- Our Mission


7 Smart, Fast Ways to Do Formative Assessment
Within these methods you’ll find close to 40 tools and tricks for finding out what your students know while they’re still learning.
Formative assessment—discovering what students know while they’re still in the process of learning it—can be tricky. Designing just the right assessment can feel high stakes—for teachers, not students—because we’re using it to figure out what comes next. Are we ready to move on? Do our students need a different path into the concepts? Or, more likely, which students are ready to move on and which need a different path?
When it comes to figuring out what our students really know, we have to look at more than one kind of information. A single data point—no matter how well designed the quiz, presentation, or problem behind it—isn’t enough information to help us plan the next step in our instruction.
Add to that the fact that different learning tasks are best measured in different ways, and we can see why we need a variety of formative assessment tools we can deploy quickly, seamlessly, and in a low-stakes way—all while not creating an unmanageable workload. That’s why it’s important to keep it simple: Formative assessments generally just need to be checked, not graded, as the point is to get a basic read on the progress of individuals, or the class as a whole.
7 Approaches to Formative Assessment
1. Entry and exit slips: Those marginal minutes at the beginning and end of class can provide some great opportunities to find out what kids remember. Start the class off with a quick question about the previous day’s work while students are getting settled—you can ask differentiated questions written out on chart paper or projected on the board, for example.
Exit slips can take lots of forms beyond the old-school pencil and scrap paper. Whether you’re assessing at the bottom of Bloom’s taxonomy or the top, you can use tools like Padlet or Poll Everywhere , or measure progress toward attainment or retention of essential content or standards with tools like Google Classroom’s Question tool , Google Forms with Flubaroo , and Edulastic , all of which make seeing what students know a snap.
A quick way to see the big picture if you use paper exit tickets is to sort the papers into three piles : Students got the point; they sort of got it; and they didn’t get it. The size of the stacks is your clue about what to do next.
No matter the tool, the key to keeping students engaged in the process of just-walked-in or almost-out-the-door formative assessment is the questions. Ask students to write for one minute on the most meaningful thing they learned. You can try prompts like:
- What are three things you learned, two things you’re still curious about, and one thing you don’t understand?
- How would you have done things differently today, if you had the choice?
- What I found interesting about this work was...
- Right now I’m feeling...
- Today was hard because...
Or skip the words completely and have students draw or circle emojis to represent their assessment of their understanding.
2. Low-stakes quizzes and polls: If you want to find out whether your students really know as much as you think they know, polls and quizzes created with Socrative or Quizlet or in-class games and tools like Quizalize , Kahoot , FlipQuiz, Gimkit , Plickers , and Flippity can help you get a better sense of how much they really understand. (Grading quizzes but assigning low point values is a great way to make sure students really try: The quizzes matter, but an individual low score can’t kill a student’s grade.) Kids in many classes are always logged in to these tools, so formative assessments can be done very quickly. Teachers can see each kid’s response, and determine both individually and in aggregate how students are doing.
Because you can design the questions yourself, you determine the level of complexity. Ask questions at the bottom of Bloom’s taxonomy and you’ll get insight into what facts, vocabulary terms, or processes kids remember. Ask more complicated questions (“What advice do you think Katniss Everdeen would offer Scout Finch if the two of them were talking at the end of chapter 3?”), and you’ll get more sophisticated insights.
3. Dipsticks: So-called alternative formative assessments are meant to be as easy and quick as checking the oil in your car, so they’re sometimes referred to as dipsticks . These can be things like asking students to:
- write a letter explaining a key idea to a friend,
- draw a sketch to visually represent new knowledge, or
- do a think, pair, share exercise with a partner.
Your own observations of students at work in class can provide valuable data as well, but they can be tricky to keep track of. Taking quick notes on a tablet or smartphone, or using a copy of your roster, is one approach. A focused observation form is more formal and can help you narrow your note-taking focus as you watch students work.
4. Interview assessments: If you want to dig a little deeper into students’ understanding of content, try discussion-based assessment methods. Casual chats with students in the classroom can help them feel at ease even as you get a sense of what they know, and you may find that five-minute interview assessments work really well. Five minutes per student would take quite a bit of time, but you don’t have to talk to every student about every project or lesson.
You can also shift some of this work to students using a peer-feedback process called TAG feedback (Tell your peer something they did well, Ask a thoughtful question, Give a positive suggestion). When you have students share the feedback they have for a peer, you gain insight into both students’ learning.
For more introverted students—or for more private assessments—use Flipgrid , Explain Everything , or Seesaw to have students record their answers to prompts and demonstrate what they can do.
5. Methods that incorporate art: Consider using visual art or photography or videography as an assessment tool. Whether students draw, create a collage, or sculpt, you may find that the assessment helps them synthesize their learning . Or think beyond the visual and have kids act out their understanding of the content. They can create a dance to model cell mitosis or act out stories like Ernest Hemingway’s “Hills Like White Elephants” to explore the subtext.
6. Misconceptions and errors: Sometimes it’s helpful to see if students understand why something is incorrect or why a concept is hard. Ask students to explain the “ muddiest point ” in the lesson—the place where things got confusing or particularly difficult or where they still lack clarity. Or do a misconception check : Present students with a common misunderstanding and ask them to apply previous knowledge to correct the mistake, or ask them to decide if a statement contains any mistakes at all, and then discuss their answers.
7. Self-assessment: Don’t forget to consult the experts—the kids. Often you can give your rubric to your students and have them spot their strengths and weaknesses.
You can use sticky notes to get a quick insight into what areas your kids think they need to work on. Ask them to pick their own trouble spot from three or four areas where you think the class as a whole needs work, and write those areas in separate columns on a whiteboard. Have you students answer on a sticky note and then put the note in the correct column—you can see the results at a glance.
Several self-assessments let the teacher see what every kid thinks very quickly. For example, you can use colored stacking cups that allow kids to flag that they’re all set (green cup), working through some confusion (yellow), or really confused and in need of help (red).
Similar strategies involve using participation cards for discussions (each student has three cards—“I agree,” “I disagree,” and “I don’t know how to respond”) and thumbs-up responses (instead of raising a hand, students hold a fist at their belly and put their thumb up when they’re ready to contribute). Students can instead use six hand gestures to silently signal that they agree, disagree, have something to add, and more. All of these strategies give teachers an unobtrusive way to see what students are thinking.
No matter which tools you select, make time to do your own reflection to ensure that you’re only assessing the content and not getting lost in the assessment fog . If a tool is too complicated, is not reliable or accessible, or takes up a disproportionate amount of time, it’s OK to put it aside and try something different.
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
- Professional learning
Teach. Learn. Grow.
Teach. learn. grow. the education blog.

27 easy formative assessment strategies for gathering evidence of student learning

- New Clothes
- Dos and Don’ts
- Three Common Misunderstandings
- Yes/No Chart
- Three Questions
- Explain What Matters
- Big Picture
- Venn Diagram
- Self-Directed Response
Combining these 10 with 10 others we’ve blogged about in the past gives teachers 20 great formative assessment strategies for checking on student learning. Be sure to click through to learn more about these formative assessment strategies.
- The Popsicle Stick
- The Exit Ticket
- The Whiteboard
- Think-Pair-Share
- Two Stars and a Wish
- Carousel Brainstorming
- Basketball Discussions
Want more? Here are seven more strategies you can use to elicit evidence of student learning.
- Entrance Tickets. We’ve blogged about and explained the Exit Ticket, so why not have an Entrance Ticket? Here, the teacher asks a question at the start of a lesson, and students write their responses on index cards or strips of paper. Answers are used to assess initial understanding of something to be discussed in that day’s lesson or as a short summary of understanding of the previous day’s lesson. The teacher designs the lesson around the fact that information on student learning will be coming in at the start of the lesson and can be used to improve the teaching and learning in that lesson. Be sure to write the question so it is easily interpreted and analyzed, allows time for you and/or the students to analyze the responses, and leaves space for you to adjust the lesson, if needed.
- Keep the Question Going. With this formative assessment strategy, you’ll ask one student a question and then ask another student if that answer seems reasonable or correct. Then, ask a third student for an explanation of why there is an agreement or not. This helps keep all the students engaged because they must be prepared to either agree or disagree with the answers given and provide explanations.
- 30-Second Share. With this strategy, students take a turn to report something learned in a lesson for up to 30 seconds each. Connections to the learning targets or success criteria are what you’ll be looking for in the language used by the student. Make this a routine at the end of a lesson so all students have the opportunity to participate, share insights, and clarify what was learned.
- Parking Lot. This is an underused strategy for students and one that can surface questions before learning, as well as during and after. This tool also offers an anonymous place for questions that may be directly related to the content or tangential to the current topic and provide insight into student thinking. Simply save a spot on your whiteboard to write down ideas or questions that aren’t completely relevant in the moment but should be revisited later.
- One-Minute Paper. This might be considered a type of exit ticket as it is typically done near the end of the day. Ask your students, either individually or with a partner, to respond in writing to a single prompt. Typical prompts include:
- Most important learning from the day and why
- Most surprising concept and why
- Most confusing topic and why
- Something I think might appear on a test or quiz and why
- 3-2-1. At the end of the learning, this strategy provides students a way to summarize or even question what they just learned. Three prompts are provided for students to respond to:
- 3 things you didn’t know before
- 2 things that surprised you about the topic
- 1 thing you want to start doing with what you’ve learned
- Assessment Reflection. This strategy is a post-assessment reflection completed individually first and then shared in a small group. After an assessment, the teacher provides a list of questions so learners can reflect on their assessment experience. During group discussion, ideas are collected as new information to support students to better prepare for and engage in future assessments. Consider the following or similar questions. You might also use strategies such as Plus, Minus, Interesting, or Plus/Delta.
- How engaged were you with this assessment? Why?
- What did you feel most confident about? Why?
- What did you do that led to your success or confidence?
- What was the most difficult part of this assessment? Why?
- What would you do differently next time?
- What was the most confusing? Why?
- What do you know about the topic that the assessment didn’t allow you to show?
All 27 of these formative assessment strategies are simple to administer and free or inexpensive to use. They’ll provide you with the evidence of student learning you need to make lesson plan adjustments and keep learning on target and moving forward. They’ll also give your students valuable information so they can adjust their learning tactics and know where to focus their energies.
If you’re not quite sure where to get started, the following discussion questions can help.
Questions for teachers
- How do you use formative assessment data to inform instructional decisions?
- How can formative assessment strategies foster a learning environment of collaboration and engagement?
- How do formative assessment strategies elicit evidence of student learning?
- What is one strategy you could try tomorrow and why?
Questions for leaders
- How do you use formative assessment data to drive school-wide instructional academic decisions?
- How can you model formative assessment strategies in staff meetings, PLCs, and meetings with teachers?
- What are three formative assessment strategies you could bring to your teachers and staff? Why do you feel these would be most effective at your school?
Get more formative assessment tips and tricks in our e-book “Making it work: How formative assessment can supercharge your practice.”
Recommended for you

12 common questions parents ask about MAP Growth

Educator assessment literacy can be strengthened by professional development

75 digital tools and apps teachers can use to support formative assessment in the classroom

Helping students grow
Students continue to rebound from pandemic school closures. NWEA® and Learning Heroes experts talk about how best to support them here on our blog, Teach. Learn. Grow.
See the post

Put the science of reading into action
The science of reading is not a buzzword. It’s the converging evidence of what matters and what works in literacy instruction. We can help you make it part of your practice.
Get the guide

Support teachers with PL
High-quality professional learning can help teachers feel invested—and supported—in their work.
Read the article
STAY CURRENT by subscribing to our newsletter
You are now signed up to receive our newsletter containing the latest news, blogs, and resources from nwea..
Formative Assessment of Teaching
What is formative assessment of teaching.
How do you know if your teaching is effective? How can you identify areas where your teaching can improve? What does it look like to assess teaching?
Formative Assessment
Formative assessment of teaching consists of different approaches to continuously evaluate your teaching. The insight gained from this assessment can support revising your teaching strategies, leading to better outcomes in student learning and experiences. Formative assessment can be contrasted with summative assessment, which is usually part of an evaluative decision-making process. The table below outlines some of the key differences between formative and summative assessment:
By participating in formative assessment, instructors connect with recent developments in the space of teaching and learning, as well as incorporate new ideas into their practice. Developments may include changes in the students we serve, changes in our understanding of effective teaching, and changes in expectations of the discipline and of higher education as a whole.
Formative assessment of teaching ultimately should guide instructors towards using more effective teaching practices. What does effectiveness mean in terms of teaching?
Effectiveness in Teaching
Effective teaching can be defined as teaching that leads to the intended outcomes in student learning and experiences. In this sense, there is no single perfect teaching approach. Effective teaching looks will depend on the stated goals for student learning and experiences. A course that aims to build student confidence in statistical analysis and a course that aims to develop student writing could use very different teaching strategies, and still both be effective at accomplishing their respective goals.
Assessing student learning and experiences is critical to determining if teaching is truly effective in its context. This assessment can be quite complex, but it is doable. In addition to measuring the impacts of your teaching, you may also consider evaluating your teaching as it aligns with best practices for evidence-based teaching especially in the disciplinary and course context or aligns with your intended teaching approach. The table below outlines these three approaches to assessing the effectiveness of your teaching:
What are some strategies that I might try?
There are multiple ways that instructors might begin to assess their teaching. The list below includes approaches that may be done solo, with colleagues, or with the input of students. Instructors may pursue one or more of these strategies at different points in time. With each possible strategy, we have included several examples of the strategy in practice from a variety of institutions and contexts.
Teaching Portfolios
Teaching portfolios are well-suited for formative assessment of teaching, as the portfolio format lends itself to documenting how your teaching has evolved over time. Instructors can use their teaching portfolios as a reflective practice to review past teaching experiences, what worked and what did not.
Teaching portfolios consist of various pieces of evidence about your teaching such as course syllabi, outlines, lesson plans, course evaluations, and more. Instructors curate these pieces of evidence into a collection, giving them the chance to highlight their own growth and focus as educators. While student input may be incorporated as part of the portfolio, instructors can contextualize and respond to student feedback, giving them the chance to tell their own teaching story from a more holistic perspective.
Teaching portfolios encourage self-reflection, especially with guided questions or rubrics to review your work. In addition, an instructor might consider sharing their entire teaching portfolio or selected materials for a single course with colleagues and engaging in a peer review discussion.
Examples and Resources:
Teaching Portfolio - Career Center
Developing a Statement of Teaching Philosophy and Teaching Portfolio - GSI Teaching & Resource Center
Self Assessment - UCLA Center for Education, Innovation, and Learning in the Sciences
Advancing Inclusion and Anti-Racism in the College Classroom Rubric and Guide
Course Design Equity and Inclusion Rubric
Teaching Demos or Peer Observation
Teaching demonstrations or peer classroom observation provide opportunities to get feedback on your teaching practice, including communication skills or classroom management.
Teaching demonstrations may be arranged as a simulated classroom environment in front of a live audience who take notes and then deliver summarized feedback. Alternatively, demonstrations may involve recording an instructor teaching to an empty room, and this recording can be subjected to later self-review or peer review. Evaluation of teaching demos will often focus on the mechanics of teaching especially for a lecture-based class, e.g. pacing of speech, organization of topics, clarity of explanations.
In contrast, instructors may invite a colleague to observe an actual class session to evaluate teaching in an authentic situation. This arrangement gives the observer a better sense of how the instructor interacts with students both individually or in groups, including their approach to answering questions or facilitating participation. The colleague may take general notes on what they observe or evaluate the instructor using a teaching rubric or other structured tool.
Peer Review of Course Instruction
Preparing for a Teaching Demonstration - UC Irvine Center for Educational Effectiveness
Based on Peer Feedback - UCLA Center for Education, Innovation, and Learning in the Sciences
Teaching Practices Equity and Inclusion Rubric
Classroom Observation Protocol for Undergraduate STEM (COPUS)
Student Learning Assessments
Student learning can vary widely across courses or even between academic terms. However, having a clear benchmark for the intended learning objectives and determining whether an instructor’s course as implemented helps students to reach that benchmark can be an invaluable piece of information to guide your teaching. The method for measuring student learning will depend on the stated learning objective, but a well-vetted instrument can provide the most reliable data.
Recommended steps and considerations for using student learning assessments to evaluate your teaching efficacy include:
Identify a small subset of course learning objectives to focus on, as it is more useful to accurately evaluate one objective vs. evaluating many objectives inaccurately.
Find a well-aligned and well-developed measure for each selected course learning objective, such as vetted exam questions, rubrics, or concept inventories.
If relevant, develop a prompt or assignment that will allow students to demonstrate the learning objective to then be evaluated against the measure.
Plan the timing of data collection to enable useful comparison and interpretation.
Do you want to compare how students perform at the start of your course compared to the same students at the end of your course?
Do you want to compare how the same students perform before and after a specific teaching activity?
Do you want to compare how students in one term perform compared to students in the next term, after changing your teaching approach?
Implement the assignment/prompt and evaluate a subset or all of the student work according to the measure.
Reflect on the results and compare student performance measures.
Are students learning as a result of your teaching activity and course design?
Are students learning to the degree that you intended?
Are students learning more when you change how you teach?
This process can be repeated as many times as needed or the process can be restarted to instead focus on a different course learning objective.
List of Concept Inventories (STEM)
Best Practices for Administering Concept Inventories (Physics)
AAC&U VALUE Rubrics
Rubric Bank | Assessment and Curriculum Support Center - University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa
Rubrics - World Languages Resource Collection - Kennesaw State University
Student Surveys or Focus Groups
Surveys or focus groups are effective tools to better understand the student experience in your courses, as well as to solicit feedback on how courses can be improved. Hearing student voices is critical as students themselves can attest to how course activities made them feel, e.g. whether they perceive the learning environment to be inclusive, or what topics they find interesting.
Some considerations for using student surveys in your teaching include:
Surveys collect individual and anonymous input from as many students as possible.
Surveys can gather both quantitative and qualitative data.
Surveys that are anonymous avoid privileging certain voices over others.
Surveys can enable students to share about sensitive experiences that they may be reluctant to discuss publicly.
Surveys that are anonymous may lend to negative response bias.
Survey options at UC Berkeley include customized course evaluation questions or anonymous surveys on bCourses, Google Forms, or Qualtrics.
Some considerations for using student focus groups in your teaching include:
Focus groups leverage the power of group brainstorming to identify problems and imagine possible solutions.
Focus groups can gather both rich and nuanced qualitative data.
Focus groups with a skilled facilitator tend to have more moderated responses given the visibility of the discussion.
Focus groups take planning, preparation, and dedicated class time.
Focus group options at UC Berkeley include scheduling a Mid-semester Inquiry (MSI) to be facilitated by a CTL staff member.
Instructions for completing question customization for your evaluations as an instructor
Course Evaluations Question Bank
Student-Centered Evaluation Questions for Remote Learning
Based on Student Feedback - UCLA Center for Education, Innovation, and Learning in the Sciences
How Can Instructors Encourage Students to Complete Course Evaluations and Provide Informative Responses?
Student Views/Attitudes/Affective Instruments - ASBMB
Student Skills Inventories - ASBMB
How might I get started?
Self-assess your own course materials using one of the available rubrics listed above.
Schedule a teaching observation with CTL to get a colleague’s feedback on your teaching practices and notes on student engagement.
Schedule an MSI with CTL to gather directed student feedback with the support of a colleague.
Have more questions? Schedule a general consultation with CTL or send us your questions by email ( [email protected] )!
References:
Evaluating Teaching - UCSB Instructional Development
Documenting Teaching - UCSC Center for Innovations in Teaching and Learning
Other Forms of Evaluation - UCLA Center for Education, Innovation, and Learning in the Sciences
Evaluation Of Teaching Committee on Teaching, Academic Senate
Report of the Academic Council Teaching Evaluation Task Force
Teaching Quality Framework Initiative Resources - University of Colorado Boulder
Benchmarks for Teaching Effectiveness - University of Kansas Center for Teaching Excellence
Teaching Practices Instruments - ASBMB
- Math for Kids
- Parenting Resources
- ELA for Kids
- Teaching Resources

How to Teach Skip Counting to Kids in 9 Easy Steps
10 Best Math Intervention Strategies for Struggling Students
How to Teach Division to Kids in 11 Easy Steps
How to Teach Place Value in 9 Easy Steps
8 Math Division Tricks: Making Division Fun & Accessible
Simple & Stress-Free After School Schedule for Kids of All Ages
When Do Kids Start Preschool: Age & Readiness Skills
Kindergarten Readiness Checklist: A Guide for Parents
How to Choose Best School For Your Kid: 12 Best Tips
Why Kids Get Bored at School: 10 Tips to Keep Them Interested
6 Effective Ways to Improve Writing Skills
40 Four Letter Words That Start With A
What Are the Stages of Spelling Development: Ultimate Guide
48 Rhyming Words for Kindergarten Kids
How to Teach Vowels to Kids: A Step-by-Step Guide
13 Challenges for Teachers and How to Address Them
12 best qualities of a good teacher.
15 Best Innovative Tech Tools for Teachers
What is Teachers Professional Development: Strategies & More
11 Best Ways to Create a Positive Learning Environment for Kids
How to Use Formative Assessment in Your Classroom: 5 Ways

Formative assessment is one of the most critical parts of teaching and learning. It helps both teachers and learners to meet the end objectives.
Every teacher uses a different approach to evaluate assessment in the classroom. However, more broadly, two types of assessments are commonly practiced – Formative and Summative Assessments . Formative assessment helps bridge learning gaps and evaluate students’ progress during the learning process, unlike summative assessment.
Thus, modern teachers use formative assessments to create an intellectual learning environment. So, let’s look better at formative assessment before adopting it in your classroom.
What is Formative Assessment?
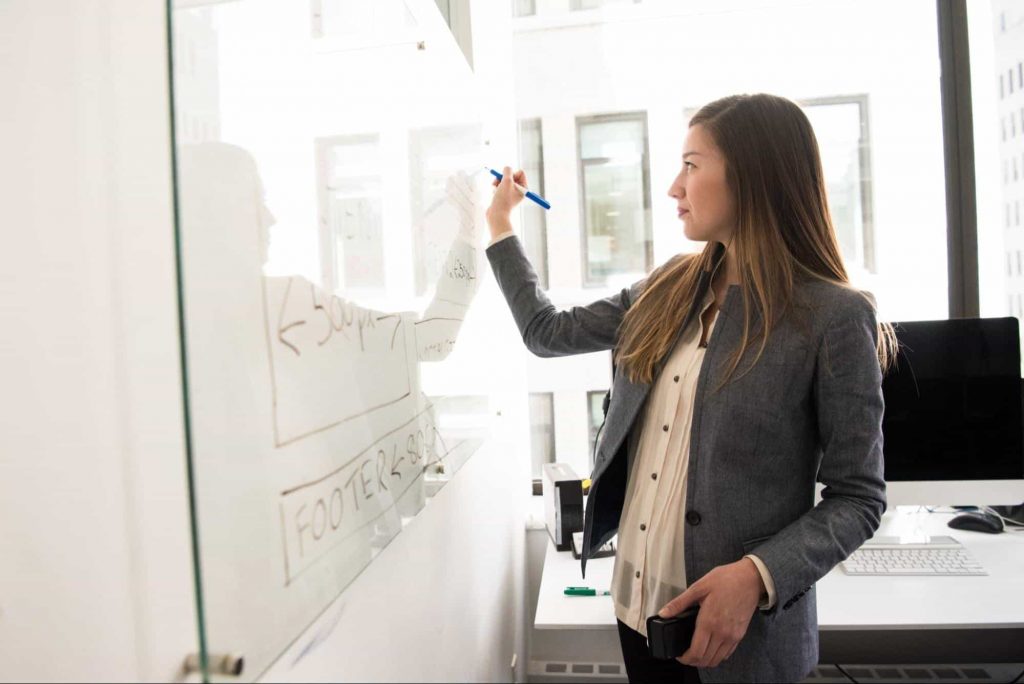

Formative assessment refers to a set of methods teachers use to monitor the in-process progress of students. Formative evaluation monitors a student’s comprehensive review, including academic, special needs, etc.
Using formative assessments in the classrooms helps teachers to assess the academic growth of a student in different manners, such as:
- Which subjects a student finds hard to learn?
- What are the learning standards of the individual students in the classroom?
- Which skills do they find difficult to acquire?
SplashLearn: Most Comprehensive Learning Program for PreK-5

SplashLearn inspires lifelong curiosity with its game-based PreK-5 learning program loved by over 40 million children. With over 4,000 fun games and activities, it’s the perfect balance of learning and play for your little one.
Once teachers run the assessment, they can adjust the lessons based on individual students’ needs and objectives.
In short, formative assessment is something that teachers ask or do to gather information about a student. For example, asking your students to raise their hands if they have any doubts is also a formative assessment.
Formative Assessment Examples

Without even knowing, you conduct various formative assessments in your classroom. Here are a few common formative assessment examples:
- Asking your students to mention subjects or topics that they find hard to understand.
- Providing a specific worksheet or journal to students for expressing their thoughts.
- Requesting class monitors to evaluate the performance of their in-mates.
- Asking students to self-evaluate their growth and performance, etc.
Formative Assessment Evaluation

Formative assessment is not a new term . It has been part of the teaching methods since 1960. However, this teaching technique has entered the mainstream in recent years.
The digitalization, intention-based studies, and modernization of the educational system have fueled formative assessments. Schools are encouraging more and more teachers to use formative assessment strategies. They motivate teachers to personalize learning to create better learning opportunities for all.
Why Should You Use Formative Assessment Strategies in Your Classroom?

Formative assessment is a debatable topic among educationists. Some find it a loose method to evaluate performance, and some think it is not an effective way to monitor performance. But, no matter what people say, it is undebatable that formative assessment offers the following benefits:
1. Goal-Based Learning
Constant progress monitoring highlights the end learning goals. It helps students remember their goals from a particular course or class. Conversely, teachers can ensure students are moving in the right direction or require extra help to achieve their academic goals.
2. Student-Centered Learning
Through formative assessments, teachers can understand the requirements of individual students. They can know the learning pace and caliber of a student. This helps to promote a student-centered learning environment in the classroom.
3. Improves Education Level
Teachers will know students’ academic growth in real-time when they gather constant feedback via different methods. They can bridge the gap between students’ learning goals and knowledge using this knowledge. Teachers can implement strategies to help slow students, like visual or audio learning.
4. Elevate Students Motivation
When students get regular progress updates and notes on achieving their learning goals, it improves their engagement. Formative assessments keep students motivated and inspired to do better every day.
5. Personalized Learning
Formative assessment allows teachers to practice personalized learning in the classroom. They can establish one-on-one relationships with every student in their classroom and understand their strengths/shortcomings. This helps teachers to utilize students’ strengths to teach them new concepts.
6. Self-Evaluation
Self-evaluation is the best way to improve students’ performance. In this, students evaluate their own progress over the period and compare it to the standards set by their teachers. This will reduce teachers’ burden to monitor students’ performance and enhance their productivity.
7. Effective Decision Making
When teachers have rigorous data, they can make effective decisions on time. If teachers find a student struggling with a subject, they can use different strategies to teach them. And, if a student is still struggling, they can suggest alternative solutions before it’s too late.
Types of Formative Assessments
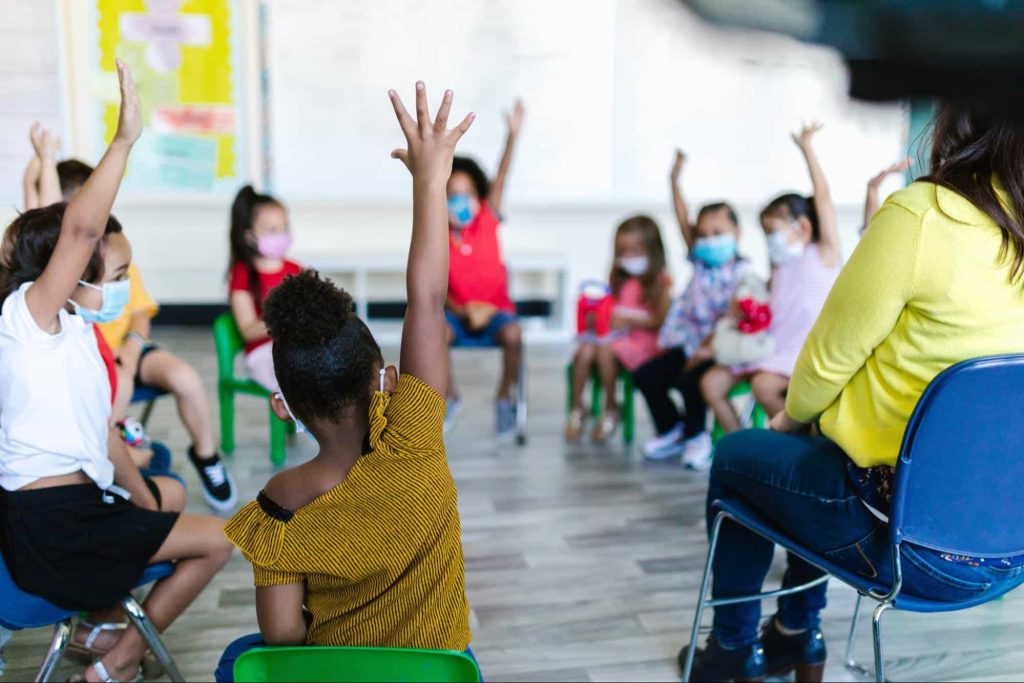

1. Quizzes
Impromptu quizzes are the most preferred way to conduct formative assessments. After teaching a lesson, many teachers ask for quizzes to know how many students have understood the concept.
2. Polls
Polls are helpful to gather instant feedback. During online studies, polls can help teachers better understand the students’ viewpoints on a specific topic.
3. Entry Slips
Teachers can ask questions before starting a new lesson to check how much students already know. This helps teachers assess the teaching level they should use to make students understand a lesson.
4. Exit Slips
Teachers use this formative assessment technique at the end of a lesson. In this approach, students are requested to write down a few points or share opinions on the lesson. This will allow teachers to evaluate how much students have learned and what they missed.
5. Dipsticks
Dipsticks are an easy and quick method to know how much students have understood in the classroom. In this formative assessment strategy, teachers can give a worksheet to students at the end of a day or week. It is like a mini-test to monitor progress.
6. Tag Feedback
It is a peer assessment method where students evaluate each other’s performance. Tag feedback provides in-depth feedback as students can discuss with their peers better than their teachers.
7. Interviews and Group Discussions
You can host a one-on-one interview with your students after a significant period to understand their needs. A 10-minute interaction with your students can help you learn much about them. Besides this, you can organize group discussions to get better insight into your students’ overall development.
8. Practical Exercise
Teachers can ask students to use the lesson in the real world. With this exercise, students can learn to implement an academic lesson in an actual situation. Plus, teachers get to know whether students understand the basic concept or not.
Another formative assessment method is asking students to take a small survey after the class. You can also send an online survey to parents. This will expand the scope of your assessment.
How to Deploy Formative Assessment Strategies in Your Classroom?
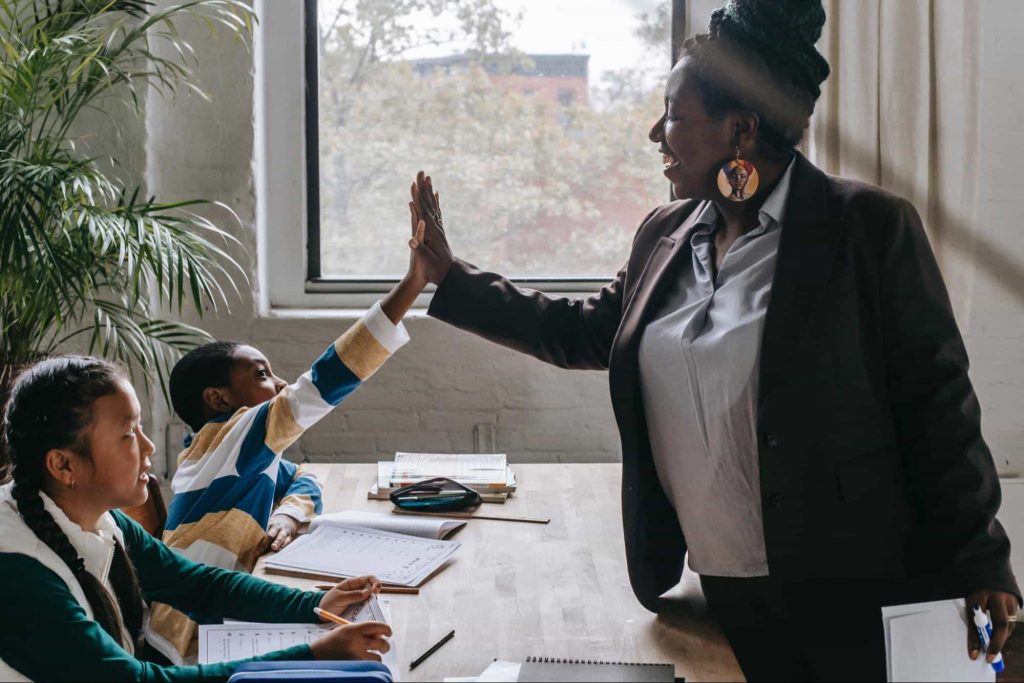

The success of your formative assessment strategies depends on how you deploy them. So, it is critical to implement formative assessments in the correct order in your class, such as:
1. Define Performance Criteria
Teachers should explain the performance evaluation criteria to students to work on self-improvement. For example, describe the requirements to grade test papers to students. Teachers can also hold class-wide discussions to define the performance criteria.
2. Boost Students’ Self-Evaluation
It would help if you asked students to use the preset criteria to evaluate their own progress. This practice will save time and make students understand their shortcomings. Teachers should ask students to rank their best work to find their strengths.
3. Provide Comprehensive Feedback
The best feedback is corrective and forward-looking. So, don’t only pinpoint problematic areas in your feedback. You should also provide a detailed solution to overcome the problem. In addition, share feedback over feedback to confirm whether students have learned something from previous feedback.
4. Encourage Peer Discussions
Teachers should invite students to discuss the formative learning process together. These discussions help teachers understand students’ concerns on courses and respond to them. Teachers can get insightful information through group discussions to define learning goals.
5. Collect Constant Data
You cannot provide accurate feedback to students based on past information. You need the latest data to help students and design formative assessment strategies. Thus, you should feel free to collect relevant data from students to provide the correct feedback. Teachers should make a constant effort to monitor their students’ performance.
Let’s Adopt Formative Assessments Today!
If you hope to provide your students with a personalized and futuristic learning environment, formative assessment is a way to do it. These assessments will allow you to teach in a better way. You can make every student grow with regular assessments.
So, we have already shared how to deploy a successful formative assessment strategy in your classroom. Let’s take a leap of faith and raise education standards using formative assessments.
With SplashLearn’s assessment-based learning, you can now elevate your students’ learning outcomes & help them become fearless learners!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the purpose of formative and summative assessment.
Formative assessment monitors students’ ongoing learning progress and provides instant feedback. Summative assessment aims to analyze a student’s learning at the end of a course. Teachers need to focus on both assessments to improve learning levels.
What is a formative assessment in the classroom?
Formative assessment provides evidence to teachers of where students are in their learning programs. So, formative assessment in the classroom means supporting reflective learning. These assessments help teachers make adjustments to the curriculum based on the students’ performance.
Is homework a formative assessment?
Yes, homework is a formative assessment if used in the right way. In formative assessment homework, students get several chances to practice, get feedback and improve. Homework is the best tool to try new skills without any pressure for students.
What is a good formative assessment?
A good formative assessment strategy revolves around asking students to answer questions like “why” and “how.” The high-order questions require in-depth thinking and provide better insight to teachers.
30 Best Preschool Graduation Ideas & Activities
13 Best Spring Bulletin Board Ideas: Spring into Creativity
What Do You Learn in 5th Grade: Overview, Subjects and Skills

Most Popular

15 Best Report Card Comments Samples

101 Best Riddles for Kids (With Explanation)

40 Best Good Vibes Quotes to Brighten Your Day
Recent posts.

15 Fun Fourth of July Activities for kids in 2024

Math & ELA | PreK To Grade 5
Kids see fun., you see real learning outcomes..
Watch your kids fall in love with math & reading through our scientifically designed curriculum.
Parents, try for free Teachers, use for free

About SplashLearn
Enter the Splashverse! Inspire lifelong curiosity with this game-based PreK-5 learning experience loved by over 40 million children. SplashLearn is the perfect balance of learning and game-play that your little one needs to build math and reading confidence.
- Games for Kids
- Worksheets for Kids
- Math Worksheets
- ELA Worksheets
- Math Vocabulary
- Number Games
- Addition Games
- Subtraction Games
- Multiplication Games
- Division Games
- Addition Worksheets
- Subtraction Worksheets
- Multiplication Worksheets
- Division Worksheets
- Times Tables Worksheets
- Reading Games
- Writing Games
- Phonics Games
- Sight Words Games
- Letter Tracing Games
- Reading Worksheets
- Writing Worksheets
- Phonics Worksheets
- Sight Words Worksheets
- Letter Tracing Worksheets
- Prime Number
- Order of Operations
- Long multiplication
- Place value
- Parallelogram
- SplashLearn Success Stories
- SplashLearn Apps
- [email protected]
© Copyright - SplashLearn

Make learning a game for your students
Unlock endless learning fun with 14,000+ games & activities, 450+ lesson plans, and more—free forever.
Teachers, Use for Free
- BookWidgets Teacher Blog

The ultimate formative assessment guide for teachers - Classroom tools, tips, and examples

Formative assessment is gaining importance in our classrooms. Evaluation is not just about a final grade anymore: it’s about pushing your students to get better learning outcomes; it’s about feedback, and growing.
Creating an effective teaching environment with formative assessment techniques and tools is important. In this formative evaluation blog post guide for teachers, I’ll show you everything you need to know about this topic.
This guide is divided into several chapters. Just click on the link below to jump to parts that interest you, or, if you’re new to formative assessment, just read everything. 👀
What is formative assessment?
- The differences between formative and summative assessment
- Types & examples of formative assessments
- Formative assessment tools
Formative assessment tips for teachers
How to give formative feedback.

The definition of formative assessment (or formative evaluation) is very clear: Formative assessment is an ongoing process of collecting information on the outcomes, strengths, and weaknesses of your students at any point in their learning process.
Teachers use this information to provide ongoing feedback to students when they are still learning. Feedback should be actionable, so students can use it to improve their learning.
The most important characteristic of formative assessment is that there are no grades! You don’t need to put a mark on a student to measure his capabilities.

The difference between formative and summative assessment
To show the differences between formative and summative evaluation, we’ve created a clear infographic for you.
Of course, I’ll spill the beans again, here.
Whereas the definition of formative assessment clearly states that it’s an ongoing process of collecting student information and providing feedback, summative assessment is used to evaluate students’ learning at the end of an instructional unit by comparing it against some standard or benchmark.
- Difference 1: When does the assessment take place in a students’ learning process? That’s the first, and biggest difference between the two evaluation strategies. As you already know now, formative assessment is an ongoing activity. The evaluation takes place during the learning process. Not just one time, but several times. A summative evaluation takes place after the learning process when a course or unit is completed.
- Difference 2: What’s the information you get from your students’ learning process? With formative assessment, you try to figure out whether a student’s doing well or needs help by monitoring the learning process. When you use summative assessments, you assign grades. The grades tell you whether the student achieved the learning goal or not.
- Difference 3: What’s the purpose of both evaluation strategies? For formative assessment, the purpose is to improve students’ learning outcomes. For summative assessment, the purpose is to evaluate students’ achievements. In other words: do you want your students to be the best at something, or do you want your students to do better than before each time over and over again?
- Difference 4: What’s the size of the evaluation packages? Formative assessment evaluates your students’ knowledge of small content areas. For example, 3 formative evaluations of 1 chapter. Summative assessment asks students to test their knowledge of complete chapters or content areas. For example, just 1 evaluation at the end of a chapter. The lesson material package is much larger now.
- Difference 5: What’s the nature of the assessment? Formative assessment considers evaluation as a process. This way, the teacher can see a student grow and steer the student in an upwards direction. With summative assessment, it’s harder for you to guide the student in the right direction. The evaluation is already done. That’s why summative assessments or evaluations are considered to be more of a “product”.
You can also take a look at this page to learn more about using BookWidgets for formative and summative assessments.

Types and examples of formative assessments
There are many methods to formatively evaluate your students. I’ll sum up a few types, including a digital example of formative assessment.
As this is a technology blog for teachers, I will focus a bit more on the digital ways of formative evaluation. You’ll see that for every traditional method, there’s a digital one too, providing the teacher with even more useful statistics in your students’ learning processes.
You can find and adapt all the digital formative assessment examples in this BookWidgets group folder .
1. Exit Tickets

An exit ticket or exit slip is a sheet of paper or a digital activity with questions that each student answers individually at the end of the lesson.
The questions can be about the lesson content (what they liked about it, what they remember) , or about how they felt after the lesson. Exit slips will give you the information you need to help your students improve, and to help you understand how they feel at that exact moment.
There are hundreds of different exit slip types, which makes it a very strong formative assessment tool for all classes and all teachers.
Exit Ticket Example
We’ve created an exit ticket guide with over 60 digital, ready-to-use exit tickets for you to use immediately.
Check out the example below: Exit in 3, 2, 1

This exit ticket is created with BookWidgets, which also has a reporting dashboard for teachers. Here, you’ll see all the submitted results and you can quickly get the information you need, and provide feedback where needed.
2. Self-assessments

It will take practice and guidance to help the students understand the importance of a thorough self-evaluation.
Self-assessment example
There are many self-assessment strategies. Exit slips are one of them. Take a look at the list with exit tickets above. You’ll certainly find some good ones. Also, check out this post with some creative self-assessment ideas .
Here’s my favorite self-assessment example: The Traffic Light

Students have to reflect on the task and indicate where they’re at. Do they understand everything? Do they still need help? Are they stuck or completely disoriented? They have to indicate and color the traffic light green, orange or red. They also have to indicate why they choose that color.
3. Worksheets and quizzes

You can use, for example, the BookWidgets worksheet or quiz activity. With over 30 different question types, the possibility to add multimedia, and set up different scoring options, this is the ultimate formative evaluation activity you’ll be able to build.
Some unique formative assessment settings in the BookWidgets Worksheet or Quiz are:
- Immediately show students the correct answers when the activity is finished: this way, students know what they have correct and where they need practicing for improvement.
- Immediately color correct student answers green: students can keep trying and dig deeper in their brain to change the other answers to green as well. Instant feedback can be quite motivating for some learners.
- Enter automatic feedback based on your students’ answers: students with a different outcome will get different feedback, adapted to where they are in their learning process.
- Return student results, solely with your personalized feedback, without grades: students receive personalized feedback are able to try again keeping the timely feedback in mind.
- Allow students to edit their answers: students can change their answers to the questions, based upon the automatic or personalized teacher feedback. This effective formative assessment technique may lead to improved learning outcomes.
- Use LIVE activity while students are working on a worksheet or quiz: Know the exact moment when a student begins to struggle or needs support. This is also a great way to see which students are successful and provide enrichment opportunities or challenges to enhance engagement.
- Provide a rationale to a response which is revealed along with the correct response after each question when your students go through the questions one by one: Rationale feedback allows learners to build knowledge sequentially in the learning process.
Digital formative worksheet example
Teachers have so many evaluation options in BookWidgets. This example utilizes the automatic feedback setting. Give it a try yourself to see how it works and what this can mean for your classroom. First, complete this worksheet really badly. Make some mistakes and click on “show score”. Now, read your feedback and edit your answers. Try to do better. What’s your feedback message now?

Digital formative Quiz example
I have another one for you here, with different settings. This is a history quiz where students have to go through the questions one by one. After each question, they also get the right explanation. Go take a look! 👇

4. Educational games

Students are often more motivated when the teacher says the magical words “complete this crossword puzzle”. Games can also be great for assessing prior knowledge or as an opening lesson reflection.
Digital formative crossword puzzle example
This crossword puzzle is also a retrieval practice strategy, where students have to summon their knowledge about the lesson again. They can complete it, see the results and then submit to the teacher. Go ahead and give it a try 👇

The teacher reviews the results and provides written feedback as needed. Finally, the teacher returns the feedback to the student.
Digital formative Pair Matching example
A pair matching game is solely for practicing, but feedback can be added to motivate and encourage students. And that’s what formative assessment is all about. In this example, students need to match the pairs, and after finishing they receive written and audio feedback from the teacher. The feedback could also be a question, asking your students to reflect on the exercise like in the example below. Go take a look!

These Crossword Puzzle and Matching pairs activities were created using BookWidgets.
5. Pop quizzes

Digital pop quiz example
Take a look and go through the quiz. In the end, students have to submit their answers to the teacher and also get the right answers to see how they did.

Since your students have to submit this pop-quiz, you can view the results. Below you can see a snapshot of the reporting data of this BookWidgets quiz. It will show you which questions are hard to solve for the complete class. Use this to get your students back on track for the questions they clearly didn’t understand.

6. Diagnostic tests

You can use a diagnostic assessment to discover diverse learners’ needs. It allows you to see data on struggling learners as well as those who will benefit from increased challenges in learning. It is after the diagnostic assessment that differentiated teaching and learning begins.
Diagnostic test example
Here are two diagnostic test examples for teachers of English as a Second Language (ESL). Both are designed to provide the teacher an understanding of students listening and reading comprehension skills.
Diagnostic test example of listening skills

Diagnostic test example of reading comprehension

Ines Neefs , an English teacher in Belgium, created these BookWidgets diagnostic tests.
7. Journals an portfolios

OR, this can be done differently. Here, a portfolio is used for daily self-reflection allowing opportunities for student to stay on task. Self-reflection allows students time to think about their thinking and learning leading to growth. Students should submit reflections to the teacher who in turn provides suggestions on how to try again, improve and even follow up with individual students.
Digital portfolio example
Portfolios can be websites your students build, or a combination of worksheets, collages, and more. For this example, I picked out a special one. It’s a self-assessment portfolio for students that are learning English. They have to keep track of what they learn, what went good, bad and how they are going to improve their learning outcome.
It’s an example created by Sandy Lapere , an English teacher in Belgium, and her team. She created this portfolio entirely with BookWidgets.

8. Peer assessments

Peer assessments have a few important advantages:
- It encourages your students to reflect on their own learning progress and performance,
- It helps students become autonomous learners,
- It encourages students to be more responsible for their own learning,
- It helps students develop their assessment and argument skills,
- It helps students be more aware of their weaknesses and strengths;
- It helps students learn more from each other.
Using their own and fellow students’ feedback, students can move forward with it and do better. Keep in mind that formative peer assessments aren’t about the grades, but about the feedback.
Peer assessment example
This is a simple but fun peer assessment. After an exercise, a performance or presentation, the fellow students need to give some tops and tips to the student in front of the class.

The teacher picks out 3 students to share their tips and tops out loud. The rest of the class send their results to the student in front of the class via e-mail. After sending it to their fellow students, they can delete their answers from the Widget and use it again for other fellow students.
9. Teacher Observation

In your classroom, you should be able to see struggling students and students that need more challenges. Of course, this is very time-intensive, and you can overlook some things.
This is where technology can be helpful. A lot of apps allow you to track student progress while they are working on an assignment. This allows you to immediately swoop in when needed.
Live Widgets observation example
BookWidgets’ Live Widgets function allows you to do just that: follow students’ progress live while they are working on an assignment. The live widgets dashboard shows you how long it took for students to complete an assignment, how well they did on each question, and if they are stuck or not. You can open individual student work as well and see where things go wrong. This is your cue to help out a student and give instant feedback so they can move on.

Formative assessment tools for teachers
In the arena of educational technology, you’ll see a lot of quiz and testing apps, but keep in mind that the focus must lie on providing your students with timely, meaningful feedback. The playing field for this type of apps narrows a bit, but there are still plenty of good fish in the sea to choose from.
Here is a list of 10 good formative assessment classroom tools for teachers. Of course, you can find many more formative evaluation tools for your classroom here .
1. BookWidgets

BookWidgets has a library with over 40 different exercise templates (or widgets). You can create formative exercises like pair matching games or crossword puzzles, and formative assessments like worksheets and quizzes with over 30 different question types.
The BookWidgets Reporting Dashboard makes sure you get the right student statistics and feedback features to support your students’ learning. And, like I already said before, you can also follow student progress live, while your students are working on an assignment, which allows you to quickly steer students in the right direction.
2. EdPuzzle

Add more value to videos in your lessons. They’re not just an introductory tool anymore. With EdPuzzle you can ask your students lots of questions during the video, so you can test their understanding right away and point out some important parts in the video.
Again, here you get some statistics to see how many times your students saw the video and how well they understood it. As a teacher, you use these statistics and address topics that are still a bit hard to understand for your students.

You can even let parents join in on the conversation. They can see their children’s tasks and comment on them too.
4. Classkick

Teachers provide personalized, real-time feedback and grading with an array of tools–directly on the canvas, in classkicks’ help center, or with pointed stickers. Students can even ask their peers for help anonymously.
5. Flipgrid

Teachers can set up assignments where students need to respond with a video recording. Students can also respond to each other’s videos.

The teacher asks a question, all your students have to answer it on their device and the results show up, on the screen, immediately.
Use this tool for anonymous surveys, brainstorm sessions, questions about the lesson material, Q&A sessions, and much more. Wooclap has a lot of fun live question formats.
7. Formative

The feedback features are really handy (written, audio, video, …) and your students get a notification in case they look over the teachers’ feedback. As a teacher, you can also track student progress in real-time.

All those slides make an amazing interactive presentation. Especially if you add activities like quizzes, open-ended questions, polls, draw questions, and others.
When your presentation is ready, your students can opt-in by entering a code in their Nearpod app or just click on the assigned link in Google Classroom.
You, as a teacher, are in charge of the presentation. when you switch to another slide, the presentation on your students’ devices will also switch to that slide.
When your students’ have to make a quiz or a poll, they can just do that on their screen, as it is a part of the presentation. The answers are gathered live! So you can see immediately what your students answered.
9. Peardeck

You can even add interactive elements such as quiz questions and whiteboards. Every student can answer these in real-time on their own device. This truly engages students, and you’re sure that your students are participating as well.
The one thing I’m most excited about here is the Google Slides Add-on. Add Pear Deck activities to your google slides to make them even more interactive

With Padlet you can create an online post-it board that you can share with any student or teacher you want. Just give them the unique Padlet link. Padlet allows you to insert ideas anonymously or with your name. It’s easy to use and very handy.
Whoever has the Padlet board opened on his device, can see what’s on it and what everyone is writing. Students just have to start adding little sticky notes online. They can see all the ideas gathered on the teacher board immediately. The teacher can allow other comments as well, which makes it the perfect tool for peer assessment.

As there are so many ways to do formative assessment, you might need some handy tips. Whatever formative assessment strategy you use in your classroom, these tips will help you out, and prevent you from making mistakes.
1. Actionable

2. Educational technology

3. Show the difficult parts

4. QR-corner

With BookWidgets, you can even bundle the exercises of the same topic into a WebQuest , creating just 1 QR-code for a complete set of extra exercises. You can also use a planner for this.
5. Video instructions

6. Mastery learning

7. Differentiate instructions

Check out this BookWidgets blog post for 20 ways to give differentiated instructions . These instructions will give students the chance to learn at their own pace or according to their own needs, competencies, and interests. Differentiated instruction strategies make sure students don’t get left behind when the teacher moves forward.

When you’re giving ongoing and regular feedback, you can speak of formative feedback. Formative feedback lies at the base for improvement and is crucial when it comes to formative assessment. Students are in need of ongoing information to identify their strengths and target areas so they know how to improve their learning process.
Make sure to read this comprehensive post about giving meaningful feedback . It will give you many good insights.
Giving meaningful feedback is not always easy. But there are a few feedback rules. Below, I give you a handy overview of the do’s and dont’s of giving feedback. These awesome tips are from Susan M. Brookhart. You can read more about it in her book: “ How to Give Effective Feedback to Your Students .”
It’s a wrap!
I hope you now have all the information about formative assessment you need. Let us know what tips you’ve just learned you’re certainly going to use in your classroom! Start the formative evaluation conversation, mention us on Twitter, @ibookwidgets , and make sure to share this post with fellow teachers.
Hooked on BookWidgets? Join our Teaching with BookWidgets Facebook community 💖. I’m Lucie Renard, and I’d love to connect with you on LinkedIn or Twitter too!
Last but not least, don’t forget to create your first formative evaluation with Bookwidgets here. 👇
Create my first formative evaluation with BookWidgets
Join hundreds of thousands of subscribers, and get the best content on technology in education.
BookWidgets enables teachers to create fun and interactive lessons for tablets, smartphones, and computers.

- Formative Assessment: Meaning, Types & Examples

Formative assessment allows you to evaluate students’ performance in real-time, and also improve the course content and delivery during the learning process. It makes it easier for teachers to track the performance of students during a course or training program.
Since formative assessment happens on the go, it is best described as a quick-fire method of monitoring the learner’s progress. To do this, the researcher needs to ask different questions and administer multiple class exercises to get valuable feedback from the students.
What is Formative Assessment?
Formative assessment is a process of evaluating the students’ knowledge as they learn. It is a method of on-going assessment and it involves putting together a series of quick-fire questions and exercises to help you monitor the learner’s progress during the course.
As students learn, they will experience challenges along the way—they may find it difficult to understand a concept or to grasp a few examples. Without formative assessments, it is almost impossible for the teacher to recognize when the student is struggling and to provide the right support.
Unlike summative assessment that happens at the end of a course, formative assessment tracks the student’s knowledge level on the go. Since it doesn’t measure the student’s knowledge against some standard, it is typically considered as having a low or no point value.
Characteristics of Formative Assessment
Understanding the characteristics of formative assessment enables you to plan and execute one effectively as an instructor. For instance, knowing that formative assessment and learning happen concurrently will help you avoid waiting till the end of a course before evaluating your students.
Other things you should know about formative assessment include:
- It evaluates the learning process and the learner’s progress at the same time.
- A formative assessment is collaborative as it measures the student’s progress and the effectiveness of the teaching method.
- Formative assessments are interwoven with the ongoing teaching and learning process.
- It is a fluid method of evaluation. The student’s progress is not measured against a standard or benchmark unlike what you will find with summative assessment methods.
- Formative assessment requires the instructors and the students to become intentional learners.
- The aim of formative assessment is to gather actionable feedback that improves the overall teaching and learning process.
- It is a diagnostic method of evaluation.
- Results from formative assessments are immediately made available.
- Formative assessments are non-graded.
Examples of Formative Assessment
- Impromptu Quiz
After a lesson, you can ask students to take part in an impromptu quiz to know how well they understood the course material. An easy way to do this is by creating a short online quiz with relevant close-ended questions using Formplus.
A poll is a way to gather instant feedback from students as they learn by asking the right questions. Formplus allows you to create simple and fun polls that help you to evaluate your students’ knowledge as part of formative assessment.
With multiple form field options, you can have different types of rating questions in your poll including heart and emoji ratings. Formplus also has an automatic poll closing option; making it easier for you to integrate the online polls into the overall teaching and learning process.
- One Minute Papers
Another way to assess students’ knowledge on the go is by asking them to create simple one-minute papers; they can do this online with Formplus. You can create a simple 1-minute survey with open-ended questions and ask your students to share their knowledge within a particular context.
- Entry Slips
Before starting off on a new topic or lesson, you can ask one or more questions to know how much the students remember from the previous lesson. You can edit any of our online surveys and list differentiated questions for the students to respond to.
Exit slips are used to measure the students’ progress at the end of the lesson. Ask learners to write some of the points they remember from the lesson on scrap paper or create a simple online questionnaire on Formplus to collect relevant responses from students.
If you hosted the class on e-learning platforms like Google Classroom and Edulastic, you can track what your students know at a glance and also measure their progress, in line with the teaching and learning goals.
Think of these as easy and quick methods to know how well the learners understand different concepts discussed in class. You can ask learners to write short letters explaining core concepts to another person or do a think-pair-share exercise with a partner.
- Visual Exercises
Ask students to interpret core ideas from the course using simple visual representations. They can create basic sketches of what they have learned or you can create a simple survey and ask them to choose the most appropriate visual representation from the image options in your Formplus form.
- Interviews and Focus Groups
At specific intervals during the class, you can organize quick interviews and focus groups to assess the students. These can be in the form of casual discussions with the learners or 10-minutes structured interviews using an online survey or questionnaire. Organizing and focus groups can provide better contexts for the assessment.
- Tag Feedback
This is a peer assessment method where the students evaluate and provide feedback on each other’s performance. As students assess their peers, you gain valuable insights into how well they understand the course material and topic(s).
Tag feedback is an effective way to get the students involved in formative assessment. Ask learners to highlight the positive contributions of their peers, or to suggest ways to improve the course content, teaching method, or overall classroom engagement.
- Self-assessment
One of the best ways to conduct formative assessments is to simply ask the students to do it themselves while you provide the needed guidance. When students evaluate themselves, they can reflect on their learning goals and discover their strengths and weaknesses.
How to Use Formplus to Conduct Formative Assessment
As a seamless data collection tool, Formplus allows you to create effective forms, questionnaires , and surveys for formative assessment. It has multiple form features and templates; making it easy for you to assess students’ knowledge as you engage with them in the classroom.
Create your questionnaire for formative assessment with these easy steps:
- Log into your Formplus dashboard and click the “create new form” button at the top of the dashboard. If you do not have a Formplus account, visit www.formpl.us and follow the prompt to create one.
- In the form builder, add the title of your online questionnaire to the title box.
- Drag and drop preferred form fields from the form fields section into your questionnaire. You can choose from more than 30 form field options located on the left side of the builder.
- Click on the pencil icon beside each field to include your question(s) and option(s), if any. You can also make the field required or read-only.
- Click on the “save icon” for all the changes you’ve made to your assessment questionnaire. When you do this, you will automatically access the form customization section.
- Use multiple form customization options to change the look and feel of your questionnaire. You can change the background color to your brand hue and add your organization’s logo to the questionnaire.
- Click on the form sharing option and choose any of the options to share your questionnaire with learners for formative assessment. Formplus allows you to send out email invitations, share the form directly on social media, and also add it to your website.
- Monitor responses in our form analytics dashboard.
Now, let’s talk about some of the features that make Formplus a great formative assessment tool.
1. Mobile-friendly Forms
Smartphones have become indispensable learning tools and this is why your formative assessment needs to go mobile too. With our mobile-friendly forms, you can conduct formative assessments and track students’ progress using mobile phone surveys and forms.
Formplus allows you to create custom mobile forms that can be viewed and filled out on any internet-enabled device on-the-go. Our mobile-responsive forms adapt to any smart device they are viewed on; making it possible for students to complete polls and questionnaires without pinching or zooming out on their screens.
2. Multiple Form Fields
Choose from our multiple form fields to help you collect feedback from students in different formats. Formplus has more than 30 form fields that support data collection the way you like. Some of the form fields you can use for formative assessment are text fields, rating fields, and image choice options.
3. Multiple Form Sharing Options
Formplus has multiple form-sharing options; making it more convenient for students to participate in formative assessment. After creating your online assessment survey, poll, or questionnaire, you can send out email invitations to students to fill the form—this is a great idea for entry and exit slips.
4. Autofill Form Data from Spreadsheet
Formplus allows you to autofill students’ data from a spreadsheet so that respondents do not have to bother about providing information from scratch as they participate in formative assessment. After mapping out the students’ data on your form or survey, send out email invitations to students to allow them to update their information via custom prefilled forms.
5. File Uploads
Formplus offers flexible and unlimited file uploads so you can collect different file types of any file size directly in your form, and save them in your preferred cloud storage. You can add numerous file upload fields directly in the Formplus form builder; choosing from 30 available form fields.
Advantages of Formative Assessment
- Formative assessment helps students to align their learning goals with the aims and objectives of the coursework or training. It keeps the learning goals in the minds of everyone and instructors can help students to resolve any challenges they face before they get off track.
- Formative assessment improves the overall learner performance. As teachers monitor learners’ progress, they can utilize the feedback to improve the learning experience and ultimately, the learner’s performance.
- It is an effective way to boost your students’ motivation. Formative assessment spurs learners to smash their goals by consistently tracking their progress towards specific knowledge objectives.
- By tracking learners’ progress using different formative assessment methods, the teacher can create personalized learning experiences for the students. Formative assessment helps you to understand the unique needs of your students and know the best ways to support them on their individual learning journeys.
- Formative assessment empowers the instructors to make data-driven decisions. Using the data gathered from frequent learning checks, the instructor can make valid and informed decisions that are grounded in real-time experiences.
- It helps instructors to adjust their teaching methods to better suit the needs of the learners.
Disadvantages of Formative Assessment
- Formative assessment can be time-consuming because the teacher needs to implement several methods to effectively monitor students’ progress as they learn.
- The more formative assessments you incorporate in the learning process, the lesser time there is for actual teaching.
- Planning formative assessment processes can be tedious and exhausting for the instructor.
- The instructor’s bias or any other form of subjectivity affects the validity of the whole process and can create an inaccurate representation of the students’ progress.
- Since formative assessments are non-graded, students may not be eager or motivated to participate in them; especially when they are accustomed to getting grades or points for their academic progress.
Formative assessment has a huge positive impact on the teaching and learning process. Teachers can use the data from formative assessment to improve their teaching methods while students use the platform to draw the teacher’s attention to areas where they need help.
It is also a great way to boost class participation because the students get involved in different quick-fire tasks as the course progresses. If you are just getting familiar with this method of course evaluation, you can start by creating an online impromptu quiz for your students using Formplus or putting a 1-minute online survey together.

Connect to Formplus, Get Started Now - It's Free!
- assessment form
- formative assessment
- online assessment
- summative assessment
- training evaluation
- busayo.longe

You may also like:
Authentic Assessment: Definition + [Examples & Types ]
Authentic assessment is one of the most practical methods of course evaluation. Unlike theoretical evaluation, authentic asse

Formative Vs Summative Assessment: 15 Key Differences & Similarities
Today, we will look at 2 of the most common methods of course evaluation—summative assessment and formative assessment. While
Alternative Assessment: Definition, Types, Examples & Strategies
If you’re looking for a course evaluation method that puts the student’s knowledge to work, then you should try the alternati
Summative Assessment: Definition + [Examples & Types]
From end-of-term examinations to teacher-designed quizzes, summative assessment is one of the most effective ways to grade a
Formplus - For Seamless Data Collection
Collect data the right way with a versatile data collection tool. try formplus and transform your work productivity today..

Formative assessments: the ultimate guide for teachers
- Categories Blog
- Date February 14, 2024
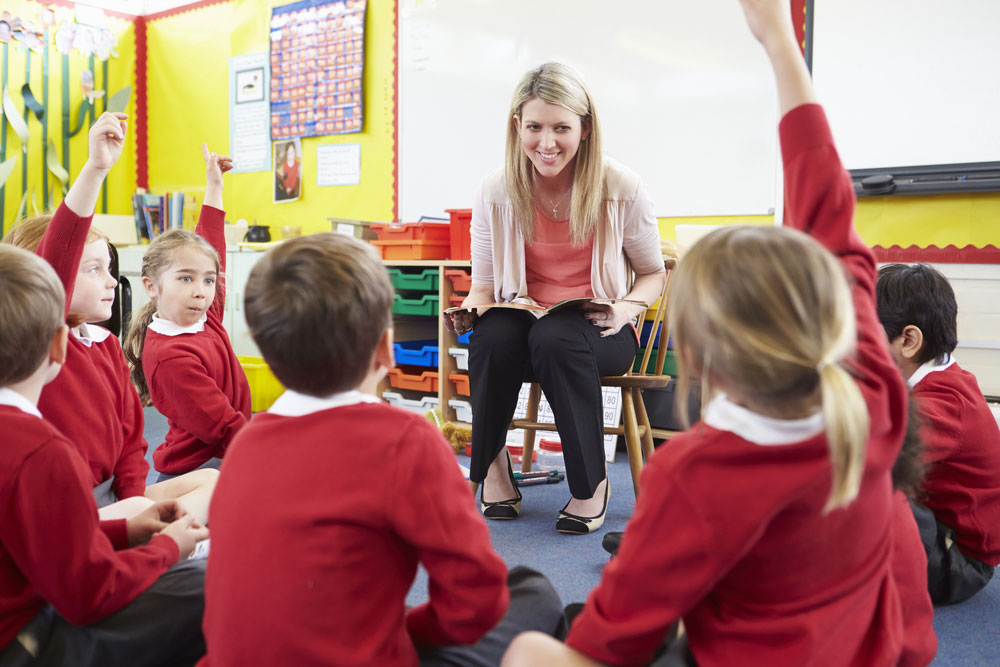

K-12 education is a construction process where students’ skills and knowledge are gradually built up, with every preceding “block” essential to keep on building.
As a teacher, it’s your job to ensure that your students have the core knowledge they need to keep advancing through their education. You need a daily understanding of their current skills and knowledge so that you can accurately gauge their progression, and decide what to teach them next.
One of the most effective, proven ways to do this is with formative assessments (OECD, 2008). 1 They’re a crucial tool in your teaching kit, helping you to provide quality education to students.
Table of contents
- What are formative assessments?
- Evidence that formative assessment works
- Formative assessment examples / types
- Formative assessment strategies for your school and classroom
1. What are formative assessments?
Formative assessments are regular low-stakes tests that help you gauge students’ understanding. They are “dipsticks” where you can quickly check learning as you might quickly check the oil in your car, allowing you to adapt your teaching and fill knowledge gaps while learning is still taking place.
Quizzes are a common example of formative assessments. They’re quick to create, complete, and mark, and give you a good impression of students’ understanding of the content and their progress for the unit. You can see which questions and topics they are struggling with, re-teach them, and then re-test – a rapid feedback and improvement cycle that boosts student outcomes and moves them along their learning journeys.
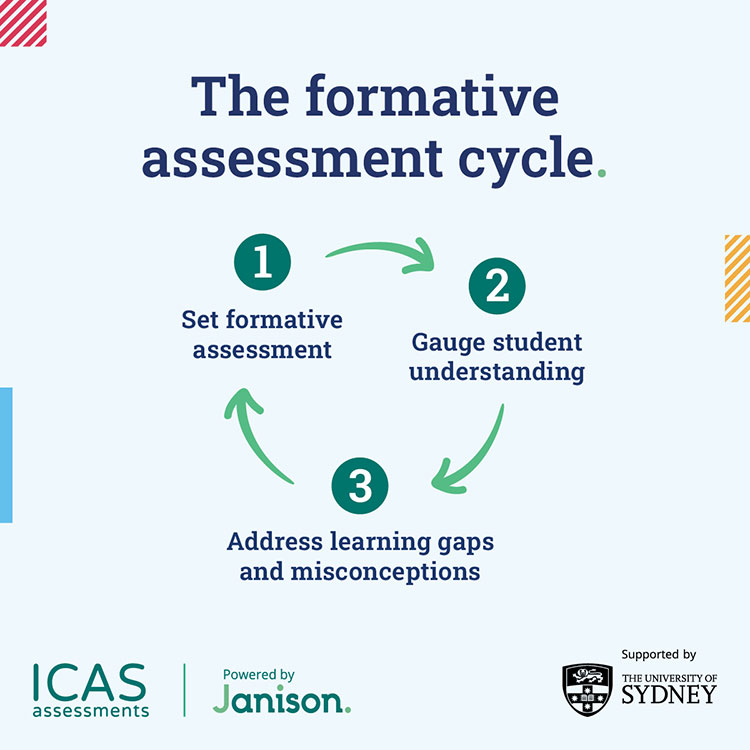
You can see how this differs from summative assessments like end-of-year exams. These are one-off tests used to evaluate student understanding after learning has finished, with no opportunity to improve. Their purpose is to grade. But with formative assessments, getting the right answers isn’t important because that isn’t the objective. Instead, the purpose is to provide you with continuous, fast “readings” of student progress which you use to adapt your teaching and advance their learning. Summative assessments are to grade, and formative assessments are to direct .
As you can imagine, this sets entirely different tones for the two types of assessment. Summative tests can be high-stakes with real consequences that shape students’ future opportunities. This makes them understandably anxious, which can significantly affect their performance (Embse et al., 2018). 2 Formative assessments, on the other hand, are low-stakes, light-touch tests that are (ideally) designed to be fun and engaging, and to boost learning outcomes (OECD, 2008). 5 Formative assessments help to improve summative assessment scores/grades (and more importantly, their education), but this doesn’t work the other way around.
To make our position clear: both types of assessment have an important place in education. They just have different purposes and effects on students. If you’d like a more detailed comparison of these two types of assessment, please check out our article here .
How formative assessments help your teaching

“Formative assessment – while not a “silver bullet” that can solve all educational challenges – offers a powerful means for meeting goals for high-performance, high-equity of student outcomes, and for providing students with knowledge and skills for lifelong learning.” 1
– OECD
In essence, formative assessments help you answer three key questions:
- Are students learning what they need to learn?
- Are students learning at a steady pace?
- What should be taught next?
The answers to these questions form an objective appraisal of your current teaching strategies and lesson plans, providing clues on what needs to change. This may include the following and more:
- Change of content – formative assessments reveal student understanding, which includes any learning gaps or misconceptions they may have. With this information, you can adjust the content being taught to ensure they are learning what they need.
- Refine learning intentions – when you have a strong understanding of your students’ knowledge and skills, you’re able to write more precise learning intentions in your lesson plans, and by extension, better plans overall that accurately address students’ needs.
- Group students based on ability – formative assessments are usually given to entire classes, which reveals students’ both individually, and as a whole. If assessment results reveal distinct groupings of students based on their knowledge and skill, and you have the capacity to group them in your class and set unique work, that’s a much more inclusive way to teach and likely to result in better learning outcomes. More broadly, this information also helps you form separate support classes or Gifted and Talented classes.
- Change frequency of assessment – if you’ve previously identified knowledge gaps, you’ll want to re-assess after learning to ensure they’re filled. While formative assessment should be a regular occurrence in your class, the frequency should change depending on the results and other feedback you get from students.
Formative assessments in action – a quick example
“Assessment is the bridge between teaching and learning. It’s only by assessment that you know what has been taught, has been learned.” 3
– Dylan Wiliam, formative assessment expert
To give you an example of formative assessments in action, let’s say you’re a Year 8 Science teacher starting a new term with students, and before proceeding with the content assigned to this term, you want to check their understanding to ensure they’ve mastered the prerequisite content, allowing you to correctly build on their knowledge.
As part of this term, students are extending their knowledge of biological sciences. So you ask them to take five minutes to create individual mind maps of everything they remember about cells – a brain dump of the content they have already been taught last term. Walking around the class, you can see maps that contain organelles, membranes, nuclei, and even little drawings of cell structures. Some students have filled their A4 sheet and others have barely touched it (mental note added). But overall, your students have covered the core concepts they learned last year.
To validate this information, you’d like them to elaborate on their mind maps to ensure they actually understand (rather than just remember) the concepts, so you write a few of the key ideas on the board and ask who would like to explain it. They seem to have a good grasp of membranes and nuclei, but even with plenty of hints, nobody can accurately describe what organelles do, or how the cells of plants and animals differ. You’ve identified two clear topics that need some refreshing, which you can either teach immediately or add to your next lesson plan.
These formative assessments may have taken no longer than 10 minutes. Of course, there needs to be a good balance between assessment and instruction, but that’s the beauty of formative assessments: they are quick and sharp and provide you with objective, real-world data that effectively directs your teaching. By incorporating formative assessments into your day-to-day teaching, you have vital feedback on student learning which you can use to identify and fill their knowledge gaps, build on their knowledge, and set them up for success.
Formative assessments help students become self-learners

Formative assessments have another effect on students that can improve their education and lives immeasurably: they help them become empowered self-learners (Clark, 2012). 3
This happens for two reasons:
They learn self-evaluation techniques
Many formative assessments have processes in which students assess their own work or the work of their peers. Rubrics are a good example. You can give students a marking rubric that allows them to assess their classmates’ abilities at reading aloud, as per below:
“By learning how to evaluate their own work, students develop the crucial meta-cognitive skills they need to progress by themselves.”
By using this rubric as a guide, they can score their classmates on volume, fluency, and clarity, and in the process, they also learn how to assess their own skills and pinpoint areas of weakness.
Informal debates are another example. You can create small groups of students and ask them to debate an issue in which they express their opinions, back them up with evidence, and listen to why their classmates agree or disagree. The conversations help them discover potential misconceptions or logical flaws, again teaching them (through modelling) how to evaluate such things by themselves.
By learning how to evaluate their own work, students develop the crucial meta-cognitive skills they need to progress by themselves. It’s giving them the proverbial fishing rod instead of a fish. They learn how to reflect, critique, review, and mark their own work, giving them a firm grip on their own learning and accelerating them to speeds far beyond what teachers can achieve by themselves. This leads to greater self-efficacy (Panadero et all., 2017) 4 and success.
They’re interactive and social
Formative assessments are highly varied, interactive tasks that students engage with during class. For most students, because the assessments are hands-on activities that require their attention, this makes them more interesting than standard instruction from the teacher. Students often become enthusiastically engaged in their learning, which creates a sense of agency and responsibility for their education. When combined with learning goals, this can be a powerful tool for improving outcomes.
Similarly, formative assessments can be co-operative social activities where students are encouraged to interact with their classmates and teachers. They might be having conversations with each other, validating their knowledge before and after learning, self-assessing using proven techniques, and many other activities (see our full list of assessment examples below) in which they are active and involved. As socially-driven creatures, this can turn your students’ learning from dull chores into genuinely fun experiences where they build friendships along the way.
2. Evidence that formative assessment works

“Teaching which incorporates formative assessment has helped to raise levels of student achievement, and has better enabled teachers to meet the needs of increasingly diverse student populations, helping to close gaps in equity of student outcomes.” 1
Formative assessments have been studied extensively, and show sweeping improvements for learning outcomes (OECD, 2008). 1
A comprehensive report on formative assessment by the Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development (OECD), backed up by numerous studies, found the practice to be one of the most important interventions for promoting high [student] performance ever studied (OECD, 2008). 1 It’s the equivalent of taking students’ scores in an average performing country and lifting them into the top five best performing countries (Beaton et al., 1996, Black and Wiliam, 1998) 5,6 .
The OECD report shows that formative assessments:
- Make education more equitable . They lift the performance of every single student, including those who are underachieving.
- Improve school attendance . Formative assessments tend to be fun and engaging for students, which makes school much more enjoyable and reduces absence rates.
- Help students retain what they’ve learned. Assessments tap into the “testing effect” – a phenomenon in which the act of testing also boosts learning. Trying to recall information from memory is a highly effective way to learn (Brown et al., 2014). 9
- Help students become self-learners . They are more involved and engaged in the learning process itself, discovering the mechanics behind learning and self-evaluation and how they can do it themselves.
- Help to clarify misconceptions. These can be immediately corrected during learning, before they are consolidated into long-term memories during sleep (Klinzing, Niethard and Born, 2019). 11
Aside from the OECD report, there are numerous studies where formative assessment has proven its worth. A 2021 meta-analysis of 32 studies found that formative assessments boosted learning outcomes considerably (Karaman, 2021). 11 For the core foundational skill of Writing, another meta-analysis of formative assessment experiments found feedback to be a crucial part of the process. When teachers and peers gave feedback, and students self-evaluated their own work, writing quality was enhanced (Graham et al., 2015). 7
Another study found formative assessment to have a positive influence on literacy as well as maths and the arts. Helping students to self-assess provided one of the biggest benefits, as did providing written feedback on quizzes (Lee et al., 2020). 8 Feedback has proven to be a crucial part of effective formative assessment, and we cover this in more detail below. For Science, high school biology teachers who completed a professional development program on formative assessment saw their abilities increase for key areas such as interpreting student ideas, eliciting questions and providing feedback (Furtak, et all., 2016). 7
Finally, in a random sample of 22 Swedish Year 4 Mathematics teachers, researchers asked them to participate in a professional development program on formative assessment. After implementing their knowledge in their respective classes, their students significantly outperformed others (Andersson, Palm, 2016). 10
We could go on. There’s so much evidence of the efficacy of formative assessment. It’s amazing to think that such drastic improvements can be made by introducing effective formative assessments into your classrooms (we talk more about effective strategies below).
3. Formative assessment examples / types and how they work
Formative assessments are extremely diverse. They range from generic to subject/content-specific, allowing you to assess knowledge and skills in a variety of ways, and cover the full breadth of K-12. You can pick and choose which formative assessments suit your students based on their age and the covered content.
Their variety and spontaneity can make learning much more fun for students of all ages. These are some of the more common formative assessment examples you’ll find in schools across the world.

Age group: all
Quizzes are one of the most popular types of formative assessment, and for good reason: they’re fun, quick to create and mark, and give you a great indication of students’ general knowledge, learning gaps and possible misconceptions for a topic. They can be given as:
- Diagnostic pre-tests before starting a new unit
- Mid-unit checkups to determine whether learning is going according to plan
- Evaluative tests that check learning before the next unit starts
- Start or end of lesson check-ups to quickly assess learning
Quizzes typically contain multiple-choice questions , which make them nice and quick to mark. But they can take other forms if needed. You can also incorporate directive feedback into each quiz’s results to show students what they might do to improve.
Discussion boards

With discussion boards, students write what they know about a topic on the whiteboard. This could be as a mind map, graffiti wall, or another format, with students writing short words or phrases, full sentences, or even drawing pictures. It’s a brain-dump of sorts that helps you understand students’ depth of knowledge for a topic, and any potential learning gaps or misconceptions you need to address.

Brain dumps are the same as discussion boards but are completed on paper or screens, either individually or in small groups. Students write everything they know about a topic in the format they prefer, which gives you an idea of their knowledge for the topic.
Traffic light system
With the traffic light system, each student is given three coloured cards – one red, one orange and one green – which they need to hold up in response to a statement. Red is disagree, orange is unsure, and green is agree. You might ask them whether 10 times 10 is 200, whether day and night is created by the moon, or whether the word “running” is a verb.
When students hold their cards up, you get a visual gauge of how many students answered correctly. It’s another super-quick, fun formative assessment for younger students.
Questions / surveys

These are the simplest formative test of all: you ask questions to the class and assess their answers on the spot. They’re a staple of teaching around the world because they give you an ultra-fast idea of what your students know about the content already taught, so that you can refresh their memories if needed. You’ll be able to gauge their knowledge from the numbers of hands raised and the quality of answers (keeping in mind the general shyness of that particular class).
Rubrics / self-evaluation
Age group: Years 3 to 10
When students learn how to assess their own work, they’re on the road to becoming self-learners who can develop a fully-fledged love of learning. Rubrics are a formative assessment that helps them on this path. They’re a simple marking criteria that students can apply to their own (or their classmates’) work to judge their performance, and what improvements they might need to make.
As already touched on previously, an example is the reading rubric shown below. Students can listen to their classmates read aloud, give them a score for each skill, and then discuss why they gave them afterwards. The rubric is one of many tools that students can use to self-evaluate and become enthusiastic independent learners.
KWL charts are a formative assessment that prepare your students for what they’re going to learn, get them invested in their own learning, and help them evaluate whether learning was successful.
Three columns are drawn on the board in class, from left to right:
- What I know
- What I want to know
- What I learned
For the content being taught in today’s class, students are invited to write about what they know about it, and what they want to know about it. They complete the “what I learned” third column at the end of class, showing them whether they achieved their desires/objectives. This is another simple, effective way for students to assess their own learning.
You can include an additional section if you wish – how will you learn it (which makes it KWHL). This encourages students to think about how to research and discover the information.
Think-Pair-Share

Age group: Years 1 to 9
With Think-Pair-Share, students write down their responses to a question and then discuss their answers with a partner. You walk around the room and listen to their discussions, to gauge their level of understanding of the topic. Finally, they share their answers with the class, which encourages them to reflect on the accuracy and logic of their own.
See, Think, Wonder
Age group: Years 1 to 5
See, Think, Wonder is a formative assessment that stimulates students’ curiosities and really gets them thinking about an image. They are given a photograph or picture and sheets with three columns that must be filled out:
- See – they describe what they see using descriptive language
- Think – they describe what they think is going on with the image
- Wonder – they write anything they’re wondering about the image
The task shows you the quality of their writing, their interpretation skills, their creativity, the accuracy of their observations, and more. Once done they can discuss their answers with students at their table, which encourages teamwork, or read them to the entire class.
Thumbs up or down

This is another quick and easy assessment that reveals general misconceptions. You offer a statement and ask them to give a thumbs up if they agree, and a thumbs down if they disagree. By judging the accuracy of their answers, you’ll know whether common misconceptions are present and resolve them if so.
For the statements, it can be a good idea to use any that your prior students have struggled with in the past.
Hot seat questioning
Hot seat questioning is an assessment that makes questions a little more fun. Anonymous questions are placed on a selection of seats, typically in front of class, and students are invited to select a seat, read the question aloud, and then try to answer. The rest of the class are encouraged to discuss the students’ answer and provide their own if appropriate.
The questions can vary in difficulty depending on the subject and year level. It can be an engaging, fun way to assess student learning and stimulate discussion.
Entry & exit slips

Age group: Years 1 to 6
Entry and exit slips are a simple form of pre- and post-tests, helping you understand whether content was successfully learned. Students fill out an entry slip with a question like “How does heat transfer?” and then an exit slip with the same question. This helps them to compare their knowledge before and after the lesson, which can be extremely satisfying and motivating. You can also check their answers for accuracy once the lesson is over and discover learning gaps or misconceptions that need to be addressed.
One-minute papers
At the end of the lesson, students are given a minute to answer a question that summarises what has been learned. For example: how does hardware and software allow people to interact with computers?
After quickly reviewing their papers, you’ll have a sense of how well they’ve remembered and understood the content, and whether you need to go over it again in the next lesson.
The limited time given to complete this task can make it stressful for some students, which impairs its accuracy. You can relax every student by telling them they have a minute, but that they can also take some extra time if they need.
Muddiest point

With the muddiest point assessment, students are asked to write down what they were most confused about after a lecture or other activity. You can select random students to discuss their answers with the class, have them talk about their answers between themselves, or review their answers once the class is over. If you notice common confusions/misunderstandings, you’ll want to address them in a future lesson.
Informal debates
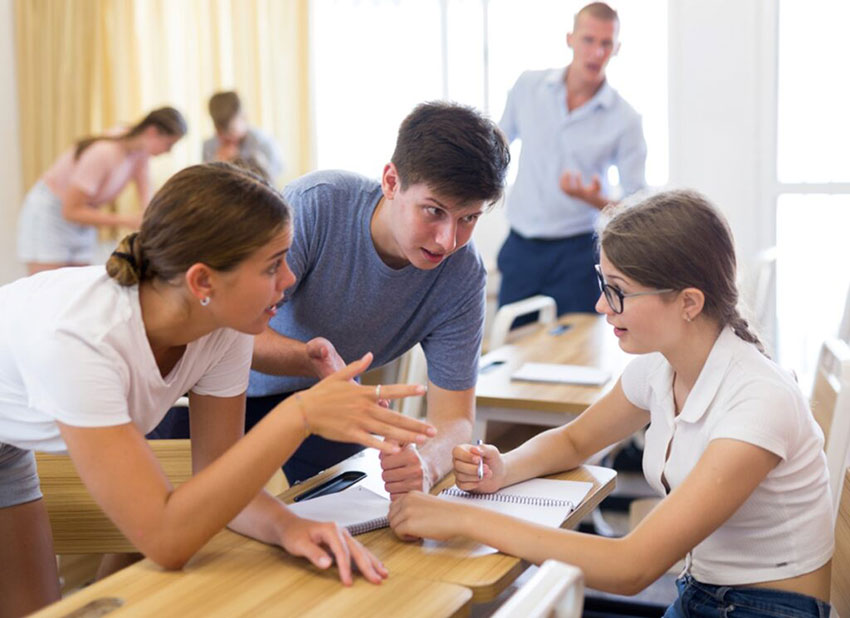

Age group: Years 5 to 12
Informal debates between groups of two or more students can be a great way to gauge their understanding of a topic. You can assign each group member a position in the debate, ask them to present evidence of their viewpoints to each other, and have them respond in turn. It works best for more “subjective” subjects that can lack concrete explanations or viewpoints, like literature, the arts, or social sciences.
This assessment tool really taps into students higher-order thinking skills, with each side bringing their arguments, supportive reasoning and passion to the conversation.
Anticipation guides
Age group: Years 3 to 9
Anticipation guides are a tool that help you discover misconceptions for students. You present them with a statement like “Products have minimal impact on the earth’s environment,” and ask them write down whether they agree with the statement before the lesson begins. Once the lesson is over, you ask them to respond to the same question.
Their answers will tell you whether they have absorbed your instruction, and can also vividly demonstrate the value of teaching to them – “in the past hour I’ve learned something new and important!”

Kids love moving their bodies, and you can use this to your advantage by asking them to “act out” certain processes in class. For example, if you want to know whether they’ve understood how gas, liquids, and solids behave differently, you can clear a space and ask them to (safely) demonstrate how they might move if they were transformed into one of these states. Or you can ask them to form expressions for how a character might feel in a story.
This exercise is not only great fun (especially for younger children), it also communicates their understanding to you.
4. Formative assessment strategies for your school and classroom
Now that we’ve covered the what and why of formative assessment, it’s time to talk about some actual strategies that you can use to implement them at your school and execute them to a high standard.
Set up a formative assessment framework
“A framework will make your formative assessments structured, purposeful, frequent, and at less risk of being dropped in favour of ‘teaching to the tests’.”
Some teachers are pressured to achieve good grades on high-visibility summative assessments, and this can come at the cost of fewer formative assessments that actually improve student outcomes (OECD, 2008). 1
So it’s crucial to create a formative assessment framework that prioritises the tests, especially if they are regularly dropped in favour of summative testing. A framework will make your formative assessments structured, purposeful, frequent, and at less risk of being dropped in favour of “teaching to the tests,” especially if they are endorsed by the school leaders.
Thankfully, the OECD has completed extensive research on formative assessments , with real case studies on teachers who have successfully made them a part of their teaching and achieved strong learning outcomes for their students. These are some of their suggestions that can form the basis of your framework, adapted and summarised:
Establish a classroom culture that encourages interaction through formative assessments

Interaction is a big part of formative assessment. Students may find themselves thrusting their thumbs in the air, holding up coloured paper, drawing mind maps, having debates and more. These hands-on, collaborative types of assessment are not only more engaging for students, but it’s showing them that learning can (and should) be fun – even for the teenagers!
Make formative assessments an integral part of your classroom culture. Factor them into your lesson plans and get every student involved. Demonstrate that the tasks themselves are important because they teach them to become more self-aware, more empathetic and cooperative with their classmates, more able to make decisions, and better equipped to assess their own work. Show them, over and over, that formative assessments are not necessarily about getting a top score or beating their classmates. They’re about carving out a path for your teaching while giving them the tools they need to become fully-fledged, self-learners. Get parents involved too and try to convince them of the value of formative assessment – it should be an easy sale!
There is no such thing as “failure” with formative assessments, and with every new one completed, students will start to realise this and become more confident and happier to take risks.
Create challenging learning goals for students and track their progress, together
Goal-setting is a long proven technique for achieving better outcomes, both inside and outside the classroom. Setting challenging goals has shown to improve task performance, boost work output, and regulate choices in favour of completing the goal (Locke et al., 1968). 12
In the context of formative assessments, goals should relate to mastery, not marks. Your students may create learning goals to improve their reading comprehension, to master their multiplication tables, or to run simple science experiments with clear predictions, conclusions and evaluations. With clear goals that have explicit, easy-to-understand success criteria, lessons can become more meaningful and students may find themselves more engaged in their learning – there’s a purpose and objective to what they’re doing. Rather than achieving an A+, it’s about becoming a more capable person. This can lead to greater intrinsic motivation, improved self-esteem, and a number of other benefits (OECD, 2008). 1
Work with your students to set learning goals that are personally meaningful to them. Have them print them off and stick them to their workbooks. For related lessons where learning goals are shared among students, ask them to quickly read their goals at the start of the lesson, and then when the lesson is over, get them to spend 30 seconds reflecting on their progress. Did they move a little closer? What might they do better next time? This is self-learning in action, and gives them the confidence and autonomy to become lifelong learners.
Use varied formative assessment methods to meet diverse student needs
Your students are all fantastically unique. Some thrive when asked to complete quizzes. Others enjoy reflecting on what they’ve learned. Some love going up to the board and writing or drawing what they know about something.

To cater to the various needs and preferences of your students, it pays to incorporate a variety of formative assessment methods into your day-to-day teaching. This not only makes things more fun for your students, it provides you with a broader, more accurate assessment of their skills and knowledge.
Involve students in the learning process
As previously discussed, one of the most incredible things about formative assessments is that they encourage students to become actively involved in their own education, teaching them self-learning strategies they can use to grow all by themselves. These “metacognitive” strategies are a fundamental soft skill that can make a big difference to their success at school and beyond.
Try to incorporate a good portion of formative assessments that teach students the value of learning and show them how to assess their own work. These include rubrics, KWL charts, entry/exit tickets and more.
Give feedback rather than marks
Marks are important to summative tests like exams, but when it comes to formative assessments, feedback is the name of the game. It’s essential for helping students self-learn. A mark is a solitary number that tells them almost nothing; high-quality feedback is rich, specific information that tells them where to go next. It can help students to feel more motivated, better equipped, and more confident, which can almost double their growth over the course of a year (Hattie and Temperley, 2007) 13 .
When offering feedback for formative assessments, try to ensure that it is:
- Timely – imagine if a driving instructor only provided suggestions after you’d got out of the car? They’d be nowhere near as effective. Our short-term memories are exactly that – short – and we are much more capable of actioning feedback if it’s delivered immediately when the tasks are still fresh in our minds. Work with your students’ short-term memories, not against them.
- Specific and constructive – what specifically did the student fail at, and how can they remedy the problem themselves? That’s what your feedback should focus on. Students need to know what they did wrong and what actionable steps they can take to fix it: key ingredients for self-learning. It may be that they can’t do this by themselves because they don’t know the content well enough, in which case it needs to be re-taught.
- Motivational – starting feedback by acknowledging students’ correct answers can make them more receptive to fixing their mistakes / filling their learning gaps. By telling them they’ve done well for certain questions, it can motivate them to do well for every A pat on the back can do wonders! You can also highlight what they’ve improved on since their last assessment, helping them to see that they’re progressing towards their learning goals.
- Where am I going?
- How am I going?
- Where to next?
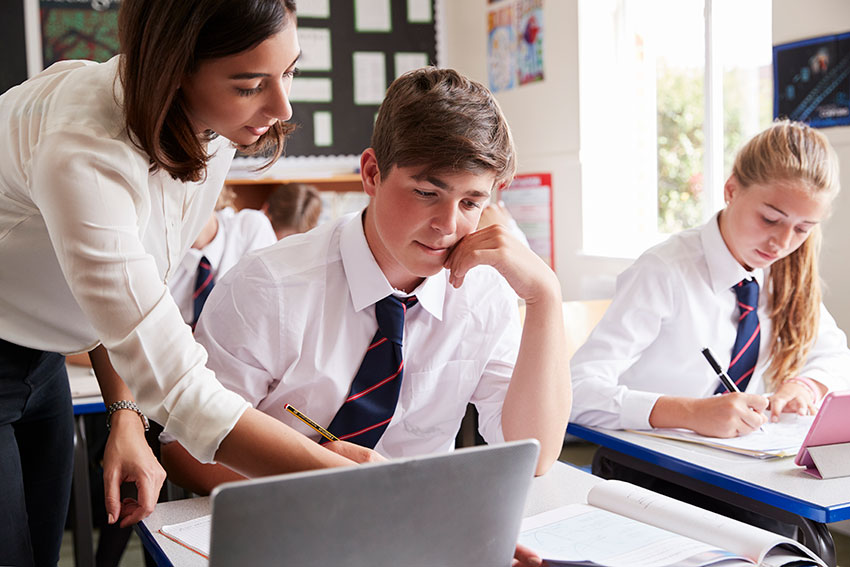

When providing formative assessment feedback to students, it can be based on four different things:
- The activity – how well the task was understood or performed.
- The learning process – what the student needs to do to complete the task.
- Managing their learning – how the student might need to plan or self-monitor.
- Qualities – personal qualities that the student shows, like an aptitude for arithmetic.
And finally, if providing praise as part of your feedback, it goes without saying that you should never focus on their intelligence or natural abilities. It creates a fixed mindset that can really hinder their learning. 14 Instead, try to praise their effort.
Teach students how to assess their own work
Self-assessment is a key part of self-learning – a process that can work like high-powered fertiliser for students’ growth. When students are taught how to self-assess, they better understand how their answers are related to their learning goals, they’re invited to reflect on their efforts, and most importantly, they can identify what they need to do to produce better quality work.
As their teacher, you use pre-defined success criteria to assess the accuracy of their work, and they can use the very same criteria to assess themselves and their peers. As you complete the different types of formative assessment, demonstrate how you use the templates, checklists, or rubrics to mark their work, and how it shapes the judgment of what is considered high-quality. Give them samples of exemplary work and explain why it’s so good. Show them, again and again, how you use the criteria to discover potential gaps in their learning and the actions that might be taken to fill them. By modelling your own assessment and feedback processes, you help them become their own teachers.
When they get better at this important skill, students can spend time marking, discussing, critiquing and demystifying their assessment results, blossoming into self-directed learners who can take ownership of their education. You’re showing them that self-assessment is a vital part of the learning process and providing them with the tools they need to achieve great things.
The NSW Government provide some more extensive examples of how to teach students self-assessment techniques , which we highly recommend reading.
Vary formative assessments to meet students’ diverse needs
Student diversity is one of the biggest challenges to providing great education, and this extends to formative assessment. With so many different learning styles, preferences, levels of progress and subject matter, you’ll need to select a variety of assessment types to suit their needs. A quiz might make sense for one subject and group of students, an informal debate for another, KWL charts for younger children, etc. It all comes down to what you think might work best for the group and the content, which takes time and patience to figure out.
Practice and experimentation is key. In time, you’ll be a formative assessment master.
Always test for misconceptions before starting a new unit
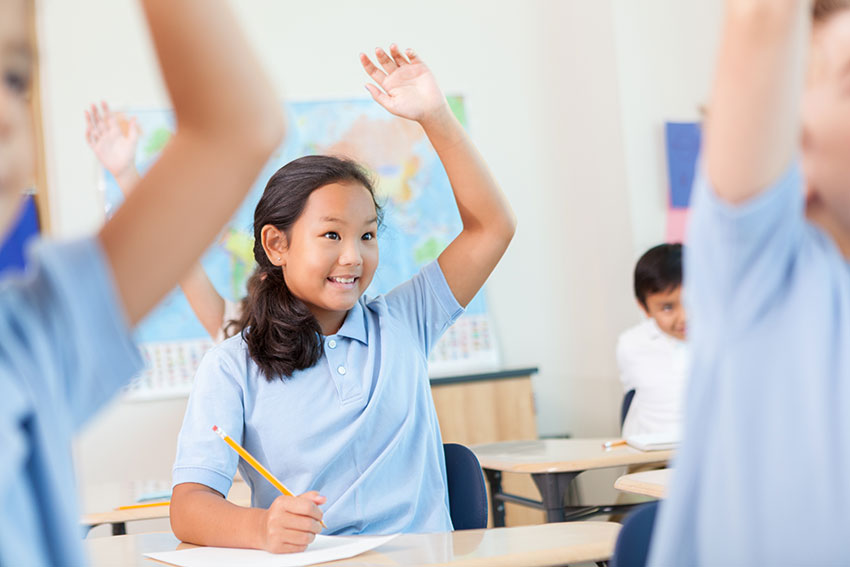

Education is a series of building blocks, and if one of those blocks is the wrong size, it compromises the entire structure. Knowledge cannot be built upon if incorrect. If students have misunderstood how basic fractions work, they’re not going to be able to understand equivalent fractions later on.
Thankfully, formative assessments are ideal for diagnosing these kinds of misconceptions . Pretty much any formative assessment can be diagnostic. Whether you’re using surveys, hot seat questioning, or another type of assessment, you’ll quickly discover common misconceptions and remedy them before they can hamper students’ learning later on. And the best time to do this is before starting a new unit, when they’re about to learn fresh content. It’s the perfect time to repair those misshapen blocks of knowledge from the previous unit so you can confidently keep building.
Make students feel safe
Formative assessment can be engaging and highly interactive, so students need to participate for it to work. But this won’t happen unless they feel safe.
Creating a safe learning environment is a big topic, but here are some effective tips you can use to make students feel secure in your classroom, and coax each of them out of their shells:
- Lay down ground rules – make it absolutely clear that there will be no laughing, teasing, or name calling in class, and that transgressions will be punished. These kinds of hurtful interactions can be burned into students’ memories and really hold them back. Make your class a judgment-free zone and enforce a strict zero-bullying policy.
- Be trustworthy – consistently treat your students with kindness, respect and a “fair but firm” attitude, and you’ll quickly win their trust. They’ll feel much safer to participate when they know the authority in the room has their back. This is especially important for the students who are particularly withdrawn or emotional, and may have a turbulent life at home. Your classroom could become their precious safe place.
- Explain the importance of mistakes – every mistake is an opportunity for the student to recognise the error, figure out where they went wrong, and do it right next time. There’s no growth without mistakes – they’re a sign that your students are pushing themselves!
- Incorporate brief social-emotional activities – brief activities like daily greetings, checking in with emotions and gratitude lists can help your students express their emotions to their peers, build stronger empathy skills, and feel emotionally safe in your class.
- Post their work around the class – most of us love to be celebrated for our achievements, and you can do this for your students by posting their great work on the classroom’s walls. It’s a visual reminder that they are skilled and capable.
- Explain why you’re giving an assessment – for formative assessments that can feel high-stakes, like quizzes or one-minute papers, briefly explain why it’s important, and remind them that there are no consequences for wrong answers.
- OECD/CERI, Assessment for Learning Formative Assessment , OECD
- Nathaniel von der Embse, Dane Jester, Devlina Roy, James Post, 2018, Test anxiety effects, predictors, and correlates: A 30-year meta-analytic review , Journal of Affective Disorders
- Ian Clark, 2012, Formative Assessment: Assessment Is for Self-regulated Learning , Educational Psychology Review
- Ernesto Panadero, Anders Jonsson, Juan Botella, 2017, Effects of self-assessment on self-regulated learning and self-efficacy: Four meta-analyses , Educational Research Review
- Beaton, A.E. et al. (1996), Mathematics Achievement in the Middle School Years, Boston College, Boston, MA.
- Black P. and D. Wiliam (1998), Assessment and Classroom Learning, Assessment in Education: Principles, Policy and Practice
- Steve Graham, Michael Hebert, and Karen R. Harris, Formative Assessment and Writing , The Elementary School Journal
- Hansol Lee, Huy Q.Chung, Yu Zhang, Jamal Abedi, Mark Warschauer, 2020, The Effectiveness and Features of Formative Assessment in US K-12 Education: A Systematic Review , Applied Measurement in Education
- Brown et al. (2014), Make It Stick, Belknap Press
- Catarina Andersson, Torulf Palm, 2017, The impact of formative assessment on student achievement: A study of the effects of changes to classroom practice after a comprehensive professional development programme , Learning and Instruction , 49
- Jens G. Klinzing, Niels Niethard, Jan Born, 2019, Mechanisms of systems memory consolidation during sleep , Nature Neuroscience
- Edwin A. Locke, 1968, Toward a theory of task motivation and incentives , Organisational Behaviour and Human Performance
- Hattie, J & Timperley, H, 2007, The Power of Feedback , Review of educational Research Vol. 77
- Carol Dweck, 2006, Mindset: The New Psychology of Success, Random House

Nardin is a former primary school teacher of 10 years. During her time as a teacher, she served as Head of Years for K-2, was a trained NAPLAN marker, and was part of the team that wrote the 2021 NSW English Syllabus 3-6. She is currently an assessment consultant for ICAS and Reach.
Tag: formative assessments
Previous post
How ICAS boosts this student's love of learning
You may also like.

How ICAS boosts this student’s love of learning

Standardised assessments: the ultimate guide for teachers

How to use Reach results to boost your school’s performance
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
FREE Poetry Worksheet Bundle! Perfect for National Poetry Month.
25 Formative Assessment Options Your Students Will Actually Enjoy
Get them excited to show you what they know!

Formative assessment is the piece of the teaching puzzle that allows us to quickly (and hopefully, accurately) gauge how well our students are understanding the material we’ve taught. From there, we make the important decisions about where our lesson will go next. Do we need to reteach, or are our students ready to progress? Do some students need additional practice? And which students need to be pushed to achieve the next level?
The best formative assessments will not only answer these questions but will also engage students in their own learning. With that in mind, here are 25 formative assessment techniques that will have your students looking forward to showing you what they know.
1. Doodle Notes

Have students doodle/draw a pic of their understanding instead of writing it. Studies have shown it has numerous beneficial effects on student learning.
2. Same Idea, New Situation
Ask your students to apply the concepts they’ve learned to a completely different situation. For example, students could apply the steps of the scientific method to figuring out how to beat an opposing soccer team. They observe data (the other team’s plays), form theories (they always rely on two main players), test theories while collecting more data (block those players and see what happens), and draw conclusions (see if that worked).
[contextly_auto_sidebar]
3. Tripwire

Tripwires are things that catch people off guard and mess them up. Ask your students to list what they believe are the three misunderstandings about the topic that are most likely to mess up a peer. By asking students to think about the key understandings from this angle, we can get an excellent view of how well they comprehend the topic.
4. Two Truths and a Lie
No longer just a get-to-know-you game or icebreaker, this well-known activity also makes a great formative assessment. Ask students to list two things that are true or accurate about the learning and one idea that sounds like it might be accurate, but isn’t. You’ll be able to assess each student’s understanding when they turn in their responses, and going over them with your class the following day makes an excellent review activity.
5. Popsicle Sticks

Formative assessment doesn’t need to be complicated or time-consuming to be meaningful and engaging. Have each student put their name on a popsicle stick in a jar or box on your desk. Let them know you’ll be pulling popsicle sticks to see who will be answering questions about the lesson. Knowing their name could be pulled makes students who might let peers do the talking focus on the learning. It dispels notions of favoritism and identifies learning gaps. And, most importantly, provides real-time feedback teachers can use in their lesson planning.
6. Explain it to a Famous Person
Ask the student to explain the day’s lesson to someone famous in an analogy that would make sense to that person. For example, the Revolutionary War was fought between the colonies and Great Britain. The colonies wanted to be independent and, after winning the war, renamed themselves the United States of America, just like when Prince left his record label and had to change his name to an unpronounceable symbol in order to break contractual obligations (I’m dating myself with this example, aren’t I?).
7. Traffic Light

Printing on post-it notes is actually pretty simple and fun! Slap a clip-art picture of a traffic light on there and you have a perfect formative assessment tool that students can complete when time is short at the end of class.
8. 30-Second Share
Challenge students to explain what the lesson they learned was all about to a peer, a small group, or the entire class in 30 seconds. At first, you might want to start at 15-seconds and build their stamina. But by encouraging students to explain everything they can for a set and relatively short amount of time, you’ll be building their confidence and public speaking skills at the same time as you get a good grasp on how much they’ve remembered about the lesson.
9. Venn Diagrams

An oldie but a goodie. Have your student compare the topic you just introduced to a tangential topic you taught in the past. This way, you’re getting a formative assessment on how well they understand the new topic and they’re getting a review of an older topic as well!
10. Poll Them
Polls are a great way to quickly assess student understanding. You can do this in person, or you can use apps like Poll Everywhere , Socrative , or Mentimeter to make free polls students can answer using their phones or computers.
11. S.O.S. Summaries
A great, quick formative assessment idea that can be used at any point throughout a lesson is the S.O.S. summary. The teacher presents the students with a statement (S). Then, asks the students to give their opinion (O) about the statement. Finally, the students are asked to support (S) their opinion with evidence from the lesson. For example, a teacher might say to the students, “Complete an S.O.S. on this statement: The Industrial Revolution produced only positive effects on society.”
S.O.S. can be used at the start of a lesson to assess prior knowledge or at the end of a unit or lesson to determine if students’ opinions have changed or if their support has grown stronger with the new information they’ve learned.
12. FOUR-Corners
This activity can be used with questions or opinions. Before asking the question/making the statement, establish each corner of the room as a different potential opinion or answer. After giving the prompt, each student goes to the corner that best represents their answer. Based on classroom discussion, students can then move from corner to corner, adjusting their answer or opinion.
13. Jigsaw Learning

Perfect when teaching complicated subjects or topics with many different parts. In this formative assessment, teachers break a large body of information into smaller sections. Each section is then assigned to a different small group. That small group is in charge of learning about their section and becoming the class experts. Then, one by one, each section teaches the others about their part of the whole. As the teacher listens to each section being taught, they can use the lesson as a method of formative assessment.
14. Anonymous Pop-Quiz
All the formative assessment power of a pop-quiz with none of the unnecessary pressure or embarrassment. To use this tool, simply quiz your students on the essential information you want to ensure they understand. Instruct each student NOT to put their name on their paper.
Once the assessment is complete, redistribute the quizzes in a way that ensures no one knows whose quiz they have in front of them. Have the students correct the quizzes and share out which answers most students got wrong and which answers everyone seemed to understand the most. You’ll know right away how well the class as a whole understands the topic without embarrassing any students individually.
15. One-Minute Write-Up

At the end of a lesson, give students one minute to write as much as they can about what they learned through the lesson or unit. If needed, provide some guiding questions to get them started.
- What was the most important learning from today, and why?
- Did anything surprise you? If so, what?
- What was the most confusing part of the lesson, and why?
- What is something that will likely appear on a test or quiz, and why?
Challenge them to write as much as they can and to write for all of the 60-seconds. To make it a bit more engaging, consider letting students do this with a partner.
16. EdPuzzle
Students love to watch videos and, because of this, we end up showing a lot of short video clips. While they’re engaging, it’s often tough to determine if our students are getting the information we hoped they would get out of watching them. EdPuzzle solves this problem. The free app allows you to link to a video and add questions that stop the video at times you determine. So you can show your students the video of the Dust Bowl, but stop at various points to ask them what they think life might have been like during this time. You can ask them to make comparisons between what they watch and the characters they’re reading about in class. All of this information is then available for you to view and use for formative assessment.
17. Historical Post Cards

Ask students to take on the role of one historical figure you’ve been learning about in class. Have them write a postcard/email/tweet (as long as it’s short) to another historical figure discussing and describing a political event.
18. 3x Summaries
Have students write a 75-100 word summary of a lesson independently. Then, in pairs, have them rewrite it using only 35-50 words. Finally, have them work with a small group to rewrite it one last time. This time, they may use only 10-15 words. Discuss what different groups decided was the most essential information and why they chose to omit certain information. The conversation about what they left out is just as useful as seeing what they left in.
19. Roses and Thorns

Ask students to write or share out two things they really liked/understood about a topic (the roses) and something they didn’t like/didn’t understand (the thorn).
20. Thumbs Up, Down, or in the Middle
Sometimes things stick around because they just work. Asking students to give you a thumbs up if they understand, thumbs down if they don’t, or thumbs somewhere in the middle if they are so-so about it, is probably one of the fastest formative assessments around. It’s also very easy to keep track of if you’re the teacher standing in the front of the room. Just make sure that you follow up with the thumbs down or thumbs in the middle folks to help them with any confusion.
21. Word Clouds

Ask your students to provide you with the three most essential words or ideas from a lesson and plug them into a word cloud generator . You’ll quickly have an excellent formative assessment that shows you what they thought was most worthy of remembering. If it doesn’t line up with what you think was most important, you know what you need to reteach.
22. Curation
Ask students to gather a bunch of examples that correctly demonstrate the concept you taught. So if you’re studying rhetorical strategies, have students send you screenshots of ads that demonstrate them. Not only will you be able to tell immediately who understood the lesson and who didn’t, but you’ll also have a bunch of great examples and non-examples ready to go for those students who need additional practice.
23. Dry Erase Boards

Another time-tested method of formative assessment that teachers often overlook is individual dry erase boards. They really are an awesome and fast way to see where each student’s level of understanding is at any given point.
24. Think-Pair-Shares
Like so many teacher tools, this one can get stale if overused. But, if used as a method to encourage all students to find their voice and share their learning, it’s perfect for formative assessment. To ensure its effectiveness, ask a question of the class. Have every student write down their own answer. Pair students up with a classmate and give them time to share and discuss their answers. After pairs have had a chance to discuss, have them share out with a larger group or the class as a whole. Circulate, listening to groups who have students you know might be more likely to struggle with the current topic. Collect the papers for extra accountability.
25. Self-Directed

This one can intimidate some students at first, but it can be incredibly powerful to let students themselves choose how they want to demonstrate learning. You can support students by giving them managed choice, but let them decide if they want to show you they understood the essential parts of your lesson by drawing a picture, writing a paragraph, creating a pop quiz, or even writing song lyrics. This shows you’re putting them in charge of their own learning.
What’s your go-to method of formative assessment? Tell us in the comments.
Get more teaching tips and ideas when you sign up for our free newsletters .
You Might Also Like

What Is Formative Assessment and How Should Teachers Use It?
Check student progress as they learn, and adapt to their needs. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2023. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256
Join the Active History Community!
Active History Teacher
Interactive, Hands-on lessons and test prep ideas for US History Classrooms
Top Ten Formative Assessments for Social Studies
July 9, 2021

Formative assessments are so important in social studies! If you teach in a state with a standardized test, then you know formative assessments are the KEY to success! In my US History classroom, I am constantly evaluating what works best in terms of the age-old question, “Did they get it?” Formative assessments are critical and the more I embed fun ways to do it, the more I know my students will be successful.
My favorite ways to check for understanding vary on the time of the year and how long I have in class any particular day.
As we get closer to our test in May each year, I build in more and more quick activities to formally assess students. These activities give me the informal data I need to drive my review moving forward.
These are my Top 10 favorite formative assessments:
- Hands-on sorting activities. Honestly, my students LOVE it when I break out with the baggies. They know we are about to do something hands-on. I love watching students make connections as they sort primary sources , vocabulary and key people in US History. They are discussing, reviewing and are engaged in the content. I can immediately tell when students are struggling and need a mini review!

I always add baggies (all sizes) and card stock to my "wish list" at the beginning of the school year.

2. Play Give a Clue! This game is a favorite of my students. Students pair up with one partner facing my screen. The other student has their back to the screen. The one facing the screen gives clues to their partner to try and have them guess the terms.
Why do I love it so much?
Students review a ton of information in a short amount of time. If I listen carefully, I can tell what terms students are struggling with. We will do a quick review before we move on. Check out the version for early American History and Modern American History.
3. Graffiti Tagging – This is one of those “have in your back pocket” strategies that works every time! Pass out the dry erase markers and call out an era. Students do a brain dump of anything they can remember about the era on their desk.
I’ll have students call out a term they have written down, if a student has that term, they circle it on their desk. We go around the room until we have exhausted the terms. I “fill in” with any terms/people/etc. they may have missed.
If time permits, they write a summary of the era using as many of the terms as they can.
4. Play a quick game of Bingo. I prepare “snack sized” baggies of squares of paper at the beginning of the school year that I can pull out quickly. If you print and laminate your Bingo cards, you can use them year after year!
5. White board races – This one is super simple! I divide my students into 3 groups and hand the 1st student in each group a dry erase marker. Students answer questions on the white board as fast as they can. Then they pass the marker to the next person on their team. The team with the most wins gets Jolly Ranchers.
I get the 10 pound bag of Jolly Ranchers in bulk off Amazon.
6. Door Slaps! – Check out this fun formative assessment from Dawn from Social Studies Success.
7. Play the “good the bad and the ugly” of an era. This is an easy activity! I call out a topic or an era. In small groups, students discuss the era. They come up with the “good, the bad and the ugly” of the era. We vote as a class on the best answers.
8. Q & A with individual white boards – I have a class set of white boards I got off Amazon. I hand each student a white board and a dry erase marker. I always give students 1 or 2 minutes to “draw whatever makes them happy” – so they can get the doodles out of their system. Then I simply ask questions and have them answer on the white board.
9. Pictionary with whiteboards – I’ve done this as a whole class activity and with individual white boards. I write key concepts on notecards. I pass out the note cards (and ask them not to show others) and have students draw an image of the concept for other students to guess.
10. Blooket, Quizlet Live and Quizlet Live are always in my back pocket. Students love to play and the data you get at the end is great! Perfect to drive your next steps of instruction!
Formative assessments don’t have to be quick writes, exit tickets or boring! Think outside the box and get students discussing, moving and interactive!
What are your favorite formative assessments?
Latest on Instagram

Latest on Pinterest
Latest on facebook.
14 Examples of Formative Assessment [+FAQs]

Traditional student assessment typically comes in the form of a test, pop quiz, or more thorough final exam. But as many teachers will tell you, these rarely tell the whole story or accurately determine just how well a student has learned a concept or lesson.
That’s why many teachers are utilizing formative assessments. While formative assessment is not necessarily a new tool, it is becoming increasingly popular amongst K-12 educators across all subject levels.
Curious? Read on to learn more about types of formative assessment and where you can access additional resources to help you incorporate this new evaluation style into your classroom.
What is Formative Assessment?
Online education glossary EdGlossary defines formative assessment as “a wide variety of methods that teachers use to conduct in-process evaluations of student comprehension, learning needs, and academic progress during a lesson, unit, or course.” They continue, “formative assessments help teachers identify concepts that students are struggling to understand, skills they are having difficulty acquiring, or learning standards they have not yet achieved so that adjustments can be made to lessons, instructional techniques, and academic support.”
The primary reason educators utilize formative assessment, and its primary goal, is to measure a student’s understanding while instruction is happening. Formative assessments allow teachers to collect lots of information about a student’s comprehension while they’re learning, which in turn allows them to make adjustments and improvements in the moment. And, the results speak for themselves — formative assessment has been proven to be highly effective in raising the level of student attainment, increasing equity of student outcomes, and improving students’ ability to learn, according to a study from the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
On the flipside of the assessment coin is summative assessments, which are what we typically use to evaluate student learning. Summative assessments are used after a specific instructional period, such as at the end of a unit, course, semester, or even school year. As learning and formative assessment expert Paul Black puts it, “when the cook tastes the soup, that’s formative assessment. When a customer tastes the soup, that’s summative assessment.”
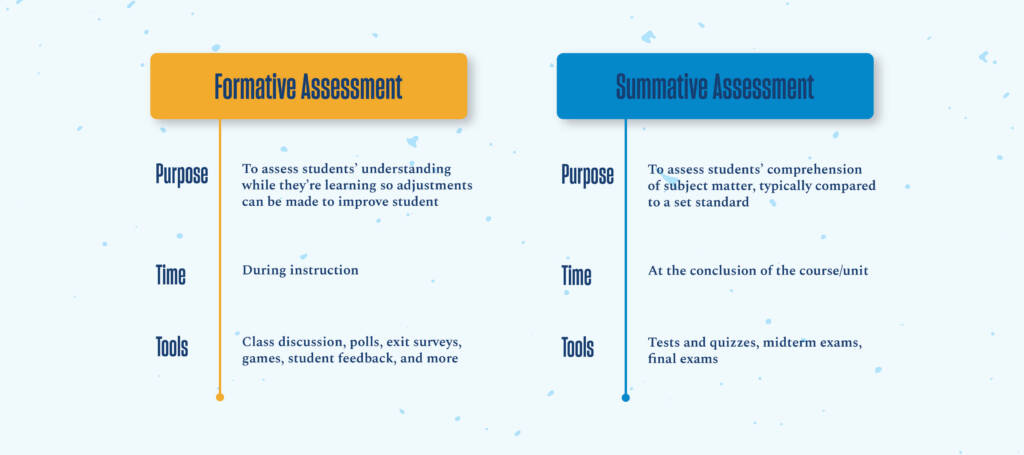
14 Examples of Formative Assessment Tools & Strategies
There are many types of formative assessment tools and strategies available to teachers, and it’s even possible to come up with your own. However, here are some of the most popular and useful formative assessments being used today.
- Round Robin Charts
Students break out into small groups and are given a blank chart and writing utensils. In these groups, everyone answers an open-ended question about the current lesson. Beyond the question, students can also add any relevant knowledge they have about the topic to their chart. These charts then rotate from group to group, with each group adding their input. Once everyone has written on every chart, the class regroups and discusses the responses.
- Strategic Questioning
This formative assessment style is quite flexible and can be used in many different settings. You can ask individuals, groups, or the whole class high-level, open-ended questions that start with “why” or “how.” These questions have a two-fold purpose — to gauge how well students are grasping the lesson at hand and to spark a discussion about the topic.
- Three-Way Summaries
These written summaries of a lesson or subject ask students to complete three separate write-ups of varying lengths: short (10-15 words), medium (30-50 words), and long (75-100). These different lengths test students’ ability to condense everything they’ve learned into a concise statement, or elaborate with more detail. This will demonstrate to you, the teacher, just how much they have learned, and it will also identify any learning gaps.
- Think-Pair-Share
Think-pair-share asks students to write down their answers to a question posed by the teacher. When they’re done, they break off into pairs and share their answers and discuss. You can then move around the room, dropping in on discussions and getting an idea of how well students are understanding.
- 3-2-1 Countdown
This formative assessment tool can be written or oral and asks students to respond to three very simple prompts: Name three things you didn’t know before, name two things that surprised you about this topic, and name one you want to start doing with what you’ve learned. The exact questions are flexible and can be tailored to whatever unit or lesson you are teaching.
- Classroom Polls
This is a great participation tool to use mid-lesson. At any point, pose a poll question to students and ask them to respond by raising their hand. If you have the capability, you can also use online polling platforms and let students submit their answers on their Chromebooks, tablets, or other devices.
- Exit/Admission Tickets
Exit and admission tickets are quick written exercises that assess a student’s comprehension of a single day’s lesson. As the name suggests, exit tickets are short written summaries of what students learned in class that day, while admission tickets can be performed as short homework assignments that are handed in as students arrive to class.
- One-Minute Papers
This quick, formative assessment tool is most useful at the end of the day to get a complete picture of the classes’ learning that day. Put one minute on the clock and pose a question to students about the primary subject for the day. Typical questions might be:
- What was the main point?
- What questions do you still have?
- What was the most surprising thing you learned?
- What was the most confusing aspect and why?
- Creative Extension Projects
These types of assessments are likely already part of your evaluation strategy and include projects like posters and collage, skit performances, dioramas, keynote presentations, and more. Formative assessments like these allow students to use more creative parts of their skillset to demonstrate their understanding and comprehension and can be an opportunity for individual or group work.
Dipsticks — named after the quick and easy tool we use to check our car’s oil levels — refer to a number of fast, formative assessment tools. These are most effective immediately after giving students feedback and allowing them to practice said skills. Many of the assessments on this list fall into the dipstick categories, but additional options include writing a letter explaining the concepts covered or drawing a sketch to visually represent the topic.
- Quiz-Like Games and Polls
A majority of students enjoy games of some kind, and incorporating games that test a student’s recall and subject aptitude are a great way to make formative assessment more fun. These could be Jeopardy-like games that you can tailor around a specific topic, or even an online platform that leverages your own lessons. But no matter what game you choose, these are often a big hit with students.
- Interview-Based Assessments
Interview-based assessments are a great way to get first-hand insight into student comprehension of a subject. You can break out into one-on-one sessions with students, or allow them to conduct interviews in small groups. These should be quick, casual conversations that go over the biggest takeaways from your lesson. If you want to provide structure to student conversations, let them try the TAG feedback method — tell your peer something they did well, ask a thoughtful question, and give a positive suggestion.
- Self Assessment
Allow students to take the rubric you use to perform a self assessment of their knowledge or understanding of a topic. Not only will it allow them to reflect on their own work, but it will also very clearly demonstrate the gaps they need filled in. Self assessments should also allow students to highlight where they feel their strengths are so the feedback isn’t entirely negative.
- Participation Cards
Participation cards are a great tool you can use on-the-fly in the middle of a lesson to get a quick read on the entire classes’ level of understanding. Give each student three participation cards — “I agree,” “I disagree,” and “I don’t know how to respond” — and pose questions that they can then respond to with those cards. This will give you a quick gauge of what concepts need more coverage.
5 REASONS WHY CONTINUING EDUCATION MATTERS FOR EDUCATORS
The education industry is always changing and evolving, perhaps now more than ever. Learn how you can be prepared by downloading our eBook.

List of Formative Assessment Resources
There are many, many online formative assessment resources available to teachers. Here are just a few of the most widely-used and highly recommended formative assessment sites available.
- Arizona State Dept of Education
FAQs About Formative Assessment
The following frequently asked questions were sourced from the Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development (ASCD), a leading education professional organization of more than 100,000 superintendents, principals, teachers, and advocates.
Is formative assessment something new?
No and yes. The concept of measuring a student’s comprehension during lessons has existed for centuries. However, the concept of formative assessment as we understand it didn’t appear until approximately 40 years ago, and has progressively expanded into what it is today.
What makes something a formative assessment?
ASCD characterized formative assessment as “a way for teachers and students to gather evidence of learning, engage students in assessment, and use data to improve teaching and learning.” Their definition continues, “when you use an assessment instrument— a test, a quiz, an essay, or any other kind of classroom activity—analytically and diagnostically to measure the process of learning and then, in turn, to inform yourself or your students of progress and guide further learning, you are engaging in formative assessment. If you were to use the same instrument for the sole purpose of gathering data to report to a district or state or to determine a final grade, you would be engaging in summative assessment.”
Does formative assessment work in all content areas?
Absolutely, and it works across all grade levels. Nearly any content area — language arts, math, science, humanities, and even the arts or physical education — can utilize formative assessment in a positive way.
How can formative assessment support the curriculum?
Formative assessment supports curricula by providing real-time feedback on students’ knowledge levels and comprehension of the subject at hand. When teachers regularly utilize formative assessment tools, they can find gaps in student learning and customize lessons to fill those gaps. After term is over, teachers can use this feedback to reshape their curricula.
How can formative assessment be used to establish instructional priorities?
Because formative assessment supports curriculum development and updates, it thereby influences instructional priorities. Through student feedback and formative assessment, teachers are able to gather data about which instructional methods are most (and least) successful. This “data-driven” instruction should yield more positive learning outcomes for students.
Can formative assessment close achievement gaps?
Formative assessment is ideal because it identifies gaps in student knowledge while they’re learning. This allows teachers to make adjustments to close these gaps and help students more successfully master a new skill or topic.
How can I help my students understand formative assessment?
Formative assessment should be framed as a supportive learning tool; it’s a very different tactic than summative assessment strategies. To help students understand this new evaluation style, make sure you utilize it from the first day in the classroom. Introduce a small number of strategies and use them repeatedly so students become familiar with them. Eventually, these formative assessments will become second nature to teachers and students.
Before you tackle formative assessment, or any new teaching strategy for that matter, consider taking a continuing education course. At the University of San Diego School of Professional and Continuing Education, we offer over 500 courses for educators that can be completed entirely online, and many at your own pace. So no matter what your interests are, you can surely find a course — or even a certificate — that suits your needs.
Be Sure To Share This Article
- Share on Twitter
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Your Salary
Browse over 500+ educator courses and numerous certificates to enhance your curriculum and earn credit toward salary advancement.
Related Posts

TeachersBuzz
Fa3 model papers 2024 / formative assessment 3 model question papers english medium(e/m) cce exam papers, fa3 / formative assessment 3 model question papers 2024 english medium (e/m) cce exam papers.

FA3 model papers / Formative Assessment 3 Model Question Papers English Medium(E/M) CCE Exam papers for 1st to 10th classes
Director of School Education,Telangana stateHyderabad has given the internal exams i.e. Formative Assessments /FA examinations scheduled to be conducted for four times i.e. FA1, FA2, FA3 and FA4 and DSE Telangana has directed to complete the Four Formative Assessment (FA) Test as per schedule in the given dates which were given here.
I-V(Primary) Classes Formative Assessment-3 Question Papers (All in one bunch pdf) TS Schools.
Examinations Schedule(AP Schools) 2023-2024:
- Revised schedule for formative and summative assessments 2024.
- Formative Assessment 3 (Class Room Based Assessment 2) : from 23-02-2024 to 29-02-2024
- Formative Assessment-4 : MARCH,2024
- Pre public Exams for X class : MARCH 2024.
- Summative Assessment-2 (Class Room Based Assessment 3) : APRIL, 2024
READ| AP FA3/ CBA2 Exams Answer Key Papers 2024 for 1st to 10th classes All Subjects Principles Of Evaluation, Model Papers
AP SCHOOLS Latest Model papers for FA 3 (Formative 3)
1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th, 5th Class Question Papers 2023-2024 – I to V (Primary) Classes Formative Assessment-3 (FA-3) Question Papers download:
* 1st Class Formative Assesment III Model Question Papers Download
* 2nd Class Formative Assesment III Model Question Papers Download
* 3rd Class Formative Assesment III Model Question Papers Download * 4th Class Formative Assesment III Model Question Papers Download * 5th Class Formative Assesment III Model Question Papers Download
FA-III TELUGU Model PAPERS SET-I & SET-II
Fa-iii hindi model papers set-i & set-ii, set-iii & set-iv, fa-iii english model papers, fa-iii maths model papers set-itm set-iitm, set-iii em set-iv em, fa-iii physical science model papers set-i em set-ii em.
FA 3 TELUGU Question Papers Class VI to X SET 1 : VI Class
FA 3 HINDI Question Papers Class VI to X
SET 1 : VI Class
SET 2 : VI Class
SET 3 : VI Class
SET 4 : VI Class
6th Class Social Studies FA3 Exam Paper Telugu Medium English Medium
7th Class Social Studies FA3 Exam Paper Telugu Medium English Medium
8th Class Social Studies FA3 Exam Paper Telugu Medium English Medium
9th Class Social Studies FA3 Exam Paper Telugu Medium English Medium
10th Class Social Studies FA3 Exam Paper Telugu Medium English Medium
Mathematics CCE FA 3 /Formative 3/Formative Assessment 3 Question Papers/Model Papers For 6th,7th,8th,9th,10th Classes/VI/VII/VIII/IX/Classes
TELUGU MEDIUM SET 1 : VI Class VII Class VIII class IX Class X Class
ENGLISH MEDIUM SET 1 : VI Class VII Class VIII class IX Class X Class
——— II Class
———– III Class
———– IV Class
——- V Class
TLM & Activity models for Telugu, English, Maths & EVS of Primary Schools – 1st to 5th classes Teaching & Learning Material
FA3/ FLN Monthly Slip Tests for DEC 2023
FA 3 & FLN December-2023 Test All Subjects Question Papers Prepared based on FLN First Step December Syllabus
FLN Telugu Class 1,2,3,4,5 SLIP TEST DEC -2022
FLN ENGLISH Class 1,2,3,4,5 SLIP TEST DEC -2022
FLN Mathematics Class 1,2,3,4,5 Slip Test – December – 2022
————————-
Telugu FA 3 Question Papers based on FLN
Click here to Download PDF 1st Class Telugu FA 3 Question Papers
FA 3 Question Papers of Telangana High Schools
VI th Class Hindi Click here to Download
TS Schools Formative Assessments 2023-24 Schedule
Examinations Schedule(TS Schools) 2023-2024:
- Formative Assessment – FA 1 : by 31.07.2023
- Formative Assessment – FA 2 : by 30.09.2023
- Summative Assessment – SA 1 : from 05.10.2023- 11.10.2023
- Formative Assessment – FA 3 : by 14.12.2023
- Formative Assessment – FA 4 : By 29.01.2024 for SSC (10th) and
- By 29.02.2024 for classes (1st-9th).
- Summative Assessment – SA 2 : For 1st to 9th Classes : 08.04.2024 – 18.04.2024
- Pre-final for Class – X : Before 29.02.2024
- SSC Board Examinations : March 2024
FA 3 Model Question Papers 2023-24
A. English Medium Question Papers
FA3 / Formative Assessment 3 Model Question Papers English Medium (E/M) 1st to 5th all subjects pdf download
Related Posts

TeachersBuzz.in
Eberly Center
Teaching excellence & educational innovation, what is the difference between formative and summative assessment, formative assessment.
The goal of formative assessment is to monitor student learning to provide ongoing feedback that can be used by instructors to improve their teaching and by students to improve their learning. More specifically, formative assessments:
- help students identify their strengths and weaknesses and target areas that need work
- help faculty recognize where students are struggling and address problems immediately
Formative assessments are generally low stakes , which means that they have low or no point value. Examples of formative assessments include asking students to:
- draw a concept map in class to represent their understanding of a topic
- submit one or two sentences identifying the main point of a lecture
- turn in a research proposal for early feedback
Summative assessment
The goal of summative assessment is to evaluate student learning at the end of an instructional unit by comparing it against some standard or benchmark.
Summative assessments are often high stakes , which means that they have a high point value. Examples of summative assessments include:
- a midterm exam
- a final project
- a senior recital
Information from summative assessments can be used formatively when students or faculty use it to guide their efforts and activities in subsequent courses.
CONTACT US to talk with an Eberly colleague in person!
- Faculty Support
- Graduate Student Support
- Canvas @ Carnegie Mellon
- Quick Links

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
3. Dipsticks: So-called alternative formative assessments are meant to be as easy and quick as checking the oil in your car, so they're sometimes referred to as dipsticks. These can be things like asking students to: write a letter explaining a key idea to a friend, draw a sketch to visually represent new knowledge, or.
A formative assessment is a teaching practice—a question, an activity, or an assignment—meant to gain information about student learning. It's formative in that it is intentionally done for the purpose of planning or adjusting future instruction and activities. Like we consider our formative years when we draw conclusions about ourselves, a ...
Formative Assessment Examples #1: Mini-White Boards. Formative Assessments Examples: Having students solve problems or answer questions and display their results on a mini-white board is a great way to instantly gauge understanding. Formative assessment is used to gauge student understanding during the learning process.
The Department of Education (DepEd) defines formative assessment as an ongoing process of providing learners with immediate feedback on how well they are learning. In the Philippines, formative assessment is commonly used in classrooms. It helps teachers determine which topics to focus on and which skills to emphasize.
Consider our formative practices workshops, where school and district teams can gain a better understanding of the role formative practice plays in instruction and the four foundational practices to use in the classroom. Or for a quick start, download our eBook "Making it work: How formative assessment can supercharge your practice."
3. Strategic Questioning. Questioning strategies may be used with individuals, small groups, or the entire class. Effective formative assessment strategies involve asking students to answer higher-order questions such as "why" and "how."
Academy for Teaching and Learning. Moody Library, Suite 201. One Bear Place. Box 97189. Waco, TX 76798-7189. [email protected]. (254) 710-4064. Assessment comes in two forms: formative and summative. Formative assessment occurs during the learning process, focuses on improvement (rather than evaluation) and is often informal and low-stakes.
A few years ago, I came across "10 assessments you can perform in 90 seconds" by TeachThought and really enjoyed the formative assessment strategies they outlined. Using formative assessment strategies in class during instruction—or "simple assessments," as they call them—is easy and provides the instant feedback teachers need to identify which learners need more help and adjust ...
Direct evaluation of student work through papers, projects, assignments, exam questions. Student surveys for intended experiences or changes in student beliefs/attitudes. Evaluation of course design components using instructor rubrics. Evaluation of live teaching practice using classroom observation protocols.
This will allow teachers to evaluate how much students have learned and what they missed. 5. Dipsticks. Dipsticks are an easy and quick method to know how much students have understood in the classroom. In this formative assessment strategy, teachers can give a worksheet to students at the end of a day or week.
Formative assessment evaluates your students' knowledge of small content areas. For example, 3 formative evaluations of 1 chapter. Summative assessment asks students to test their knowledge of complete chapters or content areas. For example, just 1 evaluation at the end of a chapter. The lesson material package is much larger now.
Formative assessment takes place while learning is still happening. In other words, teachers use formative assessment to gauge student progress throughout a lesson or activity. This can take many forms (see below), depending on the teacher, subject, and learning environment. Here are some key characteristics of this type of assessment:
Formative assessment allows you to evaluate students' performance in real-time, and also improve the course content and delivery during the learning process. It makes it easier for teachers to track the performance of students during a course or training program. Since formative assessment happens on the go, it is best described as a quick ...
St. Paul American School. There are three broad types of assessments: diagnostic, formative, and summative. These take place throughout the learning process, helping students and teachers gauge learning. Within those three broad categories, you'll find other types of assessment, such as ipsative, norm-referenced, and criterion-referenced.
3. Formative assessment examples / types and how they work. Formative assessments are extremely diverse. They range from generic to subject/content-specific, allowing you to assess knowledge and skills in a variety of ways, and cover the full breadth of K-12. ... World-class assessments driving student success. ACN 081 897 494. Call us today ...
5. Popsicle Sticks. Formative assessment doesn't need to be complicated or time-consuming to be meaningful and engaging. Have each student put their name on a popsicle stick in a jar or box on your desk. Let them know you'll be pulling popsicle sticks to see who will be answering questions about the lesson.
Door Slaps! - Check out this fun formative assessment from Dawn from Social Studies Success. 7. Play the "good the bad and the ugly" of an era. This is an easy activity! I call out a topic or an era. In small groups, students discuss the era. They come up with the "good, the bad and the ugly" of the era. We vote as a class on the best ...
You can ask individuals, groups, or the whole class high-level, open-ended questions that start with "why" or "how." These questions have a two-fold purpose — to gauge how well students are grasping the lesson at hand and to spark a discussion about the topic. ... 3-2-1 Countdown; This formative assessment tool can be written or oral ...
FA3 model papers / Formative Assessment 3 Model Question Papers English Medium(E/M) CCE Exam papers for 1st to 10th classes Director of School Education,Telangana stateHyderabad has given the internal exams i.e. Formative Assessments /FA examinations scheduled to be conducted for four times i.e. FA1, FA2, FA3 and FA4 and DSE Telangana has directed to complete the Four Formative Assessment (FA ...
Formative assessment is a process that uses informal assessment strategies to gather information on student learning. Teachers determine what students ... 3:Checklists — Class checklists are a great tool for collecting data about students during a unit of study. Before beginning a new unit,
The goal of summative assessment is to evaluate student learning at the end of an instructional unit by comparing it against some standard or benchmark. Summative assessments are often high stakes, which means that they have a high point value. Examples of summative assessments include: a midterm exam. a final project. a paper. a senior recital.