What Is A Business Continuity Plan? [+ Template & Examples]
Published: December 30, 2022
When a business crisis occurs, the last thing you want to do is panic.

The second-to-last thing you want to do is be unprepared. Crises typically arise without warning. While you shouldn't start every day expecting the worst, you should be relatively prepared for anything to happen.
A business crisis can cost your company a lot of money and ruin your reputation if you don't have a business continuity plan in place. Customers aren't very forgiving, especially when a crisis is influenced by accidents within the company or other preventable mistakes. If you want your company to be able to maintain its business continuity in the face of a crisis, then you'll need to come up with this type of plan to uphold its essential functions.

In this post, we'll explain what a business continuity plan is, give examples of scenarios that would require a business continuity plan, and provide a template that you can use to create a well-rounded program for your business.
Table of Contents:

What is a business continuity plan?
- Business Continuity Types
- Business Continuity vs Disaster Recovery
Business Continuity Plan Template
How to write a business continuity plan.
- Business Continuity Examples
A business continuity plan outlines directions and procedures that your company will follow when faced with a crisis. These plans include business procedures, names of assets and partners, human resource functions, and other helpful information that can help maintain your brand's relationships with relevant stakeholders. The goal of a business continuity plan is to handle anything from minor disruptions to full-blown threats.
For example, one crisis that your business may have to respond to is a severe snowstorm. Your team may be wondering, "If a snowstorm disrupted our supply chain, how would we resume business?" Planning contingencies ahead of time for situations like these can help your business stay afloat when you're faced with an unavoidable crisis.
When you think about business continuity in terms of the essential functions your business requires to operate, you can begin to mitigate and plan for specific risks within those functions.
.png)
Crisis Communication and Management Kit
Manage, plan for, and communicate during your corporate crises with these crisis management plan templates.
- Free Crisis Management Plan Template
- 12 Crisis Communication Templates
- Post-Crisis Performance Grading Template
- Additional Crisis Best Management Practices
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Business Continuity Planning
Business continuity planning is the process of creating a plan to address a crisis. When writing out a business continuity plan, it's important to consider the variety of crises that could potentially affect the company and prepare a resolution for each.
Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
How to Navigate Customer Service During a Business Closure

10 Crisis Communication Plan Examples (and How to Write Your Own)

I Tried 7 Crisis Management Software to See if They’re Worth It (Results & Recommendations)

20 Crisis Management Quotes Every PR Team Should Live By
![business continuity plan document sample Social Media Crisis Management: Your Complete Guide [Free Template]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/social-media-crisis-management_11.webp)
Social Media Crisis Management: Your Complete Guide [Free Template]
![business continuity plan document sample De-Escalation Techniques: 19 Best Ways to De-Escalate [Top Tips + Data]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/de-escalation-techniques_2.webp)
De-Escalation Techniques: 19 Best Ways to De-Escalate [Top Tips + Data]

Situational Crisis Communication Theory and How It Helps a Business

What Southwest’s Travel Disruption Taught Us About Customer Service

Showcasing Your Crisis Management Skills on Your Resume
![business continuity plan document sample What Is Contingency Planning? [+ Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/contingency-planning.jpg)
What Is Contingency Planning? [+ Examples]
Manage, plan for, and communicate during a corporate crisis.
Service Hub provides everything you need to delight and retain customers while supporting the success of your whole front office
How to Write a Business Continuity Plan + Template
The goal of risk management is not to eliminate all risks but to effectively reduce their likelihood and impact. One way to do that is through business continuity planning.
Having a business continuity plan in place can help your organization keep operating at some capacity during a disaster.
Below, get straightforward answers to what a business continuity plan includes, why it’s important, and how to write one. You’ll also find a business continuity template to simplify the process.
What is a business continuity plan?
A business continuity plan is a document containing a predetermined set of procedures that describe how an organization will sustain its business operations during and after a significant disruption.
This disruption may be caused by a broad range of threats, including natural disasters, technical failures, and cyberattacks .
What is business continuity management?
A business continuity plan is one part of business continuity management (BCM). BCM includes risk assessment, response planning, recovery, and long-term maintenance of the policies and procedures developed, tested, and used when a crisis occurs.
What is the primary goal of business continuity planning?
The primary goal of business continuity planning is to identify preparations and recovery actions that can assist an organization in resuming operations and services as quickly as possible during and after a crisis.
For example, most business operations depend heavily on technology and automated systems, and the disruption of these systems for even a few hours may cause severe problems. Consider a Zoom outage. This may impact meetings with colleagues, customers, and prospects and important projects and deals as a result. A company with a business continuity plan that has identified a substitute tool for video meetings will be able to recover faster than a company without one.
To ensure your business runs as smoothly as possible even when faced with system failures, cyber attacks, natural disasters, and other major disruptions, there must be an awareness of potential crises that could impact critical systems, tools, and skills of your organization and a plan to deal with them.
Business continuity planning is also important for getting and staying compliant with some privacy and security standards, including SOC 2®. Let’s take a look at this other reason for creating a BCP and keeping it up to date.
Recommended reading

SOC 2 Compliance: Requirements, Audit Process, and Benefits for Business Growth
Why is a business continuity plan important for SOC 2 compliance?
A business continuity plan is part of the documentation that a SOC 2 auditor will likely review, along with your systems and security controls, to determine your level of compliance with the Trust Services Criteria (TSC) you’ve selected. This plan is especially important if you include Availability as a TSC in your SOC 2 audit .
The Availability controls in SOC 2 focus on minimizing downtime. Risk assessment is therefore essential.
A SOC 2 auditor will most likely review whether your company has identified and thought of ways to mitigate environmental threats that could impact system availability, like hurricanes, tornados, and wildfires. The same process should be applied to “man made” threats, like theft and cyber attacks.
A SOC 2 auditor will also likely review whether your business continuity plan can be applied to unforeseen events that could impact your system availability and capacity, like a global pandemic.
An auditor will also likely review if you’ve tested your BCP within the last year (at least).
Who is responsible for business continuity planning?
Business continuity planning must be a top-down effort. Meaning, it must have the support and willing participation of a director or senior manager at the company. While they will act as the executive sponsor, another individual should be appointed as the BCP coordinator. Depending on the size of the organization, a planning team representing all major areas of operations may also need to be appointed to assist the BCP coordinator.
This coordinator and/or team should be appropriately announced and empowered to execute on a range of responsibilities, including uncovering your business’s weaknesses and making plans to mitigate them, testing those plans to make sure they’re effective for different types of crises, and updating them as new threats emerge.
What’s the difference between business continuity, disaster recovery, and incident response plans?
There are several contingency and continuity plans that can help minimize the impact of catastrophic events. Let’s take a look at the three most common plans and how they differ from each other below.
Business continuity plan vs disaster recovery plan
The key difference between a business continuity and disaster recovery plan is that a BCP provides procedures for sustaining business operations while recovering from a significant disruption, whereas a DRP provides procedures for recovering information systems operations after a significant system disruption like a major software failure or a natural disaster by relocating them to an alternate location.
Many organizations choose to combine their business continuity and disaster recovery plans into a single document. However, some choose to create them as standalone documents.
Business continuity plan vs incident response
The key difference between a business continuity plan and incident response plan is that a BCP provides procedures for sustaining business operations while recovering from a significant disruption, whereas an IRP provides procedures for mitigating and correcting a system after a security incident, like a virus or Trojan horse.
An IRP plan should detail a recovery process for when security incidents do happen.
This is another crucial document that a SOC 2 auditor will likely review to determine your level of compliance with the TSC you’ve selected.
What does a business continuity plan typically include?
A business continuity plan typically includes the following:
- Mission critical services, processes, and resources: Every BCP should include a list of mission critical services, processes, and resources. These need to be recovered first when a BCP event occurs to minimize downtime.
- Alternative location considerations: During a significant BCP event, an organization may need to use back-up data centers, back-up sites for operations, remote locations, or other alternative locations. These are typically documented in the BCP along with considerations like the accessibility of these alternative sites, transportation alternatives to these sites, the number of staff necessary to perform critical activities at these sites, and other resources that will be required.
- Vendor relationships: Organizations may categorize vendors into risk levels and evaluate the risk in their BCP plans.
- Telecommunications services and technology considerations: Organizations typically detail strategies for maintaining operations during communications disruptions in their BCP. This may include using multiple telecommunication providers, secondary phone lines, cloud technology, temporary phone lines, mobile telecom units and Wi-Fi for staff without power, as well as back-up mobile phone services with different carriers.
- Communication plans: Organizations typically establish communications plans with staff, customers, and other external third parties, including regulators, exchanges, and emergency officials, in their BCP as well.
- Regulatory and compliance considerations: Organizations typically include regulatory requirements in their BCPs and should regularly update them to include any new requirements.
- Review and testing methods: Organizations should include how their BCP is reviewed and tested and how often. For example, they may conduct full BCP tests at least annually or sooner if significant changes are made. They may also conduct employee training or require employees to review their BCP annually to ensure all personnel are familiar with the plan and their responsibilities.
- Recovery objectives: A BCP will typically include key recovery objectives that help organizations plan how quickly they need to recover data and systems in order to minimize disruptions and maintain smooth operations during unexpected events. These are defined below: - RPO (Recovery Point Objective): RPO sets the limit for how much data loss a business can tolerate after a disruption. It defines the latest acceptable point in time to recover data, minimizing potential losses. - RTO (Recovery Time Objective): RTO is the maximum acceptable downtime for systems or processes. It indicates how quickly a business needs to recover and resume normal operations after a disruption.
Business continuity plan example
This business continuity plan example from Santa Cruz Health is designed for different facilities to customize to ensure measures are taken to prepare and pre-position resources to ensure continuity of mission critical services and processes in an event that disrupts normal operations and impacts essential operations of the facility. It is broken down into several sections, including:
- General : Describes the purpose of the BCP, as stated above.
- Activation : Briefly describes when the plan should be activated.
- Overview : Briefly describes what the plan is, how it was developed, what steps need to be taken to ensure it’s effective, and what’s included.
- Continuity requirements : Lists the facility’s mission critical services, processes, equipment and supplies, IT applications, records, and business continuity personnel.
- Continuity and recovery actions : Lists procedures following the occurrence of different BCP events, including loss of power, loss of HVAC, and relocation of departmental services to an alternate location.
How to write a business continuity plan
Now it’s time to start formulating and building out your business continuity plan. To guide you through the process, we’ve broken the process down into six key steps. We’ve also provided a template below to help get you started.

1. Identify and assess your risks.
The first major task of writing a BCP is identifying the risks or threats in your environment and determining how they might impact your operations. For example, some environmental threats may be likely to cause physical damage to your building. Other types of threats may have an impact on your staff and their families.
The risks that are most threatening to your operations should be prioritized.
2. Identify critical elements of your organization.
The next major task is identifying the tools, systems, and skills that are essential to your operations and how critical they are to recover. You can kick off brainstorming by posing the question, how do we achieve our goals?
For example, let’s say one of your mission critical services is fundraising. In that case, a critical asset might be pledge cards. The vendor that prints your pledge cards would also be considered critical.
When identifying these systems, tools, and skills, you’ll also want to determine what resources would be required to restore them and therefore resume the mission critical services and processes they are part of. Examples of resource requirements are facilities, personnel, equipment, software, data files, system components, and vital records.
This will help determine priority levels for sequencing recovery activities. In other words, what needs to be restored first in order to get back to work as quickly as possible during and after a crisis?
3. Identify ways to mitigate risks.
Now that you understand your organization’s unique risks and critical elements, you’re ready to create a plan of action.
Start by identifying strategies that will eliminate the risks you identified in step 1 entirely. If that’s not possible, identify strategies that will lessen their impact. For example, it’s impossible to eliminate the threat of environmental threats like snowstorms entirely. Instead, you can create a procedure to have your employees and contractors work remotely if a snowstorm makes it impossible or difficult to get to the office. This will require that all employees and contractors have the appropriate supplies and equipment and receive the same communications.
These mitigation strategies are designed to eliminate or lessen the impact of a threat before a crisis and should therefore be implemented as quickly as possible.
4. Identify ways to prepare for and recover from the loss of any critical elements.
Since it is impossible to eliminate all threats facing your organization, your next step is to identify as many strategies as possible for dealing with the loss of each critical element identified in step 2.
For example, installing protective systems like a security system, fire alarm system, and antivirus software can all be considered strategies to prepare for and recover from the loss of critical elements caused by theft, vandalism, environmental hazards, cyber attacks, and other threats.
The goal is to come up with as many preparedness strategies as possible in order to best prepare and recover from the loss of mission critical assets during and after a crisis.
During the review or testing stage, you can remove any strategies that are too time-consuming or expensive.
5. Prepare for how you will respond after a crisis.
Now that plans and strategies are in place, you can take steps to improve the efficiency and quality of your organization’s response to a crisis to help you get back to work as quickly as possible.
Consider creating a recovery team that can assess your losses and initiate recovery actions after a crisis. The roles and responsibilities of this team can be documented in your BCP.
6. Update and test your business continuity plan.
Your business continuity plan is a living document. It should be updated to reflect the evolving risks and needs of your business. Whether you’re integrating new software that suddenly crashes or bringing on a new management team member, your BCP should reflect these changes.
If there are no major changes impacting your business, you should still test your business continuity plan once a year at a minimum. This is a best practice and compliance requirement. You can use a variety of testing methods, including tabletop exercises and simulation tests.
Testing and keeping documentation like this up to date is an important part of continuous compliance .

What Is Continuous Compliance + How To Achieve It
Business continuity plan template.
Use this template to begin identifying the risks, critical elements, mitigation actions, and preparedness strategies that will make up the basic components of your business continuity plan.

What are the benefits of a business continuity plan?
Implementing and maintaining an effective business continuity plan offers a range of benefits, including:
- reduced costs and impact on business performance when a disruption occurs
- a consistent, organization-wide approach to respond and recover from a significant disruption
- assurance for clients, suppliers, regulators, and other stakeholders that the organization has systems and processes in place for business continuity
- improved business performance and organizational resilience
- a better understanding of the business, its critical issues, and areas of vulnerability
What are the 5 components of a business continuity plan?
While every business continuity plan is unique, five key components are:
- Risks and their potential business impact and likelihood of occurrence
- Mission critical services, processes, and resources
- Risk mitigation actions
- Preparedness strategies to prepare for and recover from the loss of any critical elements
- Training, testing, and plan maintenance
What are the 4 P’s of business continuity?
The four P's of business continuity are people, processes, premises, and providers. Below are definitions of each:
- People : This includes your employees and customers.
- Processes : This includes the technology and processes your business uses to keep everything running.
- Premises : This includes the buildings and spaces from which your business operates.
- Providers : This includes partners, vendors, and suppliers that your business relies on for resources.
What is a real-life example of business continuity?
A real-life example of business continuity is the response to the Cape Town water crisis, which began in 2015. During a period of severe drought, Cape Town implemented several response and recovery strategies which averted the catastrophe of running out of water — also known as “Day Zero.” This included the introduction of innovative pressure reduction methodologies to curb water losses, sustained reduction in water use, and effective public communication and awareness programs to avoid “Day Zero.”
How do I write a BCM plan?
Below is a step-by-step process for writing a BCM plan:
- Identify and assess risks (can use the 4 P’s)
- Identify mission critical products, services, or functions
- Evaluate the potential impact of risks and disruptions to critical elements
- List actions to mitigate these risks
- List strategies to prepare for and recover from the loss of any critical elements
- Maintain, review, and continuously update the business continuity plan
Why do business continuity plans fail?
Business continuity plans fail for a variety of reasons, with the most common being a lack of buy-in from top management. Other reasons are that no one is appointed to take ownership of business continuity planning, or the plan isn’t tested and updated regularly to keep up with changes affecting the business.
Use trust to accelerate growth
Grc overview, what is grc and why is it important, the 3 components of grc, navigating cybersecurity governance, 14 common types of cybersecurity attacks in 2023, data governance: definition, principles, and frameworks, how to build a smart data governance strategy, data governance metrics and kpis, what is a risk management strategy + examples, risk assessment: purpose, process, and software + template, what is risk mitigation + strategies, how to create a risk register + template, how to create an incident response plan + template, what is a change management process + template, what is third-party risk management + policy, compliance and auditing, security compliance: how to keep your business safe & meet regulations, 15 essential regulatory and security compliance frameworks, how to conduct an effective internal compliance audit, how to implement a grc program, how to implement a grc program + checklist, success metrics for grc programs, how to measure grc maturity, grc tools and resources, grc automation, what is grc software and how does it work, top benefits of adopting grc software, how to choose a grc software solution.
SOC 1 ® , SOC 2 ® and SOC 3 ® are registered trademarks of the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants in the United States. The AICPA ® Trust Services Criteria for Security, Availability, Processing Integrity, Confidentiality, and Privacy is copyrighted by the Association of International Certified Professional Accountants. All rights reserved.
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Legal Templates
Home Business Business Continuity Plan
Business Continuity Plan Template
Use a business continuity plan to outline how your business will continue to operate in a range of disaster scenarios.

Updated December 18, 2023 Written by Sara Hostelley | Reviewed by Brooke Davis
A business continuity plan outlines the instructions and procedures a business should follow after a natural disaster or disruptive event so it can resume its operations. Events like floods and fires can interrupt your business practices, so it’s essential to have a plan in place to handle these situations and effectively get back to work.
What Is a Business Continuity Plan?
When to use a business continuity plan, benefits of a business continuity plan, elements of a business continuity plan, different types of business continuity plans, activities to complete before writing a business continuity plan, how to write a business continuity plan, business continuity plan sample.
A business continuity plan is a document establishing your organization’s strategies for dealing with a disaster. These procedures help you resume business quickly and reduce downtime and lost revenue.
It covers essential processes like protecting assets, handling human resources issues, and dealing with business partners.
Business Continuity Planning vs. Disaster Recovery Planning
An effective business continuity plan helps a company continue its overall operations after a catastrophe, while a disaster recovery plan focuses on reviving a business’s IT-related functions.
Creating a business continuity plan before you need it can help you prepare for the unexpected. It helps you be proactive so you don’t have to devise a plan amidst a disaster.
Once your continuity plan is in place, you may need to implement it during disasters like:
- Cyberattacks
- Natural disasters like hurricanes, earthquakes, tornados, and floods
- Major IT or internet disruptions
- Pandemics or health crises
- Supply chain disruptions
- Man-made disasters or times of social unrest
While a business plan guides your company’s everyday operations, a business continuity plan helps you resume company activities after severe disturbances.
Explore the benefits of a business continuity plan for your company:
Better Decision-Making
A BCP offers a structured framework for employees to make decisions during high-stress situations. Clear protocols and communication methods help your business continuity management team make rational decisions, which can promote confidence and encourage action among employees.
A More Efficient Return to Normal Business Operations
A BCP could make the difference between continued operations and further turmoil in an emergency. Returning to business operations quickly can prevent customers from seeking out competing businesses.
A business continuity plan template makes planning for contingencies in various scenarios easy and addresses the most critical roles and responsibilities necessary for keeping your company running.
Above all, a BCP limits confusion during critical situations and orients employees to the primary focus.
Increased Employee Safety
BCPs prioritize employees’ safety and well-being during emergencies. These plans include guidelines for remote work so employees don’t have to be near the disaster site. They also contain protocols for communicating with one another and evacuating plans in case a disaster happens during work hours.
A Reduction in Lost Time and Revenue
Unmitigated disruptions can financially weaken an organization quickly. Business continuity plans account for all factors necessary for continued operations. The more effort you put into planning, the more time and money you can save.
So, ensure a reliable backup plan for essential systems and enable remote access to customer, product, and company data to keep the revenue stream flowing.
Ability to Quickly Implement IT Fixes
Natural and manufactured disasters typically involve system disruptions. To remain functional, build redundancy into your critical systems. This proactivity will allow you to implement essential fixes to hardware and software assets.
Increased Organizational Resilience
A BCP prepares a company to encounter any challenges it may face. It lets the company’s employees adapt strategies as necessary and work towards continuous improvements, allowing the company to experience long-term success no matter the obstacles it encounters.
Explore some essential elements in a business continuity plan:
- Business Impact Analysis: Determine how a disaster would impact your business’s operations.
- Risk Assessment: Identify the risks that may disrupt your business’s processes.
- Business Continuity Strategy: Detail the steps you’ll take to keep your company running if an interruption occurs. Tailor this strategy to your business’s needs.
- Recovery Team: Include members from across key departments in your recovery team.
- Training: Define training procedures to ensure all members have sufficient knowledge relating to emergency protocols.
- Business Continuity Exercises: Create simulations to practice how your business continuity team would react in an emergency.
- Communication: Establish methods for distributing information internally and externally.
- Backup Locations and Physical Assets: List backup locations for conducting business operations if the primary location isn’t usable. Summarize the equipment you’ll need to continue operations.
- Periodic Review and Recommendations: Include policies for reviewing and updating your plan. Accept recommendations from employees to improve the plan’s efficiency.
- Technology: Describe the processes for retaining access to technology systems. Detail the importance of having emergency power and data backup procedures in place.
While a business continuity plan can cover various recovery strategies for specific events, it prioritizes one event. Explore some of the types of business continuity plans:
- Scope: Emphasize the restoration of normal business activities.
- Objective: To prepare for an unforeseen emergency.
- Scope: Focus on the recovery of IT data, systems, and infrastructure.
- Objective: To reduce downtime and data loss by quickly restoring IT services if they go down.
- Scope: Address communication methods and strategies after a crisis.
- Objective: To provide clear and timely communication to internal and external stakeholders, ensuring the accurate sharing of information.
- Scope: Involve the supply chain’s continuity, including procurement, manufacturing, and distribution.
- Objective: To limit supply chain disruptions and maintain the availability of services and goods.
- Scope: Address the continuity of physical facilities, including warehouses, manufacturing plants, and offices.
- Objective: To ensure the availability of operational facilities or other locations during critical events.
- Scope: Focus on employees’ well-being and safety.
- Objective: To maintain workforce availability and set up guidelines for remote work if possible.
- Scope: Involve continuity plans for key third-party parties, including partners, suppliers, and vendors.
- Objective: To account for the company’s dependencies on external parties and minimize associated disruptions.
- Scope: Address regulatory requirements relating to business continuity.
- Objective: To ensure compliance with industry standards and legal regulations.
Explore some activities to complete before writing a business continuity plan so you can create a more effective document:
1. Decide on a Writing Team
Decide on a team to write the plan. Find employees knowledgeable about various business processes so they can assign tasks accordingly.
Ask for employees’ input to create control and command teams. Appoint several people to be in charge during a crisis so they can have one another’s support. Establish a clear chain of command to minimize arguments and promote efficiency.
Nominate a team leader and a backup team leader for each department within your company. Consider recruiting third-party representatives to assist with coordinating specific activities during disasters.
2. Conduct Critical Function Analysis
Analyze your company’s critical business functions. Determine which functions it can and can’t exist without. This way, you can more easily determine what to prioritize in an emergency.
Determine how losing these functions across different departments might impact external and internal operations.
3. Analyze Potential Risks
Analyze potential risks depending on the nature of your business. Specific threats might be more imminent than others, so you can create visual representations, such as risk maps, to show the relationship between the impact and likelihood of your proposed risks.
From here, you can pinpoint high-priority risks that will require immediate attention.
4. Determine the Plan’s Scope
Determine whether the plan applies to specific departments, one location, or your entire company. Figure out what resources and critical functions you must maintain to successfully implement the plan.
5. Brainstorm Recovery Procedures
Use your risk assessment and critical function analysis to brainstorm how your team should react to a business disruption. Think about the timing for what must occur before, during, and after the business continuity planning process.
Step 1 – Write Your Company’s Information
Write your company’s information, including its name, address, and phone number. Include the name of the person writing the plan and the date you last revised it.

Step 2 – Define the Document’s Purpose
Define the document’s purpose, restating that the document is to establish procedures for the execution and recovery of business activities for your specific company. Check off the specific events you want to plan for.

Step 3 – Outline the Applicability
Clarify the applicability of the document. State which operations the document applies to, including the operation’s name, description, and impact on the business.

Step 4 – Define the Recovery Strategies
Define the recovery strategies for all the events you’ve outlined. Explain the recovery procedure and resource requirements for each event, such as a natural disaster, fire, epidemic, pandemic, technical issue, cyberattack, supply chain disruption, business site disruption, labor strike, or civil unrest.

Step 5 – Name Your Recovery Team
Name your recovery team, including a team and an alternate team lead. These individuals will restore and maintain business continuity and ensure the document’s compliant execution. Include each member’s name, role, email, phone number, and responsibilities.

Step 6 – Detail Processes for Vendor Communication
Designate a person who will be responsible for contacting vendors and partners. This way, external parties key to the business’s functions will know what’s going on and the plan for continued operation.

Step 7 – Name an Internal Communicator
Name an internal communicator, providing their name, email, phone number, and roles within the organization. This person will provide all employees with business-wide updates as the appropriate teams implement the continuity plan.

Step 8 – Describe Relocation Procedures
Describe relocation procedures, including backup offices and methods for obtaining equipment and assets for relevant business activities. Provide an estimated timeline for a transition back to normal operations.

Step 9 – Write Testing Procedures
Write testing procedures to occasionally examine the BCP’s effectiveness. This way, the company can make updates to improve the plan’s effectiveness.

Step 10 – Outline Deactivation Procedures
Outline deactivation procedures so your team knows when your company has officially restored its normal operations.

Step 11 – Provide Exceptions
Write exceptions so your team knows when the business continuity plan doesn’t apply. For example, the plan might not apply if business operations can restore themselves within a certain number of hours.

Download a business continuity plan template below in PDF or Word format:

Related Documents
- One-Page Business Plan : A simplified version of a traditional business plan that outlines the basics of your business.
- LLC Operating Agreement : An internal written document among members of a Limited Liability Company (“LLC”).
- Articles of Incorporation : Fill out this document to form an incorporated business (or "corporation").
- Social Media Policy : A document detailing the guidelines and requirements for your company's social media use.
- Emergency Action Plan : Use this form to outline a standard process that your company can use in the event of an emergency.
- Legal Resources
- Partner With Us
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell My Personal Information

The document above is a sample. Please note that the language you see here may change depending on your answers to the document questionnaire.

Thank you for downloading!
How would you rate your free template?
Click on a star to rate
Get started
- Project management
- CRM and Sales
- Work management
- Product development life cycle
- Comparisons
- Construction management
- monday.com updates
How to write a business continuity plan template
To avoid the common pitfalls associated with growing a successful business, you’ll need to come up with a long-term plan. A business continuity plan template can help you anticipate and avoid disruptions to your company.
Unanticipated threats can wipe out your assets, while risky courses of action can lead to disastrous results. Take the pandemic as an example, which wrought havoc on companies’ plans for growth. In the first year, 43% of businesses temporarily closed , something few could have anticipated.
In this article, we’ll explore why you need a business continuity plan template to help you stay on steady footing, even if the ground beneath you shakes.
Get the template
What is a business continuity plan template?
A business continuity plan (BCP) is a roadmap for long-term success that factors in common pitfalls and risks. A business continuity plan template ensures that you dot your Is and cross your Ts, and craft a reliable plan to handle unexpected events or disasters.
The template will include fields for filling in information on your current resources, recovery procedures when you face critical setbacks, and a list of personnel responsible for addressing such issues.
The primary purpose of business continuity management is to analyze the current status of your company and its state of preparedness for unexpected threats. With it, senior management can find any weak spots in the business and proactively identify solutions to problems that could hinder progress toward your goals. Of course, there are other reasons you’d benefit from this template.
Why use a business continuity plan template?
Reiterating on the above, the main function of the business continuity plans template is to provide a framework for addressing any problems that may arise in various departments and areas of the business.
Without a plan for dealing with roadblocks, your business’s growth can be stunted, or worse, screech to a halt. All it takes is a few missteps or misguided risks to steer your company off course. 90% of small businesses fail within a single year if they can’t resume full operations following an unexpected disaster.
Don’t confuse a BCP with a disaster recovery plan. A BCP doesn’t just outline what to do in case of emergencies, but it presents ideas for recovering full functionality within the business to minimize the impact on growth.
Take your company’s sensitive data as an example. Relying solely on backups to external servers or hard drives could be risky. In your BCP template, you’ll want to detail how you can protect and manage your data in the event of a breach or severe weather conditions. For instance, a hybrid approach, using both a cloud-based solution and a private server, could afford you extra data security and safety.
There were 3,950 confirmed data breaches in 2020 alone, which highlights the dangers of ignoring your data security. The faster you can get back on your feet and recover from cyberthreats or unforeseen events, the easier it’ll be to hold onto your cutting edge and stay a step ahead of the competition.
Those are the benefits in theory, but let’s take a look at specific cases where BCP templates can help.
What are examples of business continuity plan templates?
Depending on your needs, these business continuity templates can provide a little extra inspiration to get started.
Risk assessment template for business continuity
Use a risk assessment table to calculate whether various weather conditions or other events could impact your day-to-day operations. Your business continuity management team could use resources such as this to identify potential threats—however unlikely —to make sure that the company isn’t caught off guard.

( Image Source )
While nobody could have predicted the havoc wreaked by Hurricane Katrina, a rigorous risk assessment system ensures that you have most bases covered, including natural disasters.
Even if your headquarters is sheltered from severe weather conditions, there may be secondary offices or physical data servers in high-risk areas. As such, it’s important to factor in all of your infrastructure to avoid getting blindsided.
Alternate site evaluation template
If you have employees working from home or away from your primary place of work, you can use an alternate site evaluation table to evaluate the possible risks. Have your employees fill out a table like this one so that you have all the relevant contact information on your books in case of an emergency.

This information can help you better understand your employees’ work arrangements and troubleshoot any issues should they come up.
BCP committee table template
Use a simple BCP committee table to determine member’s roles and responsibilities. For each member, you can fill out contact information, along with a list of the main duties they are required to carry out.

This will make it easy for the committee members to coordinate for meetings and have a clear action plan for what to do next.
Want a template that lets you do all of this in one document? monday.com has just what the doctor ordered.
monday.com’s business continuity plan template
On the monday.com business continuity plan template, you’ll be able to enter data such as committee member contact details, disaster recovery action plans, and evacuation information.
The template covers all bases regarding potential threats you could encounter as you grow your business. With it, you’ll be able to keep all the information in a single place and enter it in an easy-to-digest way to share with your employees.

And that’s not all. With monday.com Work OS, your employees can easily share and collaborate on tables and forms, so you can ask for input regarding secondary places of work and contact information. Plus, managers can access this information from anywhere, allowing them to see crucial details at a glance for better preparation.
Part of business continuity planning is ensuring your sensitive data is secure, so you’ll appreciate that monday.com protects your information with permission-based access. Only those in the BCP committee will be privy to the plans unless you wish to grant access to other employees.
If you want to expand beyond the BCP and really detail how you’ll deal with potential disasters and risks, we’ve got a few templates for you.
Related templates from monday.com
Let’s take a look at a few templates that are related to a business continuity plan template.
Disaster recovery template
A Disaster Recovery Template falls under the scope of the business continuity plan committee. It’s just what it sounds like: a comprehensive plan for necessary actions if disaster strikes. More specifically, the plan should inform your approach for getting systems back online when they go down.
In this disaster recovery template, you can include everything from cyber-attacks and data breaches to worldwide pandemics or natural disasters. You can integrate these reports into your overall BCP to get a comprehensive overview of your recovery plans.
Operating functions template
An operating functions template gives you an idea of how you can cut costs in various processes and workflows. It can also inform how you can implement more sustainable business practices and initiatives.
Check out these different operations templates from monday.com that can be used with the BCP template to outline potential risks associated with new initiatives and suggested changes to work processes.
Program risk register
The Program Risk Register Template is for the early-stage process of identifying and evaluating potential risks to your business. It complements the business continuity plan template well — you can focus on valid, severe, likely risks in your BCP, and have a separate table for risks of all likelihoods and potential levels of impact.
FAQs about business continuity plan templates
How do you write a business continuity plan.
You can write a business continuity plan by first listing the various departments of your company and what risks or threats they might face. From there, you can assess the likelihood of these threats coming to fruition. Once you have an idea of the probability of the various threats to your company, you can prioritize them.
With a prioritized list, you can start with the most pressing threat and proactively brainstorm what actions you could take if it were to arise. The purpose of the BCP is to shield your company against anything that could hinder your progress. Coming up with potential solutions for addressing hypothetical problems can prepare you for real ones in the future.
What is a small business continuity plan?
A small business continuity plan is a document that details potential risks and threats to a small business. It’s well worth creating such a document as a small business owner, as it can save you from disaster as you strive to scale the company.
For small businesses, any hitch can prove disastrous. 38.8% of US-based small businesses were affected by supply chain issues in 2021, which, for some, would have impeded growth significantly. Over-reliance on foreign suppliers could be an example of an unnecessary risk that, without being addressed, could spell disaster for a small business.
With the business continuity plan in place, you can protect your business in its most vulnerable state of growth. The plan forces you to think laterally about the threats that could sink your business. That way, you can make necessary course corrections and increase your chances of long-term survival.
What is an example of a business continuity plan?
An example of a business continuity plan is to plan out how you’ll protect your app’s uptime in the event something happens to one data center: for example, running a clone in AWS you can always fall back on.
What are the 3 elements of business continuity?
The three most vital elements within business continuity are resilience, recovery, and contingency.
- Resilience: how you’ll make it as hard as possible for critical functions to fail.
- Recovery: how you’ll get back to normal operations if disaster strikes.
- Contingency: what you’ll do if plan A for recovery fails.
- Project risk management

Send this article to someone who’d like it.
- Human Resources
- Tools and Samples
Business Continuity Plan
A business continuity plan (BCP) is an essential business document that outlines how a business will continue its critical functions during and after an emergency event or disruption in business.
Emergency events can also include natural disasters, workplace violence, utility failures, cyber-attacks, supply shortages, economic downturns, or any event that will result in the disruption of business processes.
Try Betterteam
Post your jobs to 100+ job boards
- Reach over 250 million candidates.
- Get candidates in hours, not days.
The COVID-19 Pandemic:
The COVID-19 (Coronavirus) pandemic is a real-world example of an emergency situation in which a business continuity plan should be instituted.
Business Continuity Plan Template Download
Download this business continuity plan template in MS Word format and start using it straight away.
Why is it Important To Have a Business Continuity Plan?
In times of crisis, having a business continuity plan in place will ensure your business is able to function, before, during, and after an emergency event.
A BCP will clearly outline the people and procedures involved in running your business when the worst happens. A Busines Continuity Plan is beneficial because:
- It is required by many business regulators, investors, and stakeholders.
- It provides a sense of security for managers and staff.
- It will allow your business to provide reasonable service to your customers during and after an emergency.
- It will allow you to preserve your revenue stream and your reputation.
- It can provide additional insight into your organization.
What Should Be Included In A Business Continuity Plan:
Business continuity plans are as varied and complex as businesses themselves. Every plan is different and should be based on the needs of your company and your customers. Here are a few general examples of what a BCP should include:
- The scope and purpose of your plan.
- Your plan's goals and objectives.
- A comprehensive list of tasks required to keep your operations going.
- The roles and responsibilities of your BCM team and your staff.
- The contact information for management and key BCM staff.
- Maintenance protocols for your plan.
- Information about site and data backups.
- Information on where to go in an emergency.
- Procedures to coordinate with emergency personnel.
How to Build a Business Continuity Plan:
A step-by-step guide to creating a business continuity plan.
Identify the scope of your plan.
Perform a regulatory review..
Before you create your business continuity plan, first consider the expectations and regularity standards that come from external stakeholders including investors, external partners, and auditors.
Identify the objectives of your plan.
When creating a comprehensive business continuity plan, a key step is to identify the objectives of your plan and then set goals accordingly. Here you should be considering how detailed your plan should be and which departments and staff members should be involved.
Define the outcome of your plan.
When creating the scope of your plan, you should also define the successful outcome of your plan and which milestones should be tracked during an emergency.
Form the business continuity management team.
Decide on the size of your team..
The business continuity management team is responsible for implementing and executing your BCP. The size of your team is dependent on the size of your company and the way in which you plan on rolling out your program.
Identify your key business areas and critical functions.
Complete a risk assessment..
The next step is to perform a detailed risk assessment on your company. A risk assessment allows you to understand the physical, financial, reputational, and operational risks to your company should a major disruption occur.
Have your team create a detailed list of threats and risks that would impact your business and rate them according to the likelihood of occurrence and severity. Examples of risks and exposures include:
- Natural disasters.
- Global pandemics.
- Staffing shortages.
- Cyber attacks.
- Single point disruptions.
- Disruptions to the supply chain.
- Political instability.
Conduct a business impact analysis.
A business impact analysis will help you identify your business's core needs and determine the potential impact resulting from the disruption of business. Examples of impacts to consider include:
- Increase in customer dissatisfaction.
- Damage to company reputation.
- Loss of sales or income.
- Loss of equipment or data.
- Delay or loss of new business.
- Regulatory fines.
Identify your business processes and determine which would cause the most damage to the company if they were to fail. Classify each of these functions or processes as either:
Find out which business objectives they support, how often they occur, which departments they affect, and what other aspects of the business are dependent on these to function? Your BIA report should document the potential impact resulting from business disruptions and provide information that can be used in your recovery strategies.
Create an incident response plan.
Outline your operations plan..
This should be the most comprehensive section of your business continuity plan. You can break down operations activities into prevention strategies, response strategies, and recovery strategies.
Come up with prevention strategies.
In this section, you should detail any preventative measures that should be taken before a disruption occurs. This may include creating remote work solutions for your employees, having backup utility providers, alternative network resources, data backups, and server backups.
Detail response strategies.
Response strategies are needed when there is an emergency or sudden disruption of business. This section should detail what each member of your business continuity team should do in the event of an emergency. This includes evacuation procedures, safety protocols, and staff communications.
Plan your recovery strategies.
Recovery strategies ensure that critical business processes are restored after an emergency event or major disruption in business. Your plan should have a detailed description of the actions necessary to keep your business functional until all personal, systems, and facilities are operational again.
Develop a training curriculum.
Implement a training curriculum..
Once your business continuity plan is complete, it is important to implement a training curriculum for your business continuity management team and your company employees. Training should include a basic overview of your BCP as well as relevant and tactical exercises designed to test your continuity procedures.
It may be worth staging a mock emergency to establish the efficacy of your plan and highlight areas of improvement.
Conduct annual reviews.
Review and update your plan..
As your business grows and changes so should your business continuity plan. It is important to conduct annual reviews of your BCP to ensure that it aligns with your current processes and requirements. Updates should be made to evacuation procedures, staff contacts, and communication methods as needed.
Business Continuity Management Services:
For larger businesses, it may be worth employing the services of a business continuity consulting and management company to review your BCP. These services may include:
- A comprehensive assessment of your current business continuity plan.
- Gap analysis.
- Recommendations and long-term planning.
- Annual updates.
- Training exercises.
Layoff Letter Due to COVID-19 (Coronavirus)
What is a business continuity plan?
A business continuity plan is a document detailing how your business will continue to function during an emergency or major disruption of business.
What is the primary goal of business continuity planning?
To minimize the damage to your business in the event of an emergency or disruption of business.
What does a business continuity plan typically include?
- The scope, purpose, and policy of your plan.
Is business continuity the same as disaster recovery?
No, disaster recovery is part of a business continuity plan which is designed to ensure that your business stays functional before, during, and after an emergency. Disaster recovery focuses on restoring operations after a major disruption in business.
When should I update a business continuity plan?
Your business continuity plan should be reviewed and updated annually or whenever you make major changes to your production processes.
Related Articles:
Disaster recovery plan, recruiting strategies, life-sustaining businesses, what is full life cycle recruiting, what is strategic staffing.
ISO 22301 Business Continuity Simplified: Fortify Your Business Against Disruption
By Andy Marker | June 22, 2020 (updated September 15, 2022)
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
In this article, you’ll find expert tips and implementation guides, and you'll learn how ISO 22301 can buffer your business against disasters.
Included on this page, you’ll find an International Standards Organization (ISO) 22301 audit checklist template , a simplified ISO 22301 cheat-sheet , and an ISO 22301 self-assessment checklist , as well as examples of ISO 22301 in action and an ISO 22301 quick-start guide .
What Is ISO 22301?
ISO 22301 is a global standard for business continuity planning requirements to help organizations protect themselves against disruptions. The most current version is 22301:2019, Security and resilience - Business continuity management systems - Requirements.
The requirements in ISO 22301 address disruptive incidents that can be natural or human-made, widespread or local, intentional or unintentional, such as a snowstorm, a broken water main, an epidemic, a data breach, or a phishing attack. Large or small, for- and nonprofit organizations alike can use ISO 22301.
The Business Manager’s Quick-Start Guide to ISO 22301
The ISO 22301 standard can provide benefits for your business continuity planning, even if your organization chooses not to pursue certification, or the review process that confirms your business continuity system meets all ISO 22301 requirements.
"Certification is nice, but not required,” says Mart Rovers of InterProm. “First, seek compliance. That way, you know that your business continuity management practices are in better shape." You can start to create a solid business continuity plan with just a few simple steps, which you can also download as this ISO 22301 Quick-Start Guide .
- Check If You Already Have Continuity Plans: Find out if your organization already has business continuity plans. Search through your document management system and ask management or long-time employees. Organizations sometimes create and quickly forget about resources, or store responses locally in an informal system. As Andrew Nichols of the Michigan Manufacturing Technology Center suggests, if your organization already implements other ISO standards, such as ISO 9001 or ISO 27000, you can leverage some of the common requirement elements for your 22301 plan.
- Identify Missing Components: Conduct a gap analysis of existing policies and processes to see what business continuity resources you need. According to Mart Rovers, one way to conduct a self-assessment is to copy into a spreadsheet each phrase of the ISO 22301 standard that contains the word "shall." Then, determine gaps between your company and the standard. "Use the standard as your guide to establishing a coherent set of practices to address business continuity management for your organization," says Rovers. You can also use Smartsheet's ISO 22301 Self-Assessment Checklist and ISO 22301 Simplified Cheatsheet for your gap analysis.
- Keep It Simple: Having binders full of perfectly formatted procedures won’t help in an emergency. Create easy-to-follow guidelines and checklists and, more importantly, build "muscle memory" in your employees through training and drills. That way, in a panic, people understand what to do without having to be told.
- Make Your Plan a Living Document: Ticking off items on an audit checklist doesn't mean you’re prepared. Frequently read, revise, and practice your plan to keep it relevant and to train new staff.

- Communicate Your Plan to Staff and Other Stakeholders: Even the most well-written plan is useless if the people who can benefit from it don't know about it. Inform everyone covered by the plan that it exists, including your supply chain and other outside stakeholders.
ISO 22301 Requirements
The ISO 22301 standard offers a framework for planning, testing, and monitoring a business continuity management system (BCMS). The ISO 22301 document contains 10 sections, which introduce the standard and definitions, as well as actionable requirements of the standard.
As with other ISO requirement documents, ISO 22301 describes only what organizations must do to reach minimum proficiency — it does not prescribe how to achieve these standards. Each organization must consider its distinct conditions and obligations to find the best way to follow the requirements.
Here is an overview of the clauses in ISO 22301 that impact an organization most:
- Clause 4, Context: Your organization must understand what it is, what it does, and what outputs and processes it must sustain. You must also determine who has a stake in the continuity of your operations — in other words, the interested parties. For example, customers have a stake in your organization continuing to function.
- Clause 5, Leadership: Few organizational initiatives thrive without the sustained support and championship of top management. Management must commit to a business continuity plan and make available any resources — human, financial, or otherwise — to ensure its success.
- Clause 6, Planning: To plan for sustainability, you must understand what disruptions could potentially occur and how these incidents affect the business — in other words, potential risks and their impact. Set measurable business continuity objectives to guarantee the minimum viable products or services, as well as compliance with any legal or regulatory requirements.
- Clause 7, Support: No program can advance without resources and support. Decide what personnel, roles, and teams you need for threat response and how you can best enhance their effectiveness. Create internal and external communication procedures for reference, and communicate the continuity plan to all necessary parties before and during a crisis. Establish a document management system for key continuity documents, such as procedures.
- Clause 8, Operation: Conduct your risk assessment and business impact analysis , and plan your disruption recovery approach. Implement the recovery plan with detailed procedures, and test it regularly to verify that it works. Make sure people can find the procedures (and other documents) they need, and revise your plan as necessary.
- Clause 9, Evaluation: Establish a process to regularly measure and assess your continuity policies and procedures and their execution. Review and revise your plan and documents to ensure they are effective and relevant
- Clause 10, Improvement: Seek continual improvement in all functional and operational areas, including through periodic management reviews. Improvements in day-to-day activities help bolster the organization in times of disruption. When processes veer from the standard or fail to conform with ISO and quality management standards, implement corrective action.
Key Definitions Related to ISO 22301
Some of the following key terms and concepts originate with ISO, some with ISO 22301, and some with business continuity and risk management:
- Context: The purpose and character of the organization and the environment in which it operates. This includes internal and external influences that shape the business continuity management system.
- Disruptive Incident: A disruptive incident is an event that stops or slows the everyday work of an organization. Examples of disruptive incidents include earthquakes, internet stoppages, broken fans in a data center, or food poisoning in a cafeteria.
- Interested Parties: Interested parties are stakeholders in the successful operation and outcomes of your business continuity plan. They can include customers, employees, suppliers, or regulatory officials.
- Leadership: In ISO 22301, leadership refers to top management or the person or people who run the organization and champion the business continuity effort.
- Maximum Acceptable Outage (MAO): The length of time an activity or process can be unavailable or ineffective before the health and survival of the organization are threatened.
- Minimum Business Continuity Objective (MBCO) : The lowest level of products or services that is acceptable for a business to offer during a disruption.
- Recovery Timeframe Objectives (RTO): This refers to the prioritization of key activities and the timing that makes those activities operational.
Benefits of ISO 22301 and Business Continuity Management System
If teams are already overwhelmed with their workload, they may not like to think about disasters. Furthermore, organizations might think that ISO standards include difficult jargon and that pursuing a continuity plan adds unnecessary work. However, management systems practitioners suggest that continuity preparations produce substantial gains.

“I think it's a truism that many organizations can benefit from the principles and some of the practices of resiliency and contingency planning,” says Andrew Nichols, Quality Program Manager at the Michigan Manufacturing Technology Center .
As an example of the benefits that risk analysis and preparation can yield, Nichols relates his experience of visiting a small northeastern town during a widespread winter power outage. The whole town was closed, with the exception of one restaurant that had a generator.
“They had a line of people out the door every mealtime because nowhere else was capable,” Nichols remembers. “Somebody had the foresight to think about the loss of power. And that organization cleaned up financially because they were able to provide what the customers needed.”
Consider these specific benefits to using ISO 22301 business continuity planning:
- Protect against and recover from disruptive incidents.
- Identify and control current and future threats.
- Improve your risk management planning efforts.
- Prevent large-scale damage.
- Become proactive in preventing problems and recovering from incidents, rather than reactive to damage and disruption.
- Reduce downtime and increase recovery time.
- Keep important activities running during disruption.
- Deliver quality products consistently.
- Provide dependable service.
- Prove you’re a reputable supplier.
- Prove your resilience to all stakeholders.
Experts also assert that ISO 22301 can be a simple and effective continuity tool. “All these ISO standards, they’re like hidden gems because of how fast they can get you up to speed without having to reinvent the wheel,” says Mart Rovers, President of IT consulting firm InterProm .

“I cannot emphasize enough how within reach this standard is. Anytime people hear the word ‘ISO,’ they think, ‘Oh, that's for large organizations. Oh, that's way too formal. It's too much. It's overkill.’ I understand where this is coming from because the word ‘standard’ itself is scary for many organizations. However, the size of organization really doesn't matter. The things you should be doing in ISO 22301, you can do at a smaller scale,” says Rovers.
Some also hesitate at the thought of certification. Both Nichols and Rovers stress that certification is not necessary for every enterprise. Although certification may be a condition of doing business for some companies, those who don’t need certification can still gain advantages from following ISO 22301.
In weighing the pros and cons of ISO certification, Rovers suggests buying a copy of ISO 22301 , and then copying and pasting each sentence that contains the word “shall” into a spreadsheet (these sentences represent the requirements you must follow). From the spreadsheet, consider whether full ISO adoption and certification are too complicated for your organization. Regardless of your decision, you can always use the spreadsheet to conduct a self-audit.
ISO 22301 in Action
The following image provides a small sample of the possible outcomes to business continuity management.
How a Management System Helps Business Continuity
For those familiar with other ISO standards, the management system component of ISO 22301 might be a new concept. Rovers describes management systems as follows:
“The best way to explain a management system is to imagine opening up an old watch. It has these spinning wheels, these gears. In the case of an ISO standard, you're looking at a number of requirements to put that watch together with all these spinning wheels. That watch is a coherent system. You take out one of those gears, and then the watch fails.
“A management system for continuity follows the same idea — every requirement that the standard asks for represents one of those gears. And every requirement serves a distinct purpose (otherwise, it would not be a requirement). If you don't meet a particular requirement, the watch, so to speak, may not function as it could or should. These ISO requirements are not just there to keep you busy.”
ISO 22301 and PDCA
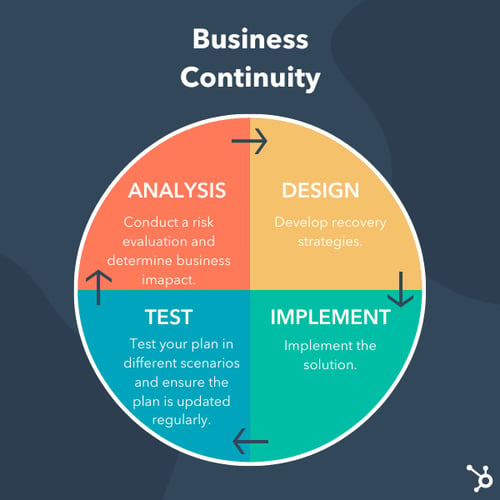
Each segment of the PDCA (plan-do-check-act) cycle for continuous improvement corresponds to at least one ISO 22301 clause. Organizations can use ISO 22301 to test continuity procedures, review outcomes, and implement updates or fix problems in a continuous cycle that leads to an increasingly resilient business continuity system.
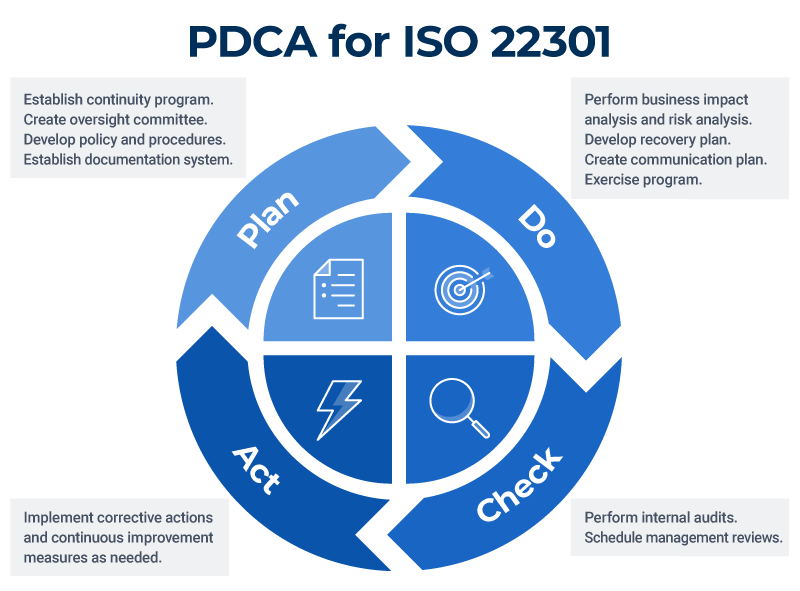
ISO 22301 and Maturity Models
A maturity model measures an organization’s ability to pursue continuous improvement in key areas. ISO 22301 does not have a maturity model.
As Rovers explains, “It was never the intent of ISO 22301 to be a maturity model. You either meet all the requirements of the standard, or you don’t. You could say that by not meeting the requirements of the standard, you’re not mature. Or better said, your business continuity management practices are not mature.”
BCM Lifecycle ISO 22301
The business continuity management (BCM) lifecycle represents industry best practices and some of the core requirements of ISO 22301. These practices offer a solid foundation for resilience, while offering flexibility to adapt to changes in the organization.
Guided by leadership, these are the key activities for the lifecycle:
- Conduct a business impact analysis and risk assessment.
- Establish a business continuity strategy.
- Establish and implement business continuity procedures.
- Exercise and test the procedures regularly before a disruption occurs.

ISO 22301 Audit Checklist Template (Excel)
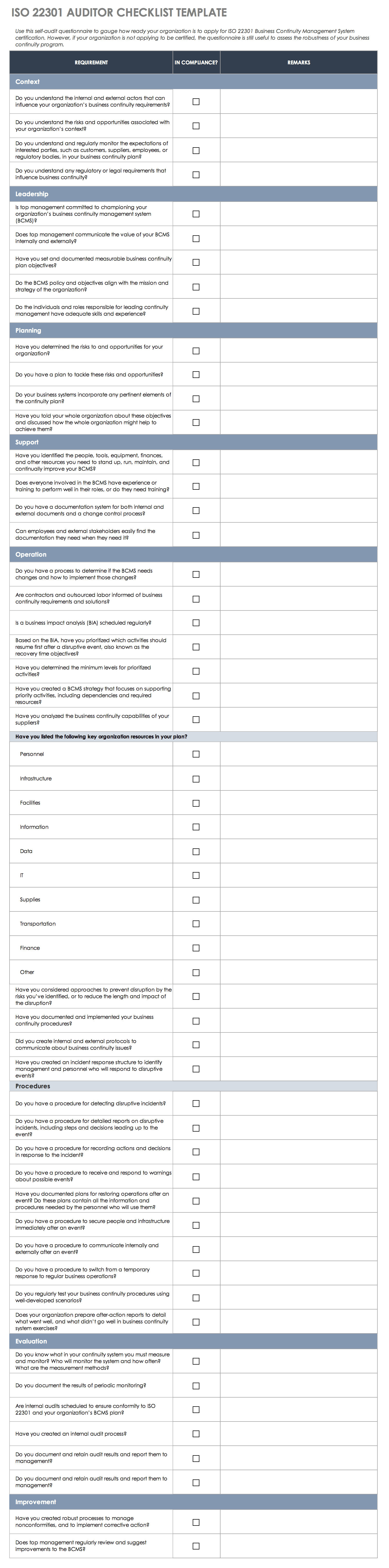
Use this detailed checklist to determine if your business continuity plan aligns with ISO 22301 standards. You can use the template whether you’re applying for certification or simply pursuing a continuity management plan.
Download ISO 22301 Audit Checklist Template
Excel | Smartsheet
ISO 22301 Self-Assessment Checklist
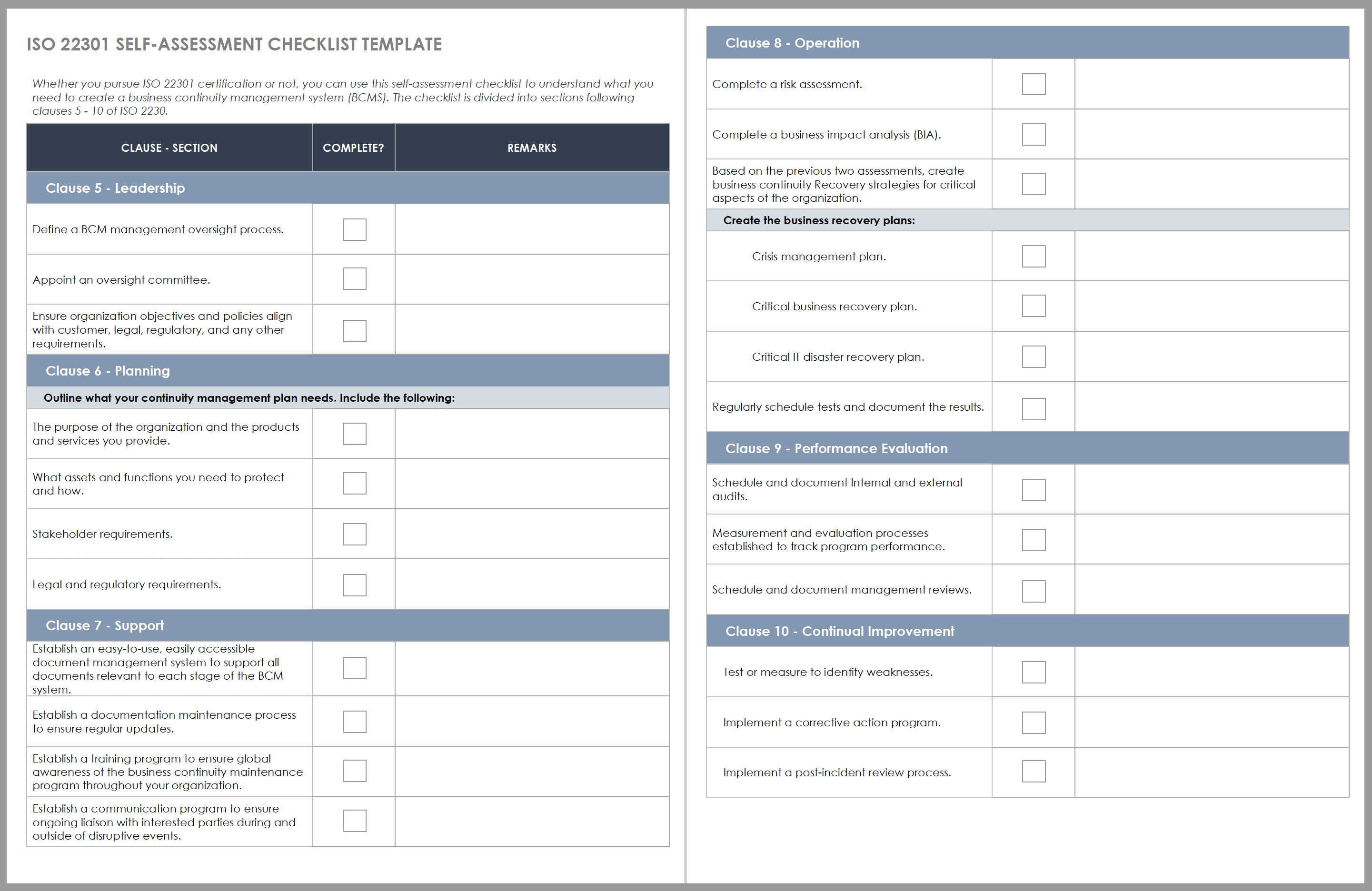
This self-assessment checklist is divided into sections that correspond to clauses in ISO 22301. Use it to confirm whether your business continuity system meets the requirements for leadership, planning, support, operation, performance evaluation, and continual improvement.
Download ISO 22301 Self-Assessment Checklist Template
Excel | Word | PDF
ISO 22301 Implementation Guide
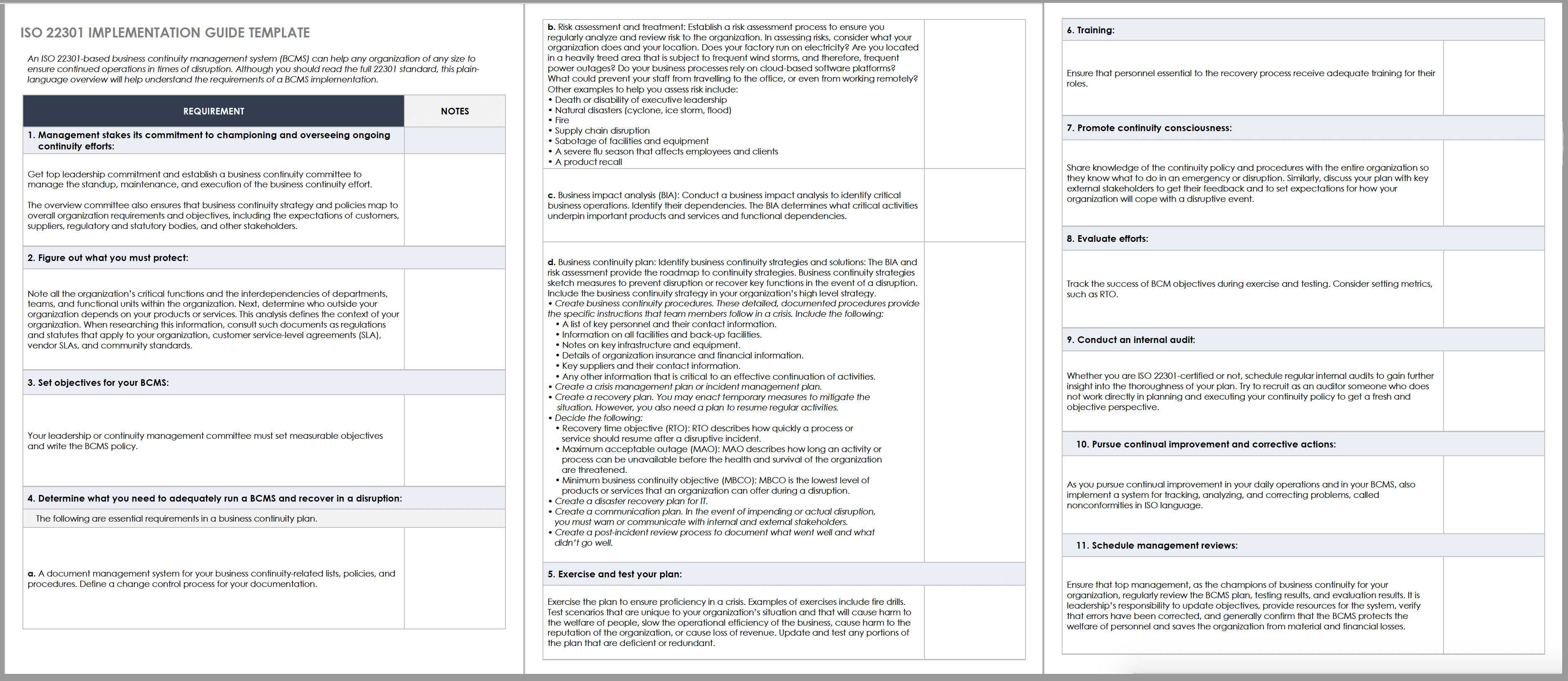
This guide states the essential information from ISO 22301 in plain English. For best results, read it with the full standard, which is currently available for free online to support the COVID-19 response.
Download ISO 22301 Implementation Guide Template
Excel | Word | PDF
ISO 22301 Simplified Cheat-Sheet
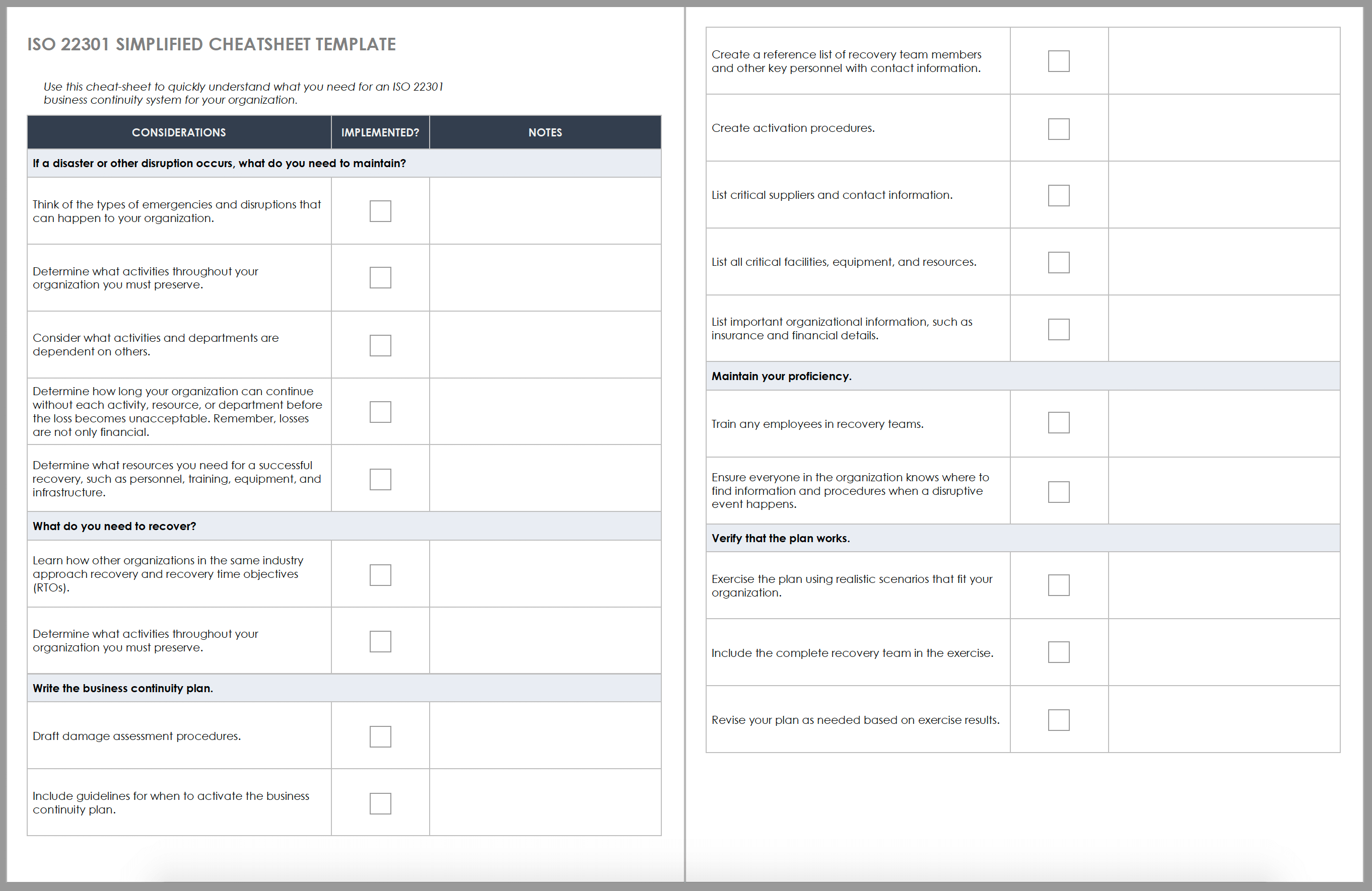
Use this simplified cheat-sheet to understand the basic elements of creating a business continuity plan. The template walks you through the process of determining critical aspects of your organization, writing the recovery plan, and exercising the plan to ensure proficiency.
Download ISO 22301 Simplified Cheat-Sheet Template
ISO 22301 Business Continuity Policy Template
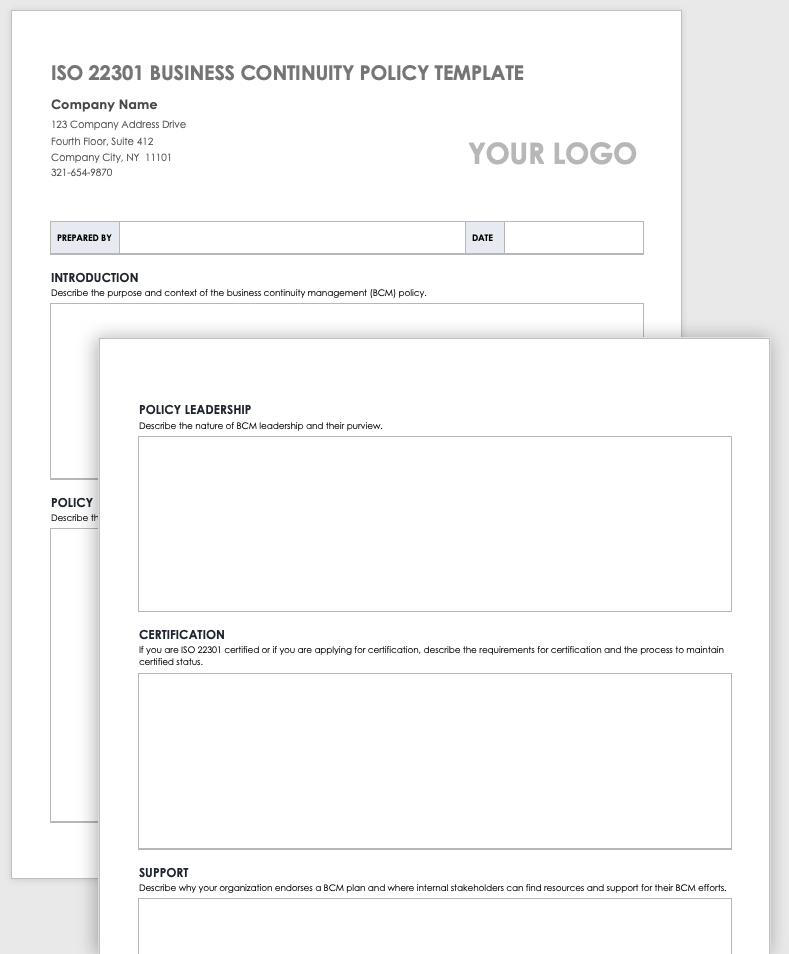
A business continuity policy describes the processes and procedures an organization needs in order to function well daily, including in times of disruption and crisis. This policy template includes space for BCMS objectives, a leadership description, a policy outline, and any certification details.
Download ISO 22301 Business Continuity Policy Template
ISO 22301 Business Continuity Template
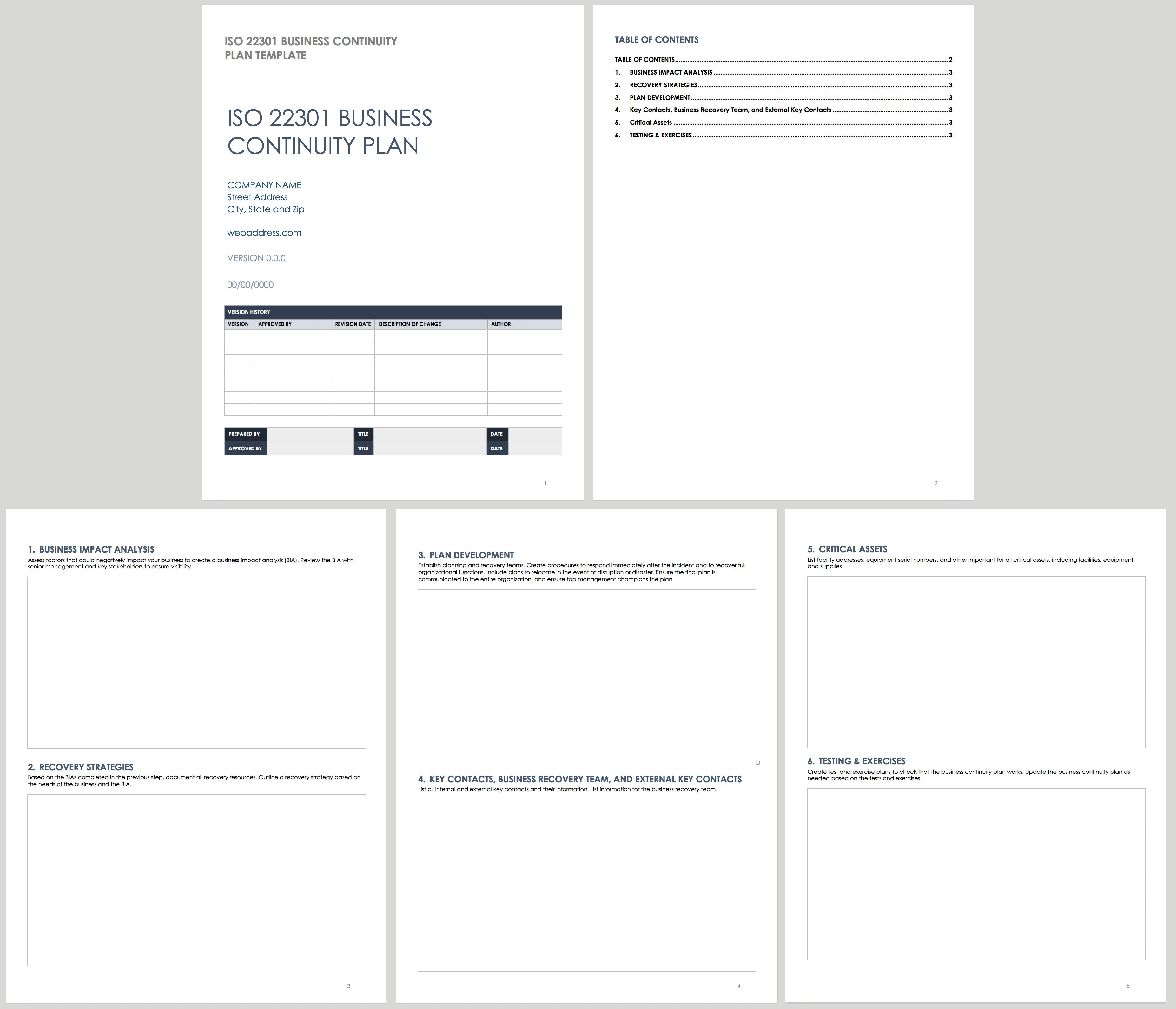
Use this template to create a business continuity plan. Describe the results of your risk analysis and business impact analysis, detail your disaster recovery and continuity procedures, and list key contacts and important assets.
Download ISO 22301 Business Continuity Template
Word | PDF
ISO 22301 Business Continuity Sample
The Community Nonprofit Center of New York made available this business continuity template to support the response to coronavirus. Find space to detail responses to minimal and critical emergencies, a risk matrix template, and lists for information about insurance, critical assets, and responses to disruptive events.
For other most useful free, downloadable business continuity plan (BCP) templates please read our "Free Business Continuity Plan Templates" article.
Disaster Recovery Plan Templates
After you perform a risk analysis and business impact analysis, consider writing a disaster recovery plan. Disaster recovery plan templates , available in different formats, provide an easy-to-use structure for documenting continuity plans. Download templates specialized for IT, payroll, small businesses, and more.
To learn about the difference between recovery plans and continuity plans, visit our "Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery: Their Differences and How They Work Together" article.
ISO 22301 Versus ISO 27301
ISO 27301 provides requirements that organizations use to ensure their information and communications technology (ICT) continuity, security, and readiness to survive a disruption. The standard is often staged with ISO 22301 because both are based on similar management system approaches.
The full name of this standard is ISO 27301 - Information Technology - Security Techniques . Originally published in 2011, it is soon to be revised.
“Both [ISO 27301 and ISO 22301] ask for top management involvement and commitment, both ask that you have the right resources, that you have documentation management, that you do performance evaluations, and that you make improvements,” explains Rovers.
They differ in the focus of the risk assessment: ISO 27001 addresses security, whereas ISO 22301 addresses business continuity. “Each area has different risks, but the approach to the risk management assessment and mitigation follows the same steps. There's enormous overlap.”
IT security continuity has significant relevance in the remote work environment. For example, while using your work laptop at home or signed into the work network, what happens when someone innocently plugs in a thumb drive that infects your laptop and corrupts the network? Both ISO 22301 and ISO 27001 work together to prevent such incidents and mitigate problems that occur.
For additional resources, visit " Free ISO 27001 Checklists and Templates ."
General Requirements Across Management System Standards
Some ISO requirements are commonly stated across the management system standards, which include ISO 22301; ISO 9001 , Quality Management; ISO 20000, IT Service Management; and ISO 27001, Information Security. Examples of common requirements include establishing objectives for the business continuity management system as appropriate to the organization, obtaining management’s commitment to supporting the system, implementing a documentation management system, conducting internal audits, and pursuing continual improvement. This functional overlap enables organizations to undertake combined audits for these standards.
Historical Foundations of ISO 22301
The concept of business continuity was borne out of the IT boom of the 1980s and 1990s. Public and private organizations realized the need to ensure continuity of service and key supplies and to mitigate the effects of disruptive events. The first formal standard reflecting these concerns was the United Kingdom’s British Standard (also known as BS) 25999, which introduced the management system concept to the business continuity discipline.
In 2012, the global standards body ISO released ISO 22301:2012 as the first international standard for business continuity. Based on the contributions and comments of continuity professionals from assorted industries in over 60 countries, ISO 22301 superseded BS 25999.
ISO’s consensus-based standards, such as 22301, cover practices and industries ranging from quality management, IT service, and food safety to environmental safety and information security. ISO standards aim to increase the quality and safety of many products and services, including most common household items, appliances, and cars. Although large enterprises and manufacturers usually follow ISO requirements and guidelines, organizations of all sizes and types can benefit from ISO principles.
For ISO 22301, the standard provides a consistent BCMS framework and a universal language among organizations for communicating about continuity and aligning processes.
When they get certified in ISO 22301 and other ISO standards, organizations can demonstrate to management, legislators, regulators, customers, and other stakeholders that they follow good practices. For ISO certification, organizations need third-party verification that they comply with all requirements of a standard.
“Certification shows you have some level of competence,” explains Rovers. “It shows you take the standard seriously. For organizations buying your goods or services, it can be a compelling reason to choose you.”
Guidance Documents for ISO 22301
For in-depth discussions of aspects of the 22301 standard, ISO offers a series of guidance documents. To those considering pursuing ISO 22301 certification, these documents provide additional insight:
- ISO 22313 - Security and resilience — Business continuity management systems — Guidance on the use of ISO 22301
- ISO 22316 - Security and resilience — Organizational resilience — Principles and attributes
- ISO 22317 - Societal security — Business continuity management systems — Guidelines for business impact analysis (BIA)
- ISO 22318 - Societal security — Business continuity management systems — Guidelines for supply chain continuity
- ISO 22330 - Security and resilience — Business continuity management systems — Guidelines for people aspects of business continuity
- ISO 22331 - Security and resilience — Business continuity management systems — Guidelines for business continuity strategy
What Is the Latest Version of ISO 22301?
The requirement document ISO 22301:2019, Security and resilience - Business continuity management systems - Requirements , was released on October 31, 2019. The update from the original 2012 version reflects changes in management system approaches and clarifies specifications around clause 8.
Build Powerful, Automated Business Processes and Workflows with Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Any articles, templates, or information provided by Smartsheet on the website are for reference only. While we strive to keep the information up to date and correct, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability, or availability with respect to the website or the information, articles, templates, or related graphics contained on the website. Any reliance you place on such information is therefore strictly at your own risk.
These templates are provided as samples only. These templates are in no way meant as legal or compliance advice. Users of these templates must determine what information is necessary and needed to accomplish their objectives.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
- Advisera Home
- ISO in General
Partner Panel
ISO 22301 Documentation Toolkits
Iso 22301 training.
- Documentation Toolkits
- White Papers
- Templates & Tools
Where to Start
New ai tool.
- Live Consultations
- Consultant Directory
- For Consultants

Dejan Kosutic
- Talk to Sales
ISO 27001 / ISO 22301 document template:
Business continuity plan.
The purpose of the Business Continuity Plan is to define precisely how the organization will manage incidents in the case of a disaster or other disruption of business, and how it will recover its critical activities within set deadlines.
The document is optimized for small and medium-sized organizations – we believe that overly complex and lengthy documents are just overkill for you.
There are 7 appendices related to this document. The appendices are not included in the price of this document and can be purchased separately: Incident Response Plan , Incident Log , List of Business Continuity Sites , Transportation Plan , Key Contacts , Disaster Recovery Plan and Activity Recovery Plan .
TEMPLATE LANGUAGE
CUSTOMERS FROM 107 COUNTRIES
THIS TEMPLATE IS ALSO AVAILABLE AS PART OF THESE DOCUMENTATION TOOLKITS

DOCUMENT FEATURES
- Price US$ 74.90
- Compliant with ISO 22301 8.4; ISO/IEC 27001 A.5.29
- Format MS Word 2013, MS Word 2016, MS Word 2019
- Number of pages 9
- Document language English. For other languages click here: Deutsch , Español , Nederlands , Français , Português
- Can I edit the document? Yes. The document is fully editable – just enter information specific to your company.
- Can I use this to become certified? Yes. The documentation template may be used for ISO 27001 and ISO 22301 certification audit purposes.
- Well-defined instructions Document templates contain an average of twenty comments each, and offer clear guidance for filling them out.
- Designed with your company in mind The template was created for small and medium-sized businesses.
VIDEO TUTORIAL INCLUDED
- The tutorial How to Write Business Continuity Plan According to ISO 22301 will show you how to insert your real data into the document. The tutorial is included in the price of the template.
Schedule a free presentation, and our representative will show you any document you're interested in.
WHAT OUR CUSTOMERS SAY ABOUT US
The documentation is brilliant. I worked through the BS 25999 package last year, combined with a bit of reading around the subject (mainly from Dejan's blog!) and we've got ourselves a business continuity plan. I'm just starting to do the same now with ISO 27001, and then we're going to work towards getting both of them certified.
Managing Director Click Travel Ltd
I am new to ISO 27001 and did not know where to start. The documentation templates helped me get started and have provided a good road map for where I need to go from here.
Compliance Manager
I used the template to aid me in preparing a third party management policy for my company. I did change a lot of the language but it was helpful to be sure of what sections needed to be included. Helped me work smarter, not harder.
It saved me hours of work, I really appreciated the template.
Sinometis International Pty Ltd
Well designed, well documented, a lot of time saved. Best ISO templates Business, no doubt.
RTI Surgical, Inc.
The document helped me to put in order the topics that needed to be covered.
Senior Partner Evolutionary Methodologies Consulting
The ISO 22301 documentation helped me reach a level of granularity which is appropriate and yet not so detailed as to bog down the implementation.
ONVENTIS GmbH
OUR CLIENTS

Preview Business Continuity Plan template
- The document is fully editable so that you can adapt it to your company design.
- Documents include placeholder marks for all information you need to complete.
- Each document includes comments and information , which guides you through completion.
- Comments with video tutorials support you with practical instructions.
Buy Business Continuity Plan
Sold in 107 countries
FAQS: PURCHASING INDIVIDUAL ISO 27001 / ISO 22301 DOCUMENT TEMPLATES
How will l receive the template.
After payment confirmation, we'll send you an email that contains a link to download the document. It's super easy.
What payments do you accept?
You may pay with major credit card, or via wire transfer from your bank account.
How do you protect my payment details?
We use Secure Socket Layer (SSL) technology, which is the industry standard and considered one of the safest systems for online payment. Your account details and credit card information are encrypted and go straight to the payment processor. We won’t have access to your payment information, and we won’t store it in any form.
Which currencies are accepted?
We can accept 50-plus common currencies for payment, including Swiss Francs, US Dollars, British Pounds and Euros.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Business Continuity Plan Basics
- Understanding BCPs
- Benefits of BCPs
- How to Create a BCP
- BCP & Impact Analysis
- BCP vs. Disaster Recovery Plan
Frequently Asked Questions
- Business Continuity Plan FAQs
The Bottom Line
What is a business continuity plan (bcp), and how does it work.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/wk_headshot_aug_2018_02__william_kenton-5bfc261446e0fb005118afc9.jpg)
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
What Is a Business Continuity Plan (BCP)?
A business continuity plan (BCP) is a system of prevention and recovery from potential threats to a company. The plan ensures that personnel and assets are protected and are able to function quickly in the event of a disaster.
Key Takeaways
- Business continuity plans (BCPs) are prevention and recovery systems for potential threats, such as natural disasters or cyber-attacks.
- BCP is designed to protect personnel and assets and make sure they can function quickly when disaster strikes.
- BCPs should be tested to ensure there are no weaknesses, which can be identified and corrected.
Understanding Business Continuity Plans (BCPs)
BCP involves defining any and all risks that can affect the company's operations, making it an important part of the organization's risk management strategy. Risks may include natural disasters—fire, flood, or weather-related events—and cyber-attacks . Once the risks are identified, the plan should also include:
- Determining how those risks will affect operations
- Implementing safeguards and procedures to mitigate the risks
- Testing procedures to ensure they work
- Reviewing the process to make sure that it is up to date
BCPs are an important part of any business. Threats and disruptions mean a loss of revenue and higher costs, which leads to a drop in profitability. And businesses can't rely on insurance alone because it doesn't cover all the costs and the customers who move to the competition. It is generally conceived in advance and involves input from key stakeholders and personnel.
Business impact analysis, recovery, organization, and training are all steps corporations need to follow when creating a Business Continuity Plan.
Benefits of a Business Continuity Plan
Businesses are prone to a host of disasters that vary in degree from minor to catastrophic. Business continuity planning is typically meant to help a company continue operating in the event of major disasters such as fires. BCPs are different from a disaster recovery plan, which focuses on the recovery of a company's information technology system after a crisis.
Consider a finance company based in a major city. It may put a BCP in place by taking steps including backing up its computer and client files offsite. If something were to happen to the company's corporate office, its satellite offices would still have access to important information.
An important point to note is that BCP may not be as effective if a large portion of the population is affected, as in the case of a disease outbreak. Nonetheless, BCPs can improve risk management—preventing disruptions from spreading. They can also help mitigate downtime of networks or technology, saving the company money.
How To Create a Business Continuity Plan
There are several steps many companies must follow to develop a solid BCP. They include:
- Business Impact Analysis : Here, the business will identify functions and related resources that are time-sensitive. (More on this below.)
- Recovery : In this portion, the business must identify and implement steps to recover critical business functions.
- Organization : A continuity team must be created. This team will devise a plan to manage the disruption.
- Training : The continuity team must be trained and tested. Members of the team should also complete exercises that go over the plan and strategies.
Companies may also find it useful to come up with a checklist that includes key details such as emergency contact information, a list of resources the continuity team may need, where backup data and other required information are housed or stored, and other important personnel.
Along with testing the continuity team, the company should also test the BCP itself. It should be tested several times to ensure it can be applied to many different risk scenarios . This will help identify any weaknesses in the plan which can then be corrected.
In order for a business continuity plan to be successful, all employees—even those who aren't on the continuity team—must be aware of the plan.
Business Continuity Impact Analysis
An important part of developing a BCP is a business continuity impact analysis. It identifies the effects of disruption of business functions and processes. It also uses the information to make decisions about recovery priorities and strategies.
FEMA provides an operational and financial impact worksheet to help run a business continuity analysis. The worksheet should be completed by business function and process managers who are well acquainted with the business. These worksheets will summarize the following:
- The impacts—both financial and operational—that stem from the loss of individual business functions and process
- Identifying when the loss of a function or process would result in the identified business impacts
Completing the analysis can help companies identify and prioritize the processes that have the most impact on the business's financial and operational functions. The point at which they must be recovered is generally known as the “recovery time objective.”
Business Continuity Plan vs. Disaster Recovery Plan
BCPs and disaster recovery plans are similar in nature, the latter focuses on technology and information technology (IT) infrastructure. BCPs are more encompassing—focusing on the entire organization, such as customer service and supply chain.
BCPs focus on reducing overall costs or losses, while disaster recovery plans look only at technology downtimes and related costs. Disaster recovery plans tend to involve only IT personnel—which create and manage the policy. However, BCPs tend to have more personnel trained on the potential processes.
Why Is Business Continuity Plan (BCP) Important?
Businesses are prone to a host of disasters that vary in degree from minor to catastrophic and business continuity plans (BCPs) are an important part of any business. BCP is typically meant to help a company continue operating in the event of threats and disruptions. This could result in a loss of revenue and higher costs, which leads to a drop in profitability. And businesses can't rely on insurance alone because it doesn't cover all the costs and the customers who move to the competition.
What Should a Business Continuity Plan (BCP) Include?
Business continuity plans involve identifying any and all risks that can affect the company's operations. The plan should also determine how those risks will affect operations and implement safeguards and procedures to mitigate the risks. There should also be testing procedures to ensure these safeguards and procedures work. Finally, there should be a review process to make sure that the plan is up to date.
What Is Business Continuity Impact Analysis?
An important part of developing a BCP is a business continuity impact analysis which identifies the effects of disruption of business functions and processes. It also uses the information to make decisions about recovery priorities and strategies.
FEMA provides an operational and financial impact worksheet to help run a business continuity analysis.
These worksheets summarize the impacts—both financial and operational—that stem from the loss of individual business functions and processes. They also identify when the loss of a function or process would result in the identified business impacts.
Business continuity plans (BCPs) are created to help speed up the recovery of an organization filling a threat or disaster. The plan puts in place mechanisms and functions to allow personnel and assets to minimize company downtime. BCPs cover all organizational risks should a disaster happen, such as flood or fire.
Federal Emergency Management Agency. " Business Process Analysis and Business Impact Analysis User Guide ." Pages 15 - 17.
Ready. “ IT Disaster Recovery Plan .”
Federal Emergency Management Agency. " Business Process Analysis and Business Impact Analysis User Guide ." Pages 15-17.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/BusinessPlanMeeting-570270145f9b5861953a6732.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices

Business Continuity Plan Template
Make a business continuity plan with business continuity plan template from venngage..
- Design Style : modern
- Colors : dark
- Size : Letter
- Plan : business
A business continuity plan template is a document that outlines the steps that need to be taken in order to ensure business continuity in the event of a disaster or emergency. It can help to ensure that your business can continue to operate in the event of a disruption. Your business continuity plan template should include information about business continuity in general, the business's mission and values statement, business description, key contacts (name, positions held), suppliers, clients/customers/donors, associates (employees who are not part of management or do not hold critical roles in operations) that may be affected by an emergency, business location(s), business phone numbers and fax numbers, business email addresses, business bank account information (name and address on file), back up services (a list of providers and contact information for restoring lost data), insurance providers (contact information on file) and billing statements. When developing your business continuity plan template, you should create a section for business activities where employees may volunteer to participate in the business continuity planning process. Additionally, business goals and objectives should be developed to ensure
Read more >
Explore more
Create your business continuity plan (with free template)

Our experts
Written and reviewed by:.
As a small business owner you may have been alarmed by the events and uncertainty of the past few years. Since COVID first hit, a barrage of tough trading conditions has seen countless businesses forced into administration or even company liquidation .
With a background of Brexit, pandemics, lockdowns, the Great Resignation, an in-and-out-and-in-again recession, and other current stressors – you will need a clear plan in place to keep operations running smoothly in these uncertain times – one that focuses on the continuity, survival and durability of your small business. That's where a Business Continuity Plan can be essential.
You may have heard about Business Continuity Plans (BCPs), but don't know exactly what they are or how to go about creating one. Whilst many small businesses have insurances in place, far less know they need a BCP or some kind of framework to deal with unexpected or unpredictable events.
We’ll guide you through the process here, explaining the key considerations and elements. By the end of this article you’ll know how to write a thorough and workable BCP, using the free template provided to get started .
In this article, we will cover:
What is a business continuity plan, why is a business continuity plan important.
- How to Create A Business Continuity Plan
Next Steps: Testing and Reviewing Your Plan
Our below guide will give you detailed advice on how to write a quality BCP.
But first, you need to know what to include – and that's where a high quality template can help.
We recommend using the free clickup.com BCP template to ensure nothing gets missed. Every step involved in the business continuity plan – coordinating your emergency response, forming your strategy to get back up and running and communicating with your customers – is already mapped out for you, ready to be filled in with your details.
We recommend creating an account with Clickup to use this free template – doing so means you may be able to keep your business protected financially and otherwise in the event of an emergency. You can see the template below, or click to try it for yourself by signing up to Clickup.

Business continuity is the ability of an organisation to continue production and delivery to an acceptable standard following a disruptive incident. A Business Continuity Plan details the steps and strategies to how you intend to do that.
Your Business Continuity Plan can take many different forms – a paper document that you could store away in a filing cabinet, or a digital document that you store on your computer (or multiple if you want to be really safe).
Ultimately it is the emergency strategy you use if you want to get your business on track in terms of regaining customers (and to avoid losing them to competitors) from supply chain issues, for example, to fixing physical damage to products or property, recovering from any losses of particularly significant people, and keeping the business from fully having to close down due to significant negative events.
You would normally use it as soon as you possibly can after said negative events to mitigate as much damage (whether physical or representational) as you can. This would also inspire confidence about you to your team and show the leadership needed to deal with stressful situations when it’s most needed.
The state of the world leaves much to be desired right now. We are seeing such unprecedented upheavals in almost every sector of everyday life – from the cost of living, to post-pandemic effects, to rising electricity prices and other forms of inflation – that Collins Dictionary chose “Permacrisis” as their 2022 word of the year.
“Permacrisis” perfectly encapsulates the ‘survival mode’ most small business owners are in right now . But having a Business Continuity Plan ensures that your company and its assets are protected and are able to function quickly in the event of a disaster – so that the business survives with as little damage as possible (financial or otherwise).
Your business continuity plan should detail such important aspects such as:
- Coordinating an emergency response
- Dealing with damaged infrastructure
- Timescales for getting systems back up and running
- Strategies for reassuring customers
How to Create a Business Continuity Plan
We know you already have a lot on your plate right now, and creating a new plan may seem like a lot of work with multiple considerations and factors – but not to worry. A solid plan is worth it, as it can be an essential asset for years to come, and we’re here to walk you through making one.
(We’re also assuming you already have your business plan in place, but if not, we also have a guide that will give you detailed advice on how to write a quality business plan here.)
Step 1: What are your potential risks and impact?
- Consider all the potential risks to your company. There are external risks (for example power cuts, natural disasters, cyber attacks and other things that are out of your control for the most part), and internal risks (for example sudden cash-flow issues, tough sales months or losing key staff).
- What parts of the business could they affect? The issues could affect anything from your premises, people, stock and equipment, operations and processes, to technology.
- What could the impact be? You could for example experience a loss of sales and income, increased expenses, decreased customer satisfaction and loyalty, delayed service delivery, poor product quality, or regulatory fines.
Let’s put it together: If you owned a hair salon and a competitor opened up next door .(potential risk), it would affect the volume of potential customers (part of business affected) and there may be a loss of sales (business impact).
Step 2: What are your critical business functions?
- A critical business function is a process that must be restored in the event of a disruption to protect the business and keep meeting expectations (up to the standards of shareholders, for example). A good Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system would help with this process, and you can find some of the best CRM for small businesses here .
- A few different business functions that exist are paperwork, employees, and production for example .
- Using paperwork that was at risk of a fire as an example, a way to mitigate this potential risk would be to have multiple backups , in different locations and the responsibility of different people in the business.
Step 3: Who holds the key roles and responsibilities?
It’s important to consider the key roles and responsibilities in your business because that way, the right information can get to the right people in a streamlined way and issues can be resolved by the right people quickly.
These may include:
- Internal staff (sales leaders, accountants, client managers etc)
- External key players (contractors and service providers, suppliers and distributors, IT consultants, utility companies etc)
- It’s important to have a list of key people (with their documented roles), and other important contacts, as well as clear instructions that clarify their responsibilities in an emergency situation.
Let’s put it together: If there was a security breach in a tech company, the customer service department (internal staff) would need to be alerted who could send out a reassuring email to customers. Next, a call would need to be made to an IT consultant to fix the issue (external key players). At the same time, a senior manager for example (key people) could also send out a message to shareholders to clear up and clarify any incorrect information showing on systems.
Step 4: What is your communication plan?
- Who needs to be contacted: in the event of a disruption or emergency? Some examples may include employees, customers, clients, or suppliers.
- How will you communicate with them: Depending on the severity of the situation and also taking into consideration the tone of your company brand and the mediums your customer base use most, you could use social media, press releases, or an email newsletter for example.
- What will the tone be? The tone can be serious, reassuring, optimistic or anything else you feel most accurately serves the situation, and that would be on brand for your company.
- Test your plan. It is extremely important to make sure your plan works BEFORE it's put into action. There would be nothing worse than to feel you have a good plan but when something serious actually happens, it all falls apart because it wasn’t properly tested or viable in actual practice.
- The various components of testing may involve training staff, practice drills where you can receive feedback on areas of improvement, and allowing yourself time to make adjustments where necessary. Project management software would be useful in organising all of this with the many different people involved – we have an article on some of the best free project management software here.
When Should You Review Your Plan?
A Business Continuity Plan should be a living, breathing entity just as your company is. As life’s natural changes occur, and shifts in your business infrastructure inevitably occur over different periods of time, you will need to ensure that your plan is regularly updated so it’s the best it can be.
Key factors that should trigger a review include:
- Changes to staff: New staff will need to be informed about the practices of your plans, and sometimes the plan may need to be adjusted to accommodate new staff, if they have specific needs for example.
- Changes to premises: Your plan should include emergency procedures for every physical premise you have, so if there is a change there make sure your plan reflects that to ensure it’s as optimal as possible.
- Changes to processes: If there are changes to your processes, your plan should reflect these changes so that everyone can stay updated and there is as little confusion as possible in the event of anything unexpected.
How Often Should You Review Your Plan?
- Timeframe: An annual review is good practice to review and update your business continuity plan, because usually in that amount of time a business, the environment of the business and the world would have naturally changed and evolved to some extent.
- Who to update: You should inform anyone within your company that the changes will affect, such as staff and employees, who will need to know in order to adjust their behaviours and processes and move forward safely. (You can use your list of key people for this).
- How / where to store your BCP: As mentioned above in the ‘critical business section’, it’s important that your BCP is stored in a few different locations, and accessible to the people who may need it.
Your business continuity plan should not just be something you create then never intend to action. You never know when an emergency event will come into play that could potentially break your business in some way or another, and you can use the free template provided by Clickup to rectify that.
Hopefully you’ll never need to use your plan, but in the worst case scenario, you can rest assured that you have yourself and your business covered.
Written by:
Leave a comment.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
We value your comments but kindly requests all posts are on topic, constructive and respectful. Please review our commenting policy.
Related Articles


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 3: Establish the business continuity plan objectives. Step 4: Evaluate the potential impact of disruptions to the business and its workers. Step 5: List actions to protect the business. Step 6: Organize contact lists. Step 7: Maintain, review, and continuously update the business continuity plan.
CREATING THE BUSINESS CONTINUITY PLAN The business continuity plan (BCP) is intended to be a dynamic plan and can be used in emergencies, disasters, and other catastrophic events where the technology, facility, or a department is severely impacted. BCPs are critical in keeping the facility open and providing care to the community.
Business Continuity Plan Template for Healthcare Organizations; ... Use this template to document and track your business operations in the event of a disruption or disaster to maintain critical processes. With space to record business function recovery priorities, recovery plans, and alternate site locations, this template allows you to plan ...
Here is an example of a BCP format: Business Name: Record the business name, which usually appears on the title page. Date: The day the BCP is completed and signed off. Purpose and Scope: This section describes the reason for and span of the plan. Business Impact Analysis: Add the results of the BIA to your plan.
6. Conduct a business impact analysis (BIA) Perform a BIA to understand the potential consequences of disruption to critical business functions. It has to be done in determining the maximum acceptable downtime and the resources needed for business continuity. 7. Start drafting the plan.
Business continuity policy templates can save you time when writing a policy. Editing an existing document takes less effort than formatting a new one and serves as a reminder to add key information. Use our free downloadable business continuity policy template available in Microsoft Word and Google Docs formats.
1. Operational. Operational continuity means that the systems and processes your business relies on are able to continue functioning without disruption. As these processes are critical to business operations, it's important to have a plan in place in case disruption occurs so you can minimize the loss of revenue. 2.
A business continuity plan is a document containing a predetermined set of procedures that describe how an organization will sustain its business operations during and after a significant disruption. ... Business continuity plan template. Use this template to begin identifying the risks, critical elements, mitigation actions, and preparedness ...
A business continuity plan is a document establishing your organization's strategies for dealing with a disaster. These procedures help you resume business quickly and reduce downtime and lost revenue. ... A business continuity plan template makes planning for contingencies in various scenarios easy and addresses the most critical roles and ...
A business continuity plan (BCP) is a roadmap for long-term success that factors in common pitfalls and risks. A business continuity plan template ensures that you dot your Is and cross your Ts, and craft a reliable plan to handle unexpected events or disasters. The template will include fields for filling in information on your current ...
To ensure the proper execution of our continuity plan, the company will have (number of drills, e.g., 2) drills over the year on (add dates). Each one will be carried out by our emergency response team during work hours. Employees will receive a reminder email a week before the drill to prepare. During each drill, we will review the ...
By Paul Peters, Updated Nov 23, 2023. A business continuity plan (BCP) is an essential business document that outlines how a business will continue its critical functions during and after an emergency event or disruption in business. Emergency events can also include natural disasters, workplace violence, utility failures, cyber-attacks, supply ...
Using the right business continuity plan template can be critical to creating the proper foundation for your company. Create one now! Business . Analytics; ... the more likely it is that you will create a truly effective business document. Business Continuity Plan Examples. Download 45 KB #11. Download 3 MB #12. Download 151 KB #13. Download 2 ...
What is a business continuity plan (BCP)? A business continuity plan is a survival tool tailored to each organization's natural course of operation. This document merges comprehensive techniques in risk assessment and crisis management. Companies employ BCPs to anticipate potential threats like pandemics, human error, and technological failures.
ISO 22301 Simplified Cheat-Sheet. Use this simplified cheat-sheet to understand the basic elements of creating a business continuity plan. The template walks you through the process of determining critical aspects of your organization, writing the recovery plan, and exercising the plan to ensure proficiency.
Business Continuity Plan (BCP) is a document which provides guidance and steps for recovery in a specified period of time for a specified function or process. It is written in enough detail so that those required will be able to execute the plan with minimal delay. It is a collection of resources, actions, procedures, and information that is
The documentation template may be used for ISO 27001 and ISO 22301 certification audit purposes. Document templates contain an average of twenty comments each, and offer clear guidance for filling them out. The template was created for small and medium-sized businesses.
Business Continuity Plan Overview Existing BC Plan Layout BCM Team Document Page: 1 Layout of Proposed BCCM Template Business Continuity Plan Components and sequencing description This document is designed to help explain the contents of an example Business Continuity Plans, so that team members will have a better understanding of how to relate ...
You are responsible for the content of the documents you create using these templates. We are not responsible for the value or accuracy of these documents, nor for the damages resulting from their use. If you do not agree with what you just read, do not use the templates. Use this business continuity plan template to help minimize the risk that ...
Business Continuity Planning - BCP: The business continuity planning (BCP) is the creation of a strategy through the recognition of threats and risks facing a company, with an eye to ensure that ...
Create. A business continuity plan template is a document that outlines the steps that need to be taken in order to ensure business continuity in the event of a disaster or emergency. It can help to ensure that your business can continue to operate in the event of a disruption. Your business continuity plan template should include information ...
How to Create A Business Continuity Plan. Next Steps: Testing and Reviewing Your Plan. Get started with Clickup's free business continuity plan template today. Our below guide will give you detailed advice on how to write a quality BCP. But first, you need to know what to include - and that's where a high quality template can help.