TechRepublic
Account information.


Share with Your Friends
How to configure a static IP address in CentOS 7
Your email has been sent
You may have set up a CentOS server and, in the process, accidentally set it up with DHCP. If your CentOS server uses a GUI, changing that IP address from dynamic to static is very simple. But what if your server is a text-only machine? What do you do then? Fortunately, it’s not all that hard to configure that GUI-less server with a static IP address–you just have to know where it’s configured and know the syntax of the configuration. Of course, by nature of what we’re working on this is all done manually, so be prepared to type.
I’ll be working on CentOS 7 . I’ll assume you already have the operating system installed and working properly, have access to the machine, and have an administrative account. With that out of the way, let’s set up that static IP address.
Find your interface
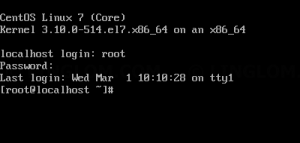
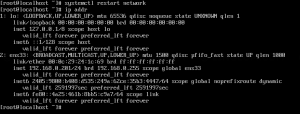
The first thing we must do is find out the name of our ethernet interface. A static IP address cannot be configured without this name. To do this, log into your server and issue the command ip a . The output of this command ( Figure A ) will include the name of the interface.
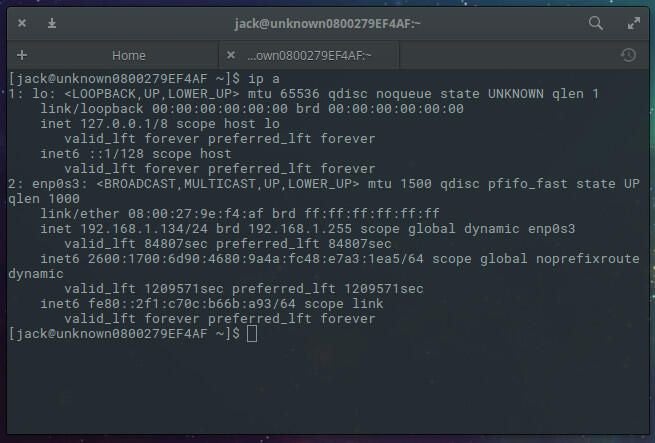
As you can see, from my output, the name of my interface is enp0s3. Now that we know the name of our interface, we can configure the static address.
Configuring the address
Within the directory /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ you should find the file ifcfg-INTERFACENAME (Where INTERFACENAME is the name of your interface). In my instance, the file is ifcfg-enp0s3. It is important that you configure that file, and not the ifcfg-eth file. Open the correct file for editing with the command sudo nano /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enp0s3 . We need to modify that file in order to not only change the protocol from dhcp to static, but to add the specific IP address. So when you open up that file, you’ll want to change:
BOOTPROTO=dhcp
BOOTPROTO=static
Now you’ll need to add the entries to set not only the IP address, but the netmask, gateway, and DNS addresses. At the bottom of that file, add the following:
IPADDR=192.168.1.200 NETMASK=255.255.255.0 GATEWAY=192.168.1.1 DNS1=1.0.0.1 DNS2=1.1.1.1 DNS3=8.8.4.4
NOTE: All fields in bold, you will edit to reflect your networking needs. If you have fewer or more DNS entries, add or remove them as needed.
Save and close that file. In order to make the changes take effect, issue the command sudo systemctl restart network. Once the networking system has restarted, issue the command ip a to see that your IP address has changed to reflect your configuration.
And that’s all there is to setting a static IP address on CentOS. That wasn’t so hard, now was it? Don’t think this technique is limited only to GUI-less CentOS servers. You can use the same method to set a static IP address on a CentOS server with a GUI as well.
Enjoy having more control over your CentOS network interfaces.
Subscribe to the Developer Insider Newsletter
From the hottest programming languages to commentary on the Linux OS, get the developer and open source news and tips you need to know. Delivered Tuesdays and Thursdays
- How to install Kloxo-Mr hosting control panel on CentOS
- How to install a GUI on top of CentOS 7
- How to install cPanel/WHM on CentOS 7
- How to use the nmcli command to gather network device information on Linux
- Learn how to run Linux on Microsoft's Azure cloud
Create a TechRepublic Account
Get the web's best business technology news, tutorials, reviews, trends, and analysis—in your inbox. Let's start with the basics.
* - indicates required fields
Sign in to TechRepublic
Lost your password? Request a new password
Reset Password
Please enter your email adress. You will receive an email message with instructions on how to reset your password.
Check your email for a password reset link. If you didn't receive an email don't forgot to check your spam folder, otherwise contact support .
Welcome. Tell us a little bit about you.
This will help us provide you with customized content.
Want to receive more TechRepublic news?
You're all set.
Thanks for signing up! Keep an eye out for a confirmation email from our team. To ensure any newsletters you subscribed to hit your inbox, make sure to add [email protected] to your contacts list.

How to Set a Static IP Address in CentOS Linux
An IP ( Internet Protocol ) Address is a unique numerical representation of a computer on a network. Every computer connected to the Internet is identified by an IP Address.
Usually, IP addresses are dynamically assigned to a computer by a dedicated server called DHCP Server ( Dynamic Host Control Protocol ), and hence change from time to time as and when the connection is lost and reestablished.
However, there are scenarios where a static IP address is more preferable; Eg. In large corporations, where it removes the load of using DHCP for each computer in the organization.
Today, we will learn how to set a static IP address on a local network in CentOS .
List Network Interface Name
A computer can be connected to one or more network interfaces, for example to a WiFi device and a LAN device, which has different IP addresses for each interface.
Run the following command to show the interface names.

The interface ‘ enp0s3 ‘ is the LAN device connected to my computer and the IP Address is ‘ 10.0.2.15 ‘. The other interface ‘ lo ‘ ( Loopback ) which is nothing but the local network of the computer within itself. Thus my computer is only connected to one interface, ‘ enp0s3 ‘.
Configuring Static IP Address in CentOS
Go to directory ‘ /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts ‘ and list the files; you should see a file corresponding to your network interface.

Open the file ‘ifcfg-enp0s3’ using ‘ Vim ‘ or any editor of your choice.
Set the following values for the variables. Change the values according to the IP address and subnet that you need to set.

Save and exit the file. Restart the networking service with the following commands:
Finally, run ‘ ifconfig ‘ again to verify if static IP has been set.

In this article, we saw an easy way to set an IP address in CentOS. The example, in this case, is a static IP on the local network, i.e., it is not a static public IP over the Internet.
To set a static public IP address over the Internet, you need to purchase the IP Address and configure it in the file as shown above, along with other details like DNS server, network prefix, which will be provided by your Internet Service Provider.
Thanks a lot for reading and let us know your thoughts in the comments below!
How to Install Software from Source in Linux
How to Disable SSH Login to Specific User in Linux
Each tutorial at UbuntuMint is created by a team of experienced writers so that it meets our high-quality standards.
RECOMMENDED ARTICLES
What are CentOS and CentOS Stream and History
How to Create Sudo User in RHEL, CentOS, Rocky & AlmaLinux
How to Install Remi Repo in RHEL, CentOS, Rocky, & AlmaLinux
How to Install Suricata on RHEL, Rocky & AlmaLinux
How to Install FTP with SSL in Rocky Linux and AlmaLinux
Learn Different Networking Options in VirtualBox
How to Install Guest Additions in Virtualbox VM
How to Install CentOS 7 Minimal in Virtualbox
How to Host a Website on NGINX Web Server
How to Host a Website on an Apache Web Server
Got something to say? Join the discussion. Cancel reply
Thanks for choosing to leave a comment. Please keep in mind that all comments are moderated according to our comment policy, and your email address will NOT be published or shared. Please Do NOT use keywords in the name field. Let's have a personal and meaningful conversation.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

How To Configure Static IP Address in CentOS 7 / RHEL 7
Setting up the network and bringing servers into the network is the primary administration task for any system administrator.
In some cases, these tasks are automated using DHCP (Dynamic Network Configuration Protocol) which takes care of assigning IP Address to Desktop/Servers.
READ: How To configure DHCP server on CentOS 7, Ubuntu 18.04 & Debian 9
But, if you go to the bigger organizations, they use static (manual) IP to avoid network issues due non-availability of DHCP servers.
Configure Static IP Address in CentOS 7 / RHEL 7
Let us configure our system for the following information.
IP Address: 192.168.1.10 Netmask: 255.255.255.0 Gateway (Router): 192.168.1.1 DNS Server 1: 192.168.1.1 DNS Server 2: 8.8.8.8 Domain Name: itzgeek.local
Find the available network interfaces on your system
You can use any one of the below commands to list down the available network interfaces on the system.
Choose the desired network interface
The output of ifconfig -a may look like below. Here, I wish to change the IP address of enp0s3.
Configure the Static IP Address
In this method, we will edit the network interface file found under /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ directory. For interface enp0s3 , the file name would be ifcfg-enp0s3 .
Update the interface file as per the requirement.
You can also use nmtui , a text-based user interface for configuring network interfaces.
Select Edit a connection and press Enter .
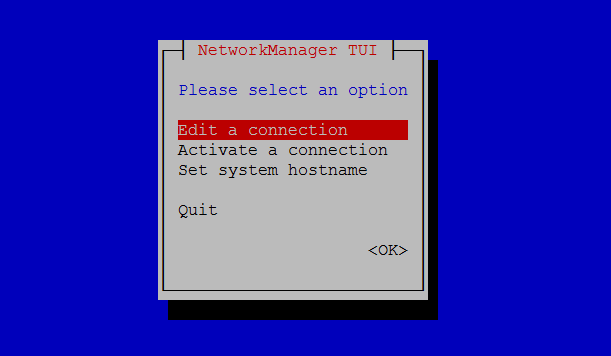
Choose the network interface and then Edit .

Set the IP Address and enter OK .
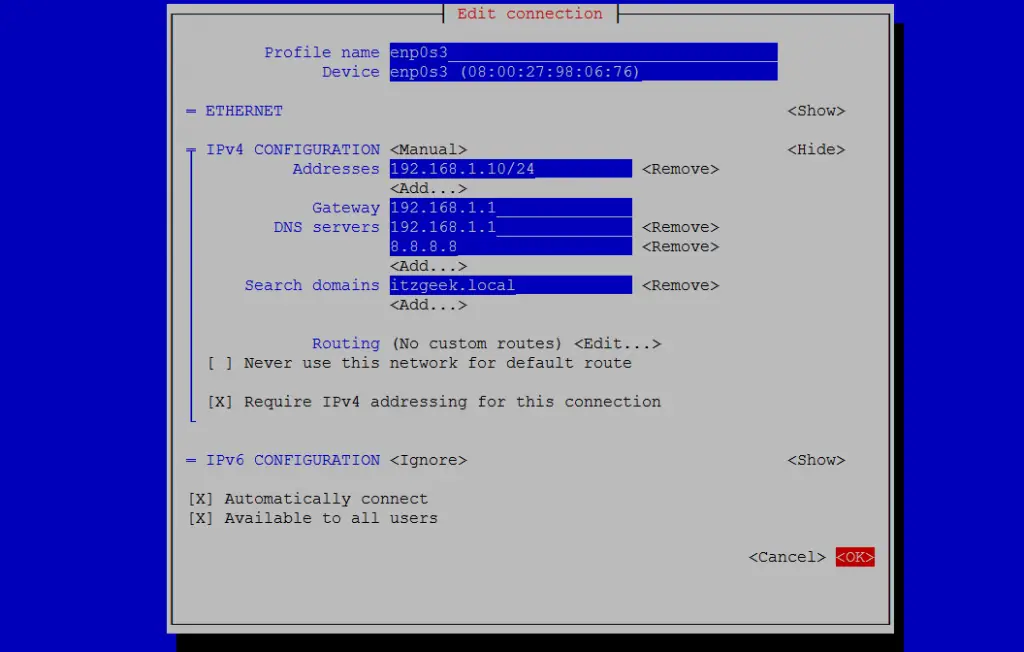
Restart Network
Finally, restart the network service using the following command to have these changes take effect.
Verify Static IP Address
Use ifconfig -a command to verify the static ip address.
Also, verify the DNS server entries.
That’s All. I hope you have learned how to configure a static IP address on CentOS 7 / RHEL 7 .
How To Install Oracle Java JDK 12 / 11 / 8 on Debian 10 / Debian 9
How to Configure Let’s Encrypt SSL in OpenLiteSpeed Web Server
How to Install Oracle Java JDK 18 on Linux
How to Install Oracle Java JDK 17 on Linux
How to Upgrade CentOS 7 to Rocky Linux 8
How To Install PHP 8.0 on CentOS 7 / RHEL 7
How To Install NTP (Chrony) On CentOS 8 / CentOS 7 & RHEL 8 / RHEL 7
How To Install Gradle on CentOS 8 / 7 & RHEL 8 / 7
- CentOS 8 / RHEL 8
- CentOS 7 / RHEL 7
- CentOS 6 / RHEL 6
- LinuxMint 20
- Linux Mint 19
- Linux Mint 18
- Rocky Linux 8
- Ubuntu 22.04
- Ubuntu 20.04
- Ubuntu 18.04
- MySQL / MariaDB
- Other Tools

How to configure a static IP address on CentOS 7
Last updated on November 7, 2020 by Dan Nanni
If you want to set up a static IP address on a network interface in CentOS 7, there are several different ways to do it, varying depending on whether or not you want to use Network Manager for that.
Network Manager is a dynamic network control and configuration system that attempts to keep network devices and connections up and active when they are available). CentOS/RHEL 7 comes with Network Manager service installed and enabled by default.
To verify the status of Network Manager service:
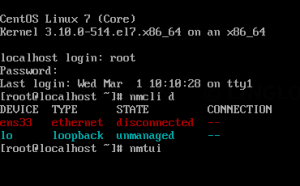
To check which network interface is managed by Network Manager, run:
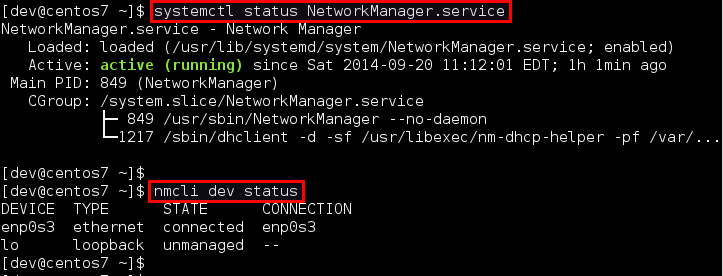
If the output of nmcli shows connected for a particular interface (e.g., enp0s3 in this example), it means that the interface is managed by Network Manager. You can easily disable Network Manager for a particular interface, so that you can configure it on your own for a static IP address.
Here are two different ways to assign a static IP address to a network interface on CentOS 7 . We will be configuring a network interface named enp0s3 .
Configure a Static IP Address without Network Manager
Go to the /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts directory, and locate the configuration file of the interface ( ifcfg-enp0s3 ). Create it if not found.
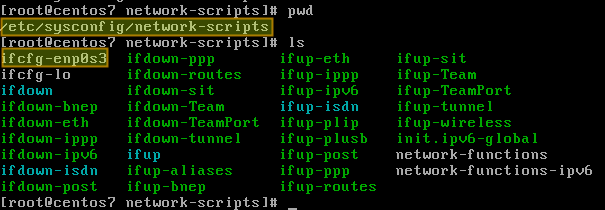
Open the configuration file and edit the following variables:
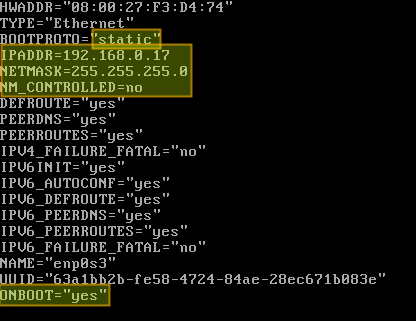
In the above, NM_CONTROLLED=no indicates that this interface will be set up using this configuration file, instead of being managed by Network Manager service. ONBOOT=yes tells the system to bring up the interface during boot.
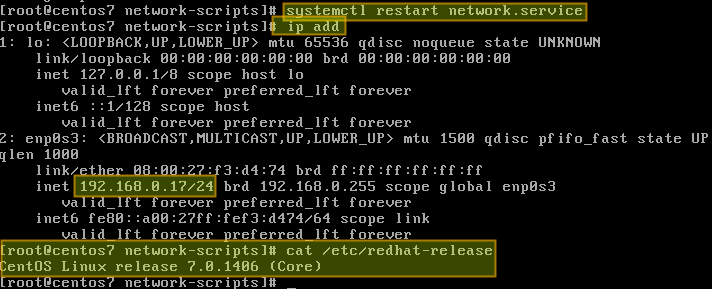
Save changes and restart the network service using the following command:
Now verify that the interface has been properly configured:
Configure a Static IP Address with Network Manager
If you want to use Network Manager to manage the interface, you can use nmtui (Network Manager Text User Interface) which provides a way to configure Network Manager in a terminal environment.
Before using nmtui , first set NM_CONTROLLED=yes in /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enp0s3 .
Now let's install nmtui as follows.
Then go ahead and edit the Network Manager configuration of enp0s3 interface:
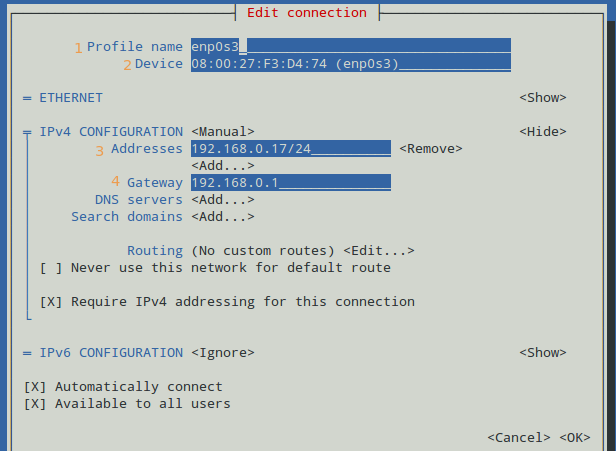
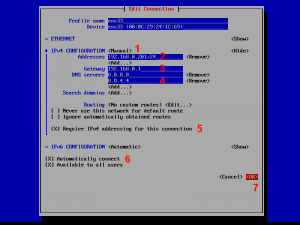
The following screen will allow us to manually enter the same information that is contained in /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enp0s3 .
Use the arrow keys to navigate this screen, press Enter to select from a list of values (or fill in the desired values), and finally click OK at the bottom right:
Finally, restart the network service.
and you're ready to go.
Support Xmodulo
This website is made possible by minimal ads and your gracious donation via PayPal or credit card
Please note that this article is published by Xmodulo.com under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License . If you would like to use the whole or any part of this article, you need to cite this web page at Xmodulo.com as the original source.

Xmodulo © 2021 ‒ About ‒ Write for Us ‒ Feed ‒ Powered by DigitalOcean

How to Configure Network Static IP Address on RHEL/CentOS 8/7
The scope of this tutorial is to explain how we can edit and make changes to Network Configurations on RHEL/CentOS 8/7 from the command line only, and, more specifically how we can set up a Static IP address on network interfaces using system network-scripts, which is a must be configured to serve Internet-facing network services, and how to configure or change RHEL/CentOS system hostname .
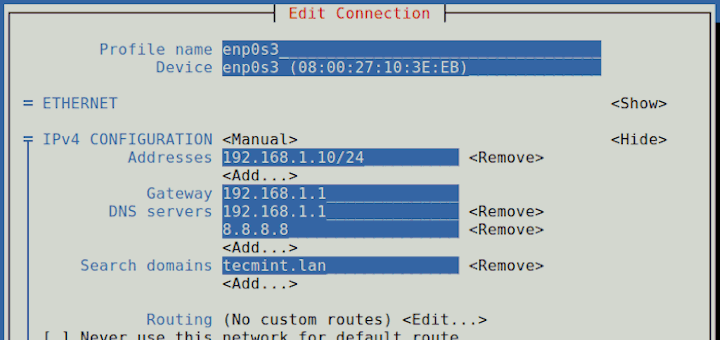
Also will show you, how we can manage or disable unwanted system services, such as Network Manager , which is no longer needed in-case you use a manual static IP configured on network scripts, Avahi-Daemon which is, also, not needed on a server and represents a seriously security gap, unless you installed the server on your Laptop and you want to instantly browse your network for other services, and on the final will present you Network Manager Text User Interface – nmtui , a system utility that can ease the job of editing your system network settings with advanced Interface configurations like creating Bond , Bridge , Team and VLAN Interfaces.
Requirements
- Installation of “CentOS 8.0″ with Screenshots
- Installation of RHEL 8 with Screenshots
- How to Enable RHEL Subscription in RHEL 8
- CentOS 7.0 Minimal System Installation
- RHEL 7.0 Minimal System Installation
- Active RHEL 7.0 Subscriptions and Functional Repositories
Also, be aware that most of the configurations offered by editing system files should not be performed from a remote location using SSH service until you establish a continued and reliable network connection using a fixed IP address.
On this page
- Disable Unwanted Services in CentOS
- Set Static IP Address on CentOS
- Set Hostname in CentOS
- Set Static IP Address on CentOS Using Nmtui Tool
Step 1: Disable Unwanted System Services in CentOS
1. Before actually starting to do anything we need to make sure that our system has some necessary editing and networking tools like netstat , ifconfig , wget , curl , and lsof installed, some of them will not be used on this step but it’s better to have them installed for future configurations.
2. After the tools have installed run ifconfig to get your Network Interfaces settings and status, and, then run netstat or lsof command to check what services are running by default on our server.
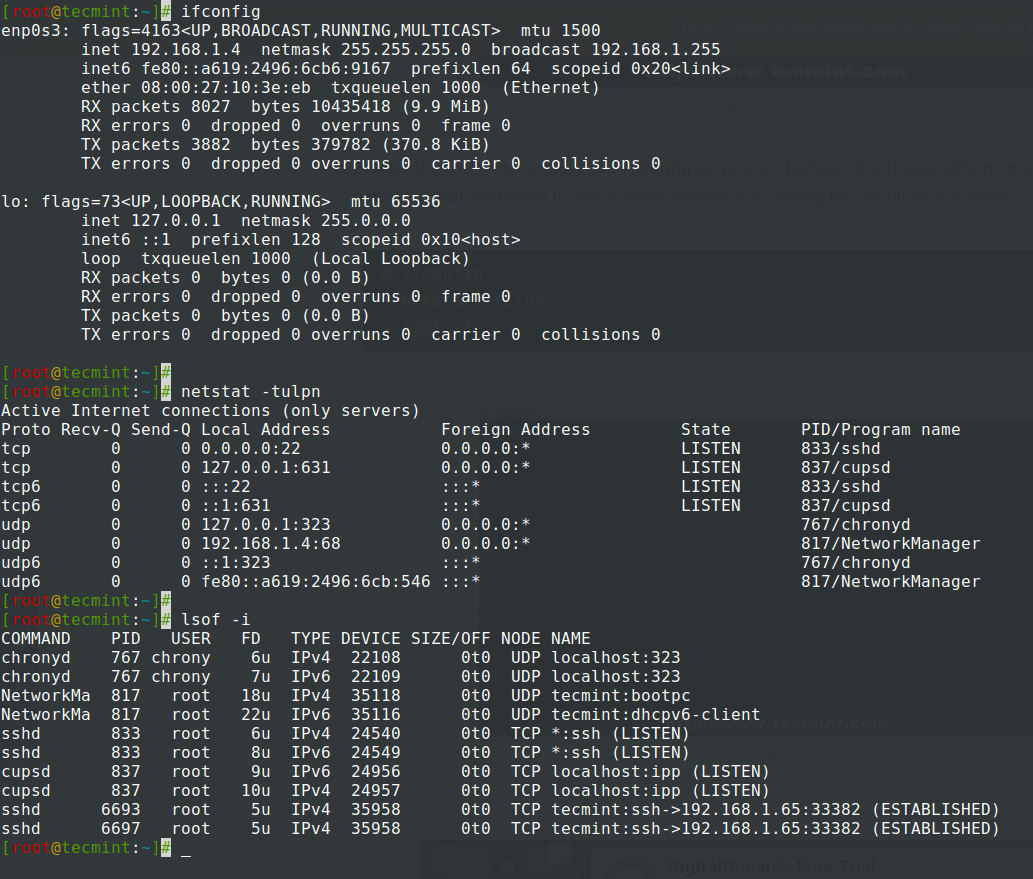
3. The netstat command output is pretty self-explanatory and shows a list of sockets associated with their running program name.
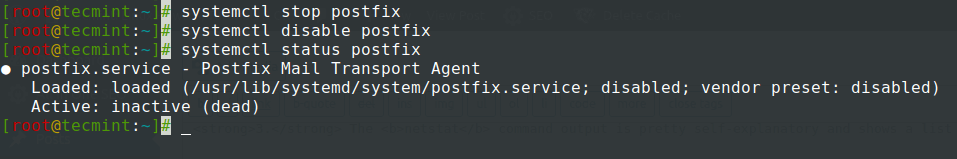
If, for example, our system will not be used as a mail service you can stop Postfix master daemon which runs on localhost and, also stop and disable other unwanted services using the following commands – the only service I advise not to stop or disable for now is SSH if you need remote control over the server.
Stop Postfix Service
Stop Avahi Daemon Service
4. You can, also, use old init commands to stop or disable services but since Red Hat now implements systemd process and service management, you should better get used to systemctl commands and use it often.
If you use Arch Linux then it should be a piece of cake to switch to systemd – although all init commands now are linked and pass-through systemd filter.
5. If you want to get a list of all started services run the service command and for an exhaustive report use systemctl .
6. To manage services run the systemctl command using the most important switches: start , stop , restart , reload , disable , enable , show , list-dependencies , is-enabled, etc. followed by your service name.
Also, another important feature that the systemctl command can also run on a remote server through SSH service on a specified host using -H option and perform the same actions as locally.
For example, see the command and screenshot below.
Step 2: Configuring Static IP Address on CentOS
7. Before start editing Network Interface Card system files make sure that from now on and until you set static IP, you have physical or any other type of access to your server, because this step requires bringing down your network interface and connections.
Although it can be done smoothly without disrupting your connectivity and activate connection after reboot . There is no way you can test it before reboot if you only have a single NIC attached. Still, I will present to you with the entire method and indicate the steps needed to be avoided in case you want to maintain your connectivity and test it afterward.
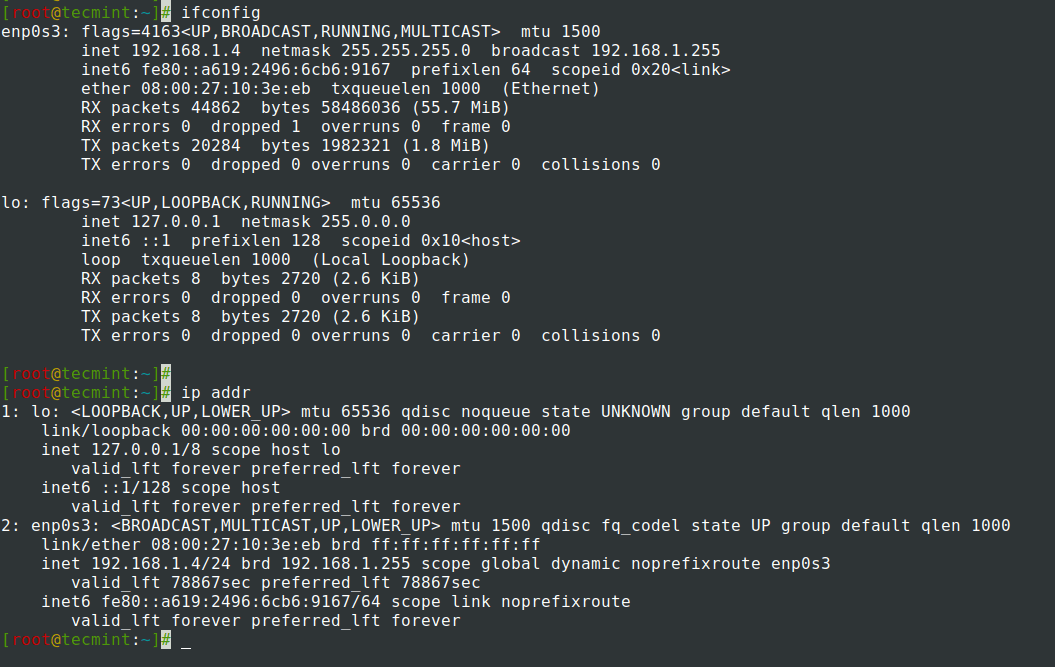
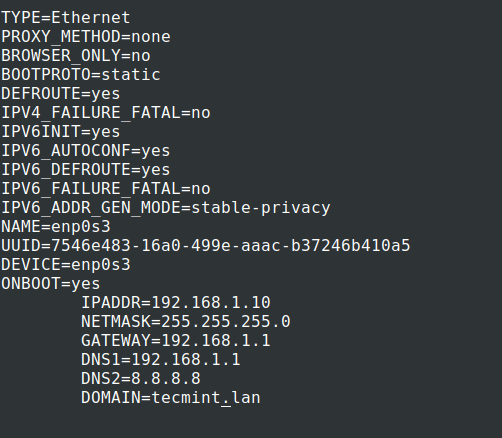
8. Now move to /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ path, open and choose your Network Interface you want to assign static IP for editing – to get all NICs names to use ifconfig or IP command as shown.
9. Next, use the following network template to edit the file and make sure that the ONBOOT statement is set on YES , BOOTPROTO is set to static or none and don’t change HWADDR and UUID values provided by default.
Make the following changes as shown.
10. After finishing editing the file, close it, and move to resolv.conf file if you want DNS servers enabled system-wide.
Here just add your DNS servers using nameserver statement.
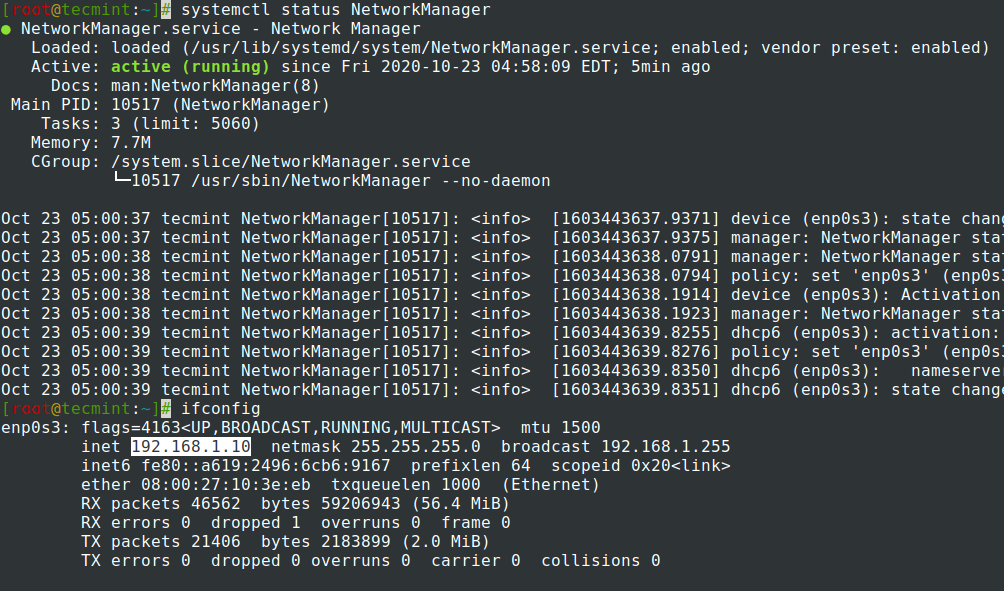
11. Now Network Interface is configured with a static IP, the only thing remaining is to restart your network or reboot your system and use ifconfig or IP command to view the IP address and test configuration using ping command.
NOTE : After restart use the newly static IP address configured to perform remote login with SSH.
Step 3: Setting Hostname in CentOS
12. To adjust system hostname system-wide, open hostname and hosts file located on /etc path and edit both the following way.
Hostname File
Here you can add just the name of the system but it’s a good idea to append the .dot domain to.
Here add the same hostname as above on the 127.0.0.1 line before the localhost.localdomain statements.

Alternatively, you can set hostname using the hostnamectl command as shown.
13. To test if your hostname is correctly set use hostname command.
Step 4: Set Static IP Address on CentOS Using Nmtui Tool
14. NetworkManager Text User Interface (TUI) tool, nmtui , is an RHEL intuitive tool which provides a text interface to configure networking by controlling Network Manager, which helps to edit advanced network settings such as assign static IP addresses to Network Interfaces, activate or disable a connection, edit WI-FI connections, set your system hostname or create advanced Network interfaces like InfiniBand, bond, bridge, team or VLAN.
NetworkManager-tui is installed by default in RHEL/CentOS 7.0, but if for some reason its missing issue the following command to install it.
14. To start Network Manager Text User Interface run the nmtui command and use TAB or arrow keys to navigate through and press Enter to select an option. If you want to directly edit or connect a specific interface run the following options.
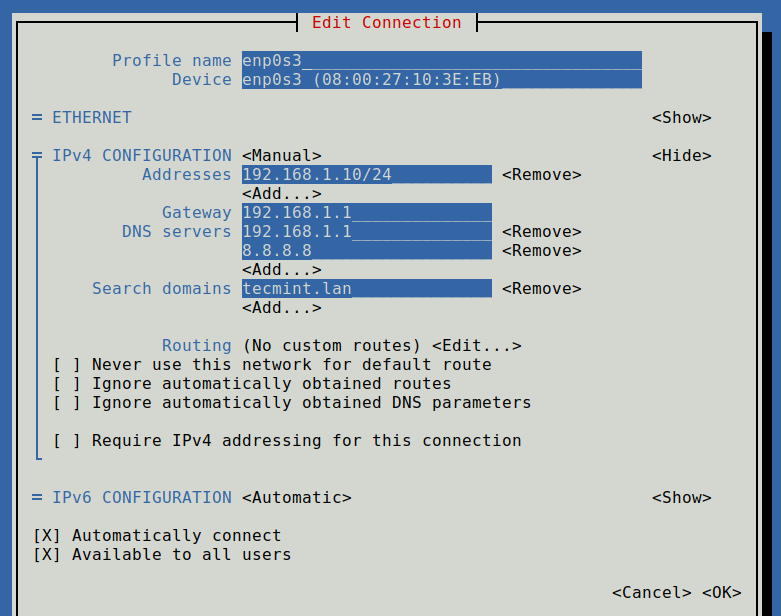
If you want to set static IP you can, also, use Network Manager Text User Interface as a facile alternative to actually edit network interfaces files, with a limited number of options that method has to offer, but make sure Network Manager service is enabled and started on your system.
Previous article:
Next article:
Each tutorial at TecMint is created by a team of experienced Linux system administrators so that it meets our high-quality standards.
Related Posts

How to Reset Forgotten Root Password in RHEL Systems
How to Install and Configure NTP in RHEL Systems

How to Install Terraform (Infrastructure as Code) in Linux
How to Install and Configure GitLab on Linux

How to Create and Run New Service Units in Systemd Using Shell Script
How to Install and Configure VNC Server in CentOS and RHEL
11 thoughts on “How to Configure Network Static IP Address on RHEL/CentOS 8/7”
After 2 hours tests, Good all be fine, it works fine, just Added : In smb.conf file configuration in [Anonymous]
1- be sure that your server has a static connection 2- added user with password : smbpasswd -a username
Thank For Author I have make a samba configuration in 2 hours
I feel learning with quick manner in this site Thank you very much
I also routinely disable NetworkManager on my servers, but do note that “nmtui” (and also nmcli) are NetworkManager clients, so you cannot use them if you have disabled NetworkManager.
Excellent!. This is the ONLY post on setting static IP on Centos which is correct. Simple flow.
All: Just follow the steps as is.
Great explanation. Great job guys.
Great article. The static IP configuration works great on my RHEL 7 server vm.
Just have a question. The Red Hat documentation says that BOOTPROTO should be set to “none”. My copy of your configuration only works with BOOTPROTO=static as you used in your example. If I set it to none the ip address does not get updated. I am having some discussions with our Linux sys admins since they are insisting that I should follow only the Red Had docs and this is a problem as I can’t make it work with BOOTPROTO=none. Is there a reason why it only works with BOOTPROTO=static?
If it works with bootptoto=static then stick with this option as long as it does the job right! As far as i know it should work also with none (none actually specifies that no boot-time protocol should be used but the IP value from IPADDR=1.2.3.4 variable should be updated for NIC at boot time).
@Ehwan Kho: Just use ip link show or ifconfig -a command and you should see all your NICs names. You can also use nmtui to edit your new card settings.
How do I add a new network card – NIC? I tried using lspci | grep Ethernet, it display that it 2 cards. My question now how could I know its name? as they are not using the eth1, eth2 et al.. And I can’t see /etc/udev/rules.d/70-persistent-net.rules. Your thoughts are highly appreciated.
In my opinion you can use both approaches, manual editing NICs interfaces or configure static IP using NM or nmtui if you dont have a GUI. But for a better control and flexibility over your NICs you should go with manual configurations, without NM. If you go with manual without NM don’t forget to use NM_CONTROLLED=no and ONBOOT=yes parameters.
please matie cezar can you teach me how to network a small firm. i will be happy if you can teach me form scratch to the level of networking a firm. i want to learn the installation and configuration
I ALWAYS disable network manager on Servers, it’s too dynamic and wastes resources. Why Red Hat is pushing that crap I don’t know, but I haven’t met anyone who wants it on a server. It’s great for desktops, and laptops, but NOT servers. Also, the DNS settings need to stick to being setup in the resolv.conf file, not spread out in the ifcfg scripts. Keeps the config manageable and easy to troubleshoot.
From going over the documentation on RHEL/CentOS 7, it appears that they’re really pushing for NetworkManager to be the default way to manage networking. For servers (not desktop) do you believe it’s best to disable NetworkManager and just assign static IPs normally as you have instructed or do you believing managing all the network through net manager is worth it?
The reason I ask is because I only deal with servers (not desktops) and I’ve seen many times NetworkManger causing major network issues. So I’m still on the fence whether or not to do things through netManager. Specially considering that rhel 7 is using it by default.
Got something to say? Join the discussion. Cancel reply
Thank you for taking the time to share your thoughts with us. We appreciate your decision to leave a comment and value your contribution to the discussion. It's important to note that we moderate all comments in accordance with our comment policy to ensure a respectful and constructive conversation.
Rest assured that your email address will remain private and will not be published or shared with anyone. We prioritize the privacy and security of our users.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
How to setup a static IP address on Centos 7 / RHEL 7

In this article we will explain how to setup a static IP address on Centos 7 / RHEL 7.There are several ways to configure a static IP address.
1. nmtui Tool ( Network Configuration Text User Interface) 2. nmcli Tool ( Network Manager Command Line ) 3. Editing /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-network_interface_name.fcg
For this tutorial, we’re going to assign to my server on my lab environment: – IP address : 192.168.1.10 – NetMask 255.255.255.0 – Gateway 192.168.1.1 – Domain Name Servers : 192.168.1.2 192.168.1.3 ( In my lab environment i’ve two Dns Servers) – Search Domains : yallalabs.com
Before starting let’s check current IP address and of our Centos 7 / RHEL 7 server :
Here, like you see, my network interface name is enp0s3 and the network configuration is automatically assigned by my DHCP server. Let’s start setting up a static ip address to our server .
1./ nmtui tool:
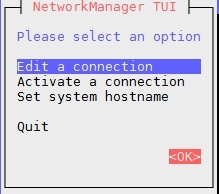
Remember to check Automatically connect to start the network device on boot and click ok .
By the way you can directly edit or connect an interface network device using:
Finally, restart the Network configuration daemon
2. nmcli Tool ( Network Manager Command Line )
First, let’s display the network connections.
Let’s start.
if you want to display list of all informations of the network connection use this command.
3. Editing /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-network_interface_name.fcg
BY default the configuration file will look like the block below.
To change the above setup to a static IP address configuration, replace BOOTPROTO value from dhcp to static or none as shown below.
Then add the IP address, network mask, gateway, domain search and Dns for the server at the end and save the file.
Finally, restart the network service to insecure change takes effect.
That’s it for now. Enjoy..
PS. If you like this post please share it with your friends on the social networks using the buttons below.Thanks. YallaLabs
Lotfi Waderni
I'm a technical writer with a background in Linux and windows server administration.
How to change the Hostname on CentOS 7 / RHEL 7
How to setup a static ip address on ubuntu 16 lts, you may also like, how to install nagios core 4 on..., how to install docker compose on centos..., how to configure nginx as a load..., how to add a new slave node..., leave a comment cancel reply.

How To Configure a Static IP Address on CentOS 7/8
- Knowledge Base
- Networking 6
- Webhosting 10
- Virtualisation 2
Introduction
This guide details howto configure a static IP on CentOS 7 or 8 on an operating system installed without a GUI. There are a number of options/methods available to do this outlined below.
Method 1 – Using Network Configuration File
1) First determinte the name of your network adapter by running the following:
2) Using your favourite text editor open the configuration file for your network adapter, replacing X with the name of your network adapter determined in the previous step.
3) Configure the variables in the file for your conneciton:
4) The most common configuration parameters with explanations are:
BOOTPROTO= none, bootp or dhcp IPADDR= DEVICE=<name> –> where <name> is the name of the physical device. DNS{1,2}=<address> –> where <address> is a name server address to be placed in /etc/resolv.conf GATEWAY= MACADDR=<MAC-address> –> Where <MAC-address> is the hardware address of the Ethernet device in the form AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:F NETMASK=
ONBOOT=<answer> –> Where <answer> is one of the following: yes — This device should be activated at boot-time. no — This device should not be activated at boot-time.
PEERDNS= yes – Modify /etc/resolv.conf if the DNS directive is set. If using DHCP, then yes is the default. no – Do not modify /etc/resolv.conf.
USERCTL= yes – Non-root users are allowed to control this device. no – Non-root users are not allowed to control this device.
4) If you have NetworkManager service running, you’ll need to instruct the network service that network manager doesn’t manage this interface (eth0). This is done by adding the line:
5) Then you can stop NetworkManager service. For CentOS 7/8, this can be done using:
6) After saving the changes, the shut down the interface and bring it back:
7) Then you can stop NetworkManager service. For CentOS 7/8, this can be done using:
8) Check the current adapter settings:

Method 2 – Using ip and ifconfig commands
The ifconfig command is now depreciated in favour of ip tool however is still part of net-tools package and can be installded with:
For clarity in the steps below both iptool and ifconfig commands are shown:
Show Adapters
To show all ip address related infoprmation is ip/config these commands are used:
Bring Up/Down an Interface
Setting a static ip.
Static IP setting can be done using ip or ifconfig. But note that changes made with these commands are not persistent against reboots:
Removing a static IP
Clearing IP information can be done as follows:
Add default route via gateway IP
A default route can be set using ip and ifconfig commands for destinations without static routes defined.
Method 3 – Using Network Manager (nmcli)
In RHEL and CentOS 7 and 8 the networking service is managed by the NetworkManager daemon and it is used to dynamically configure and control network devices and keep connections up and active when they are available.
Howto remove NetworkManager
In case you don’t want to remove network manager you can disable and remove it as follows:
Incase you do wish to use NetworkManager then a reference of commands can be found below:
Howto start NetworkManager
You can check Network Manager is running and started as follows:
Bring Up interfaces using NetworkManager
You can bring network interfaces up and down using network manager as follows:
Configure a static IP using NetworkManager
1) List current connections
2) Delete connections entering UUID or network name from Step 1
3) Create a network with name ethX
4) Configure DNS and make network configurations always be manual for this network interface.
5) Restart the network:
6) View the connection ethX

– Limited Offer –
Dual Core Xeon E3-1220L 2.20Ghz
Only £29/Month
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Steps to assign static IP address in CentOS Linux via command line?
How to configure so the Linux CentOS v8 VM I have with static IP address?
I have already set the networking parameter during the GUI installation, but after the reboot, it still reverting back with DHCP IP addressing?
Do I have to create a new interface file rather than modifying the below:
Note: I cannot even restart the network service as mentioned in the various blog:
- linux-networking
- The question is tagged as centos7, can you please confirm whether you mean 7 or 8? – tater Aug 12, 2020 at 12:53
- Run this and send the output please: ifdown ens192 && ifup ens192; ip a – Farhad Kia Aug 26, 2020 at 13:05
3 Answers 3
By default, networking on CentOS 7 and 8 is managed by NetworkManager.
It uses a plugin called ifcfg-rh to read the old network service configuration files (used in CentOS 6 and previous versions) such as the one you mentioned and translate them into the appropriate NetworkManager configuration.
What has probably happened here is that the interface name has changed from what it was during installation. This often happens with virtual machines running under VMware products. It looks like you had the interface name ens192 at install time. You can use ip link to see the current interface name.
If the name differs, you can edit the file and change the interface name within, then reload NetworkManager.
While NetworkManager excels at managing networks for desktop/laptop systems, and certainly works for servers, it's quite heavy for that purpose. I've lately begun switching my CentOS 8 servers to the much lighter systemd-networkd, which is a bit better integrated into the system, but doesn't support desktop/laptop systems (particularly WiFi) as well. You might consider doing the same.
- even after the restart and reload NetworkManager, the IP address is still not applied, despite the cat /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens192 shows updated static IP address. – Senior Systems Engineer Aug 20, 2020 at 7:13
I've managed to configure the IP networking using the text user interface tool:
If the name differs, you can edit the file and change the interface name within, then reload NetworkManage
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged linux centos7 linux-networking ..
- The Overflow Blog
- Want to be a great software engineer? Don’t be a jerk.
- Climbing the GenAI decision tree sponsored post
- Featured on Meta
- New Focus Styles & Updated Styling for Button Groups
- Upcoming initiatives on Stack Overflow and across the Stack Exchange network
Hot Network Questions
- Efficient Algorithm for Scheduling 140 Predefined 1:1 Meetings with Variable Participant Constraints Over 7 Slots?
- Why did Nicaragua file a case against only Germany at the ICJ?
- Can anyone explain this sacrifice?
- Can religions die?
- Sight reader or busker?
- Paint color consistency
- Treatment of expl3 variables - registers versus macros
- Manga about a boy whose girlfriend was drafted into war against aliens
- How to equally split college fund between 2 children going to college 5 years apart?
- What are the parameters of the Voyager high-gain antenna?
- Painting wood cabinets. Do I have to start over?
- How can I make a custom header in less? Or alternatively, how can I open two files simultaneously in less?
- What are examples of "Official Observations" in a passport?
- Are wider tires on a road bike a good idea?
- Am I in my rights to ask a colleague to not take notes on everything I say outside a meeting?
- Should I revise the sentence in bold?
- As of 2024, how can Russia escalate the war in Ukraine?
- Co-Existing with a Highly Extroverted Leader and "Forced Fun"
- Can you use existing in home coax cables to connect a Leaf antenna to TV?
- How can I get unicode-math to print ⩽ when I type ≤?
- What is the difference between mind and consciousness?
- How do I properly exit a program and return to the CCP in CP/M?
- NSF grant proposal not reviewed despite being received
- Colorbar to illustrate the change of a specific parameter
Press ESC to close

Configure IP address in Linux (RHEL/CentOS 7)
The first thing that we do after installing an operating system is to configure the IP address i.e. networking on the machine. Whether we want to connect to the internet or only to our local area network (LAN), we must provide information regarding our network to the machine. In this tutorial, we are going to discuss how to configure IP address in Linux (RHEL/CentOS 7) using three different methods.
Also if you would like to assign an IP address to your Ubuntu system, then please refer to this tutorial How to manage network in Ubuntu 18.04 – Netplan Command or you can also refer to the tutorial for IP COMMAND, using which you can manage the network on all Linux distributions that have IP command installed.
(Recommended Read: IP Aliasing: Assigning multiple IP addresses to single NIC )
Configure IP address in Linux
Method 1- by editing the network interface file.
This method works on all Linux distributions. To configure the IP address, we need to open the network configuration file & pass our network information in the file. In RHEL/CentOS 7, location for all network interfaces in ' /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts ', in our case name of network interface is 'ifcfg-en0s3'. We will now edit the file to configure a static IP address for our system. Open the network interface file,
$ cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts $ vi ifcfg-en0s3
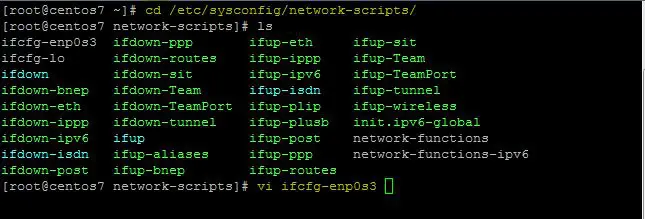
To configure a static IP address, change the ' BOOTPROTO ' to ' none ' (it's DHCP by default) & enter IP address, gateway & DNS information. Also, change ' ONBOOT ' to ' yes ' so that we don't have to start networking services every time we restart our system.
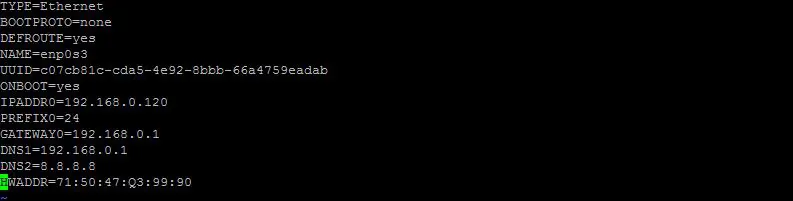
After making all the changes, save the file & then restart the networking services to implement the changes.
$ systemctl restart network $ vi ifcfg-en0s3
Method 2 - Using the Graphical interface
If we are using RHEL/CentOS with GUI then we can easily configure IP address graphically. Open 'Network' either by clicking the network icon & then selecting ' Network Settings ' on the top-left corner of the screen or goto Applications-> System Tools-> Settings-> Network.
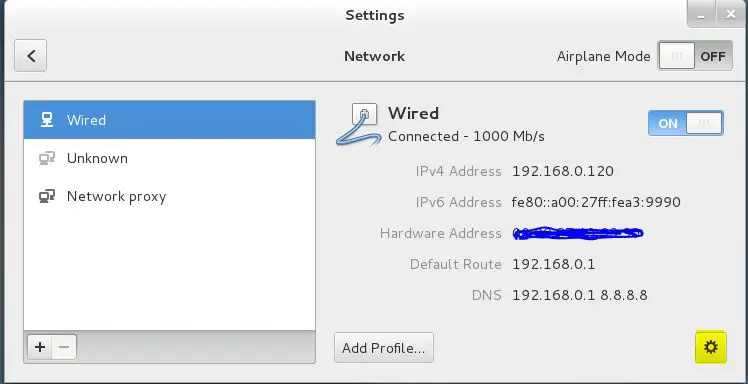
Next, click on the Settings icon (on the bottom right corner of the opened window) & select IPV4 then mention your network information on the opened window.
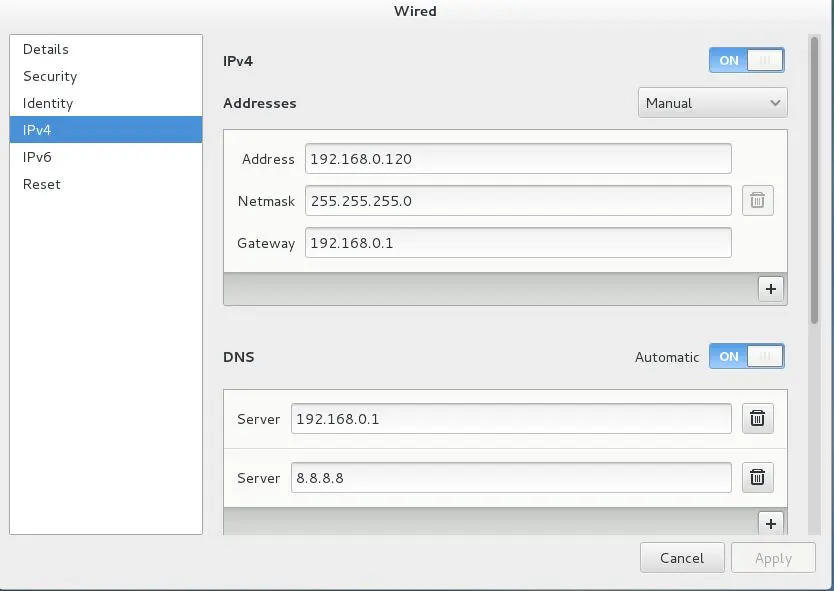
After the IP information has been edited, click on apply & exit from the menu. Lastly restart network services for implementing the changes.
Method 3- Using NMTUI command
This method can be used in GUI as well as in CLI. For using it in GUI mode, open a terminal and enter the command 'nmtui' & press enter or if using CLI, just enter the command 'nmtui' & press enter. This will open a new window with 3 options i.e. we can edit our network interface, activate a network interface, or set a hostname for our system (read our tutorial on setting hostname HERE ).
To set up networking for the system, select 'Edit a connection', select your network interface & then select 'Edit' using the arrow keys. In the 'IPv4 Configuration' select 'manual' & then enter your network information.
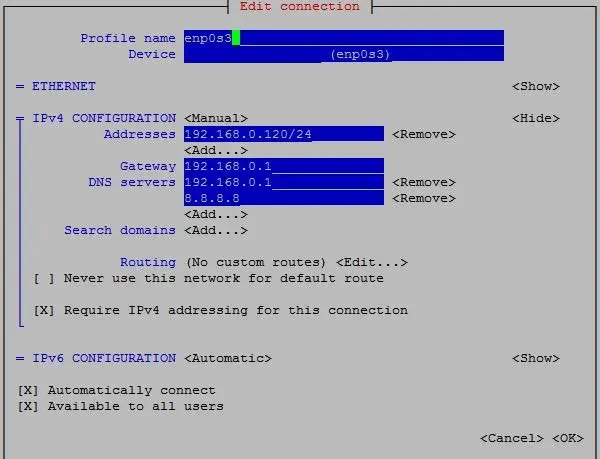
After making changes, press 'OK' to save the file & on the next screen press 'Quit' to exit from the menu. Restart your network services for changes to take effect.
Apart from these three methods, you can also configure IP address when installing operating system & also there are two more methods through which we can configure our network on RHEL/CentOS 7 machines i.e. by using ' nmcli command & ifconfig command . This wraps up our tutorial on how to configure IP address in Linux. For any queries/questions, please use the comment box below.
If you think we have helped you or just want to support us, please consider these :-
Connect to us: Facebook | Twitter
Linux TechLab is thankful for your continued support.
Share Article:
Passionate about Linux & open source. Loves to learn, read & write about Linux as well as new technologies.
Install TeamViewer on Ubuntu & CentOS /RHEL
Omd monitoring: install omd on centos 6, one comment.
That was very helpful, thank you. Best regards.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Dedicated Server
- Windows VPS
The Ultimate Guide to Change IP Address on CentOS

If you intend to change and configure your IP address in the CentOS system, you should know that the IP configuration in CentOS is done automatically. So, to change your IP in CentOS, you have to do it manually. This article examines how to change the IP address with possible methods. So apply the below steps carefully to achieve your desired result.
Prerequisites
If you want to change the IP address on CentOS distribution you have to prepare some requirements like:
- Up-to-date CentOS distribution in Linux VPS
- A user with root access
3 Simple Methods to Change IP Address on CentOS
You can configure and change your IP address using a number of options or methods available in this article. So, keep studying:
Method 1: Change IP Address on CentOS Via Network Configuration File
First, run the following command to determine the name of your network adapter:
Now use a suitable text editor to open the configuration file of your network adapter and replace x with the name of your network adapter:
As you can see below, you should configure the variables in the file:
Below are the most common configuration parameters with explanation:
If you have the network manager service and run it, you must configure it so that the network manager does not manage this interface (eth0) . You can do this by adding the following line:
Use the command below to stop the network manager service:
Save the changes, shutdown, and bring back the interface:
Now stop the network manager service using the following command:
Go through this command to check the current adapter setting:
Method 2: Change IP Address on CentOS Via IP and ifconfig commands
Note that the ifconfig command is deprecated, but it is still part of the net-tools package and can be installed with this command:

For more clarification, we will show both iptools and ifconfig commands.
If you want to show IP address-related information, use the following command:
Then to bring up or down an interface, use the command below:
You can set the static IP using ip or ifconfig commands. be careful, because changes made with these two are not persistent against reboots.
To clear the IP information , run the following command:
For destinations without static routes defined, you set the default route using ip and ifconfig commands:
Method 3: Change IP Address on CentOS Via Network Manager
The network manager service is used for CentOS management and for dynamic configuration and control of network devices. This service can also be used to keep active connections available.
You can remove the network manager, but if you just want to disable and then remove it, use the command below:
In this section, we will mention commands so that you can use the network manager service using them.
First, you should check the status of the network manager using these commands:
To bring network interfaces up and down use the network manager with the commands below:
Configuring A Static IP Via Network Manager

Use this command to list the current connections:
Enter UUID or network name from step 1 to delete connections:
By running the command below, you can create a network using ethx :
Now you need to configure DNS . You have to do the network settings manually:
Use this command to restart the network:
Running the following command, helps you to view the connection ethx :
Troubleshooting Issues About Change IP Address on CentOS
Here are some problems with changing IP address CentOS:
1- Lost connection after IP changes.
If you lose connection to the server after changing the IP, it could be due to an incorrect configuration. Revert the changes and check for typos or mistakes.
2- Incorrect Syntax in Configuration File
Ensure that the syntax in the configuration file is correct. A small typo can cause issues.
3- There may be firewall problems
Update firewall rules to allow traffic to the new IP address. Use the firewall-cmd or iptables command to configure firewall settings.
As mentioned in this article, IP is configured automatically and the service used to manage CentOS is called network manager. But if you need to change your IP, you have to do it manually. We also tried to show you how to change and configure the IP in three different ways. So follow the steps carefully and if you have any questions, contact us in the comments section.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 5 / 5. Vote count: 2
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
Step by Step to Configure Plesk on RDP Server
Have you ever heard of Plesk and its features? Well, In this article, we will provide you with step-...

Unleashing Your Artistic Potential with Linux Mint
Linux Mint is a different operating system among Linux distributions. If you are looking for an oper...
What is your opinion about this Blog?
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment
Publish Review
- 1- Prerequisites
- 2- 3 Simple Methods to Change IP Address on CentOS
- 3- Method 1: Change IP Address on CentOS Via Network Configuration File
- 4- Method 2: Change IP Address on CentOS Via IP and ifconfig commands
- 5- Method 3: Change IP Address on CentOS Via Network Manager
- 6- Configuring A Static IP Via Network Manager
- 7- Troubleshooting Issues About Change IP Address on CentOS
- 8- Conclusion

Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
How can I set a static IP address in CentOS 7?
I have a CentOS 7 Minimal VirtualBox VM that I would like to set a static IP address on. I want to assign the static IP address via a Bash script within the VM (so not using the VirtualBox network interface).
How can this be done?
So far I've tried editing the file : /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enp0s8 , and putting the below in it (per this question: https://superuser.com/a/365088 ).
But then the network adaptor doesn't restart ( service network restart ), which after a considerable amount of restarts/resets/trial, and error, and copious Google searches, it seems like it could be dozens of different things.
ip a lists two devices:
I also have a ifcfg-enp0s3 config file in the sysconfig dir (not sure why).
So, what's a nice, simple, predictable, reliable way of setting a static IP address in CentOS 7 minimal?
- 1 The answer you linked to is correct. – Ramhound Sep 9, 2017 at 19:12
- ipcfg-en0s3 – Ramhound Sep 9, 2017 at 19:50
- @Ramhound - That may be the "correct" answer, but I'm afraid it's not a working answer. Sure, if I do ip a it reports that enp0s8 is on my new, desired IP address, and I can ping that address from the client itself, but the host machine can't access it. And as noted above, in this configuration, service network restart returns FAILED, although I've just got rid of that by simply deleting the ifcfg-enps03 file. I still can't externally connect to the client despite being able to on the old address before the change. (And firewalld is stopped). – linux_confusion Sep 9, 2017 at 21:35
- Neither the answer linked nor RHEL Documentation has quoted values. Did you try your configuration without quotes? – sebasth Sep 10, 2017 at 6:57
- @sebasth - the file that already exists (and thus shipped with CentOS) has quote marks. However I've tried both with and without and they make no difference. – linux_confusion Sep 10, 2017 at 8:34
Try following:
I believe your problem is primary in the missing NM_CONTROLLED=no. Except of network restart you may try to set it UP with
You may also need to specify GATEWAY=
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged linux networking virtualbox centos ..
- The Overflow Blog
- Want to be a great software engineer? Don’t be a jerk.
- Climbing the GenAI decision tree sponsored post
- Featured on Meta
- New Focus Styles & Updated Styling for Button Groups
- Upcoming initiatives on Stack Overflow and across the Stack Exchange network
- Google Cloud will be Sponsoring Super User SE
Hot Network Questions
- What is the correct formulation of Newton's Second Law of Motion?
- Do faster responding low-pass filters exist compared to a traditional RC filter?
- What Equivalent %* of Batch in PowerShell
- Op-amp (LM348N) becomes very hot when connected to power
- How could Venus be partially terraformed?
- What is this glyph on Feb 23 1940 in a Finnish military calendar?
- What caused pink flares during the eclipse
- What is the most efficient way to find the area of a circle given three points on the rim
- Are wider tires on a road bike a good idea?
- Can ATC assign speed adjustment to aircraft on final approach course?
- AirBnB: cancel confirmed booking with low price as a host
- Can you use existing in home coax cables to connect a Leaf antenna to TV?
- What is the difference between mind and consciousness?
- Extreme anxiety before boarding a plane
- Almost sure probability in convergence, versus 0 probability in reality
- Split String Function Implementation in Python
- Clifford group without the phase gate
- Should I revise the sentence in bold?
- Do Trump's lawyers have a fiduciary duty to delay the proceedings?
- Questions About the FunctionExpand Function
- Co-Existing with a Highly Extroverted Leader and "Forced Fun"
- Is this formula already known?
- python cprofile decorator
- How can I get unicode-math to print ⩽ when I type ≤?
How to Configure CentOS 7 Network Settings

The following tutorial will guide you through configuring CentOS 7 network settings. If you are familiar with CentOS 6 or lower, you will notice that the network configuration files are largely the same.
The biggest difference between the latest major version and those below it is the naming convention for network interfaces. Prior to CentOS 7 the network interfaces were numbered, starting from 0. The first interface would also be named eth0. This is no longer the case, as the first network interface is now labeled enp3s0. To add some confusion, the next interface is labeled enp8s0.
Understanding Network Interface Naming
A predictable way of determining a network interfaces name was introduced in CentOS 6. However, it wasn’t until CentOS 7 was released that the feature was enabled by default.
The predictable naming convention assigns a name to an interface based on a number of factors. For an ethernet card, the following are used: type, bus, and slot. For example, the first network interface for a CentOS 7 server running on Virtualbox would be labeled enp3sp, or Ethernet device, bus 3, slot 0.
Disabling Predictable Naming
While it is not recommended to disable this feature, you may disable it at any time. By doing so you return to having a naming convention of etc[0,1,2,3…].
Common Settings
GATEWAY : The IP address of your network gateway. Required if you require connectivity beyond your local network subnet, such as having Internet connectivity.
IPADDR : The IP address of the network interface.
Configuration File
Configuring a static ip.
A static address is one that is permanently assigned to one host. It is an address that is manually configured by the administrator.
- Open the configuration file for your network interface. vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
- Add the following settings to the file: DEVICE=enp3s0 ONBOOT=yes IPADDR=192.168.1.10 NETMASK=255.255.255.0 GATEWAY=192.168.1.1
- Save your changes and exit
- Your new settings will not apply until the network interface is restarted or brought online. If you are remotely logged into the server and modifying the network settings of the interface you are connected to, reboot the system.
- Restarting the network interface. ifdown enp0s3 ifup enp0s3
Configuring DHCP Settings
A dynamic address is one leased from a DHCP server when a system boots or a network interface comes online. The following settings configure a network interface for DHCP.
- Open the configuration file for your network interface. vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-
- Add the following settings. If a configuration already exists, modify it to look like the following: DEVICE=enp3s0 ONBOOT=yes DHCP=yes
Validate Your Network Settings
You will want to ensure that your network interface has applied your new settings. You can use the IP command to output its settings.
The output will display basic information about the interface, such as device name, IP address, MAC address, etc. The following is an example of the output.
No related posts found
Linglom.com
Configure static ip address on centos 7.
This article shows 2 methods to enable a network interface and configure static IP address on CentOS 7 which are as following:
Configure IP address in GUI mode
Configure ip address using command line, watch on youtube.
Step-by-step
And type this command to open Network Manager.
- Change IP v4 configuration to Manual and click Show button on the right
- Enter IP address with network mask, for instance, 192.168.0.201/24
- Enter gateway address
- Enter DNS servers
- Check Require IPv4 addressing for this connection option
- Check Automatically connect option
- Click OK and click Back
systemctl restart network
vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33
Related Posts
How to find ip addresses and subnet number in a few seconds, ip addressing fundamentals, how to change hostname on centos 6.6, privacy overview.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Verify new IP settings using the ip command for the NIC named eth0: # ip a s eth0 Verify new routing settings: # ip r Next, verify DNS servers settings using the cat command or grep command to query the /etc/resolv.conf file as follows: # cat /etc/resolv.conf Finally verify the internet connectivity using the ping command: # ping -c 3 cyberciti ...
sl - Serial line IP (slip) Configuring a Static IP. You can set up a static IP via command line by modifying the network script of the interface. 1. First, find the name of the network interface you want to change using the network manager command-line tool. Prompt the system to list all network devices, along with network details: nmcli d
So when you open up that file, you'll want to change: BOOTPROTO=dhcp. To: BOOTPROTO=static. Now you'll need to add the entries to set not only the IP address, but the netmask, gateway, and DNS ...
An IP (Internet Protocol) Address is a unique numerical representation of a computer on a network.Every computer connected to the Internet is identified by an IP Address. Usually, IP addresses are dynamically assigned to a computer by a dedicated server called DHCP Server (Dynamic Host Control Protocol), and hence change from time to time as and when the connection is lost and reestablished.
Here, I wish to change the IP address of enp0s3. enp0s3: ... Configure Static IP Address in CentOS 7 - Configure Static IP Address Restart Network. Finally, restart the network service using the following command to have these changes take effect. ... systemctl restart network Verify Static IP Address. Use ifconfig -a command to verify the ...
If you want to set up a static IP address on a network interface in CentOS 7, ... Here are two different ways to assign a static IP address to a network interface on CentOS 7. ... Save changes and restart the network service using the following command:
On the other hand, nmcli is a command-line tool used to control NetworkManager and reporting network status. It can be utilized as a replacement for nm-applet or other graphical clients. nmcli can create, display, edit, delete, activate, and deactivate network connections, as well as control and display network device status.
The scope of this tutorial is to explain how we can edit and make changes to Network Configurations on RHEL/CentOS 8/7 from the command line only, and, more specifically how we can set up a Static IP address on network interfaces using system network-scripts, which is a must be configured to serve Internet-facing network services, and how to configure or change RHEL/CentOS system hostname.
- IP address : 192.168.1.10 - NetMask 255.255.255. - Gateway 192.168.1.1 - Domain Name Servers : 192.168.1.2 192.168.1.3 ( In my lab environment i've two Dns Servers) - Search Domains : yallalabs.com. Before starting let's check current IP address and of our Centos 7 / RHEL 7 server :
To assign IP address, open terminal & execute the following command, $ nmtui. You will see the following screen, Click on ' Edit a connection ', press ' Enter '. Use the ' Tab ' key to navigate. On the next screen, select the network interface from the list of interfaces & press ENTER key, Add the IP address and other necessary details ...
Method 1 - Using Network Configuration File. 1) First determinte the name of your network adapter by running the following: sudo lshw -class network -short. 2) Using your favourite text editor open the configuration file for your network adapter, replacing X with the name of your network adapter determined in the previous step.
It looks like you had the interface name ens192 at install time. You can use ip link to see the current interface name. If the name differs, you can edit the file and change the interface name within, then reload NetworkManager. [root@PRDSIEM01-VM ~]# systemctl reload NetworkManager. While NetworkManager excels at managing networks for desktop ...
This tutorial will show you how to configure the static IP address on CentOS 7 using two different methods. Prerequisites. A VPS or dedicated server with CentOS 7 installed. Configuration details. For this tutorial, we will use the following details: IP address: 192.168.12.23; Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0; Gateway: 192.168.12.1; DNS Server 1: 8.8.8.8
Method 2 - Using the Graphical interface. If we are using RHEL/CentOS with GUI then we can easily configure IP address graphically. Open 'Network' either by clicking the network icon & then selecting 'Network Settings' on the top-left corner of the screen or goto Applications-> System Tools-> Settings-> Network.. Next, click on the Settings icon (on the bottom right corner of the opened window ...
Method 1: Change IP Address on CentOS Via Network Configuration File. First, run the following command to determine the name of your network adapter: sudo lshw -class network -short. Now use a suitable text editor to open the configuration file of your network adapter and replace x with the name of your network adapter: nano /etc/sysconfig ...
@Ramhound - That may be the "correct" answer, but I'm afraid it's not a working answer. Sure, if I do ip a it reports that enp0s8 is on my new, desired IP address, and I can ping that address from the client itself, but the host machine can't access it. And as noted above, in this configuration, service network restart returns FAILED, although I've just got rid of that by simply deleting the ...
You will want to ensure that your network interface has applied your new settings. You can use the IP command to output its settings. ip a show enps3s0. The output will display basic information about the interface, such as device name, IP address, MAC address, etc. The following is an example of the output.
First we will cover the instructions to get IP address and other network information from command line. Get started by opening a command line terminal and check for your internal IP address by executing the ip command. $ ip a. Locate the requested network interface and check for assigned IP address. Additionally, the above command also reveals ...
Note: You have to change ens33 to match your device name that you want to configure. On the editor, change ONBOOT to yes. Note: To enter edit mode in vi editor, press Insert. Change BOOTPROTO to static and insert IP address, gateway, and DNS servers for this network interface.; Exit edit mode by press Esc and type :wq to save file and exit the editor.; Restart network service by type this command.
In this tutorial, we will learn how to assign static IP addresses in CentOS 7 or 8 machines. There are two ways we can assign a static IP address in CentOS 8 systems, 1- Using Network manager. 2 ...
Note that 12.34.567.8xx and 12.34.567.8yy are public IP addresses, and that 12.34.567.8__ indicates that the first 8 characters of the IP and gateway are identical. Also note that BOOTPROTO=static and NM_CONTROLLED=no need to end up in whatever results from the nmcli commands.
One common requirement is changing the IP address of a server to align with network changes, migrations, or simply to reorganize the network. This article will guide you through the process of changing the IP address on a CentOS 7 system, covering both the command line and graphical user interface methods.
122. You can use hostname command : ipaddr=$(hostname -I) -i, --ip-address : Display the IP address (es) of the host. Note that this works only if the host name can be resolved. -I, --all-ip-addresses : Display all network addresses of the host. This option enumerates all configured addresses on all network interfaces.