Eureka Math™ Homework Helper 2015–2016 Grade 1 Module 2


Related documents

Study collections
Add this document to collection(s).
You can add this document to your study collection(s)
Add this document to saved
You can add this document to your saved list
Suggest us how to improve StudyLib
(For complaints, use another form )
Input it if you want to receive answer
Standards Alignment
Assessments, professional learning, family engagement, case studies.
NEW EUREKA MATH 2 ® PILOT PACKAGE
Are you looking for new ways to advance equity and build knowledge in your math classroom with high-quality instructional materials? EdReports recently reviewed Eureka Math 2 . Scan the QR code or access the final report .
Check out our special pilot package for only $10 per student.
Shop Online

SEE THE SCIENCE OF READING IN ACTION
At Great Minds ® , we’re committed to ensuring our curricula are aligned to the latest research on how students best learn to read, write, and build knowledge.
Explore webinars, blogs, research briefs, and more to discover how we incorporate this important body of research.

FREE CLASSROOM PRINTABLES
At Great Minds®, we’re committed to supporting educators with high-quality curricula and resources.
Explore resources designed to aid students in science and engineering and spark classroom conversation.
Webinar Library
Instructional resources, trending topics, knowledge-building, the science of reading, lesson design, universal design for learning (udl), background knowledge.
Palm Springs, CA
Houston, TX
New Orleans, LA

Eureka Math Student Materials: Grades K–5
Learn, Practice, Succeed
Learn, Practice, and Succeed from Eureka Math™ offer teachers multiple ways to differentiate instruction, provide extra practice, and assess student learning. These versatile companions to A Story of Units® (Grades K–5) guide teachers in response to intervention (RTI), provide extra practice, and inform instruction.
Also available for Grades 6–8 .
Learn, Practice, Succeed can be purchased all together or bundled in any configuration. Contact your account solutions manager for more information and pricing.

The Learn book serves as a student’s in-class companion where they show their thinking, share what they know, and watch their knowledge build every day!
Application Problems: Problem solving in a real-world context is a daily part of Eureka Math , building student confidence and perseverance as students apply their knowledge in new and varied ways.
Problem Sets : A carefully sequenced Problem Set provides an in-class opportunity for independent work, with multiple entry points for differentiation.
Exit Tickets: These exercises check student understanding, providing the teacher with immediate, valuable evidence of the efficacy of that day’s instruction and informing next steps.
Templates: Learn includes templates for the pictures, reusable models, and data sets that students need for Eureka Math activities.

With Practice , students build competence in newly acquired skills and reinforce previously learned skills in preparation for tomorrow’s lesson. Together, Learn and Practice provide all the print materials a student uses for their core instruction.
Eureka Math contains multiple daily opportunities to build fluency in mathematics . Each is designed with the same notion—growing every student’s ability to use mathematics with ease . Fluency experiences are generally fast-paced and energetic, celebrating improvement and focusing on recognizing patterns and connections within the material.
Eureka Math fluency activities provide differentiated practice through a variety of formats—some are conducted orally, some use manipulatives, others use a personal whiteboard, or a handout and paper-and-pencil format.
Sprints: Sprint fluency activities in Eureka Math Practice build speed and accuracy with already acquired skills. Used when students are nearing optimum proficiency, Sprints leverage tempo to build a low-stakes adrenaline boost that increases memory and recall. Their intentional design makes Sprints inherently differentiated – the problems build from simple to complex, with the first quadrant of problems being the simplest, and each subsequent quadrant adding complexity.

Eureka Math Succeed enables students to work individually toward mastery. Teachers and tutors can use Succeed books from prior grade levels as curriculum-consistent tools for filling gaps in foundational knowledge. Students will thrive and progress more quickly, as familiar models facilitate connections to their current, grade-level content.
Additional Problem Sets: Ideal for Homework or extra practice, these additional problem sets align lesson-by-lesson with what is happening in the classroom. These problems are sequenced from simple-to-complex to naturally scaffold student practice. They align with Eureka Math and use the curriculum’s mathematical models and language, ensuring that students feel the connections and relevance to their daily instruction, whether they are working on foundational skills or getting extra practice on the current topic.
Homework Helpers: Each problem set is accompanied by a Homework Helper, a set of worked examples that illustrate how similar problems are solved. The examples, viewed side by side with the homework, support students as they reinforce the day’s learning. Homework Helpers are also a great way to keep parents informed about math class.

Bundles and Class Sets Available
Bundle options are available for all of our materials (print, digital, PD, etc.). Prices vary by grade and size of class set. Certain grade-levels do not include all packets due to the nature of the grade-level content. Student workbooks are available in class sets of 20, 25, and 30. Prices vary by size of class set .

every child is capable of greatness
- Job Openings
- Digital Support
- Print Support
- Media Inquiries
Let’s Connect
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- System Status
- CA Residents: Do Not Sell My Info
- Texas Go Math
- Big Ideas Math
- Engageny Math
- McGraw Hill My Math
- enVision Math
- 180 Days of Math
- Math in Focus Answer Key
- Math Expressions Answer Key
- Privacy Policy
Eureka Math Grade 1 Module 2 Lesson 14 Answer Key
Engage ny eureka math 1st grade module 2 lesson 14 answer key, eureka math grade 1 module 2 lesson 14 sprint answer key.
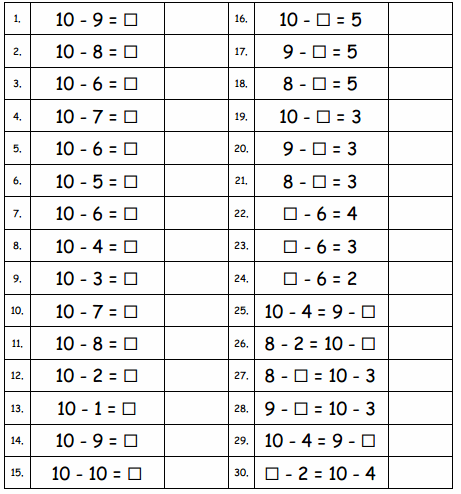
Question 1. 10 – 9 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 9 = 1 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract nine from ten then we got one.
Question 2. 10 – 8 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 8 = 2 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract eight from ten then we got two.
Question 3. 10 – 6 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 6 = 4 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract six from ten then we got four.
Question 4. 10 – 7 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 7 = 3 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract seven from ten then we got three.
Question 5. 10 – 6 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 6 = 4 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract six from ten then we got four.
Question 6. 10 – 5 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 5 = 5 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract five from ten then we got five.
Question 7. 10 – 6 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 6 = 4 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract six from ten then we got four.
Question 8. 10 – 4 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 4 = 6 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract four from ten then we got six.
Question 9. 10 – 3 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 3 = 7 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract three from ten then we got seven.
Question 10. 10 – 7 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 7 = 3 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract seven from ten then we got three.
Question 11. 10 – 8 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 8 = 2 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract eight from ten then we got two.
Question 12. 10 – 2 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 2 = 8 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract two from ten then we got eight.
Question 13. 10 – 1 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 1 = 9 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract one from ten then we got nine.
Question 14. 10 – 9 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 9 = 1 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract nine from ten then we got one.
Question 15. 10 – 10 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 10 = 0 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract ten from ten then we got zero.
Question 16. 10 – ☐ = 5 Answer: 10 – 5 = 5 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract five from ten then we got five.
Question 17. 9 – ☐ = 5 Answer: 9 – 4 = 5 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract four from nine then we got five.
Question 18. 8 – ☐ = 5 Answer: 8 – 3 = 5 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract three from eight then we got five.
Question 19. 10 – ☐ = 3 Answer: 10 – 7 = 3 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract seven from ten then we got three.
Question 20. 9 – ☐ = 3 Answer: 9 – 6 = 3 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract six from nine then we got three.
Question 21. 8 – ☐ = 3 Answer: 8 – 5 = 3 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract five from eight then we got three.
Question 22. ☐ – 6 = 4 Answer: 10 – 6 = 4 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract six from ten then we got four.
Question 23. ☐ – 6 = 3 Answer: 9 – 6 = 3 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract six from nine then we got three.
Question 24. ☐ – 6 = 2 Answer: 8 – 6 = 2 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract six from eight then we got two.
Question 25. 10 – 4 = 9 – ☐ Answer: 10 – 4 = 9 – 3 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract four from ten then we got six. Subtract three from nine then we got six. Both are equal number sentences.
Question 26. 8 – 2 = 10 – ☐ Answer: 8 – 2 = 10 – 4 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract two from eight then we got six. Subtract four from ten then we got six. Both are equal number sentences.
Question 27. 8 – ☐ = 10 – 3 Answer: 8 – 1 = 10 – 3 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract one from eight then we got seven. Subtract three from ten then we got seven. Both are equal number sentences.
Question 28. 9 – ☐ = 10 – 3 Answer: 9 – 2 = 10 – 3 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract two from nine then we got seven. Subtract three from ten then we got seven. Both are equal number sentences.
Question 29. 10 – 4 = 9 – ☐ Answer: 10 – 4 = 9 – 3 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract four from ten then we got six. Subtract three from nine then we got six. Both are equal number sentences.
Question 30. ☐ – 2 = 10 – 4 Answer: 8 – 2 = 10 – 4 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract two from eight then we got six. Subtract four from ten then we got six. Both are equal number sentences.
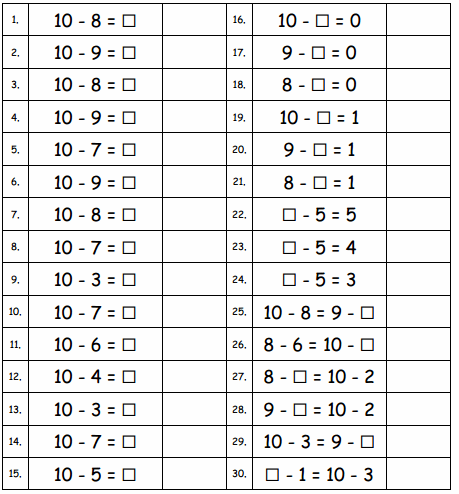
Question 1. 10 – 8 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 8 = 2 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract eight from ten then we got two.
Question 2. 10 – 9 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 9 = 1 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract nine from ten then we got one.
Question 3. 10 – 8 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 8 = 2 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract eight from ten then we got two.
Question 4. 10 – 9 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 9 = 1 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract nine from ten then we got one.
Question 5. 10 – 7 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 7 = 3 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract seven from ten then we got three.
Question 6. 10 – 9 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 9 = 1 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract nine from ten then we got one.
Question 7. 10 – 8 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 8 = 2 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract eight from ten then we got two.
Question 8. 10 – 7 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 7 = 3 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract seven from ten then we got three.
Question 11. 10 – 6 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 6 = 4 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract six from ten then we got four.
Question 12. 10 – 4 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 4 = 6 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract four from ten then we got six.
Question 13. 10 – 3 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 3 = 7 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract three from ten then we got seven.
Question 14. 10 – 7 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 7 = 3 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract seven from ten then we got three.
Question 15. 10 – 5 = ☐ Answer: 10 – 5 = 5 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract five from ten then we got five.
Question 16. 10 – ☐ = 0 Answer: 10 – 10 = 0 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract ten from ten then we got zero.
Question 17. 9 – ☐ = 0 Answer: 9 – 9 = 0 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract nine from nine then we got zero.
Question 18. 8 – ☐ = 0 Answer: 8 – 8 = 0 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract eight from eight then we got zero.
Question 19. 10 – ☐ = 1 Answer: 10 – 9 = 1 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract nine from ten then we got one.
Question 20. 9 – ☐ = 1 Answer: 9 – 8 = 1 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract eight from nine then we got one.
Question 21. 8 – ☐ = 1 Answer: 8 – 7 = 1 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract seven from eight then we got one.
Question 22. ☐ – 5 = 5 Answer: 10 – 5 = 5 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract five from ten then we got five.
Question 23. ☐ – 5 = 4 Answer: 9 – 5 = 4 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract five from nine then we got four.
Question 24. ☐ – 5 = 3 Answer: 8 – 5 = 3 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract five from eight then we got three.
Question 25. 10 – 8 = 9 – ☐ Answer: 10 – 8 = 9 – 7 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract eight from ten then we got two. Subtract seven from nine then we got two. Both are equal number sentences.
Question 26. 8 – 6 = 10 – ☐ Answer: 8 – 6 = 10 -8 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract six from eight then we got two. Subtract eight from ten then we got two. Both are equal number sentences.
Question 27. 8 – ☐ = 10 – 2 Answer: 8 – 0 = 10 – 2 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract zero from eight then we got eight. Subtract two from ten then we got eight. Both are equal number sentences.
Question 28. 9 – ☐ = 10 – 2 Answer: 9 – 1 = 10 – 2 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract one from nine then we got eight. Subtract two from ten then we got eight. Both are equal number sentences.
Question 29. 10 – 3 = 9 – ☐ Answer: 10 – 3 = 9 – 2 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract three from ten then we got seven. Subtract two from nine then we got seven. Both are equal number sentences.
Question 30. ☐ – 1 = 10 – 3 Answer: 8 – 1 = 10 – 3 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. The result of a subtraction is called a difference. Subtract one from eight then we got seven. Subtract three from ten then we got seven. Both are equal number sentences.
Eureka Math Grade 1 Module 2 Lesson 14 Problem Set Answer Key
Question 1. Match the pictures with the number sentences.
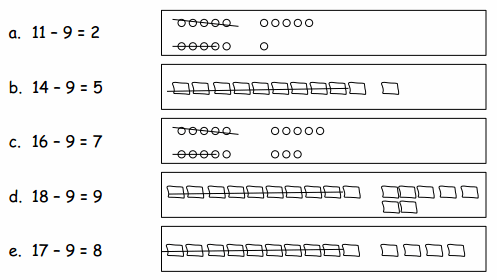
Eureka Math Grade 1 Module 2 Lesson 14 Exit Ticket Answer Key
Eureka Math Grade 1 Module 2 Lesson 14 Homework Answer Key
Circle 10 and subtract. Make a number bond.
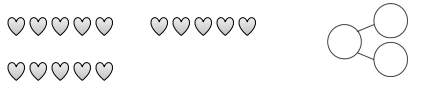
Question 6. Complete the number bond, and write the number sentence that helped you.
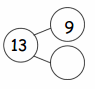
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A Story of Units 1•2 G1-M2-Lesson 8 1. Solve. Make math drawings using the ten-frame to show how you made ten to solve. 8 + 8 = 𝟏𝟏𝟏𝟏+ = a new expression, 10 + 6. 2. Make math drawings using ten-frames to solve. Circle the true number sentences. Write an X to show number sentences that are not true.
Eureka Math Grade 1 Module 2 Lesson 2 Problem Set Answer Key. the numbers that make ten. Draw a picture. Complete the number sentence. Question 1. Answer: 10 + 4 = 14. Explanation: An addition sentence is a mathematical expression that shows two or more values added together and their sum.
Maddy caught 𝟏𝟏𝟏𝟏 Lesson 1: © 2015 Great Minds eureka-math.org G1-M2-HWH-1.3.-09.2015 10 is such a friendly number! Solve word problems with three addends, two of which make ten. animals. 1 6 1•2 -1 A Story of Units 15 Homework Helper G1-M2-Lesson 2 1. Circle the numbers that make ten. Draw a picture.
Grade 1 Module 2 Collapse all Expand all. Introduction to Place Value Through Addition and Subtraction Within 20 ... Lesson 1. Lesson 2. Lesson 3. Lesson 4. Lesson 5. Lesson 6. Lesson 7. Lesson 8. Lesson 9. Lesson 10. ... This work by EMBARC.Online based upon Eureka Math and is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial ...
Engage NY Eureka Math 1st Grade Module 1 Lesson 2 Answer Key Eureka Math Grade 1 Module 1 Lesson 2 Problem Set Answer Key. Circle 2 parts you see. Make a number bond to match. Question 1. Answer: Question 2. Answer: Question 3. Answer: Question 4. Answer: Question 5. Answer: Question 6. Answer: Question 7. Answer: Question 8. Answer: Question 9.
EngageNY/Eureka Math Grade 1 Module 2 Lesson 1For more videos, please visit http://bit.ly/eurekapusdPLEASE leave a message if a video has a technical difficu...
Module 1 Lessons 1-39 Eureka Math™ Homework Helper 2015-2016. 2015-16 Lesson 1: Analyze and describe embedded numbers (to 10) using 5 groups and ... 1•1. Homework Helper . G1-M1-Lesson 2 . 1. Circle 2 parts you see. Make a number bond to match. ... G1-M1-Lesson 4 . By the end of first grade, students should know all their addition and ...
10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 G1-M1-SFA-1.3.1-05.2016 Eureka Math™ Grade 1 Module 1 Student File_A Student Workbook This file contains: • G1-M1 Problem Sets • G1-M1 Homework • G1-M1 Templates (including cut outs)1 1Note that not all lessons in this module include templates or cut outs. A Story of Units®
As the creator of Engage NY Math and Eureka Math, Great Minds is the only place where you can get print editions of the PK-12 curriculum.Our printed materials are available in two configurations: Learn, Practice, Succeed, or student workbooks, teacher editions, assessment and fluency materials. The Learn, Practice, Succeed configuration is available for grades K-8 and offers teachers ...
5.0. (30) $1.50. PDF. There are two homework sheets included in this file. These sheets coincide with Eureka Math Module 2 Lessons 1-5, 6, 8, & 10 Week 1 includes lessons 1-5. Week 2 includes lesson 6, 8, 10. Each sheet can be passed out on Monday and students can work on them the entire week as new lessons are taught in the classroom.
Grade 1, Module 2, Lesson 16, Homework 6. Grade 1, Module 2, Lesson 17, Problem Set 8 & 9. Grade 1, Module 2, Lesson 18, Problem Set 2. ... Eureka Math Grade 1 Module 3 Lesson 12 Eureka Math Grade 1 Module 3 Lesson 13. Eureka - Gr.1 - Parent Resources. Parent Guide - Gr.1 .
Bundle options are available for all of our materials (print, digital, PD, etc.). Prices vary by grade and size of class set. Certain grade-levels do not include all packets due to the nature of the grade-level content. Student workbooks are available in class sets of 20, 25, and 30. Prices vary by size of class set.
Adjust the Exit Ticket and Homework to . 2 See the Progression documents "K, Counting and Cardinality" and "K−5, Operations and Algebraic Thinking" pp. 9 and 23, ... and +1 facts for Lesson 22 and +2 facts for Lesson 23. Students can mix up their ... EUREKA MATH: GRADE 1 PACING AND PREPARATIONGUIDE
Grade 1 Module 1: Sums and Differences to 10. A 1st Grade resource for teachers using Eureka Math (EngageNY). Grade 1 Module 2: Introduction to Place Value Through Addition and Subtraction Within 20. A 1st Grade resource for teachers using Eureka Math (EngageNY). Grade 1 Module 3: Ordering and Comparing Length Measurements as Numbers.
EngageNY/Eureka Math Grade 4 Module 1 Lesson 2For more Eureka Math (EngageNY) videos and other resources, please visit http://EMBARC.onlinePLEASE leave a mes...
EngageNY/Eureka Math Grade 1 Module 1 Lesson 1For more videos, please visit http://bit.ly/eurekapusdPLEASE leave a message if a video has a technical difficu...
Eureka Math Grade 1 Module 2 Lesson 29 Homework Answer Key. Solve the problems. Write your answers to show how many tens and ones. Question 1. __ - __ = __ __ + __ = __ Answer: 0 tens and 9 ones. Explanation: In the above image we can observe 17 - 8 expression. A number bond is a simple addition of two numbers that add up to give the sum.
Lesson 2 : Use iteration with one physical unit to measure. 2•2 G2-M2-Lesson 2 1. The picture of the eraser is about _____ centimeters long. 2. John used a centimeter cube and the mark and move forward strategy to measure these pieces of tape. Use his work to answer the following questions. How long is Tape A? _____ centimeters long.
December 5, 2023 / By Prasanna. Eureka Math Grade 1 Answer Key provided facilitates learning outside the classroom. The Solutions provided bridge the gap between the way maths was once taught. Eureka Math Grade 1 Answers help you to understand the mathematical concepts much easier as well as to enhance problem-solving skills.
These sheets coincide with Eureka Math Module 2 Lessons 1-5, 6, 8, & 10 Module 3 Lessons 1-20 Module 4 Lessons There are FOUR homework sheets also included in this file. These sheets coincide with Eureka Math Module 4 Lessons 1 - 15 If you like this product, please check out my store for more Eureka Math products for 2nd grade. I have ...
Engage NY Eureka Math 1st Grade Module 2 Lesson 28 Answer Key Eureka Math Grade 1 Module 2 Lesson 28 Sprint Answer Key. A *Write the missing number. Answer: Question 1. 10 + 2 = ☐ Answer: 10 + 2 = 12 Explanation: An addition sentence is a mathematical expression that shows two or more values added together and their sum. ADD ten with two then ...
6 x GRADE New York State Common Core Mathematics Curriculum GRADE 6 • MODULE 4 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org This file derived from G6-M4-TE-1.3.-09.2015 13 Topic A: Relationships of the Operations Topic A ...
Eureka Math Grade 1 Module 2 Lesson 14 Homework Answer Key. Circle 10 and subtract. Make a number bond. Question 1. 15 - 9 = ___ Answer: 15 - 9 = 6 Explanation: Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents the operation of removing objects from a collection. In the above image we can observe a number sentence 15 - 9 = 6.