots of information. That does not mean it will not take time and effort to complete; you may even have to learn a new skill to complete the assignment.
- Ask the instructor about anything you do not understand. Do not hesitate to approach your instructor. Instructors would prefer to set you straight before you hand the paper in. That’s also when you will find their feedback most useful.
Assignment formats
Many assignments follow a basic format. Assignments often begin with an overview of the topic, include a central verb or verbs that describe the task, and offer some additional suggestions, questions, or prompts to get you started.
An Overview of Some Kind
The instructor might set the stage with some general discussion of the subject of the assignment, introduce the topic, or remind you of something pertinent that you have discussed in class. For example:
“Throughout history, gerbils have played a key role in politics,” or “In the last few weeks of class, we have focused on the evening wear of the housefly …”
The Task of the Assignment
Pay attention; this part tells you what to do when you write the paper. Look for the key verb or verbs in the sentence. Words like analyze, summarize, or compare direct you to think about your topic in a certain way. Also pay attention to words such as how, what, when, where, and why; these words guide your attention toward specific information. (See the section in this handout titled “Key Terms” for more information.)
“Analyze the effect that gerbils had on the Russian Revolution”, or “Suggest an interpretation of housefly undergarments that differs from Darwin’s.”
Additional Material to Think about
Here you will find some questions to use as springboards as you begin to think about the topic. Instructors usually include these questions as suggestions rather than requirements. Do not feel compelled to answer every question unless the instructor asks you to do so. Pay attention to the order of the questions. Sometimes they suggest the thinking process your instructor imagines you will need to follow to begin thinking about the topic.
“You may wish to consider the differing views held by Communist gerbils vs. Monarchist gerbils, or Can there be such a thing as ‘the housefly garment industry’ or is it just a home-based craft?”
These are the instructor’s comments about writing expectations:
“Be concise”, “Write effectively”, or “Argue furiously.”
Technical Details
These instructions usually indicate format rules or guidelines.
“Your paper must be typed in Palatino font on gray paper and must not exceed 600 pages. It is due on the anniversary of Mao Tse-tung’s death.”
The assignment’s parts may not appear in exactly this order, and each part may be very long or really short. Nonetheless, being aware of this standard pattern can help you understand what your instructor wants you to do.
Interpreting the assignment
Ask yourself a few basic questions as you read and jot down the answers on the assignment sheet:
Why did your instructor ask you to do this particular task?
Who is your audience.
- What kind of evidence do you need to support your ideas?
What kind of writing style is acceptable?
- What are the absolute rules of the paper?
Try to look at the question from the point of view of the instructor. Recognize that your instructor has a reason for giving you this assignment and for giving it to you at a particular point in the semester. In every assignment, the instructor has a challenge for you. This challenge could be anything from demonstrating an ability to think clearly to demonstrating an ability to use the library. See the assignment not as a vague suggestion of what to do but as an opportunity to show that you can handle the course material as directed. Paper assignments give you more than a topic to discuss—they ask you to do something with the topic. Keep reminding yourself of that. Be careful to avoid the other extreme as well: do not read more into the assignment than what is there.
Of course, your instructor has given you an assignment so that they will be able to assess your understanding of the course material and give you an appropriate grade. But there is more to it than that. Your instructor has tried to design a learning experience of some kind. Your instructor wants you to think about something in a particular way for a particular reason. If you read the course description at the beginning of your syllabus, review the assigned readings, and consider the assignment itself, you may begin to see the plan, purpose, or approach to the subject matter that your instructor has created for you. If you still aren’t sure of the assignment’s goals, try asking the instructor. For help with this, see our handout on getting feedback .
Given your instructor’s efforts, it helps to answer the question: What is my purpose in completing this assignment? Is it to gather research from a variety of outside sources and present a coherent picture? Is it to take material I have been learning in class and apply it to a new situation? Is it to prove a point one way or another? Key words from the assignment can help you figure this out. Look for key terms in the form of active verbs that tell you what to do.
Key Terms: Finding Those Active Verbs
Here are some common key words and definitions to help you think about assignment terms:
Information words Ask you to demonstrate what you know about the subject, such as who, what, when, where, how, and why.
- define —give the subject’s meaning (according to someone or something). Sometimes you have to give more than one view on the subject’s meaning
- describe —provide details about the subject by answering question words (such as who, what, when, where, how, and why); you might also give details related to the five senses (what you see, hear, feel, taste, and smell)
- explain —give reasons why or examples of how something happened
- illustrate —give descriptive examples of the subject and show how each is connected with the subject
- summarize —briefly list the important ideas you learned about the subject
- trace —outline how something has changed or developed from an earlier time to its current form
- research —gather material from outside sources about the subject, often with the implication or requirement that you will analyze what you have found
Relation words Ask you to demonstrate how things are connected.
- compare —show how two or more things are similar (and, sometimes, different)
- contrast —show how two or more things are dissimilar
- apply—use details that you’ve been given to demonstrate how an idea, theory, or concept works in a particular situation
- cause —show how one event or series of events made something else happen
- relate —show or describe the connections between things
Interpretation words Ask you to defend ideas of your own about the subject. Do not see these words as requesting opinion alone (unless the assignment specifically says so), but as requiring opinion that is supported by concrete evidence. Remember examples, principles, definitions, or concepts from class or research and use them in your interpretation.
- assess —summarize your opinion of the subject and measure it against something
- prove, justify —give reasons or examples to demonstrate how or why something is the truth
- evaluate, respond —state your opinion of the subject as good, bad, or some combination of the two, with examples and reasons
- support —give reasons or evidence for something you believe (be sure to state clearly what it is that you believe)
- synthesize —put two or more things together that have not been put together in class or in your readings before; do not just summarize one and then the other and say that they are similar or different—you must provide a reason for putting them together that runs all the way through the paper
- analyze —determine how individual parts create or relate to the whole, figure out how something works, what it might mean, or why it is important
- argue —take a side and defend it with evidence against the other side
More Clues to Your Purpose As you read the assignment, think about what the teacher does in class:
- What kinds of textbooks or coursepack did your instructor choose for the course—ones that provide background information, explain theories or perspectives, or argue a point of view?
- In lecture, does your instructor ask your opinion, try to prove their point of view, or use keywords that show up again in the assignment?
- What kinds of assignments are typical in this discipline? Social science classes often expect more research. Humanities classes thrive on interpretation and analysis.
- How do the assignments, readings, and lectures work together in the course? Instructors spend time designing courses, sometimes even arguing with their peers about the most effective course materials. Figuring out the overall design to the course will help you understand what each assignment is meant to achieve.
Now, what about your reader? Most undergraduates think of their audience as the instructor. True, your instructor is a good person to keep in mind as you write. But for the purposes of a good paper, think of your audience as someone like your roommate: smart enough to understand a clear, logical argument, but not someone who already knows exactly what is going on in your particular paper. Remember, even if the instructor knows everything there is to know about your paper topic, they still have to read your paper and assess your understanding. In other words, teach the material to your reader.
Aiming a paper at your audience happens in two ways: you make decisions about the tone and the level of information you want to convey.
- Tone means the “voice” of your paper. Should you be chatty, formal, or objective? Usually you will find some happy medium—you do not want to alienate your reader by sounding condescending or superior, but you do not want to, um, like, totally wig on the man, you know? Eschew ostentatious erudition: some students think the way to sound academic is to use big words. Be careful—you can sound ridiculous, especially if you use the wrong big words.
- The level of information you use depends on who you think your audience is. If you imagine your audience as your instructor and they already know everything you have to say, you may find yourself leaving out key information that can cause your argument to be unconvincing and illogical. But you do not have to explain every single word or issue. If you are telling your roommate what happened on your favorite science fiction TV show last night, you do not say, “First a dark-haired white man of average height, wearing a suit and carrying a flashlight, walked into the room. Then a purple alien with fifteen arms and at least three eyes turned around. Then the man smiled slightly. In the background, you could hear a clock ticking. The room was fairly dark and had at least two windows that I saw.” You also do not say, “This guy found some aliens. The end.” Find some balance of useful details that support your main point.
You’ll find a much more detailed discussion of these concepts in our handout on audience .
The Grim Truth
With a few exceptions (including some lab and ethnography reports), you are probably being asked to make an argument. You must convince your audience. It is easy to forget this aim when you are researching and writing; as you become involved in your subject matter, you may become enmeshed in the details and focus on learning or simply telling the information you have found. You need to do more than just repeat what you have read. Your writing should have a point, and you should be able to say it in a sentence. Sometimes instructors call this sentence a “thesis” or a “claim.”
So, if your instructor tells you to write about some aspect of oral hygiene, you do not want to just list: “First, you brush your teeth with a soft brush and some peanut butter. Then, you floss with unwaxed, bologna-flavored string. Finally, gargle with bourbon.” Instead, you could say, “Of all the oral cleaning methods, sandblasting removes the most plaque. Therefore it should be recommended by the American Dental Association.” Or, “From an aesthetic perspective, moldy teeth can be quite charming. However, their joys are short-lived.”
Convincing the reader of your argument is the goal of academic writing. It doesn’t have to say “argument” anywhere in the assignment for you to need one. Look at the assignment and think about what kind of argument you could make about it instead of just seeing it as a checklist of information you have to present. For help with understanding the role of argument in academic writing, see our handout on argument .
What kind of evidence do you need?
There are many kinds of evidence, and what type of evidence will work for your assignment can depend on several factors–the discipline, the parameters of the assignment, and your instructor’s preference. Should you use statistics? Historical examples? Do you need to conduct your own experiment? Can you rely on personal experience? See our handout on evidence for suggestions on how to use evidence appropriately.
Make sure you are clear about this part of the assignment, because your use of evidence will be crucial in writing a successful paper. You are not just learning how to argue; you are learning how to argue with specific types of materials and ideas. Ask your instructor what counts as acceptable evidence. You can also ask a librarian for help. No matter what kind of evidence you use, be sure to cite it correctly—see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial .
You cannot always tell from the assignment just what sort of writing style your instructor expects. The instructor may be really laid back in class but still expect you to sound formal in writing. Or the instructor may be fairly formal in class and ask you to write a reflection paper where you need to use “I” and speak from your own experience.
Try to avoid false associations of a particular field with a style (“art historians like wacky creativity,” or “political scientists are boring and just give facts”) and look instead to the types of readings you have been given in class. No one expects you to write like Plato—just use the readings as a guide for what is standard or preferable to your instructor. When in doubt, ask your instructor about the level of formality they expect.
No matter what field you are writing for or what facts you are including, if you do not write so that your reader can understand your main idea, you have wasted your time. So make clarity your main goal. For specific help with style, see our handout on style .
Technical details about the assignment
The technical information you are given in an assignment always seems like the easy part. This section can actually give you lots of little hints about approaching the task. Find out if elements such as page length and citation format (see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial ) are negotiable. Some professors do not have strong preferences as long as you are consistent and fully answer the assignment. Some professors are very specific and will deduct big points for deviations.
Usually, the page length tells you something important: The instructor thinks the size of the paper is appropriate to the assignment’s parameters. In plain English, your instructor is telling you how many pages it should take for you to answer the question as fully as you are expected to. So if an assignment is two pages long, you cannot pad your paper with examples or reword your main idea several times. Hit your one point early, defend it with the clearest example, and finish quickly. If an assignment is ten pages long, you can be more complex in your main points and examples—and if you can only produce five pages for that assignment, you need to see someone for help—as soon as possible.
Tricks that don’t work
Your instructors are not fooled when you:
- spend more time on the cover page than the essay —graphics, cool binders, and cute titles are no replacement for a well-written paper.
- use huge fonts, wide margins, or extra spacing to pad the page length —these tricks are immediately obvious to the eye. Most instructors use the same word processor you do. They know what’s possible. Such tactics are especially damning when the instructor has a stack of 60 papers to grade and yours is the only one that low-flying airplane pilots could read.
- use a paper from another class that covered “sort of similar” material . Again, the instructor has a particular task for you to fulfill in the assignment that usually relates to course material and lectures. Your other paper may not cover this material, and turning in the same paper for more than one course may constitute an Honor Code violation . Ask the instructor—it can’t hurt.
- get all wacky and “creative” before you answer the question . Showing that you are able to think beyond the boundaries of a simple assignment can be good, but you must do what the assignment calls for first. Again, check with your instructor. A humorous tone can be refreshing for someone grading a stack of papers, but it will not get you a good grade if you have not fulfilled the task.
Critical reading of assignments leads to skills in other types of reading and writing. If you get good at figuring out what the real goals of assignments are, you are going to be better at understanding the goals of all of your classes and fields of study.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Meaning of assignment in English
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
- It was a jammy assignment - more of a holiday really.
- He took this award-winning photograph while on assignment in the Middle East .
- His two-year assignment to the Mexico office starts in September .
- She first visited Norway on assignment for the winter Olympics ten years ago.
- He fell in love with the area after being there on assignment for National Geographic in the 1950s.
- act as something
- all work and no play (makes Jack a dull boy) idiom
- be at work idiom
- be in work idiom
- housekeeping
- in the line of duty idiom
- undertaking
You can also find related words, phrases, and synonyms in the topics:
assignment | American Dictionary
Assignment | business english, examples of assignment, collocations with assignment.
These are words often used in combination with assignment .
Click on a collocation to see more examples of it.
Translations of assignment
Get a quick, free translation!

Word of the Day
relating to or caused by an earthquake

Varied and diverse (Talking about differences, Part 1)

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
- on assignment
- American Noun
- Collocations
- Translations
- All translations
To add assignment to a word list please sign up or log in.
Add assignment to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
Synonyms of task
- as in purpose
- as in to entrust
- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
Thesaurus Definition of task
(Entry 1 of 2)
Synonyms & Similar Words
- responsibility
- undertaking
- participation
- involvement
Thesaurus Definition of task (Entry 2 of 2)
Synonym Chooser
How does the noun task contrast with its synonyms?
Some common synonyms of task are assignment , chore , duty , job , and stint . While all these words mean "a piece of work to be done," task implies work imposed by a person in authority or an employer or by circumstance.
When can assignment be used instead of task ?
The words assignment and task can be used in similar contexts, but assignment implies a definite limited task assigned by one in authority.
When might chore be a better fit than task ?
While in some cases nearly identical to task , chore implies a minor routine activity necessary for maintaining a household or farm.
When would duty be a good substitute for task ?
The meanings of duty and task largely overlap; however, duty implies an obligation to perform or responsibility for performance.
Where would job be a reasonable alternative to task ?
The synonyms job and task are sometimes interchangeable, but job applies to a piece of work voluntarily performed; it may sometimes suggest difficulty or importance.
In what contexts can stint take the place of task ?
While the synonyms stint and task are close in meaning, stint implies a carefully allotted or measured quantity of assigned work or service.
Phrases Containing task
- take to task
Articles Related to task

Can 'Task' Be Used as a Verb?
Taking a usage peeve to task
Thesaurus Entries Near task
Cite this entry.
“Task.” Merriam-Webster.com Thesaurus , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/thesaurus/task. Accessed 10 May. 2024.
More from Merriam-Webster on task
Nglish: Translation of task for Spanish Speakers
Britannica English: Translation of task for Arabic Speakers
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
More commonly misspelled words, your vs. you're: how to use them correctly, every letter is silent, sometimes: a-z list of examples, more commonly mispronounced words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), popular in wordplay, the words of the week - may 10, 12 star wars words, a great big list of bread words, 10 scrabble words without any vowels, 8 uncommon words related to love, games & quizzes.


Understanding your assignment questions: A short guide
- Introduction
- Breaking down the question
Directive or task words
Task works for science based essays.
- Further reading and references
It is really important to understand the directive or task word used in your assignment.
This will indicate how you should write and what the purpose of the assignment in. The following examples show some task words and their definitions.
However, it is important to note that none of these words has a fixed meaning. The definitions given are a general guide, and interpretation of the words may vary according to the context and the discipline.
If you are unsure as the exactly what a lecturer means by a particular task word, you should ask for clarification.
Analyse : Break up into parts; investigate
Comment on : Identify and write about the main issues; give your reactions based on what you've read/ heard in lectures. Avoid just personal opinion.
Compare : Look for the similarities between two things. Show the relevance or consequences of these similarities concluding which is preferable.
Contrast : Identify the differences between two items or arguments. Show whether the differences are significant. Perhaps give reasons why one is preferable.
Criticise : Requires an answer that points out mistakes or weaknesses, and which also indicates any favourable aspects of the subject of the question. It requires a balanced answer.
Critically evaluate : Weigh arguments for and against something, assessing the strength of the evidence on both sides. Use criteria to guide your assessment of which opinions, theories, models or items are preferable.
Define : Give the exact meaning of. Where relevant, show you understand how the definition may be problematic.
Describe : To describe is to give an observational account of something and would deal with what happened, where it happened, when it happened and who was involved. Spell out the main aspects of an idea or topic or the sequence in which a series of things happened.
Discuss : Investigate or examine by argument; sift and debate; give reasons for and against; examine the implications.
Evaluate : Assess and give your judgement about the merit, importance or usefulness of something using evidence to support your argument.
Examine : Look closely into something
Explain : Offer a detailed and exact rationale behind an idea or principle, or a set of reasons for a situation or attitude. Make clear how and why something happens.
Explore : Examine thoroughly; consider from a variety of viewpoints
Illustrate : Make something clear and explicit, give examples of evidence
Justify : Give evidence that supports and argument or idea; show why a decision or conclusions were made
Outline : Give the main points/features/general principles; show the main structure and interrelations; omit details and examples
State : Give the main features briefly and clearly
Summarise : Draw out the main points only; omit details and examples
To what extent... : Consider how far something is true, or contributes to a final outcome. Consider also ways in which it is not true.
Task Words:
How to write e.g., discuss, argue etc.
Subject Matter:
What you should be writing about.
Limiting Words:
May narrow or change the focus of your answer. (Important - they stop you from including irrelevant info)
Below are some examples of questions and tips on how you might think about answering them.
Compare acute and chronic pain in terms of pathophysiology and treatment
Compare - Make sure you are comparing and not just describing the two things in isolation
Acute and chronic pain - Subject matter
In terms of pathophysiology and treatment - Important limiting phrase - focus ONLY on these things. Use them as a lens to highlight the differences between acute and chronic pain.
Tip : Assignments that ask you to compare two things can be structured in different ways. You may choose to alternate continually between the two things, making direct comparisons and organising your essay according to themes. Alternatively, you may choose to discuss one thing fully and then the next. If you choose the second approach, you must make the links and comparisons between the two things completely clear.
With reference to any particular example enzyme, outline the key structural and functional properties of its active site
With reference to any particular example enzyme - Important limiting phase - focus your answer on a specific example. Use this example to help demonstrate your understanding.
Outline - Factual description is needed. You must demonstrate your knowledge and understanding.
The key structural and functional properties of its active site - Subject matter
Tip : Assignments that ask you to outline or describe are assessing your understanding of the topic. You must express facts clearly and precisely, using examples to illuminate them.
There is no convincing evidence for the existence of life outside our solar systems
There is - Task words not so obvious this time. Try turning the title into a question: 'Is there any convincing evidence for...?'
Convincing - Important limiting word- there may be evidence but you need to assess whether or not it is convincing.
For the existence of life outside of our solar system - Subject matter
Tip : Assignment titles that are on actually a question are often simply asking 'how true is this statement?' You must present reasons it could be true and reasons it might not be, supported by evidence and recognising the complexity of the statement.
To what extent can nuclear power provide a solution to environmental issues?
Discuss - Explore the topic from different angles, in a critical way (not purely descriptive)
Nuclear power - Subject matter
Provide a solution to - Limiting phrase: discuss ways it can and ways it can't- don't be afraid to take a position based on evidence.
Environmental issues - Subject matter. Might be an idea to define/ discuss what could be meant by environmental issues? This might be important for your argument.
Tip : If an assignment is asking a direct question, make sure your essay answers it. Address it directly in the introduction, make sure each paragraph contributes something towards your response to it, and reinforce your response in your conclusion.
Discuss the issue of patient autonomy in relation to at least one case study
The issue of patient autonomy - Subject matter
In relation to at least one case study - Important limiting phrase - don't just discuss the issue of patient autonomy in general; discuss it in the context of one or more case studies. You should use the case study to illustrate all of your points about patient autonomy.
Tip : Assignments that ask you to discuss in relation to a case study, or to a placement or own experience, usually want to see a clear link between theory and practice (reality).
- << Previous: Breaking down the question
- Next: Further reading and references >>
- Last Updated: Nov 13, 2023 4:28 PM
- URL: https://libguides.bham.ac.uk/asc/understandingassignments
- Privacy Policy

Home » Assignment – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Assignment – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Definition:
Assignment is a task given to students by a teacher or professor, usually as a means of assessing their understanding and application of course material. Assignments can take various forms, including essays, research papers, presentations, problem sets, lab reports, and more.
Assignments are typically designed to be completed outside of class time and may require independent research, critical thinking, and analysis. They are often graded and used as a significant component of a student’s overall course grade. The instructions for an assignment usually specify the goals, requirements, and deadlines for completion, and students are expected to meet these criteria to earn a good grade.
History of Assignment
The use of assignments as a tool for teaching and learning has been a part of education for centuries. Following is a brief history of the Assignment.
- Ancient Times: Assignments such as writing exercises, recitations, and memorization tasks were used to reinforce learning.
- Medieval Period : Universities began to develop the concept of the assignment, with students completing essays, commentaries, and translations to demonstrate their knowledge and understanding of the subject matter.
- 19th Century : With the growth of schools and universities, assignments became more widespread and were used to assess student progress and achievement.
- 20th Century: The rise of distance education and online learning led to the further development of assignments as an integral part of the educational process.
- Present Day: Assignments continue to be used in a variety of educational settings and are seen as an effective way to promote student learning and assess student achievement. The nature and format of assignments continue to evolve in response to changing educational needs and technological innovations.
Types of Assignment
Here are some of the most common types of assignments:
An essay is a piece of writing that presents an argument, analysis, or interpretation of a topic or question. It usually consists of an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Essay structure:
- Introduction : introduces the topic and thesis statement
- Body paragraphs : each paragraph presents a different argument or idea, with evidence and analysis to support it
- Conclusion : summarizes the key points and reiterates the thesis statement
Research paper
A research paper involves gathering and analyzing information on a particular topic, and presenting the findings in a well-structured, documented paper. It usually involves conducting original research, collecting data, and presenting it in a clear, organized manner.
Research paper structure:
- Title page : includes the title of the paper, author’s name, date, and institution
- Abstract : summarizes the paper’s main points and conclusions
- Introduction : provides background information on the topic and research question
- Literature review: summarizes previous research on the topic
- Methodology : explains how the research was conducted
- Results : presents the findings of the research
- Discussion : interprets the results and draws conclusions
- Conclusion : summarizes the key findings and implications
A case study involves analyzing a real-life situation, problem or issue, and presenting a solution or recommendations based on the analysis. It often involves extensive research, data analysis, and critical thinking.
Case study structure:
- Introduction : introduces the case study and its purpose
- Background : provides context and background information on the case
- Analysis : examines the key issues and problems in the case
- Solution/recommendations: proposes solutions or recommendations based on the analysis
- Conclusion: Summarize the key points and implications
A lab report is a scientific document that summarizes the results of a laboratory experiment or research project. It typically includes an introduction, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion.
Lab report structure:
- Title page : includes the title of the experiment, author’s name, date, and institution
- Abstract : summarizes the purpose, methodology, and results of the experiment
- Methods : explains how the experiment was conducted
- Results : presents the findings of the experiment
Presentation
A presentation involves delivering information, data or findings to an audience, often with the use of visual aids such as slides, charts, or diagrams. It requires clear communication skills, good organization, and effective use of technology.
Presentation structure:
- Introduction : introduces the topic and purpose of the presentation
- Body : presents the main points, findings, or data, with the help of visual aids
- Conclusion : summarizes the key points and provides a closing statement
Creative Project
A creative project is an assignment that requires students to produce something original, such as a painting, sculpture, video, or creative writing piece. It allows students to demonstrate their creativity and artistic skills.
Creative project structure:
- Introduction : introduces the project and its purpose
- Body : presents the creative work, with explanations or descriptions as needed
- Conclusion : summarizes the key elements and reflects on the creative process.
Examples of Assignments
Following are Examples of Assignment templates samples:
Essay template:
I. Introduction
- Hook: Grab the reader’s attention with a catchy opening sentence.
- Background: Provide some context or background information on the topic.
- Thesis statement: State the main argument or point of your essay.
II. Body paragraphs
- Topic sentence: Introduce the main idea or argument of the paragraph.
- Evidence: Provide evidence or examples to support your point.
- Analysis: Explain how the evidence supports your argument.
- Transition: Use a transition sentence to lead into the next paragraph.
III. Conclusion
- Restate thesis: Summarize your main argument or point.
- Review key points: Summarize the main points you made in your essay.
- Concluding thoughts: End with a final thought or call to action.
Research paper template:
I. Title page
- Title: Give your paper a descriptive title.
- Author: Include your name and institutional affiliation.
- Date: Provide the date the paper was submitted.
II. Abstract
- Background: Summarize the background and purpose of your research.
- Methodology: Describe the methods you used to conduct your research.
- Results: Summarize the main findings of your research.
- Conclusion: Provide a brief summary of the implications and conclusions of your research.
III. Introduction
- Background: Provide some background information on the topic.
- Research question: State your research question or hypothesis.
- Purpose: Explain the purpose of your research.
IV. Literature review
- Background: Summarize previous research on the topic.
- Gaps in research: Identify gaps or areas that need further research.
V. Methodology
- Participants: Describe the participants in your study.
- Procedure: Explain the procedure you used to conduct your research.
- Measures: Describe the measures you used to collect data.
VI. Results
- Quantitative results: Summarize the quantitative data you collected.
- Qualitative results: Summarize the qualitative data you collected.
VII. Discussion
- Interpretation: Interpret the results and explain what they mean.
- Implications: Discuss the implications of your research.
- Limitations: Identify any limitations or weaknesses of your research.
VIII. Conclusion
- Review key points: Summarize the main points you made in your paper.
Case study template:
- Background: Provide background information on the case.
- Research question: State the research question or problem you are examining.
- Purpose: Explain the purpose of the case study.
II. Analysis
- Problem: Identify the main problem or issue in the case.
- Factors: Describe the factors that contributed to the problem.
- Alternative solutions: Describe potential solutions to the problem.
III. Solution/recommendations
- Proposed solution: Describe the solution you are proposing.
- Rationale: Explain why this solution is the best one.
- Implementation: Describe how the solution can be implemented.
IV. Conclusion
- Summary: Summarize the main points of your case study.
Lab report template:
- Title: Give your report a descriptive title.
- Date: Provide the date the report was submitted.
- Background: Summarize the background and purpose of the experiment.
- Methodology: Describe the methods you used to conduct the experiment.
- Results: Summarize the main findings of the experiment.
- Conclusion: Provide a brief summary of the implications and conclusions
- Background: Provide some background information on the experiment.
- Hypothesis: State your hypothesis or research question.
- Purpose: Explain the purpose of the experiment.
IV. Materials and methods
- Materials: List the materials and equipment used in the experiment.
- Procedure: Describe the procedure you followed to conduct the experiment.
- Data: Present the data you collected in tables or graphs.
- Analysis: Analyze the data and describe the patterns or trends you observed.
VI. Discussion
- Implications: Discuss the implications of your findings.
- Limitations: Identify any limitations or weaknesses of the experiment.
VII. Conclusion
- Restate hypothesis: Summarize your hypothesis or research question.
- Review key points: Summarize the main points you made in your report.
Presentation template:
- Attention grabber: Grab the audience’s attention with a catchy opening.
- Purpose: Explain the purpose of your presentation.
- Overview: Provide an overview of what you will cover in your presentation.
II. Main points
- Main point 1: Present the first main point of your presentation.
- Supporting details: Provide supporting details or evidence to support your point.
- Main point 2: Present the second main point of your presentation.
- Main point 3: Present the third main point of your presentation.
- Summary: Summarize the main points of your presentation.
- Call to action: End with a final thought or call to action.
Creative writing template:
- Setting: Describe the setting of your story.
- Characters: Introduce the main characters of your story.
- Rising action: Introduce the conflict or problem in your story.
- Climax: Present the most intense moment of the story.
- Falling action: Resolve the conflict or problem in your story.
- Resolution: Describe how the conflict or problem was resolved.
- Final thoughts: End with a final thought or reflection on the story.
How to Write Assignment
Here is a general guide on how to write an assignment:
- Understand the assignment prompt: Before you begin writing, make sure you understand what the assignment requires. Read the prompt carefully and make note of any specific requirements or guidelines.
- Research and gather information: Depending on the type of assignment, you may need to do research to gather information to support your argument or points. Use credible sources such as academic journals, books, and reputable websites.
- Organize your ideas : Once you have gathered all the necessary information, organize your ideas into a clear and logical structure. Consider creating an outline or diagram to help you visualize your ideas.
- Write a draft: Begin writing your assignment using your organized ideas and research. Don’t worry too much about grammar or sentence structure at this point; the goal is to get your thoughts down on paper.
- Revise and edit: After you have written a draft, revise and edit your work. Make sure your ideas are presented in a clear and concise manner, and that your sentences and paragraphs flow smoothly.
- Proofread: Finally, proofread your work for spelling, grammar, and punctuation errors. It’s a good idea to have someone else read over your assignment as well to catch any mistakes you may have missed.
- Submit your assignment : Once you are satisfied with your work, submit your assignment according to the instructions provided by your instructor or professor.
Applications of Assignment
Assignments have many applications across different fields and industries. Here are a few examples:
- Education : Assignments are a common tool used in education to help students learn and demonstrate their knowledge. They can be used to assess a student’s understanding of a particular topic, to develop critical thinking skills, and to improve writing and research abilities.
- Business : Assignments can be used in the business world to assess employee skills, to evaluate job performance, and to provide training opportunities. They can also be used to develop business plans, marketing strategies, and financial projections.
- Journalism : Assignments are often used in journalism to produce news articles, features, and investigative reports. Journalists may be assigned to cover a particular event or topic, or to research and write a story on a specific subject.
- Research : Assignments can be used in research to collect and analyze data, to conduct experiments, and to present findings in written or oral form. Researchers may be assigned to conduct research on a specific topic, to write a research paper, or to present their findings at a conference or seminar.
- Government : Assignments can be used in government to develop policy proposals, to conduct research, and to analyze data. Government officials may be assigned to work on a specific project or to conduct research on a particular topic.
- Non-profit organizations: Assignments can be used in non-profit organizations to develop fundraising strategies, to plan events, and to conduct research. Volunteers may be assigned to work on a specific project or to help with a particular task.
Purpose of Assignment
The purpose of an assignment varies depending on the context in which it is given. However, some common purposes of assignments include:
- Assessing learning: Assignments are often used to assess a student’s understanding of a particular topic or concept. This allows educators to determine if a student has mastered the material or if they need additional support.
- Developing skills: Assignments can be used to develop a wide range of skills, such as critical thinking, problem-solving, research, and communication. Assignments that require students to analyze and synthesize information can help to build these skills.
- Encouraging creativity: Assignments can be designed to encourage students to be creative and think outside the box. This can help to foster innovation and original thinking.
- Providing feedback : Assignments provide an opportunity for teachers to provide feedback to students on their progress and performance. Feedback can help students to understand where they need to improve and to develop a growth mindset.
- Meeting learning objectives : Assignments can be designed to help students meet specific learning objectives or outcomes. For example, a writing assignment may be designed to help students improve their writing skills, while a research assignment may be designed to help students develop their research skills.
When to write Assignment
Assignments are typically given by instructors or professors as part of a course or academic program. The timing of when to write an assignment will depend on the specific requirements of the course or program, but in general, assignments should be completed within the timeframe specified by the instructor or program guidelines.
It is important to begin working on assignments as soon as possible to ensure enough time for research, writing, and revisions. Waiting until the last minute can result in rushed work and lower quality output.
It is also important to prioritize assignments based on their due dates and the amount of work required. This will help to manage time effectively and ensure that all assignments are completed on time.
In addition to assignments given by instructors or professors, there may be other situations where writing an assignment is necessary. For example, in the workplace, assignments may be given to complete a specific project or task. In these situations, it is important to establish clear deadlines and expectations to ensure that the assignment is completed on time and to a high standard.
Characteristics of Assignment
Here are some common characteristics of assignments:
- Purpose : Assignments have a specific purpose, such as assessing knowledge or developing skills. They are designed to help students learn and achieve specific learning objectives.
- Requirements: Assignments have specific requirements that must be met, such as a word count, format, or specific content. These requirements are usually provided by the instructor or professor.
- Deadline: Assignments have a specific deadline for completion, which is usually set by the instructor or professor. It is important to meet the deadline to avoid penalties or lower grades.
- Individual or group work: Assignments can be completed individually or as part of a group. Group assignments may require collaboration and communication with other group members.
- Feedback : Assignments provide an opportunity for feedback from the instructor or professor. This feedback can help students to identify areas of improvement and to develop their skills.
- Academic integrity: Assignments require academic integrity, which means that students must submit original work and avoid plagiarism. This includes citing sources properly and following ethical guidelines.
- Learning outcomes : Assignments are designed to help students achieve specific learning outcomes. These outcomes are usually related to the course objectives and may include developing critical thinking skills, writing abilities, or subject-specific knowledge.
Advantages of Assignment
There are several advantages of assignment, including:
- Helps in learning: Assignments help students to reinforce their learning and understanding of a particular topic. By completing assignments, students get to apply the concepts learned in class, which helps them to better understand and retain the information.
- Develops critical thinking skills: Assignments often require students to think critically and analyze information in order to come up with a solution or answer. This helps to develop their critical thinking skills, which are important for success in many areas of life.
- Encourages creativity: Assignments that require students to create something, such as a piece of writing or a project, can encourage creativity and innovation. This can help students to develop new ideas and perspectives, which can be beneficial in many areas of life.
- Builds time-management skills: Assignments often come with deadlines, which can help students to develop time-management skills. Learning how to manage time effectively is an important skill that can help students to succeed in many areas of life.
- Provides feedback: Assignments provide an opportunity for students to receive feedback on their work. This feedback can help students to identify areas where they need to improve and can help them to grow and develop.
Limitations of Assignment
There are also some limitations of assignments that should be considered, including:
- Limited scope: Assignments are often limited in scope, and may not provide a comprehensive understanding of a particular topic. They may only cover a specific aspect of a topic, and may not provide a full picture of the subject matter.
- Lack of engagement: Some assignments may not engage students in the learning process, particularly if they are repetitive or not challenging enough. This can lead to a lack of motivation and interest in the subject matter.
- Time-consuming: Assignments can be time-consuming, particularly if they require a lot of research or writing. This can be a disadvantage for students who have other commitments, such as work or extracurricular activities.
- Unreliable assessment: The assessment of assignments can be subjective and may not always accurately reflect a student’s understanding or abilities. The grading may be influenced by factors such as the instructor’s personal biases or the student’s writing style.
- Lack of feedback : Although assignments can provide feedback, this feedback may not always be detailed or useful. Instructors may not have the time or resources to provide detailed feedback on every assignment, which can limit the value of the feedback that students receive.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...
- Plan a Clinical Trial
- Add Your Assumptions
Define Outsourced Tasks on the Assignment Tab
On the Assignment tab, select which location the assignments apply to and a default service provider for outsourced tasks, then, for each task or assignment group, assign a service provider and billing rate location.
Select the location and default service provider for outsourced tasks
- Select the Assignment tab.
- Select Centralized Tasks/Location Defaults if you want assignments to pertain to every location in the study.
- Otherwise, select a specific location.
- If all outsourced tasks are to be performed by a single service provider, select that service provider.
- Example 1: If Values apply to is set to Centralized Tasks/Location Defaults , to assign all outsourced tasks for all locations to Major CRO, select Major CRO .
- Example 2: If Values apply to is set to a country, for example, Chile, to assign all outsourced tasks in Chile to Medium CRO, select Medium CRO .
- If a service provider is not available for selection, return to the Provider tab and add the service provider.
- Click Save .
- If a list of assignment groups and tasks doesn't appear at the bottom of the screen, click the Show Tasks link.
- To expand all task groups, in the table header bar, double click in the space to the left of the Assignment Group/Task column header.
- The Included column, which appears only if you expand the task groups, indicates whether this task is included in the study and allows you to exclude a task from the study. If this check box is grayed out, the task must be included (or excluded) from the plan based on other input assumptions you have made or other study characteristics.
- You can exclude selected tasks from the plan, which eliminates the effort and costs associated with these tasks. Tasks that cannot be excluded or specifically assigned, or whose billing rate location cannot be different from the location of subject data, are presented with the associated option(s) disabled.
- If, on the Overview tab , you selected Outsourced , you can only assign tasks to a vendor. If you selected Conducted Internally , you can only assign tasks to the sponsor. To assign some tasks to service providers and others to the sponsor, you must select Combination on the Overview tab.
The value displayed might indicate additional information when showing the assigned provider(s) for an entire group of tasks, as follows:
- Service provider name appears with no additional markers —All tasks in the group are performed by a single service provider.
- Service provider name appears with an asterisk (*) —The service provider is the default service provider selected to perform tasks in the group, but some tasks are assigned to another provider.
- You can specify a different billing rate location for each task group or individual task. For example, if data management tasks for all European sites are performed in Germany, change this field to Germany for each of the locations in Europe.
- You can select any location where this activity or activities are conducted. The location does not need to have active sites participating in the study. For example, you might have study sites in France, Germany, and Italy, but perform all data management in the UK or India.
- To choose a location that does not have sites or subjects, from the drop-down list, choose Other... . Choose the location where the work is performed (or from where the resources who will perform the task will come), and then click Ok .
- By default, centralized tasks are calculated using the back office billing rate selected on the Provider tab.
For example, if assignments made for individual tasks included in the group are not pinned, changes made to the assignment group or to the location defaults override these assignments.
- Pinned settings are lost if you remove the associated locations or service providers from the plan. However, if you replace a provider, your pinned settings are maintained.
- Task overrides migrated from plans created in earlier versions of the application are pinned by default.
- If an assigned provider is deleted from a plan, the task is automatically assigned to the primary provider in the plan.
- Repeat as necessary for multiple locations where the service provider is different or the billing rate is different from the local rate for that location.
- Override selected resources and rates or click Next to view or adjust labor fees.
- Override Resources and Rates You can specify substitutions for each resource and/or override the billing rate location and rate by location, per provider.
Parent topic: Add Your Assumptions
Override Resources and Rates
You can specify substitutions for each resource and/or override the billing rate location and rate by location, per provider.
- Click Save to save any changes you have already made.
- In the Task Assignments section, click the Override Resources or Rates link.
- On the Resource Overrides screen, in the Scope of Overrides section, from the For tasks assigned to drop-down list, select a service provider.
- In the Resources / Overrides section, specify your override for each default resource specification and pin your changes if desired. If you pin your changes, ClearTrial uses these choices throughout the plan instead of its defaults.
- Click Save & Close .
- Perform additional overrides, or click Next to view or adjust effort and labor fees .
Parent topic: Define Outsourced Tasks on the Assignment Tab

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Task assigning involves defining responsibilities and allocating resources for team members to complete a project effectively. While workplace leaders can assign tasks to team members in different departments, managers typically assign tasks to their department's members. Discovering each team member's strengths, potential, and expertise can ...
A task is something you have to do. An assignment is usually a task that someone gives you to do. Ways to use 'task'. A task describes an activity that can be done in your daily life. But you ...
Mistake #1: Using Task And Assignment Interchangeably. One of the most common mistakes people make is using the terms task and assignment interchangeably. While they may seem similar, they have different meanings. A task is a specific action or set of actions that need to be completed, while an assignment is a task that is assigned to someone.
Open the desired task, click "Assignee", and choose the right team member (s). Keyboard shortcuts: Hover over the task and press "A" to open the Assignee picker. Press the space bar to assign yourself. This way makes assigning tasks easier and quicker!
Effective task assignment ensures that the right tasks are allocated to the right people based on their skills, capabilities, and availability. This eliminates confusion, reduces the chances of mistakes, and improves efficiency. ... Define Objectives: Clearly state the purpose and outcome of each task. Relevant Skills: Assign tasks based on ...
Make a meeting with the team leads and go through the points above. Assign tasks according to each team's availability, interest, and skill required to successfully push the project forward. As team leads - assign tasks further down the pipeline. Track task completion and make necessary changes along the way.
Define the project scope and objectives: The first step in task assignment is to clearly define the project scope and objectives.This helps in identifying the tasks that need to be completed to achieve the project goals. Identify tasks: The next step is to identify the tasks required to complete the project. This involves breaking down the project into smaller, manageable tasks and activities.
The meaning of ASSIGNMENT is the act of assigning something. How to use assignment in a sentence. Synonym Discussion of Assignment.
Assignment is a task assigned as part of a job or course of study. In short, assignment = task given to you. Share. Improve this answer. ... Does Jesus mean "Salvation" or "God is Salvation"? Why does this vintage DRAM chip enable circuit require such a beefy resistor? ...
[countable] a task or piece of work that somebody is given to do, usually as part of their job or studies. Students are required to complete all homework assignments. You will need to complete three written assignments per semester. a business/special assignment ; I had set myself a tough assignment.
7 meanings: 1. something that has been assigned, such as a mission or task 2. a position or post to which a person is assigned.... Click for more definitions.
1 [countable, uncountable] a task or piece of work that someone is given to do, usually as part of their job or studies You will need to complete three written assignments per semester. She is in Greece on an assignment for one of the Sunday newspapers. one of our reporters on assignment in China I had given myself a tough assignment. a business/special assignment
task: [noun] a usually assigned piece of work often to be finished within a certain time. something hard or unpleasant that has to be done. duty, function.
In project management, a task is a work item or activity with a specific purpose related to the larger goal. It's a necessary step on the road towards project completion. For example, it could be something as complex as a mobile app bug fix. Or it could be something as simple as photocopying the latest brochure for distribution.
Synonyms for ASSIGNMENT: task, job, duty, project, mission, chore, responsibility, function; Antonyms of ASSIGNMENT: dismissal, discharge, firing, expulsion, rejection, removal, dismission, deposition ... and task. While all these words mean "a piece of work to be done," assignment implies a definite limited task assigned by one in authority. a ...
Define. Make a statement as to the meaning or interpretation of something, giving sufficient detail as to allow it to be distinguished from similar things. Describe. Spell out the main aspects of an idea or topic or the sequence in which a series of things happened. Discuss. Investigate or examine by argument.
The Task of the Assignment. Pay attention; this part tells you what to do when you write the paper. Look for the key verb or verbs in the sentence. Words like analyze, summarize, or compare direct you to think about your topic in a certain way. ... define—give the subject's meaning (according to someone or something). Sometimes you have to ...
ASSIGNMENT definition: 1. a piece of work given to someone, typically as part of their studies or job: 2. a job that…. Learn more.
Assignment definition: something assigned, as a particular task or duty. See examples of ASSIGNMENT used in a sentence.
assignment: 1 n an undertaking that you have been assigned to do (as by an instructor) Types: show 6 types... hide 6 types... school assignment , schoolwork a school task performed by a student to satisfy the teacher writing assignment , written assignment an assignment to write something classroom project a school task requiring considerable ...
Synonyms for TASK: job, duty, assignment, project, chore, mission, function, responsibility, endeavor, errand. ... While the synonyms stint and task are close in meaning, stint implies a carefully allotted or measured quantity of assigned work or service. a 2-month stint as a reporter. Phrases Containing task.
It is really important to understand the directive or task word used in your assignment. This will indicate how you should write and what the purpose of the assignment in. The following examples show some task words and their definitions. However, it is important to note that none of these words has a fixed meaning.
Definition: Assignment is a task given to students by a teacher or professor, usually as a means of assessing their understanding and application of course material. Assignments can take various forms, including essays, research papers, presentations, problem sets, lab reports, and more. Assignments are typically designed to be completed ...
To expand all task groups, in the table header bar, double click in the space to the left of the Assignment Group/Task column header.; The Included column, which appears only if you expand the task groups, indicates whether this task is included in the study and allows you to exclude a task from the study.