Hungarian Method
The Hungarian method is a computational optimization technique that addresses the assignment problem in polynomial time and foreshadows following primal-dual alternatives. In 1955, Harold Kuhn used the term “Hungarian method” to honour two Hungarian mathematicians, Dénes Kőnig and Jenő Egerváry. Let’s go through the steps of the Hungarian method with the help of a solved example.

Hungarian Method to Solve Assignment Problems
The Hungarian method is a simple way to solve assignment problems. Let us first discuss the assignment problems before moving on to learning the Hungarian method.
What is an Assignment Problem?
A transportation problem is a type of assignment problem. The goal is to allocate an equal amount of resources to the same number of activities. As a result, the overall cost of allocation is minimised or the total profit is maximised.
Because available resources such as workers, machines, and other resources have varying degrees of efficiency for executing different activities, and hence the cost, profit, or loss of conducting such activities varies.
Assume we have ‘n’ jobs to do on ‘m’ machines (i.e., one job to one machine). Our goal is to assign jobs to machines for the least amount of money possible (or maximum profit). Based on the notion that each machine can accomplish each task, but at variable levels of efficiency.
Hungarian Method Steps
Check to see if the number of rows and columns are equal; if they are, the assignment problem is considered to be balanced. Then go to step 1. If it is not balanced, it should be balanced before the algorithm is applied.
Step 1 – In the given cost matrix, subtract the least cost element of each row from all the entries in that row. Make sure that each row has at least one zero.
Step 2 – In the resultant cost matrix produced in step 1, subtract the least cost element in each column from all the components in that column, ensuring that each column contains at least one zero.
Step 3 – Assign zeros
- Analyse the rows one by one until you find a row with precisely one unmarked zero. Encircle this lonely unmarked zero and assign it a task. All other zeros in the column of this circular zero should be crossed out because they will not be used in any future assignments. Continue in this manner until you’ve gone through all of the rows.
- Examine the columns one by one until you find one with precisely one unmarked zero. Encircle this single unmarked zero and cross any other zero in its row to make an assignment to it. Continue until you’ve gone through all of the columns.
Step 4 – Perform the Optimal Test
- The present assignment is optimal if each row and column has exactly one encircled zero.
- The present assignment is not optimal if at least one row or column is missing an assignment (i.e., if at least one row or column is missing one encircled zero). Continue to step 5. Subtract the least cost element from all the entries in each column of the final cost matrix created in step 1 and ensure that each column has at least one zero.
Step 5 – Draw the least number of straight lines to cover all of the zeros as follows:
(a) Highlight the rows that aren’t assigned.
(b) Label the columns with zeros in marked rows (if they haven’t already been marked).
(c) Highlight the rows that have assignments in indicated columns (if they haven’t previously been marked).
(d) Continue with (b) and (c) until no further marking is needed.
(f) Simply draw the lines through all rows and columns that are not marked. If the number of these lines equals the order of the matrix, then the solution is optimal; otherwise, it is not.
Step 6 – Find the lowest cost factor that is not covered by the straight lines. Subtract this least-cost component from all the uncovered elements and add it to all the elements that are at the intersection of these straight lines, but leave the rest of the elements alone.
Step 7 – Continue with steps 1 – 6 until you’ve found the highest suitable assignment.
Hungarian Method Example
Use the Hungarian method to solve the given assignment problem stated in the table. The entries in the matrix represent each man’s processing time in hours.
\(\begin{array}{l}\begin{bmatrix} & I & II & III & IV & V \\1 & 20 & 15 & 18 & 20 & 25 \\2 & 18 & 20 & 12 & 14 & 15 \\3 & 21 & 23 & 25 & 27 & 25 \\4 & 17 & 18 & 21 & 23 & 20 \\5 & 18 & 18 & 16 & 19 & 20 \\\end{bmatrix}\end{array} \)
With 5 jobs and 5 men, the stated problem is balanced.
\(\begin{array}{l}A = \begin{bmatrix}20 & 15 & 18 & 20 & 25 \\18 & 20 & 12 & 14 & 15 \\21 & 23 & 25 & 27 & 25 \\17 & 18 & 21 & 23 & 20 \\18 & 18 & 16 & 19 & 20 \\\end{bmatrix}\end{array} \)
Subtract the lowest cost element in each row from all of the elements in the given cost matrix’s row. Make sure that each row has at least one zero.
\(\begin{array}{l}A = \begin{bmatrix}5 & 0 & 3 & 5 & 10 \\6 & 8 & 0 & 2 & 3 \\0 & 2 & 4 & 6 & 4 \\0 & 1 & 4 & 6 & 3 \\2 & 2 & 0 & 3 & 4 \\\end{bmatrix}\end{array} \)
Subtract the least cost element in each Column from all of the components in the given cost matrix’s Column. Check to see if each column has at least one zero.
\(\begin{array}{l}A = \begin{bmatrix}5 & 0 & 3 & 3 & 7 \\6 & 8 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\0 & 2 & 4 & 4 & 1 \\0 & 1 & 4 & 4 & 0 \\2 & 2 & 0 & 1 & 1 \\\end{bmatrix}\end{array} \)
When the zeros are assigned, we get the following:
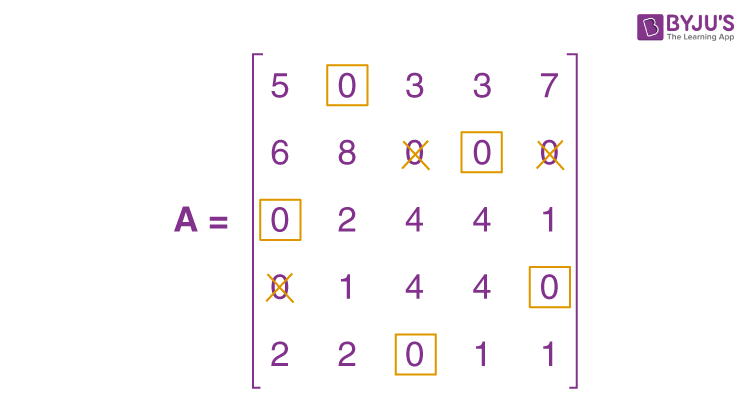
The present assignment is optimal because each row and column contain precisely one encircled zero.
Where 1 to II, 2 to IV, 3 to I, 4 to V, and 5 to III are the best assignments.
Hence, z = 15 + 14 + 21 + 20 + 16 = 86 hours is the optimal time.
Practice Question on Hungarian Method
Use the Hungarian method to solve the following assignment problem shown in table. The matrix entries represent the time it takes for each job to be processed by each machine in hours.
\(\begin{array}{l}\begin{bmatrix}J/M & I & II & III & IV & V \\1 & 9 & 22 & 58 & 11 & 19 \\2 & 43 & 78 & 72 & 50 & 63 \\3 & 41 & 28 & 91 & 37 & 45 \\4 & 74 & 42 & 27 & 49 & 39 \\5 & 36 & 11 & 57 & 22 & 25 \\\end{bmatrix}\end{array} \)
Stay tuned to BYJU’S – The Learning App and download the app to explore all Maths-related topics.
Frequently Asked Questions on Hungarian Method
What is hungarian method.
The Hungarian method is defined as a combinatorial optimization technique that solves the assignment problems in polynomial time and foreshadowed subsequent primal–dual approaches.
What are the steps involved in Hungarian method?
The following is a quick overview of the Hungarian method: Step 1: Subtract the row minima. Step 2: Subtract the column minimums. Step 3: Use a limited number of lines to cover all zeros. Step 4: Add some more zeros to the equation.
What is the purpose of the Hungarian method?
When workers are assigned to certain activities based on cost, the Hungarian method is beneficial for identifying minimum costs.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

- Data Structures
- Linked List
- Binary Tree
- Binary Search Tree
- Segment Tree
- Disjoint Set Union
- Fenwick Tree
- Red-Black Tree
- Advanced Data Structures
Hungarian Algorithm for Assignment Problem | Set 1 (Introduction)
- Hungarian Algorithm for Assignment Problem | Set 2 (Implementation)
- Introduction to Exact Cover Problem and Algorithm X
- Greedy Approximate Algorithm for Set Cover Problem
- Job Assignment Problem using Branch And Bound
- Implementation of Exhaustive Search Algorithm for Set Packing
- Channel Assignment Problem
- Chocolate Distribution Problem | Set 2
- Transportation Problem | Set 1 (Introduction)
- OLA Interview Experience | Set 11 ( For Internship)
- Top 20 Greedy Algorithms Interview Questions
- Job Sequencing Problem - Loss Minimization
- Prim's Algorithm (Simple Implementation for Adjacency Matrix Representation)
- Data Structures and Algorithms | Set 21
- Adobe Interview Experience | Set 55 (On-Campus Full Time for MTS profile)
- Amazon Interview Experience | Set 211 (On-Campus for Internship)
- OYO Rooms Interview Experience | Set 3 (For SDE-II, Gurgaon)
- C# Program for Dijkstra's shortest path algorithm | Greedy Algo-7
- Algorithms | Dynamic Programming | Question 7
- Amazon Interview | Set 46 (On-campus for Internship)
- For each row of the matrix, find the smallest element and subtract it from every element in its row.
- Do the same (as step 1) for all columns.
- Cover all zeros in the matrix using minimum number of horizontal and vertical lines.
- Test for Optimality: If the minimum number of covering lines is n, an optimal assignment is possible and we are finished. Else if lines are lesser than n, we haven’t found the optimal assignment, and must proceed to step 5.
- Determine the smallest entry not covered by any line. Subtract this entry from each uncovered row, and then add it to each covered column. Return to step 3.
Try it before moving to see the solution
Explanation for above simple example:
An example that doesn’t lead to optimal value in first attempt: In the above example, the first check for optimality did give us solution. What if we the number covering lines is less than n.
Time complexity : O(n^3), where n is the number of workers and jobs. This is because the algorithm implements the Hungarian algorithm, which is known to have a time complexity of O(n^3).
Space complexity : O(n^2), where n is the number of workers and jobs. This is because the algorithm uses a 2D cost matrix of size n x n to store the costs of assigning each worker to a job, and additional arrays of size n to store the labels, matches, and auxiliary information needed for the algorithm.
In the next post, we will be discussing implementation of the above algorithm. The implementation requires more steps as we need to find minimum number of lines to cover all 0’s using a program. References: http://www.math.harvard.edu/archive/20_spring_05/handouts/assignment_overheads.pdf https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dQDZNHwuuOY

Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Mathematical
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

Unbalanced Assignment Problem: Definition, Formulation, and Solution Methods
Table of Contents
Are you familiar with the assignment problem in Operations Research (OR)? This problem deals with assigning tasks to workers in a way that minimizes the total cost or time needed to complete the tasks. But what if the number of tasks and workers is not equal? In this case, we face the Unbalanced Assignment Problem (UAP). This blog will help you understand what the UAP is, how to formulate it, and how to solve it.
What is the Unbalanced Assignment Problem?
The Unbalanced Assignment Problem is an extension of the Assignment Problem in OR, where the number of tasks and workers is not equal. In the UAP, some tasks may remain unassigned, while some workers may not be assigned any task. The objective is still to minimize the total cost or time required to complete the assigned tasks, but the UAP has additional constraints that make it more complex than the traditional assignment problem.
Formulation of the Unbalanced Assignment Problem
To formulate the UAP, we start with a matrix that represents the cost or time required to assign each task to each worker. If the matrix is square, we can use the Hungarian algorithm to solve the problem. But when the matrix is not square, we need to add dummy tasks or workers to balance the matrix. These dummy tasks or workers have zero costs and are used to make the matrix square.
Once we have a square matrix, we can apply the Hungarian algorithm to find the optimal assignment. However, we need to be careful in interpreting the results, as the assignment may include dummy tasks or workers that are not actually assigned to anything.
Solutions for the Unbalanced Assignment Problem
Besides the Hungarian algorithm, there are other methods to solve the UAP, such as the transportation algorithm and the auction algorithm. The transportation algorithm is based on transforming the UAP into a transportation problem, which can be solved with the transportation simplex method. The auction algorithm is an iterative method that simulates a bidding process between the tasks and workers to find the optimal assignment.
In summary, the Unbalanced Assignment Problem is a variant of the traditional Assignment Problem in OR that deals with assigning tasks to workers when the number of tasks and workers is not equal. To solve the UAP, we need to balance the matrix by adding dummy tasks or workers and then apply algorithms such as the Hungarian algorithm, the transportation algorithm, or the auction algorithm. Understanding the UAP can help businesses and organizations optimize their resource allocation and improve their operational efficiency.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 1 / 5. Vote count: 1
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you! 😔
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Operations Research
1 Operations Research-An Overview
- History of O.R.
- Approach, Techniques and Tools
- Phases and Processes of O.R. Study
- Typical Applications of O.R
- Limitations of Operations Research
- Models in Operations Research
- O.R. in real world
2 Linear Programming: Formulation and Graphical Method
- General formulation of Linear Programming Problem
- Optimisation Models
- Basics of Graphic Method
- Important steps to draw graph
- Multiple, Unbounded Solution and Infeasible Problems
- Solving Linear Programming Graphically Using Computer
- Application of Linear Programming in Business and Industry
3 Linear Programming-Simplex Method
- Principle of Simplex Method
- Computational aspect of Simplex Method
- Simplex Method with several Decision Variables
- Two Phase and M-method
- Multiple Solution, Unbounded Solution and Infeasible Problem
- Sensitivity Analysis
- Dual Linear Programming Problem
4 Transportation Problem
- Basic Feasible Solution of a Transportation Problem
- Modified Distribution Method
- Stepping Stone Method
- Unbalanced Transportation Problem
- Degenerate Transportation Problem
- Transhipment Problem
- Maximisation in a Transportation Problem
5 Assignment Problem
- Solution of the Assignment Problem
- Unbalanced Assignment Problem
- Problem with some Infeasible Assignments
- Maximisation in an Assignment Problem
- Crew Assignment Problem
6 Application of Excel Solver to Solve LPP
- Building Excel model for solving LP: An Illustrative Example
7 Goal Programming
- Concepts of goal programming
- Goal programming model formulation
- Graphical method of goal programming
- The simplex method of goal programming
- Using Excel Solver to Solve Goal Programming Models
- Application areas of goal programming
8 Integer Programming
- Some Integer Programming Formulation Techniques
- Binary Representation of General Integer Variables
- Unimodularity
- Cutting Plane Method
- Branch and Bound Method
- Solver Solution
9 Dynamic Programming
- Dynamic Programming Methodology: An Example
- Definitions and Notations
- Dynamic Programming Applications
10 Non-Linear Programming
- Solution of a Non-linear Programming Problem
- Convex and Concave Functions
- Kuhn-Tucker Conditions for Constrained Optimisation
- Quadratic Programming
- Separable Programming
- NLP Models with Solver
11 Introduction to game theory and its Applications
- Important terms in Game Theory
- Saddle points
- Mixed strategies: Games without saddle points
- 2 x n games
- Exploiting an opponent’s mistakes
12 Monte Carlo Simulation
- Reasons for using simulation
- Monte Carlo simulation
- Limitations of simulation
- Steps in the simulation process
- Some practical applications of simulation
- Two typical examples of hand-computed simulation
- Computer simulation
13 Queueing Models
- Characteristics of a queueing model
- Notations and Symbols
- Statistical methods in queueing
- The M/M/I System
- The M/M/C System
- The M/Ek/I System
- Decision problems in queueing
Assignment Problem: Maximization
There are problems where certain facilities have to be assigned to a number of jobs, so as to maximize the overall performance of the assignment.
The Hungarian Method can also solve such assignment problems , as it is easy to obtain an equivalent minimization problem by converting every number in the matrix to an opportunity loss.
The conversion is accomplished by subtracting all the elements of the given matrix from the highest element. It turns out that minimizing opportunity loss produces the same assignment solution as the original maximization problem.
- Unbalanced Assignment Problem
- Multiple Optimal Solutions
Example: Maximization In An Assignment Problem
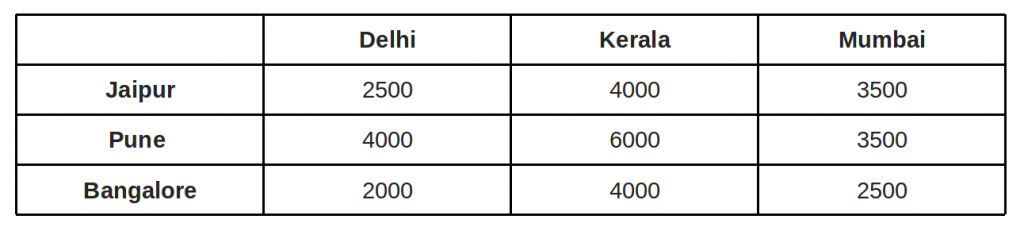
At the head office of www.universalteacherpublications.com there are five registration counters. Five persons are available for service.
How should the counters be assigned to persons so as to maximize the profit ?
Here, the highest value is 62. So we subtract each value from 62. The conversion is shown in the following table.
On small screens, scroll horizontally to view full calculation
Now the above problem can be easily solved by Hungarian method . After applying steps 1 to 3 of the Hungarian method, we get the following matrix.
Draw the minimum number of vertical and horizontal lines necessary to cover all the zeros in the reduced matrix.
Select the smallest element from all the uncovered elements, i.e., 4. Subtract this element from all the uncovered elements and add it to the elements, which lie at the intersection of two lines. Thus, we obtain another reduced matrix for fresh assignment. Repeating step 3, we obtain a solution which is shown in the following table.
Final Table: Maximization Problem
Use Horizontal Scrollbar to View Full Table Calculation
The total cost of assignment = 1C + 2E + 3A + 4D + 5B
Substituting values from original table: 40 + 36 + 40 + 36 + 62 = 214.
Share This Article
Operations Research Simplified Back Next
Goal programming Linear programming Simplex Method Transportation Problem

4. Unbalanced Assignment Problem


COMMENTS
The Hungarian method is a computational optimization technique that addresses the assignment problem in polynomial time and foreshadows following primal-dual alternatives. In 1955, Harold Kuhn used the term "Hungarian method" to honour two Hungarian mathematicians, Dénes Kőnig and Jenő Egerváry. Let's go through the steps of the Hungarian method with the help of a solved example.
Here is the video about unbalanced Assignment problem using Hungarian method,In this video we have seen how to solve unbalanced assignment problem using step...
Hungarian method for assignment problem Step 1. Subtract the entries of each row by the row minimum. Step 2. Subtract the entries of each column by the column minimum. Step 3. Make an assignment to the zero entries in the resulting matrix. A = M 17 10 15 17 18 M 6 10 20 12 5 M 14 19 12 11 15 M 7 16 21 18 6 M −10
Time complexity : O(n^3), where n is the number of workers and jobs. This is because the algorithm implements the Hungarian algorithm, which is known to have a time complexity of O(n^3). Space complexity : O(n^2), where n is the number of workers and jobs.This is because the algorithm uses a 2D cost matrix of size n x n to store the costs of assigning each worker to a job, and additional ...
📒⏩Comment Below If This Video Helped You 💯Like 👍 & Share With Your Classmates - ALL THE BEST 🔥Do Visit My Second Channel - https://bit.ly/3rMGcSAThis vi...
The Hungarian Method: The following algorithm applies the above theorem to a given n × n cost matrix to find an optimal assignment. Step 1. Subtract the smallest entry in each row from all the entries of its row. Step 2. Subtract the smallest entry in each column from all the entries of its column. Step 3.
The existing Hungarian method for solving unbalanced assignment problems is based on the assumptions to assign some jobs to dummy or pseudo machines, those jobs assigned to dummy machines are actually left without execution. In real world situations one may be interested to execute all the jobs on actual machines.
Solutions for the Unbalanced Assignment Problem. Besides the Hungarian algorithm, there are other methods to solve the UAP, such as the transportation algorithm and the auction algorithm. The transportation algorithm is based on transforming the UAP into a transportation problem, which can be solved with the transportation simplex method.
The existing Hungarian method for solving unbalanced assignment problems is based on the assumptions to assign some jobs to dummy or pseudo machines, those jobs assigned to dummy machines are ...
This purpose can be served by assigning multiple jobs to a single machine. The present paper proposes a Modified Hungarian Method for solving unbalanced assignment problems which gives the optimal policy of assignment of jobs to machines. A stepwise algorithm of proposed method is presented and the developed algorithm is also coded in Java SE 11.
In this video you will learn about how to solve unbalanced Assignment problem using Hungarian method in Operation research.After watching full video you wil...
Example: Unbalanced Assignment Problem. Solution. Since the number of persons is less than the number of jobs, we introduce a dummy person (D) with zero values. The revised assignment problem is given below: Table. Now use the Hungarian method to obtain the optimal solution yourself. Ans. = 20 + 17 + 17 + 0 = 54.
Hungarian method, the simplex method for linear programming was modified to solve the assignment problem [3],[4],[5]. Also the signature method for the assignment problem was presented by Balinski [6]. Kore [7] proposed a new approach to solve an unbalanced assignment problem without balancing it.
The Hungarian Method can also solve such assignment problems, as it is easy to obtain an equivalent minimization problem by converting every number in the matrix to an opportunity loss. The conversion is accomplished by subtracting all the elements of the given matrix from the highest element. It turns out that minimizing opportunity loss ...
Hungarian method calculator. 1. A computer centre has 3expert programmers. The centre wants 3 application programmes to be developed. The head of thecomputer centre, after studying carefully the programmes to be developed, estimates the computer time in minutes required by the experts for the application programmes as follows. Programmers.
Introduction to Umbalanced Assignment Problem Hungarian Meethod|Linear Programming|Dream MathsInstagram:- https://Instagram.com/dreammathsTelegram:-https://t...
The Unbalanced Assignment Problem Alternative Optimal Solutions Restriction on Assignments ... Assignment Problems 7 Hungarian Method of Solving an Assignment Problem The steps for obtaining an optimal solution of an assignment problem are as follows: 1. Check whether the given matrix is square. If not, make it square by adding
Many practitioners and researchers used the Hungarian method in the past to solve assignment problems (Kuhn 1955) ; (Chopra et al. 2017). The existing Hungarian method for solving unbalanced assignment problems is based on the assumption that some jobs should be assigned to dummy or pseudo machines, but those jobs are left unexecuted by
The present paper proposes a Modified Hungarian Method for solving unbalanced assignment problems which gives the optimal policy of assignment of jobs to machines. A stepwise algorithm of proposed ...
Before applying Hungarian method, form a balanced / square matrix..Add dummy rows ..Add dummy columns ..
So to solve this problem, we have to add dummy rows or columns with cost 0, to make it a square matrix. ExampleFind Solution of Assignment problem using Hungarian method (MIN case) Here given problem is unbalanced and add 1 new column to convert it into a balance. 9 `9=9-0`.
#unbalancedassignmentproblemHere is the video of unbalanced assignment problem using hungarian method in hindi in operation Research . In this video we discu...