- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- *New* Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →

Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
3 Business Strategy Examples to Inspire Your Own

- 03 Nov 2022
Successful businesses often change the way the world lives. Consider Apple, Google, and Netflix and the immense value each offers customers. Despite ambitious profit margins, the companies' business strategies didn't stem solely from financial goals. Each prioritized consumer value through innovations such as smartphones, faster search engines, and video streaming.
If you want to develop a successful business strategy, here's an overview of value creation, how to create value, and examples of companies successfully implementing it into their business models.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is a Value-Based Business Strategy?
Creating value for the customer and company determines whether a business strategy is successful. According to Harvard Business School Professor Felix Oberholzer-Gee in the HBS Online course Business Strategy , "These companies don't win by having the best product or most impressive service. They win by creating the most value."
While this can be difficult to visualize, the value stick framework illustrates how a company can maximize profit while creating more value for its customers, suppliers, and stakeholders.

The value stick is a graph comprised of four components: willingness to pay (WTP), price, cost, and willingness to sell (WTS). Each segment represents how a sale's value is split between a firm, its customers, and suppliers. While each component leads to value, two levers create it: WTP and WTS.
To better understand how these components aid value-based business strategies , here are examples of how you can implement them in your organization.
Raising WTP
Willingness to pay (WTP) refers to the highest price a customer is willing to pay for a product or service. This calculation determines the threshold at which customers are more likely to make a purchase. Any slight imbalance in this number can deter, or even dissuade, consumers from purchasing. Only when a customer is delighted by a product or service are they willing to pay more.
Companies need to know their customer's WTP to remain profitable. According to HBS Online's Business Strategy course, it's influenced by the functional attributes of the product or service and other considerations, including:
- Business sustainability: Is the product or service environmentally sound?
- Social status: Does the media give your product or service additional value?
- Market influence: Does your product or service inspire your competition?
Raising WTP can be an effective strategy for companies interested in increasing profit margins. This difficult balancing act requires an understanding of the product and target consumer. Business Strategy identifies three main mechanisms for raising WTP:
- Conferring status: Earning "status" granted by media and the consumers to gain more value through public attention and brand legitimacy
- Reducing uncertainty: Ensuring quality and purpose within an organization, so customers know what to expect with your product and service every time
- Forming tastes: Taking the time to get your brand to the consumer as soon as possible because of nostalgic drivers
Lowering WTS
Willingness to sell (WTS) is the lowest price suppliers are willing to accept in exchange for materials needed to create products or services. Just as customers must weigh personal versus monetary value in determining whether they want to participate in a transaction, so do suppliers.
Another way to measure WTS is by considering employee engagement and retention. One of the most valuable assets a company has is its talent. Effective leaders nurture and develop employees to ensure salary isn't their only motivator.
Lowering WTS for one or both of these groups can be an effective business strategy for companies that can't raise their WTP. For example, companies that can motivate employees to work for a lower cost by providing value in other ways—such as benefits packages, flexible work hours, and generous paid time off—can lower WTS. Another method of lowering WTS is creating value for suppliers. This can take the form of additional warehouse space or long-term contracts.

3 Companies With Successful Business Strategies
One of the best ways to learn about business strategy is from real-world examples. Here are three companies that faced numerous challenges but overcame them through value-based business strategies.
1. Best Buy
Best Buy, the multinational electronics retailer, is an excellent example of how a shift in business strategy can lead to rapid growth. In 2012, Best Buy faced fierce market competition with online platforms like Amazon and big-box stores like Walmart and Home Depot. As a result, the company lost over a billion dollars in revenue in a single quarter.
Rather than closing stores or developing new products, Best Buy's leadership decided to leverage an existing asset not being utilized to its full potential: its storefronts. Best Buy started using its stores as "mini warehouses," providing faster shipping times, easier customer pick-up, and improved product availability. As a result of enhancing convenience for the customer, Best Buy increased its WTP.
Best Buy is an exceptional example of a value-based business strategy because it subsequently lowered WTS with this initiative. By keeping the vast network of stores intact and allowing vendors to build showrooms within its stores, Best Buy provided a cost-effective option for its vendors. This additional value lowered vendors' WTS, leading to product discounts.
As the largest sportswear manufacturer of shoes, clothing, and accessories, Nike has become one of the world's leading global sports brands. While much of Nike's success has come from its iconic products, it's also resulted from effective business strategies that out-compete in today's crowded sportswear market.
Value-based pricing greatly contributed to the company's reported global revenue of more than $44 billion in 2021 . For example, Nike has consistently leveraged consumers' perceptions of its products to drive prices up within their WTP. Nike can do this by creating the highest quality products to justify charging a premium price.
Many of Nike's competitors struggle to follow this same business model because of Nike's most valuable asset: its image. Company leadership at Nike has long understood that its pricing model isn't just reflected in the quality of its products but in the influence of its logo. By understanding its social and market influence, Nike's exclusive products, such as Air Jordans, have contributed to driving its perceived value to an even higher level. As a result, brand value and customer loyalty are two major pillars of Nike's long-term success at consistently raising its customer's WTP.
3. Starbucks
The world's largest coffeehouse chain, Starbucks, also needed to adopt a value-based strategy to gain market domination. In 2008, Starbucks faced immense financial pressure from increasing fast-food chain competition, rising prices in food and supplies, and global strains on coffee trading. In fact, by March 30, 2008, its profits had fallen nearly 28 percent compared to the previous year, leading to 300 closed stores and 6,700 employee layoffs.
To combat these challenges, Starbucks focused on better understanding the company's WTP. According to a letter by Starbucks CEO Howard Shultz, "The company must shift its focus away from bureaucracy and back to customers. We need to reignite the emotional attachment with our customers."
One method of doing this was the "My Starbucks Idea." Its goal was to create a space for customers to exchange ideas with each other and the company about Starbucks' products, services, stores, and corporate social responsibility . With nearly 93,000 ideas recorded and 1.3 million newly generated on social media, Starbucks tapped into what their customers cared about most.
Understanding what drives customer value led to many business model changes synonymous with Starbucks today. For example, free Wi-Fi, lounge chairs, and Starbucks' rewards program all sparked from customer feedback and forums. As a result, Starbucks is widely known as one of the fast-food chains with the highest WTP because of its loyal customer base.

Making Profits the Outcome, Not the Goal
Companies considering a shift in business strategy are often facing financial hardships. Whether an impending bankruptcy, decreasing profit margins, or increasing employee turnover, business strategies are meant to solve these problems. Yet, this isn't where your strategy should start.
"Profit is not the goal," says Oberholzer-Gee in HBS Online's Business Strategy course. "You treat it as an outcome. It's people first, then business."
Business leaders need an in-depth understanding of customer value to succeed in today's competitive marketplace. While real-world examples illustrate the implementation of these value-based strategies, taking an online course like Business Strategy can help you create an effective business strategy that wins over customers while generating a profit.
Are you interested in learning how customer value relates to financially successful business strategies? Explore our online course Business Strategy , or other strategy courses , to develop your strategic planning skills. To determine which strategy course is right for you, download our free flowchart .

About the Author
- Scroll to top
- / Sign Up
- HOW WE HELP CLIENTS
- schedule your conversation
Strategic Planning Process Definition, Steps and Examples
Published: 03 January, 2024
Social Share:

Digital Strategy

Table of Contents
Organizations use Strategic Planning to gather all their stakeholders to evaluate the collection of current circumstances and decide upon their ongoing goals and benchmarks. They decide upon long-term objectives and establish a vision for the company’s future.
The efforts behind an organization’s Strategic Planning Processes are vital to its success, and yet, while many organizations acknowledge they need to do this kind of planning, they often don’t understand how to make it a reality. In this article, we explain the reasons behind Strategic Planning and how to make your Strategic Planning Process as powerful as possible.
As always, Digital Leadership welcomes the opportunity to partner with you and your business. Our innovation consulting services and digital transformation services assist organizations in navigating the strategic planning process and beyond. By leveraging our collaborative approach, we aim to align your vision with actionable goals. As an initial step to assist businesses in selecting tailored services that align with their specific needs and objectives for innovation, we offer an Innovation Blueprint to evaluate current innovation practices. If you have questions or comments or would like to leverage the experience of one of our global experts, schedule a free consultation by visiting our CONTACT US page today!

Find out how we can help you
Corporate training, innovation consulting and much more.
What is a Strategic Plan
Strategic planning is a systematic process wherein the leaders of an organization articulate their vision for the future and delineate the goals and objectives that will guide the trajectory of the organization.
Much more about Strategic planning and how to go through the Strategic planning process and other approaches to innovation strategy you will find in our brand-new FREE book “How to Create Innovation” Register for the download now !

The Only Book On Innovation You’ll Ever Need
+FREE access to 50+ complimentary download packages covering the details with plenty of helpful background information
What is the Strategic Planning Process
Strategic planning is a process of defining an organization’s direction and making decisions on allocating its resources to pursue this direction . It involves creating a long-term plan that outlines the organization’s vision, mission, values, and objectives, as well as the strategies and tactics that will be used to achieve them.
Strategy is often misunderstood, which is surprising because fundamentally it’s a pretty basic concept. Strategy is a clearly expressed direction and a verified plan on how to get there. Your Strategic Planning Process formalizes the steps you’ll take to decide on your plan. The Strategic Planning Process facilitates using a Strategic Execution Framework that articulates where you’ll invest in innovation and where you can cut costs.
As far as business development planning is concerned, your Strategic Execution Framework is a vital tool for driving innovation, but first you must define the process you’ll undertake to determine how you and your team see the future of your organization. In this article, we discuss how to create your Strategic Plan and define its relationship to other concepts and documents that direct your business and its activities.

While it’s true that every business is different and must develop their own processes, we believe there are some process of strategic planning stepsthat benefit all organizations.
Below are our recommendations for the steps to take when undergoing your Strategic Planning Process, along with the questions we suggest you answer during each specific step.
Step One: Analyze your Business Environment
- Who are your competitors?
- What relevant market data do you have, and what do you still need?
- What technology has emerged that impacts your business model?
- How have customer expectations changed since your last Strategic Plan?
- What advantages do you have over competitors?
- Where is your company weaker compared to competitors?
- What predictable complications are on the horizon?
- Which unpredictable complications seem most likely or most potentially impactful?
Step Two: Set your Strategic Direction
- What is your overall Business Purpose ?
- How have your operations reflected your Purpose and Goals recently?
- How should your operations reflect your Purpose and Goals?
- Where do you see your business going in the next year?
- In two years? In three years?
- What are the metrics you’ll use to measure success?
- What are your make-or-break necessities?
Step Three: Set and develop Strategic Goals and Strategic Objectives
- Have you considered short-, mid-, and long-term business goals , and what are they?
- How do your Strategic Goals reflect your Mission Statement?
- How do your Strategic Goals reflect your company values and vision?
- What daily operations must be completed to work toward your Strategic Objectives?
- How will you communicate your Strategic Goals and Strategic Objectives?
- Who is responsible for reporting on success?
- How will strategic data be collected?
Related: Strategic Goals: Examples, Importance, Definitions and How to Set Them
Step Four: Drill down to Department-Level Objectives
- What are specific department concerns?
- How will your budget influence and be influenced by your Strategic Goals and Objectives?
- Which departments have resources that could be shared to better advantage?
- What roles do individual departments play in your overall Strategic Goals?
- What ongoing projects become a priority because of your new Strategic Goals?
- Are Departmental Objectives complementing each other and the overall Business Model?
Step Five: Manage and Analyze Performance
- Who is on the Strategic Planning team?
- Are tasks and job descriptions properly aligned to ensure the right work is getting completed?
- What is the schedule for the meeting for Strategic Planning?
- What are your metrics for measuring performance and success?
- Have you clearly articulated and shared KPIs?
- Who is responsible for gathering data?
- How will data be collected?
- How will data be reported?
- What’s at stake for strategy success or failure?
Step Six: Review and develop your Strategic Plan
- How should your Strategic Plan look on paper?
- What is your Strategy Execution Framework —how will you guarantee the Strategic Plan Team’s decisions are respected and executed?
- What is the review process?
- How often do you evaluate your Strategic Plan?
- How will you communicate your final Strategic Plan?
Strategic Planning Process Examples
1) apple strategic plan process.
- Vision and Mission: Apple’s strategic planning begins with a clear vision and mission. Apple’s vision is to create innovative products that inspire and enrich people’s lives.
- Environmental Analysis: Apple conducts thorough environmental analyses, considering technological trends, market demands, and competitive landscapes. This includes staying at the forefront of cutting-edge technologies.
- SWOT Analysis: Apple evaluates its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. For example, one of Apple’s strengths is its strong brand image, while a weakness might be dependence on a limited product line.
- Setting business Goals and Objectives: Apple sets specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals. This could include objectives like maintaining a certain market share, launching new products, or achieving specific financial targets.
- Strategies and Tactics: Apple develops strategies based on its goals. For instance, a strategic move might be expanding its ecosystem by integrating hardware, software, and services. Tactics could include aggressive marketing campaigns and product launches.
- Implementation and Execution: Apple’s strategic plans are meticulously executed. The launch of iconic products like the iPhone, iPad, and Mac series demonstrates effective implementation of their strategies.
- Monitoring and Adjusting: Apple constantly monitors its performance metrics, customer feedback, and market dynamics. If necessary, adjustments are made to the strategic plan to stay responsive to changing conditions.
2) Tesla Strategic Plan Process
- Vision and Mission: Tesla’s strategic planning revolves around its mission to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy. The vision includes producing electric vehicles and renewable energy solutions.
- Market Analysis: Tesla analyzes global markets for electric vehicles, renewable energy, and energy storage. This involves understanding regulatory environments, consumer behaviours, and technological advancements.
- Risk Assessment: Tesla conducts risk assessments related to manufacturing, supply chain, and market volatility. For instance, it considers risks associated with battery production and global economic conditions.
- Setting Bold Objectives: Tesla is known for setting ambitious objectives, such as achieving mass-market electric vehicle adoption and establishing a robust network of charging stations worldwide.
- Innovative Strategies: Tesla’s strategic planning involves innovation in technology and business models . For instance, the “Gigafactories” for mass production of batteries and the “Autopilot” feature in vehicles reflect innovative strategies.
- Agile Adaptation: Due to the rapidly changing automotive and energy sectors, Tesla maintains an agile approach. The company adapts its plans swiftly to capitalize on emerging opportunities, as seen in the expansion of its energy products.
- Continuous Improvement: Tesla places emphasis on continuous improvement. The iterative development of electric vehicle models, software updates, and advancements in battery technology showcase a commitment to refinement.
These examples demonstrate how strategic planning is a dynamic and integral part of the business processes of leading companies. They highlight the importance of a well-defined vision, rigorous analysis, adaptability, and innovation in the strategic planning process.
Tactical vs. Strategic Planning Process
An easy way to distinguish your company’s Tactical Planning from your Strategic Planning is to separate your wants from your HOWs.
In your Strategic Planning, you identify what you WANT for the company. These are big-picture dreams (achievable, but big ) that are your definition of success. In your Tactical Planning, you identify the HOW for reaching those dreams, including the smaller necessary steps.
Each kind of planning is vital for securing the organization’s future, but they require different sorts of attention and philosophy, and teams that are good at planning one way may not necessarily be good at the other kind of planning.
Strategic Planning vs. Your Business Purpose
Your Strategic Planning Process will of course be deeply connected to your Business Purpose .
We like to think of Business Purpose in broad terms, choosing especially to think of a business’s role in massive transformation. Embedded within a Business Purpose is the Business Plan that directs operations and how a company delivers value to its customers.
What is the relationship between your Strategic Planning and your Business Purpose ? One feeds into the other. Your Business Purpose must point to a larger impact you’ll have on the people who purchase your goods and services, and your Strategic Planning takes into account how you’ll grow and expand that Purpose as you reach more customers more successfully.
Strategic Planning vs Business Planning
Strategic planning and business planning are two distinct processes that are often used interchangeably, but they have some key differences.
Strategic planning is a top-level process that focuses on determining the direction of an organization over the long term. It involves setting goals, determining the key resources and actions necessary to achieve those goals, and allocating those resources in a way that best serves the organization’s future. The outcome of strategic planning is typically a long-term strategic plan that outlines the organization’s vision, mission, values, and objectives.
Business planning , on the other hand, is a more tactical process that focuses on the implementation of specific initiatives and projects to support the organization’s long-term goals. Business plans typically outline the steps necessary to launch a new product, enter a new market, or achieve a specific objective. They may also include budgets, marketing plans, and other operational details.
In short, strategic planning is about setting the direction for an organization, while business planning is about implementing specific initiatives to support that direction. Both processes are important for the success of an organization and should be used in conjunction to ensure that resources are allocated effectively and that the organization is moving in the right direction.
Why is Strategic Planning Important?
Imagine this scenario: A warehouse full of goods sits, unsold and unmoved. A collection of brilliant people languishes at desks all day. Outside, the world spins and changes. It’s ready for what these people could do, can do, and yet nothing happens. Needs remain unmet. Progress is halted. Everyday life takes several backwards steps. This is what your business will look like without proper Strategic Planning.
Strategic Planning forces you to consider your Strategic Objectives and critically compare them to the resources you have available. As you continuously evaluate the circumstances of your business and your customers, your Strategic Plan evolves to match your goals and business capabilities.
The process involved pushes decision-makers to practice Strategic Thinking . It limits wasteful spending, especially when upper-level managers are willing to forgo pet projects in favor of operations with a broader use and appeal.
Strategic Planning is important because it directs your resources to efficiently meet your overall Business Goals . Without Strategic Planning, you are likely to waste resources, make conflicting decisions, or fail to grow your business to its greatest potential.
When Do You Create a Strategic Plan?
Most businesses find value in reviewing their Strategic Plan every three years. This allows enough time to pass that you can evaluate the success of previous plans, reflect on the achievement of your Strategic Goals, consider developments outside your organization that affect your business, and begin formulating new goals that will become the next version of your plans.
When businesses first begin, they often have too many fires burning at once. They remain focused on existing today rather than planning for tomorrow. Most entrepreneurs remember those stressful early days of starting their businesses and can understand why formalities like Strategic Plans can fall by the wayside. We believe if your business lasts longer than a year it’s important to develop a plan for the future. Think of Strategic Planning as a celebration of a first anniversary—a sign that you’re poised to continue moving forward for years to come.
However, Strategic Planning is not a one-off event that is over once the cookies are all gone and the room clears. Your Strategic Planning team should meet regularly to measure how effective the plans are at helping you reach your Strategic Goals . Ad hoc subcommittees can play a role in gathering evidence to ensure that your plans remain appropriate, especially if conditions change.
For example, we recommended a close review of Strategic Plans and Strategic Goals once the COVID-19 pandemic made it clear that business was going to be affected at least short- to mid-term. We continue to recommend teams regularly revisit their Strategic Plans with global circumstances in mind to recognize opportunities and prepare for challenges.
The Benefits of Strategic Planning
As we’ve mentioned, there are many benefits of Strategic Planning . Some of those benefits include:
- Shared sense of power and importance
- United direction
- Clear path and purpose for decision-making and operations
- Boosted operational effectiveness
- Responsible, efficient use of available resources
- Meaningful work done on a daily basis
- Tracking of progress
- Ability to adjust to changing circumstances
What is a business without Strategic Planning? In most cases, it’s not much, nor is it long for the world. While it’s possible to accidentally find success without much planning, most successful businesses are a result of careful thought mixed with the urge to pounce on the opportunity.
What prepares you to pounce?
Your Strategic Planning and the processes that make it possible.
The UNITE Business Model Framework: A Framework for Innovation Success

50 Innovation Examples: Exciting Innovative Ideas in Business
In the Business environment, strategic innovation has taken centre stage as a...

Innovation Strategy: Developing Innovative Strategies in Business
Innovation has become an imperative for organizations worldwide, yet the multitude of...
Free guide to improve your innovation success rate*
Our 35-page comprehensive innovation guide covers the key areas why innovation fails. While it cannot cover all the solutions (that would take books to fill), it provides you with a convenient starting point for your analysis and provides further resources and links to the corresponding UNITE models, ultimately allowing you to work towards a doubling and tripling your chances of success.

Discover the largest library of innovation & transformation tools on the entire Internet!
LOG IN VIA E-MAIL
Forgot password?
New to Digital Leadership? Create your account

Get access to the UNITE Models now!
Discover the largest library of innovation & transformation tools on the internet!
First name *
Last name *
Professional E-mail *
Choose Your Password *
Confirm Your Password *
I want to be kept up-to-date and accept the privacy statement *
By signing up, you agree to receive news and accept the privacy statement (mandatory)
Already have an account? Log in
Verify your e-mail address now by entering the 6-digit code we’ve just sent to your inbox
Don't receive Code? Resend code
Country * Please Select Afghanistan Albania Algeria Andorra Angola Antigua and Barbuda Argentina Armenia Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belarus Belgium Belize Benin (Dahomey) Bolivia Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana Brazil Brunei Brunswick and Lüneburg Bulgaria Burkina Faso (Upper Volta) Burundi Cabo Verde Cambodia Cameroon Canada Cayman Islands Central African Republic Central American Federation Chad Chile China Colombia Comoros Congo Free State Costa Rica Cote d’Ivoire (Ivory Coast) Croatia Cuba Cyprus Czechia Democratic Republic of the Congo Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic Ecuador Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Eswatini Ethiopia Fiji Finland France Gabon Gambia Georgia Germany Ghana Grand Duchy of Tuscany Greece Grenada Guatemala Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Holy See Honduras Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iran Iraq Ireland Israel Italy Jamaica Japan Jordan Kazakhstan Kenya Kiribati Korea Kosovo Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Laos Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Libya Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Marshall Islands Mauritania Mauritius Mexico Micronesia Moldova Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Morocco Mozambique Namibia Nassau Nauru Nepal Netherlands New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria North Macedonia Norway Oman Pakistan Palau Panama Papal States Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Piedmont-Sardinia Poland Portugal Qatar Republic of Congo Republic of Korea (South Korea) Republic of the Congo Romania Russia Rwanda Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Samoa San Marino Sao Tome and Principe Saudi Arabia Schaumburg-Lippe Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Slovakia Slovenia Solomon Islands Somalia South Africa South Sudan Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Sweden Switzerland Syria Tajikistan Tanzania Thailand Timor-Leste Togo Tonga Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Tuvalu Uganda Ukraine United Arab Emirates United Kingdom Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Venezuela Vietnam Württemberg Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe Industry * Please Select Automotive, mobilty & transport Financial Services Chemical & agriculture Construction & Real Estate Consulting Education Energy Banking, insurance & FS FMCG Food Gov / Public Industry Health & lifestyle Logistics, Aero & Shipping Media & Entertainment Natural resources & mining Pharma & Biotech Retail & trade Tech & E-Commerce Telco Tourism design Information technology & services Management consulting Retail Pharmaceuticals International trade & development Professional training & coaching luxury goods & jewelry Automotive Insurance Mechanical or industrial engineering Company Size * XS - 1-10 S - 10-100 M - 100-1000 L - 1000-5000 XL - > 5000
Seniority * Please Select Junior Consultant Senior Consultant Manager Senior Manager Director VP SVP Partner CXO Board Member
Areas of interest * Innovation Digital Transformation Culture & Organization IT Strategy & Bus. Alignment Customer Experience
Editable UNITE models (PowerPoint) included
Most of our models and canvases are designed to be applied!
To help you personalize them to your exact business requirements, you can download fully editable versions of the UNITE models available (PowerPoint format)!
They are straightforward to work with, and you can directly incorporate them into your presentations as you need…thus saving countless hours of replication!
PS: did you know that you are also getting hi-res print-ready versions for your workshops?
Monthly live webinars
Each month we host our exclusive, invitation-only webinar series where one of our industry-leading experts updates our members on the latest news, progress and concepts around business strategy, innovation and digital transformation, as well as other related topics.
You will receive the book in PDF and EPUB formats, ideal for your computer, Kindle, Tablet or other eReading device.
Bi-weekly live group Q&A sessions
These sessions are your opportunity to bring any questions or challenges you’re facing and receive expert guidance on the spot.
Come and be a part of engaging discussions where your unique concerns are heard and addressed.
1x personal coaching session / month
If you are occasionally looking for a sparring partner or you need limited support, then this option will be ideal for you. Coaching sessions are 1-2 hours where we can discuss any challenge or opportunity you are currently facing.
If you need a few more hours outside of this provision, then these could be billed transparently.
Unlimited video call support! – it’s like always making the right decision!
We believe support shouldn’t be limited. Because we typically find that the occasional hour just doesn’t cut it – particularly if you and your team are in the midst of a large and complex project.
Your time with Stefan is therefore unlimited (fair usage applies) – in his function as coach and sparring partner. That does mean that you will still have to do the work – we cannot take that off you, unless you hire us as consultants. But you will get valuable strategic insight and direction to make sure you are always focusing your efforts where they will lead to the best results.
One personal coaching session / month + unlimited support via e-mail & WhatsApp
We believe support shouldn’t be limited. If you generally know what you are doing but want a sparring partner to frequently raise questions to, this is the perfect choice!
In addition to your monthly 1-1 live coaching sessions with Stefan, you will also get unlimited support from him via email and WhatsApp messaging (fair usage applies). This not only allows you to get valuable strategic direction in your calls, but also gives you instant access to expert help as you work through your plans each month.
The fact that support is text-based means that we can speed up our responses to you while keeping the overall cost of support down.
Welcome gift of our book “How to Create Innovation” (digital + physical editions)*
As a welcome gift, you will receive the both the digital and physical version of our book “How to Create Innovation”, which covers numerous relevant resources and provides additional deep dives into our UNITE models and concepts.
The print version will be shipped out to you on sign-up. The digital version will be emailed to you, and comes in PDF and EPUB formats, ideal for your computer, Kindle, Tablet or other eReading device.
1x major workshop or 2x smaller workshops / month
1x major or 2x smaller workshops based on the UNITE models.
- Topics covered: almost any challenge under the header of #strategy, #innovation or #transformation, leveraging the UNITE models.
- Hands-On Learning: solve your challenges while learning the practical application of the UNITE models and walk away with concrete plans and tools to take your next steps.
- Industry thought leadership: facilitated by Stefan, the founder of Digital Leadership and the main author of the UNITE models, ensuring top-tier guidance and knowledge sharing.
- Collaborative approach: engage in interactive sessions that foster collaboration, idea exchange, and real-time problem-solving among peers and industry leaders.
- Continuous Improvement: Regular workshops ensure ongoing development in your organization staying ahead of industry trends and customer needs.
Access all of our UNITE models, (incl. editable & print versions)
All of our Professional plans offer full access to the following:
- 6x UNITE model package downloads are included per month, if you need something in addition to these however, please let us know!
- Hi-res, print-ready versions you can use in your workshops
- Fully editable PowerPoint versions where applicable – personalize to your needs.
- Exclusive access to our vault of never-before-published strategic materials. We have much more to share – a lot of our concepts have never been published!
Exclusive access to our private UNITE community (upcoming)
We are currently in the process of launching our brand new community., we are designing our community to specifically help you:.
- Get answers to questions (“How do I …”)
- Share leading practices & knowledge
- Jointly develop new models
- Network amongst a highly qualified group of peers
Please, select the reason
Cancelling your plan will deactivate your plan after the current billing period ends. You will not be charged further, but also won’t be able to access [exclusive features/services].
- Cost-related issues
- Unsatisfied with the service
- Features I need are missing
- Switching to a different service
- Other (Please specify)
Book Your Initial Blueprint Session Now
Simply fill out the below form and book in a time for our initial session that works for you. This initial session is free, no strings attached, and is where we can discuss your Blueprint needs more in-depth before moving forward.

Stefan F. Dieffenbacher
Founder of digital leadership.
Adam D. Wisniewski
Partner for it strategy & business alignment.

Get in touch with Digital Leadership
Speak to our team today to find the best solution for your business to grow and scale.
We are here to support you across the entire lifecycle in all topics related to #digital, #innovation, #transformation and #marketing!

Stefan F. Dieffenbacher Founder of Digital Leadership
Contact Us!
Contact form, contact details, book a call.
Title, first name & last name * Email address * Phone number Please let us know how we can best support you! *
By clicking “Send”, I agree to Terms of Service and Privacy Policy.
Let’s have a conversation!
“Please be invited to reach out! We are happy to help and look forward to a first meeting!”
+41 (0) 44 562 42 24
Schedule Your Call With Our Team
Find a time on our calender that best suits you !

Founder and CEO of Digital Leadership
SCHEDULE YOUR INITIAL CALL
A Quick Survey!
Help us better understand the UNITE community
What is the main challenge you're currently facing in your business?
One Last Step..
Seniority * Please Select Junior Consultant Senior Consultant Manager Senior Manager Director VP SVP Partner CXO Board Member
Areas of interest * Innovation Digital Transformation Culture & Organization IT Strategy & Bus. Alignment Customer Experience
You Want To Drive Change?
Let’s find the best solution for your business to grow and scale sustainably!
Let’s kick start it!
We will uncover your current business situation and goals and provide you with a bespoke solution that helps you drastically grow your business working with us.

Stefan F. Dieffenbacher, M.B.A.
Feedback about our consulting that we are proud of
Read the reviews and make sure that this is not a waste of time, but a super effective tool.
You want to drive change?
Schedule your free business assessment call with our founder.
On this call, we will uncover your current business situation and goals and talk about how to drive change and solve your need.
Choose the meeting type that applies to your needs and schedule a time to meet with someone from our team. We look forward to speaking with you soon!
Thanks, We’ve Received Your Updated Details

Schedule Your Free Business Assessment

Schedule Your Free Business Assessment Call With Adam D. Wisniewski
Welcome to our scheduling page.

Let’s Design your Customer Experience Blueprint !
In a uniquely designed 60 or 90 minute session* , we will …
- > identify where to start with near-certainty
- > define what approach it takes to create success in your organization
Based on the Blueprinting session, you will receive a tailored blueprint that aligns with your objectives, vision and goals, ensuring that your initiative is a success from start to finish.

In this session, you will be working together with Patrick Zimmermann, Associate Partner for Customer Experience

Let’s Design your Culture & Org-Change Blueprint !

In this session, you will be working together with Dr. Andreas Rein, Partner at Digital Leadership for Culture & Org Change
Let’s Design your Innovation Blueprint !

In this session, you will be working together with Sascha Martini, Partner at Digital Leadership for Innovation and Digital Transformation
Let’s Design your Transformation Blueprint !

In this session, you will be working together with Stefan F. Dieffenbacher, Founder of Digital Leadership Stefan is a global thought leader in the innovation space
Let’s Design your IT Strategy & Business Alignment Blueprint !

In this session, you will be working together with Adam D. Wisniewski, Partner for IT Strategy & Business Alignment

Patrick Zimmermann

Sascha Martini

Dr. Andreas Rein
Write a personalized review! Log in
Create Review


Strategic Plans for Long-Term Growth: Examples and Strategies
.png)
This is a comprehensive guide on strategic planning for small to midsize companies.
If you want to:
- Move your organization in the direction you intend for long-term success,
- Implement your plan smoothly for greater growth,
- Use a better platform for developing a truly effective strategic plan,
… then you’ll love this guide. Let’s get started.
What’s Covered in This Guide
Click on each to jump to that section.
What is Strategic Planning?
What does strategic planning mean, what is the goal of strategic planning.
- What is Strategic Leadership?
4 Strategic Planning Strategies
The strategic planning process [11 steps], what does strategic planning involve.
- How to Implement Your Strategic Plan
Examples of Strategic Plans
Get your strategic planning done on ninety.
Strategic planning is the process you use to:
- Establish and document a clear direction for your organization.
- Identify business goals and set priorities that create growth for your company.
- Formulate a long-term plan of action designed to achieve these objectives.
- Determine an internal system tracking and evaluating performance.
When organizations want to, they use a strategic plan to:
- Strengthen their operation.
- Focus on collective energy and resources.
- Enable leaders, teams, and other stakeholders to work toward common goals.
- Make agreements around desired results.
- Refresh direction and prevail over a changing or challenging environment.
Thinking strategically helps companies take the right action for more success and better outcomes. Some even call it an art.
Strategic planning is one of three essential ways to pursue important objectives for your company. When tackling challenges and determining action plans, you can think strategically, tactically, or operationally. These three thought processes often work in concert to help you create a framework that achieves your desired objectives.
- Strategic plans are designed for multilevel involvement throughout the entire organization. Leaders will look ahead to where they want to be in three, five, and ten years and develop a mission.
- Tactical plans support strategic plans. They outline the specific responsibilities and functionalities at the department level so employees know how to do their part to make the strategic plan successful.
- Operational plans focus on the highly detailed procedures, processes, and routine tasks that frontline employees must accomplish to achieve desired outcomes.
The goal of your strategic plan is to determine:
- Where your company stands in relation to the current business environment. Understand how your business operates, how you create value, and how you differentiate from your competitors.
- Where you want to take the business based on long-term objectives such as your company’s vision, mission, culture, values, and goals. Envision how you see the company five or ten years from now.
- What you need to do to get there. You come away from your planning sessions with a roadmap that helps deliver on your strategic objectives. Determine better ways to enable and implement change, schedule deadlines, and structure goals, so they’re achievable.
The main purpose of your strategic plan is to create clearly defined goals for achieving the growth and success of your organization. These goals are connected to your organization’s mission and long-term vision.
What is Strategic Leadership?
Strategic leadership is how you create, implement, and sustain your strategic plan, so your organization moves in the direction you intend for long-term success. This usually involves establishing ongoing practices and benchmarks, allocating resources, and providing leadership that supports your strategic mission and vision statement.
Strategic leadership, also known as strategy execution, can employ two different approaches:
- A prescriptive approach is analytical and focuses on how strategies are created to account for risks and opportunities.
- A descriptive approach is principle-driven and focuses on how strategies are implemented to account for risks and opportunities.
Most people agree that a strategic plan is only as good as the company’s ability to research, create, implement, evaluate, and adjust when needed. The benefits can be great when:
- Your entire organization supports the plan.
- Your business is set up to succeed.
- Your employees are more likely to stay on track without being distracted or derailed.
- You make better decisions based on metrics that facilitate course correction.
- Everyone in your company is involved and invested in better outcomes.
- Departments and teams are aligned across your company.
- People are committed to learning and training.
- Productivity increases, and performance improves.
- Creativity is encouraged and rewarded.
What are the four main points of strategic planning? You engage in strategic thinking so you can create effective company goals that are:
Purpose-driven
Align your strategic plan with the company’s purpose and values as you understand them.
Actionable strategic goals are worth spending your time and resources on to reach organizational objectives.
It’s critical for you to track your strategy's progress and success, enabling your teams to take action and meet the goals more effectively.
Focused Long-term
A long-term focus distinguishes a strategic plan from operational goals, which involve daily activities and milestones required for success. When planning strategically, you’re looking ahead to the company’s future.
A strategic plan isn’t written in a day. Critical thinking evolves over several months. Those involved in the strategic planning are usually a team of leaders and employees from your company and possibly other stakeholders.
When should strategic planning be done?
You should plan strategically for start-ups and newer organizations from the start. But even if your company is more established, it’s not too late to start working on strategy.
Flexible timing that’s tailored to the needs of your organization is smart. Although the frequency of strategy sessions is up to you, many leaders use these milestones as a guide:
- When the economy, your market, and industry trends change, or a global event occurs (like the onset of a pandemic).
- Following a change in senior leadership.
- Before a product launch or when a new division is added to your business.
- After your company merges with another organization.
- During a convenient time frame such as a quarterly and annual review.
Many organizations opt to schedule regular strategic reviews such as quarterly or annually. Especially when crafting a plan, your strategic planning team should meet regularly. They will often follow predetermined steps in the development of your long-term plan.
What are the 11 steps of strategic planning?
Identify your company’s strategic position in the marketplace. .
Gather market data and research information from both internal and external sources. You may want to conduct a comprehensive SWOT analysis to determine your company’s Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats against success. Your strengths and weaknesses are directly related to your current competitive advantage within your industry. They are what you use to balance challenges to your success. They also influence the likelihood of increased market share in the future.
Define your unique vision and mission.
What would success look like for you in three years? Five years? Ten years? Articulate that in a vision statement. How do you intend to realize your vision? That’s articulated in your mission statement. Formulating purpose-driven strategic goals articulates why your company does what it does. Your organizational values inform your mission and vision and connect them to specific objectives.
Determine your company’s value.
Many companies use financial forecasting for this purpose. A forecast can assign anticipated measurable results, return on investment (ROI), or profits and cost of investment.
Set your organizational direction.
Defining the impact you want to have and the time frame for achieving helps focus a too-broad or over-ambitious first draft. This way, your plan will have objectives that will have the most impact.
Create specific strategic objectives.
Your strategic objectives identify the conditions for your success. For instance, they may cover:
- Value: Increasing revenue and shareholder value, budgeting cost, allocating resources aligned with the strategic plan, forecasting profitability, and ensuring financial stability.
- Customer Experience: Identifying target audiences, solution-based products and services, value for the cost, better service, and increased market share.
- Operational Efficiency: Streamlining internal processes, investing in research and development, total quality and performance priorities, reducing cost, and improving workplace safety.
- Learning and Growth: Training leaders and teams to address change and sustain growth, improving employee productivity and retention, and building high-performing teams.
Set specific strategic initiatives.
Strategic initiatives are your company's actions to reach your strategic objectives, such as raising brand awareness, a commitment to product development, purpose-driven employee training, and more.
Develop cascading goals.
Cascading goals are like cascading messages : They filter your strategy throughout the company from top to bottom. The highest-level goals align with mid-level goals to individual goals employees must accomplish to achieve overall outcomes. This helps everyone see how their performance will influence overall success, which improves engagement and productivity.
Create alignment across the entire company.
The success of your strategy is directly impacted by your commitment to inform and engage your entire workforce in strategy implementation. This involves ensuring everyone is connected and working together to achieve your goals. Overall decision-making becomes easier and more aligned.
Consider strategy mapping.
A strategy map is an easy-to-understand diagram, graphic, or illustration that shows the logical, cause-and-effect relationship among various strategic objectives. They are used to quickly communicate how your organization creates value. It will help you communicate the details of your strategic plan better to people by tapping into their visual learning abilities.
Use metrics to measure performance.
When your strategy informs the creation of SMART organizational goals , benchmarks can be established and metrics can be assigned to evaluate performance within time frames. Key performance indicators (KPIs) align performance and productivity with long-term strategic objectives.
Evaluate the performance of your plan regularly.
You write a strategic plan to improve your company’s overall performance. Evaluating your progress at regular intervals will tell you whether you’re on your way to achieving your objectives or whether your plan needs an adjustment.
Effective strategic planning involves creating a company culture of good communication and accountability. It involves creating and embracing the opportunity for positive change.
Consider these statistics:
- In many companies, only 42% of leaders and 27% of employees have access to a strategic plan.
- Even if they have access, 95% of employees do not understand their organization's strategy.
- 5.2% of a strategy’s potential is lost to poor communication.
- What leaders care about makes up at least 80% of the content of their communications. But those messages do not tap into around 80% of their employees’ primary motivators for putting extra energy into a change program.
- 28% of leaders say one of the main reasons strategic initiatives succeed is the ability to attract skilled personnel; 25% say it’s good communication; 25% say it’s the ability to manage organizational change.
Here’s what you can do to embrace a culture of good communication and accountability:
Make your strategic plan visible. Talk about what's working and what isn't. People want to know where and how they fit into the organization and why their contribution is valuable. Even if they don't understand every element of the plan.
Build accountability. If you've agreed on a plan with clear objectives and priorities, your leaders have to take responsibility for what's in it. They must own the objectives and activities in your plan.
Create an environment for change. It’s much more difficult to implement a strategy if you think there will be no support or collaboration from your coworkers. Addressing their concerns will help build a culture that understands how to champion change.
Implementing Your Strategic Plan
- 98% of leaders think strategy implementation takes more time than strategy formulation.
- 61% of leaders acknowledge that their organizations often struggle to bridge the gap between strategy formulation and its day-to-day implementation.
- 45% of leaders say ensuring employees take different actions or demonstrate different behaviors is the toughest implementation challenge; 37% of leaders say it’s gaining support across the whole organization.
- 39% of leaders say one of the main reasons strategic plans succeed is skilled implementation.
The reality for so many is that it’s harder to implement a strategic plan than to craft one. Great strategic ideas and a clear direction are key to success, no matter what. But so is:
- Turning strategic ideas into an easy-to-implement framework that enables meaningful managing, tracking, and adapting.
- Getting everyone in the organization on the same strategic page, from creation to execution.
When your plan is structured to support implementation, you're more likely to get it done.
What are examples of good strategic planning? There are lots of templates out there to help you create a plan document with pen and paper.
But Ninety has a better way.
The Vision planner is essentially a strategic planning template on Ninety’s cloud-based platform that allows you to:
- Set goals, establish how you will meet them, and share them with those who need to know.
- Gain visibility around your company values.
- Create core values, a niche, and long-term goals that are accessible to everyone in your company.
- Create a vision of the future that lets you know what needs to happen now.
- Streamline and organize your processes.
- Easily update and track changes.
- Bring alignment to your entire organization.
And you can do all this with only two digitized pages.
In your Vision tool inside Ninety, you can easily access all the things that make strategic plans effective:
- Executive Summary
- Elevator Pitch
- Mission Statement
- Vision Statement
- SWOT Analysis
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
- Industry Analysis
- Marketing Plan
- Operations Plan
- Financial Projections
Vision + Goals is also completely integrated with all other features on Ninety, such as Scorecards, 90-Day Goals, To-Dos, Issues, Roles & Responsibilities Chart, Meetings, One-on-Ones, and more:
- Create a clear vision for each team.
- Determine one- and three-year goals.
- Reference past versions in a Vision archive.
- Share your Vision with all teams, or keep it private.
Now that you’ve learned how to grow your company using strategic planning, it’s time to put your knowledge into practice:
Build your strategic plan on Ninety now.
Do you want more step-by-step guides on strategy, strategic planning, and creating actionable strategic plans? Subscribe to our blog!
You might also like:

Is Team Health at the Forefront in Your Annual Planning Meeting?
Leadership • 7 Minute Read

Explore 7 Business Strategy Types for Sustainable Growth
Productivity • 17 Minute Read

Setting Business Goals: How to Write, Track and Align Them for Growth
Goals • 16 Minute Read
.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} Join us: Learn how to build a trusted AI strategy to support your company's intelligent transformation, featuring Forrester .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Register now .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Business strategy |
- 7 strategic planning models, plus 8 fra ...
7 strategic planning models, plus 8 frameworks to help you get started

Strategic planning is vital in defining where your business is going in the next three to five years. With the right strategic planning models and frameworks, you can uncover opportunities, identify risks, and create a strategic plan to fuel your organization’s success. We list the most popular models and frameworks and explain how you can combine them to create a strategic plan that fits your business.
A strategic plan is a great tool to help you hit your business goals . But sometimes, this tool needs to be updated to reflect new business priorities or changing market conditions. If you decide to use a model that already exists, you can benefit from a roadmap that’s already created. The model you choose can improve your knowledge of what works best in your organization, uncover unknown strengths and weaknesses, or help you find out how you can outpace your competitors.
In this article, we cover the most common strategic planning models and frameworks and explain when to use which one. Plus, get tips on how to apply them and which models and frameworks work well together.
Strategic planning models vs. frameworks
First off: This is not a one-or-nothing scenario. You can use as many or as few strategic planning models and frameworks as you like.
When your organization undergoes a strategic planning phase, you should first pick a model or two that you want to apply. This will provide you with a basic outline of the steps to take during the strategic planning process.
![strategic planning in business examples [Inline illustration] Strategic planning models vs. frameworks (Infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/89236d14-1abf-4f49-8b91-4187147f1c63/inline-business-strategy-strategic-planning-models-1-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
During that process, think of strategic planning frameworks as the tools in your toolbox. Many models suggest starting with a SWOT analysis or defining your vision and mission statements first. Depending on your goals, though, you may want to apply several different frameworks throughout the strategic planning process.
For example, if you’re applying a scenario-based strategic plan, you could start with a SWOT and PEST(LE) analysis to get a better overview of your current standing. If one of the weaknesses you identify has to do with your manufacturing process, you could apply the theory of constraints to improve bottlenecks and mitigate risks.
Now that you know the difference between the two, learn more about the seven strategic planning models, as well as the eight most commonly used frameworks that go along with them.
![strategic planning in business examples [Inline illustration] The seven strategic planning models (Infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/23048ae4-8a18-4b9b-ad9e-33b0fc5d04ee/inline-business-strategy-strategic-planning-models-2-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
1. Basic model
The basic strategic planning model is ideal for establishing your company’s vision, mission, business objectives, and values. This model helps you outline the specific steps you need to take to reach your goals, monitor progress to keep everyone on target, and address issues as they arise.
If it’s your first strategic planning session, the basic model is the way to go. Later on, you can embellish it with other models to adjust or rewrite your business strategy as needed. Let’s take a look at what kinds of businesses can benefit from this strategic planning model and how to apply it.
Small businesses or organizations
Companies with little to no strategic planning experience
Organizations with few resources
Write your mission statement. Gather your planning team and have a brainstorming session. The more ideas you can collect early in this step, the more fun and rewarding the analysis phase will feel.
Identify your organization’s goals . Setting clear business goals will increase your team’s performance and positively impact their motivation.
Outline strategies that will help you reach your goals. Ask yourself what steps you have to take in order to reach these goals and break them down into long-term, mid-term, and short-term goals .
Create action plans to implement each of the strategies above. Action plans will keep teams motivated and your organization on target.
Monitor and revise the plan as you go . As with any strategic plan, it’s important to closely monitor if your company is implementing it successfully and how you can adjust it for a better outcome.
2. Issue-based model
Also called goal-based planning model, this is essentially an extension of the basic strategic planning model. It’s a bit more dynamic and very popular for companies that want to create a more comprehensive plan.
Organizations with basic strategic planning experience
Businesses that are looking for a more comprehensive plan
Conduct a SWOT analysis . Assess your organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats with a SWOT analysis to get a better overview of what your strategic plan should focus on. We’ll give into how to conduct a SWOT analysis when we get into the strategic planning frameworks below.
Identify and prioritize major issues and/or goals. Based on your SWOT analysis, identify and prioritize what your strategic plan should focus on this time around.
Develop your main strategies that address these issues and/or goals. Aim to develop one overarching strategy that addresses your highest-priority goal and/or issue to keep this process as simple as possible.
Update or create a mission and vision statement . Make sure that your business’s statements align with your new or updated strategy. If you haven’t already, this is also a chance for you to define your organization’s values.
Create action plans. These will help you address your organization’s goals, resource needs, roles, and responsibilities.
Develop a yearly operational plan document. This model works best if your business repeats the strategic plan implementation process on an annual basis, so use a yearly operational plan to capture your goals, progress, and opportunities for next time.
Allocate resources for your year-one operational plan. Whether you need funding or dedicated team members to implement your first strategic plan, now is the time to allocate all the resources you’ll need.
Monitor and revise the strategic plan. Record your lessons learned in the operational plan so you can revisit and improve it for the next strategic planning phase.
The issue-based plan can repeat on an annual basis (or less often once you resolve the issues). It’s important to update the plan every time it’s in action to ensure it’s still doing the best it can for your organization.
You don’t have to repeat the full process every year—rather, focus on what’s a priority during this run.
3. Alignment model
This model is also called strategic alignment model (SAM) and is one of the most popular strategic planning models. It helps you align your business and IT strategies with your organization’s strategic goals.
You’ll have to consider four equally important, yet different perspectives when applying the alignment strategic planning model:
Strategy execution: The business strategy driving the model
Technology potential: The IT strategy supporting the business strategy
Competitive potential: Emerging IT capabilities that can create new products and services
Service level: Team members dedicated to creating the best IT system in the organization
Ideally, your strategy will check off all the criteria above—however, it’s more likely you’ll have to find a compromise.
Here’s how to create a strategic plan using the alignment model and what kinds of companies can benefit from it.
Organizations that need to fine-tune their strategies
Businesses that want to uncover issues that prevent them from aligning with their mission
Companies that want to reassess objectives or correct problem areas that prevent them from growing
Outline your organization’s mission, programs, resources, and where support is needed. Before you can improve your statements and approaches, you need to define what exactly they are.
Identify what internal processes are working and which ones aren’t. Pinpoint which processes are causing problems, creating bottlenecks , or could otherwise use improving. Then prioritize which internal processes will have the biggest positive impact on your business.
Identify solutions. Work with the respective teams when you’re creating a new strategy to benefit from their experience and perspective on the current situation.
Update your strategic plan with the solutions. Update your strategic plan and monitor if implementing it is setting your business up for improvement or growth. If not, you may have to return to the drawing board and update your strategic plan with new solutions.
4. Scenario model
The scenario model works great if you combine it with other models like the basic or issue-based model. This model is particularly helpful if you need to consider external factors as well. These can be government regulations, technical, or demographic changes that may impact your business.
Organizations trying to identify strategic issues and goals caused by external factors
Identify external factors that influence your organization. For example, you should consider demographic, regulation, or environmental factors.
Review the worst case scenario the above factors could have on your organization. If you know what the worst case scenario for your business looks like, it’ll be much easier to prepare for it. Besides, it’ll take some of the pressure and surprise out of the mix, should a scenario similar to the one you create actually occur.
Identify and discuss two additional hypothetical organizational scenarios. On top of your worst case scenario, you’ll also want to define the best case and average case scenarios. Keep in mind that the worst case scenario from the previous step can often provoke strong motivation to change your organization for the better. However, discussing the other two will allow you to focus on the positive—the opportunities your business may have ahead.
Identify and suggest potential strategies or solutions. Everyone on the team should now brainstorm different ways your business could potentially respond to each of the three scenarios. Discuss the proposed strategies as a team afterward.
Uncover common considerations or strategies for your organization. There’s a good chance that your teammates come up with similar solutions. Decide which ones you like best as a team or create a new one together.
Identify the most likely scenario and the most reasonable strategy. Finally, examine which of the three scenarios is most likely to occur in the next three to five years and how your business should respond to potential changes.
5. Self-organizing model
Also called the organic planning model, the self-organizing model is a bit different from the linear approaches of the other models. You’ll have to be very patient with this method.
This strategic planning model is all about focusing on the learning and growing process rather than achieving a specific goal. Since the organic model concentrates on continuous improvement , the process is never really over.
Large organizations that can afford to take their time
Businesses that prefer a more naturalistic, organic planning approach that revolves around common values, communication, and shared reflection
Companies that have a clear understanding of their vision
Define and communicate your organization’s cultural values . Your team can only think clearly and with solutions in mind when they have a clear understanding of your organization's values.
Communicate the planning group’s vision for the organization. Define and communicate the vision with everyone involved in the strategic planning process. This will align everyone’s ideas with your company’s vision.
Discuss what processes will help realize the organization’s vision on a regular basis. Meet every quarter to discuss strategies or tactics that will move your organization closer to realizing your vision.
6. Real-time model
This fluid model can help organizations that deal with rapid changes to their work environment. There are three levels of success in the real-time model:
Organizational: At the organizational level, you’re forming strategies in response to opportunities or trends.
Programmatic: At the programmatic level, you have to decide how to respond to specific outcomes or environmental changes.
Operational: On the operational level, you will study internal systems, policies, and people to develop a strategy for your company.
Figuring out your competitive advantage can be difficult, but this is absolutely crucial to ensure success. Whether it’s a unique asset or strength your organization has or an outstanding execution of services or programs—it’s important that you can set yourself apart from others in the industry to succeed.
Companies that need to react quickly to changing environments
Businesses that are seeking new tools to help them align with their organizational strategy
Define your mission and vision statement. If you ever feel stuck formulating your company’s mission or vision statement, take a look at those of others. Maybe Asana’s vision statement sparks some inspiration.
Research, understand, and learn from competitor strategy and market trends. Pick a handful of competitors in your industry and find out how they’ve created success for themselves. How did they handle setbacks or challenges? What kinds of challenges did they even encounter? Are these common scenarios in the market? Learn from your competitors by finding out as much as you can about them.
Study external environments. At this point, you can combine the real-time model with the scenario model to find solutions to threats and opportunities outside of your control.
Conduct a SWOT analysis of your internal processes, systems, and resources. Besides the external factors your team has to consider, it’s also important to look at your company’s internal environment and how well you’re prepared for different scenarios.
Develop a strategy. Discuss the results of your SWOT analysis to develop a business strategy that builds toward organizational, programmatic, and operational success.
Rinse and repeat. Monitor how well the new strategy is working for your organization and repeat the planning process as needed to ensure you’re on top or, perhaps, ahead of the game.
7. Inspirational model
This last strategic planning model is perfect to inspire and energize your team as they work toward your organization’s goals. It’s also a great way to introduce or reconnect your employees to your business strategy after a merger or acquisition.
Businesses with a dynamic and inspired start-up culture
Organizations looking for inspiration to reinvigorate the creative process
Companies looking for quick solutions and strategy shifts
Gather your team to discuss an inspirational vision for your organization. The more people you can gather for this process, the more input you will receive.
Brainstorm big, hairy audacious goals and ideas. Encouraging your team not to hold back with ideas that may seem ridiculous will do two things: for one, it will mitigate the fear of contributing bad ideas. But more importantly, it may lead to a genius idea or suggestion that your team wouldn’t have thought of if they felt like they had to think inside of the box.
Assess your organization’s resources. Find out if your company has the resources to implement your new ideas. If they don’t, you’ll have to either adjust your strategy or allocate more resources.
Develop a strategy balancing your resources and brainstorming ideas. Far-fetched ideas can grow into amazing opportunities but they can also bear great risk. Make sure to balance ideas with your strategic direction.
Now, let’s dive into the most commonly used strategic frameworks.
8. SWOT analysis framework
One of the most popular strategic planning frameworks is the SWOT analysis . A SWOT analysis is a great first step in identifying areas of opportunity and risk—which can help you create a strategic plan that accounts for growth and prepares for threats.
SWOT stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Here’s an example:
![strategic planning in business examples [Inline illustration] SWOT analysis (Example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/cfab4ed2-46d1-4636-b801-14b3d86c8367/inline-project-management-SWOT-analysis-4-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
9. OKRs framework
A big part of strategic planning is setting goals for your company. That’s where OKRs come into play.
OKRs stand for objective and key results—this goal-setting framework helps your organization set and achieve goals. It provides a somewhat holistic approach that you can use to connect your team’s work to your organization’s big-picture goals. When team members understand how their individual work contributes to the organization’s success, they tend to be more motivated and produce better results
10. Balanced scorecard (BSC) framework
The balanced scorecard is a popular strategic framework for businesses that want to take a more holistic approach rather than just focus on their financial performance. It was designed by David Norton and Robert Kaplan in the 1990s, it’s used by companies around the globe to:
Communicate goals
Align their team’s daily work with their company’s strategy
Prioritize products, services, and projects
Monitor their progress toward their strategic goals
Your balanced scorecard will outline four main business perspectives:
Customers or clients , meaning their value, satisfaction, and/or retention
Financial , meaning your effectiveness in using resources and your financial performance
Internal process , meaning your business’s quality and efficiency
Organizational capacity , meaning your organizational culture, infrastructure and technology, and human resources
With the help of a strategy map, you can visualize and communicate how your company is creating value. A strategy map is a simple graphic that shows cause-and-effect connections between strategic objectives.
The balanced scorecard framework is an amazing tool to use from outlining your mission, vision, and values all the way to implementing your strategic plan .
You can use an integration like Lucidchart to create strategy maps for your business in Asana.
11. Porter’s Five Forces framework
If you’re using the real-time strategic planning model, Porter’s Five Forces are a great framework to apply. You can use it to find out what your product’s or service’s competitive advantage is before entering the market.
Developed by Michael E. Porter , the framework outlines five forces you have to be aware of and monitor:
![strategic planning in business examples [Inline illustration] Porter’s Five Forces framework (Infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/d63265bc-23e2-4ce6-9b91-b3da5a756619/inline-business-strategy-strategic-planning-models-3-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Threat of new industry entrants: Any new entry into the market results in increased pressure on prices and costs.
Competition in the industry: The more competitors that exist, the more difficult it will be for you to create value in the market with your product or service.
Bargaining power of suppliers: Suppliers can wield more power if there are less alternatives for buyers or it’s expensive, time consuming, or difficult to switch to a different supplier.
Bargaining power of buyers: Buyers can wield more power if the same product or service is available elsewhere with little to no difference in quality.
Threat of substitutes: If another company already covers the market’s needs, you’ll have to create a better product or service or make it available for a lower price at the same quality in order to compete.
Remember, industry structures aren’t static. The more dynamic your strategic plan is, the better you’ll be able to compete in a market.
12. VRIO framework
The VRIO framework is another strategic planning tool designed to help you evaluate your competitive advantage. VRIO stands for value, rarity, imitability, and organization.
It’s a resource-based theory developed by Jay Barney. With this framework, you can study your firmed resources and find out whether or not your company can transform them into sustained competitive advantages.
Firmed resources can be tangible (e.g., cash, tools, inventory, etc.) or intangible (e.g., copyrights, trademarks, organizational culture, etc.). Whether these resources will actually help your business once you enter the market depends on four qualities:
Valuable : Will this resource either increase your revenue or decrease your costs and thereby create value for your business?
Rare : Are the resources you’re using rare or can others use your resources as well and therefore easily provide the same product or service?
Inimitable : Are your resources either inimitable or non-substitutable? In other words, how unique and complex are your resources?
Organizational: Are you organized enough to use your resources in a way that captures their value, rarity, and inimitability?
It’s important that your resources check all the boxes above so you can ensure that you have sustained competitive advantage over others in the industry.
13. Theory of Constraints (TOC) framework
If the reason you’re currently in a strategic planning process is because you’re trying to mitigate risks or uncover issues that could hurt your business—this framework should be in your toolkit.
The theory of constraints (TOC) is a problem-solving framework that can help you identify limiting factors or bottlenecks preventing your organization from hitting OKRs or KPIs .
Whether it’s a policy, market, or recourse constraint—you can apply the theory of constraints to solve potential problems, respond to issues, and empower your team to improve their work with the resources they have.
14. PEST/PESTLE analysis framework
The idea of the PEST analysis is similar to that of the SWOT analysis except that you’re focusing on external factors and solutions. It’s a great framework to combine with the scenario-based strategic planning model as it helps you define external factors connected to your business’s success.
PEST stands for political, economic, sociological, and technological factors. Depending on your business model, you may want to expand this framework to include legal and environmental factors as well (PESTLE). These are the most common factors you can include in a PESTLE analysis:
Political: Taxes, trade tariffs, conflicts
Economic: Interest and inflation rate, economic growth patterns, unemployment rate
Social: Demographics, education, media, health
Technological: Communication, information technology, research and development, patents
Legal: Regulatory bodies, environmental regulations, consumer protection
Environmental: Climate, geographical location, environmental offsets
15. Hoshin Kanri framework
Hoshin Kanri is a great tool to communicate and implement strategic goals. It’s a planning system that involves the entire organization in the strategic planning process. The term is Japanese and stands for “compass management” and is also known as policy management.
This strategic planning framework is a top-down approach that starts with your leadership team defining long-term goals which are then aligned and communicated with every team member in the company.
You should hold regular meetings to monitor progress and update the timeline to ensure that every teammate’s contributions are aligned with the overarching company goals.
Stick to your strategic goals
Whether you’re a small business just starting out or a nonprofit organization with decades of experience, strategic planning is a crucial step in your journey to success.
If you’re looking for a tool that can help you and your team define, organize, and implement your strategic goals, Asana is here to help. Our goal-setting software allows you to connect all of your team members in one place, visualize progress, and stay on target.
Related resources

Solve your tech overload with an intelligent transformation

9 steps to craft a successful go-to-market (GTM) strategy

Unmanaged business goals don’t work. Here’s what does.
How Asana uses work management to effectively manage goals

How To Write A Strategic Plan That Gets Results + Examples

Are you feeling overwhelmed with the thought of writing a strategic plan for your business? Do you want to create a plan that will help you move your team forward with inspired alignment and disciplined execution? You're not alone.
Gone are the days of rigid, 5- or 10-year planning cycles that do not leave room for flexibility and innovation. To stay ahead of the curve, you need a dynamic and execution-ready strategic plan that can guide your business through the ever-evolving landscape.
At Cascade, we understand that writing a strategic plan can be dreadful, especially in today's unpredictable environment. That's why we've developed a simple model that can help you create a clear, actionable plan to achieve your organization's goals. With our tested and proven strategic planning template , you can write a strategic plan that is both adaptable and effective .
Whether you're a seasoned strategy professional or a fresh strategy planner, this guide will walk you through the process step-by-step on how to write a strategic plan. By the end, you'll have a comprehensive, easy-to-follow strategic plan that will help you align your organization on the path to success.

Follow this guide step-by-step or skip to the part you’re most interested in:
- Pre-Planning Phase: Build The Foundation
Cascade Model For Strategic Planning: What You Need To Know
- Key Elements of a Strategic Plan
How To Write A Strategic Plan In 6 Simple Steps
3 strategic plan examples to get you started, how to achieve organizational alignment with your strategic plan.
- Quick Overview of Key Steps In Writing A Strategic Plan

Create An Execution-Ready Strategic Plan With Cascade 🚀
*Editor’s note: This article is part of our ‘How to create a Strategy’ collection. At the end of this article, you’ll find a link to each piece within this collection so you can dig deeper into each element of an effective strategic plan and more related resources to master strategy execution.
Pre-Planning Phase: Build The Foundation
Before we dive into writing a strategic plan, it's essential to know the basics you should cover before the planning phase. The pre-planning phase is where you'll begin to gather the data and strategic insights necessary to create an effective strategic plan.
1. Run a strategic planning workshop
The first step is to run a strategic planning workshop with your team. Get your team in the room, get their data, and gather their insights. By running this workshop, you'll foster collaboration and bring fresh perspectives to the table. And that’s not all.
The process of co-creating and collaborating to put that plan together with stakeholders is one of the most critical factors in strategy execution . According to McKinsey’s research , initiatives in which employees contribute to development are 3.4 times more likely to be successful. They feel like the plan is a result of their efforts, and they feel ownership of it, so they're more likely to execute it.
💡 Tip: Use strategy frameworks to structure your strategy development sessions, such as GAP analysis , SWOT analysis , Porter’s Five Forces , Ansoff matrix , McKinsey 7S model , or GE matrix . You can even apply the risk matrix that will help you align and decide on key strategic priorities.
2. Choose your strategic planning model
Before creating your strategic plan, you need to decide which structure you will use. There are hundreds of ways to structure a strategic plan. You’ve likely heard of famous strategic models such as OKRs and the Balanced Scorecard .
But beyond the well-known ones, there's also a myriad of other strategic planning models ranging from the extremely simple to the absurdly complex.
Many strategic models work reasonably well on paper, but in reality, they don't show you how to write a strategic plan that fits your organization's needs.
Here are some common weaknesses most popular strategic models have:
- They're too complicated. People get lost in terminology rather than focus on execution.
- They don’t scale. They work well for small organizations but fail when you try to extend them across multiple teams.
- They're too rigid. They force people to add layers for the sake of adding layers.
- They're neither tangible nor measurable. They’re great at stating outcomes but lousy at helping you measure success.
- They're not adaptable. As we saw in the last years, the business environment can change quickly. Your model needs to be able to work in your current situation and adapt to changing economic landscapes.
Our goal in this article is to give you a simpler, more effective way to write a strategic plan. This is a tested and proven strategic planning model that has been refined over years of working with +20,000 teams around the world. We call it the Cascade Strategy Model.
This approach has proven to be more effective than any other model we have tried when it comes to executing and implementing the strategy .
It’s easy to use and it works for small businesses, fast-growing startups, as well as multinationals trying to figure out how to write a fail-proof strategic plan.
We’ve created a simple diagram below to illustrate what a strategic plan following the Cascade Model will look like when it's completed:
.jpeg)
Rather than a traditional roadmap , imagine your strategy as a flowchart. Each row is a mandatory step before moving on to the next.
We call our platform Cascade for a reason: strategy must cascade throughout an organization along with values, focus areas, and objectives.
Above all, the Cascade Model is intended to be execution-ready —in other words, it has been proven to deliver success far beyond strategic planning. It adds to a successful strategic management process.Key elements of a Strategic Plan
Key Elements Of A Strategic Plan
The key elements of a strategic plan include:
- Vision : Where do you want to get to?
- Values : How will you behave on the journey?
- Focus Areas : What are going to be your strategic priorities?
- Strategic objectives : What do you want to achieve?
- Actions and projects : How are you going to achieve the objectives?
- KPIs : How will you measure success?
In this part of the article, we will give you an overview of each element within the Cascade Model. You can follow this step-by-step process in a spreadsheet , or sign up to get instant access to a free Cascade strategic planning template and follow along as we cover the key elements of an effective strategic plan.
Your vision statement is your organization's anchor - it defines where you want to get to and is the executive summary of your organization's purpose. Without it, your strategic plan is like a boat without a rudder, at the mercy of strong winds and currents like Covid and global supply chain disruptions.
A good vision statement can help funnel your strategy towards long-term goals that matter the most to your organization, and everything you write in your plan from this point on will help you get closer to achieving your vision.
Trying to do too much at once is a surefire way to sink your strategic plan. By creating a clear and inspiring vision statement , you can avoid this trap and provide guidance and inspiration for your team. A great vision statement might even help attract talent and investment into your organization.
For example, a bike manufacturing company might have a vision statement like, “To be the premier bike manufacturer in the Pacific Northwest.” This statement clearly articulates the organization's goals and is a powerful motivator for the team.
In short, don't start your strategic plan without a clear vision statement. It will keep your organization focused and help you navigate toward success.
📚 Recommended read: How to Write a Vision Statement (With Examples, Tips, and Formulas)
Values are the enablers of your vision statement —they represent how your organization will behave as you work towards your strategic goals. Unfortunately, many companies throw around meaningless words just for the purpose of PR, leading to a loss of credibility.
To avoid this, make sure to integrate your organization’s core values into everyday operations and interactions. In today's highly-competitive world, it's crucial to remain steadfast in your values and cultivate an organizational culture that's transparent and trustworthy.
Companies with the best company cultures consistently outperform competitors and their average market by up to 115.6%, as reported by Glassdoor .
For example, a bike manufacturing company might have core values like:
- Accountability
These values reflect the organization's desire to become the leading bike manufacturer, while still being accountable to employees, customers, and shareholders.
👉 Here’s how to add vision and values to your strategic plan in Cascade:
After you sign up and invite your team members to collaborate on the plan, navigate to Plans and Teams > Teams page, and add the vision, mission and values. This will help you to ensure that the company’s vision, mission statement, and values are always at top of mind for everyone.
📚When you're ready to start creating some company values, check out our guide, How To Create Company Values .
3. Focus Areas
Your focus areas are the strategic priorities that will keep your team on track and working toward the company’s mission and vision. They represent the high-level areas that you need to focus on to achieve desired business outcomes.
In fact, companies with clearly defined priorities are more likely to achieve their objectives. According to a case study by the Harvard Business Review , teams that focus on a small number of key initiatives are more likely to succeed than those that try to do too much.
That’s also something that we usually recommend to our customers when they set up their strategic plan in Cascade. Rather than spreading your resources too thin over multiple focus areas, prioritize three to five.
Following our manufacturing example above, some good focus areas include:
- Aggressive growth
- Producing the nation's best bikes
- Becoming a modern manufacturer
- Becoming a top place to work
Your focus areas should be tighter in scope than your vision statement, but broader than specific goals, time frames, or metrics.
By defining your focus areas, you'll give your teams a guardrail to work within, which can help inspire innovation and creative problem-solving.
With a clear set of focus areas, your team will be better able to prioritize their work and stay focused on the most important things, which will ultimately lead to better business results.
👉Here’s how you can set focus areas in Cascade:
In Cascade, you can add focus areas while creating or importing an existing strategic plan from a spreadsheet. With Cascade’s Focus Area deep-dive functionality , you will be able to:
- Review the health of your focus areas in one place.
- Get a breakdown by plans, budgets, resources, and people behind each strategic priority.
- See something at-risk? Drill down into each piece of work regardless of how many plans it's a part of.

📚 Recommended read: Strategic Focus Areas: How to create them + Examples
4. Strategic Objectives
The importance of setting clear and specific objectives for your strategic plan cannot be overstated.
Strategic objectives are the specific and measurable outcomes you want to achieve . While they should align with your focus areas, they should be more detailed and have a clear deadline.
According to the 2022 State of High Performing Teams report , there is a strong correlation between goals and success not only at the individual and team level but also at the organizational level. Here’s what they found:
- Employees who are unaware of their company's goals are over three times more likely to work at a company that is experiencing a decline in revenue than employees who are aware of the goals.
- Companies with shrinking revenues are almost twice as likely to have employees with unclear work expectations.
Jumping straight into actions without defining clear objectives is a common mistake that can lead to missed opportunities or misalignment between strategy and execution.
To avoid this pitfall, we recommend you add between three and six objectives to each focus area .
It's here that we need to start being a bit more specific for the first time in your strategic planning process . Let's take a look at an example of a well-written strategic objective:
- Continue top-line growth that outpaces the industry by 31st Dec 2023.
This is too specific to be a focus area. While it's still very high level, it indicates what the company wants to accomplish and includes a clear deadline. Both these aspects are critical to a good strategic objective.
Your strategic objectives are the heart and soul of your plan, and you need to ensure they are well-crafted. So, take the time to create well-planned objectives that will help you achieve your vision and lead your organization to success.
👉Here’s how you can set objectives in Cascade:
Adding objectives in Cascade is intuitive, straightforward, and accessible from almost anywhere in the workspace. With one click, you’ll open the objective sidebar and fill out the details. These can include a timeline, the objective’s owner, collaborators, and how your objective will be measured (success criteria).
📚 Recommended read: What are Strategic Objectives? How to write them + Examples
5. Actions and projects
Once you’ve defined your strategic objectives, the next step is to identify the specific strategic initiatives or projects that will help you achieve those objectives . They are short-term goals or actionable steps you or your team members will take to accomplish objectives. They should leverage the company’s resources and core competencies.
Effective projects and actions in your strategic plan should:
- Be extremely specific.
- Contain a deadline.
- Have an owner.
- Align with at least one of your strategic objectives.
- Provide clarity on how you or your team will achieve the strategic objective.
Let's take a look at an example of a well-written project continuing with our bike manufacturing company using the strategic objective from above:
Strategic objective: Continue top-line growth that outpaces the industry by 31st Dec 2023.
Project: Expand into the fixed gear market by 31st December 2023.
This is more specific than the objective it links to, and it details what you will do to achieve the objective.
Another common problem area for strategic plans is that they never quite get down to the detail of what you're going to do.
It's easier to state "we need to grow our business," but without concrete projects and initiatives, those plans will sit forever within their PowerPoint templates, never to see the light of day after their initial creation.
Actions and projects are where the rubber meets the road. They connect the organizational strategic goals with the actual capabilities of your people and the resources at their disposal. Defining projects is a vital reality check every strategic plan needs.
👉Here’s how you create actions and projects in Cascade:
From the Objective sidebar, you can choose to add a project or action under your chosen objective. In the following steps, you can assign an owner and timeline to each action or project.
Plus, in Cascade, you can track the progress of each project or action in four different ways. You can do it manually, via milestones, checklists, or automatically by integrating with Jira and 1000+ other available integrations .
📚 Recommended read: How to create effective projects
Measuring progress towards strategic objectives is essential to effective strategic control and business success. That's where Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) come in. KPIs are measurable values that track progress toward achieving key business objectives . They keep you on track and help you stay focused on the goals you set for your organization.
To get the most out of your KPIs, make sure you link them to a specific goal or objective. In this way, you'll avoid creating KPIs that don't contribute to your objectives and distract you from focusing on what matters.
Ideally, you will add both leading and lagging KPIs to each objective so you can get a more balanced view of how well you're progressing. Leading KPIs can indicate future performance while lagging KPIs show how well you’ve done in the past. Both types of KPIs are critical for operational planning and keeping your business on track.
Think of KPIs as a form of signpost in your organization. They provide critical insights that inform business leaders of their organization’s progress toward key business objectives. Plus, they can help you identify opportunities faster and capitalize on flexibility.
👉Here’s how you can set and track KPIs in Cascade:
In Cascade , you can add measures while creating your objectives or add them afterward. Open the Objective sidebar and add your chosen measure.
When you create your Measure, you can choose how to track it. Using Cascade, you can track it manually or automatically. You can automate tracking via 1000+ integrations , including Excel spreadsheets and Google Sheets. In this way, you can save time and ensure that your team has up-to-date information for faster and more confident decision-making.
📚 Recommended reads:
- 10 Popular KPI Software Tools To Connect & Visualize Your Data (2023 Guide)
- How To Track KPIs To Hit Your Business Goals
Corporate Strategic Plan
Following the steps outlined above, you should end up with a strategic plan that looks something like this:

This is a preview of a corporate strategic plan template that is pre-filled with examples. Here you can use the template for free and begin filling it out to align with your organization's needs. Plus, it’s suitable for organizations of all sizes and any industry.
Once you fill in the template, you can also switch to the timeline view. You’ll get a complete overview of how the different parts of your plan are distributed across the roadmap in a Gantt chart view.

This template will help you create a structured approach to the strategic planning process, focus on key strategic priorities, and drive accountability to achieve necessary business outcomes.
👉 Get your free corporate strategic plan template here.
Coca-Cola Strategic Plan
Need a bit of extra inspiration to start writing your organization’s strategic plan? Check out this strategic plan example, inspired by Coca-Cola’s business plan:

This template is pre-filled with Coca-Cola’s examples so you can inspire your strategic success on one of the most iconic brands on the planet.
👉 Grab your free example of a Coca-Cola strategic plan here.
The Ramsay Health Care expansion strategy
Ramsay Health Care is a multinational healthcare provider with a strong presence in Australia, Europe, and Asia.
Almost all of its growth was organic and strategic. The company founded its headquarters in Sydney, Australia, but in the 21st century, it decided to expand globally through a primary strategy of making brownfield investments and acquisitions in key locations.
Ramsay's strategy was simple yet clever. By becoming a majority shareholder of the biggest local players, the company expanded organically in each region by leveraging and expanding their expertise.
Over the last two decades, Ramsay's global network has grown to 460 locations across 10 countries with over $13 billion in annual revenue.
📚 Recommended read: Strategy study: The Ramsay Health Care Growth Study
✨ Bonus resource: We've created a list of the most popular and free strategic plan templates in our library that will help you build a strategic plan based on the Cascade model explained in this article. You can use these templates to create a plan on a corporate, business unit, or team level.
We highlighted before that other strategic models often fail to scale strategic plans and goals scales across multiple teams and organizational levels.
In an ideal world, you want to have a maximum of two layers of detail underneath each of your focus areas. This means you'll have a focus area, followed by a layer of objectives. Underneath the objectives, you'll have a layer of actions, projects, and KPIs.

If you have a single team that’s responsible for the strategy execution, this works well. However, how do you implement a strategy across multiple and cross-functional teams? And why is it important?
According to LSA research of 410 companies across 8 industries, highly aligned companies grow revenue 58% faster and are 72% more profitable. And this is what Cascade can help you achieve.
To achieve achieve organization-wide alignment with your strategic plan and impact the bottom line, there are two ways to approach it in Casade: through contributing objectives or shared objectives .
1. Contributing objectives
This approach involves adding contributing objectives that link to your main strategic objectives, like this:

For each contributing objective, you simply repeat the Objective → Action/Project → KPI structure as follows:

Here's how you can create contributing objectives in Cascade:
Option A: Create contributing objectives within the same plan
This means creating multiple contributing objectives within the same strategic plan that contribute to the main objective.
However, be aware that if you have a lot of layers, your strategic plan can become cluttered, and people might have difficulty understanding how their daily efforts contribute to the strategic plan at the top level.
For example, the people responsible for managing contributing objectives at the bottom of the plan ( functional / operational level ) will lose visibility on how are their objectives linked to the main focus areas and objectives (at a corporate / business level ).
This approach is best suited to smaller organizations that only need to add a few layers of objectives to their plan.
Option B: Create contributing objectives from multiple plans linking to the main objective
This approach creates a network of aligned strategic plans within your organization. Each plan contains a set of focus areas and one single layer of objectives, each with its own set of projects, actions, and KPIs. This concept looks like this:

This example illustrates an objective that is a main objective in the IT strategic plan , but also contributes to the main strategic plan's objective.
For example, let’s say that your main business objective is to improve customer satisfaction by reducing product delivery time by 25% in the next quarter. This objective requires multiple operational teams within your organization to work together to achieve a shared objective.
Each team will create its own objective in its plan to contribute to the main objective:
- Logistics team: Reduce the shipment preparation time by 30%
- IT team: Implement new technology to reduce manual handling in the warehouse
- Production team: Increase production output by hour for 5%
Here’s how this example would look like within Cascade platform:

Although each contributing objective was originally created in its own plan, you can see how each contributing objective relates to the main strategic objective and its status in real-time.
2. Shared objectives
In Cascade, shared objectives are the same objectives shared across different strategic plans.
For example, you can have an objective that is “Achieve sustainable operations”. This objective can be part of the Corporate Strategy Plan, but also part of the Operations Plan , Supply Chain Plan , Production Plan, etc. In short, this objective becomes a shared objective between multiple teams and strategic plan.
This approach helps you to:
- Cascade your business strategy as deep as you want across a near-infinite number of people while maintaining strategic alignment throughout your organization .
- Create transparency and a much higher level of engagement in the strategy throughout your organization since objective owners are able to identify how their shared efforts contribute to the success of the main business objectives.
The more shared objectives you have across your organization, the more your teams will be aligned with the overarching business strategy. This is what we call " alignment health ”.
Here’s how you can see the shared objectives in the alignment map and analyze alignment health within Cascade:

You get a snapshot of how is your corporate strategic plan aligned with sub-plans from different business units or departments and the status of shared objectives. This helps you quickly identify misaligned initiatives and act before it’s too late. Plus, cross-functional teams have better visibility of how their efforts contribute to shared objectives.
So whether you choose contributing objectives or shared objectives, Cascade has the tools and features to help you achieve organization-wide alignment and boost your bottom line.
Quick Overview Of Key Steps In Writing A Strategic Plan
Here’s a quick infographic to help you remember how everything connects and why each element is critical to creating an effective strategic plan:

This simple answer to how to write a strategic plan avoids confusing jargon and has elements that the whole organization can both get behind and understand.
💡Tip: Save this image or bookmark this article for your next strategic planning session.
If you're struggling to write an execution-ready strategic plan, the Cascade model is the solution you've been looking for. With its clear, easy-to-understand terminology, and simple linkages between objectives, projects, and KPIs, you can create a plan that's both scalable and flexible.
But why is a flexible and execution-ready strategic plan so important? It's simple: without a clear and actionable plan, you'll never be able to achieve your business objectives. By using the Cascade Strategic Planning Model, you'll be able to create a plan that's both tangible and measurable, with KPIs that help you track progress towards your goals.
However, the real value of the Cascade framework lies in its flexibility . By creating links between main business objectives and your teams’ objectives, you can easily scale your plan without losing focus. Plus, the model's structure of linked layers means that you can always adjust your strategy in response to new challenges or opportunities and keep everyone on the same page.
So if you want to achieve results with your strategic plan, start using Cascade today. With its unique combination of flexibility and focus, it's the perfect tool for any organization looking to master strategy execution and succeed in today's fast-paced business world.
Want to see Cascade in action? Get started for free or book a 1:1 demo with Cascade’s in-house strategy expert.
This article is part one of our mini-series "How to Write a Strategic Plan". This first article will give you a solid strategy model for your plan and get the strategic thinking going.
Think of it as the foundation for your new strategy. Subsequent parts of the series will show you how to create the content for your strategic plan.
Articles in our How to Write a Strategic Plan series
- How To Write A Strategic Plan: The Cascade Model (This article)
- How to Write a Good Vision Statement
- How To Create Company Values
- Creating Strategic Focus Areas
- How To Write Strategic Objective
- How To Create Effective Projects
- How To Write KPIs + Ultimate Guide To Strategic Planning
More resources on strategic planning and strategy execution:
- 6 Steps to Successful Strategy Execution
- 4-Step Strategy Reporting Process (With Template)
- Annual Planning: Plan Like a Pro In 5 Steps (+ Template)
- 18 Free Strategic Plan Templates (Excel & Cascade) 2023
- The Right Way To Set Team Goals
- 23 Best Strategy Tools For Your Organization in 2023
Popular articles

Viva Goals Vs. Cascade: Goal Management Vs. Strategy Execution

What Is A Maturity Model? Overview, Examples + Free Assessment
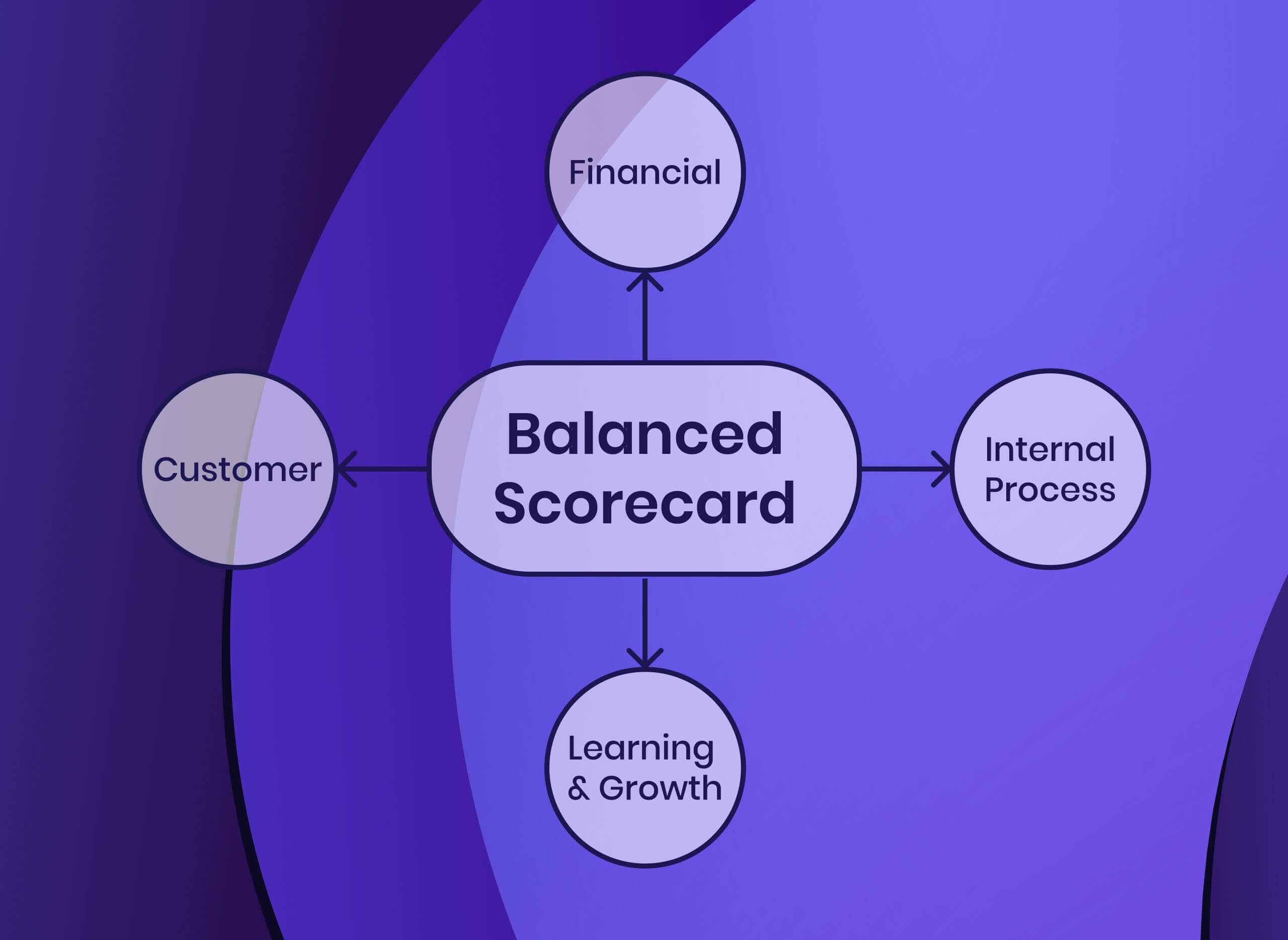
How To Implement The Balanced Scorecard Framework (With Examples)

The Best Management Reporting Software For Strategy Officers (2024 Guide)
Your toolkit for strategy success.

Essential Guide to the Strategic Planning Process
By Joe Weller | April 3, 2019 (updated March 26, 2024)
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
In this article, you’ll learn the basics of the strategic planning process and how a strategic plan guides you to achieving your organizational goals. Plus, find expert insight on getting the most out of your strategic planning.
Included on this page, you'll discover the importance of strategic planning , the steps of the strategic planning process , and the basic sections to include in your strategic plan .
What Is Strategic Planning?
Strategic planning is an organizational activity that aims to achieve a group’s goals. The process helps define a company’s objectives and investigates both internal and external happenings that might influence the organizational path. Strategic planning also helps identify adjustments that you might need to make to reach your goal. Strategic planning became popular in the 1960s because it helped companies set priorities and goals, strengthen operations, and establish agreement among managers about outcomes and results.
Strategic planning can occur over multiple years, and the process can vary in length, as can the final plan itself. Ideally, strategic planning should result in a document, a presentation, or a report that sets out a blueprint for the company’s progress.
By setting priorities, companies help ensure employees are working toward common and defined goals. It also aids in defining the direction an enterprise is heading, efficiently using resources to achieve the organization’s goals and objectives. Based on the plan, managers can make decisions or allocate the resources necessary to pursue the strategy and minimize risks.
Strategic planning strengthens operations by getting input from people with differing opinions and building a consensus about the company’s direction. Along with focusing energy and resources, the strategic planning process allows people to develop a sense of ownership in the product they create.

“Strategic planning is not really one thing. It is really a set of concepts, procedures, tools, techniques, and practices that have to be adapted to specific contexts and purposes,” says Professor John M. Bryson, McKnight Presidential Professor of Planning and Public Affairs at the Hubert H. Humphrey School of Public Affairs, University of Minnesota and author of Strategic Planning for Public and Nonprofit Organizations: A Guide to Strengthening and Sustaining Organizational Achievement . “Strategic planning is a prompt to foster strategic thinking, acting, and learning, and they all matter and they are all connected.”
What Strategic Planning Is Not
Strategic planning is not a to-do list for the short or long term — it is the basis of a business, its direction, and how it will get there.
“You have to think very strategically about strategic planning. It is more than just following steps,” Bryson explains. “You have to understand strategic planning is not some kind of magic solution to fixing issues. Don’t have unrealistic expectations.”
Strategic planning is also different from a business plan that focuses on a specific product, service, or program and short-term goals. Rather, strategic planning means looking at the big picture.
While they are related, it is important not to confuse strategic planning with strategic thinking, which is more about imagining and innovating in a way that helps a company. In contrast, strategic planning supports those thoughts and helps you figure out how to make them a reality.
Another part of strategic planning is tactical planning , which involves looking at short-term efforts to achieve longer-term goals.
Lastly, marketing plans are not the same as strategic plans. A marketing plan is more about introducing and delivering a service or product to the public instead of how to grow a business. For more about marketing plans and processes, read this article .
Strategic plans include information about finances, but they are different from financial planning , which involves different processes and people. Financial planning templates can help with that process.
Why Is Strategic Planning Important?
In today’s technological age, strategic plans provide businesses with a path forward. Strategic plans help companies thrive, not just survive — they provide a clear focus, which makes an organization more efficient and effective, thereby increasing productivity.

“You are not going to go very far if you don’t have a strategic plan. You need to be able to show where you are going,” says Stefan Hofmeyer, an experienced strategist and co-founder of Global PMI Partners . He lives in the startup-rich environment of northern California and says he often sees startups fail to get seed money because they do not have a strong plan for what they want to do and how they want to do it.
Getting team members on the same page (in both creating a strategic plan and executing the plan itself) can be beneficial for a company. Planners can find satisfaction in the process and unite around a common vision. In addition, you can build strong teams and bridge gaps between staff and management.
“You have to reach agreement about good ideas,” Bryson says. “A really good strategy has to meet a lot of criteria. It has to be technically workable, administratively feasible, politically acceptable, and legally, morally, and ethically defensible, and that is a pretty tough list.”
By discussing a company’s issues during the planning process, individuals can voice their opinions and provide information necessary to move the organization ahead — a form of problem solving as a group.
Strategic plans also provide a mechanism to measure success and progress toward goals, which keeps employees on the same page and helps them focus on the tasks at hand.
When Is the Time to Do Strategic Planning?
There is no perfect time to perform strategic planning. It depends entirely on the organization and the external environment that surrounds it. However, here are some suggestions about when to plan:
If your industry is changing rapidly
When an organization is launching
At the start of a new year or funding period
In preparation for a major new initiative
If regulations and laws in your industry are or will be changing
“It’s not like you do all of the thinking and planning, and then implement,” Bryson says. “A mistake people make is [believing] the thinking has to precede the acting and the learning.”
Even if you do not re-create the entire planning process often, it is important to periodically check your plan and make sure it is still working. If not, update it.
What Is the Strategic Planning Process?
Strategic planning is a process, and not an easy one. A key is to make sure you allow enough time to complete the process without rushing, but not take so much time that you lose momentum and focus. The process itself can be more important than the final document due to the information that comes out of the discussions with management, as well as lower-level workers.

“There is not one favorite or perfect planning process,” says Jim Stockmal, president of the Association for Strategic Planning (ASP). He explains that new techniques come out constantly, and consultants and experienced planners have their favorites. In an effort to standardize the practice and terms used in strategic planning, ASP has created two certification programs .
Level 1 is the Strategic Planning Professional (SPP) certification. It is designed for early- or mid-career planners who work in strategic planning. Level 2, the Strategic Management Professional (SMP) certification, is geared toward seasoned professionals or those who train others. Stockmal explains that ASP designed the certification programs to add structure to the otherwise amorphous profession.
The strategic planning process varies by the size of the organization and can be formal or informal, but there are constraints. For example, teams of all sizes and goals should build in many points along the way for feedback from key leaders — this helps the process stay on track.
Some elements of the process might have specific start and end points, while others are continuous. For example, there might not be one “aha” moment that suddenly makes things clear. Instead, a series of small moves could slowly shift the organization in the right direction.
“Don’t make it overly complex. Bring all of the stakeholders together for input and feedback,” Stockmal advises. “Always be doing a continuous environmental scan, and don’t be afraid to engage with stakeholders.”
Additionally, knowing your company culture is important. “You need to make it work for your organization,” he says.
There are many different ways to approach the strategic planning process. Below are three popular approaches:
Goals-Based Planning: This approach begins by looking at an organization’s mission and goals. From there, you work toward that mission, implement strategies necessary to achieve those goals, and assign roles and deadlines for reaching certain milestones.
Issues-Based Planning: In this approach, start by looking at issues the company is facing, then decide how to address them and what actions to take.
Organic Planning: This approach is more fluid and begins with defining mission and values, then outlining plans to achieve that vision while sticking to the values.
“The approach to strategic planning needs to be contingent upon the organization, its history, what it’s capable of doing, etc.,” Bryson explains. “There’s such a mistake to think there’s one approach.”
For more information on strategic planning, read about how to write a strategic plan and the different types of models you can use.
Who Participates in the Strategic Planning Process?
For work as crucial as strategic planning, it is necessary to get the right team together and include them from the beginning of the process. Try to include as many stakeholders as you can.
Below are suggestions on who to include:
Senior leadership
Strategic planners
Strategists
People who will be responsible for implementing the plan
People to identify gaps in the plan
Members of the board of directors
“There can be magic to strategic planning, but it’s not in any specific framework or anybody’s 10-step process,” Bryson explains. “The magic is getting key people together, getting them to focus on what’s important, and [getting] them to do something about it. That’s where the magic is.”
Hofmeyer recommends finding people within an organization who are not necessarily current leaders, but may be in the future. “Sometimes they just become obvious. Usually they show themselves to you, you don’t need to look for them. They’re motivated to participate,” he says. These future leaders are the ones who speak up at meetings or on other occasions, who put themselves out there even though it is not part of their job description.
At the beginning of the process, establish guidelines about who will be involved and what will be expected of them. Everyone involved must be willing to cooperate and collaborate. If there is a question about whether or not to include anyone, it is usually better to bring on extra people than to leave someone out, only to discover later they should have been a part of the process all along. Not everyone will be involved the entire time; people will come and go during different phases.
Often, an outside facilitator or consultant can be an asset to a strategic planning committee. It is sometimes difficult for managers and other employees to sit back and discuss what they need to accomplish as a company and how they need to do it without considering other factors. As objective observers, outside help can often offer insight that may escape insiders.
Hofmeyer says sometimes bosses have blinders on that keep them from seeing what is happening around them, which allows them to ignore potential conflicts. “People often have their own agendas of where they want to go, and if they are not aligned, it is difficult to build a strategic plan. An outsider perspective can really take you out of your bubble and tell you things you don’t necessarily want to hear [but should]. We get into a rhythm, and it’s really hard to step out of that, so bringing in outside people can help bring in new views and aspects of your business.”
An outside consultant can also help naysayers take the process more seriously because they know the company is investing money in the efforts, Hofmeyer adds.
No matter who is involved in the planning process, make sure at least one person serves as an administrator and documents all planning committee actions.
What Is in a Strategic Plan?
A strategic plan communicates goals and what it takes to achieve them. The plan sometimes begins with a high-level view, then becomes more specific. Since strategic plans are more guidebooks than rulebooks, they don’t have to be bureaucratic and rigid. There is no perfect plan; however, it needs to be realistic.
There are many sections in a strategic plan, and the length of the final document or presentation will vary. The names people use for the sections differ, but the general ideas behind them are similar: Simply make sure you and your team agree on the terms you will use and what each means.
One-Page Strategic Planning Template
“I’m a big fan of getting a strategy onto one sheet of paper. It’s a strategic plan in a nutshell, and it provides a clear line of sight,” Stockmal advises.
You can use the template below to consolidate all your strategic ideas into a succinct, one-page strategic plan. Doing so provides you with a high-level overview of your strategic initiatives that you can place on your website, distribute to stakeholders, and refer to internally. More extensive details about implementation, capacity, and other concerns can go into an expanded document.
Download One-Page Strategic Planning Template Excel | Word | Smartsheet
The most important part of the strategic plan is the executive summary, which contains the highlights of the plan. Although it appears at the beginning of the plan, it should be written last, after you have done all your research.
Of writing the executive summary, Stockmal says, “I find it much easier to extract and cut and edit than to do it first.”
For help with creating executive summaries, see these templates .
Other parts of a strategic plan can include the following:
Description: A description of the company or organization.
Vision Statement: A bold or inspirational statement about where you want your company to be in the future.
Mission Statement: In this section, describe what you do today, your audience, and your approach as you work toward your vision.
Core Values: In this section, list the beliefs and behaviors that will enable you to achieve your mission and, eventually, your vision.
Goals: Provide a few statements of how you will achieve your vision over the long term.
Objectives: Each long-term goal should have a few one-year objectives that advance the plan. Make objectives SMART (specific, measurable, achievable, and time-based) to get the most out of them.
Budget and Operating Plans: Highlight resources you will need and how you will implement them.
Monitoring and Evaluation: In this section, describe how you will check your progress and determine when you achieve your goals.
One of the first steps in creating a strategic plan is to perform both an internal and external analysis of the company’s environment. Internally, look at your company’s strengths and weaknesses, as well as the personal values of those who will implement your plan (managers, executives, board members). Externally, examine threats and opportunities within the industry and any broad societal expectations that might exist.
You can perform a SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) analysis to sum up where you are currently and what you should focus on to help you achieve your future goals. Strengths shows you what you do well, weaknesses point out obstacles that could keep you from achieving your objectives, opportunities highlight where you can grow, and threats pinpoint external factors that could be obstacles in your way.
You can find more information about performing a SWOT analysis and free templates in this article . Another analysis technique, STEEPLE (social, technological, economic, environmental, political, legal, and ethical), often accompanies a SWOT analysis.
Basics of Strategic Planning
How you navigate the strategic planning process will vary. Several tools and techniques are available, and your choice depends on your company’s leadership, culture, environment, and size, as well as the expertise of the planners.
All include similar sections in the final plan, but the ways of driving those results differ. Some tools are goals-based, while others are issues- or scenario-based. Some rely on a more organic or rigid process.
Hofmeyer summarizes what goes into strategic planning:
Understand the stakeholders and involve them from the beginning.
Agree on a vision.
Hold successful meetings and sessions.
Summarize and present the plan to stakeholders.
Identify and check metrics.
Make periodic adjustments.
Items That Go into Strategic Planning
Strategic planning contains inputs, activities, outputs, and outcomes. Inputs and activities are elements that are internal to the company, while outputs and outcomes are external.
Remember, there are many different names for the sections of strategic plans. The key is to agree what terms you will use and define them for everyone involved.
Inputs are important because it is impossible to know where you are going until you know what is around you where you are now.
Companies need to gather data from a variety of sources to get a clear look at the competitive environment and the opportunities and risks within that environment. You can think of it like a competitive intelligence program.
Data should come from the following sources:
Interviews with executives
A review of documents about the competition or market that are publicly available
Primary research by visiting or observing competitors
Studies of your industry
The values of key stakeholders
This information often goes into writing an organization’s vision and mission statements.
Activities are the meetings and other communications that need to happen during the strategic planning process to help everyone understand the competition that surrounds the organization.
It is important both to understand the competitive environment and your company’s response to it. This is where everyone looks at and responds to the data gathered from the inputs.
The strategic planning process produces outputs. Outputs can be as basic as the strategic planning document itself. The documentation and communications that describe your organization’s strategy, as well as financial statements and budgets, can also be outputs.
The implementation of the strategic plan produces outcomes (distinct from outputs). The outcomes determine the success or failure of the strategic plan by measuring how close they are to the goals and vision you outline in your plan.
It is important to understand there will be unplanned and unintended outcomes, too. How you learn from and adapt to these changes influence the success of the strategic plan.
During the planning process, decide how you will measure both the successes and failures of different parts of the strategic plan.
Sharing, Evaluating, and Monitoring the Progress of a Strategic Plan
After companies go through a lengthy strategic planning process, it is important that the plan does not sit and collect dust. Share, evaluate, and monitor the plan to assess how you are doing and make any necessary updates.
“[Some] leaders think that once they have their strategy, it’s up to someone else to execute it. That’s a mistake I see,” Stockmal says.
The process begins with distributing and communicating the plan. Decide who will get a copy of the plan and how those people will tell others about it. Will you have a meeting to kick off the implementation? How will you specify who will do what and when? Clearly communicate the roles people will have.
“Before you communicate the plan [to everyone], you need to have the commitment of stakeholders,” Hofmeyer recommends. Have the stakeholders be a part of announcing the plan to everyone — this keeps them accountable because workers will associate them with the strategy. “That applies pressure to the stakeholders to actually do the work.”
Once the team begins implementation, it’s necessary to have benchmarks to help measure your successes against the plan’s objectives. Sometimes, having smaller action plans within the larger plan can help keep the work on track.
During the planning process, you should have decided how you will measure success. Now, figure out how and when you will document progress. Keep an eye out for gaps between the vision and its implementation — a big gap could be a sign that you are deviating from the plan.
Tools are available to assist with tracking performance of strategic plans, including several types of software. “For some organizations, a spreadsheet is enough, but you are going to manually enter the data, so someone needs to be responsible for that,” Stockmal recommends.
Remember: strategic plans are not written in stone. Some deviation will be necessary, and when it happens, it’s important to understand why it occurred and how the change might impact the company's vision and goals.
Deviation from the plan does not mean failure, reminds Hofmeyer. Instead, understanding what transpired is the key. “Things happen, [and] you should always be on the lookout for that. I’m a firm believer in continuous improvement,” he says. Explain to stakeholders why a change is taking place. “There’s always a sense of re-evaluation, but do it methodically.”
Build in a schedule to review and amend the plan as necessary; this can help keep companies on track.
What Is Strategic Management?
Strategic planning is part of strategic management, and it involves the activities that make the strategic plan a reality. Essentially, strategic management is getting from the starting point to the goal effectively and efficiently using the ongoing activities and processes that a company takes on in order to keep in line with its mission, vision, and strategic plan.
“[Strategic management] closes the gap between the plan and executing the strategy,” Stockmal of ASP says. Strategic management is part of a larger planning process that includes budgeting, forecasting, capital allocation, and more.
There is no right or wrong way to do strategic management — only guidelines. The basic phases are preparing for strategic planning, creating the strategic plan, and implementing that plan.
No matter how you manage your plan, it’s key to allow the strategic plan to evolve and grow as necessary, due to both the internal and external factors.
“We get caught up in all of the day-to-day issues,” Stockmal explains, adding that people do not often leave enough time for implementing the plan and making progress. That’s what strategic management implores: doing things that are in the plan and not letting the plan sit on a shelf.
Improve Strategic Planning with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.

- Our Approach
- Strategic planning facilitation
- Aligned Strategy Course
- Strategy and Leadership Podcast
- SME Strategy on Youtube
- Strategy and Leadership Community
Strategic Plan Examples: Case Studies and Free Strategic Planning Template
By Anthony Taylor - May 29, 2023

As you prepare for your strategic planning process, it's important to explore relevant strategic plan examples for inspiration.
In today's competitive business landscape, a well-defined strategic plan holds immense significance. Whether you're a private company, municipal government, or nonprofit entity, strategic planning is essential for achieving goals and gaining a competitive edge. By understanding the strategic planning process, you can gain valuable insights to develop an effective growth roadmap for your organization.
In this blog, we will delve into real-life examples of strategic plans that have proven successful. These examples encompass a wide range of organizations, from Credit Unions that have implemented SME Strategy's Aligned Strategy process to the Largest Bank in Israel. By examining these cases, we can gain a deeper understanding of strategic planning and extract relevant insights that can be applied to your organization.
- Strategic Plan Example (Global Financial Services Firm)
- Strategic Plan Example (Joint Strategic Plan)
- Strategic Plan Example: (Government Agency)
- Strategic Plan Example (Multinational Corporation)
- Strategic Plan Example: (Public Company)
- Strategic Plan Example (Non Profit)
- Strategic Plan Example: (Small Nonprofit)
- Strategic Plan example: (Municipal Government)
- Strategic Plan Example: (Environmental Start-up)
When analyzing strategic plan examples, it is crucial to recognize that a strategic plan goes beyond being a mere document. It should encapsulate your organization's mission and vision comprehensively while also being actionable. Your strategic plan needs to be tailored to your organization's specific circumstances, including factors such as size, industry, budget, and personnel. Simply replicating someone else's plan will not suffice.
Have you ever invested significant time and resources into creating a plan, only to witness its failure during execution? We believe that a successful strategic plan extends beyond being a static document. It necessitates meticulous follow-through, execution, documentation, and continuous learning. It serves as the foundation upon which your future plans are built.
It is important to note that a company's success is not solely determined by the plan itself, but rather by how effectively it is executed. Our intention is to highlight the diverse roles that a company's mission, vision, and values play across different organizations, whether they are large corporations or smaller nonprofits.
Strategic plans can vary in terms of their review cycles, which can range from annual evaluations to multi-year periods. There is no one-size-fits-all example of a strategic plan, as each organization possesses unique needs and circumstances that must be taken into account.
Strategic planning is an essential process for organizations of all sizes and types. It assists in setting a clear direction, defining goals, and effectively allocating resources. To gain an understanding of how strategic plans are crafted, we will explore a range of examples, including those from private companies, nonprofit organizations, and government entities.
Throughout this exploration, we will highlight various frameworks and systems employed by profit-driven and nonprofit organizations alike, providing valuable insights to help you determine the most suitable approach for your own organization.
Watch: Examples of Strategic Plans from Real-Life Organizations
Strategic Plan Example - The Bank Hapoalim Vision: To be a leading global financial services firm, with its core in Israel, focused on its clients and working to enhance their financial freedom.
Bank Hapoalim, one of Israel's largest banks with 8,383 branches across 5 different countries as of 2022, has recently provided insights into its latest strategic plan. The plan highlights four distinct strategic priorities:
- Continued leadership in corporate banking and capital markets
- Adaptation of the retail banking operating model
- Resource optimization and greater productivity
- Differentiating and influential innovation
Check out their strategic plan here: Strategic Plan (2022-2026)
We talked to Tagil Green, the Chief Strategy Officer at Bank Hapoalim, where we delved into various aspects of their strategic planning process. We discussed the bank's strategic planning timeline, the collaborative work they engaged in with McKinsey, and the crucial steps taken to secure buy-in and ensure successful implementation of the strategy throughout the organization. In our conversation, Tagil Green emphasized the understanding that there is no universal template for strategic plans. While many companies typically allocate one, two, or three days for strategic planning meetings during an offsite, Bank Hapoalim recognized the significance of their size and complexity. As a result, their strategic plan took a comprehensive year-long effort to develop. How did a Large Global Organization like Bank Hapoalim decide on what strategic planning timeline to follow?
"How long do you want to plan? Some said, let's think a decade ahead. Some said it's irrelevant. Let's talk about two years ahead. And we kind of negotiated into the like, five years ahead for five years and said, Okay, that's good enough, because some of the complexity and the range depends on the field that you work for. So for banking in Israel, four or five years ahead, is good enough. " Tagil Green, Chief Strategy Officer, Bank Hapoalim
Another important aspect you need to consider when doing strategic planning is stakeholder engagement, We asked Tagil her thoughts and how they conducted stakeholder engagement with a large employee base.
Listen to the Full Conversation with Tagil:
Strategic Planning and Execution: Insights from the Chief Strategy Officer of Israel's Leading Bank
Strategic Plan Example: Region 16 and DEED (Joint Strategic Plan)
Mission Statement: We engage state, regional, tribal, school, and community partners to improve the quality and equity of education for each student by providing evidence-based services and supports.
In this strategic plan example, we'll explore how Region 16 and DEED, two government-operated Educational Centers with hundreds of employees, aligned their strategic plans using SME Strategy's approach . Despite facing the challenges brought on by the pandemic, these organizations sought to find common ground and ensure alignment on their mission, vision, and values, regardless of their circumstances.
Both teams adopted the Aligned Strategy method, which involved a three day onsite strategic planning session facilitated by a strategic planning facilitator . Together, they developed a comprehensive 29-page strategic plan outlining three distinct strategic priorities, each with its own objectives and strategic goals. Through critical conversations, they crafted a clear three year vision, defined their core customer group as part of their mission, refined their organizational values and behaviors, and prioritized their areas of focus.
After their offsite facilitation, they aligned around three key areas of focus:
- Effective Communication, both internally and externally.
- Streamlining Processes to enhance efficiency.
- Developing Effective Relationships and Partnerships for mutual success.
By accomplishing their goals within these strategic priorities, the teams from Region 16 and DEED aim to make progress towards their envisioned future.
To read the full review of the aligned strategy process click here
Download Now Starting your strategic planning process soon? Get our free Strategic Planning Template
Strategic Plan Example: (Government Agency) - The City of Duluth Workforce Development Board
What they do:
The Duluth Workforce Development Board identifies and aligns workforce development strategies to meet the needs of Duluth area employers and job seekers through comprehensive and coordinated systems.
An engaged and diverse workforce, where all individuals, regardless of background, have or are on a path to meaningful employment and a family sustaining wage, and all employers are able to fill jobs in demand.
The City of Duluth provides an insightful example of a strategic plan focused on regional coordination to address workforce needs in various industry sectors and occupations. With multiple stakeholders involved, engaging and aligning them becomes crucial. This comprehensive plan, spanning 82 pages, tackles strategic priorities and initiatives at both the state and local levels.
What sets this plan apart is its thorough outline of the implementation process. It covers everything from high-level strategies to specific meetings between different boards and organizations. Emphasizing communication, coordination, and connectivity, the plan ensures the complete execution of its objectives. It promotes regular monthly partner meetings, committee gatherings, and collaboration among diverse groups. The plan also emphasizes the importance of proper documentation and accountability throughout the entire process.
By providing a clear roadmap, the City of Duluth's strategic plan effectively addresses workforce needs while fostering effective stakeholder engagement . It serves as a valuable example of how a comprehensive plan can guide actions, facilitate communication, and ensure accountability for successful implementation.
Read this strategic plan example here: Strategic Plan (2021-2024)
Strategic Plan Example: McDonald's (Multinational Corporation)
McDonald's provides a great strategic plan example specifically designed for private companies. Their "Velocity Growth Plan" covers a span of three years from 2017 to 2020, offering a high-level strategic direction. While the plan doesn't delve into specific implementation details, it focuses on delivering an overview that appeals to investors and aligns the staff. The plan underscores McDonald's commitment to long-term growth and addressing important environmental and societal challenges. It also highlights the CEO's leadership in revitalizing the company and the active oversight provided by the Board of Directors.
The Board of Directors plays a crucial role in actively overseeing McDonald's strategy. They engage in discussions about the Velocity Growth Plan during board meetings, hold annual strategy sessions, and maintain continuous monitoring of the company's operations in response to the ever-changing business landscape.
The McDonald's strategic plan revolved around three core pillars:
- Retention: Strengthening and expanding areas of strength, such as breakfast and family occasions.
- Regain: Focusing on food quality, convenience, and value to win back lost customers.
- Convert: Emphasizing coffee and other snack offerings to attract casual customers.
These pillars guide McDonald's through three initiatives, driving growth and maximizing benefits for customers in the shortest time possible.
Read the strategic plan example of Mcdonlald's Velocity growth plan (2017-2020)
Strategic Plan Example: Nike (Public Company)
Nike's mission statement is “ to bring inspiration and innovation to every athlete in the world .”
Nike, as a publicly traded company, has developed a robust global growth strategy outlined in its strategic plan. Spanning a five-year period from 2021 to 2025, this plan encompasses 29 strategic targets that reflect Nike's strong commitment to People, Planet, and Pay. Each priority is meticulously defined, accompanied by tangible actions and measurable metrics. This meticulous approach ensures transparency and alignment across the organization.
The strategic plan of Nike establishes clear objectives, including the promotion of pay equity, a focus on education and professional development, and the fostering of business diversity and inclusion. By prioritizing these areas, Nike aims to provide guidance and support to its diverse workforce, fostering an environment that values and empowers its employees.
Read Nike's strategic plan here
Related Content: Strategic Planning Process (What is it?)
The Cost of Developing a Strategic Plan (3 Tiers)
Strategic Plan Example (Non Profit) - Alternatives Federal Credit Union
Mission: To help build and protect wealth for people with diverse identities who have been historically marginalized by the financial industry, especially those with low wealth or identifying as Black, Indigenous, or people of color.
AFCU partnered with SME Strategy in 2021 to develop a three year strategic plan. As a non-profit organization, AFCU recognized the importance of strategic planning to align its team and operational components. The focus was on key elements such as Vision, Mission, Values, Priorities, Goals, and Actions, as well as effective communication, clear responsibilities, and progress tracking.
In line with the Aligned Strategy approach, AFCU developed three strategic priorities to unite its team and drive progress towards their vision for 2024. Alongside strategic planning, AFCU has implemented a comprehensive strategy implementation plan to ensure the effective execution of their strategies.
Here's an overview of AFCU's 2024 Team Vision and strategic priorities: Aligned Team Vision 2024:
To fulfill our mission, enhance efficiency, and establish sustainable community development approaches, our efforts will revolve around the following priorities: Strategic Priorities:
Improving internal communication: Enhancing communication channels and practices within AFCU to foster collaboration and information sharing among team members.
Improving organizational performance: Implementing strategies to enhance AFCU's overall performance, including processes, systems, and resource utilization.
Creating standard operating procedures: Developing standardized procedures and protocols to streamline operations, increase efficiency, and ensure consistency across AFCU's activities.
By focusing on these strategic priorities, AFCU aims to strengthen its capacity to effectively achieve its mission and bring about lasting change in its community. Watch the AFCU case study below:
Watch the Full Strategic Plan Example Case Study with the VP and Chief Strategy Officer of AFCU
Strategic Plan Example: (Small Nonprofit) - The Hunger Project
Mission: To end hunger and poverty by pioneering sustainable, grassroots, women-centered strategies and advocating for their widespread adoption in countries throughout the world.
The Hunger Project, a small nonprofit organization based in the Netherlands, offers a prime example of a concise and effective three-year strategic plan. This plan encompasses the organization's vision, mission, theory of change, and strategic priorities. Emphasizing simplicity and clarity, The Hunger Project's plan outlines crucial actions and measurements required to achieve its goals. Spanning 16 pages, this comprehensive document enables stakeholders to grasp the organization's direction and intended impact. It centers around three overarching strategic goals, each accompanied by its own set of objectives and indicators: deepening impact, mainstreaming impact, and scaling up operations.
Read their strategic plan here
Strategic Plan example: (Municipal Government)- New York City Economic Development Plan
The New York City Economic Development Plan is a comprehensive 5-year strategic plan tailored for a municipal government. Spanning 68 pages, this plan underwent an extensive planning process with input from multiple stakeholders.
This plan focuses on the unique challenges and opportunities present in the region. Through a SWOT analysis, this plan highlights the organization's problems, the city's strengths, and the opportunities and threats it has identified. These include New York's diverse population, significant wealth disparities, and high demand for public infrastructure and services.
The strategic plan was designed to provide a holistic overview that encompasses the interests of a diverse and large group of business, labor, and community leaders. It aimed to identify the shared values that united its five boroughs and define how local objectives align with the interests of greater New York State. The result was a unified vision for the future of New York City, accompanied by a clear set of actions required to achieve shared goals.
Because of its diverse stakeholder list including; council members, local government officials, and elected representatives, with significant input from the public, their strategic plan took 4 months to develop.
Read it's 5 year strategic plan example here
Strategic Plan Example: Silicon Valley Clean Energy
Silicon Valley Clean Energy provides a strategic plan that prioritizes visual appeal and simplicity. Despite being in its second year of operation, this strategic plan example effectively conveys the organization's mission and values to its Board of Directors. The company also conducts thorough analyses of the electric utility industry and anticipates major challenges in the coming years. Additionally, it highlights various social initiatives aimed at promoting community, environmental, and economic benefits that align with customer expectations.
"This plan recognizes the goals we intend to accomplish and highlights strategies and tactics we will employ to achieve these goals. The purpose of this plan is to ensure transparency in our operations and to provide a clear direction to staff about which strategies and tactics we will employ to achieve our goals. It is a living document that can guide our work with clarity and yet has the flexibility to respond to changing environments as we embark on this journey." Girish Balachandran CEO, Silicon Valley Clean Energy
This strategic plan example offers flexibility in terms of timeline. It lays out strategic initiatives for both a three-year and five-year period, extending all the way to 2030. The plan places emphasis on specific steps and targets to be accomplished between 2021 and 2025, followed by goals for the subsequent period of 2025 to 2030. While this plan doesn't go into exhaustive detail about implementation steps, meeting schedules, or monitoring mechanisms, it effectively communicates the organization's priorities and desired long term outcomes. Read its strategic plan example here
By studying these strategic plan examples, you can create a strategic plan that aligns with your organization's goals, communicates effectively, and guides decision-making and resource allocation. Strategic planning approaches differ among various types of organizations.
Private Companies: Private companies like McDonald's and Nike approach strategic planning differently from public companies due to competitive market dynamics. McDonald's provides a high-level overview of its strategic plan in its investor overview.
Nonprofit Organizations: Nonprofit organizations, like The Hunger Project, develop strategic plans tailored to their unique missions and stakeholders. The Hunger Project's plan presents a simple yet effective structure with a clear vision, mission, theory of change, strategic priorities, and action items with measurable outcomes.
Government Entities: Government entities, such as the New York City Development Board, often produce longer, comprehensive strategic plans to guide regional or state development. These plans include implementation plans, stakeholder engagement, performance measures, and priority projects.
When creating a strategic plan for your organization, consider the following key points:
Strategic Priorities: Define clear strategic priorities that are easy to communicate and understand.
Stakeholder Engagement: Ensure your plan addresses the needs and interests of your stakeholders.
Measurements: Include relevant measurements and KPIs, primarily for internal use, to track, monitor and report your progress effectively.
Conciseness vs. Thoroughness: Adapt the level of detail in your plan based on the size of your organization and the number of stakeholders involved.
By learning from these examples, you can see that developing a strategic plan should be a process that fits your organization, effectively communicates your goals, and provides guidance for decision-making and resource allocation. Remember that strategic planning is an ongoing process that requires regular review and adjustment to stay relevant and effective.
Need assistance in maximizing the impact of your strategic planning? Learn how our facilitators can lead you through a proven process, ensuring effectiveness, maintaining focus, and fostering team alignment.

Our readers' favourite posts
Subscribe to our bi-weekly newsletter: leaders digest, quick links.
- Podcast (Spotify)
- Speaker & Media
- Alignment Book
- Privacy Policy
Free Resources
- Strategic planning session agenda (Sample)
- Strategic plan template
- How to create a strategic plan (Start here)
- Weekly Strategy Tips
- Non profit program
Products and Services
- Strategic Planning Facilitator
- Strategy Implementation Consulting
- Strategic Planning Course
- 1-855-895-5446

Copyright © 2011-2023 SME Strategy Consulting | Strategic Planning Facilitator + Strategy Implementation Consulting. All rights reserved.
How to improve strategic planning
In conference rooms everywhere, corporate planners are in the midst of the annual strategic-planning process. For the better part of a year, they collect financial and operational data, make forecasts, and prepare lengthy presentations with the CEO and other senior managers about the future direction of the business. But at the end of this expensive and time-consuming process, many participants say they are frustrated by its lack of impact on either their own actions or the strategic direction of the company.
This sense of disappointment was captured in a recent McKinsey Quarterly survey of nearly 800 executives: just 45 percent of the respondents said they were satisfied with the strategic-planning process. 1 1. “ Improving strategic planning: A McKinsey Survey ,” The McKinsey Quarterly , Web exclusive, September 2006. The survey, conducted in late July and early August 2006, received 796 responses from a panel of executives from around the world. All panelists have mostly financial or strategic responsibilities and work in a wide range of industries for organizations with revenues of at least $500 million. Moreover, only 23 percent indicated that major strategic decisions were made within its confines. Given these results, managers might well be tempted to jettison the planning process altogether.
But for those working in the overwhelming majority of corporations, the annual planning process plays an essential role. In addition to formulating at least some elements of a company’s strategy, the process results in a budget, which establishes the resource allocation map for the coming 12 to 18 months; sets financial and operating targets, often used to determine compensation metrics and to provide guidance for financial markets; and aligns the management team on its strategic priorities. The operative question for chief executives is how to make the planning process more effective—not whether it is the sole mechanism used to design strategy. CEOs know that strategy is often formulated through ad hoc meetings or brand reviews, or as a result of decisions about mergers and acquisitions.
Our research shows that formal strategic-planning processes play an important role in improving overall satisfaction with strategy development. That role can be seen in the responses of the 79 percent of managers who claimed that the formal planning process played a significant role in developing strategies and were satisfied with the approach of their companies, compared with only 21 percent of the respondents who felt that the process did not play a significant role. Looked at another way, 51 percent of the respondents whose companies had no formal process were dissatisfied with their approach to the development of strategy, against only 20 percent of those at companies with a formal process.
So what can managers do to improve the process? There are many ways to conduct strategic planning, but determining the ideal method goes beyond the scope of this article. Instead we offer, from our research, five emergent ideas that executives can employ immediately to make existing processes run better. The changes we discuss here (such as a focus on important strategic issues or a connection to core-management processes) are the elements most linked with the satisfaction of employees and their perceptions of the significance of the process. These steps cannot guarantee that the right strategic decisions will be made or that strategy will be better executed, but by enhancing the planning process—and thus increasing satisfaction with the development of strategy—they will improve the odds for success.
Start with the issues
Ask CEOs what they think strategic planning should involve and they will talk about anticipating big challenges and spotting important trends. At many companies, however, this noble purpose has taken a backseat to rigid, data-driven processes dominated by the production of budgets and financial forecasts. If the calendar-based process is to play a more valuable role in a company’s overall strategy efforts, it must complement budgeting with a focus on strategic issues. In our experience, the first liberating change managers can make to improve the quality of the planning process is to begin it by deliberately and thoughtfully identifying and discussing the strategic issues that will have the greatest impact on future business performance.
Granted, an approach based on issues will not necessarily yield better strategic results. The music business, for instance, has discussed the threat posed by digital-file sharing for years without finding an effective way of dealing with the problem. But as a first step, identifying the key issues will ensure that management does not waste time and energy on less important topics.
We found a variety of practical ways in which companies can impose a fresh strategic perspective. For instance, the CEO of one large health care company asks the leaders of each business unit to imagine how a set of specific economic, social, and business trends will affect their businesses, as well as ways to capture the opportunities—or counter the threats—that these trends pose. Only after such an analysis and discussion do the leaders settle into the more typical planning exercises of financial forecasting and identifying strategic initiatives.
One consumer goods organization takes a more directed approach. The CEO, supported by the corporate-strategy function, compiles a list of three to six priorities for the coming year. Distributed to the managers responsible for functions, geographies, and brands, the list then becomes the basis for an offsite strategy-alignment meeting, where managers debate the implications of the priorities for their particular organizations. The corporate-strategy function summarizes the results, adds appropriate corporate targets, and shares them with the organization in the form of a strategy memo, which serves as the basis for more detailed strategic planning at the division and business-unit levels.
A packaged-goods company offers an even more tailored example. Every December the corporate senior-management team produces a list of ten strategic questions tailored to each of the three business units. The leaders of these businesses have six months to explore and debate the questions internally and to come up with answers. In June each unit convenes with the senior-management team in a one-day meeting to discuss proposed actions and reach decisions.
Some companies prefer to use a bottom-up rather than top-down process. We recently worked with a sales company to design a strategic-planning process that begins with in-depth interviews (involving all of the senior managers and selected corporate and business executives) to generate a list of the most important strategic issues facing the company. The senior-management team prioritizes the list and assigns managers to explore each issue and report back in four to six weeks. Such an approach can be especially valuable in companies where internal consensus building is an imperative.
Bring together the right people
An issues-based approach won’t do much good unless the most relevant people are involved in the debate. We found that survey respondents who were satisfied with the strategic-planning process rated it highly on dimensions such as including the most knowledgeable and influential participants, stimulating and challenging the participants’ thinking, and having honest, open discussions about difficult issues. In contrast, 27 percent of the dissatisfied respondents reported that their company’s strategic planning had not a single one of these virtues. Such results suggest that too many companies focus on the data-gathering and packaging elements of strategic planning and neglect the crucial interactive components.
Strategic conversations will have little impact if they involve only strategic planners from both the business unit and the corporate levels. One of our core beliefs is that those who carry out strategy should also develop it. The key strategy conversation should take place among corporate decision makers, business unit leaders, and people with expertise essential to the discussion. In addition to leading the corporate review, the CEO, aided by members of the executive team, should as a rule lead the strategy review for business units as well. The head of a business unit, supported by four to six people, should direct the discussion from its side of the table (see sidebar, "Things to ask in any business unit review").
Things to ask in any business unit review
Are major trends and changes in your business unit’s environment affecting your strategic plan? Specifically, what potential developments in customer demand, technology, or the regulatory environment could have enough impact on the industry to change the entire plan?
How and why is this plan different from last year’s?
What were your forecasts for market growth, sales, and profitability last year, two years ago, and three years ago? How right or wrong were they? What did the business unit learn from those experiences?
What would it take to double your business unit’s growth rate and profits? Where will growth come from: expansion or gains in market share?
If your business unit plans to take market share from competitors, how will it do so, and how will they respond? Are you counting on a strategic advantage or superior execution?
What are your business unit’s distinctive competitive strengths, and how does the plan build on them?
How different is the strategy from those of competitors, and why? Is that a good or a bad thing?
Beyond the immediate planning cycle, what are the key issues, risks, and opportunities that we should discuss today?
What would a private-equity owner do with this business?
How will the business unit monitor the execution of this strategy?
One pharmaceutical company invites business unit leaders to take part in the strategy reviews of their peers in other units. This approach can help build a better understanding of the entire company and, especially, of the issues that span business units. The risk is that such interactions might constrain the honesty and vigor of the dialogue and put executives at the focus of the discussion on the defensive.
Corporate senior-management teams can dedicate only a few hours or at most a few days to a business unit under review. So team members should spend this time in challenging yet collaborative discussions with business unit leaders rather than trying to absorb many facts during the review itself. To provide some context for the discussion, best-practice companies disseminate important operational and financial information to the corporate review team well in advance of such sessions. This reading material should also tee up the most important issues facing the business and outline the proposed strategy, ensuring that the review team is prepared with well-thought-out questions. In our experience, the right 10 pages provide ample fuel to fire a vigorous discussion, but more than 25 pages will likely douse the level of energy or engagement in the room.
Adapt planning cycles to the needs of each business
Managers are justifiably concerned about the resources and time required to implement an issues-based strategic-planning approach. One easy—yet rarely adopted—solution is to free business units from the need to conduct this rigorous process every single year. In all but the most volatile, high-velocity industries, it is hard to imagine that a major strategic redirection will be necessary every planning cycle. In fact, forcing businesses to undertake this exercise annually is distracting and may even be detrimental. Managers need to focus on executing the last plan’s major initiatives, many of which can take 18 to 36 months to implement fully.
Some companies alternate the business units that undergo the complete strategic-planning process (as opposed to abbreviated annual updates of the existing plan). One media company, for example, requires individual business units to undertake strategic planning only every two or three years. This cadence enables the corporate senior-management team and its strategy group to devote more energy to the business units that are “at bat.” More important, it frees the corporate-strategy group to work directly with the senior team on critical issues that affect the entire company—issues such as developing an integrated digitization strategy and addressing unforeseen changes in the fast-moving digital-media landscape.
Other companies use trigger mechanisms to decide which business units will undergo a full strategic-planning exercise in a given year. One industrial company assigns each business unit a color-coded grade—green, yellow, or red—based on the unit’s success in executing the existing strategic plan. “Code red,” for example, would slate a business unit for a strategy review. Although many of the metrics that determine the grade are financial, some may be operational to provide a more complete assessment of the unit’s performance.
Freeing business units from participating in the strategic-planning process every year raises a caveat, however. When important changes in the external environment occur, senior managers must be able to engage with business units that are not under review and make major strategic decisions on an ad hoc basis. For instance, a major merger in any industry would prompt competitors in it to revisit their strategies. Indeed, one advantage of a tailored planning cycle is that it builds slack into the strategic-review system, enabling management to address unforeseen but pressing strategic issues as they arise.
Implement a strategic-performance-management system
In the end, many companies fail to execute the chosen strategy. More than a quarter of our survey respondents said that their companies had plans but no execution path. Forty-five percent reported that planning processes failed to track the execution of strategic initiatives. All this suggests that putting in place a system to measure and monitor their progress can greatly enhance the impact of the planning process.
Most companies believe that their existing control systems and performance-management processes (including budgets and operating reviews) are the sole way to monitor progress on strategy. As a result, managers attempt to translate the decisions made during the planning process into budget targets or other financial goals. Although this practice is sensible and necessary, it is not enough. We estimate that a significant portion of the strategic decisions we recommend to companies can’t be tracked solely through financial targets. A company undertaking a major strategic initiative to enhance its innovation and product-development capabilities, for example, should measure a variety of input metrics, such as the quality of available talent and the number of ideas and projects at each stage in development, in addition to pure output metrics such as revenues from new-product sales. One information technology company, for instance, carefully tracks the number and skill levels of people posted to important strategic projects.
Strategic-performance-management systems, which should assign accountability for initiatives and make their progress more transparent, can take many forms. One industrial corporation tracks major strategic initiatives that will have the greatest impact, across a portfolio of a dozen businesses, on its financial and strategic goals. Transparency is achieved through regular reviews and the use of financial as well as nonfinancial metrics. The corporate-strategy team assumes responsibility for reviews (chaired by the CEO and involving the relevant business-unit leaders) that use an array of milestones and metrics to assess the top ten initiatives. One to expand operations in China and India, for example, would entail regular reviews of interim metrics such as the quality and number of local employees recruited and the pace at which alliances are formed with channel partners or suppliers. Each business unit, in turn, is accountable for adopting the same performance-management approach for its own, lower-tier top-ten list of initiatives.
When designed well, strategic-performance-management systems can give an early warning of problems with strategic initiatives, whereas financial targets alone at best provide lagging indicators. An effective system enables management to step in and correct, redirect, or even abandon an initiative that is failing to perform as expected. The strategy of a pharmaceutical company that embarked on a major expansion of its sales force to drive revenue growth, for example, presupposed that rapid growth in the number of sales representatives would lead to a corresponding increase in revenues. The company also recognized, however, that expansion was in turn contingent on several factors, including the ability to recruit and train the right people. It therefore put in place a regular review of the key strategic metrics against its actual performance to alert managers to any emerging problems.
Integrate human-resources systems into the strategic plan
Simply monitoring the execution of strategic initiatives is not sufficient: their successful implementation also depends on how managers are evaluated and compensated. Yet only 36 percent of the executives we surveyed said that their companies’ strategic-planning processes were integrated with HR processes. One way to create a more valuable strategic-planning process would be to tie the evaluation and compensation of managers to the progress of new initiatives.
Although the development of strategy is ostensibly a long-term endeavor, companies traditionally emphasize short-term, purely financial targets—such as annual revenue growth or improved margins—as the sole metrics to gauge the performance of managers and employees. This approach is gradually changing. Deferred-compensation models for boards, CEOs, and some senior managers are now widely used. What’s more, several companies have added longer-term performance targets to complement the short-term ones. A major pharmaceutical company, for example, recently revamped its managerial-compensation structure to include a basket of short-term financial and operating targets as well as longer-term, innovation-based growth targets.
Although these changes help persuade managers to adopt both short- and long-term approaches to the development of strategy, they don’t address the need to link evaluation and compensation to specific strategic initiatives. One way of doing so is to craft a mix of performance targets that more appropriately reflect a company’s strategy. For example, one North American services business that launched strategic initiatives to improve its customer retention and increase sales also adjusted the evaluation and compensation targets for its managers. Rather than measuring senior managers only by revenue and margin targets, as it had done before, it tied 20 percent of their compensation to achieving its retention and cross-selling goals. By introducing metrics for these specific initiatives and linking their success closely to bonus packages, the company motivated managers to make the strategy succeed.
An advantage of this approach is that it motivates managers to flag any problems early in the implementation of a strategic initiative (which determines the size of bonuses) so that the company can solve them. Otherwise, managers all too often sweep the debris of a failing strategy under the operating rug until the spring-cleaning ritual of next year’s annual planning process.
Some business leaders have found ways to give strategic planning a more valuable role in the formulation as well as the execution of strategy. Companies that emulate their methods might find satisfaction instead of frustration at the end of the annual process.
Renée Dye is a consultant in McKinsey’s Atlanta office, and Olivier Sibony is a director in the Paris office.
This article was first published in the Autumn 2007 issue of McKinsey on Finance . Visit McKinsey’s corporate finance site to view the full issue.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Distortions and deceptions in strategic decisions
Tired of strategic planning.
- Contact sales
Start free trial
Strategic Planning in Business

Table of Contents
What is business strategic planning, the strategic planning process in 3 steps, what is a business strategic plan, key components of a business strategic plan, business strategic plan example, strategic plan vs. business plan.
Strategic planning is key for success in business. By planning strategically for the future, a business can achieve its goals. It’s easier said than done, but the more you know about strategic planning, the better chance you have at succeeding.
Business strategic planning is the process of creating a business strategy and an accompanying business strategic plan to implement a company’s vision and achieve its goals over time. The main goal of strategic planning is to take a company from its current state to its desired state through a series of business actions.
The business strategic planning process usually consists of defining business goals, doing a SWOT analysis to assess the company’s business environment and developing a business strategy. The leadership team is in charge of business strategic planning, as it has a very important impact on the overall direction of a company.
Get your free
Strategic Plan Template
Use this free Strategic Plan Template for Word to manage your projects better.
Strategic Planning is one of the three levels of organizational planning, which is the process that allows organizations to define its objectives for the future and make action plans to guide the efforts of each of its departments, employees and management levels .
The other two levels of organizational planning are tactical and operational planning. Let’s see how these three types of organizational planning differ from each other.
Strategic Planning vs. Tactical Planning
While a strategic plan is created by the top management team and defines the high-level strategic goals of an entire organization, a tactical plan has a narrower scope. A tactical plan is created by the middle management level of a business and describes the specific goals, initiatives, challenges and resources for each department and how its efforts contribute to the completion of the larger strategic plan of the business.
Strategic Planning vs. Operational Planning
An operational plan allows you to establish guidelines, procedures and best practices for the daily operations of your business. The main objective of operational planning is to ensure that your business operations contribute to the accomplishment of the strategic objectives defined in the strategic plan.
Strategic planning is very important, but it doesn’t need to be overly complex. Let’s simplify this process by breaking it down into three simple steps.
1. Set Business Goals
A business goal is simply an accomplishment that a company wants to achieve in the short, medium or long term. Business goals can take many forms such as increasing sales, revenue, customer satisfaction levels and brand positioning, among many other things.
2. Conduct a SWOT Analysis
The goal of a business strategy is to leverage the strengths of a business and minimize the impact of its weaknesses. Those two things are internal factors. The strengths of a company can become competitive advantages that can lead to business growth. There are many types of business strengths and weaknesses such as scale, speed, or R&D, just to name a few.
Threats and opportunities refer to external factors such as competitors or an untapped market. A successful business strategy considers all of these factors to define how a product or service will be created, marketed and sold, and a SWOT analysis is a great starting point.
3. Develop a Business Strategy & Strategic Plan
Once you’ve completed your SWOT analysis, you can create a business strategy that’s designed to help position your company in the market. Your business strategy guides how you produce, market and sell your product or service based on internal and external analysis.
Then, you’ll need a strategic plan to explain how you plan to execute that business strategy. To oversee the execution of a business strategic plan, managers need to manage time, costs and tasks. ProjectManager is a project planning tool that allows managers to plan, schedule and manage their team’s work. Plan your work with professional tools such as Gantt charts, kanban boards, task lists and calendars. Then track your progress in real time to stick to your strategic plan. Get started for free.
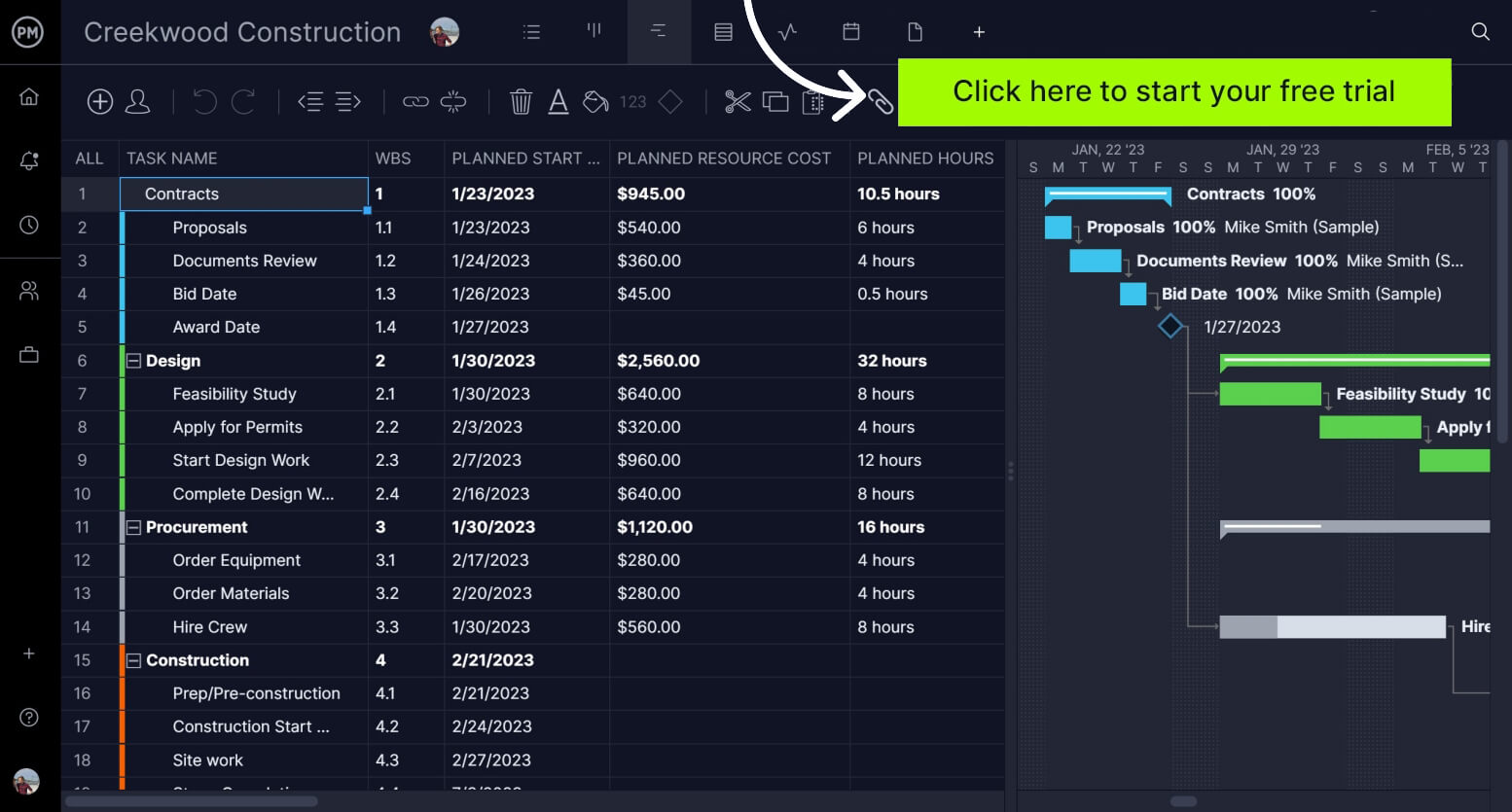
A business strategic plan is an implementation plan that’s meant to turn a business strategy into action items that can be executed over time. Business strategic plans are usually executed over the course of 3-5 years.
How to Develop a Strategic Plan
To develop a strategic plan, you should ask yourself the following three questions.
- Where Is the Business Now? Gather as much information on your business as possible including internal operations and what drives its profitability. Compare the business to competitors and note the similarities and differences in detail. This isn’t a day-to-day operational study, but a broader look at the business in context to itself and its environment. But don’t go crazy; stay realistic in terms of your business goals. Be detached and critical in your analysis.
- Where Do You Want to Go? Now it’s time to decide what your top-level objectives are for the future. Start with a vision statement , objectives, values, techniques and goals. Look forward to five years or more to forecast where you want the business to be at that time. This means figuring out what the focus of the business will be in the future. Will that focus differ from what it is now, and what competitive advantages do have you in the marketplace? This is where you build the foundation and initiate changes.
- How Can You Get There? Once you know where you are and where you want to go, it’s time to plan. What are the changes to the structure, financing, etc., necessary for the business to get there? Decide on the best way to implement those changes, the timeframe with deadlines and how to finance it. Remember, this is looking at the business at large, so consider major endeavors such as diversification, existing growth, acquisition and other functional matters. A gap analysis can be a big help here.
Once you’ve answered the above questions and have a way to achieve the long-term goals laid out in the strategic plan, the next step is making sure you have the right person to manage all of its moving parts. They must be analytical, a creative thinker and able to grasp operational detail.
That doesn’t mean the strategic plan is led by one person. It’s best to not do it alone; seek other opinions. The people in your organization, from bottom to top, are all great resources to offer perspectives from their standpoints. Don’t forget to take in the advice of stakeholders, including customers, clients, advisors and consultants.
To create a strong strategic plan, one must first have a strong understanding of the business that is to expand. How does the business work? Where does the business stand in relation to competitors in the marketplace? A strategic plan is built on the bones of the following foundational elements:
- Mission Statement: The mission statement describes what your company does.
- Vision Statement: The vision statement explains where your company expects to be in the future.
- Core Values: Guiding principles that shape your company’s organizational culture.
- Business Objectives: Consider using the SMART goal-setting technique . This simply means setting up specific, measurable, attainable, relevant and time-bound objectives that your company wants to achieve.
- SWOT Analysis: External and internal factors that make up your company’s business competitive environment.
- Action Plan: A plan outlining steps that will be taken to achieve the business objectives of your organization.
- Financials: A section that shows the financial performance expectations, the budget and the resources that will be required to implement the action plan.
- Performance Measurements: Performance indicators that will be used to measure the effectiveness of the action plan.
Never forget to check your strategic plan against reality. In addition to being achievable, it must be practical for your business environment, resources and marketplace.
Now let’s look at a simple business strategic plan example. This is a strategic plan for a small construction company.
1. Mission, Vision & Core Values
- Mission Statement: To build residential spaces that provide wellbeing for our clients.
- Vision Statement: To offer the best construction experience for our clients and expand our brand throughout the globe.
- Core Values: Sustainable innovation and respect for the environment.
2. Business Objectives
- Business Objective 1: Grow operating margin from 15% to 20% over the next year.
- Business Objective 2: Reduce operating costs by 5% over the next quarter
- Business Objective 3: Increase the number of new contracts generated by 10% over the next year
3. SWOT Analysis
- Strengths: Available financing, brand visibility and know-how.
- Weaknesses: Lack of PPE, human capital and expertise in construction areas such as plumbing, electrical work and masonry, which requires subcontractors.
- Opportunities: Lack of environmentally-friendly construction companies in the market.
- Threats: Larger construction companies compete for contracts in the area.
4. Action Plan
- Business Objective 1: To grow operating margin, new employees with plumbing, electrical work and masonry experience will be hired to cut down subcontractor costs. This must be done by the end of the first quarter.
- Business Objective 2: To reduce operating costs, the company will acquire property, plant and equipment. By doing this, the company will no longer rent equipment from third parties, which will reduce operating costs significantly in the medium and long term.
- Business Objective 3: To increase the number of new contracts generated, the leadership team will invest more in the PR, marketing and advertising departments. The company will also invest in key positions for the construction bidding process such as contract estimators.
- Financials: This section will explain in detail what are the costs associated with the work items in the action plan as well as the expected financial benefits for the company.
Our free strategic plan template helps leadership teams gather important information about their business strategy, which makes it the perfect tool to start shaping a strategic plan for your business or project.
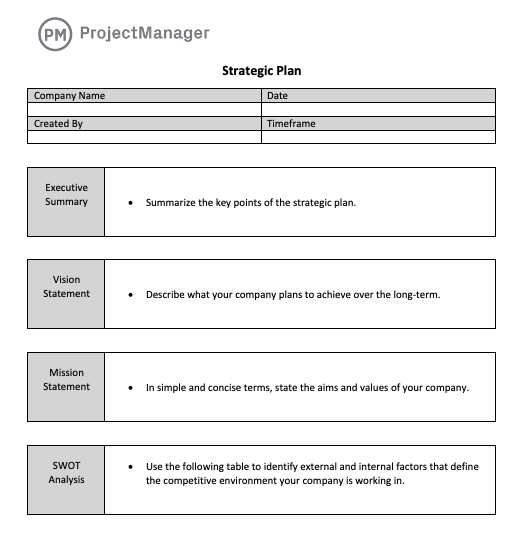
More Free Strategic Planning Templates
Here are some free strategic planning templates for Word and Excel that will help you with key aspects of the strategic planning process. Use them individually or add them to your strategic plan template for Word so you don’t miss any detail about your organizational strategy.
Strategic Roadmap Template
This strategic roadmap template allows you to map the activities, strategic projects and initiatives that each business department will execute to accomplish the objectives defined in the strategic plan of an organization.
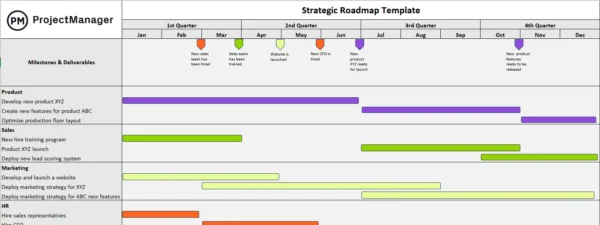
Strategic Map Template
This strategic map template it’s a strategic planning tool that allows you to visualize all the strategic objectives of your organization and understand how they’re interrelated.
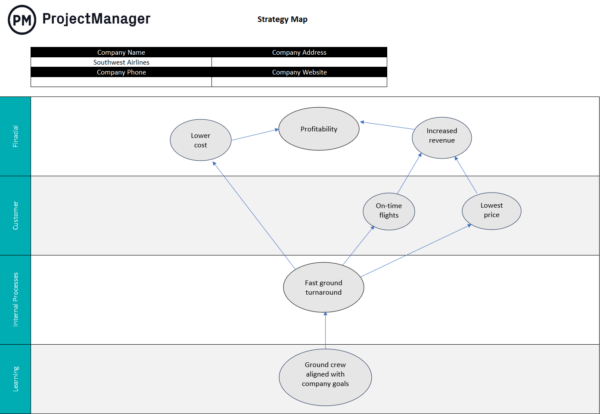
Balanced Scorecard Template
A balanced scorecard is a chart that allows you to set strategic objectives that will benefit your business in one of four key areas, its finances, internal processes, customer satisfaction and organizational learning.
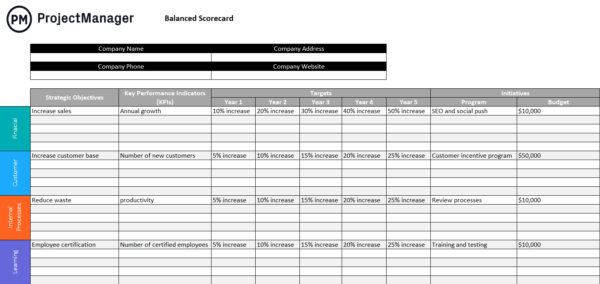
Vision Statement Template
The vision statement is one of the most important aspects of the organizational strategy of a business. It’s a short but powerful statement that describes the overall direction of a company and what it intends to achieve in the future. This free vision statement template will help you focus on what matters most and define the vision of your business.
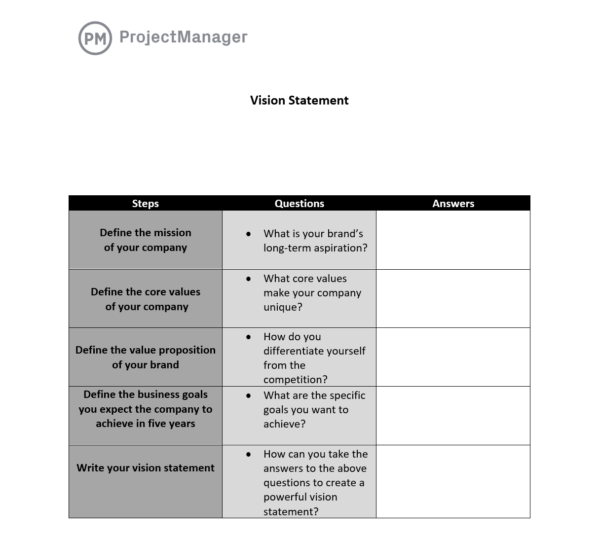
A strategic plan is a type of business plan, but there are distinctions between the two. Whereas a strategic plan is for implementing and managing the strategic direction of a business, a business plan is more often the document that starts a business.
A business plan is used primarily to get funding for the venture or direct the operation, and the two plans target different timeframes in business history. A strategic plan is used to investigate a future period, usually between three-to-five years. A business plan is more routinely a year out.
A Different Intent
A strategic plan offers a business focus, direction and action to help the business grow from the point it presently resides to a greater market share in the future. A business plan, on the other hand, is more focused on offering a structure to capture and implement ideas that initially define a business.
With a strategic plan, existing resources are prioritized to increase revenue and return on investment. The business plan is different in that it’s seeking funding for a venture that doesn’t yet exist. Where a strategic plan is building a sustainable competitive advantage in the future, a business plan is designed to take advantage of a current business opportunity.
So, a strategic plan is communicating direction to teams and stakeholders in order to achieve future goals. A business plan isn’t talking to staff, which is likely nonexistent or minimal at this point. It’s speaking to banks and other financial supporters.
Related Strategic Planning Content
- Strategic Project Management: Planning Strategic Projects
- Strategic Planning Models: An Introduction to 5 Popular Models
- A Quick Guide to Strategic Initiatives
- How to Create a Strategic Roadmap for Your Organization
- Project Alignment: Aligning Your Project to Business Strategy
Strategic planning, like any planning, requires keeping a lot of balls in the air. That means having the right tool to plan, monitor and report on all the various tasks and resources. ProjectManager is online project management software that gives you control over every aspect of creating and implementing a strategic plan. Try it today with this free 30-day trial.

Deliver your projects on time and under budget
Start planning your projects.
New Articles
- Tools and Techniques for Successful Lean Implementation: Streamlining Your Processes
- The Power of Six Sigma: Revolutionizing Process Improvement
- Increasing Efficiency and Saving Costs: The Benefits of Hiring Consultancy Services
- Understanding the Importance of Strategic Planning
- Best practices for successful automation
- Benefits of automating processes
- Tools and technologies for automation
- Streamlining workflows
- Case studies of successful workflow improvements
- Strategies for streamlining workflows
- Identifying inefficiencies in workflows
- Outsourcing
- Managing outsourced processes for maximum efficiency
- When to consider outsourcing for increased efficiency
- Choosing the right outsourcing partner
- How Kaizen can improve processes and increase efficiency
- Examples of successful Kaizen projects
- What is Kaizen?
- Understanding the Six Sigma methodology
- Key tools and techniques for Six Sigma implementation
- Benefits of using Six Sigma for process improvement
- Lean methodology
- Tools and techniques for successful lean implementation
- Benefits of implementing lean methodology
- What is lean methodology?
- Expertise and experience
- Examples of successful projects with consultancy services
- Why expertise is crucial in improving processes and operations
- How consultancy services bring valuable experience to the table
- Fresh perspective
- Real-world examples of fresh perspectives leading to improved operations
- How consultancy services can offer new solutions and ideas
- The importance of an outside perspective in identifying inefficiencies
- Efficiency and cost savings
- Case studies of cost-saving projects with consultancy services
- Ways in which consultancy services can increase efficiency and save costs
- ROI of hiring a consultancy service
- Strategic planning
- Real-world examples of effective strategic planning
- What is strategic planning and why is it important?
- Key elements of a successful strategic plan
- Supply chain management
- Case studies of successful supply chain management
- Understanding the supply chain and its impact on business operations
- Strategies for efficient supply chain management
- Project management
- Key principles of effective project management
- Examples of successful project management in different industries
- Tools and techniques for successful project management
- Business strategy and operations management
Welcome to our article on real-world examples of effective strategic planning. Strategic planning is a crucial aspect of business strategy and operations management, and it plays a vital role in the success of any organization. In today's fast-paced and constantly evolving business landscape, having a solid strategic plan is more important than ever before. In this article, we will explore the concept of strategic planning and provide you with real-world examples of how it has been effectively implemented by successful companies. We will also discuss the benefits of strategic planning and how it can help organizations stay ahead of the competition. Whether you are a business owner, a manager, or simply interested in learning more about strategic planning, this article is for you.
So, let's dive in and discover the power of effective strategic planning in driving business success. The success of any business relies heavily on effective strategic planning. It involves setting goals, making decisions, and taking actions that will ultimately help a company achieve its objectives. In this article, we will explore real-world examples of how strategic planning has been successfully implemented by businesses, and why it is an essential aspect of operations management. The first example we will look at is Apple Inc. Under the leadership of Steve Jobs, Apple implemented a strategic plan that focused on innovation and customer experience.
By consistently improving their products and creating a strong brand image, Apple was able to dominate the tech industry and become one of the most valuable companies in the world. Their strategic planning not only enabled them to stay ahead of their competitors but also allowed them to continuously meet the ever-changing demands of their customers. Another example is Starbucks, which used strategic planning to expand its global presence and increase its market share. By analyzing consumer trends and adapting to changing preferences, Starbucks was able to maintain its position as a leading coffee chain. Their strategic planning helped them identify new markets and tailor their products and services to fit the needs of different cultures and regions. Additionally, Procter & Gamble (P&G) is another company that has successfully utilized strategic planning in their operations.
P&G's strategic planning focused on innovation and product development, allowing them to continuously introduce new and improved products to the market. This approach not only helped them stay ahead of their competitors but also maintained customer loyalty and satisfaction. Furthermore, Walmart is another prime example of a company that has effectively incorporated strategic planning into their business strategy. With a relentless focus on cost-cutting and efficiency, Walmart has been able to offer competitive prices to their customers while maintaining profitability. Their strategic planning has also enabled them to expand globally and cater to diverse markets while still maintaining their brand identity. Lastly, Coca-Cola is a company that has consistently used strategic planning to remain a market leader in the beverage industry.
Real-life Examples of Successful Strategic Planning
Benefits of strategic planning.
By setting clear goals and objectives, strategic planning can lead to increased profitability for a business. This is because it allows companies to focus their resources and efforts on areas that will bring the most return on investment. Additionally, effective strategic planning can improve the efficiency of a business. By analyzing and optimizing processes, businesses can reduce waste, save time, and ultimately improve their bottom line. This also leads to better decision-making as companies have a clear understanding of their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Another benefit of strategic planning is that it promotes teamwork and collaboration within an organization.
The Importance of Strategic Planning
Effective strategic planning.
By considering various scenarios, businesses can create backup strategies that can be implemented if needed. This helps companies stay prepared and adaptable in an ever-changing business landscape. Moreover, strategic planning also helps businesses maximize resources and minimize potential risks. By carefully planning and allocating resources, companies can ensure that they are utilizing their assets effectively and efficiently to achieve their goals. Additionally, by identifying potential risks, businesses can take steps to mitigate them and minimize their impact on operations. In today's competitive market, strategic planning is more important than ever.
It allows companies to stay ahead of the competition by constantly evaluating their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. By regularly revisiting and adjusting their strategies, businesses can stay relevant and successful in the long run. In conclusion, strategic planning is an essential aspect of business strategy and operations management . By studying real-world examples of successful strategic planning , companies can learn valuable lessons and implement effective strategies to achieve their goals and stay ahead of the competition.

Kimberly Greenfield
Passionate food junkie. Typical burrito fan. Infuriatingly humble pop culture trailblazer. Wannabe internet junkie. Hipster-friendly web aficionado.
- The Power of Kaizen: Improving Processes for Better Results
Discover the fundamentals of Kaizen and how it can benefit your business's processes.

- The Importance of Expertise in Improving Processes and Operations
Discover the benefits of hiring a consultancy service and how expertise plays a vital role.

- The Power of Lean Methodology: Unlocking the Benefits
Discover the benefits of implementing lean methodology and revolutionize your process improvement techniques.
- Examples of Successful Kaizen Projects
Learn about successful Kaizen projects and how they can improve your processes.
Leave Message
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
I agree with the terms of service
- Best Practices for Successful Automation: Streamline Your Operations
- How Kaizen Can Revolutionize Your Processes and Boost Efficiency
Case Studies of Successful Workflow Improvements: Boosting Operational Efficiency
- Understanding the Six Sigma Methodology: A Comprehensive Overview
- Examples of Successful Projects with Consultancy Services
- The Benefits of Automating Processes for Increased Operational Efficiency
- Key Tools and Techniques for Six Sigma Implementation
- Streamlining Workflows: Strategies for Increasing Operational Efficiency
Identifying Inefficiencies in Workflows: How to Streamline Your Operations for Greater Efficiency
- Tools and Technologies for Automation: Streamlining Your Business Processes
- How Consultancy Services Bring Valuable Experience to the Table
- Maximizing Efficiency through Outsourcing
- Understanding Lean Methodology: A Comprehensive Guide
- When to Outsource for Increased Efficiency: A Comprehensive Guide
- How to Choose the Right Outsourcing Partner: A Comprehensive Guide
- The Power of Consultancy Services: Real-Life Cost-Saving Case Studies
- Case Studies of Successful Supply Chain Management: Maximizing Business Strategy and Operations
- Key Principles of Effective Project Management: A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding the Supply Chain and its Impact on Business Operations
- How Consultancy Services Can Offer New Solutions and Ideas
- The Power of a Fresh Perspective: Identifying and Eliminating Inefficiencies
- Strategies for Efficient Supply Chain Management
Examples of Successful Project Management in Different Industries: How to Achieve Success in Your Business
- Understanding the ROI of Hiring a Consultancy Service
- Tools and Techniques for Successful Project Management: Maximizing Efficiency and Delivering Results
- The Key Elements of a Successful Strategic Plan
Recent Posts

Which cookies do you want to accept?

Strategic Plan Examples | Best 11 Tools For Effective Strategic Planning | Updated in 2024
Jane Ng • 14 Jan 2024 • 10 min read
Looking for Strategic Plan Examples? Having a strategic plan is essential for any business or organization’s growth. A well-crafted plan can make all the difference in the success of your venture. It helps you have a realistic vision for the future and maximize the company’s potential.
So, if you struggle to develop a strategic plan for your business or organization. In this blog post, we will discuss a strategic plan example along with few fun ideas for strategic planning and tools that can serve as a guide to help you create a successful plan.
Table of Contents
What is a strategic plan, strategic plan examples, tools for effective strategic planning, how ahaslides help you with strategic planning, key takeaways, frequently asked questions, tips for better engagement.
- Strategy Formulation
- Scenario Planning Examples
- What is Career Planning?
- Stress Management

Looking for a tool to engage your team?
Gather your team members by a fun quiz on AhaSlides. Sign up to take free quiz from AhaSlides template library!
A strategic plan is a plan that outlines an organization’s long-term goals, objectives, and strategies for achieving them.
It is a roadmap that helps your organization prepare and allocate resources, efforts, and actions to achieve its vision and mission.

Specifically, a strategic plan usually lasts 3-5 years and may require the organization to evaluate its current position with its strengths, weaknesses, potential, and competitive level. Based on this analysis, the organization will define its strategic goals and objectives (they need to be SMART: specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound).
Following that, the plan will list the required steps and actions to achieve these goals, as well as the resources needed, timelines, and performance measures to track progress and success.
To guarantee success, your strategic plan needs tools that help with planning, management, communication, collaboration, and accountability to help the organization stay focused and stick to the workflow.
Here are some strategic planning models your business can use:
1/ SWOT Analysis – Strategic Plan Example
The SWOT Analysis model was developed by Albert Humphrey . This model is a well-known business analysis model for organizations that want to create a strategic plan by evaluating four factors:
- S – Strengths
- W – Weaknesses
- O – Opportunities
- T – Threats
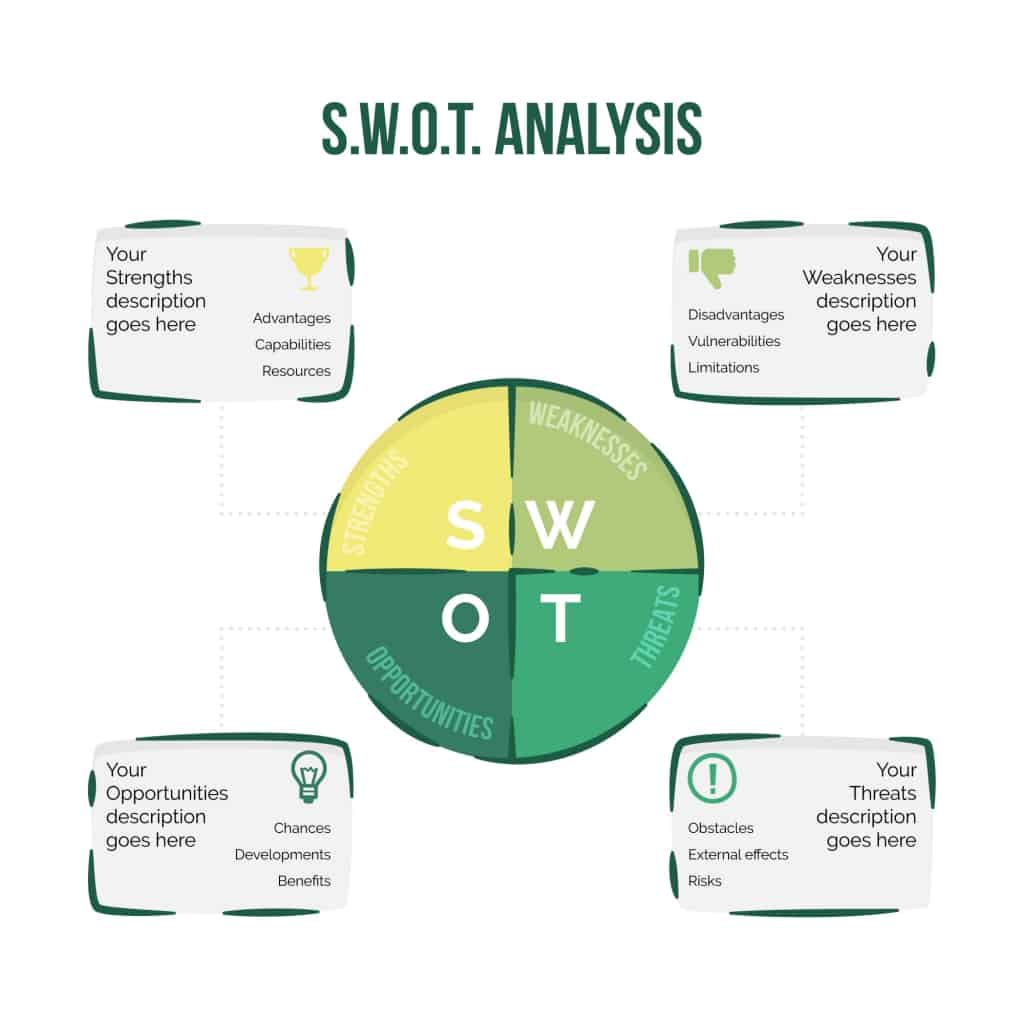
With these factors, your organization can understand its current situation, advantages, and areas where need to improve. In addition, your organization can identify the external threats that may affect it and the opportunities to seize in the present or the future.
After having such an overview, organizations will have a solid basis for effective planning, avoiding risks later.
Strategic Plan Example: To help you better understand how to use SWOT analysis to develop a strategic plan, we will give an example.
You have a small business that sells handmade soap products. Here is a SWOT analysis of your business:
Based on this SWOT analysis, your business can develop a strategic plan that focuses on
- Expand product distribution channels
- Developing new product lines
- Improve online marketing and advertising
With this strategy, you can leverage your strengths, such as high-quality products and personalized customer service.
2/ Balanced Scorecard Model – Strategic Plan Example
Balanced Scorecard Model is a strategic planning model that helps businesses develop sustainably and reliably through all 4 aspects:
- Financial: Organizations need to measure and monitor financial results, including fixed costs, depreciation expenses, return on investment, return on investment, revenue growth rate, etc.
- Customers: Organizations need to measure and evaluate customer satisfaction, along with their ability to meet customer needs.
- Internal process: Organizations need to measure and evaluate how well they are doing.
- Learning & Growth: Organizations focus on training and helping their employees develop, helping them improve their knowledge and skills to maintain a competitive edge in the market.
Strategic Plan Example: Here is an example to help you understand more about this model:
Assuming you are the owner of a famous coffee brand, here is how you apply this model to your strategic plan.
The Balanced Scorecard model ensures that a business is considering all aspects of its operations and provides a framework for measuring progress and adjusting strategies as needed.
3/ Blue Ocean Strategy Model – Strategic Plan Example
Blue Ocean Strategy Model is a strategy of developing and expanding a new market in which there is no competition or competition is unnecessary.
There are six basic principles for the successful implementation of a blue ocean strategy.
- Reconstruct market boundaries: Businesses need to rebuild market boundaries to break out of competition and form blue oceans.
- Focus on the big picture, not the numbers: Businesses need to focus on the big picture when planning their strategy. Don’t get bogged down in details.
- Go beyond the existing demands: Instead of focusing on existing products or services, they need to identify those who are non-customers or potential customers.
- Get the strategic sequence right: Businesses need to create a value proposition that differentiates them and adjust internal processes, systems, and people.
- Overcome organizational obstacles. To successfully implement the Blue Ocean Strategy, the business will need buy-in from all levels of the organization and communicate strategy effectively.
- Strategy Execution. Businesses implement strategy while minimizing operational risks and preventing sabotage from within.

Strategic Plan Example: The following is an example of applications of the Blue Ocean Model.
Let’s continue to assume that you are an organic soap business owner.
- Reconstruct market boundaries: Your business can define a new market space by creating a line of soaps that are only for sensitive skin.
- Focus on the big picture, not the numbers: Instead of just focusing on profits, your business can create value for customers by emphasizing natural and organic ingredients in soap products.
- Go beyond the existing demands: You can tap into new demand by identifying non-customers, such as those with sensitive skin. Then create compelling reasons for them to use your product.
- Get the strategic sequence right: Your business can create a value proposition that sets it apart from competitors, in this case with natural and organic ingredients. Then align its internal processes, systems, and people to deliver on that promise.
- Overcome organizational obstacles: To successfully implement this strategy, your business needs support from all levels of stakeholders for this new product.
- Strategy Execution: Your business can build performance metrics and adjust the strategy over time to ensure they’re performing effectively.
Here are some popular tools to help you have an effective strategic plan:
Tools For Data Gathering and Analysis
#1 – pest analysis.
PEST is an analysis tool that helps your business understand the “big picture” of the business environment (usually macro-environmental) in which you are participating, thereby identifying opportunities and potential threats.

PEST Analysis will evaluate this environment through the following 4 factors:
- Politics: Institutional and legal factors can affect the viability and development of any industry.
- Economics: Organizations need to pay attention to both short-term and long-term economic factors and government intervention to decide which industries and areas to invest in.
- Social: Each country and territory has its own unique cultural values and social factors. These factors create the characteristics of consumers in those regions, which make a huge impact on all products, services, markets, and consumers.
- Technology: Technology is an important factor because it has a profound impact on products, services, markets, suppliers, distributors, competitors, customers, manufacturing processes, marketing practices, and the position of organizations.
PEST analysis helps your business understand the business environment. From there, you can map out a clear strategic plan, make the most of the opportunities that come your way, minimize the threats and easily overcome the challenges.
#2 – Porter’s Five Forces
Five Forces represent 5 competitive forces that need to be analyzed to assess the long-term attractiveness of a market or a segment in a particular industry, thereby helping your business have an effective development strategy.
Here are those 5 forces
- Threat from new opponents
- Power of suppliers
- Threat from substitute products and services
- Power of customers
- The fierce competition of competitors in the same industry
These five factors have a dialectical relationship with each other, showing the competition in the industry. Therefore, you need to analyze these factors and develop strategies to identify what is particularly attractive and outstanding for the business.
#3 – SWOT Analysis
More than being a model for strategic planning, SWOT is a valuable tool for conducting market analysis. By utilizing SWOT, you can pinpoint the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of your organization before implementing a successful strategy.
Tools For Strategy Development and Implementation
#4 – scenario planning .
Scenario planning is a strategic planning tool that considers multiple future scenarios and evaluates their potential for an organization.
The scenario planning process has two stages:
- Identifying the key uncertainties and trends that could shape the future.
- Developing multiple response scenarios based on those factors.
Each scenario describes a different possible future, with its own unique set of assumptions and outcomes. By considering these scenarios, your organization can better understand various possible futures it may face, and develop strategies that are more resilient and adaptable.

#5 – Value Chain Analysis
The Value Chain Analysis model is an analytical tool for understanding how the activities within your organization will create value for customers.
There are three steps to performing a value chain analysis for an organization:
- Divide the organization’s activities into main activities and supporting activities
- Cost breakdown for each activity
- Identify the fundamental activities that create customer satisfaction and organizational success
From the three steps above, your organization can more effectively measure its capabilities by identifying and evaluating each activity. Then each value-creation activity is considered a resource to create a competitive advantage for the organization.
#6 – Critical Success Factors
Critical Success Factors (CSF) refer to the causes that lead to the success of a business or set out what employees need to do to help their business to achieve success.
Some helpful questions for determining your business’s CSF include:
- What factors are likely to lead to the desired outcome of the business?
- What requirements must exist to produce that result?
- What tools does the business need to achieve that goal?
- What skills does the business need to achieve that goal?
By defining the CSF, your business can create a common reference point for what it needs to do to achieve its goals, thereby motivating the workforce to get there.

#7 – A Balanced Scorecard
Besides being a model for strategic planning, A Balanced Scorecard is a performance management tool that helps you track progress toward your strategic objectives. It also helps you to measure and communicate your progress to stakeholders.
#8 – Blue Ocean Strategy Canvas
Apart from functioning as a strategic planning model, the Blue Ocean Strategy Canvas assists in recognizing new market opportunities by aligning your organization’s offerings with those of your competitors.
By using this tool, you can identify areas where your organization can stand out and generate new demand.
Tools For Measurement and Evaluation
#9 – key performance indicators.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is a tools to measure and evaluate work performance. KPIs are usually expressed through numbers, ratios, and quantitative indicators, to reflect the performance of groups or divisions of the business.
KPIs help businesses monitor and evaluate the performance of employees in a transparent, clear, specific, and fair manner thanks to specific data.

>> Learn more about KPI versus OKR
Tools For Brainstorming
#10 – mind mapping.
Mind mapping is a visual tool that can be used during the strategic planning process to help with brainstorming and organizing ideas. It is a method of visually representing information and ideas by drawing a diagram.
Besides helping discover new ideas, it helps to find connections between various strategic objectives, which can ensure that the strategic plan is comprehensive and effective.
AhaSlides offers several features that can be useful for your strategic planning.
AhaSlides allows you to create engaging and interactive presentations that can be used to communicate complex ideas or gather feedback. Along with pre-made templates , we also have features like live polls , quizzes , and live Q&A sessions that help you encourage engagement. As well as ensuring that all stakeholders have a voice and can provide input into the planning process.
Besides, the word cloud allows team members to collaborate and generate new ideas during strategic planning, which can help identify new opportunities or solutions to challenges that may arise.
Overall, AhaSlides is a valuable tool for strategic planning since it promotes communication, cooperation, and data-driven decision-making.
Having a well-defined strategic plan example is critical for any organization to achieve its goals and objectives. Therefore, with the information in the article, your organization may develop a complete strategic plan that is in line with its vision and mission, resulting in long-term growth and success.
And do not forget by using various strategic planning tools and models such as SWOT analysis, Balanced Scorecard, and Blue Ocean Strategy,… your organization can identify its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, track progress toward its goals, and develop innovative strategies to differentiate itself in the market.
Besides, digital tools like AhaSlides can aid in the effectiveness of the strategic planning process.
Best IT strategic plan example?
Creating a comprehensive IT strategic plan is essential for organizations to align their technology initiatives with their overall business goals. While there isn’t a single “best” IT strategic plan that fits all organizations, please remember that the Key Initiatives should include: (1) Identification of major IT initiatives and projects for the planning period. (2) Detailed descriptions of each initiative, including objectives, scope, and expected outcomes. and (3) Alignment of each initiative with specific strategic goals.
What is effective strategic planning?
Effective strategic planning is a structured and forward-thinking process that organizations use to define their long-term vision, set clear objectives, and determine the actions required to achieve their goals. Effective strategic planning goes beyond creating a document; it involves engaging stakeholders, aligning resources, and continually adapting to changing circumstances.

A writer who wants to create practical and valuable content for the audience
More from AhaSlides

- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
6 Strategic Concepts That Set High-Performing Companies Apart
- Kaihan Krippendorff

Lessons from Microsoft, NVIDIA, Netflix, Tesla, and others.
Strategic concepts come in and out of fashion as the needs and dynamics of the marketplace change. Research and analysis of today’s landscape identifies six key strategic concepts that set outperforming companies apart: Borrow someone’s road, partner with a third party, reveal your strategy, be good, let the competition go, and adopt small scale attacks.
At the close of 2023, the California-based chip company Nvidia announced yet another quarter of record sales — an achievement that came hot on the heels of its entry to the elite club of U.S. enterprises with a $1 trillion market valuation earlier in the year. The company, whose success has been fueled by the AI boom, now holds approximately 80% of the global market share for GPU semiconductor chips .
- Kaihan Krippendorff is the co-author, with Robert C. Wolcott, of Proximity: How Coming Breakthroughs in Just-in-Time Transform Business, Society, and Daily Life and founder of Outthinker Networks .
Partner Center
Get full control of all your budgets in one place
Resource Planning
See where your agency stands this quarter, and in the next few
Get access to over 50 prebuilt agency reports or build and customize on your own
Project Management
Set up, streamline, and deliver projects
Time Tracking
With each tracked hour, get more precise data so you can run a more profitable agency
Shape your agency's sustainable growth
Eliminate hours spent on invoicing
Create documents and collaborate with your teammates
Software Development
Marketing Agency
Design Studio
In-house Team
Success Stories
Read how agencies transform using Productive
Agency management, product updates & how tos
End-to-end Agency Management
Future proof your business with an agency management system
Agency Resource Management
Gain more control over your agency’s resources
Learn how to run a more successful agency in Productive
Billable Hours Calculator
Find out your billable hours, team utilization rate, and ideal billable hourly rate
Get advice and support from the team
The Bold Community
Join the community for agency professionals by Productive
Book a Demo
Try Productive
Comparisons
{{minutes}} min read
Strategic Human Resource Planning (SHRM): Guide to Human Resources & Management
Lucija Bakić
April 5, 2024
Strategic human resource planning (SHRM) is a proactive process that aligns human resource capabilities with long-term business goals.
In this guide, we’ll go through the basics of why this foward-thinking approach is so important for resource planning success . This includes its definition, the main steps, and best business practices. Key Takeaways
- Strategic HR management (SHRM) is a key step to ensuring that businesses are resilient and sustainable in the long run.
- Key steps of the process include: analyzing current capacity, forecasting needs, gap analysis, HR strategy implementation and monitoring.
- Many of the challenges of SHRM, such as resistance to change or tracking KPIs, can be addressed by implementing a modern ERP software solution .
What Is Strategic Human Resource Planning?
Strategic human resource planning is part of the broader human resource plan ning (HRP) strategy. This process targets long-term objectives, spanning from one to five years, and ensures that businesses have enough capacity to meet future needs. Strategic HR planning must be aligned with short-term resource planning, which handles daily concerns, such as employee schedules and workloads. Long-term strategies should also be aligned across departments, such as the finances or management, to ensure that initiatives contribute to shared organizational goals. See more : What Is Human Resource Planning ?
Why Businesses Need Strategic HRP
Some of the critical business questions that strategic HRP addresses can include:
- Will you have enough human resources for future needs?
- Which type of talent will you need (regarding skills, seniority, etc.)
- Which conflicts or gaps could appear in your business workflows ?
- Do you have contingency plans for various risk factors?
Additionally, it can cover broader concerns, such as the need for organizational flexibility or continuous improvement. As an ongoing process, strategic management provides the perfect answer for businesses to tackle and address complex issues.
5 Main Steps of the Strategic HR Planning Process
The four main steps of strategic HRM include analyzing current capacity, needs forecasting, gap analysis, and strategy development and implementation.
1. Analyzing Current Capacity
This step involves analyzing both internal and external business circumstances that are important for future demand. Internal factors usually include details about your current employees, including their productivity, specific skills, availability, and engagement levels. External factors encompass market trends, economic conditions, and industry-specific demands that could influence future resource requirements.
Align Your HR Management With Strategic Goals
Get an all-in-one solution and improve your business performance with employee scheduling, time off management, billable hours tracking, and more.
Start Free Trial
Book a demo
2. Needs Forecasting
Accurate needs forecasting is one of the most challenging parts of the developing workforce plans . It involves predicting the skills, overall capacity, and roles needed to keep a business relevant during changing market conditions and technological advancements. Therefore, it requires a thorough understanding of your human capital and the industry. Needs forecasting includes:
- Supply forecasting: Assesses the current workforce and external labor market trends to identify whether there will be an excess or shortage of talent in the future.
- Demand forecasting: Focuses more on demand, i.e., quantifying future labor requirements to ensure that business goals will be met.
3. Gap Analysis
Gap analysis takes the first two steps of the human resource management process to pinpoint specific areas of improvement — it compares the current workforce capabilities with future needs to identify conflicts or discrepancies. For example, a retail chain looking to expand its online presence might consider its current capacity, and realize that it has enough technical roles to go into e-commerce. However, by conducting needs forecasting of the competitors, it may recognize the need for marketing professionals skilled in SEO or digital marketing to drive more of their customer base to their website.
4. Strategy Development
The next step involves developing specific strategies to address resource conflicts and help your business reach its goals. Some of these may include:
- Talent management strategies can be developed to address issues with workforce management. It can include processes such as recruiting, retaining, and developing employees.
- Employee engagement strategies are usually developed to tackle low morale and productivity. Organizational strategies might include improving collaboration, manager-to-employee feedback, or capacity building initiatives .
- Development programs are a specific part of talent management, aimed to address skill gaps through upskilling or reskilling employees. Strategies may include mentoring by senior employees, workshops, or other training opportunities.
- Succession planning is utilized to mitigate the risk of key positions becoming vacant unexpectedly. It usually involves identifying high-risk positions and then selecting and preparing potential employees to fill them in the future.
5. Implementation and Monitoring
To ensure that your strategies are effective across time, it’s necessary to closely monitor progress, usually by analyzing various key capacity performance indicators (KPIs). Setting desired targets can be a good way of determining if you’re on the right track — for example, an agency with low productivity might set its desired utilization rates at 80%.
Manage and visualize your employee productivity with Productive
However, it’s equally important to keep in mind that some benefits of successful ERP can be difficult to quantify or determine in a short amount of time. This can include better workplace culture or increased employee satisfaction. See more: ERP benefits for businesses
Documenting Your Strategic HR Plan
The strategic HR document should include an outline of the organization’s human resource objectives, the strategies for achieving them, and the steps for implementation. Putting your initiatives into writing can help drive alignment across various teams and ensure that everything is progressing according to plan.
How and Where to Create Documentation?
According to research by Forrester, 97% of organizations have minimal or no digitally documented processes. While traditional documentation can be better than no documentation, consider the benefits of automating information gathering and sharing with ERP software solutions .
We used to have a project management tool, a time tracking tool, a support tool, a way we handled opportunities and sales-driven processes. Those were all separate tools that we had, and it wasn’t good. It also meant that all that data was being lost every time we switched between tools , or we had to find a way to normalize the data between them. And now, the fact that it’s all in one, it’s really a game changer.
BRYAN CASLER, VICE PRESIDENT OF DIGITAL STRATEGY AT 4SITE INTERACTIVE STUDIOS
For example, the resource and agency management tool Productive can help you automate the work scheduling process with its resource planning model template, provide real-time reporting on utilization rates, manage employee availability and time off, and more. Another great feature you can consider is collaborative documentation with AI content creation. This can help you keep all essential project data on a single platform.
ON DEMAND WEBINAR
Using ai – not getting used by ai.
Get a sneak peek into our Bold Community and learn how agencies can benefit from AI in 2023 with Nicholas Petroski from Promethean Research.
Challenges & Best Practices for Strategic HRP
Some of the main challenges of strategic HRP include ensuring buy-in at all organizational levels, handling resistance to change, efficiently monitoring performance, and fostering continuous improvement.
Getting Business-Wide Buy-In
Organizational changes need to be effected from the top to the ground-level staff. Getting buy-in for new initiatives from leaders and other key stakeholders is essential to get the most out of your HRP initiatives. Silos can cause issues for adoption and cause miscommunications across teams, where one part of the company may not be aware of the changes or understand their role in implementation.
Overcoming Resistance to Change
According to Deloitte, some of the biggest roadblocks to new initiatives include resistance to change (82%) and inadequate sponsorship (72%). Both can be addressed with clear communication and transparency, so that all employees understand why and how initiatives are being implemented. Asigning change ambassadors within teams can facilitate a smoother transition. Learn more: Efficient resource management for multiple projects
Reviewing and Analyzing Progress
Good initiatives can stumble and fall if there’s no way to measure actual performance. Selecting the right key performance indicators and implementing a way to analyze them is important for the success of HRP initiatives. For example, a consulting firm that has issues with turnover might implement additional benefits or hire more staff to balance workloads — the KPIs to be monitored would be employee satisfaction, the utilization rate , and the attrition rate.
Productive can forecast KPIs for professional services agencies, like revenue and profit margins
Incremental Changes and Continuous Innovation
Another reason why monitoring KPIs is so important is that incremental but timely improvements are always better than extensive changes. Smaller adjustments allow businesses to remain flexible and agile to adapt to market demands and internal changes without causing disruptions.
The Role of Analytics & HRP Software
Finally, most, if not all challenges mentioned above can be streamlined with the right tools for resource planning and HR management. The benefits of using such tools include:
- Improved timeline estimation (60%)
- More effective use of resources (55%)
- Enhanced team communication (49%)
- More accurate metrics (38%)
There are many potential options on the market, but consider using a comprehensive software for your strategic planning. These types of solutions can give you a competitive advantage with benefits such as centralized workflows, unified data, and reduced costs for tech stacks.
Get the most out of your agency’s resources with Productive
As an all-in-one solution tailored to agencies of all shapes and sizes, Productive can help you manage both day-to-day resource management and create strategic plans. Key features include: resource allocation, employee performance management, real-time reporting, project budgeting, workflow automations, and much more. Learn more about Productive by booking a demo today.
What are the 4 HR strategies?
The 4 HR strategies include talent acquisition and retention, learning and development, performance management, and workforce planning and forecasting. Each strategy addresses a part of the human resource planning process and contributes to achieving organizational success.
What is strategic resource planning?
Strategic resource planning is a part of human resource management that examines the capacity and needs of your future workforce for sustainable business growth. It’s focused on ensuring that your business has the critical skills for meeting business goals over a long period of time.
What are the 5 steps in human resource planning?
The 5 main steps in human resource planning include: analyzing current HR availability, forecasting future needs, gap analysis, developing strategies for human resource management, and implementing and monitoring your initiatives.
What is SHRM and its importance?
SHRM or strategic human resources management is a forward-looking approach to managing human resources and aligning HR practices with organizational goals. It allows businesses to remain competitive, sustainable, and flexible in dynamic market conditions.
Connect With Agency Peers
Access agency-related Slack channels, exchange business insights, and join in on members-only live sessions.
Content Specialist
Related articles
Agency Management
Top 5 Capacity Report Types for Effective Project Management
The best capacity planning template for agencies, resource capacity planning: the definitive guide.
Questions not answered yet? Our sales is here to help
+1 (415) 287-3073
Integrations
Automations
Business Consultancy
Customer Stories
Product Updates
Agency Valuation Calculator
Building Productive
Brand Guidelines
Trust Center
© 2024 The Productive Company, Inc.
Privacy Policy
Terms & Conditions
We need your consent to continue
Necessary cookies
Cookies for the basic functionality of the Productive website.
Functional cookies
Cookies for additional functionality and increased website security.
Targeting cookies
Advertising and analytics service cookies that create day-to-day statistics and show ads on their site and on the advertiser’s partners websites.
Save changes
Manage cookies and help us deliver our services. By using our services, you agree to our use of cookies.
Try Productive for free
Free 14-day trial. No credit card required. Cancel any time.
Already using Productive? Sign in with an existing account

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Goals, Priorities and Strategies. Outlines the goals, priorities, and strategies to meet the mission. 3 -4 overarching goals aligned with mission. Priorities, activities, objectives, strategies are in more depth, have more specificity - each goal could have a few different objectives / strategies associated with it.
Step 1: Assess your current business strategy and business environment. Before you can define where you're going, you first need to define where you are. Understanding the external environment, including market trends and competitive landscape, is crucial in the initial assessment phase of strategic planning.
One of the best ways to learn about business strategy is from real-world examples. Here are three companies that faced numerous challenges but overcame them through value-based business strategies. 1. Best Buy. Best Buy, the multinational electronics retailer, is an excellent example of how a shift in business strategy can lead to rapid growth.
These examples demonstrate how strategic planning is a dynamic and integral part of the business processes of leading companies. They highlight the importance of a well-defined vision, rigorous analysis, adaptability, and innovation in the strategic planning process.
Identify business goals and set priorities that create growth for your company. Formulate a long-term plan of action designed to achieve these objectives. Determine an internal system tracking and evaluating performance. When organizations want to, they use a strategic plan to: Strengthen their operation.
1. Basic model. The basic strategic planning model is ideal for establishing your company's vision, mission, business objectives, and values. This model helps you outline the specific steps you need to take to reach your goals, monitor progress to keep everyone on target, and address issues as they arise.
Step 2: Build out your five-year plan. Develop the framework that will hold your high-level priorities. You can use your OAS or Strategic Shift exercises to help you define your priorities and objectives—but more importantly, you need a way to manage these elements.The way to do that is by selecting and developing a strategy management framework that will bring all your priorities together ...
1. Run a strategic planning workshop. The first step is to run a strategic planning workshop with your team. Get your team in the room, get their data, and gather their insights. By running this workshop, you'll foster collaboration and bring fresh perspectives to the table. And that's not all.
Strategy and strategic plans: How they are different and why it matters. Strategy creates a common understanding of what an organization wants to achieve and what it needs to do to meet its goals. Strategic plans bridge the gap from overall direction to specific projects and day-to-day actions that ultimately execute the strategy. Job No. 1 is ...
Strategic management is part of a larger planning process that includes budgeting, forecasting, capital allocation, and more. There is no right or wrong way to do strategic management — only guidelines. The basic phases are preparing for strategic planning, creating the strategic plan, and implementing that plan.
Strategic Plan example: (Municipal Government)- New York City Economic Development Plan. The New York City Economic Development Plan is a comprehensive 5-year strategic plan tailored for a municipal government. Spanning 68 pages, this plan underwent an extensive planning process with input from multiple stakeholders.
One industrial company assigns each business unit a color-coded grade—green, yellow, or red—based on the unit's success in executing the existing strategic plan. "Code red," for example, would slate a business unit for a strategy review.
In the normal course of operations, it can be easy to lose your grasp on what a strategic plan is (or should be). The best examples of good strategic plans all set clear priorities for an organization and focus employees and resources on established goals. While a strategic plan does share common elements with a business plan, or even execution plan, it is very distinct from both of those things.
The models for strategic planning in business include the following: Basic Model: The basic model establishes the company's mission, business objectives, and values. This model helps outline a company's steps to reach its goals. ... Let us go through the following examples to understand this planning process: Example #1. Suppose Jennifer ...
Importance and Benefits of Strategic Planning. A strategic plan is more than just a business tool, it also plays a key role in defining operational, cultural, and workplace ethics. Here are some of the key aspects of the importance of strategic planning: 1. Provides a unified goal.
Business Strategic Plan Example. Now let's look at a simple business strategic plan example. This is a strategic plan for a small construction company. 1. Mission, Vision & Core Values. Mission Statement: To build residential spaces that provide wellbeing for our clients.
1. Clarify the company's vision. One of the first steps in strategic planning is defining the vision, values and mission for the organization. The vision is the long-term objective of the business, and you should base it on ambitious but realistic goals. Values are beliefs that create the foundation for the company, and affect every part of ...
In this article, we will explore real-world examples of how strategic planning has been successfully implemented by businesses, and why it is an essential aspect of operations management. The first example we will look at is Apple Inc. Under the leadership of Steve Jobs, Apple implemented a strategic plan that focused on innovation and customer ...
Strategic Plan Example: The following is an example of applications of the Blue Ocean Model. Let's continue to assume that you are an organic soap business owner. Reconstruct market boundaries: Your business can define a new market space by creating a line of soaps that are only for sensitive skin.
A business strategy guides top-level executives, as well as departments, about what should and should not be done, according to the organization's core values. It helps everyone stay on the same page and with the same goals. 3. SWOT analysis. SWOT stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats.
Research and analysis of today's landscape identifies six key strategic concepts that set outperforming companies apart: Borrow someone's road, partner with a third party, reveal your strategy ...
However, enthusiasm for strategic business planning was revived in the 1990s and strategic planning remains relevant in modern business. ... For example, after implementing a strategy to improve customer service, a company may discover that it needs to adopt a new customer relationship management (CRM) software program in order to attain the ...
A strategic plan is a document written by leaders of an organization that enables the organization to be innovative, adaptable, and increase its competitive advantage for a time span of 3 to 10 ...
Strategic planning is the process in which a business defines and executes a long-term plan to achieve organizational objectives through analysis of present and the desired future state, the company's environment, and its existing gaps. This planning is done to respond to internal and external changes, so that the company remains competitive ...
Strategic human resource planning (SHRM) is a proactive process that aligns human resource capabilities with long-term business goals. In this guide, we'll go through the basics of why this foward-thinking approach is so important for resource planning success. This includes its definition, the main steps, and best business practices ...