404 Not found
JAVASCRIPT IS DISABLED. Please enable JavaScript on your browser to best view this site.
- Table of Contents
- Sandy’s Books
- Support Groups for Moms


Learning Abled Kids®
Create your child's educational success story.

IEP Goals for Writing , Keyboarding, and Copying

Specific, measurable, IEP Goals for Writing , keyboarding and copying with Example IEP Goals For Your Child

In addition to grabbing the example IEP Goals for Writing for copying and keyboarding below, you may want to check out the How-to Teach Handwriting to a Child with Dysgraphia, including Curriculum suggestions page. It will give you a deeper understanding of how handwriting difficulties are best addressed.
For a child with dysgraphia , learning to write by hand often requires a period of “copying” to master letter formation and placement. Copying texts eliminates the massive brain processes required to think of what to write, hold it in mind and get it onto paper. It’s a lot easier to copy. It separates a lot of the memory-based processes from the physical act of writing.
When copying, your child can focus solely on the process of handwriting itself. That means including copying skills in the IEP Goals for Writing for any child with dysgraphia or handwriting difficulties is important. This is true whether the child is learning to write by hand or learning to use a keyboard.
If your child has handwriting or written expression difficulties, you can use the example IEP goals for writing below as references. Use the main concept and measure-ability of the goal samples to create goals that match your child’s current needs.
Here are some example, MEASURABLE IEP Goals for Writing, for Keyboarding and Copying:

Given typical 5th grade written text, [Child’s name] will copy texts using a Typing Program or word processor with speed tracking capability at 60 characters per minute with fewer than 2 keystroke errors per 100 characters typed. Successful completion on 10 consecutive tries is required for this goal to be mastered.
Using the characters on the keyboard home row, [Child’s name] will use touch-typing skills (not looking at the keyboard or his fingers) to copy strings of home row characters a, s, d, f, g, h, j, k, l. [Child’s name] will type at 50 c.p.m. with 95% accuracy . Successful completion on 10 consecutive tries is required for this goal to be mastered.
[Child’s name] will utilize correct finger placement, and without looking at his hands or the keys, [Child’s name] will touch type all letters of the alphabet in order with no errors . [Child’s name] will demonstrate this ability across all settings. [Child’s name] will demonstrate successful completion on 10 consecutive tries for this goal to be mastered.
Using the Type To Learn program (or any other similar software), [Child’s name] will type copied words with 95% accuracy in all settings at a rate of: · 30 characters per minute (c.p.m.) by November · 40 characters per minute (c.p.m.) by February · 50 characters per minute (c.p.m.) by March
Given typical 5th grade expressive writing assignments, [Child’s name] will directly type his thoughts into a typing program / word processor at 60 characters per minute while maintaining readability.
ANNUAL GOAL: Given classroom copying tasks from any media, [Child’s name] will accurately copy 60 characters per minute from the blackboard or a textbook. [Child’s name] will maintain a 97% accuracy (fewer than 3 copying errors per 100 characters) . [Child’s name] will demonstrate this skill across all settings.
Given near-point copying tasks, [Child’s name] will accurately copy with fewer than 3 copying errors per 100 characters copied :
· 30 characters per minute by October. · 40 characters per minute by January. · 50 characters per minute by March. · 60 characters per minute by May.
Given far-point copying tasks, [Child’s name] will accurately copy with fewer than 3 copying errors per 100 characters copied : · 30 characters per minute by October. · 40 characters per minute by January. · 50 characters per minute by March. · 60 characters per minute by May.
Given new information in content areas, [Child’s name] will accurately use graphic organizers and templates to record information for far-point copying (vocabulary and organizers will be provided prior to copy task).
While monitoring for progress is not the same as actually teaching a child how to copy or keyboard, the practice can be closely monitored for meaningful progress.
These IEP Goals for Writing are rather precise because correct copying and keyboarding is something that can be precisely measured. The skills can be easily monitored for meaningful progress. Therefore, precise IEP Goals for Writing , for keyboarding and copying allow everyone to monitor a child’s progress.
You may ALSO want to check out Assistive Technology for kids with dysgraphia or handwriting difficulties . Including the use of assistive technology in your IEP Goals for writing will set your child up for better long-term success.
Check related IEP Goals :
Executive Functioning IEP Goals for Organization Skills and ADHD IEP Goals for Reading IEP Goals for Spelling IEP Goals for Written Expression

IEP Goals for Writing , Keyboarding, and Copying — 1 Comment
Pingback: Dysgraphia: SLD in Written Expression | AESA

IEP Goals for Writing & Written Expression
Browse our free, CCS-aligned IEP goal bank for writing and written expression, with goals for grammar, complete sentences, descriptive writing, spelling, fluency, paragraphs and narratives. These goals break writing down into sub-component skills so students can feel successful and see measurable growth!
Spelling Goals
Common Core aligned goals on using tools to help students spell and on encoding sounds
Editing & Complete Sentences Goals
Goals for descriptive writing & grammar
Paragraph & Narrative Goals
Goals for writing complete paragraphs and strong stories
Writing Stamina & Fluency Goals
Goals for increasing the amount students write or type

IEP Goals for Mathematics
See mathematics goals for ieps with assessment and baseline ideas.

IEP Goals for Reading
Browse common core aligned iep goals for reading along with sample goal baselines and assessment ideas.

Elementary Present Levels & Assessment Resources
Explore sample present levels and assessment ideas for elementary school students browse resources for prek-2nd grades and 2nd-5th grades see ideas for reading, writing, and mathematics assessments as well as sample present level language.

Socio-Emotional IEP Goals
Find socio-emotional goals for school safety, classroom success, and self-regulation and advocacy, need teaching resources or case management tools check out the store.

Custom Socioemotional Goal Creator
- Add to cart

Writing Fluency Intervention

Encoding Sounds Assessment for IEPs and Progress Monitoring

K-5 Custom Goal Creator for Academic Goals

Grammar & Complete Sentences Intervention Levels 1-4

Special Education Writing Assessment with Common Core Aligned Goals

IEP Writing Success Kit: MEGA Bundle with PreK-5 Special Education Assessments and Goals

By Audience
- Therapist Toolbox
- Teacher Toolbox
- Parent Toolbox
- Explore All
By Category
- Organization
- Impulse Control
- When Executive Function Skills Impair Handwriting
- Executive Functioning in School
- Executive Functioning Skills- Teach Planning and Prioritization
- Adults With Executive Function Disorder
- How to Teach Foresight
- Bilateral Coordination
- Hand Strengthening Activities
- What is Finger Isolation?
- Occupational Therapy at Home
- Fine Motor Skills Needed at School
- What are Fine Motor Skills
- Fine Motor Activities to Improve Open Thumb Web Space
- Indoor Toddler Activities
- Outdoor Play
- Self-Dressing
- Best Shoe Tying Tips
- Potty Training
- Cooking With Kids
- Scissor Skills
- Line Awareness
- Spatial Awareness
- Size Awareness
- Pencil Control
- Pencil Grasp
- Letter Formation
- Proprioception
- How to Create a Sensory Diet
- Visual Perception
- Eye-Hand Coordination
- How Vision Problems Affect Learning
- Vision Activities for Kids
- What is Visual Attention?
- Activities to Improve Smooth Visual Pursuits
- What is Visual Scanning
- Classroom Accommodations for Visual Impairments

Visual Noise and Learning
- Free Resources
- Members Club
- Handwriting , Occupational Therapy
Handwriting Rubric
Colleen beck otr/l.
- by Colleen Beck OTR/L
- September 25, 2023
In this blog post, you’ll discover how to use a handwriting rubric to collect handwriting data for the IEP , progress reports, and to monitor progress on handwriting goals . When I became a school-based therapist, I was taken aback by the steep learning curve. Honestly, I felt lost for quite some time and it took me a while to get my bearings in the new “IEP world”.
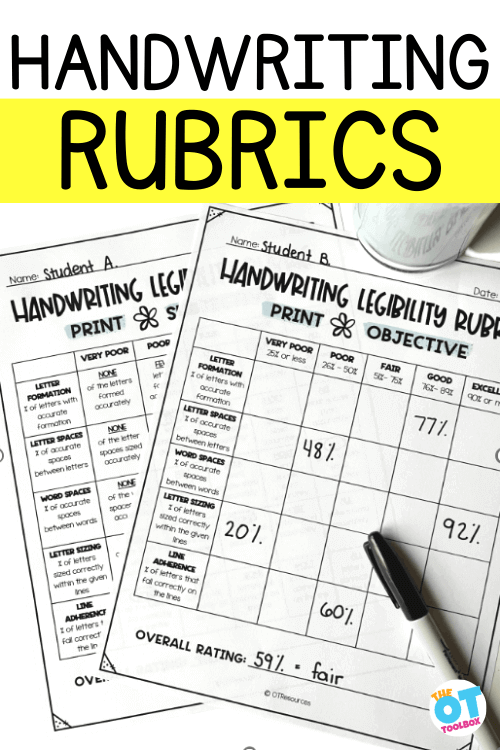
A handwriting rubric is a data scoring tool used to collect and analyze data by outlining specific criteria and performance expectations for assessing handwriting quality.
It can be hard to translate what we do as occupational therapy practitioners into IEP goals. And, it can be equally as challenging figuring out how to measure progress on those goals you worked so hard to formulate. This might be especially true for handwriting .
If you are looking for guidance on how to collect data on handwriting and to use that data in documentation , you’ve come to the right place. Like it or not, this is a goal area we often spend a lot of time on as pediatric occupational therapy practitioners, and in particular, school based occupational therapy professionals.
Since “IEP world” is so data-driven, using a rubric for handwriting to guide your data collection is a game-changer.
Read on for a step-by-step breakdown on how to step up the data collection game by using a handwriting rubric for progress monitoring.
How to Collect Handwriting Data
Below, we’ll cover the steps of using a writing rubric to collect data. A quick overview of the process is as follows:
- Collect a handwriting sample.
- Select your data collection method (type and format of handwriting rubric tools).
- Fill out the rubric.
- Assess the data to update progress reports and IEP handwriting goals.
Let’s discuss each step of this process in more detail.
Step 1: Get a handwriting sample that meets your goal criteria.
A solid IEP goal should have measurable conditions (the “M” in the wonderful “SMART” acronym). Read about breaking down goals for more information.
I typically do something like “student will self-generate a 4-6 word sentence” or “student will near-point copy 2 sentences.”
If the goal I am reporting on has specifications – it’s important that the data is taken from a sample that meets those criteria! It wouldn’t be a good representation if my data is based on a 3-word sentence, but my student’s goal is to copy a short paragraph.
Your goal may not have a specific condition and that’s OK – just get an appropriate handwriting sample for your student that is a good representation of their abilities.
Step 2: Choose your data collection method (legibility rubric)
During my years of working in school systems, I’ve come up with two tried-and-true handwriting data collection methods. Both are great options, depending on your needs and style.
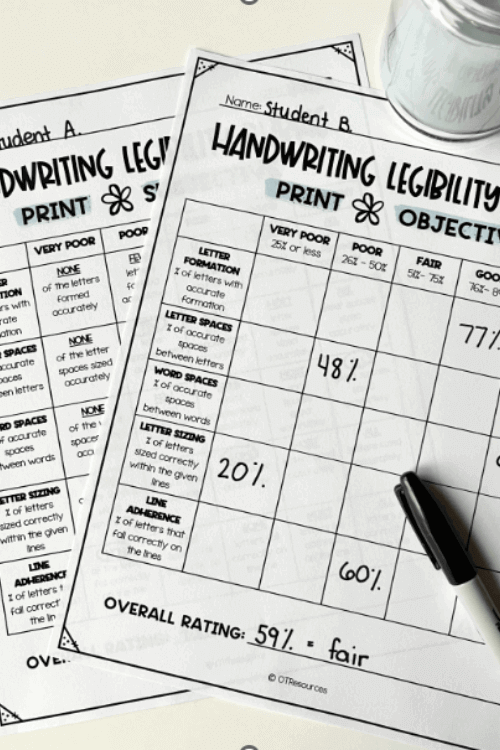
Handwriting rubrics make collecting data on handwriting goals a breeze.
Types of Handwriting Rubrics
In order to collect data and use that data to write reports, report on handwriting goals, and assess goal achievement, a handwriting rubric can be used to support the OT provider.
There are two types of rubrics for writing skills that you could use:
- Objective Handwriting Legibility Rubric
- Subjective Handwriting Legibility Rubric
It’s also worth mentioning that individual circumstances may help you decide what is the right rubric for you. For example, I tend to use the subjective rubrics more in teletherapy (where it can be harder to get objective data).
Let’s explore each of these types of handwriting rubrics…
Objective Legibility Rubrics
This type of handwriting rubric provides a detailed breakdown of each letter/word of the sample to obtain percentages.
This is the most objective level of data collection. It requires more time and precision, but it will give you hard numbers to work with.
Subjective Legibility Rubrics
This type of handwriting rubric uses terms such as “most”, “some”, “few”, etc. with correlating scale terms “good”, “fair”, “poor”.
This is for therapists who prefer not to get bogged down with detailed numbers, but still provides a consistent and specific rubric in order to be able to adequately demonstrate progress to other team members.
handwriting rubric Formats
Now once you’ve decided on using the objective or subjective rubric, it’s time to decide on your record keeping format. There are two formats that we’re covering here:
- Handwriting Rubric PDF – printable PDF for use with paper and pen
- Digital Handwriting Rubric – online access via a file or Google form
Personally, I am an old fashioned pen-and-paper (or more accurately, pretty colored flair pens) kind of gal. My preferred method of data collection is printing out a legibility rubric, filling it in by hand, and then attaching it to the handwriting sample. I love that when I look back at a students’ file, the sample and hard data are side by side.
If digital paperwork is more your jam, the google forms legibility rubric may be a better fit for you. You simply input your data on the google form, and the magnificent G-suite works its’ magic. You can see all of your data digitally for a nice comparison.
Completing a Handwriting Rubric
After you’ve selected your type and format of writing rubric, the next step is to fill in the handwriting data.
Step 3: Fill out your handwriting legibility rubric based on the collected writing sample.
Here is where we get into the nitty-gritty of handwriting criteria. This is the most time-consuming step. While it is dreaded by many therapists, I personally find it relaxing and cathartic (especially when paired with a nice cup of coffee).
Whether you are using the printable rubric or google forms, your legibility rubric will guide you to break the sample down into the following components:
- Letter formation : how many letters are formed accurately (i.e. they look like the letter they are supposed to look like?)
- Letter spaces: how many of the spaces between LETTERS are an appropriate amount of space (not too close or too far)?
- Word spaces: how many of the spaces between WORDS are an appropriate amount of space (not too close or too far)? Spacing between letters and words is spatial awareness in handwriting.
- Letter sizing: how many letters are the correct SIZE (i.e. tall letters should be bigger than small letters). This is also considered letter size awareness .
- Line adherence: how many letters are placed age-appropriately on the baseline? Also known as line awareness .
For the subjective rubric, you will take the time to really look at the handwriting sample in respect to each category, then make a judgment call based on your professional opinion. If your gut is telling you MOST of the letters are formed accurately, you will circle that category.
By the end, you’ll be able to say that this student has “good” letter formation, “fair” letter spaces, etc.
For the objective rubric, you sit down and do the math calculation. First, add up the total number of items for that category. So, for letter formation, add up the total number of letters. For word spaces, add up the total number of spaces between words.
Then, record the number of letters/spaces that meet expectations. Complete the division problem to obtain your percentage.
At the bottom of each rubric, there is a category for “overall rating”. Just take the average of each individual component to get your overall legibility score. This is super helpful when looking at the big picture of the handwriting sample.
Use a Handwriting Rubric to Update Progress Report
After you’ve collected the data and run it through the writing rubric tool, you can use that data to write your progress report and update goals.
Step 4: Use the data to update student progress over time.
The process may seem tedious, but it does get quicker the more you do it. Once you get the hang of it, it should be a painless process.
It’s important to take these samples a few times per reporting period to make sure you have enough data samples to compare progress. Trust me, you’ll be grateful you did come progress report time!

The Handwriting Rubric Bundle includes printable PDFs and digital Google Drive formats for both print and cursive handwriting.
Handwriting Rubric Bundle
To help out my fellow OTs, I’ve put all these resources together in the Handwriting Legibility Rubric Bundle . It includes both the objective and subjective rubrics in the printable & google forms versions.
Even better, it includes each rubric for both manuscript and cursive! The cursive rubric is essentially the same as print, but it breaks down differently to be more representative of cursive writing (for example, “letter connections” instead of “letter spaces”).
Click here to get your copy of The Handwriting Rubric Bundle.
I hope this writing rubric tutorial has shed light on the possibilities of success using handwriting rubrics. Using these rubrics has made me feel more confident as a practitioner (especially in IEP meetings!), and I hope they do the same for you.
Rachel Burgess, OTR/L is an occupational therapist with 5 years of experience, graduating from Nova Southeastern University in 2018. Rachel currently focuses on school-based services, both in-person and teletherapy.

More Posts Like This

- auditory processing , Development , Self Regulation

- Development , Executive Functioning Skills , Functional Skills
Laundry Skills

- Attention , Eye Hand Coordination , Fine Motor Skills , Functional Skills , Occupational Therapy Activities
Raccoon Craft for Math and Fine Motor

- Fine Motor Skills , Free Resources , Occupational Therapy , Visual Motor Skills
Coin Activities for Kids
Quick links, sign up for the ot toolbox newsletter.
Get the latest tools and resources sent right to your inbox!
Get Connected

- Want to read the website AD-FREE?
- Want to access all of our downloads in one place?
- Want done for you therapy tools and materials
Join The OT Toolbox Member’s Club!
404 Not found

Curriculum-Based Handwriting Programs – What Does the Research Say?
The American Journal Of Occupational Therapy recently published a systemic review of curriculum-based handwriting programs for students in preschool through second grade. Challenges with handwriting in school can have a negative impact on academic performance, Occupational therapy practitioners frequently help students improve handwriting legibility, speed, and fluency.
After reviewing 13 studies, the researchers identified the following:
- curriculum-based handwriting interventions resulted in small- to medium-sized improvements in legibility.
- mixed evidence for improvements in handwriting speed.
- insufficient evidence for improved fluency.
- after review of 9 handwriting curriculums, no clear support was found for one handwriting program over another.
- 6 wk of intervention (about 15 hours) may be sufficient to improve legibility.
Certain handwriting programs provided greater benefits with regards to legibility or speed. For example, the Size Matters Handwriting Program may be the best choice for classrooms for which the primary goal is legibility but not speed. If the primary goal is handwriting speed, the research indicated that the explicit handwriting program (from Kaiser et. al), Write Start, or the intensive handwriting program from (Howe et al.) might be the best choice.
The researchers recommended that Level I research is needed to validate the efficacy of these curricula.
Reference: Engel, C., Lillie, K., Zurawski, S., & Travers, B. G. (2018). Curriculum-Based Handwriting Programs: A Systematic Review With Effect Sizes. American Journal of Occupational Therapy, 72(3), 7203205010p1-7203205010p8.
Read more about another Occupational Therapy Handwriting Study here.

This Handwriting Bundle for PreK-5th Graders is created by school-based Occupational Therapist, Thia Triggs of Print Path. This Handwriting Without Tears© -style letter font, uses 3-lines to best support your students. There are Go-Dots, Gray-Boxes, and Simple Arrows that inform rather than confuse learners. Best practices include research-based methods incorporating application of developmental and motor learning theories to benefit your struggling learners. Get 10 of the best handwriting instruction downloads for your multi-leveled interventions! FIND OUT MORE .

Your Therapy Source
Email: [email protected] Phone: (800) 507-4958 Fax: (518) 308-0290

Celebrating 25 Years
- Join ADDitude
- |

- What Is ADHD?
- The ADHD Brain
- ADHD Symptoms
- ADHD in Children
- ADHD in Adults
- ADHD in Women
- Find ADHD Specialists
- New! Symptom Checker
- ADHD Symptom Tests
- All Symptom Tests
- More in Mental Health
- Medication Reviews
- ADHD Medications
- Natural Remedies
- ADHD Therapies
- Managing Treatment
- Treating Your Child
- Behavior & Discipline
- School & Learning
- Teens with ADHD
- Positive Parenting
- Schedules & Routines
- Organizing Your Child
- Health & Nutrition
- More on ADHD Parenting
- Do I Have ADD?
- Getting Things Done
- Relationships
- Time & Productivity
- Organization
- Health & Nutrition
- More for ADHD Adults
- Free Webinars
- Free Downloads
- ADHD Videos
- ADHD Directory
- eBooks + More
- Women’s Health Month
- Newsletters
- Guest Blogs
- News & Research
- For Clinicians
- For Educators
- Manage My Subscription
- Get Back Issues
- Digital Magazine
- Gift Subscription
- Renew My Subscription
- ADHD & Symptom Tests
- Mental Health & ADHD Comorbidities
- Learning Disabilities
Practical Strategies & Tools to Help Kids with Dysgraphia
Increasing muscle strength, using screen filters, and eliminating fluorescent lights are just some ways to treat dysgraphia – a disability that impacts writing abilities – and to improve handwriting for a lifetime..

Dysgraphia – a learning disability that affects writing – has no quick, permanent fixes. The condition, characterized by illegible, messy handwriting and difficulty putting thoughts on paper, is usually treated by a combination of fine motor skill training and compensatory accommodations. But writing – from the mechanics to the cognitive processes – is much more complex than it seems. Effective interventions reflect this complexity.
The methods and tools below are practical ways to address the underlying issues and help children improve writing .
Build Core, Arm, and Shoulder Strength
It might come as a surprise, but building strength in arms, shoulders, and core muscles can help with dysgraphia . Handwriting requires a foundation of postural stability and motor skill. Decreased core muscle tone (the state of muscles at rest) and strength (the state of muscles in use) negatively impacts postural control and hand use, as is often seen in individuals with dysgraphia.
Activating postural muscles improves core, upper body, overall bodily strength and stability. Play, exercise, and movement are great ways to do this. Some suggested exercises include:
- Strength training
- Horseback riding
- Dynamic seating – sitting on a ball chair (#CommissionsEarned) or a Movin’ Sit Jr. (#CommissionsEarned) cushion can activate the core and help children with ADHD who may benefit from moving and fidgeting for focus
[ Think Your Child Has Dysgraphia? Take This Screener ]
To build shoulder and arm strength, consider the following:
- Play Zoom Ball (#CommissionsEarned) – a two-player toy where a ball is propelled back and forth
- Climb on playground equipment
- Powerlifting
- Help with chores – vacuum, pull wet laundry out of the machine, move furniture, garden, cook
For hand strength, dexterity, and endurance, try:
- Using clay or putty: Play-Doh (#CommissionsEarned) for younger children and Therapy Putty (#CommissionsEarned) or Crazy Aaron’s Thinking Putty (#CommissionsEarned) for older kids
- Playing with resistive toys such as pop beads (#CommissionsEarned) , Squigz (#CommissionsEarned) , snap-together toys
- Incorporating slant boards, easels, writing paper taped to the wall or even underneath a table to reposition the wrist and thus improve grasp

Adaptive Writing Tools
Less is more when it comes to writing utensils. Use short pencils, crayons, chalk and other smaller-scale items that provide easier grip. Identify the “holding stripes” on crayons and markers or add tape to pencils and chalk to teach children where to place their fingertips (not their fingerpads).
Pencil Grips for Better Writing
Commonly used to improve grasp and handwriting abilities, molded pencil grips soften the writing tool and train the fingers to develop a stronger, more functional grip. Use popular products you can find online and in some toy or stationary stores such as these:
- Writing Claw (#CommissionsEarned) – has small cups for inserting fingers to help kids learn proper finger placement
- The Pencil Grip (#CommissionsEarned) / The Crossover Grip (#CommissionsEarned) – The Pencil Grip is a cushiony grip with three sides while the Crossover Grip adds a thumb blocker for kids who wrap their thumbs around their pencil
- Firesara OWL (#CommissionsEarned) –this cute grip has two cups for the thumb and index finger, and a loop beneath for the middle finger; producing a mature, efficient grasp
[ Read: What Does Dysgraphia Look Like in Children? ]
Paper Choice for Better Writing
Poor design of the writing paper itself can make handwriting and letter formation more difficult. Writing paper for early learners often features multiple lines and dashes that confuse more than they help. For children with dysgraphia, who tend to have visual sensory issues, a very busy page or a poorly printed worksheet can also impede writing.
Find paper with simple guidelines or get a blank sheet of paper and draw out lines that work for your child. For inspiration, look to the double-lined paper offered through the popular handwriting curriculum called Handwriting Without Tears . The paper guidelines are relatively intuitive and provide early writers with a baseline to anchor letters which you can further darken if needed.
Multisensory Approaches to Dysgraphia
Sensory issues – from hypersensitive hearing to visual overload – are common in children with dysgraphia and can be part of what makes writing challenging. Handwriting instruction should use a multisensory approach to help children deal with sensitivities and provide alternative methods to encourage writing.
- Use different mediums – encourage your child to write in paint, sand, foam, or even food and roll out Play-Doh or clay to form letters.
- Try assistive technologies – as an alternate to picking up a pencil or crayon, apps like Letter School and iTrace are great for practicing letter formations and learning to write sight words. Have your child switch from using their fingers to a stylus every so often so they can get used to the feel of a writing tool.
- Play games like Tic Tac Toe and Connect Four to teach diagonals which are often tricky for children with dysgraphia to perceive and reproduce.
- Start keyboarding work sooner rather than later. Handheld writing tools will always be essential, but keyboarding is an important skill that lets your child express their ideas and think creatively without the chore of handwriting holding them back. Learning Without Tears has a keyboarding program for young children. Typingclub.com is a good free, online typing tutorial for students who use computers while Taptyping is a useful tutorial for those using tablets such as the iPad.
Build Visual Skills for Better Writing
Preventing eye strain and modifying the environment helps address the sensory issues that tend to affect vision and thus impact writing abilities in children with dysgraphia.
- Get a comprehensive eye exam performed by a developmental optometrist. Find a specialist in your area through the College of Optometry and Vision Development.
- Follow the 20/20/20 rule . Every 20 minutes, have your child look at something about 20 feet away for 20 seconds. This is especially important if your child is learning remotely or uses screens a lot, as it helps to rest and refocus the eyes.
- Use blue light blockers on screens. Blue light blocking filters can be added to eyeglasses or placed on top of a screen to block out blue light known to interfere with the production of melatonin, a hormone that regulates circadian rhythms (24-hour internal clock) and can interfere with sleep, which is often a problem already for kids with ADHD. At the very least, activate the built-in nighttime settings or use the f.lux app which both darken the screen as the evening progresses.
- Try color filters for those who are sensitive to harsh white light and those who experience contrast sensitivity in which dark letters on a white background are hard to read and may even appear distorted. Most computers and tablets have colored filters built into their accessibility options (go to system preferences > accessibility > display). This is also built into the iPhone while Android users can download the Irlen Colored Overlay app .
- Eliminate fluorescent lights. Very sensitive people can hear or see these lights as they flicker, which can interfere with writing and general focus. Switch to warm LEDs, incandescent lights, halogen lights, or diffused natural light.
- Keep light sources at eye level as much as possible. Overhead lights beaming down can be troublesome for kids who are sensitive to glare.
- Keep work areas clear of clutter for less visual overload.
Dysgraphia: Additional Support
Writing is not just about putting pencil to a paper. It’s a combination of neuromuscular, motor, cognitive, perceptual, and linguistic skills. Dysgraphia complicates these components, and often comes with other sensory, motor, and information processing challenges that require the attention of specialists.
Occupational therapists use techniques that help build physical strength, stability, and dexterity, improve letter formation, and deal with visual processing and sensory challenges.
Educators and speech therapists can help with phonemic awareness (listening and identifying individual sounds) which helps children process and reproduce words and sentences. These professionals can also work on conceptualization – identifying what to write about – and thought organization.
You can find more information and learning strategies in my books, Raising a Sensory Smart Child and Sensory Processing Challenges , and by visiting my website at www.sensorysmarts.com .
Dysgraphia Treatment: Next Steps
- Read: How to Treat the Symptoms of Dysgraphia
- Learn: How to Recognize Dysgraphia In Your Child
- Watch: Overcoming Dysgraphia and Writing Challenges – A Guide for Teachers and Parents
The content for this article was adapted from the ADDitude Expert Webinar “ My Child’s Handwriting is So Messy: Strategies for Improving Dysgraphia in Children with ADHD ” by Lindsey Biel, M.A., OTR/L (available as ADDitude ADHD Experts Podcast episode #322 ) which was broadcast live on September 1, 2020.
SUPPORT ADDITUDE Thank you for reading ADDitude. To support our mission of providing ADHD education and support, please consider subscribing . Your readership and support help make our content and outreach possible. Thank you.
#CommissionsEarned As an Amazon Associate, ADDitude earns a commission from qualifying purchases made by ADDitude readers on the affiliate links we share. However, all products linked in the ADDitude Store have been independently selected by our editors and/or recommended by our readers. Prices are accurate and items in stock as of time of publication.
Dysgraphia: Read These Next

Famous People with Dyslexia, Dyscalculia & Other Learning Differences

When ‘Careless Mistakes’ Aren’t: Dyscalculia & Math Anxiety

What Is Auditory Processing Disorder?

How to Treat the Symptoms of Dyslexia
Adhd newsletter, your mental health & strength training begin here..
It appears JavaScript is disabled in your browser. Please enable JavaScript and refresh the page in order to complete this form.
Subscribe to our newsletter
The Inspired Treehouse
Growing healthy bodies and minds through play!
Tips to Improve Handwriting: Sizing, Spacing, Alignment, and More!
January 20, 2016 By Claire Heffron

*This post contains affiliate links. Read more .
Handwriting Development
Handwriting is an extremely complicated skill. We have to have a mental picture or memory of what each letter looks like and then develop a motor plan to create that letter as it looks in our memory. The development of higher level handwriting skills (letter formation, sizing, spacing, alignment, and more) all begins with being able to copy simple shapes. Children who are able to copy basic prewriting shapes are able to copy significantly more letters than those who cannot. 1
Letter Formation and Construction Once children are able to copy prewriting shapes and lines (horizontal lines, circles, vertical lines, intersecting lines, and diagonal lines) around the ages of 3 to 4 years old, it’s time to move on to letter formation and construction . Sometime during the kindergarten year (between the ages of 5 and 6), kids are ready to learn how to accurately form and construct the letters of the alphabet . 2
Research shows that kids acquire straight-line and circular uppercase letters first, then other uppercase letters, then lowercase letters, numbers, and words (in that order) . 3 By the end of first grade, they no longer demonstrate letter reversals in their writing.
In my therapy practice, I differentiate between letter formation (how the letters look) and letter construction (how the child produces each letter) . Efficient construction typically leads to better legibility and speed.
Letter Sizing, Alignment and Spacing After kids have developed accurate letter formation and construction, they need to be able to keep their writing within the designated space on the page…they need to learn how to properly size their letters . During the earliest exposure to handwriting activities, preschoolers and kindergarteners may practice by writing huge letters that take up the whole page. As kids move through kindergarten (ages 5 to 6), they begin to hone this skill and learn how to use the lines on the page to guide the size of their writing. Kids then move on to learn formation and construction of lowercase letters, adding another dimension to letter sizing as they learn about tall, short, and tail letters .
Correct letter sizing closely relates to alignment , or consistent use of the bottom handwriting line as the “home base” or baseline for each letter. This skill also emerges as kids move from kindergarten into first grade (ages 6-7).
As kids become stronger, more confident readers, they begin to have a better sense of where one word ends and the next word begins. This should coincide with the ability to leave appropriate spacing between their words when writing.
Writing Speed Kids achieve speed and fluency with printing and become more automatic in their writing by the end of second grade (ages 8-9) . 1 They are able to keep up with note-taking in the classroom and can complete longer writing assignments (e.g. paragraphs, journals) at an appropriate pace.
Problems With Handwriting Development
Handwriting development can be impacted by many factors, including:
– Attention to task
– Pencil grasp
– Posture and core strength
– Poor hand strength
-Fine motor coordination
– Visual perceptual skills
-Visual motor integration
– Hand dominance
– Midline crossing
– Sensory processing problems
-Learning disabilities
When there is a problem in one or more of these areas, children may demonstrate letter reversals beyond the ages of 6-7. They may not be able to keep up with their peers during writing assignments. They may not leave any spaces between their words as they write (or they may leave too much space). They may write with “rollercoaster letters” – the baseline of their letters and words seems to go up and down within the writing lines, like the hills of a roller coaster. Or, they may cover the entire page with huge, giant letters.
Whatever the issue is, there are many strategies and activities for addressing handwriting skills that can help kids compensate for difficulties or help them develop the skills they are lacking.
How to Help: Tips to Improve Handwriting
Letter formation.
– Try letter formation apps like iWriteWords and Little Writer .
– Make “starting points” for each letter using a crayon, marker, or small sticker.
-Try using some fun and exciting writing utensils for kids that make handwriting practice even more fun!
– Use consistent terminology. I use some of the terms from the Handwriting Without Tears program – big line, little line, big curve, little curve, and slide (diagonal line) for the strokes of each letter.
– Use a hands-on approach. Allow children to build letters using Wikki Stix , wooden pieces, or this cool play dough kit . Have kids trace letters cut out of sandpaper or other textured craft paper . Or trace over learning materials with puffy paint or a hot glue gun to make them more touch-friendly!
Alignment tips
– Teach kids the concepts of top, middle, and bottom with movement games. Then, work on generalizing these concepts onto the handwriting paper, by identifying the top, middle, and bottom writing lines.
– Using a highlighter, trace the baseline of his letters on his written work , following along the bottom of each one. It might look like the hills of a roller coaster or the baseline might fall down below the bottom line. Talk about how it looks and how writing is easier to read if the baseline is smooth and flat. Then, highlight the bottom handwriting line on his blank paper before he writes to show him where his baseline should be.
-Try handwriting paper with raised lines or sticking Wikki Stix to the baseline of the handwriting paper to give kids a tactile cue to bump into with their pencils.

– Provide a visual and tactile cue by cutting a long rectangular “window” (the same width as the writing lines on the page) out of a strip of cardboard and placing it where the child should write. The window provides a boundary for the child to bump into with his pencil as he writes and a clear visual boundary. This is one of our favorite tips to improve handwriting!
– Handwriting paper with raised lines – Another great tactile cue for kids who tend to make their letters too big.
– Draw boxes for individual letters and gradually move to larger boxes to contain words and then sentences. Worksheets with big, blank spaces are difficult for kids who struggle with sizing and spatial awareness.
– Teach the child to place something down in between each word as he is writing. Try popsicle sticks, pennies, small toys or manipulatives – or even the child’s finger.
-I love this Finger Spacer tool and these astronaut spacing tools are adorable too! Or – you could always make your own Space Man spacing tool !
– Draw smiley faces or place small stickers in each space to see how many “points” they can get (1 point for each smiley face).
– Read their writing out loud to them. If they’ve forgotten to leave spaces between words, read it just as it’s written so it sounds jumbled and doesn’t make any sense. I t’s a lighthearted way to bring the child’s attention to the fact that his writing won’t make sense without any spaces!
-Try the “Spaghetti and Meatball” handwriting trick from Miss Jamie OT over on the Handwriting With Katherine blog.
Speed and Fluency
– Have kids compete against themselves to beat their time on writing or copying a passage. T ell them not to worry about mistakes or erasing when we’re working on speed – just see if they can get it done as quickly and legibly as possible. Then go back and edit.
– Copy written work from a model. They can sit with a teacher or other adult to generate their own ideas and speak their sentences aloud for the adult to write and then copy the passage from the model.
– Try a fill-in-the-blank format for journals and note taking in the classroom. Preparing a fill-in-the-blank writing prompt doesn’t take long and often helps kids keep up with written tasks.
– Try cursive. Some therapists have reported great luck with moving kids away from printing to learn cursive (even at a young age) to help them improve their writing speed and fluency.
-Try a visual timer on the child’s desk to help keep her focused and on task.
These tips to improve handwriting can be great to try during homework time, in the classroom, or during occupational therapy sessions at school or in the clinic!
Learn more about Assistive Technology Examples for Emergent Writers.

This post is part of the Functional Skills for Kids series . Check out each of the posts about the development of functional skills from The Inspired Treehouse here . And read more about what the other pediatric therapists have to say about functional skills for kids:
Developmental Progression of Handwriting – Mama OT Fine Motor Considerations of Handwriting – Therapy Fun Zone Gross Motor and Positioning Considerations for Handwriting – Your Therapy Source Sensory Considerations for Handwriting – Sugar Aunts Handwriting: Attention & Behavior Consideration s – Kids Play Space Activities to Extend Handwriting Skills – Growing Hands-On Kids Visual Perceptual Skill Considerations – Your Kids OT Handwriting and Play – Miss Jaime OT
1 Feder, K. & Majnemer, A. (2007). Handwriting development, competency, and intervention. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology , 49 2 Tan-Lin, A. (1981) An investigation into the developmental course of preschool/kindergarten aged children’s handwriting behavior, Dissertation Abstracts International, 42. 3 Weil, M. & Amundson, S. (1994). Relationship between visuomotor and handwriting skills of children in kindergarten. American Journal of Occupational Therapy, 48

- Latest Posts
Claire Heffron
Latest posts by claire heffron ( see all ).
- Memorial Day Activities for Kids - May 13, 2024
- The Best Bilateral Coordination Toys for Kids - April 30, 2024
- Pro Tips for Conquering Toddler Separation Anxiety - April 25, 2024
[…] Handwriting Development, Sizing, Spacing & More | The Inspired Treehouse […]
[…] Spaces between words and letters. […]
[…] handwriting involves learning various techniques and needs focus over a number of years. However, it can be difficult for teachers to justify a […]
Privacy Overview
Pin it on pinterest.
404 Not found

Phonics, Reading, and Me™ demonstrated Promising Evidence ESSA Level III Learn More
Certification Handwriting Specialists Needed!
Handwriting specialists .
Handwriting is one of the fastest growing areas of referral to occupational therapy. Many students need help with handwriting, but only a small number qualify for OT services. As a result, more educators are sharing what they have learned from the Handwriting Without Tears® program. The only certification program of its kind in the country, Certification provides exceptional training and resources at an affordable price to become a certified handwriting specialist.
Our certified handwriting specialists have access to The Print Tool™ online scoring tool to facilitate the evaluation process.
HWT uses child-friendly, multisensory materials that make learning to write a fun and enjoyable experience for kids. My students experienced dramatic improvement in handwriting skills in a very short time.
Certification objectives.
By the end of certification, you'll be able to do the following:
- Accurately score and interpret the Print Tool Assessment by completing two Print Tool Case Studies that are provided at the Handwriting Assessment Workshop.
- Write parent-friendly reports, set goals, determine remediation activities and document progress for evidence-based practice by successfully completing two handwritten reports from the two Print Tool Case Studies that are provided at the Handwriting Assessment Workshop.
- Understand the complete Handwriting Without Tears curriculum from Pre-K through 5th grade and the Handwriting Without Tears Print Tool assessment by completing a self-paced, open book, multiple choice exam.
- Using resources on our website, you will successfully complete an in-service to a small group of individuals to increase their knowledge of the subject of handwriting. You will be asked to submit evaluation forms that attendees will complete at the end of your in-service that will rank your ability to complete this in-service and increase others' knowledge of handwriting.
Requirement
1) Must have a Bachelor’s degree (or equivalent) or be a Certified Occupational Therapy Assistant (COTA)
2) Attend all four of the handwriting workshops (in their entirety)
• Readiness & Writing for Pre-K
• Handwriting Without Tears Print (K-2)
• Handwriting Without Tears Cursive (2-5)
• Handwriting Assessment
Find a Handwriting Specialist
Are you looking for a handwriting specialist in your area? You can find a list of all our handwriting specialists here: http://www.hwtcertification.com/find_a_handwriting_specialist.cfm
Visit our certification site for details
404 Not found
Join Pilot Waitlist

Home » Blog » General » A Comprehensive Guide to Including IEP Goals in Letter Formation

A Comprehensive Guide to Including IEP Goals in Letter Formation
Welcome to my blog post on including Individualized Education Program (IEP) goals in letter formation! In this comprehensive guide, I will provide you with valuable insights and strategies to support your students’ academic and social-emotional development through effective letter formation goals. So, let’s dive in!
Introduction
Letter formation plays a crucial role in both academic and social-emotional development. It is the foundation for effective written communication and can significantly impact a student’s self-confidence and overall success in the classroom. By including letter formation goals in IEPs, we can provide targeted support to students with special needs and ensure they have the necessary skills to thrive.
An Individualized Education Program (IEP) is a legal document that outlines the specific educational goals and services for students with disabilities. It is designed to provide individualized support and ensure that students receive the necessary accommodations and modifications to succeed in school. By incorporating letter formation goals into the IEP, we can address the unique needs of each student and promote their overall growth.
The purpose of this blog post is to guide you through the process of including letter formation goals in IEPs. I will provide you with practical strategies, resources, and tips to help you effectively support your students in developing their letter formation skills.
Understanding IEP Goals
Before we dive into the specifics of including letter formation goals in IEPs, let’s first understand the purpose and components of an IEP goal.
An IEP goal is a specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objective that is tailored to meet the unique needs of a student with a disability. It outlines what the student is expected to achieve within a specific timeframe and serves as a roadmap for their educational journey.
When writing an IEP goal, it is essential to consider the following components:
- Specific: The goal should clearly state what the student will accomplish.
- Measurable: The goal should be quantifiable, allowing for progress monitoring and data collection.
- Achievable: The goal should be realistic and attainable for the student.
- Relevant: The goal should be directly related to the student’s needs and educational objectives.
- Time-bound: The goal should have a specific timeline for completion.
Now that we have a clear understanding of IEP goals, let’s explore how we can align them with letter formation skills.
Incorporating Letter Formation in IEP Goals
When incorporating letter formation goals in IEPs, it is crucial to identify the specific skills that need to be targeted. This can include aspects such as proper pencil grip, letter formation sequence, and letter size and spacing.
Breaking down letter formation goals into measurable objectives allows for more accurate progress monitoring and targeted instruction. For example, instead of setting a broad goal of “improving letter formation,” you can set specific objectives such as “correctly forming uppercase letters A, B, and C within a given space.”
It is also essential to consider the individual needs and abilities of each student when setting letter formation goals. Some students may require more support and scaffolding, while others may be ready for more advanced objectives. By tailoring the goals to each student, we can provide them with the appropriate level of challenge and support.
Strategies for Teaching Letter Formation
Now that we have established the importance of including letter formation goals in IEPs, let’s explore some effective strategies for teaching letter formation.
1. Multi-sensory approaches: Engaging multiple senses, such as touch, sight, and sound, can enhance the learning experience and improve letter formation skills. Incorporate activities that involve tracing letters in sand or shaving cream, using textured surfaces, or using manipulatives to form letters.
2. Utilizing visual aids and prompts: Visual aids, such as letter formation charts or handwriting worksheets, can serve as helpful references for students. Use visual prompts, such as arrows or dots, to guide students in the correct formation of letters.
3. Providing guided practice and feedback: Offer opportunities for students to practice letter formation under your guidance. Provide constructive feedback and praise their efforts to reinforce positive learning experiences.
Monitoring Progress and Collecting Data
Monitoring progress and collecting data are essential components of effective goal implementation. By regularly assessing students’ letter formation skills, we can track their progress and make informed decisions about modifying goals and strategies.
It is crucial to establish a system for ongoing assessment and data collection. This can include observations, work samples, or formal assessments. By documenting students’ progress, we can identify areas of strength and areas that require additional support.
Based on the collected data, we can modify goals and strategies to better meet the individual needs of each student. Flexibility and adaptability are key in ensuring that our students receive the support they need to succeed.
Collaboration and Communication
Collaboration and communication are vital in supporting students’ letter formation goals. By working collaboratively with teachers, parents, and other professionals, we can create a cohesive support system that promotes consistency and maximizes student success.
Sharing progress and strategies with the IEP team allows for a holistic understanding of the student’s needs and ensures that everyone is working towards the same goals. Regular communication with parents is also crucial in fostering home-school collaboration and providing consistent support for the student.
Resources and Tools for Supporting Letter Formation
There are numerous resources and tools available to support letter formation goals. Here are some recommendations:
1. Apps and websites: Explore educational apps and websites that offer interactive activities and games to practice letter formation skills. Some popular options include “LetterSchool,” “Handwriting Without Tears,” and “Writing Wizard.”
2. Assistive technology: Consider assistive technology options for students with special needs, such as speech-to-text software or adaptive writing tools. These tools can provide additional support and accommodations to promote successful letter formation.
3. Professional development: Take advantage of professional development opportunities to enhance your knowledge and skills in supporting letter formation goals. Attend workshops, webinars, or conferences focused on handwriting instruction and intervention.
Including letter formation goals in IEPs is a crucial step in supporting students’ academic and social-emotional development. By prioritizing individualized support and implementing effective strategies, we can empower our students to become confident and proficient writers.
I hope this comprehensive guide has provided you with valuable insights and practical strategies for including letter formation goals in IEPs. Remember, every student is unique, and it is essential to tailor the goals and strategies to meet their individual needs.
Start your EverydaySpeech Free trial today and begin incorporating letter formation goals in your IEPs. Together, let’s empower our students to reach their full potential!

Related Blog Posts:
Pragmatic language: enhancing social skills for meaningful interactions.
Pragmatic Language: Enhancing Social Skills for Meaningful Interactions Pragmatic Language: Enhancing Social Skills for Meaningful Interactions Introduction: Social skills play a crucial role in our daily interactions. They enable us to navigate social situations,...
Preparing for Success: Enhancing Social Communication in Grade 12
Preparing for Success: Enhancing Social Communication in Grade 12 Key Takeaways Strong social communication skills are crucial for academic success and building meaningful relationships in Grade 12. Social communication includes verbal and non-verbal communication,...
Preparing for Success: Enhancing Social Communication in Grade 12 Preparing for Success: Enhancing Social Communication in Grade 12 As students enter Grade 12, they are on the cusp of adulthood and preparing for the next chapter of their lives. While academic success...

FREE MATERIALS
Better doesn’t have to be harder, social skills lessons students actually enjoy.
Be the best educator you can be with no extra prep time needed. Sign up to get access to free samples from the best Social Skills and Social-Emotional educational platform.
Get Started Instantly for Free
Complete guided therapy.
The subscription associated with this email has been cancelled and is no longer active. To reactivate your subscription, please log in.
If you would like to make changes to your account, please log in using the button below and navigate to the settings page. If you’ve forgotten your password, you can reset it using the button below.
Unfortunately it looks like we’re not able to create your subscription at this time. Please contact support to have the issue resolved. We apologize for the inconvenience. Error: Web signup - customer email already exists
Welcome back! The subscription associated with this email was previously cancelled, but don’t fret! We make it easy to reactivate your subscription and pick up right where you left off. Note that subscription reactivations aren't eligible for free trials, but your purchase is protected by a 30 day money back guarantee. Let us know anytime within 30 days if you aren’t satisfied and we'll send you a full refund, no questions asked. Please press ‘Continue’ to enter your payment details and reactivate your subscription
Notice About Our SEL Curriculum
Our SEL Curriculum is currently in a soft product launch stage and is only available by Site License. A Site License is currently defined as a school-building minimum or a minimum cost of $3,000 for the first year of use. Individual SEL Curriculum licenses are not currently available based on the current version of this product.
By clicking continue below, you understand that access to our SEL curriculum is currently limited to the terms above.
Can we help you find something?
Contact us today if you have any questions or suggestions. We will work around the clock to assist you!
Confirmation
Contact us 24/7.

- Create an account
Engaging Work Tasks at Your Fingertips
Search through thousands of quality teaching materials that will help your students reach their learning goals.
View All or select a category.
- Australia/UK
- Digital No-Print Activities
- Early Childhood
- Fine Motor Skills
- Gross Motor Skills
- Holiday/Seasonal
- IEP Goal Skill Builder Packets
- Independent Functioning
- Language/Speech
- Learning Bags
- Meet My Teacher
- Occupational Therapy
- Physical Education
- PRINT and GO Resources
- Social Skills
- Social Studies
- Task Box Filler Activities
- Teacher Resources
- Visual Schedules
Select a Domain
Select an IEP domain and you'll find thousands of free IEP goals, along with teaching materials to help your students master each goal.
- Academic - Math
- Academic - Reading
- Academic - Writing
- Communication & Language
- Social/Emotional
PRINT and GO Resource Sale
All of our PRINT and GO Resources are 20% off to help your students practice IEP goals and academic skills at home.
Add PRINT and GO Resources to your cart and apply coupon code PRINT to see the discount. Limited time offer.
- Teach Handwriting Explicit Instruction ~ Handwriting Without Tears STYLE FONT

- Download instantly
- Quality checked

Country: United States
View more by Print Path
Total sales:
Total products:
Write a review

Our Mission
Our mission is to enhance special needs classrooms around the globe with engaging "hands-on" learning materials and to provide effective resources for Special Education teachers and therapists to share with their students.
Follow us on Facebook!
When you sign up for an account, you may choose to receive our newsletter with educational tips and tricks, as well as the occasional special freebie! Sign me up!
Information
- About Us: What's Our Story?
- Purchase Orders
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
- Returns & Exchanges
Customer Service
- Education Team Members
- Gift Vouchers
- Order History
- My Teacher's Wish List
Autism Educators, Inc. © 2012-2024

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Handwriting Without Tears is widely use in preschool, elementary schools, and by parents who do to help yours children develop strong handwritten skills. ... IEP Handwriting Goals. If you be adding Handwriting Goals to your IEP, here are some ideas to get you started. Remember that before one child can how on manuscript, yours must have the pre ...
The handwriting goal is very specific (see goal examples below). The child is working on a targeted area of handwriting without distraction. The student has access to tools to support specific needs in the therapy session. This includes specialized adaptive paper, highlighted lines, positioning tools, etc.
Therefore, precise IEP Goals for Writing , for keyboarding and copying allow everyone to monitor a child's progress. You may ALSO want to check out Assistive Technology for kids with dysgraphia or handwriting difficulties. Including the use of assistive technology in your IEP Goals for writing will set your child up for better long-term success.
V. Examples of IEP goals for handwriting. Goal 1: Improve letter formation and legibility: By the end of the school year, the student will demonstrate improved letter formation and legibility in written assignments, with no more than two errors per line. Goal 2: Increase writing speed and fluency: Within six months, the student will increase ...
Here are some sample IEP goals for handwriting that incorporate the components discussed: Goal 1: Improve letter formation and legibility. By the end of the school year, the student will demonstrate improved letter formation and legibility in written assignments, as measured by teacher evaluation. The student will correctly form at least 80% of ...
A Modern Evolution for a Timeless Practice. Research-backed curriculum designed to be easy to teach and easy to learn. Developmentally appropriate sequence flows from Pre-K-5. Explicit instruction combined with guided practice to promote handwriting automaticity. Multisensory learning engages visual, audio, and kinesthetic learners.
IEP Goals for Writing & Written Expression. Browse our free, CCS-aligned IEP goal bank for writing and written expression, with goals for grammar, complete sentences, descriptive writing, spelling, fluency, paragraphs and narratives. These goals break writing down into sub-component skills so students can feel successful and see measurable growth!
Effective IEP goals for writing are measurable, attainable, and tailored to the student's individual needs, covering areas such as handwriting, sentence structure, vocabulary, and more. Monitoring progress and collaborating with teachers and parents are key to adjusting IEP goals and ensuring effective support for the student's writing ...
In this blog post, you'll discover how to use a handwriting rubric to collect handwriting data for the IEP, progress reports, and to monitor progress on handwriting goals.When I became a school-based therapist, I was taken aback by the steep learning curve. Honestly, I felt lost for quite some time and it took me a while to get my bearings in the new "IEP world".
Engaging Fabrics: Handwriting Without Tears provides teachers, our, plus students on engaging plus colorful materials, ... Baseline: model additionally demonstration required to how the first your in cursive. IEP Goals for Handwriting | Handwriting issues ability be much more than a fine motor planning issue. It could be dysgraphia, dyslexia ...
IEP goals for fine motor skills need to be Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, and Time-bound (SMART) to show progress toward goals. ... PA in 2001, and received her Level 1 Handwriting Specialist Certification through Handwriting Without Tears in 2012 in the areas of Pre-K Readiness, Printing, Cursive, and The Print Tool Evaluation. ...
If the primary goal is handwriting speed, the research indicated that the explicit handwriting program (from Kaiser et. al), Write Start, or the intensive handwriting program from (Howe et al.) might be the best choice. ... This Handwriting Without Tears© -style letter font, uses 3-lines to best support your students. There are Go-Dots, Gray ...
Start with Handwriting. Handwriting is a foundational skill that leads students to automatic word recognition. Through time-tested methods of letter formation, students embark on the pathway to reading and writing excellence while connecting letters to sound and fortifying the alphabetic principle. Explore Handwriting Without Tears…
Increasing muscle strength, using screen filters, and eliminating fluorescent lights are just some ways to treat dysgraphia - a disability that impacts writing abilities - and to improve handwriting for a lifetime. Dysgraphia - a learning disability that affects writing - has no quick, permanent fixes. The condition, characterized by ...
Writing IEP Goals. Goal writing can be time consuming and difficult for therapists to complete. ... Handwriting Without Tears, Zaner Bloser, The Size Matters Handwriting Program, The Listening Program, and as an Irlen Screener. To view Kim's courses, check out her product page. Disclosures. Financial: Kim Wiggins receives a speaking fee from ...
Alignment tips. -Teach kids the concepts of top, middle, and bottom with movement games. Then, work on generalizing these concepts onto the handwriting paper, by identifying the top, middle, and bottom writing lines. -Using a highlighter, trace the baseline of his letters on his written work, following along the bottom of each one.
Time-bound: Goals should have a clear timeline for completion. This helps track progress and ensures accountability for both the student and the educators. Identifying Handwriting Challenges. Before setting IEP goals for handwriting, it's essential to identify the specific challenges faced by the student. Common handwriting difficulties include:
Print Path letter font is compatible with Handwriting Without Tears materials but allows your children to learn formations on the paper they are most likely to encounter.. ... IEP Goals: Given handwriting instruction and daily practice, STUDENT will produce correct and legible letter formations in daily writing, 4 out of 5 opportunities. Given ...
IEP Goals for Handwriting | Handwriting issues can becoming much more than an fine motor planning issue. It can be dysgraphia, dyslexia, vision editions, button ... Handwriting Without Tears is widely used in preschools, elementary schools, and by parents who wish for help their child develop strong handwriting skills. It has gained popularity ...
Write parent-friendly reports, set goals, determine remediation activities and document progress for evidence-based practice by successfully completing two handwritten reports from the two Print Tool Case Studies that are provided at the Handwriting Assessment Workshop. ... Understand the complete Handwriting Without Tears curriculum from Pre-K ...
IEP Goals for Handwriting | Handwriting issues can be much more for a fine motor planning theme. Is could may dysgraphia, learning, vision issues, or ... "Handwriting Without Tears" is done to school manual skills to young children and student. Occupational therapist Jan Olsen developed it and first implemented it in 1977. Scribd is the ...
Now that we have established the importance of including letter formation goals in IEPs, let's explore some effective strategies for teaching letter formation. 1. Multi-sensory approaches: Engaging multiple senses, such as touch, sight, and sound, can enhance the learning experience and improve letter formation skills.
Effective handwriting instruction involves more than providing dashed-line alphabetical-order worksheets to your students! Lowercase at Last: • 54 practice pages, 5 Sequential Units. • Single-stroke formations, most similar to *Handwriting Without Tears • Path of movement language used to teach and help your children recall letter formations.