
How To Write A Research Paper
Step-By-Step Tutorial With Examples + FREE Template
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewer: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | March 2024
For many students, crafting a strong research paper from scratch can feel like a daunting task – and rightly so! In this post, we’ll unpack what a research paper is, what it needs to do , and how to write one – in three easy steps. 🙂
Overview: Writing A Research Paper
What (exactly) is a research paper.
- How to write a research paper
- Stage 1 : Topic & literature search
- Stage 2 : Structure & outline
- Stage 3 : Iterative writing
- Key takeaways
Let’s start by asking the most important question, “ What is a research paper? ”.
Simply put, a research paper is a scholarly written work where the writer (that’s you!) answers a specific question (this is called a research question ) through evidence-based arguments . Evidence-based is the keyword here. In other words, a research paper is different from an essay or other writing assignments that draw from the writer’s personal opinions or experiences. With a research paper, it’s all about building your arguments based on evidence (we’ll talk more about that evidence a little later).
Now, it’s worth noting that there are many different types of research papers , including analytical papers (the type I just described), argumentative papers, and interpretative papers. Here, we’ll focus on analytical papers , as these are some of the most common – but if you’re keen to learn about other types of research papers, be sure to check out the rest of the blog .
With that basic foundation laid, let’s get down to business and look at how to write a research paper .

Overview: The 3-Stage Process
While there are, of course, many potential approaches you can take to write a research paper, there are typically three stages to the writing process. So, in this tutorial, we’ll present a straightforward three-step process that we use when working with students at Grad Coach.
These three steps are:
- Finding a research topic and reviewing the existing literature
- Developing a provisional structure and outline for your paper, and
- Writing up your initial draft and then refining it iteratively
Let’s dig into each of these.
Need a helping hand?
Step 1: Find a topic and review the literature
As we mentioned earlier, in a research paper, you, as the researcher, will try to answer a question . More specifically, that’s called a research question , and it sets the direction of your entire paper. What’s important to understand though is that you’ll need to answer that research question with the help of high-quality sources – for example, journal articles, government reports, case studies, and so on. We’ll circle back to this in a minute.
The first stage of the research process is deciding on what your research question will be and then reviewing the existing literature (in other words, past studies and papers) to see what they say about that specific research question. In some cases, your professor may provide you with a predetermined research question (or set of questions). However, in many cases, you’ll need to find your own research question within a certain topic area.
Finding a strong research question hinges on identifying a meaningful research gap – in other words, an area that’s lacking in existing research. There’s a lot to unpack here, so if you wanna learn more, check out the plain-language explainer video below.
Once you’ve figured out which question (or questions) you’ll attempt to answer in your research paper, you’ll need to do a deep dive into the existing literature – this is called a “ literature search ”. Again, there are many ways to go about this, but your most likely starting point will be Google Scholar .
If you’re new to Google Scholar, think of it as Google for the academic world. You can start by simply entering a few different keywords that are relevant to your research question and it will then present a host of articles for you to review. What you want to pay close attention to here is the number of citations for each paper – the more citations a paper has, the more credible it is (generally speaking – there are some exceptions, of course).

Ideally, what you’re looking for are well-cited papers that are highly relevant to your topic. That said, keep in mind that citations are a cumulative metric , so older papers will often have more citations than newer papers – just because they’ve been around for longer. So, don’t fixate on this metric in isolation – relevance and recency are also very important.
Beyond Google Scholar, you’ll also definitely want to check out academic databases and aggregators such as Science Direct, PubMed, JStor and so on. These will often overlap with the results that you find in Google Scholar, but they can also reveal some hidden gems – so, be sure to check them out.
Once you’ve worked your way through all the literature, you’ll want to catalogue all this information in some sort of spreadsheet so that you can easily recall who said what, when and within what context. If you’d like, we’ve got a free literature spreadsheet that helps you do exactly that.

Step 2: Develop a structure and outline
With your research question pinned down and your literature digested and catalogued, it’s time to move on to planning your actual research paper .
It might sound obvious, but it’s really important to have some sort of rough outline in place before you start writing your paper. So often, we see students eagerly rushing into the writing phase, only to land up with a disjointed research paper that rambles on in multiple
Now, the secret here is to not get caught up in the fine details . Realistically, all you need at this stage is a bullet-point list that describes (in broad strokes) what you’ll discuss and in what order. It’s also useful to remember that you’re not glued to this outline – in all likelihood, you’ll chop and change some sections once you start writing, and that’s perfectly okay. What’s important is that you have some sort of roadmap in place from the start.

At this stage you might be wondering, “ But how should I structure my research paper? ”. Well, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution here, but in general, a research paper will consist of a few relatively standardised components:
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Methodology
Let’s take a look at each of these.
First up is the introduction section . As the name suggests, the purpose of the introduction is to set the scene for your research paper. There are usually (at least) four ingredients that go into this section – these are the background to the topic, the research problem and resultant research question , and the justification or rationale. If you’re interested, the video below unpacks the introduction section in more detail.
The next section of your research paper will typically be your literature review . Remember all that literature you worked through earlier? Well, this is where you’ll present your interpretation of all that content . You’ll do this by writing about recent trends, developments, and arguments within the literature – but more specifically, those that are relevant to your research question . The literature review can oftentimes seem a little daunting, even to seasoned researchers, so be sure to check out our extensive collection of literature review content here .
With the introduction and lit review out of the way, the next section of your paper is the research methodology . In a nutshell, the methodology section should describe to your reader what you did (beyond just reviewing the existing literature) to answer your research question. For example, what data did you collect, how did you collect that data, how did you analyse that data and so on? For each choice, you’ll also need to justify why you chose to do it that way, and what the strengths and weaknesses of your approach were.
Now, it’s worth mentioning that for some research papers, this aspect of the project may be a lot simpler . For example, you may only need to draw on secondary sources (in other words, existing data sets). In some cases, you may just be asked to draw your conclusions from the literature search itself (in other words, there may be no data analysis at all). But, if you are required to collect and analyse data, you’ll need to pay a lot of attention to the methodology section. The video below provides an example of what the methodology section might look like.
By this stage of your paper, you will have explained what your research question is, what the existing literature has to say about that question, and how you analysed additional data to try to answer your question. So, the natural next step is to present your analysis of that data . This section is usually called the “results” or “analysis” section and this is where you’ll showcase your findings.
Depending on your school’s requirements, you may need to present and interpret the data in one section – or you might split the presentation and the interpretation into two sections. In the latter case, your “results” section will just describe the data, and the “discussion” is where you’ll interpret that data and explicitly link your analysis back to your research question. If you’re not sure which approach to take, check in with your professor or take a look at past papers to see what the norms are for your programme.
Alright – once you’ve presented and discussed your results, it’s time to wrap it up . This usually takes the form of the “ conclusion ” section. In the conclusion, you’ll need to highlight the key takeaways from your study and close the loop by explicitly answering your research question. Again, the exact requirements here will vary depending on your programme (and you may not even need a conclusion section at all) – so be sure to check with your professor if you’re unsure.
Step 3: Write and refine
Finally, it’s time to get writing. All too often though, students hit a brick wall right about here… So, how do you avoid this happening to you?
Well, there’s a lot to be said when it comes to writing a research paper (or any sort of academic piece), but we’ll share three practical tips to help you get started.
First and foremost , it’s essential to approach your writing as an iterative process. In other words, you need to start with a really messy first draft and then polish it over multiple rounds of editing. Don’t waste your time trying to write a perfect research paper in one go. Instead, take the pressure off yourself by adopting an iterative approach.
Secondly , it’s important to always lean towards critical writing , rather than descriptive writing. What does this mean? Well, at the simplest level, descriptive writing focuses on the “ what ”, while critical writing digs into the “ so what ” – in other words, the implications. If you’re not familiar with these two types of writing, don’t worry! You can find a plain-language explanation here.
Last but not least, you’ll need to get your referencing right. Specifically, you’ll need to provide credible, correctly formatted citations for the statements you make. We see students making referencing mistakes all the time and it costs them dearly. The good news is that you can easily avoid this by using a simple reference manager . If you don’t have one, check out our video about Mendeley, an easy (and free) reference management tool that you can start using today.
Recap: Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground here. To recap, the three steps to writing a high-quality research paper are:
- To choose a research question and review the literature
- To plan your paper structure and draft an outline
- To take an iterative approach to writing, focusing on critical writing and strong referencing
Remember, this is just a b ig-picture overview of the research paper development process and there’s a lot more nuance to unpack. So, be sure to grab a copy of our free research paper template to learn more about how to write a research paper.
You Might Also Like:

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Writing a Paper: Writing a Paper
Writing a paper.
The Walden Writing Center staff is dedicated to ensuring your transition to a writing intensive program is a smooth one. In the pages listed on the left you will find all the information you need to master the craft of scholarly writing.
If you are new to scholarly writing, it may be helpful to remember that writing is a process, not an event. Some common steps in the life cycle of a writing project are outlined below. Click each step to access information and resources on that topic, or navigate through our interactive "Life Cycle of a Paper" project at the bottom of the page.
Good luck with your scholarly writing, and if you have questions, Ask OASIS .
Writing Process
Click on each step to find out more about each part of the writing process.
Crash Course in Scholarly Writing Video Playlist
Note that these videos were created while APA 6 was the style guide edition in use. There may be some examples of writing that have not been updated to APA 7 guidelines.


Related Resources
Didn't find what you need? Search our website or email us .
Read our website accessibility and accommodation statement .
- Next Page: Goal Setting
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
- How to write a research paper
Last updated
11 January 2024
Reviewed by
With proper planning, knowledge, and framework, completing a research paper can be a fulfilling and exciting experience.
Though it might initially sound slightly intimidating, this guide will help you embrace the challenge.
By documenting your findings, you can inspire others and make a difference in your field. Here's how you can make your research paper unique and comprehensive.
- What is a research paper?
Research papers allow you to demonstrate your knowledge and understanding of a particular topic. These papers are usually lengthier and more detailed than typical essays, requiring deeper insight into the chosen topic.
To write a research paper, you must first choose a topic that interests you and is relevant to the field of study. Once you’ve selected your topic, gathering as many relevant resources as possible, including books, scholarly articles, credible websites, and other academic materials, is essential. You must then read and analyze these sources, summarizing their key points and identifying gaps in the current research.
You can formulate your ideas and opinions once you thoroughly understand the existing research. To get there might involve conducting original research, gathering data, or analyzing existing data sets. It could also involve presenting an original argument or interpretation of the existing research.
Writing a successful research paper involves presenting your findings clearly and engagingly, which might involve using charts, graphs, or other visual aids to present your data and using concise language to explain your findings. You must also ensure your paper adheres to relevant academic formatting guidelines, including proper citations and references.
Overall, writing a research paper requires a significant amount of time, effort, and attention to detail. However, it is also an enriching experience that allows you to delve deeply into a subject that interests you and contribute to the existing body of knowledge in your chosen field.
- How long should a research paper be?
Research papers are deep dives into a topic. Therefore, they tend to be longer pieces of work than essays or opinion pieces.
However, a suitable length depends on the complexity of the topic and your level of expertise. For instance, are you a first-year college student or an experienced professional?
Also, remember that the best research papers provide valuable information for the benefit of others. Therefore, the quality of information matters most, not necessarily the length. Being concise is valuable.
Following these best practice steps will help keep your process simple and productive:
1. Gaining a deep understanding of any expectations
Before diving into your intended topic or beginning the research phase, take some time to orient yourself. Suppose there’s a specific topic assigned to you. In that case, it’s essential to deeply understand the question and organize your planning and approach in response. Pay attention to the key requirements and ensure you align your writing accordingly.
This preparation step entails
Deeply understanding the task or assignment
Being clear about the expected format and length
Familiarizing yourself with the citation and referencing requirements
Understanding any defined limits for your research contribution
Where applicable, speaking to your professor or research supervisor for further clarification
2. Choose your research topic
Select a research topic that aligns with both your interests and available resources. Ideally, focus on a field where you possess significant experience and analytical skills. In crafting your research paper, it's crucial to go beyond summarizing existing data and contribute fresh insights to the chosen area.
Consider narrowing your focus to a specific aspect of the topic. For example, if exploring the link between technology and mental health, delve into how social media use during the pandemic impacts the well-being of college students. Conducting interviews and surveys with students could provide firsthand data and unique perspectives, adding substantial value to the existing knowledge.
When finalizing your topic, adhere to legal and ethical norms in the relevant area (this ensures the integrity of your research, protects participants' rights, upholds intellectual property standards, and ensures transparency and accountability). Following these principles not only maintains the credibility of your work but also builds trust within your academic or professional community.
For instance, in writing about medical research, consider legal and ethical norms, including patient confidentiality laws and informed consent requirements. Similarly, if analyzing user data on social media platforms, be mindful of data privacy regulations, ensuring compliance with laws governing personal information collection and use. Aligning with legal and ethical standards not only avoids potential issues but also underscores the responsible conduct of your research.
3. Gather preliminary research
Once you’ve landed on your topic, it’s time to explore it further. You’ll want to discover more about available resources and existing research relevant to your assignment at this stage.
This exploratory phase is vital as you may discover issues with your original idea or realize you have insufficient resources to explore the topic effectively. This key bit of groundwork allows you to redirect your research topic in a different, more feasible, or more relevant direction if necessary.
Spending ample time at this stage ensures you gather everything you need, learn as much as you can about the topic, and discover gaps where the topic has yet to be sufficiently covered, offering an opportunity to research it further.
4. Define your research question
To produce a well-structured and focused paper, it is imperative to formulate a clear and precise research question that will guide your work. Your research question must be informed by the existing literature and tailored to the scope and objectives of your project. By refining your focus, you can produce a thoughtful and engaging paper that effectively communicates your ideas to your readers.
5. Write a thesis statement
A thesis statement is a one-to-two-sentence summary of your research paper's main argument or direction. It serves as an overall guide to summarize the overall intent of the research paper for you and anyone wanting to know more about the research.
A strong thesis statement is:
Concise and clear: Explain your case in simple sentences (avoid covering multiple ideas). It might help to think of this section as an elevator pitch.
Specific: Ensure that there is no ambiguity in your statement and that your summary covers the points argued in the paper.
Debatable: A thesis statement puts forward a specific argument––it is not merely a statement but a debatable point that can be analyzed and discussed.
Here are three thesis statement examples from different disciplines:
Psychology thesis example: "We're studying adults aged 25-40 to see if taking short breaks for mindfulness can help with stress. Our goal is to find practical ways to manage anxiety better."
Environmental science thesis example: "This research paper looks into how having more city parks might make the air cleaner and keep people healthier. I want to find out if more green spaces means breathing fewer carcinogens in big cities."
UX research thesis example: "This study focuses on improving mobile banking for older adults using ethnographic research, eye-tracking analysis, and interactive prototyping. We investigate the usefulness of eye-tracking analysis with older individuals, aiming to spark debate and offer fresh perspectives on UX design and digital inclusivity for the aging population."
6. Conduct in-depth research
A research paper doesn’t just include research that you’ve uncovered from other papers and studies but your fresh insights, too. You will seek to become an expert on your topic––understanding the nuances in the current leading theories. You will analyze existing research and add your thinking and discoveries. It's crucial to conduct well-designed research that is rigorous, robust, and based on reliable sources. Suppose a research paper lacks evidence or is biased. In that case, it won't benefit the academic community or the general public. Therefore, examining the topic thoroughly and furthering its understanding through high-quality research is essential. That usually means conducting new research. Depending on the area under investigation, you may conduct surveys, interviews, diary studies, or observational research to uncover new insights or bolster current claims.
7. Determine supporting evidence
Not every piece of research you’ve discovered will be relevant to your research paper. It’s important to categorize the most meaningful evidence to include alongside your discoveries. It's important to include evidence that doesn't support your claims to avoid exclusion bias and ensure a fair research paper.
8. Write a research paper outline
Before diving in and writing the whole paper, start with an outline. It will help you to see if more research is needed, and it will provide a framework by which to write a more compelling paper. Your supervisor may even request an outline to approve before beginning to write the first draft of the full paper. An outline will include your topic, thesis statement, key headings, short summaries of the research, and your arguments.
9. Write your first draft
Once you feel confident about your outline and sources, it’s time to write your first draft. While penning a long piece of content can be intimidating, if you’ve laid the groundwork, you will have a structure to help you move steadily through each section. To keep up motivation and inspiration, it’s often best to keep the pace quick. Stopping for long periods can interrupt your flow and make jumping back in harder than writing when things are fresh in your mind.
10. Cite your sources correctly
It's always a good practice to give credit where it's due, and the same goes for citing any works that have influenced your paper. Building your arguments on credible references adds value and authenticity to your research. In the formatting guidelines section, you’ll find an overview of different citation styles (MLA, CMOS, or APA), which will help you meet any publishing or academic requirements and strengthen your paper's credibility. It is essential to follow the guidelines provided by your school or the publication you are submitting to ensure the accuracy and relevance of your citations.
11. Ensure your work is original
It is crucial to ensure the originality of your paper, as plagiarism can lead to serious consequences. To avoid plagiarism, you should use proper paraphrasing and quoting techniques. Paraphrasing is rewriting a text in your own words while maintaining the original meaning. Quoting involves directly citing the source. Giving credit to the original author or source is essential whenever you borrow their ideas or words. You can also use plagiarism detection tools such as Scribbr or Grammarly to check the originality of your paper. These tools compare your draft writing to a vast database of online sources. If you find any accidental plagiarism, you should correct it immediately by rephrasing or citing the source.
12. Revise, edit, and proofread
One of the essential qualities of excellent writers is their ability to understand the importance of editing and proofreading. Even though it's tempting to call it a day once you've finished your writing, editing your work can significantly improve its quality. It's natural to overlook the weaker areas when you've just finished writing a paper. Therefore, it's best to take a break of a day or two, or even up to a week, to refresh your mind. This way, you can return to your work with a new perspective. After some breathing room, you can spot any inconsistencies, spelling and grammar errors, typos, or missing citations and correct them.
- The best research paper format
The format of your research paper should align with the requirements set forth by your college, school, or target publication.
There is no one “best” format, per se. Depending on the stated requirements, you may need to include the following elements:
Title page: The title page of a research paper typically includes the title, author's name, and institutional affiliation and may include additional information such as a course name or instructor's name.
Table of contents: Include a table of contents to make it easy for readers to find specific sections of your paper.
Abstract: The abstract is a summary of the purpose of the paper.
Methods : In this section, describe the research methods used. This may include collecting data, conducting interviews, or doing field research.
Results: Summarize the conclusions you drew from your research in this section.
Discussion: In this section, discuss the implications of your research. Be sure to mention any significant limitations to your approach and suggest areas for further research.
Tables, charts, and illustrations: Use tables, charts, and illustrations to help convey your research findings and make them easier to understand.
Works cited or reference page: Include a works cited or reference page to give credit to the sources that you used to conduct your research.
Bibliography: Provide a list of all the sources you consulted while conducting your research.
Dedication and acknowledgments : Optionally, you may include a dedication and acknowledgments section to thank individuals who helped you with your research.
- General style and formatting guidelines
Formatting your research paper means you can submit it to your college, journal, or other publications in compliance with their criteria.
Research papers tend to follow the American Psychological Association (APA), Modern Language Association (MLA), or Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS) guidelines.
Here’s how each style guide is typically used:
Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS):
CMOS is a versatile style guide used for various types of writing. It's known for its flexibility and use in the humanities. CMOS provides guidelines for citations, formatting, and overall writing style. It allows for both footnotes and in-text citations, giving writers options based on their preferences or publication requirements.
American Psychological Association (APA):
APA is common in the social sciences. It’s hailed for its clarity and emphasis on precision. It has specific rules for citing sources, creating references, and formatting papers. APA style uses in-text citations with an accompanying reference list. It's designed to convey information efficiently and is widely used in academic and scientific writing.
Modern Language Association (MLA):
MLA is widely used in the humanities, especially literature and language studies. It emphasizes the author-page format for in-text citations and provides guidelines for creating a "Works Cited" page. MLA is known for its focus on the author's name and the literary works cited. It’s frequently used in disciplines that prioritize literary analysis and critical thinking.
To confirm you're using the latest style guide, check the official website or publisher's site for updates, consult academic resources, and verify the guide's publication date. Online platforms and educational resources may also provide summaries and alerts about any revisions or additions to the style guide.
Citing sources
When working on your research paper, it's important to cite the sources you used properly. Your citation style will guide you through this process. Generally, there are three parts to citing sources in your research paper:
First, provide a brief citation in the body of your essay. This is also known as a parenthetical or in-text citation.
Second, include a full citation in the Reference list at the end of your paper. Different types of citations include in-text citations, footnotes, and reference lists.
In-text citations include the author's surname and the date of the citation.
Footnotes appear at the bottom of each page of your research paper. They may also be summarized within a reference list at the end of the paper.
A reference list includes all of the research used within the paper at the end of the document. It should include the author, date, paper title, and publisher listed in the order that aligns with your citation style.
10 research paper writing tips:
Following some best practices is essential to writing a research paper that contributes to your field of study and creates a positive impact.
These tactics will help you structure your argument effectively and ensure your work benefits others:
Clear and precise language: Ensure your language is unambiguous. Use academic language appropriately, but keep it simple. Also, provide clear takeaways for your audience.
Effective idea separation: Organize the vast amount of information and sources in your paper with paragraphs and titles. Create easily digestible sections for your readers to navigate through.
Compelling intro: Craft an engaging introduction that captures your reader's interest. Hook your audience and motivate them to continue reading.
Thorough revision and editing: Take the time to review and edit your paper comprehensively. Use tools like Grammarly to detect and correct small, overlooked errors.
Thesis precision: Develop a clear and concise thesis statement that guides your paper. Ensure that your thesis aligns with your research's overall purpose and contribution.
Logical flow of ideas: Maintain a logical progression throughout the paper. Use transitions effectively to connect different sections and maintain coherence.
Critical evaluation of sources: Evaluate and critically assess the relevance and reliability of your sources. Ensure that your research is based on credible and up-to-date information.
Thematic consistency: Maintain a consistent theme throughout the paper. Ensure that all sections contribute cohesively to the overall argument.
Relevant supporting evidence: Provide concise and relevant evidence to support your arguments. Avoid unnecessary details that may distract from the main points.
Embrace counterarguments: Acknowledge and address opposing views to strengthen your position. Show that you have considered alternative arguments in your field.
7 research tips
If you want your paper to not only be well-written but also contribute to the progress of human knowledge, consider these tips to take your paper to the next level:
Selecting the appropriate topic: The topic you select should align with your area of expertise, comply with the requirements of your project, and have sufficient resources for a comprehensive investigation.
Use academic databases: Academic databases such as PubMed, Google Scholar, and JSTOR offer a wealth of research papers that can help you discover everything you need to know about your chosen topic.
Critically evaluate sources: It is important not to accept research findings at face value. Instead, it is crucial to critically analyze the information to avoid jumping to conclusions or overlooking important details. A well-written research paper requires a critical analysis with thorough reasoning to support claims.
Diversify your sources: Expand your research horizons by exploring a variety of sources beyond the standard databases. Utilize books, conference proceedings, and interviews to gather diverse perspectives and enrich your understanding of the topic.
Take detailed notes: Detailed note-taking is crucial during research and can help you form the outline and body of your paper.
Stay up on trends: Keep abreast of the latest developments in your field by regularly checking for recent publications. Subscribe to newsletters, follow relevant journals, and attend conferences to stay informed about emerging trends and advancements.
Engage in peer review: Seek feedback from peers or mentors to ensure the rigor and validity of your research. Peer review helps identify potential weaknesses in your methodology and strengthens the overall credibility of your findings.
- The real-world impact of research papers
Writing a research paper is more than an academic or business exercise. The experience provides an opportunity to explore a subject in-depth, broaden one's understanding, and arrive at meaningful conclusions. With careful planning, dedication, and hard work, writing a research paper can be a fulfilling and enriching experience contributing to advancing knowledge.
How do I publish my research paper?
Many academics wish to publish their research papers. While challenging, your paper might get traction if it covers new and well-written information. To publish your research paper, find a target publication, thoroughly read their guidelines, format your paper accordingly, and send it to them per their instructions. You may need to include a cover letter, too. After submission, your paper may be peer-reviewed by experts to assess its legitimacy, quality, originality, and methodology. Following review, you will be informed by the publication whether they have accepted or rejected your paper.
What is a good opening sentence for a research paper?
Beginning your research paper with a compelling introduction can ensure readers are interested in going further. A relevant quote, a compelling statistic, or a bold argument can start the paper and hook your reader. Remember, though, that the most important aspect of a research paper is the quality of the information––not necessarily your ability to storytell, so ensure anything you write aligns with your goals.
Research paper vs. a research proposal—what’s the difference?
While some may confuse research papers and proposals, they are different documents.
A research proposal comes before a research paper. It is a detailed document that outlines an intended area of exploration. It includes the research topic, methodology, timeline, sources, and potential conclusions. Research proposals are often required when seeking approval to conduct research.
A research paper is a summary of research findings. A research paper follows a structured format to present those findings and construct an argument or conclusion.
Get started today
Go from raw data to valuable insights with a flexible research platform
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 21 December 2023
Last updated: 16 December 2023
Last updated: 6 October 2023
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 25 November 2023
Last updated: 15 February 2024
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 10 April 2023
Last updated: 20 December 2023
Latest articles
Related topics.
- 10 research paper
Log in or sign up
Get started for free
Writing an Academic Paper: A Beginner’s Guide

Table of contents

Catherine Miller
An academic paper might be quite different from other writing you’ve done before. But never fear — with my experience of writing as an undergraduate, Master’s student, and teacher, I’m here to help you understand the ins and outs of writing an academic paper so you’ll ace your next assignment.
Academic writing is done by scholars for an audience of other scholars. This means your audience is likely to be quite informed about your field of study, so you won’t need to start from the absolute basics. But, it also means your piece needs to be well-researched, with a clearly thought-out argument or informative literature review supported by academic sources.
In this article, I’ll give you a step-by-step guide to putting together an academic paper that will get you a top grade.

Topic Selection
If you need to write an academic paper as part of your class assignment, you might have clear instructions on what the topic needs to be. This could be a question to answer, an argument statement to support or refute, or a general topic area to research which you can then develop your own specific paper title for. Make sure you double check the grading requirements and any other guidelines provided by your teacher or institution.
If you’ve got some freedom to come up with your own ideas, spending some time reading around your subject and brainstorming potential topics could be a good place to start.
Brainstorming Ideas
It’s wise to start by reading the recommended course material, especially the key texts. If you’re not sure what the best books and articles for additional reading might be, ask your professor for some recommendations.
As you read, keep an eye out for ideas that might be ripe for exploration. If your paper is supposed to be an argument, look out for areas of the topic that seem to generate debate.
It’s a good idea to make notes as you go, keeping track of potential citations and the information you’ll need to include in your bibliography. Organized notes can make all the difference when it comes to putting your finished paper together! You could do this using software like Notion , Evernote , or Google Keep , a spreadsheet, or even good old pen and paper.
Selecting a Focused Topic
Most academic papers will require you to come up with an argument, and a good place to start is narrowing down your thesis statement, i.e. the main point of your paper. This needs to be a defendable statement, so picking something for the sake of being controversial might leave you in a tricky position if there aren’t enough sources to back it up. Additionally, it needs to be something focused enough to explore in a few pages, rather than needing a whole book to explain.
For example ‘ The economic situation of 1930s Germany was the key reason for Hitler’s rise to power.’ The thesis statement takes a clear position, can be defended, and isn’t too wide-ranging.
Your own opinion on what you’ve read will be important, but you should also engage with the existing scholarship in the field. Whether you decide to stick with the consensus, or go against the grain, you will need to have a good understanding of what others have said.
Exploring the Background Information
Once you’ve reviewed any provided course materials and recommended reading, it’s important to recognize and address any glaring gaps in your knowledge. Are there any terms you don’t understand? Do you need to build an understanding of any particular events, people, or themes? Check the citations and bibliography of your readings to find and jump off to other works to build an understanding of how scholarship on the topic has progressed.
Finding Scholarly Sources for Research
Depending on your subject area, you may need to find and use both primary and secondary sources for your research. Primary sources may include:
- Newspaper articles
- Historical documents
- Eyewitness accounts or interviews
- Documentary materials
- Photographs
- Novels, plays, and/or poems
- Pieces of art
- Government reports
- Lab data/reports
Secondary sources are usually other academic papers, critical works, or books that review a range of evidence and comment upon primary sources. These can include textbooks, biographies, literary criticism, etc., depending on your field of study.
Your college library is a great place to start your research, especially if you need to use works that are not yet available digitally. However, many academic journals are now online, meaning you can find a wealth of other papers to read and reference within a few clicks. You should check which journals your college subscribes to, and you can search sites like JSTOR and Google Scholar .
Read the full article - Best Research Tools of 2023
Outline Creation
Before you start writing, it’s a good idea to create a paper outline. This will help you fix your structure, clarify your points, and can ultimately make it quicker to write up the final piece.
Read the full article - Creating an Outline with AI .
Creating an Overall Structure
The structure of an academic paper is likely to be more complex and developed than essays you may have written for school. You will need to make your thesis statement clear and support this with both evidence and analysis, as well as refuting other, competing ideas. Your work should reach a clear conclusion that leaves your reader in no doubt of your main argument. Nailing down your thesis statement, the key supporting points, and the main points you want to refute, should provide you with an overall structure for your academic paper.
Identifying and Summarizing Key Points
As you read around the topic, you should start to find repeated ideas that will become the main themes of your work. For example, if you are exploring how a theme is presented by a particular poet, you might find five or six ways the writer handles this idea. You will need to decide which one you find most persuasive by deciding which one has the most compelling evidence. This will become your thesis statement. The other ideas can be refuted as you develop your argument.
It’s a good idea to create a summary of each main idea you want to include by boiling it down into a few sentences at most. You can use software like Wordtune Read to help you. This AI (artificial intelligence) reader automatically summarizes longer documents to make it easier for you to condense the main ideas you will later re-expand.
As you write out your plan, these summaries will form kernels of your developed paragraphs, saving you lots of time in writing the final piece.

Essential Steps of the Writing Process
Writing up your academic paper might feel intimidating, but once you’ve got your structure plotted out, fleshing out the bones of the argument is the fun part. Make sure you leave enough time to write the paper and review it in plenty of time before the deadline, ideally taking some time away from the paper so you can come back to it with fresh ideas (which makes it easier to see any mistakes!).
Thesis Statement
Your thesis statement should come towards the start of your academic paper. This sets up the purpose of your paper, and establishes a trail of thought that your reader should be able to follow throughout the piece. It’s good practice to return to the thesis statement regularly throughout your work, and make sure you restate it in the conclusion (paraphrased if necessary to avoid robotic repetition).
Before you begin writing the whole paper, work on your thesis statement by condensing the main argument of your paper into just one sentence. If you’re not sure if you have enough evidence for the argument you want to make by the time you finish your plan, you might need to revise your thesis statement before you write the whole paper. Trust me: it’s easier to change the thesis before you write all the paragraphs.
Read the full article - How to Write a Thesis Statement with AI
Writing an Introduction
The introduction of an academic paper must make your argument clear, and should be concise and free of any fluff. You need to clearly lay out your argument, but should also set the scene for your work by summarizing the major scholarship, or history of the field, which most writers do first. You should also consider if the information you include in the introduction is definitely relevant to or necessary for the rest of the piece. For example, throwing in dates or definitions at this point may well be a distraction. Someone should be able to read just your introduction and already have a clear idea of your argument.
Additionally, your introduction needs to engage the audience by giving them a hint of the argument to come and suggesting why this topic is important. From a pile of 200+ papers, will your professor enjoy reading yours? A good introduction can help you to make a great first impression.
Read the full article - A Step-by-Step Guide to Writing Compelling Introductions
Body Paragraphs
Each paragraph of your paper should clearly support your thesis statement, or refute an alternative idea. Topic sentences (sentences that lay out the main point of each paragraph, before you go on to flesh out the detail) can be a good way to establish a clear thrust for each paragraph. However, it’s better to avoid formulaic or repetitive paragraph structures where you can.
The key idea of each paragraph should be supported by evidence, which you will want to comment on, either to establish how you agree with it or to argue against it. Drawing connections between different pieces of evidence, or synthesizing and/or comparing ideas, can make your use of evidence more complex and nuanced, and therefore more effective.
Consider how the paragraphs flow into one another. Referencing the previous paragraph and setting up the purpose of the next can create a more coherent structure for your paper and therefore make it easier to follow.
Drafting a Conclusion
The conclusion should bring the reader back to your thesis statement, and leave them in no doubt as to the strength of your argument. This is not a place to introduce new information or ideas at any length, although you may want to suggest further areas of study or research.
Keep your conclusion concise, too. If possible, finishing with a memorable closing sentence can round off your paper with a flourish and leave a lasting impression on your audience.
Don’t forget that revising your work is a crucial step! You should re-read your work a number of times to check if the structure and argument work well. You could try re-summarizing each paragraph, too, to make sure your points are clear.
Once you are confident that the content of the paper is solid, it’s time to look at the technical construction of your phrases and sentences, which is where editing and proofreading come in.
Editing and proofreading
Editing and proofreading are very important. The last thing you want to do is hand in a paper that’s difficult to read and follow because of technical errors. However, for many people, this is also an intimidating step.
One technique to try with your paper is to read it aloud. This can often highlight phrases or sentences that don’t work well or that don’t feel natural. You could also try reading your paper backwards, sentence by sentence. This forces your eye to stop skimming the page, which can lead to you missing mistakes.
It’s not just technical features that may need editing. As you re-read, you might notice words and phrases that can be upgraded to make your ideas stronger, or to help you communicate in a more engaging way. Luckily, you don’t need to do this all yourself; a digital tool like Wordtune can help you improve your work by suggesting alternative ways to express your ideas. You can even direct it to make suggestions in a particular tone (for example, more or less formal). Wordtune will also check your work for spelling and grammar mistakes, which can also save you time and stress.

Including Citations
The evidence you use in your academic paper needs to be cited correctly. Check the guidelines your institution follows for citation, as there are a few different models out there. However, most models will share the following in common:
- For each quotation from a source, provide the author’s name, date of publication, and page number (this can be in-text or as a footnote, depending on style guidelines). Some models also like you to provide the title of the text and the location of production.
- Use quotation marks to indicate where you have taken text from another source (to avoid plagiarism)
- To include a bibliography at the end of your paper (a full list of works cited). This should only include the texts you have cited, and usually references the title of the academic journal or book, date of publication, volume number (if it’s a journal), page numbers (if referencing a chapter or article), publishing company and location of production.
Citing correctly is a crucial part of how to write an academic paper, but it can also be fiddly and time consuming. Keeping accurate and organized notes while you research can make this bit easier.
Practice makes perfect
Learning how to write an academic paper is a process, so give yourself plenty of time to write your first one. As you progress in your studies, you will become more efficient and quicker at writing papers. And, don’t forget, you’re not alone! There are loads of resources out there to help you write an academic paper, including digital tools like Wordtune, online help guides, and support from your professor and institution, too. Before you know it, you’ll be turning in high quality, engaging academic papers that will help you ace your courses.
Share This Article:

Title Case vs. Sentence Case: How to Capitalize Your Titles

How to Properly Conduct Research with AI: Tools, Process, and Approach

What’s a Double Negative? + How To Fix It
Looking for fresh content, thank you your submission has been received.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
13.1 Formatting a Research Paper
Learning objectives.
- Identify the major components of a research paper written using American Psychological Association (APA) style.
- Apply general APA style and formatting conventions in a research paper.
In this chapter, you will learn how to use APA style , the documentation and formatting style followed by the American Psychological Association, as well as MLA style , from the Modern Language Association. There are a few major formatting styles used in academic texts, including AMA, Chicago, and Turabian:
- AMA (American Medical Association) for medicine, health, and biological sciences
- APA (American Psychological Association) for education, psychology, and the social sciences
- Chicago—a common style used in everyday publications like magazines, newspapers, and books
- MLA (Modern Language Association) for English, literature, arts, and humanities
- Turabian—another common style designed for its universal application across all subjects and disciplines
While all the formatting and citation styles have their own use and applications, in this chapter we focus our attention on the two styles you are most likely to use in your academic studies: APA and MLA.
If you find that the rules of proper source documentation are difficult to keep straight, you are not alone. Writing a good research paper is, in and of itself, a major intellectual challenge. Having to follow detailed citation and formatting guidelines as well may seem like just one more task to add to an already-too-long list of requirements.
Following these guidelines, however, serves several important purposes. First, it signals to your readers that your paper should be taken seriously as a student’s contribution to a given academic or professional field; it is the literary equivalent of wearing a tailored suit to a job interview. Second, it shows that you respect other people’s work enough to give them proper credit for it. Finally, it helps your reader find additional materials if he or she wishes to learn more about your topic.
Furthermore, producing a letter-perfect APA-style paper need not be burdensome. Yes, it requires careful attention to detail. However, you can simplify the process if you keep these broad guidelines in mind:
- Work ahead whenever you can. Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” includes tips for keeping track of your sources early in the research process, which will save time later on.
- Get it right the first time. Apply APA guidelines as you write, so you will not have much to correct during the editing stage. Again, putting in a little extra time early on can save time later.
- Use the resources available to you. In addition to the guidelines provided in this chapter, you may wish to consult the APA website at http://www.apa.org or the Purdue University Online Writing lab at http://owl.english.purdue.edu , which regularly updates its online style guidelines.
General Formatting Guidelines
This chapter provides detailed guidelines for using the citation and formatting conventions developed by the American Psychological Association, or APA. Writers in disciplines as diverse as astrophysics, biology, psychology, and education follow APA style. The major components of a paper written in APA style are listed in the following box.
These are the major components of an APA-style paper:
Body, which includes the following:
- Headings and, if necessary, subheadings to organize the content
- In-text citations of research sources
- References page
All these components must be saved in one document, not as separate documents.
The title page of your paper includes the following information:
- Title of the paper
- Author’s name
- Name of the institution with which the author is affiliated
- Header at the top of the page with the paper title (in capital letters) and the page number (If the title is lengthy, you may use a shortened form of it in the header.)
List the first three elements in the order given in the previous list, centered about one third of the way down from the top of the page. Use the headers and footers tool of your word-processing program to add the header, with the title text at the left and the page number in the upper-right corner. Your title page should look like the following example.

The next page of your paper provides an abstract , or brief summary of your findings. An abstract does not need to be provided in every paper, but an abstract should be used in papers that include a hypothesis. A good abstract is concise—about one hundred fifty to two hundred fifty words—and is written in an objective, impersonal style. Your writing voice will not be as apparent here as in the body of your paper. When writing the abstract, take a just-the-facts approach, and summarize your research question and your findings in a few sentences.
In Chapter 12 “Writing a Research Paper” , you read a paper written by a student named Jorge, who researched the effectiveness of low-carbohydrate diets. Read Jorge’s abstract. Note how it sums up the major ideas in his paper without going into excessive detail.

Write an abstract summarizing your paper. Briefly introduce the topic, state your findings, and sum up what conclusions you can draw from your research. Use the word count feature of your word-processing program to make sure your abstract does not exceed one hundred fifty words.
Depending on your field of study, you may sometimes write research papers that present extensive primary research, such as your own experiment or survey. In your abstract, summarize your research question and your findings, and briefly indicate how your study relates to prior research in the field.
Margins, Pagination, and Headings
APA style requirements also address specific formatting concerns, such as margins, pagination, and heading styles, within the body of the paper. Review the following APA guidelines.
Use these general guidelines to format the paper:
- Set the top, bottom, and side margins of your paper at 1 inch.
- Use double-spaced text throughout your paper.
- Use a standard font, such as Times New Roman or Arial, in a legible size (10- to 12-point).
- Use continuous pagination throughout the paper, including the title page and the references section. Page numbers appear flush right within your header.
- Section headings and subsection headings within the body of your paper use different types of formatting depending on the level of information you are presenting. Additional details from Jorge’s paper are provided.

Begin formatting the final draft of your paper according to APA guidelines. You may work with an existing document or set up a new document if you choose. Include the following:
- Your title page
- The abstract you created in Note 13.8 “Exercise 1”
- Correct headers and page numbers for your title page and abstract
APA style uses section headings to organize information, making it easy for the reader to follow the writer’s train of thought and to know immediately what major topics are covered. Depending on the length and complexity of the paper, its major sections may also be divided into subsections, sub-subsections, and so on. These smaller sections, in turn, use different heading styles to indicate different levels of information. In essence, you are using headings to create a hierarchy of information.
The following heading styles used in APA formatting are listed in order of greatest to least importance:
- Section headings use centered, boldface type. Headings use title case, with important words in the heading capitalized.
- Subsection headings use left-aligned, boldface type. Headings use title case.
- The third level uses left-aligned, indented, boldface type. Headings use a capital letter only for the first word, and they end in a period.
- The fourth level follows the same style used for the previous level, but the headings are boldfaced and italicized.
- The fifth level follows the same style used for the previous level, but the headings are italicized and not boldfaced.
Visually, the hierarchy of information is organized as indicated in Table 13.1 “Section Headings” .
Table 13.1 Section Headings
A college research paper may not use all the heading levels shown in Table 13.1 “Section Headings” , but you are likely to encounter them in academic journal articles that use APA style. For a brief paper, you may find that level 1 headings suffice. Longer or more complex papers may need level 2 headings or other lower-level headings to organize information clearly. Use your outline to craft your major section headings and determine whether any subtopics are substantial enough to require additional levels of headings.
Working with the document you developed in Note 13.11 “Exercise 2” , begin setting up the heading structure of the final draft of your research paper according to APA guidelines. Include your title and at least two to three major section headings, and follow the formatting guidelines provided above. If your major sections should be broken into subsections, add those headings as well. Use your outline to help you.
Because Jorge used only level 1 headings, his Exercise 3 would look like the following:
Citation Guidelines
In-text citations.
Throughout the body of your paper, include a citation whenever you quote or paraphrase material from your research sources. As you learned in Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” , the purpose of citations is twofold: to give credit to others for their ideas and to allow your reader to follow up and learn more about the topic if desired. Your in-text citations provide basic information about your source; each source you cite will have a longer entry in the references section that provides more detailed information.
In-text citations must provide the name of the author or authors and the year the source was published. (When a given source does not list an individual author, you may provide the source title or the name of the organization that published the material instead.) When directly quoting a source, it is also required that you include the page number where the quote appears in your citation.
This information may be included within the sentence or in a parenthetical reference at the end of the sentence, as in these examples.
Epstein (2010) points out that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (p. 137).
Here, the writer names the source author when introducing the quote and provides the publication date in parentheses after the author’s name. The page number appears in parentheses after the closing quotation marks and before the period that ends the sentence.
Addiction researchers caution that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (Epstein, 2010, p. 137).
Here, the writer provides a parenthetical citation at the end of the sentence that includes the author’s name, the year of publication, and the page number separated by commas. Again, the parenthetical citation is placed after the closing quotation marks and before the period at the end of the sentence.
As noted in the book Junk Food, Junk Science (Epstein, 2010, p. 137), “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive.”
Here, the writer chose to mention the source title in the sentence (an optional piece of information to include) and followed the title with a parenthetical citation. Note that the parenthetical citation is placed before the comma that signals the end of the introductory phrase.
David Epstein’s book Junk Food, Junk Science (2010) pointed out that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (p. 137).
Another variation is to introduce the author and the source title in your sentence and include the publication date and page number in parentheses within the sentence or at the end of the sentence. As long as you have included the essential information, you can choose the option that works best for that particular sentence and source.
Citing a book with a single author is usually a straightforward task. Of course, your research may require that you cite many other types of sources, such as books or articles with more than one author or sources with no individual author listed. You may also need to cite sources available in both print and online and nonprint sources, such as websites and personal interviews. Chapter 13 “APA and MLA Documentation and Formatting” , Section 13.2 “Citing and Referencing Techniques” and Section 13.3 “Creating a References Section” provide extensive guidelines for citing a variety of source types.
Writing at Work
APA is just one of several different styles with its own guidelines for documentation, formatting, and language usage. Depending on your field of interest, you may be exposed to additional styles, such as the following:
- MLA style. Determined by the Modern Languages Association and used for papers in literature, languages, and other disciplines in the humanities.
- Chicago style. Outlined in the Chicago Manual of Style and sometimes used for papers in the humanities and the sciences; many professional organizations use this style for publications as well.
- Associated Press (AP) style. Used by professional journalists.
References List
The brief citations included in the body of your paper correspond to the more detailed citations provided at the end of the paper in the references section. In-text citations provide basic information—the author’s name, the publication date, and the page number if necessary—while the references section provides more extensive bibliographical information. Again, this information allows your reader to follow up on the sources you cited and do additional reading about the topic if desired.
The specific format of entries in the list of references varies slightly for different source types, but the entries generally include the following information:
- The name(s) of the author(s) or institution that wrote the source
- The year of publication and, where applicable, the exact date of publication
- The full title of the source
- For books, the city of publication
- For articles or essays, the name of the periodical or book in which the article or essay appears
- For magazine and journal articles, the volume number, issue number, and pages where the article appears
- For sources on the web, the URL where the source is located
The references page is double spaced and lists entries in alphabetical order by the author’s last name. If an entry continues for more than one line, the second line and each subsequent line are indented five spaces. Review the following example. ( Chapter 13 “APA and MLA Documentation and Formatting” , Section 13.3 “Creating a References Section” provides extensive guidelines for formatting reference entries for different types of sources.)

In APA style, book and article titles are formatted in sentence case, not title case. Sentence case means that only the first word is capitalized, along with any proper nouns.
Key Takeaways
- Following proper citation and formatting guidelines helps writers ensure that their work will be taken seriously, give proper credit to other authors for their work, and provide valuable information to readers.
- Working ahead and taking care to cite sources correctly the first time are ways writers can save time during the editing stage of writing a research paper.
- APA papers usually include an abstract that concisely summarizes the paper.
- APA papers use a specific headings structure to provide a clear hierarchy of information.
- In APA papers, in-text citations usually include the name(s) of the author(s) and the year of publication.
- In-text citations correspond to entries in the references section, which provide detailed bibliographical information about a source.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
- U.S. Locations
- UMGC Europe
- Learn Online
- Find Answers
- 855-655-8682
- Current Students
Online Guide to Writing and Research
The research process, explore more of umgc.
- Online Guide to Writing
Planning and Writing a Research Paper
Work Your Sources into Your Research Writing
Working your sources into your writing is a very important part of the writing process and gets easier over time. You must also decide whether you will quote , paraphrase , or summarize the material when incorporating resources into your writing.
Academic integrity encompasses the practice of engaging with source material meaningfully and ethically, to the benefit of your own learning and the discourse community with which you interact. UMGC has carefully developed a philosophy of, approach to, and tutorial about academic integrity that can be found here: Philosophy of Academic Integrity Please review this material and familiarize yourself with both the best practices in this area and how to avoid running afoul of expectations.
Quoting, Paraphrasing, Summarizing, and Citing Your Sources
How to incorporate your sources.
How you incorporate your sources into your writing depends on how you are using them and why you are writing your paper. Many students have difficulty deciding when to quote, paraphrase, or summarize, and then when to cite a source.
Understanding Why We Use Citations
Understanding why writers use citations in academic research can help you decide when to use them. Citing reliable sources gives your research and writing credibility, showing your familiarity with the work of a scholarly community and your understanding of how you are contributing to it. It also shows the reader that you have done the research and have gone to great lengths to make your paper as strong and clear as possible.
How to Work Citations and Paraphrasing Into Your Own Writing
Keep in mind that sometimes it is difficult to figure out how to work the quotations and paraphrases into your own style of writing. You want to avoid using lengthy blocks of quotations or lengthy paraphrases of the sources. For more information about quoting and paraphrasing resources, check out Chapter 5, “ Academic Integrity and Documentation .” Also, please take a look at the UMGC library Citing and Writing LibGuide .
Research Styles
- OBJECTIVE RESEARCHER
- CONTEXT CREATOR
At this level, you are expected to remain objective and impartial when presenting the research, with no personal opinions given. You report the information, taking on the role of an experimental researcher or even an investigative reporter.
Here, you are expected to put your sources in the context of a greater issue or debate. You have to offer enough explanation and discussion (through your own comprehension and interpretation) to help your reader see the connection between the material you are researching and the other references.
At this level, you help the reader understand the relationship, significance, and authority of the reference material by introducing and discussing its sources.
Here, you are asked to judge the source materials and their usefulness for your research project. This last position, most commonly found in literary, musical, or other fine arts criticism, involves you, the researcher, as a critical thinker in assessing the sources.
Key Takeaways
- Acknowledging intellectual ownership shows respect for those who have contributed to the field of knowledge and for the achievements in that field.
- Citing reliable sources gives your research and writing credibility, showing your familiarity with the work of a scholarly community and your understanding of how you are contributing to it.
Mailing Address: 3501 University Blvd. East, Adelphi, MD 20783 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License . © 2022 UMGC. All links to external sites were verified at the time of publication. UMGC is not responsible for the validity or integrity of information located at external sites.
Table of Contents: Online Guide to Writing
Chapter 1: College Writing
How Does College Writing Differ from Workplace Writing?
What Is College Writing?
Why So Much Emphasis on Writing?
Chapter 2: The Writing Process
Doing Exploratory Research
Getting from Notes to Your Draft
Introduction
Prewriting - Techniques to Get Started - Mining Your Intuition
Prewriting: Targeting Your Audience
Prewriting: Techniques to Get Started
Prewriting: Understanding Your Assignment
Rewriting: Being Your Own Critic
Rewriting: Creating a Revision Strategy
Rewriting: Getting Feedback
Rewriting: The Final Draft
Techniques to Get Started - Outlining
Techniques to Get Started - Using Systematic Techniques
Thesis Statement and Controlling Idea
Writing: Getting from Notes to Your Draft - Freewriting
Writing: Getting from Notes to Your Draft - Summarizing Your Ideas
Writing: Outlining What You Will Write
Chapter 3: Thinking Strategies
A Word About Style, Voice, and Tone
A Word About Style, Voice, and Tone: Style Through Vocabulary and Diction
Critical Strategies and Writing
Critical Strategies and Writing: Analysis
Critical Strategies and Writing: Evaluation
Critical Strategies and Writing: Persuasion
Critical Strategies and Writing: Synthesis
Developing a Paper Using Strategies
Kinds of Assignments You Will Write
Patterns for Presenting Information
Patterns for Presenting Information: Critiques
Patterns for Presenting Information: Discussing Raw Data
Patterns for Presenting Information: General-to-Specific Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Problem-Cause-Solution Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Specific-to-General Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Summaries and Abstracts
Supporting with Research and Examples
Writing Essay Examinations
Writing Essay Examinations: Make Your Answer Relevant and Complete
Writing Essay Examinations: Organize Thinking Before Writing
Writing Essay Examinations: Read and Understand the Question
Chapter 4: The Research Process
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Ask a Research Question
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Cite Sources
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Collect Evidence
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Decide Your Point of View, or Role, for Your Research
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Draw Conclusions
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Find a Topic and Get an Overview
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Manage Your Resources
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Outline
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Survey the Literature
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Work Your Sources into Your Research Writing
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Human Resources
Research Resources: What Are Research Resources?
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found?
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Electronic Resources
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Print Resources
Structuring the Research Paper: Formal Research Structure
Structuring the Research Paper: Informal Research Structure
The Nature of Research
The Research Assignment: How Should Research Sources Be Evaluated?
The Research Assignment: When Is Research Needed?
The Research Assignment: Why Perform Research?
Chapter 5: Academic Integrity
Academic Integrity
Giving Credit to Sources
Giving Credit to Sources: Copyright Laws
Giving Credit to Sources: Documentation
Giving Credit to Sources: Style Guides
Integrating Sources
Practicing Academic Integrity
Practicing Academic Integrity: Keeping Accurate Records
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Paraphrasing Your Source
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Quoting Your Source
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Summarizing Your Sources
Types of Documentation
Types of Documentation: Bibliographies and Source Lists
Types of Documentation: Citing World Wide Web Sources
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - APA Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - CSE/CBE Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - Chicago Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - MLA Style
Types of Documentation: Note Citations
Chapter 6: Using Library Resources
Finding Library Resources
Chapter 7: Assessing Your Writing
How Is Writing Graded?
How Is Writing Graded?: A General Assessment Tool
The Draft Stage
The Draft Stage: The First Draft
The Draft Stage: The Revision Process and the Final Draft
The Draft Stage: Using Feedback
The Research Stage
Using Assessment to Improve Your Writing
Chapter 8: Other Frequently Assigned Papers
Reviews and Reaction Papers: Article and Book Reviews
Reviews and Reaction Papers: Reaction Papers
Writing Arguments
Writing Arguments: Adapting the Argument Structure
Writing Arguments: Purposes of Argument
Writing Arguments: References to Consult for Writing Arguments
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Anticipate Active Opposition
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Determine Your Organization
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Develop Your Argument
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Introduce Your Argument
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - State Your Thesis or Proposition
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Write Your Conclusion
Writing Arguments: Types of Argument
Appendix A: Books to Help Improve Your Writing
Dictionaries
General Style Manuals
Researching on the Internet
Special Style Manuals
Writing Handbooks
Appendix B: Collaborative Writing and Peer Reviewing
Collaborative Writing: Assignments to Accompany the Group Project
Collaborative Writing: Informal Progress Report
Collaborative Writing: Issues to Resolve
Collaborative Writing: Methodology
Collaborative Writing: Peer Evaluation
Collaborative Writing: Tasks of Collaborative Writing Group Members
Collaborative Writing: Writing Plan
General Introduction
Peer Reviewing
Appendix C: Developing an Improvement Plan
Working with Your Instructor’s Comments and Grades
Appendix D: Writing Plan and Project Schedule
Devising a Writing Project Plan and Schedule
Reviewing Your Plan with Others
By using our website you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about how we use cookies by reading our Privacy Policy .
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
- Research Papers
How to Write a Paper
Last Updated: April 8, 2024 Approved
This article was co-authored by Matthew Snipp, PhD . C. Matthew Snipp is the Burnet C. and Mildred Finley Wohlford Professor of Humanities and Sciences in the Department of Sociology at Stanford University. He is also the Director for the Institute for Research in the Social Science’s Secure Data Center. He has been a Research Fellow at the U.S. Bureau of the Census and a Fellow at the Center for Advanced Study in the Behavioral Sciences. He has published 3 books and over 70 articles and book chapters on demography, economic development, poverty and unemployment. He is also currently serving on the National Institute of Child Health and Development’s Population Science Subcommittee. He holds a Ph.D. in Sociology from the University of Wisconsin—Madison. There are 12 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. In this case, 100% of readers who voted found the article helpful, earning it our reader-approved status. This article has been viewed 320,945 times.
Whether you’re in high school or university, writing papers is probably a big part of your grade for at least some of your classes. Writing an essay on any topic can be challenging and time consuming. But, when you know how to break it down into parts and write each of those parts, it’s much easier! Follow the steps in this article for help writing your next paper from start to finish.
Pre-Writing

- If you have an idea for a topic that isn’t listed, feel free to ask your instructor if it would be okay to write about something that isn’t on the list they provided.
- In some cases, the teacher or professor might just provide an assignment sheet covering the logistics of the paper, but leave the topic choice up to you. If this happens, it can be helpful to come up with a short list of ideas on your own, then choose the best one.
- Don’t hesitate to ask your instructor for guidance on choosing a topic if you’re having trouble deciding.

- Note that there are different types of papers including research papers, opinion papers, and analytical essays. All of them need a thesis statement and all of them require you to do research and review various sources in order to write them.
- Keep in mind that a thesis is not a topic, a fact, or an opinion. It is an argument based on observations and findings that you are trying to prove in your paper, like a hypothesis statement in a science experiment.

- An example of a thesis statement for a research paper is: “The Soviet Union collapsed because of the ruling class’s inability to tackle the economic problems of the common people.” This tells the reader what point you are going to back up with evidence in the rest of your paper.
- A thesis statement for an opinion paper might read something like: “Libraries are an essential community resource and as such should receive more funding from local municipal governments.”
- An analytical essay’s thesis statement could be: “JD Salinger makes heavy use of symbolism in The Catcher in the Rye in order to create feelings of melancholy and uncertainty in the novel.”

- For example, if your thesis is about why the government needs to do more to protect wetland ecosystems, main supporting points could be: “effects of wetland loss in the US,” “current lack of laws protecting wetlands,” and “benefits of saving wetlands.”
- These major points form the body of your paper, in between your introduction and your conclusion.

- For example, under a main point that says “employment conditions affect the mental health of workers,” your sub-points might be: “high levels of stress are directly related to mental health” and “workers in low-skill positions tend to have higher levels of stress.”

- For example, you could write something like: “Did you know that cattle ranching is the leading cause of deforestation in the Amazon rainforest?”

- For example, you might write something like: “It’s common for apps and social media to be demonized as a waste of time and brain space, but not all such technology should be considered mindless entertainment. In fact, many apps and social media networks can be used for educational and academic purposes.”

- Make sure the background information about your topic that you include in your intro flows nicely into your thesis.

- Think of each paragraph as kind of a mini essay in and of itself. Each paragraph should be a self-contained chunk of information that relates to the overall topic and thesis of your paper.
- Supporting evidence can be things like statistics, data, facts, and quotes from your sources

- For example, put a paragraph about the reasons behind the collapse of the Soviet Union before a paragraph about the changes to Eastern European societies in the 90s, because the collapse of the Soviet Union directly led to many of those changes.
- If your first body paragraph discusses the extent of deforestation in the Amazon over the past decade, and your second paragraph is going to explain how that affects animal extinction, state the shift in focus by writing something like: “The deforestation of the Amazon over the last decade has resulted in a drastic reduction of natural habitats for many species.”

- For example, if your thesis in your intro was “The use of technology can benefit children because it improves developmental skills,” restate it something like this: “The use of technology contributes to children’s well-rounded development from a young age.”

- For example, you might write something like: “Deforestation is directly linked to climate change and increasingly extreme weather across the world, which is why global governments must take more action to stop illegal logging.”

- For example, say something like: “Ignoring the realities of deforestation and climate change has grave implications for all of us. If we don’t start putting more pressure on governments to act, your children or grandchildren will be living in a very different world from that which we inhabit today.”
Citing Sources

- Humanities subjects include language arts and cultural studies.
- Note that these are just the basic rules for writing an MLA-style works cited page. For a full list of rules regarding all things MLA and citations, refer to an MLA handbook.
- Note that there is some crossover between certain subjects, in which case more than 1 style of works cited or reference page may be acceptable.
- Always review your assignment rubric or ask your professor which style of citations they prefer before writing your reference or works cited page.

- Social sciences include psychology, sociology, and anthropology.
- Refer to an APA style guide for complete rules about how to list different types of sources.

- Check a Chicago Manual of Style for more specific instructions about citations.
- Note that Chicago style is more commonly used for published works. If you’re a student, your professor might instruct you to use MLA format for your papers.
Revising, Editing, and Proofreading

- Anywhere from a few hours to a day is a good amount of time to wait before you start revising your paper. The point is to come back to it with a fresh set of eyes.
- If you can, get a roommate, a family member, a friend, or a classmate to read your paper too. Ask them for advice on ways you could make your argument and your evidence more clear or relevant.
- Here are 3 questions to ask yourself as you read each sentence and piece of information in your paper: Is this really worth saying? Does this say what I want it to say? Will readers understand what I’m saying?

- It helps to read your paper out loud as you do this. Listen for awkward pauses, phrases, and sentence structure, and revise them so the writing flows better.
- Try copying and pasting your essay into the free online tool called “Hemingway.” The app suggests many different ways to make your writing clearer, more direct, and more readable.

- Take this sentence as an example: “The collapse of the Soviet Union resulted in the collapse of local governments and economies across Eastern Europe.” Instead of using “collapse” twice, replace the second instance with “crumbling.”

- It’s also a good idea to paste your paper into a third-party tool, like Grammarly, for a final spelling and grammar check. Not every program catches everything, so it’s better to be on the safe side!
Sample Research Papers

Sample Essays

Expert Q&A

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/common_writing_assignments/research_papers/choosing_a_topic.html
- ↑ https://writingcenter.fas.harvard.edu/pages/developing-thesis
- ↑ Matthew Snipp, PhD. Research Fellow, U.S. Bureau of the Census. Expert Interview. 26 March 2020.
- ↑ https://library.piedmont.edu/c.php?g=521348&p=3564584
- ↑ https://academicguides.waldenu.edu/writingcenter/writingprocess/outlining
- ↑ https://writingcenter.uagc.edu/introductions-conclusions
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_works_cited_page_basic_format.html
- ↑ https://aut.ac.nz.libguides.com/APA6th/referencelist
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/chicago_manual_17th_edition/cmos_formatting_and_style_guide/general_format.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/proofreading/steps_for_revising.html
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/revising-drafts/
About This Article

To write a paper, review the assignment sheet and rubric, and begin your research. Decide what you want to argue in your paper, and form it into your thesis statement, which is a sentence that sums up your argument and main points. Make an outline of the argument, and then start writing the introduction to the paper, which grabs your reader's attention and states the thesis. Then, include at least 3 paragraphs of supporting evidence for your argument, which makes up the body of the paper. Finally, end the paper with a conclusion that wraps up your points and restate your thesis. For tips from our academic reviewer on refining your paper and making a strong argument, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Jun 6, 2016

Did this article help you?

Reza Siahaan
Nov 30, 2016
Dec 15, 2016
Juliet Janeway
Jun 23, 2016
Logan Markland
Feb 21, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve
× All floors of the JFK Library are open for summer quarter. For details see Library Access
Research Guides
Eastern Washington University Libraries
APA Style 7th Edition Tutorials for Students in Psychology and Social Work
What is apa style.
- The Importance of Citing
Why is APA Style needed?
How do i get started with apa style, let us practice what we have learned, attribution and acknowledgement.
- Basics of APA Style Tutorial
- Reference Entry Elements
- Reference Examples
- Reference List
- In-Text Citations
- Student Paper Format
- Managing References - Zotero
Origination of APA Style
- Where did APA Style come from?
Commonly Used APA Related Terms
Abstract : Abstract is a brief synopses of article. It provides a brief but comprehensive summary of the article.
Citing : In the context of academic writing, citing is the act of acknowledging the sources of information you have used when writing your work.
Citation: A citation gives credit to a source, and contains publication information such as author(s), title and date.
DOI (digital object identifier): It is a unique alphanumeric string assigned to a digital object, mainly a scholarly article, to provide a persistent link to its location on the internet.
In-Text Citation : It is a brief note that appears within the body of the paper and briefly identifies the cited work by its author and date of publication. An in-text citation should always match the corresponding entry in the reference list at the end of paper.
Paraphrasing : A paraphrase restates another’s idea (or your own previously published idea) in your own words.
Plagiarism : It is the act of presenting the words, ideas, or images of another as your own; it denies creators of content the credit they are due.
Quoting : It is the act of reproducing the exact wording used by the original author. Direct quotations appear within quotation marks and end with a citation.
Reference : It contains details about one cited work, generally including four elements: author, date, title, and source.
Reference List : It identifies all the sources you cited in the text of your paper. It generally is at the end of the paper and definitely on a new page after the text of your paper.
APA Style is the most common writing style used in college and career. Its purpose is to promote excellence in communication by helping writers create clear, precise, and inclusive sentences with a straightforward scholarly tone. It addresses areas of writing such as how to
- format a paper so it looks professional;
- credit other people’s words and ideas via citations and references to avoid plagiarism; and
- describe other people with dignity and respect using inclusive, bias-free language.
APA Style is primarily used in the behavioral sciences, which are subjects related to people, such as psychology, education, and nursing. It is also used by students in business, engineering, communications, and other classes. Students use it to write academic essays and research papers in college, and professionals use it to conduct, report, and publish scientific research.
In addition, APA Style provides you with a powerful tool that will hep you avoid deliberate or unintentional plagiarism. Please review the Avoiding Plagiarism Guide created by the APA experts to understand what two common types of plagiarism are and how to avoid them.
Why is learning citations important? Citations help readers understand where the information used in your paper comes from, enabling them to trace the path of that information. When readers wish to explore a specific point or reference cited in the text, citations make it easier by providing information about your sources in a standardized format.
Besides showing readers where you obtained information, using citations also has a strong ethical purpose. In academic writing, it is important to credit ideas that are not your own. Citations allow you to integrate the ideas of others with your own thoughts in a fair and honest way.
The reference formats for APA Style manuals are as follows:
APA Style provides a foundation for effective scholarly communication because it helps authors present their ideas in a clear and concise, and organized manner. Uniformity and consistency enable readers to (a) focus on the ideas being presented rather than formatting and (b) scan works quickly for key points, findings, and sources. When style works best, ideas flow logically, sources are credited appropriately, and papers are organized predictably and consistently.
Students are encouraged to first learn about APA Style by reading works written in APA Style. A couple of guides created by APA experts from the American Psychological Association can help you with that:
Anatomy of a Journal Article https://apastyle.apa.org/instructional-aids/anatomy-journal-article.pdf
Scholarly journal articles share a common anatomy or structure. Each part of an article serves a specific purpose. The handout of Anatomy of a Journal Article explains how journal articles are structured and how to become more efficient at reading and understanding them. Understanding the structure of a scholarly article and the purpose of each part helps you grasp a strategy called targeted reading. Targeted reading means to read specific sections of research articles first to determine if the article seems useful for your research topic. This way you will save time, find useful article faster, and choose which articles to read in full.
Reading and Understanding Abstracts https://apastyle.apa.org/instructional-aids/reading-abstracts.pdf
Abstracts are short summaries of scientific research articles. The handout of Reading & Understanding Abstracts explains the definition and purpose of abstracts and the benefits of reading them, including analysis of a sample abstract. The skill of reading and understanding abstracts of scholarly articles not only saves time but also helps you conduct better research and write more effectively.
APA Style Writing Principles https://apastyle.apa.org/instructional-aids/writing-principles.pdf
The poster created by APA experts shows the three main principles of APA Style: clarity, precision, and inclusion and lists steps on how to achieve them. As a student writer, you always should write your academic paper with clarity, precision, and inclusion.
Research Article Activity https://apastyle.apa.org/instructional-aids/apa-style-research-activity.pdf
Reading research articles is not an easy task for you as a student. The Research Article Activity designed by APA Style experts aims to make it easy to read and understand a scholarly article. This activity worksheet helps you find, cite, analyze, and summarize a research article. Completing this activity breaks down a lengthy research article into easily understandable chunks. This way helps you better understand the study in the article before you write about it.
The information in this Guide is courtesy of the official APA Style website by the American Psychological Association.
Source Credit: Information on this LibGuide comes from APA Style website https://apastyle.apa.org/ This website has a wealth of free and authoritative resources designed to help anyone new to APA Style.
- Next: Basics of APA Style Tutorial >>
- Last Updated: Apr 6, 2024 12:06 PM
- URL: https://research.ewu.edu/APAStyleTutorial
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
MLA Formatting and Style Guide

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9 th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
The following overview should help you better understand how to cite sources using MLA 9 th edition, including how to format the Works Cited page and in-text citations.
Please use the example at the bottom of this page to cite the Purdue OWL in MLA. See also our MLA vidcast series on the Purdue OWL YouTube Channel .
Creating a Works Cited list using the ninth edition
MLA is a style of documentation that may be applied to many different types of writing. Since texts have become increasingly digital, and the same document may often be found in several different sources, following a set of rigid rules no longer suffices.
Thus, the current system is based on a few guiding principles, rather than an extensive list of specific rules. While the handbook still describes how to cite sources, it is organized according to the process of documentation, rather than by the sources themselves. This gives writers a flexible method that is near-universally applicable.
Once you are familiar with the method, you can use it to document any type of source, for any type of paper, in any field.
Here is an overview of the process:
When deciding how to cite your source, start by consulting the list of core elements. These are the general pieces of information that MLA suggests including in each Works Cited entry. In your citation, the elements should be listed in the following order:
- Title of source.
- Title of container,
- Other contributors,
- Publication date,
Each element should be followed by the corresponding punctuation mark shown above. Earlier editions of the handbook included the place of publication and required different punctuation (such as journal editions in parentheses and colons after issue numbers) depending on the type of source. In the current version, punctuation is simpler (only commas and periods separate the elements), and information about the source is kept to the basics.
Begin the entry with the author’s last name, followed by a comma and the rest of the name, as presented in the work. End this element with a period.
Bhabha, Homi K. The Location of Culture. Routledge, 1994.
Title of source
The title of the source should follow the author’s name. Depending upon the type of source, it should be listed in italics or quotation marks.
A book should be in italics:
Henley, Patricia. The Hummingbird House . MacMurray, 1999.
An individual webpage should be in quotation marks. The name of the parent website, which MLA treats as a "container," should follow in italics:
Lundman, Susan. "How to Make Vegetarian Chili." eHow, www.ehow.com/how_10727_make-vegetarian-chili.html.*
A periodical (journal, magazine, newspaper) article should be in quotation marks:
Bagchi, Alaknanda. "Conflicting Nationalisms: The Voice of the Subaltern in Mahasweta Devi's Bashai Tudu." Tulsa Studies in Women's Literature , vol. 15, no. 1, 1996, pp. 41-50.
A song or piece of music on an album should be in quotation marks. The name of the album should then follow in italics:
Beyoncé. "Pray You Catch Me." Lemonade, Parkwood Entertainment, 2016, www.beyonce.com/album/lemonade-visual-album/.
*The MLA handbook recommends including URLs when citing online sources. For more information, see the “Optional Elements” section below.
Title of container
The eighth edition of the MLA handbook introduced what are referred to as "containers," which are the larger wholes in which the source is located. For example, if you want to cite a poem that is listed in a collection of poems, the individual poem is the source, while the larger collection is the container. The title of the container is usually italicized and followed by a comma, since the information that follows next describes the container.
Kincaid, Jamaica. "Girl." The Vintage Book of Contemporary American Short Stories, edited by Tobias Wolff, Vintage, 1994, pp. 306-07.
The container may also be a television series, which is made up of episodes.
“94 Meetings.” Parks and Recreation, created by Greg Daniels and Michael Schur, performance by Amy Poehler, season 2, episode 21, Deedle-Dee Productions and Universal Media Studios, 2010.
The container may also be a website, which contains articles, postings, and other works.
Wise, DeWanda. “Why TV Shows Make Me Feel Less Alone.” NAMI, 31 May 2019, www.nami.org/Blogs/NAMI-Blog/May-2019/How-TV-Shows-Make-Me-Feel-Less-Alone . Accessed 3 June 2019.
In some cases, a container might be within a larger container. You might have read a book of short stories on Google Books , or watched a television series on Netflix . You might have found the electronic version of a journal on JSTOR. It is important to cite these containers within containers so that your readers can find the exact source that you used.
“94 Meetings.” Parks and Recreation , season 2, episode 21, NBC , 29 Apr. 2010. Netflix, www.netflix.com/watch/70152031?trackId=200256157&tctx=0%2C20%2C0974d361-27cd-44de-9c2a-2d9d868b9f64-12120962.
Langhamer, Claire. “Love and Courtship in Mid-Twentieth-Century England.” Historical Journal , vol. 50, no. 1, 2007, pp. 173-96. ProQuest, doi:10.1017/S0018246X06005966. Accessed 27 May 2009.
Other contributors
In addition to the author, there may be other contributors to the source who should be credited, such as editors, illustrators, translators, etc. If their contributions are relevant to your research, or necessary to identify the source, include their names in your documentation.
Foucault, Michel. Madness and Civilization: A History of Insanity in the Age of Reason. Translated by Richard Howard , Vintage-Random House, 1988.
Woolf, Virginia. Jacob’s Room . Annotated and with an introduction by Vara Neverow, Harcourt, Inc., 2008.
If a source is listed as an edition or version of a work, include it in your citation.
The Bible . Authorized King James Version, Oxford UP, 1998.
Crowley, Sharon, and Debra Hawhee. Ancient Rhetorics for Contemporary Students. 3rd ed., Pearson, 2004.
If a source is part of a numbered sequence, such as a multi-volume book or journal with both volume and issue numbers, those numbers must be listed in your citation.
Dolby, Nadine. “Research in Youth Culture and Policy: Current Conditions and Future Directions.” Social Work and Society: The International Online-Only Journal, vol. 6, no. 2, 2008, www.socwork.net/sws/article/view/60/362. Accessed 20 May 2009.
Quintilian. Institutio Oratoria. Translated by H. E. Butler, vol. 2, Loeb-Harvard UP, 1980.
The publisher produces or distributes the source to the public. If there is more than one publisher, and they are all are relevant to your research, list them in your citation, separated by a forward slash (/).
Klee, Paul. Twittering Machine. 1922. Museum of Modern Art, New York. The Artchive, www.artchive.com/artchive/K/klee/twittering_machine.jpg.html. Accessed May 2006.
Women's Health: Problems of the Digestive System . American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, 2006.
Daniels, Greg and Michael Schur, creators. Parks and Recreation . Deedle-Dee Productions and Universal Media Studios, 2015.
Note : The publisher’s name need not be included in the following sources: periodicals, works published by their author or editor, websites whose titles are the same name as their publisher, websites that make works available but do not actually publish them (such as YouTube , WordPress , or JSTOR ).
Publication date
The same source may have been published on more than one date, such as an online version of an original source. For example, a television series might have aired on a broadcast network on one date, but released on Netflix on a different date. When the source has more than one date, it is sufficient to use the date that is most relevant to your writing. If you’re unsure about which date to use, go with the date of the source’s original publication.
In the following example, Mutant Enemy is the primary production company, and “Hush” was released in 1999. Below is a general citation for this television episode:
“Hush.” Buffy the Vampire Slayer , created by Joss Whedon, performance by Sarah Michelle Gellar, season 4, Mutant Enemy, 1999 .
However, if you are discussing, for example, the historical context in which the episode originally aired, you should cite the full date. Because you are specifying the date of airing, you would then use WB Television Network (rather than Mutant Enemy), because it was the network (rather than the production company) that aired the episode on the date you’re citing.
“Hush.” Buffy the Vampire Slayer, created by Joss Whedon, performance by Sarah Michelle Gellar, season 4, episode 10, WB Television Network, 14 Dec. 1999 .
You should be as specific as possible in identifying a work’s location.
An essay in a book or an article in a journal should include page numbers.
Adiche, Chimamanda Ngozi. “On Monday of Last Week.” The Thing around Your Neck, Alfred A. Knopf, 2009, pp. 74-94 .
The location of an online work should include a URL. Remove any "http://" or "https://" tag from the beginning of the URL.
Wheelis, Mark. "Investigating Disease Outbreaks Under a Protocol to the Biological and Toxin Weapons Convention." Emerging Infectious Diseases , vol. 6, no. 6, 2000, pp. 595-600, wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/6/6/00-0607_article. Accessed 8 Feb. 2009.
When citing a physical object that you experienced firsthand, identify the place of location.
Matisse, Henri. The Swimming Pool. 1952, Museum of Modern Art, New York .
Optional elements
The ninth edition is designed to be as streamlined as possible. The author should include any information that helps readers easily identify the source, without including unnecessary information that may be distracting. The following is a list of optional elements that can be included in a documented source at the writer’s discretion.
Date of original publication:
If a source has been published on more than one date, the writer may want to include both dates if it will provide the reader with necessary or helpful information.
Erdrich, Louise. Love Medicine. 1984. Perennial-Harper, 1993.
City of publication:
The seventh edition handbook required the city in which a publisher is located, but the eighth edition states that this is only necessary in particular instances, such as in a work published before 1900. Since pre-1900 works were usually associated with the city in which they were published, your documentation may substitute the city name for the publisher’s name.
Thoreau, Henry David. Excursions . Boston, 1863.
Date of access:
When you cite an online source, the MLA Handbook recommends including a date of access on which you accessed the material, since an online work may change or move at any time.
Bernstein, Mark. "10 Tips on Writing the Living Web." A List Apart: For People Who Make Websites, 16 Aug. 2002, alistapart.com/article/writeliving. Accessed 4 May 2009.
As mentioned above, while the MLA handbook recommends including URLs when you cite online sources, you should always check with your instructor or editor and include URLs at their discretion.
A DOI, or digital object identifier, is a series of digits and letters that leads to the location of an online source. Articles in journals are often assigned DOIs to ensure that the source is locatable, even if the URL changes. If your source is listed with a DOI, use that instead of a URL.
Alonso, Alvaro, and Julio A. Camargo. "Toxicity of Nitrite to Three Species of Freshwater Invertebrates." Environmental Toxicology , vol. 21, no. 1, 3 Feb. 2006, pp. 90-94. Wiley Online Library, doi: 10.1002/tox.20155.
Creating in-text citations using the previous (eighth) edition
Although the MLA handbook is currently in its ninth edition, some information about citing in the text using the older (eighth) edition is being retained. The in-text citation is a brief reference within your text that indicates the source you consulted. It should properly attribute any ideas, paraphrases, or direct quotations to your source, and should direct readers to the entry in the Works Cited list. For the most part, an in-text citation is the author’s name and the page number (or just the page number, if the author is named in the sentence) in parentheses :
When creating in-text citations for media that has a runtime, such as a movie or podcast, include the range of hours, minutes and seconds you plan to reference. For example: (00:02:15-00:02:35).
Again, your goal is to attribute your source and provide a reference without interrupting your text. Your readers should be able to follow the flow of your argument without becoming distracted by extra information.
How to Cite the Purdue OWL in MLA
Entire Website
The Purdue OWL . Purdue U Writing Lab, 2019.
Individual Resources
Contributors' names. "Title of Resource." The Purdue OWL , Purdue U Writing Lab, Last edited date.
The new OWL no longer lists most pages' authors or publication dates. Thus, in most cases, citations will begin with the title of the resource, rather than the developer's name.
"MLA Formatting and Style Guide." The Purdue OWL, Purdue U Writing Lab. Accessed 18 Jun. 2018.
- Write great papers Article
- Captivate the class Article
- Stage your story Article

Write great papers
Write great papers with microsoft word.
You may already use Microsoft Word to write papers, but you can also use for many other tasks, such as collecting research, co-writing with other students, recording notes on-the-fly, and even building a better bibliography!
Explore new ways to use Microsoft Word below.
Getting started
Let’s get started by opening Microsoft Word and choosing a template to create a new document. You can either:
Select Blank document to create a document from scratch.
Select a structured template.
Select Take a tour for Word tips.
Next, let’s look at creating and formatting copy. You can do so by clicking onto the page and beginning to type your content. The status bar at the bottom of the document shows your current page number and how many words you've typed, in case you’re trying to stay maintain a specific word count.

To format text and change how it looks, select the text and select an option on the Home tab: Bold, Italic, Bullets, Numbering , etc.
To add pictures, shapes, or other media, simply navigate to the Insert tab, then select any of the options to add media to your document.
Word automatically saves your content as you work, so you don’t have to stress about losing your progress if you forget to press Save .
Here are some of the advanced tools you can try out while using Microsoft Word.
Type with your voice
Have you ever wanted to speak, not write, your ideas? Believe it or not, there’s a button for that! All you have to do is navigate to the Home tab, select the Dictate button, and start talking to “type” with your voice. You’ll know Dictate is listening when the red recording icon appears.
Tips for using Dictate
Speak clearly and conversationally.
Add punctuation by pausing or saying the name of the punctuation mark.
If you make a mistake, all you have to do is go back and re-type your text.
Finding and citing sources
Get a head start on collecting sources and ideas for a big paper by searching key words in Researcher in the References tab of your document.
Researcher uses Bing to search the web and deliver high-quality research sources to the side of your page. Search for people, places, or ideas and then sort by journal articles and websites. Add a source to your page by selecting the plus sign.
As you write, Researcher saves a record of your searches. Just select My Research to see the complete list.
Keep track of all your sources by using Word's built-in bibliography maker. Simply navigate to the References tab.
First, choose the style you want your citations to be in. In this example, we’ve selected APA style.
Select Insert Citation and Add New Source .
In the next window, choose what kind of work you’re citing—an article, book, etc.—and fill in the required details. Then select OK to cite your source.
Keep writing. At the ends of sentences that need sources, select Insert Citation to keep adding new sources, or pick one you already entered from the list.
As you write, Word will keep track of all the citations you’ve entered. When you’re finished, select Bibliography and choose a format style. Your bibliography will appear at the end of your paper, just like that.
Make things look nice
Make your report or project look extra professional in the Design tab! Browse different themes, colors, fonts, and borders to create work you're proud of!
Illustrate a concept with a chart or a model by navigating to the Insert tab and choosing SmartArt . In this example, we chose Cycle and filled in text from the writing process to make a simple graphic. Choose other graphic types to represent hierarchies, flow charts, and more.
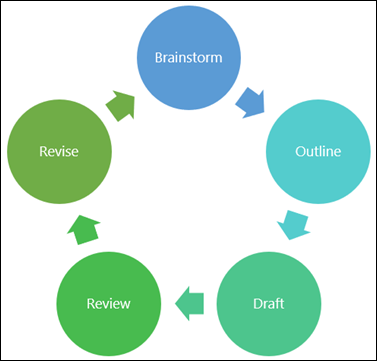
To insert a 3D model, select Insert > 3D Models to choose from a library of illustrated dioramas from different course subjects and 3D shapes.
Invite someone to write with you
If you’re working on a group project, you can work on a document at the same time without emailing the file back and forth. Select Share at the top of your page and create a link you can send to other students.
Now, everybody can open the same file and work together.
Keep learning
Check out more Microsoft Word training and support
Microsoft paper and report templates

Need more help?
Want more options.
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.

Microsoft 365 subscription benefits

Microsoft 365 training

Microsoft security

Accessibility center
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.

Ask the Microsoft Community

Microsoft Tech Community

Windows Insiders
Microsoft 365 Insiders
Was this information helpful?
Thank you for your feedback.
Best Tips on How to Write a Term Paper

Writing a Term Paper: What You Need to Know
If you've landed here by searching on Google for tips on how to write term paper, you're in the right spot! You can be upfront about your deadline and share the number of pages you need to complete with us.
This article will analyze and cover every aspect of the term paper writing process. Here, you can learn how to create an outline, structure every paragraph, and what to include in each section. After finishing the article, you can create a perfect paper yourself. But if you prefer a professional to write it instead of you, just use the magic words ' write my term paper ,' and it'll be done perfectly for you.
To write it yourself next time, let's dive in to learn every aspect of writing academic papers.
Understanding What is Term Paper
The first question we must answer to start our article is - what is term paper?! According to the definition, a term paper is a research paper you write at the end of a semester or academic year. This task will evaluate your understanding of the course material and assess your proficiency in the curriculum's essential components.
In addition to its primary goal, writing a term paper also has other purposes. It enhances your critical, analytical thinking, and writing abilities, which are valuable not only during your academic journey but also in your professional career beyond university. As you work on the parts of the document, you delve further into the subject matter and familiarize yourself with its key issues and complexities.
Depending on the course content, your professor may assign you a particular topic to write about. On other occasions, you may be free to choose a topic of your own or select a narrower theme from a more extensive list of options.
Term Paper Format
It’s imperative to grasp the meaning of a term paper format when delving into the realm of academic paper writing. A crucial initial step in formatting your paper is to consult your professor regarding specific requirements. Notably, certain term papers necessitate the inclusion of visual aids such as pictures and diagrams, as well as an abstract, while others may prefer a minimalist approach with minimal to no visual elements and no separate abstract.
The fundamental and prevalent components of the format encompass the following:
Title Page : This section contains essential information, including the author's name, the course name, the date of submission, and the instructor's name.
Abstract : An encapsulation of the paper's content, offering a concise overview.
Literature Review : This segment involves an analysis of prior research conducted by others, providing context for your study.
Methodology : In this section, the paper discusses the methods and approaches employed in the student's research.
Results : The substantive portion of the term paper, where the findings and their implications are thoroughly discussed.
Future Recommendations : This segment offers insights and guidance for those intending to pursue further study in the same field.
References List : This section compiles all the sources utilized in the research. It is essential that these sources have a correct MLA or APA format citation listed alphabetically for easy reference.
Term Paper Outline
To make any term paper writing process easier, outlining is your way out. When your term paper format is created, including writing the title page, you can start outlining your thoughts and ideas. Brainstorm the theme you're exploring, look for different ideas from various sources, further research the topic, and organize them all together.

Introduction
Starting is always challenging, and beginning the writing of a research paper is no exception. Many students, and sometimes even professionals, often face difficulties with how to start a term paper or any kind of writing. Fortunately, this brief guide will explain the purpose of the term paper format and its introduction and offer helpful tips for creating a strong one.
The introduction of the term paper is where you should set up your topic and approach for your audience; it must include the following:
Introduce the topic - The intro's initial goal is to communicate the topic's significance and interest to the reader, usually with a catchy hook .
Analyze the background - Provide some background information about the theme you're exploring and why this specific topic is essential.
Define the Problem - This part specifies how your research fits in and what problem it aims to solve.
State the Thesis Statement - The introduction should end with a thesis statement, representing the position you'll provide evidence and arguments for.
Considering these tips, you can create a perfect paper, but if you don't have time and deadlines are approaching, just text us - ' write my research paper for me ' and consider it done.
In term paper writing, body paragraphs are your central part. The worth of your entire paper depends on the information you present in these sections. When you start creating your term paper outline, always remember to include these parts in your body paragraphs:
Literature Review - This part examines scholarly articles, relevant books, and other sources related to a specific issue, research area, or theory. It presents a detailed overview, assessment, and summary of these works concerning the research problem being investigated.
Methodology Section - In this section, you should describe how you conducted the research. This information enables readers to verify the accuracy and reliability of your approach. An effective methodology can increase the reader's confidence in the validity of your findings.
Results - Here, you provide what you found while analyzing the data and answer the question posed in the introduction using the data collected.
Discussion - This section involves your analysis, description, and interpretation of your findings. They explain the significance of the results and connect them back to the research question.
Writing a term paper conclusion can often be tricky. It should be clear and summarize what you've already presented in previous sections. Every term paper needs a concluding paragraph, so let's analyze what you should include there:
Restate the research topic - A concise statement can effectively reiterate the topic, but it's essential to explain why this topic is important.
Restate the thesis statement - Write your thesis statement in different words and make it just one sentence long.
Summarize the main points of the research - Include the main arguments and facts presented in your writing and remind the reader of the significance of your topic.
Concluding sentence - Create a thought-provoking concluding sentence to make an impression on readers and leave them with something to think about.
Many students consider restating the thesis statement to be one of the most challenging parts of writing a conclusion. So, we prepared an article on how to write a thesis statement where our experts shared their tips and personal tricks of the trade.
Looking for a Professional to Write a Term Paper for You?
Order a paper today and let our experts help you achieve academic success!

How to Write a Term Paper?
Prior to immersing yourself in the process of research and writing, it is imperative to prepare a term paper proposal. Essentially, it serves as a means to present and substantiate your chosen topic to your instructor, a crucial step before commencing the actual manuscript.
In your proposal, it is vital to incorporate recent studies or research findings pertaining to your selected topic, along with appropriate references to support your assertions. Clearly articulate the relevance of your chosen topic to the course through the submission of a concise article. Additionally, delineate your objectives and adeptly structure the progression of your ideas, facilitating your instructor's comprehension of the trajectory you intend to pursue in your writing.
Should you require assistance, consider the option of procuring a term paper from our proficient writers as an alternative solution!
Start with the Abstract
In the initial section addressing the art of writing term paper, your primary objective revolves around elucidating the essence of your research. However, it is advisable to compose this section after completing all subsequent components. Ensure to highlight the principal discoveries of your research, making them accessible to readers unacquainted with the subject matter. Simplicity and informativeness are key considerations.
An effectively structured abstract should encompass the following elements:
Introduction: Introduce the problem you are tackling in your paper and elucidate the significance of your chosen topic. Furthermore, expound on the practical, scientific, or theoretical objectives of your research.
Body: Emphasize the core aspects of your research and outline your investigative approach. Provide an overview of the nature of your findings.
Conclusion: Elaborate on the practical applications or implications of your results.
When composing a term paper abstract, revisit your paper and identify pivotal statements related to your research objectives, methods, findings, and conclusions. Extract these sentences, and you will have the initial draft of your abstract.
PRO TIP: Adhere to the assignment instructions, ensuring your abstract falls within the prescribed word limit of 120-250 words.
What sets the introduction apart from the abstract? The abstract encapsulates the essence of your paper, succinctly presenting its key elements and encompassing results and conclusions. Conversely, the introduction provides contextual information about the topic, introduces the proposition (or thesis statement), and outlines the primary issues to be explored in the paper.
Write an Introduction
Prepare to captivate your readers right from the outset with a compelling term paper introduction. A robust beginning can create a compelling inertia, making it difficult for them to divert their attention from your paper. So, how can you arouse their interest and sustain their engagement?
- Seize attention: Commence with a captivating fact, a startling statement, or a thought-provoking paradox that underscores the significance of your subject matter. Initiate their curiosity from the very first sentence in your term paper.
- Offer an overview: Provide a succinct delineation of the issue you are tackling and articulate the principal objective of your paper. Additionally, elucidate how your specific topic interconnects with broader contexts, establishing the framework for a more profound exploration.
- Formulate the thesis statement: Express the fundamental argument or central question that your paper will address. Provide a glimpse of what lies ahead without divulging all the intricacies.
It's essential to bear in mind that the term paper introduction should be both inviting and concise. Avoid excessive examples or superfluous details that may obscure the initial impact.
Proceed to the Main Body
Once you have gathered your research results and notes, it's time to conduct a meticulous examination of your findings. Capture the essential outcomes of your research while eliminating any superfluous materials, thereby streamlining your work.
To write term paper body sections, an effective approach involves initiating the process by formulating topic sentences based on your outline. Subsequently, expand these topic sentences into full-fledged paragraphs, incorporating pertinent supporting details to reinforce your arguments.
The number of paragraphs required for your body section can vary, contingent on the specific topic and the instructions provided in the assignment. In many instances, a term paper's body entails a literature review followed by the presentation of your research results.
Here's a valuable tip for maintaining coherence and lucidity: Initiate each paragraph with a well-crafted topic sentence. This serves as a clear introduction to the central idea of the paragraph, ensuring a seamless progression of ideas throughout your paper. By employing this technique, your term paper will exhibit a well-structured organization and will be easily comprehensible for your readers.
Finish with a Conclusion
As you draw the main body of your term paper to a close, it is paramount to deliver a considerate and succinct conclusion. This conclusion should serve to recapitulate the information presented and explore the broader ramifications of your research. Here are key considerations for shaping your conclusion:
IMPORTANT NOTE:
- Avoid introducing any novel information in this section.
- Summarize the final outcomes of your research.
- Articulate the implications for future investigations.
Now, take a moment to assess your research findings by reflecting on the following inquiries:
What significance does my research hold?
How does my chosen topic intersect with other relevant subjects or domains?
Ultimately, bring all these elements together with a potent concluding sentence that leaves a lasting and resonant impression.
Upon successfully completing your initial draft and finding yourself with some remaining time, it's crucial to recognize the significance of proofreading your text. Devoting a moment to reviewing paper can yield remarkable results. After all, many professors perceive misspellings, punctuation errors, and grammatical inaccuracies as reflections of negligence, potentially overshadowing your original ideas and substantial findings. Let's elevate the quality of your text!
Begin by meticulously perusing your first draft and considering how to refine your paper for greater clarity and persuasiveness. Identify ideas that may not seamlessly fit the context and either eliminate or adapt them accordingly. Additionally, pinpoint areas where more comprehensive support is needed. To enhance the fluidity of your paper, incorporate transitional phrases or words to ensure a smooth connection of ideas.
Subsequently, once your content is logically structured, it's time to rectify any errors. Thoroughly address all grammatical, punctuation, and spelling mistakes with care.
Lastly, ensure that your paper adheres to the correct format (e.g., Chicago style format ) and layout. Verify the accuracy of page numbering and make certain that any visual elements, such as images, tables, and diagrams, are appropriately numbered and titled. Just as you do when finalizing your term paper, devote the same level of attention to these details during the proofreading process. Your dedication will culminate in a polished and impressive final paper.
Need PRO Help in Creating Term Paper Proposals?
Let our experts make the perfect final draft for you!

Term Paper Writing Tips
You can create the best term paper by considering all the tips and structures we provided for you, and you must now be able to craft a term paper template that can impress your professor.
To better immerse how to write a term paper, we have some additional tips you can use to practice your writing skills and make the writing process easier:

- Implement Mind Mapping Strategies - Develop 3-5 main ideas and use a mind mapping strategy to connect them and choose the one you'll explore in your paper.
- Use Case Studies - Case studies can not only help in writing your paper, but they can also help to create a term paper proposal to make the significance of the theme more plausible.
- Choose a Doable Topic - Pick a subject you can effectively address within the given time frame. Narrow down a topic that is captivating and inspiring to you.
- Avoid Being Wordy - Are your sentences concise? Evaluate each one and determine if you've used a minimum number of words necessary to convey meaning.
- Double-check and Proofread - Run a spelling-checker to eliminate errors in your paper. Ask someone else to read it for you and listen to their feedback. You can also use AI to make it read your paper and listen to how every word and sentence sounds and if anything needs to be corrected.
How to Choose Sources for Citing in Your Term Papers
Prioritizing the search for the most effective sources is of utmost importance when you write a term paper. Before delving into the writing process, it is imperative to assemble all the sources you require, as they will serve as the foundation for constructing the Literature Review chapter. But how do you discern the most credible and influential sources?
Rely on reputable databases: Look to trusted databases such as JSTOR and Google Scholar as exemplary sources of credibility. These repositories host the latest peer-reviewed articles, expediting your research process.
Verify the site's address: Pay close attention to the website's URL. Links with .gov, .org, and .edu domains typically offer reliable and authoritative information. Conversely, steer clear of sources such as news portals, blogs, and Wikipedia, as they often contain personal opinions without substantial evidence.
Do impartial research: Authors frequently imbue their work with their personal political and social beliefs. In the context of your article, prioritize sources with minimal bias. Investigate the author's background and assess their trustworthiness.
Seek most recent sources: Given the dynamic nature of many research fields, aim for sources not exceeding five years. This is particularly crucial if your paper pertains to the sciences, where up-to-date studies are paramount.
Stay on topic: Remember that your term paper essay must adhere closely to the chosen subject. Even if a source appears impressive, it is incompatible with your paper if it slightly relates to your topic.
Use Our Academic Help
Now, you have all the information to begin writing your first draft for a successful term paper. But if writing a term paper definitely isn't a thing you want to be doing right now, you can text us and your assignment will be perfectly done with no further effort on your behalf.
Our Latest Blog Posts
.webp)
Your path to academic success
Improve your paper with our award-winning Proofreading Services , Plagiarism Checker , Citation Generator , AI Detector & Knowledge Base .
Proofreading & Editing
Get expert help from Scribbr’s academic editors, who will proofread and edit your essay, paper, or dissertation to perfection.
Plagiarism Checker
Detect and resolve unintentional plagiarism with the Scribbr Plagiarism Checker, so you can submit your paper with confidence.
Citation Generator
Generate accurate citations with Scribbr’s free citation generator and save hours of repetitive work.

Happy to help you
You’re not alone. Together with our team and highly qualified editors , we help you answer all your questions about academic writing.
Open 24/7 – 365 days a year. Always available to help you.
Very satisfied students
This is our reason for working. We want to make all students happy, every day.
Ease of use and excellent citation…
Ease of use and excellent citation support
It works exceptionally well
It works exceptionally well, some references that are not open to the public, you sometimes have to manually cite. But as research should be public as students don't have 40€ to pay for a research paper, I find it acceptable as I would not want to us those papers anyway for everything else it works great.
Simplistic and Efficient
Very helpful in creating citations while also creating the in paragraph citations, saves so much time very simple and easy to use. Even when it cannot cite it aids in helping me create my own citations.
Awesome experience!
Scribbr has helped me in my college…
Scribbr has helped me in my college citations. It is an excellent tool to do a better job.
Huge time saver!
I have used Scribbr for the duration of my degree program. It is a huge time saver and allows me to focus on content rather than worrying about if I put the date in the correct location in my citation.
Very user friendly and gives accurate…
Very user friendly and gives accurate information.
This is a fantastic site to cite your…
This is a fantastic site to cite your references in the correct format quickly! I know I was able to cite all of my references correctly in my last paper because of this program.
It always helps get the job done.
Easy and efficient to use.
This tool has helped me write many…
This tool has helped me write many papers in my doctoral program. The citation tool is the best, and the fact that it keeps me on track from making plagiarism mistakes is very helpful.
The majority of the time it's correct, but sometimes manual entry is needed.
Great time saver
Great time saver, easy to use and accurate in most situations.
Having the resource of rephrasing…
Having the resource of rephrasing sections of text for my graduate papers has been helpful when my thoughts were just not coming together.
Great for Citation generator
I can only speak for the citation generator as that is the only product I've used by Scribbr all these years. By far a must-use for any college course. Scribbr is a free citation generator that provides so much value for users. No BS here. It's helped me properly cite papers for many years. Worth the check.
It is very accurate and has helped me…
It is very accurate and has helped me with citations tremendously.
I love Scribbr.
I love Scribbr.. it does glitch at times and give incorrect citations (i've contact support a few times) but overall, it works very well. The paraphraser if also very useful!!
Everything was so simple
Instant citations
It's really helpful to be able to generate citations in whatever style you need, directly from your browser. I use it every day.
I LOVE Scribbr
I LOVE Scribbr. It's the best citation tool I have used.
Everything you need to write an A-grade paper
Free resources used by 5,000,000 students every month.
Bite-sized videos that guide you through the writing process. Get the popcorn, sit back, and learn!

Lecture slides
Ready-made slides for teachers and professors that want to kickstart their lectures.
- Academic writing
- Citing sources
- Methodology
- Research process
- Dissertation structure
- Language rules
Accessible how-to guides full of examples that help you write a flawless essay, proposal, or dissertation.

Chrome extension
Cite any page or article with a single click right from your browser.
Time-saving templates that you can download and edit in Word or Google Docs.

Help you achieve your academic goals
Whether we’re proofreading and editing , checking for plagiarism or AI content , generating citations, or writing useful Knowledge Base articles , our aim is to support students on their journey to become better academic writers.
We believe that every student should have the right tools for academic success. Free tools like a paraphrasing tool , grammar checker, summarizer and an AI Proofreader . We pave the way to your academic degree.
Ask our team
Want to contact us directly? No problem. We are always here for you.
- Email [email protected]
- Start live chat
- Call +1 (510) 822-8066
- WhatsApp +31 20 261 6040

Frequently asked questions
Our team helps students graduate by offering:
- A world-class citation generator
- Plagiarism Checker software powered by Turnitin
- Innovative Citation Checker software
- Professional proofreading services
- Over 300 helpful articles about academic writing, citing sources, plagiarism, and more
Scribbr specializes in editing study-related documents . We proofread:
- PhD dissertations
- Research proposals
- Personal statements
- Admission essays
- Motivation letters
- Reflection papers
- Journal articles
- Capstone projects
Scribbr’s Plagiarism Checker is powered by elements of Turnitin’s Similarity Checker , namely the plagiarism detection software and the Internet Archive and Premium Scholarly Publications content databases .
The add-on AI detector is powered by Scribbr’s proprietary software.
The Scribbr Citation Generator is developed using the open-source Citation Style Language (CSL) project and Frank Bennett’s citeproc-js . It’s the same technology used by dozens of other popular citation tools, including Mendeley and Zotero.
You can find all the citation styles and locales used in the Scribbr Citation Generator in our publicly accessible repository on Github .
to submit an obituary
Monday-Friday 8:30am-4:00pm, Call 610-915-2226
(Proofs will be provided for accuracy only, they will not be styled/formatted like the finished product)
Obituaries submitted on Saturday, Sunday and Holidays are accepted from 8:30 a.m. to 3:00 p.m. by email only [email protected]
(No proofs will be furnished. Pricing will not be available until the next business day after 10:00am by calling Dianne at 610-915-2226)
Obituaries received after Deadline will not be published in the following edition of the paper.
Sending Procedure:
Email is the preferable method for receiving Obituaries (and the only method on Saturday, Sunday and Holidays), they can be sent to [email protected] (Feel free to call and confirm that we’ve received the email)
Formatting:
Obituaries will continue to visually look the same as they currently do, but you will no longer be restricted in what you can say (ex. As much Family can be listed as you’d like; Wording like “Went to rest with the Lord” is now permissible)
There is a cost for each obituary. Pricing and payments are only available Monday through Friday, 8:30 am to 4:00 pm. All weekend and holiday submissions will be provided a cost the next business day.
Exceptions:
All New accounts, Out of State Funeral Homes and Private Parties will require prepayment upon approval of the obituary. Weekend and Holiday staff are not authorized to set up a new account or process payments
Deadline for the above is before 4:00 PM Mon – Fri. only (Holiday schedules may vary).
Prepayment required submissions will be handled on the very first business day following the weekend and/or holiday schedule. A complete name, address and best contact phone number are required upon submittal of your obituary request to set up your account. A proof will then be emailed for review but placed on hold until payment is received.

Sponsored Content | Best Research Paper Writing Services: Top 5…
Share this:.
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window)
Sponsored Content
Sponsored content | best research paper writing services: top 5 u.s. companies, after a thorough search, we’ve narrowed down the five leading research paper writing sites. our comparison is based on their quality, affordability, and several other aspects to ensure you pick the best service for your needs..

On all of the factors that we judged these 5 paper writing services by, PaperHelp consistently impressed on all fronts. With prices starting at just $13 for a 1-page essay, PaperHelp provides professional standards of writing at a budget-friendly price.
You can get a paper written for high school, undergraduate, bachelor’s, and even professional education levels. PaperHelp not only offers academic writing samples, but they also have an editing and proofreading service. This allows you to send them a draft of your paper, and get tailored feedback on improvements and corrections.
When you make an order on their website, PaperHelp matches your criteria to one of their hundreds of writers. They have experts in almost every subject area, who provide fast service — they can even write your paper in time for a same-day deadline!
All purchases from PaperHelp also come with a free revision policy, allowing you to tailor your essay to the smallest of details. You can request up to 3 free revisions of your paper. Every essay you buy is also checked thoroughly for plagiarism.
Overall, this is our pick for the best research paper writing service. We love PaperHelp for its easy-to-use website, its generous free revision policy, and its great value for money. If you require research paper writing help, this is the website to choose.
2. BBQPapers : Best For Complex College Papers

Sometimes you need a specialist essay on a niche or complicated topic — and this is exactly the situation where BBQPapers excels. They promise that they have a top 2% expert for every subject area, no matter how broad or specific, and their papers have fast turnarounds of as little as 3 hours.
The professional writers at BBQPapers can help you with not only papers but also presentations — making them one of the few sites to offer help with different types of assignments.
Prices at BBQPapers start at $5.85 for 100 words. If you find yourself needing their services often, or requesting a lot of lengthy papers, then you can take advantage of their loyalty program. This gives you lifetime discounts of 5%, 10%, and 15% off all of your future papers.
Every paper comes with accurate referencing (in the style that you request), a review by a trained editor, and unlimited free revisions within 10 days. If even after this you’re not satisfied with the essay that you receive, you have a 60-day money-back guarantee.
If you’re looking for a specialized, completely confidential service with services available up to Ph.D. level of study, then look no further than BBQPapers.
3. EssayTerritory : Best Value

Saving money everywhere you can as a student is important, which is why great value paper writing services like EssayTerritory are great to find. You can expect a cheap, reliable, and fast service, for both education and business assignments!
A high school level paper with a 14-day deadline from EssayTerritory costs just $10 — and this price includes high-quality editing and proofreading, relevant case studies and sources, and unlimited free revisions. This service has one of the largest varieties of assignment types to choose from, including job applications, dissertation chapters, and thesis proposals.
Essays and college assignments from EssayTerritory can be written for Ph.D. level, and even then, prices are still very competitive. The highest price you’ll pay for Ph.D. projects with a 1-day turnaround is $81, much less than other paper writing services.
If you’re not satisfied with your paper, it’s easy to reach out to EssayTerritory 24/7 customer support. They can guide you through the process of requesting revisions or even give you a full refund thanks to their money-back guarantee.
If you’re looking for a high-quality, fast service at the best possible price that you can find, EssayTerritory can help you to pass your assignments without breaking the bank.
4. SpeedyPaper : Best Customer Support

What sets SpeedyPaper apart from the competition is its commitment to providing excellent service. With their friendly and dedicated customer support, at every stage of your purchase, you can feel confident and assured of the progress of your paper.
Their customer reviews praise the fast delivery, great price, and the communication that was received throughout the process. Their writers are professional and know how to deal with different subject areas to minute levels of detail.
We were impressed with how transparent SpeedyPaper is about its services. They outline their criteria for recruiting writers on their website, which includes academic verification using university degree qualifications, GPA, and high grammar test scores. They even outline how much their writers are paid.
SpeedyPaper pride themselves on their good customer reputation, which is maintained thanks to their reliable service and high quality customer care team. They have samples of previous work available to view on their website, which will give you an idea of the quality you can expect from the finished product.
SpeedyPaper is our recommendation for the research paper writing site that provides the best customer service and dedication to customer satisfaction.
5. EssayPro : Best for Choice and Flexibility

Any good essay writing service will assign writers to papers based on their expertise, knowledge, and education level. But some of these sites do this using an algorithm, which is efficient, but can make mistakes…and there’s no true substitute for a human eye.
EssayPro takes a revolutionary approach to this model, and instead of leaving your paper in the hands of AI, allows you to choose which of their writers you want to take care of your assignment. This unique service means that you can find the best possible writer who matches the needs of your paper.
EssayPro acts as an intermediary service that connects you with freelance writers who are highly qualified, and have often been working as professional writers for years. All of the writers on EssayPro have 5+ years of experience of academic writing, and have a Masters degree or higher qualification.
Thanks to the site-wide policy, you are entitled to unlimited free revisions with your order, no matter which writer you choose. You will also be guaranteed a fast, friendly, and professional writing service.
If you want to make sure that your paper is written by someone you can trust, then make sure to check out EssayPro!
FAQs About Research Paper Writing Services
How do essay writing services work.
If you’ve never ordered from an essay writing service before, then you might not know what to expect — or where to start. More and more college students are turning to these sites to help them with the increasing number of essays that they are assigned every semester — but how do essay writing services work?
The research paper writing services connect you with professional and academic writers, who are either employed by the site or work as self-employed freelancers, to work on your paper. The professional research paper writer will see the subject area you request, the number of words or pages that are needed, the deadline for the paper, and other information that you provide.
The research paper helper may contact you to request additional information, or to keep you updated on the progress of your paper. Because the writer that has been assigned to your paper will have knowledge of your subject area, they will use a variety of specialized resources to write your assignment.
Once your paper has been completed, you will receive a PDF draft from the professional writer — this is the stage where you can ask for any revisions to be made. If you’re happy with what has been written, the full version of the paper will be released to you, and is officially all yours!
Are research paper writing websites legit?
Contrary to popular belief, there is nothing illegal about using a custom research paper writing website. As long as you follow the correct procedures of your university, you also can’t get into trouble for academic misconduct.
Writers who work for research paper writing services are normal human beings, who happen to have a passion and a talent for writing. Usually, these writers are paid a large percentage of what you pay to the research paper help site — sometimes, they are also paid to work specific hours.
Before you start spending money though, it’s important to verify the integrity of the site you’re looking to use. The essay writing services space has exploded in popularity in recent years, which means that some people want to take advantage of this. There are plenty of sites that will take your payment and run, leaving you out of pocket and without an essay for your upcoming deadline.
Make sure to check the reviews of the sites you’re looking at — especially those on impartial sites such as TrustPilot. It can also be helpful to look at the About Us section on the website, to learn more about the company. Finally, if it seems too good to be true, it likely is — don’t trust sites that are charging something like $10 for thousands of words, with a same-day turnaround.
Can I entrust someone to write my research paper? Is it safe?
Research paper assistance sites mentioned on this list are 100% safe to use, and you don’t need to worry about any negative repercussions from using their services. The most reputable sites will have a confidentiality policy, where your interaction with their research paper writers will remain anonymous. Nobody will know you have used the site unless you share this information yourself.
Most sites put their professional paper writers through strict verification processes — this ensures not only their writing ability, but also that they are a real and trustworthy person. They may ask their writers to provide government issued ID, and proof of their employment or academic qualifications.
You may also be concerned about if your payment is secure when using a term paper writing service — many of these sites use secure payment methods such as PayPal, Google Pay, Apple Pay and more. There is also support for a number of international, fee-free payment options.
A good research paper writing service will also have stringent anti-plagiarism measures. This includes checking the finished product a number of times through different services, and some sites will have their own purpose-built plagiarism checkers.
Will my essay be plagiarism-free?
One of the main concerns when ordering an essay from a writing service is whether it will be flagged for plagiarism. Having this happen to one of your assignments can get you into serious trouble. You may be investigated by your school’s academic misconduct department, and you could even be expelled from your high school, university, or college.
Professional research paper services include a guarantee of plagiarism-free content. Your paper will contain only unique content, with no copy-pasted information. All sources will also be properly referenced in the style that you request.
To achieve this, sites use plagiarism checkers from a variety of sources. Many custom research papers and term papers are checked multiple times, and every effort is taken to reduce the similarity percentage of the finished product.
Specifically, many sites will ensure that their research papers pass the plagiarism check enforced by Turnitin — one of the most popular assignment submission platforms that many universities use. The platform has a strict plagiarism checker that will flag an assignment if it is above a certain similarity percentage.
You can be confident that your essay will be plagiarism-free when ordering from a paper writing service; and if it isn’t, you may be entitled for a free refund under their money back guarantee.
How much does it cost to hire professional research paper writers?
The price to buy a research paper online will vary depending on a few factors. Many sites will allow you to input your basic requirements, and give you an estimation of the price based on this. The factors that can increase or decrease the cost of your paper include its length, the deadline for submission, the education level, and sometimes the subject area.
The specific cost of paying for an essay may be calculated per page, or per 100 words. In most cases, our research found that the standard price for a 1 page, high-school level essay with a 2 week turnaround was between $10 and $12.
If you want to save on your research paper, then make sure to request the services of a writing site well in advance — the more time you give them to complete your paper, the less it will cost.
Can you get caught using term paper writing services?
This is a common concern for people who are looking to find a research paper service to write academic papers for them. Plagiarism not only includes using uncited sources from the internet, but also trying to pass off someone else’s work as your own. As we covered earlier, this can get you into a lot of trouble.
When buying an essay to use as a model answer, as reference material, or ideas, you cannot get caught or punished for using it. Your professors won’t need to see the essay that you bought, and you won’t need to cite your usage of it; because for all intents and purposes, it does not exist.
Things become less clear when you consider, or intend to submit a research paper that you bought. Many sites do not encourage this, and it should not be the main reason that you look for a service to write your essay for you. You have a much higher chance of being caught for submitting a bought research paper as your own, but you may also get away with it … do so at your own risk!
So, to conclude, our overall choice for the best research paper writing service is PaperHelp. We’re crowning them as our winner based on their high quality services, low prices, and fast delivery. Their customer reviews and testimonials show that people trust them to deliver on-time, and to take attention to detail in their work.
Whether you’re looking for inspiration, editing and proofreading, or just expert advice on your research paper, you can be sure of receiving an A+ service from PaperHelp.
The news and editorial staff of the Delco Daily Times had no role in this post’s preparation.
More in Sponsored Content

Sponsored Content | Best 15 Trusted Platforms to Buy Instagram Likes (2024)

Sponsored Content | Buy Instagram followers from these 16 best sites (2024)

Sponsored Content | Buy TikTok Followers From These 17 Best & Trusted Sites

Sponsored Content | The 7 Best Essay Writing Services in the U.S.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 1: Find a topic and review the literature. As we mentioned earlier, in a research paper, you, as the researcher, will try to answer a question.More specifically, that's called a research question, and it sets the direction of your entire paper. What's important to understand though is that you'll need to answer that research question with the help of high-quality sources - for ...
Step 1: Prewriting. Step 2: Planning and outlining. Step 3: Writing a first draft. Step 4: Redrafting and revising. Step 5: Editing and proofreading. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the writing process.
Develop a thesis statement. Create a research paper outline. Write a first draft of the research paper. Write the introduction. Write a compelling body of text. Write the conclusion. The second draft. The revision process. Research paper checklist.
Writing a Paper. The Walden Writing Center staff is dedicated to ensuring your transition to a writing intensive program is a smooth one. In the pages listed on the left you will find all the information you need to master the craft of scholarly writing. If you are new to scholarly writing, it may be helpful to remember that writing is a ...
8. Write a research paper outline. Before diving in and writing the whole paper, start with an outline. It will help you to see if more research is needed, and it will provide a framework by which to write a more compelling paper. Your supervisor may even request an outline to approve before beginning to write the first draft of the full paper.
Essay writing process. The writing process of preparation, writing, and revisions applies to every essay or paper, but the time and effort spent on each stage depends on the type of essay.. For example, if you've been assigned a five-paragraph expository essay for a high school class, you'll probably spend the most time on the writing stage; for a college-level argumentative essay, on the ...
Writing an Introduction. The introduction of an academic paper must make your argument clear, and should be concise and free of any fluff. You need to clearly lay out your argument, but should also set the scene for your work by summarizing the major scholarship, or history of the field, which most writers do first.
This can help guide you through both your research and outline creation process. 2. Select the topic of your paper. After reviewing the guidelines of your paper, you can choose the topic you'd like to cover. Take your time researching different topics relevant to the guidelines of your paper.
Just get your thoughts on paper. Draft an introduction that grabs your reader's attention, states your topic, and explains the point of your paper. Write body paragraphs that logically support your thesis statement. Put the information you researched into your own words. Draft a conclusion that reflects on and summarizes the main points of ...
Set the top, bottom, and side margins of your paper at 1 inch. Use double-spaced text throughout your paper. Use a standard font, such as Times New Roman or Arial, in a legible size (10- to 12-point). Use continuous pagination throughout the paper, including the title page and the references section.
Work Your Sources into Your Research Writing. Working your sources into your writing is a very important part of the writing process and gets easier over time. You must also decide whether you will quote, paraphrase, or summarize the material when incorporating resources into your writing. Academic integrity encompasses the practice of engaging ...
Pre-Writing. Download Article. 1. Choose a topic and research it. Typically, your teacher or instructor provides a list of topics to choose from for an essay. Read the assignment rubric, make sure you understand it, and pick a topic that interests you and that you think you can write a strong paper about. [1]
the essence of your argument or idea. See our handout on Writing a Thesis Statement for more. The roadmap Not all academic papers include a roadmap, but many do. Usually following the thesis, a roadmap is a narrative table of contents that summarizes the flow of the rest of the paper. Below, see an example
Abstract: Abstract is a brief synopses of article.It provides a brief but comprehensive summary of the article. Citing: In the context of academic writing, citing is the act of acknowledging the sources of information you have used when writing your work.. Citation: A citation gives credit to a source, and contains publication information such as author(s), title and date.
This article walks through the formatting steps needed to create an APA Style student paper, starting with a basic setup that applies to the entire paper (margins, font, line spacing, paragraph alignment and indentation, and page headers). It then covers formatting for the major sections of a student paper: the title page, the text, tables and ...
§Write something, even a few lines, every day §"Don't fall in love with your prose: writing and rewriting is what every author does to create papers that are both convincing and clear" -[Dr. Rob Fish] §Use headers andsub-headers -helps illuminate logical flow of paper 36
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and ...
- The Writing Process: These features show all the steps taken to write a paper, allowing you to follow it from initial idea to published article. - Into the Essay: Excerpts from actual papers show the ideas from the chapters in action because you learn to write best by getting examples rather than instructions. Much of my approach to ...
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9 th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
Finding and citing sources. Get a head start on collecting sources and ideas for a big paper by searching key words in Researcher in the References tab of your document. Researcher uses Bing to search the web and deliver high-quality research sources to the side of your page. Search for people, places, or ideas and then sort by journal articles and websites.
Summarize the main points of the research - Include the main arguments and facts presented in your writing and remind the reader of the significance of your topic. Concluding sentence - Create a thought-provoking concluding sentence to make an impression on readers and leave them with something to think about.
Improve your paper with our Proofreading & Editing Service, Plagiarism Checker, Citation Generator, and extensive Knowledge Base. ... Fast and easy helps a lot with my school work! Read review on Trustpilot Jeremy 7 April 2024 Excellent app ... Everything you need to write an A-grade paper. Free resources used by 5,000,000 students every month.
1. PaperHelp: Best Research Paper Writing Service Overall. On all of the factors that we judged these 5 paper writing services by, PaperHelp consistently impressed on all fronts. With prices ...
'A masterpiece of statesmanship," declared The Daily Telegraph.. "Un résultat considérable," judged Le Figaro.It is relatively rare for diplomats to secure such coverage of our work.
After the amount of the bond was slashed to $175 million by a New York appeals court, the Trump team eventually reached back out to Knight Specialty, according to Hankey. At first, Trump planned ...