- Data Center and Cloud
- vSphere 7.x

Steps to Configure IP Address and Hostname in vSphere ESXi 7
Once you install VMware ESXi on the physical host, the next basic step will be to configure IP address and hostname . By default, IP address is set to receive IP from DHCP server and the hostname is set to localhost . This article will show steps to configure IP Address and hostname in vSphere ESXi 7 .
Step 1. Log on to the VMware ESXi Direct Console User Interface (DCUI) . When you finish installing ESXi server, you are presented with DCUI interface as shown below. DCUI isn’t accessible remotely and is something you will have to access directly from the server with keyboard and monitor hooked onto the server. Once you have access to the DCUI, press on F2 to customize the system settings.

This will bring up a login screen as shown below. Enter root credentials and press Enter .
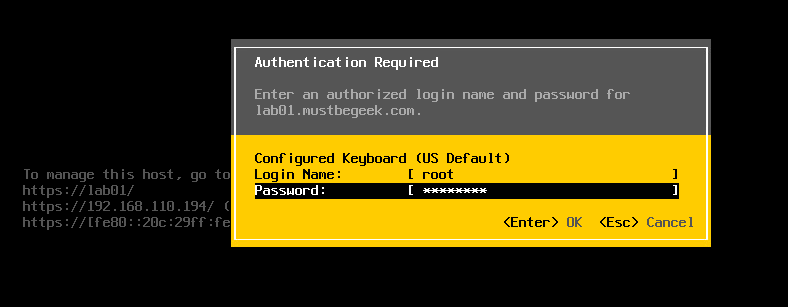
Step 2. Once you login successfully, System Customization setting will be displayed as shown in screenshot below. Use your keyboard arrow keys to select Configure Management Network option and click Enter .

Now Configure Management Network setting will be displayed as shown below. This is where you can setup IP address, hostname and other network settings of the ESXi server. Select IPv4 configuration option and press Enter .

Step 3. Under IPv4 Configuration options as shown below, there are three options to choose from. The second option “Use dynamic IPv4 address and network configuration” is selected by default, which means the ESXi host will receive IP from DHCP server if there is any in the network. Use arrow keys to select the third option “Set static IPv4 address and network configuration” and press space bar to select the option. You can then type static IP Address , Subnet Mask and Default Gateway as shown below. After configuring this, press Enter to continue.

Step 4. You will then be taken back to Configure Management Network options. Select DNS configuration and click Enter .

Choose the second option “Use the following DNS server addresses and hostname” . From here you will be able to configure the DNS server and hostname . Once completed press Enter .

Step 5. This will take you back to Configure the Management Network options. The last and most crucial step, which is very easy to forget is to save all these changes made. To do this, press ESC from the configure management network screen below.

Step 6. You will be presented with screen below. Press Y to apply the changes and restart management network. It will take less than a minute to restart the management network interface.

Step 7. You will now see the new IP address and host name you configured as shown below. Notice the IP address now is ending with (STATIC) word, before it was (DHCP) .

In this way you can configure IP Address and Hostname in vSphere ESXi 7. Now you can log in to the ESXi host using the URL https://192.168.110.194/ in your browser. Then you can start creating virtual machines and manage the ESXi host.
You may also like -

- Latest Posts
Latest posts by Bipin ( see all )
- Install Exchange 2019 in Windows Server 2019 - November 28, 2020
- Why Backup your Microsoft Office 365 - November 27, 2020
- What’s New in VMware vSphere 7 - September 18, 2020
VMware Arena
Reserved space for virtualization, configuring ip address for esxi host.
Login with the root credentials
Select the Network Adapter for your ESXi host management network and Hit enter
Select the IP configuration to change the IP address from DHCP assigned to static IP address and Hit Enter
Enter the IP address, Subnet mask and Default gateway for the ESXi server management network and Hit Enter to OK.
Provide the Primary and secondary DNS server. Enter the Host name for your ESXi host and Hit Enter to OK.
Thanks For Reading!!!!
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
How does vSphere DHCP assign IP addresses?
I have installed Ubuntu in a vSphere VM and due to some error, it got the wrong IP address. I asked IT to fix the DHCP entry and they did but the VM kept getting assigned the wrong IP. I could get it the correct IP address running dhclient but this was not persistent. The solution was to add
to /etc/netplan/99-dhcp.yaml .
Can someone explain how assigning IP addresses works by default in this case and why I have to manually set it to use the MAC address for DHCP?
- vmware-vsphere
- vSphere doesn't. Talk with your IT department. – vidarlo Apr 11, 2023 at 12:25
- 1 @vidarlo - not strictly true sorry, see below. – Chopper3 Apr 11, 2023 at 12:46
Generally vSphere doesn't deal with IP, only ethernet - but there's two exceptions to this; if you're using NSX and if you've configured a 'Network Protocol Profile'.
Firstly just ask you VMware people if they use NSX, if they do then they'll have a lot of control of how DHCP works and can help you based on their designs.
If they don't have NSX then it could well be one of these 'Network Protocol Profiles' - this is a v7 name (it used to have a different name in previous versions but I've forgotten its name sorry) anyway it's set at the 'Datacenter' level, if you have appropriate permissions you could select the datacenter that contains thew cluster/host that manages your VM, then under 'Configure' you should see 'Network Protocol Profiles' - if one or more are in there then you can find the one that applies to your VM (they're usually assigned to port-groups or networks) and see how it's setup.
If you have none of these then I suspect you have an external/non-VMware-provided DHCP service running, again your server/networking people should be able to help.
- Thanks for the answer. My current knowledge is that Ubuntu uses /etc/machine-id and sends that identifier to the dhcp server instead of the mac address. The config change just forces it to use the mac address instead of /etc/machine-id . So this would have nothing to do with VMWare. Does this make sense? – gdkrmr Apr 13, 2023 at 11:02
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged dhcp vmware-vsphere ..
- The Overflow Blog
- Why do only a small percentage of GenAI projects actually make it into...
- Spreading the gospel of Python
- Featured on Meta
- Our Partnership with OpenAI
- Imgur image URL migration: Coming soon to a Stack Exchange site near you!
Hot Network Questions
- Why is Afghanistan experiencing extreme deflation?
- What could cause a society to collectively forget about an event?
- How to retrieve the index of a subset in Subsets[list,nspec,{s}]?
- Book series where the young male protagonist learns he's part of a magical family, uses his crutch to slay one of them
- Is the asq.in.th website an official resource of the Thai government?
- What does なんたら mean?
- Does this sequence ever end?
- What is the purpose of the top tube on bicycles?
- For what kind of distributions, the joint distribution could be determined uniquely by marginal distribution and correlation?
- Frank Stella's Protractor Series - Can we reproduce Lac Laronge IV?
- Thistle-ish plant in Texas
- Hash as filename to protect data
- Can I use a hose clamp to ground a wire to EMT?
- Using Dragon and Polaris Dawn to dock with near Earth asteroids
- How can use this pcb header (rated voltage, nominal voltage etc.)?
- ADRS in WOTS+ signature scheme
- Water in attic AC air handler pan
- Why my super-capacitor self-discharge so fast?
- Extract Value from Kafka-Topics Command
- “Out of the mouths of babes”: Is this idiom strictly used to refer to children?
- 2008 iMac screen problem
- Is it true that |X| vanishes at infinity, then X is integrable?
- Which comma(s) can I remove in this sentence? I feel like there are too many here but all seem necessary to me
- Extra NESTED LOOP / INNER JOIN causing NO JOIN PREDICATE warning
- Interview Questions
- Advertise here
While deploying the vSphere Replication Appliance, I wrongly miss configured the IP address of management interface. Later I realized that it was not reachable and I was unable to access VAMI console of vSphere Replication. I had to change the IP address of appliance without rebuilding this. If you are in same situation then you may follow this blog to change the IP address using Command line. You just need to access console of vSphere replication VM through Web client. Follow below steps:
- Login to vSphere Replication appliance Console. Use ROOT credentials.
- Run below command.
/opt/vmware/share/vami/vami_config_net
- Follow these options as showing in below figure.
- IPv4 Configuration has been done.
Share this on Social Media
About the author.
Public profile: user/profile/99900000
* Name
* email id, subscribe us, get emails on latest blogging tips and news from vmwareinsight.
VMware Insight

- Applications
- Cloud & SDDC
- Community Home
Change IP Adres in Windows based vCenter server
Peter Van Den Bosch Sep 21, 2017 10:24 AM
Finikiez Sep 21, 2017 11:24 AM
MAIESGH55 Nov 18, 2023 09:08 PM
MOMOBRIANBIZ Nov 18, 2023 10:27 PM
Finikiez sep 21, 2017 02:17 pm.
Rahul Parmar Sep 26, 2017 10:44 AM
1. change ip adres in windows based vcenter server.

Hi! i need to change the IP adres on an Windows based vCenter server. Allthough this is not supported what issues can i come across?
2. RE: Change IP Adres in Windows based vCenter server

It's not true. You can change VC IP and it shouldn't cause serious issues.
Maybe this one VMware vCenter Server IP address change causes VMware ESX hosts to disconnect (1001493) | VMware KB or possibly you will need modify accordingly your external solutions if they are configured using VC IP instead of FQDN.
3. RE: Change IP Adres in Windows based vCenter server

4. RE: Change IP Adres in Windows based vCenter server

thank you
5. RE: Change IP Adres in Windows based vCenter server
Google it carefully :smileyhappy: this doc is for vFabric Data Director product
6. RE: Change IP Adres in Windows based vCenter server

Changing the vCenter server IP leads to ESXi hosts disconnection from the vCenter as the hosts store the IP address of the vCenter server in configuration files of each of the individual servers. This incorrect address continues to be used for heartbeat packets to vCenter Server and hosts get disconnected. Changing the vCenter IP address also affects any other VMware/third party components registered with vCenter using the IP address.
In case, if you still want to change the vCenter IP address, you can change it using the below steps. Ensure to perform this activity in a maintenance window as it will impact your complete environment.
1. Change the DNS to reflect the new IP address
2. Change the 'Managed IP address' in vCenter advanced settings .For more information see Verifying the VMware vCenter Server Managed IP Address (1008030)
3. ESXi hosts must be made aware of this change as they will continue to heartbeat to the old vCenter IP address .Follow the steps in vCenter Server IP address change causes ESX hosts to disconnect (1001493)
4. Re-register SSO & Inventory Service to vCenter Server by following the steps in Re-pointing and re-registering VMware vCenter Server 5.1 / 5.5 and components (2033620)
New Best Answer
- Terms of Use
Changing the ESXi server management IP address
Article id: 323615, updated on:, issue/introduction, environment.
When an ESXi management IP address is changed and if it fails to connect to the vCenter then restart vCenter agent and management agents on ESXi host. Workaround: Before proceeding, ensure that:
- The new IP address and required network setup are ready.
- You have disabled High Availability (HA) in the cluster to prevent a failover event. For more information, see Disabling VMware High Availability (HA) (1008025) .
- Disabled lockdown mode if enabled For more information, see Enabling or disabling Lockdown mode on an ESXi host.
- The ESXi host is placed in maintenance mode as the host may disconnect during the change of IP address.
To change the ESXi server management IP address:
- Change ESXi Server Management IP Address:
Use DCUI Change ESXi Server Management IP Address:
- Log in to the Direct Console User Interface of the ESXi.
- Select Configure Management Network and press Enter
- From the Configure Management Network Options menu, select IPv4 Configuration or IPv6 Configuration press Enter
- Set new IPv4 or IPv6 config then Press Enter
- Press Esc to Exit DCUI pop alert "Configure Management Network: Confirm"
- Press Y to apply changes and restart management network.
- Open a SSH session to the host with root credentials. For more information, see Opening a command or shell prompt (1003892)
- Alternatively, you can also change the IP address from the KVM or the remote console.
- Run this command: esxcli network ip interface ipv4 set -i vmk1 -I ip address -N subnet -t static
- Update the DNS server entries to reflect the required changes.
- Restart ESXi Server Management Network.
Log in to the Direct Console User Interface of the vCenter Server Appliance. Select Restart Management Network and press Enter. Press F11.
- Restart the Management agents (vpxa) in ESXi . Please see the detail in https://kb.vmware.com/s/article/1003490
- Reconnect host to vCenter
- Login to vCenter Server Web Client and Select a host in the inventory.
- Right click host and select Connection -> Connect
You can adjust other options to ensure that HA does not activate for a momentary disconnect from vCenter Server instead of a host failure, resulting in failure of virtual machines. For example, the key feature is Datastore heart-beating. If this feature is enabled, virtual machines are identified as running on the ESXi host and HA does not activate. You can also adjust the host monitoring or network isolation responses while making changes. Note : This is the safest and simplest method:
- Place the ESXi host in maintenance mode.
- Remove the ESXi host from vCenter Server.
- Connect directly using the ESXi Host UI Client or KVM.
- NOTE: Ensure you have console access to the ESXi server before doing the step.
Additional Information

Platform products
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux A flexible, stable operating system to support hybrid cloud innovation.
- Red Hat OpenShift A container platform to build, modernize, and deploy applications at scale.
- Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform A foundation for implementing enterprise-wide automation.
- Start a trial Assess a product with a no-cost trial.
- Buy online Buy select products and services in the Red Hat Store.

- Red Hat Enterprise Linux AI
- Red Hat OpenShift AI
- Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization
- Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS
- Microsoft Azure Red Hat OpenShift
By category
- Application platform
Artificial intelligence
Edge computing.
- IT automation
- Linux standardization
By organization type
- Financial services
- Industrial sector
- Media and entertainment
- Public sector
- Telecommunications
By customer
- British Army
- HCA Healthcare
- Macquarie Bank
- Tata Consultancy Services
- Search all success stories
- Open Innovation Labs
- Technical Account Management
Training & certification
- All courses and exams
- All certifications
- Verify a certification
- Skills assessment
- Learning subscription
- Learning community
- Red Hat Academy
- Connect with learning experts
- Ansible Basics: Automation Technical Overview (DO007) [No cost]
- Containers, Kubernetes and Red Hat OpenShift Technical Overview (DO080) [No cost]
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux Technical Overview (RH024) [No cost]
- Red Hat Certified System Administrator (RHCSA) exam
- Red Hat System Administration I (RH124)
- Application modernization
- Cloud computing
- Cloud-native applications
- Virtualization
- See all topics
- What is InstructLab?
- What are cloud services?
- What is edge computing?
- What is hybrid cloud?
- Why build a Red Hat cloud?
- Cloud vs. edge
- Red Hat OpenShift vs. Kubernetes
- Learning Ansible basics
- What is Linux?
More to explore
- Customer success stories
- Events and webinars
- Podcasts and video series
- Resource library
- Training and certification
For customers
- Our partners
- Red Hat Ecosystem Catalog
- Find a partner
For partners
- Partner Connect
- Become a partner
- Access the partner portal
- Our company
- How we work
- Our social impact
- Development model
- Subscription model
- Product support
Open source
- Open source commitments
- How we contribute
- Red Hat on GitHub
Company details
- Analyst relations

Communities
- For system administrators
- For architects
- Customer advocacy
Recommendations
As you browse redhat.com, we'll recommend resources you may like. For now, try these.
- All Red Hat products
- Tech topics
- Red Hat resources
Select a language
- Training & services
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux
- Red Hat OpenShift
- Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform
Applications
- Cloud services
Infrastructure
Open hybrid cloud, original shows, how to perform an ipi installation of openshift on vsphere with static ip addresses.
- Back to all posts
Tags: Topics , Networking , Products
Deploying OpenShift on vSphere is quick and simple when performing an IPI installation. However, IPI installations require using Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). Many organizations do not allow the use of DHCP on their networks. Additionally, use cases such as external load balancers are difficult to manage with DHCP-assigned addresses. OpenShift 4.14 allows static IP addresses with Tech Preview IPI installations.
Static IP addresses are provisioned at install time by configuring install-config.yaml. After installation, additional machines may be scaled in to the cluster with static IPs by providing IP addresses in the machine API machine specs or using a controller that assigns IP addresses to the systems.
Prerequisites
- A network administrator has allocated IP addresses for the bootstrap, control plane, compute nodes, API VIP, and ingress VIP.
- install-config.yaml is configured with a static IPs bootstrap, control plane, compute nodes, API VIP, and ingress VIP.
- install-config.yaml is configured with the TechPreviewNoUpgrade feature set.
Note: Allocating an API and ingress VIP is optional if the cluster is being installed with an external load balancer. Sample install-config.yaml file:
These annotations apply to the settings in the file above:
- (0) - The role of the network definition. Valid values are bootstrap , control-plane , or compute .
- (1) - IPv4 and/or IPv6 addresses to be applied to the network interface.
- (2) - The default gateway to be applied to the network interface.
- (3) - Up to three nameservers to be used for DNS resolution.
Note: The number of control-plane and compute network definitions must match the master and worker machine pool replicas, respectively.
In addition, you must provide one bootstrap network definition.
Machine scaling with static IP addresses
There are two options for scaling in new machines with static IPs:
- Create a new machine resource with static IP configuration set in the machine YAML.
- Scale up new machines with a machineset.
Scaling individual machines
1. Create a machine resource YAML that includes the required network definition.
The following annotations apply to the file above:
- (1) - The default gateway to be applied to the network interface.
- (2) - IPv4 and/or IPv6 addresses to be applied to the network interface.
Run the following command to implement the YAML file:
Scaling with machinesets
Machinesets may be used to scale machines with static IPs. However, the machine API machine controller does not directly interface with an IP management API. Rather, when a machineset is configured to request a static IP, the machine API machine controller will create an IPAddressClaim in the openshift-machine-api namespace. Note: Organizations may use any number of IP management services. To enable the use of these services, the OpenShift administrator is responsible for handling the creation and binding of IPAddressClaims . As such, automation capable of interfacing with the IP management service and the OpenShift API must be implemented. In Kubernetes, controllers typically handle this type of reconciliation. It is recommended that a controller be written that can interface with the IP management service and the OpenShift API. The example at github.com/rvanderp3/machine-ipam-controller implements such a controller. The following section describes how IPAddresses can be bound with a series of oc commands.
Binding IPAddressClaims
When an IPAddressClaim is created in association with a machine, a virtual machine associated with that machine will not be created until outstanding IPAddressClaim (s) are bound. Here is an overview of machine API machine controller reconciliation as related to IPAddressClaims :
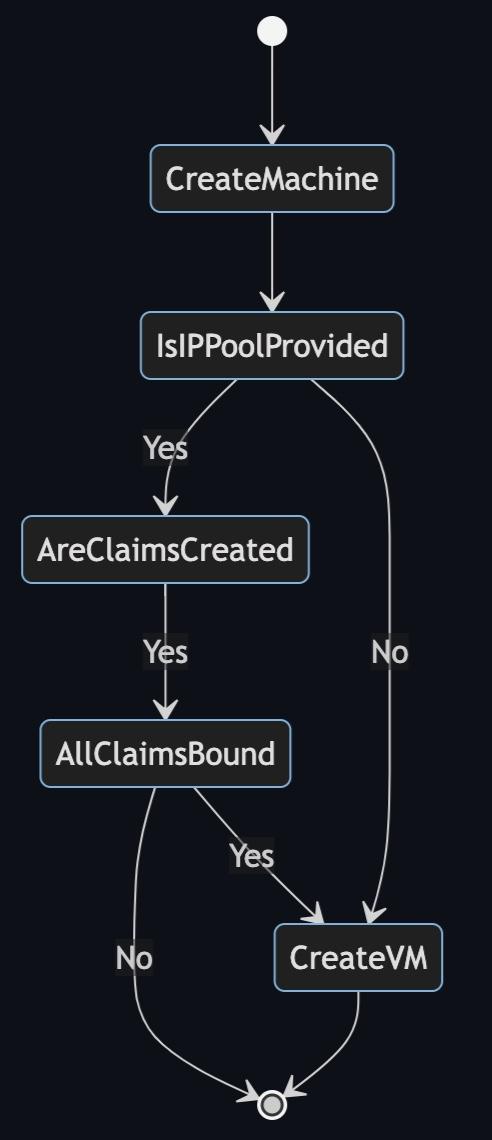
IPAddressClaims may be bound manually by using oc invocations or creating a customer controller. The diagram below describes how to reconcile IPAddressClaims . Here's an overview of IPAddressClaim binding:
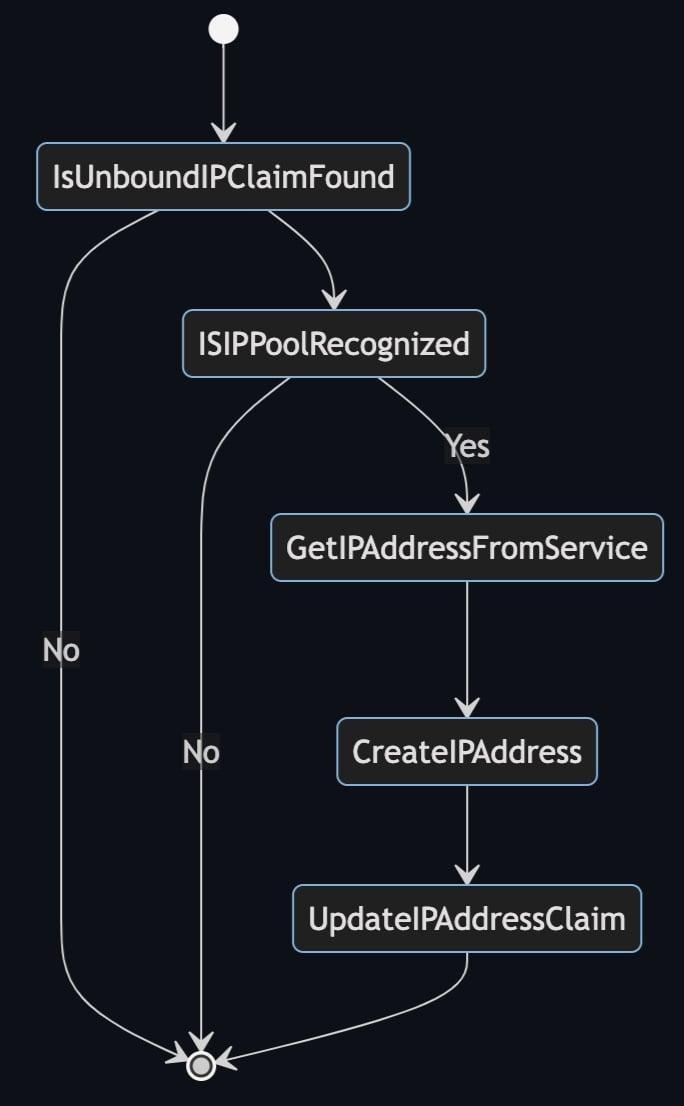
1. Configure a machineset with an IPPool reference. The IPPool reference is included in IPAddressClaims created by the machine API.
Note the following references in the file above:
- (1) - A reference to an IPPool . An IPPool reference may refer to a registered CRD or could simply be a reference that is recognized by the administrator or controller handling IPAddressClaims . IPPools allow a machineset to specify a configuration to be used by the administrator or controller when allocating an IP Address.
- (2) - IPAddress resources do not define nameservers. As such, at least one nameserver should be provided.
2. Scale up a machine:
3. After scaling up a machine, an IPAddressClaim will be created by the machine API controller. To check for IPAddressClaims :
Below is an example of the structure of an IPAddressClaim :
4. Allocate an IP address and create an IPAddress to bind to the IPAddressClaim . Below is an example of the structure of an IPAddress :
- (1) - The name of the associated IPAddressClaim
- (2) - The reference to the IPPool associated with the IPAddressClaim
5. Update the IPAddressClaim status with a reference to the IPAddress . Once an IPAddress has been created, the IPAddressClaim must be updated to include a reference to the IPAddress .
To do this with the oc client:
By enabling static IP addresses for vSphere IPI installations, administrators now have more control over how OpenShift nodes are deployed. We are interested in hearing your thoughts on this feature. Please let us know in the comments.
About the author
Richard vanderpool, more like this, meet the hybrid cloud console’s virtual assistant, getting started with red hat insights and fedramp, compiler: legacies | ossified operating systems, compiler: ready to launch, browse by channel.
The latest on IT automation for tech, teams, and environments
Updates on the platforms that free customers to run AI workloads anywhere
Explore how we build a more flexible future with hybrid cloud
The latest on how we reduce risks across environments and technologies
Updates on the platforms that simplify operations at the edge
The latest on the world’s leading enterprise Linux platform
Inside our solutions to the toughest application challenges
Entertaining stories from the makers and leaders in enterprise tech
- See all products
- Developer resources
- Customer support
- Red Hat value calculator
Try, buy, & sell
- Product trial center
- Red Hat Marketplace
- Red Hat Store
- Buy online (Japan)
Communicate
- Contact sales
- Contact customer service
- Contact training
- About Red Hat
We’re the world’s leading provider of enterprise open source solutions—including Linux, cloud, container, and Kubernetes. We deliver hardened solutions that make it easier for enterprises to work across platforms and environments, from the core datacenter to the network edge.
Red Hat legal and privacy links
- Contact Red Hat
- Red Hat Blog
- Diversity, equity, and inclusion
- Cool Stuff Store
- Red Hat Summit
- Privacy statement
- Terms of use
- All policies and guidelines
- Digital accessibility

Proxmox Install Beginners Guide

Quick Summary
- After getting the ISO image in a position to install from, we can mount the ISO and boot from the ISO, either on bare metal or in a virtual machine.
After you select the Proxmox VE menu option for installation, the server will boot and grab a DHCP address if DHCP is available, and then it will move forward to the next phase of the installation.
- The ISO image is the installation medium we will use to install Proxmox VE server virtualization on our bare metal or VM instance.
Most IT admins are at least familiar with VMware vSphere and Microsoft Hyper-V in the enterprise. These have been staples in the enterprise data center for years now. Many are giving attention to KVM-based hypervisors like Proxmox due to the shakeup of VMware pricing with the Broadcom buyout. Let’s take a look at the Proxmox install for beginners and see how you can get one of the most popular KVM-based hypervisors configured for running virtual machines.
Table of contents
Requirements, download the proxmox iso, burn proxmox to a usb drive, installing proxmox ve server, first boot of proxmox and login, troubleshooting, wrapping up, proxmox installation.
Like most other hypervisors, Proxmox virtual environment is easily installed by simply downloading the ISO file, “burning” this to a USB key or uploading it to your datastore (nested virtualization). This is the method we will look at for the purposes of this beginner guide.
Note the following requirements for installing Proxmox VE Server:
- Intel EMT64 or AMD64 CPU with Intel VT or AMD-V support.
- Memory Requirements: Minimum of 2 GB for Proxmox VE and its core services. Additional memory is necessary for guest systems. For setups using Ceph or ZFS, allocate roughly 1GB of memory per terabyte of utilized storage.
- For optimal performance, use fast and redundant storage solutions, with SSDs providing the best results.
- OS Storage Recommendations: You can choose hardware RAID with a battery-protected write cache (BBU) or use ZFS without RAID, optionally enhancing it with an SSD for the ZIL.
VM Storage Solutions:
- For local setups, select between a hardware RAID with a battery-backed write cache (BBU) or a non-RAID configuration suitable for ZFS and Ceph. Note that ZFS and Ceph are not compatible with traditional hardware RAID controllers .
- Shared and distributed storage configurations are feasible.
- For performance, SSDs with Power-Loss-Protection (PLP) are advised, while consumer-grade SSDs are not recommended.
- Ensure redundancy with multiple Gigabit NICs, scaled according to your storage technology and cluster requirements.
- CPU compatibility with VT-d/AMD-d is essential for PCI(e) passthrough.
You can download the Proxmox ISO image at the following official link from Proxmox: Download Proxmox software, datasheets, agreements . Download the Proxmox VE <version> ISO Installer . The ISO image is the installation medium we will use to install Proxmox VE server virtualization on our bare metal or VM instance.

You can “burn” the ISO image you download for the Proxmox server installation to a USB flash drive. To do this, use a tool like Rufus or Ventoy , to place the ISO image on the USB drive.
After getting the ISO image in a position to install from, we can mount the ISO and boot from the ISO, either on bare metal or in a virtual machine. When booting, select the correct usb device and it will boot into the Proxmox VE iso image.
When you boot from the Proxmox ISO image, you will be taken to the Proxmox GUI installer. You have three options here:
- Install Proxmox VE (Graphical)
- Install Proxmox VE (Terminal UI)
- Advanced Options
For a normal installation, we will select install Proxmox VE (Graphical) option.

The next step of the Proxmox installation is accepting the end user license agreement (EULA) in the Proxmox installation wizard. Click the I agree button in the lower right corner of the screen.

Select the storage target where you want to install the Proxmox installation.

Next, the Proxmox installer will have you configure the location and language settings. This includes the following:
- Keyboard layout

Configure the administration password and email address. This step will configure the root account password and email address associated with the account for your Proxmox VE server.

Next, we configure the management network configuration, including the hostname, IP address, subnet (CIDR format), gateway, and DNS configuration.

Finally, we make it to the summary screen. Here, we want to review the configuration settings and make sure all the settings are configured correctly. By default, the checkbox “Automatically reboot after successful installation” is checked.
Click the Install button in the lower right corner of the installation screen.

The installation process begins.

The installation completes successfully. Before the server reboots, the informational screen will be displayed below, including the web address and port configuration for accessing the web GUI.

After the Proxmox VE Server reboots, it will display the GRUB startup screen below, giving you to the option to boot into diagnostics modes or boot normally.

Once the server boots, it will boot to the terminal console displayed below. The terminal console will display the URL for accessing the web GUI. Note the special port that Proxmox VE Server uses for the web admin console, port 8006.

After you launch a browser and browse to the URL displayed in the terminal console, you will be promoted to log into the Proxmox VE Server. Here, you will use root and the password you configured during the installation of Proxmox VE Server.

Once you log in to the Proxmox VE web interface, you will see the default dashboard displayed for Proxmox. You will see your node listed under the Datacenter node. From the main dashboard, you will see various menus that will display relative to the context of where you have clicked in the left-hand pane.

Note the following troubleshooting tips during a Proxmox VE Server installation.
- Note the specific error displayed in the console. View the low-level logs on the Proxmox VE Server host and any other output. Also, make sure your hardware meets the minimum requirements for installing Proxmox VE Server. Make sure you have met the installation requirements for installing Proxmox.
Other general troubleshooting steps with installation issues:
- Check BIOS/UEFI Settings: Ensure Intel VT-x/AMD-V is enabled for virtualization support
- Verify Installation Media: Test the Proxmox VE installation ISO for corruption and confirm its integrity.
- Review Hardware Compatibility: Make sure the server’s hardware is compatible with Proxmox VE requirements
- Inspect Disk Health: Check for any disk errors or failures that could impede installation.
- Analyze Installation Logs: Look at the logs generated during installation to identify any specific errors or warnings.
- Test Network Connectivity: Make sure you have a stable and active network connections necessary for downloading installation updates and packages
- Update Server Firmware: Keep the BIOS/UEFI and other firmware up to date to avoid compatibility issues
- Disable Unnecessary Hardware: Temporarily turn off unneeded hardware for the installation process and rule out conflicts
- Consult Proxmox Forums: Use the Proxmox community forums for guidance specific to your installation issues
Proxmox is a powerful KVM-based hypervisor that many use in the home lab and production environments. The installation process is straightforward. Pay attention to the installation requirements, BIOS settings, and any output messages received. Using the troubleshooting steps listed, you can generally get to the bottom of any issues during the installation process.
Subscribe to VirtualizationHowto via Email 🔔
Enter your email address to subscribe to this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
Email Address
Brandon Lee
Related articles.

Proxmox Docker Containers Monster – 13000 containers on a single host

Proxmox Update No Subscription Repository Configuration

Proxmox 8: New Features and Home Lab Upgrade Instructions

Proxmox add disk storage space – NVMe drive
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of new posts by email.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Change the hostname of your AL2 instance
When you launch an instance into a private VPC, Amazon EC2 assigns a guest OS hostname. The type of hostname that Amazon EC2 assigns depends on your subnet settings. For more information about EC2 hostnames, see Amazon EC2 instance hostname types in the Amazon EC2 User Guide for Linux Instances .
A typical Amazon EC2 private DNS name for an EC2 instance configured to use IP-based naming with an IPv4 address looks something like this: ip-12-34-56-78.us-west-2.compute.internal , where the name consists of the internal domain, the service (in this case, compute ), the region, and a form of the private IPv4 address. Part of this hostname is displayed at the shell prompt when you log into your instance (for example, ip-12-34-56-78 ). Each time you stop and restart your Amazon EC2 instance (unless you are using an Elastic IP address), the public IPv4 address changes, and so does your public DNS name, system hostname, and shell prompt.
This information applies to Amazon Linux. For information about other distributions, see their specific documentation.
Change the system hostname
If you have a public DNS name registered for the IP address of your instance (such as webserver.mydomain.com ), you can set the system hostname so your instance identifies itself as a part of that domain. This also changes the shell prompt so that it displays the first portion of this name instead of the hostname supplied by AWS (for example, ip-12-34-56-78 ). If you do not have a public DNS name registered, you can still change the hostname, but the process is a little different.
In order for your hostname update to persist, you must verify that the preserve_hostname cloud-init setting is set to true . You can run the following command to edit or add this setting:
If the preserve_hostname setting is not listed, add the following line of text to the end of the file:
To change the system hostname to a public DNS name
Follow this procedure if you already have a public DNS name registered.
For AL2: Use the hostnamectl command to set your hostname to reflect the fully qualified domain name (such as webserver.mydomain.com ).
For Amazon Linux AMI: On your instance, open the /etc/sysconfig/network configuration file in your favorite text editor and change the HOSTNAME entry to reflect the fully qualified domain name (such as webserver.mydomain.com ).
Reboot the instance to pick up the new hostname.
Alternatively, you can reboot using the Amazon EC2 console (on the Instances page, select the instance and choose Instance state , Reboot instance ).
Log into your instance and verify that the hostname has been updated. Your prompt should show the new hostname (up to the first ".") and the hostname command should show the fully-qualified domain name.
To change the system hostname without a public DNS name
For AL2: Use the hostnamectl command to set your hostname to reflect the desired system hostname (such as webserver ).
For Amazon Linux AMI: On your instance, open the /etc/sysconfig/network configuration file in your favorite text editor and change the HOSTNAME entry to reflect the desired system hostname (such as webserver ).
Open the /etc/hosts file in your favorite text editor and change the entry beginning with 127.0.0.1 to match the example below, substituting your own hostname.
You can also implement more programmatic solutions, such as specifying user data to configure your instance. If your instance is part of an Auto Scaling group, you can use lifecycle hooks to define user data. For more information, see Run commands on your Linux instance at launch and Lifecycle hook for instance launch in the AWS CloudFormation User Guide .
Change the shell prompt without affecting the hostname
If you do not want to modify the hostname for your instance, but you would like to have a more useful system name (such as webserver ) displayed than the private name supplied by AWS (for example, ip-12-34-56-78 ), you can edit the shell prompt configuration files to display your system nickname instead of the hostname.
To change the shell prompt to a host nickname
Create a file in /etc/profile.d that sets the environment variable called NICKNAME to the value you want in the shell prompt. For example, to set the system nickname to webserver , run the following command.
Open the /etc/bashrc (Red Hat) or /etc/bash.bashrc (Debian/Ubuntu) file in your favorite text editor (such as vim or nano ). You need to use sudo with the editor command because /etc/bashrc and /etc/bash.bashrc are owned by root .
Edit the file and change the shell prompt variable ( PS1 ) to display your nickname instead of the hostname. Find the following line that sets the shell prompt in /etc/bashrc or /etc/bash.bashrc (several surrounding lines are shown below for context; look for the line that starts with [ "$PS1" ):
Change the \h (the symbol for hostname ) in that line to the value of the NICKNAME variable.
(Optional) To set the title on shell windows to the new nickname, complete the following steps.
Create a file named /etc/sysconfig/bash-prompt-xterm .
Make the file executable using the following command.
Open the /etc/sysconfig/bash-prompt-xterm file in your favorite text editor (such as vim or nano ). You need to use sudo with the editor command because /etc/sysconfig/bash-prompt-xterm is owned by root .
Add the following line to the file.
Log out and then log back in to pick up the new nickname value.
Change the hostname on other Linux distributions
The procedures on this page are intended for use with Amazon Linux only. For more information about other Linux distributions, see their specific documentation and the following articles:
How do I assign a static hostname to a private Amazon EC2 instance running RHEL 7 or Centos 7?

To use the Amazon Web Services Documentation, Javascript must be enabled. Please refer to your browser's Help pages for instructions.
Thanks for letting us know we're doing a good job!
If you've got a moment, please tell us what we did right so we can do more of it.
Thanks for letting us know this page needs work. We're sorry we let you down.
If you've got a moment, please tell us how we can make the documentation better.
K000138732: BIG-IP Next Central Manager OData Injection vulnerability CVE-2024-21793
Final- This article is marked as 'Final' because the security issue described in this article either affected F5 products at one time and was resolved or it never affected F5 products. Unless new information is discovered, F5 will no longer update the article.
Security Advisory Description
An OData injection vulnerability exists in the BIG-IP Next Central Manager API (URI). ( CVE-2024-21793 )
An unauthenticated attacker can exploit this vulnerability to execute malicious SQL statements through the BIG-IP NEXT Central Manager API (URI).
Security Advisory Status
F5 Product Development has assigned ID 1518641 (BIG-IP NEXT CM) to this vulnerability. This issue has been classified as CWE-200: Exposure of Sensitive Information to an Unauthorized Actor .
To determine if your product and version have been evaluated for this vulnerability, refer to the Evaluated products box. To determine if your release is known to be vulnerable, the components or features that are affected by the vulnerability, and for information about releases, point releases, or hotfixes that address the vulnerability, refer to the following tables. You can also use iHealth to diagnose a vulnerability for BIG-IP and BIG-IQ systems. For more information about using iHealth, refer to K27404821: Using F5 iHealth to diagnose vulnerabilities . For more information about security advisory versioning, refer to K51812227: Understanding security advisory versioning .
In this section
BIG-IP Next
BIG-IP and BIG-IQ
F5 Distributed Cloud Services
Other products
Note : After a fix is introduced for a given minor branch, that fix applies to all subsequent maintenance and point releases for that branch, and no additional fixes for that branch will be listed in the table. For example, when a fix is introduced in 20.0.2, the fix also applies to 20.0.3, and all later 20.1.x releases. For more information, refer to K51812227: Understanding security advisory versioning .
1 F5 evaluates only software versions that have not yet reached the End of Technical Support (EoTS) phase of their lifecycle. For more information, refer to the Security hotfixes section of K4602: Overview of the F5 security vulnerability response policy .
2 The CVSSv3 score link takes you to a resource outside of MyF5, and it is possible that the document may be removed without our knowledge.
Note : After a fix is introduced for a given minor branch, that fix applies to all subsequent maintenance and point releases for that branch, and no additional fixes for that branch will be listed in the table. For example, when a fix is introduced in 16.1.2.1, the fix also applies to 16.1.2.2, and all later 16.1.x releases (16.1.3.x., 16.1.4.x). For more information, refer to K51812227: Understanding security advisory versioning .
Security Advisory Recommended Actions
If you are running a version listed in the Versions known to be vulnerable column, you can eliminate this vulnerability by installing a version listed in the Fixes introduced in column. If the Fixes introduced in column does not list a version for your branch, then no update candidate currently exists for that branch and F5 recommends that you upgrade to a version with the fix (refer to the tables).
If the Fixes introduced in column lists a version prior to the one you are running, in the same branch, then your version should have the fix.
To mitigate this vulnerability for affected F5 products, you should restrict management access to F5 products to only trusted users and devices over a secure network.
Acknowledgments
F5 acknowledges Vladyslav Babkin of Eclypsium for bringing this issue to our attention and following the highest standards of coordinated disclosure.
Related Content
- K41942608: Overview of MyF5 security advisory articles
- K12201527: Overview of Quarterly Security Notifications
- K51812227: Understanding security advisory versioning
- K4602: Overview of the F5 security vulnerability response policy
- K4918: Overview of the F5 critical issue hotfix policy
- K39757430: F5 product and services lifecycle policy index
- K9502: BIG-IP hotfix and point release matrix
- K13123: Managing BIG-IP product hotfixes (11.x - 17.x)
- K000090258: Download F5 products from MyF5
- K9970: Subscribing to email notifications regarding F5 products
- K9957: Creating a custom RSS feed to view new and updated documents
- K000135931: Contact F5 Support
AI Recommended Content
- K10866411 : Creating a custom cipher group using the Configuration utility
- K5903 : BIG-IP software support policy
- K000139508 : rust-openssl vulnerability CVE-2024-3296
- K000135931 : Contact F5 Support
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.
When deploying to vSphere in Automation Assembler , you can assign a static IP address but must take care not to introduce conflicts between cloudConfig initialization commands and customization specifications.
Sample designs
The following designs safely apply a static IP address without any conflict between cloud template initialization commands and customization specifications. All contain the assignment: static network setting.
Day 2 customizations
Like an initial deployment, a Day 2 action also might include network configuration. To skip customization during Day 2 actions, add the following property:
customizeGuestOsDay2: false
Designs that won't work or might produce unwanted results
Neither initialization commands nor customization spec are present to configure network settings.
Initialization commands aren't present, but ovfProperties blocked the customization spec.
Application of the customization spec conflicts with initialization commands.
Other workarounds for cloud-init and customization specs
When deploying to vSphere , you can also customize an image to work around cloud-init and customization spec conflicts. See the following external repository for more information.
- vSphere Image Preparation Scripts


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Procedure. Log in to the vCenter Server from the vSphere Client. Select the host in the inventory. On the Configure tab, expand Networking. Select VMkernel adapters. Select vmk0 Management Network and click the edit icon. Select IPv4 settings. Select Use static IPv4 settings. Enter or change the static IPv4 address settings.
Use your keyboard arrow keys to select Configure Management Network option and click Enter. Now Configure Management Network setting will be displayed as shown below. This is where you can setup IP address, hostname and other network settings of the ESXi server. Select IPv4 configuration option and press Enter. Step 3.
0. In vSphere go to config->networking->properties of vswitch (or create a new vswitch->vmkerkenel port (or a a new vmkernel port)->edit and you should see the IP settings tab. Share. Improve this answer.
This video demonstrates configuring IPv4 on the management network from the console of an ESXi 7 host.This is a video in a series to demonstrate the completi...
How to change the IP Address for a VMware ESXi Server.In this video, you will learn how to change the IP Address of the server.Go to networking and click on ...
Learn how to perform the Vmware ESXi IP address configuration. Our tutorial will teach you all the steps required in 10 minutes or less.
The default network is VM Network, if you accidently removed it navigate to vSwitch0, click Properties, Add, Virtual Machine, enter Network Label (the name that will appear when you create a new virtual NIC for every server, i.e. VM Network) and VLAN ID if applicable (default 0), Next, Finish. After you created the network you will be able to ...
Once logged in, select the Administration menu from the home page and on the left-hand side select System Configuration: Next, select Nodes and then choose the VCenter server that you would like to change the IP Address on. Select the Manage tab and then under Networking click the Edit button: You can now enter your desired networking ...
Select the IP configuration to change the IP address from DHCP assigned to static IP address and Hit Enter. Enter the IP address, Subnet mask and Default gateway for the ESXi server management network and Hit Enter to OK. Select the DNS configuration and hit Enter to Chnage the DNS infomration. Provide the Primary and secondary DNS server.
Open Network and Sharing Center. Click on Change Adapter Settings. Right Click on Adapter. Select Properties. open Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) if using IPv4. Select the Radio Button "User the Following IP address". Do the Same for the DNS if you want Select "Use the Following IP Address". End Result Static IP within a VM.
By default, DHCP sets the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway. For future reference, write down the IP address. For DHCP to work, your network environment must have a DHCP server. If DHCP is not available, the host assigns the link local IP address, which is in the subnet 169.254.x.x/16. The assigned IP address appears on the direct ...
I have installed Ubuntu in a vSphere VM and due to some error, it got the wrong IP address. I asked IT to fix the DHCP entry and they did but the VM kept getting assigned the wrong IP. I could get it the correct IP address running dhclient but this was not persistent. The solution was to add. dhcp-identifier: mac
If you are in same situation then you may follow this blog to change the IP address using Command line. You just need to access console of vSphere replication VM through Web client. Follow below steps: Login to vSphere Replication appliance Console. Use ROOT credentials. Run below command. Follow these options as showing in below figure.
Ordering an IP Block. To order an IP block for your vCenter environment, go to the OVHcloud Control Panel. In the Bare Metal Cloud section, click IP on the left-hand sidebar. Then click Order additional IPs. Select the vCenter environment to which you wish to add IPs. You will need to follow the pop-up menu and fill in the proper fields to ...
Depending on which version of ESXi you're using, you should be able to right click within the GUI and add a column for IP address. Note: in order for the IP addresses of guests to be presented up through the ESXi host, VMware Tools will need to be installed and running.
ESXi hosts must be made aware of this change as they will continue to heartbeat to the old vCenter IP address .Follow the steps in vCenter Server IP address change causes ESX hosts to disconnect (1001493) 4. Re-register SSO & Inventory Service to vCenter Server by following the steps in Re-pointing and re-registering VMware vCenter Server 5.1 ...
This article provides steps to change the ESXi server management IP address, assigning a new IP subnet to the kernel port group or management interface for the host in the cluster and to maintain the ESXi host connectivity to vCenter Server. Environment. VMware ESXi 3.5.x Installable
Configuring Network Settings. ESXi requires one IP address for the management network. To configure basic network settings, use the vSphere Client or the direct console. Use the vSphere Client if you are satisfied with the IP address assigned by the DHCP server. You are not satisfied with the IP address assigned by the DHCP server.
OpenShift 4.14 allows static IP addresses with Tech Preview IPI installations. Overview. Static IP addresses are provisioned at install time by configuring install-config.yaml. After installation, additional machines may be scaled in to the cluster with static IPs by providing IP addresses in the machine API machine specs or using a controller ...
Most IT admins are at least familiar with VMware vSphere and Microsoft Hyper-V in the enterprise. ... The proxmox installation grabs an ip address. The next step of the Proxmox installation is accepting the end user license agreement (EULA) in the Proxmox installation wizard. ... Configure the administration password and email address. This ...
Change the system hostname. If you have a public DNS name registered for the IP address of your instance (such as webserver.mydomain.com), you can set the system hostname so your instance identifies itself as a part of that domain.This also changes the shell prompt so that it displays the first portion of this name instead of the hostname supplied by AWS (for example, ip-12-34-56-78).
In the Manage address lists, click Add address list. Enter a name for the address list. For example, Sophos Phish Threat. Enter the domain names. For more information about the IP addresses that Phish Threat uses, see IP addresses and domains. Turn off the authentication requirement for all the domains, and click Save. In Spam, click Use ...
Security Advisory Description An OData injection vulnerability exists in the BIG-IP Next Central Manager API (URI). (CVE-2024-21793) Impact An unauthenticated attacker can exploit this vulnerability to execute malicious SQL statements through the BIG-IP NEXT Central Manager API (URI). Security Advisory Status F5 Product Development has assigned ID 1518641 (BIG-IP NEXT CM) to this vulnerability.
When deploying to vSphere in Automation Assembler, you can assign a static IP address but must take care not to introduce conflicts between cloudConfig initialization commands and customization specifications.. Sample designs. The following designs safely apply a static IP address without any conflict between cloud template initialization commands and customization specifications.