Don't bother with copy and paste.
Get this complete sample business plan as a free text document.

Government Services Business Plan
Start your own government services business plan
ASTI - Advanced Science and Technology Institute
Executive summary executive summary is a brief introduction to your business plan. it describes your business, the problem that it solves, your target market, and financial highlights.">.
The Advanced Science and Technology Institute (ASTI) supports research faculty and staff at **State University, University of AnyState, AnyState Health Sciences University and AnyCity State University in its management of new discoveries. This support includes the management of new discoveries having commercial applications, as well as the management of corporate research agreements leading to new discovery.
**(Editor’s Note: Names disguised for confidentiality.)
1.1 Keys to Success
- Building a strong support base with the private sector within State and the Northwest.
- Creating an effective network between researchers to facilitate cross-disciplinary contact.
- Raising the viability of ASTI as the one-stop resource for all transferable technology that is being developed on the campuses of State’s four largest universities.
1.2 Mission
The mission of the ASTI is to bring technologies from **State University, University of AnyState, AnyState Health Sciences University and AnyCity State University into public use; thereby providing economic development assistance to state and federal agencies and companies to benefit State constituents, providing service to the technology transfer staff of each institution by assisting in identifying, protecting, developing and transferring technology to the private sector and generating income. ASTI’s unique perspective is in its ability to link researchers from various institutions to create new technologies that can then be marketed to the private sector.
Historically, State has received less attention from companies that develop long-term relationships with the university research community. With SouthernState universities to the south and the University of AnyState to the north, State has had a difficult time reaching the level of viability necessary to draw the interest of companies outside the state.
It is a problem of economy of scale. Currently, State University, University of AnyState, AnyState Health Sciences University and AnyCity State University have 128 technologies available for licensing. One university in SouthernState, The University of Southern State (USS), has over 200 technologies available for licensing. In addition, USS has received $20 million in corporate research funding last year. This far exceeds the total for all corporate research funding for the four State schools ($3 million) during the same period. In State, the State Technology Center has secured $91 million in private funding for technology transfer from the University of State. It is critical that the four major universities in State pool its resources in order to be competitive in drawing corporate attention to the excellent researchers working within their institutions.
It is ASTI’s mission to create a resource for the private sector that rivals USC by providing an aggressive one-stop center for all the pivotal research that is occuring in State.
1.3 Objectives
- Establish a 42-member corporate research support council and increase corporate membership in ASTI’s Technology Development Council by 20% each year.
- Facilitate two new industry sponsored research agreements the first year and increase the number of agreements each year.
- Create new research linkages between the four campuses and develop new collaborative relationships between researchers.
- Develop a cross-disciplinary research database that will link researchers throughout the state.
Organization Summary organization overview ) is an overview of the most important points about your company—your history, management team, location, mission statement and legal structure.">
ASTI is a focused program that offers a powerful resource to researchers who are seeking corporate support for research and corporations seeking new technologies. The program also seeks linkages between the four campus researchers in developing new partnerships that will generate additional corporate interest.
2.1 Legal Entity
State University, University of AnyState, AnyState Health Sciences University, and AnyCity State University are all share holders in ASTI.
2.2 Start-up Summary
Start-up costs and initial financing are shown on the following table. Each institution will contribute $40,000 to ASTI’s operating budget.

2.3 Program Location
ASTI will be located in AnyCity, AnyState. This is a good central location for a state-wide program. AnyCity State University is located in AnyCity. AnyState Health Sciences University and State University are located in NewTown 60 miles to the north. The University of State is located in OldTown which is 40 miles south of AnyCity.
ASTI’s services include:
New Technology Assist in identifying new invention disclosures for new discoveries and evaluation of these new discoveries to determine commercial potential. A research database will be created and maintained by ASTI in order to respond quickly to requests for information from the private sector, especially when it links researchers on multiple campuses. Companies will have a quick and accessible resource that will identify researchers that match their interest areas. ASTI will also assist in the establishment of new businesses to develop emerging technologies.
Research Collaborations ASTI will actively seek cross-disciplinary collaboration opportunities between researchers on the four member campuses.
Technology Conferences ASTI will sponsor two conferences in Portland each year focusing on the areas of Biotechnology, Material Science, Computer Science, and Medical Technology.
Newsletter and Promotional Publications ASTI will produce a monthly newsletter and quarterly promotional publications directed toward the private sector which will focus on current research on the four campuses and researcher profiles. This material will also highlight researchers seeking corporate support.
Market Analysis Summary how to do a market analysis for your business plan.">
The research enterprise at State University, University of AnyState, AnyState Health Sciences University and AnyCity State University is remarkably broad, deep and diverse, spanning activities in twenty-two academic colleges and more than 40 multidisciplinary programs, centers, programs, and institutes.
ASTI will first focus on creating the information base necessary to satisfy high-technology corporations that are currently prospecting for new technologies. These are mostly larger companies, but also include medium- to small-sized companies.
Our most important group of potential customers are the researchers in these companies. They do not want to waste their time or resources looking for a needle in a haystack. It is critical that they find ASTI an excellent tool in quickly identifying technologies and researchers that will lead to profitable products.
ASTI will provide a two-tier service that will correspond to a company’s membership in ASTI’s Technology Development Council. There will be both a full and associate membership option in the Technology Development Council. We anticipate that larger companies will select the full membership option because it will offer additional research services. An associate membership is tailored for the medium- to small-sized companies whose contacts will be less frequent.
4.1 Market Segmentation
Larger Companies: It is critical to create major stakeholders in the development of a better delivery system for technology transfer. Currently, there are several large companies that have an ongoing relationship with researchers on the four major campuses. Recruiting these companies as full members of the Technology Development Council is an important first step in improving corporate interest in high-tech members in State. These companies will be responsive to ASTI’s ability to ferret out the research and researchers that they are interested in reviewing. ASTI will also facilitate any cross-disciplinary linkages that will lead to the pursuit of research that these companies are interested in. Involvement in the growth of ASTI will attract companies of simular size and stature.
Medium to Small Companies: These companies are critical to the growth of ASTI because they represent the state’s developing high-tech industries. Their focus in not only on a specific technology that is being developed at one of the member campuses but also on the graduate students that are working on the research. As associate members of the Technology Development Council, these companies will gain greater access to all the research opportunities that will meet their technology and staff needs.
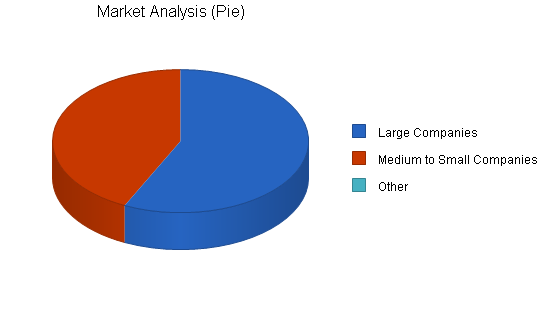
4.2 Target Market Segment Strategy
As indicated by the previous table, we must first focus on all companies that have current relationships with researchers on the member campuses.
4.3 Service Providers Analysis
The private sector’s access to researchers at the member campuses range from excellent in selected disciplines, to completely chaotic and frustrating in most others areas.
ASTI’s goal is to assure access to all critical research through a streamlined process that leaves the company both satisfied with the results as well as the time invested in the search.
Strategy and Implementation Summary
The initial funding from the four member institutions will provide the foundation for launching ASTI. Its survival will depend on the program’s ability to grow a membership base to its Technology Development Council. The program will not survive if it is unable to meet its goal of increasing membership in the Council by 20% each year.
ASTI’s information products and services will add real value to the companies search for emerging technology. As stated before, our most important group of potential customers are the researchers in these companies. Their input into the kind of services they want will be critical to the evolution of ASTI. Our focus will be to add value in everything connected with ASTI.
5.1 Competitive Edge
ASTI’s competitive advantage is their comprehensive approach to providing unequalled access to researchers. ASTI’s focus is to support the companies in their successful pursuit of emerging technologies. The most critical component is the responsiveness of the program to company inquiries into selected research areas.
The best scenario is the company responding to research highlights provided by ASTI before initial inquires are made. ASTI will strive to open doors for companies so that long-term relationships will develop and companies will become members of the Technology Development Council.
The approach is decidedly sales-oriented in focus. This is a critical advantage when in competition with universities in SouthernState and NorthernState. Companies will find State research viable and easy to access.
Yet the key to ASTI’s success will be in how the program evolves in response to companies demands. ASTI’s Technology Development Council was a vehicle for that evolution. The Council will provide companies with the access to fine-tune services to improve the program’s ability to meet industry demands.
5.2 Marketing Strategy
ASTI’s marketing strategy will be to build the Technology Development Council as a base of support for technology transfer. The plan is to use existing members of the Council as lead contact for other companies. The best description of the strategy is the ever-widening ripples when a stone is thrown in a pond. The first step is to capture all the companies the are currently quite aware of the excellent researchers at the four member institutions. From that base, begin to recruit new companies that current members will invite into the Council.
Though it is possible that fresh contacts to ASTI, from inquiries about technology highlighted in promotional material, can lead to companies joining the Council, it will be the membership of the Council that will drive the success of the program.
5.3 Fundraising Strategy
The fund raising strategy will be the payment of annual membership fees in the Technology Development Council. A full membership will be $3,000 a year. An associate membership will be $1,000.
5.3.1 Funding Forecast
During the first year, ASTI will recruit 20 full members and 21 associate members to the Technology Development Council.

5.4 Milestones
ASTI’s milestones are as follows:
- Within the first six months of operation to assemble the Technology Development Council membership.
- Publish the first ASTI monthly newsletter in December.
- Stage high tech conferences in AnyCity during the month of March and September in 2002.
- Achieve two new industry sponsored research agreements with researchers at the member institutions during the first year of operation.
Management Summary management summary will include information about who's on your team and why they're the right people for the job, as well as your future hiring plans.">
ASTI’s director is John Doe. He is excited about the state’s vision of establishing a technology transfer consortium involving the state’s strongest corporate citizens. “These are ideas that many people have shared and promoted,” Doe said. “I’m hoping to work with units around the state to implement these and other ideas related to research agreements with industry.” Doe understands the need for State to strengthen connections with the private sector.
He joins ASTI from Pacific Northwest National Laboratory in MoneyCity, State, where he worked as technology transfer manager in the Environmental Technology Division. He has a Ph.D. in low-temperature geochemistry from The Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, Md., and a post-doctoral fellow from Yale University.
He believes the technology transfer consortium is a natural mechanism to allow large and small enterprises to make use of the expertise at the member institutions and allow faculty to participate in entrepreneurial pursuits. “I will promote ideas such as an entrepreneurial sabbatical for faculty where they could pursue business start-ups and the universities will receive some benefit in return,” Doe said. “I’m excited about the opportunities and look forward to working with the Technology Development Council and promoting the critical research efforts occuring at the institutions that ASTI represents.”
6.1 Personnel Plan
ASTI’s director position is full-time. In addition, ASTI will also have three full-time employees; a research associate that will be responsible for research data collection, a communication associate who will be responsible for the program’s publications, and a full-time administrative assistant.
Financial Plan investor-ready personnel plan .">
The following sections will outline important financial information.
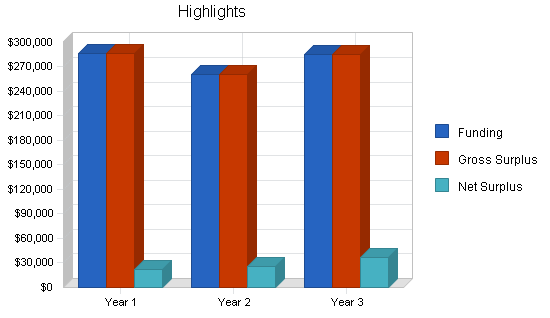
7.1 Break-even Analysis
The following table shows what our break-even point will be to cover our montuhly costs.

7.2 Projected Surplus or Deficit
The following table will indicate projected surplus and deficit.

7.3 Projected Cash Flow
The following table and chart illustrate the projected cash flow.

7.4 Standard Ratios
The following table compares our standard ratios with the Standard Industry Code #8748, Other Management Consulting Services.
Tax Season Savings
Get 40% off LivePlan
The #1 rated business plan software
Discover the world’s #1 plan building software


Build plans, manage results, & achieve more
Learn about the AchieveIt Difference vs other similar tools
We're more than just a software, we're a true partner
- Strategic Planning
- Business Transformation
- Enterprise PMO
- Project + Program Management
- Operational Planning + Execution
- Integrated Plan Management
- Federal Government
- State + Local Government
- Banks + Credit Unions
- Manufacturing
Best practices on strategy, planning, & execution
Real-world examples of organizations that have trusted AchieveIt
Ready-to-use templates to take planning to the next level
Research-driven guides to help your strategy excel
Pre-recorded & upcoming webinars on everything strategy & planning
- *NEW!* Podcast 🎙️
How to Create a Strategic Plan for Your Government Department or Agency

RELATED TAGS:
blog , government , Strategic Planning
Budgets and deadlines are two of the most crucial elements when it comes to getting things done in a local government. To be as efficient as possible, you’ll need a robust strategic plan for your government department that outlines how you’ll spend your provincial budget and how you and your subcontractors will achieve public project deadlines. Building a long-term and multiyear strategic plan with goals and objectives can be challenging. We also understand how complicated it is to transform your ideas into tangible results for your community, and we’re here to help.
In This Article
Why Government Departments and Agencies Need Strategic Plans
Why current government strategic processes and tools fall short, conduct internal and external analysis, consider the vision and mission , perform a holistic risk-assessment , list the focus areas , develop strategic objectives, set up an actionable game plan , utilize measurable kpis , put the plan into action , evaluate the results , transform government strategic planning and execution with achieveit, ready to accelerate your planning and execution efforts let’s actually do this..
Why should the state and municipal governments consider strategic planning? Isn’t having a yearly budget sufficient? After all, things may change when heavy rains overflow the city sewers or roadway repairs exceed the budget. What difference does additional planning make? What exactly is department strategic planning?
A department strategic plan is a comprehensive and systematic management tool that assists governmental departments, agencies and organizations in assessing their current environment, anticipating changes and responding appropriately to issues. Strategic planning involves envisioning the future, improving effectiveness, developing commitment to the department’s mission and reaching a consensus on strategies and objectives for achieving that mission. It involves influencing the future rather than merely preparing for or responding to it.
While combining community vision with available resources is critical, the resources should not stifle the vision. The objectives of a departmental strategic plan will involve identifying how the resources available may be linked to future ambitions. A long-term financial plan, created with the department strategy plan, is crucial to the departmental strategic planning process. A government should have an established financial planning mechanism that evaluates the long-term economic consequences of current and planned policies and programs. A financial plan depicts the expected financial repercussions of certain activities.
Regarding strategic planning in government positions, the notion is that leaders must be good strategists if their departments and agencies are to achieve their goals, accomplish their mandates and, most importantly, satisfy their communities in the coming years. The strategic planning department must lay out effective strategies to deal with changing conditions and governmental leaders must create a cohesive and defensible framework for their judgments. Ultimately, a department strategy provides a big-picture document that directs resources and activities toward a well-defined vision.
A state department strategic plan is a long-term commitment to various governmental objectives. Selecting the correct solutions to support the department’s strategic plan is critical to attaining them. The strategic planning department requires integrated and holistic systems and tools to increase productivity and improve the overall management of the various objectives while keeping operations running smoothly. An adequate system also keeps communication channels open between different departments.
Many procedures and systems on the market can help manage a department’s strategic plan but mainly focuses on short-term success. Business intelligence, project management, strategy development tools and other mainstream options focus on something other than integrated plans that span departments and locations. Each focuses on a specific function of planning, developing, executing or reporting strategies, so finding a single system that keeps everything in one secure place is challenging.

Taking an analytical look into these traditional options, we can see some pros to utilizing them. Still, some cons can lead to your government’s strategic processes falling short:
- Business intelligence tools: Although business intelligence tools provide visual dashboards, reports and a data-driven understanding of how the government is performing, they miss the “why” behind the strategic plan — the vision and future forecasts.
- Project management tools: These tools are excellent for providing detailed project statuses but lack the big-picture view and are typically challenging to use and connect with other projects.
- Strategy management tools: Strategy development tools can most certainly help organize plans and foster project alignment. However, these tools are less proficient at enabling the effective execution of these plans. They have limited flexibility and make it difficult to manage multiple plans across the agency.
- Mainstream tools: You might recognize mainstream and user-friendly tools like PowerPoint and Excel. Despite being customizable, these tools lack format and version control.
Strategic planning in government can be challenging. You must include stakeholder input, ensure that your department’s strategy is consistent across all municipal agencies, connect capital projects to multiple plans and ensure that everyone engaged is on board with the strategy. The good news is that it’s possible and the approach may be more straightforward than you think.
Follow these tips for creating your government agency’s strategic plan:

Conduct an environmental scan, where the local government can investigate and assess the current and developing factors within their own area’s internal and external environments. The internal and external analysis provides detailed information on the government’s existing conditions, including prospective opportunities, strengths, threats and weaknesses to control or prevent.
An internal analysis looks at the government’s internal environment to analyze its abilities, resources and competitive advantages. An internal analysis helps you identify strengths and weaknesses and the opportunities and threats that government departments or agencies face. This information assists government officials in making strategic decisions as they carry out the strategy development and implementation process. In a nutshell, the following topics should be included in your internal analysis:
- SWOT Analysis: Conducting a SWOT analysis can help you comprehensively understand your area’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats.
- Strategy analysis: This analysis assists you in evaluating how well you performed against your current department strategy plan, what you can improve on and where you can focus your efforts.
- Internal stakeholder analysis: This analysis enables you to gain insight into the issues and perspectives of your area’s internal stakeholders and their influence.
- VRIO Analysis: A VRIO analysis can assist you in identifying any competitive advantages you may have and how to convert them into long-term competitive advantages.
An external analysis investigates and evaluates the government’s external environment to understand possibilities and risks in its area. Forces outside a local government’s immediate control affect them, and they need to be able to plan accordingly. For example, changes in legislation and policies, demographic shifts or climate concerns can influence a government’s decisions. An external analysis should usually consider the following:
- PESTEL analysis: Conducting a PESTEL analysis can help you discover the many scopes that may influence an area.
- External stakeholder analysis: This analysis enables you to gain insight into the issues and perspectives of your local government’s external stakeholders and their influence.
The government’s vision statement defines where they want to go — it’s the anchor that keeps them from being stranded at sea. A clear vision statement will aid in directing the strategic plan toward the best results for the community. Everything written into the plan will eventually help the government department or agency get closer to its vision. Additionally, your local government should base its department’s strategic plan on its mission statement. Consider asking the following questions to articulate the critical components of the strategy:
- What are the top concerns that your government must address?
- Which forthcoming public projects are most important to your constituents?
Every government has risks that require attention through policy and infrastructure developments. A comprehensive assessment of the different risks to your community may include the following:
- National issues: At the federal level, social and economic concerns arise and citizens on both sides may be dissatisfied with their government’s shortcomings. Considering which issues are most essential at the national level can enable your community to make localized efforts to address them.
- Constituent dissatisfaction: Angry constituents equals a poor reelection campaign. To avoid unfavorable government-constituent relations, your local government should examine which topics are most beneficial to your community and analyze these concerns.
- Economic hardship: Local governments must examine the impact of inflation on local companies, citizens and budgets.
- Natural disasters: Which natural disasters are the greatest threat to your area? What steps have been taken or are being made to address these events, reduce risks and communicate with the public?
- Cybercrime: Cybercriminals have been creating data breaches in municipal governments for years, and attacks are increasing daily. Have your local government invested in cyber-safe technologies and backed up its data?
- International challenges: Do you need help attracting new government employees due to intergovernmental challenges? Do your internal procedures need to be more effective and costly? Do you have an up-to-date information technology strategy? One of the leading reasons for inefficient bureaucracy is a failure to recognize and handle such difficulties.
- Public policies: Which national and state legislation are the most important for your municipality to handle in the near future in terms of public policy? What consequences will you face if you do not address these policies?
After reviewing all the significant risks, it’s time to prioritize the most critical ones and develop a strategy to manage them. List the top focus areas that are crucial to your citizens or represent significant risks to your community’s health, safety, quality and economy. Your focus areas should also align with the local government’s and community’s future aspirations. Although it would be ideal to address all areas immediately, it could be more realistic. Try to prioritize a few critical issues.
Strategic objectives indicate what your city genuinely wants to achieve — they’re quite high-priority and should have a date attached. Your strategic goals should align with one or more of your focus areas and provide some tangibility to how you envision attaining your focus areas. Similar to selecting a few focus areas at a time, you can develop a few realistic and achievable strategic objectives. An example of a strategic objective can be to “improve the community’s safety by implementing a new reporting system by June 30, 2023.”
Now that you’ve decided on the primary focus areas and objectives, it’s time to consider how to execute them. A game plan defines what the government will need to do to achieve its goals. An actionable game plan assists in breaking down the bigger picture into smaller, more attainable results and activities. At this phase in your strategic planning process, you will begin to define the steps you will take to attain specific goals and the talents, expertise and resources required.

KPIs track progress toward your strategic goals. KPIs are quantitative metrics that demonstrate your government’s progress toward essential strategic objectives. KPIs tell you whether or not you have met your strategic target. Once KPIs have been determined, describe who is responsible for what and give them a job using your local government management tool to keep everyone organized and accountable.
Following your department’s strategy’s completion and policymakers’ approval of budgets and deadlines for major projects, it’s time to begin implementing your government initiatives. File requests for proposals (RFPs) for private-sector partnerships, fill out the necessary documentation and clarify who is doing what and when.
Taking strategic action to address concerns entails some risk in and of itself. You’ll need to pay close attention to your KPIs and adjust if problems with fulfilling timelines and budgets develop. If such problems arise, you must assess whether parts of the process may be expedited using government technology. Automation will save you time and money while increasing the likelihood of project success in your management planning.
A government strategic plan is the first vital step toward achieving governmental goals. The execution of these plans also plays a pivotal role in the goals’ success. A government runs high-level plans that cascade down and across multiple departments — which can make managing the execution of strategic plans more challenging. This is because different departments work with tools that support their specific work and role. As a result, information is stockpiled across these departments, making planning and organization a manual process.
Transform your strategic planning and execution process with strategic planning software built for your organization. AchieveIt is a FedRAMP-authorized cloud-based platform that connects, manages and executes mission-critical plans and activities for federal government agencies. AchieveIt is a platform that easily tracks the performance of all your integrated plans while automating time-consuming update collection. Managing all these moving parts goes from multiple spreadsheets to a single, easy-to-use platform.
By utilizing AchieveIt, federal government agencies can:
- Establish uniformity in data collection and reporting.
- Create visibility across plans and initiatives to know what needs attention.
- Promote accountability for mission execution.
- Make informed decisions with real-time data and proper context.
- Monitor the performance of long-term initiatives with dashboards and reports.
- Connect all its plans and strategies in one single place.

Do you need help developing and aligning your plans? Since planning and executing is more than just software, AcieveIt’s expert team will partner with you. Our strategy experts can ensure you stay on track and offer advice on how other federal agencies approach planning and execution. Allow AchieveIt to make your agency more efficient, so you can better serve the public while focusing on achieving mission-critical objectives. Request a demo or give us a call at 1-800-535-1559 today.
Related Posts

Measuring Progress: KPIs for Tracking Strategy Implementation

How to Leverage Strategic Leadership in Turbulent Times

How to Create a Long-Term Business Strategy in 7 Steps
Hear directly from our awesome customers
See first-hand why the world's best leaders use AchieveIt
See AchieveIt in action
Stay in the know. Join our community of subscribers.
Subscribe for plan execution content sent directly to your inbox.

- Executive Mosaic
- Executive Biz
- Executive Gov
- Submit your news
- Tuesday, April 9, 2024

How To Start A Government Contracting Business In 2022
- July 1, 2022
The entire commercial business industry was dealt with difficult cards for the past few years—from the COVID-19 shutdowns to the global supply chain disruptions. Countless small businesses closed their shutters for good, negatively impacting several industries. However, the government contracting industry stood its ground .
The stability in the face of uncertainty and the opportunity to earn lucrative profits are just some of the reasons why starting a government contracting business benefits you.
Table of Contents
What should your prepare to become a government contractor?
Evaluate whether government contracting aligns with your business goals.
The federal contracting industry is not an overnight miracle. Given how complicated this industry is, it requires patience, dedication, and strategy to make your business thrive in this industry.
Entering the federal contracting field unprepared will cost you. So before you decide to take the risk, make sure that this endeavor will be beneficial to your business’s overall growth. Study the pros and cons of government contracting, then measure it against your company’s goals. Once you have done that, see if this business opportunity plays to your strengths.
Seek government assistance for small businesses
The government contracting field is dominated by established government contracting firms. This may create an uneven playing field for small businesses, which is why government assistance programs, loans, and grants are available for qualified businesses.
The Small Business Administration ( SBA ), the official federal agency that promotes and protects small businesses, administers a number of contracting assistance programs, such as these:
8(a) Business Development Program
This program helps small businesses gear up to win local, state, and federal government contracts. Under the 8(a) program, small businesses can compete for set-aside contracts and participate in SBA’s Mentor-Protégé Program.
Participating small businesses will also receive one-on-one training with Business Opportunity Specialists and procurement and compliance experts. They can help budding government contractors assess their business readiness in competing for federal contracts.
Women-Owned Small Business Program
Women still face discrimination in various industries. So to ensure female business leaders will have equal access to contracting opportunities, this program gives them the opportunity for more contracting opportunities through set-asides .
Additionally, certified women-owned small businesses and economically-disadvantaged women-owned small businesses are given preferential consideration for open and full competition government contracts.
HUBZone Program
If your business is located in a Historically Underutilized Business Zone ( HUBZone ) and at least 35% of your employees reside in a HUBZone, you can apply for this federal assistance program. Small businesses under this program can compete for set-asides .
Veteran Assistance Programs
Retired veterans, particularly the service-disabled veterans who own small businesses, can apply for various assistance programs to kickstart their careers. Like other federal programs, veteran-owned small businesses are eligible to compete for exclusive government contracts for small businesses or set-asides .
Study your federal contracting market
Most businesses who enter the government contracting field want to earn ludicrous profits. But, the government contracting industry is a massive field, and shooting blindly will get you nowhere. If you want to make it big, you have to make a game plan—market research.
With that in mind, you must set your target federal agencies as early as possible. And once you have nailed down your prospective government agencies, you should dive deeper: study their demands and spending trends—and above all, get to know who you’ll be competing with.
For starters, you can get an overview of the government contracting field by checking previously awarded contracts at SAM.gov and viewing competitor profiles at Dynamic Small Business Search ( DSBS ). You can also use the forecast tool for contracting opportunities by the General Services Administration (GSA).
Get familiar with FAR
The Federal Acquisition Regulation ( FAR ) is the playbook of every government contractor and contracting officer in the industry. FAR illustrates the rules and regulations governing the government’s acquisition of goods and services using public funds.
Understanding the intricate government contracting processes requires time, dedication, and effort. You can also consult a legal representative or federal contracting assistance centers to help you understand it better.
Study the government regulations on businesses
To qualify as a government contractor, your business must be compliant with federal, state, and local business regulations. There are around 90,000 business laws and regulations in effect right now. But you can learn the major business regulations that you should pay closer attention to.
Additionally, there are contracting assistance centers that can connect you with compliance experts. They will help you understand the legal implications of failing to follow the regulations and assess your business’s regulatory compliance.
What are the requirements to start a government contracting business?

Acquire the necessary business permits and licenses
As previously stated, the government is very particular about the companies it does business with. In addition to being a regulation-compliant business, it must possess the necessary licenses to prove its capabilities in performing the required services.
Register at SAM
SAM , or System for Award Management, is a one-stop platform for federal agencies and government contractors. On this website, government agencies can publish open contracts for bidding, and federal contractors can take a shot at bidding for the said contracts.
However, only SAM-registered entities can qualify for government contracts. You can view the complete list of requirements needed to register at SAM, but in general, here are the primary documents you have to prepare before your registration:
Unique Entity ID (UEI)
The federal government has finally moved away from requiring its contractors to request their DUNS Numbers. To streamline this process, government contractors can get their UEI at SAM.gov . Here is the guide on how you can request your UEI.
North American Industry Classification Code (NAICS Code)
NAICS Codes are a special set of codes representing your company’s industry. This code is used by contracting officers to identify the nature of your business and see if you fit the contract.
You can get your NAICS Codes by visiting this self-service website . Select which among the codes best describes your business. If your business belongs to two or more categories, you can select more than one NAICS Code.
Core Business Information
The Core Business Information refers to your business details, such as your business structure, physical and mailing address, organization start date, and more .
Financial Information
The government will ask for your financial information to know your preferred payment method. Additionally, the government will also use this to set up your Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT).
CAGE / NCAGE Code
The CAGE and NCAGE codes are identifiers assigned by the government, particularly by defense agencies. CAGE Codes are assigned to U.S. entities, while NCAGE Codes are awarded to businesses outside the U.S. and its territories.
The Commercial and Government Entity (CAGE) Code is automatically assigned to a U.S. entity after registering at SAM.gov . Meanwhile, non-U.S. entities should request their NATO Commercial and Government Entity (NCAGE) Code before registering at SAM.gov .
Keep tabs on federal contracting opportunities
Once you have successfully registered your business at SAM.gov , you should now learn how to scout for contract opportunities. Fortunately, you don’t have to search high and low to explore the latest contract opportunities—you can do it at SAM.gov !
Back then, the federal government used the Federal Business Opportunities Website (FedBizOpps) to publish contract opportunities. But the government has integrated the functionalities of this website into the SAM.gov website for a more streamlined experience.

Explore subcontracting
The road to becoming a federal contractor can be challenging, especially for a green small business owner. But, businesses can try their hand first in subcontracting for prime contractors.
Subcontractors do not work directly with government agencies. Instead, they lend their specialized expertise to prime contractors to fulfill one area of a federal contract. The requirements to become a subcontractor are less demanding than a prime contractor , making contracting more accessible to small businesses.
Get your business known
Building a solid reputation and portfolio is crucial in this line of work. However, getting your business known by your target government agencies can be pretty daunting, especially if you don’t know where to begin. But we got your back!
Attend Networking Events
Being in the same room with other federal contracting giants can be overwhelming. But if you look at it from another angle, you will realize that you are surrounded by opportunities.
Networking , when done right, can give you access to a myriad of opportunities that grow your business and expand your vision as a leader. Contrary to popular belief, networking is not merely “politicking.” It means fostering meaningful relationships with your peers.
Build Social Media Presence
On top of attending networking events, you should not forget the power of the internet. Platforms like LinkedIn and Facebook are excellent places to build your online presence and network with other contracting professionals.

Learn how to write bids for government contracts
Once you have laid out your foundations, the next thing you need to do is learn how to write bids for federal contracts. Winning a contract bid is your ticket to becoming a full-fledged federal government contractor. So, here are some bid writing tips that can help you finally board the plane of government contracting:
Choose federal contracts that align with your business’s strengths and goals
Sending out contract bids en masse in hopes of landing a single win is a wasteful endeavor.
Writing a contract bid proposal will consume time, money, and effort. Therefore, to write a winning contract bid, you must select which federal opportunities are most suited for your businesses.
Analyze the RFP document
The Request for Proposal (RFP) is among the ways the federal government solicits contract proposals.
The RFP document is usually a hundred-page document that states everything you need to know about a contract opportunity—timeframe, task, budget, and other related details. At a glance, reading through a hundred-page material might be too cumbersome. But, this will ultimately help you craft your proposal.
There are several factors to consider when reviewing this document, but you must pay closer attention to sections B, C, L, and M.
Strictly adhere to the instructions stated in the RFP
It pays to be detail-oriented in this phase of writing. In Section L of the RFP document, the requesting federal agency will lay out its detailed requirements for the proposal—from the document’s font style and size to the proper email address to which the proposal should be submitted.
Neglecting to follow their instructions can eliminate your contract proposal from the pool.
Create a bid outline
The next step of the writing process is to draft an outline. This will prevent your proposal from being derailed and, ultimately, speed up your writing.
When creating an outline for your proposal, consider several factors that the federal agency will look for, such as your business identity, capability statement, portfolio, and plan on how you will execute the contract.
Price your contract competitively
When pricing your goods and services, you should be in the know of its market prices. You can neither price it too low nor too high.
Price it cheap and you may endanger the financial stability of your company, and even cast doubt on your ability to deliver quality products and services. On the other hand, if you price it ludicrously, the federal government will simply look for other cost-efficient government contractors.
Going to the extreme ends of the spectrum will not do you any good. Keep in mind that the federal government is looking for contractors who can deliver quality work that falls within justifiable costs.
Review your proposal before submitting
The last thing you want is your contract bid to be discarded due to technicalities. To avoid this from happening, bring in a trusted set of eyes to review your federal contract bid to catch any errors and point out questionable details that you have missed out on before.
Learn the terms, the contract bid writing process, and how contracting officers will evaluate your proposal in this contract bid writing guide .
The federal government offers some of the best opportunities, especially for small companies. But to become eligible for these contract opportunities, you must first make the necessary preparations to become a government contractor. Once you have laid out your foundations, you should sharpen your writing skills to win a contract bid.
Video of the Day
Register Here
How to Optimize Your Federal Business Development Workflow

IN THIS ARTICLE
How to Define Your Federal Business Development Strategy
Difficulties in federal business development, tools and intelligence to streamline your workflow.
[Use Bloomberg Government’s focused data sets, proprietary tools, and expert analysis to fill your pipeline and grow your business now.]
Managing federal business development workflows can quickly become an unwieldy process, especially when it involves large government contracts that need input and coordination across multiple parties. Building and monitoring the entire opportunity pipeline, from the initial draft request for proposal to winning the final contract, often requires extensive research on information that’s fragmented across multiple platforms, spreadsheets, emails, and messages.
For business developers, this means a lot of time spent finding and gathering both quantitative and qualitative data on individual opportunities, market trends, government spending, networks and partnerships. Optimizing this workflow is essential to building robust pipelines, closing contracts, and growing your federal business.
Winning Federal Contracts on the Top 20 Contract Vehicles
With the right strategy in place, contractors can find and win new contracts for a predictable pipeline.
Before you’re able to optimize your workflow, you must first define your business development strategy. This is the plan of action your company will use to identify new opportunities, build out their pipeline, write the proposals, and ultimately win contracts. Accomplishing this goal requires a detailed plan and an immense amount of research into market conditions, government spending trends, and competitor analysis.
To define your company’s business development strategy and optimize your workflow, consider conducting both a Black Hat and White Hat review. These assessments provide valuable insights into the current market size, your company’s current position in it, and your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses.
The Data You Need
Gain the certainty you need for your business through key information on all federal budget, solicitation, and spending activities.
Black Hat Review
A Black Hat review is all about the competition. You’ll want to write a proposal from their point of view to gain a better understanding of how they would secure the deal. Make a note of any advantages your competitors might have, either in the products or services themselves or their opportunity funnels, and keep track of their weak points.
This exercise can help you determine how your company stacks up to the competition, the right competitive price point at which to market your solution, and whether or not you can win the contract. You’ll also gain key insights on how to position your company against your competitors while building customer relationships with program managers and contracting officers.
White Hat Review
Whereas a Black Hat review focuses on your competitors, a White Hat review targets your company’s capabilities and solutions. This is when you utilize the actionable information from research and assessments to improve your win probability.
Assess and minimize your own weak spots, and explore how your market solutions compare to the competition. It might reveal that you need a partner for a contract or that a niche is oversaturated. In any case, you can use this time to tackle any internal issues, adjust pipeline goals, and target competitor pitfalls with your solutions.
[Explore the tenth annual BGOV200 Federal Industry Leader rankings and download the full report.]
While it might be easy to say “define your business development strategy,” taking the necessary actions to create and implement a detailed pipeline plan is no simple feat. Business developers face many challenges throughout their workflows, from time-consuming research on opportunities to qualifying partnerships and contract leads.
Some common frustrations among business development teams include:
- Identifying areas of opportunity in a niche market.
- A shortage of pipeline opportunities and inaccurate information.
- Aggregating and analyzing accurate, reliable data and contracts to win work.
- Staying up-to-date on government spending trends and market conditions.
- Finding the right agency and vendor contacts.
- Facilitating calls or meetings to gain information and expand their networks.
- Clearly communicating with contracting officers.
- Ensuring accurate release dates for RFPs.
With information buried across a multitude of channels, business developers spend most of their time tracking it down or contacting people. These difficulties often hinder strategic growth planning, resulting in companies falling short of their pipeline goals. However, there are strategies and solutions that can help you overcome these hurdles with numerous added benefits.
Bloomberg Government offers a powerful suite of features designed to optimize your entire federal contracting workflow. With BGOV, business developers can easily create viable pipelines that win task orders on contracts and close deals.
Opportunity Search is the market’s most comprehensive search tool. With fast, accurate, and reliable information and access to a vast database of 31+ million contracts, BGOV provides business developers with the resources they need to save time while pursuing government contract opportunities.
BGOV Alerts offers proactive email updates on opportunities and markets of interest. Based on recompete data, machine learning algorithms can forecast which competitors might bid on the same project. BGOV Workspaces can also help you build your pipeline, qualify potential opportunities, and collaborate with team tools.
Backed by the power of Bloomberg News and proprietary expert analytics combined with powerful market intelligence tools provide business developers with a centralized platform for reliable information on current market conditions, government spending trends, and new contract opportunities. Not only does this present valuable context for current strategies and business decisions, it also saves time researching information by organizing disparate data stored on separate systems platforms.
With enhanced pipeline visibility and access to key market insights and information, BGOV enables business developers to produce accurate forecasting and strong opportunity pipelines. This translates into more contracts won and deals closed, growing your federal contracting business and network.
Market Intelligence to Inform Business Development
Bloomberg Government is your source for news, analysis, and data that covers mission-critical developments. From purchasing trends to supply chain, with BGOV, you’re always a step ahead.
Bloomberg Government helps you streamline the process of taking an opportunity search result from potential to pipeline – and proposal ready. Unparalleled document search capabilities allow you to seek out undiscovered opportunities, gaining a competitive advantage. Track these solicitations and perform competitive analysis to better understand your current market position. Competitive and contract intelligence provides you with accurate, up-to-date information so you can save time on research and focus on business development.
With Bloomberg Government, you receive reliable, actionable data that can propel your opportunities through your pipeline and deliver results. To learn more about how BGOV can help optimize your business development workflows, request a demo .
Find the right opportunities with BGOV’s unmatched data sets.Enhance your view of the market. Opportunity Search enables you to find and exclude keywords in documents attached to solicitation notices to surface relevant opportunities in no time at all.
Request a demo
Reference Shelf
- Report: BGOV200 Federal Industry Leader rankings
- Webinar: Contracts to Watch: GWACs & MACs
- Article: Partnering with 8(a) companies as a large contracting firm
- Article: The Top 10 IT Contractors
- Article: Federal Contract Spending Trends in Five Charts
- Article: How to Build Your Pipeline With the Right Federal Contracts
- Article: How to Size Your Market to Strategically Grow Your Federal Business
How Lobbying Firms are Changing their Structures and Advocacy Strategy
Contractor impacts: fy24 defense appropriations, artificial intelligence market profile.
Mobile Menu Overlay
The White House 1600 Pennsylvania Ave NW Washington, DC 20500
Fact Sheet: The New Small Business Boom Under the Biden- Harris Administration
Since day one in office, President Biden has focused on providing America’s small businesses with the tools and resources they need to reopen, rehire, and build back better. To-date, the Biden-Harris Administration has distributed more than $400 billion in critical relief to more than 6 million small businesses.
President Biden’s efforts have not only helped millions of Main Street businesses keep their lights on and employees on payroll, they have enabled a remarkable rebound in small business activity, with small business demand for labor and inventories near record highs. According to a leading survey of small business owners, the share of small businesses planning to create new jobs in the next three months is higher than it ever was at any point during the previous Administration. Another recent survey of small business owners found that 71 percent are optimistic about their own performance in 2022, up from 63 percent one year ago. The broader economic recovery – one of the fastest on record – has also helped spur a surge in entrepreneurship. Americans are applying to start new businesses at a record rate, up about 30 percent compared to before the pandemic.

The historically high level of new business applications has taken place amidst the Biden-Harris Administration’s historic bottom-up approach to economic recovery. Soon after taking office, the Biden-Harris Administration enacted the American Rescue Plan (ARP), which provided direct relief to families and small businesses and supported the vaccination of more than 200 million Americans. Through the combination of ARP investments and existing emergency relief programs, the Biden-Harris Administration distributed more than $400 billion in critical relief to more than 6 million small businesses. The ARP also provided thousands of entrepreneurs with the personal and financial security to launch their own business. This support included $1,400 per-person Economic Impact Payments, expanded Child Tax Credit payments of up to $300 per child per month, Affordable Care Act credits and COBRA premium support to ensure health care coverage remained available, and an expansion of the Employer Retention Credit, including expanding eligibility to recent startups.
Despite the historic progress made to-date, the Biden-Harris Administration remains committed to helping America’s new small businesses grow, create jobs, and provide the essential goods and services our communities depend on. Specifically, the Biden-Harris Administration is:
- Expanding access to low cost loans and investments. The Treasury Department is working with all states and territories plus 400 Tribal governments on standing up small business lending and investment programs as part of the $10 billion State Small Business Credit Initiative (SSBCI) established through the ARP. and By this summer, the first wave of programs will launch, unlocking billions of dollars in new lending and investment capital for small businesses in big cities and small towns all across America. Small businesses can also continue to access the Small Business Administration’s (SBA) traditional 7a, 504, and microloan programs, which collectively reached record high loan volume in Fiscal Year 2021 by providing $44.8 billion through more than 61,000 loans .
- Increasing access to billions of dollars in federal contracts for small businesses. Last year, the Biden-Harris Administration announced its strategy for increasing the share of federal procurement dollars that go to socially disadvantaged businesses by 50% by 2025. President Biden’s Bipartisan Infrastructure Law also includes a historic procurement effort designed to support small businesses and tackle long standing inequities in the contracting system. Among other things, the legislation directs DOT to attempt to award more than $37 billion in federal contracts to small disadvantaged business contractors.
- Helping small businesses hire new employees and reach new customers by providing universal broadband . Broadband internet is necessary for Americans to do their jobs and increasingly important for small business owners all across America. President Biden’s Bipartisan Infrastructure Law will invest $65 billion in broadband infrastructure, helping ensure that every American has access to reliable high-speed internet and creating new opportunities for small businesses nationwide.
- Connecting small businesses to the resources they need to grow and succeed. The SBA Community Navigator program launched last year and is deploying trusted messengers in underrepresented communities to offer small businesses a broad array of support services. The Bipartisan Infrastructure Law made permanent the Minority Business Development Agency (MBDA), elevated its Director to Under Secretary of Commerce, and gave the agency more tools and authority. SBA also recently launched the Small Business Digital Alliance , a public-private partnership to offer small businesses with critical tech resources to start and expand their e-commerce business, with an eye toward scaling for success.
Stay Connected
We'll be in touch with the latest information on how President Biden and his administration are working for the American people, as well as ways you can get involved and help our country build back better.
Opt in to send and receive text messages from President Biden.
Get the Best GovCon News Straight to your Inbox

- Mission & Vision
- Upcoming events
- Past Events
- Events available now
- Sponsorship
- Executive Profiles
- Future Trends
- Member News
- Speaker News
- Cybersecurity
- Defense and Intelligence
- Federal Civilian
- Digital Modernization

How To Set Business Goals As A Government Contractor
It is already 2022, yet the U.S. government remains one of the biggest clients any business can have. Each year, the government spends billions to mobilize government contractors to accelerate the nation’s recovery and development. With a lucrative opportunity just within your reach, it makes sense to prime your business to be a government contractor.

But, you are not the only one who thinks like that.
Aside from you, countless other businesses are also gunning to win contracts from the government. And once you have entered the industry, you will be competing with government contracting giants, corporations, and many more. Scary, right?
But despite having the odds stacked against you, you can still make a name in the government contracting industry. You can secure more government contracts by setting up your business for success—and it starts by learning how to set business goals.

Table of Contents

What are business goals?
Business goals are your organization’s guiding beacon to which you direct all of your efforts to achieve them. And that is why skipping on planning your business goals can spell disaster to your business. Without concrete business goals, your organization will not have a clear direction to follow for its growth.
Why are business goals important?

It lets you measure success
Business goals are one of the best metrics of success.
Setting clear goals for your business gives your team a clear picture of what success will look like. If your team sees that their combined efforts bring them a step closer to your goals, they will feel more motivated to give their best. If your team hits a slump and can’t seem to progress forward, then you can evaluate the areas that need improvement.

It enables you to integrate and enhance your current workflow
Setting business goals allows you to evaluate which of your current efforts are crucial to achieving your goals and which still needs improvement.
Integrating your current work process into your game plan will increase your chances of success. Doing this will create a more healthy and confident business environment since your team is already familiar existing workflow. There is no need to transition anything, and your team will feel a renewed sense of purpose if their current workflow is used as means to achieve business success.

It lets you rally your team under a common goal
Different departments operate differently. But once you have defined a business goal, all departments can realign their business objectives and workflow to achieve their target. Depending on the nature of their team, your department leaders can come up with other strategies to maximize their team’s skills and expertise to bring your business a step closer to achieving the goal.
Let’s say that you want your company to win 10% more government contracts compared to the previous fiscal year. With a business goal as massive as this, each of your business’s departments, using their strategy, will pitch in their efforts to achieve this goal. Your HR department can look into more federal training to educate your employees regarding the latest policies. Your marketing department can devise a new advertising campaign to promote your products and services to your target federal clientele.
As you can see, defining a business goal for your company brings together your employees and lets you maximize their unique capabilities for the greater good.

It promotes accountability across the board
As a business leader, you should master the skill of delegation. By breaking down the business goals into manageable chunks, you can assign a specific task to every team member to achieve the ultimate goal. Once your people have their duties laid out, they can move with purpose.
Regardless of their rank, making your employees accountable for fulfilling their tasks does not only serve as a motivation for them but also helps their managers track their performance to see whether they need further guidance or not.

It helps you make informed decisions
Your business goals are not just targets you have to hit—they can also be your company’s solid foundation to help you withstand the test of time. So as a best practice, ensure that you implement a work process dedicated to monitoring and evaluating your company’s performance and progress in achieving your business goals. That way, you can use the gathered data, assess what works and not, then enhance your company’s approach for your future endeavors based on your findings.

What is the difference between business goals and business objectives?
It is pretty common to get confused with the concepts. A business goal is an overarching target that your company desires to achieve. In contrast, a business objective is a specific and measurable milestone that fulfills the ultimate goal.
For example, your business goal is to increase your overall government contract success rate by 10% compared to the previous year. Then, your business objective might be investing in the latest technologies to fulfill more complex contracts. So to put it simply, the business goal is the stairs to success, and your business objective is the steps.

Short-term business goals vs. Long-term business goals
Similar to the previously discussed comparison, short-term and long-term business goals function pretty much the same. They are not mutually exclusive; instead, they coexist as two parts of a whole. You need to employ both types of goals to achieve business success.
The bottom line is you set short-term goals to tackle specific goals that you can accomplish within a year. This goal is often viewed as “stepping stones” to success. On the other hand, long-term goals are overarching goals that are achievable within a three to five-year timeframe. Usually, long-term business goals are made up of more manageable short-term goals.
Knowing how to plan and execute these types of business goals properly is essential when you have to develop an effective business plan that will guide your company.

How to create effective business goals
Goal setting requires you to dedicate ample time to strategize methods that address your company’s desired goals and ensure that you maximize the expertise of your team members in achieving them.
So to start, here is a guide on setting business goals that cover all fronts.

Identify long-term goals
You should define your long-term business goals before you get into the nitty-gritty of setting business goals. This means that you should visualize where you want to see your business ten years from now.
By identifying your long-term targets, you can now break them down into short-term business goals that will help guide the efforts of your team members.

Set SMART goals
You should not simply put “to increase profits” as your long-term business goal when setting goals. This goal is too vague and thus, rendering it unactionable. So instead, you should aim to create SMART goals.
The SMART formula is a well-known goal-setting method that helps business leaders like you refine their goals to ensure they are aligned with your vision. The SMART approach is, in fact, an acronym that characterizes an effective business goal: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
To elaborate further on how to set SMART goals, let’s talk about these two examples of a business goal:
Goal A: “I want to be a successful government contractor.”
Goal B: “This year, I want to increase my federal client’s satisfaction to 15% compared to last fiscal year.”
Having a specific business goal removes any uncertainties in determining your progress to success. Goal A is too vague—there are countless factors of being a successful government contractor. On the other hand, Goal B clearly states that its metric of success is a 15% increase in federal client satisfaction.
When setting business goals, it is essential to have a specific number in mind that determines whether you are progressing towards your target or not. With Goal B, you can identify whether you have achieved your target 15% increase in client satisfaction by devising a customer feedback form.
Setting ambitious goals won’t hurt. But setting lucrative goals may adversely impact your team’s morale. Goal B’s target 15% increase is a realistic and achievable goal that has factored in the company’s current capabilities and limitations and the future complications that may arise during the specified time frame.
When you set business goals, they must remain aligned with your company values and vision. Although Goal A describes what you want to achieve in the long run, it is not an actionable goal that can take you there. It is more of a motivation.
On the other hand, Goal B is aligned with your desire to succeed in the government contracting industry.
Time-bound.
And, of course, you should set a realistic timeframe to achieve your goals. This can maintain accountability across all levels and motivate your team to do their best. Goal B specified a target end date for the current year, whereas Goal A did not.

Work backward from the goal
You might feel overwhelmed and lost from plotting out your business goals with all of that in mind. So to help you keep on track, you can try working backward. Since you are putting yourself at the finish line, you can get a clearer vision of the big picture without losing sight of your ultimate goal. Additionally, this change in mindset might also give you fresh insights that may help you achieve your business goals.

Break long-term goals into small, attainable steps
Long-term goals are motivating and ambitious. But without a solid plan on making it to reality, it is all for naught. Once you have laid out your long-term business goals, you should break them into smaller, more manageable business objectives.
For example, suppose your long-term goal is to have a solid staff adept in managing and executing government contracts. In that case, your business objectives can be to provide necessary federal policy training, increase employee engagement on federal projects, and award incentives to displays of excellence.
How do you ensure that you fulfill your business goals?
Regularly keep track of your progress
How would you know if your efforts are bearing fruit if you don’t monitor it regularly, right? So as a business leader, it is essential always to keep track of your company’s progress. That way, you can properly evaluate whether your business is heading in the right direction or not.

How can you monitor your progress?
You can do different methods to see your company’s current standing. Here are some of the best business practices you should take note of:
- Establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and see whether your employee, their manager, their department, or your company as a whole is meeting their set KPIs.
- Ask your clients for satisfaction feedback regularly to see which area are you operating best and which needs improvement.
- Make use of Pictoral History. Take photos of your establishment, your team, your products and services, and all your milestones to see how far you have come.
- Regularly review your financial statements and assess your business’s cash flow.

Adjust goals as priorities change
Although it is relatively easy to predict the federal government’s demands, you should not be lax in staying updated about the trends and factors that may cause a change in the federal marketplace. So to keep your business flexible in adapting to change, you should encourage a mindset that your business goals are not set in stone.
No one was prepared when the COVID-19 pandemic wreaked havoc globally last 2019. Even if it is implausible to experience an industry disruption as massive as that, you should be prepared to revisit your business goals as your priorities change. Don’t be afraid of change. Instead, embrace it. Who knows, maybe you will find an exciting opportunity in the face of the unknown.

Allocate some of your resources in marketing
Small businesses usually don’t have the resources to execute a wide-scale advertising campaign to promote their goods and services. And if you can relate to that, don’t worry! This doesn’t mean that this will be the end of the line for you.
Although you can’t mount a massive advertising campaign yet, you can still promote your business effectively by using fewer resources— networking . There are paid and free events that you can try out where your target federal agencies and key industry players usually attend.
With this new marketing strategy, you expose yourself to the opportunity of creating business connections that may lead you to quality referrals. Participating in networking events is also an excellent way to meet your fellow industry players in the field whom you can partner with for future government projects.
Additionally, don’t forget to perform social media marketing efforts whenever you attend an event. It may be as simple as posting a photo of you in the event of publishing a thought piece about your experience. With social media, you can increase traffic to your web page and garner the attention of your target market.

Modernize your workflow
Ever since society has shifted to a remote work setup, there has been a noticeable rise in digital tools that can streamline a business’s workflow to improve overall productivity. These digital tools automate repetitive administrative tasks and help business leaders manage and monitor tasks.
Here are some of the productivity tools you can try out for your business:
Managing and monitoring different tasks simultaneously can get overwhelming and confusing. So to avoid overlooking anything, you can try out this online collaboration tool that features everything you will need to manage your business successfully. In just a glance, Basecamp can let you see the progress of your projects and deadlines. It enables you to share files with your team swiftly and even communicate with your staff in real-time.
Google Workspace
Google has developed a collection of cloud-based productivity tools that you will need to manage your business. From drafting a contract proposal via Google Docs to brainstorming with your team via Jamboard, Google has it all. You can use its services for free, but they offer premium plans for businesses if you want more storage capacity and improved workflow.
Time Doctor
If your team is still working remotely, Time Doctor is perfect for you! It is an application that lets you monitor your employees’ activity and productivity levels regularly.
Who wouldn’t miss out on this online conferencing tool, right? Zoom lets you host video calls with an employee, team, department, or your entire company! Your group can maximize its free version or upgrade to a paid plan to enjoy uninterrupted calls.

Invest in your employees
It is more expensive to hire established industry professionals than invest in your workforce. So to ensure that your employees remain loyal to you, don’t forget to recognize their hard work and offer an excellent work-life balance.
Instead of working them to the bone for more than 80 hours every week, give them a well-deserved break so they can take care of their wellbeing and attend to their other personal duties. Hold regular meetings with each of your employees to check upon them. Ask if the company is helping them achieve their financial goals and personal goals.
If you notice that your company is struggling if you cut down work hours, maybe it is time to reevaluate your goals, workload, and your workflow to see where you can improve.
Keeping your employees in the best shape keeps their minds focused and renews their drive for excellence. And this will result in a more productive team that will contribute significantly to your company’s success.

Setting the right business goals is just the tip of the iceberg. To achieve your desired success, you have to be dedicated, creative, flexible, and above all, compassionate to your people.

Sign Up Now! Potomac Officers Club provides you with Daily Updates and News Briefings about Articles
Category: Articles

April 01, 2024

March 22, 2024

March 12, 2024

Register Here
Business Plan Template for Government Officials
- Great for beginners
- Ready-to-use, fully customizable Subcategory
- Get started in seconds

Government officials play a crucial role in shaping the future of our communities. To ensure their initiatives are successful, they need a solid business plan that outlines objectives, strategies, and action plans. That's where ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Government Officials comes in!
With this template, government officials can:
- Clearly define their goals and objectives for public programs and initiatives
- Develop comprehensive strategies to achieve those goals, taking into account available resources and budget constraints
- Create actionable plans with defined timelines and responsibilities
Whether it's promoting economic development, improving public services, or addressing social issues, ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Government Officials provides a structured framework to drive results and make a positive impact. Get started today and lead your community towards a brighter future!
Business Plan Template for Government Officials Benefits
Crafting a comprehensive business plan using ClickUp's template can provide numerous benefits for government officials:
- Streamlined communication and alignment of goals among government departments and agencies
- Clear identification of key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress and measure success
- Enhanced transparency and accountability in the implementation of government programs and initiatives
- Facilitation of strategic decision-making based on data-driven insights and analysis
- Improved resource allocation and budget management for optimal utilization
- Empowerment of government officials to effectively communicate their vision and objectives to stakeholders
- Promotion of economic development and public welfare through effective planning and execution.
Main Elements of Government Officials Business Plan Template
To help government officials streamline their business planning process, ClickUp offers a comprehensive Business Plan Template designed specifically for government officials.
Key elements of ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Government Officials include:
- Custom Statuses: Keep track of the progress of each section of your business plan with statuses like Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do.
- Custom Fields: Utilize custom fields like Reference, Approved, and Section to add relevant information and track the approval status of different sections of your business plan.
- Custom Views: Access different views such as Topics, Status, Timeline, Business Plan, and Getting Started Guide to gain a comprehensive understanding of your business plan, track its progress, and effectively communicate it to stakeholders.
- Collaboration Tools: Collaborate with your team and stakeholders using features like comments, mentions, task assignments, and real-time editing to ensure everyone is on the same page and contribute to the success of your business plan.
- Integrations: Seamlessly integrate with other tools and platforms used by government officials, such as Google Docs, Microsoft Office, and more, to enhance productivity and streamline your workflow.
With ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Government Officials, you can effectively plan, execute, and track your government initiatives, driving economic growth and public welfare.
How To Use Business Plan Template for Government Officials
Writing a business plan can be overwhelming, especially for government officials. However, using the Business Plan Template in ClickUp, you can simplify the process by following these four steps:
1. Define your objectives and mission
Start by clearly defining the objectives and mission of your government office. What are you trying to achieve? What services or initiatives do you want to prioritize? By setting clear goals, you can create a roadmap for success.
Use the Goals feature in ClickUp to outline your objectives and track your progress.
2. Analyze the market and competition
Next, conduct a thorough analysis of the market and identify your competition. Understand the needs of your constituents and identify any gaps or opportunities that your office can address. This will help you position your office effectively and differentiate yourself from others.
Utilize the Table view in ClickUp to organize and analyze market research data, including competitor analysis and market trends.
3. Develop your strategies and action plans
Based on your objectives and market analysis, develop strategies and action plans to achieve your goals. Outline specific initiatives, programs, or policies that your government office will implement. Break down these plans into actionable steps and assign responsibilities to team members.
Create tasks and subtasks in ClickUp to outline your strategies and action plans, assign them to team members, and set due dates to ensure timely execution.
4. Monitor progress and make adjustments
Once your business plan is in motion, it's crucial to monitor progress regularly. Track key performance indicators (KPIs) and measure the success of your initiatives. If necessary, make adjustments to your strategies or action plans to ensure that you stay on track and continue to meet your goals.
Utilize the Dashboards feature in ClickUp to create visual representations of your KPIs and monitor the progress of your government office in real-time.
By following these steps and utilizing the Business Plan Template in ClickUp, government officials can develop a comprehensive and effective business plan that sets them up for success in serving their constituents.
Get Started with ClickUp’s Business Plan Template for Government Officials
Government officials can use the Business Plan Template for Government Officials in ClickUp to streamline their planning and implementation processes for government programs and initiatives.
To get started, hit “Add Template” to sign up for ClickUp and add the template to your Workspace. Make sure you designate which Space or location in your Workspace you’d like this template applied.
Next, invite relevant members or guests to your Workspace to start collaborating.
Now you can take advantage of the full potential of this template to create a comprehensive business plan:
- Use the Topics View to organize your business plan by different topics or sections
- The Status View will help you track the progress of each task and ensure that everything is on track
- The Timeline View will give you a visual representation of the project timeline and help you manage deadlines effectively
- The Business Plan View provides a holistic overview of your entire plan, allowing you to see how different sections are interconnected
- The Getting Started Guide View will help you outline the initial steps and key considerations for implementing your plan
Customize your business plan template by adding the following custom fields:
- Reference: Use this field to link relevant documents, reports, or external resources to each task
- Approved: Indicate whether each task has been approved or not, ensuring accountability and transparency
- Section: Categorize each task into different sections or areas of focus, making it easier to navigate and prioritize tasks
Organize tasks into four different statuses: Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, To Do, to track the progress and status of each task accurately.
Update statuses as you progress through tasks to keep stakeholders informed of progress.
Monitor and analyze tasks to ensure maximum productivity and successful implementation of government programs and initiatives.
- Business Plan Template for Metalworkers
- Business Plan Template for Casino Employees
- Business Plan Template for Pharmacists
- Business Plan Template for Finance Teams
- Business Plan Template for Quantity Surveyor
Template details
Free forever with 100mb storage.
Free training & 24-hours support
Serious about security & privacy
Highest levels of uptime the last 12 months
- Product Roadmap
- Affiliate & Referrals
- On-Demand Demo
- Integrations
- Consultants
- Gantt Chart
- Native Time Tracking
- Automations
- Kanban Board
- vs Airtable
- vs Basecamp
- vs MS Project
- vs Smartsheet
- Software Team Hub
- PM Software Guide
- Insights & Analysis
- Nonprofit Jobs
Business Planning for Nonprofits
Business planning is a way of systematically answering questions such as, “What problem(s) are we trying to solve?” or “What are we trying to achieve?” and also, “Who will get us there, by when, and how much money and other resources will it take?”
The business planning process takes into account the nonprofit’s mission and vision, the role of the board, and external environmental factors, such as the climate for fundraising.
Ideally, the business planning process also critically examines basic assumptions about the nonprofit’s operating environment. What if the sources of income that exist today change in the future? Is the nonprofit too reliant on one foundation for revenue? What happens if there’s an economic downturn?
A business plan can help the nonprofit and its board be prepared for future risks. What is the likelihood that the planned activities will continue as usual, and that revenue will continue at current levels – and what is Plan B if they don't?
Narrative of a business plan
You can think of a business plan as a narrative or story explaining how the nonprofit will operate given its activities, its sources of revenue, its expenses, and the inevitable changes in its internal and external environments over time. Ideally, your plan will tell the story in a way that will make sense to someone not intimately familiar with the nonprofit’s operations.
According to Propel Nonprofits , business plans usually should have four components that identify revenue sources/mix; operations costs; program costs; and capital structure.
A business plan outlines the expected income sources to support the charitable nonprofit's activities. What types of revenue will the nonprofit rely on to keep its engine running – how much will be earned, how much from government grants or contracts, how much will be contributed? Within each of those broad categories, how much diversification exists, and should they be further diversified? Are there certain factors that need to be in place in order for today’s income streams to continue flowing?
The plan should address the everyday costs needed to operate the organization, as well as costs of specific programs and activities.
The plan may include details about the need for the organization's services (a needs assessment), the likelihood that certain funding will be available (a feasibility study), or changes to the organization's technology or staffing that will be needed in the future.
Another aspect of a business plan could be a "competitive analysis" describing what other entities may be providing similar services in the nonprofit's service and mission areas. What are their sources of revenue and staffing structures? How do their services and capacities differ from those of your nonprofit?
Finally, the business plan should name important assumptions, such as the organization's reserve policies. Do your nonprofit’s policies require it to have at least six months of operating cash on hand? Do you have different types of cash reserves that require different levels of board approval to release?
The idea is to identify the known, and take into consideration the unknown, realities of the nonprofit's operations, and propose how the nonprofit will continue to be financially healthy. If the underlying assumptions or current conditions change, then having a plan can be useful to help identify adjustments that must be made to respond to changes in the nonprofit's operating environment.
Basic format of a business plan
The format may vary depending on the audience. A business plan prepared for a bank to support a loan application may be different than a business plan that board members use as the basis for budgeting. Here is a typical outline of the format for a business plan:
- Table of contents
- Executive summary - Name the problem the nonprofit is trying to solve: its mission, and how it accomplishes its mission.
- People: overview of the nonprofit’s board, staffing, and volunteer structure and who makes what happen
- Market opportunities/competitive analysis
- Programs and services: overview of implementation
- Contingencies: what could change?
- Financial health: what is the current status, and what are the sources of revenue to operate programs and advance the mission over time?
- Assumptions and proposed changes: What needs to be in place for this nonprofit to continue on sound financial footing?
More About Business Planning
Budgeting for Nonprofits
Strategic Planning
Contact your state association of nonprofits for support and resources related to business planning, strategic planning, and other fundamentals of nonprofit leadership.
Additional Resources
- Components of transforming nonprofit business models (Propel Nonprofits)
- The matrix map: a powerful tool for nonprofit sustainability (Nonprofit Quarterly)
- The Nonprofit Business Plan: A Leader's Guide to Creating a Successful Business Model (David La Piana, Heather Gowdy, Lester Olmstead-Rose, and Brent Copen, Turner Publishing)
- Nonprofit Earned Income: Critical Business Model Considerations for Nonprofits (Nonprofit Financial Commons)
- Nonprofit Sustainability: Making Strategic Decisions for Financial Viability (Jan Masaoka, Steve Zimmerman, and Jeanne Bell)
Disclaimer: Information on this website is provided for informational purposes only and is neither intended to be nor should be construed as legal, accounting, tax, investment, or financial advice. Please consult a professional (attorney, accountant, tax advisor) for the latest and most accurate information. The National Council of Nonprofits makes no representations or warranties as to the accuracy or timeliness of the information contained herein.
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Business and self-employed
- Business finance and support
Write a business plan
Download free business plan templates and find help and advice on how to write your business plan.
Business plan templates
Download a free business plan template on The Prince’s Trust website.
You can also download a free cash flow forecast template or a business plan template on the Start Up Loans website to help you manage your finances.
Business plan examples
Read example business plans on the Bplans website.
How to write a business plan
Get detailed information about how to write a business plan on the Start Up Donut website.
Why you need a business plan
A business plan is a written document that describes your business. It covers objectives, strategies, sales, marketing and financial forecasts.
A business plan helps you to:
- clarify your business idea
- spot potential problems
- set out your goals
- measure your progress
You’ll need a business plan if you want to secure investment or a loan from a bank. Read about the finance options available for businesses on the Business Finance Guide website.
It can also help to convince customers, suppliers and potential employees to support you.
Related content
Is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. We’ll send you a link to a feedback form. It will take only 2 minutes to fill in. Don’t worry we won’t send you spam or share your email address with anyone.

Business Plan Development Guide
(6 reviews)
Lee Swanson, University of Saskatchewan
Copyright Year: 2017
Publisher: OPENPRESS.USASK.CA
Language: English
Formats Available
Conditions of use.
Learn more about reviews.
Reviewed by Kevin Heupel, Affiliate Faculty, Metropolitan State University of Denver on 3/4/20
The text does a good job of providing a general outline about writing and developing a written business plan. All of the important steps and components are included. However, the text is light on details, examples, and rationale for each element... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 3 see less
The text does a good job of providing a general outline about writing and developing a written business plan. All of the important steps and components are included. However, the text is light on details, examples, and rationale for each element of the business plan. Some examples from actual business plans would be helpful.
Content Accuracy rating: 4
For the most part, the content is accurate. The content covers all important aspects of drafting a business plan. I thought the industry analysis could use more information about collecting primary and secondary sources; instead, this information was referenced in the marketing plan section.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 5
Most of the content relies on cites as far back as 2006; however, when it comes to developing and writing a business plan nothing has changed. Thus, the content is current and there is no concern about it becoming obsolete in the near future.
Clarity rating: 4
The text is clear. There are no difficult terms used and the writing is simple. The text uses a lot of bullet points though, which gets tedious to read for a few pages.
Consistency rating: 5
The text does a good job of maintaining consistency in terms of framework and terminology. The text is organized where it's easy to find the information you want in a quick manner.
Modularity rating: 3
The text has a lot of bullet points and the paragraphs are dense. However, the use of subheading is excellent.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 5
The book is organized as if you're writing a business plan from start to finish, which is helpful as a practical guide.
Interface rating: 5
There are no navigation problems, distortion of images/charts, or any other display features that may distract or confuse the reader.
Grammatical Errors rating: 5
The text is free of grammatical errors. The sentence structure is simple with many bullet points, which helps to avoid any grammatical issues.
Cultural Relevance rating: 5
This book was written by a Canadian professor and provides references to Canadian sources. However, the information in this text can be used for U.S. schools.
This book is very short and provides a good, general overview about the process of creating and writing a business plan. It won't help a reader if he/she is confused about a certain part of the business plan. The reader will have to find another source, such as "Preparing Effective Business Plans" by Bruce Barringer, Ph.D. The book provides links to good resources and a finished business plan that the reader can reference. I would recommend the book for undergraduate courses.
Reviewed by Kenneth Lacho, Professor of Management, The University of New Orleans on 6/19/18
1. Text is relevant to Canada. Not the United States 2. Needs to cover resources available to entrepreneur, e.g., federal government agencies, trade associations, chambers of commerce, economic development agencies. 3. Discuss local economy or... read more
1. Text is relevant to Canada. Not the United States 2. Needs to cover resources available to entrepreneur, e.g., federal government agencies, trade associations, chambers of commerce, economic development agencies. 3. Discuss local economy or economic area relevant to this proposed business. 4. Business model ok as a guide. 5. Suggested mission statement to cover: product/business, target customer, geographical area covered. 6. Need detailed promotion plan, e.g., personal selling, advertising, sales promotion, networking publicity, and social media. 7. How do you find the target market? 8. Chapter 6 too much detail on debt and equity financing. 9. Discuss how to find sources of financing, e.g., angels. 10. Expand coverage of bootstring, crowdfunding. 11. Chapter 4 – good checklist. 12. Chapter 3 - overlaps. 13. Chapter 7 – 3 pages of executive summary – double or single spaced typing. Number all tables, graphs. 14. Some references out-of-date, mostly academic. Bring in trade magazines such as Entrepreneur.
Content Accuracy rating: 5
In my opinion, the content is accurate and error free.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 4
The material is relevant to writing a business plan. I wonder if the Porter, SWOT VRIO, etc. material is too high level for students who may not be seniors or have non-business degrees (e.g., liberal arts). Porter has been around for a while and does have longevity. The author has to be more alert to changes in promotion, e.g., social media and sources of financing, e.g., crowdfunding.
Clarity rating: 3
As noted in No. 9, the tone of the writing is too academic, thus making the material difficult to understand. Paragraphs are too long. Need to define: Porter, TOWS Matrix, VRIO, PESTEL. A student less from a senior or a non-business major would not be familiar with these terms.
Consistency rating: 4
The text is internally consistent. The model approach helps keep the process consistent.
Modularity rating: 4
The process of developing a business plan is divided into blocks which are parts of the business plan. Paragraphs tend to be too long in some spots.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 4
The topics are presented in a logical step-wise flow. The language style is too academic in parts, paragraphs too long. Leaves out the citations. Provides excellent check lists.
There are no display features which confuse the reader.
Grammatical Errors rating: 4
The text has no grammatical errors. On the other hand, I found the writing to be too academic in nature. Some paragraphs are too long. The material is more like an academic conference paper or journal submission. Academic citations references are not needed. The material is not exciting to read.
The text is culturally neutral. There are no examples which are inclusive of a variety of races, ethnicities, and backgrounds.
This book best for a graduate class.
Reviewed by Louis Bruneau, Part Time Faculty, Portland Community College on 6/19/18
The text provides appropriate discussion and illustration of all major concepts and useful references to source and resource materials. read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 5 see less
The text provides appropriate discussion and illustration of all major concepts and useful references to source and resource materials.
Contents of the book were accurate, although it could have benefited from editing/proofreading; there was no evidence of bias. As to editing/proofreading, a couple of examples: A. “Figure 1 – Business Plan… “ is shown at the top of the page following the diagram vs. the bottom of the page the diagram is on. (There are other problems with what is placed on each page.) B. First paragraph under heading “Essential Initial Research” there is reference to pages 21 to 30 though page numbering is missing from the book. (Page numbers are used in the Table of Contents.)
The book is current in that business planning has been stable for sometime. The references and resources will age in time, but are limited and look easy to update.
Clarity rating: 5
The book is written in a straightforward way, technical terms that needed explanations got them, jargon was avoided and generally it was an easy read.
The text is internally consistent in terms of terminology and framework.
Modularity rating: 5
The book lends itself to a multi-week course. A chapter could be presented and students could work on that stage of Plan development. It could also be pre-meeting reading for a workshop presentation. Reorganizing the book would be inappropriate.
The topics in the text are presented in a logical, clear fashion.
Generally, the book is free of interface problems. The financial tables in the Sample Plan were turned 90° to maintain legibility. One potential problem was with Figure 6 – Business Model Canvas. The print within the cells was too small to read; the author mitigated the problem by presenting the information, following Figure 6, in the type font of the text.
I found no grammatical errors.
The text is not culturally insensitive or offensive in any way.
I require a business plan in a course I teach; for most of the students the assignment is a course project that they do not intend to pursue in real life. I shared the book with five students that intended to develop an actual start-up business; three of them found it helpful while the other two decided not to do that much work on their plans. If I were planning a start-up, I would use/follow the book.
Reviewed by Todd Johnson, Faculty of Business, North Hennepin Community College on 5/21/18
The text is a thorough overview of all elements of a business plan. read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 4 see less
The text is a thorough overview of all elements of a business plan.
The content is accurate and seems to lack bias.
Content seems relevant and useful . It does not help an entrepreneur generate ideas, and is very light on crowdfunding and other novel funding source content. It is more traditional. This can be easily updated in future versions, however. "Social Media" appears once in the book, as does "Crowd Funding".
The book is comprehensive, but perhaps not written in the most lucid, accessible prose. I am not sure any college student could pick this up and just read and learn. It would be best used as a "teach along guide" for students to process with an instructor.
The text seems consistent. The author does a nice job of consistently staying on task and using bullets and brevity.
Here I am not so certain. The table of contents is not a good guide for this book. It does make the book look nicely laid out, but there is a lot of complexity within these sections. I read it uncertain that it was well organized. Yes there are many good bits of information, however it is not as if I could spend time on one swathe of text at a time. I would need to go back and forth throughout the text.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 2
Similar to the above. I did not like the flow and organization of this. An editor would help things be in a more logical order.
Interface rating: 2
The interface is just OK. It is not an attractice interface, as it presents text in a very dense manner. The images and charts are hard to follow.
I did not find any grammatical errors.
Cultural Relevance rating: 4
I a not certain of the origins of Saskatchewan, but I do feel this is a different read. It is more formal and dense than it has to be. This would be a difficult read for my students. I do not feel it is insensitive in any way, or offensive in any way.
I would not adopt this book if given the chance. It is too dense, and not organized very well, even though the information is very good. The density and lack of modularity are barriers to understanding what is obviously very good information.
Reviewed by Mariana Mitova, Lecturer, Bowling Green State University on 2/1/18
Though this textbook has a prescriptive nature, it is quite comprehensive. The author strikes a good balance between presenting concepts in a concise way and providing enough information to explain them. Many every-day examples and live links to... read more
Though this textbook has a prescriptive nature, it is quite comprehensive. The author strikes a good balance between presenting concepts in a concise way and providing enough information to explain them. Many every-day examples and live links to other resources add to the completeness of the textbook.
Content seems accurate.
Since the content is somewhat conceptual, the text will not become obsolete quickly. In addition, the author seems to be updating and editing content often hence the relevance to current developments is on target.
The text is very clear, written in clear and straight-to-the point language.
The organization of content is consistent throughout the entire text.
The textbook is organized by chapters, beginning with overview of the model used and followed by chapters for each concept within the model. Nicely done.
The flow is clear, logical and easy to follow.
Overall, images, links, and text are well organized. Some headlines were misaligned but still easy to follow.
No concerns for grammar.
No concerns for cultural irrelevance.
Reviewed by Darlene Weibye, Cosmetology Instructor, Minnesota State Community and Technical College on 2/1/18
The text is comprehensive and covers the information needed to develop a business plan. The book provides all the means necessary in business planning. read more
The text is comprehensive and covers the information needed to develop a business plan. The book provides all the means necessary in business planning.
The text was accurate, and error-free. I did not find the book to be biased.
The content is up-to-date. I am reviewing the book in 2017, the same year the book was published.
The content was very clear. A business plan sample included operation timelines, start up costs, and all relevant material in starting a business.
The book is very consistent and is well organized.
The book has a table of contents and is broken down into specific chapters. The chapters are not divided into sub topics. I do not feel it is necessary for sub topics because the chapters are brief and to the point.
There is a great flow from chapter to chapter. One topic clearly leads into the next without repeating.
The table of contents has direct links to each chapter. The appearance of the chapters are easy to read and the charts are very beneficial.
Does not appear to have any grammatical errors.
The text is not culturally insensitive or offensive.
I am incorporating some of the text into the salon business course. Very well written book.
Table of Contents
Introduction
- Chapter 1 – Developing a Business Plan
- Chapter 2 – Essential Initial Research
- Chapter 3 – Business Models
- Chapter 4 – Initial Business Plan Draft
- Chapter 5 – Making the Business Plan Realistic
- Chapter 6 – Making the Plan Appeal to Stakeholders and Desirable to the Entrepreneur
- Chapter 7 – Finishing the Business Plan
- Chapter 8 – Business Plan Pitches
References Appendix A – Business Plan Development Checklist and Project Planner Appendix B – Fashion Importers Inc. Business Plan Business Plan Excel Template
Ancillary Material
About the book.
This textbook and its accompanying spreadsheet templates were designed with and for students wanting a practical and easy-to-follow guide for developing a business plan. It follows a unique format that both explains what to do and demonstrates how to do it.
About the Contributors
Dr. Lee Swanson is an Associate Professor of Management and Marketing at the Edwards School of Business at the University of Saskatchewan. His research focuses on entrepreneurship, social entrepreneurship, Aboriginal entrepreneurship, community capacity-building through entrepreneurship, and institutional-stakeholder engagement. Dr. Swanson’s current research is funded through a Social Sciences Humanities Research Council grant and focuses on social and economic capacity building in Northern Saskatchewan and Northern Scandinavia. He is also actively studying Aboriginal community partnerships with resource based companies, entrepreneurship centres at universities, community-based entrepreneurship, and entrepreneurial attitudes and intentions. He teaches upper-year and MBA entrepreneurship classes and conducts seminars on business planning and business development.
Contribute to this Page

Certification of Health IT
Health information technology advisory committee (hitac), health equity, hti-1 final rule, information blocking, interoperability, patient access to health records, clinical quality and safety, global health it efforts, health it and health information exchange basics, health it in health care settings, health it resources, laws, regulation, and policy, onc funding opportunities, onc hitech programs, privacy, security, and hipaa, scientific initiatives, standards & technology, usability and provider burden, draft 2024-2030 federal health it strategic plan.
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), through the Office of the National Coordinator for Health IT (ONC), released the draft 2024-2030 Federal Health IT Strategic Plan for public comment. The draft plan was developed in collaboration with more than 25 federal organizations that regulate, purchase, develop, and use health IT to help deliver care and improve patient health.
2024-2030 Draft Federal Health IT Strategic Plan [PDF - 2.3 MB]
The draft plan defines a set of goals, objectives, and strategies the federal government will pursue to improve health experiences and outcomes for individuals, populations, and communities while also promoting opportunities for improving health equity, advancing scientific discovery and innovation, and modernizing the nation’s public health infrastructure. The draft plan also places an emphasis on addressing the policy and technology components essential for securely catering to the diverse data requirements of all health IT users.

The final 2024-2030 strategic plan will serve as a roadmap for federal agencies and a catalyst for alignment outside the federal government. Federal organizations will be able to utilize the final plan to prioritize resources, align and coordinate efforts across agencies, signal priorities to the private sector, and benchmark and assess progress over time.
ONC encourages review and comments on the draft plan. Please submit your comments via our feedback form . Attachments should be in Microsoft Word, Excel, PPT, or Adobe PDF format. The comment period is open for 60 days and the deadline for submission is May 28, 2024 at 11:59:59 PM ET .
Submit Comments
Additional Information
- Read blog post on the Health IT Buzz Blog
- Read press release
Open Survey
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.
Go to homepage business.govt.nz business.govt.nz
Business.govt.nz, in association with, how to write a business plan.
There isn’t a one-size-fits-all formula to write a business plan. But there are some key things to consider. Check out our free templates — one for start-ups and a quick-focus template for growing businesses.
Tips for preparing a business plan
- Be clear and focused about what you want to achieve – this will help align your team so you’re all working toward the same thing.
- Choose the type of business plan that works for you – you may like to have a document, or a business canvas might work better.
- Keep it short, simple and easy to understand.
- Keep your goals realistic and relevant to what is going on in the economy and in your industry.
- Use Stats NZ’s Data for Business website to find useful business tools and statistics.
- Contact Stats NZ to get useful business data.
- Get out and speak with your customers to gain understanding of how your product works for them and whether it’s something they would pay for.
- Do a SWOT analysis to determine your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats.
- Ask your advisor or mentor to review your plan and give you feedback and suggested improvements.
Data for Business (external link) — Stats NZ
Call Stats NZ toll-free on 0508 525 525
Use this free template to help you write a great plan for launching your new business.
A business plan helps you set goals for your business, and plan how you’re going to reach them. When you’re starting out it’s a good idea to do a full and thorough business plan.
Quick-focus business plan
Quick-focus planning to make sure you work on the right things for your growing business - every day.
It’s important to take time to reflect on your business strategies and plan. It doesn’t have to be a difficult or time-consuming task.
Implementing your business plan
- Keep your business plan as a living document – don’t leave it to gather dust on a shelf.
- Make sure it’s easily accessible and top-of-mind for you and your team.
- Reflect your goals in the day-to-day operations of your business.
- Outline the most practical and cost-effective way to achieve each goal – make a note of any extra resources you’ll need.
- Make it clear these goals are the top priority for the business.
SWOT your business, and your competition
A SWOT analysis is a great way to assess what your business does well, and where you’ll need to improve. It can also help you identify ways you can exploit opportunities, and to identify and prepare for potential threats to your business success.
Strengths and weaknesses are typically inside your business — what are you good at, what are you not so good at — while opportunities and threats are external factors.
It can be as simple as drawing a large square, and dividing it into four quadrants – one for each element of the SWOT analysis.
Think about what you, your team, and your business are good at – all the attributes that will help you achieve your goals, for example, what you (and your team) do well, any unique skills or expert knowledge, what you/your business do better than your competitors, good processes and systems, and where your business is most profitable.
Think about the things that could stop you from achieving your objectives. This might include what costs you time and/or money, the areas you or your company need to improve in, what resources you lack, which parts of the business aren’t profitable, poor brand awareness, disorganised processes, or a poor online presence. Think about what you can do to minimise your weaknesses.
Opportunities
Think about the external conditions that will help you achieve your goals. How can you do more for your existing customers, or reach new markets? Are there related products and services that could provide opportunities for your business, and how could you use technology to enhance your business?
Consider the external conditions that could damage your business's performance – things like what’s going on in your industry, and in the economy, the obstacles you face, the strengths of your biggest competitors, and things your competitors are doing that you're not. Think about how you could try to minimise or manage the threats.
Repeat the exercise for your competition too – it’ll help you identify areas where you can beat them, to fine-tune your niche market, and make sure you’re prepared to address the challenge they pose.
Refine and review
Craig Jackson has dabbled in business planning before. But when he set up his ice pop business Dr Feelgood, he decided to work with a mentor.
“She was instrumental to pushing us to a very healthy product. Our first business plan was 47 pages long. It came down to four pages, which distilled down what we were doing and how we look at it,” says Jackson.
“It’s really important to ask ‘do people want your product’ and then ‘are there enough of them to buy it’? Our market validation was me going around gas stations, cafes, dairies and looking in freezers and talking to freezer managers and talking to our friends.”
Jackson regularly reviews progress against his business plan. “We’ve hit all our targets, but have learnt a lot in the first six months of operating. Places I thought we’d really sell, we don’t, and places I thought we’d never go is where we’re going.”
Review your business plan
- Check how you’re tracking to reach key milestones in your business plan every month, and celebrate when these have been reached.
- Stay on top of industry trends and stay connected with your customers – this will help you keep ahead of any changes needed in your business.
- Update your business plan with any changes affecting your business or industry.
Tips on when business planning is right for your business
Tips on types of advice you’ll need
Common mistakes
Not being able to clearly articulate your business and the value it offers to customers.
Making assumptions about your customers rather than speaking with them.
Not reviewing and monitoring your business plan.
Setting unrealistic or uninformed targets.
Subscribe to our newsletter
Sign up to the business.govt.nz monthly newsletter for news, advice and information from across government to save your business time and money.
You must enable JavaScript to submit this form
How helpful was this information?
"Rate this" is required
Related content
Research your market.
Knowing about your market and rivals is crucial, whether you’re starting, growing or well established.
Test if you’re ready to grow
Are you and your business ripe to expand? Take our self-assessment test and find out.
News for business
Get updates for small businesses from across government about new services, law changes and more.
Guide to starting a business
Business planning advice.
Whether you’re growing fast or new to business, expert advice can kick-start your planning.
- Side Hustles
- Power Players
- Young Success
- Save and Invest
- Become Debt-Free
- Land the Job
- Closing the Gap
- Science of Success
- Pop Culture and Media
- Psychology and Relationships
- Health and Wellness
- Real Estate
- Most Popular
Related Stories
- Earn Over 150,000 student loan borrowers will soon have their debt forgiven
- Become Debt-Free Student debt relief due to financial hardship could be on its way
- Become Debt-Free President Biden forgives student debt for nearly 78,000 borrowers through PSLF
- Become Debt-Free Some student loan borrowers will start seeing their debt forgiven in February
- Spend The No. 1 money mistake to avoid after being laid off
25 million student loan borrowers could see their balances shrink under Biden’s new forgiveness plan

President Joe Biden and his administration are moving forward with plans to provide student debt relief to as many people as possible.
The administration announced Monday the details of its new plan to reduce student debt balances for millions of borrowers. The proposed regulations — which were drafted as part of the months-long negotiated rulemaking process — feature several different ways for borrowers to see their debt balances reduced, if not eliminated entirely.
The provisions of the plan include forgiving excessive interest that has accrued, discharging balances that have been in repayment for 20 years or more and relief for borrowers who attended now-closed or insolvent institutions.
"[The] plan is focused on the reasons that people are struggling with their student loan debt," James Kvaal, Under Secretary of Education, told CNBC Make It.
"People who are upside down on their student loans because interest has racked up faster than they could pay it, people who have been making payments on their loans for decades and still owe those loans — it's a sign of how aggressive the President is [being] in tackling the student loan crisis," he said.
The relief provisions will soon be open for a public comment period where the administration will consider revisions to its proposal before it goes into effect. Some provisions are expected to roll out as early as this fall, the administration said.
As with Biden's previous student debt forgiveness proposals, it's possible this plan will come under legal scrutiny if challenged by opponents. But this plan differs from his previous action by using a different legal authority — the Higher Education Act — and narrowing the scope of borrowers eligible for relief.
In the event this plan is enacted and a future presidential administration wanted to repeal it, it would need to go through the same lengthy rulemaking process, Kvaal said.
Here's the relief borrowers may expect to see in the coming months.
Up to $20,000 of accrued interest forgiven
Interest accrues daily on student loans and some borrowers have interest rates as high as 8%. As a result, many borrowers wind up with balances higher than what they initially took out for school, despite making regular payments.
Biden's plan aims to address that "runaway interest" by canceling up to $20,000 of the amount a borrower's balance has grown due to unpaid interest after entering repayment. Single borrowers who earn $120,000 or less and married borrowers earning $240,000 or less who enroll in an income-driven repayment plan would be eligible to have their entire excess interest balances discharged, the administration said.
Some 25 million borrowers stand to benefit from their interest balances being reduced if the plan goes into effect as proposed. An estimated 23 million of those borrowers will have their entire balance growth forgiven, according to the administration.
Automatic loan discharge for forgiveness-eligible borrowers
The Biden administration has canceled debt for over 1 million borrowers through existing forgiveness programs, including Public Service Loan Forgiveness , income-driven repayment and closed school loan discharges.
The administration estimates another 2 million borrowers are eligible to have their debt forgiven under these programs, but have not yet applied .
The new plan will allow the administration to use available data to identify and automatically clear balances for these borrowers as they are eligible, without borrower action.
Debt forgiveness for long-term borrowers
Another 2 million borrowers could benefit from a provision that will clear debt balances that are at least 20 years old for undergraduate borrowers and 25 years for graduate borrowers. It will apply to undergraduate borrowers with direct loans or direct consolidation loans who entered repayment on or before July 1, 2005, and graduate school borrowers who entered repayment on or before or July 1, 2000.
Currently, borrowers enrolled in the Saving on a Valuable Education plan or other income-driven repayment plans are eligible to have their remaining balances discharged after 20 or 25 years, but the new regulation would eliminate the IDR requirement.
Relief for attendees of 'low-financial-value' programs
The Biden administration has made a concerted effort to "hold colleges accountable when they leave students with mountains of debt and without good job prospects," it said in its statement.
As such, the new plan would waive loans for borrowers who attended institutions or programs the administration identifies as "low-financial-value."
That includes schools that have lost eligibility to receive federal student aid or were denied recertification due to cheating or taking advantage of students, as well as programs that have since closed or have a history of leaving students with high debt loads and poor earnings outcomes.
Help for borrowers facing financial hardship
The administration says it is committed to pursuing a "specific action" for student loan borrowers experiencing a variety of financial hardships , although it's not yet clear who may receive relief and to what degree their balances will be reduced.
"This could include delivering automatic forgiveness to borrowers predicted to be likely to default on their loans, or through an individualized applications where borrowers could detail their financial hardship that is preventing them from being able to fully pay back their loan, such as a child care or medical expense," the administration said in its statement.
Want to make extra money outside of your day job? Sign up for CNBC's new online course How to Earn Passive Income Online to learn about common passive income streams, tips to get started and real-life success stories. Register today and save 50% with discount code EARLYBIRD.
Plus, sign up for CNBC Make It's newsletter to get tips and tricks for success at work, with money and in life.

- Share full article
Advertisement
Trump Spoke Recently With Saudi Leader
It is not clear what the former president discussed with Prince Mohammed bin Salman, but news of their call came amid Biden administration negotiations with the Saudis over a Middle East peace plan.

By Maggie Haberman and Jonathan Swan
- April 3, 2024
Former President Donald J. Trump spoke recently with Saudi Arabia’s de facto ruler, Prince Mohammed bin Salman, their first publicly disclosed conversation since Mr. Trump left office in January 2021, according to two people briefed on the discussion who were not authorized to speak publicly about it.
It was unclear what the two men discussed and whether it was their only conversation since Mr. Trump’s departure from the White House. Neither representatives for Mr. Trump nor an official of the Saudi government responded to requests for comment.
But news of their discussion comes at a time when the Biden administration is engaged in delicate negotiations with the Saudis aimed at establishing a lasting peace in the Middle East, building on diplomatic ties between Israel and a number of Arab states forged through the work of the Trump administration.
If President Biden manages to clinch a trilateral megadeal — which would probably include a Saudi-Israeli peace agreement, an Israeli commitment to a two-state solution, a U.S.-Saudi defense treaty and U.S.-Saudi understandings on a civilian nuclear program in Saudi Arabia — he will need support from two-thirds of senators to ratify the U.S.-Saudi treaty. Mr. Trump, as the presumptive Republican nominee in firm command of his party, could potentially either block any deal or greenlight it for congressional Republicans.
Mr. Trump has other reasons to maintain warm relations with Prince Mohammed. The former president and Jared Kushner, his son-in-law and former senior White House adviser, established close ties with the crown prince while in office and have capitalized on that good will in their private businesses since leaving government.
Saudi Arabia was the first stop on Mr. Trump’s first foreign trip as president — a sign of the value Mr. Trump placed on the relationship. Mr. Trump pursued major deals with the Saudis, including arms sales, and he defended Prince Mohammed at his moment of greatest international pressure, after the C.I.A. concluded that the crown prince had ordered the killing of the dissident journalist Jamal Khashoggi in 2018.
Nine months after the killing, Mr. Trump called Prince Mohammed “a friend of mine” and praised the “spectacular job” he had done in liberalizing Saudi Arabia’s laws, including allowing women to drive. While still in office, Mr. Trump told the journalist Bob Woodward that “I saved his ass” when Prince Mohammed was under intense criticism from officials in the U.S. Congress.
“I was able to get Congress to leave him alone. I was able to get them to stop,” Mr. Trump added.
For his part, Mr. Biden promised during his 2020 campaign to treat Prince Mohammed as a “pariah” because of the killing of Mr. Khashoggi. Once in office, however, he concluded that it was unsustainable to sideline the Saudi crown prince, and his team has sought to mend the fractured relationship.
Since leaving the presidency, Mr. Trump has made use of his Saudi connections. At the same time as he was preparing to announce his presidential campaign, in November 2022, the Trump Organization was putting the final touches on a deal with the Omani government and a Saudi firm for a multibillion-dollar Trump-branded real estate development in Oman. Mr. Trump has also worked with Saudi Arabia’s sovereign wealth fund to host the Saudi-backed LIV golf tour at some of his golf courses.
Mr. Kushner has benefited from Prince Mohammed’s support on an even larger scale. Only six months after leaving government, Mr. Kushner’s investment firm, Affinity Partners, secured $2 billion from Saudi Arabia’s Public Investment Fund, in what was described in internal documents as a “ strategic relationship ” with Mr. Kushner. A panel of advisers to the Saudi sovereign wealth fund had recommended against investing with Mr. Kushner, citing his lack of experience, but Prince Mohammed overruled them.
The Saudi crown prince is not the only foreign leader with whom Mr. Trump has engaged recently. Last month, he hosted Prime Minister Viktor Orban of Hungary at his Mar-a-Lago estate in Florida for a meeting, the second they have held in the last two years. A person close to Mr. Trump said it was Mr. Orban who sought the meeting.
At some of his rallies, Mr. Trump has lauded Mr. Orban — who has been criticized for eroding democratic institutions in Hungary — as an admirably strong leader.
Maggie Haberman is a senior political correspondent reporting on the 2024 presidential campaign, down ballot races across the country and the investigations into former President Donald J. Trump. More about Maggie Haberman
Jonathan Swan is a political reporter covering the 2024 presidential election and Donald Trump’s campaign. More about Jonathan Swan

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Government Agencies is designed to help government agencies effectively outline and manage their strategic goals, objectives, and action plans. Here are the main elements of this template: Custom Statuses: Easily track progress with four custom statuses - Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do - to ...
Total Capital and Liabilities. $154,200. Total Funding. $160,000. Need real financials. We recommend using LivePlan as the easiest way to create automatic financials for your own business plan. Create your own business plan.
A government strategic plan is the first vital step toward achieving governmental goals. The execution of these plans also plays a pivotal role in the goals' success. A government runs high-level plans that cascade down and across multiple departments — which can make managing the execution of strategic plans more challenging.
To qualify as a government contractor, your business must be compliant with federal, state, and local business regulations. There are around 90,000 business laws and regulations in effect right ...
A work plan is a department's operational plan (sometimes referred to as a department business plan). Generally speaking, it's more tactical and operational in nature than the high-level government strategic plan. The work plan typically covers only 1-2 years of the strategic plan, and is linked to the budget directly, so it can be more ...
Accomplishing this goal requires a detailed plan and an immense amount of research into market conditions, government spending trends, and competitor analysis. To define your company's business development strategy and optimize your workflow, consider conducting both a Black Hat and White Hat review.
Small businesses can also continue to access the Small Business Administration's (SBA) traditional 7a, 504, and microloan programs, which collectively reached record high loan volume in Fiscal ...
Goal A: "I want to be a successful government contractor.". Goal B: "This year, I want to increase my federal client's satisfaction to 15% compared to last fiscal year.". Specific. Having a specific business goal removes any uncertainties in determining your progress to success.
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States. ... Socio economic categories Check your eligibility for small-business set-asides. Training and videos Suggested training for doing business ... Plan a trip expand menu. Per diem rates. Transportation (airfare rates, POV rates, etc.) ...
Step 4: Develop Your Federal Marketing Plan. • Know your competitive position and what distinguishes your product or service from your competition. Clearly outline what makes your small business stand out. Effectively communicate these factors to Federal agencies. • Assess the strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities of your small business ...
Government officials play a crucial role in shaping the future of our communities. To ensure their initiatives are successful, they need a solid business plan that outlines objectives, strategies, and action plans. That's where ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Government Officials comes in! With this template, government officials can:
According to Propel Nonprofits, business plans usually should have four components that identify revenue sources/mix; operations costs; program costs; and capital structure. A business plan outlines the expected income sources to support the charitable nonprofit's activities. What types of revenue will the nonprofit rely on to keep its engine ...
Government activity Departments. Departments, agencies and public bodies. News. News stories, speeches, letters and notices ... A business plan is a written document that describes your business ...
A business plan sets you up for success when you start, and helps you adapt as your business grows. Develop your marketing plan A marketing plan can help you understand who your customers are, how to reach them and how to define your brand.
Chapter 1 - Developing a Business Plan. Chapter 2 - Essential Initial Research. Chapter 3 - Business Models. Chapter 4 - Initial Business Plan Draft. Chapter 5 - Making the Business Plan Realistic. Chapter 6 - Making the Plan Appeal to Stakeholders and Desirable to the Entrepreneur. Chapter 7 - Finishing the Business Plan.
5. Review your plan regularly. As your business changes, your plan will need to change to ensure your business is still heading in the right direction. Having your plan up-to-date can keep you focused on where you are heading. It's a good idea to keep a record of each version of your business plan. 6.
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), through the Office of the National Coordinator for Health IT (ONC), released the draft 2024-2030 Federal Health IT Strategic Plan for public comment. The draft plan was developed in collaboration with more than 25 federal organizations that regulate, purchase, develop, and use health IT to help deliver care and improve patient health.
2022-25 Business plans. The following documents were released with Budget 2022: Government of Alberta Strategic Plan. Ministry Business Plans - Complete Volume. Ministry Business Plan Reader's Guide. Advanced Education. Agriculture, Forestry and Rural Economic Development. Children's Services. Community and Social Services.
April 2, 2024 at 11:01 AM PDT. Listen. 4:24. The Biden administration wants to tackle rampant shortages of drugs for cancer and other diseases with a multibillion-dollar plan that calls for ...
Implementing your business plan. Keep your business plan as a living document - don't leave it to gather dust on a shelf. Make sure it's easily accessible and top-of-mind for you and your team. Reflect your goals in the day-to-day operations of your business. Outline the most practical and cost-effective way to achieve each goal - make ...
Biden's plan aims to address that "runaway interest" by canceling up to $20,000 of the amount a borrower's balance has grown due to unpaid interest after entering repayment. Single borrowers who ...
President Biden announced his new plan to provide student debt relief to millions of Americans in Wisconsin, a battleground state that is pivotal to his reelection bid. The White House on Monday ...
Mr. Kushner has benefited from Prince Mohammed's support on an even larger scale. Only six months after leaving government, Mr. Kushner's investment firm, Affinity Partners, secured $2 billion ...