Assignment Problem: Meaning, Methods and Variations | Operations Research
After reading this article you will learn about:- 1. Meaning of Assignment Problem 2. Definition of Assignment Problem 3. Mathematical Formulation 4. Hungarian Method 5. Variations.

Meaning of Assignment Problem:
An assignment problem is a particular case of transportation problem where the objective is to assign a number of resources to an equal number of activities so as to minimise total cost or maximize total profit of allocation.
The problem of assignment arises because available resources such as men, machines etc. have varying degrees of efficiency for performing different activities, therefore, cost, profit or loss of performing the different activities is different.
Thus, the problem is “How should the assignments be made so as to optimize the given objective”. Some of the problem where the assignment technique may be useful are assignment of workers to machines, salesman to different sales areas.
Definition of Assignment Problem:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Suppose there are n jobs to be performed and n persons are available for doing these jobs. Assume that each person can do each job at a term, though with varying degree of efficiency, let c ij be the cost if the i-th person is assigned to the j-th job. The problem is to find an assignment (which job should be assigned to which person one on-one basis) So that the total cost of performing all jobs is minimum, problem of this kind are known as assignment problem.
The assignment problem can be stated in the form of n x n cost matrix C real members as given in the following table:
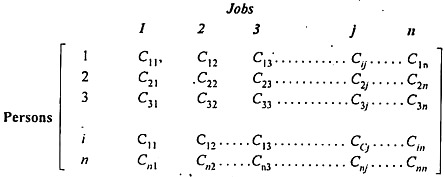
Check it out now on O’Reilly
Dive in for free with a 10-day trial of the O’Reilly learning platform—then explore all the other resources our members count on to build skills and solve problems every day.

A Comparative Analysis of Assignment Problem
- Conference paper
- First Online: 06 June 2023
- Cite this conference paper

- Shahriar Tanvir Alam ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0567-3381 5 ,
- Eshfar Sagor 5 ,
- Tanjeel Ahmed 5 ,
- Tabassum Haque 5 ,
- Md Shoaib Mahmud 5 ,
- Salman Ibrahim 5 ,
- Ononya Shahjahan 5 &
- Mubtasim Rubaet 5
Part of the book series: EAI/Springer Innovations in Communication and Computing ((EAISICC))
Included in the following conference series:
- International Conference on Big Data Innovation for Sustainable Cognitive Computing
128 Accesses
The aim of a supply chain team is to formulate a network layout that minimizes the total cost. In this research, the lowest production cost of the final product has been determined using a generalized plant location model. Furthermore, it is anticipated that units have been set up appropriately so that one unit of input from a source of supply results in one unit of output. The assignment problem is equivalent to distributing a job to the appropriate machine in order to meet customer demand. This study concentrates on reducing the cost of fulfilling the overall customer demand. Many studies have been conducted, and various algorithms have been proposed to achieve the best possible result. The purpose of this study is to present an appropriate model for exploring the solution to the assignment problem using the “Hungarian Method.” To find a feasible output of the assignment problem, this study conducted a detailed case study. The computational results indicate that the “Hungarian Method” provides an optimum solution for both balanced and unbalanced assignment problems. Moreover, decision-makers can use the study’s findings as a reference to mitigate production costs and adopt any sustainable market policy.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or Ebook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others
Optimization model for a production, inventory, distribution and routing problem in small furniture companies.

New Hybrid Algorithm for Supply Chain Optimization
Bi-objective optimization model with economic and environmental consideration for an integrated supply chain with random demand and flexible production rate
Z. Xiang, J. Yang, X. Liang, M.H. Naseem, Application of discrete Grey Wolf Algorithm in balanced transport problem, in 2021 3rd International Academic Exchange Conference on Science and Technology Innovation, IAECST 2021 , (2021), pp. 1312–1318. https://doi.org/10.1109/IAECST54258.2021.9695827
Chapter Google Scholar
C. Woodyard, New York City Is Costliest Place to Park in USA (2018). https://content.usatoday.com/communities/driveon/post/2011/07/new-york-city-costliest-place-to-park-your-car/1#.WWUoFoQrJdg . Accessed 23 Apr 2022
K. McCoy, Drivers spend an average of 17 hours a year searching for parking spots. USA Today (2017). https://www.usatoday.com/story/money/2017/07/12/parking-pain-causes-financial-and-personal-strain/467637001/ . Accessed 23 Apr 2022
W. Ho, P. Ji, A genetic algorithm for the generalised transportation problem. Int. J. Comput. Appl. Technol. 22 (4), 190–197 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1504/IJCAT.2005.006959
Article Google Scholar
Z. Nakat, S. Herrera, Y. Cherkaoui, Cairo Traffic Congestion Study (World Bank, Washington, DC, 2013)
Google Scholar
S. Bussmann, K. Schild, An agent-based approach to the control of flexible production systems, in IEEE International Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation, ETFA , vol. 2, (2001), pp. 481–488. https://doi.org/10.1109/etfa.2001.997722
S. Emde, M. Gendreau, Scheduling in-house transport vehicles to feed parts to automotive assembly lines. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 260 (1), 255–267 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2016.12.012
Article MathSciNet MATH Google Scholar
S. Chopra, G. Notarstefano, M. Rice, M. Egerstedt, A distributed version of the Hungarian method for multirobot assignment. IEEE Trans. Robot. 33 (4), 932–947 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TRO.2017.2693377
H.A. Hussein, M.A.K. Shiker, Two new effective methods to find the optimal solution for the assignment problems. J. Adv. Res. Dyn. Control Syst. 12 (7), 49–54 (2020). https://doi.org/10.5373/JARDCS/V12I7/20201983
M. Chen, D. Zhu, A workload balanced algorithm for task assignment and path planning of inhomogeneous autonomous underwater vehicle system. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Develop. Syst. 11 (4), 483–493 (2018)
C. Cubukcuoglu, P. Nourian, M.F. Tasgetiren, I.S. Sariyildiz, S. Azadi, Hospital layout design renovation as a quadratic assignment problem with geodesic distances. J. Build. Eng. 44 , 102952 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2021.102952
U. Tosun, A new tool for automated transformation of quadratic assignment problem instances to quadratic unconstrained binary optimisation models. Expert Syst. Appl. 201 , 116953 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2022.116953
S.M. Homayouni, D.B.M.M. Fontes, Production and transport scheduling in flexible job shop manufacturing systems. J. Glob. Optim. 79 (2), 463–502 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10898-021-00992-6
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
R. Wang, J. Yan, X. Yang, Neural graph matching network: Learning Lawler’s quadratic assignment problem with extension to hypergraph and multiple-graph matching. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 44 (9), 5261–5279 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3078053
T. Dokeroglu, E. Sevinc, A. Cosar, Artificial bee colony optimization for the quadratic assignment problem. Appl. Soft Comput. J. 76 , 595–606 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2019.01.001
X. Xiang, C. Liu, An almost robust optimization model for integrated berth allocation and quay crane assignment problem. Omega (United Kingdom) 104 , 102455 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omega.2021.102455
Ö. Karsu, M. Azizoğlu, K. Alanlı, Exact and heuristic solution approaches for the airport gate assignment problem. Omega (United Kingdom) 103 , 102422 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omega.2021.102422
A.S. Hameed, M.L. Mutar, H.M.B. Alrikabi, Z.H. Ahmed, A.A. Abdul-Razaq, H.K. Nasser, A hybrid method integrating a discrete differential evolution algorithm with tabu search algorithm for the quadratic assignment problem: A new approach for locating hospital departments. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6653056
S.T. Ngo, J. Jaafar, I.A. Aziz, B.N. Anh, A compromise programming for multi-objective task assignment problem. Computers 10 (2), 1–16 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/computers10020015
X. Zheng, D. Zhou, N. Li, T. Wu, Y. Lei, J. Shi, Self-adaptive multi-task differential evolution optimization: With case studies in weapon–target assignment problem. Electronics 10 (23), 2945 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10232945
X. Hu, C. Liang, D. Chang, Y. Zhang, Container storage space assignment problem in two terminals with the consideration of yard sharing. Adv. Eng. Inform. 47 , 101224 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aei.2020.101224
Q. Rabbani, A. Khan, A. Quddoos, Modified Hungarian method for unbalanced assignment problem with multiple jobs. Appl. Math. Comput. 361 , 493–498 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2019.05.041
A. Kumar, A modified method for solving the unbalanced assignment problems. Appl. Math. Comput. 176 (1), 76–82 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2005.09.056
A. Iampang, V. Boonjing, P. Chanvarasuth, A cost and space efficient method for unbalanced assignment problems, in IEEM2010 – IEEE International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management , (2010), pp. 985–988. https://doi.org/10.1109/IEEM.2010.5674228
L. Wang, Z. He, C. Liu, Q. Chen, Graph based twin cost matrices for unbalanced assignment problem with improved ant colony algorithm. Results Appl. Math. 12 , 100207 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinam.2021.100207
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Military Institute of Science and Technology, Department of Industrial and Production Engineering, Dhaka, Bangladesh
Shahriar Tanvir Alam, Eshfar Sagor, Tanjeel Ahmed, Tabassum Haque, Md Shoaib Mahmud, Salman Ibrahim, Ononya Shahjahan & Mubtasim Rubaet
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Shahriar Tanvir Alam .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Sri Eshwar College of Engineering, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India
Anandakumar Haldorai
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, CMR University, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India
Arulmurugan Ramu
Sri Eshwar College of Engineering, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India
Sudha Mohanram
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper.
Alam, S.T. et al. (2023). A Comparative Analysis of Assignment Problem. In: Haldorai, A., Ramu, A., Mohanram, S. (eds) 5th EAI International Conference on Big Data Innovation for Sustainable Cognitive Computing. BDCC 2022. EAI/Springer Innovations in Communication and Computing. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-28324-6_11
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-28324-6_11
Published : 06 June 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-28323-9
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-28324-6
eBook Packages : Engineering Engineering (R0)
Share this paper
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Travelling Salesman Problem
This humorously named problem refers to the following situation:
A travelling salesman , named Rover plans to visit each of n cities. He wishes to visit each city once and only once, arriving back to city from where he started. The distance between City i and City j is c ij . What is the shortest tour Rover can take?
If there are n cities, there are (n - 1)! possible ways for his tour. For example, if the number of cities to be visited is 5, then there are 4! different combinations. Such type of problems can be solved by the assignment method.
Let c ij be the distance (or cost or time) between City i to City j and
Use Horizontal Scrollbar to View Full Details
| x = | 1 if a tour includes travelling from city i to city j (for i ≠ j) | |
| 0 otherwise |
The following example will help you in understanding the travelling salesman problem of operation research.
Example: Travelling Salesman Problem
A travelling salesman, named Rolling Stone plans to visit five cities 1, 2, 3, 4 & 5. The travel time (in hours) between these cities is shown below:
| To | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| From | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 1 | ∞ | 5 | 8 | 4 | 5 |
| 2 | 5 | ∞ | 7 | 4 | 5 |
| 3 | 8 | 7 | ∞ | 8 | 6 |
| 4 | 4 | 4 | 8 | ∞ | 8 |
| 5 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 8 | ∞ |
How should Mr. Rolling Stone schedule his touring plan in order to minimize the total travel time , if he visits each city once a week?
"As every thread of gold is valuable, so is every minute of time." - John Mason
After applying steps 1 to 3 of the Hungarian method, we get the following assignments.
Use Horizontal Scrollbar to View Full Table.
| To | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| From | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 1 | ∞ | 1 | 3 | 1 | |
| 2 | 1 | ∞ | 2 | 1 | |
| 3 | 2 | 1 | ∞ | 2 | |
| 4 | 3 | ∞ | 4 | ||
| 5 | 3 | ∞ | |||
Draw the minimum number of vertical and horizontal lines necessary to cover all the zeros in the reduced matrix.
Select the smallest element from all the uncovered elements. Subtract this smallest element from all the uncovered elements and add it to the elements, which lie at the intersection of two lines. Thus, we obtain another reduced matrix for fresh assignment. Repeating step 3 on the reduced matrix, we get the following assignments.
| To | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| From | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 1 | ∞ | 2 | 1 | ||
| 2 | ∞ | 1 | 1 | ||
| 3 | 1 | ∞ | 2 | ||
| 4 | 3 | ∞ | 5 | ||
| 5 | 4 | ∞ | |||
The above solution suggests that the salesman should go from city 1 to city 4, city 4 to city 2, and then city 2 to 1 (original starting point). The above solution is not a solution to the travelling salesman problem as he visits city 1 twice.
The next best solution can be obtained by bringing the minimum non-zero element, i.e., 1 into the solution. Please note that the value 1 occurs at four places. We will consider all the cases separately until the acceptable solution is obtained. To make the assignment in the cell (2, 3), delete the row & the column containing this cell so that no other assignment can be made in the second row and third column.
Now, make the assignments in the usual manner as shown in the following table.
He starts from city 1 and goes to city 4; from city 4 to city 2; from city 2 to city 3; from city 3 to city 5; from city 5 to city 1.
Substituting values from original table: 4 + 7 + 6+ 4 + 5 = 26 hours.
In this chapter, we focussed on a special type of transportation problem where the objective was to allocate n different facilities to n different tasks. Although an assignment problem can be formulated as a linear programming problem, it is solved by a special method known as Hungarian Method. If the number of persons is the same as the number of jobs, the assignment problem is said to be balanced. If the number of jobs is different from the number of persons, the assignment problem is said to be unbalanced. Some assignment problems entail maximizing the profit, effectiveness, or layoff of an assignment of persons to tasks or of jobs to machines. The Hungarian Method can also solve such problems. Further, the Hungarian method can also be utilized for solving crew assignment problem and the travelling salesman problem.
Share This Article
Operations Research Simplified Back Next
Goal programming Linear programming Simplex Method Transportation Problem
MBA Knowledge Base
Business • Management • Technology
Home » Management Science » Transportation and Assignment Models in Operations Research
Transportation and Assignment Models in Operations Research
Transportation and assignment models are special purpose algorithms of the linear programming. The simplex method of Linear Programming Problems(LPP) proves to be inefficient is certain situations like determining optimum assignment of jobs to persons, supply of materials from several supply points to several destinations and the like. More effective solution models have been evolved and these are called assignment and transportation models.
The transportation model is concerned with selecting the routes between supply and demand points in order to minimize costs of transportation subject to constraints of supply at any supply point and demand at any demand point. Assume a company has 4 manufacturing plants with different capacity levels, and 5 regional distribution centres. 4 x 5 = 20 routes are possible. Given the transportation costs per load of each of 20 routes between the manufacturing (supply) plants and the regional distribution (demand) centres, and supply and demand constraints, how many loads can be transported through different routes so as to minimize transportation costs? The answer to this question is obtained easily through the transportation algorithm.
Similarly, how are we to assign different jobs to different persons/machines, given cost of job completion for each pair of job machine/person? The objective is minimizing total cost. This is best solved through assignment algorithm.
Uses of Transportation and Assignment Models in Decision Making
The broad purposes of Transportation and Assignment models in LPP are just mentioned above. Now we have just enumerated the different situations where we can make use of these models.
Transportation model is used in the following:
- To decide the transportation of new materials from various centres to different manufacturing plants. In the case of multi-plant company this is highly useful.
- To decide the transportation of finished goods from different manufacturing plants to the different distribution centres. For a multi-plant-multi-market company this is useful.
- To decide the transportation of finished goods from different manufacturing plants to the different distribution centres. For a multi-plant-multi-market company this is useful. These two are the uses of transportation model. The objective is minimizing transportation cost.
Assignment model is used in the following:
- To decide the assignment of jobs to persons/machines, the assignment model is used.
- To decide the route a traveling executive has to adopt (dealing with the order inn which he/she has to visit different places).
- To decide the order in which different activities performed on one and the same facility be taken up.
In the case of transportation model, the supply quantity may be less or more than the demand. Similarly the assignment model, the number of jobs may be equal to, less or more than the number of machines/persons available. In all these cases the simplex method of LPP can be adopted, but transportation and assignment models are more effective, less time consuming and easier than the LPP.
Related posts:
- Operations Research approach of problem solving
- Introduction to Transportation Problem
- Procedure for finding an optimum solution for transportation problem
- Initial basic feasible solution of a transportation problem
- Top 7 Best Ways of Getting MBA Assignment Writing Help
- Introduction to Decision Models
- Transportation Cost Elements
- Modes of Transportation in Logistics
- Factors Affecting Transportation in Logistics
- Export/Import Transportation Systems
One thought on “ Transportation and Assignment Models in Operations Research ”
Exclussive dff. And easy understude
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Procedure, Example Solved Problem | Operations Research - Solution of assignment problems (Hungarian Method) | 12th Business Maths and Statistics : Chapter 10 : Operations Research
Chapter: 12th business maths and statistics : chapter 10 : operations research.
Solution of assignment problems (Hungarian Method)
First check whether the number of rows is equal to the numbers of columns, if it is so, the assignment problem is said to be balanced.
Step :1 Choose the least element in each row and subtract it from all the elements of that row.
Step :2 Choose the least element in each column and subtract it from all the elements of that column. Step 2 has to be performed from the table obtained in step 1.
Step:3 Check whether there is atleast one zero in each row and each column and make an assignment as follows.
Step :4 If each row and each column contains exactly one assignment, then the solution is optimal.
Example 10.7
Solve the following assignment problem. Cell values represent cost of assigning job A, B, C and D to the machines I, II, III and IV.
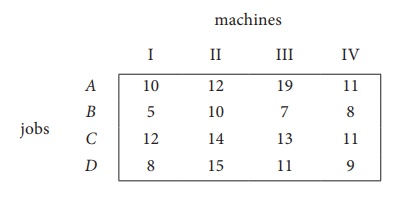
Here the number of rows and columns are equal.
∴ The given assignment problem is balanced. Now let us find the solution.
Step 1: Select a smallest element in each row and subtract this from all the elements in its row.
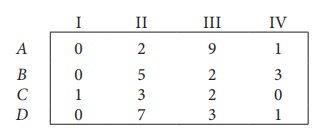
Look for atleast one zero in each row and each column.Otherwise go to step 2.
Step 2: Select the smallest element in each column and subtract this from all the elements in its column.
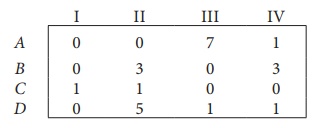
Since each row and column contains atleast one zero, assignments can be made.
Step 3 (Assignment):
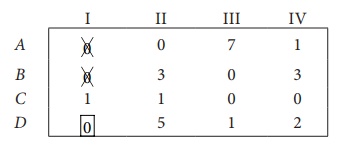
Thus all the four assignments have been made. The optimal assignment schedule and total cost is
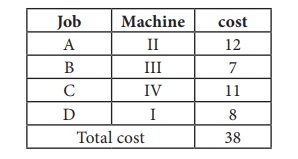
The optimal assignment (minimum) cost
Example 10.8
Consider the problem of assigning five jobs to five persons. The assignment costs are given as follows. Determine the optimum assignment schedule.
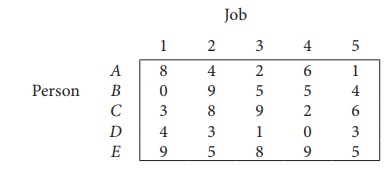
∴ The given assignment problem is balanced.
Now let us find the solution.
The cost matrix of the given assignment problem is
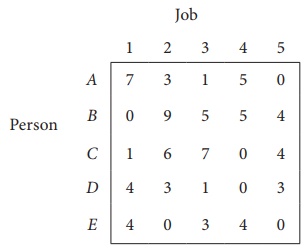
Column 3 contains no zero. Go to Step 2.
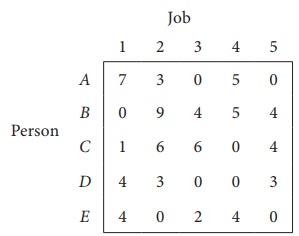
Thus all the five assignments have been made. The Optimal assignment schedule and total cost is
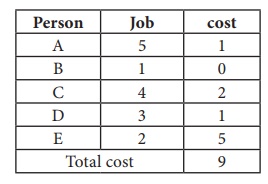
The optimal assignment (minimum) cost = ` 9
Example 10.9
Solve the following assignment problem.
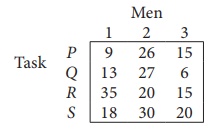
Since the number of columns is less than the number of rows, given assignment problem is unbalanced one. To balance it , introduce a dummy column with all the entries zero. The revised assignment problem is
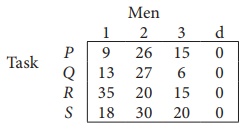
Here only 3 tasks can be assigned to 3 men.
Step 1: is not necessary, since each row contains zero entry. Go to Step 2.
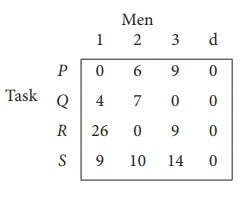
Step 3 (Assignment) :
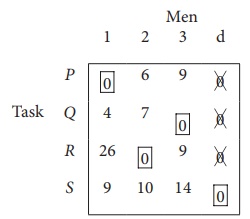
Since each row and each columncontains exactly one assignment,all the three men have been assigned a task. But task S is not assigned to any Man. The optimal assignment schedule and total cost is
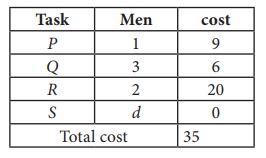
The optimal assignment (minimum) cost = ₹ 35
Related Topics
Privacy Policy , Terms and Conditions , DMCA Policy and Compliant
Copyright © 2018-2023 BrainKart.com; All Rights Reserved. Developed by Therithal info, Chennai.

Unbalanced Assignment Problem: Definition, Formulation, and Solution Methods
Table of Contents
Are you familiar with the assignment problem in Operations Research (OR)? This problem deals with assigning tasks to workers in a way that minimizes the total cost or time needed to complete the tasks. But what if the number of tasks and workers is not equal? In this case, we face the Unbalanced Assignment Problem (UAP). This blog will help you understand what the UAP is, how to formulate it, and how to solve it.
What is the Unbalanced Assignment Problem?
The Unbalanced Assignment Problem is an extension of the Assignment Problem in OR, where the number of tasks and workers is not equal. In the UAP, some tasks may remain unassigned, while some workers may not be assigned any task. The objective is still to minimize the total cost or time required to complete the assigned tasks, but the UAP has additional constraints that make it more complex than the traditional assignment problem.
Formulation of the Unbalanced Assignment Problem
To formulate the UAP, we start with a matrix that represents the cost or time required to assign each task to each worker. If the matrix is square, we can use the Hungarian algorithm to solve the problem. But when the matrix is not square, we need to add dummy tasks or workers to balance the matrix. These dummy tasks or workers have zero costs and are used to make the matrix square.
Once we have a square matrix, we can apply the Hungarian algorithm to find the optimal assignment. However, we need to be careful in interpreting the results, as the assignment may include dummy tasks or workers that are not actually assigned to anything.

Solutions for the Unbalanced Assignment Problem
Besides the Hungarian algorithm, there are other methods to solve the UAP, such as the transportation algorithm and the auction algorithm. The transportation algorithm is based on transforming the UAP into a transportation problem, which can be solved with the transportation simplex method. The auction algorithm is an iterative method that simulates a bidding process between the tasks and workers to find the optimal assignment.
In summary, the Unbalanced Assignment Problem is a variant of the traditional Assignment Problem in OR that deals with assigning tasks to workers when the number of tasks and workers is not equal. To solve the UAP, we need to balance the matrix by adding dummy tasks or workers and then apply algorithms such as the Hungarian algorithm, the transportation algorithm, or the auction algorithm. Understanding the UAP can help businesses and organizations optimize their resource allocation and improve their operational efficiency.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 1.5 / 5. Vote count: 2
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you! 😔
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Operations Research
1 Operations Research-An Overview
- History of O.R.
- Approach, Techniques and Tools
- Phases and Processes of O.R. Study
- Typical Applications of O.R
- Limitations of Operations Research
- Models in Operations Research
- O.R. in real world
2 Linear Programming: Formulation and Graphical Method
- General formulation of Linear Programming Problem
- Optimisation Models
- Basics of Graphic Method
- Important steps to draw graph
- Multiple, Unbounded Solution and Infeasible Problems
- Solving Linear Programming Graphically Using Computer
- Application of Linear Programming in Business and Industry
3 Linear Programming-Simplex Method
- Principle of Simplex Method
- Computational aspect of Simplex Method
- Simplex Method with several Decision Variables
- Two Phase and M-method
- Multiple Solution, Unbounded Solution and Infeasible Problem
- Sensitivity Analysis
- Dual Linear Programming Problem
4 Transportation Problem
- Basic Feasible Solution of a Transportation Problem
- Modified Distribution Method
- Stepping Stone Method
- Unbalanced Transportation Problem
- Degenerate Transportation Problem
- Transhipment Problem
- Maximisation in a Transportation Problem
5 Assignment Problem
- Solution of the Assignment Problem
- Unbalanced Assignment Problem
- Problem with some Infeasible Assignments
- Maximisation in an Assignment Problem
- Crew Assignment Problem
6 Application of Excel Solver to Solve LPP
- Building Excel model for solving LP: An Illustrative Example
7 Goal Programming
- Concepts of goal programming
- Goal programming model formulation
- Graphical method of goal programming
- The simplex method of goal programming
- Using Excel Solver to Solve Goal Programming Models
- Application areas of goal programming
8 Integer Programming
- Some Integer Programming Formulation Techniques
- Binary Representation of General Integer Variables
- Unimodularity
- Cutting Plane Method
- Branch and Bound Method
- Solver Solution
9 Dynamic Programming
- Dynamic Programming Methodology: An Example
- Definitions and Notations
- Dynamic Programming Applications
10 Non-Linear Programming
- Solution of a Non-linear Programming Problem
- Convex and Concave Functions
- Kuhn-Tucker Conditions for Constrained Optimisation
- Quadratic Programming
- Separable Programming
- NLP Models with Solver
11 Introduction to game theory and its Applications
- Important terms in Game Theory
- Saddle points
- Mixed strategies: Games without saddle points
- 2 x n games
- Exploiting an opponent’s mistakes
12 Monte Carlo Simulation
- Reasons for using simulation
- Monte Carlo simulation
- Limitations of simulation
- Steps in the simulation process
- Some practical applications of simulation
- Two typical examples of hand-computed simulation
- Computer simulation
13 Queueing Models
- Characteristics of a queueing model
- Notations and Symbols
- Statistical methods in queueing
- The M/M/I System
- The M/M/C System
- The M/Ek/I System
- Decision problems in queueing

- Advanced Search
A Target-Assignment Problem
- 25 citation
New Citation Alert added!
This alert has been successfully added and will be sent to:
You will be notified whenever a record that you have chosen has been cited.
To manage your alert preferences, click on the button below.
New Citation Alert!
Please log in to your account
Information & Contributors
Bibliometrics & citations, view options.
- Lawrence B Vinod C (2023) Multi-Modal Honey Bee Foraging Optimizer for Weapon Target Assignment Problem Advances in Swarm Intelligence 10.1007/978-3-031-36622-2_4 (43-54) Online publication date: 14-Jul-2023 https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1007/978-3-031-36622-2_4
- Elfeky E Cochrane M Marsh L Elsayed S Sims B Crase S Essam D Sarker R (2022) Coevolutionary Algorithm for Evolving Competitive Strategies in the Weapon Target Assignment Problem Proceedings of the 2022 6th International Conference on Intelligent Systems, Metaheuristics & Swarm Intelligence 10.1145/3533050.3533052 (9-18) Online publication date: 9-Apr-2022 https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3533050.3533052
- Yadav K Alshudukhi J Dhiman G Viriyasitavat W (2022) iTSA: an improved Tunicate Swarm Algorithm for defensive resource assignment problem Soft Computing - A Fusion of Foundations, Methodologies and Applications 10.1007/s00500-022-06979-z 26 :10 (4929-4937) Online publication date: 1-May-2022 https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1007/s00500-022-06979-z
- Show More Cited By
Index Terms
Mathematics of computing
Mathematical analysis
Mathematical optimization
Continuous optimization
Linear programming
Theory of computation
Design and analysis of algorithms
Recommendations
The fleet assignment problem: solving a large-scale integer program.
Given a flight schedule and set of aircraft, the fleet assignment problem is to determine which type of aircraft should fly each flight segment. This paper describes a basic daily, domestic fleet assignment problem and then presents chronologically the ...
Lagrangean decomposition/relaxation for the routing and wavelength assignment problem
This work deals with solving the Routing and Wavelength Assignment problem where the number of accepted connections is to be maximized. Lagrangean decomposition as well as Lagrangean relaxation are studied for both node-arc formulations and arc-path ...
On the Maximum Quadratic Assignment Problem
Quadratic assignment is a basic problem in combinatorial optimization that generalizes several other problems such as traveling salesman, linear arrangement, dense k subgraph, and clustering with given sizes. The input to the quadratic assignment ...
Information
Published in.
Linthicum, MD, United States
Publication History
Contributors, other metrics, bibliometrics, article metrics.
- 25 Total Citations View Citations
- 0 Total Downloads
- Downloads (Last 12 months) 0
- Downloads (Last 6 weeks) 0
- Salgo A Banks J Rivest F Onuţ I Zulkernine F (2021) Exploring decision support systems in task scheduling Proceedings of the 31st Annual International Conference on Computer Science and Software Engineering 10.5555/3507788.3507814 (184-189) Online publication date: 22-Nov-2021 https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.5555/3507788.3507814
- Shi X Zou S Song S Guo R (2021) A multi-objective sparse evolutionary framework for large-scale weapon target assignment based on a reward strategy Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems: Applications in Engineering and Technology 10.3233/JIFS-202679 40 :5 (10043-10061) Online publication date: 1-Jan-2021 https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.3233/JIFS-202679
- Karasakal O Karasakal E Silav A (2021) A multi-objective approach for dynamic missile allocation using artificial neural networks for time sensitive decisions Soft Computing - A Fusion of Foundations, Methodologies and Applications 10.1007/s00500-021-05923-x 25 :15 (10153-10166) Online publication date: 1-Aug-2021 https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1007/s00500-021-05923-x
- Kline A Ahner D Lunday B (2020) A heuristic and metaheuristic approach to the static weapon target assignment problem Journal of Global Optimization 10.1007/s10898-020-00938-4 78 :4 (791-812) Online publication date: 1-Dec-2020 https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1007/s10898-020-00938-4
- Ghanbari A Alaei H (2020) Meta-heuristic algorithms for resource Management in Crisis Based on OWA approach Applied Intelligence 10.1007/s10489-020-01808-y 51 :2 (646-657) Online publication date: 24-Aug-2020 https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1007/s10489-020-01808-y
- Gibbons D Lim C Shi P (2019) Deep Learning for Bipartite Assignment Problems * 2019 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics (SMC) 10.1109/SMC.2019.8914228 (2318-2325) Online publication date: 6-Oct-2019 https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1109/SMC.2019.8914228
- Kline A Ahner D Lunday B (2019) Real-time heuristic algorithms for the static weapon target assignment problem Journal of Heuristics 10.1007/s10732-018-9401-1 25 :3 (377-397) Online publication date: 1-Jun-2019 https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1007/s10732-018-9401-1
View options
Login options.
Check if you have access through your login credentials or your institution to get full access on this article.
Full Access
Share this publication link.
Copying failed.
Share on social media
Affiliations, export citations.
- Please download or close your previous search result export first before starting a new bulk export. Preview is not available. By clicking download, a status dialog will open to start the export process. The process may take a few minutes but once it finishes a file will be downloadable from your browser. You may continue to browse the DL while the export process is in progress. Download
- Download citation
- Copy citation
We are preparing your search results for download ...
We will inform you here when the file is ready.
Your file of search results citations is now ready.
Your search export query has expired. Please try again.
- Show all results for " "

Operations Research: Assignment Problem
Study Flashcards
8 Questions
The personnel assignment problem involves assigning multiple tasks to each worker., the goal of the assignment problem is to maximize the total resource expenditure to complete all tasks., the hungarian technique is used to solve scheduling issues involving irregular cost functions., the case study involves assigning employees to deliver packets to destination locations based on a single criterion., the assignment problem is a subset of the transportation problem., sasaki devised a technique to solve two-sided assignment challenges., a sensitivity analysis is not necessary to avoid changing the optimal assignment from the original problem., the case study involves using the branch-and-bound technique to solve the personnel assignment problem., study notes, assignment problem.
- The assignment problem is a subset of the people assignment problem, which appears in various decision-making scenarios.
- It involves assigning n jobs to n workers, each with varying levels of competency in executing each task.
- The goal is to assign each task to the most appropriate worker, minimizing the total resource expenditure to complete all tasks.
Characteristics of the Assignment Problem
- Each worker is assigned to only one task.
- Assignment price, time spent completing tasks, travel, and other factors can be used to optimize a resource.
Researchers' Contributions
- Sasaki developed a novel technique to address one-sided assignment challenges.
- Maxon and Bhadury proposed a problem with repetitive work and included a human factor in the research.
- Bogomolnaia and Moulin developed a simple random assignment problem with a unique solution.
- Nuass described a specific branch-and-bound technique for tackling assignment problems.
- Sourd investigated the continuous assignment problem to solve scheduling issues involving irregular cost functions.
- Odior et al. addressed the efficacy of plausible solutions to assignment difficulties.
Case Study: Central Post Office in Bandung
- The Hungarian technique was used to solve a personnel assignment problem in the central post office in Bandung.
- The problem involved assigning employees to deliver packets to destination locations based on several criteria owned by each employee.
- A sensitivity analysis of data changes was conducted to avoid changing the optimal assignment from the original problem.
Methodology
- The assignment problem was addressed using the concept of journey time based on Hungarian methodologies.
Learn about the assignment problem, a classic problem in operations research, which involves assigning jobs to workers based on their varying levels of competency. Understand the characteristics of the assignment problem and its goal of minimizing resource expenditure.
Make Your Own Quizzes and Flashcards
Convert your notes into interactive study material.
More Quizzes Like This

The Hungarian Method and Combinatorial Optimization Quiz
Assignment Problem Quiz
Bus Route Assignment Problem in Logistics and Transportation Systems
Operations Research: Assignment Problem Case Study
Upgrade to continue
Today's Special Offer
Save an additional 20% with coupon: SAVE20
Upgrade to a paid plan to continue
Trusted by students, educators, and businesses worldwide.
We are constantly improving Quizgecko and would love to hear your feedback. You can also submit feature requests here: feature requests.
Create your free account
By continuing, you agree to Quizgecko's Terms of Service and Privacy Policy .
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
Title: unlocking the potential of operations research for multi-graph matching.
Abstract: We consider the incomplete multi-graph matching problem, which is a generalization of the NP-hard quadratic assignment problem for matching multiple finite sets. Multi-graph matching plays a central role in computer vision, e.g., for matching images or shapes, so that a number of dedicated optimization techniques have been proposed. While the closely related NP-hard multi-dimensional assignment problem (MDAP) has been studied for decades in the operations research community, it only considers complete matchings and has a different cost structure. We bridge this gap and transfer well-known approximation algorithms for the MDAP to incomplete multi-graph matching. To this end, we revisit respective algorithms, adapt them to incomplete multi-graph matching, and propose their extended and parallelized versions. Our experimental validation shows that our new method substantially outperforms the previous state of the art in terms of objective and runtime. Our algorithm matches, for example, 29 images with more than 500 keypoints each in less than two minutes, whereas the fastest considered competitor requires at least half an hour while producing far worse results.
| Subjects: | Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV) |
| Cite as: | [cs.CV] |
| (or [cs.CV] for this version) | |
| Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite |
Submission history
Access paper:.
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
After reading this article you will learn about:- 1. Meaning of Assignment Problem 2. Definition of Assignment Problem 3. Mathematical Formulation 4. Hungarian Method 5. Variations. Meaning of Assignment Problem: An assignment problem is a particular case of transportation problem where the objective is to assign a number of resources to an equal number of activities so as to minimise total ...
Solving the Assignment Problem. There are various methods for solving the assignment problem, including the Hungarian method, the brute force method, and the auction algorithm. Here, we will focus on the steps involved in solving the assignment problem using the Hungarian method, which is the most commonly used and efficient method. Step 1: Set ...
The assignment problem is a fundamental combinatorial optimization problem. In its most general form, the problem is as follows: The problem instance has a number of agents and a number of tasks. Any agent can be assigned to perform any task, incurring some cost that may vary depending on the agent-task assignment.
Problem 4. Job shop needs to assign 4 jobs to 4 workers. The cost of performing a job is a function of the skills of the workers. Table summarizes the cost of the assignments. Worker1 cannot do job3, and worker 3 cannot do job 4. Determine the optimal assignment using the Hungarian method. Job. Worker.
The assignment problem is one of the fundamental combinatorial optimization problems in the branch of optimization or operations research in mathematics. In an assignment problem , we must find a maximum matching that has the minimum weight in a weighted bipartite graph .
Assignment Problem. The assignment problem is a special case of linear programming problem; it is one of the fundamental combinational optimization problems in the branch of optimization or operations research in mathematics. Its goal consists in assigning m resources (usually workers) to n tasks (usually jobs) one a one to one basis while ...
The Assignment Problem is a special type of Linear Programming Problem based on the following assumptions: However, solving this task for increasing number of jobs and/or resources calls for…
5 Assignment Problem 5.1 INTRODUCTION The assignment problem is one of the special type of transportation problem for which more efficient (less-time consuming) solution method has been devised by KUHN … - Selection from Operations Research [Book]
The problem is a special form of the transportation problem and, as such, has an optimal solution in which each variable is either zero or one. The problem can be solved by the simplex method, but special assignment problem algorithms tend to be computationally more efficient.
The problem is to find an assignment of the operations to the machines, for which the total time for completing all the jobs is minimized". Case 2 : If jobs in the same category may be processed simultaneously, but the different categories must be processed in sequence, then the objective is: Minimize P ∑ k = 1 r max j ∈ S k { c P ( j ...
Textbooks: https://amzn.to/2VgimyJhttps://amzn.to/2CHalvxhttps://amzn.to/2Svk11kIn this video, we'll talk about how to solve a special case of the transporta...
Assignment problems involve optimally matching the elements of two or more sets, where the dimension of the problem refers to the number of sets of elements to be matched. ... of the assignment problem is discussed in almost every textbook for an introductory course in either management science/operations research or production and operations ...
Title: "Cracking the Balanced Assignment Problem in Operations Research!"🔍 Uncover the secrets of the Balanced Assignment Problem in this quick guide to Ope...
as the transportation problem, the assignment problem, the shortest path problem, the maximum flow problem, and the minimum cost flow problem. Very efficient algorithms exist which are many times more efficient than linear programming in the utilization of computer time and space resources. Introduction to Operations Research - p.6
Operations Research I. Assignment problems. Ing. Lenka Skanderová, Ph.D. Description and definition. • Assignees are assigned to do the tasks • Asignee: • Employee, machine, vehicle, etc. The assignment problem satisfies these assumptions: 1. The number of assignees equals to the number of tasks 2. Each assignee can be assigned to do ...
assignment problem occurs frequently in practice and is a basic problem in network flow theory since it can be reduced to a number of other problems, including ... research is to develop an optimal result for an assignment problem and to provide an example of how to handle a balanced and unbalanced assignment problem. ... operations for ...
Some assignment problems entail maximizing the profit, effectiveness, or layoff of an assignment of persons to tasks or of jobs to machines. The Hungarian Method can also solve such problems. Further, the Hungarian method can also be utilized for solving crew assignment problem and the travelling salesman problem.
Transportation and assignment models are special purpose algorithms of the linear programming. The simplex method of Linear Programming Problems(LPP) proves to be inefficient is certain situations like determining optimum assignment of jobs to persons, supply of materials from several supply points to several destinations and the like. More effective solution models have been evolved and these ...
Solve the following assignment problem. Solution: Since the number of columns is less than the number of rows, given assignment problem is unbalanced one. To balance it , introduce a dummy column with all the entries zero. The revised assignment problem is. Here only 3 tasks can be assigned to 3 men.
The Unbalanced Assignment Problem is an extension of the Assignment Problem in OR, where the number of tasks and workers is not equal. In the UAP, some tasks may remain unassigned, while some workers may not be assigned any task. The objective is still to minimize the total cost or time required to complete the assigned tasks, but the UAP has ...
Operations Research (OR) is a field in which people use mathematical and engineering methods to study optimization problems in Business and Management, Economics, Computer Science, Civil Engineering, Industrial Engineering, etc. This course introduces frameworks and ideas about various types of optimization problems in the business world.
Abstract. This paper is concerned with a target assignment model of a probabilistic and nonlinear nature, but nevertheless one which is closely related to the "personnel-assignment" problem. It is shown here that, despite the apparent nonlinearities, it is possible to devise a linear programming formulation that will ordinarily provide a ...
Learn about the assignment problem, a classic problem in operations research, which involves assigning jobs to workers based on their varying levels of competency. Understand the characteristics of the assignment problem and its goal of minimizing resource expenditure.
We consider the incomplete multi-graph matching problem, which is a generalization of the NP-hard quadratic assignment problem for matching multiple finite sets. Multi-graph matching plays a central role in computer vision, e.g., for matching images or shapes, so that a number of dedicated optimization techniques have been proposed. While the closely related NP-hard multi-dimensional ...