- Search Search Please fill out this field.

What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans for May 2024 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How To Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
Setting Business Goals & Objectives: 4 Considerations

- 31 Oct 2023
Setting business goals and objectives is important to your company’s success. They create a roadmap to help you identify and manage risk , gain employee buy-in, boost team performance , and execute strategy . They’re also an excellent marker to measure your business’s performance.
Yet, meeting those goals can be difficult. According to an Economist study , 90 percent of senior executives from companies with annual revenues of one billion dollars or more admitted they failed to reach all their strategic goals because of poor implementation. In order to execute strategy, it’s important to first understand what’s attainable when developing organizational goals and objectives.
If you’re struggling to establish realistic benchmarks for your business, here’s an overview of what business goals and objectives are, how to set them, and what you should consider during the process.
Access your free e-book today.
What Are Business Goals and Objectives?
Business objectives dictate how your company plans to achieve its goals and address the business’s strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities. While your business goals may shift, your objectives won’t until there’s an organizational change .
Business goals describe where your company wants to end up and define your business strategy’s expected achievements.
According to the Harvard Business School Online course Strategy Execution , there are different types of strategic goals . Some may even push you and your team out of your comfort zone, yet are important to implement.
For example, David Rodriguez, global chief human resources officer at Marriott, describes in Strategy Execution the importance of stretch goals and “pushing people to not accept today's level of success as a final destination but as a starting point for what might be possible in the future.”
It’s important to strike a balance between bold and unrealistic, however. To do this, you must understand how to responsibly set your business goals and objectives.
Related: A Manager’s Guide To Successful Strategy Implementation
How to Set Business Goals and Objectives
While setting your company’s business goals and objectives might seem like a simple task, it’s important to remember that these goals shouldn’t be based solely on what you hope to achieve. There should be a correlation between your company’s key performance indicators (KPIs)—quantifiable success measures—and your business strategy to justify why the goal should, and needs to, be achieved.
This is often illustrated through a strategy map —an illustration of the cause-and-effect relationships that underpin your strategy. This valuable tool can help you identify and align your business goals and objectives.
“A strategy map gives everyone in your business a road map to understand the relationship between goals and measures and how they build on each other to create value,” says HBS Professor Robert Simons in Strategy Execution .
While this roadmap can be incredibly helpful in creating the right business goals and objectives, a balanced scorecard —a tool to help you track and assess non-financial measures—ensures they’re achievable through your current business strategy.
“Ask yourself, if I picked up a scorecard and examined the measures on that scorecard, could I infer what the business's strategy was,” Simon says. “If you've designed measures well, the answer should be yes.”
According to Strategy Execution , these measures are necessary to ensure your performance goals are achieved. When used in tandem, a balanced scorecard and strategy map can also tell you whether your goals and objectives will create value for you and your customers.
“The balanced scorecard combines the traditional financial perspective with additional perspectives that focus on customers, internal business processes, and learning and development,” Simons says.
These four perspectives are key considerations when setting your business goals and objectives. Here’s an overview of what those perspectives are and how they can help you set the right goals for your business.
4 Things to Consider When Setting Business Goals and Objectives
1. financial measures.
It’s important to ensure your plans and processes lead to desired levels of economic value. Therefore, some of your business goals and objectives should be financial.
Some examples of financial performance goals include:
- Cutting costs
- Increasing revenue
- Improving cash flow management
“Businesses set financial goals by building profit plans—one of the primary diagnostic control systems managers use to execute strategy,” Simons says in Strategy Execution . “They’re budgets drawn up for business units that have both revenues and expenses, and summarize the anticipated revenue inflows and expense outflows for a specified accounting period.”
Profit plans are essential when setting your business goals and objectives because they provide a critical link between your business strategy and economic value creation.
According to Simons, it’s important to ask three questions when profit planning:
- Does my business strategy generate enough profit to cover costs and reinvest in the business?
- Does my business generate enough cash to remain solvent through the year?
- Does my business create sufficient financial returns for investors?
By mapping out monetary value, you can weigh the cost of different strategies and how likely it is you’ll meet your company and investors’ financial expectations.
2. Customer Satisfaction
To ensure your business goals and objectives aid in your company’s long-term success, you need to think critically about your customers’ satisfaction. This is especially important in a world where customer reviews and testimonials are crucial to your organization’s success.
“Everything that's important to the business, we have a KPI and we measure it,” says Tom Siebel, founder, chairman, and CEO of C3.ai, in Strategy Execution . “And what could be more important than customer satisfaction?”
Unlike your company’s reputation, measuring customer satisfaction has a far more personal touch in identifying what customers love and how to capitalize on it through future strategic initiatives .
“We do anonymous customer satisfaction surveys every quarter to see how we're measuring up to our customer expectations,” Siebel says.
While this is one example, your customer satisfaction measures should reflect your desired market position and focus on creating additional value for your audience.
Related: 3 Effective Methods for Assessing Customer Needs
3. Internal Business Processes
Internal business processes is another perspective that should factor into your goal setting. It refers to several aspects of your business that aren’t directly affected by outside forces. Since many goals and objectives are driven by factors such as business competition and market shifts, considering internal processes can create a balanced business strategy.
“Our goals are balanced to make sure we’re holistically managing the business from a financial performance, quality assurance, innovation, and human talent perspective,” says Tom Polen, CEO and president of Becton Dickinson, in Strategy Execution .
According to Strategy Execution , internal business operations are broken down into the following processes:
- Operations management
- Customer management
While improvements to internal processes aren’t driven by economic value, these types of goals can still reap a positive return on investment.
“We end up spending much more time on internal business process goals versus financial goals,” Polen says. “Because if we take care of them, the financial goals will follow at the end of the day.”
4. Learning and Growth Opportunities
Another consideration while setting business goals and objectives is learning and growth opportunities for your team. These are designed to increase employee satisfaction and productivity.
According to Strategy Execution , learning and growth opportunities touch on three types of capital:
- Human: Your employees and the skills and knowledge required for them to meet your company’s goals
- Information: The databases, networks, and IT systems needed to support your long-term growth
- Organization: Ensuring your company’s leadership and culture provide people with purpose and clear objectives
Employee development is a common focus for learning and growth goals. Through professional development opportunities , your team will build valuable business skills and feel empowered to take more risks and innovate.
To create a culture of innovation , it’s important to ensure there’s a safe space for your team to make mistakes—and even fail.
“We ask that people learn from their mistakes,” Rodriguez says in Strategy Execution . “It's really important to us that people feel it’s safe to try new things. And all we ask is people extract their learnings and apply it to the next situation.”

Achieve Your Business Goals
Business goals aren’t all about your organization’s possible successes. It’s also about your potential failures.
“When we set goals, we like to imagine a bright future with our business succeeding,” Simons says in Strategy Execution . “But to identify your critical performance variables, you need to engage in an uncomfortable exercise and consider what can cause your strategy to fail.”
Anticipating potential failures isn’t easy. Enrolling in an online course—like HBS Online’s Strategy Execution —can immerse you in real-world case studies of past strategy successes and failures to help you better understand where these companies went wrong and how to avoid it in your business.
Do you need help setting your business goals and objectives? Explore Strategy Execution —one of our online strategy courses —and download our free strategy e-book to gain the insights to create a successful strategy.

About the Author
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Write a Business Plan, Step by Step

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
What is a business plan?
1. write an executive summary, 2. describe your company, 3. state your business goals, 4. describe your products and services, 5. do your market research, 6. outline your marketing and sales plan, 7. perform a business financial analysis, 8. make financial projections, 9. summarize how your company operates, 10. add any additional information to an appendix, business plan tips and resources.
A business plan outlines your business’s financial goals and explains how you’ll achieve them over the next three to five years. Here’s a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan that will offer a strong, detailed road map for your business.

ZenBusiness
A business plan is a document that explains what your business does, how it makes money and who its customers are. Internally, writing a business plan should help you clarify your vision and organize your operations. Externally, you can share it with potential lenders and investors to show them you’re on the right track.
Business plans are living documents; it’s OK for them to change over time. Startups may update their business plans often as they figure out who their customers are and what products and services fit them best. Mature companies might only revisit their business plan every few years. Regardless of your business’s age, brush up this document before you apply for a business loan .
» Need help writing? Learn about the best business plan software .
This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your business offers and a broad summary of your financial growth plans.
Though the executive summary is the first thing your investors will read, it can be easier to write it last. That way, you can highlight information you’ve identified while writing other sections that go into more detail.
» MORE: How to write an executive summary in 6 steps
Next up is your company description. This should contain basic information like:
Your business’s registered name.
Address of your business location .
Names of key people in the business. Make sure to highlight unique skills or technical expertise among members of your team.
Your company description should also define your business structure — such as a sole proprietorship, partnership or corporation — and include the percent ownership that each owner has and the extent of each owner’s involvement in the company.
Lastly, write a little about the history of your company and the nature of your business now. This prepares the reader to learn about your goals in the next section.
» MORE: How to write a company overview for a business plan

The third part of a business plan is an objective statement. This section spells out what you’d like to accomplish, both in the near term and over the coming years.
If you’re looking for a business loan or outside investment, you can use this section to explain how the financing will help your business grow and how you plan to achieve those growth targets. The key is to provide a clear explanation of the opportunity your business presents to the lender.
For example, if your business is launching a second product line, you might explain how the loan will help your company launch that new product and how much you think sales will increase over the next three years as a result.
» MORE: How to write a successful business plan for a loan
In this section, go into detail about the products or services you offer or plan to offer.
You should include the following:
An explanation of how your product or service works.
The pricing model for your product or service.
The typical customers you serve.
Your supply chain and order fulfillment strategy.
You can also discuss current or pending trademarks and patents associated with your product or service.
Lenders and investors will want to know what sets your product apart from your competition. In your market analysis section , explain who your competitors are. Discuss what they do well, and point out what you can do better. If you’re serving a different or underserved market, explain that.
Here, you can address how you plan to persuade customers to buy your products or services, or how you will develop customer loyalty that will lead to repeat business.
Include details about your sales and distribution strategies, including the costs involved in selling each product .
» MORE: R e a d our complete guide to small business marketing
If you’re a startup, you may not have much information on your business financials yet. However, if you’re an existing business, you’ll want to include income or profit-and-loss statements, a balance sheet that lists your assets and debts, and a cash flow statement that shows how cash comes into and goes out of the company.
Accounting software may be able to generate these reports for you. It may also help you calculate metrics such as:
Net profit margin: the percentage of revenue you keep as net income.
Current ratio: the measurement of your liquidity and ability to repay debts.
Accounts receivable turnover ratio: a measurement of how frequently you collect on receivables per year.
This is a great place to include charts and graphs that make it easy for those reading your plan to understand the financial health of your business.
This is a critical part of your business plan if you’re seeking financing or investors. It outlines how your business will generate enough profit to repay the loan or how you will earn a decent return for investors.
Here, you’ll provide your business’s monthly or quarterly sales, expenses and profit estimates over at least a three-year period — with the future numbers assuming you’ve obtained a new loan.
Accuracy is key, so carefully analyze your past financial statements before giving projections. Your goals may be aggressive, but they should also be realistic.
NerdWallet’s picks for setting up your business finances:
The best business checking accounts .
The best business credit cards .
The best accounting software .
Before the end of your business plan, summarize how your business is structured and outline each team’s responsibilities. This will help your readers understand who performs each of the functions you’ve described above — making and selling your products or services — and how much each of those functions cost.
If any of your employees have exceptional skills, you may want to include their resumes to help explain the competitive advantage they give you.
Finally, attach any supporting information or additional materials that you couldn’t fit in elsewhere. That might include:
Licenses and permits.
Equipment leases.
Bank statements.
Details of your personal and business credit history, if you’re seeking financing.
If the appendix is long, you may want to consider adding a table of contents at the beginning of this section.
How much do you need?
with Fundera by NerdWallet
We’ll start with a brief questionnaire to better understand the unique needs of your business.
Once we uncover your personalized matches, our team will consult you on the process moving forward.
Here are some tips to write a detailed, convincing business plan:
Avoid over-optimism: If you’re applying for a business bank loan or professional investment, someone will be reading your business plan closely. Providing unreasonable sales estimates can hurt your chances of approval.
Proofread: Spelling, punctuation and grammatical errors can jump off the page and turn off lenders and prospective investors. If writing and editing aren't your strong suit, you may want to hire a professional business plan writer, copy editor or proofreader.
Use free resources: SCORE is a nonprofit association that offers a large network of volunteer business mentors and experts who can help you write or edit your business plan. The U.S. Small Business Administration’s Small Business Development Centers , which provide free business consulting and help with business plan development, can also be a resource.
On a similar note...
Find small-business financing
Compare multiple lenders that fit your business

Home > Business > Business Startup
How To Write a Business Plan

We are committed to sharing unbiased reviews. Some of the links on our site are from our partners who compensate us. Read our editorial guidelines and advertising disclosure .

Starting a business is a wild ride, and a solid business plan can be the key to keeping you on track. A business plan is essentially a roadmap for your business — outlining your goals, strategies, market analysis and financial projections. Not only will it guide your decision-making, a business plan can help you secure funding with a loan or from investors .
Writing a business plan can seem like a huge task, but taking it one step at a time can break the plan down into manageable milestones. Here is our step-by-step guide on how to write a business plan.
Table of contents
- Write your executive summary
- Do your market research homework
- Set your business goals and objectives
- Plan your business strategy
- Describe your product or service
- Crunch the numbers
- Finalize your business plan

By signing up I agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
Step 1: Write your executive summary
Though this will be the first page of your business plan , we recommend you actually write the executive summary last. That’s because an executive summary highlights what’s to come in the business plan but in a more condensed fashion.
An executive summary gives stakeholders who are reading your business plan the key points quickly without having to comb through pages and pages. Be sure to cover each successive point in a concise manner, and include as much data as necessary to support your claims.
You’ll cover other things too, but answer these basic questions in your executive summary:
- Idea: What’s your business concept? What problem does your business solve? What are your business goals?
- Product: What’s your product/service and how is it different?
- Market: Who’s your audience? How will you reach customers?
- Finance: How much will your idea cost? And if you’re seeking funding, how much money do you need? How much do you expect to earn? If you’ve already started, where is your revenue at now?
Step 2: Do your market research homework
The next step in writing a business plan is to conduct market research . This involves gathering information about your target market (or customer persona), your competition, and the industry as a whole. You can use a variety of research methods such as surveys, focus groups, and online research to gather this information. Your method may be formal or more casual, just make sure that you’re getting good data back.
This research will help you to understand the needs of your target market and the potential demand for your product or service—essential aspects of starting and growing a successful business.
Step 3: Set your business goals and objectives
Once you’ve completed your market research, you can begin to define your business goals and objectives. What is the problem you want to solve? What’s your vision for the future? Where do you want to be in a year from now?
Use this step to decide what you want to achieve with your business, both in the short and long term. Try to set SMART goals—specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound benchmarks—that will help you to stay focused and motivated as you build your business.
Step 4: Plan your business strategy
Your business strategy is how you plan to reach your goals and objectives. This includes details on positioning your product or service, marketing and sales strategies, operational plans, and the organizational structure of your small business.
Make sure to include key roles and responsibilities for each team member if you’re in a business entity with multiple people.
Step 5: Describe your product or service
In this section, get into the nitty-gritty of your product or service. Go into depth regarding the features, benefits, target market, and any patents or proprietary tech you have. Make sure to paint a clear picture of what sets your product apart from the competition—and don’t forget to highlight any customer benefits.
Step 6: Crunch the numbers
Financial analysis is an essential part of your business plan. If you’re already in business that includes your profit and loss statement , cash flow statement and balance sheet .
These financial projections will give investors and lenders an understanding of the financial health of your business and the potential return on investment.
You may want to work with a financial professional to ensure your financial projections are realistic and accurate.
Step 7: Finalize your business plan
Once you’ve completed everything, it's time to finalize your business plan. This involves reviewing and editing your plan to ensure that it is clear, concise, and easy to understand.
You should also have someone else review your plan to get a fresh perspective and identify any areas that may need improvement. You could even work with a free SCORE mentor on your business plan or use a SCORE business plan template for more detailed guidance.
Compare the Top Small-Business Banks
Data effective 1/10/23. At publishing time, rates, fees, and requirements are current but are subject to change. Offers may not be available in all areas.
The takeaway
Writing a business plan is an essential process for any forward-thinking entrepreneur or business owner. A business plan requires a lot of up-front research, planning, and attention to detail, but it’s worthwhile. Creating a comprehensive business plan can help you achieve your business goals and secure the funding you need.
Related content
- 5 Best Business Plan Software and Tools in 2023 for Your Small Business
- How to Get a Business License: What You Need to Know
- What Is a Cash Flow Statement?
Best Small Business Loans
5202 W Douglas Corrigan Way Salt Lake City, UT 84116
Accounting & Payroll
Point of Sale
Payment Processing
Inventory Management
Human Resources
Other Services
Best Inventory Management Software
Best Small Business Accounting Software
Best Payroll Software
Best Mobile Credit Card Readers
Best POS Systems
Best Tax Software
Stay updated on the latest products and services anytime anywhere.
By signing up, you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
Disclaimer: The information featured in this article is based on our best estimates of pricing, package details, contract stipulations, and service available at the time of writing. All information is subject to change. Pricing will vary based on various factors, including, but not limited to, the customer’s location, package chosen, added features and equipment, the purchaser’s credit score, etc. For the most accurate information, please ask your customer service representative. Clarify all fees and contract details before signing a contract or finalizing your purchase.
Our mission is to help consumers make informed purchase decisions. While we strive to keep our reviews as unbiased as possible, we do receive affiliate compensation through some of our links. This can affect which services appear on our site and where we rank them. Our affiliate compensation allows us to maintain an ad-free website and provide a free service to our readers. For more information, please see our Privacy Policy Page . |
© Business.org 2024 All Rights Reserved.
- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Small Business Guide
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- For Subscribers
- Write for Entrepreneur
- Entrepreneur Store
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
Plan Your Business Plan Before you put pen to paper, find out how to assess your business's goals and objectives.
You've decided to write a business plan, and you're ready to get started. Congratulations. You've just greatly increased the chances that your business venture will succeed. But before you start drafting your plan, you need to--you guessed it--plan your draft.
One of the most important reasons to plan your plan is that you may be held accountable for the projections and proposals it contains. That's especially true if you use your plan to raise money to finance your company. Let's say you forecast opening four new locations in the second year of your retail operation. An investor may have a beef if, due to circumstances you could have foreseen, you only open two. A business plan can take on a life of its own, so thinking a little about what you want to include in your plan is no more than common prudence.
Second, as you'll soon learn if you haven't already, business plans can be complicated documents. As you draft your plan, you'll be making lots of decisions on serious matters, such as what strategy you'll pursue, as well as less important ones, like what color paper to print it on. Thinking about these decisions in advance is an important way to minimize the time you spend planning your business and maximize the time you spend generating income.
To sum up, planning your plan will help control your degree of accountability and reduce time-wasting indecision. To plan your plan, you'll first need to decide what your goals and objectives in business are. As part of that, you'll assess the business you've chosen to start, or are already running, to see what the chances are that it will actually achieve those ends. Finally, you'll take a look at common elements of most plans to get an idea of which ones you want to include and how each will be treated.
Determine Your Objectives Close your eyes. Imagine that the date is five years from now. Where do you want to be? Will you be running a business that hasn't increased significantly in size? Will you command a rapidly growing empire? Will you have already cashed out and be relaxing on a beach somewhere, enjoying your hard-won gains?
Answering these questions is an important part of building a successful business plan. In fact, without knowing where you're going, it's not really possible to plan at all.
Now is a good time to free-associate a little bit--to let your mind roam, exploring every avenue that you'd like your business to go down. Try writing a personal essay on your business goals. It could take the form of a letter to yourself, written from five years in the future, describing all you have accomplished and how it came about.
As you read such a document, you may make a surprising discovery, such as that you don't really want to own a large, fast-growing enterprise but would be content with a stable small business. Even if you don't learn anything new, though, getting a firm handle on your goals and objectives is a big help in deciding how you'll plan your business.
Goals and Objectives Checklist If you're having trouble deciding what your goals and objectives are, here are some questions to ask yourself:
- How determined am I to see this succeed?
- Am I willing to invest my own money and work long hours for no pay, sacrificing personal time and lifestyle, maybe for years?
- What's going to happen to me if this venture doesn't work out?
- If it does succeed, how many employees will this company eventually have?
- What will be its annual revenues in a year? Five years?
- What will be its market share in that time frame?
- Will it be a niche marketer, or will it sell a broad spectrum of good and services?
- What are my plans for geographic expansion? Local? National? Global?
- Am I going to be a hands-on manager, or will I delegate a large proportion of tasks to others?
- If I delegate, what sorts of tasks will I share? Sales? Technical? Others?
- How comfortable am I taking direction from others? Could I work with partners or investors who demand input into the company's management?
- Is it going to remain independent and privately owned, or will it eventually be acquired or go public?
Your Financing Goals
It doesn't necessarily take a lot of money to make a lot of money, but it does take some. That's especially true if, as part of examining your goals and objectives, you envision very rapid growth.
Energetic, optimistic entrepreneurs often tend to believe that sales growth will take care of everything, that they'll be able to fund their own growth by generating profits. However, this is rarely the case, for one simple reason: You usually have to pay your own suppliers before your customers pay you. This cash flow conundrum is the reason so many fast-growing companies have to seek bank financing or equity sales to finance their growth. They are literally growing faster than they can afford.
Start by asking yourself what kinds of financing you're likely to need--and what you'd be willing to accept. It's easy when you're short of cash, or expect to be short of cash, to take the attitude that almost any source of funding is just fine. But each kind of financing has different characteristics that you should take into consideration when planning your plan. These characteristics take three primary forms:
- First, there's the amount of control you'll have to surrender. An equal partner may, quite naturally, demand approximately equal control. Venture capitalists often demand significant input into management decisions by, for instance, placing one or more people on your board of directors. Angel investors may be very involved or not involved at all, depending on their personal style. Bankers, at the other end of the scale, are likely to offer no advice whatsoever as long as you make payments of principal and interest on time and are not in violation of any other terms of your loan.
- You should also consider the amount of money you're likely to need. Any amount less than several million dollars is too small to be considered for a standard initial public offering of stock, for example. Venture capital investors are most likely to invest amounts of $250,000 to $3 million. On the other hand, only the richest angel investor will be able to provide more than a few hundred thousand dollars, if that.
Almost any source of funds, from a bank to a factor, has some guidelines about the size of financing it prefers. Anticipating the size of your needs now will guide you in preparing your plan.
- The third consideration is cost. This can be measured in terms of interest rates and shares of ownership as well as in time, paperwork and plain old hassle.
How Will You Use Your Plan
Believe it or not, part of planning your plan is planning what you'll do with it. No, we haven't gone crazy--at least not yet. A business plan can be used for several things, from monitoring your company's progress toward goals to enticing key employees to join your firm. Deciding how you intend to use yours is an important part of preparing to write it.
Do you intend to use your plan to help you raise money? In that case, you'll have to focus very carefully on the executive summary, the management, and marketing and financial aspects. You'll need to have a clearly focused vision of how your company is going to make money. If you're looking for a bank loan, you'll need to stress your ability to generate sufficient cash flow to service loans. Equity investors, especially venture capitalists, must be shown how they can cash out of your company and generate a rate of return they'll find acceptable.
Do you intend to use your plan to attract talented employees? Then you'll want to emphasize such things as stock options and other aspects of compensation as well as location, work environment, corporate culture and opportunities for growth and advancement.
Do you anticipate showing your plan to suppliers to demonstrate that you're a worthy customer? A solid business plan may convince a supplier of some precious commodity to favor you over your rivals. It may also help you arrange supplier credit. You may want to stress your blue-ribbon customer list and spotless record of repaying trade debts in this plan.
Assessing Your Company's Potential
For most of us, unfortunately, our desires about where we would like to go aren't as important as our businesses' ability to take us there. Put another way, if you choose the wrong business, you're going nowhere.
Luckily, one of the most valuable uses of a business plan is to help you decide whether the venture you have your heart set on is really likely to fulfill your dreams. Many, many business ideas never make it past the planning stage because their would-be founders, as part of a logical and coherent planning process, test their assumptions and find them wanting.
Test your idea against at least two variables. First, financial, to make sure this business makes economic sense. Second, lifestyle, because who wants a successful business that they hate?
Answer the following questions to help you outline your company's potential. There are no wrong answers. The objective is simply to help you decide how well your proposed venture is likely to match up with your goals and objectives.
- What initial investment will the business require?
- How much control are you willing to relinquish to investors?
- When will the business turn a profit?
- When can investors, including you, expect a return on their money?
- What are the projected profits of the business over time?
- Will you be able to devote yourself full time to the business, financially?
- What kind of salary or profit distribution can you expect to take home?
- What are the chances the business will fail?
- What will happen if it does?
- Where are you going to live?
- What kind of work are you going to be doing?
- How many hours will you be working?
- Will you be able to take vacations?
- What happens if you get sick?
- Will you earn enough to maintain your lifestyle?
- Does your family understand and agree with the sacrifices you envision?
Sources: The Small Business Encyclopedia , Business Plans Made Easy, Start Your Own Business and Entrepreneur magazine.
Continue on to the next section of our Business Plan How-To >> Elements of a Business Plan
Want to be an Entrepreneur Leadership Network contributor? Apply now to join.
Editor's Pick Red Arrow
- This Mother and Daughter Were 'Kind of Fringe Weirdos' When They Started an Uncommon Business in Their Garage. Now They're in Major Retailers — and Victoria Beckham Is a Fan.
- Lock A Leadership Shortage Is Coming. Here's What Needs to Happen to Prevent It.
- Lock The Author of 'Million Dollar Weekend' Says This Is the Only Difference Between You and the Many 'Very, Very Dumb People' Making a Lot of Money
- What the NLRB Appeal of the Expanded Joint Employer Rule Judgment Means for Your Business
- Lock 12 Books That Self-Made Millionaires Swear By
- The Sweet Side Hustle She Started in an Old CVS Made $800,000 in One Year. Now She's Repeating the Success With Her Daughter — and They've Already Exceeded 8 Figures.
Most Popular Red Arrow
Want to start a simple business that helps the planet after 'one night's worth of research,' he started an eco-friendly gig and now makes $200k a year.
Environmentally-conscious laws are picking up steam across the country. When one went into effect in Zach Cavacas's home state, he saw a lucrative business opportunity. Chances are, a similar law is coming to your state, or is already there.
Jack Dorsey Explains Bluesky Exit: 'Literally Repeating All the Mistakes We Made' at Twitter
Dorsey left the Bluesky board and deleted his account earlier this week.
Warren Buffett Had to Work From His iPhone After Telephone Lines Went Down at Berkshire Hathaway: 'I'm Glad We Didn't Sell All of Our Apple'
Berkshire sold around $20 billion worth of Apple recently.
My Startup Couldn't Raise VC Funding, So We Became Profitable. Here's How We Did It — And How You Can Too.
Four months ago, my startup reached profitability for the first time. It came after more than a year of active work and planning, and here's what it took.
63 Small Business Ideas to Start in 2024
We put together a list of the best, most profitable small business ideas for entrepreneurs to pursue in 2024.
McDonald's Is Responding to Sky-High Fast Food Prices By Rolling Out a Much Cheaper Value Meal: Report
The news comes as the chain looks to redirect back to customer "affordability."
Successfully copied link
What is a Business Plan? Definition and Resources

9 min. read
Updated May 10, 2024
If you’ve ever jotted down a business idea on a napkin with a few tasks you need to accomplish, you’ve written a business plan — or at least the very basic components of one.
The origin of formal business plans is murky. But they certainly go back centuries. And when you consider that 20% of new businesses fail in year 1 , and half fail within 5 years, the importance of thorough planning and research should be clear.
But just what is a business plan? And what’s required to move from a series of ideas to a formal plan? Here we’ll answer that question and explain why you need one to be a successful business owner.
- What is a business plan?

A business plan lays out a strategic roadmap for any new or growing business.
Any entrepreneur with a great idea for a business needs to conduct market research , analyze their competitors , validate their idea by talking to potential customers, and define their unique value proposition .
The business plan captures that opportunity you see for your company: it describes your product or service and business model , and the target market you’ll serve.
It also includes details on how you’ll execute your plan: how you’ll price and market your solution and your financial projections .
Reasons for writing a business plan
If you’re asking yourself, ‘Do I really need to write a business plan?’ consider this fact:
Companies that commit to planning grow 30% faster than those that don’t.
Creating a business plan is crucial for businesses of any size or stage. It helps you develop a working business and avoid consequences that could stop you before you ever start.
If you plan to raise funds for your business through a traditional bank loan or SBA loan , none of them will want to move forward without seeing your business plan. Venture capital firms may or may not ask for one, but you’ll still need to do thorough planning to create a pitch that makes them want to invest.
But it’s more than just a means of getting your business funded . The plan is also your roadmap to identify and address potential risks.
It’s not a one-time document. Your business plan is a living guide to ensure your business stays on course.
Related: 14 of the top reasons why you need a business plan
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
What research shows about business plans
Numerous studies have established that planning improves business performance:
- 71% of fast-growing companies have business plans that include budgets, sales goals, and marketing and sales strategies.
- Companies that clearly define their value proposition are more successful than those that can’t.
- Companies or startups with a business plan are more likely to get funding than those without one.
- Starting the business planning process before investing in marketing reduces the likelihood of business failure.
The planning process significantly impacts business growth for existing companies and startups alike.
Read More: Research-backed reasons why writing a business plan matters
When should you write a business plan?
No two business plans are alike.
Yet there are similar questions for anyone considering writing a plan to answer. One basic but important question is when to start writing it.
A Harvard Business Review study found that the ideal time to write a business plan is between 6 and 12 months after deciding to start a business.
But the reality can be more nuanced – it depends on the stage a business is in, or the type of business plan being written.
Ideal times to write a business plan include:
- When you have an idea for a business
- When you’re starting a business
- When you’re preparing to buy (or sell)
- When you’re trying to get funding
- When business conditions change
- When you’re growing or scaling your business
Read More: The best times to write or update your business plan
How often should you update your business plan?
As is often the case, how often a business plan should be updated depends on your circumstances.
A business plan isn’t a homework assignment to complete and forget about. At the same time, no one wants to get so bogged down in the details that they lose sight of day-to-day goals.
But it should cover new opportunities and threats that a business owner surfaces, and incorporate feedback they get from customers. So it can’t be a static document.
Related Reading: 5 fundamental principles of business planning
For an entrepreneur at the ideation stage, writing and checking back on their business plan will help them determine if they can turn that idea into a profitable business .
And for owners of up-and-running businesses, updating the plan (or rewriting it) will help them respond to market shifts they wouldn’t be prepared for otherwise.
It also lets them compare their forecasts and budgets to actual financial results. This invaluable process surfaces where a business might be out-performing expectations and where weak performance may require a prompt strategy change.
The planning process is what uncovers those insights.
Related Reading: 10 prompts to help you write a business plan with AI
- How long should your business plan be?
Thinking about a business plan strictly in terms of page length can risk overlooking more important factors, like the level of detail or clarity in the plan.
Not all of the plan consists of writing – there are also financial tables, graphs, and product illustrations to include.
But there are a few general rules to consider about a plan’s length:
- Your business plan shouldn’t take more than 15 minutes to skim.
- Business plans for internal use (not for a bank loan or outside investment) can be as short as 5 to 10 pages.
A good practice is to write your business plan to match the expectations of your audience.
If you’re walking into a bank looking for a loan, your plan should match the formal, professional style that a loan officer would expect . But if you’re writing it for stakeholders on your own team—shorter and less formal (even just a few pages) could be the better way to go.
The length of your plan may also depend on the stage your business is in.
For instance, a startup plan won’t have nearly as much financial information to include as a plan written for an established company will.
Read More: How long should your business plan be?
What information is included in a business plan?
The contents of a plan business plan will vary depending on the industry the business is in.
After all, someone opening a new restaurant will have different customers, inventory needs, and marketing tactics to consider than someone bringing a new medical device to the market.
But there are some common elements that most business plans include:
- Executive summary: An overview of the business operation, strategy, and goals. The executive summary should be written last, despite being the first thing anyone will read.
- Products and services: A description of the solution that a business is bringing to the market, emphasizing how it solves the problem customers are facing.
- Market analysis: An examination of the demographic and psychographic attributes of likely customers, resulting in the profile of an ideal customer for the business.
- Competitive analysis: Documenting the competitors a business will face in the market, and their strengths and weaknesses relative to those competitors.
- Marketing and sales plan: Summarizing a business’s tactics to position their product or service favorably in the market, attract customers, and generate revenue.
- Operational plan: Detailing the requirements to run the business day-to-day, including staffing, equipment, inventory, and facility needs.
- Organization and management structure: A listing of the departments and position breakdown of the business, as well as descriptions of the backgrounds and qualifications of the leadership team.
- Key milestones: Laying out the key dates that a business is projected to reach certain milestones , such as revenue, break-even, or customer acquisition goals.
- Financial plan: Balance sheets, cash flow forecast , and sales and expense forecasts with forward-looking financial projections, listing assumptions and potential risks that could affect the accuracy of the plan.
- Appendix: All of the supporting information that doesn’t fit into specific sections of the business plan, such as data and charts.
Read More: Use this business plan outline to organize your plan
- Different types of business plans
A business plan isn’t a one-size-fits-all document. There are numerous ways to create an effective business plan that fits entrepreneurs’ or established business owners’ needs.
Here are a few of the most common types of business plans for small businesses:
- One-page plan : Outlining all of the most important information about a business into an adaptable one-page plan.
- Growth plan : An ongoing business management plan that ensures business tactics and strategies are aligned as a business scales up.
- Internal plan : A shorter version of a full business plan to be shared with internal stakeholders – ideal for established companies considering strategic shifts.
Business plan vs. operational plan vs. strategic plan
- What questions are you trying to answer?
- Are you trying to lay out a plan for the actual running of your business?
- Is your focus on how you will meet short or long-term goals?
Since your objective will ultimately inform your plan, you need to know what you’re trying to accomplish before you start writing.
While a business plan provides the foundation for a business, other types of plans support this guiding document.
An operational plan sets short-term goals for the business by laying out where it plans to focus energy and investments and when it plans to hit key milestones.
Then there is the strategic plan , which examines longer-range opportunities for the business, and how to meet those larger goals over time.
Read More: How to use a business plan for strategic development and operations
- Business plan vs. business model
If a business plan describes the tactics an entrepreneur will use to succeed in the market, then the business model represents how they will make money.
The difference may seem subtle, but it’s important.
Think of a business plan as the roadmap for how to exploit market opportunities and reach a state of sustainable growth. By contrast, the business model lays out how a business will operate and what it will look like once it has reached that growth phase.
Learn More: The differences between a business model and business plan
- Moving from idea to business plan
Now that you understand what a business plan is, the next step is to start writing your business plan .
The best way to start is by reviewing examples and downloading a business plan template. These resources will provide you with guidance and inspiration to help you write a plan.
We recommend starting with a simple one-page plan ; it streamlines the planning process and helps you organize your ideas. However, if one page doesn’t fit your needs, there are plenty of other great templates available that will put you well on your way to writing a useful business plan.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Tim Berry is the founder and chairman of Palo Alto Software , a co-founder of Borland International, and a recognized expert in business planning. He has an MBA from Stanford and degrees with honors from the University of Oregon and the University of Notre Dame. Today, Tim dedicates most of his time to blogging, teaching and evangelizing for business planning.

Table of Contents
- Reasons to write a business plan
- Business planning research
- When to write a business plan
- When to update a business plan
- Information to include
- Business vs. operational vs. strategic plans
Related Articles

13 Min. Read
How to Write an Online Fitness Business Plan

12 Min. Read
Free Amazon FBA Business Plan PDF [2024 Template + Sample Plan]

8 Min. Read
How to Format a Business Plan in 8 Simple Steps

6 Min. Read
How to Write Your Business Plan Cover Page + Template
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} AI that works. Coming June 5, Asana redefines work management—again. .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Get early access .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Product overview
- All features
- App integrations
CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana Intelligence
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Marketing strategic planning
- Request tracking
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- View all uses arrow-right icon
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- What's new Learn about the latest and greatest from Asana
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Support Need help? Contact the Asana support team
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- 22 types of business objectives to meas ...
22 types of business objectives to measure success

Clear business objectives help you achieve your mission statement and long-term company vision. These objectives can range from financial objectives to organization specific objectives. Take a look at 22 types of business objectives you can set—plus, learn when to use business objectives vs. 14 other goal frameworks.
Whether you work at a small business, a start up, or as a team lead at a larger enterprise, as a key business owner, you’re responsible for identifying the business objectives that will help your organization hit its long-term goals. Setting goals and strategic objectives is the best way to know where you’re going and how to get there.
In this article, learn about 22 different types of business objectives and how to make them achievable. Then, take a look at the 15 different types of goals you can set, depending on why you’re setting those goals.
What is a business objective?
Business objectives are the results you are aiming to achieve in order to accomplish your longer-term company vision. Think of business objectives as metrics to measure your overall business success.
Hitting your business objectives means you’re on the path towards achieving larger company goals. As such, business objectives should focus on large-scale organizational impact. Good business objectives are measurable, specific, and time-bound.
22 types of business objectives
Set business objectives based on factors that measure and impact your organization’s success. For example, you might set the following business objectives:
Financial business objectives
1. Profitability: A profitability-focused business objective is important if your company is relying on outside investors. Achieving—and maintaining—profitability ensures your long-term success so you can make progress towards your overall company mission.
2. Revenue: Revenue-focused business objectives help you balance your income with your costs in order to stay in business. You might set business objectives to achieve a certain annual revenue goal, or to increase revenue by a certain percentage over a period of time.
3. Costs: Costs refer to how much money you’re spending on your business. Reducing costs can help you increase revenue and achieve profitability. Business objectives related to cost can help you control production or operations cost to improve your business’s financial performance.
4. Cash flow: Cash flow refers to the money moving into and out of your business. Cash flow can be positive—when you’re making more than you’re spending—or negative—when you’re spending more than you’re making. Similar to profitability, a cash flow-oriented business objective can help set you up for long term financial success.
5. Sustainable growth: In order to grow as a business, you need to grow sustainably. Setting business objectives around sustainable growth can help you plan your financial projections, employee costs, and other financial considerations.
Customer-centric business objectives
6. Competitive positioning: A big element of your business strategy is thinking about how your product or service compares to others in the same market. By setting a business objective focused on competitive positioning, you can ensure your product or service reaches parity with what’s expected in the market, or use competitive positioning to outdo your competitors in a key area.
8. Customer satisfaction: In order to succeed as a business, you need happy customers. Focusing on a customer satisfaction-based business objective can help you better serve your customers. Depending on the business objective, this might focus on a customer advocacy program, a better help desk, or something similarly customer-facing.
9. Brand awareness: Your brand is what makes your organization stand out from the crowd. Brand awareness is an important way to understand how your customers think of your brand, and how aware they are of your distinct brand vs. your competitors. Understanding—and increasing—brand awareness is a key part of your long-term marketing strategy .
10. Sales: You’ll often find business objectives related to improving or refining the sales cycle. This could include anything from reducing customer acquisition cost (CAC), developing better lead tracking, increasing cross-selling, or something else.
11. Churn: In business, your churn rate refers to how many customers you lose over a set period of time. Reducing churn is a great way to increase your revenue and ensure your customers are satisfied with the product or service you provide.
Internal business objectives
12. Employee satisfaction and engagement: Part of your business is how your employees feel about working there, too. Increasing employee satisfaction and engagement leads to happier employees, reduced burnout , and more effective teams.
13. Employee retention: A key internal business objective is how long your employees spend at your company. Increasing tenure and reducing turnover can help you achieve more complex projects with knowledgeable employees.
14. Company growth: In order to grow your business, you also need to grow the number of people you employ. Growing your company sustainably can be difficult—which is why businesses often set company growth as a key business objective.
15. Organizational culture: Organizational culture is the ideals, values, and group norms that shape how team members interact within your company. Good culture drives employee engagement and increases retention, which is one of the key reasons so many companies set organizational culture-focused business objectives.
16. Change management: Smoothly implement large-scale organizational change with change management . Though you typically won’t see organizations set this type of business objective year after year, it can be a helpful objective to set if you have large changes on the horizon.
17. Productivity: At Asana, we don’t think of productivity as “doing the most you can,” but rather as a way to optimize your time and get your best work done. Increasing employee productivity can help your teams achieve their high-impact work more efficiently.
18. Employee effectiveness: Teams don’t just need to be efficient—they also need to know the right things to work on. The best companies aim for efficiency and effectiveness—which is where an effectiveness-based business objective comes into play. To learn more, read our article about the difference between efficiency and effectiveness .
19. Diversity and inclusion: A big part of a welcoming company culture is making sure your employees feel like they belong. Investing in diversity and inclusion programs can help your business be more welcoming to your current and potential employees.
Regulation related business objectives
20. Quality control: Implementing quality control measures as a business objective can help you ensure your product or services are at the level you want them to be. This in turn leads to better customer relationships and overall increase in revenue.
21. Compliance: If your business has any compliance needs to meet in the near future, setting those compliance requirements as a business objective will ensure you hit your targets on time.
22. Sustainability or waste reduction: Some businesses set business objectives to reduce waste or increase sustainability. While this may not directly impact your business, proving that you’re environmentally minded can help you reach specific audiences you’re targeting.
Which goal framework is right for you?
Figuring out exactly what type of goal you need to set can be tricky. Each goal framework is slightly different—and implementing the right one can help you achieve success.
The type of goal you set will depend on the business activities you’re running and the specific goals you have. If your goals have a set time frame, you may want to go with short-term objectives, whereas larger goals have their own unique frameworks.
If you’re not sure where to start, check out these 15 goal frameworks for different situations:
1. Business objectives: Set goals based on operating factors that impact your company’s long-term success.
2. Business plan : Also called a business strategy plan. Document your business’ goals and plan out how you’ll get there.
3. Vision statement : Set an organization-wide North Star.
4. Big Hairy Audacious Goals (BHAGs) : Set organization-sized stretch goals .
5. Company values : Align your team around core principles.
6. Strategic plan : Clarify your three to five year company goals during the strategic planning process.
7. Strategic goal : Set the goals you want to achieve by the end of your strategic plan.
8. Critical success factors : Clarify the high-level goals you need to achieve in order to achieve your strategic goals.
9. Strategic management : Execute against your strategic plan in order to achieve your company goals.
10. Business goals : Set predetermined targets to achieve in a set period of time.
11. Objectives and key results (OKRs) : Set and communicate annual company goals.
12. Key performance indicators (KPIs) : Set quantitative goals.
13. Project objectives : Share what you want to achieve by the end of a project.
14. Project deliverables : Identify a project’s output.
15. Project milestones : Mark specific checkpoints along a project’s timeline.
More goal setting resources
Clear goals are critical to keep your organization functioning. In addition to business objectives, check out our goal setting resource hub for tips on setting goals and achieving high-impact results. Then when you’re ready, get started with Asana for goal tracking. With Asana , you can connect your company goals to the work that supports them—all in one place.
Related resources

7 steps to complete a social media audit (with template)

How to accomplish big things with long-term goals

What are objectives and key results (OKRs)?

Fix these common onboarding challenges to boost productivity
How to Set, Track, and Achieve Business Objectives with 60 Examples
By Kate Eby | April 10, 2023
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
Businesses that set objectives make better decisions. Business objectives allow companies to focus their efforts, track progress, and visualize future success. We’ve worked with experts to create the most comprehensive guide to business objectives.
Included in this article, you’ll find the differences between business objectives and business goals , the four main business objectives , and the benefits of setting business objectives . Plus, find 60 examples of business objectives , which you can download in Microsoft Word.
What Is a Business Objective?
A business objective is a specific, measurable outcome that a company works to achieve. Company leaders set business objectives that help the organization meet its long-term goals. Business objectives should be recorded so that teams can easily access them.
Business objectives cover many different factors of a company’s success, such as financial health, operations, productivity, and growth.
One easy way to make sure that you are setting the right business objectives is to follow the SMART goal framework . SMART objectives are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
To learn about setting project objectives using the SMART framework, see this comprehensive guide to writing SMART project objectives .
Business Objectives vs. Business Goal
A business goal is a broad, long-term outcome that a company works toward. Goals usually inform which strategies that department leaders will implement. A business objective , however, is a specific, short-term outcome or action that helps the company achieve long-term goals.
Although the terms are often used interchangeably, goals and objectives are not the same . In general, goals are broad in scope and describe an outcome, while objectives are narrow in scope and describe a specific action or step.
While these differences are important to understand, many of the common frameworks for successful goal-setting — such as SMART, objectives and key results ( OKRs ), and management by objectives (MBO) — can be useful when writing business objectives.
When deciding on objectives for a team or department, keep in mind the overarching goals of a business. Each objective should move the company closer to its long-term goals.
Project Goals and Objectives Template
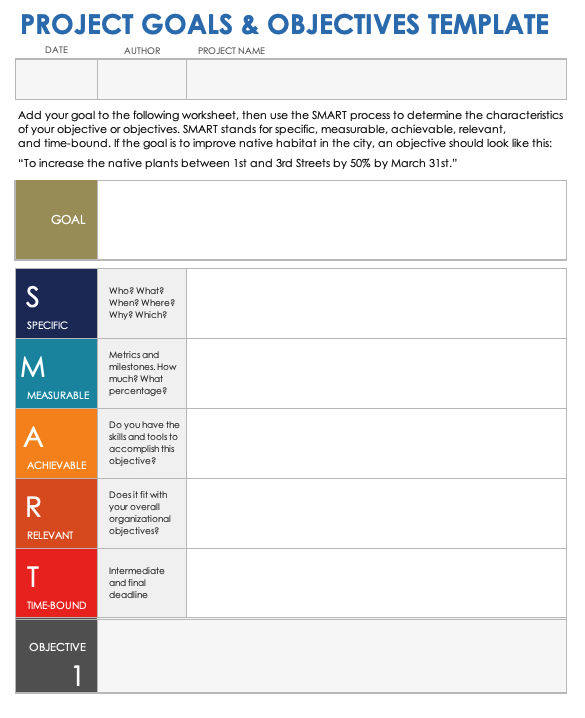
Download the Project Goals and Objectives Template for Excel | Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF
Use this free, printable template to learn how to break down project goals into individual objectives using the SMART framework. Write the primary goal at the top of the worksheet, then follow the SMART process to create one or more specific objectives that will help you achieve that goal.
For resources to help with setting and tracking goals at your company, see this all-inclusive list of goal tracking and setting templates .
What Are the Four Main Business Objectives?
The four main business objectives are economic, social, human, and organic. Each can help a business ensure their prolonged health and growth. For example, human objectives refer to employees’ well-being, while economic objectives refer to the company’s financial health.
These are the four main business objectives:
- Example: Reduce spending on paid advertisements by 20 percent.
- Example: Reduce average customer wait times from eight minutes to four minutes.
- Example: Hire two new chemical engineers by the end of Q2.
- Example: Improve the efficiency of a specific software product by 15 percent.
Types of Business Objectives
There are many types of business objectives beyond the main four. These range from regulation objectives to environmental objectives to municipal objectives. For example, a global objective might be to distribute a product to a new country.
In addition to economic, social, human, and organic objectives, here are some other types of business objectives companies might set:
- Regulatory: These objectives relate to compliance requirements, such as meeting quality standards or conducting internal audits.
- National: These objectives relate to a company’s place in and how they contribute to the country they operate in, such as promoting social justice causes and creating employment opportunities.
- Global: These objectives relate to a company’s place in and its contribution to many countries, such as improving living standards and responding to global demands for products and services.
- Environmental: These objectives relate to a company’s environmental impact, such as reducing chemical waste or making eco-friendly investments.
- Healthcare: These objectives relate to the health and well-being of a population, whether within or outside an organization. These objectives might be improving healthcare benefit options for employees or refining a drug so that it has fewer side effects.
The Importance of Having Business Objectives
Teams need business objectives to stay focused on the company’s long-term goals. Business objectives help individual employees understand how their roles contribute to the larger mission of the organization. Setting business objectives facilitates effective planning.
Here are some benefits to setting business objectives:

- Develops Leadership: Company leaders are more effective when they have a clear vision and can delegate tasks to make it a reality. Setting objectives is a great way to improve one’s leadership skills.
- Increases Motivation: People tend to be more invested in work when they have clear, attainable objectives to achieve. Plus, each completed objective provides a morale boost to keep teams happy and productive.
- Encourages Innovation and Productivity: With increased motivation and workplace satisfaction come more innovations. Set attainable but challenging objectives, and watch teams come up with creative solutions to get things done.
- Improves Strategy: Setting objectives that align with overarching company goals means that everyone across the company can stay aligned on strategic implementation.
- Enhances Customer Satisfaction: Overall customer satisfaction is more likely to increase over time when measurable quality improvements are in place.
- Improves Prioritization: When they are being able to see all of the current objectives, team members can more easily prioritize their work, which in turn makes their workloads feel more manageable.
- Improves Financial Health: Setting economic objectives in particular can help companies stay on top of their financial goals.
60 Examples of Business Objectives
Company leaders can use business objectives to improve every facet of an organization, from customer satisfaction to market share to employee well-being. Here are 60 examples of business objectives that can help a company achieve its goals.
Economic Business Objectives
- Increase profit margins by 5 percent by the end of the Q4.
- Recover 50 percent of total outstanding debts from each quarter the following quarter for the next year.
- “Increase revenue by 10 percent each year for the next five years,” suggests Tyler.
- Offer three new holiday sales events in the coming year.
- Move 30 percent of surplus stock by the end of Q2.
- “Reduce costs by 10 percent each year for the next five years,” suggests Tyler.
- Reduce monthly interest payments by 1.5 percent by consolidating debt.
- Introduce a new credit payment option to expand the potential customer base.
- Apply for six government grants by the end of the year.
- Hire an accountant to track expenses and file the company’s taxes.
- Secure a $100,000 loan to start a business.
- Pitch your business ideas to a venture capital firm.
- Improve your business credit score from 75 to 85 in two years.
- Invest in solar panels for your company headquarters to reduce building energy costs by 75 percent.
- Establish a monthly practice to analyze your cash flow statement.
Social Business Objectives
- Decrease customer average customer wait times by 20 percent in two months.
- Improve the average customer service satisfaction rating from 3.2/5 to 3.8/5 in six months through targeting trainings.
- Hire a contract UX designer to redesign the company website interface in four months.
- Decrease customer churn by 15 percent in one year.
- “Triple the customer base within two years,” suggests Tyler.
- Offer 20 percent more customer discounts and specials over the course of two years.
- Increase market share by 5 percent in three years.
- Increase monthly sales quotas for sales associates by 10 percent.
- Develop a sales incentive program to reward top-performing sales associates with vacations, bonuses, and other prizes.
- Donate $10,000 to local causes, such as public school funds or local charities.
- Partner with a charitable organization to host a company-wide 5K.
- Increase your marketing budget by 15 percent.
- Hire a new marketing director by the end of Q3.
- Donate 40 percent of surplus stock to a relevant charity.
- Increase engagement across all social media platforms by 10 percent with a multiplatform ad campaign.
Human Business Objectives
- Hire three new employees by the end of Q1.
- Hire a contractor to train your IT team on new software.
- Rewrite and distribute your company values statement.
- Conduct a quarterly, company-wide productivity training over the next two years.
- Establish a diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) committee.
- Design and implement a mentorship program for diverse employees.
- Create an incentive program that grants additional vacation days for all employees when company-wide productivity goals are met.
- Offer a free monthly happy hour to improve the employee experience.
- Select change leaders across multiple teams to provide support for a corporate reorg.
- Start three employee resource groups (ERGs) within the next six months.
- Diversify websites and career fairs where the hiring team recruits applicants to encourage a more diverse pool of candidates for new jobs.
- Invest in an office redesign that improves the office atmosphere and provides more in-office resources, such as free coffee and snacks, to on-site employees.
- Upgrade employee laptops to improve productivity and employee satisfaction.
- Conduct a yearly, comprehensive employee experience survey to identify areas of improvement.
- Throw office parties to celebrate change milestones.
Organic Business Objectives
- Increase the top line by 15 percent every year for the next five years.
- Achieve 20 percent net profit from 10 product enhancements in the next two years.
- Decrease raw materials costs by 10 percent by the end of the year.
- Reduce downtime by 25 percent by the end of the year.
- Within two years, attain a rate of 25 percent new revenue from products released within the last year.
- Improve customer acquisition ration by 10 percent every quarter for the next two years.
- Reduce total inventory levels by 20 percent over four months.
- Interact with at least 20 Instagram users every month for one year.
- Have a new product launch covered by at least three reputable industry publications within two months of the launch date.
- Grow both the top line and the bottom line by 60 percent every year for three years.
- Reduce product defects by 15 percent every year for four years.
- Increase on-time delivery dates for top customers by 25 percent over the span of three quarters.
- Conduct yearly workplace safety reviews.
- Decrease average customer wait times for responses to social media queries from 45 minutes to 15 minutes by the end of Q4.
- Improve your company website to be on the first page of search results within six months.
Download 60 Example Business Objectives for
Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF
Track the Progress of Business Objectives with Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.

Business Plan Goals and Examples for Success
Written by Dave Lavinsky

A well-crafted business plan serves as a roadmap for entrepreneurs and businesses to achieve their objectives. One crucial aspect of a business plan is outlining clear and measurable goals. Business plan goals are the specific targets and milestones that a company aims to achieve within a defined timeframe. They provide a direction and purpose for the business, guiding decision-making, resource allocation, and strategic planning. In this article, we will explore the importance of setting business plan goals and provide examples of common goals.
How to Finish Your Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Why are Business Plan Goals Important?
Business plan goals are essential for several reasons:
- Strategic Focus : Goals help businesses define their strategic direction and focus their efforts on what matters most. They align the company’s efforts and resources towards achieving specific objectives, ensuring that everyone is working towards a common purpose.
- Measurable Outcomes : Goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). By setting SMART goals, businesses can track progress, measure success, and identify areas for improvement.
- Motivation and Accountability : Goals provide motivation and drive for entrepreneurs and employees. They create a sense of purpose and urgency, encouraging individuals to work towards achieving the desired outcomes. Goals also establish accountability, as progress is monitored and reviewed regularly.
- Decision-Making : Goals serve as a reference point for decision-making. They help businesses prioritize initiatives, allocate resources, and evaluate opportunities based on their alignment with the established goals.
Examples of Business Plan Goals
Business plan goals can vary depending on the nature, size, and stage of the business. Here are some common examples of business plan goals:
Financial Goals:
- Achieve a specific revenue target within a defined timeframe.
- Increase profitability by a certain percentage or dollar amount.
- Reduce costs or increase efficiency in a particular area of the business.
- Secure funding or investment to support business growth.
Market Penetration Goals:
- Expand market share in a specific geographic region or target market.
- Increase brand awareness and recognition among the target audience.
- Launch new products or services in the market.
- Increase customer retention or loyalty.
Operational Goals:
- Improve production or service delivery processes to enhance quality or reduce lead times.
- Enhance supply chain management to optimize inventory levels or reduce costs.
- Implement new technologies or systems to streamline operations or improve customer experience.
- Achieve certifications or industry standards to improve credibility and competitiveness.
Human Resources Goals:
- Hire and retain top talent to support business growth.
- Provide training and development opportunities for employees to enhance their skills and performance.
- Improve employee engagement and satisfaction levels.
- Establish a diverse and inclusive workforce.
Social Responsibility Goals:
- Implement environmentally sustainable practices in the business operations.
- Contribute to the local community through philanthropic initiatives or social impact programs.
- Promote diversity, equity, and inclusion within the organization.
- Establish ethical and responsible business practices.
Business Plan Goals Conclusion
Business plan goals are critical for defining the direction and purpose of a business. They provide measurable outcomes, motivation, and accountability, guiding decision-making and resource allocation. Examples of business plan goals can include financial, market penetration, operational, human resources, and social responsibility objectives. When setting business plan goals, it’s essential to make them SMART – specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound – to increase their effectiveness in driving business success. Regular monitoring and review of progress towards these goals can help businesses stay on track and adapt their strategies as needed to achieve their desired outcomes.

Need a business plan? Call now:
Talk to our experts:
- Business Plan for Investors
- Bank/SBA Business Plan
- Operational/Strategic Planning
- L1 Visa Business Plan
- E1 Treaty Trader Visa Business Plan
- E2 Treaty Investor Visa Business Plan
- EB1 Business Plan
- EB2 Visa Business Plan
- EB5 Business Plan
- Innovator Founder Visa Business Plan
- UK Start-Up Visa Business Plan
- UK Expansion Worker Visa Business Plan
- Manitoba MPNP Visa Business Plan
- Start-Up Visa Business Plan
- Nova Scotia NSNP Visa Business Plan
- British Columbia BC PNP Visa Business Plan
- Self-Employed Visa Business Plan
- OINP Entrepreneur Stream Business Plan
- LMIA Owner Operator Business Plan
- ICT Work Permit Business Plan
- LMIA Mobility Program – C11 Entrepreneur Business Plan
- USMCA (ex-NAFTA) Business Plan
- Franchise Business Planning
- Landlord Business Plan
- Nonprofit Start-Up Business Plan
- USDA Business Plan
- Cannabis business plan
- eCommerce business plan
- Online Boutique Business Plan
- Mobile Application Business Plan
- Daycare business plan
- Restaurant business plan
- Food Delivery Business Plan
- Real Estate Business Plan
- Business Continuity Plan
- Buy Side Due Diligence Services
- ICO whitepaper
- ICO consulting services
- Confidential Information Memorandum
- Private Placement Memorandum
- Feasibility study
- Fractional CFO
- How it works
- Business Plan Examples
Goals and Objectives for Business Plan with Examples
Nov.05, 2023
Average rating 5 / 5. Vote count: 2
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.

Table of Content
Every business needs a clear vision of what it wants to achieve and how it plans to get there. A business plan is a document that outlines the goals and objectives of a business, as well as the strategies and actions to achieve them. A well-written business plan from business plan specialists can help a business attract investors, secure funding, and guide its growth.
Understanding Business Objectives
Business objectives are S pecific, M easurable, A chievable, R elevant, and T ime-bound (SMART) statements that describe what a business wants to accomplish in a given period. They are derived from the overall vision and mission of the business, and they support its strategic direction.
Business plan objectives can be categorized into different types, depending on their purpose and scope. Some common types of business objectives are:
- Financial objectives
- Operational objectives
- Marketing objectives
- Social objectives
For example, a sample of business goals and objectives for a business plan for a bakery could be:
- To increase its annual revenue by 20% in the next year.
- To reduce its production costs by 10% in the next six months.
- To launch a new product line of gluten-free cakes in the next quarter.
- To improve its customer satisfaction rating by 15% in the next month.
The Significance of Business Objectives
Business objectives are important for several reasons. They help to:
- Clarify and direct the company and stakeholders
- Align the company’s efforts and resources to a common goal
- Motivate and inspire employees to perform better
- Measure and evaluate the company’s progress and performance
- Communicate the company’s value and advantage to customers and the market
For example, by setting a revenue objective, a bakery can focus on increasing its sales and marketing efforts, monitor its sales data and customer feedback, motivate its staff to deliver quality products and service, communicate its unique selling points and benefits to its customers, and adjust its pricing and product mix according to market demand.
Advantages of Outlining Business Objectives
Outlining business objectives is a crucial step in creating a business plan. It serves as a roadmap for the company’s growth and development. Outlining business objectives has several advantages, such as:
- Clarifies the company’s vision, direction, scope, and boundaries
- Break down the company’s goals into smaller tasks and milestones
- Assigns roles and responsibilities and delegates tasks
- Establishes standards and criteria for success and performance
- Anticipates risks and challenges and devises contingency plans
For example, by outlining its business objective for increasing the average revenue per customer in its business plan, a bakery can:
- Attract investors with its viable business plan for investors
- Secure funding from banks or others with its realistic financial plan
- Partner with businesses or organizations that complement or enhance its products or services
- Choose the best marketing, pricing, product, staff, location, etc. for its target market and customers
Setting Goals and Objectives for a Business Plan
Setting goals and objectives for a business plan is not a one-time task. It requires careful planning, research, analysis, and evaluation. To set effective goals and objectives for a business plan, one should follow some best practices, such as:
OPTION 1: Use the SMART framework. A SMART goal or objective is clear, quantifiable, realistic, aligned with the company’s mission and vision, and has a deadline. SMART stands for:
- Specific – The goal or objective should be clear, concise, and well-defined.
- Measurable – The goal or objective should be quantifiable or verifiable.
- Achievable – The goal or objective should be realistic and attainable.
- Relevant – The goal or objective should be aligned with the company’s vision, mission, and values.
- Time-bound – The goal or objective should have a deadline or timeframe.
For example, using the SMART criteria, a bakery can refine its business objective for increasing the average revenue per customer as follows:
- Specific – Increase revenue with new products and services from $5 to $5.50.
- Measurable – Track customer revenue monthly with sales reports.
- Achievable – Research the market, develop new products and services, and train staff to upsell and cross-sell.
- Relevant – Improve customer satisfaction and loyalty, profitability and cash flow, and market competitiveness.
- Time-bound – Achieve this objective in six months, from January 1st to June 30th.
OPTION 2: Use the OKR framework. OKR stands for O bjectives and K ey R esults. An OKR is a goal-setting technique that links the company’s objectives with measurable outcomes. An objective is a qualitative statement of what the company wants to achieve. A key result is a quantitative metric that shows how the objective will be achieved.
OPTION 3: Use the SWOT analysis. SWOT stands for S trengths, W eaknesses, O pportunities, and T hreats. A SWOT analysis is a strategic tool that helps the company assess the internal and external factors that affect its goals and objectives.
- Strengths – Internal factors that give the company an advantage over others.
- Weaknesses – Internal factors that limit the company’s performance or growth.
- Opportunities – External factors that allow the company to improve or expand.
- Threats – External factors that pose a risk or challenge to the company.
For example, using these frameworks, a bakery might set the following goals and objectives for its SBA business plan :
Objective – To launch a new product line of gluten-free cakes in the next quarter.
Key Results:
- Research gluten-free cake market demand and preferences by month-end.
- Create and test 10 gluten-free cake recipes by next month-end.
- Make and sell 100 gluten-free cakes weekly online or in-store by quarter-end.
SWOT Analysis:
- Expertise and experience in baking and cake decorating.
- Loyal and satisfied customer base.
- Strong online presence and reputation.
Weaknesses:
- Limited production capacity and equipment.
- High production costs and low-profit margins.
- Lack of knowledge and skills in gluten-free baking.
Opportunities:
- Growing demand and awareness for gluten-free products.
- Competitive advantage and differentiation in the market.
- Potential partnerships and collaborations with health-conscious customers and organizations.
- Increasing competition from other bakeries and gluten-free brands.
- Changing customer tastes and preferences.
- Regulatory and legal issues related to gluten-free labeling and certification.
Examples of Business Goals and Objectives
To illustrate how to write business goals and objectives for a business plan, let’s use a hypothetical example of a bakery business called Sweet Treats. Sweet Treats is a small bakery specializing in custom-made cakes, cupcakes, cookies, and other baked goods for various occasions.
Here are some examples of possible startup business goals and objectives for Sweet Treats:
Earning and Preserving Profitability
Profitability is the ability of a company to generate more revenue than expenses. It indicates the financial health and performance of the company. Profitability is essential for a business to sustain its operations, grow its market share, and reward its stakeholders.
Some possible objectives for earning and preserving profitability for Sweet Treats are:
- To increase the gross profit margin by 5% in the next quarter by reducing the cost of goods sold
- To achieve a net income of $100,000 in the current fiscal year by increasing sales and reducing overhead costs
Ensuring Consistent Cash Flow
Cash flow is the amount of money that flows in and out of a company. A company needs to have enough cash to cover its operating expenses, pay its debts, invest in its growth, and reward its shareholders.
Some possible objectives for ensuring consistent cash flow for Sweet Treats are:
- Increase monthly operating cash inflow by 15% by the end of the year by improving the efficiency and productivity of the business processes
- Increase the cash flow from investing activities by selling or disposing of non-performing or obsolete assets
Creating and Maintaining Efficiency
Efficiency is the ratio of output to input. It measures how well a company uses its resources to produce its products or services. Efficiency can help a business improve its quality, productivity, customer satisfaction, and profitability.
Some possible objectives for creating and maintaining efficiency for Sweet Treats are:
- To reduce the production time by 10% in the next month by implementing lean manufacturing techniques
- To increase the customer service response rate by 20% in the next week by using chatbots or automated systems
Winning and Keeping Clients
Clients are the people or organizations that buy or use the products or services of a company. They are the source of revenue and growth for a company. Therefore, winning and keeping clients is vital to generating steady revenue, increasing customer loyalty, and enhancing word-of-mouth marketing.
Some possible objectives for winning and keeping clients for Sweet Treats are:
- To acquire 100 new clients in the next quarter by launching a referral program or a promotional campaign
- To retain 90% of existing clients in the current year by offering loyalty rewards or satisfaction guarantees
Building a Recognizable Brand
A brand is the name, logo, design, or other features distinguishing a company from its competitors. It represents the identity, reputation, and value proposition of a company. Building a recognizable brand is crucial for attracting and retaining clients and creating a loyal fan base.
Some possible objectives for building a recognizable brand for Sweet Treats are:
- To increase brand awareness by 50% in the next six months by creating and distributing engaging content on social media platforms
- To improve brand image by 30% in the next year by participating in social causes or sponsoring events that align with the company’s values
Expanding and Nurturing an Audience with Marketing
An audience is a group of people interested in or following a company’s products or services. They can be potential or existing clients, fans, influencers, or partners. Expanding and nurturing an audience with marketing is essential for increasing a company’s visibility, reach, and engagement.
Some possible objectives for expanding and nurturing an audience with marketing for Sweet Treats are:
- To grow the email list by 1,000 subscribers in the next month by offering a free ebook or a webinar
- To nurture leads by sending them relevant and valuable information through email newsletters or blog posts
Strategizing for Expansion
Expansion is the process of increasing a company’s size, scope, or scale. It can involve entering new markets, launching new products or services, opening new locations, or forming new alliances. Strategizing for expansion is important for diversifying revenue streams, reaching new audiences, and gaining competitive advantages.
Some possible objectives for strategizing for expansion for Sweet Treats are:
- To launch a new product or service line by developing and testing prototypes
- To open a new branch or franchise by securing funding and hiring staff
Template for Business Objectives
A template for writing business objectives is a format or structure that can be used as a guide or reference for creating your objectives. A template for writing business objectives can help you to ensure that your objectives are SMART, clear, concise, and consistent.
To use this template, fill in the blanks with your information. Here is an example of how you can use this template:
Example of Business Objectives
Our business is a _____________ (type of business) that provides _____________ (products or services) to _____________ (target market). Our vision is to _____________ (vision statement) and our mission is to _____________ (mission statement).
Our long-term business goals and objectives for the next _____________ (time period) are:
S pecific: We want to _____________ (specific goal) by _____________ (specific action).
M easurable: We will measure our progress by _____________ (quantifiable indicator).
A chievable: We have _____________ (resources, capabilities, constraints) that will enable us to achieve this goal.
R elevant: This goal supports our vision and mission by _____________ (benefit or impact).
T ime-bound: We will complete this goal by _____________ (deadline).
Repeat this process for each goal and objective for your business plan.
How to Monitor Your Business Objectives?
After setting goals and objectives for your business plan, you should check them regularly to see if you are achieving them. Monitoring your business objectives can help you to:
- Track your progress and performance
- Identify and overcome any challenges
- Adjust your actions and strategies as needed
Some of the tools and methods that you can use to monitor your business objectives are:
- Dashboards – Show key data and metrics for your objectives with tools like Google Data Studio, Databox, or DashThis.
- Reports – Get detailed information and analysis for your objectives with tools like Google Analytics, Google Search Console, or SEMrush.
- Feedback – Learn from your customers and their needs and expectations with tools like SurveyMonkey, Typeform, or Google Forms.
Strategies for Realizing Business Objectives
To achieve your business objectives, you need more than setting and monitoring them. You need strategies and actions that support them. Strategies are the general methods to reach your objectives. Actions are the specific steps to implement your strategies.
Different objectives require different strategies and actions. Some common types are:
- Marketing strategies
- Operational strategies
- Financial strategies
- Human resource strategies
- Growth strategies
To implement effective strategies and actions, consider these factors:
- Alignment – They should match your vision, mission, values, goals, and objectives
- Feasibility – They should be possible with your capabilities, resources, and constraints
- Suitability – They should fit the context and needs of your business
How OGSCapital Can Help You Achieve Your Business Objectives?
We at OGSCapital can help you with your business plan and related documents. We have over 15 years of experience writing high-quality business plans for various industries and regions. We have a team of business plan experts who can assist you with market research, financial analysis, strategy formulation, and presentation design. We can customize your business plan to suit your needs and objectives, whether you need funding, launching, expanding, or entering a new market. We can also help you with pitch decks, executive summaries, feasibility studies, and grant proposals. Contact us today for a free quote and start working on your business plan.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the goals and objectives in business.
Goals and objectives in a business plan are the desired outcomes that a company works toward. To describe company goals and objectives for a business plan, start with your mission statement and then identify your strategic and operational objectives. To write company objectives, you must brainstorm, organize, prioritize, assign, track, and review them using the SMART framework and KPIs.
What are the examples of goals and objectives in a business plan?
Examples of goals and objectives in a business plan are: Goal: To increase revenue by 10% each year for the next five years. Objective: To launch a new product line and create a marketing campaign to reach new customers.
What are the 4 main objectives of a business?
The 4 main objectives of a business are economic, social, human, and organic. Economic objectives deal with financial performance, social objectives deal with social responsibility, human objectives deal with employee welfare, and organic objectives deal with business growth and development.
What are goals and objectives examples?
Setting goals and objectives for a business plan describes what a business or a team wants to achieve and how they will do it. For example: Goal: To provide excellent customer service. Objective: To increase customer satisfaction scores by 20% by the end of the quarter.
At OGSCapital, our business planning services offer expert guidance and support to create a realistic and actionable plan that aligns with your vision and mission. Get in touch to discuss further!
OGSCapital’s team has assisted thousands of entrepreneurs with top-rate business plan development, consultancy and analysis. They’ve helped thousands of SME owners secure more than $1.5 billion in funding, and they can do the same for you.

Vegetable Farming Business Plan

Trading Business Plan

How To Write A Textile Manufacturing Business Plan

Start a Vending Machine Business in 2024: A Detailed Guide

Oil and Gas Business Plan

What Is Strategic Planning: Definition and Process

Any questions? Get in Touch!
We have been mentioned in the press:
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Search the site:
Business Plan Template
Collaborate with your team, craft your business plan, and present your ideas visually with the Business Plan Template.
Trusted by 65M+ users and leading companies
About the Business Plan Template
A solid business plan is the key to the success of any project. That's why we have designed a comprehensive business plan template that makes organizing and outlining your business objectives a breeze. This template will help you streamline your process and visualize your goals, creating a roadmap for your business journey.
What's a business plan template?
A business plan template is a pre-structured framework that outlines the core aspects of a business plan. It helps organize and detail key components, providing a clear picture of what the business aims to achieve. Miro's business plan template includes:
Problem: Identify the core problem that the business plans to solve.
Solution: Outline the solution to address the problem.
Resources: Detail the resources required, including time, workforce, and materials.
Benefit: Define the benefits of implementing the proposed solution.
Risks: Analyze potential risks and how they will be mitigated.
Scope: Describe the extent and limitations of the project.
Stakeholders: List the parties involved and their interests.
Costs: Estimate the financial aspects of the project.
Metrics: Identify the key performance indicators to measure success.
How to use the business plan template in Miro
Using Miro's business plan template is an effortless and effective way to craft your business strategy. Here's a step-by-step guide to making the most of this template:
Choose the template: Select the business plan template from Miro's Template Library, tailored to fit any business type.
Define the problem: Identify the core problem your business intends to solve. Use Miro's tagging feature to add relevant tags for easy reference.
Outline the solution: Describe how your product or service addresses the problem. Use Miro's automated diagramming to create flow diagrams or charts illustrating the solution process.
List the resources: Detail all necessary resources, including time, workforce, and materials. Create categories and use color coding to organize them effectively.
Highlight the benefit: Define the benefits and why your solution is preferable. Incorporate visual aids like icons to emphasize key points.
Analyze the risks: List potential risks and their mitigation strategies. Use sticky notes to jot down thoughts and ideas collaboratively.
Describe the scope: Clarify the project's limitations and extent.
Identify stakeholders: List the parties involved using symbols or avatars to represent various stakeholders.
Estimate costs: Break down the financial aspects using tables or charts to present the information clearly.
Determine metrics: Set key performance indicators and use Miro's graphs to visualize the success measures.
Customize your plan: Add, remove, or change any fields to suit your specific project. You can expand the quadrants, adding data or other artifacts as needed.
Collaborate and share: Invite team members to collaborate in real time, adding comments and feedback. Miro's collaboration features support seamless teamwork.
To finish, prepare a presentation. With features like frames and the Presentation Mode , you can visually guide stakeholders through your strategy. And remember, ensure that all details are accurate and aligned with your goals.
With this quick guide and Miro's various sets of features, creating a business plan becomes a collaborative and creative process. The ability to visualize, tag, and present your plan ensures a rich and engaging experience for everyone involved. Whether you're a startup or an established business, Miro's business plan template offers the flexibility and robustness needed to succeed in today's competitive landscape.
Can I customize the business plan template in Miro?
Yes, add, remove, or change any fields to fit the specific needs of your project.
How can I share the business plan template with my team?
Miro's collaboration tools make it easy to share your template with team members, either through a direct link or by inviting them to your workspace.
Is the business plan template suitable for small businesses and startups?
Yes, the template is designed to be flexible and can be adapted to businesses of any size, including startups and small enterprises.
Get started with this template right now.
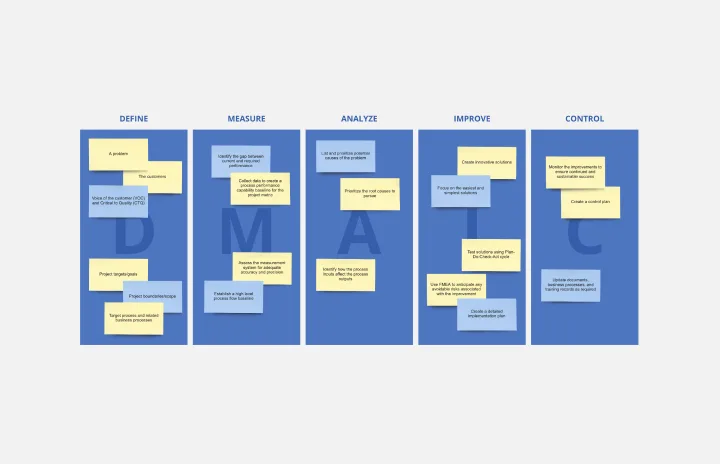
DMAIC Analysis Template
Works best for:.
Agile Methodology, Design Thinking, Operations
Processes might not seem like the funnest thing to dive into and examine, but wow can it pay off—a more efficient process can lead to serious cost savings and a better product. That’s what DMAIC analysis does. Developed as part of the Six Sigma initiative, DMAIC is a data-driven quality strategy for streamlining processes and resolving issues. The technique is broken into five fundamental steps that are followed in order: Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control.
Budget Planning Template
A budget template is a comprehensive yet flexible framework that allows you to monitor and control your finances. With user-friendly functions and numerous customization options, this tool helps you create a budget tailored to your specific needs and goals. Whether new to budgeting or an experienced financial planner, a budget template is an excellent tool to help you manage finances effectively.
Vision Board Template
Strategy & Planning, Product Development
Miro's Vision Board Template helps teams to bring their vision to life. From visual representation to real time collaboration, this template facilitates planning, execution, and achievement of any project's goals.
Feature Planning Template
Desk Research, Agile Methodology, Product Management
Features are what make a product or service fun, but adding new ones is no walk in the park. It takes many steps—ideating, designing, refining, building, testing, launching, and promoting—and just as many stakeholders. Feature Planning lets you put a smooth, sturdy process in place, so you can add a feature successfully, and spend less time and resources doing it. That makes our Feature Planning Template a smart starting point for anyone looking to add new product features, especially members of product, engineering, marketing, and sales teams.

Work Plan Template
Mapping, Project Planning
A work plan is essentially a roadmap for a project. It articulates the steps you must take to achieve the desired goal, sets demonstrable objectives, and establishes measurable deliverables. An effective work plan guides you throughout the project lifecycle, allowing you to realize an outcome by collaborating with your team. Although work plans vary, they generally contain four core components: goals, strategy, tactics, and deliverables.
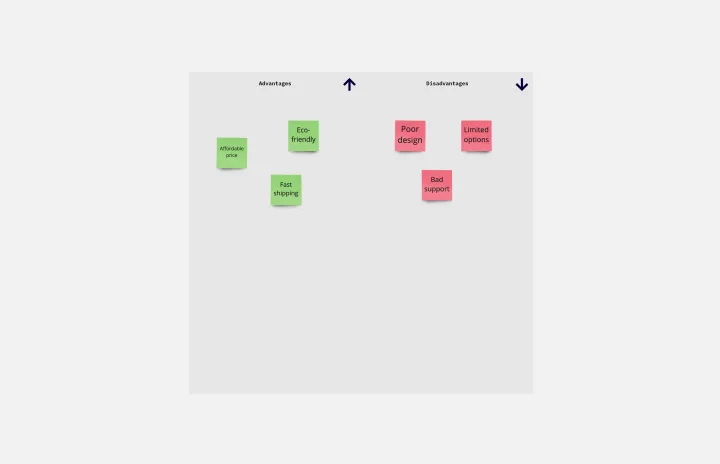
T-Chart Template
Ideation, Operations, Strategic Planning
T-Charts can help you compare and contrast two different ideas, group information into different categories, and prove a change through “before” and “after” analysis. T-Charts are visual organizational tools that enable you to compare ideas, so you can evaluate pros and cons, facts and opinions, strengths and weaknesses, or big-picture views versus specific details. Designers and content creators can use T-Charts to turn possibilities into actionable ideas. T-Charts are useful for discussing differences and similarities with your team or clients and can help you to reach a decision together.
- 212 best farm names
How to Write a Business Plan (Plus Examples & Templates)
May 24, 2021

Have you ever wondered how to write a business plan step by step? Mike Andes, told us:
This guide will help you write a business plan to impress investors.
Throughout this process, we’ll get information from Mike Andes, who started Augusta Lawn Care Services when he was 12 and turned it into a franchise with over 90 locations. He has gone on to help others learn how to write business plans and start businesses. He knows a thing or two about writing business plans!
We’ll start by discussing the definition of a business plan. Then we’ll discuss how to come up with the idea, how to do the market research, and then the important elements in the business plan format. Keep reading to start your journey!
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan is simply a road map of what you are trying to achieve with your business and how you will go about achieving it. It should cover all elements of your business including:
- Finding customers
- Plans for developing a team
- Competition
- Legal structures
- Key milestones you are pursuing
If you aren’t quite ready to create a business plan, consider starting by reading our business startup guide .
Get a Business Idea
Before you can write a business plan, you have to have a business idea. You may see a problem that needs to be solved and have an idea how to solve it, or you might start by evaluating your interests and skills.
Mike told us, “The three things I suggest asking yourself when thinking about starting a business are:
- What am I good at?
- What would I enjoy doing?
- What can I get paid for?”

If all three of these questions don’t lead to at least one common answer, it will probably be a much harder road to success. Either there is not much market for it, you won’t be good at it, or you won’t enjoy doing it.
As Mike told us, “There’s enough stress starting and running a business that if you don’t like it or aren’t good at it, it’s hard to succeed.”
If you’d like to hear more about Mike’s approach to starting a business, check out our YouTube video
Conduct Market Analysis
Market analysis is focused on establishing if there is a target market for your products and services, how large the target market is, and identifying the demographics of people or businesses that would be interested in the product or service. The goal here is to establish how much money your business concept can make.
Product and Service Demand

A search engine is your best friend when trying to figure out if there is demand for your products and services. Personally, I love using presearch.org because it lets you directly search on a ton of different platforms including Google, Youtube, Twitter, and more. Check out the screenshot for the full list of search options.
With quick web searches, you can find out how many competitors you have, look through their reviews, and see if there are common complaints about the competitors. Bad reviews are a great place to find opportunities to offer better products or services.
If there are no similar products or services, you may have stumbled upon something new, or there may just be no demand for it. To find out, go talk to your most honest friend about the idea and see what they think. If they tell you it’s dumb or stare at you vacantly, there’s probably no market for it.
You can also conduct a survey through social media to get public opinion on your idea. Using Facebook Business Manager , you could get a feel for who would be interested in your product or service.
I ran a quick test of how many people between 18-65 you could reach in the U.S. during a week. It returned an estimated 700-2,000 for the total number of leads, which is enough to do a fairly accurate statistical analysis.
Identify Demographics of Target Market
Depending on what type of business you want to run, your target market will be different. The narrower the demographic, the fewer potential customers you’ll have. If you did a survey, you’ll be able to use that data to help define your target audience. Some considerations you’ll want to consider are:
- Other Interests
- Marital Status
- Do they have kids?
Once you have this information, it can help you narrow down your options for location and help define your marketing further. One resource that Mike recommended using is the Census Bureau’s Quick Facts Map . He told us,
“It helps you quickly evaluate what the best areas are for your business to be located.”
How to Write a Business Plan

Now that you’ve developed your idea a little and established there is a market for it, you can begin writing a business plan. Getting started is easier with the business plan template we created for you to download. I strongly recommend using it as it is updated to make it easier to create an action plan.
Each of the following should be a section of your business plan:
- Business Plan Cover Page
- Table of Contents
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- Description of Products and Services
SWOT Analysis
- Competitor Data
- Competitive Analysis
- Marketing Expenses Strategy
Pricing Strategy
- Distribution Channel Assessment
- Operational Plan
- Management and Organizational Strategy
- Financial Statements and/or Financial Projections
We’ll look into each of these. Don’t forget to download our free business plan template (mentioned just above) so you can follow along as we go.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 1. Create a Cover Page
The first thing investors will see is the cover page for your business plan. Make sure it looks professional. A great cover page shows that you think about first impressions.
A good business plan should have the following elements on a cover page:
- Professionally designed logo
- Company name
- Mission or Vision Statement
- Contact Info
Basically, think of a cover page for your business plan like a giant business card. It is meant to capture people’s attention but be quickly processed.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 2. Create a Table of Contents
Most people are busy enough that they don’t have a lot of time. Providing a table of contents makes it easy for them to find the pages of your plan that are meaningful to them.
A table of contents will be immediately after the cover page, but you can include it after the executive summary. Including the table of contents immediately after the executive summary will help investors know what section of your business plan they want to review more thoroughly.
Check out Canva’s article about creating a table of contents . It has a ton of great information about creating easy access to each section of your business plan. Just remember that you’ll want to use different strategies for digital and hard copy business plans.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 3. Write an Executive Summary

An executive summary is where your business plan should catch the readers interest. It doesn’t need to be long, but should be quick and easy to read.
Mike told us,
How long should an executive summary bein an informal business plan?
For casual use, an executive summary should be similar to an elevator pitch, no more than 150-160 words, just enough to get them interested and wanting more. Indeed has a great article on elevator pitches . This can also be used for the content of emails to get readers’ attention.
It consists of three basic parts:
- An introduction to you and your business.
- What your business is about.
- A call to action
Example of an informal executive summary
One of the best elevator pitches I’ve used is:
So far that pitch has achieved a 100% success rate in getting partnerships for the business.
What should I include in an executive summary for investors?
Investors are going to need a more detailed executive summary if you want to secure financing or sell equity. The executive summary should be a brief overview of your entire business plan and include:
- Introduction of yourself and company.
- An origin story (Recognition of a problem and how you came to solution)
- An introduction to your products or services.
- Your unique value proposition. Make sure to include intellectual property.
- Where you are in the business life cycle
- Request and why you need it.
Successful business plan examples
The owner of Urbanity told us he spent 2 months writing a 75-page business plan and received a $250,000 loan from the bank when he was 23. Make your business plan as detailed as possible when looking for financing. We’ve provided a template to help you prepare the portions of a business plan that banks expect.
Here’s the interview with the owner of Urbanity:
When to write an executive summary?
Even though the summary is near the beginning of a business plan, you should write it after you complete the rest of a business plan. You can’t talk about revenue, profits, and expected expenditures if you haven’t done the market research and created a financial plan.
What mistakes do people make when writing an executive summary?
Business owners commonly go into too much detail about the following items in an executive summary:
- Marketing and sales processes
- Financial statements
- Organizational structure
- Market analysis
These are things that people will want to know later, but they don’t hook the reader. They won’t spark interest in your small business, but they’ll close the deal.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 4. Company Description
Every business plan should include a company description. A great business plan will include the following elements while describing the company:
- Mission statement
- Philosophy and vision
- Company goals
Target market
- Legal structure
Let’s take a look at what each section includes in a good business plan.
Mission Statement
A mission statement is a brief explanation of why you started the company and what the company’s main focus is. It should be no more than one or two sentences. Check out HubSpot’s article 27 Inspiring Mission Statement for a great read on informative and inspiring mission and vision statements.
Company Philosophy and Vision

The company philosophy is what drives your company. You’ll normally hear them called core values. These are the building blocks that make your company different. You want to communicate your values to customers, business owners, and investors as often as possible to build a company culture, but make sure to back them up.
What makes your company different?
Each company is different. Your new business should rise above the standard company lines of honesty, integrity, fun, innovation, and community when communicating your business values. The standard answers are corporate jargon and lack authenticity.
Examples of core values
One of my clients decided to add a core values page to their website. As a tech company they emphasized the values:
- Prioritize communication.
- Never stop learning.
- Be transparent.
- Start small and grow incrementally.
These values communicate how the owner and the rest of the company operate. They also show a value proposition and competitive advantage because they specifically focus on delivering business value from the start. These values also genuinely show what the company is about and customers recognize the sincerity. Indeed has a great blog about how to identify your core values .
What is a vision statement?
A vision statement communicate the long lasting change a business pursues. The vision helps investors and customers understand what your company is trying to accomplish. The vision statement goes beyond a mission statement to provide something meaningful to the community, customer’s lives, or even the world.
Example vision statements
The Alzheimer’s Association is a great example of a vision statement:
A world without Alzheimer’s Disease and other dementia.
It clearly tells how they want to change the world. A world without Alzheimers might be unachievable, but that means they always have room for improvement.
Business Goals
You have to measure success against goals for a business plan to be meaningful. A business plan helps guide a company similar to how your GPS provides a road map to your favorite travel destination. A goal to make as much money as possible is not inspirational and sounds greedy.
Sure, business owners want to increase their profits and improve customer service, but they need to present an overview of what they consider success. The goals should help everyone prioritize their work.
How far in advance should a business plan?
Business planning should be done at least one year in advance, but many banks and investors prefer three to five year business plans. Longer plans show investors that the management team understands the market and knows the business is operating in a constantly shifting market. In addition, a plan helps businesses to adjust to changes because they have already considered how to handle them.
Example of great business goals
My all time-favorite long-term company goals are included in Tesla’s Master Plan, Part Deux . These goals were written in 2016 and drive the company’s decisions through 2026. They are the reason that investors are so forgiving when Elon Musk continually fails to meet his quarterly and annual goals.
If the progress aligns with the business plan investors are likely to continue to believe in the company. Just make sure the goals are reasonable or you’ll be discredited (unless you’re Elon Musk).

You did target market research before creating a business plan. Now it’s time to add it to the plan so others understand what your ideal customer looks like. As a new business owner, you may not be considered an expert in your field yet, so document everything. Make sure the references you use are from respectable sources.
Use information from the specific lender when you are applying for lending. Most lenders provide industry research reports and using their data can strengthen the position of your business plan.
A small business plan should include a section on the external environment. Understanding the industry is crucial because we don’t plan a business in a vacuum. Make sure to research the industry trends, competitors, and forecasts. I personally prefer IBIS World for my business research. Make sure to answer questions like:
- What is the industry outlook long-term and short-term?
- How will your business take advantage of projected industry changes and trends?
- What might happen to your competitors and how will your business successfully compete?
Industry resources
Some helpful resources to help you establish more about your industry are:
- Trade Associations
- Federal Reserve
- Bureau of Labor Statistics
Legal Structure
There are five basic types of legal structures that most people will utilize:
- Sole proprietorships
- Limited Liability Companies (LLC)
Partnerships
Corporations.
- Franchises.
Each business structure has their pros and cons. An LLC is the most common legal structure due to its protection of personal assets and ease of setting up. Make sure to specify how ownership is divided and what roles each owner plays when you have more than one business owner.
You’ll have to decide which structure is best for you, but we’ve gathered information on each to make it easier.
Sole Proprietorship
A sole proprietorship is the easiest legal structure to set up but doesn’t protect the owner’s personal assets from legal issues. That means if something goes wrong, you could lose both your company and your home.
To start a sole proprietorship, fill out a special tax form called a Schedule C . Sole proprietors can also join the American Independent Business Alliance .
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
An LLC is the most common business structure used in the United States because an LLC protects the owner’s personal assets. It’s similar to partnerships and corporations, but can be a single-member LLC in most states. An LLC requires a document called an operating agreement.
Each state has different requirements. Here’s a link to find your state’s requirements . Delaware and Nevada are common states to file an LLC because they are really business-friendly. Here’s a blog on the top 10 states to get an LLC.
Partnerships are typically for legal firms. If you choose to use a partnership choose a Limited Liability Partnership. Alternatively, you can just use an LLC.
Corporations are typically for massive organizations. Corporations have taxes on both corporate and income tax so unless you plan on selling stock, you are better off considering an LLC with S-Corp status . Investopedia has good information corporations here .

There are several opportunities to purchase successful franchises. TopFranchise.com has a list of companies in a variety of industries that offer franchise opportunities. This makes it where an entrepreneur can benefit from the reputation of an established business that has already worked out many of the kinks of starting from scratch.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 5. Products and Services
This section of the business plan should focus on what you sell, how you source it, and how you sell it. You should include:
- Unique features that differentiate your business products from competitors
- Intellectual property
- Your supply chain
- Cost and pricing structure
Questions to answer about your products and services
Mike gave us a list of the most important questions to answer about your product and services:
- How will you be selling the product? (in person, ecommerce, wholesale, direct to consumer)?
- How do you let them know they need a product?
- How do you communicate the message?
- How will you do transactions?
- How much will you be selling it for?
- How many do you think you’ll sell and why?
Make sure to use the worksheet on our business plan template .
How to Write a Business Plan Step 6. Sales and Marketing Plan
The marketing and sales plan is focused on the strategy to bring awareness to your company and guides how you will get the product to the consumer. It should contain the following sections:
SWOT Analysis stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Not only do you want to identify them, but you also want to document how the business plans to deal with them.
Business owners need to do a thorough job documenting how their service or product stacks up against the competition.
If proper research isn’t done, investors will be able to tell that the owner hasn’t researched the competition and is less likely to believe that the team can protect its service from threats by the more well-established competition. This is one of the most common parts of a presentation that trips up business owners presenting on Shark Tank .
SWOT Examples

Examples of strengths and weaknesses could be things like the lack of cash flow, intellectual property ownership, high costs of suppliers, and customers’ expectations on shipping times.
Opportunities could be ways to capitalize on your strengths or improve your weaknesses, but may also be gaps in the industry. This includes:
- Adding offerings that fit with your current small business
- Increase sales to current customers
- Reducing costs through bulk ordering
- Finding ways to reduce inventory
- And other areas you can improve
Threats will normally come from outside of the company but could also be things like losing a key member of the team. Threats normally come from competition, regulations, taxes, and unforeseen events.
The management team should use the SWOT analysis to guide other areas of business planning, but it absolutely has to be done before a business owner starts marketing.
Include Competitor Data in Your Business Plan
When you plan a business, taking into consideration the strengths and weaknesses of the competition is key to navigating the field. Providing an overview of your competition and where they are headed shows that you are invested in understanding the industry.
For smaller businesses, you’ll want to search both the company and the owners names to see what they are working on. For publicly held corporations, you can find their quarterly and annual reports on the SEC website .
What another business plans to do can impact your business. Make sure to include things that might make it attractive for bigger companies to outsource to a small business.
Marketing Strategy
The marketing and sales part of business plans should be focused on how you are going to make potential customers aware of your business and then sell to them.
If you haven’t already included it, Mike recommends:
“They’ll want to know about Demographics, ages, and wealth of your target market.”
Make sure to include the Total addressable market . The term refers to the value if you captured 100% of the market.
Advertising Strategy
You’ll explain what formats of advertising you’ll be using. Some possibilities are:
- Online: Facebook and Google are the big names to work with here.
- Print : Print can be used to reach broad groups or targeted markets. Check out this for tips .
- Radio : iHeartMedia is one of the best ways to advertise on the radio
- Cable television : High priced, hard to measure ROI, but here’s an explanation of the process
- Billboards: Attracting customers with billboards can be beneficial in high traffic areas.
You’ll want to define how you’ll be using each including frequency, duration, and cost. If you have the materials already created, including pictures or links to the marketing to show creative assets.
Mike told us “Most businesses are marketing digitally now due to Covid, but that’s not always the right answer.”
Make sure the marketing strategy will help team members or external marketing agencies stay within the brand guidelines .

This section of a business plan should be focused on pricing. There are a ton of pricing strategies that may work for different business plans. Which one will work for you depends on what kind of a business you run.
Some common pricing strategies are:
- Value-based pricing – Commonly used with home buying and selling or other products that are status symbols.
- Skimming pricing – Commonly seen in video game consoles, price starts off high to recoup expenses quickly, then reduces over time.
- Competition-based pricing – Pricing based on competitors’ pricing is commonly seen at gas stations.
- Freemium services – Commonly used for software, where there is a free plan, then purchase options for more functionality.
HubSpot has a great calculator and blog on pricing strategies.
Beyond explaining what strategy your business plans to use, you should include references for how you came to this pricing strategy and how it will impact your cash flow.
Distribution Plan
This part of a business plan is focused on how the product or service is going to go through the supply chain. These may include multiple divisions or multiple companies. Make sure to include any parts of the workflow that are automated so investors can see where cost savings are expected and when.
Supply Chain Examples
For instance, lawn care companies would need to cover aspects such as:
- Suppliers for lawn care equipment and tools
- Any chemicals or treatments needed
- Repair parts for sprinkler systems
- Vehicles to transport equipment and employees
- Insurance to protect the company vehicles and people.
Examples of Supply Chains
These are fairly flat supply chains compared to something like a clothing designer where the clothes would go through multiple vendors. A clothing company might have the following supply chain:
- Raw materials
- Shipping of raw materials
- Converting of raw materials to thread
- Shipping thread to produce garments
- Garment producer
- Shipping to company
- Company storage
- Shipping to retail stores
There have been advances such as print on demand that eliminate many of these steps. If you are designing completely custom clothing, all of this would need to be planned to keep from having business disruptions.
The main thing to include in the business plan is the list of suppliers, the path the supply chain follows, the time from order to the customer’s home, and the costs associated with each step of the process.
According to BizPlanReview , a business plan without this information is likely to get rejected because they have failed to research the key elements necessary to make sales to the customer.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 7. Company Organization and Operational Plan
This part of the business plan is focused on how the business model will function while serving customers. The business plan should provide an overview of how the team will manage the following aspects:
Quality Control
- Legal environment
Let’s look at each for some insight.
Production has already been discussed in previous sections so I won’t go into it much. When writing a business plan for investors, try to avoid repetition as it creates a more simple business plan.
If the organizational plan will be used by the team as an overview of how to perform the best services for the customer, then redundancy makes more sense as it communicates what is important to the business.

Quality control policies help to keep the team focused on how to verify that the company adheres to the business plan and meets or exceeds customer expectations.
Quality control can be anything from a standard that says “all labels on shirts can be no more than 1/16″ off center” to a defined checklist of steps that should be performed and filled out for every customer.
There are a variety of organizations that help define quality control including:
- International Organization for Standardization – Quality standards for energy, technology, food, production environments, and cybersecurity
- AICPA – Standard defined for accounting.
- The Joint Commission – Healthcare
- ASHRAE – HVAC best practices
You can find lists of the organizations that contribute most to the government regulation of industries on Open Secrets . Research what the leaders in your field are doing. Follow their example and implement it in your quality control plan.
For location, you should use information from the market research to establish where the location will be. Make sure to include the following in the location documentation.
- The size of your location
- The type of building (retail, industrial, commercial, etc.)
- Zoning restrictions – Urban Wire has a good map on how zoning works in each state
- Accessibility – Does it meet ADA requirements?
- Costs including rent, maintenance, utilities, insurance and any buildout or remodeling costs
- Utilities – b.e.f. has a good energy calculator .
Legal Environment
The legal requirement section is focused on defining how to meet the legal requirements for your industry. A good business plan should include all of the following:
- Any licenses and/or permits that are needed and whether you’ve obtained them
- Any trademarks, copyrights, or patents that you have or are in the process of applying for
- The insurance coverage your business requires and how much it costs
- Any environmental, health, or workplace regulations affecting your business
- Any special regulations affecting your industry
- Bonding requirements, if applicable
Your local SBA office can help you establish requirements in your area. I strongly recommend using them. They are a great resource.
Your business plan should include a plan for company organization and hiring. While you may be the only person with the company right now, down the road you’ll need more people. Make sure to consider and document the answers to the following questions:
- What is the current leadership structure and what will it look like in the future?
- What types of employees will you have? Are there any licensing or educational requirements?
- How many employees will you need?
- Will you ever hire freelancers or independent contractors?
- What is each position’s job description?
- What is the pay structure (hourly, salaried, base plus commission, etc.)?
- How do you plan to find qualified employees and contractors?
One of the most crucial parts of a business plan is the organizational chart. This simply shows the positions the company will need, who is in charge of them and the relationship of each of them. It will look similar to this:

Our small business plan template has a much more in-depth organizational chart you can edit to include when you include the organizational chart in your business plan.

How to Write a Business Plan Step 8. Financial Statements
No business plan is complete without financial statements or financial projections. The business plan format will be different based on whether you are writing a business plan to expand a business or a startup business plan. Let’s dig deeper into each.
Provide All Financial Income from an Existing Business
An existing business should use their past financial documents including the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement to find trends to estimate the next 3-5 years.
You can create easy trendlines in excel to predict future revenue, profit and loss, cash flow, and other changes in year-over-year performance. This will show your expected performance assuming business continues as normal.
If you are seeking an investment, then the business is probably not going to continue as normal. Depending on the financial plan and the purpose of getting financing, adjustments may be needed to the following:
- Higher Revenue if expanding business
- Lower Cost of Goods Sold if purchasing inventory with bulk discounts
- Adding interest if utilizing financing (not equity deal)
- Changes in expenses
- Addition of financing information to the cash flow statement
- Changes in Earnings per Share on the balance sheet
Financial modeling is a challenging subject, but there are plenty of low-cost courses on the subject. If you need help planning your business financial documentation take some time to watch some of them.
Make it a point to document how you calculated all the changes to the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement in your business plan so that key team members or investors can verify your research.
Financial Projections For A Startup Business Plan
Unlike an existing business, a startup doesn’t have previous success to model its future performance. In this scenario, you need to focus on how to make a business plan realistic through the use of industry research and averages.
Mike gave the following advice in his interview:
Financial Forecasting Mistakes
One of the things a lot of inexperienced people use is the argument, “If I get one percent of the market, it is worth $100 million.” If you use this, investors are likely to file the document under bad business plan examples.
Let’s use custom t-shirts as an example.
Credence Research estimated in 2018 there were 11,334,800,000 custom t-shirts sold for a total of $206.12 Billion, with a 6% compound annual growth rate.
With that data, you can calculate that the industry will grow to $270 Billion in 2023 and that the average shirt sold creates $18.18 in revenue.
Combine that with an IBIS World estimate of 11,094 custom screen printers and that means even if you become an average seller, you’ll get .009% of the market.
Here’s a table for easier viewing of that information.

The point here is to make sure your business proposal examples make sense.
You’ll need to know industry averages such as cost of customer acquisition, revenue per customer, the average cost of goods sold, and admin costs to be able to create accurate estimates.
Our simple business plan templates walk you through most of these processes. If you follow them you’ll have a good idea of how to write a business proposal.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 9. Business Plan Example of Funding Requests
What is a business plan without a plan on how to obtain funding?
The Small Business Administration has an example for a pizza restaurant that theoretically needed nearly $20k to make it through their first month.
In our video, How to Start a $500K/Year T-Shirt Business (Pt. 1 ), Sanford Booth told us he needed about $200,000 to start his franchise and broke even after 4 months.
Freshbooks estimates it takes on average 2-3 years for a business to be profitable, which means the fictitious pizza company from the SBA could need up to $330k to make it through that time and still pay their bills for their home and pizza shop.
Not every business needs that much to start, but realistically it’s a good idea to assume that you need a fairly large cushion.
Ways to get funding for a small business
There are a variety of ways to cover this. the most common are:
- Bootstrapping – Using your savings without external funding.
- Taking out debt – loans, credit cards
- Equity, Seed Funding – Ownership of a percentage of the company in exchange for current funds
- Crowdsourcing – Promising a good for funding to create the product
Keep reading for more tips on how to write a business plan.
How funding will be used
When asking for business financing make sure to include:
- How much to get started?
- What is the minimum viable product and how soon can you make money?
- How will the money be spent?
Mike emphasized two aspects that should be included in every plan,
How to Write a Business Plan Resources
Here are some links to a business plan sample and business plan outline.
- Sample plan
It’s also helpful to follow some of the leading influencers in the business plan writing community. Here’s a list:
- Wise Plans – Shares a lot of information on starting businesses and is a business plan writing company.
- Optimus Business Plans – Another business plan writing company.
- Venture Capital – A venture capital thread that can help give you ideas.
How to Write a Business Plan: What’s Next?
We hope this guide about how to write a simple business plan step by step has been helpful. We’ve covered:
- The definition of a business plan
- Coming up with a business idea
- Performing market research
- The critical components of a business plan
- An example business plan
In addition, we provided you with a simple business plan template to assist you in the process of writing your startup business plan. The startup business plan template also includes a business model template that will be the key to your success.
Don’t forget to check out the rest of our business hub .
Have you written a business plan before? How did it impact your ability to achieve your goals?
80% of businesses fail... Learn how not to.
Learn from business failures and successes in 5 min or less. The stories, frameworks, and tactics that will make you a 10x better founder.
Brandon Boushy
Related articles
How to Start a 7-Figure Poultry Farm (2024)
Step 1. Learn About Poultry Farming
- Why poultry is better than beef
- Different feeds for different chickens
How much to start a chicken farm?

- 32 broiler chickens : $75
- One chicken tractor : $220
- 150 pounds feed : $100
- Gravity water dispenser : $60
- Total : Under $500
How much does it cost to start a chicken farm if you don’t own land?

Is chicken farming profitable?
Poultry companies selling dtc, selling as a commodity, poultry industry.
- A processing plant (or slaughterhouse)
- A wholesale processor
- Supermarkets and retailers
- The final consumer

- Land : It’s best to be near but not in big cities. Prices of land can vary dramatically. For example, you might find two to five acres ranging from $5,000 per acre to $2.5 million per acre.
- Chicken coop : Later on, we’ll explain how to build a chicken coop, but if you’re building with three square feet per chicken, you’ll probably end up spending a ton on your chicken house.
- Chickens: You might find day-old chickens for approximately $1 to $2.50 per chick based on the quantity, sex, and whether they are GMO-raised.
- Feed: You’ll need to feed the chickens, and you’ll probably want to buy in bulk. Per pound, smaller bags are much more expensive than when you buy a ton of feed.
- Transportation costs : IRS mileage deductions change each year, but have been over $.50 per mile since 2008. You can deduct actual costs instead.
- Employees: If you have over 500 chickens per owner, plan to spend $15 per hour according to the BLS .
- Purchase price per pound: $.99
- Additional expenses per pound: $.75
- Profit per pound: $.09
- Sell to the wholesaler by the pound: $1.83

Poultry Wholesalers
- Purchase price per pound: $1.83
- Additional expenses per pound: $.40 per pound
- Profit per pound: $.57
- Sell to supermarkets by the pound: $2.80
Supermarkets

- Payment to wholesaler: $2.80
- Profit: $.07
- Other expenses: $1.13
- Consumer price per pound: $4
Why does this matter to a poultry farm?
Governing laws.
- EPA rules on animal feed operations
- USDA policies regarding livestock
- Farmers Service Agency (FSA, a division of the USDA specifically to help farmers succeed)
- State agencies may have policies about farming permits, licensing, or inspection. Check the FSA map to find experts on your state regulations.
- Many cities and counties may have regulations that apply to starting a chicken farm. I would suggest talking to your local SBA office and health district.
Market Forces
Choose a poultry sector next.
- Sell chickens for meat
- Create feed to sell for poultry farmers
- Hatchery and breeding chicks
- Egg and meat processing
- Broiler farm : meat per pound of feed
- Laying eggs : Eggs per pound of feed
Type of Bird

- Number of eggs per year
- Growth potential
- Aggressiveness
- Space requirements
- And other considerations
Step 2. Write a Poultry Farming Business Plan
Step 3. poultry business loans, step 4. find a location of chicken farm.

Step 5. How to Make a Chicken Farm
- Establish how to position everything on your land.
- Decide how to make the most of your space.
- Build a chicken coop.
- Manage your supply chain.
- Purchase and care for your chickens.
- Process and sell your poultry products.
How to start a poultry farm: Build a Chicken Coop

- Nine 2” x 2” wood beams : $4 each = $36
- Seven 8’ x 2’ corrugated steel panels : $22 each = $154
- Chicken wire : $39 (should be approximately 1 roll)
- Nails and screws: $5
- Estimated Total: $234 + tax, shipping, and handling
How to start a poultry farm: Buy Feed
- Baby chickens: Starter food is best for ages that range from day old chicks to 20 weeks.
- Chicken broilers: If you’re just trying to raise chicks to sell the meat, get food specifically for broilers.
- Teenage chickens: If you want to keep your chicks properly cared for until they each become an adult chicken, you might want to change from starter food to grower food at six weeks. You’ll want to change this when they start laying eggs.
- Egg layers: Once chickens start laying eggs, they need layer feed to help produce healthier eggs. It’s like grower feed but with more calcium and minerals.
How to start a poultry farm: Other Equipment
- Waste removal system(s)
- Lighting instruments
- Brooders (for breeding)
- Heaters (for cold weather)
- Crates (for collecting eggs)
- Egg trays (for handling and selling eggs)
- Perches (for laying hens)
- Nests (for laying hens and breeding)
- Incubator (for breeding)
Get Your Chickens

- Jenks : Business success is often measured by profitability, but longevity is also important. As the longest operating poultry company supplier, they know they understand the poultry farm business.
- Cackle Hatchery : If you are looking to buy from only one supplier, Cackle is probably the place. They sell pretty much everything you need for raising and selling chickens. Plus, they’ve been around for over 80 years.
- Privett Hatchery : If you are on the west coast, you might consider getting your chickens from Privett. It’s in New Mexico making it more convenient for a farmer located in the southwest United States.
Step 6. How to Run a Chicken Farm

- Feed your birds the proper nutrients: We discussed this in the section on feed. This will help promote chicken health.
- Treat against poultry diseases: If your flock catches a chicken disease, you need to separate the sick ones and care for them. You may also have to hire a vet. Learn more about diseases chickens catch .
- Protect against predators: We discussed this during the section on design.
- Dispose of their waste: You’ll need a waste disposal system to help keep the chicken coop clean.
- The deep litter system is a method of composting inside the coop.
- You can also use an automated system.
- Treat against poultry diseases : If your flock catches a chicken disease, you have to separate sick ones and care for them. You may also have to hire a vet.
- Maintain documentation of care: You'll need a great system to document your date of purchase, care, date of processing, and more. Check out USDA documentation requirements .
Step 7. Process the Birds
Step 8. sell the chickens or eggs.

- Consumers: Reach this target market through websites, social media, your own retail location, and farmers' markets.
- Restaurants: Get in touch with restaurant owners through similar channels as consumers but also through trade organizations.
- Poultry processors and wholesalers : Join trade associations or keep reading to find out how to farm for Perdue or Tyson.
How to start a chicken farm for Perdue
- Some of the most advanced systems in the industry
- A consistent supply of industry best practices
- A regional vet dedicated to helping provide care for your poultry
- Flock advisors to help you maximize gross income and profit
- Technical assistance to maintain your systems
How to start a chicken farm for Tyson
How to start a chicken farm to sell eggs, step 9. other business functions.

- Bartering (unique to farming)
How to start a poultry farm: Hiring
- Skill: Do they at least somewhat understand the job?
- Personality: Are they fun to be around? Similar values? Work Ethic?
How to start a poultry farm: Accounting
How to start a poultry farm: marketing.

Go start your own business!
Food Truck for Sale: Ultimate Buying Guide 2024
Buying a food truck is the single largest investment a food truck business owner will make. That’s why we offer this guide on buying a food truck for sale.
We’ve interviewed a lot of business owners and they’ve provided advice on how to buy a food truck. We’ve also added additional information from research to help you buy or lease a food truck.
[su_note note_color="#dbeafc"] Click on any of the links below to find information about a food truck for sale.
Find creative food truck ideas
Create a food truck mockup, find food trucks for sale, get food truck financing, get food truck equipment, how to build a food truck, how to start a food truck business.
- Find a food truck to buy [/su_note]
How to buy a food truck for sale

You’ll want to perform the following process while buying a food truck:
- Build a food truck
- Start a food truck business
Before you even think about buying a food truck for sale, you need to know how the food truck business will make you money. That means you must decide what food and drinks you’ll serve in the food truck. Some food truck ideas include a:
- Pizza truck
- Concession trailer
- Mobile coffee shop
- Ice cream truck
- Breakfast food truck
- Seafood truck
- Lunch truck
- Dinner truck
- Food truck bar
Check out our interview with Saied Samaiel, who started Aybla Grill, which makes more than $50K a month.
Once you’ve decided what you’ll serve as a new food truck business owner, you’ll need to consider how to set up your food truck. If you don’t do it right, your food business success could be much slower.
It will be much easier for your new food truck to succeed if you plan before shopping for a food truck. You’ll want to create a concept design for your food truck, which means you’ll need to:
Measure food truck dimensions
Get a list of equipment you need (and all dimensions), draw the food truck layout.
Let’s look at each step to understand what you’ll need in a food truck for sale.

During the design stage, you’ll need to know the exterior and interior dimensions of food trucks. The outside dimensions of a food truck are useful to know so you can estimate how much it costs to wrap a food truck.
You’ll need the interior dimensions to know whether you can fit the equipment in the space. A food truck can be as small as a postal truck or up to 34 feet long. Most food trucks will be seven feet wide. You’ll also want to ensure the food truck is at least seven feet tall so people can stand comfortably.
In addition to considering different truck dimensions, your food truck business will need additional equipment to operate effectively. You’ll need to know the types of equipment you need and the size to make sure you can fit all the cooking equipment in the food truck you purchase.
Depending on the type of food truck offerings you’ll provide, you’ll need a variety of mobile cooking equipment. Your mobile commercial kitchen will need:
- Fire suppression system
- Food truck menu board
- Cash register/payment processor
- Outdoor furniture for guests (optional)
- Cooking equipment
- Food truck exhaust fan (or food truck vent hood)
- Refrigerator and freezer
- Food truck sink
- Storage for dry food
- Food truck awning
- Space for food truck supplies
- Drink machine
- Food truck oven
- Ice machine
- Food truck window
- Cooking utensils
- Air conditioning and heater
- Food truck water tank
As you can see, there are a lot of food truck appliances that need to fit into a fairly small cooking space. Fortunately, you have the option of buying food trucks fully equipped, which makes starting a food truck business much easier than designing your own storage setup and prep space from scratch.
Once you know the sizes of food trucks and the commercial equipment you need, you’ll need to map out the best way to fit it all in the vehicle.
A new business owner can choose three methods of planning the equipment layout.
- Do-it-yourself (DIY) design
Look for fully equipped food trucks for sale
Hire a mobile commercial kitchen design company.
There are pros and cons to taking each approach when buying a food truck for sale. Keep reading to find out more.
DIY food truck design

When you design your own food truck layout before buying a truck, you’ll want to look for a multipurpose food truck. You can choose to buy a new or used food truck that does not come with commercial equipment for cooking.
Designing the truck layout yourself comes with some challenges. For instance, you’re probably not trained to design and install a professional fire suppression system, work with gas appliances, or install HVAC equipment.
This may be the least expensive way of buying a new food truck for your dream food business, but if you can buy a used food truck for sale, you will probably find it much quicker and easier than building a food truck yourself.
Suggested layout for food trucks
A food truck owner will want to dispense the weight so it is as evenly distributed as possible to reduce the risk of fishtailing .
Whether you choose to have your food truck laid out clockwise (as pictured) or counterclockwise, you’ll want to consider the order in which you or your employees will perform your food prep and service processes.
For instance, a pizza truck might not have condiments and have a pizza-cutting station instead.
You’ll want dedicated spaces for the following, arranged in this order:
- Processing sales
- Cool storage
- Packaging or plating and finishing touches
Finally, you’ll serve your customers out of the second window.
If you serve drinks, you can have a self-service drink machine near the cashier or at the other end of the serving window. Either way, I suggest having it on the same side.
While the exact features of each food truck business will be different, the concepts are the same.

If you buy a fully equipped food truck, there’s no need to do design work. These will normally be more expensive than buying a truck without equipment, but you’ll know the food truck was designed by a professional.
There are plenty of places for a new owner to buy a food truck that is fully equipped with everything you need to start your mobile food truck business. Just search online for the type of food trucks you want to buy. Some common searches include:
- Food trucks for sale
- Used food trucks for sale
- Coffee truck for sale
- Food truck for sale near me
- Used food trailers for sale
- Food carts for sale
- Taco truck for sale
- Food truck trailers for sale
- Lunch truck for sale
- Food truck trailer for sale
- New food truck for sale
- Food trailer for sale
- Used food truck for sale
- Step van for sale
- Food cart for sale
You might also want to add modifiers to your search like “Near me”, state name, city name, or state abbreviation. Some popular searches for local food trucks for sale include:
- Food truck for sale Texas
- Food truck sale California
- Food trucks for sale Los Angeles
- Food trucks for sale Dallas
- Food trucks for sale in Georgia
You can buy custom food trucks if you need a unique system for your food business. That said, before you spend the extra time and money to have engineers design a pro fire suppression system and select the equipment for a custom-designed food truck, make sure you can’t find them premade.

You don’t want to request a custom design, then have the company you work with turn it into a commercially available option. This actually occurred when my dad had custom designs built. He commissioned someone to create a mold, then they started selling the design as a standard product.
While it was great for the company, it meant my dad fully paid for the product development process. Read your contracts when you commission custom work. To keep a product one of a kind, you’ll need to own all design work and any custom fabrications used to create the product.
The next step is looking at food trucks for sale. You’ll want to:
Choose the type of food truck for sale
- Establish how much the food truck will cost
- Decide where to buy the food truck

You can choose from a variety of food trucks. Here are some of the options:
- Concession trailers
Let’s look at the benefits of each of these options when you decide to become a mobile food vendor.
Why should I buy a food truck?
When you look for a food truck for sale, you’ll get a vehicle that has the kitchen and the driving equipment all in one piece. This makes the vehicle safer and easier to drive because there is no trailer attached to the food truck.
A new owner can buy a food truck fully equipped for a specific type of food sales, purchase a multipurpose food truck, or buy an empty food truck that can be fully customized.
Why should I consider concession trailers?

If you own a truck, you might save money buying a concession trailer. There’s also more space in a food trailer than in a food truck because there is no engine, transmission, or passenger space in the trailer.
A food trailer has the benefit of separating the food truck trailer from the engine and transmission. That means you can buy or sell the food truck trailer and the truck together or separately.
You can also leave the food trailer at a location if you’ll be working there for multiple days. This saves you money because you don’t have to tow the concession trailer with you everywhere.
What are the benefits of a food cart?
A food cart is less beneficial than a food truck because most are not motorized. These are a budget way of starting a mobile food business.
Food carts can make a great entry-level food business that is a stepping stone to eventually buying a food truck for sale. Some common food cart business ideas include:
- Ice cream cart
- Hot dog stand
- Drink stand
- Coffee shop
These machines will roll, but the owner must pull or push them to where they want to serve customers.
What are the benefits of a step van?

A step van is a type of food truck that allows you to access the cooking area from the cab.
This is advantageous because you can stop the truck and get to the cooking section without going outside, which is why many food truck business owners use them instead of box trucks.
How much is a food truck?
A food truck for sale can range anywhere from a couple of thousand dollars for a used food truck in poor condition to $200K for a brand-new, fully equipped food truck.
Saied explained:
[su_quote]A stationary food truck (one that stays at the same location each day) is more profitable than one you are driving to a different location each day.[/su_quote]
We’ll talk more about choosing a location for your food truck later.
How much is a food truck to rent?

Food truck rentals cost between $1,000 and $5,000 per month, depending on the terms of the fully equipped food truck rental. You will want to consider terms like:
- Equipment in the food truck
- Duration of services
- Licensing and health department inspections (included and excluded)
Consider renting a food truck so you can get your business started, earn revenue, and then qualify for food truck financing after you have proven your business model.
How much does a food truck cost to buy?
You can buy a food truck for as little as $6,000, but you can find less expensive alternatives.
How much is a used food truck?
According to Roaming Hunger, used food trucks will cost at least $6,000 unequipped or $8,000 with equipment. The prices can go up from there depending on the age of the equipment and the truck and whether it includes a business.
Where to buy a food truck

You can find a food truck for sale through companies like:
- Roaming Hunger
- Local food truck dealers
- Online marketplaces
- Food truck auction sites
- Business brokers
- Local food truck association
Food truck manufacturer
On the West Coast, Mobile Cuisine ranks Prime Design Food Trucks as their top manufacturer. The company builds, remodels, and repairs food trailers and trucks, so you can go to them to get all your equipment and your truck from one place.
On the East Coast, Mobile Cuisine suggests going to Mr. Trailers , which provides food trucks and mobile medical units.
Check out their blog for a list of manufacturers by state. Most food truck manufacturers are located in California, Texas, and Florida, but there are some in other states.
Now that you can answer “How much for a food truck?” and know where to buy them, let’s discuss getting food truck financing.

You can get food truck financing using seven different loan strategies.
- Business line of credit
- Business term loan
- Equipment financing
- Merchant cash advance
- Small Business Administration loan
- Vendor leasing programs
- Working capital loan
Check out our blog about food truck financing , then head over to National Business Capital to apply for food truck loans from the number one provider of online business loans.
This step will vary depending on whether you buy a fully equipped food truck or an empty step van, trailer, or box truck. If you bought a fully equipped vehicle, skip to the section about starting a food truck business. If you didn’t, make sure to read this and the next section.
What food truck equipment do I need?

When you enter the food truck industry, you’ll need:
- An enticing menu
- A refrigerator and freezer
- Exhaust fans
- Huge exterior lightboxes
- Storage space
- Cash register or point-of-sale (POS) machine
Don’t forget to get any specialized equipment based on your food truck needs.
Where to buy food truck equipment
Next, you’ll need to buy the equipment for your step van or trailer. You can purchase these products from some of the following places.
Restaurant supply house
A restaurant supply house is a place that sells food items to serve customers as well as equipment. Most are equipped to help you establish what you need to prep, cook, and serve food. You can go to your local store or shop online. Some popular restaurant supply houses include:
- RestaurantSupply.com: They carry equipment including Manitowac refrigeration machines, cooking equipment, and other products, but not food. They are a supplier for employee-owned Winco grocery stores. Check out Restaurant Supply .
- Web Restaurant Store: Check out Web Restaurant Store’s page for food truck tabletop equipment. They advertise having more than 400K products for sale.
- Amazon: Like every industry, you can get your storage and food prep products from Amazon Business .
Keep reading for other solutions a food truck owner could pursue.
Customization shop

A food truck business owner can also go to auto repair shops that focus on upgrading work vehicles. These companies should be located near you and offer services like:
- Food Truck Wraps: Help people see what you’re serving in your food truck van.
- Huge Exterior Light Boxes: At night, these will help people see the food truck name, menu, and price.
- Food Truck Logos: Nothing builds food truck brand awareness like a logo.
- Equipment Mounting: A mobile kitchen must have the equipment mounted to the food truck interior so it doesn’t fly around.
You might look for people who specialize in car wraps, mobile HVAC, and other features. Check out some food truck wrap ideas below.
Building a food truck requires the following steps.
Create a drawing of the food truck layout
- Strip the food truck
Gather all the equipment
Install concession window, install flooring, install electrical, install gas lines.
- Install plumbing in your food truck
Install a three-compartment sink
Install cooking equipment, install fire suppression system.
The following subsections are a summary of the step-by-step tutorials from Mobile Cuisine combined with my experience in construction management.
Keep reading for more information on how to build a food truck.
You want to have your step van or food trailer design mapped out before you begin. Otherwise, you might not be able to fit everything in the food truck. We discussed how to do this earlier in the blog. Revisit the section on creating a food truck mockup and measuring for equipment (above) for a refresher.
Next, you’ll want to gather all your storage, equipment, and tools so it is easy to start working on the food truck. I suggest laying out the equipment you want in the truck in the same relative position it will go into the step van so you can visualize it before installing it.
Strip the truck

When you buy a multipurpose food truck or trailer, you’ll need to strip out anything that could hinder you from doing business. This includes seats, trim, and anything else you don’t need.
Many people include this step later in the steps for building a food truck, but you need to at least cut out the hole before you do anything else.
Can you imagine how frustrating it would be to install something and then have to redo it because it doesn’t line up with the windows?

Once you have the window cut out for the step van, it’s time to install the floors. You’ll want to make sure you have slip-resistant materials that will not be damaged by heat, cold, or spills (meaning no carpet!).
Make sure the floor is level before installing the flooring materials onto the multipurpose food truck. You might also get slip-resistant kitchen mats like the ones pictured below. You’ll put them in once your food truck is complete.
You’ll need to install a breaker panel, electrical wiring, and lighting fixtures. You’ll probably want to hire or consult with an electrician to make sure you size them right.
If you decide to install the electrical yourself, please refrain from turning it on until after you install safety devices to prevent fires. It would be devastating if your food truck caught fire before you even used it.

A fire prevention system may be required for a food truck. Related equipment may include:
- Fire extinguishers
- Splash guards
- Gas monitors
- Properly secured appliances
- Flexible gas hoses
- Shut-off valves
- Other requirements depending on the business location
Once your multipurpose food truck is equipped with the proper security features, it’s time to install gas lines.
Gas lines will be used in many food truck applications to cook the food. Installing them is not hard, but you need to know what you’re doing.
Most states have laws holding people criminally liable for improper gas line installation.
For this reason, we won’t be providing step-by-step information. Please hire or at least consult a professional. Most HVAC providers are happy to help with work like this for a reasonable cost.
Install plumbing

You’ll need a freshwater reservoir, a waste water reservoir, and a pump in addition to piping and fittings. Check with your local health department about any special rules they’ll require you to follow.
Local health departments normally require a three-compartment sink in every food truck. The sink wells are for washing, rinsing, and sanitizing and make it possible to keep clean and dirty utensils separate.

Next, you’ll want to install the appliances to cook food. Secure them to the food truck wall and connect them to the electrical or gas power source.
At this point, you’ll likely need to get a fire inspection or health audit to make sure the unit meets all local requirements. We discuss this process in detail in the portion about how to start a food truck business below.
Buying a food truck for sale is only a portion of starting a food truck business. There are 11 steps to follow when you start and expand your food truck business.
- Learn about the food truck industry
- Generate food truck ideas
- Know how much it costs to start a food truck business
- Figure business operating costs
- Write a food truck business plan
- Determine financing options
- Obtain licenses and permits
- Buy your truck
- Secure your suppliers
- Streamline the process
- Build your food truck business and brand
Read our blog about starting a food truck for more details on the full process.
Find a food truck to buy

Now that you know how to find a food truck for sale, it’s up to you to find a seller, contact them, and buy your food truck. Sign up for our mailing list to be the first to know when we release our food truck business course. We’ll be sure to make room for you.
What else would you like to know about buying a food truck for sale?
How to Start $417K/Year Food Truck Business
Step #1. Learn about the food truck industry
Step #2. generate food truck ideas, step #3. how much does it cost to start a food truck business, step #4. figure business operating costs, step #5. write a food truck business plan, step #6. determine financing options, step #7. obtain licenses and permits, step #8. buy your truck, step #9. secure your suppliers.
- Step #10. Streamline the process
Step #11: Build your food truck business/brand
Are you ready to start a food truck business, how to start a food truck business.

- Learn About the Food Truck Industry
- Choose Your Food Truck Concept
- Estimate Food Truck Startup Costs
- Plan for Business Operating Costs
- Write a Food Truck Business Plan
- Get Food Truck Financing
- Obtain Licenses and Permits
- Buy Your Truck
- Purchase a POS System
- Streamline the Process
- Build Your Food Truck Business/Brand
How much do food trucks make a year?
Are food trucks profitable.
- Overhead: 25%
- Profit: 20%[/su_quote]

How do I price my food truck menu?
- Actual Food Cost / Food Cost Percentage=Customer Price
- (Choose a Value between 3.33 and 5) x Actual Food Costs=Customer Price
Other startup costs

How to start a food truck business with no money

What licenses are needed to start a food truck?
- Business License –This depends on the city/county/state where you work and is based on the type of service you provide, whether events, catering, etc. In addition to licensing fees, a percentage of the revenue may also go to the government agency, so be sure to factor this into your budget.
- Employer Identification Number – You need this in order to start legally paying employees, withholding taxes, etc.
- Business Permits – This is usually issued by local municipalities. These can change over time, so be sure to review this annually so you understand what is required in the way of food truck permits.
- Vehicle Licensing – Make sure the person driving the food truck is appropriately licensed and insured for that particular vehicle. Find out if you need a commercial driver's license in order to drive the food truck (this is often related to the size/length/weight of the truck.)
- Food Handler's Permit – This may require you and your employees to take a Food Safety Course. Often done online and fairly inexpensive, it may be necessary for truck owners and all employees to complete this in order to comply with food safety requirements.
- Health Department Permit – This differs between states but is typically similar to what a restaurant requires since, technically, your food truck is a restaurant on wheels.
- Fire Certificate – This requires a local fire department inspection. Your equipment must be safety certified, whether electric, propane, generator, etc. If you purchase your truck new and/or have it retrofitted, the vehicle supplier should already know these requirements and have it ready for this inspection.
- Parking Permits – If your food truck is invited to a festival or a private event, this shouldn't be an issue. But if you plan to simply park your food truck on the side of the road, you'll need to do your homework about local parking ordinances in your area.
Where should I park my food truck?

What types of food trucks are there?

Step #10. Streamline the process
Should my food truck have a pos system.

Why do food trucks fail?

nice work https://binarychemist.com/
My Name is PRETTY NGOMANE. A south African female. Aspiring to do farming. And finding a home away from home for the differently abled persons in their daily needs.
Become a business owner in less than 90 days
Start your 10-day free trial of the UpFlip Academy and learn how to start your own business from scratch.
Get business advice straight to your Inbox

24 of My Favorite Sample Business Plans & Examples For Your Inspiration
Published: February 06, 2024
I believe that reading sample business plans is essential when writing your own.

hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(53, 'e9d2eacb-6b01-423a-bf7a-19d42ba77eaa', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"});
As you explore business plan examples from real companies and brands, it’s easier for you to learn how to write a good one.
But what does a good business plan look like? And how do you write one that’s both viable and convincing. I’ll walk you through the ideal business plan format along with some examples to help you get started.
Table of Contents
Business Plan Format
Business plan types, sample business plan templates, top business plan examples.
Ask any successful sports coach how they win so many games, and they’ll tell you they have a unique plan for every single game. To me, the same logic applies to business.
If you want to build a thriving company that can pull ahead of the competition, you need to prepare for battle before breaking into a market.
Business plans guide you along the rocky journey of growing a company. And if your business plan is compelling enough, it can also convince investors to give you funding.
With so much at stake, I’m sure you’re wondering where to begin.
.webp)
Free Business Plan Template
The essential document for starting a business -- custom built for your needs.
- Outline your idea.
- Pitch to investors.
- Secure funding.
- Get to work!
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Fill out the form to get your free template.
First, you’ll want to nail down your formatting. Most business plans include the following sections.
1. Executive Summary
I’d say the executive summary is the most important section of the entire business plan.
Why? Essentially, it's the overview or introduction, written in a way to grab readers' attention and guide them through the rest of the business plan. This is important, because a business plan can be dozens or hundreds of pages long.
There are two main elements I’d recommend including in your executive summary:
Company Description
This is the perfect space to highlight your company’s mission statement and goals, a brief overview of your history and leadership, and your top accomplishments as a business.
Tell potential investors who you are and why what you do matters. Naturally, they’re going to want to know who they’re getting into business with up front, and this is a great opportunity to showcase your impact.
Need some extra help firming up those business goals? Check out HubSpot Academy’s free course to help you set goals that matter — I’d highly recommend it
Products and Services
To piggyback off of the company description, be sure to incorporate an overview of your offerings. This doesn’t have to be extensive — just another chance to introduce your industry and overall purpose as a business.
In addition to the items above, I recommend including some information about your financial projections and competitive advantage here too.:
Keep in mind you'll cover many of these topics in more detail later on in the business plan. So, keep the executive summary clear and brief, and only include the most important takeaways.
Executive Summary Business Plan Examples
This example was created with HubSpot’s business plan template:

This executive summary is so good to me because it tells potential investors a short story while still covering all of the most important details.
.webp?width=500&height=418&name=executive-summary-business-plans-examples%20(1).webp)
Image Source
Tips for Writing Your Executive Summary
- Start with a strong introduction of your company, showcase your mission and impact, and outline the products and services you provide.
- Clearly define a problem, and explain how your product solves that problem, and show why the market needs your business.
- Be sure to highlight your value proposition, market opportunity, and growth potential.
- Keep it concise and support ideas with data.
- Customize your summary to your audience. For example, emphasize finances and return on investment for venture capitalists.
Check out our tips for writing an effective executive summary for more guidance.
2. Market Opportunity
This is where you'll detail the opportunity in the market.
The main question I’d ask myself here is this: Where is the gap in the current industry, and how will my product fill that gap?
More specifically, here’s what I’d include in this section:
- The size of the market
- Current or potential market share
- Trends in the industry and consumer behavior
- Where the gap is
- What caused the gap
- How you intend to fill it
To get a thorough understanding of the market opportunity, you'll want to conduct a TAM, SAM, and SOM analysis and perform market research on your industry.
You may also benefit from creating a SWOT analysis to get some of the insights for this section.
Market Opportunity Business Plan Example
I like this example because it uses critical data to underline the size of the potential market and what part of that market this service hopes to capture.

Tips for Writing Your Market Opportunity Section
- Focus on demand and potential for growth.
- Use market research, surveys, and industry trend data to support your market forecast and projections.
- Add a review of regulation shifts, tech advances, and consumer behavior changes.
- Refer to reliable sources.
- Showcase how your business can make the most of this opportunity.
3. Competitive Landscape
Since we’re already speaking of market share, you'll also need to create a section that shares details on who the top competitors are.
After all, your customers likely have more than one brand to choose from, and you'll want to understand exactly why they might choose one over another.
My favorite part of performing a competitive analysis is that it can help you uncover:
- Industry trends that other brands may not be utilizing
- Strengths in your competition that may be obstacles to handle
- Weaknesses in your competition that may help you develop selling points
- The unique proposition you bring to the market that may resonate with customers
Competitive Landscape Business Plan Example
I like how the competitive landscape section of this business plan below shows a clear outline of who the top competitors are.
.webp?width=500&height=405&name=competitive-landscape-business-plans-examples%20(1).webp)
It also highlights specific industry knowledge and the importance of location, which shows useful experience in this specific industry.
This can help build trust in your ability to execute your business plan.
Tips for Writing Your Competitive Landscape
- Complete in-depth research, then emphasize your most important findings.
- Compare your unique selling proposition (USP) to your direct and indirect competitors.
- Show a clear and realistic plan for product and brand differentiation.
- Look for specific advantages and barriers in the competitive landscape. Then, highlight how that information could impact your business.
- Outline growth opportunities from a competitive perspective.
- Add customer feedback and insights to support your competitive analysis.
4. Target Audience
Use this section to describe who your customer segments are in detail. What is the demographic and psychographic information of your audience?
If your immediate answer is "everyone," you'll need to dig deeper. Here are some questions I’d ask myself here:
- What demographics will most likely need/buy your product or service?
- What are the psychographics of this audience? (Desires, triggering events, etc.)
- Why are your offerings valuable to them?
I’d also recommend building a buyer persona to get in the mindset of your ideal customers and be clear on why you're targeting them.
Target Audience Business Plan Example
I like the example below because it uses in-depth research to draw conclusions about audience priorities. It also analyzes how to create the right content for this audience.
Tips for Writing Your Target Audience Section
- Include details on the size and growth potential of your target audience.
- Figure out and refine the pain points for your target audience , then show why your product is a useful solution.
- Describe your targeted customer acquisition strategy in detail.
- Share anticipated challenges your business may face in acquiring customers and how you plan to address them.
- Add case studies, testimonials, and other data to support your target audience ideas.
- Remember to consider niche audiences and segments of your target audience in your business plan.
5. Marketing Strategy
Here, you'll discuss how you'll acquire new customers with your marketing strategy. I’d suggest including information:
- Your brand positioning vision and how you'll cultivate it
- The goal targets you aim to achieve
- The metrics you'll use to measure success
- The channels and distribution tactics you'll use
I think it’s helpful to have a marketing plan built out in advance to make this part of your business plan easier.
Marketing Strategy Business Plan Example
This business plan example includes the marketing strategy for the town of Gawler.
In my opinion, it really works because it offers a comprehensive picture of how they plan to use digital marketing to promote the community.
Tips for Writing Your Marketing Strategy
- Include a section about how you believe your brand vision will appeal to customers.
- Add the budget and resources you'll need to put your plan in place.
- Outline strategies for specific marketing segments.
- Connect strategies to earlier sections like target audience and competitive analysis.
- Review how your marketing strategy will scale with the growth of your business.
- Cover a range of channels and tactics to highlight your ability to adapt your plan in the face of change.
6. Key Features and Benefits
At some point in your business plan, you'll need to review the key features and benefits of your products and/or services.
Laying these out can give readers an idea of how you're positioning yourself in the market and the messaging you're likely to use. It can even help them gain better insight into your business model.
Key Features and Benefits Business Plan Example
In my opinion, the example below does a great job outlining products and services for this business, along with why these qualities will attract the audience.

Tips for Writing Your Key Features and Benefits
- Emphasize why and how your product or service offers value to customers.
- Use metrics and testimonials to support the ideas in this section.
- Talk about how your products and services have the potential to scale.
- Think about including a product roadmap.
- Focus on customer needs, and how the features and benefits you are sharing meet those needs.
- Offer proof of concept for your ideas, like case studies or pilot program feedback.
- Proofread this section carefully, and remove any jargon or complex language.
7. Pricing and Revenue
This is where you'll discuss your cost structure and various revenue streams. Your pricing strategy must be solid enough to turn a profit while staying competitive in the industry.
For this reason, here’s what I’d might outline in this section:
- The specific pricing breakdowns per product or service
- Why your pricing is higher or lower than your competition's
- (If higher) Why customers would be willing to pay more
- (If lower) How you're able to offer your products or services at a lower cost
- When you expect to break even, what margins do you expect, etc?
Pricing and Revenue Business Plan Example
I like how this business plan example begins with an overview of the business revenue model, then shows proposed pricing for key products.

Tips for Writing Your Pricing and Revenue Section
- Get specific about your pricing strategy. Specifically, how you connect that strategy to customer needs and product value.
- If you are asking a premium price, share unique features or innovations that justify that price point.
- Show how you plan to communicate pricing to customers.
- Create an overview of every revenue stream for your business and how each stream adds to your business model as a whole.
- Share plans to develop new revenue streams in the future.
- Show how and whether pricing will vary by customer segment and how pricing aligns with marketing strategies.
- Restate your value proposition and explain how it aligns with your revenue model.
8. Financials
To me, this section is particularly informative for investors and leadership teams to figure out funding strategies, investment opportunities, and more.
According to Forbes , you'll want to include three main things:
- Profit/Loss Statement - This answers the question of whether your business is currently profitable.
- Cash Flow Statement - This details exactly how much cash is incoming and outgoing to give insight into how much cash a business has on hand.
- Balance Sheet - This outlines assets, liabilities, and equity, which gives insight into how much a business is worth.
While some business plans might include more or less information, these are the key details I’d include in this section.
Financials Business Plan Example
This balance sheet is a great example of level of detail you’ll need to include in the financials section of your business plan.
Tips for Writing Your Financials Section
- Growth potential is important in this section too. Using your data, create a forecast of financial performance in the next three to five years.
- Include any data that supports your projections to assure investors of the credibility of your proposal.
- Add a break-even analysis to show that your business plan is financially practical. This information can also help you pivot quickly as your business grows.
- Consider adding a section that reviews potential risks and how sensitive your plan is to changes in the market.
- Triple-check all financial information in your plan for accuracy.
- Show how any proposed funding needs align with your plans for growth.
As you create your business plan, keep in mind that each of these sections will be formatted differently. Some may be in paragraph format, while others could be charts or graphs.
The formats above apply to most types of business plans. That said, the format and structure of your plan will vary by your goals for that plan.
So, I’ve added a quick review of different business plan types. For a more detailed overview, check out this post .
1. Startups
Startup business plans are for proposing new business ideas.
If you’re planning to start a small business, preparing a business plan is crucial. The plan should include all the major factors of your business.
You can check out this guide for more detailed business plan inspiration .
2. Feasibility Studies
Feasibility business plans focus on that business's product or service. Feasibility plans are sometimes added to startup business plans. They can also be a new business plan for an already thriving organization.
3. Internal Use
You can use internal business plans to share goals, strategies, or performance updates with stakeholders. In my opinion, internal business plans are useful for alignment and building support for ambitious goals.
4. Strategic Initiatives
Another business plan that's often for sharing internally is a strategic business plan. This plan covers long-term business objectives that might not have been included in the startup business plan.
5. Business Acquisition or Repositioning
When a business is moving forward with an acquisition or repositioning, it may need extra structure and support. These types of business plans expand on a company's acquisition or repositioning strategy.
Growth sometimes just happens as a business continues operations. But more often, a business needs to create a structure with specific targets to meet set goals for expansion. This business plan type can help a business focus on short-term growth goals and align resources with those goals.
Now that you know what's included and how to format a business plan, let's review some of my favorite templates.
1. HubSpot's One-Page Business Plan
Download a free, editable one-page business plan template..
The business plan linked above was created here at HubSpot and is perfect for businesses of any size — no matter how many strategies we still have to develop.
Fields such as Company Description, Required Funding, and Implementation Timeline give this one-page business plan a framework for how to build your brand and what tasks to keep track of as you grow.
Then, as the business matures, you can expand on your original business plan with a new iteration of the above document.
Why I Like It
This one-page business plan is a fantastic choice for the new business owner who doesn’t have the time or resources to draft a full-blown business plan. It includes all the essential sections in an accessible, bullet-point-friendly format. That way, you can get the broad strokes down before honing in on the details.
2. HubSpot's Downloadable Business Plan Template

We also created a business plan template for entrepreneurs.
The template is designed as a guide and checklist for starting your own business. You’ll learn what to include in each section of your business plan and how to do it.
There’s also a list for you to check off when you finish each section of your business plan.
Strong game plans help coaches win games and help businesses rocket to the top of their industries. So if you dedicate the time and effort required to write a workable and convincing business plan, you’ll boost your chances of success and even dominance in your market.
This business plan kit is essential for the budding entrepreneur who needs a more extensive document to share with investors and other stakeholders.
It not only includes sections for your executive summary, product line, market analysis, marketing plan, and sales plan, but it also offers hands-on guidance for filling out those sections.
3. LiveFlow’s Financial Planning Template with built-in automation
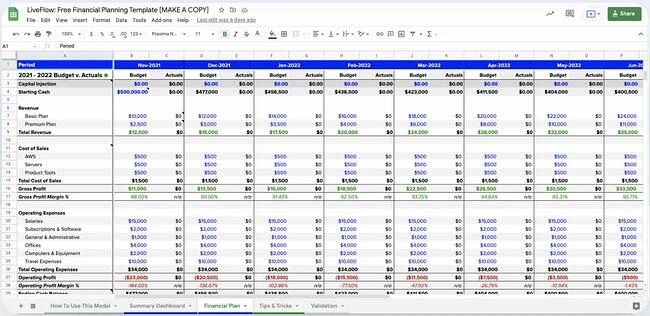
This free template from LiveFlow aims to make it easy for businesses to create a financial plan and track their progress on a monthly basis.
The P&L Budget versus Actual format allows users to track their revenue, cost of sales, operating expenses, operating profit margin, net profit, and more.
The summary dashboard aggregates all of the data put into the financial plan sheet and will automatically update when changes are made.
Instead of wasting hours manually importing your data to your spreadsheet, LiveFlow can also help you to automatically connect your accounting and banking data directly to your spreadsheet, so your numbers are always up-to-date.
With the dashboard, you can view your runway, cash balance, burn rate, gross margins, and other metrics. Having a simple way to track everything in one place will make it easier to complete the financials section of your business plan.
This is a fantastic template to track performance and alignment internally and to create a dependable process for documenting financial information across the business. It’s highly versatile and beginner-friendly.
It’s especially useful if you don’t have an accountant on the team. (I always recommend you do, but for new businesses, having one might not be possible.)
4. ThoughtCo’s Sample Business Plan

One of the more financially oriented sample business plans in this list, BPlan’s free business plan template dedicates many of its pages to your business’s financial plan and financial statements.
After filling this business plan out, your company will truly understand its financial health and the steps you need to take to maintain or improve it.
I absolutely love this business plan template because of its ease-of-use and hands-on instructions (in addition to its finance-centric components). If you feel overwhelmed by the thought of writing an entire business plan, consider using this template to help you with the process.
6. Harvard Business Review’s "How to Write a Winning Business Plan"
Most sample business plans teach you what to include in your business plan, but this Harvard Business Review article will take your business plan to the next level — it teaches you the why and how behind writing a business plan.
With the guidance of Stanley Rich and Richard Gumpert, co-authors of " Business Plans That Win: Lessons From the MIT Enterprise Forum ", you'll learn how to write a convincing business plan that emphasizes the market demand for your product or service.
You’ll also learn the financial benefits investors can reap from putting money into your venture rather than trying to sell them on how great your product or service is.
This business plan guide focuses less on the individual parts of a business plan, and more on the overarching goal of writing one. For that reason, it’s one of my favorites to supplement any template you choose to use. Harvard Business Review’s guide is instrumental for both new and seasoned business owners.
7. HubSpot’s Complete Guide to Starting a Business
If you’re an entrepreneur, you know writing a business plan is one of the most challenging first steps to starting a business.
Fortunately, with HubSpot's comprehensive guide to starting a business, you'll learn how to map out all the details by understanding what to include in your business plan and why it’s important to include them. The guide also fleshes out an entire sample business plan for you.
If you need further guidance on starting a business, HubSpot's guide can teach you how to make your business legal, choose and register your business name, and fund your business. It will also give small business tax information and includes marketing, sales, and service tips.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of starting a business, in addition to writing your business plan, with a high level of exactitude and detail. So if you’re in the midst of starting your business, this is an excellent guide for you.
It also offers other resources you might need, such as market analysis templates.
8. Panda Doc’s Free Business Plan Template

PandaDoc’s free business plan template is one of the more detailed and fleshed-out sample business plans on this list. It describes what you should include in each section, so you don't have to come up with everything from scratch.
Once you fill it out, you’ll fully understand your business’ nitty-gritty details and how all of its moving parts should work together to contribute to its success.
This template has two things I love: comprehensiveness and in-depth instructions. Plus, it’s synced with PandaDoc’s e-signature software so that you and other stakeholders can sign it with ease. For that reason, I especially love it for those starting a business with a partner or with a board of directors.
9. Small Business Administration Free Business Plan Template

The Small Business Administration (SBA) offers several free business plan templates that can be used to inspire your own plan.
Before you get started, you can decide what type of business plan you need — a traditional or lean start-up plan.
Then, you can review the format for both of those plans and view examples of what they might look like.
We love both of the SBA’s templates because of their versatility. You can choose between two options and use the existing content in the templates to flesh out your own plan. Plus, if needed, you can get a free business counselor to help you along the way.
I’ve compiled some completed business plan samples to help you get an idea of how to customize a plan for your business.
I chose different types of business plan ideas to expand your imagination. Some are extensive, while others are fairly simple.
Let’s take a look.
1. LiveFlow
One of the major business expenses is marketing. How you handle your marketing reflects your company’s revenue.
I included this business plan to show you how you can ensure your marketing team is aligned with your overall business plan to get results. The plan also shows you how to track even the smallest metrics of your campaigns, like ROI and payback periods instead of just focusing on big metrics like gross and revenue.
Fintech startup, LiveFlow, allows users to sync real-time data from its accounting services, payment platforms, and banks into custom reports. This eliminates the task of pulling reports together manually, saving teams time and helping automate workflows.
"Using this framework over a traditional marketing plan will help you set a profitable marketing strategy taking things like CAC, LTV, Payback period, and P&L into consideration," explains LiveFlow co-founder, Lasse Kalkar .
When it came to including marketing strategy in its business plan, LiveFlow created a separate marketing profit and loss statement (P&L) to track how well the company was doing with its marketing initiatives.
This is a great approach, allowing businesses to focus on where their marketing dollars are making the most impact. Having this information handy will enable you to build out your business plan’s marketing section with confidence. LiveFlow has shared the template here . You can test it for yourself.
2. Lula Body

Sometimes all you need is a solid mission statement and core values to guide you on how to go about everything. You do this by creating a business plan revolving around how to fulfill your statement best.
For example, Patagonia is an eco-friendly company, so their plan discusses how to make the best environmentally friendly products without causing harm.
A good mission statement should not only resonate with consumers but should also serve as a core value compass for employees as well.
Patagonia has one of the most compelling mission statements I’ve seen:
"Together, let’s prioritise purpose over profit and protect this wondrous planet, our only home."
It reels you in from the start, and the environmentally friendly theme continues throughout the rest of the statement.
This mission goes on to explain that they are out to "Build the best product, cause no unnecessary harm, and use business to protect nature."
Their mission statement is compelling and detailed, with each section outlining how they will accomplish their goal.
4. Vesta Home Automation

This executive summary for a smart home device startup is part of a business plan created by students at Mount Royal University .
While it lacks some of the sleek visuals of the templates above, its executive summary does a great job of demonstrating how invested they are in the business.
Right away, they mention they’ve invested $200,000 into the company already, which shows investors they have skin in the game and aren’t just looking for someone else to foot the bill.
This is the kind of business plan you need when applying for business funds. It clearly illustrates the expected future of the company and how the business has been coming along over the years.
5. NALB Creative Center
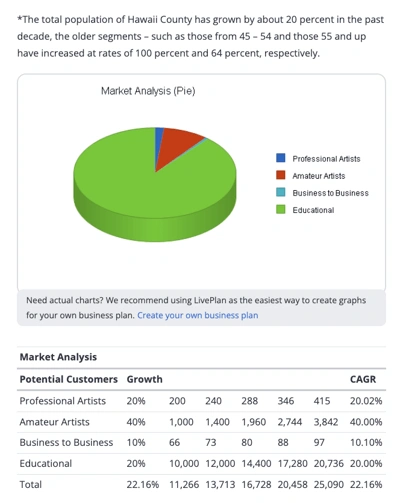
This fictional business plan for an art supply store includes everything one might need in a business plan: an executive summary, a company summary, a list of services, a market analysis summary, and more.
One of its most notable sections is its market analysis summary, which includes an overview of the population growth in the business’ target geographical area, as well as a breakdown of the types of potential customers they expect to welcome at the store.
This sort of granular insight is essential for understanding and communicating your business’s growth potential. Plus, it lays a strong foundation for creating relevant and useful buyer personas .
It’s essential to keep this information up-to-date as your market and target buyer changes. For that reason, you should carry out market research as often as possible to ensure that you’re targeting the correct audience and sharing accurate information with your investors.
Due to its comprehensiveness, it’s an excellent example to follow if you’re opening a brick-and-mortar store and need to get external funding to start your business .
6. Curriculum Companion Suites (CSS)
If you’re looking for a SaaS business plan example, look no further than this business plan for a fictional educational software company called Curriculum Companion Suites.
Like the business plan for the NALB Creative Center, it includes plenty of information for prospective investors and other key stakeholders in the business.
One of the most notable features of this business plan is the executive summary, which includes an overview of the product, market, and mission.
The first two are essential for software companies because the product offering is so often at the forefront of the company’s strategy. Without that information being immediately available to investors and executives, then you risk writing an unfocused business plan.
It’s essential to front-load your company’s mission if it explains your "Why?" and this example does just that. In other words, why do you do what you do, and why should stakeholders care? This is an important section to include if you feel that your mission will drive interest in the business and its offerings.
7. Culina Sample Business Plan

Culina's sample business plan is an excellent example of how to lay out your business plan so that it flows naturally, engages readers, and provides the critical information investors and stakeholders need.
You can use this template as a guide while you're gathering important information for your own business plan. You'll have a better understanding of the data and research you need to do since Culina’s plan outlines these details so flawlessly for inspiration.
8. Plum Sample Business Plan

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
![business aims in a business plan How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/executive-summary-example_5.webp)
How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]

What is a Business Plan? Definition, Tips, and Templates

Maximizing Your Social Media Strategy: The Top Aggregator Tools to Use

The Content Aggregator Guide for 2023
![business aims in a business plan 7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/gantt-chart-example.jpg)
7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]
![business aims in a business plan The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/flowchart%20templates.jpg)
The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]

16 Best Screen Recorders to Use for Collaboration

The 25 Best Google Chrome Extensions for SEO

Professional Invoice Design: 28 Samples & Templates to Inspire You
Customers’ Top HubSpot Integrations to Streamline Your Business in 2022
2 Essential Templates For Starting Your Business
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
- Sources of Business Finance
- Small Business Loans
- Small Business Grants
- Crowdfunding Sites
- How to Get a Business Loan
- Small Business Insurance Providers
- Best Factoring Companies
- Types of Bank Accounts
- Best Banks for Small Business
- Best Business Bank Accounts
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Bank Accounts for Small Businesses
- Free Business Checking Accounts
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Business Credit Cards for Bad Credit
- Build Business Credit Fast
- Business Loan Eligibility Criteria
- Small-Business Bookkeeping Basics
- How to Set Financial Goals
- Business Loan Calculators
- How to Calculate ROI
- Calculate Net Income
- Calculate Working Capital
- Calculate Operating Income
- Calculate Net Present Value (NPV)
- Calculate Payroll Tax
12 Key Elements of a Business Plan (Top Components Explained)
Starting and running a successful business requires proper planning and execution of effective business tactics and strategies .
You need to prepare many essential business documents when starting a business for maximum success; the business plan is one such document.
When creating a business, you want to achieve business objectives and financial goals like productivity, profitability, and business growth. You need an effective business plan to help you get to your desired business destination.
Even if you are already running a business, the proper understanding and review of the key elements of a business plan help you navigate potential crises and obstacles.
This article will teach you why the business document is at the core of any successful business and its key elements you can not avoid.
Let’s get started.
Why Are Business Plans Important?
Business plans are practical steps or guidelines that usually outline what companies need to do to reach their goals. They are essential documents for any business wanting to grow and thrive in a highly-competitive business environment .
1. Proves Your Business Viability
A business plan gives companies an idea of how viable they are and what actions they need to take to grow and reach their financial targets. With a well-written and clearly defined business plan, your business is better positioned to meet its goals.
2. Guides You Throughout the Business Cycle
A business plan is not just important at the start of a business. As a business owner, you must draw up a business plan to remain relevant throughout the business cycle .
During the starting phase of your business, a business plan helps bring your ideas into reality. A solid business plan can secure funding from lenders and investors.
After successfully setting up your business, the next phase is management. Your business plan still has a role to play in this phase, as it assists in communicating your business vision to employees and external partners.
Essentially, your business plan needs to be flexible enough to adapt to changes in the needs of your business.
3. Helps You Make Better Business Decisions
As a business owner, you are involved in an endless decision-making cycle. Your business plan helps you find answers to your most crucial business decisions.
A robust business plan helps you settle your major business components before you launch your product, such as your marketing and sales strategy and competitive advantage.
4. Eliminates Big Mistakes
Many small businesses fail within their first five years for several reasons: lack of financing, stiff competition, low market need, inadequate teams, and inefficient pricing strategy.
Creating an effective plan helps you eliminate these big mistakes that lead to businesses' decline. Every business plan element is crucial for helping you avoid potential mistakes before they happen.
5. Secures Financing and Attracts Top Talents
Having an effective plan increases your chances of securing business loans. One of the essential requirements many lenders ask for to grant your loan request is your business plan.
A business plan helps investors feel confident that your business can attract a significant return on investments ( ROI ).
You can attract and retain top-quality talents with a clear business plan. It inspires your employees and keeps them aligned to achieve your strategic business goals.
Key Elements of Business Plan
Starting and running a successful business requires well-laid actions and supporting documents that better position a company to achieve its business goals and maximize success.
A business plan is a written document with relevant information detailing business objectives and how it intends to achieve its goals.
With an effective business plan, investors, lenders, and potential partners understand your organizational structure and goals, usually around profitability, productivity, and growth.
Every successful business plan is made up of key components that help solidify the efficacy of the business plan in delivering on what it was created to do.
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan.
1. Executive Summary
One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
In the overall business plan document, the executive summary should be at the forefront of the business plan. It helps set the tone for readers on what to expect from the business plan.
A well-written executive summary includes all vital information about the organization's operations, making it easy for a reader to understand.
The key points that need to be acted upon are highlighted in the executive summary. They should be well spelled out to make decisions easy for the management team.
A good and compelling executive summary points out a company's mission statement and a brief description of its products and services.

An executive summary summarizes a business's expected value proposition to distinct customer segments. It highlights the other key elements to be discussed during the rest of the business plan.
Including your prior experiences as an entrepreneur is a good idea in drawing up an executive summary for your business. A brief but detailed explanation of why you decided to start the business in the first place is essential.
Adding your company's mission statement in your executive summary cannot be overemphasized. It creates a culture that defines how employees and all individuals associated with your company abide when carrying out its related processes and operations.
Your executive summary should be brief and detailed to catch readers' attention and encourage them to learn more about your company.
Components of an Executive Summary
Here are some of the information that makes up an executive summary:
- The name and location of your company
- Products and services offered by your company
- Mission and vision statements
- Success factors of your business plan
2. Business Description
Your business description needs to be exciting and captivating as it is the formal introduction a reader gets about your company.
What your company aims to provide, its products and services, goals and objectives, target audience , and potential customers it plans to serve need to be highlighted in your business description.
A company description helps point out notable qualities that make your company stand out from other businesses in the industry. It details its unique strengths and the competitive advantages that give it an edge to succeed over its direct and indirect competitors.
Spell out how your business aims to deliver on the particular needs and wants of identified customers in your company description, as well as the particular industry and target market of the particular focus of the company.
Include trends and significant competitors within your particular industry in your company description. Your business description should contain what sets your company apart from other businesses and provides it with the needed competitive advantage.
In essence, if there is any area in your business plan where you need to brag about your business, your company description provides that unique opportunity as readers look to get a high-level overview.
Components of a Business Description
Your business description needs to contain these categories of information.
- Business location
- The legal structure of your business
- Summary of your business’s short and long-term goals
3. Market Analysis
The market analysis section should be solely based on analytical research as it details trends particular to the market you want to penetrate.
Graphs, spreadsheets, and histograms are handy data and statistical tools you need to utilize in your market analysis. They make it easy to understand the relationship between your current ideas and the future goals you have for the business.
All details about the target customers you plan to sell products or services should be in the market analysis section. It helps readers with a helpful overview of the market.
In your market analysis, you provide the needed data and statistics about industry and market share, the identified strengths in your company description, and compare them against other businesses in the same industry.
The market analysis section aims to define your target audience and estimate how your product or service would fare with these identified audiences.

Market analysis helps visualize a target market by researching and identifying the primary target audience of your company and detailing steps and plans based on your audience location.
Obtaining this information through market research is essential as it helps shape how your business achieves its short-term and long-term goals.
Market Analysis Factors
Here are some of the factors to be included in your market analysis.
- The geographical location of your target market
- Needs of your target market and how your products and services can meet those needs
- Demographics of your target audience
Components of the Market Analysis Section
Here is some of the information to be included in your market analysis.
- Industry description and statistics
- Demographics and profile of target customers
- Marketing data for your products and services
- Detailed evaluation of your competitors
4. Marketing Plan
A marketing plan defines how your business aims to reach its target customers, generate sales leads, and, ultimately, make sales.
Promotion is at the center of any successful marketing plan. It is a series of steps to pitch a product or service to a larger audience to generate engagement. Note that the marketing strategy for a business should not be stagnant and must evolve depending on its outcome.
Include the budgetary requirement for successfully implementing your marketing plan in this section to make it easy for readers to measure your marketing plan's impact in terms of numbers.
The information to include in your marketing plan includes marketing and promotion strategies, pricing plans and strategies , and sales proposals. You need to include how you intend to get customers to return and make repeat purchases in your business plan.

5. Sales Strategy
Sales strategy defines how you intend to get your product or service to your target customers and works hand in hand with your business marketing strategy.
Your sales strategy approach should not be complex. Break it down into simple and understandable steps to promote your product or service to target customers.
Apart from the steps to promote your product or service, define the budget you need to implement your sales strategies and the number of sales reps needed to help the business assist in direct sales.
Your sales strategy should be specific on what you need and how you intend to deliver on your sales targets, where numbers are reflected to make it easier for readers to understand and relate better.

6. Competitive Analysis
Providing transparent and honest information, even with direct and indirect competitors, defines a good business plan. Provide the reader with a clear picture of your rank against major competitors.
Identifying your competitors' weaknesses and strengths is useful in drawing up a market analysis. It is one information investors look out for when assessing business plans.

The competitive analysis section clearly defines the notable differences between your company and your competitors as measured against their strengths and weaknesses.
This section should define the following:
- Your competitors' identified advantages in the market
- How do you plan to set up your company to challenge your competitors’ advantage and gain grounds from them?
- The standout qualities that distinguish you from other companies
- Potential bottlenecks you have identified that have plagued competitors in the same industry and how you intend to overcome these bottlenecks
In your business plan, you need to prove your industry knowledge to anyone who reads your business plan. The competitive analysis section is designed for that purpose.
7. Management and Organization
Management and organization are key components of a business plan. They define its structure and how it is positioned to run.
Whether you intend to run a sole proprietorship, general or limited partnership, or corporation, the legal structure of your business needs to be clearly defined in your business plan.
Use an organizational chart that illustrates the hierarchy of operations of your company and spells out separate departments and their roles and functions in this business plan section.
The management and organization section includes profiles of advisors, board of directors, and executive team members and their roles and responsibilities in guaranteeing the company's success.
Apparent factors that influence your company's corporate culture, such as human resources requirements and legal structure, should be well defined in the management and organization section.
Defining the business's chain of command if you are not a sole proprietor is necessary. It leaves room for little or no confusion about who is in charge or responsible during business operations.
This section provides relevant information on how the management team intends to help employees maximize their strengths and address their identified weaknesses to help all quarters improve for the business's success.
8. Products and Services
This business plan section describes what a company has to offer regarding products and services to the maximum benefit and satisfaction of its target market.
Boldly spell out pending patents or copyright products and intellectual property in this section alongside costs, expected sales revenue, research and development, and competitors' advantage as an overview.
At this stage of your business plan, the reader needs to know what your business plans to produce and sell and the benefits these products offer in meeting customers' needs.
The supply network of your business product, production costs, and how you intend to sell the products are crucial components of the products and services section.
Investors are always keen on this information to help them reach a balanced assessment of if investing in your business is risky or offer benefits to them.
You need to create a link in this section on how your products or services are designed to meet the market's needs and how you intend to keep those customers and carve out a market share for your company.
Repeat purchases are the backing that a successful business relies on and measure how much customers are into what your company is offering.
This section is more like an expansion of the executive summary section. You need to analyze each product or service under the business.
9. Operating Plan
An operations plan describes how you plan to carry out your business operations and processes.
The operating plan for your business should include:
- Information about how your company plans to carry out its operations.
- The base location from which your company intends to operate.
- The number of employees to be utilized and other information about your company's operations.
- Key business processes.
This section should highlight how your organization is set up to run. You can also introduce your company's management team in this section, alongside their skills, roles, and responsibilities in the company.
The best way to introduce the company team is by drawing up an organizational chart that effectively maps out an organization's rank and chain of command.
What should be spelled out to readers when they come across this business plan section is how the business plans to operate day-in and day-out successfully.
10. Financial Projections and Assumptions
Bringing your great business ideas into reality is why business plans are important. They help create a sustainable and viable business.
The financial section of your business plan offers significant value. A business uses a financial plan to solve all its financial concerns, which usually involves startup costs, labor expenses, financial projections, and funding and investor pitches.
All key assumptions about the business finances need to be listed alongside the business financial projection, and changes to be made on the assumptions side until it balances with the projection for the business.
The financial plan should also include how the business plans to generate income and the capital expenditure budgets that tend to eat into the budget to arrive at an accurate cash flow projection for the business.
Base your financial goals and expectations on extensive market research backed with relevant financial statements for the relevant period.
Examples of financial statements you can include in the financial projections and assumptions section of your business plan include:
- Projected income statements
- Cash flow statements
- Balance sheets
- Income statements
Revealing the financial goals and potentials of the business is what the financial projection and assumption section of your business plan is all about. It needs to be purely based on facts that can be measurable and attainable.
11. Request For Funding
The request for funding section focuses on the amount of money needed to set up your business and underlying plans for raising the money required. This section includes plans for utilizing the funds for your business's operational and manufacturing processes.
When seeking funding, a reasonable timeline is required alongside it. If the need arises for additional funding to complete other business-related projects, you are not left scampering and desperate for funds.
If you do not have the funds to start up your business, then you should devote a whole section of your business plan to explaining the amount of money you need and how you plan to utilize every penny of the funds. You need to explain it in detail for a future funding request.
When an investor picks up your business plan to analyze it, with all your plans for the funds well spelled out, they are motivated to invest as they have gotten a backing guarantee from your funding request section.
Include timelines and plans for how you intend to repay the loans received in your funding request section. This addition keeps investors assured that they could recoup their investment in the business.
12. Exhibits and Appendices
Exhibits and appendices comprise the final section of your business plan and contain all supporting documents for other sections of the business plan.
Some of the documents that comprise the exhibits and appendices section includes:
- Legal documents
- Licenses and permits
- Credit histories
- Customer lists
The choice of what additional document to include in your business plan to support your statements depends mainly on the intended audience of your business plan. Hence, it is better to play it safe and not leave anything out when drawing up the appendix and exhibit section.
Supporting documentation is particularly helpful when you need funding or support for your business. This section provides investors with a clearer understanding of the research that backs the claims made in your business plan.
There are key points to include in the appendix and exhibits section of your business plan.
- The management team and other stakeholders resume
- Marketing research
- Permits and relevant legal documents
- Financial documents
Was This Article Helpful?
Martin luenendonk.
Martin loves entrepreneurship and has helped dozens of entrepreneurs by validating the business idea, finding scalable customer acquisition channels, and building a data-driven organization. During his time working in investment banking, tech startups, and industry-leading companies he gained extensive knowledge in using different software tools to optimize business processes.
This insights and his love for researching SaaS products enables him to provide in-depth, fact-based software reviews to enable software buyers make better decisions.
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.
- Updated Terms of Use
- New Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
- Closed Captioning Policy
Quotes displayed in real-time or delayed by at least 15 minutes. Market data provided by Factset . Powered and implemented by FactSet Digital Solutions . Legal Statement .
This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed. ©2024 FOX News Network, LLC. All rights reserved. FAQ - New Privacy Policy
Americans adjust retirement goals up 15% but savings drop: survey
Gen zers start building retirement nest eggs earlier.

Gen Z and millennials have bigger retirement goals, according to a recent Northwestern Mutual survey. ( iStock )
The amount Americans believe they will need to retire comfortably has increased faster than inflation, but what they are saving has dropped, a recent survey said.
U.S. adults believe they will need at least $1.46 million to retire in style, according to a Northwestern Mutual survey . This figure is up 15% from the $1.27 million Americans said they needed last year. In 2020, survey respondents thought having $951,000 stashed away would provide a good enough cushion.
At the same time, the average amount Americans have saved for retirement dropped to $88,400 from $89,300 in 2023, and is more than $10,000 off its five-year peak of $98,800 in 2021.
"People's 'magic number' to retire comfortably has exploded to an all-time high, and the gap between their goals and progress has never been wider," says Aditi Javeri Gokhale, chief strategy officer, head of institutional investments and president of retail investments at Northwestern Mutual. "Inflation is expanding our expectations for retirement savings, and putting the pressure on to plan and stay disciplined."
If you're struggling to save for retirement in the current economy, you could consider paying down high-interest debt with a personal loan at a lower interest rate, which can help you lower your monthly payments. Visit Credible to compare options from multiple lenders at once and choose the one that's the best for you.
GAS, HOUSING AND CAR INSURANCE COSTS SOAR, FUELING INFLATION IN MARCH
Young Americans start saving sooner
Gen Zers have bigger retirement goals and will need $1.6 million to retire comfortably, the survey said. Despite the bigger goal, this generation of U.S. adults plan to retire by age 60 because they started saving for retirement earlier.
While the average American started saving at age 31, Gen Zers began building their retirement nest at age 22—nearly a decade earlier. By comparison, Baby Boomers started building retirement savings a full 15 years after this age and said they expect to work until the age of 72. Millennials and Gen X'ers, who began their savings at ages 27 and 31, respectively, expect to work until 64 and 67.
"These numbers tell a fascinating story about the profound shift in financial planning that has taken shape in America," Javeri Gokhale said in a statement . "Young people today recognize the value of retirement planning and building wealth early on in life and are getting a significant head start over their parents and grandparents."
"At the same time, Gen Z is redefining retirement and signaling that they plan to have long and fulfilling post-career lives," Javeri Gokhale continued. "The good news is that they are investing earlier so they can save the money they need to enjoy it."
If high-interest debt is preventing you from saving more for retirement, you could consider paying it off with a personal loan at a lower interest rate. Visit Credible to find your personalized rate in minutes without affecting your credit score.
AMERICANS TAP INTO SAVINGS AS THEY STRUGGLE WITH INFLATION: SURVEY
Only half of Boomers believe they are ready to retire
More than 4 million U.S. adults will turn 65 this year. Still, among the generations closest to retirement, only half of Boomers (49%) and Gen Xers (48%) believe they will be financially prepared to retire comfortably, with many expecting that they will likely outlive their savings.
Even more problematic is that while many older Americans across both generations anticipate a retirement shortfall, more than a third (37% and 38%, respectively) have not addressed it. One way older adults can prepare is by minimizing the taxes they pay on their retirement savings, yet only 37% have a plan in place.
"Putting money into a 401K may not be enough to retire comfortably if the financial plan doesn't address the impact of taxes on retirement income," Javeri Gokhale said. "Most people don't realize that their retirement income may be taxed about 20% or 30% when they withdraw and spend it. When they recognize the impact, it's often too late for them to adjust."
If you are retired or are preparing to retire, paying down debt with a personal loan can help you reduce your interest rate and your monthly expenses. You can visit Credible to compare multiple personal loan lenders at once and choose the one with the best interest rate for you.
REPUBLICAN STATES FILE SUIT TO STOP BIDEN'S SAVE STUDENT LOAN REPAYMENT PLAN
Have a finance-related question, but don't know who to ask? Email The Credible Money Expert at [email protected] and your question might be answered by Credible in our Money Expert column.
Biden and oil companies like this climate tech. Many Americans do not.
Carbon dioxide pipelines and underground injection can cut greenhouse gas, but community opposition is fierce.

The remote stretch of public grazing land in southeastern Montana has hardly changed since homesteading days, but underneath this wind-swept expanse lies a hidden asset in high demand: thousands of acres of porous rock where oil company executives say greenhouse gas could be piped in from afar and stored forever.
ExxonMobil and the Biden administration see in the grassy 100,000 acres a launchpad for one of the world’s most audacious climate experiments, a plan to take emissions spewing from power plants and factories and trap them underground where they cannot contribute to global warming. The scheme is inching forward despite criticism it will permit polluters to keep polluting while slowing the transition to solar and wind energy. And now sponsors face the additional hurdle of intense local opposition.
In the ranching community of Carter County, Mont., the prospect of shipping in all that carbon pollution and injecting it underneath an area called Snowy River is about as popular as an outbreak of hoof-and-mouth disease.
“The question I keep hearing is, ‘Why are they making us the dumping ground for the rest of the country?’” said Rod Tauck, chairman of the Carter County Board of Commissioners and a descendant of homesteaders who more than a century ago settled his family ranch. “Not a single constituent I know wants this.”
Such tensions are emerging nationwide, throwing an industrial-size wrench into the quest by the White House and major energy companies to advance a vast network of “carbon capture” infrastructure across the country. It would involve tens of thousands of miles of new pipelines , and scores of remote storage sites on the scale of Snowy River, targeted because the porous rock underneath them can act like a carbon sponge.
This vision for using technology to reverse climate change was once viewed widely as far-fetched.
Now, proposals to divert carbon dioxide from smokestacks to vast subterranean wells are regarded by the White House , the United Nations and the International Energy Agency as crucial to preserving any hope of meeting the world’s climate goals. The Biden administration’s plan to zero out emissions from the power grid by 2035 increasingly hinges on the success of colossal carbon capture deployment. The government has made billions of dollars of incentives available to motivate companies like ExxonMobil and Chevron to rapidly develop it.
The urgency is only increasing as a surge in forecasted energy use — driven by the insatiable electricity appetite of artificial-intelligence developers and a national boom in manufacturing — is delaying retirement of old fossil-fuel power plants and pushing utilities to build new ones.
New clean energy like wind and solar is not coming online quickly enough to meet all the projected demand, prompting government to lean on plans to stow away carbon pollution.
“We have to stop fossil fuels from causing global warming before the world stops using fossil fuels,” Myles Allen, a climate scientist at the University of Oxford in England who has served on the U.N. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, said recently at CERAWeek, an energy conference sponsored by S&P Global. “This is the way to stop fossil fuels from causing global warming.”
But early carbon capture projects are floundering.
Hostile community reception is undermining plans from the Gulf Coast of Louisiana to the prairies of South Dakota. Energy companies racing ahead are facing tough questions around safety, environmental impact and technological viability.
In Montana, the federal Bureau of Land Management in 2022 identified the Snowy River site as one of the first stretches of public land that may be suitable for carbon sequestration. ExxonMobil wants to inject 450 million cubic feet of carbon dioxide per day into the ground. The company is not identifying where that gas would come from, but one likely source is a carbon dioxide pipeline currently used to support oil and gas extraction projects (the pressurized gas is used to force fossil fuels to the surface).
That pipeline is connected to a large ExxonMobil natural gas plant 500 miles away in Wyoming. ExxonMobil says Snowy River’s storage capacity is equal to a year’s worth of polluting greenhouse gas from 1.6 million cars.
Legacy energy companies like ExxonMobil are eager to deploy technologies that could extend the life of fossil fuels by mitigating their role in global warming. Plus, federal incentives are potentially lucrative. The single Montana project could generate as much as $12.7 billion in federal tax subsidies. ExxonMobil took it over when it acquired carbon capture and pipeline developer Denbury for $4.9 billion in November.
Company officials say they have not yet made a final decision to build in Montana. But assessing the project’s viability, they say, requires they get the BLM permit to store the carbon now, so they can do testing on-site. Montana Gov. Greg Gianforte supports the company’s plan.
“We are fully committed to working with the community,” said Kathleen Ash, CEO of Denbury, now a fully owned ExxonMobil subsidiary. “This is a safe and proven technology.”
Many in the local community see something else: big corporations looking for a payday partnering with an administration turning a blind eye to a flawed technology. They point to problems that carbon capture projects are encountering around the world, such as Chevron’s sprawling Gorgon operation at a massive natural gas field in Australia. It is not trapping even half the carbon dioxide planned, amid persistent technological troubles.
BLM officials counter that carbon dioxide has been safely injected underground as part of the oil production process for decades. They call the projects an “important tool” for fighting climate change and advancing the administration’s agenda to erase emissions.
“They are presenting this as a climate solution and I don’t know that it is,” said Liz Barbour, who manages Cinch Buckle Ranch, an operation bordering Snowy River that uses low-impact, conservation-focused agricultural practices. “The only thing I do know is that it is part of their plan to continue producing oil and gas.” Barbour is among several ranchers working with a grass-roots group called the Northern Plains Resource Council to fight the project.
Local landowners with sharply contrasting politics and views on climate change are finding common cause in the battle. The council’s argument that carbon capture is “an unproven, government hand-out to large out of state corporations” was echoed repeatedly in interviews in this county of 1,415 people defined by wide-open spaces and dirt roads, where visiting a neighbor can involve an hour-long journey. Carter County cast 89 percent of its ballots for Donald Trump in 2020.
“Many of us are willing to accept the premise that this is a dangerous compound that needs to be gotten rid of,” said Jack Owen, a 72-year-old who ranches on land his ancestors homesteaded. “The question is, ‘Why here?’”
ExxonMobil’s assurances that the project would be almost entirely underground, with little noticeable impact on the landscape are met skeptically. Local landowners counter that upgrading the roads, drilling wells, and installing new pipelines would take a heavy toll on the landscape.
The scale of carbon that must be effectively stored nationwide to make a dent in global warming is enormous. Claude Letourneau, the CEO of Svante, one of North America’s leading carbon capture technology firms, said containing the emissions created by manufacturing processes like cement- and steel-making could require 10,000 plants to trap the gas, compress it and then pipe or truck it to places like Snowy River.
An ambitious proposal in the Midwest recently collapsed. The proposed 1,200-mile Heartland Greenway pipeline was supposed to span five states, bringing 15 million tons of carbon dioxide captured at ethanol plants each year to storage sites where it would be buried.
The project, proposed by Navigator CO2, appeared to have early advantages. Ethanol plants emit uncontaminated carbon dioxide that is less complicated to capture and compress than the gas from other industries. And many landowners along the proposed route already hosted oil and gas pipelines.
But community opposition was intense. Landowners and local regulators worried about safety and environmental fallout. The CEO of Williams, one of the biggest natural gas pipeline companies in the world, said in an interview that even his board chairman, who owns farmland in Iowa, wants nothing to do with the carbon dioxide pipelines.
“He said, ‘I don’t want it damaging this very valuable cropland,” Williams CEO Alan Armstrong said.
Navigator CO2 canceled the Heartland Greenway project in October. It blamed “the unpredictable nature of the regulatory and government processes involved.”
Armstrong is one of many energy executives who said the project faltered because the developers spent too little time educating communities about the technology and talking through concerns. Companies more practiced in securing permits for pipelines, it was argued, would win local buy-in.
But it is not turning out that way for ExxonMobil in Montana.
Assurances from ExxonMobil that disruption would be minimal are met with worries that the project will disrupt the ecosystem, leave water tables vulnerable to the leaching of carbon dioxide, and create a safety hazard.
A rupture in the existing pipeline several years ago left one Carter County ranch looking as if a meteor had hit it. Pictures from 2018 show a deep, truck-size crater in the ground covered with what looks like dry ice residue, caused by the compressed carbon dioxide’s combustion.
Since that time, another major pipeline accident had dire consequences for the town of Satartia, Miss. The pipeline was also owned by Denbury, now an ExxonMobil subsidiary.
The 2020 rupture filled the air above a section of the pipeline with dangerous amounts of carbon dioxide, resulting in a medical emergency that sent 45 people to the hospital with respiratory and other problems, according to a U.S. Department of Transportation investigation.
The gas caused three men driving through the area to pass out in their car and the engine to stop running. Fire department officials had to break the windows to pull them out, according to local 911 call tapes and public records obtained by the nonprofit Climate Investigations Center. Residents desperately called 911 for help — in one case, a mother reported that her child couldn’t breathe, and in another, a caller said her friend was on the ground shaking and drooling, as if suffering a seizure.
Denbury paid a $2.8 million fine as part of a settlement with the federal government in which it did “not admit to any of the alleged violations or risks identified.” Some of the residents injured in the incident — and their doctors — say they are still suffering serious ailments because of it.
ExxonMobil officials said new training protocols for emergency responders have been initiated since the incident. They say that there has never been a fatality associated with piping carbon dioxide and that accidents involving such pipelines are rare. The company said it also supports stepped-up federal safety regulations amid the planned expansion of carbon dioxide pipelines.
Energy companies say they are undeterred.
Among the projects inching forward is one on a 140,000-acre coastal stretch between Houston and the petrochemical facilities of Port Arthur, Tex., called Bayou Bend, where Chevron plans to store as much as 1 billion tons of carbon dioxide. The company is hoping the proximity to factories will make the project more palatable to regulators and landowners.
Chevron is also aiming to bury carbon in wells off the coast of Bayou Bend, a plan that alarms marine biologists but could prove less vulnerable to community protest.
A visit to Bayou Bend punctuates the immensity of it all. The site stretches for miles, with the flat, grassy landscape interrupted only by the occasional cow chomping on weeds or alligator sunning itself in a marsh.
Developers promoting the projects are adamant that most of the work will happen out of sight, with the carbon buried as deep as 10,000 feet and hardly any industrial activity above ground.
“This has to happen,” said Chris Powers, Chevron’s vice president for carbon capture, utilization and storage, pointing to the forecasting models showing that carbon capture is crucial to curbing global warming. “To make this grow at scale, it is going to take hundreds of projects.”
Back in Montana, rancher Mike Hansen says if it is all so harmless, project boosters in the nation’s capital should just start burying carbon pollution there.
“We asked them, ‘Why don’t you do this under Washington, D.C.?’” he said. “They told us, ‘We can’t do that. There are too many people there.’”
“That is not saying much for us.”

Trump's team wants to restructure the Fed and let him have a say on interest rate decisions: WSJ
- Some members of Trump's team want to restructure the Federal Reserve, the WSJ reported.
- That could include allowing the president to have a direct say on interest rate decisions.
- It would also allow him to get rid of Fed Chair Jerome Powell before his term ends in 2026.

The nation's central bank might look quite different if former President Donald Trump wins the upcoming election.
The Wall Street Journal reported on Thursday night that members of Trump's team are creating plans that would restructure the Federal Reserve and allow Trump to influence the Fed's actions, according to people familiar — a move that would erode the Fed's independence from political entities.
According to the Journal, the proposals would give Trump a say on interest-rate decisions , along with giving him the authority to oust Fed Chair Jerome Powell from his position before his term is up in 2026.
Trump's advisors cautioned that the campaign has not confirmed these plans:
"Let us be very specific here: unless a message is coming directly from President Trump or an authorized member of his campaign team, no aspect of future presidential staffing or policy announcements should be deemed official," Trump senior advisors Susie Wiles and Chris LaCivita told the Journal.
The Journal also reported that the proposal would require the Fed to be subject to review by the Office of Management and Budget when issuing new rules — a process that other federal agencies have to undergo and would be another effort to diminish the central bank's independence on matters of banking regulation.
Trump has previously been critical of Powell's handling of interest rates during the pandemic. To help the Fed achieve its 2% inflation target, the Federal Open Market Committee has hiked interest rates 11 consecutive times since March 2022. In September, the Fed paused the hikes and held rates steady since then , and Powell has emphasized the importance of being confident in economic data before cutting rates this year.
Related stories
Trump hasn't been on board with Powell's timing. In Februrary, Trump told Fox News that Powell is being "political" by potentially choosing to cut rates right around the time of the presidential election.
"I think he's going to do something to probably help the Democrats, I think, if he lowers interest rates," Trump said, adding that "it looks to me like he's trying to lower interest rates for the sake of maybe getting people elected."
Powell has long maintained that the Fed is not a political entity, saying during an April discussion that "our analysis is free from any personal or political bias, in service to the public."
"We will not always get it right — no one does," he said. "But our decisions will always reflect our painstaking assessment of what is best for our economy in the medium and longer term — and nothing else."
None of this can be done without Trump back in the White House
The former president is the Republican Party's presumptive nominee, having handily defeated Florida Gov. Ron DeSantis, former South Carolina Gov. Nikki Haley, entrepreneur Vivek Ramaswamy, and others in the ongoing GOP primary election.
Despite many polls showing Trump ahead of President Joe Biden in head-to-head matchups, the outcomes change when 3rd party candidates are introduced into the mix, especially Democrat-turned-Independent Robert F. Kennedy Jr .
After losing to Biden in 2020, Trump has an unexpected advantage this time around: much more interest from young voters than before. Biden previously led Trump with the group by a nearly 20-point margin, but recent polls show that lead has fallen to just 1 to 2 percentage points.
There is, however, a catch: younger voters are historically much less likely to vote than older ones, and several GOP-led state legislatures introduced bills in recent years restricting which forms of identification can be used at the voting booth, which could further reduce young voter turnout.
Trump has also been hampered in recent weeks by his many legal troubles, such as the ongoing hush-money case in New York and his team's appeal to the Supreme Court on Thursday to give presidents sweeping immunity for their actions in office.
Watch: Meet the Republicans who are Trump's likely successors
- Main content

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
1. Create Your Executive Summary. The executive summary is a snapshot of your business or a high-level overview of your business purposes and plans. Although the executive summary is the first section in your business plan, most people write it last. The length of the executive summary is not more than two pages.
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating a business plan and what key components you need to include. 1. Create an executive summary. Start with a brief overview of your entire plan. The executive summary should cover your business plan's main points and key takeaways.
4. Learning and Growth Opportunities. Another consideration while setting business goals and objectives is learning and growth opportunities for your team. These are designed to increase employee satisfaction and productivity. According to Strategy Execution, learning and growth opportunities touch on three types of capital: Human: Your ...
Learn about the best business plan software. 1. Write an executive summary. This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your ...
Step 2: Do your market research homework. The next step in writing a business plan is to conduct market research. This involves gathering information about your target market (or customer persona), your competition, and the industry as a whole. You can use a variety of research methods such as surveys, focus groups, and online research to ...
To plan your plan, you'll first need to decide what your goals and objectives in business are. As part of that, you'll assess the business you've chosen to start, or are already running, to see ...
A Harvard Business Review study found that the ideal time to write a business plan is between 6 and 12 months after deciding to start a business. But the reality can be more nuanced - it depends on the stage a business is in, or the type of business plan being written. Ideal times to write a business plan include: When you have an idea for a ...
Many professionals use the terms business goal and business objective interchangeably. Generally, a business goal is a broad, long-term outcome an organization works toward, while a business objective is a specific and measurable task, project, or initiative.. Think of business objectives as the steps an organization takes toward their broader, long-term goals.
A business plan is a document that communicates a company's goals and ambitions, along with the timeline, finances, and methods needed to achieve them. Additionally, it may include a mission statement and details about the specific products or services offered. A business plan can highlight varying time periods, depending on the stage of your company and its goals.
A business plan is a written document that defines your business goals and the tactics to achieve those goals. A business plan typically explores the competitive landscape of an industry, analyzes a market and different customer segments within it, describes the products and services, lists business strategies for success, and outlines ...
8. Critical success factors: Clarify the high-level goals you need to achieve in order to achieve your strategic goals. 9. Strategic management: Execute against your strategic plan in order to achieve your company goals. 10. Business goals: Set predetermined targets to achieve in a set period of time. 11.
Economic Business Objective: Also called financial objectives, economic objectives relate to the financial health and growth of the company. These objectives can involve profits, revenue, costs, cash flow, sustainable growth, debt management, and investments. Example: Reduce spending on paid advertisements by 20 percent.
1. Executive summary. This short section introduces the business plan as a whole to the people who will be reading it, including investors, lenders, or other members of your team. Start with a sentence or two about your business, development goals, and why it will succeed. If you are seeking funding, summarise the basics of the financial plan. 2.
Business plan goals are critical for defining the direction and purpose of a business. They provide measurable outcomes, motivation, and accountability, guiding decision-making and resource allocation. Examples of business plan goals can include financial, market penetration, operational, human resources, and social responsibility objectives.
Social objectives. For example, a sample of business goals and objectives for a business plan for a bakery could be: To increase its annual revenue by 20% in the next year. To reduce its production costs by 10% in the next six months. To launch a new product line of gluten-free cakes in the next quarter.
Although this is the last part of the business plan that you'll write, it's the first section (and maybe the only section) that stakeholders will read. The executive summary of a business plan sets the stage for the rest of the document. It includes your company's mission or vision statement, value proposition, and long-term goals. 3.
What's a business plan template? A business plan template is a pre-structured framework that outlines the core aspects of a business plan. It helps organize and detail key components, providing a clear picture of what the business aims to achieve. Miro's business plan template includes: Problem: Identify the core problem that the business plans ...
How to Write a Business Plan Step 1. Create a Cover Page. The first thing investors will see is the cover page for your business plan. Make sure it looks professional. A great cover page shows that you think about first impressions. A good business plan should have the following elements on a cover page:
8. Panda Doc's Free Business Plan Template. PandaDoc's free business plan template is one of the more detailed and fleshed-out sample business plans on this list. It describes what you should include in each section, so you don't have to come up with everything from scratch.
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan. 1. Executive Summary. One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
Clawback. v. t. e. A business plan is a formal written document containing the goals of a business, the methods for attaining those goals, and the time-frame for the achievement of the goals. It also describes the nature of the business, background information on the organization, the organization's financial projections, and the strategies it ...
Simply put, your business plan helps you create clarity by helping you to define your objectives and goals for the year. Perhaps, you want to: Increase your sales volume
A business aim is the overall target or goal of the business, whereas business objectives are the steps a business needs to take to meet its overall aims. A business may have several different ...
Takeda Pharmaceutical Co. said it will streamline its workforce and lean more heavily on data and technology in a restructuring plan intended to improve growth and profit margins.
Gen Zers have bigger retirement goals and will need $1.6 million to retire comfortably, the survey said. Despite the bigger goal, this generation of U.S. adults plan to retire by age 60 because ...
ExxonMobil and the Biden administration see in the grassy 100,000 acres a launchpad for one of the world's most audacious climate experiments, a plan to take emissions spewing from power plants ...
The Wall Street Journal reported that Trump's advisors are making a plan that would give Trump the authority to oust Powell from the Federal Reserve. Menu icon A vertical stack of three evenly ...