.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} Join us: Learn how to build a trusted AI strategy to support your company's intelligent transformation, featuring Forrester .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Register now .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Business strategy |
- What is strategic planning? A 5-step gu ...

What is strategic planning? A 5-step guide

Strategic planning is a process through which business leaders map out their vision for their organization’s growth and how they’re going to get there. In this article, we'll guide you through the strategic planning process, including why it's important, the benefits and best practices, and five steps to get you from beginning to end.
Strategic planning is a process through which business leaders map out their vision for their organization’s growth and how they’re going to get there. The strategic planning process informs your organization’s decisions, growth, and goals.
Strategic planning helps you clearly define your company’s long-term objectives—and maps how your short-term goals and work will help you achieve them. This, in turn, gives you a clear sense of where your organization is going and allows you to ensure your teams are working on projects that make the most impact. Think of it this way—if your goals and objectives are your destination on a map, your strategic plan is your navigation system.
In this article, we walk you through the 5-step strategic planning process and show you how to get started developing your own strategic plan.
How to build an organizational strategy
Get our free ebook and learn how to bridge the gap between mission, strategic goals, and work at your organization.
What is strategic planning?
Strategic planning is a business process that helps you define and share the direction your company will take in the next three to five years. During the strategic planning process, stakeholders review and define the organization’s mission and goals, conduct competitive assessments, and identify company goals and objectives. The product of the planning cycle is a strategic plan, which is shared throughout the company.
What is a strategic plan?
![what is strategic plan in business [inline illustration] Strategic plan elements (infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/7d1f14e4-b008-4ea6-9579-5af6236ce367/inline-business-strategy-strategic-planning-1-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
A strategic plan is the end result of the strategic planning process. At its most basic, it’s a tool used to define your organization’s goals and what actions you’ll take to achieve them.
Typically, your strategic plan should include:
Your company’s mission statement
Your organizational goals, including your long-term goals and short-term, yearly objectives
Any plan of action, tactics, or approaches you plan to take to meet those goals
What are the benefits of strategic planning?
Strategic planning can help with goal setting and decision-making by allowing you to map out how your company will move toward your organization’s vision and mission statements in the next three to five years. Let’s circle back to our map metaphor. If you think of your company trajectory as a line on a map, a strategic plan can help you better quantify how you’ll get from point A (where you are now) to point B (where you want to be in a few years).
When you create and share a clear strategic plan with your team, you can:
Build a strong organizational culture by clearly defining and aligning on your organization’s mission, vision, and goals.
Align everyone around a shared purpose and ensure all departments and teams are working toward a common objective.
Proactively set objectives to help you get where you want to go and achieve desired outcomes.
Promote a long-term vision for your company rather than focusing primarily on short-term gains.
Ensure resources are allocated around the most high-impact priorities.
Define long-term goals and set shorter-term goals to support them.
Assess your current situation and identify any opportunities—or threats—allowing your organization to mitigate potential risks.
Create a proactive business culture that enables your organization to respond more swiftly to emerging market changes and opportunities.
What are the 5 steps in strategic planning?
The strategic planning process involves a structured methodology that guides the organization from vision to implementation. The strategic planning process starts with assembling a small, dedicated team of key strategic planners—typically five to 10 members—who will form the strategic planning, or management, committee. This team is responsible for gathering crucial information, guiding the development of the plan, and overseeing strategy execution.
Once you’ve established your management committee, you can get to work on the planning process.
Step 1: Assess your current business strategy and business environment
Before you can define where you’re going, you first need to define where you are. Understanding the external environment, including market trends and competitive landscape, is crucial in the initial assessment phase of strategic planning.
To do this, your management committee should collect a variety of information from additional stakeholders, like employees and customers. In particular, plan to gather:
Relevant industry and market data to inform any market opportunities, as well as any potential upcoming threats in the near future.
Customer insights to understand what your customers want from your company—like product improvements or additional services.
Employee feedback that needs to be addressed—whether about the product, business practices, or the day-to-day company culture.
Consider different types of strategic planning tools and analytical techniques to gather this information, such as:
A balanced scorecard to help you evaluate four major elements of a business: learning and growth, business processes, customer satisfaction, and financial performance.
A SWOT analysis to help you assess both current and future potential for the business (you’ll return to this analysis periodically during the strategic planning process).
To fill out each letter in the SWOT acronym, your management committee will answer a series of questions:
What does your organization currently do well?
What separates you from your competitors?
What are your most valuable internal resources?
What tangible assets do you have?
What is your biggest strength?
Weaknesses:
What does your organization do poorly?
What do you currently lack (whether that’s a product, resource, or process)?
What do your competitors do better than you?
What, if any, limitations are holding your organization back?
What processes or products need improvement?
Opportunities:
What opportunities does your organization have?
How can you leverage your unique company strengths?
Are there any trends that you can take advantage of?
How can you capitalize on marketing or press opportunities?
Is there an emerging need for your product or service?
What emerging competitors should you keep an eye on?
Are there any weaknesses that expose your organization to risk?
Have you or could you experience negative press that could reduce market share?
Is there a chance of changing customer attitudes towards your company?
Step 2: Identify your company’s goals and objectives
To begin strategy development, take into account your current position, which is where you are now. Then, draw inspiration from your vision, mission, and current position to identify and define your goals—these are your final destination.
To develop your strategy, you’re essentially pulling out your compass and asking, “Where are we going next?” “What’s the ideal future state of this company?” This can help you figure out which path you need to take to get there.
During this phase of the planning process, take inspiration from important company documents, such as:
Your mission statement, to understand how you can continue moving towards your organization’s core purpose.
Your vision statement, to clarify how your strategic plan fits into your long-term vision.
Your company values, to guide you towards what matters most towards your company.
Your competitive advantages, to understand what unique benefit you offer to the market.
Your long-term goals, to track where you want to be in five or 10 years.
Your financial forecast and projection, to understand where you expect your financials to be in the next three years, what your expected cash flow is, and what new opportunities you will likely be able to invest in.
Step 3: Develop your strategic plan and determine performance metrics
Now that you understand where you are and where you want to go, it’s time to put pen to paper. Take your current business position and strategy into account, as well as your organization’s goals and objectives, and build out a strategic plan for the next three to five years. Keep in mind that even though you’re creating a long-term plan, parts of your plan should be created or revisited as the quarters and years go on.
As you build your strategic plan, you should define:
Company priorities for the next three to five years, based on your SWOT analysis and strategy.
Yearly objectives for the first year. You don’t need to define your objectives for every year of the strategic plan. As the years go on, create new yearly objectives that connect back to your overall strategic goals .
Related key results and KPIs. Some of these should be set by the management committee, and some should be set by specific teams that are closer to the work. Make sure your key results and KPIs are measurable and actionable. These KPIs will help you track progress and ensure you’re moving in the right direction.
Budget for the next year or few years. This should be based on your financial forecast as well as your direction. Do you need to spend aggressively to develop your product? Build your team? Make a dent with marketing? Clarify your most important initiatives and how you’ll budget for those.
A high-level project roadmap . A project roadmap is a tool in project management that helps you visualize the timeline of a complex initiative, but you can also create a very high-level project roadmap for your strategic plan. Outline what you expect to be working on in certain quarters or years to make the plan more actionable and understandable.
Step 4: Implement and share your plan
Now it’s time to put your plan into action. Strategy implementation involves clear communication across your entire organization to make sure everyone knows their responsibilities and how to measure the plan’s success.
Make sure your team (especially senior leadership) has access to the strategic plan, so they can understand how their work contributes to company priorities and the overall strategy map. We recommend sharing your plan in the same tool you use to manage and track work, so you can more easily connect high-level objectives to daily work. If you don’t already, consider using a work management platform .
A few tips to make sure your plan will be executed without a hitch:
Communicate clearly to your entire organization throughout the implementation process, to ensure all team members understand the strategic plan and how to implement it effectively.
Define what “success” looks like by mapping your strategic plan to key performance indicators.
Ensure that the actions outlined in the strategic plan are integrated into the daily operations of the organization, so that every team member's daily activities are aligned with the broader strategic objectives.
Utilize tools and software—like a work management platform—that can aid in implementing and tracking the progress of your plan.
Regularly monitor and share the progress of the strategic plan with the entire organization, to keep everyone informed and reinforce the importance of the plan.
Establish regular check-ins to monitor the progress of your strategic plan and make adjustments as needed.
Step 5: Revise and restructure as needed
Once you’ve created and implemented your new strategic framework, the final step of the planning process is to monitor and manage your plan.
Remember, your strategic plan isn’t set in stone. You’ll need to revisit and update the plan if your company changes directions or makes new investments. As new market opportunities and threats come up, you’ll likely want to tweak your strategic plan. Make sure to review your plan regularly—meaning quarterly and annually—to ensure it’s still aligned with your organization’s vision and goals.
Keep in mind that your plan won’t last forever, even if you do update it frequently. A successful strategic plan evolves with your company’s long-term goals. When you’ve achieved most of your strategic goals, or if your strategy has evolved significantly since you first made your plan, it might be time to create a new one.
Build a smarter strategic plan with a work management platform
To turn your company strategy into a plan—and ultimately, impact—make sure you’re proactively connecting company objectives to daily work. When you can clarify this connection, you’re giving your team members the context they need to get their best work done.
A work management platform plays a pivotal role in this process. It acts as a central hub for your strategic plan, ensuring that every task and project is directly tied to your broader company goals. This alignment is crucial for visibility and coordination, allowing team members to see how their individual efforts contribute to the company’s success.
By leveraging such a platform, you not only streamline workflow and enhance team productivity but also align every action with your strategic objectives—allowing teams to drive greater impact and helping your company move toward goals more effectively.
Strategic planning FAQs
Still have questions about strategic planning? We have answers.
Why do I need a strategic plan?
A strategic plan is one of many tools you can use to plan and hit your goals. It helps map out strategic objectives and growth metrics that will help your company be successful.
When should I create a strategic plan?
You should aim to create a strategic plan every three to five years, depending on your organization’s growth speed.
Since the point of a strategic plan is to map out your long-term goals and how you’ll get there, you should create a strategic plan when you’ve met most or all of them. You should also create a strategic plan any time you’re going to make a large pivot in your organization’s mission or enter new markets.
What is a strategic planning template?
A strategic planning template is a tool organizations can use to map out their strategic plan and track progress. Typically, a strategic planning template houses all the components needed to build out a strategic plan, including your company’s vision and mission statements, information from any competitive analyses or SWOT assessments, and relevant KPIs.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. business plan?
A business plan can help you document your strategy as you’re getting started so every team member is on the same page about your core business priorities and goals. This tool can help you document and share your strategy with key investors or stakeholders as you get your business up and running.
You should create a business plan when you’re:
Just starting your business
Significantly restructuring your business
If your business is already established, you should create a strategic plan instead of a business plan. Even if you’re working at a relatively young company, your strategic plan can build on your business plan to help you move in the right direction. During the strategic planning process, you’ll draw from a lot of the fundamental business elements you built early on to establish your strategy for the next three to five years.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. mission and vision statements?
Your strategic plan, mission statement, and vision statements are all closely connected. In fact, during the strategic planning process, you will take inspiration from your mission and vision statements in order to build out your strategic plan.
Simply put:
A mission statement summarizes your company’s purpose.
A vision statement broadly explains how you’ll reach your company’s purpose.
A strategic plan pulls in inspiration from your mission and vision statements and outlines what actions you’re going to take to move in the right direction.
For example, if your company produces pet safety equipment, here’s how your mission statement, vision statement, and strategic plan might shake out:
Mission statement: “To ensure the safety of the world’s animals.”
Vision statement: “To create pet safety and tracking products that are effortless to use.”
Your strategic plan would outline the steps you’re going to take in the next few years to bring your company closer to your mission and vision. For example, you develop a new pet tracking smart collar or improve the microchipping experience for pet owners.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. company objectives?
Company objectives are broad goals. You should set these on a yearly or quarterly basis (if your organization moves quickly). These objectives give your team a clear sense of what you intend to accomplish for a set period of time.
Your strategic plan is more forward-thinking than your company goals, and it should cover more than one year of work. Think of it this way: your company objectives will move the needle towards your overall strategy—but your strategic plan should be bigger than company objectives because it spans multiple years.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. a business case?
A business case is a document to help you pitch a significant investment or initiative for your company. When you create a business case, you’re outlining why this investment is a good idea, and how this large-scale project will positively impact the business.
You might end up building business cases for things on your strategic plan’s roadmap—but your strategic plan should be bigger than that. This tool should encompass multiple years of your roadmap, across your entire company—not just one initiative.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. a project plan?
A strategic plan is a company-wide, multi-year plan of what you want to accomplish in the next three to five years and how you plan to accomplish that. A project plan, on the other hand, outlines how you’re going to accomplish a specific project. This project could be one of many initiatives that contribute to a specific company objective which, in turn, is one of many objectives that contribute to your strategic plan.
What’s the difference between strategic management vs. strategic planning?
A strategic plan is a tool to define where your organization wants to go and what actions you need to take to achieve those goals. Strategic planning is the process of creating a plan in order to hit your strategic objectives.
Strategic management includes the strategic planning process, but also goes beyond it. In addition to planning how you will achieve your big-picture goals, strategic management also helps you organize your resources and figure out the best action plans for success.
Related resources

Solve your tech overload with an intelligent transformation

9 steps to craft a successful go-to-market (GTM) strategy

Unmanaged business goals don’t work. Here’s what does.
How Asana uses work management to effectively manage goals
- Contact sales
Start free trial
Strategic Planning in Business

Table of Contents
What is business strategic planning, the strategic planning process in 3 steps, what is a business strategic plan, key components of a business strategic plan, business strategic plan example, strategic plan vs. business plan.
Strategic planning is key for success in business. By planning strategically for the future, a business can achieve its goals. It’s easier said than done, but the more you know about strategic planning, the better chance you have at succeeding.
Business strategic planning is the process of creating a business strategy and an accompanying business strategic plan to implement a company’s vision and achieve its goals over time. The main goal of strategic planning is to take a company from its current state to its desired state through a series of business actions.
The business strategic planning process usually consists of defining business goals, doing a SWOT analysis to assess the company’s business environment and developing a business strategy. The leadership team is in charge of business strategic planning, as it has a very important impact on the overall direction of a company.
Get your free
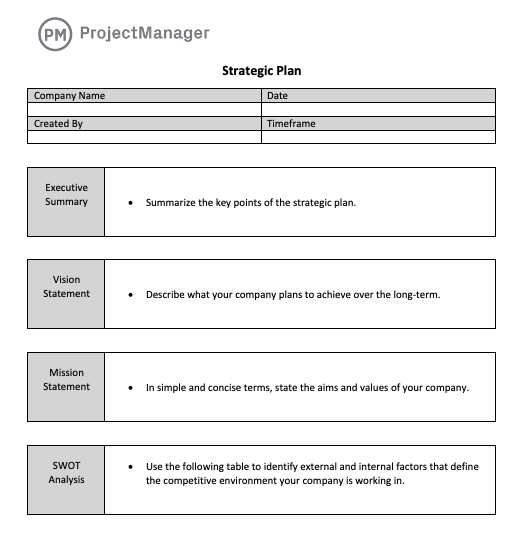
Strategic Plan Template
Use this free Strategic Plan Template for Word to manage your projects better.
Strategic Planning is one of the three levels of organizational planning, which is the process that allows organizations to define its objectives for the future and make action plans to guide the efforts of each of its departments, employees and management levels .
The other two levels of organizational planning are tactical and operational planning. Let’s see how these three types of organizational planning differ from each other.
Strategic Planning vs. Tactical Planning
While a strategic plan is created by the top management team and defines the high-level strategic goals of an entire organization, a tactical plan has a narrower scope. A tactical plan is created by the middle management level of a business and describes the specific goals, initiatives, challenges and resources for each department and how its efforts contribute to the completion of the larger strategic plan of the business.
Strategic Planning vs. Operational Planning
An operational plan allows you to establish guidelines, procedures and best practices for the daily operations of your business. The main objective of operational planning is to ensure that your business operations contribute to the accomplishment of the strategic objectives defined in the strategic plan.
Strategic planning is very important, but it doesn’t need to be overly complex. Let’s simplify this process by breaking it down into three simple steps.
1. Set Business Goals
A business goal is simply an accomplishment that a company wants to achieve in the short, medium or long term. Business goals can take many forms such as increasing sales, revenue, customer satisfaction levels and brand positioning, among many other things.
2. Conduct a SWOT Analysis
The goal of a business strategy is to leverage the strengths of a business and minimize the impact of its weaknesses. Those two things are internal factors. The strengths of a company can become competitive advantages that can lead to business growth. There are many types of business strengths and weaknesses such as scale, speed, or R&D, just to name a few.
Threats and opportunities refer to external factors such as competitors or an untapped market. A successful business strategy considers all of these factors to define how a product or service will be created, marketed and sold, and a SWOT analysis is a great starting point.
3. Develop a Business Strategy & Strategic Plan
Once you’ve completed your SWOT analysis, you can create a business strategy that’s designed to help position your company in the market. Your business strategy guides how you produce, market and sell your product or service based on internal and external analysis.
Then, you’ll need a strategic plan to explain how you plan to execute that business strategy. To oversee the execution of a business strategic plan, managers need to manage time, costs and tasks. ProjectManager is a project planning tool that allows managers to plan, schedule and manage their team’s work. Plan your work with professional tools such as Gantt charts, kanban boards, task lists and calendars. Then track your progress in real time to stick to your strategic plan. Get started for free.
A business strategic plan is an implementation plan that’s meant to turn a business strategy into action items that can be executed over time. Business strategic plans are usually executed over the course of 3-5 years.
How to Develop a Strategic Plan
To develop a strategic plan, you should ask yourself the following three questions.
- Where Is the Business Now? Gather as much information on your business as possible including internal operations and what drives its profitability. Compare the business to competitors and note the similarities and differences in detail. This isn’t a day-to-day operational study, but a broader look at the business in context to itself and its environment. But don’t go crazy; stay realistic in terms of your business goals. Be detached and critical in your analysis.
- Where Do You Want to Go? Now it’s time to decide what your top-level objectives are for the future. Start with a vision statement , objectives, values, techniques and goals. Look forward to five years or more to forecast where you want the business to be at that time. This means figuring out what the focus of the business will be in the future. Will that focus differ from what it is now, and what competitive advantages do have you in the marketplace? This is where you build the foundation and initiate changes.
- How Can You Get There? Once you know where you are and where you want to go, it’s time to plan. What are the changes to the structure, financing, etc., necessary for the business to get there? Decide on the best way to implement those changes, the timeframe with deadlines and how to finance it. Remember, this is looking at the business at large, so consider major endeavors such as diversification, existing growth, acquisition and other functional matters. A gap analysis can be a big help here.
Once you’ve answered the above questions and have a way to achieve the long-term goals laid out in the strategic plan, the next step is making sure you have the right person to manage all of its moving parts. They must be analytical, a creative thinker and able to grasp operational detail.
That doesn’t mean the strategic plan is led by one person. It’s best to not do it alone; seek other opinions. The people in your organization, from bottom to top, are all great resources to offer perspectives from their standpoints. Don’t forget to take in the advice of stakeholders, including customers, clients, advisors and consultants.
To create a strong strategic plan, one must first have a strong understanding of the business that is to expand. How does the business work? Where does the business stand in relation to competitors in the marketplace? A strategic plan is built on the bones of the following foundational elements:
- Mission Statement: The mission statement describes what your company does.
- Vision Statement: The vision statement explains where your company expects to be in the future.
- Core Values: Guiding principles that shape your company’s organizational culture.
- Business Objectives: Consider using the SMART goal-setting technique . This simply means setting up specific, measurable, attainable, relevant and time-bound objectives that your company wants to achieve.
- SWOT Analysis: External and internal factors that make up your company’s business competitive environment.
- Action Plan: A plan outlining steps that will be taken to achieve the business objectives of your organization.
- Financials: A section that shows the financial performance expectations, the budget and the resources that will be required to implement the action plan.
- Performance Measurements: Performance indicators that will be used to measure the effectiveness of the action plan.
Never forget to check your strategic plan against reality. In addition to being achievable, it must be practical for your business environment, resources and marketplace.
Now let’s look at a simple business strategic plan example. This is a strategic plan for a small construction company.
1. Mission, Vision & Core Values
- Mission Statement: To build residential spaces that provide wellbeing for our clients.
- Vision Statement: To offer the best construction experience for our clients and expand our brand throughout the globe.
- Core Values: Sustainable innovation and respect for the environment.
2. Business Objectives
- Business Objective 1: Grow operating margin from 15% to 20% over the next year.
- Business Objective 2: Reduce operating costs by 5% over the next quarter
- Business Objective 3: Increase the number of new contracts generated by 10% over the next year
3. SWOT Analysis
- Strengths: Available financing, brand visibility and know-how.
- Weaknesses: Lack of PPE, human capital and expertise in construction areas such as plumbing, electrical work and masonry, which requires subcontractors.
- Opportunities: Lack of environmentally-friendly construction companies in the market.
- Threats: Larger construction companies compete for contracts in the area.
4. Action Plan
- Business Objective 1: To grow operating margin, new employees with plumbing, electrical work and masonry experience will be hired to cut down subcontractor costs. This must be done by the end of the first quarter.
- Business Objective 2: To reduce operating costs, the company will acquire property, plant and equipment. By doing this, the company will no longer rent equipment from third parties, which will reduce operating costs significantly in the medium and long term.
- Business Objective 3: To increase the number of new contracts generated, the leadership team will invest more in the PR, marketing and advertising departments. The company will also invest in key positions for the construction bidding process such as contract estimators.
- Financials: This section will explain in detail what are the costs associated with the work items in the action plan as well as the expected financial benefits for the company.
Our free strategic plan template helps leadership teams gather important information about their business strategy, which makes it the perfect tool to start shaping a strategic plan for your business or project.
More Free Strategic Planning Templates
Here are some free strategic planning templates for Word and Excel that will help you with key aspects of the strategic planning process. Use them individually or add them to your strategic plan template for Word so you don’t miss any detail about your organizational strategy.
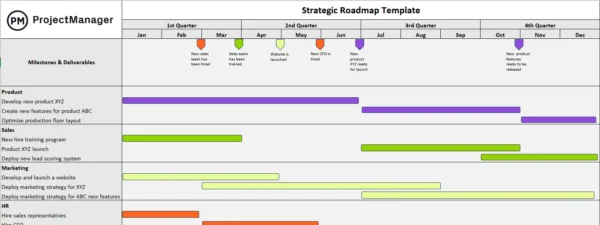
Strategic Roadmap Template
This strategic roadmap template allows you to map the activities, strategic projects and initiatives that each business department will execute to accomplish the objectives defined in the strategic plan of an organization.
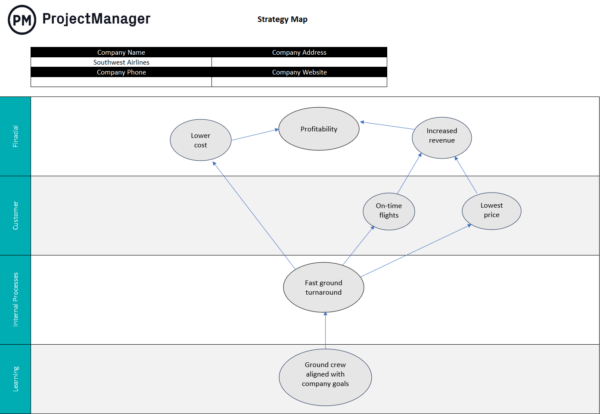
Strategic Map Template
This strategic map template it’s a strategic planning tool that allows you to visualize all the strategic objectives of your organization and understand how they’re interrelated.
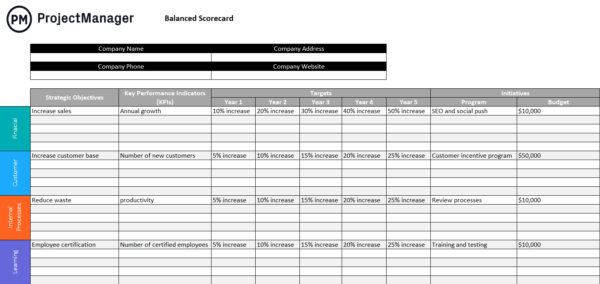
Balanced Scorecard Template
A balanced scorecard is a chart that allows you to set strategic objectives that will benefit your business in one of four key areas, its finances, internal processes, customer satisfaction and organizational learning.
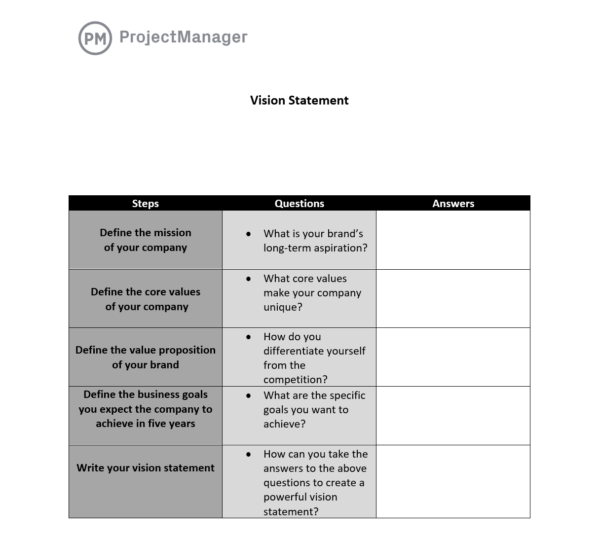
Vision Statement Template
The vision statement is one of the most important aspects of the organizational strategy of a business. It’s a short but powerful statement that describes the overall direction of a company and what it intends to achieve in the future. This free vision statement template will help you focus on what matters most and define the vision of your business.
A strategic plan is a type of business plan, but there are distinctions between the two. Whereas a strategic plan is for implementing and managing the strategic direction of a business, a business plan is more often the document that starts a business.
A business plan is used primarily to get funding for the venture or direct the operation, and the two plans target different timeframes in business history. A strategic plan is used to investigate a future period, usually between three-to-five years. A business plan is more routinely a year out.
A Different Intent
A strategic plan offers a business focus, direction and action to help the business grow from the point it presently resides to a greater market share in the future. A business plan, on the other hand, is more focused on offering a structure to capture and implement ideas that initially define a business.
With a strategic plan, existing resources are prioritized to increase revenue and return on investment. The business plan is different in that it’s seeking funding for a venture that doesn’t yet exist. Where a strategic plan is building a sustainable competitive advantage in the future, a business plan is designed to take advantage of a current business opportunity.
So, a strategic plan is communicating direction to teams and stakeholders in order to achieve future goals. A business plan isn’t talking to staff, which is likely nonexistent or minimal at this point. It’s speaking to banks and other financial supporters.
Related Strategic Planning Content
- Strategic Project Management: Planning Strategic Projects
- Strategic Planning Models: An Introduction to 5 Popular Models
- A Quick Guide to Strategic Initiatives
- How to Create a Strategic Roadmap for Your Organization
- Project Alignment: Aligning Your Project to Business Strategy
Strategic planning, like any planning, requires keeping a lot of balls in the air. That means having the right tool to plan, monitor and report on all the various tasks and resources. ProjectManager is online project management software that gives you control over every aspect of creating and implementing a strategic plan. Try it today with this free 30-day trial.

Deliver your projects on time and under budget
Start planning your projects.
The Complete Guide to Writing a Strategic Plan
By Joe Weller | April 12, 2019 (updated March 26, 2024)
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
Writing a strategic plan can be daunting, as the process includes many steps. In this article, you’ll learn the basics of writing a strategic plan, what to include, common challenges, and more.
Included on this page, you'll find details on what to include in a strategic plan , the importance of an executive summary , how to write a mission statement , how to write a vision statement , and more.
The Basics of Writing a Strategic Plan
The strategic planning process takes time, but the payoff is huge. If done correctly, your strategic plan will engage and align stakeholders around your company’s priorities.
Strategic planning, also called strategy development or analysis and assessment , requires attention to detail and should be performed by someone who can follow through on next steps and regular updates. Strategic plans are not static documents — they change as new circumstances arise, both internally and externally.
Before beginning the strategic planning process, it’s important to make sure you have buy-in from management, a board of directors, or other leaders. Without it, the process cannot succeed.
Next, gather your planning team. The group should include people from various departments at different levels, and the planning process should be an open, free discussion within the group. It’s important for leaders to get input from the group as a whole, but they don’t necessarily need approval from everyone — that will slow down the process.
The plan author is responsible for writing and putting the final plan together and should work with a smaller group of writers to establish and standardize the tone and style of the final document or presentation.
Sometimes, it’s a good idea to hire an external party to help facilitate the strategic planning process.

“It often can be helpful to have a really good facilitator to organize and pursue strategic conversations,” says Professor John M. Bryson, McKnight Presidential Professor of Planning and Public Affairs at the Hubert H. Humphrey School of Public Affairs, University of Minnesota and author of Strategic Planning for Public and Nonprofit Organizations: A Guide to Strengthening and Sustaining Organizational Achievement .
Byson says the facilitator can be in-house or external, but they need experience. “You need to make sure someone is good, so there needs to be a vetting process,” he says.
One way to gauge a facilitator’s experience is by asking how they conduct conversations. “It’s important for facilitators to lead by asking questions,” Bryson says.
Bryson says that strong facilitators often ask the following questions:
What is the situation we find ourselves in?
What do we do?
How do we do it?
How do we link our purposes to our capabilities?
The facilitators also need to be able to handle conflict and diffuse situations by separating idea generation from judgement. “Conflict is part of strategic planning,” Bryson admits. “[Facilitators] need to hold the conversations open long enough to get enough ideas out there to be able to make wise choices.”
These outside helpers are sometimes more effective than internal facilitators since they are not emotionally invested in the outcome of the process. Thus, they can concentrate on the process and ask difficult questions.
A strategic plan is a dynamic document or presentation that details your company’s present situation, outlines your future plans, and shows you how the company can get there. You can take many approaches to the process and consider differing ideas about what needs to go into it, but some general concepts stand.
“Strategic planning is a prompt or a facilitator for fostering strategic thinking, acting, and learning,” says Bryson. He explains that he often begins planning projects with three questions:
What do you want to do?
How are we going to do it?
What would happen if you did what you want to do?
The answers to these questions make up the meat of the planning document.
A strategic plan is only effective when the writing and thinking is clear, since the intent is to help an organization keep to its mission through programs and capacity, while also building stakeholder engagement.
Question 1: Where Are We Now?
The answer (or answers) to the first question — where are we now? — addresses the foundation of your organization, and it can serve as an outline for the following sections of your strategic plan:
Mission statement
Core values and guiding principles
Identification of competing organizations
Industry analysis (this can include a SWOT or PEST analysis)
Question 2: Where Are We Going?
The answers to this question help you identify your goals for the future of the business and assess whether your current trajectory is the future you want. These aspects of the plan outline a strategy for achieving success and can include the following:
Vision statement about what the company will look like in the future
What is happening (both internally and externally) and what needs to change
The factors necessary for success
Question 3: How Do We Get There?
The answers to this question help you outline the many routes you can take to achieve your vision and match your strengths with opportunities in the market. A Gantt chart can help you map out and keep track of these initiatives.
You should include the following sections:
Specific and measurable goals
An execution plan that identifies who manages and monitors the plan
An evaluation plan that shows how you plan to measure the successes and setbacks that come with implementation
What to Include in a Strategic Plan
Strategic planning terminology is not standardized throughout the industry, and this can lead to confusion. Instead, strategic planning experts use many names for the different sections of a strategic plan.

“The terms are all over the map. It’s really the concept of what the intention of the terms are [that is important],” says Denise McNerney, President and CEO of iBossWell, Inc. , and incoming president of the Association for Strategic Planning (ASP). She recommends coming up with a kind of glossary that defines the terms for your team. “One of the most important elements when you’re starting the strategic planning process is to get some clarity on the nomenclature. It’s just what works for your organization. Every organization is slightly different.”
No matter what terms you use, the general idea of a strategic plan is the same. “It’s like drawing a map for your company. One of the first steps is committing to a process, then determining how you’re going to do it,” McNerney explains.
She uses a basic diagram that she calls the strategic plan architecture . The areas above the red dotted line are the strategic parts of the plan. Below the red dotted line are the implementation pieces.

While the specific terminology varies, basic sections of a strategic plan include the following in roughly this order:
Executive summary
Elevator pitch or company description
Vision statement
Industry analysis
Marketing plan
Operations plan
Financial projections
Evaluation methods
Signature page
Some plans will contain all the above sections, but others will not — what you include depends on your organization’s structure and culture.
“I want to keep it simple, so organizations can be successful in achieving [the strategic plan],” McNerney explains. “Your plan has to be aligned with your culture and your culture needs to be aligned with your plan if you’re going to be successful in implementing it.”
The following checklist will help you keep track of what you have done and what you still need to do.
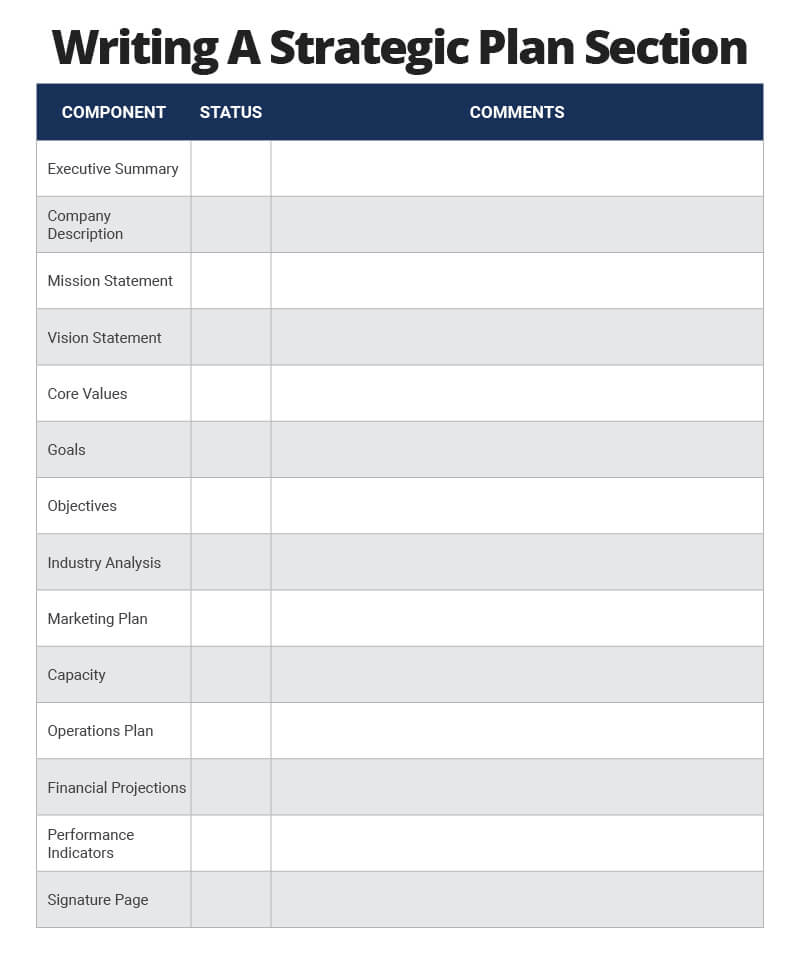
Download Strategic Plan Sections Checklist
How to Write a Strategic Plan
Once you’ve assembled your team and defined your terms, it’s time to formalize your ideas by writing the strategic plan. The plan may be in the form of a document, a presentation, or another format.
You can use many models and formats to create your strategic plan (read more about them in this article ). However, you will likely need to include some basic sections, regardless of the particular method you choose (even if the order and way you present them vary). In many cases, the sections of a strategic plan build on each other, so you may have to write them in order.
One tip: Try to avoid jargon and generic terms; for example, words like maximize and succeed lose their punch. Additionally, remember that there are many terms for the same object in strategic planning.
The following sections walk you through how to write common sections of a strategic plan.
How to Write an Executive Summary
The key to writing a strong executive summary is being clear and concise. Don’t feel pressured to put anything and everything into this section — executive summaries should only be about one to two pages long and include the main points of the strategic plan.
The idea is to pique the reader’s interest and get them to read the rest of the plan. Because it functions as a review of the entire document, write the executive summary after you complete the rest of your strategic plan.

“If you have a plan that’s really lengthy, you should have a summary,” says Jim Stockmal, President of the Association for Strategic Planning (ASP). He always writes summaries last, after he has all the data and information he needs for the plan. He says it is easier to cut than to create something.
For more information about writing an effective executive summary, a checklist, and free templates, read this article .
If you want a one-page executive summary, this template can help you decide what information to include.
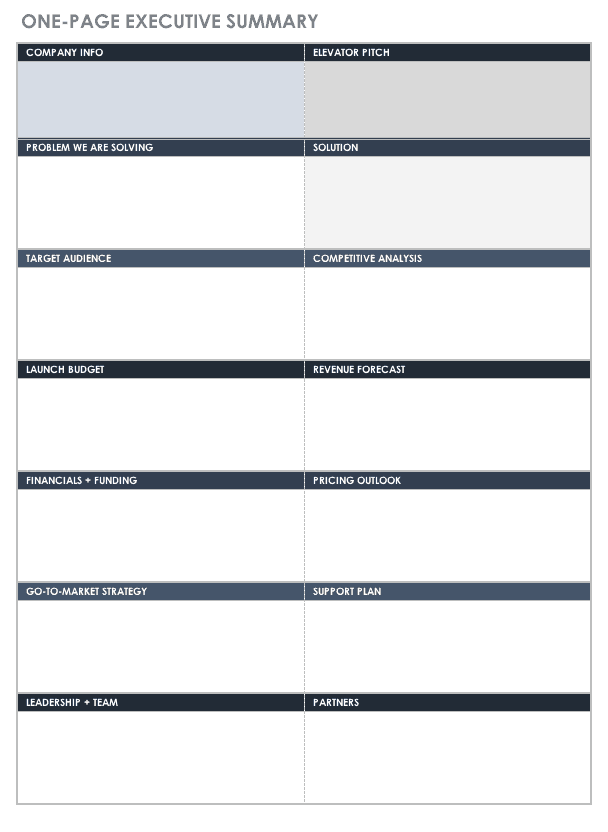
Download One-Page Executive Summary Template
Excel | Word | PDF
How to Write a Company Description
Also called an elevator pitch , the company description is a brief outline of your organization and what it does. It should be short enough that it can be read or heard during the average elevator ride.
The company description should include the history of your company, the major products and services you provide, and any highlights and accomplishments, and it should accomplish the following:
Define what you are as a company.
Describe what the company does.
Identify your ideal client and customer.
Highlight what makes your company unique.
While this may seem basic, the company description changes as your company grows and changes. For example, your ideal customer five years ago might not be the same as the current standard or the one you want in five years.
Share the company description with everyone in your organization. If employees cannot accurately articulate what you do to others, you might miss out on opportunities.
How to Write a Mission Statement
The mission statement explains what your business is trying to achieve. In addition to guiding your entire company, it also helps your employees make decisions that move them toward the company’s overall mission and goals.
“Ideally, [the mission statement is] something that describes what you’re about at the highest level,” McNerney says. “It’s the reason you exist or what you do.”
Strong mission statements can help differentiate your company from your competitors and keep you on track toward your goals. It can also function as a type of tagline for your organization.
Mission statements should do the following:
Define your company’s purpose. Say what you do, who you do it for, and why it is valuable.
Use specific and easy-to-understand language.
Be inspirational while remaining realistic.
Be short and succinct.
This is your chance to define the way your company will make decisions based on goals, culture, and ethics. Mission statements should not be vague or generic, and they should set your business apart from others. If your mission statement could define many companies in your line of work, it is not a good mission statement.
Mission statements don’t have to be only outward-facing for customers or partners. In fact, it is also possible to include what your company does for its employees in your mission statement.
Unlike other parts of your strategic plan that are designed to be reviewed and edited periodically, your company’s mission statement should live as is for a while.
That said, make the effort to edit and refine your mission statement. Take out jargon like world class, best possible, state of the art, maximize, succeed , and so on, and cut vague or unspecific phrasing. Then let your strategic planning committee review it.
How to Write a Vision Statement
Every action your company does contributes to its vision. The vision statement explains what your company wants to achieve in the long term and can help inspire and align your team.
“The vision is the highest-ordered statement of the desired future or state of what you want your business to achieve,” McNerney explains.
A clear vision statement can help all stakeholders understand the meaning and purpose of your company. It should encourage and inspire employees while setting your company’s direction. It also helps you rule out elements that might not align with your vision.
Vision statements should be short (a few sentences). They should also be memorable, specific, and ambitious. But there is a fine line between being ambitious and creating a fantasy. The vision should be clearly attainable if you follow the goals and objectives you outline later in your strategic planning plan.
Because you need to know your company’s goals and objectives to create an accurate vision statement, you might need to wait until you have more information about the company’s direction to write your vision statement.
Below are questions to ask your team as you craft your vision statement:
What impact do we want to have on our community and industry?
How will we interact with others as a company?
What is the culture of the business?
Avoid broad statements that could apply to any company or industry. For example, phrases like “delivering a wonderful experience” could apply to many industries. Write in the present tense, avoid jargon, and be clear and concise.
Vision statements should accomplish the following:
Be inspiring.
Focus on success.
Look at and project about five to 10 years ahead.
Stay in line with the goals and values of your organization.
Once you write your vision statement, communicate it to everyone in your company. Your team should be able to easily understand and repeat the company’s vision statement. Remember, the statements can change as the environment in and around your company changes.
The Difference Between Mission and Vision Statements
Mission and vision statements are both important, but they serve very different purposes.
Mission statements show why a business exists, while vision statements are meant to inspire and provide direction. Mission statements are about the present, and vision statements are about the future. The mission provides items to act upon, and the vision offers goals to aspire to.
For example, if a vision statement is “No child goes to bed hungry,” the accompanying mission would be to provide food banks within the city limits.
While many organizations have both mission and vision statements, it’s not imperative. “Not everyone has a vision statement,” McNerney says. “Some organizations just have one.”
If you choose to have only one statement, McNerney offers some advice: “Any statement you have, if you have just one, needs to include what [you do], how [you do it], why [you do it], and who you do it for.”
During the planning process, these key statements might change. “Early on in the process, you need to talk about what you are doing and why and how you are doing it. Sometimes you think you know where you want to go, but you’re not really sure,” McNerney says. “You need to have flexibility both on the plan content and in the process.”
How to Write Your Company’s Core Values
Company core values , sometimes called organizational values , help you understand what drives the company to do what it does. In this section, you’ll learn a lot about your company and the people who work with you. It should be relatively easy to write.
“The values are the core of how you operate [and] how you treat your people, both internally and externally. Values describe the behaviors you really want to advance,” McNerney says.
There are both internal and external values looking at your employees and coworkers, as well as customers and outside stakeholders. Pinpointing values will help you figure out the traits of the people you want to hire and promote, as well as the qualities you’re looking for in your customers.
Your values should align with your vision statement and highlight your strengths while mitigating weaknesses. McNerney says many organizations do not really consider or are not honest about their company’s values when working on strategic plans, which can lead to failure.
“Your strategies have to align with your values and vice versa,” she explains.
Many companies’ values sound like meaningless jargon, so take the time to figure out what matters to your company and push beyond generic language.
How to Write about Your Industry
When planning ahead for your business, it’s important to look around. How are matters inside your company? What are your competitors doing? Who are your target customers?
“[If you don’t do a thorough industry analysis], you’re doing your planning with your head in the sand. If you’re not looking at the world around you, you’re missing a whole dimension about what should inform your decision making,” McNerney advises.
Writing about your industry helps you identify new opportunities for growth and shows you how you need to change in order to take advantage of those opportunities. Identify your key competitors, and define what you see as their strengths and weaknesses. Performing this analysis will help you figure out what you do best and how you compare to your competition. Once you know what you do well, you can exploit your strengths to your advantage.
In this section, also include your SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) analysis. You can choose from many templates to help you write this section.
Next, identify your target customers. Think about what they want and need, as well as how you can provide it. Do your competitors attract your target customers, or do you have a niche that sets you apart?
The industry analysis carries a price, but also provides many benefits. “It takes some time and money to do [a thorough industry analysis], but the lack of that understanding says a lot about the future of your organization. If you don’t know what is going on around you, how can you stay competitive?” explains McNerney.
How to Write Strategic Plan Goals and Objectives
This section is the bulk of your strategic plan. Many people confuse goals and objectives, thinking the terms are interchangeable, but many argue that the two are distinct. You can think of them this way:
Goals : Goals are broad statements about what you want to achieve as a company, and they’re usually qualitative. They function as a description of where you want to go, and they can address both the short and long term.
Objectives : Objectives support goals, and they’re usually quantitative and measurable. They describe how you will measure the progress needed to arrive at the destination you outlined in the goal. More than one objective can support one goal.
For example, if your goal is to achieve success as a strategic planner, your objective would be to write all sections of the strategic plan in one month.
iBossWell, Inc.’s McNerney reiterates that there are not hard and fast definitions for the terms goals and objectives , as well as many other strategic planning concepts. “I wouldn’t attempt to put a definition to the terms. You hear the terms goals and objectives a lot, but they mean different things to different people. What some people call a goal , others call an objective . What some people call an objective , others would call a KPI. ” They key, she explains, is to decide what the terms mean in your organization, explain the definitions to key stakeholders, and stick to those definitions.
How to Write Goals
Goals form the basis of your strategic plan. They set out your priorities and initiatives, and therefore are critical elements and define what your plan will accomplish. Some planning specialists use the term strategic objectives or strategic priorities when referring to goals, but for clarity, this article will use the term goals.
“[Goals] are the higher level that contain several statements about what your priorities are,” McNerney explains. They are often near the top of your plan’s hierarchy.
Each goal should reflect something you uncovered during the analysis phase of your strategic planning process. Goals should be precise and concise statements, not long narratives. For example, your goals might be the following:
Eliminate case backlog.
Lower production costs.
Increase total revenue.
Each goal should have a stated outcome and a deadline. Think of goal writing as a formula: Action + detail of the action + a measurable metric + a deadline = goal. For example, your goal might be: Increase total revenue by 5 percent in three product areas by the third quarter of 2020.
Another way to look at it: Verb (action) + adjective (description) = noun (result). An example goal: Increase website fundraising.
Your goals should strike a balance between being aspirational and tangible. You want to stretch your limits, but not make them too difficult to reach. Your entire organization and stakeholders should be able to remember and understand your goals.
Think about goals with varying lengths. Some should go out five to 10 years, others will be shorter — some significantly so. Some goals might even be quarterly, monthly, or weekly. But be careful to not create too many goals. Focus on the ones that allow you to zero in on what is critical for your company’s success. Remember, several objectives and action steps will likely come from each goal.
How to Write Objectives
Objectives are the turn-by-turn directions of how to achieve your goals. They are set in statement and purpose with no ambiguity about whether you achieve them or not.
Your goals are where you want to go. Next, you have to determine how to get there, via a few different objectives that support each goal. Note that objectives can cover several areas.
“You need implementation elements of the plan to be successful,” McNerney says, adding that some people refer to objectives as tactics , actions , and many other terms.
Objectives often begin with the words increase or decrease because they are quantifiable and measurable. You will know when you achieve an objective. They are action items, often with start and end dates.
Use the goal example from earlier: Increase total revenue by 5 percent in three product areas by the third quarter of 2020. In this example, your objectives could be:
Approach three new possible clients each month.
Promote the three key product areas on the website and in email newsletters.
Think of the acronym SMART when writing objectives: Make them specific, measurable, achievable, realistic/relevant, and time-bound.
Breaking down the process further, some strategic planners use the terms strategies and tactics to label ways to achieve objectives. Using these terms, strategies describe an approach or method you will use to achieve an objective. A tactic is a specific activity or project that achieves the strategy, which, in turn, helps achieve the objective.
How to Write about Capacity, Operations Plans, Marketing Plans, and Financial Plans
After you come up with your goals and objectives, you need to figure out who will do what, how you will market what they do, and how you will pay for what you need to do.
“If you choose to shortchange the process [and not talk about capacity and finances], you need to know what the consequences will be,” explains McNerney. “If you do not consider the additional costs or revenues your plan is going to drive, you may be creating a plan you cannot implement.”
To achieve all the goals outlined in your strategic plan, you need the right people in place. Include a section in your strategic plan where you talk about the capacity of your organization. Do you have the team members to accomplish the objectives you have outlined in order to reach your goals? If not, you may need to hire personnel.
The operations plan maps out your initiatives and shows you who is going to do what, when, and how. This helps transform your goals and objectives into a reality. A summary of it should go into your strategic plan. If you need assistance writing a comprehensive implementation plan for your organization, this article can guide you through the process.
A marketing plan describes how you attract prospects and convert them into customers. You don’t need to include the entire marketing plan in your strategic plan, but you might want to include a summary. For more information about writing marketing plans, this article can help.
Then there are finances. We would all like to accomplish every goal, but sometimes we do not have enough money to do so. A financial plan can help you set your priorities. Check out these templates to help you get started with a financial plan.
How to Write Performance Indicators
In order to know if you are reaching the goals you outline in your strategic plan, you need performance indicators. These indicators will show you what success looks like and ensure accountability. Sadly, strategic plans have a tendency to fail when nobody periodically assesses progress.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) can show you how your business is progressing. KPIs can be both financial and nonfinancial measures that help you chart your progress and take corrective measures if actions are not unfolding as they should. Other terms similar to KPIs include performance measures and performance indicators .
Performance indicators are not always financial, but they must be quantifiable. For example, tracking visitors to a website, customers completing a contact form, or the number of proposals that close with deals are all performance indicators that keep you on track toward achieving your goals.
When writing your performance indicators, pay attention to the following:
Define how often you need to report results.
Every KPI must have some sort of measure.
List a measure and a time period.
Note the data source where you will get your information to measure and track.
ASP’s Stockmal has some questions for you to ask yourself about picking performance indicators.
Are you in control of the performance measure?
Does the performance measure support the strategic outcomes?
Is it feasible?
Is data available?
Who is collecting that data, and how will they do it?
Is the data timely?
Is it cost-effective to collect that data?
ls the goal quantifiable, and can you measure it over time?
Are your targets realistic and time-bound?
Stockmal also says performance indicators cannot focus on only one thing at the detriment of another. “Don’t lose what makes you good,” he says. He adds that focusing on one KPI can hurt other areas of a company’s performance, so reaching a goal can be short-sided.
Some performance indicators can go into your strategic plan, but you might want to set other goals for your organization. A KPI dashboard can help you set up and track your performance and for more information about setting up a KPI dashboard, this article can help.
Communicating Your Strategic Plan
While writing your strategic plan, you should think about how to share it. A plan is no good if it sits on a shelf and nobody reads it.

“After the meetings are over, you have to turn your strategy into action,” says Stefan Hofmeyer, an experienced strategist and co-founder of Global PMI Partners . “Get in front of employees and present the plan [to get everyone involved].” Hofmeyer explains his research has shown that people stay with companies not always because of money, but often because they buy into the organization’s vision and want to play a part in helping it get where it wants to go. “These are the people you want to keep because they are invested,” he says.
Decide who should get a physical copy of the entire plan. This could include management, the board of directors, owners, and more. Do your best to keep it from your competitors. If you distribute it outside of your company, you might want to attach a confidentiality waiver.
You can communicate your plan to stakeholders in the following ways:
Hold a meeting to present the plan in person.
Highlight the plan in a company newsletter.
Include the plan in new employee onboarding.
Post the plan on the employee intranet, along with key highlights and a way to track progress.
If you hold a meeting, make sure you and other key planners are prepared to handle the feedback and discussion that will arise. You should be able to defend your plan and reinforce its key areas. The goal of the plan’s distribution is to make sure everyone understands their role in making the plan successful.
Remind people of your company’s mission, vision, and values to reinforce their importance. You can use posters or other visual methods to post around the office. The more that people feel they play an important part in the organization’s success, they more successful you will be in reaching your goals of your strategic plan.
Challenges in Writing a Strategic Plan
As mentioned, strategic planning is a process and involves a team. As with any team activity, there will be challenges.
Sometimes the consensus can take priority over what is clear. Peer pressure can be a strong force, especially if a boss or other manager is the one making suggestions and people feel pressured to conform. Some people might feel reluctant to give any input because they do not think it matters to the person who ultimately decides what goes into the plan.
Team troubles can also occur when one or more members does not think the plan is important or does not buy into the process. Team leaders need to take care of these troubles before they get out of hand.
Pay attention to your company culture and the readiness you have as a group, and adapt the planning process to fit accordingly. You need to find the balance between the process and the final product.
The planning process takes time. Many organizations do not give themselves enough time to plan properly, and once you finish planning, writing the document or presentation also takes time, as does implementation. Don’t plan so much that you ignore how you are going to put the plan into action. One symptom of this is not aligning the plan to fit the capacity or finances of the company.
Stockmal explains that many organizations often focus too much on the future and reaching their goals that they forget what made them a strong company in the first place. Business architecture is important, which Stockmal says is “building the capabilities the organization needs to fulfill its strategy.” He adds that nothing happens if there is no budget workers to do the work necessary to drive change.
Be careful with the information you gather. Do not take shortcuts in the research phase — that will lead to bad information coming out further in the process. Also, do not ignore negative information you may learn. Overcoming adversity is one way for companies to grow.
Be wary of cutting and pasting either from plans from past years or from other similar organizations. Every company is unique.
And while this may sound obvious, do not ignore what your planning process tells you. Your research might show you should not go in a direction you might want to.
Writing Different Types of Strategic Plans
The strategic planning process will differ based on your organization, but the basic concepts will stay the same. Whether you are a nonprofit, a school, or a for-profit entity, strategic plans will look at where you are and how you will get to where you want to go.
How to Write a Strategic Plan for a Nonprofit
For a nonprofit, the strategic plan’s purpose is mainly how to best advance the mission. It’s imperative to make sure the mission statement accurately fits the organization.
In addition to a SWOT analysis and other sections that go into any strategic plan, a nonprofit needs to keep an eye on changing factors, such as funding. Some funding sources have finite beginnings and endings. Strategic planning is often continuous for nonprofits.
A nonprofit has to make the community care about its cause. In a for-profit organization, the marketing department works to promote the company’s product or services to bring in new revenue. For a nonprofit, however, conveying that message needs to be part of the strategic plan.
Coming up with an evaluation method and KPIs can sometimes be difficult for a nonprofit, since they are often focused on goals other than financial gain. For example, a substance abuse prevention coalition is trying to keep teens from starting to drink or use drugs, and proving the coalition’s methods work is often difficult to quantify.
This template can help you visually outline your strategic plan for your nonprofit.
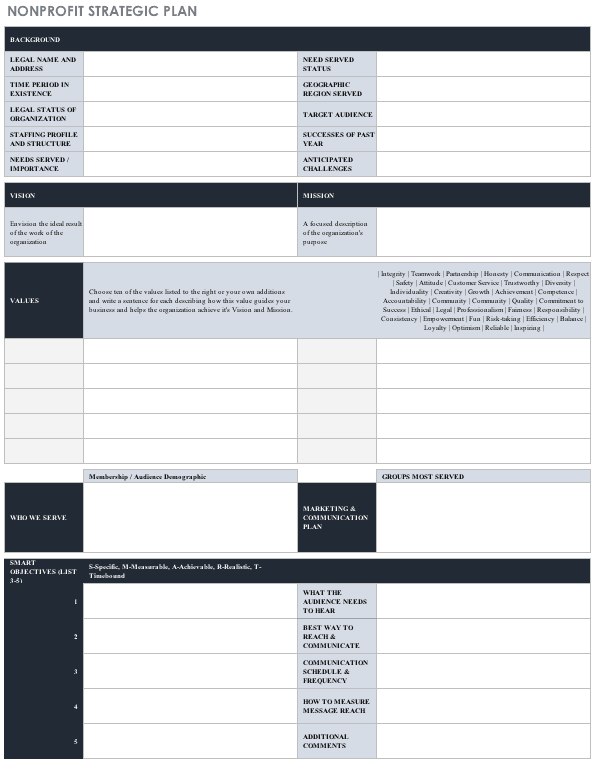
Download Nonprofit Strategic Plan Template
Excel | Smartsheet
How to Write a Strategic Plan for a School
Writing a strategic plan for a school can be difficult because of the variety of stakeholders involved, including students, teachers, other staff, and parents.
Strategic planning in a school is different from others because there are no markets to explore, products to produce, clients to woo, or adjustable timelines. Schools often have set boundaries, missions, and budgets.
Even with the differences, the same planning process and structure should be in place for schools as it is for other types of organizations.
This template can help your university or school outline your strategic plan.
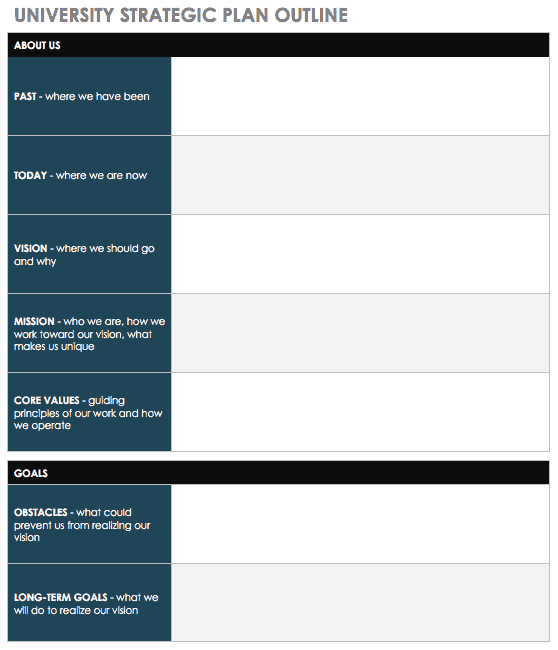
Download University Strategic Plan Outline – Word
How to Write a 5-Year Strategic Plan
There is no set time period for a strategic plan, but five years can be a sweet spot. In some cases, yearly planning might keep you continually stuck in the planning process, while 10 years might be too far out.
In addition to the basic sections that go into any strategic plan, when forecasting five years into the future, put one- and three-year checkpoints into the plan so you can track progress intermittently.
How to Write a 3-Year Strategic Plan
While five years is often the strategic planning sweet spot, some organizations choose to create three-year plans. Looking too far ahead can be daunting, especially for a new or changing company.
In a three-year plan, the goals and objectives have a shorter timeframe and you need to monitor them more frequently. Build those checkpoints into the plan.
“Most organizations do a three- to five-year plan now because they recognize the technology and the changes in business that are pretty dynamic now,” Stockmal says.
How to Write a Departmental Strategic Plan
The first step in writing a strategic plan for your department is to pay attention to your company’s overall strategic plan. You want to make sure the plans align.
The steps in creating a plan for a department are the same as for an overall strategic plan, but the mission statement, vision, SWOT analysis, goals, objectives, and so on are specific to only the people in your department. Look at each person separately and consider their core competencies, strengths, capabilities, and weaknesses. Assign people who will be responsible for certain tasks and tactics necessary to achieve your goals.
If you have access to a plan from a previous year, see how your department did in meeting its goals. Adjust the new plan accordingly.
When you finish your departmental plan, make sure to submit it to whomever is responsible for your company’s overall plan. Expect to make changes.
How to Write a Strategic Plan for a Project
A strategic plan is for the big picture, not for a particular project for an organization. Instead of a strategic plan, this area would fall under project management.
If you have a failing project and need to turn it around, this article might help.
How to Write a Personal Strategic Plan
Creating a strategic plan isn’t only for businesses. You can also create a strategic plan to help guide both your professional and personal life. The key is to include what is important to you. This process takes time and reflection.
Be prepared for what you discover about yourself. Because you will be looking at your strengths and weaknesses, you might see things you do not like. It is important to be honest with yourself. A SWOT analysis on yourself will give you some honest feedback if you let it.
Begin with looking at your life as it is now. Are you satisfied? What do you want to do more or less? What do you value most in your life? Go deeper than saying family, happiness, and health. This exercise will help you clarify your values.
Once you know what is important to you, come up with a personal mission statement that reflects the values you cherish. As it does within a business, this statement will help guide you in making future decisions. If something does not fit within your personal mission, you shouldn’t do it.
Using the information you discovered during your SWOT and mission statement process, come up with goals that align with your values. The goals can be broad, but don’t forget to include action items and timeframes to help you reach your goals.
As for the evaluation portion, identify how you will keep yourself accountable and on track. You might involve a person to remind you about your plan, calendar reminders, small rewards when you achieve a goal, or another method that works for you.
Below is additional advice for personal strategic plans:
There are things you can control and things you cannot. Keep your focus on what you can act on.
Look at the positive instead of what you will give up. For example, instead of focusing on losing weight, concentrate on being healthier.
Do not overcommit, and do not ignore the little details that help you reach your goals.
No matter what, do not dwell on setbacks and remember to celebrate successes.
Improve Strategic Planning with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
Strategic planning — what it is and how to do it well

It can be difficult to reach your business goals and ambitions, regardless of what preparation you’ve done. But if you have a strategic plan in place, you’ll be more likely to achieve a favorable outcome.
This post will explain the importance of strategic planning, when and how to make a strategic plan, and how to manage it and stay on course. It will allow the audience to move forward with their planning efforts.
Read on to learn:
- What strategic planning is

Benefits of strategic planning
- When you should do strategic planning
Steps in strategic planning
- What strategic management is
Strategic mapping
What is strategic planning.
Strategic planning is the process of defining your business’s direction and outlining a path toward a preferred future. The goal of a strategic plan is to capture an organization’s mission and core principles — to envision the fulfillment of these ideals. Strategic planning is both conceptual and practical, as it presents both high-level goals and specific approaches to achieve them.
A strategic plan needs to answer the following questions:
- Where are we now?
- Where are we going?
- How do we get there?
Strategic planning helps businesses set and maintain a clear vision and ensure they’re moving in the right direction. Once the plan has been put in place, it helps maintain alignment between various stakeholders and teams within your business. This plan can make resource allocation simpler — by determining if certain resources are being used in ways that don’t align with the broader strategic plan.
Running a business without a strategic plan is like planning a vacation with no destination in mind. How will you get there? What do you need to bring with you? The same applies to planning for your business. Strategic planning:
- Gives a sense of purpose and direction. A strategic plan provides a clear goal and end result so all other business functions can work to get you closer to that outcome. This clarity helps keep employees aligned on their efforts, make better decisions, and work towards a shared goal.
- Makes you aware of opportunities for success. Tying your plans to strategy helps your organization identify opportunities that you discover along your journey. If you find an opportunity that aligns with your strategy — and desired outcomes — you can more easily adapt to take advantage of the situation.
- Alerts you to risks to avoid. Part of the strategic planning process is scanning the external environment and competitive landscape, which allows you to identify potential roadblocks you may encounter.
- Helps you understand what resources you will need. When you have a strategic plan in place, you can more effectively allocate your resources. By aligning resources with strategic goals, businesses can focus on the initiatives, projects, and investments that maximize their ROI.
- Helps prioritize critical tasks. When deciding which tasks are most important and which can be put on hold, a strategic plan streamlines that decision making. Tasks that don’t contribute to your mission can wait, while mission-critical tasks get prioritized.
- Fosters teamwork and communication. Without a strategic plan, team members can feel isolated and siloed. However, when that strategic plan is clearly communicated to everyone, your team will feel more connected as they work towards a common goal.
- Increases motivation. And when your team understands the desired outcomes and bigger goals behind their daily tasks, they’ll be more motivated to do high-quality work in a timely manner.
- Helps measure and evaluate results. Because you’ve likely identified key performance indicators (KPIs) in your planning process, you’ll have an easier time tracking your progress. When you measure your progress, you can more easily identify areas for improvement and make changes on the fly.
When should you do strategic planning?
When and how often your business does strategic planning depends on the size and stage of your company, the speed of your business, and the scope of the projects you’re working on. Strategic planning should not be a one-time event. It should be an iterative process with continuous monitoring, evaluation, and adjustment.
If you’re a new business, you’ll want to create a business plan first, before you move into strategic planning. Once your business is established you can then set a strategic plan to outline your goals and manage your business’s strategic direction. For planning more short-term projects, use a project plan .
Once you’ve created a strategic plan, you should review it regularly — quarterly and yearly, for example — to make sure it is still aligned with your business’s goals and industry landscape. Generally, you should create a new strategic plan every 3–5 years. However, newer or faster-moving companies may need to create a new strategic plan every 1–2 years. Another scenario when you should rework your strategic plan is when you’re preparing to make a major pivot in your business.
How to write a strategic plan for a project
Learn how to write a strategic plan, why you need to create one, and the topics it should cover.

While every strategic plan might look a little different depending on the organization, industry, and other context, there is still a general outline of the process that you can follow to get you started.
Before you get started, there are a few preliminary steps you can take to make sure your planning process goes smoothly. You need to decide who is involved in the process and what documentation they’ll need. You’ll also want to revisit your company’s vision and mission statements which define where your business is aiming to go.
These are the steps you can take to create a strategic plan for your business:
1. Identify and assess your current position
To understand where you’re headed, you first need to look at where you are now. I n this stage you should:
- Collect customer and employee feedback to understand what is working well for you and what could use improvement.
- Perform a needs assessment or SWOT analysis to understand more about the current state of your business.
- Assess your available resources so you can understand what you have enough of and what you may need to reach your goals.
2. Set goals
Next, you can set goals that you’d like your business to achieve over the short and long term. It’s important to choose goals that align with your company mission and vision. You can use marketing and sales forecasts to give you an idea of what types of goals are realistic. In this phase you’ll also want to prioritize the goals you set — so you know which to choose if conflicts arise.
When setting goals, remember to set SMART goals that are specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time bound.
3. Develop your plan
In this phase it’s time to put your plan together and map out a project roadmap. This is where your plan becomes clearer both to your planning committee and to your team members who will execute based on the plan.
You want to make sure that your plan is achievable with your current resources — so that you aren’t setting yourself up for failure. You’ll also want to set measurable milestones so you can track your progress along the way. You also need to set KPIs so you have objective numbers to determine if you’re heading in the right direction.
When developing your plan, you should make sure that any short-term action items align with long-term goals. And finally, you’ll need to get approval from leadership and stakeholders.
4. Implement your plan
Now that you’ve created your strategic plan it’s time to act. In fact, the first step of implementation is creating a strategic action plan. Your action plan will outline the specific tactics you’ll use to execute your strategic plan.
In this phase, you’ll also assign tasks to your team members so everyone knows what they are responsible for and what they will be contributing to your mission. It’s important to distribute and communicate your plan across your organization. This helps encourage transparency and will drive buy-in from everyone on your team.
As you are executing on your plan, you should rely on metrics and KPIs to track your performance.
5. Revise your plan as necessary
Next, you’ll want to revise your plan as you encounter roadblocks or market changes. Even the best strategic plans will change as you gather more data or feedback. Using tools — like a project management solution — can help you monitor the progress your team is making. You should schedule periodic evaluations to see which parts of the plan are going well and which need to be revised or reevaluated.
You can conduct reviews on a quarterly basis, so you have information at the end of the year to revise your plan if needed. Even if things are going well, you should make minor adjustments every year to keep your teams aligned and your strategy up to date. Any major revisions you make will require a new planning process — because a major adjustment could derail the rest of your strategic plan.
What is strategic management?
Strategic management is the process of formulating, implementing, and evaluating strategies to achieve the larger goals and objectives of an organization. It can sometimes be used interchangeably with the term strategic planning — but within strategic planning, strategic management means managing the plan being put into action.
Part of strategic management is being adaptive and adjusting to headwinds or organizational changes. You’ll also need to maintain a strong team culture, so your plan stays on track and team members stay engaged.
There are several models that strategic management can follow. Each takes a different approach to the management process, and how it solves problems that may arise.
One of these frameworks is the balanced scorecard method. This method looks at the strategic measures of a business beyond just financial metrics to get a more “balanced” look at performance. The phrase “balanced scorecard” refers to the management report that leaders may use to drive decision making within the business, since this approach looks at more than just numbers, it provides a more wholistic view of a business.
A strategic map is a visual representation of a business’s strategic objectives and their cause-and-effect relationships between each objective. This diagram helps visualize the strategic plan and understand which tasks are dependent on others. This map should be drawn during the development of the strategic plan to get a better understanding of how things should get done and in what order.
Strategic mapping can turn complex strategic plans into easily understandable visual representations. These can be helpful tools for communicating your strategy more clearly to team members and stakeholders within your organization. Strategic maps also help organizations identify success factors, prioritize initiatives, allocate resources, and monitor progress.
A strategic map can be designed in several ways, but needs to address the four main facets of business:

- Financial. This section of the map should identify how the strategy helps meet the financial goals of the business.
- Customer. This section should address the benefits that the customer will see from the specific strategy.
- Internal business processes (IBPs). This section shares the benefits of the strategy to the processes of the business and their efficiency.
- Learning and growth. This section will address how the business’s capabilities and knowledge will improve by using a given strategy.
Getting started with strategic planning
Strategic planning is a helpful tool for aligning everyone in your organization with your objectives and long-term goals. It can also help you gain a better understanding of your place in the market and how you can improve your business outcomes.
When you’re ready to get started, assemble your leadership team, draft your mission and vision statements, and begin by assessing the current state of your business. But you can’t get the most out of your strategic plan without a platform to drive the process forward.
That’s where Adobe Workfront can help. Workfront is an enterprise work management tool that connects work to strategy and drives better collaboration to deliver measurable business outcomes. It integrates people, data, processes, and technology across an organization so you can manage the entire lifecycle of projects from start to finish. By centralizing digital projects, cross-functional teams can connect, collaborate, and execute from anywhere to help them do their best work.
Take a product tour or watch an overview video to see how Workfront can help you execute on your strategic plan to improve your business outcomes.
https://business.adobe.com/blog/perspectives/workfront-and-the-employee-experience
https://business.adobe.com/blog/perspectives/get-the-most-out-of-workfront-discovery-by-avoiding-common-challenges
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/annual-planning

- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Business Essentials
The Importance of Strategic Planning
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/david-kindness-cpa-headshot1-beab5f883dec4a11af658fd86cb9009c.jpg)
Every successful business has a plan and knows where it is heading in the future. Setting a plan with goals, target dates, and a purpose should be finalized before embarking on a business. Taking the time on an ongoing basis to review the company's past performance, and predict its future performance, gives it a road map to follow.
Without strategic planning , which is knowing the current state of your business and where you want it to go, most businesses will fail. A strategic plan allows you to see what is important, how to get there, the pitfalls to avoid, and the noise to ignore. Below we discuss some of the reasons why strategic planning is important and how to implement it.
Key Takeaways
- Strategic planning is crucial for a business as it creates a map for a business to follow and course correct when need be.
- The first part of a strategic plan is the business plan, which outlines the purpose of the business, budgets, goals, and the mission statement.
- Making time to evaluate your business on an ongoing basis will allow you to determine how well your results are adhering to your plan. This will allow you to make adjustments or double-down on how the business is being run.
- Communicating your strategic plan to your employees is critical so that everyone is on the same page and working towards the same goals.
- Reviewing and following up on your business will highlight strengths and weaknesses in your business so that you can continue with what works well and eliminate what is hindering the growth of your business.
Making a Business Plan
The very first strategic planning most businesses do is a business plan . When you first start your business, you will likely have prepared a mission statement , a budget, and a marketing and promotion plan. The business plan is a good first step, but it needs to be reviewed and updated as the business continues and grows. If you shove it in a drawer and let dust gather on it, it won't serve as the foundation of your business, as it was meant to.
Using Goal-Based Planning
How you go about conducting strategic planning will depend on many variables, including the size of your business, the time frame included, and your personal preferences. The most common style of plan is goals-based. In this type of plan, you set goals for the business (financial and non-financial) and map out the steps needed to meet those goals.
For example, if your goal is to have $100,000 in revenues next year, the steps to get there might include bringing in five new clients a month and attending three trade shows. Whatever the goals you set for your business, they should be concrete and measurable so that you know when you reach them. Another method of strategic planning is mission-based.
When you first started your business, you likely developed a mission or values statement, outlining the purpose of your company and its overall reason for being. A mission-based strategic plan ties each part of the plan into the mission, to ensure that the company is always operating in the service of that mission.
For example, if your mission statement is to be recognized as a leader in the financial services sector and to help families become financially independent, your strategic plans should address how you will meet those goals.
Making Time
It can be difficult to find the time to plan your business. Other, more pressing priorities, like trying to bring in revenue , may grab your attention; however, carving out time regularly will help you keep on top of your business.
Blocking off a few hours a day or week to focus on your plan should be part of your business operations. During that time, you can examine the prior week's financial performance and update any marketing initiatives to make sure that your business is on track with your initial plan. If it's not, then you'll need to make adjustments to get back on track.
Regardless of how often you plan, make sure that you set it in stone in your day planner. Block off the time and don't let anything else get in the way. Turn off your cell phone and, if at all possible, go somewhere away from your office to plan in order to minimize distractions.
Promoting Communication
As a business owner, you will most likely have employees. It is critical to inform them of your strategic plan so that they are on the same page and working towards the same goal as you.
Including your staff in your strategic plan will instill a feeling of responsibility in their jobs that will help ensure productivity.
For example, if you have a sales team and your strategic plan involves bringing in five new clients a month, your sales team needs to be aware of this so that they know the goal to achieve. If they don't, perhaps they would be under the assumption that bringing in two new clients a month is excellent, when in actuality, it is only 40% of your goal. Without clear communication to your employees, your business will be a boat set adrift without any course to follow.
Following Up
A critical part of the planning process is reviewing your previous plan and comparing it to your actual results. Were you able to bring in five new clients last month? If not, why not? Tweak the plan going forward to account for changes in your business or the general economic climate. The more experience you get with the planning process and with the operational side of your business, the more accurately you will be able to plan.
Once you have had your business running for a while and block out time to follow up on your strategic plan, you will be able to determine where the strengths and weaknesses in your business lie. This would allow you to correct course, perhaps changing your business plan and goals slightly to focus on your strengths, while allowing you to eliminate your weakness, making your business stronger and increasing the likelihood of achieving your goals.
The Bottom Line
Planning out the future of your business is the best way to ensure success. Creating an initial plan and communicating that plan to your employees will ensure that everyone is working towards the same goal.
Taking out time to review your business's results and comparing them to your plan will help ensure that the right policies and procedures continue whereas those that are not benefiting the company will be removed. It may seem awkward and difficult at first to create a strategic plan, but with practice, you will be able to move your business in the right direction.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Term-b-business-plan-70c26342d5374095b3cd7e860d016168.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Strategic Planning Should Be a Strategic Exercise
- Graham Kenny
Don’t create a plan. Create a system.
Many managers complain that strategy-making often reduces to an operational action plan that resembles the last one. To prevent that from happening they need to remember that strategy is about creating a system whereby a company’s stakeholders interact to create a sustainable advantage for the company. Strategic planning is how the company designs that system, which is very different from an operational action plan in that it is never a static to-do list but constantly evolves as strategy makers acquire more insights into how their system of stakeholders can create value.
Over the years I’ve facilitated many strategic planning workshops for business, government, and not-for-profit organizations. We reflect on recent changes and future trends and consider how to engage with them for corporate success.
- Graham Kenny is the CEO of Strategic Factors and author of Strategy Discovery . He is a recognized expert in strategy and performance measurement who helps managers, executives, and boards create successful organizations in the private, public, and not-for-profit sectors. He has been a professor of management in universities in the U.S. and Canada.
Partner Center
What Is a Strategic Business Plan?
- Small Business
- Business Planning & Strategy
- Strategic Business Plans
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Pinterest" aria-label="Share on Pinterest">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Reddit" aria-label="Share on Reddit">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Flipboard" aria-label="Share on Flipboard">
Objectives in Workforce Planning
Projected profit and loss statement, rationales for marketing strategies.
- How to Find a DSL Modem's IP Address
- Why Is the Business Research Process Necessary to Assist Managers?
Long-term strategic business planning is necessary for company growth and success, explains Entrepreneur magazine . Business plans provide companies with the tools to track growth, establish a budget and prepare for unforeseen changes in the market place. A strategic business plan focuses on long-term growth objectives, rather than near-term operating goals and addresses different business strategy types.
A strategic plan includes many elements a business can utilize to attract financing and manage company objectives. To optimize strategic business planning, businesses must clearly define company goals and conduct extensive research to properly understand industry trends. Looking at different strategic planning models will help you decide how to set long-term goals for your small business.
What is a Strategic Business Plan?
A strategic business plan is a written document that pairs the objectives of a company with the needs of the market place. Although a strategic business plan contains similar elements of a traditional plan, a strategic plan takes planning a step further by not only defining company goals but utilizing those goals to take advantage of available business opportunities.
This is achieved by carefully analyzing a particular business industry and being honest about your company's strength and weakness in meeting the needs of the industry. A strategic business plan is followed by tactical plans to help achieve the strategic goals.
Reasons for Strategics Plans
A strategic business plan is necessary to optimize market research and to attain optimum market share for your business. The plan allows businesses to focus on a particular niche in the marketplace, which makes sales, advertising and customer management more effective. The plan allows a company to know as much as possible about the needs of its customers and gaps in the marketplace that need to be filled. A strategic business plan helps a company provide better, more targeted service to its clients.
Strategy vs. Tactics
A strategic business plan might set a goal of diversification for the business. Tactics for achieving this strategic goal might include acquiring a business with different product lines, or adding new products to the company's line. For example, a tennis racquet manufacturer might decided to add strings to its product line, either acquiring a string maker or sourcing its own strings.
A strategic business plan includes extensive market research, industry trends and competitor analyses. A strategic plan will include the components of a traditional plan, such as an executive summary, marketing analysis and financial statements, but a strategic plan will be more specific on how the company will go about achieving company goals.
For example, a strategic business plan will attempt to identify a target market, narrow it down to a manageable size, and establish a strategy for acquiring those customers.
Benefits of Strategic Business Plans
Writing a strategic business plan has many advantages. The plan can serve as an outline for successful completion of company milestones. Company owners are in a better position to not only understand their business but become experts in their industries.
A strategic plan helps executives understand the direction in which their company is headed by reviewing past progress and making changes to improve and grow. The plan is an organizational tool that helps to keep a company on track to meet growth and financial objectives.
Misconceptions About These Plans
Many small business owners feel that strategic business plans are for large companies and big businesses. However, according to the U.S. Small Business Administration, a strategic business plan can benefit companies of all sizes and can be a great advantage to small businesses. Small businesses may utilize different types of planning activities to develop the strategies necessary to attract and retain the customers it needs to succeed.
- Entrepreneur.com: Building a Strategy Pyramid
Sherrie Scott is a freelance writer in Las Vegas with articles appearing on various websites. She studied political science at Arizona State University and her education has inspired her to write with integrity and seek precision in all that she does.
Related Articles
Why create a business plan, business planning & analysis, the importance of a business plan, what is the meaning of corporate planning, differences between strategy, plans and tactics, difference between business plan & strategic plan, tactical and operational planning, how does a business strategy differ from strategic marketing management, business enterprise planning, most popular.
- 1 Why Create a Business Plan?
- 2 Business Planning & Analysis
- 3 The Importance of a Business Plan
- 4 What Is the Meaning of Corporate Planning?
Get full control of all your budgets in one place
Resource Planning
See where your agency stands this quarter, and in the next few
Get access to over 50 prebuilt agency reports or build and customize on your own
Project Management
Set up, streamline, and deliver projects
Time Tracking
With each tracked hour, get more precise data so you can run a more profitable agency
Shape your agency's sustainable growth
Eliminate hours spent on invoicing
Create documents and collaborate with your teammates
Software Development
Marketing Agency
Design Studio
In-house Team
Success Stories
Read how agencies transform using Productive
Agency management, product updates & how tos
End-to-end Agency Management
Future proof your business with an agency management system
Agency Resource Management
Gain more control over your agency’s resources
Learn how to run a more successful agency in Productive
Billable Hours Calculator
Find out your billable hours, team utilization rate, and ideal billable hourly rate
Get advice and support from the team
The Bold Community
Join the community for agency professionals by Productive
Book a Demo
Try Productive
Comparisons
{{minutes}} min read
Strategic Human Resource Planning (SHRM): Guide to Human Resources & Management
Lucija Bakić
April 5, 2024
Strategic human resource planning (SHRM) is a proactive process that aligns human resource capabilities with long-term business goals.
In this guide, we’ll go through the basics of why this foward-thinking approach is so important for resource planning success . This includes its definition, the main steps, and best business practices. Key Takeaways
- Strategic HR management (SHRM) is a key step to ensuring that businesses are resilient and sustainable in the long run.
- Key steps of the process include: analyzing current capacity, forecasting needs, gap analysis, HR strategy implementation and monitoring.
- Many of the challenges of SHRM, such as resistance to change or tracking KPIs, can be addressed by implementing a modern ERP software solution .
What Is Strategic Human Resource Planning?
Strategic human resource planning is part of the broader human resource plan ning (HRP) strategy. This process targets long-term objectives, spanning from one to five years, and ensures that businesses have enough capacity to meet future needs. Strategic HR planning must be aligned with short-term resource planning, which handles daily concerns, such as employee schedules and workloads. Long-term strategies should also be aligned across departments, such as the finances or management, to ensure that initiatives contribute to shared organizational goals. See more : What Is Human Resource Planning ?
Why Businesses Need Strategic HRP
Some of the critical business questions that strategic HRP addresses can include:
- Will you have enough human resources for future needs?
- Which type of talent will you need (regarding skills, seniority, etc.)
- Which conflicts or gaps could appear in your business workflows ?
- Do you have contingency plans for various risk factors?
Additionally, it can cover broader concerns, such as the need for organizational flexibility or continuous improvement. As an ongoing process, strategic management provides the perfect answer for businesses to tackle and address complex issues.
5 Main Steps of the Strategic HR Planning Process
The four main steps of strategic HRM include analyzing current capacity, needs forecasting, gap analysis, and strategy development and implementation.
1. Analyzing Current Capacity
This step involves analyzing both internal and external business circumstances that are important for future demand. Internal factors usually include details about your current employees, including their productivity, specific skills, availability, and engagement levels. External factors encompass market trends, economic conditions, and industry-specific demands that could influence future resource requirements.
Align Your HR Management With Strategic Goals
Get an all-in-one solution and improve your business performance with employee scheduling, time off management, billable hours tracking, and more.
Start Free Trial
Book a demo
2. Needs Forecasting
Accurate needs forecasting is one of the most challenging parts of the developing workforce plans . It involves predicting the skills, overall capacity, and roles needed to keep a business relevant during changing market conditions and technological advancements. Therefore, it requires a thorough understanding of your human capital and the industry. Needs forecasting includes:
- Supply forecasting: Assesses the current workforce and external labor market trends to identify whether there will be an excess or shortage of talent in the future.
- Demand forecasting: Focuses more on demand, i.e., quantifying future labor requirements to ensure that business goals will be met.
3. Gap Analysis
Gap analysis takes the first two steps of the human resource management process to pinpoint specific areas of improvement — it compares the current workforce capabilities with future needs to identify conflicts or discrepancies. For example, a retail chain looking to expand its online presence might consider its current capacity, and realize that it has enough technical roles to go into e-commerce. However, by conducting needs forecasting of the competitors, it may recognize the need for marketing professionals skilled in SEO or digital marketing to drive more of their customer base to their website.
4. Strategy Development
The next step involves developing specific strategies to address resource conflicts and help your business reach its goals. Some of these may include:
- Talent management strategies can be developed to address issues with workforce management. It can include processes such as recruiting, retaining, and developing employees.
- Employee engagement strategies are usually developed to tackle low morale and productivity. Organizational strategies might include improving collaboration, manager-to-employee feedback, or capacity building initiatives .
- Development programs are a specific part of talent management, aimed to address skill gaps through upskilling or reskilling employees. Strategies may include mentoring by senior employees, workshops, or other training opportunities.
- Succession planning is utilized to mitigate the risk of key positions becoming vacant unexpectedly. It usually involves identifying high-risk positions and then selecting and preparing potential employees to fill them in the future.
5. Implementation and Monitoring
To ensure that your strategies are effective across time, it’s necessary to closely monitor progress, usually by analyzing various key capacity performance indicators (KPIs). Setting desired targets can be a good way of determining if you’re on the right track — for example, an agency with low productivity might set its desired utilization rates at 80%.
Manage and visualize your employee productivity with Productive
However, it’s equally important to keep in mind that some benefits of successful ERP can be difficult to quantify or determine in a short amount of time. This can include better workplace culture or increased employee satisfaction. See more: ERP benefits for businesses
Documenting Your Strategic HR Plan
The strategic HR document should include an outline of the organization’s human resource objectives, the strategies for achieving them, and the steps for implementation. Putting your initiatives into writing can help drive alignment across various teams and ensure that everything is progressing according to plan.
How and Where to Create Documentation?
According to research by Forrester, 97% of organizations have minimal or no digitally documented processes. While traditional documentation can be better than no documentation, consider the benefits of automating information gathering and sharing with ERP software solutions .
We used to have a project management tool, a time tracking tool, a support tool, a way we handled opportunities and sales-driven processes. Those were all separate tools that we had, and it wasn’t good. It also meant that all that data was being lost every time we switched between tools , or we had to find a way to normalize the data between them. And now, the fact that it’s all in one, it’s really a game changer.
BRYAN CASLER, VICE PRESIDENT OF DIGITAL STRATEGY AT 4SITE INTERACTIVE STUDIOS
For example, the resource and agency management tool Productive can help you automate the work scheduling process with its resource planning model template, provide real-time reporting on utilization rates, manage employee availability and time off, and more. Another great feature you can consider is collaborative documentation with AI content creation. This can help you keep all essential project data on a single platform.
ON DEMAND WEBINAR
Using ai – not getting used by ai.
Get a sneak peek into our Bold Community and learn how agencies can benefit from AI in 2023 with Nicholas Petroski from Promethean Research.
Challenges & Best Practices for Strategic HRP
Some of the main challenges of strategic HRP include ensuring buy-in at all organizational levels, handling resistance to change, efficiently monitoring performance, and fostering continuous improvement.
Getting Business-Wide Buy-In
Organizational changes need to be effected from the top to the ground-level staff. Getting buy-in for new initiatives from leaders and other key stakeholders is essential to get the most out of your HRP initiatives. Silos can cause issues for adoption and cause miscommunications across teams, where one part of the company may not be aware of the changes or understand their role in implementation.
Overcoming Resistance to Change
According to Deloitte, some of the biggest roadblocks to new initiatives include resistance to change (82%) and inadequate sponsorship (72%). Both can be addressed with clear communication and transparency, so that all employees understand why and how initiatives are being implemented. Asigning change ambassadors within teams can facilitate a smoother transition. Learn more: Efficient resource management for multiple projects
Reviewing and Analyzing Progress
Good initiatives can stumble and fall if there’s no way to measure actual performance. Selecting the right key performance indicators and implementing a way to analyze them is important for the success of HRP initiatives. For example, a consulting firm that has issues with turnover might implement additional benefits or hire more staff to balance workloads — the KPIs to be monitored would be employee satisfaction, the utilization rate , and the attrition rate.
Productive can forecast KPIs for professional services agencies, like revenue and profit margins
Incremental Changes and Continuous Innovation
Another reason why monitoring KPIs is so important is that incremental but timely improvements are always better than extensive changes. Smaller adjustments allow businesses to remain flexible and agile to adapt to market demands and internal changes without causing disruptions.
The Role of Analytics & HRP Software
Finally, most, if not all challenges mentioned above can be streamlined with the right tools for resource planning and HR management. The benefits of using such tools include:
- Improved timeline estimation (60%)
- More effective use of resources (55%)
- Enhanced team communication (49%)
- More accurate metrics (38%)
There are many potential options on the market, but consider using a comprehensive software for your strategic planning. These types of solutions can give you a competitive advantage with benefits such as centralized workflows, unified data, and reduced costs for tech stacks.
Get the most out of your agency’s resources with Productive
As an all-in-one solution tailored to agencies of all shapes and sizes, Productive can help you manage both day-to-day resource management and create strategic plans. Key features include: resource allocation, employee performance management, real-time reporting, project budgeting, workflow automations, and much more. Learn more about Productive by booking a demo today.
What are the 4 HR strategies?
The 4 HR strategies include talent acquisition and retention, learning and development, performance management, and workforce planning and forecasting. Each strategy addresses a part of the human resource planning process and contributes to achieving organizational success.
What is strategic resource planning?
Strategic resource planning is a part of human resource management that examines the capacity and needs of your future workforce for sustainable business growth. It’s focused on ensuring that your business has the critical skills for meeting business goals over a long period of time.
What are the 5 steps in human resource planning?
The 5 main steps in human resource planning include: analyzing current HR availability, forecasting future needs, gap analysis, developing strategies for human resource management, and implementing and monitoring your initiatives.
What is SHRM and its importance?
SHRM or strategic human resources management is a forward-looking approach to managing human resources and aligning HR practices with organizational goals. It allows businesses to remain competitive, sustainable, and flexible in dynamic market conditions.
Connect With Agency Peers
Access agency-related Slack channels, exchange business insights, and join in on members-only live sessions.
Content Specialist
Related articles
Agency Management
Top 5 Capacity Report Types for Effective Project Management
The best capacity planning template for agencies, resource capacity planning: the definitive guide.
Questions not answered yet? Our sales is here to help
+1 (415) 287-3073
Integrations
Automations
Business Consultancy
Customer Stories
Product Updates
Agency Valuation Calculator
Building Productive
Brand Guidelines
Trust Center
© 2024 The Productive Company, Inc.
Privacy Policy
Terms & Conditions
We need your consent to continue
Necessary cookies
Cookies for the basic functionality of the Productive website.
Functional cookies
Cookies for additional functionality and increased website security.
Targeting cookies
Advertising and analytics service cookies that create day-to-day statistics and show ads on their site and on the advertiser’s partners websites.
Save changes
Manage cookies and help us deliver our services. By using our services, you agree to our use of cookies.
Try Productive for free
Free 14-day trial. No credit card required. Cancel any time.
Already using Productive? Sign in with an existing account
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- *New* Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
What Is Business Strategy & Why Is It Important?

- 20 Oct 2022
Every business leader wants their organization to succeed. Turning a profit and satisfying stakeholders are worthy objectives but aren’t feasible without an effective business strategy.
To attain success, leaders must hone their skills and set clear business goals by crafting a strategy that creates value for the firm, customers, suppliers, and employees. Here's an overview of business strategy and why it's essential to your company’s success.
Access your free e-book today.
What’s a Business Strategy?
Business strategy is the strategic initiatives a company pursues to create value for the organization and its stakeholders and gain a competitive advantage in the market. This strategy is crucial to a company's success and is needed before any goods or services are produced or delivered.
According to Harvard Business School Online's Business Strategy course, an effective strategy is built around three key questions:
- How can my business create value for customers?
- How can my business create value for employees?
- How can my business create value by collaborating with suppliers?
Many promising business initiatives don’t come to fruition because the company failed to build its strategy around value creation. Creativity is important in business , but a company won't last without prioritizing value.
The Importance of Business Strategy
A business strategy is foundational to a company's success. It helps leaders set organizational goals and gives companies a competitive edge. It determines various business factors, including:
- Price: How to price goods and services based on customer satisfaction and cost of raw materials
- Suppliers: Whether to source materials sustainably and from which suppliers
- Employee recruitment: How to attract and maintain talent
- Resource allocation: How to allocate resources effectively
Without a clear business strategy, a company can't create value and is unlikely to succeed.
Creating Value
To craft a successful business strategy, it's necessary to obtain a thorough understanding of value creation. In the online course Business Strategy , Harvard Business School Professor Felix Oberholzer-Gee explains that, at its core, value represents a difference. For example, the difference between a customer's willingness to pay for a good or service and its price represents the value the business has created for the customer. This difference can be visualized with a tool known as the value stick.
The value stick has four components, representing the value a strategy can bring different stakeholders.

- Willingness to pay (WTP) : The maximum amount a customer is willing to pay for a company's goods or services
- Price : The actual price of the goods or services
- Cost : The cost of the raw materials required to produce the goods or services
- Willingness to sell (WTS) : The lowest amount suppliers are willing to receive for raw materials, or the minimum employees are willing to earn for their work
The difference between each component represents the value created for each stakeholder. A business strategy seeks to widen these gaps, increasing the value created by the firm’s endeavors.
Increasing Customer Delight
The difference between a customer's WTP and the price is known as customer delight . An effective business strategy creates value for customers by raising their WTP or decreasing the price of the company’s goods or services. The larger the difference between the two, the more value is created for customers.
A company might focus on increasing WTP with its marketing strategy. Effective market research can help a company set its pricing strategy by determining target customers' WTP and finding ways to increase it. For example, a business might differentiate itself and increase customer loyalty by incorporating sustainability into its business strategy. By aligning its values with its target audiences', an organization can effectively raise consumers' WTP.
Increasing Firm Margin
The value created for the firm is the difference between the price of an item and its cost to produce. This difference is known as the firm’s margin and represents the strategy's financial success. One metric used to quantify this margin is return on invested capital (ROIC) . This metric compares a business's operating income with the capital necessary to generate it. The formula for ROIC is:
Return on Invested Capital = Net Operating Cost After Tax (NOCAT) / Invested Capital (IC)
ROIC tells investors how successful a company is at turning its investments into profit. By raising WTP, a company can risk increasing prices, thereby increasing firm margin. Business leaders can also increase this metric by decreasing their costs. For example, sustainability initiatives—in addition to raising WTP—can lower production costs by using fewer or more sustainable resources. By focusing on the triple bottom line , a firm can simultaneously increase customer delight and margin.
Increasing Supplier Surplus & Employee Satisfaction
By decreasing suppliers' WTS, or increasing costs, a company can create value for suppliers—or supplier surplus . Since increasing costs isn't sustainable, an effective business strategy seeks to create value for suppliers by decreasing WTS. How a company accomplishes this varies. For example, a brick-and-mortar company might partner with vendors to showcase its products in exchange for a discount. Suppliers may also be willing to offer a discount in exchange for a long-term contract.
In addition to supplier WTS, companies are also responsible for creating value for another key stakeholder: its employees. The difference between employee compensation and the minimum they're willing to receive is employee satisfaction . There are several ways companies can increase this difference, including:
- Increasing compensation: While most companies hesitate to raise salaries, some have found success in doing so. For example, Dan Price, CEO of Gravity Payments, increased his company's minimum wage to $80,000 per year and enjoyed substantial growth and publicity as a result.
- Increasing benefits: Companies can also decrease WTS by making working conditions more desirable to prospective employees. Some offer remote or hybrid working opportunities to give employees more flexibility. Several have also started offering four-day work weeks , often experiencing increased productivity as a result.
There are several ways to increase supplier surplus and employee satisfaction without hurting the company's bottom line. Unfortunately, most managers only devote seven percent of their time to developing employees and engaging stakeholders. Yet, a successful strategy creates value for every stakeholder—both internal and external.

Strategy Implementation
Crafting a business strategy is just the first step in the process. Implementation takes a strategy from formulation to execution . Successful implementation includes the following steps :
- Establish clear goals and key performance indicators (KPIs)
- Set expectations and ensure employees are aware of their roles and responsibilities
- Delegate work and allocate resources effectively
- Put the plan into action and continuously monitor its progress
- Adjust your plan as necessary
- Ensure your team has what they need to succeed and agrees on the desired outcome
- Evaluate the results of the plan
Throughout the process, it's important to remember to adjust your plan throughout its execution but to avoid second-guessing your decisions. Striking this balance is challenging, but crucial to a business strategy's success.

Learn More About Creating a Successful Business Strategy
Business strategy constantly evolves with changing consumer expectations and market conditions. For this reason, business leaders should continuously educate themselves on creating and executing an effective strategy.
One of the best ways to stay up-to-date on best practices is to take an online course, such as HBS Online's Business Strategy program. The course will provide guidance on creating a value-driven strategy for your business.
Do you want to learn how to craft an effective business strategy and create value for your company's stakeholders? Explore our online course Business Strategy , or other strategy courses , to develop your strategic planning skills. To determine which strategy course is right for you, download our free flowchart .

About the Author
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.

Statistics for the Public Good

2024/25 Strategic Business Plan
National statistician's foreword.
The UK Statistics Authority (UKSA) strategy, Statistics for the Public Good, sets out the need for high quality statistics and data to inform the United Kingdom (UK), improve lives and build for the future. The strategy empowers the statistical and analytical system to step up to inform the country, providing and communicating evidence to inform decisions, while reducing the potential for misrepresentation.
The Office for National Statistics (ONS) and wider Government Statistical Service (GSS) produce key statistics which provide insight into the health, society and economy of our nation. These are required to evolve quicker than ever, using new data sources and methods which are more frequent and granular to show how the UK is changing and developing. The ONS is also responsible for key aspects of the Digital Economy Act (DEA), which provides access to data in support of its remit from across the UK. The ONS also has an important role in ensuring that the country’s evidence is inclusive and reflective of the full characteristics of the UK.
The UKSA strategy was published just after the start of the COVID-19 pandemic and since then the statistical and analytical system has responded to the challenges of rising cost of living; economic and social impacts of industrial action; inactivity in the labour market; trade disruption in the Red Sea and the Russian invasion of Ukraine among others. We maintained our agility to respond innovatively to this changing environment. To sustain this level of responsiveness to user needs and the quality of our core statistics, we are changing the format, frequency and content of some of our outputs.
However, the work of the statistical and analytical system is also taking place against a tight financial and human resources backdrop – one in which cash budgets are being stretched by inflation and pay pressures, and in which some increasingly important skills are harder and more expensive to attract and retain, for example in data science. This has required tough decisions on prioritisation not only within the Authority but also across the whole system.
User demands for information on new topics and the need to maintain and enhance quality statistics have required us to prioritise and align our ambitions and obligations within our available resources. Over the past three years the ONS has been working at an incredible pace, and like other organisations it has been necessary to review our priorities and spending. Added to this and in line with other countries, the ONS has been facing the challenge of falling response rates for many of our household surveys in recent years.
Despite this, we continue to deliver our suite of core statistics including Gross Domestic Product (GDP), inflation and labour market participation, as well as crucial insight on areas such as the size of the population, migration patterns, health, and crime rates, striving to ensure all outputs are of the highest quality standard.
We have continued to engage our users at a strategic and operational level including identifying priorities and needs through government networks, local engagement, social listening and stakeholder insights research. We have continued to run the ONS Assembly to support regular dialogue on delivering inclusive data with charities and bodies representing the interests of different groups of the population.
Users also inform the ONS’s policy development and delivery through our expert user advisory groups, stakeholder engagement events and through specific consultations.
As we continue to deliver against the strategy in its final year, we have introduced a set of priority outcomes that focus on our statutory functions and provide the nation with the data it most needs, while driving forward innovation using radical and ambitious approaches to modernise how we work. These five priority outcomes form the basis of our 2024/25 Strategic Business Plan and are:
- An enhanced reputation and trustworthiness for delivering independent and high-quality statistics and analysis.
- Top quality published statistics on health, population and migration.
- Top quality published statistics on prices, GDP and employment.
- Greater linked data capabilities that result in faster, evidence-based decisions across government.
- Modernised and sustainable digital infrastructure using a secure, modularised approach.
Professor Sir Ian Diamond National Statistician UK Statistics Authority
More From Forbes
Why qurate’s qvc and hsn believe the future of tv shopping is on streaming.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
This July 7, 2017, photo shows QVC facility in West Chester, Pa. (AP Photo/Matt Rourke)
The traditional business of TV shopping is at an inflection point as it competes with other retailers for consumers’ discretionary spending and the entertainment industry for their attention. Cracks in the traditional TV shopping business model are beginning to show.
While the nation’s number three shopping channel iMedia Brand ’s ShopHQ is still broadcasting, it is in Chapter 11 bankruptcy proceedings and been delisted from the Nasdaq. QVC, the number one shopping channel and number two HSN, jointly owned by Qurate Retail, have had a rough time too.
In May of last year, Qurate received a Nasdaq delisting notice but got a last-minute reprieve after selling off Zulily . Still, in October, it topped CreditRiskMonitor ’s list of retailers on the verge of bankruptcy along with Farfetch FTCH , Joann and Rite Aid RAD , and we know what happened with them.
CEO David Rawlinson is tasked with righting the Qurate ship. Since joining the company in October 2021, he had scant good news to report in earnings calls.
But that changed in the company’s latest 2023 earnings report . The results of Project Athens’ three-year transformation plan, which was implemented a year after his arrival, are starting to bear fruit.
Best High-Yield Savings Accounts Of 2024
Best 5% interest savings accounts of 2024, new business model needed.
Project Athens is a plan to not just make over the company but to transform its entire business model.
Qurate is keeping the best of the highly personal and entertaining TV shopping model perfected over the last 40-odd years by QVC and HSN and adapting it to a 21st-century video-commerce business model that expands beyond cable television and e-commerce to large-screen and small-screen/mobile streaming services, social streaming (e.g. TikTok, Facebook, X), livestream “fast” services (i.e. free ad-supported streaming services) and in-app purchasing.
“I don’t mind people using the term ‘TV shopping,’ but the better description is ‘video shopping’ or v-commerce,” he shared with me after the earnings call.
As more consumers cut the cable cord, streaming is v-commerce’s future. “We have near universal coverage in the streaming universe on Apple TV, Roku, YouTube, Sling, Amazon Fire TV, Google TV and more. We had 23% growth in that universe, making it the fastest growing part of our business, yet it’s still only about 5% of our total minutes viewed. Every day it’s becoming a bigger and bigger part of our business.”
Topline Turnaround
On the topline, Qurate’s revenues continued to slide in 2023, but the hemorrhaging slowed, even turned the corner. After reaching a high of $14.2 billion in 2020 and dropping only 1% in 2021, revenues declined 14% in 2023 and another 5% in 2023, from $11.2 billion to $10.6 billion, excluding Zulily.
But nearly two-thirds of the decline came from electronics, which were soft across the industry. And it saw growth in apparel, fitness, beauty devices, fashion accessories, footwear and fine jewelry where a lab-grown diamond collection priced from $1,300 to $5,000 was introduced on QVC with many pieces selling out immediately.
Because the company gets instant feedback on what’s hot and what’s not, it can quickly adjust presentations to shift the mix to higher-margin, faster-selling items. For example, it generated $5.7 million in sales of 19,000 Ninja Woodfire electric smoker and grill combo for $300 each, and a Barefoot Dreams throw yielded $6 million on Cyber Monday alone.
Qurate also started to add new customers in the third and fourth quarter 2023, after experiencing a steady drop over the past several years. The fourth quarter saw a 21% increase in new customers. QVC/HSN boasts some 8.1 million active customers with a mix of about half steady customers, one-fourth reactivated past customers, and one-fourth new customers.
Building customer loyalty pays off for the company. Existing customers account for roughly 31 items purchased and $1.6K in annual spend and generate 90% of QVC/HSN’s $7 billion in revenues.
QVC’s best customers, roughly 20% of its base who purchase at least 20 times per year, generate some three-fourths of revenues, purchasing on average 76 items in the year. The best customers’ spending increased on average 9% to $3,900.
One pillar of the Athens Project plan was to better differentiate QVC and HSN in the market, which were near identical twin sisters since HSN was acquired at the end of 2017. Rawlinson describes QVC as a “premium luxury retailer,” and its stable of long- time hosts have established a special relationship with their customers as trusted advisors, even friends. The average tenure for its most popular hosts is nearly 30 years.
“Our hosts build quality relationships with our viewers in ways that really surprised me,” Rawlinson related. “I get letters on a daily/weekly basis, often from people going through a hard time who feel a real connection with a host talking about their personal journey. David Venable has been very courageous talking about his weight loss journey. That makes a powerful connection and builds deep relationships of understanding, vulnerability and trust with our viewers.”
HSN, by contrast, is described as “a little more playful, irreverent at times, and moves a little faster.” It’s customer base is a bit younger than QVC, which is more focused on women 50+ with greater discretion to spend, and more ethnically diverse.
There’s also slightly more emphasis on celebrity presenters, like Dolly Parton, Iman, Giuliana Rancic, Jessica Simpson, Kathy Ireland, Christian Sirano and Wolfgang Puck, who just celebrated his 25th year with HSN and has generated $600 million in sales for the company.
Bottom Line Recovery
With things looking up on Qurate’s topline, Rawlinson can take a victory lap from the company’s bottom line performance in 2023. It turned an operating loss of $1.5 billion last year to a $647 million gain. It unlocked $577 million in free cash flow in 2023 versus use of $9 million last year. And it reduced debt by $956 million in 2023.
It also turned the corner on adjusted OIBDA starting in the third quarter that picked up steam in the fourth, rising 73% to $340 million over fourth quarter 2022, including the divestiture of Zulily, and up 46% excluding it.
OIBDA improvements are credited to:
- Gross margin expansion with a shift to higher-quality products with higher average selling prices and profit margins
- Reduction in fulfillment expenses by renegotiating shipping and delivery rates and executing other operational enhancements
- Reducing inventory balance by 22% year-over-year, which opened the door for newer product assortments
Rawlinson and his team have kept the wolf threatening its door last October at bay, but according to James Gellert, executive chair of financial health analytics firm RapidRatings, it still has work to do.
“Qurate improved its financial health in 2023 but needs to work itself out of this multi-year earnings volatility before the market can have confidence in the stock and the company,” he shared.
“Significant swings in profitability are hard for management and employees; this can lead to inconsistent financial health. Through product tweaks, asset sales, and management changes, the company is trying to adjust and innovate in the evolving retail landscape,” Gellert added.
Restoring The Human Connection To Retail
The ancient Chinese philosopher Lao Tzu said, “If you do not change direction, you may end up where you are heading.” Over the last few years, the signs were there about where Qurate was heading, and just in time, Rawlinson stepped in to change direction.
And not being an industry insider has worked to his advantage since it gives him a more objective and broader line of sight than someone steeped in the industry might have. He quickly recognized that a business model transformation was needed not just a doubling down on industry-standard strategies and processes.
Rawlinson was opportunistically recruited from NielsenIQ, where he was CEO before an ownership change, though he still serves on its board. Prior to that, he was president of Grainger Global Online, the fastest growing division of B2B industrial products supplier W W .W. Grainger.
He also held executive positions with engineering and manufacturing company ITT and worked under Presidents George W. Bush and Barack Obama administrations, during the later serving as a senior economic policy advisor in the White House National Economic Council.
B2C retailing was new to him, but he’s a quick study, having a J.D. from the University of South Carolina and a Harvard M.B.A. He immediately got that retail is first and foremost a people, not a product business.
“Retail really starts at the human level,” he shard. “As I look at the future of retail, there are two clear winners. One is the big-box stores with fluorescent lighting, concrete floors, self-checkout and largely impersonal. The other is e-commerce which is algorithmic driven. They have all kinds of products consumers need, but for ordinary people, big boxes and e-commerce are really cold environments.
“In retail there is a need for something more human and more connected. Our hosts are really critical to creating that sense of human connection. A lot of retailers forgot how important it is to have a person who you trust speak to you about the product. We are prepared to take advantage of that,” he concluded.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
- New Terms of Use
- New Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
- Closed Captioning Policy
Quotes displayed in real-time or delayed by at least 15 minutes. Market data provided by Factset . Powered and implemented by FactSet Digital Solutions . Legal Statement .
This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed. ©2024 FOX News Network, LLC. All rights reserved. FAQ - New Privacy Policy
Biden admin cancels plan to refill emergency oil reserve amid high prices
Action represents major setback to biden's spr replenishment plans.

There's 'no factor' that will pull oil prices down: Brad McMillan
Commonwealth Financial Network CIO Brad McMillan argues the Baltimore bridge disaster will 'complicate' freight along the East Coast.
The Biden administration has abruptly canceled a plan announced last month to purchase up to three million barrels of oil as part of its effort to refill the Strategic Petroleum Reserve (SPR) .
The SPR — which Congress established for emergency situations — currently contains 363.6 million barrels of oil, a 43% decline from January 2021 when President Biden took office, federal data shows. Biden began depleting the reserve in late 2021 to combat high fuel prices.
The Department of Energy said that while it remains committed to refilling the SPR, it would pull back its most recent solicitation for oil amid increasing prices . On March 14, DOE's Office of Petroleum Reserves announced the solicitation for three million barrels of oil to be delivered in August and September to its Bayou Choctaw site in Louisiana, one of four major SPR storage facilities.
"Keeping the taxpayer’s interest at the forefront, we will not award for the Bayou Choctaw SPR site in August and September, and will continue to solicit available capacity as market conditions allow," a DOE spokesperson said. "As always, we monitor market dynamics to remain nimble and innovative in our successful replenishment approach to protect this critical national security asset."
The spokesperson added that the administration has already taken steps to replenish the emergency reserve, the largest of its kind in the world, and deliver "a good deal for American taxpayers."
BIDEN ENERGY SECRETARY GRANHOLM PRESSED ON TALKS WITH TOP CCP OFFICIAL BEFORE SPR RELEASES

Secretary of Energy Jennifer Granholm hosts a news conference on Dec. 13, 2022. (Mary F. Calver/File Photo / Reuters)
When DOE first announced the Bayou Choctaw refill plan last month, it said it would aim to purchase oil priced at $79 per barrel or below. Since then, oil prices have increased, with the U.S. benchmark hitting $85.71 earlier on Wednesday.
WHITE HOUSE PROHIBITING OFFICIAL TRAVEL TO FOSSIL FUEL CONFERENCES, INTERNAL MEMO SHOWS
The solicitation, though, is one of several to be announced by DOE. The agency has in recent months executed several of those purchases , but the reserve still remains at a historically low level.

President Biden announces the release of 50 million barrels of oil from the U.S. Strategic Petroleum Reserve on Nov. 23, 2021. (Evelyn Hockstein / Reuters Photos)
Overall, the president ordered DOE to release a total of about 260 million barrels of oil from the SPR in 2021 and 2022. Although the administration has recently initiated the process of refilling the reserve, Republican lawmakers and energy experts have warned its actions make the U.S. vulnerable to short-term supply shocks.
GET FOX BUSINESS ON THE GO BY CLICKING HERE
"It’s pure insanity to watch the Biden administration cut American oil production and then claim they can’t refill our critical reserve because of the price," said Daniel Turner, founder and executive director of watchdog group Power the Future.
"Joe Biden drained the SPR for political reasons, cut our domestic production for his climate agenda, and now he’s leaving our critical reserve more vulnerable because he’s incompetent," he continued. "As a result, Americans are paying more at the pump, more at the grocery store and our SPR is less full during a time of rising turmoil in the Middle East."

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Strategic planning is a process in which organizational leaders determine their vision for the future as well as identify their goals and objectives for the organization. The process also includes establishing the sequence in which those goals should fall so that the organization is enabled to reach its stated vision .
Strategic planning is the art of creating specific business strategies, implementing them, and evaluating the results of executing the plan, in regard to a company's overall long-term goals or desires.
What is strategic planning? Strategic planning is a business process that helps you define and share the direction your company will take in the next three to five years. During the strategic planning process, stakeholders review and define the organization's mission and goals, conduct competitive assessments, and identify company goals and ...
Strategic planning is the ongoing organizational process of using available knowledge to document a business's intended direction. This process is used to prioritize efforts, effectively allocate resources, align shareholders and employees on the organization's goals, and ensure those goals are backed by data and sound reasoning. It's ...
The goal of developing a strategic plan is to ensure everyone in the business is aligned when it comes to your small business's goals and objectives, as well as to create a formal strategic plan document. 1. Discussion Phase. The discussion phase is meant to gather as much information, opinions, and input as possible.
Strategic planning is also different from a business plan that focuses on a specific product, service, or program and short-term goals. Rather, strategic planning means looking at the big picture. While they are related, it is important not to confuse strategic planning with strategic thinking, which is more about imagining and innovating in a ...
Business strategic planning is the process of creating a business strategy and an accompanying business strategic plan to implement a company's vision and achieve its goals over time. The main goal of strategic planning is to take a company from its current state to its desired state through a series of business actions.
A strategic plan is more than just a business tool, it also plays a key role in defining operational, cultural, and workplace ethics. Here are some of the key aspects of the importance of strategic planning: 1. Provides a unified goal . A strategic plan is like a unified action plan for the whole company in order to achieve common outcomes.
Strategic plans bridge the gap from overall direction to specific projects and day-to-day actions that ultimately execute the strategy. Job No. 1 is to know the difference between strategy and strategic plans — and why it matters. Strategy defines the long-term direction of the enterprise. It articulates what the enterprise will do to compete ...
Business strategy is the development, alignment, and integration of an organization's strategic initiatives to give it a competitive edge in the market. Devising a business strategy can ensure you have a clear plan for reaching organizational goals and continue to survive and thrive.
Highlight the plan in a company newsletter. Include the plan in new employee onboarding. Post the plan on the employee intranet, along with key highlights and a way to track progress. If you hold a meeting, make sure you and other key planners are prepared to handle the feedback and discussion that will arise.
How to Create a Strategic Plan for Your Business in 5 Steps. The most successful small businesses, corporations, and organizations never remain static for long. Their leaders continually look to the future, pursuing a slate of both short-term goals and long-term goals while angling for competitive advantages over rivals.
What Is Strategic Planning? Strategic planning is the ongoing organizational process of using available knowledge to document a business's intended direction. This process is used to prioritize efforts, effectively allocate resources, align shareholders and employees, and ensure organizational goals are backed by data and sound reasoning.
Strategic planning is the process of defining your business's direction and outlining a path toward a preferred future. The goal of a strategic plan is to capture an organization's mission and core principles — to envision the fulfillment of these ideals. Strategic planning is both conceptual and practical, as it presents both high-level ...
Strategic planning is crucial for a business as it creates a map for a business to follow and course correct when need be. The first part of a strategic plan is the business plan, which outlines ...
Goals, Priorities and Strategies. Outlines the goals, priorities, and strategies to meet the mission. 3 -4 overarching goals aligned with mission. Priorities, activities, objectives, strategies are in more depth, have more specificity - each goal could have a few different objectives / strategies associated with it.
An annual strategic business plan should include 8 key sections. Follow these steps to write an effective annual strategic business plan: State information that defines the company. Perform a SWOT analysis. Identify business goals. Identify key performance indicators. Perform and summarize market research. Outline the business marketing plan.
Strategic planning is how the company designs that system, which is very different from an operational action plan in that it is never a static to-do list but constantly evolves as strategy makers ...
The strategic plan and business plan also offer different uses and benefits as well. Benefits of using a strategic plan One of the primary benefits of a strategic plan is that it helps a company to increase its profitability, allowing for greater flexibility in how it can allocate funds for components like buying newer technologies and hiring ...
A strategic business plan is a written document that pairs the objectives of a company with the needs of the market place. Although a strategic business plan contains similar elements of a ...
A strategic plan for your company is one of the best ways to ensure that every move you make gets you closer to your business goals. Forbes Business Development Council is an invitation-only ...
A strategic plan is a document written by leaders of an organization that enables the organization to be innovative, adaptable, and increase its competitive advantage for a time span of 3 to 10 ...
Strategic human resource planning (SHRM) is a proactive process that aligns human resource capabilities with long-term business goals. In this guide, we'll go through the basics of why this foward-thinking approach is so important for resource planning success .
Business strategy is the strategic initiatives a company pursues to create value for the organization and its stakeholders and gain a competitive advantage in the market. This strategy is crucial to a company's success and is needed before any goods or services are produced or delivered. According to Harvard Business School Online's Business ...
The new plan, which Riley said was developed via years of engaging university and community stakeholders. It included use of an outside consultant, surveys, SWOT (strengths, weaknesses ...
Spotify Technology SA plans to raise the price of its popular audio service in several key markets for the second time in a year, a crucial step toward reaching long-term profitability.
These five priority outcomes form the basis of our 2024/25 Strategic Business Plan and are: An enhanced reputation and trustworthiness for delivering independent and high-quality statistics and analysis. Top quality published statistics on health, population and migration. Top quality published statistics on prices, GDP and employment.
The goals of the new strategic plan the city is creating, would establish a vision for the character and unique urban core of downtown, while also creating priorities for public policy and ...
New Business Model Needed. Project Athens is a plan to not just make over the company but to transform its entire business model. Qurate is keeping the best of the highly personal and entertaining ...
The Biden administration has abruptly canceled a plan announced last month to purchase up to three million barrels of oil as part of its effort to refill the Strategic Petroleum Reserve (SPR). The ...