

How to fix “self-assigned IP address” issue on Mac
Key Takeaways
- The self-assigned IP address error occurs when your Mac assigns itself an IP address instead of getting one from the router.
- This usually happens due to network configuration issues, DHCP server problems, glitches in the firewall settings, unstable Wi-Fi connection, etc.
- To fix the “self-assigned IP address” error on your Mac, renew DHCP lease, restart your network devices , rejoin your Wi-Fi , or check your network settings .
Is your MacBook struggling to access the internet, though your Wi-Fi or Ethernet works fine? This can be due to the self-assigned IP address error on your Mac. Worry not!
Here, I’ll share how to fix the internet not working due to a self-assigned IP address error on your Mac to regain a stable network connection. But before we jump into the troubleshooting steps, let’s understand what a self-assigned IP error is.
What does “self-assigned IP address” mean on Mac?
The “self-assigned IP address” error on Mac refers to a situation where your device assigns an IP address and sets up an ad-hoc network instead of obtaining one from the network router or DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server.
This self-assigned IP address is not legitimate or acknowledged on the network. That’s why your Mac cannot connect to the internet or other devices on the network, resulting in limited or no network connectivity.
This issue occurs due to several reasons such as:
- Network configuration conflicts
- DHCP server unavailability
- Problems with Mac’s network
- Unstable Wi-Fi connection
- Wrong Firewall settings
- Outdated macOS
But you can fix the issue with a few simple methods. Let’s learn them!
How to fix “self-assigned IP address” error on Mac
There are 12 ways to fix the problem, from simple checks to more advanced changes. It would help if you tried them in the order provided.
1. Check your connection
Before diving into Mac-specific settings, ensure that your router is functioning correctly and located near your Mac to obtain a valid IP address. Besides, if you are using an Ethernet connection, plug in the cable snugly.
I also check to validate that the cable has no fault and is in good condition. Moreover, If you are using an old Wi-Fi router, discard it and get a new one to obtain a smoother connection.
2. Reboot your network devices
Restarting both your modem and router can often resolve temporary network glitches. Power off the devices, unplug the cables, and wait a few seconds. It will help them cool down, as excessive heat can cause malfunctions.
After that, plug all cables, connect them to the power outlet, and turn them back on. In the meantime, restart your Mac once to iron out any bugs in macOS.
- Click the Apple logo .
3. Renew DHCP Lease on macOS
This method is effective when the assigned IP address may have expired or encountered conflicts. When you renew the DHCP Lease, your Mac requests a new IP address from the DHCP server. It ensures a valid configuration and resolves connectivity issues.
- Open the same TCP/IP tab window from Wi-Fi Details, as shown above.
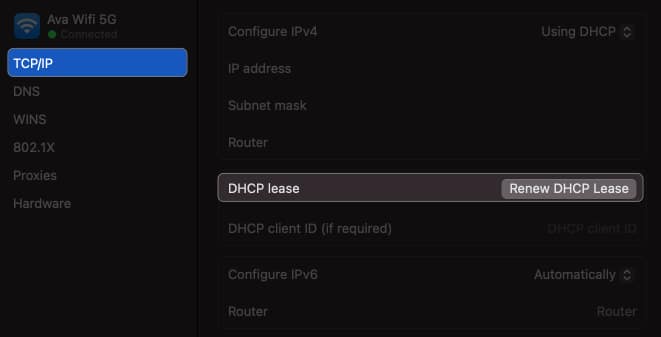
After renewing the lease, check if you can connect to your network. If that doesn’t help, try creating a New Network Location and renewing the lease.
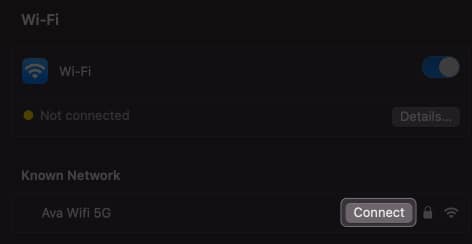
4. Rejoin your Wi-Fi network
Sometimes, simply forgetting and rejoining your Wi-Fi network can solve the self-assigned IP address error on your Mac.
- Turn off Wi-Fi for a few seconds and toggle it on.
5. Check your connection settings
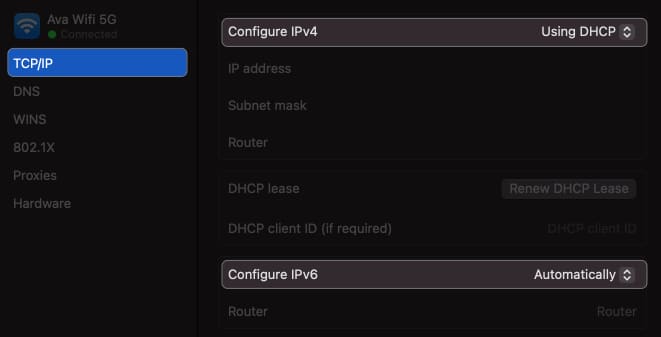
Verify that your Mac’s network settings are configured correctly. You must opt for the appropriate network settings to obtain IP addresses and DNS information automatically.
- Go to your Wi-Fi Details . I have shown the steps above.
- Select TCP/IP from the left panel.
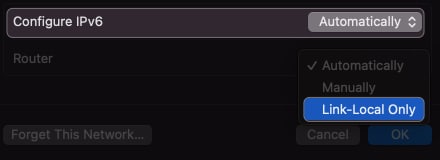
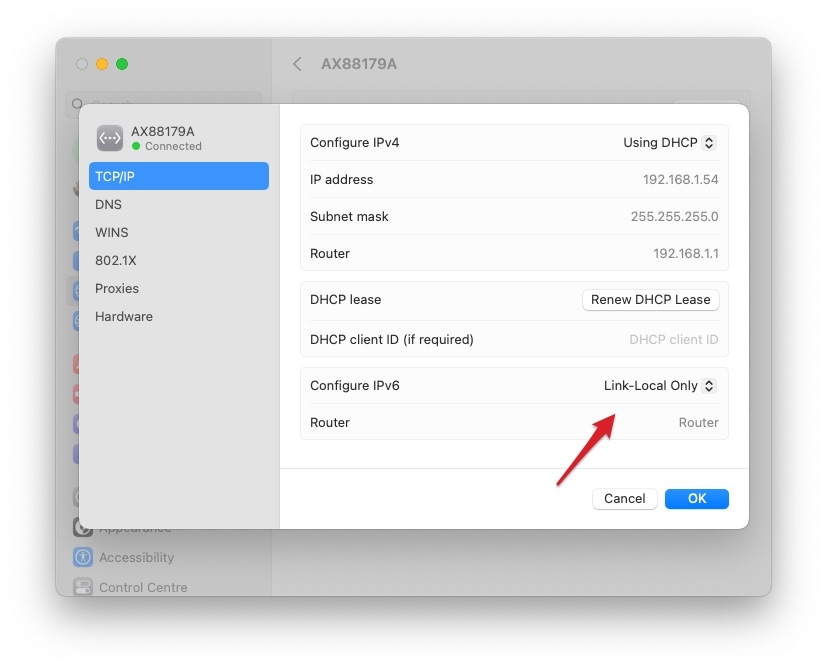
You may also try turning off the IPv6, as some users reported it conflicted with the IP address assigning procedure.
- Click on the drop-down arrow beside Configure IPv6 .
6. Reset your Network Preferences on Mac
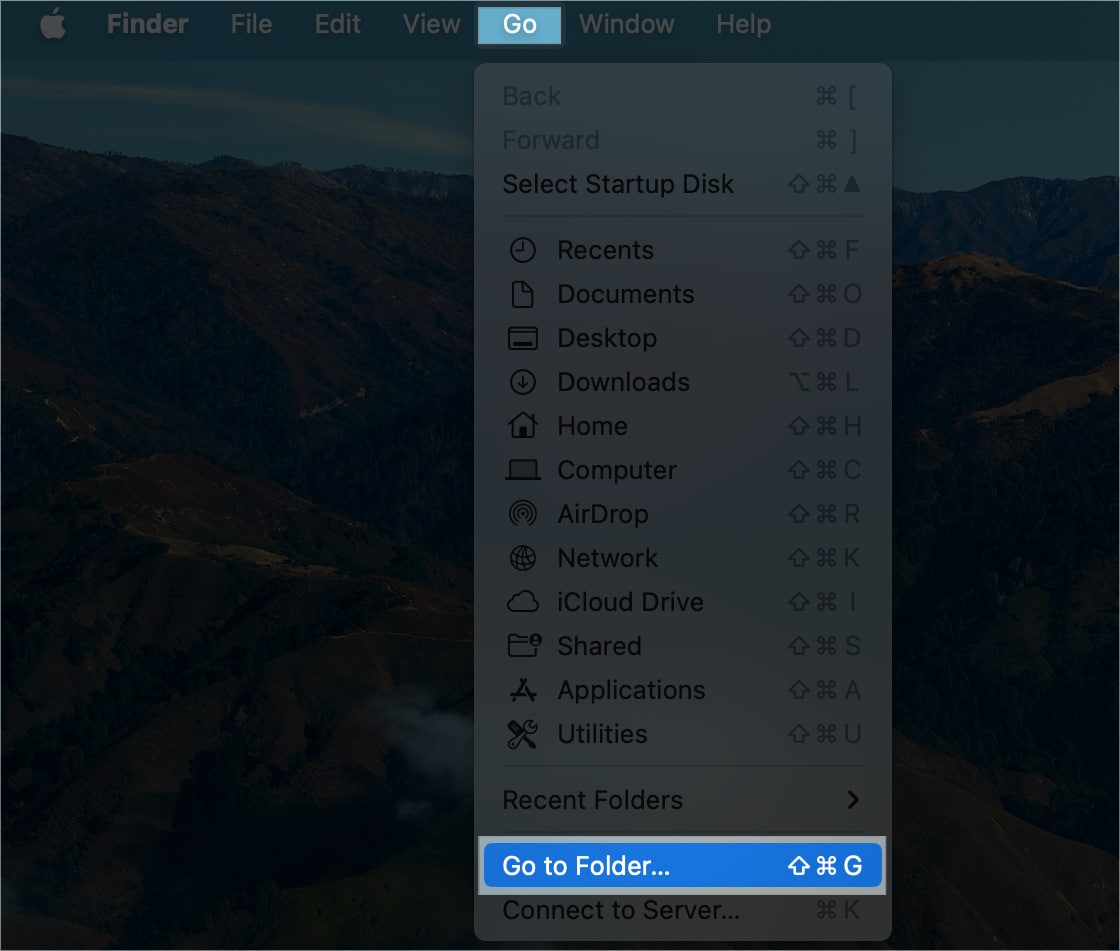
Resetting the network preferences can help eliminate IP address misconfiguration, causing the internet to not work. So, you must delete specific network connectivity-related files from your MacBook.
- Launch Finder .
- Enter your Mac password to authenticate the deletion.
- Restart your Mac. It will automatically recreate the deleted files.
- Log in and connect to your Wi-Fi network.
- Go to the TCP/IP setting again and check the router files.
7. Create a new network location
Creating a new network location lets your Mac start fresh with network settings and eliminate a self-assigned IP address.
- Click the Apple logo → System Settings .
- Wait for a few seconds until your Mac connects to your Wi-Fi.
Repeat the steps of renewing the DHCP lease on your Mac, and then try connecting to your network.
When you try to perform configuration changes to the system, your Mac’s firewall experiences configuration issues. Let’s fix this problem by resetting the Firewall.
8. Reset the Firewall on your Mac
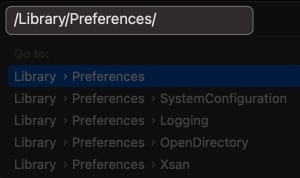
- In the menu bar, click Go → Go to Folder .
- Restart your Mac.
After your system boots, it’ll ask you to allow access to numerous programs and services. Enable access depending upon your choice. Then, try connecting to your network and check if the self-assigned IP address error persists.
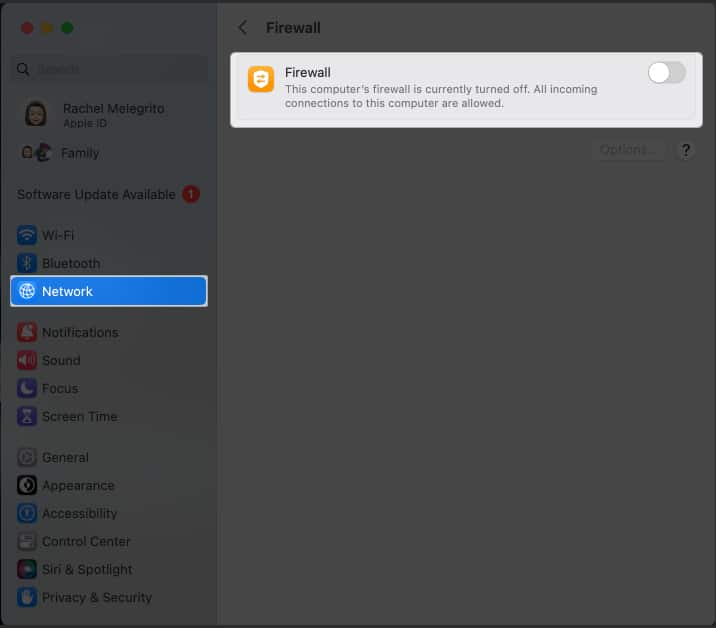
If you are unsure about deleting the Firewall files, you may temporarily disable it. Toggling off the Firewall on your Mac can help determine if it’s causing conflicts with network connectivity.
- Select Network from the left panel → Choose Firewall .
- Restart your Mac and turn it on again.
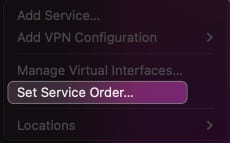
9. Set Service Order from Mac’s network settings
Adjusting the service order can prioritize the network interface, ensuring your Mac connects to your preferred network.
- Click the Apple logo → System Settings → Network .
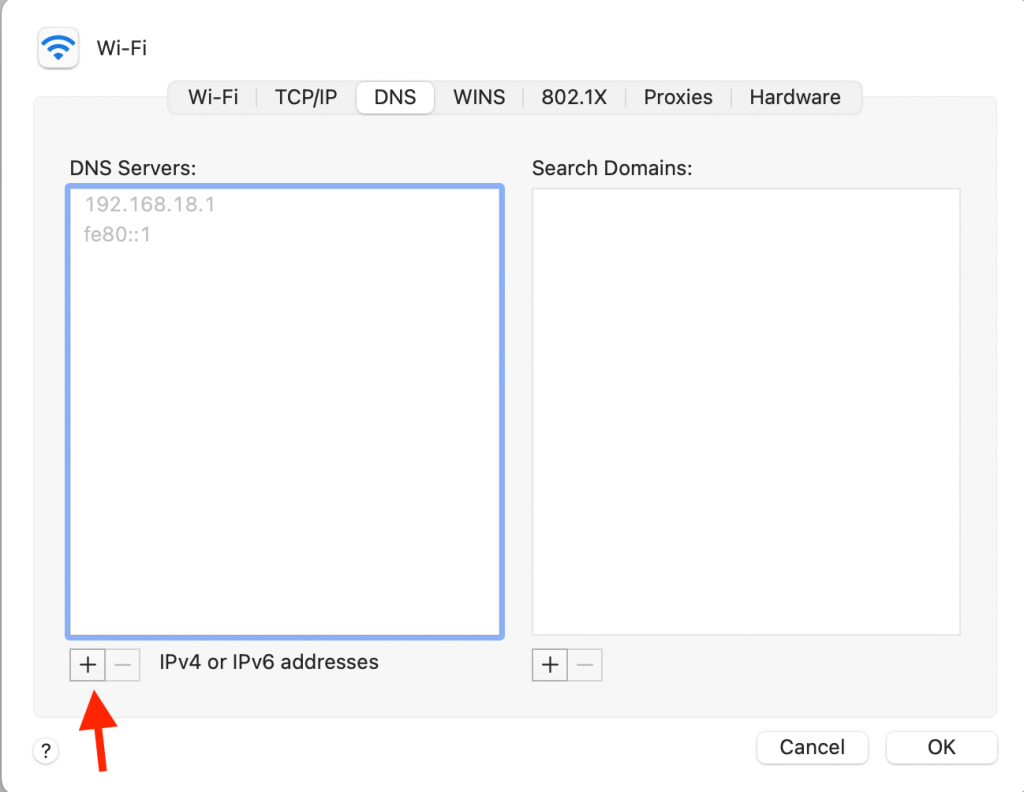
10. Change DNS Servers on macOS
Discarding existing DNS and switching to alternative DNS servers can resolve DNS-related issues that may contribute to the self-assigned IP address error.
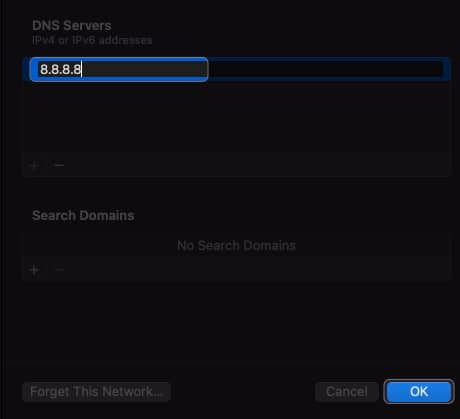
- Open System Settings → Wi-Fi → Click Details beside your Wi-Fi name.
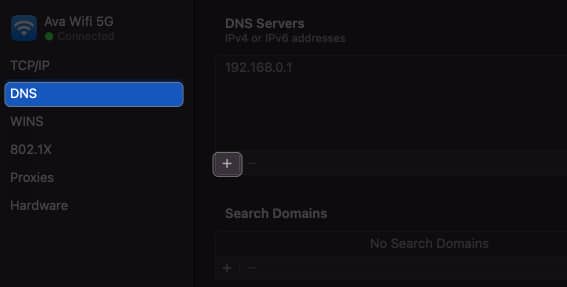
- Add these numbers: 8.8.8.8 8.8.4.4 1.1.1.1 9.9.9.9
11. Check for conflicting IP address
Ensure that no other devices on your network use the same IP address as your Mac. Check your router’s DHCP client list and verify that all devices have unique IP addresses assigned.
12. Disable VPN
If you have a VPN service enabled, disable it temporarily to see if it resolves the self-assigned IP address error. Open your Mac’s VPN settings and turn off the VPN connection.
Bonus fixes
You may need to attempt more complex fixes if the troubleshooting techniques outlined above do not fix the self-assigned IP address problem on your Mac:
- Update your Mac to the latest OS version.
- Verify your Mac is not infected with any malware or viruses.
- Ensure your network devices are operating well and there are no hardware problems.
- Restart your router or modem
- Reset NVRAM or PRAM on Mac to clear up the system settings memory.
Tips to prevent self-assigned IP address issues on Mac
Self-assigned IP address error is indeed frustrating as it prevents your Mac from accessing the internet. So, you must take some precautions to avoid such a nuisance in the future.
- Regularly update your Mac
- Try to restart your Mac, router, or other network devices once in a while
- If your router or modem is outdated, replace it with a new one to get optimal performance. Also, configure the network with high-quality equipment.
- Connect your Mac to only one active network. I suggest using an ethernet cable for a stable connection.
- Don’t connect too many devices to your Wi-Fi at a time, as it may create network overcrowding.
Get back your smooth internet access!
Encountering a self-assigned IP address error on your Mac hampers your work, so you should address it ASAP. You can tackle the issue and restore a stable and reliable network connection using these troubleshooting techniques.
If the problem isn’t resolved, contact Apple Support and seek assistance.
Explore more…
- MacBook connects to Wi-Fi but has no Internet? 12 Fixes
- Wi-Fi not working on Mac? 10 Ways to fix!
- How to Run Wi-Fi Diagnostics on Mac for Better Network Connections
- How to fix IP address conflict on Mac: Simple solutions to fix it!
🗣️ Our site is supported by our readers like you. When you purchase through our links, we earn a small commission. Read Disclaimer .
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

How To Connect Xbox Controller To iPhone Or iPad
How to refresh airtag location for improved tracking, iphone unavailable error here’s how to fix it, when did the iphone 15 come out.
- Zip-rar tool
- Zip browser
How To Fix Internet Not Working Due To Self-Assigned IP Address Issue
If your Mac is connected to a working Wi-Fi network but the Internet is still not working, then we have got the solution for you. A lot of times your Mac is issued a self-assigned IP, which causes the Internet to not work on the machine.
Despite the same Wi-Fi network working on other devices, the Mac will simply show no internet connection error and Internet will not work on it. In these situations Wi-Fi has the self-assigned IP address and will not connect to the Internet despite the Internet working on other devices.
On Mac’s Wi-Fi page the Wi-Fi will also show the Self-Assigned IP Address text instead of connected. This is a very annoying problem that can cause Internet to not work on your Mac. Not having a working Internet connection on your Mac due to Mac’s self assigned IP problem can prevent you for doing work and render your Mac useless.
Good thing is self-assigned IP issue on Mac is quite easy to solve. You can fix the self-assigned IP address issue and get the Internet to work again on your Mac by simply deleting a few files on your machine.
Simply follow the steps below from an administrator account and put the mentioned files in trash.
This solution works on all recent versions of macOS including macOS Ventura, macOS Monterey, macOS Big Sur and macOS Catalina.
Fix Self-Assigned IP Address Issue on Mac
You can use to solve the self-assigned IP address issue on your Mac running macOS Ventura, macOS Monterey, macOS Big Sur, macOS Catalina etc.
1. On your Mac launch finder and click on Macintosh HD. (Don’t see Macintosh HD? See here )
2. Click on the Library folder and go to Preferences.
3. Now click on the SystemConfiguration folder.
4. Next put the following files in trash.
- com.apple.airport.preferences.plist
- com.apple.network.identification.plist
- NetworkInterfaces.plist
5. Restart your Mac.
Once the reboot has taken place the Internet will start working and self assigned IP address issue will be resolved.
If you don’t see all the files mentioned above, then just delete the ones that are present and reboot your machine.
How to Reset Mac’s IP address
In case you’re looking to reset your Mac’s IP address to solve internet connection problems with your computer, then the following instructions will help. If deleting the files mentioned above does not help, then the steps to reset Mac IP address can also prove helpful in fixing self-assigned IP Mac problem.
On macOS Ventura or later
Below you can find instructions on how to reset Mac IP address if you are running macOS Ventura or later.
1. Click on the Apple logo from the top menu bar and then click on System Settings .
2. Now click on Wi-Fi option from the side pane.
3. Make sure your Mac is connected to your Wi-Fi network. Then click on ‘ Details… ‘ located next to Wi-Fi’s name.
4. Now click on TCP/IP button from the left side pane.
5. Next find the ‘ Renew DHCP Lease ‘ button on the right side of the window and click on it.
6. Click on OK button and using the toggle next to Wi-Fi turn off Wi-Fi and turn it back on after a few seconds.
By performing these steps you should be able to solve self-assigned IP issue on your Mac and Internet should start working once again.
On macOS Monterey or earlier
Here’s how you can reset Mac IP address if you are running macOS Monterey or earlier on your Mac.
1. On your Mac open System Preferences.
2. Click on Network icon.
3. Make sure Wi-Fi is selected from the side pane and then click on ‘Advanced’ button.
4. Now click on TCP/IP from the top navigation bar.
5. Next click on ‘Renew DHCP Lease’ button.
6. Click OK to exit and from the top menu click on the Wi-Fi button and turn off Wi-Fi.
7. After a few seconds turn Wi-Fi back on and connect your Mac to your Wi-Fi network.
8. At this point Self-Assigned IP address issue should get solved and Internet should start working again.
There you have it, this is how you can easily and quickly fix Self-Assigned IP address issue on Mac and get your Internet connection working once again. If you have any questions regarding this tutorial, then feel free to let us know in the comments section below.
- troubleshooting
Hello I recently instakked BIG SUR on my late 2013 macbook pro and I am having trouble tethering my Iphone XR to it. I can tether using wifi, but when I attempt to tether using bluetooth, my phone shows as connected in bluetooth preferences on my macbook and iphone, with the connection/link symbol shown on my iphone, but the internet will not work. In Network the bluetooth Pan shows an orange dot, STATUS: CONNECTED, but underneath it says ‘internet-not-working-self-assigned-ip-address-issue’. Do you have any ideas on how to fix this, I followed your instructions from the link ( https://ioshacker.com/how-to/fix-internet-not-working-self-assigned-ip-address-issue ) on your website, but each time I restart the computer the files that I put into the trash and delete from the trash re-appear in the system configuration folder. Only 2 of the 3 files you suggested to trash are in the folder, – com.apple.network.identification.plist – is not in the folder. Any advice appreciated.
I’m running Monterrey on my MacBook Pro and was having problem with the self-assigned IP and cannot connect to the Internet. I followed what your article suggested, several times, but was still unable to resolve the problem. Are there other suggestions that you think I should try? Thank you.
I just had the same issue and none of the fixes found online worked. I have McAfee Security software installed and there was a service running called McAfeeSystemExtensions. I deactivated the service within the Network settings and problem resolved.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Sign Up for Our Newsletters
Related posts, forgot apple id password here’s how to find it it on iphone, ipad and mac.

What is Self-Assigned IP and How to Fix it
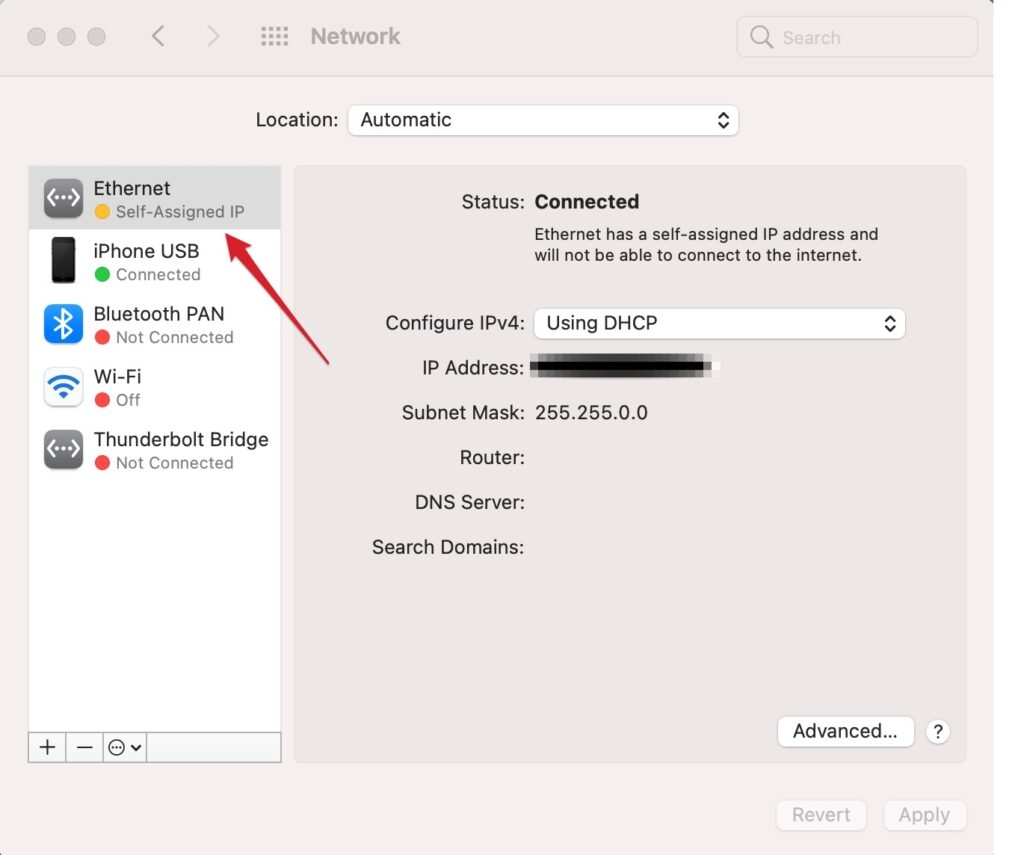
The self-assigned IP error may prevent your Mac from connecting to the Internet. You may get an Internet connection error messages such as “Wi-Fi has the self-assigned IP address and will not be able to connect to the Internet.” If you investigate this issue further, you will see that the Network pane in System Preferences will also show a notification message saying “Self-Assigned IP” with a yellow dot instead of the regular “Connected” message under the network service, as you can see in the screenshot below. This problem may occur when Mac is connected to a wired, wireless (Wi-Fi), or hotspot connection.
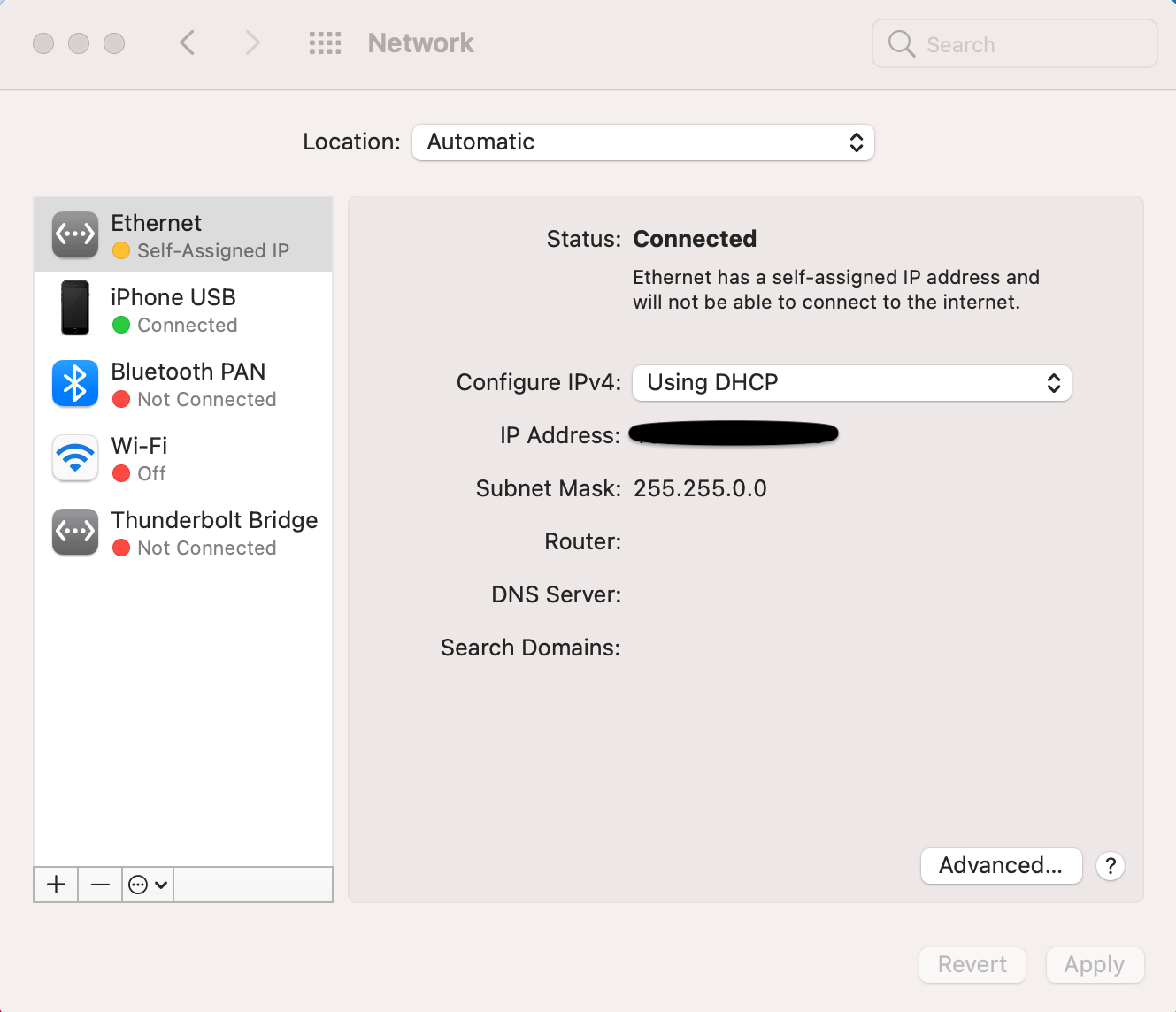
This problem occurs when a self-assigned IP address is issued to network interfaces. When this issue happens, not all computers connected to the same network may be affected. For example, in the same home, one Mac may have this problem while other similarly configured Macs may have no problem at all, even though they all are using the same Wi-Fi connection. This may mean that the root of the problem is how the problem Mac is configured. Several factors may cause this issue, such as:
- Bad cable connections.
- Not getting an IP from the router or modem.
- Failure of the DHCP server.
Follow the steps below to address this problem. Please try the steps in this order. After trying each step, check to see if your problem is fixed. If it is not fixed and if you still see the Self-Assigned IP error, move to the next step.
Self-Assigned error troubleshooting steps
Check your router/modem : If you are connected over Wi-Fi, ensure that your Mac is not too far away from the router/modem.
Restart your router/modem and your Mac : You can do this easily. Simply disconnect the power cable to your router/modem. Wait 30 seconds. Then reconnect. Then restart your Mac. Click the Apple menu and select Restart .
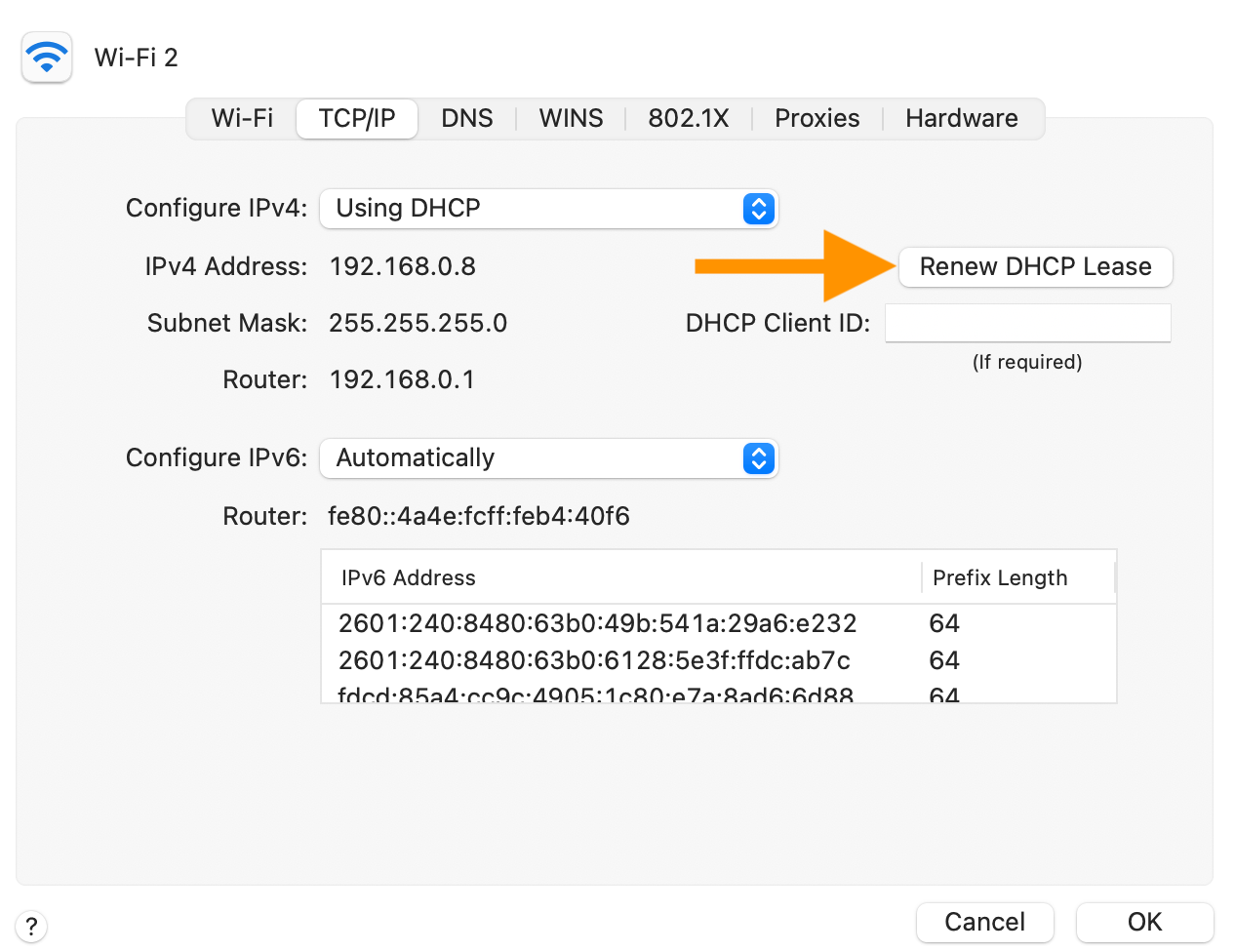
Renew DHCP Lease : On your Mac, open System Preferences and click on Network . Select the network service you want to connect to (e.g., Wi-Fi or Ethernet) and click on Advanced . This will open a new window. Select the TCP/IP tab and click the Renew DHCP Lease . Then click OK .
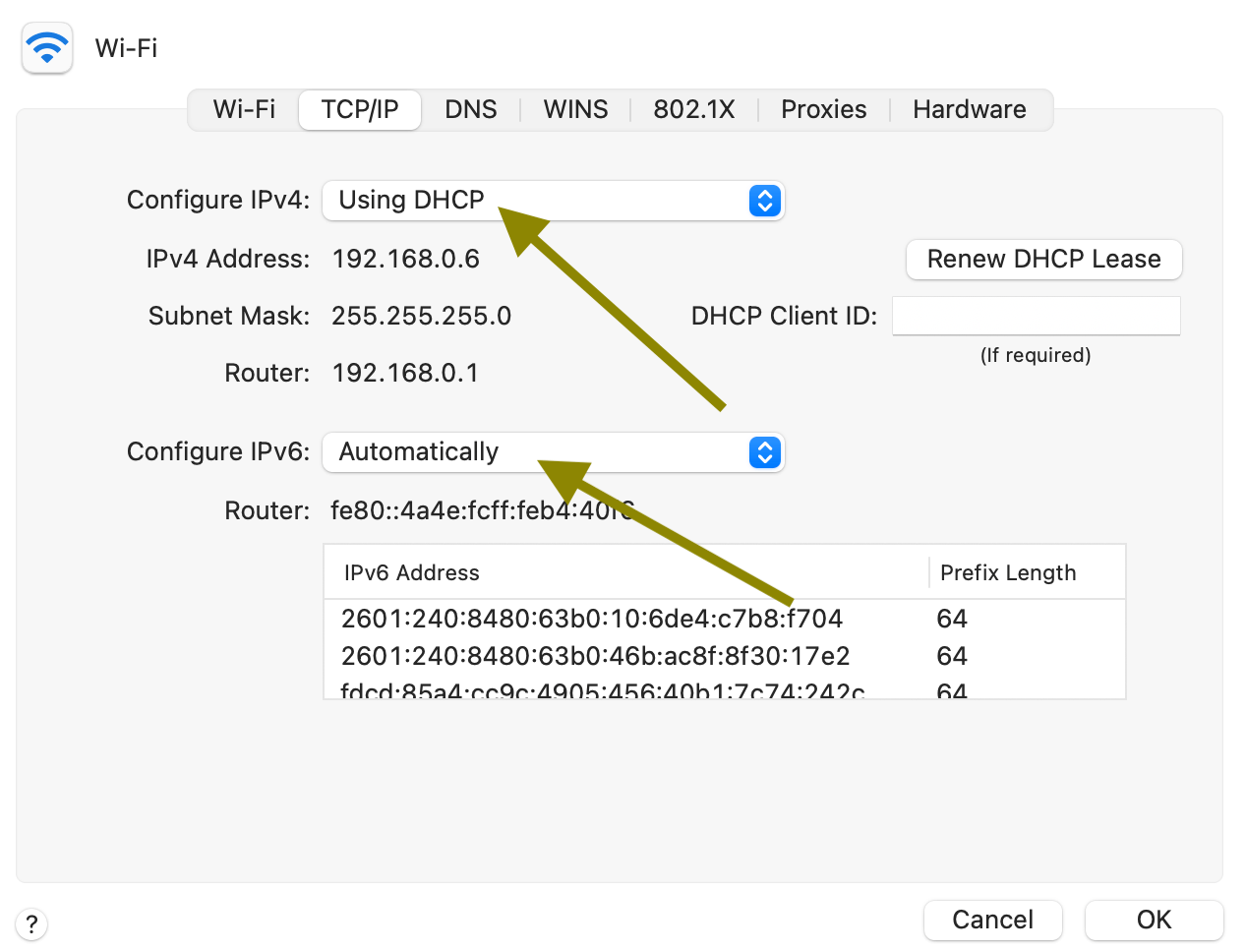
Check your connection settings : On your Mac, go to System Preferences > Network . Then select the network that shows this error and click Advanced . Select the TCP/IP tab and then make sure that “Configure IPv4” and “Configure IPv6” are set to Using DHCP and Automatically , respectively.
Then click on the DNS tab, and delete any DNS servers that are listed there. Select them one by one and click on the minus button to remove them. Do not forget to click OK and Apply when you are done.
Create a new network location : On your Mac, open System Preferences and Network . Open the Location drop-down menu and select Edit Locations . Click the plus (+) button and add a new location, give it a name and click Done . Now you have two locations: Automatic and your new location. Select this new location and then click Apply .
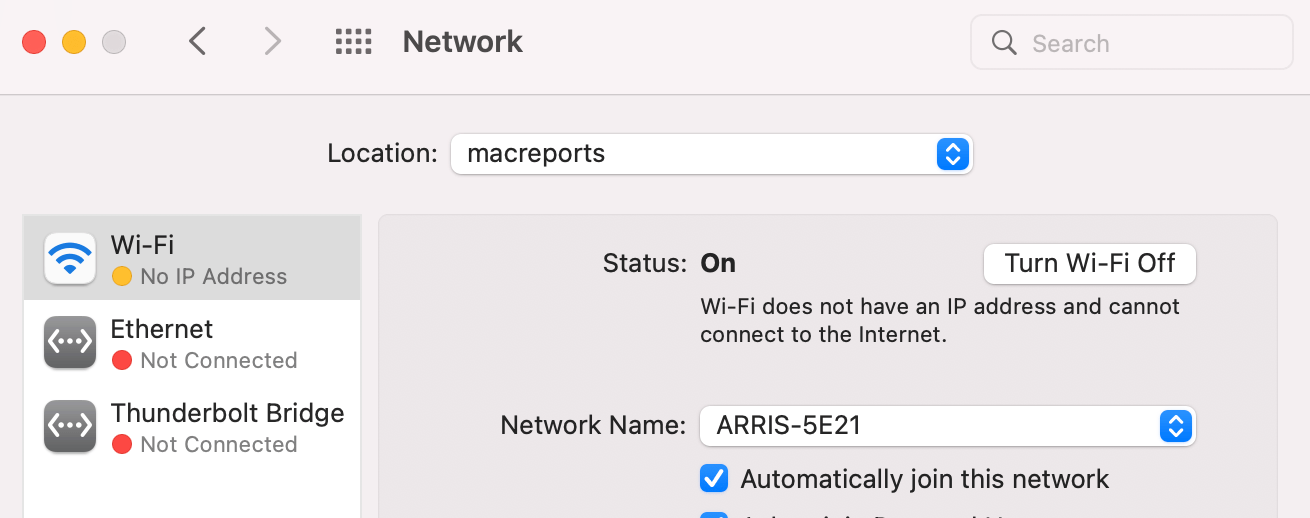
Now, we will add a new Wi-Fi or Ethernet service, whichever you are using. Click the plus (+) sign under the network services on the left, select the Interface (Wi-Fi, Ethernet, etc.) and name it, then click Create . Then click Apply .
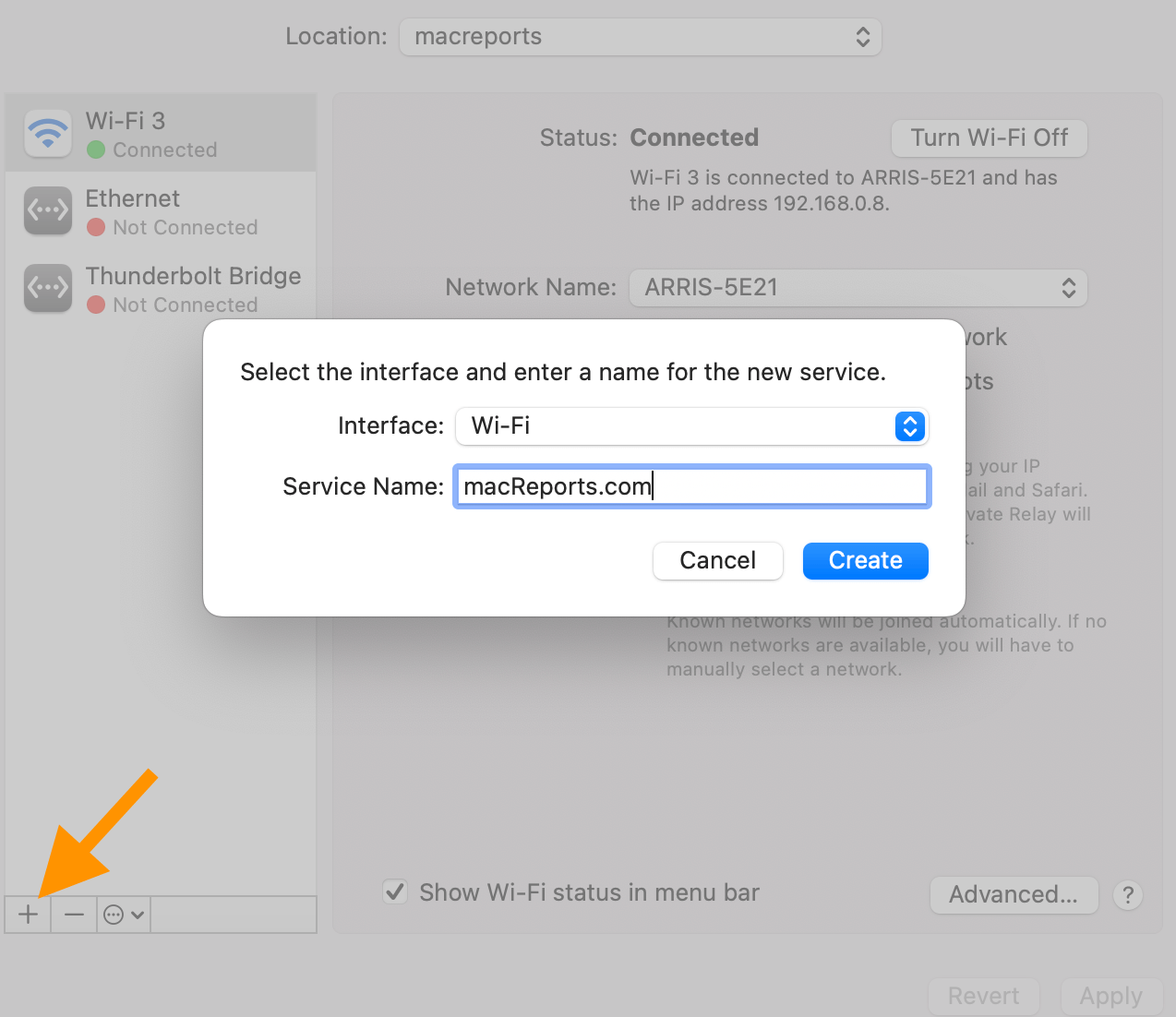
Now select the Self-Assigned IP network and then click the minus (-) button to delete it. Then click Apply . Does this newly created service connect?
Reset the system firewall: We can do that by deleting its preference file . Open a Finder window and then click Go and Go to Folder from the top menu bar. Enter /Library/Preferences/ and click Go .
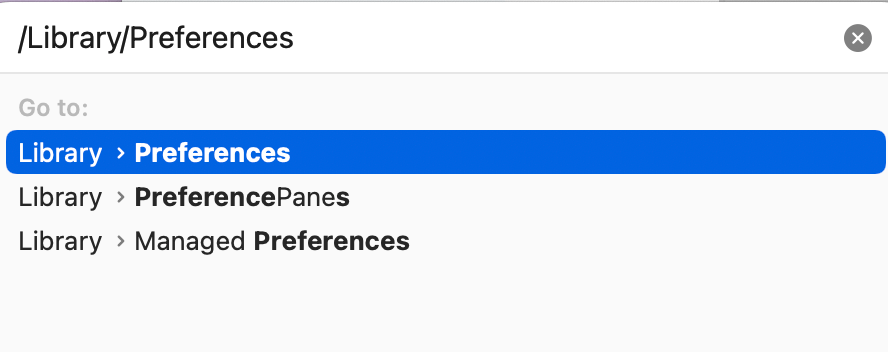
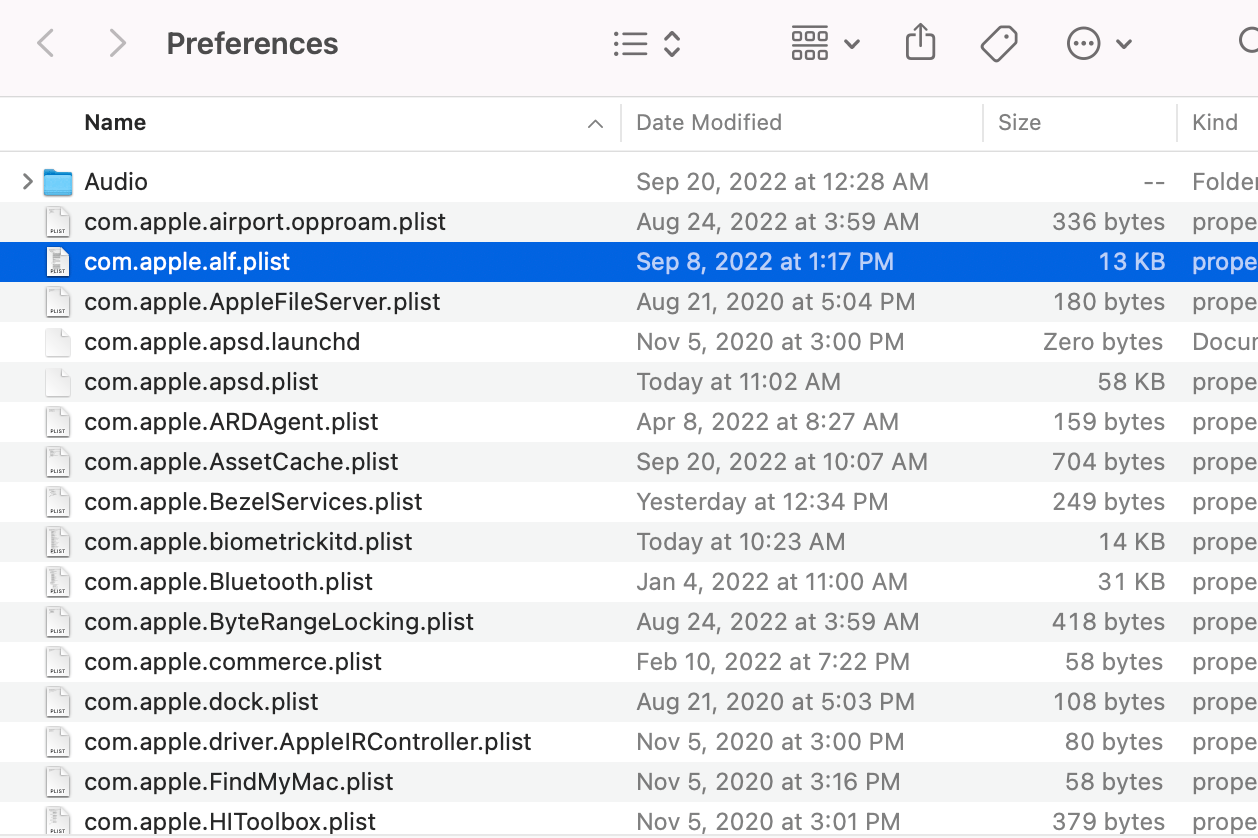
Once the Preferences folder is open, find the com.apple.alf.plist file. Delete this file (or place it on your Desktop; if you are not happy with what happens, you can put it back). Then restart your Mac.
Related articles
- How To Reset Network Settings On Mac
- How To Use Network Utility on Mac
- Mac Wi-Fi Connected But No Internet Access
- iPhone Will Not Connect To A Known Wi-Fi Network, Fix
Dr. Serhat Kurt worked as a Senior Technology Director specializing in Apple solutions for small and medium-sized educational institutions. He holds a doctoral degree (or doctorate) from the University of Illinois at Urbana / Champaign and a master’s degree from Purdue University. He is a former faculty member. Here is his LinkedIn profile and Google Scholar profile . Email Serhat Kurt .
Similar Posts
How to Stop ‘Would You Like to Save this Password’ iCloud Keychain Popups on iPhone or Mac
Keychain is the built-in password manager for Apple devices. It saves your login information for websites and apps and shares them across your devices. When it detects that you have entered a password…
What to do if you see Account Offline in Mail
When you open your Mail app on your Mac, you might see Account Offline – along with a little lightning bolt icon – on the right side of your Favorites bar at the…
How to Make your Mac Show File Extensions
Your Mac has a neat setting that allows you to configure macOS to show all common filename extensions, such as .txt, .docx, or .jpg. This setting will let you differentiate what type of…
How To Disable Screenshot Thumbnail On Mac
When you take a screenshot or screen recording, a little screenshot thumbnail preview will appear for a few seconds, and if you do nothing and if you ignore it, your screenshot (or video…
iMessage is Signed Out Error in Messages on iPhone, How to Fix
When you open the Messages app on your iPhone and try to send a message, you may see an error message saying, “iMessage is Signed Out,” as you can see in the screenshot…
Siri Not Working On Your Mac? Fix
This article explains how you can fix various Siri problems on your Mac. There are many things that can cause Siri to stop working. Mac Siri is Apple’s virtual digital assistant. This article…
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Categories:

Press ESC to close

How to Fix the Self Assigned IP Address Issue on Mac
At times macOS users face the self-assigned IP address malfunction on their computer. Your Mac will keep alerting you to the ‘internet not working’ pop-up even if you have a Wi-Fi network connection.
It allows the network interface to make a malfunctioning ad-hoc network. There can be many reasons for network issues like a broken cable, DHCP server problem, network location, etc. But, it gets better if you know the correct way to troubleshoot the issue.
Table of Contents

Fixes for the self-assigned IP address issue
Self-assigned IP issues can frustrate users and cause internet issues. But, fret not, you can fix self-assigned IP address malfunction using any of the methods mentioned below:
- Restart your modem
Before trying any other method to fix the internet issue restart your modem to see if it works. Click the ‘Wi-Fi’ button from the top menu on the Mac to turn it off. Please wait for a few minutes and then turn it back on. Check to see if the issue is fixed.
If this hack works, you will see the Wi-Fi connection running on your Mac with a proper IP address.
- Re-enable the network preferences
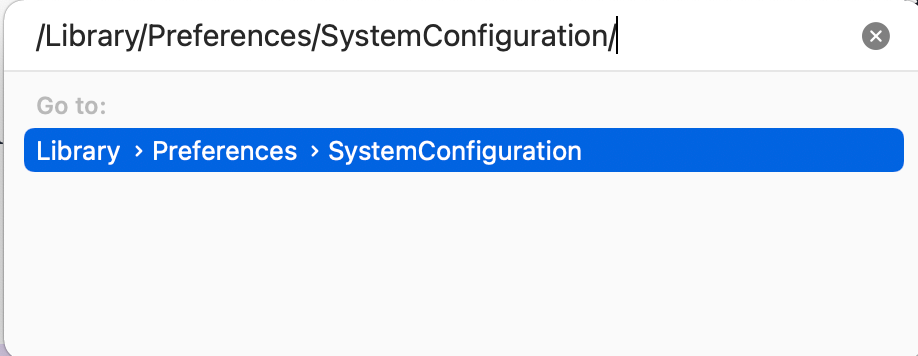
To reset network preferences on your computer, follow these steps:
- Open Mac, launch ‘Finder,’ and in the top menu bar, tap on ‘Go to Folder’ from the drop-down menu of the ‘Go’ bar
- A new window will appear, type ''/Library/Preferences/SystemConfiguration/'' and press enter
- The System Configuration window will open. Then delete the following commands: ‘ com.apple .airport.preferences.plist, Networkinterface.plist and preferences.plist’ to reset network configurations
- Please only delete the files if you have no issue losing the network configuration
- Please switch off the Mac and then switch it back on; try and link to the Wi-Fi again
- Open TCP/IP settings again and look for the files that you deleted
- You will find the removed files back in the old folder
- Renew DHCP lease
One of the most common fixes to the ‘self-assigned IP issue’ is to renew the DHCP lease. A DHCP lease temporarily assigns an IP address to a device connected to the internet.
If the internet connection is malfunctioning, follow these steps to renew your DHCP lease:
- Tap the Apple logo on the top-left menu bar, then visit the ‘System preferences’ section
- Then click on ‘Network settings’ and click ‘Advanced’ in the Wi-Fi section
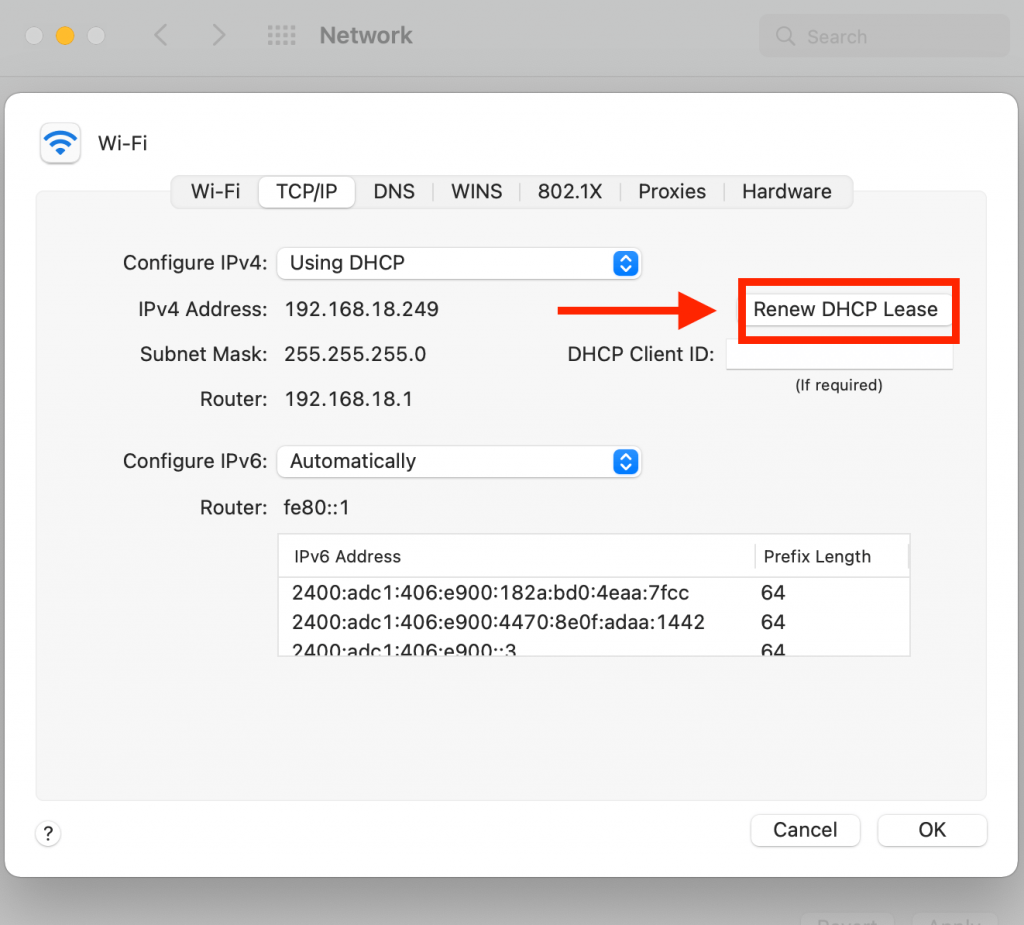
- Then select the ‘TCP/IP’ section and tap on the ‘Renew DHCP lease’ button and select OK
- After renewing the lease, check if you can connect to your Wi-Fi
- Make a different network location/ new location
One way to fix self-assigned IP is to set up new network locations on your Mac. Follow the steps below to make a new network location:
- Tap on the Apple logo from the menu bar and select ‘System preferences’
- Enter the ‘Network settings’ then tap on ‘Drop-down menu’ near the Location tab
- Then tap on ‘Edit locations’ and tap on the ‘+’ button and add a ‘new network location’ and tap on done
- Choose ‘Wi-Fi’ or Ethernet; if not selected automatically
- Then press on ‘Advanced’ button and again press the ‘Renew DHCP lease button’ and enter
- This will set a ‘new location’ on the device
- Reset Firewall
Primarily self-assigned IP address malfunction occurs when the system’s Firewall undergoes configuration problems. If you have performed significant configuration changes on a Mac, settings may not migrate properly. It causes a Firewall issue and might disrupt the network connection.
To fix the firewall configuration issue, follow these steps:
- Click the ‘Finder’ icon to launch it, then select ‘Go to folder’ in the ‘Go’ menu bar
- In the pop-up window, enter the following command /Macintosh HD/Library/Preferences/
- In the new window, delete the ‘com.apple.alf.plist’ command
- After the Mac restarts, reboot it and check if the Wi-Fi connects
Note that after the system boots, you would have to allow connections for the numerous programs temporarily.
- Setup the service order in network settings
If your Mac has a self-assigned IP address issue, try resetting the service order of Wi-Fi in the network settings.
To set ‘Service order’ on Mac, follow these steps:
- Select the Apple logo on the screen and click ‘system preferences’
- Click on ‘Network icon and then press on the gear icon
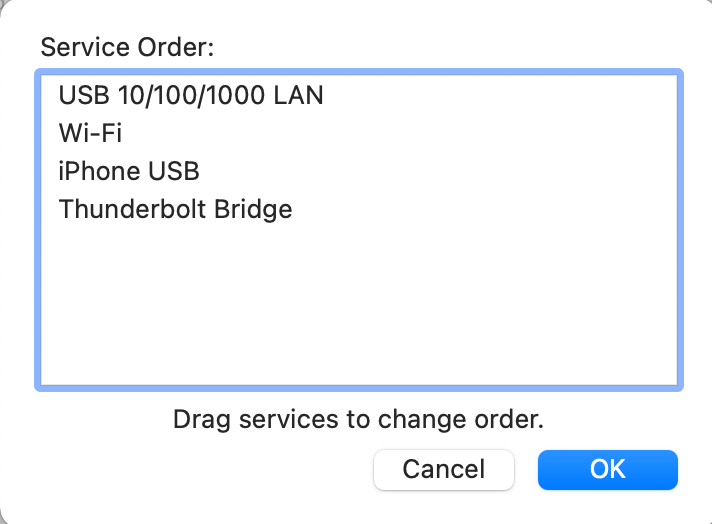
- Then tap ‘Set service order,’ and drag the services you are using at the start of the file
- For example, if you are utilizing Wi-Fi, select ‘Wi-Fi’ and put it on the first number
- Change DNS servers
DNS servers change the domain name to IP addresses. Try changing the DNS servers to see if the issue fixes. Follow these steps:
- Select the Apple logo and click ‘system preferences,’ then click on the ‘Network’ icon
- Select the Wi-Fi icon or Ethernet you use (if not selected already)
- Then choose the ‘DNS’ tab in the ‘Advanced’ section and press ‘+.’
- Add the following numbers to the DNS server list: ‘8.8.8.8, 8.8.4.4, 1.1.1.1, 9.9.9.9’ and click ‘OK’
- It will most likely fix the self-assigned IP address problem in your Mac
Contact an Apple support team tech. If the above methods do not fix your Mac’s self-assigned IP address issue.
What does self-assigned IP mean on Mac?
Self-assigned IP is one of the reasons why you are unable to use the internet on your device. It mainly occurs when your network router does not provide your device’s IP address, causing internet connection issues.
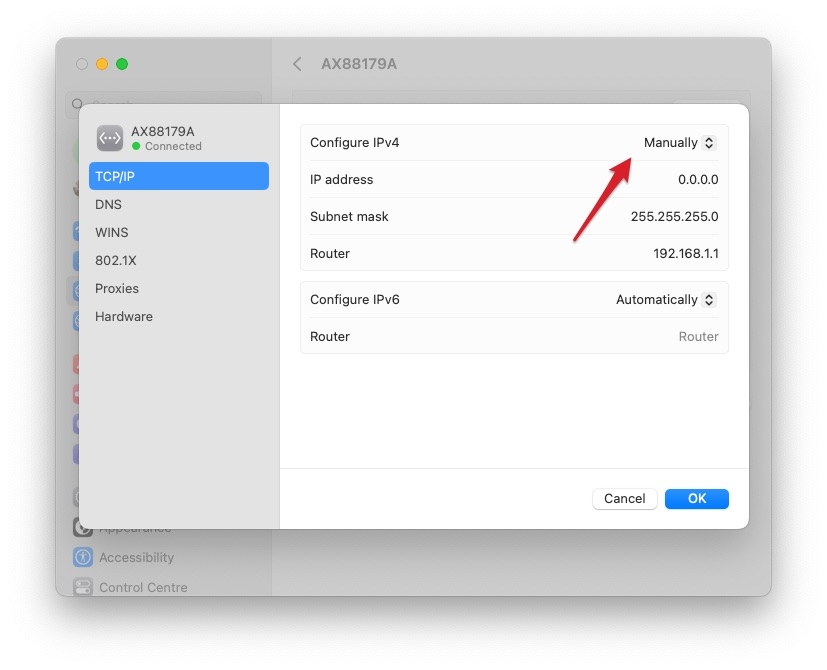
How do I give my Mac a static IP address?
You can give your Mac a static IP by following the steps below:
- Select the Apple logo and click ‘System preferences’
- Click on the ‘Network’ tab and then select the ‘Advanced button’
- ON TCP/IP section, open the configure IPv4 list and select ‘manually’
- Enter your IP settings in the field, and the static IP address will the assigned
Conclusion
By now, you must have learned how to fix self-assigned IP on your computer. Though it is not a huge problem, it does cause a lot of frustration among users. Hopefully, you found the article helpful and learned how to fix network malfunctions on your mac OS.
Share Article:
Marid is a lifelong tech enthusiast and is the lead editor of Macdentro.com. An expert on all things Apple and a lifelong Mac user. Marid has over 10 years of experience using Apple products including the Apple watch, Ipad and etc
How to Set Alarm On Mac? 6 Methods
Restoring trash on mac – a guide for mac trash recovery to recover deleted files, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

How to Fix Self-assigned IP Address Error on Mac

The self-assigned IP address error on a MAC is a common issue when the device cannot obtain an IP address from the router or DHCP server. It can cause Internet connectivity problems and make it difficult to access local network resources.
In this article, you will learn the causes of this error and provide troubleshooting steps to resolve it.
Content Table
What Does it Mean When It Says WiFi Has a Self-Assigned IP Address?
When a device says it has a “ self-assigned IP address ” on a WiFi network, it cannot obtain a valid IP address from the router. It can happen for various reasons, such as a conflict with another device on the network with the same IP address or an issue with the router’s DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) settings.
Without a valid IP address, the device cannot access the internet or communicate with other devices on the network. To fix this issue, try restarting the device and router, checking for firmware updates, or manually changing the IP address.
What Are The Reasons for Self-Assigned IP Address Errors?
Several reasons for a self-assigned IP address error can occur on a MAC . Some of the most common causes include:
- Incorrect network settings: The network settings on the MAC may be configured incorrectly, which can prevent it from obtaining an IP address from the router or DHCP server.
- DHCP server issues: The DHCP server may be down or not working properly, which can prevent the MAC from obtaining an IP address.
- Router issues: The router may malfunction or not be configured properly, which can prevent the MAC from obtaining an IP address.
- Malware or viruses: Malware can infect the MAC and cause it to assign itself an IP address, preventing it from connecting to the internet or local network resources.
Troubleshooting Steps to Fix a Self-Assigned IP Address Error on a Mac
To fix a self-assigned IP address error on a MAC , you can try the following troubleshooting steps:
- Check network connection: Ensure that the MAC is connected to the network and that the network cable is securely plugged in.

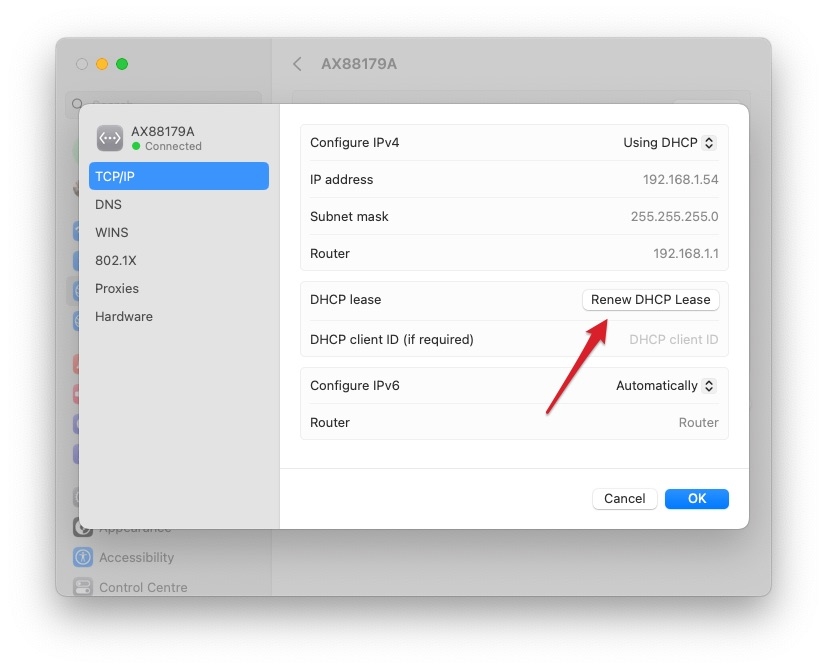
- Renew DHCP lease: Try renewing the DHCP lease on the MAC by going to the “ System Preferences ” > “ Network ” > “Select Network” >” Advanced ” > “ TCP/IP ” tab, then click on the “Renew DHCP Lease” button.
- Reset the router: Try resetting it by unplugging it for 30 seconds, then plugging it back in.

- Check for updates: Make sure the MAC runs the latest software updates.
- Disable VPN: If you are using a VPN, disable it and see if it helps.
- Check for conflicting IP addresses: Make sure that no other devices on the network use the same IP address as the MAC.
- Disable IPv6: Some users have reported disabling IPv6 on the MAC can fix the issue.
Some Bonus Fixes:
If the troubleshooting steps above do not resolve the self-assigned IP address error on your MAC , you may need to try some advanced solutions:
- Check for malware or viruses: Make sure that the MAC is not infected with malware or viruses which can cause this issue.
- Reinstall network adapter driver: Try reinstalling the network adapter driver on the MAC.
- Check for hardware issues: Make sure that the network adapter on the MAC is functioning properly and that there are no hardware issues.
- Reset NVRAM or PRAM: Try resetting the NVRAM or PRAM on the MAC.

- Contact technical support: If none of the above steps resolves the issue, contact technical support for further assistance.
It’s important to note that maintaining a stable network connection is crucial for the smooth operation of any device. A self-assigned IP address error can be a frustrating problem to deal with, but by following the steps outlined in this blog post, you should be able to resolve it quickly and get back to using your MAC as usual.
Additionally, it is always a good practice to keep your MAC updated, regularly check for malware and viruses, and ensure that the network adapter is working properly. It can help prevent self-assigned IP address errors and other network-related issues from occurring in the future.
How do I Fix the 169.254 IP Address on Mac?
If you’re experiencing an IP address of 169.254 on your Mac, your computer cannot obtain an IP address from your router. Various issues, such as a malfunctioning router or a conflict with another device on your network, can cause it.
To fix this, you can restart your router and Mac and check for any conflicting devices on your network. Depending on whether the problem persists, you may need to configure your IP address settings on your Mac manually.
You can do it by going to System Preferences > Network > Advanced > TCP/IP . Consult your router’s manual or contact your internet service provider for specific instructions.
How do I Fix DHCP on Mac?
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, or DHCP, is a crucial network component in most networks. The device assigns IP addresses to devices connected to the network. Without it, devices may be unable to connect to the internet or communicate with other devices on the network. If you are experiencing issues with DHCP on your Mac, there are a few steps you can take to fix the problem.
The first step is to check your network settings. Make sure that your Mac is set to obtain an IP address automatically and that DHCP is enabled. If these settings are incorrect, you may need to enter them manually. If this does not fix the issue, try restarting your router or modem. Sometimes, a simple reboot can resolve DHCP issues.
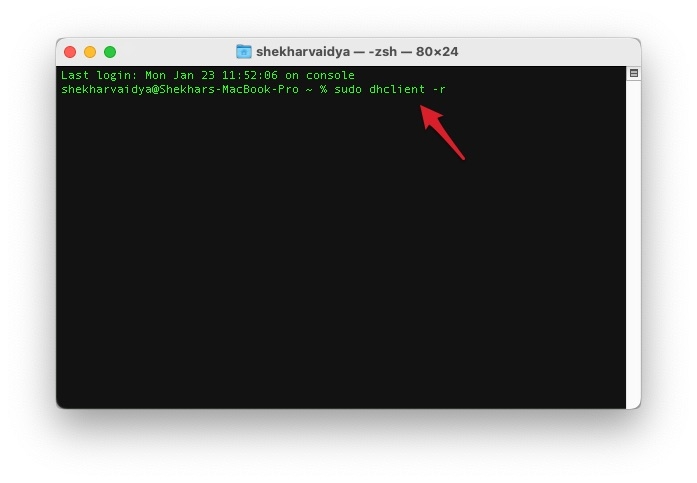
Another solution is to clear your DHCP lease. It will force your Mac to request a new IP address from the DHCP server. To do this, open the Terminal app on your Mac, then type in “ sudo dhclient -r ,” followed by your admin password. It will release the current DHCP lease, and your Mac will request a new one.
If none of the above solutions works, your router may malfunction, or you might have a problem with your modem. Try contacting your internet service provider for assistance or checking for firmware updates for your router.
Various issues, including incorrect network settings, DHCP server issues, and router problems, can cause a self-assigned IP address error on a MAC. To fix this issue, you can try troubleshooting steps such as renewing the DHCP lease, resetting network settings, and resetting the router.
In case these steps fail, you can try advanced solutions such as checking for malware or viruses, reinstalling the network adapter driver, and checking for hardware issues. If the problem persists, you may need to contact technical support.
Read : How to Fix if Mac Keyboard Not Working Properly?

Resolve "Self-Assigned IP" Errors for Apple Mac
Authored by: Support.com Tech Pro Team
1. Introduction: Apple Mac: Resolve Self-Assigned IP Address
One possible result of the inability to get online is that you have what is referred to as a self assigned IP address. This usually happens when your router (which normally provides you an IP address) does not provide you an IP address to talk to other computers.

This guide will help you to troubleshoot self assigned IP addresses.
2. Network: Reboot
One of the main causes with the inability to get on the Internet is that your networking equipment could have malfunctioned. Sometimes performing a reboot will resolve this issue.
Your network may consist of one or more of the following networking devices.
This is the primary device used to get you on the Internet.
- Has either a coaxial cable, fiber cable, or phone cord plugged into it.
- Typically has 1 or 2 Ethernet ports which connect to a router.
This is an all-in-one device that has both a modem and a router built in. It is a primary device used to get you on the Internet.
- Typically has 3 or 4 Ethernet ports which connect to a your computers and smart devices.
- Typically has Wi-Fi built into it
This device allows you to connect multiple devices to your Internet connection using a single external IP address.
- Typically has Wi-Fi built into it.
This device helps to extend the wired functionallity of devices by provuding your additional Ethernet ports.
- These are typically plug and play.
- This device is not a router.
AccessPoint
This device will provide wireless access to your existing network.
- Used to extend the range of your network
- Usually plugged into a router/gateway via Ethernet connection.
RangeExtender
This device will extend the range of your existing Wi-Fi network by rebroadcasting your Wi-Fi network.
- Standalone device plugged into a power source.
- Usually located 15-30 feet from the router.
Next we will want to power cycle the networking devices.
Modem / Gateway
- Unplug the power from the device.
- Wait 30 seconds.
- Plug the power back into the device.
- Wait for the device to go online.
Access Point / Range Extender
3. macos: restart.
- From the menu bar across the top of the screen, select the Apple menu (1), then select Restart... (2).
Any unsaved work will be lost.
4. Network: Determine Connection Type
Next we need to know how your device connects to the Internet.
- Wireless - You connect using a wireless router or access point.
- Wired - You use an Ethernet cable plugged into your gateway/router/switch and the other end is plugged into your device.
5. macOS: Renew DHCP
- Click the Apple Menu and then click on System Preferences .

- Click on Network .
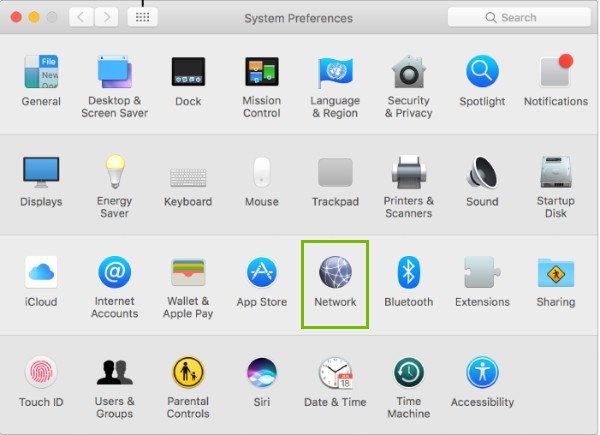
- Click the connection you are having a problem with on the left.

- Make sure Configure IPV4 is Using DHCP .
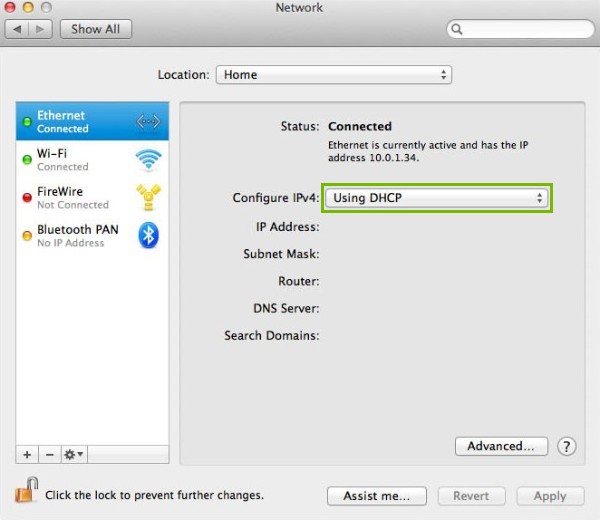
- Click on Advanced .

- Click Renew DHCP lease .

6. macOS: Forget Network
- Click the Wi-Fi icon in the menu bar. By default it will be in the upper right corner near the time and date.

- If Wi-Fi is off, choose Turn Wi-Fi on .
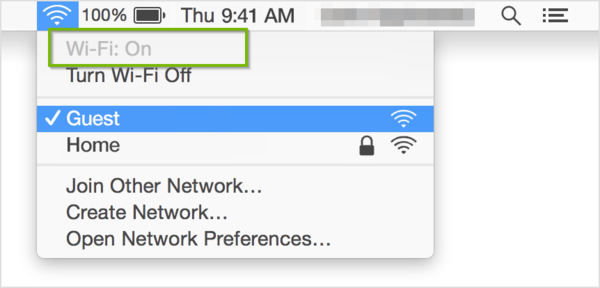
- Select Open Network Preferences .
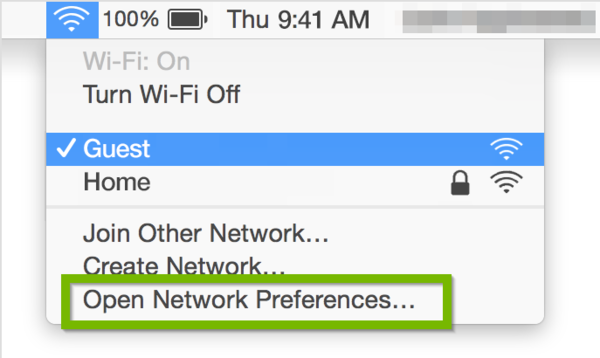
- Select Advanced within the Network window.
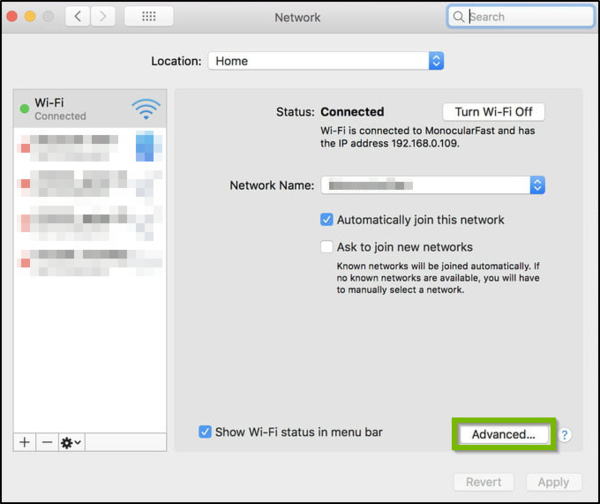
- In the Preferred Networks list, select the network you wish to forget. Tap the minus icon ( - ) to forget the network.

- Your device will no longer join this Wi-Fi network unless you reconnect once again.
7. macOS: Connect to Wi-Fi
- The strength of each nearby network is shown next to its name. More darkened bars indicate a stronger network connection.
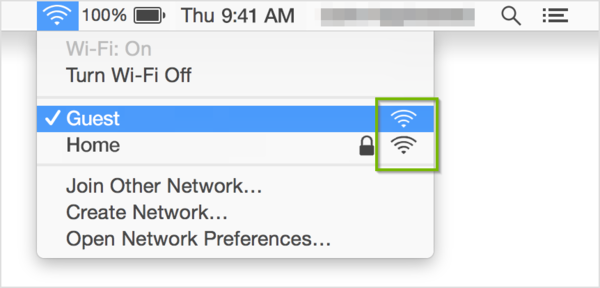
- Select the Wireless Network Name (SSID) of the network you want to connect to.
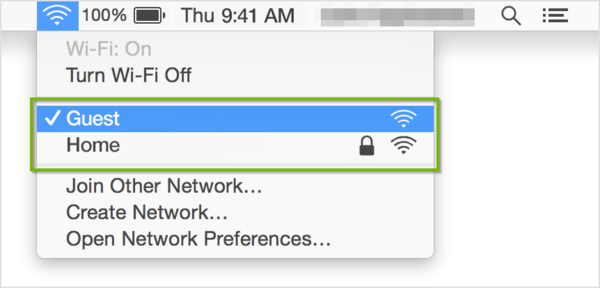
- Networks that have a lock icon next to their name require a password. After you select your network, enter the network password when you're prompted. If you don't know the network password, check with the owner of the Wi-Fi network you're trying to join.
8. macOS: Reset Firewall
- Open the Finder from the dock.

- Click on the Go menu.

- Click on Go To Folder.. .
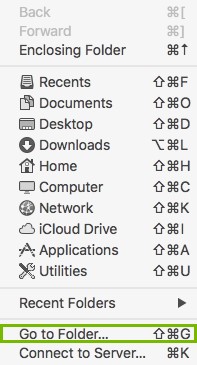
- Type " /Library/Preferences " in the box.
- Click the Go button.
- Find the file named " com.apple.alf.plist " and drag it to the trash .
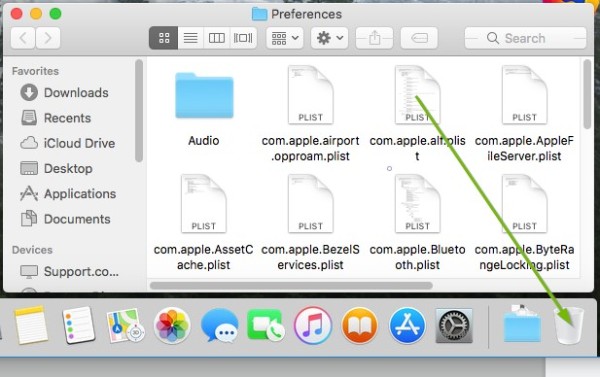
9. macOS: Restart
10. check other devices.
To help troubleshoot the problem we should check if other devices can connect to the wireless network.
11. What's next?
12. what's next, 13. macos: renew dhcp, 14. network: ethernet troubleshooting.
While Ethernet connections are typically the most reliable connection to the Internet, there are still some issues that can arise. Test your connection after each of these steps.
- Plug your Ethernet cable into another port on your Gateway/Router/Switch.
- Try using another Ethernet cable.
- If you are plugged into a switch, try plugging directly into your Gateway or Router.
15. macOS: Reset Firewall
16. macos: restart, 17. check other devices, 18. what's next, 19. what's next, privacy matters.
Support.com is committed to your privacy We do not share or sell your data to third parties. We do use cookies and other third-party technologies to improve our site and services. The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) gives you the ability to opt out of the use of cookies, third-party technologies and/or the future sale of your data. Do not sell my personal information .
Support.com is committed to your privacy Read our Privacy Policy for a clear explanation of how we collect, use, disclose and store your information
Fix self-assigned IP addresses in OS X
One common issue that has affected OS X systems is when network interfaces are issued a self-assigned IP address. Here is how to address this problem.

One common issue that has affected OS X systems is when network interfaces are issued a self-assigned IP address, even though the system is connected to a network with a properly configured DHCP server. When this happens, other systems on the same network (often including similarly configured Macs) will be working just fine, indicating the problem lies with the Mac's configuration and is not a compatibility issue with the networking hardware.
Often when I encounter this issue, I find that people have recently made a relatively major configuration change to their systems, either by updating their OS version, performing an upgrade to another major release of OS X, migrating to a new system, or have just restored their systems from backup. Initial attempts to address the problem include creating new network locations to refresh the network port configurations, or manually refresh the DHCP lease to force a reconfiguration for the port. While these are good attempts, many times they do not fix the problem.
The reason OS X issues self-assigned IP addresses is to allow a network interface to create an ad-hoc network if needed, without the presence of an established network. However, this is only done if the network port detects a proper hardware connection but cannot communicate with the DHCP server to obtain an IP address. Usually the main culprit for this is configuration problems with the system's firewall.
When people perform major configuration changes to their systems, sometimes the settings may not migrate properly. One that seems particularly vulnerable to odd problems is the system firewall. Luckily the fix is a relatively easy one; all you have to do is remove the firewall's preferences and then reboot the system.
To reset the firewall, go to the /Macintosh HD/Library/Preferences/ folder and remove the file called "com.apple.alf.plist," and then restart your computer. After the system boots, you may be prompted to allow incoming connections to numerous programs and services, so accept these for now (you can always go to the Firewall settings and deny or remove entries later on) and then try connecting to the network again. While configuration changes from migrating or restoring a system can lead to this problem, at other times major system crashes or power outages can do the same.
Questions? Comments? Have a fix? Post them below or e-mail us ! Be sure to check us out on Twitter and the CNET Mac forums .
Computing Guides
- Best Laptop
- Best Chromebook
- Best Budget Laptop
- Best Cheap Gaming Laptop
- Best 2-in-1 Laptop
- Best Windows Laptop
- Best Macbook
- Best Gaming Laptop
- Best Macbook Deals
- Best Desktop PC
- Best Gaming PC
- Best Monitor Under 200
- Best Desktop Deals
- Best Monitors
- M2 Mac Mini Review
- Best PC Speakers
- Best Printer
- Best External Hard Drive SSD
- Best USB C Hub Docking Station
- Best Keyboard
- Best Webcams
- Best Laptop Backpack
- Best Camera to Buy
- Best Vlogging Camera
- Best Tripod
- Best Waterproof Camera
- Best Action Camera
- Best Camera Bag and Backpack
- Best E-Ink Tablets
- Best iPad Deals
- Best E-Reader
- Best Tablet
- Best Android Tablet
- Best 3D Printer
- Best Budget 3D Printer
- Best 3D Printing Filament
- Best 3D Printer Deals
- Dell Coupon Codes
- Newegg Promo Codes
- HP Coupon Codes
- Microsoft Coupons
- Anker Coupons
- Logitech Promo Codes
- Western Digital Coupons
- Monoprice Promo Codes
- A4C Coupons
Newsletters
- Our sponsors
- Watch Store
- Hot topics:
- Apple legal battles
- Apple deals
- Editor’s picks
- Buying guides
How To Fix Self-Assigned IP Addresses In Mac OS X [Video How-To]
By Michael Steeber • 6:06 am, March 5, 2011
![How To Fix Self-Assigned IP Addresses In Mac OS X [Video How-To] DHCP](https://www.cultofmac.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/03/DHCP.png)
Not being able to get online can be a frustrating problem. It can cost hours of time and test your patience. See, Mac OS X doesn’t always work properly all of the time, and will occasionally assign itself an IP address, which will result in you being unable to connect to the internet. Luckily, there is an easy solution. You can use System Preferences to set a new Network Location, as well as renew your DHCP lease to fix the problem. This video will show you how to quickly fix the problem of self assigned IP addresses through System Preferences.
Daily round-ups or a weekly refresher, straight from Cult of Mac to your inbox.

Cult of Mac Today
Our daily roundup of Apple news, reviews and how-tos. Plus the best Apple tweets, fun polls and inspiring Steve Jobs bons mots. Our readers say: "Love what you do" -- Christi Cardenas. "Absolutely love the content!" -- Harshita Arora. "Genuinely one of the highlights of my inbox" -- Lee Barnett.

The Weekender
The week's best Apple news, reviews and how-tos from Cult of Mac, every Saturday morning. Our readers say: "Thank you guys for always posting cool stuff" -- Vaughn Nevins. "Very informative" -- Kenly Xavier.
Popular This Week
How to take solar eclipse photos with iphone, these are the best games on apple arcade, iwork 14 brings useful tweaks to pages, numbers and keynote, here’s the new batch of classic movies on apple tv+ in april, share passwords with your family on iphone, bodycam, dashcam, security camera: this tiny gadget can do it all [deals], big logitech sale: up to half off keyboards, mice, webcams and more [deals], ‘best of tech’ sale pushes surprising apple items [deals], ios 17.5 beta 1: all the new features and changes, apple opens the iphone app store to retro game emulators.
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Determining the self-assigned IP address of a directly-connected counterpart
I have connected two computers, A and B, NIC-to-NIC using an ethernet cable. They have self-assigned their IP addresses—at least, I can see that A has done so, so I infer that B must have also done so. Computer A is a laptop running Windows 10, but I have no keyboard and mouse available for B. From A, how can I determine B's IP address?
On A, this is what I see:
What I've tried (based on https://serverfault.com/a/30742 ):
...which just says "Host is up" and doesn't report anybody else being on the network. I don't claim to understand what nmap is doing (for example, I have no idea what's special about the number 24) but I do know that the same command with 192.168.1.0/24 successfully finds devices on the wireless network to which A is also attached.
for example, I have no idea what's special about the number 24
It's a short way of writing the "255.255.255.0" netmask. (Also called "CIDR syntax" from its origins, or "prefix length" because it indicates that the network is specified by the first 24 bits. If you convert 255.255.255.0 from decimal to binary, you'll see it begins with exactly 24 'one' bits.)
However, your actual netmask is not 255.255.255.0 – it's 255.255.0.0, as shown in the ifconfig output. That's a /16. The whole "self-assigned" range is in fact 169.254.0.0/16.
Hosts will send out a few ARP probes as part of the self-assignment process (to ensure that the address isn't already in use). If you connect the computers while Wireshark or tcpdump is already running a capture on the Ethernet interface, you should see both of them revealing their addresses this way.
- Relative to everything else I had so far stumbled across, this is a stunningly intelligible explanation of the /24 - thanks. So I conclude that nmap -sn 169.254.0.0/16 would be the way to go. I actually managed the equivalent of that in the end by adapting one of the nmap --help examples to nmap -sn 169.254.0-255.0-255 and found the IP by letting it run for 45 minutes. In future I'll bear in mind the tcpdump tip. I presume there's no way of unilaterally configuring A to say "hey, let's self assign, but with a 24-bit prefix"? That would make it a lot quicker to find... – jez Apr 1, 2021 at 15:39
- No, this autoconf mechanism (APIPA) is defined to always use this specific /16 prefix. However, the idea was that it would be accompanied by other Zeroconf services such as mDNS for dynamic discovery. (For example, Windows has mDNS and a few similar alternatives, so as long as both computers run Windows and have the network mode set to “private” you should be able to reach the other computer by its name without needing the exact address. Same goes for macOS and (to some extent) Linux.) – u1686_grawity Apr 1, 2021 at 16:18
- But to answer the question, if you specifically wanted to change the prefix, you would have to run DHCP in order to do that instead of relying on autoconf. (And once you have DHCP you no longer need nmap nor tcpdump, as you can just look in the DHCP server’s “lease” table to find the address...) – u1686_grawity Apr 1, 2021 at 16:22
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged windows networking ..
- The Overflow Blog
- Want to be a great software engineer? Don’t be a jerk.
- Climbing the GenAI decision tree sponsored post
- Featured on Meta
- New Focus Styles & Updated Styling for Button Groups
- Upcoming initiatives on Stack Overflow and across the Stack Exchange network
- Google Cloud will be Sponsoring Super User SE
Hot Network Questions
- Am I in my rights to ask a colleague to not take notes on everything I say outside a meeting?
- Split String Function Implementation in Python
- Where is the large cook promotion?
- I need a word for the atmosphere between two people
- Colorbar to illustrate the change of a specific parameter
- Re-selecting best sales forecasting model each month. Is this overfitting?
- Determining the CR of a monster with a 50% chance of absorbing damage
- How can I get unicode-math to print ⩽ when I type ≤?
- python cprofile decorator
- Are the subjective experience of the "inner witness of the Holy Spirit" and the subjective experience of an external world of equal epistemic value?
- Fixed Repeating Output
- What are examples of "Official Observations" in a passport?
- NSF grant proposal not reviewed despite being received
- When teaching Computer Architecture, why are universities using obscure or even made-up CPUs? Why not x86, ARM or RISC-V?
- Do Trump's lawyers have a fiduciary duty to delay the proceedings?
- Can you use existing in home coax cables to connect a Leaf antenna to TV?
- Paint color consistency
- What is the correct formulation of Newton's Second Law of Motion?
- Can You Train A Neural Network By Simply Giving It Ratings Each Time It Runs?
- What do I do if my players are acting in a way that is meta-gaming and are refusing to accept my decision?
- I have begun to write a science fiction story, is this description of a super soldier a viable, and grounded, creation?
- Why did Nicaragua file a case against only Germany at the ICJ?
- Op-amp (LM348N) becomes very hot when connected to power
- How to equally split college fund between 2 children going to college 5 years apart?

- OPNsense Forum »
- English Forums »
- General Discussion »
- Getting self-assigned IP on VLAN
Author Topic: Getting self-assigned IP on VLAN (Read 61 times)
Blackholesun.
- Full Member
Re: Getting self-assigned IP on VLAN
- SMF 2.0.19 | SMF © 2021 , Simple Machines Privacy Policy | XHTML | RSS | WAP2

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Enter your Mac password to authenticate the deletion.; Restart your Mac. It will automatically recreate the deleted files. Log in and connect to your Wi-Fi network.; Go to the TCP/IP setting again and check the router files. 7. Create a new network location. Creating a new network location lets your Mac start fresh with network settings and eliminate a self-assigned IP address.
MacOs Sonoma Ethernet "Self-Assigned IP" problem. HELP. The ethernet circle is at yellow and not connected. Tried: Updating the DHCP lease. Turning off the Mac's firewall and my computer's firewall. Changing the network connection option to bridged and NAT. VMware Workstation 17.5.0 build-22583795.
It reports as "Self Assigned IP" with yellow in Network preferences. This presents as the computer having no internet and showing an assigned IP outside of the range of the DHCP server. I've tried: reboot all devices including router and switch. manual IP address. assigning random number value in "DHCP Client ID" in the TCP/IP ...
Go to "System settings" and tap on "Network.". Select the network connected to the self-assigned IP address. Go to the "TCP/IP" tab and ensure that "Configure IPv4" is set to "Using DHCP" and "Configure IPv6" is set to "Automatically.". Click on the "DNS" tab and delete the DNS servers listed there by tapping the ...
Video showing how to fix issue - Self-Assigned IP address MacDetailed instructions - https://blog.pcrisk.com/mac/13307-fix-self-assigned-ip-address-issue-on-mac
Here is a list of what I have tried: Using a different patch cable from my switch to the female Ethernet cable leading to the room with the iMac. Unplugging the Ethernet cable from the back of the iMac, from the patch panel, from the switch, from the router. Turning the switch on and off. Rebooting my router. Power cycling the router.
Click on the Library folder and go to Preferences. 3. Now click on the SystemConfiguration folder. 4. Next put the following files in trash. 5. Restart your Mac. Once the reboot has taken place the Internet will start working and self assigned IP address issue will be resolved.
A self-assigned IP address is essentially a private IP address within three number ranges reserved for the computers or devices in local networks. These private addresses are assigned to the computers in the network by the DHCP server and aren't visible on the internet.
Now select the Self-Assigned IP network and then click the minus (-) button to delete it. Then click Apply. Does this newly created service connect? Reset the system firewall: We can do that by deleting its preference file. Open a Finder window and then click Go and Go to Folder from the top menu bar. Enter /Library/Preferences/ and click Go.
The very simple fix goes as follows: On your phone, go to bluetooth settings and connect your Hackintosh. On your hackintosh, go to network settings. Wait about a minute, and Bluetooth PAN should return a yellow dot stating "Self Assigned IP-Adress". Now you can simply try to connect to your hotspot and everything should work flawelessly.
One way to fix self-assigned IP is to set up new network locations on your Mac. Follow the steps below to make a new network location: Tap on the Apple logo from the menu bar and select 'System preferences'. Enter the 'Network settings' then tap on 'Drop-down menu' near the Location tab. Then tap on 'Edit locations' and tap on ...
When a device says it has a "self-assigned IP address" on a WiFi network, it cannot obtain a valid IP address from the router.It can happen for various reasons, such as a conflict with another device on the network with the same IP address or an issue with the router's DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) settings.
This guide will help you to troubleshoot self assigned IP addresses. 2. Network: Reboot. One of the main causes with the inability to get on the Internet is that your networking equipment could have malfunctioned. Sometimes performing a reboot will resolve this issue. Your network may consist of one or more of the following networking devices ...
3. A self assigned IP address suggests that your system did not receive an IP address from a DHCP or similar protocol. As Otto Andy Heiskanen mentions, restarting the DHCP server (by rebooting the router) can solve this issue often. However you mention your Linux environment does get an IP address, which could point at a different cause.
Leave just the switch plugged in to the Belkin. Now, reboot the Belkin. Once it is online, plug in the Mac to the switch. See if you get a valid IP address. Now, one by one power on/re-connect other devices. If all these devices were 'ON' when you were adding this switch there could be a conflict of IP addresses. - Appleoddity.
I sometimes have problems dropping IP addresses after changing networks and get stuck with a self-assigned IP that I cannot drop by hitting the renew "DHCP Lease" button on my Mac OS X.5 Leopard. The only work around is to manually give myself a "good" IP, shut down my computer, then boot up and switch back to regular DHCP.
If you know the IP of the Airport base station, you could try setting up your IP address manually (with Router and DNS set to base station address). Just add 10 to the last IP address number to create your IP address, and you should be safe. If that works, it is obviously a problem with DHCP. Try IntelMausiEthernet.
Getting a self assigned IP address means you didn't get a DHCP offer (and accept it). Manually assigning a known good IP and still not being able to browse means your computer is blocked from accessing the network. This could be due to many factors: The port is disabled on a switch. This is done to eliminate the possibility of a rogue actor ...
Getting a self assigned IP address in Mac OS X 10.10 (Yosemite) on a Mac Mini. Ask Question Asked 7 years, 6 months ago. Modified 7 years, 6 months ago. Viewed 4k times 1 I have had a situation where I cannot access the internet and the network preferences list ethernet interface connected to DSL modem has self assigned IP address and cannot ...
The reason OS X issues self-assigned IP addresses is to allow a network interface to create an ad-hoc network if needed, without the presence of an established network. However, this is only done ...
Luckily, there is an easy solution. You can use System Preferences to set a new Network Location, as well as renew your DHCP lease to fix the problem. This video will show you how to quickly fix ...
That's a /16. The whole "self-assigned" range is in fact 169.254../16. Hosts will send out a few ARP probes as part of the self-assignment process (to ensure that the address isn't already in use). If you connect the computers while Wireshark or tcpdump is already running a capture on the Ethernet interface, you should see both of them ...
Locate the below (search "virtualDev" or "e1000e") in your VM's VMX file (option+right click on your VM, select "Open config file in editor". Replace "e1000e" with "vmxnet3". Once that's done, restart the VM. If this doesn't work, rebuild your VM with this option set from the start.
OPNSense Router -> MikroTik Switch -> Netgear PoE Switch -> Unifi APs. I have a Guest VLAN configured with tag 20. An interface has been assigned, and DHCPv4 has been enabled to assign IP addresses between 192.168.20.10 and 192.168.20.245. The APs have also been configured to tag 20 on a Guest SSID.