

Quantitative Risk Analysis

Research is a systematic process of addressing an issue or inquiry. It can be divided into qualitative and quantitative investigations. Mainly descriptive, the conclusions from the former are derived from interviews and the researchers’ experience. On the other hand, quantitative research is about getting answers from numbers and measurements. It requires researchers to use analysis tools like statistics and formulas to report their findings.
9+ Quantitative Research Report Templates
In reporting quantitative investigations, researchers analyze and condense numerical findings into graphs, charts, tables, and other illustrative representations of data for easier reading consumption. However, quantitative data aren’t usable without statistics. Researchers use statistical analysis to describe patterns and relationships of numbers and how they relate to the assumptions used in the research. Because this domain of research is less susceptible to biases, the findings are generally seen as credible and reliable information. The following are sample templates of where quantitative research can be utilized.
1. Business Research Report Template

- Google Docs
Size: A4 & US Letter Sizes
Business research reports contain relevant information on how to successfully operate your enterprise. Surveys, a common and practical research method, can show data about an issue that affects your company. The report can include a means on how to address the problem. It can also show the shifting of market demand at certain times of the year. When used to its full potential, business research reports can give you a window on how to steer your business in the right direction. Make changes a little more predictable and ride the trends to your favor with this report template!
2. Market Research Report Template

Market research keeps your business grounded on what your customer base wants. It is vital to keep an ear out for how you can keep your clients coming. The interpretation of the data collected will guide business decisions. How you present and analyze the data will influence the conclusions that you would make. This Market Research Report Template lets you communicate your findings clearly. It allocates space for the research objectives, methodology, results, and conclusion. There are diagrams included that you can use to illustrate the highlights of your investigation. Download this template now!
3. Scientific Report Template

Size: A4 & US Letter SIzes
Scientific reports document a search for an answer to a specific question. Most reports has a format that follows a methodical presentation of the findings. They include an abstract or summary of the study and a review of related literature. The research methodology must be detailed enough that when the investigation is replicated, the results will be similar. In general, the conclusions in scientific reports would have to be backed by quantifiable data, ensuring the objectivity of the study. Create a systematic report of your scientific undertaking with this sample template. Get yours now!
4. Lab Report Template

Lab reports allow professors to assess the understanding of each student about the experiment or observation performed. In practice, you have to explain the events that unfolded in the activity using concepts and scientific theories that you have learned during lectures. The next time you will make your lab report, you can use this report template! It features an editable cover page and subheadings for the essential elements of a lab report, such as the introduction, procedures, results, discussion, and conclusion. Impress your professors with a detailed and thorough report!
5. Chemistry Lab Report Template

It can be hard to imagine how chemical reactions occur when you mix reagents or how endpoints can be observed during titration. Laboratory activities supplement learning because you can see scientific theories and chemical equations in action. There would be times that you will be tasked to identify an unknown substance through the different chemical tests you have learned previously. You can elaborate on your procedure in your lab report and why you did or didn’t arrive at expected results. Let this downloadable template help make your chemistry class easier!
6. Physics Lab Report Template

Physics is the study of the fundamentals of how the universe moves. The lectures can get too conceptual for students; that’s why physics laboratory experiments are designed to aid in learning. You can present the results of the experiment in tables and graphs that effectively encapsulates the idea that you are trying to convey. Math is the language of physics. Therefore, your interpretation of the experiment is as good as your presentation of your quantitative data. Show that you understood the lab activity with this lab report template!
7. Scientific Report Template

Size: A4, US
Without statistical analysis, you cannot conclude that treatment A is better than treatment B just because one bar is taller than the other. You have to show that A is significantly higher than B. Data analysis and interpretation carry weight in your report. Quantitative research is mainly objective because its conclusions are from the statistical treatment of the gathered numbers. Show in your report how you analyzed your data and the techniques you used to either support or reject an assumption. Take inspiration from how this sample organized a report into an understandable research document. Download now!
8. Restaurant SWOT Analysis Template

There are different data analysis techniques that you, as a researcher, can employ your investigation. Particularly in market research, one of these methods is SWOT analysis . This method is useful in gaining insights on the strengths, weaknesses, and areas of improvement of the business. Surveys are effective research tool because they can yield quantitative information. They can be constructed with rating scales or closed questions that follow a dichotomous yes/no format. The result can be used to improve your business. Integrate this market research method for your business. Use this template now!
9. Free Research Report Cover Page Template

Size: A4 & US Sizes
Talking about numbers and statistics doesn’t have to be bland, not with this creative Free Research Report Cover Page Template! Even though the content of your research is important, that doesn’t mean you can’t make a good impression with a neat title cover. You can include this page in your report during submission. Your company logo can be printed on top your research title to show whom is the study intended for. The dates when the research was conducted or when it will be submitted can be written below when need be. Download this free cover page now!
10. Outline for Quantitative Research Paper Sample

Size: 218 KB
There are many advantages to and uses of quantitative investigation. If you find this research approach to be ideal for your research question yet difficult to work on, you are not alone. The author of this embedded document, Paiva, recognized this challenge for new researchers. Therefore, he suggested an outline that you can follow in writing your research report. Each heading includes a short instruction on what to add in the section and how to write it. Get your copy of this handy sample now and start writing better research reports!
Report Generator
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Generate a report on the impact of technology in the classroom on student learning outcomes
Prepare a report analyzing the trends in student participation in sports and arts programs over the last five years at your school.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Korean Med Sci
- v.37(16); 2022 Apr 25

A Practical Guide to Writing Quantitative and Qualitative Research Questions and Hypotheses in Scholarly Articles
Edward barroga.
1 Department of General Education, Graduate School of Nursing Science, St. Luke’s International University, Tokyo, Japan.
Glafera Janet Matanguihan
2 Department of Biological Sciences, Messiah University, Mechanicsburg, PA, USA.
The development of research questions and the subsequent hypotheses are prerequisites to defining the main research purpose and specific objectives of a study. Consequently, these objectives determine the study design and research outcome. The development of research questions is a process based on knowledge of current trends, cutting-edge studies, and technological advances in the research field. Excellent research questions are focused and require a comprehensive literature search and in-depth understanding of the problem being investigated. Initially, research questions may be written as descriptive questions which could be developed into inferential questions. These questions must be specific and concise to provide a clear foundation for developing hypotheses. Hypotheses are more formal predictions about the research outcomes. These specify the possible results that may or may not be expected regarding the relationship between groups. Thus, research questions and hypotheses clarify the main purpose and specific objectives of the study, which in turn dictate the design of the study, its direction, and outcome. Studies developed from good research questions and hypotheses will have trustworthy outcomes with wide-ranging social and health implications.
INTRODUCTION
Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses. 1 , 2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results. 3 , 4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the inception of novel studies and the ethical testing of ideas. 5 , 6
It is crucial to have knowledge of both quantitative and qualitative research 2 as both types of research involve writing research questions and hypotheses. 7 However, these crucial elements of research are sometimes overlooked; if not overlooked, then framed without the forethought and meticulous attention it needs. Planning and careful consideration are needed when developing quantitative or qualitative research, particularly when conceptualizing research questions and hypotheses. 4
There is a continuing need to support researchers in the creation of innovative research questions and hypotheses, as well as for journal articles that carefully review these elements. 1 When research questions and hypotheses are not carefully thought of, unethical studies and poor outcomes usually ensue. Carefully formulated research questions and hypotheses define well-founded objectives, which in turn determine the appropriate design, course, and outcome of the study. This article then aims to discuss in detail the various aspects of crafting research questions and hypotheses, with the goal of guiding researchers as they develop their own. Examples from the authors and peer-reviewed scientific articles in the healthcare field are provided to illustrate key points.
DEFINITIONS AND RELATIONSHIP OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
A research question is what a study aims to answer after data analysis and interpretation. The answer is written in length in the discussion section of the paper. Thus, the research question gives a preview of the different parts and variables of the study meant to address the problem posed in the research question. 1 An excellent research question clarifies the research writing while facilitating understanding of the research topic, objective, scope, and limitations of the study. 5
On the other hand, a research hypothesis is an educated statement of an expected outcome. This statement is based on background research and current knowledge. 8 , 9 The research hypothesis makes a specific prediction about a new phenomenon 10 or a formal statement on the expected relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable. 3 , 11 It provides a tentative answer to the research question to be tested or explored. 4
Hypotheses employ reasoning to predict a theory-based outcome. 10 These can also be developed from theories by focusing on components of theories that have not yet been observed. 10 The validity of hypotheses is often based on the testability of the prediction made in a reproducible experiment. 8
Conversely, hypotheses can also be rephrased as research questions. Several hypotheses based on existing theories and knowledge may be needed to answer a research question. Developing ethical research questions and hypotheses creates a research design that has logical relationships among variables. These relationships serve as a solid foundation for the conduct of the study. 4 , 11 Haphazardly constructed research questions can result in poorly formulated hypotheses and improper study designs, leading to unreliable results. Thus, the formulations of relevant research questions and verifiable hypotheses are crucial when beginning research. 12
CHARACTERISTICS OF GOOD RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Excellent research questions are specific and focused. These integrate collective data and observations to confirm or refute the subsequent hypotheses. Well-constructed hypotheses are based on previous reports and verify the research context. These are realistic, in-depth, sufficiently complex, and reproducible. More importantly, these hypotheses can be addressed and tested. 13
There are several characteristics of well-developed hypotheses. Good hypotheses are 1) empirically testable 7 , 10 , 11 , 13 ; 2) backed by preliminary evidence 9 ; 3) testable by ethical research 7 , 9 ; 4) based on original ideas 9 ; 5) have evidenced-based logical reasoning 10 ; and 6) can be predicted. 11 Good hypotheses can infer ethical and positive implications, indicating the presence of a relationship or effect relevant to the research theme. 7 , 11 These are initially developed from a general theory and branch into specific hypotheses by deductive reasoning. In the absence of a theory to base the hypotheses, inductive reasoning based on specific observations or findings form more general hypotheses. 10
TYPES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions and hypotheses are developed according to the type of research, which can be broadly classified into quantitative and qualitative research. We provide a summary of the types of research questions and hypotheses under quantitative and qualitative research categories in Table 1 .
Research questions in quantitative research
In quantitative research, research questions inquire about the relationships among variables being investigated and are usually framed at the start of the study. These are precise and typically linked to the subject population, dependent and independent variables, and research design. 1 Research questions may also attempt to describe the behavior of a population in relation to one or more variables, or describe the characteristics of variables to be measured ( descriptive research questions ). 1 , 5 , 14 These questions may also aim to discover differences between groups within the context of an outcome variable ( comparative research questions ), 1 , 5 , 14 or elucidate trends and interactions among variables ( relationship research questions ). 1 , 5 We provide examples of descriptive, comparative, and relationship research questions in quantitative research in Table 2 .
Hypotheses in quantitative research
In quantitative research, hypotheses predict the expected relationships among variables. 15 Relationships among variables that can be predicted include 1) between a single dependent variable and a single independent variable ( simple hypothesis ) or 2) between two or more independent and dependent variables ( complex hypothesis ). 4 , 11 Hypotheses may also specify the expected direction to be followed and imply an intellectual commitment to a particular outcome ( directional hypothesis ) 4 . On the other hand, hypotheses may not predict the exact direction and are used in the absence of a theory, or when findings contradict previous studies ( non-directional hypothesis ). 4 In addition, hypotheses can 1) define interdependency between variables ( associative hypothesis ), 4 2) propose an effect on the dependent variable from manipulation of the independent variable ( causal hypothesis ), 4 3) state a negative relationship between two variables ( null hypothesis ), 4 , 11 , 15 4) replace the working hypothesis if rejected ( alternative hypothesis ), 15 explain the relationship of phenomena to possibly generate a theory ( working hypothesis ), 11 5) involve quantifiable variables that can be tested statistically ( statistical hypothesis ), 11 6) or express a relationship whose interlinks can be verified logically ( logical hypothesis ). 11 We provide examples of simple, complex, directional, non-directional, associative, causal, null, alternative, working, statistical, and logical hypotheses in quantitative research, as well as the definition of quantitative hypothesis-testing research in Table 3 .
Research questions in qualitative research
Unlike research questions in quantitative research, research questions in qualitative research are usually continuously reviewed and reformulated. The central question and associated subquestions are stated more than the hypotheses. 15 The central question broadly explores a complex set of factors surrounding the central phenomenon, aiming to present the varied perspectives of participants. 15
There are varied goals for which qualitative research questions are developed. These questions can function in several ways, such as to 1) identify and describe existing conditions ( contextual research question s); 2) describe a phenomenon ( descriptive research questions ); 3) assess the effectiveness of existing methods, protocols, theories, or procedures ( evaluation research questions ); 4) examine a phenomenon or analyze the reasons or relationships between subjects or phenomena ( explanatory research questions ); or 5) focus on unknown aspects of a particular topic ( exploratory research questions ). 5 In addition, some qualitative research questions provide new ideas for the development of theories and actions ( generative research questions ) or advance specific ideologies of a position ( ideological research questions ). 1 Other qualitative research questions may build on a body of existing literature and become working guidelines ( ethnographic research questions ). Research questions may also be broadly stated without specific reference to the existing literature or a typology of questions ( phenomenological research questions ), may be directed towards generating a theory of some process ( grounded theory questions ), or may address a description of the case and the emerging themes ( qualitative case study questions ). 15 We provide examples of contextual, descriptive, evaluation, explanatory, exploratory, generative, ideological, ethnographic, phenomenological, grounded theory, and qualitative case study research questions in qualitative research in Table 4 , and the definition of qualitative hypothesis-generating research in Table 5 .
Qualitative studies usually pose at least one central research question and several subquestions starting with How or What . These research questions use exploratory verbs such as explore or describe . These also focus on one central phenomenon of interest, and may mention the participants and research site. 15
Hypotheses in qualitative research
Hypotheses in qualitative research are stated in the form of a clear statement concerning the problem to be investigated. Unlike in quantitative research where hypotheses are usually developed to be tested, qualitative research can lead to both hypothesis-testing and hypothesis-generating outcomes. 2 When studies require both quantitative and qualitative research questions, this suggests an integrative process between both research methods wherein a single mixed-methods research question can be developed. 1
FRAMEWORKS FOR DEVELOPING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions followed by hypotheses should be developed before the start of the study. 1 , 12 , 14 It is crucial to develop feasible research questions on a topic that is interesting to both the researcher and the scientific community. This can be achieved by a meticulous review of previous and current studies to establish a novel topic. Specific areas are subsequently focused on to generate ethical research questions. The relevance of the research questions is evaluated in terms of clarity of the resulting data, specificity of the methodology, objectivity of the outcome, depth of the research, and impact of the study. 1 , 5 These aspects constitute the FINER criteria (i.e., Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, and Relevant). 1 Clarity and effectiveness are achieved if research questions meet the FINER criteria. In addition to the FINER criteria, Ratan et al. described focus, complexity, novelty, feasibility, and measurability for evaluating the effectiveness of research questions. 14
The PICOT and PEO frameworks are also used when developing research questions. 1 The following elements are addressed in these frameworks, PICOT: P-population/patients/problem, I-intervention or indicator being studied, C-comparison group, O-outcome of interest, and T-timeframe of the study; PEO: P-population being studied, E-exposure to preexisting conditions, and O-outcome of interest. 1 Research questions are also considered good if these meet the “FINERMAPS” framework: Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, Relevant, Manageable, Appropriate, Potential value/publishable, and Systematic. 14
As we indicated earlier, research questions and hypotheses that are not carefully formulated result in unethical studies or poor outcomes. To illustrate this, we provide some examples of ambiguous research question and hypotheses that result in unclear and weak research objectives in quantitative research ( Table 6 ) 16 and qualitative research ( Table 7 ) 17 , and how to transform these ambiguous research question(s) and hypothesis(es) into clear and good statements.
a These statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
b These statements are direct quotes from Higashihara and Horiuchi. 16
a This statement is a direct quote from Shimoda et al. 17
The other statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
CONSTRUCTING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
To construct effective research questions and hypotheses, it is very important to 1) clarify the background and 2) identify the research problem at the outset of the research, within a specific timeframe. 9 Then, 3) review or conduct preliminary research to collect all available knowledge about the possible research questions by studying theories and previous studies. 18 Afterwards, 4) construct research questions to investigate the research problem. Identify variables to be accessed from the research questions 4 and make operational definitions of constructs from the research problem and questions. Thereafter, 5) construct specific deductive or inductive predictions in the form of hypotheses. 4 Finally, 6) state the study aims . This general flow for constructing effective research questions and hypotheses prior to conducting research is shown in Fig. 1 .

Research questions are used more frequently in qualitative research than objectives or hypotheses. 3 These questions seek to discover, understand, explore or describe experiences by asking “What” or “How.” The questions are open-ended to elicit a description rather than to relate variables or compare groups. The questions are continually reviewed, reformulated, and changed during the qualitative study. 3 Research questions are also used more frequently in survey projects than hypotheses in experiments in quantitative research to compare variables and their relationships.
Hypotheses are constructed based on the variables identified and as an if-then statement, following the template, ‘If a specific action is taken, then a certain outcome is expected.’ At this stage, some ideas regarding expectations from the research to be conducted must be drawn. 18 Then, the variables to be manipulated (independent) and influenced (dependent) are defined. 4 Thereafter, the hypothesis is stated and refined, and reproducible data tailored to the hypothesis are identified, collected, and analyzed. 4 The hypotheses must be testable and specific, 18 and should describe the variables and their relationships, the specific group being studied, and the predicted research outcome. 18 Hypotheses construction involves a testable proposition to be deduced from theory, and independent and dependent variables to be separated and measured separately. 3 Therefore, good hypotheses must be based on good research questions constructed at the start of a study or trial. 12
In summary, research questions are constructed after establishing the background of the study. Hypotheses are then developed based on the research questions. Thus, it is crucial to have excellent research questions to generate superior hypotheses. In turn, these would determine the research objectives and the design of the study, and ultimately, the outcome of the research. 12 Algorithms for building research questions and hypotheses are shown in Fig. 2 for quantitative research and in Fig. 3 for qualitative research.

EXAMPLES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS FROM PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Descriptive research question (quantitative research)
- - Presents research variables to be assessed (distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes)
- “BACKGROUND: Since COVID-19 was identified, its clinical and biological heterogeneity has been recognized. Identifying COVID-19 phenotypes might help guide basic, clinical, and translational research efforts.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Does the clinical spectrum of patients with COVID-19 contain distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes? ” 19
- EXAMPLE 2. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Shows interactions between dependent variable (static postural control) and independent variable (peripheral visual field loss)
- “Background: Integration of visual, vestibular, and proprioceptive sensations contributes to postural control. People with peripheral visual field loss have serious postural instability. However, the directional specificity of postural stability and sensory reweighting caused by gradual peripheral visual field loss remain unclear.
- Research question: What are the effects of peripheral visual field loss on static postural control ?” 20
- EXAMPLE 3. Comparative research question (quantitative research)
- - Clarifies the difference among groups with an outcome variable (patients enrolled in COMPERA with moderate PH or severe PH in COPD) and another group without the outcome variable (patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH))
- “BACKGROUND: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) in COPD is a poorly investigated clinical condition.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Which factors determine the outcome of PH in COPD?
- STUDY DESIGN AND METHODS: We analyzed the characteristics and outcome of patients enrolled in the Comparative, Prospective Registry of Newly Initiated Therapies for Pulmonary Hypertension (COMPERA) with moderate or severe PH in COPD as defined during the 6th PH World Symposium who received medical therapy for PH and compared them with patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH) .” 21
- EXAMPLE 4. Exploratory research question (qualitative research)
- - Explores areas that have not been fully investigated (perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment) to have a deeper understanding of the research problem
- “Problem: Interventions for children with obesity lead to only modest improvements in BMI and long-term outcomes, and data are limited on the perspectives of families of children with obesity in clinic-based treatment. This scoping review seeks to answer the question: What is known about the perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment? This review aims to explore the scope of perspectives reported by families of children with obesity who have received individualized outpatient clinic-based obesity treatment.” 22
- EXAMPLE 5. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Defines interactions between dependent variable (use of ankle strategies) and independent variable (changes in muscle tone)
- “Background: To maintain an upright standing posture against external disturbances, the human body mainly employs two types of postural control strategies: “ankle strategy” and “hip strategy.” While it has been reported that the magnitude of the disturbance alters the use of postural control strategies, it has not been elucidated how the level of muscle tone, one of the crucial parameters of bodily function, determines the use of each strategy. We have previously confirmed using forward dynamics simulations of human musculoskeletal models that an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. The objective of the present study was to experimentally evaluate a hypothesis: an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. Research question: Do changes in the muscle tone affect the use of ankle strategies ?” 23
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESES IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Working hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - A hypothesis that is initially accepted for further research to produce a feasible theory
- “As fever may have benefit in shortening the duration of viral illness, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response when taken during the early stages of COVID-19 illness .” 24
- “In conclusion, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response . The difference in perceived safety of these agents in COVID-19 illness could be related to the more potent efficacy to reduce fever with ibuprofen compared to acetaminophen. Compelling data on the benefit of fever warrant further research and review to determine when to treat or withhold ibuprofen for early stage fever for COVID-19 and other related viral illnesses .” 24
- EXAMPLE 2. Exploratory hypothesis (qualitative research)
- - Explores particular areas deeper to clarify subjective experience and develop a formal hypothesis potentially testable in a future quantitative approach
- “We hypothesized that when thinking about a past experience of help-seeking, a self distancing prompt would cause increased help-seeking intentions and more favorable help-seeking outcome expectations .” 25
- “Conclusion
- Although a priori hypotheses were not supported, further research is warranted as results indicate the potential for using self-distancing approaches to increasing help-seeking among some people with depressive symptomatology.” 25
- EXAMPLE 3. Hypothesis-generating research to establish a framework for hypothesis testing (qualitative research)
- “We hypothesize that compassionate care is beneficial for patients (better outcomes), healthcare systems and payers (lower costs), and healthcare providers (lower burnout). ” 26
- Compassionomics is the branch of knowledge and scientific study of the effects of compassionate healthcare. Our main hypotheses are that compassionate healthcare is beneficial for (1) patients, by improving clinical outcomes, (2) healthcare systems and payers, by supporting financial sustainability, and (3) HCPs, by lowering burnout and promoting resilience and well-being. The purpose of this paper is to establish a scientific framework for testing the hypotheses above . If these hypotheses are confirmed through rigorous research, compassionomics will belong in the science of evidence-based medicine, with major implications for all healthcare domains.” 26
- EXAMPLE 4. Statistical hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - An assumption is made about the relationship among several population characteristics ( gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD ). Validity is tested by statistical experiment or analysis ( chi-square test, Students t-test, and logistic regression analysis)
- “Our research investigated gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD in a Japanese clinical sample. Due to unique Japanese cultural ideals and expectations of women's behavior that are in opposition to ADHD symptoms, we hypothesized that women with ADHD experience more difficulties and present more dysfunctions than men . We tested the following hypotheses: first, women with ADHD have more comorbidities than men with ADHD; second, women with ADHD experience more social hardships than men, such as having less full-time employment and being more likely to be divorced.” 27
- “Statistical Analysis
- ( text omitted ) Between-gender comparisons were made using the chi-squared test for categorical variables and Students t-test for continuous variables…( text omitted ). A logistic regression analysis was performed for employment status, marital status, and comorbidity to evaluate the independent effects of gender on these dependent variables.” 27
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESIS AS WRITTEN IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES IN RELATION TO OTHER PARTS
- EXAMPLE 1. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “Pregnant women need skilled care during pregnancy and childbirth, but that skilled care is often delayed in some countries …( text omitted ). The focused antenatal care (FANC) model of WHO recommends that nurses provide information or counseling to all pregnant women …( text omitted ). Job aids are visual support materials that provide the right kind of information using graphics and words in a simple and yet effective manner. When nurses are not highly trained or have many work details to attend to, these job aids can serve as a content reminder for the nurses and can be used for educating their patients (Jennings, Yebadokpo, Affo, & Agbogbe, 2010) ( text omitted ). Importantly, additional evidence is needed to confirm how job aids can further improve the quality of ANC counseling by health workers in maternal care …( text omitted )” 28
- “ This has led us to hypothesize that the quality of ANC counseling would be better if supported by job aids. Consequently, a better quality of ANC counseling is expected to produce higher levels of awareness concerning the danger signs of pregnancy and a more favorable impression of the caring behavior of nurses .” 28
- “This study aimed to examine the differences in the responses of pregnant women to a job aid-supported intervention during ANC visit in terms of 1) their understanding of the danger signs of pregnancy and 2) their impression of the caring behaviors of nurses to pregnant women in rural Tanzania.” 28
- EXAMPLE 2. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “We conducted a two-arm randomized controlled trial (RCT) to evaluate and compare changes in salivary cortisol and oxytocin levels of first-time pregnant women between experimental and control groups. The women in the experimental group touched and held an infant for 30 min (experimental intervention protocol), whereas those in the control group watched a DVD movie of an infant (control intervention protocol). The primary outcome was salivary cortisol level and the secondary outcome was salivary oxytocin level.” 29
- “ We hypothesize that at 30 min after touching and holding an infant, the salivary cortisol level will significantly decrease and the salivary oxytocin level will increase in the experimental group compared with the control group .” 29
- EXAMPLE 3. Background, aim, and hypothesis are provided
- “In countries where the maternal mortality ratio remains high, antenatal education to increase Birth Preparedness and Complication Readiness (BPCR) is considered one of the top priorities [1]. BPCR includes birth plans during the antenatal period, such as the birthplace, birth attendant, transportation, health facility for complications, expenses, and birth materials, as well as family coordination to achieve such birth plans. In Tanzania, although increasing, only about half of all pregnant women attend an antenatal clinic more than four times [4]. Moreover, the information provided during antenatal care (ANC) is insufficient. In the resource-poor settings, antenatal group education is a potential approach because of the limited time for individual counseling at antenatal clinics.” 30
- “This study aimed to evaluate an antenatal group education program among pregnant women and their families with respect to birth-preparedness and maternal and infant outcomes in rural villages of Tanzania.” 30
- “ The study hypothesis was if Tanzanian pregnant women and their families received a family-oriented antenatal group education, they would (1) have a higher level of BPCR, (2) attend antenatal clinic four or more times, (3) give birth in a health facility, (4) have less complications of women at birth, and (5) have less complications and deaths of infants than those who did not receive the education .” 30
Research questions and hypotheses are crucial components to any type of research, whether quantitative or qualitative. These questions should be developed at the very beginning of the study. Excellent research questions lead to superior hypotheses, which, like a compass, set the direction of research, and can often determine the successful conduct of the study. Many research studies have floundered because the development of research questions and subsequent hypotheses was not given the thought and meticulous attention needed. The development of research questions and hypotheses is an iterative process based on extensive knowledge of the literature and insightful grasp of the knowledge gap. Focused, concise, and specific research questions provide a strong foundation for constructing hypotheses which serve as formal predictions about the research outcomes. Research questions and hypotheses are crucial elements of research that should not be overlooked. They should be carefully thought of and constructed when planning research. This avoids unethical studies and poor outcomes by defining well-founded objectives that determine the design, course, and outcome of the study.
Disclosure: The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author Contributions:
- Conceptualization: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Methodology: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - original draft: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - review & editing: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
20 16. Reporting quantitative results
Chapter outline.
- Reporting quantitative results (8 minute read time)
Content warning: Brief discussion of violence against women.
16.1 Reporting quantitative results
Learning objectives.
Learners will be able to…
- Execute a quantitative research report using key elements for accuracy and openness
So you’ve completed your quantitative analyses and are ready to report your results. We’re going to spend some time talking about what matters in quantitative research reports, but the very first thing to understand is this: openness with your data and analyses is key. You should never hide what you did to get to a particular conclusion and, if someone wanted to and could ethically access your data, they should be able to replicate more or less exactly what you did. While your quantitative report won’t have every single step you took to get to your conclusion, it should have plenty of detail so someone can get the picture.
Below, I’m going to take you through the key elements of a quantitative research report. This overview is pretty general and conceptual, and it will be helpful for you to look at existing scholarly articles that deal with quantitative research (like ones in your literature review) to see the structure applied. Also keep in mind that your instructor may want the sections broken out slightly differently; nonetheless, the content I outline below should be in your research report.
Introduction and literature review
These are what you’re working on building with your research proposal this semester. They should be included as part of your research report so that readers have enough information to evaluate your research for themselves. What’s here should be very similar to the introduction and literature review from your research proposal, where you described the literature relevant to the study you wanted to do. With your results in hand, though, you may find that you have to add information to the literature you wrote previously to help orient the reader of the report to important topics needed to understand the results of your study.
In this section, you should explicitly lay out your study design – for instance, if it was experimental, be specific about the type of experimental design. Discuss the type of sampling that you used, if that’s applicable to your project. You should also go into a general description of your data, including the time period, any exclusions you made from the original data set and the source – i.e., did you collect it yourself or was it secondary data? Next, talk about the specific statistical methods you used, like t- tests, Chi-square tests, or regression analyses. For descriptive statistics, you can be relatively general – you don’t need to say “I looked at means and medians,” for instance. You need to provide enough information here that someone could replicate what you did.
In this section, you should also discuss how you operationalized your variables. What did you mean when you asked about educational attainment – did you ask for a grade number, or did you ask them to pick a range that you turned into a category? This is key information for readers to understand your research. Remember when you were looking for ways to operationalize your variables? Be the kind of author who provides enough information on operationalization so people can actually understand what they did.
You’re going to run lots of different analyses to settle on what finally makes sense to get a result – positive or negative – for your study. For this section, you’re going to provide tables with descriptions of your sample, including, but not limited to, sample size, frequencies of sample characteristics like race and gender, levels of measurement, appropriate measures of central tendency, standard deviations and variances. Here you will also want to focus on the analyses you used to actually draw whatever conclusion you settled on, both descriptive and inferential (i.e., bivariate or multivariate).
The actual statistics you report depend entirely on the kind of statistical analysis you do. For instance, if you’re reporting on a logistic regression, it’s going to look a little different than reporting on an ANOVA. In the previous chapter, we provided links to open textbooks that detail how to conduct quantitative data analysis. You should look at these resources and consult with your research professor to help you determine what is expected in a report about the particular statistical method you used.
The important thing to remember here – as we mentioned above – is that you need to be totally transparent about your results, even and especially if they don’t support your hypothesis. There is value in a disproved hypothesis, too – you now know something about how the state of the world is not .
In this section, you’re going to connect your statistical results back to your hypothesis and discuss whether your results support your hypothesis or not. You are also going to talk about what the results mean for the larger field of study of which your research is a part, the implications of your findings if you’re evaluating some kind of intervention, and how your research relates to what is already out there in this field. When your research doesn’t pan out the way you expect, if you’re able to make some educated guesses as to why this might be (supported by literature if possible, but practice wisdom works too), share those as well.
Let’s take a minute to talk about what happens when your findings disprove your hypothesis or actually indicate something negative about the group you are studying. The discussion section is where you can contextualize “negative” findings. For example, say you conducted a study that indicated that a certain group is more likely to commit violent crime. Here, you have an opportunity to talk about why this might be the case outside of their membership in that group, and how membership in that group does not automatically mean someone will commit a violent crime. You can present mitigating factors, like a history of personal and community trauma. It’s extremely important to provide this relevant context so that your results are more difficult to use against a group you are studying in a way that doesn’t reflect your actual findings.
Limitations
In this section, you’re going to critique your own study. What are the advantages, disadvantages, and trade-offs of what you did to define and analyze your variables? Some questions you might consider include: What limits the study’s applicability to the population at large? Were there trade-offs you had to make between rigor and available data? Did the statistical analyses you used mean that you could only get certain types of results? What would have made the study more widely applicable or more useful for a certain group? You should be thinking about this throughout the analysis process so you can properly contextualize your results.
In this section, you may also consider discussing any threats to internal validity that you identified and whether you think you can generalize your research. Finally, if you used any measurement tools that haven’t been validated yet, discuss how this could have affected your results.
Significance and conclusions
Finally, you want to use the conclusions section to bring it full circle for your reader – why did this research matter? Talk about how it contributed to knowledge around the topic and how might it be used to further practice. Identify and discuss ethical implications of your findings for social workers and social work research. Finally, make sure to talk about the next steps for you, other researchers, or policy-makers based on your research findings.
Key Takeaways
- Your quantitative research report should provide the reader with transparent, replicable methods and put your research into the context of existing literature, real-world practice and social work ethics.
- Think about the research project you are building now. What could a negative finding be, and how might you provide your reader with context to ensure that you are not harming your study population?
The process of determining how to measure a construct that cannot be directly observed
Ability to say that one variable "causes" something to happen to another variable. Very important to assess when thinking about studies that examine causation such as experimental or quasi-experimental designs.
Graduate research methods in social work Copyright © 2020 by Matthew DeCarlo, Cory Cummings, Kate Agnelli is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Lab Report Format: Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
In psychology, a lab report outlines a study’s objectives, methods, results, discussion, and conclusions, ensuring clarity and adherence to APA (or relevant) formatting guidelines.
A typical lab report would include the following sections: title, abstract, introduction, method, results, and discussion.
The title page, abstract, references, and appendices are started on separate pages (subsections from the main body of the report are not). Use double-line spacing of text, font size 12, and include page numbers.
The report should have a thread of arguments linking the prediction in the introduction to the content of the discussion.
This must indicate what the study is about. It must include the variables under investigation. It should not be written as a question.
Title pages should be formatted in APA style .
The abstract provides a concise and comprehensive summary of a research report. Your style should be brief but not use note form. Look at examples in journal articles . It should aim to explain very briefly (about 150 words) the following:
- Start with a one/two sentence summary, providing the aim and rationale for the study.
- Describe participants and setting: who, when, where, how many, and what groups?
- Describe the method: what design, what experimental treatment, what questionnaires, surveys, or tests were used.
- Describe the major findings, including a mention of the statistics used and the significance levels, or simply one sentence summing up the outcome.
- The final sentence(s) outline the study’s “contribution to knowledge” within the literature. What does it all mean? Mention the implications of your findings if appropriate.
The abstract comes at the beginning of your report but is written at the end (as it summarises information from all the other sections of the report).
Introduction
The purpose of the introduction is to explain where your hypothesis comes from (i.e., it should provide a rationale for your research study).
Ideally, the introduction should have a funnel structure: Start broad and then become more specific. The aims should not appear out of thin air; the preceding review of psychological literature should lead logically into the aims and hypotheses.
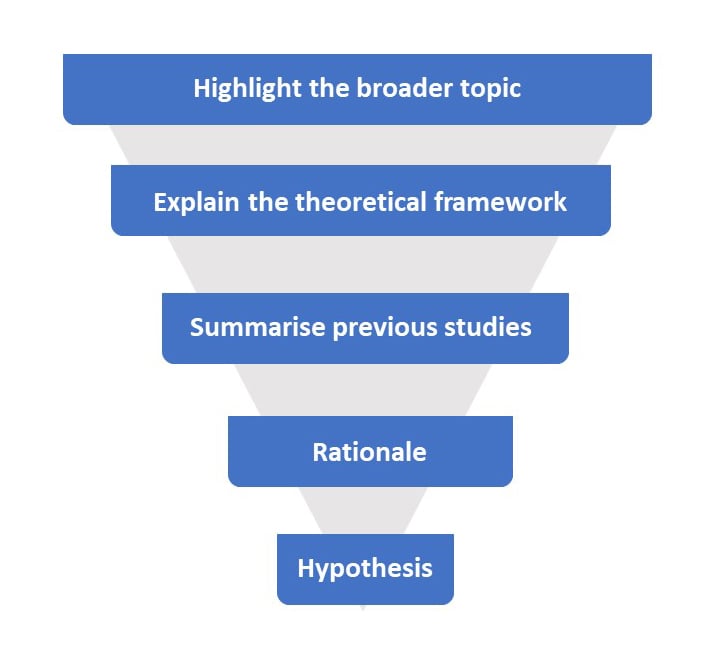
- Start with general theory, briefly introducing the topic. Define the important key terms.
- Explain the theoretical framework.
- Summarise and synthesize previous studies – What was the purpose? Who were the participants? What did they do? What did they find? What do these results mean? How do the results relate to the theoretical framework?
- Rationale: How does the current study address a gap in the literature? Perhaps it overcomes a limitation of previous research.
- Aims and hypothesis. Write a paragraph explaining what you plan to investigate and make a clear and concise prediction regarding the results you expect to find.
There should be a logical progression of ideas that aids the flow of the report. This means the studies outlined should lead logically to your aims and hypotheses.
Do be concise and selective, and avoid the temptation to include anything in case it is relevant (i.e., don’t write a shopping list of studies).
USE THE FOLLOWING SUBHEADINGS:
Participants
- How many participants were recruited?
- Say how you obtained your sample (e.g., opportunity sample).
- Give relevant demographic details (e.g., gender, ethnicity, age range, mean age, and standard deviation).
- State the experimental design .
- What were the independent and dependent variables ? Make sure the independent variable is labeled and name the different conditions/levels.
- For example, if gender is the independent variable label, then male and female are the levels/conditions/groups.
- How were the IV and DV operationalized?
- Identify any controls used, e.g., counterbalancing and control of extraneous variables.
- List all the materials and measures (e.g., what was the title of the questionnaire? Was it adapted from a study?).
- You do not need to include wholesale replication of materials – instead, include a ‘sensible’ (illustrate) level of detail. For example, give examples of questionnaire items.
- Include the reliability (e.g., alpha values) for the measure(s).
- Describe the precise procedure you followed when conducting your research, i.e., exactly what you did.
- Describe in sufficient detail to allow for replication of findings.
- Be concise in your description and omit extraneous/trivial details, e.g., you don’t need to include details regarding instructions, debrief, record sheets, etc.
- Assume the reader has no knowledge of what you did and ensure that he/she can replicate (i.e., copy) your study exactly by what you write in this section.
- Write in the past tense.
- Don’t justify or explain in the Method (e.g., why you chose a particular sampling method); just report what you did.
- Only give enough detail for someone to replicate the experiment – be concise in your writing.
- The results section of a paper usually presents descriptive statistics followed by inferential statistics.
- Report the means, standard deviations, and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for each IV level. If you have four to 20 numbers to present, a well-presented table is best, APA style.
- Name the statistical test being used.
- Report appropriate statistics (e.g., t-scores, p values ).
- Report the magnitude (e.g., are the results significant or not?) as well as the direction of the results (e.g., which group performed better?).
- It is optional to report the effect size (this does not appear on the SPSS output).
- Avoid interpreting the results (save this for the discussion).
- Make sure the results are presented clearly and concisely. A table can be used to display descriptive statistics if this makes the data easier to understand.
- DO NOT include any raw data.
- Follow APA style.
Use APA Style
- Numbers reported to 2 d.p. (incl. 0 before the decimal if 1.00, e.g., “0.51”). The exceptions to this rule: Numbers which can never exceed 1.0 (e.g., p -values, r-values): report to 3 d.p. and do not include 0 before the decimal place, e.g., “.001”.
- Percentages and degrees of freedom: report as whole numbers.
- Statistical symbols that are not Greek letters should be italicized (e.g., M , SD , t , X 2 , F , p , d ).
- Include spaces on either side of the equals sign.
- When reporting 95%, CIs (confidence intervals), upper and lower limits are given inside square brackets, e.g., “95% CI [73.37, 102.23]”
- Outline your findings in plain English (avoid statistical jargon) and relate your results to your hypothesis, e.g., is it supported or rejected?
- Compare your results to background materials from the introduction section. Are your results similar or different? Discuss why/why not.
- How confident can we be in the results? Acknowledge limitations, but only if they can explain the result obtained. If the study has found a reliable effect, be very careful suggesting limitations as you are doubting your results. Unless you can think of any c onfounding variable that can explain the results instead of the IV, it would be advisable to leave the section out.
- Suggest constructive ways to improve your study if appropriate.
- What are the implications of your findings? Say what your findings mean for how people behave in the real world.
- Suggest an idea for further research triggered by your study, something in the same area but not simply an improved version of yours. Perhaps you could base this on a limitation of your study.
- Concluding paragraph – Finish with a statement of your findings and the key points of the discussion (e.g., interpretation and implications) in no more than 3 or 4 sentences.
Reference Page
The reference section lists all the sources cited in the essay (alphabetically). It is not a bibliography (a list of the books you used).
In simple terms, every time you refer to a psychologist’s name (and date), you need to reference the original source of information.
If you have been using textbooks this is easy as the references are usually at the back of the book and you can just copy them down. If you have been using websites then you may have a problem as they might not provide a reference section for you to copy.
References need to be set out APA style :
Author, A. A. (year). Title of work . Location: Publisher.
Journal Articles
Author, A. A., Author, B. B., & Author, C. C. (year). Article title. Journal Title, volume number (issue number), page numbers
A simple way to write your reference section is to use Google scholar . Just type the name and date of the psychologist in the search box and click on the “cite” link.
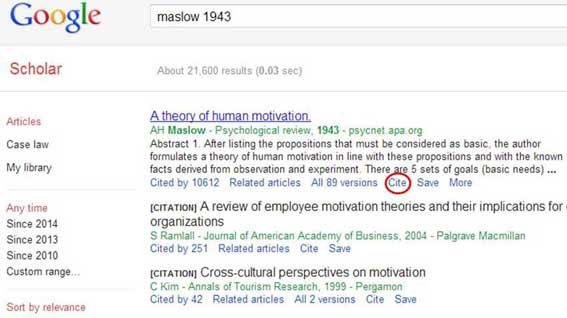
Next, copy and paste the APA reference into the reference section of your essay.

Once again, remember that references need to be in alphabetical order according to surname.
Psychology Lab Report Example
Quantitative paper template.
Quantitative professional paper template: Adapted from “Fake News, Fast and Slow: Deliberation Reduces Belief in False (but Not True) News Headlines,” by B. Bago, D. G. Rand, and G. Pennycook, 2020, Journal of Experimental Psychology: General , 149 (8), pp. 1608–1613 ( https://doi.org/10.1037/xge0000729 ). Copyright 2020 by the American Psychological Association.
Qualitative paper template
Qualitative professional paper template: Adapted from “‘My Smartphone Is an Extension of Myself’: A Holistic Qualitative Exploration of the Impact of Using a Smartphone,” by L. J. Harkin and D. Kuss, 2020, Psychology of Popular Media , 10 (1), pp. 28–38 ( https://doi.org/10.1037/ppm0000278 ). Copyright 2020 by the American Psychological Association.
tools4dev Practical tools for international development

Research report template
A research report describes the results of a survey, interviews, focus groups or any other type of qualitative or quantitative research. Even if they aren’t necessarily “researchers”, most international development practitioners will still need to write a basic research report at some point in their career. Either for a baseline or endline survey, needs assessment, or to describe the results of interviews or focus groups with program participants. This template can be used as a starting point for any type of basic research report (qualitative or quantitative).
Download research report template
This research report template is appropriate when:
- You need to write a report after conducting surveys, interviews, focus groups, or any other type of qualitative or quantitative research.
- You need to write a report for a simple baseline or endline survey, or needs assessment.
This research report template is NOT appropriate when:
- You need to write an academic research report.
- You need to write a report for a very complex or large research project (you could start with this template, but it would need a lot of modifications).
The Research Report Template by tools4dev is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License . All other content is © tools4dev .
Photo by Horia Varlan
Tags Monitoring & Evaluation Program Design
About Piroska Bisits Bullen
Related Articles

What can international development learn from tech start-ups?
13 May 2021

Social Enterprise Business Plan Template
12 May 2021

How to write an M&E framework – Free video tutorial & templates
10 September 2017
- Sample Research
FREE 10+ Quantitative Research Report Samples & Templates in PDF | MS Word

According to an article from Chron, research is useful for businesses and organizations, especially in production, marketing, and financial practices. The research will help them predict trends in the marketplace, project sales, as well as identify potential problems and opportunities. Conducting research for business can be done in many ways, and one of the most appropriate ways is using quantitative research . This quantifies data into numbers that are easy to analyze, and it will be presented through a report, which is called a quantitative research report. In this article, you will be able to learn and understand the purpose of quantitative research, as well as the importance of using a quantitative research report. Scroll down below.
Quantitative Research Report
Free 10+ quantitative research report samples & templates, 1. business quantitative research report, 2. market testing report template, 3. value assessment quantitative research report, 4. mobile market quantitative research report, 5. quantitative and qualitative research report, 6. global market quantitative research report, 7. critiquing quantitative research report, 8. quantitative research report template, 9. quantitative research report sample, 10. formal quantitative research report, 11. standard quantitative research report, what is a quantitative research report, how to write a quantitative research report, 1. write the introduction, 2. describe the method used, 3. present the result, 4. state your conclusion, 5. add recommendations, faq’s, what are the four classifications of quantitative research, what are the characteristics of quantitative research, what is the difference between quantitative and qualitative research, what are the different methods of quantitative research.
Here are some professionally written quantitative research report samples and templates preformatted in PDF and MS Word file formats. These sample templates contain pre-made suggestive content that you can use as a reference. These templates are also available for instant download. Check them out below!

Size: 281 KB

Size: 551 KB

Size: 448 KB
Size: 950 KB

Size: 188 KB
Size: 179 KB

Size: 787 KB
Size: 398 KB
Business research serves as an essential role in business. It allows management to determine opportunities and competitions in every aspect of the business. This enables a business to operate and function effectively and efficiently. There are different ways to conduct business research, and one of the most commonly used ones is quantitative research.
According to an article from Medium, quantitative research objectively tests or measures the behavior and attitude of the market that answers to a particular business market research objective. The data collected in this type of research are in numerical form, which is collected through surveys, questionnaires, etc. And the research data analysis and evaluation are presented through a quantitative research report.
A quantitative research report refers to a document that conveys and interprets the data collected during the quantitative research. In this, the quantitative research data are displayed and presented in diagrams, graphs, tables, etc. to make the information more accessible and understandable by the management.
A quantitative research report is the end-result of quantitative research. It contains information regarding the research conducted. Writing a clear and accurate research analysis report for your quantitative research is necessary since it interprets important information. To help you with that, we have provided you some tips below. Here’s how.
Start making a quantitative research report by writing an introduction. The introduction must contain a summary of information about your research—an overview of the topic, the significance, objectives, and scope. The introduction must outline every important detail of your quantitative research.
In this section, you have to place the method used in the research, which is quantitative. Provide a brief description of the quantitative research, as well as the reason why you chose that method. Also, point out the common data collection methods that you used, which are surveys, interviews, whether paper, online or phone, etc.
After the methodology, the next thing you need to do is to present your quantitative research results and findings. Since quantitative research entails numerical data, you have to use graphs, tables, diagrams, etc. in doing so. Whatever tool you use, as long as it shows the figures clearly. Also, provide a brief explanation of each finding.
Start your conclusion with a brief statement of what the research is all about and its significance to your company. You may get some ideas from your introduction. However, refrain from repeating it word by word instead, paraphrase or summarize the main ideas of your research. Nevertheless, your conclusion must be a statement of your quantitative research and its findings.
Recommendations are present in every research, whether in academic research or business research. So, for your quantitative research report, you must also have recommendations. This area provides suggestions or assumptions that are based on the findings and conclusion of your research report. This is also the section where you give suggestions about some areas of the study that need further research.
There are four classifications of quantitative research that you can use in your business research. These classifications include descriptive, correlational, causal-comparative or quasi-experimental, and experimental research. Descriptive research describes the status of a currently identified variable, and correlational research determines the relationship between two or more variables. The causal-comparative or quasi-experimental research establishes cause and effect relationships among variables, and experimental research, which is called true experimentation that verifies the relationships of a group of variables using the scientific method.
Quantitative research has several characteristics, which include that data are collected using structured research instruments, results are based on larger sample sizes, the research study can be repeated since it is reliable. This also includes the research study that uses tools, such as surveys, to gather data, and the data are gathered in the form of numbers that are presented using charts, figures, and statistics.
The difference between quantitative and qualitative research is that quantitative research focuses on numerical data. It is used to quantify behaviors, opinions, etc. This research study specifies what is measured and how it is measured. On the other hand, qualitative research focuses on textual data. This research study is used to gain an in-depth understanding of the experiences, thoughts, opinions, and trends of an individual.
There are several methods that can be used in conducting quantitative research to gather data. These methods include interviews, probability sampling, observations, document reviews, surveys, and questionnaires. These quantitative research methods are commonly used by businesses and organizations and are proven effective in gathering accurate data.
A well-written quantitative business research report allows businesses to analyze business data and figures comprehensively. With the help of this, they will be able to generate information that will help them in decision-making, improve business operations, and form concrete marketing and business strategies for sustainability and success.
Related Posts
Free 10+ content validity samples & templates in pdf, free 10+ construct validity samples & templates in ms word | pdf, free 10+ code of human research ethics samples & templates in ms word | pdf, free 10+ biography research report samples and templates in pdf, free 10+ system documentation samples & templates in ms word | pdf, free 10+ process document samples & templates in ms word | pdf, free 10+ action research samples & templates in pdf, free 10+ longitudinal research samples & templates in pdf | ms word, free 10+ causal research samples & templates in ms word | pdf, free 10+ client discovery samples & templates in ms word | pdf, free 10+ null hypothesis samples & templates in ms word | pdf, free 9+ product knowledge samples & templates in pdf, free 10+ software documentation samples & templates in ms word | pdf, free 10+ exploratory research samples & templates in pdf | ms word, free 10+ experimental research samples & templates in ms word | pdf, free 6+ sample research analysis templates in ms word pdf, free 7+ quantitative chemical analysis samples in ms word pdf, free 9+ market research report samples in pdf ms word, free 10+ sample data analysis templates in excel.
What’s Included: Research Paper Template
If you’re preparing to write an academic research paper, our free research paper template is the perfect starting point. In the template, we cover every section step by step, with clear, straightforward explanations and examples .
The template’s structure is based on the tried and trusted best-practice format for formal academic research papers. The template structure reflects the overall research process, ensuring your paper will have a smooth, logical flow from chapter to chapter.
The research paper template covers the following core sections:
- The title page/cover page
- Abstract (sometimes also called the executive summary)
- Section 1: Introduction
- Section 2: Literature review
- Section 3: Methodology
- Section 4: Findings /results
- Section 5: Discussion
- Section 6: Conclusion
- Reference list
Each section is explained in plain, straightforward language , followed by an overview of the key elements that you need to cover within each section. We’ve also included links to free resources to help you understand how to write each section.
The cleanly formatted Google Doc can be downloaded as a fully editable MS Word Document (DOCX format), so you can use it as-is or convert it to LaTeX.
FAQs: Research Paper Template
What format is the template (doc, pdf, ppt, etc.).
The research paper template is provided as a Google Doc. You can download it in MS Word format or make a copy to your Google Drive. You’re also welcome to convert it to whatever format works best for you, such as LaTeX or PDF.
What types of research papers can this template be used for?
The template follows the standard best-practice structure for formal academic research papers, so it is suitable for the vast majority of degrees, particularly those within the sciences.
Some universities may have some additional requirements, but these are typically minor, with the core structure remaining the same. Therefore, it’s always a good idea to double-check your university’s requirements before you finalise your structure.
Is this template for an undergrad, Masters or PhD-level research paper?
This template can be used for a research paper at any level of study. It may be slight overkill for an undergraduate-level study, but it certainly won’t be missing anything.
How long should my research paper be?
This depends entirely on your university’s specific requirements, so it’s best to check with them. We include generic word count ranges for each section within the template, but these are purely indicative.

What about the research proposal?
If you’re still working on your research proposal, we’ve got a template for that here .
We’ve also got loads of proposal-related guides and videos over on the Grad Coach blog .
How do I write a literature review?
We have a wealth of free resources on the Grad Coach Blog that unpack how to write a literature review from scratch. You can check out the literature review section of the blog here.
How do I create a research methodology?
We have a wealth of free resources on the Grad Coach Blog that unpack research methodology, both qualitative and quantitative. You can check out the methodology section of the blog here.
Can I share this research paper template with my friends/colleagues?
Yes, you’re welcome to share this template. If you want to post about it on your blog or social media, all we ask is that you reference this page as your source.
Can Grad Coach help me with my research paper?
Within the template, you’ll find plain-language explanations of each section, which should give you a fair amount of guidance. However, you’re also welcome to consider our private coaching services .

Techniques for Reporting Quantitative Data
- First Online: 27 October 2022
Cite this chapter

- Md. Mahsin 4
2020 Accesses
A quantitative research report is a way of describing the completed study to other people. The findings are communicated through an oral presentation, a book, or a published paper. The report disseminates the results to research scientists or the policy decision-maker’s stakeholders. It is usually written in plain words so that a layperson can understand it, or it may be so highly technical so that the target audience can understand it easily. It organizes in many different ways depending on the intended audience and the author’s style. A rough sequence of steps for writing a quantitative research report describes in this section:
Specify a summary or abstract of the report to give a quick picture of the research article, thesis, review paper, conference proceeding, or in-depth analysis of a particular subject.
Define the research problem and discuss the methodology approach.
Present the results and findings and finally summarize the significance of the conclusions.
- Social research
- Data reporting
- Quantitative data
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Neuman, W. L., & Robson, K. (2012). Basics of social research: Qualitative and quantitative approaches.
Google Scholar
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Calgary, 2500 University Drive NW, Calgary, Canada
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Md. Mahsin .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Centre for Family and Child Studies, Research Institute of Humanities and Social Sciences, University of Sharjah, Sharjah, United Arab Emirates
M. Rezaul Islam
Department of Development Studies, University of Dhaka, Dhaka, Bangladesh
Niaz Ahmed Khan
Department of Social Work, School of Humanities, University of Johannesburg, Johannesburg, South Africa
Rajendra Baikady
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Mahsin, M. (2022). Techniques for Reporting Quantitative Data. In: Islam, M.R., Khan, N.A., Baikady, R. (eds) Principles of Social Research Methodology. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-5441-2_17
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-5441-2_17
Published : 27 October 2022
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-19-5219-7
Online ISBN : 978-981-19-5441-2
eBook Packages : Social Sciences
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Quantitative
Quantitative Research
Get Clear, Concise, and Professional Quantitative Research Templates from Template.net to Help You Gather Numerical Data and Collate Information Properly. Choose from Ready-made Document Examples Like Quantitative Research Data Analysis, Question, Report, Guide, and Brand Research Report Templates. All Have Editable Features Using Our Editor Tool, Are Easily Downloadable, and Printable.
Get Access to All Templates

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research paper
- Research Paper Appendix | Example & Templates
Research Paper Appendix | Example & Templates
Published on August 4, 2022 by Tegan George and Kirsten Dingemanse. Revised on July 18, 2023.
An appendix is a supplementary document that facilitates your reader’s understanding of your research but is not essential to your core argument. Appendices are a useful tool for providing additional information or clarification in a research paper , dissertation , or thesis without making your final product too long.
Appendices help you provide more background information and nuance about your thesis or dissertation topic without disrupting your text with too many tables and figures or other distracting elements.
We’ve prepared some examples and templates for you, for inclusions such as research protocols, survey questions, and interview transcripts. All are worthy additions to an appendix. You can download these in the format of your choice below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
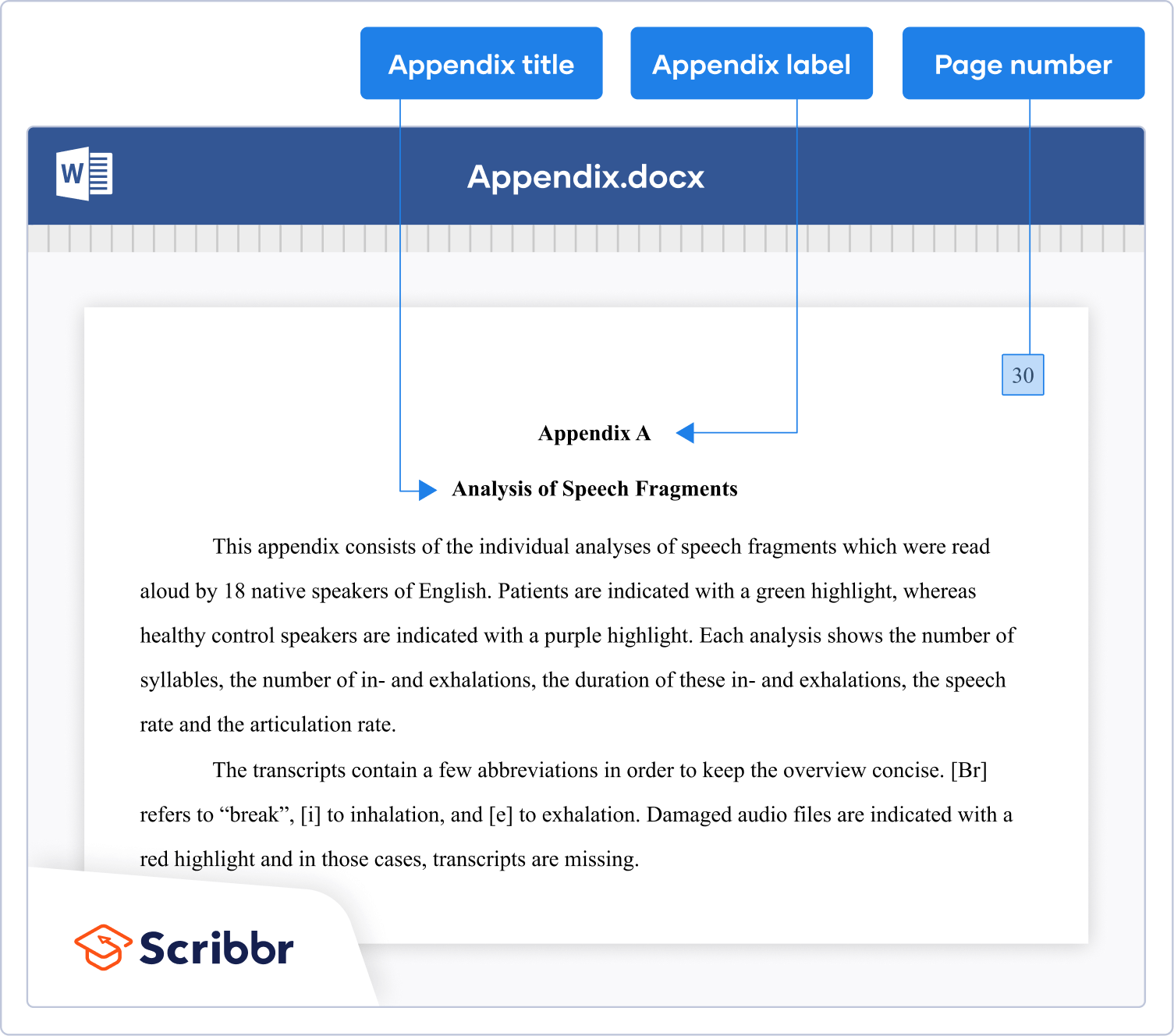
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is an appendix in a research paper, what to include in an appendix, how to format an appendix, how to refer to an appendix, where to put your appendices, other components to consider, appendix checklist, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about appendices.
In the main body of your research paper, it’s important to provide clear and concise information that supports your argument and conclusions . However, after doing all that research, you’ll often find that you have a lot of other interesting information that you want to share with your reader.
While including it all in the body would make your paper too long and unwieldy, this is exactly what an appendix is for.
As a rule of thumb, any detailed information that is not immediately needed to make your point can go in an appendix. This helps to keep your main text focused but still allows you to include the information you want to include somewhere in your paper.
Scribbr Citation Checker New
The AI-powered Citation Checker helps you avoid common mistakes such as:
- Missing commas and periods
- Incorrect usage of “et al.”
- Ampersands (&) in narrative citations
- Missing reference entries

An appendix can be used for different types of information, such as:
- Supplementary results : Research findings are often presented in different ways, but they don’t all need to go in your paper. The results most relevant to your research question should always appear in the main text, while less significant results (such as detailed descriptions of your sample or supplemental analyses that do not help answer your main question), can be put in an appendix.
- Statistical analyses : If you conducted statistical tests using software like Stata or R, you may also want to include the outputs of your analysis in an appendix.
- Further information on surveys or interviews : Written materials or transcripts related to things such as surveys and interviews can also be placed in an appendix.
You can opt to have one long appendix, but separating components (like interview transcripts, supplementary results, or surveys ) into different appendices makes the information simpler to navigate.
Here are a few tips to keep in mind:
- Always start each appendix on a new page.
- Assign it both a number (or letter) and a clear title, such as “Appendix A. Interview transcripts.” This makes it easier for your reader to find the appendix, as well as for you to refer back to it in your main text.
- Number and title the individual elements within each appendix (e.g., “Transcripts”) to make it clear what you are referring to. Restart the numbering in each appendix at 1.
It is important that you refer to each of your appendices at least once in the main body of your paper. This can be done by mentioning the appendix and its number or letter, either in parentheses or within the main part of a sentence. It’s also possible to refer to a particular component of an appendix.
Appendix B presents the correspondence exchanged with the fitness boutique. Example 2. Referring to an appendix component These results (see Appendix 2, Table 1) show that …
It is common to capitalize “Appendix” when referring to a specific appendix, but it is not mandatory. The key is just to make sure that you are consistent throughout your entire paper, similarly to consistency in capitalizing headings and titles in academic writing .
However, note that lowercase should always be used if you are referring to appendices in general. For instance, “The appendices to this paper include additional information about both the survey and the interviews .”
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
The simplest option is to add your appendices after the main body of your text, after you finish citing your sources in the citation style of your choice. If this is what you choose to do, simply continue with the next page number. Another option is to put the appendices in a separate document that is delivered with your dissertation.
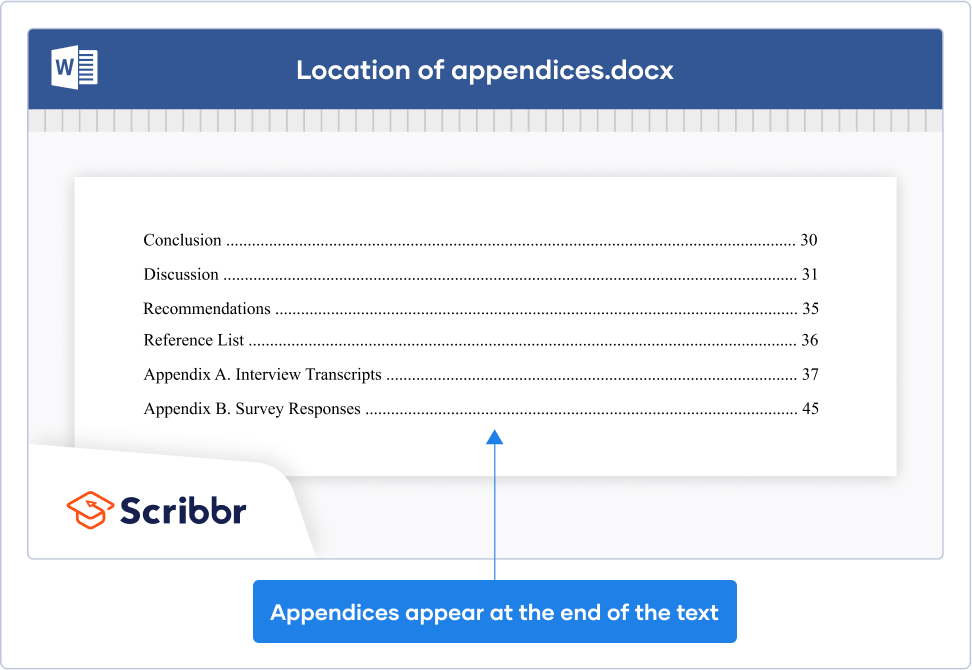
Remember that any appendices should be listed in your paper’s table of contents .
There are a few other supplementary components related to appendices that you may want to consider. These include:
- List of abbreviations : If you use a lot of abbreviations or field-specific symbols in your dissertation, it can be helpful to create a list of abbreviations .
- Glossary : If you utilize many specialized or technical terms, it can also be helpful to create a glossary .
- Tables, figures and other graphics : You may find you have too many tables, figures, and other graphics (such as charts and illustrations) to include in the main body of your dissertation. If this is the case, consider adding a figure and table list .
Checklist: Appendix
All appendices contain information that is relevant, but not essential, to the main text.
Each appendix starts on a new page.
I have given each appendix a number and clear title.
I have assigned any specific sub-components (e.g., tables and figures) their own numbers and titles.
My appendices are easy to follow and clearly formatted.
I have referred to each appendix at least once in the main text.
Your appendices look great! Use the other checklists to further improve your thesis.
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Anchoring bias
- Halo effect
- The Baader–Meinhof phenomenon
- The placebo effect
- Nonresponse bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Yes, if relevant you can and should include APA in-text citations in your appendices . Use author-date citations as you do in the main text.
Any sources cited in your appendices should appear in your reference list . Do not create a separate reference list for your appendices.
An appendix contains information that supplements the reader’s understanding of your research but is not essential to it. For example:
- Interview transcripts
- Questionnaires
- Detailed descriptions of equipment
Something is only worth including as an appendix if you refer to information from it at some point in the text (e.g. quoting from an interview transcript). If you don’t, it should probably be removed.
When you include more than one appendix in an APA Style paper , they should be labeled “Appendix A,” “Appendix B,” and so on.
When you only include a single appendix, it is simply called “Appendix” and referred to as such in the main text.
Appendices in an APA Style paper appear right at the end, after the reference list and after your tables and figures if you’ve also included these at the end.
You may have seen both “appendices” or “appendixes” as pluralizations of “ appendix .” Either spelling can be used, but “appendices” is more common (including in APA Style ). Consistency is key here: make sure you use the same spelling throughout your paper.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. & Dingemanse, K. (2023, July 18). Research Paper Appendix | Example & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved April 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/appendix/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, dissertation table of contents in word | instructions & examples, what is a glossary | definition, templates, & examples, figure and table lists | word instructions, template & examples, what is your plagiarism score.
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Research Report – Example, Writing Guide and Types
Research Report – Example, Writing Guide and Types
Table of Contents

Research Report
Definition:
Research Report is a written document that presents the results of a research project or study, including the research question, methodology, results, and conclusions, in a clear and objective manner.
The purpose of a research report is to communicate the findings of the research to the intended audience, which could be other researchers, stakeholders, or the general public.
Components of Research Report
Components of Research Report are as follows:
Introduction
The introduction sets the stage for the research report and provides a brief overview of the research question or problem being investigated. It should include a clear statement of the purpose of the study and its significance or relevance to the field of research. It may also provide background information or a literature review to help contextualize the research.
Literature Review
The literature review provides a critical analysis and synthesis of the existing research and scholarship relevant to the research question or problem. It should identify the gaps, inconsistencies, and contradictions in the literature and show how the current study addresses these issues. The literature review also establishes the theoretical framework or conceptual model that guides the research.
Methodology
The methodology section describes the research design, methods, and procedures used to collect and analyze data. It should include information on the sample or participants, data collection instruments, data collection procedures, and data analysis techniques. The methodology should be clear and detailed enough to allow other researchers to replicate the study.
The results section presents the findings of the study in a clear and objective manner. It should provide a detailed description of the data and statistics used to answer the research question or test the hypothesis. Tables, graphs, and figures may be included to help visualize the data and illustrate the key findings.
The discussion section interprets the results of the study and explains their significance or relevance to the research question or problem. It should also compare the current findings with those of previous studies and identify the implications for future research or practice. The discussion should be based on the results presented in the previous section and should avoid speculation or unfounded conclusions.
The conclusion summarizes the key findings of the study and restates the main argument or thesis presented in the introduction. It should also provide a brief overview of the contributions of the study to the field of research and the implications for practice or policy.
The references section lists all the sources cited in the research report, following a specific citation style, such as APA or MLA.
The appendices section includes any additional material, such as data tables, figures, or instruments used in the study, that could not be included in the main text due to space limitations.
Types of Research Report
Types of Research Report are as follows:
Thesis is a type of research report. A thesis is a long-form research document that presents the findings and conclusions of an original research study conducted by a student as part of a graduate or postgraduate program. It is typically written by a student pursuing a higher degree, such as a Master’s or Doctoral degree, although it can also be written by researchers or scholars in other fields.
Research Paper
Research paper is a type of research report. A research paper is a document that presents the results of a research study or investigation. Research papers can be written in a variety of fields, including science, social science, humanities, and business. They typically follow a standard format that includes an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion sections.
Technical Report
A technical report is a detailed report that provides information about a specific technical or scientific problem or project. Technical reports are often used in engineering, science, and other technical fields to document research and development work.
Progress Report
A progress report provides an update on the progress of a research project or program over a specific period of time. Progress reports are typically used to communicate the status of a project to stakeholders, funders, or project managers.
Feasibility Report
A feasibility report assesses the feasibility of a proposed project or plan, providing an analysis of the potential risks, benefits, and costs associated with the project. Feasibility reports are often used in business, engineering, and other fields to determine the viability of a project before it is undertaken.
Field Report
A field report documents observations and findings from fieldwork, which is research conducted in the natural environment or setting. Field reports are often used in anthropology, ecology, and other social and natural sciences.
Experimental Report
An experimental report documents the results of a scientific experiment, including the hypothesis, methods, results, and conclusions. Experimental reports are often used in biology, chemistry, and other sciences to communicate the results of laboratory experiments.
Case Study Report
A case study report provides an in-depth analysis of a specific case or situation, often used in psychology, social work, and other fields to document and understand complex cases or phenomena.
Literature Review Report
A literature review report synthesizes and summarizes existing research on a specific topic, providing an overview of the current state of knowledge on the subject. Literature review reports are often used in social sciences, education, and other fields to identify gaps in the literature and guide future research.
Research Report Example
Following is a Research Report Example sample for Students:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Academic Performance among High School Students
This study aims to investigate the relationship between social media use and academic performance among high school students. The study utilized a quantitative research design, which involved a survey questionnaire administered to a sample of 200 high school students. The findings indicate that there is a negative correlation between social media use and academic performance, suggesting that excessive social media use can lead to poor academic performance among high school students. The results of this study have important implications for educators, parents, and policymakers, as they highlight the need for strategies that can help students balance their social media use and academic responsibilities.
Introduction:
Social media has become an integral part of the lives of high school students. With the widespread use of social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and Snapchat, students can connect with friends, share photos and videos, and engage in discussions on a range of topics. While social media offers many benefits, concerns have been raised about its impact on academic performance. Many studies have found a negative correlation between social media use and academic performance among high school students (Kirschner & Karpinski, 2010; Paul, Baker, & Cochran, 2012).
Given the growing importance of social media in the lives of high school students, it is important to investigate its impact on academic performance. This study aims to address this gap by examining the relationship between social media use and academic performance among high school students.
Methodology:
The study utilized a quantitative research design, which involved a survey questionnaire administered to a sample of 200 high school students. The questionnaire was developed based on previous studies and was designed to measure the frequency and duration of social media use, as well as academic performance.
The participants were selected using a convenience sampling technique, and the survey questionnaire was distributed in the classroom during regular school hours. The data collected were analyzed using descriptive statistics and correlation analysis.
The findings indicate that the majority of high school students use social media platforms on a daily basis, with Facebook being the most popular platform. The results also show a negative correlation between social media use and academic performance, suggesting that excessive social media use can lead to poor academic performance among high school students.
Discussion:
The results of this study have important implications for educators, parents, and policymakers. The negative correlation between social media use and academic performance suggests that strategies should be put in place to help students balance their social media use and academic responsibilities. For example, educators could incorporate social media into their teaching strategies to engage students and enhance learning. Parents could limit their children’s social media use and encourage them to prioritize their academic responsibilities. Policymakers could develop guidelines and policies to regulate social media use among high school students.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, this study provides evidence of the negative impact of social media on academic performance among high school students. The findings highlight the need for strategies that can help students balance their social media use and academic responsibilities. Further research is needed to explore the specific mechanisms by which social media use affects academic performance and to develop effective strategies for addressing this issue.
Limitations:
One limitation of this study is the use of convenience sampling, which limits the generalizability of the findings to other populations. Future studies should use random sampling techniques to increase the representativeness of the sample. Another limitation is the use of self-reported measures, which may be subject to social desirability bias. Future studies could use objective measures of social media use and academic performance, such as tracking software and school records.
Implications:
The findings of this study have important implications for educators, parents, and policymakers. Educators could incorporate social media into their teaching strategies to engage students and enhance learning. For example, teachers could use social media platforms to share relevant educational resources and facilitate online discussions. Parents could limit their children’s social media use and encourage them to prioritize their academic responsibilities. They could also engage in open communication with their children to understand their social media use and its impact on their academic performance. Policymakers could develop guidelines and policies to regulate social media use among high school students. For example, schools could implement social media policies that restrict access during class time and encourage responsible use.
References:
- Kirschner, P. A., & Karpinski, A. C. (2010). Facebook® and academic performance. Computers in Human Behavior, 26(6), 1237-1245.
- Paul, J. A., Baker, H. M., & Cochran, J. D. (2012). Effect of online social networking on student academic performance. Journal of the Research Center for Educational Technology, 8(1), 1-19.
- Pantic, I. (2014). Online social networking and mental health. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 17(10), 652-657.
- Rosen, L. D., Carrier, L. M., & Cheever, N. A. (2013). Facebook and texting made me do it: Media-induced task-switching while studying. Computers in Human Behavior, 29(3), 948-958.
Note*: Above mention, Example is just a sample for the students’ guide. Do not directly copy and paste as your College or University assignment. Kindly do some research and Write your own.
Applications of Research Report
Research reports have many applications, including:
- Communicating research findings: The primary application of a research report is to communicate the results of a study to other researchers, stakeholders, or the general public. The report serves as a way to share new knowledge, insights, and discoveries with others in the field.
- Informing policy and practice : Research reports can inform policy and practice by providing evidence-based recommendations for decision-makers. For example, a research report on the effectiveness of a new drug could inform regulatory agencies in their decision-making process.
- Supporting further research: Research reports can provide a foundation for further research in a particular area. Other researchers may use the findings and methodology of a report to develop new research questions or to build on existing research.
- Evaluating programs and interventions : Research reports can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of programs and interventions in achieving their intended outcomes. For example, a research report on a new educational program could provide evidence of its impact on student performance.
- Demonstrating impact : Research reports can be used to demonstrate the impact of research funding or to evaluate the success of research projects. By presenting the findings and outcomes of a study, research reports can show the value of research to funders and stakeholders.
- Enhancing professional development : Research reports can be used to enhance professional development by providing a source of information and learning for researchers and practitioners in a particular field. For example, a research report on a new teaching methodology could provide insights and ideas for educators to incorporate into their own practice.
How to write Research Report
Here are some steps you can follow to write a research report:
- Identify the research question: The first step in writing a research report is to identify your research question. This will help you focus your research and organize your findings.
- Conduct research : Once you have identified your research question, you will need to conduct research to gather relevant data and information. This can involve conducting experiments, reviewing literature, or analyzing data.
- Organize your findings: Once you have gathered all of your data, you will need to organize your findings in a way that is clear and understandable. This can involve creating tables, graphs, or charts to illustrate your results.
- Write the report: Once you have organized your findings, you can begin writing the report. Start with an introduction that provides background information and explains the purpose of your research. Next, provide a detailed description of your research methods and findings. Finally, summarize your results and draw conclusions based on your findings.
- Proofread and edit: After you have written your report, be sure to proofread and edit it carefully. Check for grammar and spelling errors, and make sure that your report is well-organized and easy to read.
- Include a reference list: Be sure to include a list of references that you used in your research. This will give credit to your sources and allow readers to further explore the topic if they choose.
- Format your report: Finally, format your report according to the guidelines provided by your instructor or organization. This may include formatting requirements for headings, margins, fonts, and spacing.
Purpose of Research Report
The purpose of a research report is to communicate the results of a research study to a specific audience, such as peers in the same field, stakeholders, or the general public. The report provides a detailed description of the research methods, findings, and conclusions.
Some common purposes of a research report include:
- Sharing knowledge: A research report allows researchers to share their findings and knowledge with others in their field. This helps to advance the field and improve the understanding of a particular topic.
- Identifying trends: A research report can identify trends and patterns in data, which can help guide future research and inform decision-making.
- Addressing problems: A research report can provide insights into problems or issues and suggest solutions or recommendations for addressing them.
- Evaluating programs or interventions : A research report can evaluate the effectiveness of programs or interventions, which can inform decision-making about whether to continue, modify, or discontinue them.
- Meeting regulatory requirements: In some fields, research reports are required to meet regulatory requirements, such as in the case of drug trials or environmental impact studies.
When to Write Research Report
A research report should be written after completing the research study. This includes collecting data, analyzing the results, and drawing conclusions based on the findings. Once the research is complete, the report should be written in a timely manner while the information is still fresh in the researcher’s mind.
In academic settings, research reports are often required as part of coursework or as part of a thesis or dissertation. In this case, the report should be written according to the guidelines provided by the instructor or institution.
In other settings, such as in industry or government, research reports may be required to inform decision-making or to comply with regulatory requirements. In these cases, the report should be written as soon as possible after the research is completed in order to inform decision-making in a timely manner.
Overall, the timing of when to write a research report depends on the purpose of the research, the expectations of the audience, and any regulatory requirements that need to be met. However, it is important to complete the report in a timely manner while the information is still fresh in the researcher’s mind.
Characteristics of Research Report
There are several characteristics of a research report that distinguish it from other types of writing. These characteristics include:
- Objective: A research report should be written in an objective and unbiased manner. It should present the facts and findings of the research study without any personal opinions or biases.
- Systematic: A research report should be written in a systematic manner. It should follow a clear and logical structure, and the information should be presented in a way that is easy to understand and follow.
- Detailed: A research report should be detailed and comprehensive. It should provide a thorough description of the research methods, results, and conclusions.
- Accurate : A research report should be accurate and based on sound research methods. The findings and conclusions should be supported by data and evidence.
- Organized: A research report should be well-organized. It should include headings and subheadings to help the reader navigate the report and understand the main points.
- Clear and concise: A research report should be written in clear and concise language. The information should be presented in a way that is easy to understand, and unnecessary jargon should be avoided.
- Citations and references: A research report should include citations and references to support the findings and conclusions. This helps to give credit to other researchers and to provide readers with the opportunity to further explore the topic.
Advantages of Research Report
Research reports have several advantages, including:
- Communicating research findings: Research reports allow researchers to communicate their findings to a wider audience, including other researchers, stakeholders, and the general public. This helps to disseminate knowledge and advance the understanding of a particular topic.
- Providing evidence for decision-making : Research reports can provide evidence to inform decision-making, such as in the case of policy-making, program planning, or product development. The findings and conclusions can help guide decisions and improve outcomes.
- Supporting further research: Research reports can provide a foundation for further research on a particular topic. Other researchers can build on the findings and conclusions of the report, which can lead to further discoveries and advancements in the field.
- Demonstrating expertise: Research reports can demonstrate the expertise of the researchers and their ability to conduct rigorous and high-quality research. This can be important for securing funding, promotions, and other professional opportunities.
- Meeting regulatory requirements: In some fields, research reports are required to meet regulatory requirements, such as in the case of drug trials or environmental impact studies. Producing a high-quality research report can help ensure compliance with these requirements.
Limitations of Research Report
Despite their advantages, research reports also have some limitations, including:
- Time-consuming: Conducting research and writing a report can be a time-consuming process, particularly for large-scale studies. This can limit the frequency and speed of producing research reports.
- Expensive: Conducting research and producing a report can be expensive, particularly for studies that require specialized equipment, personnel, or data. This can limit the scope and feasibility of some research studies.
- Limited generalizability: Research studies often focus on a specific population or context, which can limit the generalizability of the findings to other populations or contexts.
- Potential bias : Researchers may have biases or conflicts of interest that can influence the findings and conclusions of the research study. Additionally, participants may also have biases or may not be representative of the larger population, which can limit the validity and reliability of the findings.
- Accessibility: Research reports may be written in technical or academic language, which can limit their accessibility to a wider audience. Additionally, some research may be behind paywalls or require specialized access, which can limit the ability of others to read and use the findings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Because this domain of research is less susceptible to biases, the findings are generally seen as credible and reliable information. The following are sample templates of where quantitative research can be utilized. 1. Business Research Report Template. Details. File Format. MS Word. Pages. Google Docs.
FREE 10+ Quantitative Research Report Templates in MS Word | PDF. In the natural and social sciences, and perhaps in other areas, quantitative analysis refers to the comprehensive empirical study of observed phenomena by statistical, computational and/or mathematical techniques. Quantitative research aims to establish and utilize phenomena-related mathematical hypotheses, models, and theories.
INTRODUCTION. Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses.1,2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results.3,4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the ...
These sample papers demonstrate APA Style formatting standards for different student paper types. Students may write the same types of papers as professional authors (e.g., quantitative studies, literature reviews) or other types of papers for course assignments (e.g., reaction or response papers, discussion posts), dissertations, and theses.
Reporting Research Results in APA Style | Tips & Examples. Published on December 21, 2020 by Pritha Bhandari.Revised on January 17, 2024. The results section of a quantitative research paper is where you summarize your data and report the findings of any relevant statistical analyses.. The APA manual provides rigorous guidelines for what to report in quantitative research papers in the fields ...
Quantitative Research Design (JARS-Quant) The current JARS-Quant standards, released in 2018, expand and revise the types of research methodologies covered in the original JARS, which were published in 2008. JARS-Quant include guidance for manuscripts that report. In addition, JARS-Quant now divides hypotheses, analyses, and conclusions ...
Revised on June 22, 2023. Quantitative research is the process of collecting and analyzing numerical data. It can be used to find patterns and averages, make predictions, test causal relationships, and generalize results to wider populations. Quantitative research is the opposite of qualitative research, which involves collecting and analyzing ...
Execute a quantitative research report using key elements for accuracy and openness. So you've completed your quantitative analyses and are ready to report your results. We're going to spend some time talking about what matters in quantitative research reports, but the very first thing to understand is this: openness with your data and ...
The most logical way to structure quantitative results is to frame them around your research questions or hypotheses. For each question or hypothesis, share: A reminder of the type of analysis you used (e.g., a two-sample t test or simple linear regression). A more detailed description of your analysis should go in your methodology section.
The abstract provides a concise and comprehensive summary of a research report. Your style should be brief but not use note form. Look at examples in journal articles. It should aim to explain very briefly (about 150 words) the following: ... Quantitative paper template. Quantitative professional paper template: Adapted from "Fake News, Fast ...
Download research report template. This research report template is appropriate when: You need to write a report after conducting surveys, interviews, focus groups, or any other type of qualitative or quantitative research. You need to write a report for a simple baseline or endline survey, or needs assessment.
FREE 10+ Quantitative Research Report Samples & Templates. Here are some professionally written quantitative research report samples and templates preformatted in PDF and MS Word file formats. These sample templates contain pre-made suggestive content that you can use as a reference. These templates are also available for instant download.
Abstract. Summarizing quantitative data and its effective presentation and discussion can be challenging for students and researchers. This chapter provides a framework for adequately reporting findings from quantitative analysis in a research study for those contemplating to write a research paper. The rationale underpinning the reporting ...
The research paper template covers the following core sections: The title page/cover page. Abstract (sometimes also called the executive summary) Section 1: Introduction. Section 2: Literature review. Section 3: Methodology. Section 4: Findings /results. Section 5: Discussion. Section 6: Conclusion.
time, and because the original JARS Working Group focused exclusively on quantitative research, the P&C Board appointed a separate committee to develop reporting standards for qualitative research.3 The book you are reading presents the revised reporting stan-dards that came out of the efforts related to quantitative research. A separate volume is
A rough sequence of steps for writing a quantitative research report describes in this section: 1. Specify a summary or abstract of the report to give a quick picture of the research article, thesis, review paper, conference proceeding, or in-depth analysis of a particular subject. 2. Define the research problem and discuss the methodology ...
Types of Quantitative Research Methods. Quantitative research can be conducted in two different methods: Primary Quantitative Research Methods. The most commonly used form of performing market research is primary quantitative analysis. The distinctive feature of primary research is that the researcher focuses on specifically collecting data, rather than on data collected from previously ...
Quantitative Research Paper Template. Quantitative Research Checklist Template. Quantitative Research Survey. Research Report Gantt Chart Template. APA Research Template. Research on Effective Post-Sale Incentives Template. Research on the Impact of Post-Sale Support on Customer Loyalty Template. Research on Predicting Commission Payouts Based ...
Recent years have seen dramatic changes in research practices in psychological science. In particular, preregistration of study plans before conducting a study has been identified as an important tool to help increase the transparency of science and to improve the robustness of psychological research findings. This article presents the Psychological Research Preregistration-Quantitative (PRP ...
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management".
Quantitative Research; Quantitative Research. Get Clear, Concise, and Professional Quantitative Research Templates from Template.net to Help You Gather Numerical Data and Collate Information Properly. Choose from Ready-made Document Examples Like Quantitative Research Data Analysis, Question, Report, Guide, and Brand Research Report Templates.
Research Paper Appendix | Example & Templates. Published on August 4, 2022 by Tegan George and Kirsten Dingemanse. Revised on July 18, 2023. An appendix is a supplementary document that facilitates your reader's understanding of your research but is not essential to your core argument. Appendices are a useful tool for providing additional information or clarification in a research paper ...
Following is a Research Report Example sample for Students: Title: The Impact of Social Media on Academic Performance among High School Students. ... The study utilized a quantitative research design, which involved a survey questionnaire administered to a sample of 200 high school students. The findings indicate that there is a negative ...