
- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.


9.1: The Pythagorean Theorem
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 35449

- David Arnold
- College of the Redwoods
Pythagoras was a Greek mathematician and philosopher, born on the island of Samos (ca. 582 BC). He founded a number of schools, one in particular in a town in southern Italy called Crotone, whose members eventually became known as the Pythagoreans. The inner circle at the school, the Mathematikoi, lived at the school, rid themselves of all personal possessions, were vegetarians, and observed a strict vow of silence. They studied mathematics, philosophy, and music, and held the belief that numbers constitute the true nature of things, giving numbers a mystical or even spiritual quality.
Today, nothing is known of Pythagoras’s writings, perhaps due to the secrecy and silence of the Pythagorean society. However, one of the most famous theorems in all of mathematics does bear his name, the Pythagorean Theorem.
Prior to revealing the contents of the Pythagorean Theorem, we pause to provide the definition of a right triangle and its constituent parts.
Right Triangle
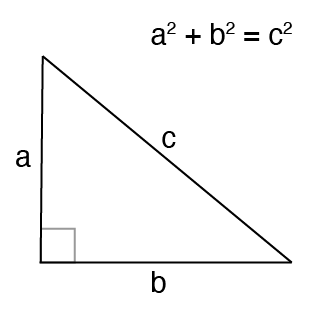
A triangle with one right angle (90 ◦ ) is called a right triangle . In the figure below, the right angle is marked with a little square.

The side of the triangle that is directly opposite the right angle is called the hypotenuse . The sides of the triangle that include the right angle are called the legs of the right triangle.
Now we can state one of the most ancient theorems of mathematics, the Pythagorean Theorem .
Pythagorean Theorem
Let \(c\) represent the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle, and let a and b represent the lengths of its legs, as pictured in the image that follows.

The relationship involving the legs and hypotenuse of the right triangle, given by
\[a^2 + b^2 = c^2,\nonumber \]
is called the Pythagorean Theorem .
Here are two important observations.
Observations Regarding the Hypotenuse
Two important facts regarding the hypotenuse of the right triangle are:
- The hypotenuse is the longest side of the triangle and lies directly opposite the right angle.
- In the Pythagorean equation \(a^2 + b^2 = c^2\), the hypotenuse lies by itself on one side of the equation.
The Pythagorean Theorem can only be applied to right triangles.
Let’s look at a simple application of the Pythagorean Theorem.
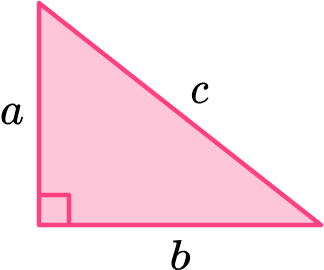
The legs of a right triangle measure 3 and 4 meters, respectively. Find the length of the hypotenuse.
Let’s follow the Requirements for Word Problem Solutions .
1. Set up a Variable Dictionary . Let c represent the length of the hypotenuse, as pictured in the following sketch.
2. Set up an Equation . The Pythagorean Theorem says that
\[a^2 + b^2 = c^2.\nonumber \]
In this example, the legs are known. Substitute 4 for a and 3 for b (3 for a and 4 for b works equally well) into the Pythagorean equation.
\[4^2 + 3^2 = c^2\nonumber \]
3. Solve the Equation .
\[ \begin{aligned} 4^2 + 3^2 = c^2 ~ & \textcolor{red}{ \text{ The Pythagorean equation.}} \\ 16 + 9 = c^2 ~ & \textcolor{red}{ \text{ Exponents first: } 4^2 = 16 \text{ and } 3^2 = 9.} \\ 25 = c^2 ~ & \textcolor{red}{ \text{ Add: } 16+9=25.} \\ 5 = c~ & \textcolor{red}{ \text{ Take the nonnegative square root.}} \end{aligned}\nonumber \]
Technically, there are two answers to c 2 = 25, i.e., c = −5 or c = 5. However, c represents the hypotenuse of the right triangle and must be nonnegative. Hence, we must choose c = 5.
4. Answer the Question . The hypotenuse has length 5 meters.
5. Look Back . Do the numbers satisfy the Pythagorean Theorem? The sum of the squares of the legs should equal the square of the hypotenuse. Let’s check.
\[\begin{aligned} 4^2 + 3^2 = 5^2 \\ 16 + 9 = 25 \\ 25 = 25 \end{aligned}\nonumber \]
All is well!
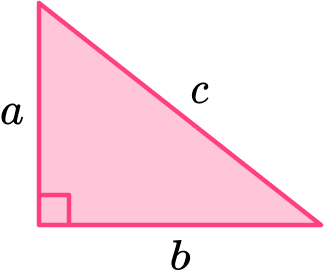
The legs of a right triangle measure 5 and 12 feet, respectively. Find the length of the hypotenuse.
Given the following right triangle, find the length of the missing side.

Note that the hypotenuse (across from the right angle) has length 13. This quantity should lie on one side of the Pythagorean equation all by itself. The sum of the squares of the legs go on the other side. Hence,
\[5^2 + x^2 = 13^2\nonumber \]
Solve the equation for x .
\[ \begin{aligned} 25+x^2 = 169 ~ & \textcolor{red}{ \text{ Exponents first: } 5^2 = 25 \text{ and } 13^2 = 169.} \\ 25 + x^2 -25 = 169 - 25 ~ & \textcolor{red}{ \text{ Subtract 25 from both sides.}} \\ x^2 = 144 ~ & \textcolor{red}{ \text{ Simplify both sides.}} \\ x= 12 ~ & \textcolor{red}{ \text{ Take the nonnegative square root of 144.}} \end{aligned}\nonumber \]
The hypotenuse of a right triangle measures 25 centimeters. One leg of the right triangle measures 24 centimeters. Find the length of the remaining leg.
7 centimeters
Perfect squares are nice, but not required.
Given the following right triangle, find the exact length of the missing side.

Note that the hypotenuse (across from the right angle) has length 12. This quantity should lie on one side of the Pythagorean equation all by itself. The sum of the squares of the legs go on the other side. Hence,
\[x^2 + 7^2 = 12^2\nonumber \]
\[ \begin{aligned} x^2 + 49 = 144 ~ & \textcolor{red}{ \text{ Exponents first: } 7^2 = 49 \text{ and } 12^2 = 144.} \\ x^2 + 49-49 = 144 - 49 ~ & \textcolor{red}{ \text{ Subtract 49 from both sides.}} \\ x^2 = 95 ~ & \textcolor{red}{ \text{ Simplify both sides.}} \\ x = \sqrt{95} ~ & \textcolor{red}{ \text{ Take the nonnegative square root of 95.}} \end{aligned}\nonumber \]
Hence, the exact length of the missing side is \(\sqrt{95}\).
The hypotenuse and one leg of a right triangle measure 9 and 7 inches, respectively. Find the length of the remaining leg.
Add texts here. Do not delete this text first.
Important Observation
Any attempt to use your calculator to approximate 95 in Example 3 would be an error as the instructions asked for an exact answer.
Sometimes an approximate answer is desired, particularly in applications.
Ginny want to create a vegetable garden in the corner of her yard in the shape of a right triangle. She cuts two boards of length 8 feet which will form the legs of her garden. Find the length of board she should cut to form the hypotenuse of her garden, correct to the nearest tenth of a foot.
We follow the Requirements for Word Problem Solutions .
1. Set up a Variable Dictionary . We begin with a labeled sketch. Let x represent the length of the unknown hypotenuse.

2. Set Up an Equation . The hypotenuse is isolated on one side of the Pythagorean equation.
\[x^2 = 8^2 + 8^2\nonumber \]
\[ \begin{aligned} x^2 = 8^2 + 8^2 ~ & \textcolor{red}{ \text{ The Pythagorean equation.}} \\ x^2 = 64 + 64 ~ & \textcolor{red}{ \text{ Exponents first: } 8^2 = 64 \text{ and } 8^2 = 64.} \\ x^2 = 128 ~ & \textcolor{red}{ \text{ Add: } 64 + 64 = 128.} \\ x = \sqrt{128} ~ & \textcolor{red}{ \text{ Take the nonnegative square root.}} \end{aligned}\nonumber \]
4. Answer the Question . The exact length of the hypotenuse is \(\sqrt{128}\) feet, but we’re asked to find the hypotenuse to the nearest tenth of a foot. Using a calculator, we find an approximation for \(\sqrt{128}\).
\[\sqrt{128} \approx 11.313708499\nonumber \]
To round to the nearest tenth, first identify the rounding and test digits.

The test digit is less than five. So we leave the rounding digit alone and truncate. Therefore, correct to the nearest tenth of a foot, the length of the hypotenuse is approximately 11.3 feet.
5. Look Back . The sum of the squares of the legs is
\[ \begin{aligned} 8^2 + 8^2 = 64 + 64 \\ = 128. \end{aligned}\nonumber \]
The square of the hypotenuse is
\[(11.3)^2 = 127.69\nonumber \]
These are almost the same, the discrepancy due to the fact that we rounded to find an approximation for the hypotenuse.
A 15 foot ladder leans against the wall of a building. The base of the ladder lies 5 feet from the base of the wall. How high up the wall does the top of the ladder reach? Round your answer to the nearest tenth of a foot.
In Exercises 1-16, your solutions should include a well-labeled sketch.
1. The length of one leg of a right triangle is 15 meters, and the length of the hypotenuse is 25 meters. Find the exact length of the other leg.
2. The length of one leg of a right triangle is 7 meters, and the length of the hypotenuse is 25 meters. Find the exact length of the other leg.
3. The lengths of two legs of a right triangle are 12 meters and 16 meters. Find the exact length of the hypotenuse.
4. The lengths of two legs of a right triangle are 9 meters and 12 meters. Find the exact length of the hypotenuse.
5. The length of one leg of a right triangle is 13 meters, and the length of the hypotenuse is 22 meters. Find the exact length of the other leg.
6. The length of one leg of a right triangle is 6 meters, and the length of the hypotenuse is 15 meters. Find the exact length of the other leg.
7. The lengths of two legs of a right triangle are 2 meters and 21 meters. Find the exact length of the hypotenuse.
8. The lengths of two legs of a right triangle are 7 meters and 8 meters. Find the exact length of the hypotenuse.
9. The length of one leg of a right triangle is 12 meters, and the length of the hypotenuse is 19 meters. Find the exact length of the other leg.
10. The length of one leg of a right triangle is 5 meters, and the length of the hypotenuse is 10 meters. Find the exact length of the other leg.
11. The lengths of two legs of a right triangle are 6 meters and 8 meters. Find the exact length of the hypotenuse.
12. The lengths of two legs of a right triangle are 5 meters and 12 meters. Find the exact length of the hypotenuse.
13. The length of one leg of a right triangle is 6 meters, and the length of the hypotenuse is 10 meters. Find the exact length of the other leg.
14. The length of one leg of a right triangle is 9 meters, and the length of the hypotenuse is 15 meters. Find the exact length of the other leg.
15. The lengths of two legs of a right triangle are 6 meters and 22 meters. Find the exact length of the hypotenuse.
16. The lengths of two legs of a right triangle are 9 meters and 19 meters. Find the exact length of the hypotenuse.
In Exercises 17-24, your solutions should include a well-labeled sketch.
17. The lengths of two legs of a right triangle are 3 meters and 18 meters. Find the length of the hypotenuse. Round your answer to the nearest hundredth.
18. The lengths of two legs of a right triangle are 10 feet and 16 feet. Find the length of the hypotenuse. Round your answer to the nearest tenth.
19. The length of one leg of a right triangle is 2 meters, and the length of the hypotenuse is 17 meters. Find the length of the other leg. Round your answer to the nearest tenth.
20. The length of one leg of a right triangle is 4 meters, and the length of the hypotenuse is 12 meters. Find the length of the other leg. Round your answer to the nearest hundredth.
21. The lengths of two legs of a right triangle are 15 feet and 18 feet. Find the length of the hypotenuse. Round your answer to the nearest hundredth.
22. The lengths of two legs of a right triangle are 6 feet and 13 feet. Find the length of the hypotenuse. Round your answer to the nearest tenth.
23. The length of one leg of a right triangle is 4 meters, and the length of the hypotenuse is 8 meters. Find the length of the other leg. Round your answer to the nearest hundredth.
24. The length of one leg of a right triangle is 3 meters, and the length of the hypotenuse is 15 meters. Find the length of the other leg. Round your answer to the nearest tenth.
25. Greta and Fritz are planting a 13-meter by 18-meter rectangular garden, and are laying it out using string. They would like to know the length of a diagonal to make sure that right angles are formed. Find the length of a diagonal. Round your answer to the nearest hundredth. Your solution should include a well-labeled sketch.
26. Markos and Angelina are planting an 11- meter by 19-meter rectangular garden, and are laying it out using string. They would like to know the length of a diagonal to make sure that right angles are formed. Find the length of a diagonal. Round your answer to the nearest tenth. Your solution should include a well-labeled sketch.
27. The base of a 24-meter long guy wire is located 10 meters from the base of the telephone pole that it is anchoring. How high up the pole does the guy wire reach? Round your answer to the nearest hundredth. Your solution should include a well-labeled sketch.
28. The base of a 30-foot long guy wire is located 9 feet from the base of the telephone pole that it is anchoring. How high up the pole does the guy wire reach? Round your answer to the nearest hundredth. Your solution should include a well-labeled sketch.
29. Hiking Trail. A hiking trail runs due south for 8 kilometers, then turns west for about 15 kilometers, and then heads northeast on a direct path to the starting point. How long is the entire trail?
30. Animal Trail. An animal trail runs due east from a watering hole for 12 kilometers, then goes north for 5 kilometers. Then the trail turns southwest on a direct path back to the watering hole. How long is the entire trail?
31. Upper Window. A 10-foot ladder leans against the wall of a house. How close to the wall must the bottom of the ladder be in order to reach a window 8 feet above the ground?
32. How high? A 10-foot ladder leans against the wall of a house. How high will the ladder be if the bottom of the ladder is 4 feet from the wall? Round your answer to the nearest tenth.
1. 20 meters
3. 20 meters
5. √315 meters
7. \(\sqrt{445}\) meters
9. \(\sqrt{217}\) meters
11. 10 meters
13. 8 meters
15. \(\sqrt{520}\) meters
17. 18.25 meters
19. 16.9 meters
21. 23.43 feet
23. 6.93 meters
25. 22.20 meters
27. 21.82 meters
29. 40 kilometers

Pythagorean Theorem
How to Use The Pythagorean Theorem
The Formula
The picture below shows the formula for the Pythagorean theorem. For the purposes of the formula, side $$ \overline{c}$$ is always the hypotenuse . Remember that this formula only applies to right triangles .

Examples of the Pythagorean Theorem
When you use the Pythagorean theorem, just remember that the hypotenuse is always 'C' in the formula above. Look at the following examples to see pictures of the formula.

Conceptual Animation of Pythagorean Theorem
Demonstration #1.
More on the Pythagorean theorem
Demonstration #2
Video tutorial on how to use the pythagorean theorem.
Step By Step Examples of Using the Pythagorean Theorem
Example 1 (solving for the hypotenuse).
Use the Pythagorean theorem to determine the length of X.

Identify the legs and the hypotenuse of the right triangle .
The legs have length 6 and 8 . $$X $$ is the hypotenuse because it is opposite the right angle.

Substitute values into the formula (remember 'C' is the hypotenuse).
$ A^2+ B^2= \red C^2 \\ 6^2+ 8^2= \red X^2 $
$A^2+ B^2= \red X^2 \\ 100= \red X^2 \\ \sqrt {100} = \red X \\ 10= \red X $
Example 2 (solving for a Leg)

The legs have length 24 and $$X$$ are the legs. The hypotenuse is 26.

$ \red A^2+ B^2= C^2 \\ \red x^2 + 24^2= {26}^2 $
$ \red x^2 + 24^2= 26^2 \\ \red x^2 + 576= 676 \\ \red x^2 = 676 - 576 \\ \red x^2 = 100 \\ \red x = \sqrt { 100} \\ \red x = 10 $
Practice Problems
Find the length of X.

Remember our steps for how to use this theorem. This problems is like example 1 because we are solving for the hypotenuse .
The legs have length 14 and 48 . The hypotenuse is X.
$ A^2 + B^2 = C^2 \\ 14^2 + 48^2 = x^2 $
Solve for the unknown.
$ 14^2 + 48^2 = x^2 \\ 196 + 2304 = x^2 \\ \sqrt{2500} = x \\ \boxed{ 50 = x} $

Use the Pythagorean theorem to calculate the value of X. Round your answer to the nearest tenth.

Remember our steps for how to use this theorem. This problems is like example 2 because we are solving for one of the legs .
The legs have length 9 and X . The hypotenuse is 10.
$ A^2 + B^2 = C^2 \\ 9^2 + x^2 = 10^2 $
$ 9^2 + x^2 = 10^2 \\ 81 + x^2 = 100 \\ x^2 = 100 - 81 \\ x^2 = 19 \\ x = \sqrt{19} \approx 4.4 $
Use the Pythagorean theorem to calculate the value of X. Round your answer to the nearest hundredth.

The legs have length '10' and 'X'. The hypotenuse is 20.
$ A^2 + B^2 = C^2 \\ 10^2 + \red x^2 = 20^2 $
$ 10^2 + \red x^2 = 20^2 \\ 100 + \red x^2 = 400 \\ \red x^2 = 400 -100 \\ \red x^2 = 300 \\ \red x = \sqrt{300} \approx 17.32 $
- Pythagorean Theorem Shell Problem Cool challenging problem from involving pythagoren theorem, isosceles triangles and pattern recognition
- Free Triangle Worksheets
- Pythagorean Theorem Calculator
Ultimate Math Solver (Free) Free Algebra Solver ... type anything in there!
Popular pages @ mathwarehouse.com.
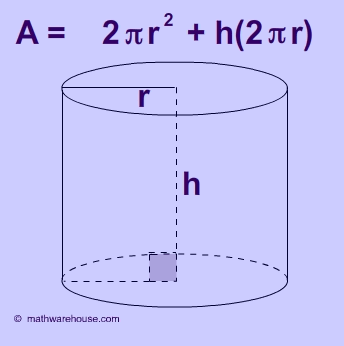
Pythagoras Theorem Questions (with Answers)
Pythagoras theorem.
In a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides.

- Length of the hypotenuse is c
- The hypotenuse is the longest side
- Lengths of the other sides are a, b
Right Triangle Questions – using the theorem
The Theorem helps us in:
- Finding Sides: If two sides are known, we can find the third side.
- Determining if a triangle is right-angled: If the sides of a triangle are known and satisfy the Pythagoras Formula, it is a right-angled triangle.
There is a proof of this theorem by a US president. Its simplicity makes it is easy enough for the grade 8 kids to understand.
Finding the missing sides (side lengths) of a Right Triangle
The theorem gives a relation among the three sides of a right-angled triangle. We can find one side if we know the other two sides. How?
Example: We are given (see figure) below the two sides of the right triangle. Find the third side.

Given: a = 3, c = 5
Which side is the hypotenuse?
✩ Always identify the hypotenuse first
Unknown side = BC = b ?
Putting the values in the Pythagoras Formula: a 2 + b 2 = c 2
3 2 + b 2 = 5 2
9 + b 2 = 25
b 2 = 25 − 9 = 16 = 4 2
Finding the Hypotenuse of a Triangle
Using the Pythagoras formula, finding hypotenuse is no different from any other side.
Example: Sides of a right triangle are 20 cm and 21 cm, find its hypotenuse.

Pythagoras Formula: a 2 + b 2 = c 2
- c is the length of the hypotenuse
- a, b are the lengths of the other two sides (you can assume any length as a or b ).
Let AB = a = 20, BC = b = 21
Putting values in the formula:
20 2 + 21 2 = c 2
400 + 441 = c 2
Finding Right Triangle
Given the sides, we can determine if a triangle is right-angled by applying the Pythagoras Formula. How?
- Assume the longest side to be hypotenuse Length = c . Find its square ( = c 2 )
- Find the sum of squares of the other two sides ( = a 2 + b 2 )
- If a 2 + b 2 ≠ c 2 it is a not right triangle
- If a 2 + b 2 = c 2 it is a right triangle
Example: A triangle has sides 8 cm, 11 cm, and 15 cm. Determine if it is a right triangle
Longest side = 15 cm. Let us assume it to be hypotenuse = c (as we know that it is always the longest)
c 2 = 15 2 = 225
Other sides a = 8 cm b = 11 cm. (You can assume any side length to be a or b ).
a 2 + b 2 = 8 2 + 11 2 = 64 + 121 = 185
a 2 + b 2 ≠ c 2
So this is not a right-angled triangle.
Example: The sides of a triangle are 8 cm, 17 cm, and 15 cm. Find if it is a right triangle.
Longest side = 17 cm. Let us assume it to be hypotenuse = c
c 2 = 17 2 = 289
Other sides a = 8 cm, b = 15 cm.
a 2 + b 2 = 8 2 + 15 2 = 64 + 225 = 289
So a 2 + b 2 = c 2
It is a right-angled triangle.
Pythagoras Questions Types
You will encounter the following types of questions related to this theorem:
- Find a side, given two sides These questions are the direct application of the theorem (formula) and are easiest to solve.
- Express the relation between the two sides in an equation
- Substitute one side by the other using the first equation in the Pythagoras Formula
- Given the Perimeter and one side, find other sides – Perimeter is the sum of the three sides. Since one side is known, we subtract it from the perimeter to get a relationship between the other two sides.
- Given Area and one side find other sides – Area = 2 1 × ( ba se × a lt i t u d e ) . Base and altitude can be the sides with the right angle OR the hypotenuse and the altitude.
Pythagoras Questions
The questions chosen have minimal use of other concepts, yet, some of these are hard Pythagoras questions (See Ques 4 and Ques 10 ).
1 Question
ABC is a right triangle. AC is its hypotenuse. Length of side AB is 2√5 . Side BC is twice of side AB. Find the length of AC.
Can you express BC in terms of AB and apply the Pythagoras Theorem?
Ans. AC = 10
2 Question
The hypotenuse of a right triangle is 6 cm . Its area is 9 cm 2 . Find its sides.

Can you form two equations – one using area and the other using the Pythagoras formula?
Ans. Each side is 3√2 cm.
3 Question
One side of a right triangle is 4 10 cm. Find the length of its other side if the hypotenuse is 13 cm.
Can you directly apply the Pythagoras Theorem?
Ans. 3 cm
4 Question
In a right triangle ABC, length of the medians to the sides AB and BC are 2 61 and 601 respectively. Find the length of its hypotenuse.

CE = 2 61
Let AE = EB = x
BD = DC = y
Can you use the Pythagorean Theorem to form an equation between x, y, and AD?
Can you form another equation involving x, y, and EC?
Can you use this result to find A C 2 ? Use the triangle ABC.
Ans. AC = 26
5 Question
In a right triangle, the longest side is 8 cm. One of the remaining sides is 4√3 cm long. Find the length of the other side.
Can you apply the Pythagoras Theorem directly?
Ans. 4 cm
6 Question
The first side of a right triangle is shorter than the second side by 1 cm. It is longer than the third side by 31 cm. Find the sides of the triangle.
Can you form equations between the first side and the other two sides? Which side is the hypotenuse?
Ans. 9 cm, 40 cm, 41 cm
7 Question
The perimeter of a right triangle is equal to 30 cm. The length of one of its sides is 10 cm. Find its hypotenuse.

Can you find the relation between the unknown side and the perimeter in terms of the hypotenuse?
Ans. 12.5 cm
8 Question
The sides of a triangle are 5 cm, 9 cm, and 12 cm. Is it a right-angled triangle?
Can you identify the possible hypotenuse? Also, test if the sides satisfy the Pythagoras Formula.
Ans. Not a right triangle.
9 Question
In a right triangle, two sides are equal. The longest side is 7√2 cm, find the remaining sides.
Ans. 7 cm
10 Question
In the following right triangle altitude BD = 9 10 cm and DC = 27 10 cm. Find the sides of the triangle.

Can you apply the Pythagoras Theorem to the triangle BCD?
Can you form an equation between a and x using the triangle ABD?
Can you find the value of x using above equations and triangle ABC?
Ans. AB = 30cm, BC = 90cm, A C = 30 10 c m
Answers to Pythagoras Questions
1 answer.
Let AB = a , BC = b and AC = c .
AB = a = 2√5
BC is twice of AB, b = 2a = 4√5
AC = Hypotenuse = c
Applying the Pythagoras Theorem a 2 + b 2 = c 2 :
(2√5) 2 + (4√5) 2 = c 2
4(5) + 16(5) = c 2
c 2 = 20 + 80 = 100
2 Answer
Let AB = a , BC = b
In triangle ABC, base = b and altitude = a
Area of Triangle = 2 1 × ( ba se × a lt i t u d e ) . So:
2 1 × ( ab ) = 9
ab = 18 (Equation 1)
Using the Pythagoras Formula:
a 2 + b 2 = 6 2 = 36
We add and subtract 2ab to complete the square :
a 2 + b 2 − 2ab + 2ab = 36
(a − b) 2 + 2ab = 36
(a − b) 2 + 36 = 36 Using ab = 18 from Equation 1
(a − b) 2 = 0
Substituting a by b in Equation 1:
Side AB = BC = 3√2 cm

3 Answer
Let the length of sides be a, b and c , such that:
a = 4 10 cm
b = unknown
From the Pythagoras formula a 2 + b 2 = c 2 , we get:
( 4 10 ) 2 + b 2 = 1 3 2
(16 × 10) + b 2 = 169
160 + b 2 = 169
b 2 = 169 − 160 = 9
4 Answer
Using triangle ABD:
AB 2 + BD 2 = AD 2
( 2 x ) 2 + y 2 = ( 601 ) 2
4 x 2 + y 2 = 601 (Equation 1)
Using triangle EBC :
EB 2 + BC 2 = EC 2
x 2 + ( 2 y ) 2 = ( 2 61 ) 2
x 2 + 4 y 2 = ( 2 61 ) 2
x 2 + 4 y 2 = 244 (Equation 2)
Adding Equation 1 and 2:
4x 2 + y 2 + x 2 + 4y 2 = 601 + 244
5x 2 + 5y 2 = 845
x 2 + y 2 = 169 (Equation 3)
Let us solve for the hypotenuse using the triangle ABC:
AB 2 + BC 2 = AC 2
(2x) 2 + (2y) 2 = AC 2
4x 2 + 4y 2 = AC 2
4(x 2 + y 2 ) = AC 2
Substituting the value of x 2 + y 2 from Equation 3:
4(169) = AC 2
A C = 4 ( 169 )
AC = 2 × 13 = 26
5 Answer
Let the lengths of sides be a, b and c (hypotenuse).
Hypotenuse is the longest side. So c = 8 .
Let b = 4√3 .
From the Pythagoras Theorem:
a 2 + b 2 = c 2
a 2 + (4√3) 2 = 8 2
a 2 + 16(3) = 64
a 2 + 48 = 64
The third side is 4 cm.
6 Answer
The second side is the longest. It is the hypotenuse. Let its length be c .
Let the length of first side be b and third side a .
Applying the Pythagoras formula:
(b − 31) 2 + b 2 = (b + 1) 2
b 2 − 62b + 31 2 + b 2 = b 2 + 2b + 1
b 2 − 62b + 961 = 2b + 1
b 2 − 64b + 960 = 0
b 2 − 24b − 40b + 960 = 0
b(b − 24) − 40(b − 24) = 0
(b − 40)(b − 24) = 0
b = 40 Or b = 24
For b = 24 , we get a = 24 − 31 = − 7 . Length of a side cannot be negative, so we reject b = 24 .
For b = 40 , we get a = 40 − 31 = 9 and c = 40 + 1 = 41
The sides of triangle are 9 cm, 40 cm and 41 cm.
7 Answer
Side BC = b = 10 cm
Perimeter = Sum of the sides
= a + b + c = 30 (Given)
a + 10 + c = 30
a = 20 − c ( Equation 1 )
Applying the Pythagoras Theorem to find the hypotenuse:
Using Equation 1 to substitute the value of a
(20 − c) 2 + (10) 2 = c 2
400 − 40c + c 2 + 100 = c 2
500 − 40c = 0
The length of hypotenuse = 12.5 cm
8 Answer
Longest side = 12 cm. Let us assume it to be the hypotenuse = c
So c 2 = 12 2 = 144
The Pythagoras Formula: a 2 + b 2 = c 2
We can assume any side to be a or b.
Let a = 5 cm, b = 9 cm.
a 2 + b 2 = 5 2 + 9 2 = 25 + 81 = 106
So a 2 + b 2 ≠ c 2
This is a not a right angled triangle.
9 Answer
Let the length of the sides be a, b , and c (hypotenuse).
In a right triangle hypotenuse is the longest side. So c = 7√2
Other sides are equal. So a = b .
Applying the Pythagoras theorem:
b 2 + b 2 = (7√2) 2
2b 2 = 49(2)
Each side is 7 cm.
10 Answer
Let AB = a, BC = b, AC = c and AD = x
Given B D = 9 10 D C = 27 10
Applying Pythagoras Theorem to triangle BCD:
BD 2 + DC 2 = BC 2
( 9 10 ) 2 + ( 27 10 ) 2 = B C 2
(9 2 × 10) + (27 2 × 10) = b 2
810 + 7290 = b 2
Applying Pythagoras Theorem to triangle ABD:
BD 2 + AD 2 = AB 2
a 2 = ( 9 10 ) 2 + x 2 (Equation 1)
From the figure:
AC = AD + BD
c = x + 27 10 (Equation 2)
Applying Pythagoras Theorem to triangle ABC:
Using b = 90 and value of a 2 from Equation 1 and c from Equation 2:
( 9 10 ) 2 + x 2 + 9 0 2 = ( x + 27 10 ) 2
9 2 ( 10 ) + x 2 + 9 0 2 = x 2 + 54 10 x + 2 7 2 ( 10 )
810 + 8100 = 54 10 x + 7290
54 10 x = 8910 − 7290 = 1620
x = 10 30
Putting value of x in Equation 1:
a 2 = ( 9 10 ) 2 + ( 3 10 ) 2
a 2 = 810 + 90 = 900
Using value of a and b in Pythagoras Formula for triangle ABC:
30 2 + 90 2 = c 2
900 + 8100 = c 2
c = 30 10
AB = 30cm, BC = 90cm, A C = 30 10 c m
Difficult Pythagoras Questions (Year 10, Guided Answers) ➤
James Garfield Pythagorean Theorem (Illustration & Proof) ➤
Pythagorean Theorem Calculator
How to use the pythagorean theorem calculator, what is the pythagorean theorem, how do i use pythagorean theorem, what is the hypotenuse formula, other considerations when dealing with triangles, the pythagorean theorem calculator in the making.
This Pythagorean theorem calculator will calculate the length of any of the missing sides of a right triangle, provided you know the lengths of its other two sides. This includes calculating the hypotenuse. The hypotenuse of the right triangle is the side opposite the right angle, and is the longest side. This side can be found using the hypotenuse formula, another term for the Pythagorean theorem when it's solving for the hypotenuse.
Recall that a right triangle is a triangle with an angle measuring 90 degrees. The other two angles must also total 90 degrees, as the sum of the measures of the angles of any triangle is 180. Read on to answer "what is the Pythagorean theorem and how is it used?"
The Pythagorean theorem calculator is one of the most accessible tools you will come across, despite the name being scary. All you need is any two of the three sides of a right triangle, and you are all set.
Let's take a look at the steps to use our Pythagorean theorem calculator.
Input leg a of the right triangle.
Next, input leg b of the right triangle.
And that is it. The tool will display the following results:
a. The hypotenuse (c) of the right triangle.
b. The area of the triangle.
c. And the perimeter of the triangle.
You don't necessarily have to input legs a and b. If you know the hypotenuse value and need to know any other legs, input the information accordingly.
The default unit is centimeter (cm) for length and cm² for area. You can change these to one of the listed of options according to your requirements. Remember to change the unit before you input the values.
How about we try to understand an example ? For instance, you are climbing a ladder to your roof, and you get curious about the length of the ladder . You notice that the distance from the roof to the ground is leg a , and the distance from the wall to the ladder's base is leg b . And the ladder itself is the hypotenuse. You input the measurements in the tool as leg a and b, 4 m and 3 m , respectively. (Remember to change the units from centimeters to meters first). The calculator instantly determines the hypotenuse as 5 m , the area as 6 m² , and the perimeter as 12 m .
Next time you get curious about any setup that looks like a right triangle, you can use our Pythagorean theorem calculator to determine the lengths of the legs.
The Pythagorean theorem describes how the three sides of a right triangle are related in Euclidean geometry. It states that the sum of the squares of the legs of a right triangle equals the square of the hypotenuse . You can also think of this theorem as the hypotenuse formula. If the legs of a right triangle are a and b and the hypotenuse is c , the formula is:
a² + b² = c²
The theorem was credited to the ancient Greek philosopher and mathematician Pythagoras, who lived in the sixth century BC. Although it was previously used by the Indians and Babylonians, Pythagoras (or his students) were credited with being the first to prove the theorem. It should be noted that there is no concrete evidence that Pythagoras himself worked on or proved this theorem.
Here's how to use Pythagorean theorem:
- Input the two lengths that you have into the formula. For example, suppose you know one leg a = 4 and the hypotenuse c = 8.94 . We want to find the length of the other leg b .
- After the values are put into the formula, we have 4² + b² = 8.94² .
- Square each term to get 16 + b² = 80 .
- Combine like terms to get b² = 64 .
- Take the square root of both sides of the equation to get b = 8 . Go ahead and check it with an online Pythagorean theorem calculator!
Note that if you are solving for a or b , rearrange the equation to isolate the desired variable before combining like terms and taking the square root
The Pythagorean theorem calculator will solve for the sides in the same manner that we displayed above. We have included the method to show you how you can solve your problem if you prefer to do it by hand.
The hypotenuse formula simply takes the Pythagorean theorem and solves for the hypotenuse, c . To solve for the hypotenuse, we simply take the square root of both sides of the equation a² + b² = c² and solve for c . When doing so, we get c = √(a² + b²) . This is just a reformulation of the Pythagorean theorem and is often associated with the name hypotenuse formula .
Notice the sides of a triangle have a certain degree of gradient or slope. We can use the slope calculator to determine the slope of each side. In a right triangle, the sides that form the right angle will have slopes whose product is -1. The formula for slope, if you wish to calculate by hand, is:
(y₂ − y₁)/(x₂ − x₁)
You can also figure out the missing side lengths and angles of a right triangle using the right triangle calculator . If the angles given in the problem are in degrees and you want to convert to radians or radians to degrees, check out our angle converter . There is an easy way to convert degrees to radians and radians to degrees.
If the angle is in radians:
- Multiply by 180/π .
If the angle is in degrees:
- Multiply by π/180 .
Sometimes you may encounter a problem where two lengths are missing. In such cases, the Pythagorean theorem calculator won't help – you will use trigonometric functions to solve for these missing pieces. Don't worry! We have an excellent trigonometric functions calculator available for you.
Indeed, all maths enthusiasts would be happy to have access to a Pythagorean theorem calculator. Even the students who have to complete their assignments would be thrilled. Now imagine how happy Mateusz and Piotr were when they decided to make a tool for one of the most sought-after mathematics concepts and successfully did so.
Mateusz Mucha is the brain behind Omni Calculator. His deep love for numbers with strategic vision and operational expertise is a testament to his career. He believes in a hands-on approach in all aspects of life, whether it is leadership, building some innovative calculator or digital product, or participating in a cycling marathon. He is a well-balanced blend of exemplary leadership and vision, with strategic thinking, innovation, and attention to detail being a few of the skills in his arsenal.
Piotr Małek is creative, athletic, and curious by nature, which makes him a person of remarkable discipline, high credibility, and determination. As a content writer, his ability to explain complex topics with a fairytale-like ease is genuinely fascinating. The diverse experiences he has gained over the years, his intellectual curiosity, and his lifestyle of continuous learning make him a credible voice in any field he is interested in exploring.
We ensure our tools are based on authentic information and proper research. After an expert makes the calculator, another expert in the field reviews it thoroughly. Then, a native language speaker proofreads the content, ensuring further refinement; only then is the tool released for our users. To learn more about our commitment to quality, please refer to our Editorial Policies page .
What is the hypotenuse given legs 7 and 9?
The hypotenuse is 11.40 .
You need to apply the Pythagorean theorem:
- Recall the formula a² + b² = c² , where a , and b are the legs and c is the hypotenuse.
- Put the length of the legs into the formula: 7² + 9² = c² .
- Squaring gives 49 + 81 = c² . That is, c² = 150 .
- Taking the square root, we obtain c = 11.40 . You can verify the result with an online Pythagorean theorem calculator.
What is the leg in an isosceles triangle with hypotenuse 10?
Each leg has length 10/√2 ≈ 7.07 . To arrive at this answer, we apply the Pythagorean theorem:
- In our case, a = b , so the formula reads 2a² = c² .
- Solving for a , we get a = c/√2 .
- Plugging in c = 10 , we get the final answer: a = 10/√2 ≈ 7.07 .
Circle skirt
Irregular trapezoid area.
- Biology (100)
- Chemistry (98)
- Construction (144)
- Conversion (292)
- Ecology (30)
- Everyday life (261)
- Finance (569)
- Health (440)
- Physics (509)
- Sports (104)
- Statistics (182)
- Other (181)
- Discover Omni (40)
Math teaching support you can trust

resources downloaded

one-on-one tutoring sessions

schools supported
[FREE] Fun Math Games & Activities
Engage your students with our ready-to-go packs of no-prep games and activities for a range of abilities across Kindergarten to Grade 5!
15 Pythagorean Theorem Practice Problems For 8th Grade
Beki christian.
Pythagorean Theorem practice problems involve using the relationship between the sides of a right triangle to calculate missing side lengths in triangles. The Pythagorean Theorem is introduced in 8th grade and is used to solve a variety of problems across high school.
Here, you’ll find a selection of Pythagorean Theorem questions that demonstrate the different types of questions students are likely to encounter in 8th grade.
What is the Pythagorean Theorem?
How to answer pythagorean theorem questions, pythagorean theorem in real life, pythagorean theorem in 8th grade, pythagorean theorem practice problems.
The Pythagorean Theorem is the geometric theorem that states that the square of the hypotenuse (longest side) of a right triangle is equal to the sum of the squares of the two shorter sides of the triangle.
This can be written as a^2+b^2=c^2 for a triangle labeled like this:
15 Pythagoras Theorem Practice Problems
Wish you could have the 15 Pythagoras Theorem questions from this blog in a ready-to-go worksheet? We've done just that!
1 – Label the sides of the triangle a , b , and c . Note that the hypotenuse, the longest side of a right triangle, is opposite the right angle and will always be labeled .
2 – Write down the formula and substitute the values>
3 – Calculate the answer. You may be asked to give your answer in an exact form or round to a given degree of accuracy, such as a certain number of decimal places or significant figures.
Pythagorean Theorem has many real-life uses, including in architecture and construction, navigation and surveying.
Pythagorean Theorem is usually introduced in middle school, as it is a part of the 8th grade Common Core Math Standards.
The emphasis in middle school is on students being able to:
- Explain the Pythagorean Theorem;
- Use the theorem to solve mathematical and real-world problems – with both 2D and 3D figures;
- Use the theorem to calculate the distance between two points on a coordinate grid.
The process for solving any Pythagoras Theorem problem always begins by identifying the relevant right-angled triangle and labeling the sides a , b , c. If there is not a diagram in the question, it can be helpful to draw one.
Where necessary, round your answers to 3 significant figures.
1. A ship sails 6 \, km East and then 8 \, km North. Find the ship’s distance from its starting point.
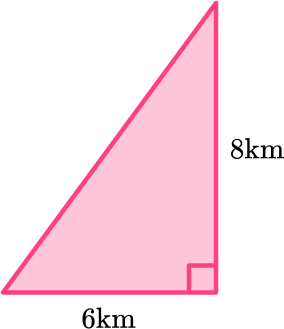
The ship is 10 kilometers from its starting point.
2. A ladder is 5 \, m long. The base of the ladder is 3 \, m from the base of a vertical wall. How far up the wall does the ladder reach?
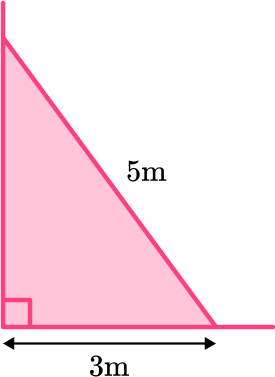
The ladder reaches 4 meters up the wall.
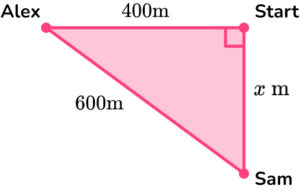
3. Alex and Sam start from the same point. Alex walks 400 meters west. Sam walks x meters south, until they are 600 \, m apart from each other. How far does Sam walk?
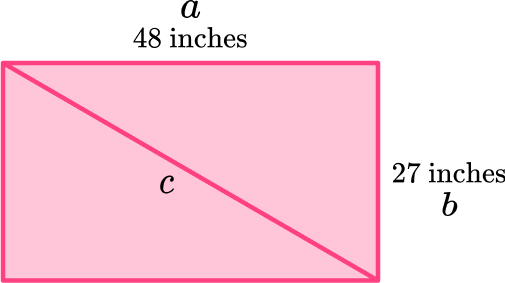
4. A television’s size is the measurement from the upper left hand corner of the television to the bottom right hand corner. Find the size of this television.

39.7 inches
55.1 inches
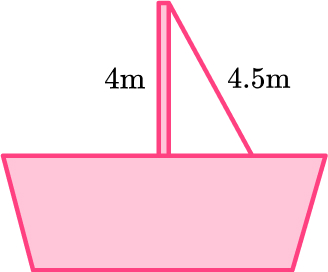
5. The pole of a sailing boat is supported by a rope from the top of the pole to an anchor point on the deck. The pole is 4 \, m long and the rope is 4.5 \, m long. Calculate the distance from the base of the pole to the anchor point of the rope on the deck.
6. Work out the length of the diagonal of a square with 8 \, cm sides.
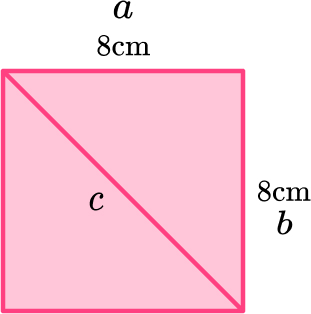
The diagonal of the square has a length of 11.3 centimeters.
7. ABC is an isosceles triangle.
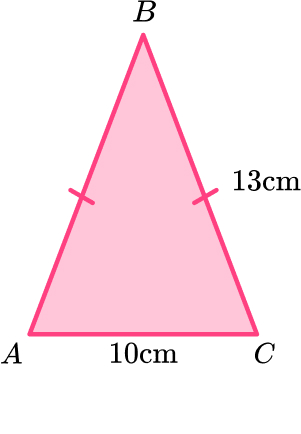
Work out the height of the triangle.
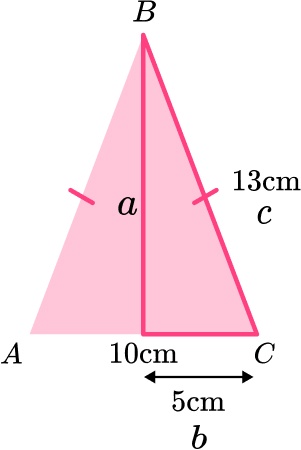
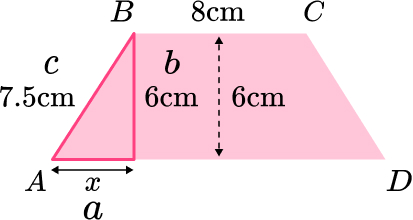
8. ABCD is an isosceles trapezoid.
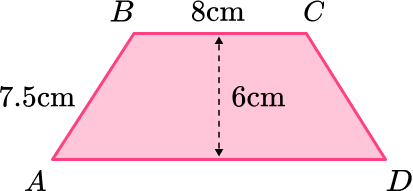
Work out the length of AD.
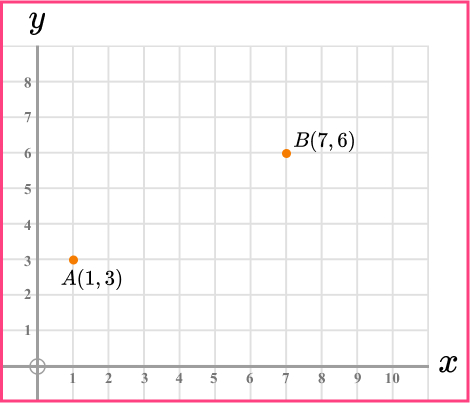
9. Here is a cm square grid. Calculate the distance between the points A and B.
10. Which is a right angled triangle?
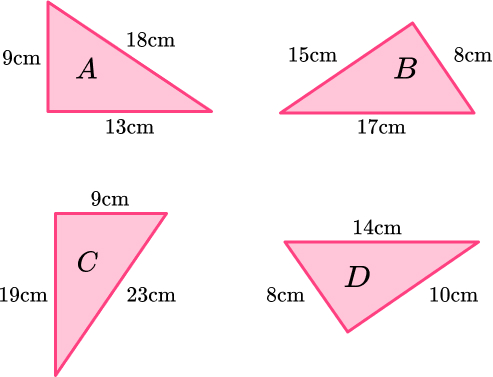
Not a right angled triangle because Pythagorean Theorem doesn’t work.
Right angled triangle because Pythagorean Theorem works.
11. PQRS is made from two right angled triangles.
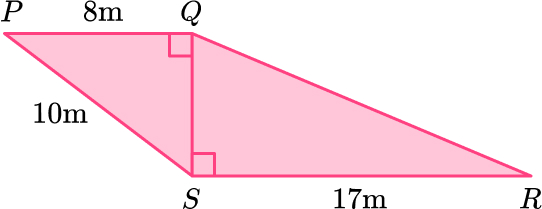
Work out the length of QR.
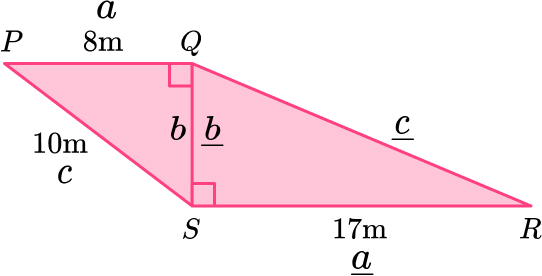
Triangle \text{PQS:}
Triangle \text{QRS}
12. Here is a pattern made from right angled triangles. Work out the length x.
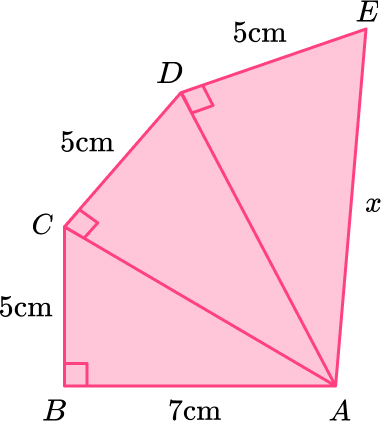
Triangle \text{ABC:}
Triangle \text{ACD:}
13. Here is a pyramid.
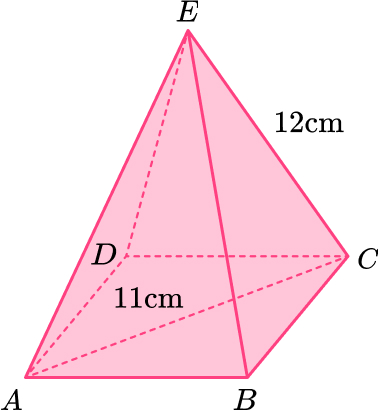
Work out the height of the pyramid.
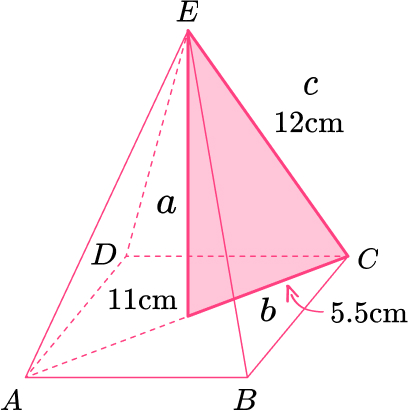
14. Here is a cuboid.
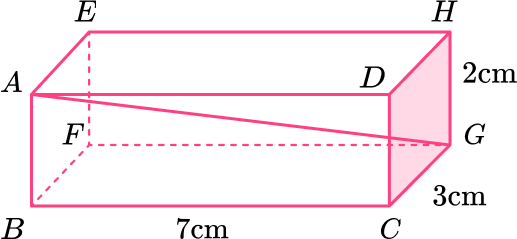
Work out the length AG.
Give your answer in its exact form.
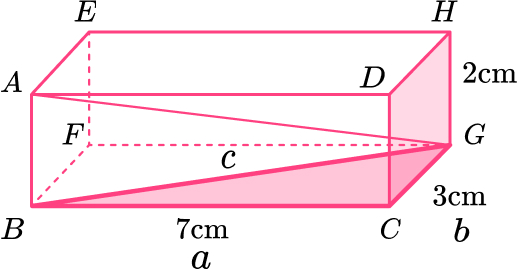
Length of \text{BG:}
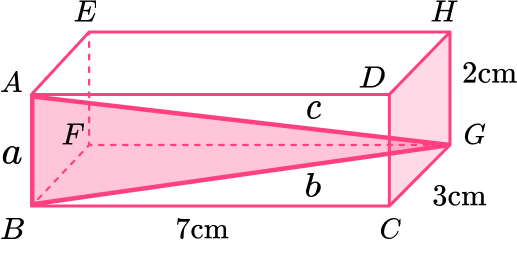
Length of \text{AG:}
15. Here is a right angled triangle.
Form an equation and use it to work out the value of x.
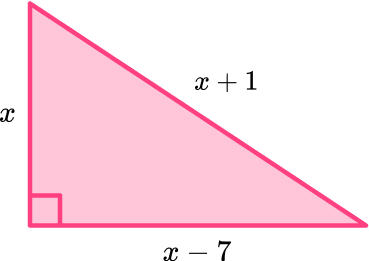
x=4 \, or \, x=12
x cannot be 4 as you can’t have a negative side length so x=12
In middle school, students…
- prove the Pythagorean Theorem;
- use the Pythagorean Theorem with trigonometric ratios to solve problems;
- use the Pythagorean Theorem in proofs.
Pythagoras Theorem may feature in questions alongside other topics, such as trigonometry, circle theorems or algebra.
The Pythagorean Theorem is used to calculate a missing length in a right triangle . If you have a right angled triangle and you know two of the lengths, label the sides of the triangle a,b and c (c must be the hypotenuse – the longest side). Pythagorean Theorem is a^2+b^2=c^2. Substitute the values you know into Pythagorean Theorem and solve to find the missing side.
The hypotenuse of a right triangle is the longest side. If you know the lengths of the other two sides, you can find the length of the hypotenuse by squaring the two shorter sides, adding those values together and then taking the square root. By doing this you are finding c in a^2+b^2=c^2
If your triangle is a right triangle and you know two of the sides, you can use Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of the third side. To do this, label the sides a , b and c (with c being the hypotenuse – the longest side). Substitute the values you know into a^2+b^2=c^2 and solve to find the missing side.
Looking for more Pythagorean theorem math questions?
- Ratio questions
- Algebra questions
- Probability questions
- Trigonometry questions
- Venn diagram questions
- Long division questions
Do you have students who need extra support in math? Give your students more opportunities to consolidate learning and practice skills through personalized math tutoring with their own dedicated online math tutor. Each student receives differentiated instruction designed to close their individual learning gaps, and scaffolded learning ensures every student learns at the right pace. Lessons are aligned with your state’s standards and assessments, plus you’ll receive regular reports every step of the way. Personalized one-on-one math tutoring programs are available for: – 2nd grade tutoring – 3rd grade tutoring – 4th grade tutoring – 5th grade tutoring – 6th grade tutoring – 7th grade tutoring – 8th grade tutoring Why not learn more about how it works ?
The content in this article was originally written by former UK Secondary teacher Beki Christian and has since been revised and adapted for US schools by elementary and middle school teacher Kathleen Epperson.
Math Games for 6th Graders [FREE]
On the lookout to make your math lessons fun and interactive while building math skills? Try our 6 printable math games for 6th graders.
Playable in pairs, teams or a whole class, our accompanying instructions and printable resources make preparation a breeze!
Privacy Overview
Calculator Soup ®
Online Calculators
Pythagorean Theorem Calculator
Pythagorean Theorem for Right Triangles
What is the Pythagorean Theorem?
The Pythagorean Theorem states that the sum of the squared sides of a right triangle equals the length of the hypotenuse squared.
You might recognize this theorem in the form of the Pythagorean equation:
If you know the length of any 2 sides of a right triangle you can use the Pythagorean equation formula to find the length of the third side.
Calculator Use
This calculator solves the Pythagorean Theorem equation for sides a or b , or the hypotenuse c . The hypotenuse is the side of the triangle opposite the right angle.
For right triangles only, enter any two values to find the third. See the solution with steps using the Pythagorean Theorem formula.
This calculator also finds the area A of the right triangle with sides a and b . The formula for area of a right triangle is:
Pythagorean Theorem Formula
For a right triangle with hypotenuse c and legs a and b , the area of the square whose side is c is equal to the sum of the two areas of the two squares whose sides are a and b . Since a square area is equal to one of its sides squared, the formula can be written:
Using the Pythagorean Theorem formula for right triangles you can find the length of the third side if you know the length of any two other sides. Read below to see solution formulas derived from the Pythagorean Theorem formula:
Solve for the Length of the Hypotenuse c
The length of the hypotenuse is the square root of the sum of the sides squared.
Solve for Length of Side a
The length of side a is the square root of the squared hypotenuse minus the square of side b .
Solve for the Length of Side b
The length of side b is the square root of the squared hypotenuse minus the square of side a .
Solve for Area A of the Right Triangle
The area of a right triangle is side a multiplied by side b divided by 2.
What are Pythagorean Triples?
A Pythagorean triple is a set of 3 positive integers for sides a and b and hypotenuse c that satisfy the Pythagorean Theorem formula a 2 + b 2 = c 2
The smallest known Pythagorean triple is 3, 4, and 5. Showing the work:
References:
Weisstein, Eric W. "Pythagorean Theorem" From MathWorld --A Wolfram Web Resource. Pythagorean Theorem .
Wikipedia "Pythagorean Theorem" at Pythagorean Theorem last accessed May 4, 2020.
Cite this content, page or calculator as:
Furey, Edward " Pythagorean Theorem Calculator " at https://www.calculatorsoup.com/calculators/geometry-plane/pythagorean-theorem.php from CalculatorSoup, https://www.calculatorsoup.com - Online Calculators
Last updated: February 6, 2024

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A simple equation, Pythagorean Theorem states that the square of the hypotenuse (the side opposite to the right angle triangle) is equal to the sum of the other two sides. Following is how the Pythagorean equation is written: a²+b²=c². In the aforementioned equation, c is the length of the hypotenuse while the length of the other two sides ...
The Pythagorean Theorem deals with which relationship in a right triangle? The lengths of the legs and the length of the hypotenuse. The triangle shown is a right triangle. Create the equation to be used to find the missing lengths. (Enter the smaller leg of the triangle first.) Do not solve the equation. x^2=4^2+7^2.
Here's the Pythagorean Theorem formula for your quick reference. Note: drawings not to scale. Problem 1: Find the value of [latex]x [/latex] in the right triangle. Problem 2: Find the value of [latex]x [/latex] in the right triangle. Problem 3: Find the value of [latex]x [/latex] in the right triangle. Problem 4: The legs of a right triangle ...
Learn. Test your understanding of Pythagorean theorem with these NaN questions. The Pythagorean theorem describes a special relationship between the sides of a right triangle. Even the ancients knew of this relationship. In this topic, we'll figure out how to use the Pythagorean theorem and prove why it works.
The sum of the smaller squares (orange and yellow) is equal to the largest square (blue). The Pythagorean Theorem relates the three sides in a right triangle. To be specific, relating the two legs and the hypotenuse, the longest side. The Pythagorean Theorem can be summarized in a short and compact equation as shown below.
Pythagorean Theorem formula shown with triangle ABC is: a^2+b^2=c^2 . Side c is known as the hypotenuse. The hypotenuse is the longest side of a right triangle. Side a and side b are known as the adjacent sides. They are adjacent, or next to, the right angle. You can only use the Pythagorean Theorem with right triangles. For example,
About. Transcript. The Pythagorean theorem is a cornerstone of math that helps us find the missing side length of a right triangle. In a right triangle with sides A, B, and hypotenuse C, the theorem states that A² + B² = C². The hypotenuse is the longest side, opposite the right angle. Created by Sal Khan.
The Pythagorean Theorem. Find the length of the unknown side 'x'. Find the length of the unknown side 'x'. Find the length of the unknown side 'x'. Find the length of the unknown side 'x'. Is this a RIGHT triangle? If the longest side of a triangle is 10 . meters, and the other two sides are 6 and 8 meters long, is it a RIGHT ...
Pythagorean Theorem. Let \(c\) represent the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle, and let a and b represent the lengths of its legs, as pictured in the image that follows. The relationship involving the legs and hypotenuse of the right triangle, given by \[a^2 + b^2 = c^2,\nonumber \] is called the Pythagorean Theorem.
Answers: Identify whether the following triangles is a right triangle using Pythagorean Theorem. 1. 2,5,6 Solution: 22+52=62. 4+25=36 29≠36 Not a right triangle 2. 9,16,15 Solution: 92+152=162. 81+225=256 306≠256 Not a right triangle 2. 8, 15,17 Solution: 82+152=172. 64+225=289 289=289 Right Triangle 4.
12. Which side length would be considered c? 9,12,10. 12. Find b: a=5 b=? c=13. Either of the two shortest sides of a right triangle, they meet at a common vertex to form a right angle. leg. The longest side of a right triangle. It is always opposite of, and never is a part of, the right angle. hypotenuse.
Use the Pythagorean theorem to determine the length of X. Step 1. Identify the legs and the hypotenuse of the right triangle . The legs have length 6 and 8. X X is the hypotenuse because it is opposite the right angle. Step 2. Substitute values into the formula (remember 'C' is the hypotenuse). A2 + B2 = C2 62 + 82 = X2 A 2 + B 2 = C 2 6 2 + 8 ...
Section 6.2 The Pythagorean Theorem 239 EXAMPLE 2 Finding the Length of a Leg Find the missing length of the triangle. a 2 + b 2 = c 2 Write the Pythagorean Theorem. a 2 + 2.12 = 2.9 2 Substitute 2.1 for b and 2.9 for c. a 2 + 4.41 = 8.41 Evaluate powers. a 2 = 4 Subtract 4.41 from each side. a = 2 Take positive square root of each side. The length of the leg is 2 centimeters.
Right Triangle Questions - using the theorem. The Theorem helps us in: Finding Sides: If two sides are known, we can find the third side. Determining if a triangle is right-angled: If the sides of a triangle are known and satisfy the Pythagoras Formula, it is a right-angled triangle. There is a proof of this theorem by a US president.
Create the equation to be used to find the missing lengths. y^2 = 3^2 + 3^2. The triangle shown is a right triangle. Create the equation to be used to find the missing lengths. Format your answer in the sequence: hypotenuse, unknown leg, known leg. 9^2 = x^2 + 5^2. Create the equation to be used to find the missing lengths.
The Pythagorean Theorem Worksheet is an excellent way to expand your understanding of the Pythagorean Theorem. As you use the worksheet, it is important to remember that 'a' and 'b' represent the shorter lengths on the triangle while c represents the hypotenuse, which is the longest side. Pythagoras Theorem worksheets present you with ...
The hypotenuse formula simply takes the Pythagorean theorem and solves for the hypotenuse, c.To solve for the hypotenuse, we simply take the square root of both sides of the equation a² + b² = c² and solve for c.When doing so, we get c = √(a² + b²).This is just a reformulation of the Pythagorean theorem and is often associated with the name hypotenuse formula.
How to answer Pythagorean Theorem questions. 1 - Label the sides of the triangle a, b, and c. Note that the hypotenuse, the longest side of a right triangle, is opposite the right angle and will always be labeled. 2 - Write down the formula and substitute the values>. a^2+b^2=c^2 a2 +b2 = c2. 3 - Calculate the answer.
This calculator solves the Pythagorean Theorem equation for sides a or b, or the hypotenuse c. The hypotenuse is the side of the triangle opposite the right angle. For right triangles only, enter any two values to find the third. See the solution with steps using the Pythagorean Theorem formula. This calculator also finds the area A of the ...
Lesson 2. The Pythagorean Theorem and Its Converse. LESSON/HOMEWORK. LECCIÓN/TAREA. LESSON VIDEO. ANSWER KEY. EDITABLE LESSON. EDITABLE KEY. SMART NOTEBOOK.
Pythagorean Theorem. a²+b²=c² where a and b represent the legs of a right triangle and c represents the hypotenuse. right angle. An angle that measures 90°. Right angles are often marked with a special square symbol. Perpendicular lines form right angles. right cone. A cone whose vertex is directly over the center of its circular base.
5.3 Answers - tfvfv fbdbalvf fdavgtedf. History 100% (16) 2. Unit 3 - Land-Based Empires 1450-1750 Part 1 Graphic Organizer-7c2150-2e5483. History 93% (163) 1. US History 3.05. History 100% (9) In mathematics, the Pythagorean theorem, or Pythagoras' theorem, is a fundamental relation in Euclidean geometry among the three sides of a right ...
2. The sides of an equilateral triangle are 8 units long. What is the length of the attitude of the triangle? 4 square root of 3. What is the length of side TS? 6 square root of 6. In a proof of the Pythagorean theorem using similarity, what allows you to state that the triangles are similar in order to write the true proportions c/a = a/f and ...