

Biomedical Engineering
IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering contains basic and applied papers dealing with biomedical engineering. Papers range from engineering development in methods and techniques with biomedical applications to experimental and clinical investigations with engineering contributions.
Submit Your Manuscript
Impact factor, eigenfactor, article influence score.
Join the EMBS
In an era where technology is expanding at a rapid rate and the needs for medical application of these technologies has never been greater, the intersection between engineering, medicine and biology is a critical place to be. The IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society is well-positioned to serve as a central gathering point for both of these major disciplines.
Featured Articles
- March 29, 2024
Transmission Coefficient-Based Monitoring of Microwave Ablation: Development and Experimental Evaluation in Ex Vivo Tissue
We demonstrate the feasibility of monitoring microwave ablation zone growth with the same antennas used for delivering ablation, potentially offering a means for real-time intraprocedural assessment.

Measurement and Analysis of In Vivo Gastroduodenal Slow Wave Patterns Using Anatomically-Specific Cradles and Electrodes
This study describes novel measurement and analysis methods for in vivo bioelectrical slow waves and documents physiological phenomena in high-resolution across the gastroduodenal junction for the first time.
Sensing and Controlling Strategy for Upper Extremity Prosthetics Based on Piezoelectric Micromachined Ultrasound Transducer
A novel wearable A-mode ultrasound system based on PMUTs enables accurate gesture recognition, simplifies probes, eliminates the need for gel and complex circuits, promising simplified prosthetic control.
FLEX: FLexible transducer with EXternal tracking for ultrasound imaging with patient-specific geometry estimation
This study presents the patient-specific flexible ultrasound probe geometry estimation for real-time imaging with accurate anatomical structure and encourages utilizing the proposed imaging concept for image-guided interventions.
Biomechanical MEMS Electrostatic Energy Harvester for Pacemaker Application: a study of optimal interface circuit
This work presents a solution to extend the battery lifetime by converting biomechanical heartbeats energy into electricity using an innovative electrostatic MEMS energy harvesting device. Based on the energy consumed by the latest generation of leadless commercial pacemakers, this solution has experimentally demonstrated the possibility of extending pacemaker battery life by up to 44%, and holds out the prospect of total battery replacement.

A Novel Articulating Chip–on–Tip Endoscope for Dynamic Middle Ear Surgical Visualization
A novel Articulating Chip-on-Tip Endoscope (ACoT Endo) to enhance visualization during pediatric middle ear surgeries, reducing mastoidectomy instances. It integrates a cable-driven distal end and Chip-on-Tip cameras for improved visualization.
Current Issue
TBME, Volume 70, Issue 4, April 2024
IEEE Account
- Change Username/Password
- Update Address
Purchase Details
- Payment Options
- Order History
- View Purchased Documents
Profile Information
- Communications Preferences
- Profession and Education
- Technical Interests
- US & Canada: +1 800 678 4333
- Worldwide: +1 732 981 0060
- Contact & Support
- About IEEE Xplore
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Nondiscrimination Policy
- Privacy & Opting Out of Cookies
A not-for-profit organization, IEEE is the world's largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity. © Copyright 2024 IEEE - All rights reserved. Use of this web site signifies your agreement to the terms and conditions.

Volumes and issues
Volume 39 march - december 2023 mar - dec 2023.
- Issue 4 December 2023
- Issue 3 September 2023
- Issue 2 June 2023
- Issue 1 March 2023
Volume 38 March - December 2022 Mar - Dec 2022
- Issue 4 December 2022
- Issue 3 September 2022
- Issue 2 June 2022
Emerging Technologies for Fighting COVID-19
Volume 37 March - December 2021 Mar - Dec 2021
- Issue 4 December 2021
- Issue 3 September 2021
- Issue 2 June 2021
- Issue 1 March 2021
Volume 36 March - December 2020 Mar - Dec 2020
- Issue 4 December 2020
- Issue 3 September 2020
- Issue 2 June 2020
- Issue 1 March 2020
Volume 35 March - December 2019 Mar - Dec 2019
- Issue 3-4 December 2019
- Issue 2 June 2019
- Issue 1 March 2019
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Search by keyword
- Search by citation
Page 1 of 44
Noninvasive spinal stimulation improves walking in chronic stroke survivors: a proof-of-concept case series
After stroke, restoring safe, independent, and efficient walking is a top rehabilitation priority. However, in nearly 70% of stroke survivors asymmetrical walking patterns and reduced walking speed persist. Th...
- View Full Text
Classification of vasovagal syncope from physiological signals on tilt table testing
The diagnostic test for vasovagal syncope (VVS), the most common cause of syncope is head-up tilt test (HUTT) assessment. During the test, subjects experienced clinical symptoms such as nausea, sweating, pallo...
Effects of immediate loading directionality on the mechanical sensing protein PIEZO1 expression and early-stage healing process of peri-implant bone
The reduced treatment time of dental implants with immediate loading protocol is an appealing solution for dentists and patients. However, there remains a significant risk of early peri-implant bone response f...
Enhancing automated lower limb rehabilitation exercise task recognition through multi-sensor data fusion in tele-rehabilitation
Tele-rehabilitation is the provision of physiotherapy services to individuals in their own homes. Activity recognition plays a crucial role in the realm of automatic tele-rehabilitation. By assessing patient m...
A novel in-bed body posture monitoring for decubitus ulcer prevention using body pressure distribution mapping
Decubitus ulcers are prevalent among the aging population due to a gradual decline in their overall health, such as nutrition, mental health, and mobility, resulting in injury to the skin and tissue. The most ...
Construction of in vitro liver-on-a-chip models and application progress
The liver is the largest internal organ of the human body. It has a complex structure and function and plays a vital role in drug metabolism. In recent decades, extensive research has aimed to develop in vitro...
Evaluating imaging repeatability of fully self-service fundus photography within a community-based eye disease screening setting
This study aimed to investigate the imaging repeatability of self-service fundus photography compared to traditional fundus photography performed by experienced operators.
Three-dimensional visualization of thyroid ultrasound images based on multi-scale features fusion and hierarchical attention
Ultrasound three-dimensional visualization, a cutting-edge technology in medical imaging, enhances diagnostic accuracy by providing a more comprehensive and readable portrayal of anatomical structures compared...
Effects of hyperbaric oxygen combined cabin ventilator on critically ill patients with liberation difficulty after tracheostomy
Critically ill patients undergoing liberation often encounter various physiological and clinical complexities and challenges. However, whether the combination of hyperbaric oxygen and in-cabin ventilator thera...
Diagnostic value of bedside lung ultrasound and 12-zone score in the 65 cases of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome and its severity
To explore the predictive value of bedside lung ultrasound score in the severity of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome (NRDS) and mechanical ventilation and extubation.
Designing and validating an experimental protocol to induce airway narrowing in older adults with and without asthma
Persons with asthma may experience excessive airway narrowing due to exercise or exposure to cold air, worsening their daily functionality. Exercise has several benefits for asthma control, but it may induce a...
Application of visual transformer in renal image analysis
Deep Self-Attention Network (Transformer) is an encoder–decoder architectural model that excels in establishing long-distance dependencies and is first applied in natural language processing. Due to its comple...
A concept for human use of real-time and remote monitoring of diabetic subjects using intermittent scanned continuous glucose measurement
Flash glucose monitoring systems like the FreeStyle Libre (FSL) sensor have gained popularity for monitoring glucose levels in people with diabetes mellitus. This sensor can be paired with an off-label convert...
HM_ADET: a hybrid model for automatic detection of eyelid tumors based on photographic images
The accurate detection of eyelid tumors is essential for effective treatment, but it can be challenging due to small and unevenly distributed lesions surrounded by irrelevant noise. Moreover, early symptoms of...
Simulating impaired left ventricular–arterial coupling in aging and disease: a systematic review
Aortic stenosis, hypertension, and left ventricular hypertrophy often coexist in the elderly, causing a detrimental mismatch in coupling between the heart and vasculature known as ventricular−vascular (VA) cou...
Non-invasive parameters of autonomic function using beat-to-beat cardiovascular variations and arterial stiffness in hypertensive individuals: a systematic review
Non-invasive, beat-to-beat variations in physiological indices provide an opportunity for more accessible assessment of autonomic dysfunction. The potential association between the changes in these parameters ...
Kinematic difference and asymmetries during level walking in adolescent patients with different types of mild scoliosis
Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS), three-dimensional spine deformation, affects body motion. Previous research had indicated pathological gait patterns of AIS. However, the impact of the curve number on th...
The effectiveness of simple heuristic features in sensor orientation and placement problems in human activity recognition using a single smartphone accelerometer
Human activity Recognition (HAR) using smartphone sensors suffers from two major problems: sensor orientation and placement. Sensor orientation and sensor placement problems refer to the variation in sensor si...
StairNet: visual recognition of stairs for human–robot locomotion
Human–robot walking with prosthetic legs and exoskeletons, especially over complex terrains, such as stairs, remains a significant challenge. Egocentric vision has the unique potential to detect the walking en...
Feasibility of using a depth camera or pressure mat for visual feedback balance training with functional electrical stimulation
Individuals with incomplete spinal-cord injury/disease are at an increased risk of falling due to their impaired ability to maintain balance. Our research group has developed a closed-loop visual-feedback bala...
Screening ovarian cancer by using risk factors: machine learning assists
Ovarian cancer (OC) is a prevalent and aggressive malignancy that poses a significant public health challenge. The lack of preventive strategies for OC increases morbidity, mortality, and other negative conseq...
Deep neural networks for wearable sensor-based activity recognition in Parkinson’s disease: investigating generalizability and model complexity
The research gap addressed in this study is the applicability of deep neural network (NN) models on wearable sensor data to recognize different activities performed by patients with Parkinson’s Disease (PwPD) ...
Abnormal interlimb coordination of motor developmental delay during infant crawling based on kinematic synergy analysis
Previous studies have reported that abnormal interlimb coordination is a typical characteristic of motor developmental delay (MDD) during human movement, which can be visually manifested as abnormal motor post...
Detecting bulbar amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) using automatic acoustic analysis
Automatic speech assessments have the potential to dramatically improve ALS clinical practice and facilitate patient stratification for ALS clinical trials. Acoustic speech analysis has demonstrated the abilit...
Advantages of transformer and its application for medical image segmentation: a survey
Convolution operator-based neural networks have shown great success in medical image segmentation over the past decade. The U-shaped network with a codec structure is one of the most widely used models. Transf...
Beyond timing and step counting in 360° turning-in-place assessment: a scoping review
Turning in place is a challenging motor task and is used as a brief assessment test of lower limb function and dynamic balance. This review aims to examine how research of instrumented analysis of turning in p...
Protocol for metadata and image collection at diabetic foot ulcer clinics: enabling research in wound analytics and deep learning
The escalating impact of diabetes and its complications, including diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs), presents global challenges in quality of life, economics, and resources, affecting around half a billion people. ...
Joint angle estimation during shoulder abduction exercise using contactless technology
Tele-rehabilitation, also known as tele-rehab, uses communication technologies to provide rehabilitation services from a distance. The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of tele-rehab, where the ...
A dry polymer nanocomposite transcutaneous electrode for functional electrical stimulation
Functional electrical stimulation (FES) can be used in rehabilitation to aid or improve function in people with paralysis. In clinical settings, it is common practice to use transcutaneous electrodes to apply ...
Left main coronary artery morphological phenotypes and its hemodynamic properties
Atherosclerosis may be linked to morphological defects that lead to variances in coronary artery hemodynamics. Few objective strategies exit at present for generalizing morphological phenotypes of coronary art...
Multimodal diagnosis model of Alzheimer’s disease based on improved Transformer
Recent technological advancements in data acquisition tools allowed neuroscientists to acquire different modality data to diagnosis Alzheimer’s disease (AD). However, how to fuse these enormous amount differen...
Pulse wave-based evaluation of the blood-supply capability of patients with heart failure via machine learning
Pulse wave, as a message carrier in the cardiovascular system (CVS), enables inferring CVS conditions while diagnosing cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). Heart failure (HF) is a major CVD, typically requiring exp...
Effects of workload and saddle height on muscle activation of the lower limb during cycling
Cycling workload is an essential factor in practical cycling training. Saddle height is the most studied topic in bike fitting, but the results are controversial. This study aims to investigate the effects of ...
A neural network with a human learning paradigm for breast fibroadenoma segmentation in sonography
Breast fibroadenoma poses a significant health concern, particularly for young women. Computer-aided diagnosis has emerged as an effective and efficient method for the early and accurate detection of various s...
Unsupervised corneal contour extraction algorithm with shared model for dynamic deformation videos: improving accuracy and noise resistance
In this study, an automatic corneal contour extraction algorithm with a shared model is developed to extract contours from dynamic corneal videos containing noise, which improves the accuracy of corneal biomec...
Bioelectricity in dental medicine: a narrative review
Bioelectric signals, whether exogenous or endogenous, play crucial roles in the life processes of organisms. Recently, the significance of bioelectricity in the field of dentistry is steadily gaining greater a...

Effect of test duration and sensor location on the reliability of standing balance parameters derived using body-mounted accelerometers
Balance parameters derived from wearable sensor measurements during postural sway have been shown to be sensitive to experimental variables such as test duration, sensor number, and sensor location that influe...
Cycling using functional electrical stimulation therapy to improve motor function and activity in post-stroke individuals in early subacute phase: a systematic review with meta-analysis
Stroke necessitates interventions to rehabilitate individuals with disabilities, and the application of functional electrical stimulation therapy (FEST) has demonstrated potential in this regard. This study ai...
A weakly supervised deep learning model integrating noncontrasted computed tomography images and clinical factors facilitates haemorrhagic transformation prediction after intravenous thrombolysis in acute ischaemic stroke patients
Haemorrhage transformation (HT) is a serious complication of intravenous thrombolysis (IVT) in acute ischaemic stroke (AIS). Accurate and timely prediction of the risk of HT before IVT may change the treatment...
RAGE plays key role in diabetic retinopathy: a review
RAGE is a multiligand receptor for the immunoglobulin superfamily of cell surface molecules and is expressed in Müller cells, vascular endothelial cells, nerve cells and RPE cells of the retina. Diabetic retin...
Assessment of the functional severity of coronary lesions from optical coherence tomography based on ensembled learning
Atherosclerosis is one of the most frequent cardiovascular diseases. The dilemma faced by physicians is whether to treat or postpone the revascularization of lesions that fall within the intermediate range giv...
Artificial intelligence in glaucoma: opportunities, challenges, and future directions
Artificial intelligence (AI) has shown excellent diagnostic performance in detecting various complex problems related to many areas of healthcare including ophthalmology. AI diagnostic systems developed from f...
Radiotranscriptomics of non-small cell lung carcinoma for assessing high-level clinical outcomes using a machine learning-derived multi-modal signature
Multi-omics research has the potential to holistically capture intra-tumor variability, thereby improving therapeutic decisions by incorporating the key principles of precision medicine. The purpose of this st...
Wireless capsule endoscopy multiclass classification using three-dimensional deep convolutional neural network model
Wireless capsule endoscopy (WCE) is a patient-friendly and non-invasive technology that scans the whole of the gastrointestinal tract, including difficult-to-access regions like the small bowel. Major drawback...
Prediction of non-perfusion volume ratio for uterine fibroids treated with ultrasound-guided high-intensity focused ultrasound based on MRI radiomics combined with clinical parameters
Prediction of non-perfusion volume ratio (NPVR) is critical in selecting patients with uterine fibroids who will potentially benefit from ultrasound-guided high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) treatment, a...
Comparison of plugin and redundant marker sets to analyze gait kinematics between different populations
Gait model consists of a marker set and a segment pose estimation algorithm. Plugin marker set and inverse kinematic algorithm (IK.) are prevalent in gait analysis, especially musculoskeletal motion analysis. ...
Effects of vibration therapy for post-stroke spasticity: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
The efficacy of vibration therapy (VT) in people with post-stroke spasticity (PSS) remains uncertain. This study aims to conduct a comprehensive meta-analysis to assess the effectiveness of VT in PSS.
Evaluating the ability of a predictive vision-based machine learning model to measure changes in gait in response to medication and DBS within individuals with Parkinson’s disease
Gait impairments in Parkinson’s disease (PD) are treated with dopaminergic medication or deep-brain stimulation (DBS), although the magnitude of the response is variable between individuals. Computer vision-ba...
Bactericidal effect of low-temperature atmospheric plasma against the Shigella flexneri
Shigella flexneri ( S. flexneri ) is a common intestinal pathogenic bacteria that mainly causes bacillary dysentery, especially in low socioeconomic countries. This study aimed to apply cold atmospheric plasma (CAP...
Selective peripheral nerve recording using simulated human median nerve activity and convolutional neural networks
It is difficult to create intuitive methods of controlling prosthetic limbs, often resulting in abandonment. Peripheral nerve interfaces can be used to convert motor intent into commands to a prosthesis. The E...
- Editorial Board
- Manuscript editing services
- Instructions for Editors
- Sign up for article alerts and news from this journal
- ISSN: 1475-925X (electronic)
BioMedical Engineering OnLine
ISSN: 1475-925X
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
Journal of Biological Engineering

Call for new submissions to our emerging leaders collection
Journal of Biological Engineering invites submissions from emerging leaders in biological engineering to contribute to our special collection. Launched in 2018, this collection has re-opened for new submissions, subject to editorial approval. Read more .
- Most accessed
- Collections
3D-printed nanohydroxyapatite/methylacrylylated silk fibroin scaffold for repairing rat skull defects
Authors: Wu Huiwen, Liang Shuai, Xie Jia, Deng Shihao, Wei Kun, Yang Runhuai, Qian Haisheng and Li Jun
Construction and applications of the EOMA spheroid model of Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma
Authors: Yanan Li, Xinglong Zhu, Li Li, Chunjuan Bao, Qin Liu, Ning zhang, Ziyan He, Yi Ji and Ji Bao
Structural and practical identifiability analysis in bioengineering: a beginner’s guide
Authors: Linda Wanika, Joseph R. Egan, Nivedhitha Swaminathan, Carlos A. Duran-Villalobos, Juergen Branke, Stephen Goldrick and Mike Chappell
An innovative lab-scale production for a novel therapeutic DNA vaccine candidate against rheumatoid arthritis
Authors: Juan Long, Xiao Zhao, Fei Liang, Yang Zeng, Nan Liu, Yuying Sun and Yongzhi Xi
Chitosan as a promising materials for the construction of nanocarriers for diabetic retinopathy: an updated review
Authors: Yan Lv, Chenglei Zhai, Gang Sun and Yangfang He
Most recent articles RSS
View all articles
Recent advances in 3D printing of biomaterials
Authors: Helena N Chia and Benjamin M Wu
Efficient extraction method to collect sugar from sweet sorghum
Authors: Fei Jia, Jeerwan Chawhuaymak, Mark R Riley, Werner Zimmt and Kimberly L Ogden
Solving a Hamiltonian Path Problem with a bacterial computer
Authors: Jordan Baumgardner, Karen Acker, Oyinade Adefuye, Samuel Thomas Crowley, Will DeLoache, James O Dickson, Lane Heard, Andrew T Martens, Nickolaus Morton, Michelle Ritter, Amber Shoecraft, Jessica Treece, Matthew Unzicker, Amanda Valencia, Mike Waters, AMalcolm Campbell…
Engineering BioBrick vectors from BioBrick parts
Authors: Reshma P Shetty, Drew Endy and Thomas F Knight Jr
Engineering bacteria to solve the Burnt Pancake Problem
Authors: Karmella A Haynes, Marian L Broderick, Adam D Brown, Trevor L Butner, James O Dickson, W Lance Harden, Lane H Heard, Eric L Jessen, Kelly J Malloy, Brad J Ogden, Sabriya Rosemond, Samantha Simpson, Erin Zwack, A Malcolm Campbell, Todd T Eckdahl, Laurie J Heyer…
Most accessed articles RSS
Thematic series Biological Engineering Research in South Korea Edited by Jeong-Yeol Yoon
Thematic series Emerging leaders in biological engineering Edited by Raj R Rao
Thematic series Stem cell engineering and regenerative medicine Edited by Raj R Rao
Thematic series Convergence of biosensors and technologies Edited by Jeong-Yeol Yoon
Thematic series Emerging biomaterials for translational medicine Edited by Jeong-Yeol Yoon
Announcing the launch of In Review
Journal of Biological Engineering , in partnership with Research Square, is now offering In Review . Authors choosing this free optional service will be able to:
- Share their work with fellow researchers to read, comment on, and cite even before publication
- Showcase their work to funders and others with a citable DOI while it is still under review
- Track their manuscript - including seeing when reviewers are invited, and when reports are received
Aims and scope
Biological engineering is an emerging discipline that encompasses engineering theory and practice connected to and derived from the science of biology, just as mechanical engineering and electrical engineering are rooted in physics and chemical engineering in chemistry. Topical areas include, but are not limited to:
- Synthetic biology and cellular design
- Biomolecular, cellular and tissue engineering
- Bioproduction and metabolic engineering
- Ecological and environmental engineering
- Biological engineering education and the biodesign process
As the official journal of the Institute of Biological Engineering , Journal of Biological Engineering provides a home for all research on the continuum of biological information science, molecules and cells, product formation, wastes and remediation, and educational advances in curriculum content and pedagogy at the undergraduate and graduate-levels.
Manuscripts should explore commonalities with other fields of application by providing some discussion of the broader context of the work and how it connects to other areas within the field.
Featured collection: Biological Engineering Research in South Korea
We believe that Journal of Biological Engineering is moving on a positive trajectory towards world-class journal in biological engineering. To better showcase this positive trend, we are initiating the region-specific thematic series focused on specific country or region. Our first country/region is South Korea. The number of JBE articles from South Korea has steadily increased in recent years and we would like to see a higher number of top-quality contributions from this country. Read more .

About the Society
The Institute of Biological Engineering (IBE) is a professional organization which encourages inquiry and interest in biological engineering. IBE supports advances in our understanding of biological engineering across education, research, industry, government and the public. Through publications, meetings, and distribution of information and services, IBE encourages cooperation and collaboration between biological engineers, and the dissemination of knowledge in the field.
Do you have an idea for a thematic series? Let us know!
About the editors.


Official journal of

Journal of Biological Engineering is affiliated with the Institute of Biological Engineering (IBE). Join the IBE.
Annual Journal Metrics
2022 Citation Impact 5.6 - 2-year Impact Factor 5.5 - 5-year Impact Factor 1.173 - SNIP (Source Normalized Impact per Paper) 0.851 - SJR (SCImago Journal Rank)
2023 Speed 9 days submission to first editorial decision for all manuscripts (Median) 99 days submission to accept (Median)
2023 Usage 612,507 downloads 417 Altmetric mentions
- More about our metrics
ISSN: 1754-1611
- General enquiries: [email protected]
biomedical engineering Recently Published Documents
Total documents.
- Latest Documents
- Most Cited Documents
- Contributed Authors
- Related Sources
- Related Keywords
Ophthalmological instruments of Al-Halabi fill in a gap in the biomedical engineering history
Virus-like particles: revolutionary platforms for developing vaccines against emerging infectious diseases.
Virus-like particles (VLPs) are nanostructures that possess diverse applications in therapeutics, immunization, and diagnostics. With the recent advancements in biomedical engineering technologies, commercially available VLP-based vaccines are being extensively used to combat infectious diseases, whereas many more are in different stages of development in clinical studies. Because of their desired characteristics in terms of efficacy, safety, and diversity, VLP-based approaches might become more recurrent in the years to come. However, some production and fabrication challenges must be addressed before VLP-based approaches can be widely used in therapeutics. This review offers insight into the recent VLP-based vaccines development, with an emphasis on their characteristics, expression systems, and potential applicability as ideal candidates to combat emerging virulent pathogens. Finally, the potential of VLP-based vaccine as viable and efficient immunizing agents to induce immunity against virulent infectious agents, including, SARS-CoV-2 and protein nanoparticle-based vaccines has been elaborated. Thus, VLP vaccines may serve as an effective alternative to conventional vaccine strategies in combating emerging infectious diseases.
Biomedical Engineering Technologies
Biocybernetics and biomedical engineering – current trends and challenges, deep learning models principles applied to biomedical engineering, deep learning models evolution applied to biomedical engineering, ieee transactions on biomedical engineering (t-bme), biomedical engineering and occupational therapy approach in technologies for enhancement human labor and defense abilities, artificial intelligence models applied to biomedical engineering, introduction to cognitive science, cognitive computing, and human cognitive relation to help in the solution of artificial intelligence biomedical engineering problems, export citation format, share document.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- BMC Biomed Eng

BMC Biomedical Engineering: a home for all biomedical engineering research
Alexandros houssein.
1 Springer Nature, 4 Crinan Street, London, N1 9XW UK
Alan Kawarai Lefor
2 Department of Surgery, Jichi Medical University, Shimotsuke, Tochigi Japan
Antonio Veloso
3 Laboratory of Biomechanics and Functional Morphology, Faculty of Human Kinetics, Lisbon, Portugal
4 Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN USA
Jong Chul Ye
5 Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Daejeon, Republic of Korea
Dimitrios I. Zeugolis
6 Regenerative, Modular and Developmental Engineering Laboratory (REMODEL), Biomedical Sciences Building, National University of Ireland Galway (NUI Galway), Galway, Ireland
Sang Yup Lee
7 Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Daejeon, Republic of Korea
Associated Data
Not applicable.
This editorial accompanies the launch of BMC Biomedical Engineering , a new open access, peer-reviewed journal within the BMC series, which seeks to publish articles on all aspects of biomedical engineering. As one of the first engineering journals within the BMC series portfolio, it will support and complement existing biomedical communities, but at the same time, it will provide an open access home for engineering research. By publishing original research, methodology, database, software and review articles, BMC Biomedical Engineering will disseminate quality research, with a focus on studies that further the understanding of human disease and that contribute towards the improvement of human health.
Introduction
Biomedical engineering is a multidisciplinary field that integrates principles from engineering, physical sciences, mathematics and informatics for the study of biology and medicine, with the ultimate goal of improving human health and quality of life.
Biomedical engineering is not a new concept; however, it was not until the 1900s when rapid technological advancements in the chemical, physical and life sciences influenced breakthroughs in the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of disease. The invention of the electrocardiograph, the concept of x-ray imaging, the electron microscope, the mechanical heart valve and human genome sequencing, are just a few examples of technological innovations that revolutionised science and medicine and changed the approach to human healthcare. Current biomedical engineering technologies are a growing part of clinical decision making, which can now be influenced from multiscale observations, ranging from the nano to the macro-scale.
Today, the need for innovation in health technologies is ever more prominent. The annual global healthcare spending has seen continued growth and is projected to reach a staggering $8.7 trillion by 2020 [ 1 ]. Global health challenges are becoming more complex, wide spread and difficult to control. Resources are scarce and with a growing population, our society has a need for affordable, portable and sustainable solutions. The World Health Organisation has pledged to make a billion lives healthier by 2023 [ 2 ], a goal that will require widespread commitment by governments, funding agencies, researchers and clinicians. Biomedical engineers will be at the heart of this movement and face a responsibility for continuous innovation. Biomedical engineering research is expected to create health technologies that will drastically improve the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of disease, as well as patient rehabilitation. As an example, the NIH 2016–2020 strategic plan focuses on point of care and precision medicine technologies including genetic engineering, microfluidics, nanomedicine, imaging, digital/mobile-Health and big data [ 3 ].
BMC Biomedical Engineering will strive to complement these efforts and provide an open access venue for the dissemination of all biomedical engineering research. As part of the BMC series, a portfolio of journals serving communities across all sciences, the Journal will act as a resource for a wide range of disciplines. It aims to support scientists, engineers and clinicians by making their research openly and permanently available, irrespective of their location or affiliation.
Aims and scope
BMC Biomedical Engineering considers articles on all aspects of biomedical engineering, including fundamental, translational and clinical research. It combines tools and methods from biology and medicine with mathematics, physical sciences and engineering towards the understanding of human biology and disease and the improvement of human health. The Journal will publish a range of article types, including research, methodology, software, database and review articles.
As part of the BMC series, a collection of open access, peer-reviewed and community focused journals covering all areas of science, editorial decisions will not be made on the basis of the interest of a study or its likely impact. Studies must be scientifically valid. For research articles this includes a scientifically sound research question, the use of suitable methods and analysis, and following community-agreed standards relevant to the research field.
BMC Biomedical Engineering aims to publish work that undergoes a thorough peer review process by appropriate peer-reviewers and is deemed to be a coherent and valid addition to the scientific knowledge. It aims to provide an open access venue which allows for immediate and effective dissemination of research and enables our readers to explore and understand the latest developments, trends and practices in biomedical engineering. We believe that open access and the Creative Commons Attribution License [ 4 ] are essential to this, allowing universal and free access to all articles published in the Journal and allowing them to be read and the data re-used without restrictions. BMC Biomedical Engineering will work closely with the rest of the journals in the BMC series portfolio [ 5 ] to help authors find the right home for their research. We will highlight selected journal content through various promotional channels to ensure the research reaches its target audience and receives the attention it deserves.
Editorial sections
Many new technologies that have revolutionised biomedical engineering require the coalition of previously independent communities. 3D bioprinting of tissues and organs brings together methods from cell biology, biomaterials, nanotechnology and engineering and is being used for the transplantation of tissues, including skin, bone, muscle, soft tissue, cartilage and others [ 6 , 7 ]. The concept of tissue and disease modelling is being driven towards drug discovery and toxicology studies, aiming to increase the yield of drug testing by tackling limitations of current cell and animal models [ 8 ].
New approaches in natural and synthetic biomaterials have redefined bioelectronics. Silk fibroins and other unconventional interfaces can form flexible electronics and challenge the use of silicon-based technologies. For biomedical applications, these new approaches present advantages not only due to their biocompatibility and low cost, but also for their electromechanical and optical virtues [ 9 ]. Implantable probes are being redesigned so that they facilitate long term stability and high resolution, without perturbing the biological system or creating an immune response. Such technologies are now able to facilitate recordings of single neurons in vivo, in a chronically stable manner, with applications to the restoration of vision and retinal prosthetics [ 10 ].
For many years biomedical imaging has been connecting microscopic discoveries with macroscopic observations. Photoacoustic tomography (PAT) is now able to image large spatial scales, from organelles to small animals, at very high speeds [ 11 ]. In fact, single-shot real-time imaging can operate at 10 trillion frames per second and is finding applications in breast cancer diagnosis [ 12 , 13 ].
In the field of medical robotics, new approaches combine machine learning and artificial intelligence to strengthen the clinician’s decision making. Others are leveraging augmented reality (AR) to facilitate better immersion and more natural surgical workflows for computer assisted orthopaedic surgery [ 14 ].
BMC Biomedical Engineering celebrates the interdisciplinary nature of the field. In order to navigate the wide range of biomedical engineering research, the Journal is structured in six editorial sections.
- Biomaterials, nanomedicine and tissue engineering
- Medical technologies, robotics and rehabilitation engineering
- Biosensors and bioelectronics
- Computational and systems biology
- Biomechanics
- Biomedical Imaging
We are delighted to welcome our founding Section Editors along with a growing international group of Editorial board Members [ 15 , 16 ]. The Journal is supported by an expert Editorial Advisory group of senior engineers and scientists, which is chaired by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee. Together with the in-house Editor, this group will provide academic leadership and expertise and will work together to transverse into multiple clinical and engineering disciplines. The Editorial Board will keep growing and developing to reflect and adapt to the nature of this diverse community.
Biomaterials, nanomedicine and tissue engineering section
This section primarily focuses on the development of biofunctional tissue substitutes, which possess the highest level of biomimicry, through recapitulation of nature’s innate sophistication and thorough processes. It considers research, methods, clinical trials, leading opinion and review articles on the development, characterisation and application of nano- and micro- biofunctional biomaterials, cell-assembled tissue substitutes, diagnostic tools, microfluidic devices and drug/gene discovery and delivery methods. Manuscripts focusing on permanently differentiated, engineered and stem cell biology and application are welcome. This section will place a substantial focus on clinical translation and technologies that advance the current status-quo. As such, articles that enhance the scalability and robustness of tissue engineering methodologies, or that enable new and improved industrial or clinical applications of biomedical engineering discoveries, tools and technologies are strongly encouraged.
Medical technologies, robotics and rehabilitation engineering section
This section seeks to represent research in engineering that encompasses a wide range of interests across medical specialties, including orthopaedic, cardiovascular, musculoskeletal, craniofacial, neurological, urologic and other medical technologies. It will consider research on medical robotics, computer assisted technologies, medical devices, e/m-health and other medical instrumentation. It aims to improve the prevention, diagnosis, intervention and treatment of injury or disease and it welcomes articles that represent new approaches to engineering that may be useful in the care of patients. Technical and practical aspects of rehabilitation engineering, from concept to clinic and papers on improving the quality of life of patients with a disability are encouraged. The section also seeks to represent clinically important research that is based on new and emerging technologies. This could include clinical studies of new approaches to robotic-assisted surgery, clinical studies of new devices, or other studies that are close to patient care or rehabilitation.
Biosensors and bioelectronics section
This section considers articles on the theory, design, development and application on all aspects of biosensing and bioelectronics technologies. The section will consider approaches that combine biology and medicine with sensing and circuits and systems technologies on a wide variety of subjects, including lab-on-chips, microfluidic devices, biosensor interfaces, DNA chips and bioinstrumentation. It also considers articles on the development of computational algorithms (such as deep learning, reinforcement learning, etc.) that interpret the acquired signals, hardware acceleration and implementation of the algorithms, brain-inspired or brain-like computational schemes, and bioelectronics technologies that can have a wide impact in the research and clinical community. Articles on implantable and wearable electronics, low-power, wireless and miniaturised imaging systems, organic semiconductors, smart sensors and neuromorphic circuits and systems are strongly encouraged.
Computational and systems biology section
Computational, integrative and systemic approaches are at the heart of biomedical engineering. This section considers papers on all aspects of mathematical, computational, systems and synthetic biology that result in the improvement of patient health. Integrative and multi-scale approaches, in the network and mechanism-based definition of injury and disease, or its prevention, diagnosis and treatment are welcome. Papers on high precision, interactive and personalised medicine, on digital/mobile health, on complex/big data analytics and machine learning, or on systemic and informatics approaches in a healthcare or clinical setting are encouraged.
Biomechanics section
This section represents the interdisciplinary field of biomechanics and investigates the relationship of structure with function in biological systems from the micro- to the macro- world. It considers papers on all aspects of analytical and applied biomechanics at all scales of observation, that improve the diagnosis, therapy and rehabilitation of patients or that advance their kinetic performance. The topics of interest range from mechanobiology and cell biomechanics to clinical biomechanics, orthopaedic biomechanics and human kinetics. Articles on the mechanics and wear of bones and joints, artificial prostheses, body-device interaction, musculoskeletal modelling biomechanics and solid/fluid computational approaches are strongly encouraged.
Biomedical imaging section
Biomedical imaging has been connecting microscopic discoveries with macroscopic observations for the diagnosis and treatment of disease and has seen considerable advances in recent years. This section will consider articles on all biomedical imaging modalities including medical imaging (MRI, CT, PET, ultrasound, x-ray, EEG/MEG), bio-imaging (microscopy, optical imaging) and neuroimaging across all scales of observation. Its primary focus will be to foster integrative approaches that combine techniques in biology, medicine, mathematics, computation, hardware development and image processing. Articles on new methodologies or on technical perspectives involving novel imaging concepts and reconstruction methods, machine learning, sparse sampling and statistical analysis tool development are encouraged.
The motivation for the launch of BMC Biomedical Engineering is to create an authoritative, unbiased and community-focused open access journal. We are committed to working together with our authors, editors and reviewers to provide an inclusive platform for the publication of high-quality manuscripts that span all aspects of biomedical engineering research. We welcome articles from all over the world and we will devote our efforts to ensure a robust and fair peer-review process for all. We believe in continuous improvement and we encourage the community to get in touch with us to provide ideas and feedback on how to improve the Journal and serve the community better.
We hope you will find the first group of articles an interesting and valuable read, and we look forward to working with you all to disseminate research into the exciting field of biomedical engineering.
Acknowledgements
Availability of data and materials, abbreviations, authors’ contributions.
AH wrote the introduction, aims and scope and conclusion. AH, AKL, AV, ZY, JCY, DIZ and SYL wrote the editorial sections. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Consent for publication, competing interests.
AH is the Editor of BMC Biomedical Engineering and an employee of Springer Nature. AL, AV, ZY, JY, DZ and SL are members of the Editorial Board of BMC Biomedical Engineering .
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Help | Advanced Search
Electrical Engineering and Systems Science > Image and Video Processing
Title: annotated biomedical video generation using denoising diffusion probabilistic models and flow fields.
Abstract: The segmentation and tracking of living cells play a vital role within the biomedical domain, particularly in cancer research, drug development, and developmental biology. These are usually tedious and time-consuming tasks that are traditionally done by biomedical experts. Recently, to automatize these processes, deep learning based segmentation and tracking methods have been proposed. These methods require large-scale datasets and their full potential is constrained by the scarcity of annotated data in the biomedical imaging domain. To address this limitation, we propose Biomedical Video Diffusion Model (BVDM), capable of generating realistic-looking synthetic microscopy videos. Trained only on a single real video, BVDM can generate videos of arbitrary length with pixel-level annotations that can be used for training data-hungry models. It is composed of a denoising diffusion probabilistic model (DDPM) generating high-fidelity synthetic cell microscopy images and a flow prediction model (FPM) predicting the non-rigid transformation between consecutive video frames. During inference, initially, the DDPM imposes realistic cell textures on synthetic cell masks which are generated based on real data statistics. The flow prediction model predicts the flow field between consecutive masks and applies that to the DDPM output from the previous time frame to create the next one while keeping temporal consistency. BVDM outperforms state-of-the-art synthetic live cell microscopy video generation models. Furthermore, we demonstrate that a sufficiently large synthetic dataset enhances the performance of cell segmentation and tracking models compared to using a limited amount of available real data.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- HTML (experimental)
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
Biomedical Engineering
- Most Cited Papers
- Most Downloaded Papers
- Newest Papers
- Save to Library
- Last »
- Tissue Engineering Follow Following
- Biomaterials Follow Following
- Medical Imaging Follow Following
- Biomechanics Follow Following
- Biomedical signal and image processing Follow Following
- Electronics and biomedical engineering Follow Following
- Bioengineering Follow Following
- Medical Image Processing Follow Following
- Image Processing Follow Following
- Microfluidics Follow Following
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- Academia.edu Publishing
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

How To Become a Biomedical Engineer

Industry Advice Engineering
Modern advances in medical technology have drastically improved the quality of care doctors are able to provide to patients. From diagnosis to treatment, biomedical devices continue to play a critical role in improving human health. Much of the credit for the development of these advanced technologies goes to biomedical engineers.
Here’s an overview of what a biomedical engineer does, how to become one, and why it’s an excellent career choice.
What Is Biomedical Engineering?
Biomedical engineering is a multidisciplinary field that applies engineering principles and techniques to biology and healthcare. It requires an in-depth understanding of life-science subjects such as biology, chemistry, and physics, as well as engineering knowledge in mathematics and design.
What Do Biomedical Engineers Do?
Biomedical engineers are tasked with a wide range of responsibilities depending on their industry. Common roles include:
- Designing medical devices: Developing medical imaging devices like MRIs, sonograms, ultrasound devices, and other medical technology
- Developing new innovations: Researching and contributing to the development of innovative medical advancements such as artificial organs, or replacement of body parts
- Collaborating with medical staff: Training other professionals on safety and the proper use of biomedical equipment, helping maintain medical devices, and troubleshooting medical equipment when necessary
- Research: Conducting statistical analysis, writing research papers, and offering valuable contributions to the overall scientific community on biomedical engineering methods and results
Biomedical engineers typically work behind the scenes and don’t have much interaction with patients. However, their work plays a critical role in patient recovery or improved quality of life. For this reason, many individuals are motivated to pursue a career as a biomedical engineer.
How to Become a Biomedical Engineer
For individuals interested in biological sciences, mathematics, engineering, and other related sub-disciplines, a position in biotechnology is the perfect career path. The steps to become a biomedical engineer are:
- Fulfill the educational requirements
- Obtain relevant experience
- Develop in-demand skills
- Obtain relevant qualifications, if required by employers
Educational Requirements
The first step to becoming a biomedical engineer is fulfilling the educational requirements of the role. Biomedical engineers typically need at least a bachelor’s in life sciences, biotechnology, or engineering. Many, however, continue their education by pursuing a graduate or doctoral degree as well. According to government data, almost 71 percent of biomedical engineers have a bachelor’s degree; of those, 42 percent also hold a master’s, and 14 percent earned a doctoral or professional degree.

Background Experience
Experience is an important aspect of any professional job posting. Many times employers want to know if applicants have been successful performing job responsibilities in other settings. According to government data, the largest percentage of experience requirements for biomedical engineer job postings is between four and six years of prior experience, comprising 31 percent of job postings. Only 18 percent of postings require one year of experience or less.
Since this industry values prior work experience, prospective biomedical engineers hoping to obtain relevant, hands-on experience, can greatly benefit from a program like the Master of Science in Biotechnology . These programs are designed specifically to prepare students for the workforce, presenting them with opportunities to collaborate with industry professionals and work with real-world projects.
In-Demand Skills
In addition to the experience and educational requirements, prospective biomedical engineers can set themselves apart from competing applicants by developing in-demand skills employers frequently look for.
Specialized Skills
Specialized, or “hard” skills, refer to job-specific skills required to achieve success in a biomedical engineering position. The top hard skills employers list on biomedical engineering job postings are:
- Biomedical Engineering
- Medical Devices
- Electrical Engineering

Common Skills
Common, or “soft” skills, are the personal attributes required for biomedical engineers to succeed in their position. These skills aren’t job-specific, but often promote success in interpersonal interactions with team members, or in rare cases, patients. The most commonly listed soft skills in job postings are:
- Communications
- Troubleshooting (Problem Solving)

Top Qualifications
On top of any specialized skills specific to the industry, some biomedical engineering positions require certain credentials and certifications. Many of these certifications are job or industry specific, so you don’t need to pursue them unless you know they’re necessary. Nevertheless, it’s good to be aware that some jobs may require these credentials. According to a government report, some of the credentials listed in biomedical engineering job postings include:
- Engineer in Training (EIT)/Professional Engineer (PE): The EIT and PE certifications demonstrate a proficiency in the engineering field. Some positions give preference to applicants with these credentials, but in most cases biomedical engineers, particularly entry-level, don’t need this certification.
- Security Clearance: Some government positions require security clearance due to the sensitive nature of the position, but it’s not a typical requirement for biomedical engineering positions.
Jared Auclair , associate dean of the Professional Program and Graduate Affairs in the College of Science at Northeastern, recommends that prospective biomedical engineers not worry about these qualifications unless employers require them. “I wouldn’t pursue [these credentials] before I had a job,” he explains. “I would wait to see what was required for me to do that job, and then I would find a way to get those credentials, post-employment.”
Why Should You Consider Biomedical Engineering?
Biomedical engineering is a challenging career, but a rewarding one. A biomedical career typically offers several benefits, including a high average salary, job growth, and opportunities to make a difference.
High Average Salary
Biomedical engineers can obtain a wide range of salaries spanning from $24,000 to $160,000, depending on seniority, education, background, and whether the role is part time or full time. However, according to government data, the median salary of biomedical engineers is approximately $83,800 per year.

A relevant master’s degree can increase your earning potential. According to Auclair, “With a master’s degree, you can advance quickly and pretty far in a company, and the jobs pay pretty well.”
Additional data confirms that job postings requiring a master’s degree advertise a salary approximately 14 percent higher than those requiring a bachelor’s. Master’s-level biomedical engineers earn a median annual salary of nearly $95,000. Conversely, postings that require a bachelor’s degree advertise a median salary of $83,300 per year, and of those postings, 60 percent still prefer graduate-level applicants.
Growth Opportunities
Biomedical engineering is one of the most in-demand careers in the biotechnology industry . In terms of job opportunities, biomedical engineers have many choices. The healthcare industry offers a wide range of jobs for prospective biomedical engineers, including working in medical imaging, pharmaceuticals, neural engineering, mechanical engineering, and a variety of other options. Biomedical engineers can also advance their careers to management positions.
Make a Meaningful Difference
Healthcare professionals who take more of a hands-on role in patient care often receive the credit for patient recovery. While this credit is definitely well-deserved, they wouldn’t be able to provide the same quality of care without the work of biomedical engineers. The reality is that although biomedical engineers operate behind the scenes, they play an essential role in the healthcare industry.
One of biomedical engineers’ primary objectives is to improve patients’ quality of life by applying their engineering problem-solving skills to the medical field. They’re able to make a meaningful difference in others’ lives by increasing the efficiency of medical procedures through innovative technologies, or easing the diagnosis process for medical professionals by improving diagnostic technology. Individuals who are motivated to improve others’ quality of life will likely find biotechnology a rewarding career.
Take the Next Step Toward a Meaningful Career
For many, biomedical engineering is an appealing career. However, the educational requirements for higher-paying positions can be daunting. Auclair assures prospective students that pursuing an advanced degree in biotechnology is “definitely worth the investment, especially in the experiential master’s space.”
If you’re interested in developing the skills required to succeed in the biotechnology industry, consider applying for Northeastern’s Master of Science in Biotechnology program to expedite your biomedical engineering career and obtain valuable, real-world experience and in-demand skills.
Subscribe below to receive future content from the Graduate Programs Blog.
About michael boyles, related articles.
11 Data Science Careers Shaping Our Future

How Data Science is Disrupting Supply Chain Management

What Does a Data Scientist Do?
Did you know.
Advanced degree holders earn a salary an average 25% higher than bachelor's degree holders. (Economic Policy Institute, 2021)
Northeastern University Graduate Programs
Explore our 200+ industry-aligned graduate degree and certificate programs.
Most Popular:
Tips for taking online classes: 8 strategies for success, public health careers: what can you do with an mph, 7 international business careers that are in high demand, edd vs. phd in education: what’s the difference, 7 must-have skills for data analysts, in-demand biotechnology careers shaping our future, the benefits of online learning: 8 advantages of online degrees, how to write a statement of purpose for graduate school, the best of our graduate blog—right to your inbox.
Stay up to date on our latest posts and university events. Plus receive relevant career tips and grad school advice.
By providing us with your email, you agree to the terms of our Privacy Policy and Terms of Service.
Keep Reading:

The 8 Highest-Paying Master’s Degrees in 2024

Graduate School Application Tips & Advice

How To Get a Job in Emergency Management

Join Us at Northeastern’s Virtual Graduate Open House | March 5–7, 2024
- Browse Works
- Engineering
- Biomedical Engineering
Biomedical Engineering Research Papers/Topics
Sweat sensors in the smart wearables era - a review.
In recent years, there has been significant interest in developing wearable devices to mimic the integrated sensing of life forms, which enhances their performance and survival capabilities. Progress in the development of physical sensors and wearable electronics has been promising, leading to numerous consumer products that measure activity, posture, heart rate, respiration rate, and blood oxygen level. Despite the challenges in retrieving and processing bodily fluids, wearable chemical sens...
Effect of Magnetic field on Micro-organisms
This study uses the model organism, C. elegans, to investigate its sensitivity and response to static magnetic fields. Wild-type C. elegans are put into microfluidic channels and exposed to permanent magnets for five cycles of thirty-second time intervals at field strengths ranging from 5 milli Tesla to 120 milli Tesla. Recorded and analyzed with custom software, the results of the worm's movement - the average velocity, turning and curling percentage - were compared to control experiments...
Worm Egg Counting using Machine learning
To evaluate the level of infestation of the soybean cyst nematode (SCN), Heterodera glycines, in the field, egg population densities are determined from soil samples. Sucrose centrifugation is a common technique for separating debris from the extracted SCN eggs. We have developed a procedure, however, that employs OptiPrep as a density gradient medium, with improved extraction and recovery of the eggs compared to the sucrose centrifugation technique. Also, we have built computerized methods t...
Paralysis modes of worms in drugs
The emergence of new drugs is often driven by the escalating resistance of parasites to existing drugs and the accessibility of more advanced technology platforms. Microfluidic devices have allowed for quicker testing of compounds, regulated sampling/sorting of entire animals, and automated behavioral pattern detection. In the majority of microfluidic devices, the effects of drugs on small animals (e.g. Caenorhabditis elegans)elegant are quantified by an endpoint, dose response curve that sho...
Modes of paralysis of worms in anthelmintic drugs
Microfluidic chip for culturing gene-edited bacteria.
By utilizing a low-cost engineering tool, we have created a microfluidic platform to study bacteria at the single cell level, allowing us to unlock insights into microbial physiology and genetics that would otherwise not be possible. The platform is composed of 3D devices made of adhesive tapes, an agarose membrane as the resting substrate, a temperature-controlled environmental chamber, and an autofocusing module. With this technology, we have been able to observe Escherichia coli morphologi...
Wearable devices at Work
The effects of the workplace on the safety, health, and productivity of personnel can be seen at various levels. To protect and boost general worker health, innovative hardware and software tools have been developed for the detection, elimination, substitution, and regulation of occupational hazards. Wearable technologies make it possible for constant tracking of workers and their environment, whereas connected worker solutions provide contextual information and support for decision-making. H...
Video Capsule Endoscopy : A Review of Technologies
In this review, we focus on the hardware and software technologies used for the purpose of gastrointestinal tract monitoring in a safe and comfortable manner. We review the FDA guidelines for ingestible wireless telemetric medical devices, and the features incorporated in capsule systems such as microrobotics, closed-loop feedback, physiological sensing, nerve stimulation, sampling and delivery, panoramic imaging and rapid reading software. Both experimental and commercialized capsule systems...
Animal Behavior Sensing Electronics
We propose a remote monitoring device for measuring behavioral indicators like posture, gait, vocalization, and external temperature which can help in evaluating the health and welfare of pigs. The multiparameter electronic sensor board was tested in a laboratory and on animals. Machine learning algorithms and decision support tools can be used to detect lameness, lethargy, pain, injury, and distress. The roadmap for technology adoption, potential benefits, and further challenges are discusse...
Electrical field effects on micro-organisms
We present the NERV, a nonmechanical, unidirectional valve, to control the locomotion of Caenorhabditis elegant (C. elegans) in microfluidic devices. This valve is created by establishing a region of lateral electric field which can be toggled between on and off states. We observed that C. elegans do not prefer to advance into this region when the field lines are facing their movement, so when they reach the boundary of the NERV, they partway enter the field, retreat, and switch direction. We...
Anthelmintic resistance in nematodes
It is becoming more essential to identify and recognize the phenotypes of anti-parasitic drug-resistant isolates. Current molecular methods of doing so are restricted. In this paper, we showcase a microfluidic bioassay to measure phenotype using parameters of nematode locomotion, using larvae of the animal parasite Oesophagostomum dentatum. Parameters of sinusoidal movement, including propagation speed, wavelength, wave amplitude, and oscillation frequency, were dependent on the levamisole-se...
Robotic Manipulator using an Inductive Sensor
This project involves the use of an inductive sensor to control a robotic arm system. The signals generated in the induction coil will help in controlling the manipulator to perform certain gripping and grabbing actions. Also, the report describes the method used to acquire and process these induced signals before they are sent (induced signals) to the manipulator through the help of two programmed microcontrollers.
A Hybrid Technique for Speckle Noise Reduction in ultrasound images
Abstract In the field of biomedical imaging, Ultrasound is an incontestable vital tool for diagnosis, it provides in non-invasive manner the internal structure of the body to detect eventually diseases or abnormalities tissues. These images are obtained with a simple linear or sector scan US probe, which show a granular appearance called speckle. . Unfortunately, the presence of speckle noise affects edges and fine details which limit the contrast resolution and make diagnostic more difficult...
Comparative Studies of Needle Free Injection Systems and Hypodermic Needle Injection: A Global Perspective
Needle-free injection (NFI) is a novel transdermal either intramuscularly or subcutaneously drug delivery system, where innovative ways to introduce a variety of medicines like as antibiotics, iron, or vaccines comfortably, accurately, easily and rapidly without, piercing the skin compared to traditional needle. While hypodermic needle is inject substances into body by intradermal, intramuscular, subcutaneous, intravenous, etc or extract fluids from the body body, for example taking blood fro...
Design and Implementation of a Mechanical Ventilator
Africa’s healthcare system is challenged by inadequate medical equipment, stemming from the fact that it does not manufacture its own medical devices but depends mostly on used medical equipment donations, many of which do not function and require extensive repairs. The World Health Organization estimates that 50 to 80 percent of medical equipment in developing countries are not working, therefore creating a barrier in the health system delivery of health services. Mechanical ventilators ...
Popular Papers/Topics
Study of blood glucose measurement based on blood resistivity, design for real time heart sounds recognition system, design of a hybrid artificial hip joint using finite element analysis, design of a programmed oxygen delivery system, early detection of stomach pain using reflexology, design of management programme for a clinical engineering department, adaptive techniques for cardiac arrhythmia detection by using artificial neural network, improvement u-net for mri brain tumour segmentation by searching for suitable activation function, a study of optical and thermal effectsof gold nanoparticles, noise reducing using hybrid technique in magnetic resonances image, central medical waste treatment facility, detection of breast cancer using artificial neural networks (ann), designing a tele-pediatric system based on the internet, short messages technique in health level 7(hl7), heart beat rate variability analysis using statistical methods.
Privacy Policy | Refund Policy | Terms | Copyright | © 2024, Afribary Limited. All rights reserved.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
Articles in 2024
A serine-conjugated butyrate prodrug with high oral bioavailability suppresses autoimmune arthritis and neuroinflammation in mice
The esterification of butyrate to serine makes for an odourless and tasteless oral prodrug that ameliorated disease severity and reduced inflammatory responses in mouse models of rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis.
- Erica Budina
- Jeffrey A. Hubbell
Mesenchymal stromal cells with chimaeric antigen receptors for enhanced immunosuppression
Antigen-specific immunosuppression can be enhanced by genetically modifying mesenchymal stromal cells with chimaeric antigen receptors, as shown for the treatment of graft-versus-host disease in mice.
- Olivia Sirpilla
- R. Leo Sakemura
- Saad S. Kenderian
Oncolytic mineralized bacteria as potent locally administered immunotherapeutics
Intratumourally administered bacteria coated with manganese dioxide modulate the immunosuppressive tumour microenvironment and potently activate antitumour immune responses, as shown in multiple solid tumours in small animals.
- Chenya Wang
- Liping Zhong
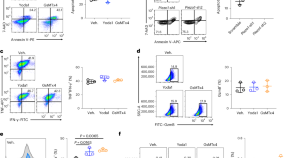
PIEZO1 mechanically regulates the antitumour cytotoxicity of T lymphocytes
Blocking the mechanical sensor PIEZO1 in cytotoxic T lymphocytes strengthens their traction forces and augments their cytotoxicity against tumour cells.
- Ruiyang Pang
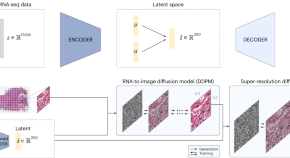
Generation of synthetic whole-slide image tiles of tumours from RNA-sequencing data via cascaded diffusion models
Cascaded diffusion models can be used to synthesize realistic whole-slide image tiles from latent representations of RNA-sequencing data from human tumours.
- Francisco Carrillo-Perez
- Marija Pizurica
- Olivier Gevaert
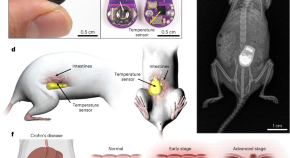
Miniaturized implantable temperature sensors for the long-term monitoring of chronic intestinal inflammation
Wireless miniaturized implantable temperature sensors enable real-time monitoring of the progression of inflammatory bowel diseases, as shown in a mouse model of Crohn’s-disease-like ileitis.
- Surabhi R. Madhvapathy
- Matthew I. Bury
- John A. Rogers
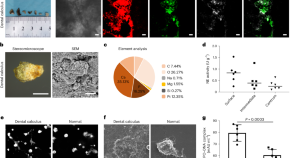
Bacteria-mediated resistance of neutrophil extracellular traps to enzymatic degradation drives the formation of dental calculi
The development of dental calculi involves bacteria in local mature biofilms converting the DNA in neutrophil extracellular traps from being degradable by the enzyme DNase I to being degradation resistant.
- Mei-chen Wan
In vivo affinity maturation of mouse B cells reprogrammed to express human antibodies
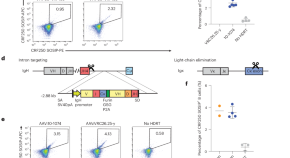
Mouse B cells can be reprogrammed via Cas12a to express human antibodies that when affinity-matured in recipient mice generate broader and more potent antibody variants.
- Michael Farzan
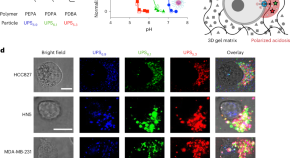
Severely polarized extracellular acidity around tumour cells
Hydronium ions bordering cancer cells are highly concentrated into a small extracellular region, and in tumour tissue such severely polarized acidity correlates with the expression of monocarboxylate transporters and with the exclusion of cytotoxic T cells.
- Zachary Bennett
- Jinming Gao
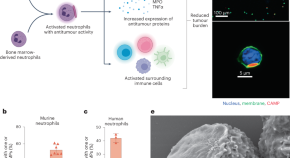
Neutrophils bearing adhesive polymer micropatches as a drug-free cancer immunotherapy
The intravenous injection of neutrophils bearing discoidal polymer microscale ‘patches’ on their surfaces reduces tumour burden in mice owing to the patch-induced polarization of the neutrophils towards an antitumour phenotype.
- Ninad Kumbhojkar
- Supriya Prakash
- Samir Mitragotri
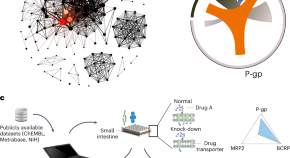
Screening oral drugs for their interactions with the intestinal transportome via porcine tissue explants and machine learning
A machine-learning model trained on interactions between oral drugs and intestinal drug transporters obtained by modulating their expression in intact porcine tissue can be used to predict drug–transporter and drug–drug interactions.
- Daniel Reker
- Giovanni Traverso
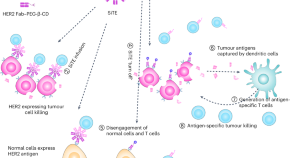
Small-molecule-mediated control of the anti-tumour activity and off-tumour toxicity of a supramolecular bispecific T cell engager
The off-tumour toxicity of a supramolecular bispecific T cell engager can be halted by disengaging T cells from the tumour cells via the disassembly of the supramolecular aggregate through the infusion of the small-molecule drug amantadine.
- Ningqiang Gong
- Xuexiang Han
- Michael J. Mitchell
Extracellular vesicles incorporating retrovirus-like capsids for the enhanced packaging and systemic delivery of mRNA into neurons
The delivery of mRNAs into neurons at inflammatory sites in vivo can be enhanced by engineering leucocytes to produce extracellular vesicles incorporating mRNA-packaging retrovirus-like capsids.
- Sijin Luozhong
- Shaoyi Jiang
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Cover design: Alex Wing. Nature Biomedical Engineering ( Nat. Biomed. Eng) ISSN 2157-846X (online) Nature Biomedical Engineering publishes original research, reviews and commentary of high ...
Research on Biomedical Engineering is an online, peer-reviewed journal dedicated to all fields of Biomedical Engineering. Multidisciplinary in nature, catering to readers and authors interested in developing tools based on engineering and physical sciences to solve biological and medical problems. Publishes Original Research Articles, Reviews ...
Biomedical engineering is a branch of engineering that applies principles and design concepts of engineering to healthcare. ... Research Highlights 27 Feb 2024 Nature Reviews Bioengineering ...
Biomedical Engineering. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering contains basic and applied papers dealing with biomedical engineering. Papers range from engineering development in methods and techniques with biomedical applications to experimental and clinical investigations with engineering contributions.
A comprehensive study of optic disc detection in artefact retinal images using a deep regression neural network for a fused distance-intensity map. Research on Biomedical Engineering is an online, peer-reviewed journal dedicated to all fields of Biomedical Engineering. Multidisciplinary in nature, ...
Aims and scope. BioMedical Engineering OnLine is an open access, peer-reviewed journal that is dedicated to publishing research in all areas of biomedical engineering. BioMedical Engineering OnLine is aimed at readers and authors throughout the world with an interest in using tools of the physical and data sciences, and techniques in ...
The motivation for the launch of BMC Biomedical Engineering is to create an authoritative, unbiased and community-focused open access journal. We are committed to working together with our authors, editors and reviewers to provide an inclusive platform for the publication of high-quality manuscripts that span all aspects of biomedical engineering research.
Communications Preferences. Profession and Education. Technical Interests. Need Help? US & Canada:+1 800 678 4333. Worldwide: +1 732 981 0060. Contact & Support. About IEEE Xplore. Contact Us.
Volume 37 March - December 2021. Issue 4 December 2021. Issue 3 September 2021. Issue 2 June 2021. Issue 1 March 2021.
Tele-rehabilitation is the provision of physiotherapy services to individuals in their own homes. Activity recognition plays a crucial role in the realm of automatic tele-rehabilitation. By assessing patient m... Alireza Ettefagh and Atena Roshan Fekr. BioMedical Engineering OnLine 2024 23 :35. Research Published on: 19 March 2024.
Biological Engineering Research in South Korea Edited by Jeong-Yeol Yoon. 2019. ... He received his second Ph.D. degree in Biomedical Engineering from University of California, Los Angeles in 2004, ... 1.173 - SNIP (Source Normalized Impact per Paper) 0.851 - SJR (SCImago Journal Rank) 2023 Speed
With the recent advancements in biomedical engineering technologies, commercially available VLP-based vaccines are being extensively used to combat infectious diseases, whereas many more are in different stages of development in clinical studies. Because of their desired characteristics in terms of efficacy, safety, and diversity, VLP-based ...
Read the latest Research articles in Biomedical engineering from Scientific Reports. ... Biomedical engineering articles within Scientific Reports. ... Calls for Papers
The published papers include nine research papers and one review. We appreciate all the authors who have decided to publish their research in this Special Issue. Thanks to these authors, we could provide the state of the art of the recent research of intelligent techniques in applications of biomedical engineering. Below, we summarize the ...
The paper further identified and discussed significant applications of Biomedical engineering for healthcare. Biomedical engineering is a fascinating field of life science that can change ...
Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. A Feature Paper should be a substantial original Article that involves several techniques or approaches, provides an outlook for future research directions and describes possible research applications. ... (Engineering, Biomedical) Rapid ...
This manuscript was written with two readers in mind. Firstly, it is intended for mathematical modelers with a background in physics, mathematics, or engineering who want to jump into biomedicine. We provide them with ideas to motivate the use of mathematical modelling when discussing with experimental partners.
Biomedical engineering research is expected to create health technologies that will drastically improve the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of disease, as well as patient rehabilitation. ... Technical and practical aspects of rehabilitation engineering, from concept to clinic and papers on improving the quality of life of patients with a ...
The segmentation and tracking of living cells play a vital role within the biomedical domain, particularly in cancer research, drug development, and developmental biology. These are usually tedious and time-consuming tasks that are traditionally done by biomedical experts. Recently, to automatize these processes, deep learning based segmentation and tracking methods have been proposed. These ...
Fig. 1: Synthesis and antitumour process of oncolytic mineralized bacteria. The strong antitumour immunity triggered by mineralized bacteria could be attributed to several different mechanisms ...
Download. by Maria Vulpiani. 15. Mechanical Engineering , Biomedical Engineering , Treatment Outcome , Adolescent. The use of reduced healing times on ITIR implants with a sandblasted and acid-etched (SLA) surface:. Early results from clinical trials on ITIR SLA implants. Download. by David Cochran. 3.
The first step to becoming a biomedical engineer is fulfilling the educational requirements of the role. Biomedical engineers typically need at least a bachelor's in life sciences, biotechnology, or engineering. Many, however, continue their education by pursuing a graduate or doctoral degree as well. According to government data, almost 71 ...
Biomedical Engineering Research Papers/Topics . Sweat sensors in the smart wearables era - A Review. In recent years, there has been significant interest in developing wearable devices to mimic the integrated sensing of life forms, which enhances their performance and survival capabilities. Progress in the development of physical sensors and ...
BMC Biomedical Engineering considers articles on all as-pects of biomedical engineering, including fundamental, translational and clinical research. It combines tools and methods from biology and medicine with mathematics, physical sciences and engineering towards the under-standing of human biology and disease and the improve-ment of human ...
The development of dental calculi involves bacteria in local mature biofilms converting the DNA in neutrophil extracellular traps from being degradable by the enzyme DNase I to being degradation ...