You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser or activate Google Chrome Frame to improve your experience.
Begin typing your search above and press return to search. Press Esc to cancel.

Linux Genie

How to Set Static IP Address on Debian 12?
A static IP address is an IP address that does not change/modify with time. It is useful for setting up servers, remote access, or other network services that require a fixed IP address (need to be reachable at a fixed location). By default, Debian 12 uses a dynamic IP address that is allocated by a DHCP server. However, you can configure your Debian 12 system to use a static IP address by editing the network configuration files.
This guide will explain all possible methods to set up a static IP address on Debian 12 along with the step-by-step instructions.
Prerequisite: Create a Backup File
Before network configuration, it is good practice to create a backup of the existing network settings via the “ cp ” command:
How to Set Up a Static IP Address on Debian 12?
There are different methods to set up a static IP address on Debian 12, depending on the network interface you are using. You can use either the command line or graphical interface to configure your network settings.
To set up a static IP address on Debian 12, follow these:
- Method 1: Editing the /etc/network/interfaces File
- Method 2: Using the nmcli (Command-line Tool)
- Method 3: Using the nmtui (Text-based Interface)
- Method 4: Using NetworkManager (Graphical-based Interface)
Let’s begin with the first method.
Method 1: Set Up a Static IP Address on Debian 12 Editing the /etc/network/interfaces File
The “ /etc/network/interfaces ” file is a configuration file that defines how the network interfaces are configured on the system. To change an interface’s IP address, first check its current IP address:
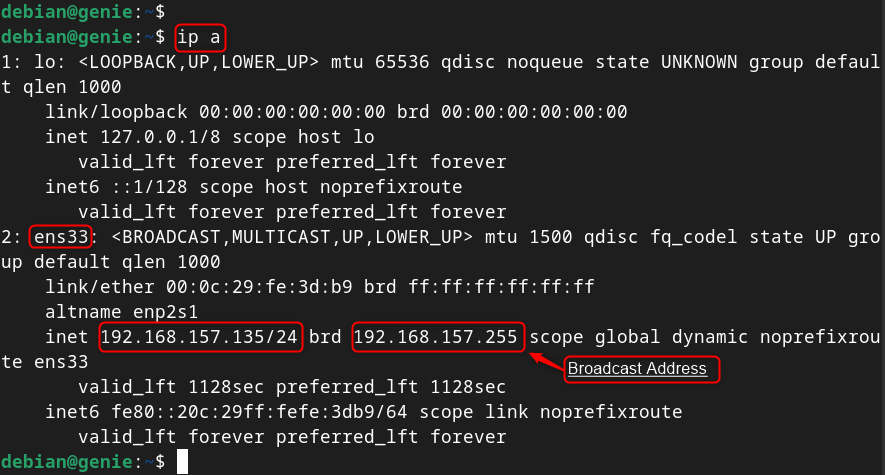
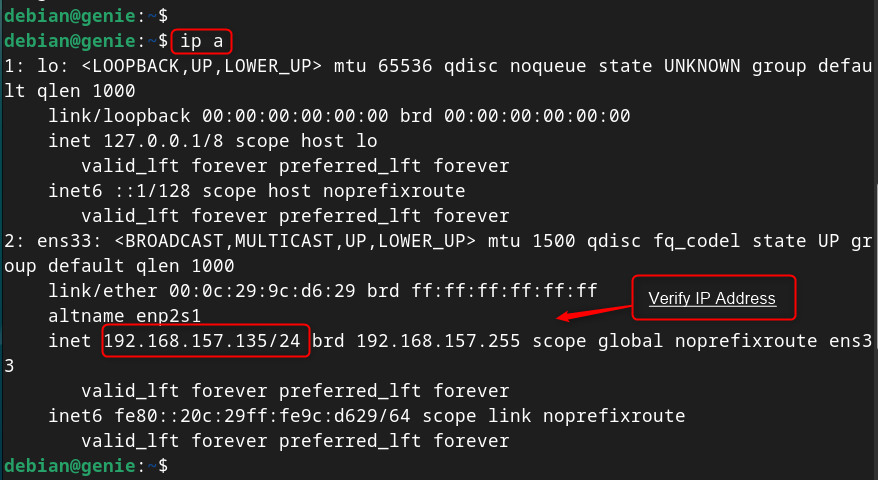
Here, the network interface “ ens33 ” has the IP address “ 192.168.157.135 ”. The last IP address on the network is “ 192.168.157.255 ”, which is the broadcast address. The IP address must be in the range of “ 192.168.157.135 ” to “ 192.168.157.255 ”.
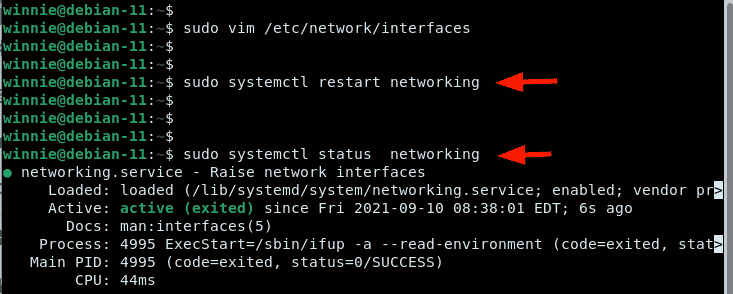
To set up a static IP address on Debian 12, edit the “/ etc/network/interfaces ” file and add the desired IP address, netmask, gateway, and DNS server for your interface. After saving the file, restart the network service to take effect as follow:
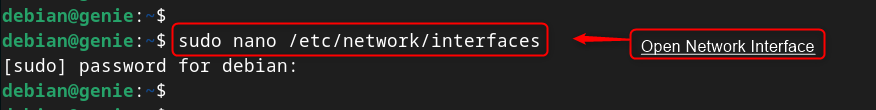
Step 1: Open /etc/network/interfaces File
First, access the /etc/network/interfaces file to edit the desired networking file via nano (editor):
Step 2: Configure Network Interface
Find the line that starts with “ iface ” and match to the network interface for configuration. For instance, to configure the ethernet interface “ ens33 ”, add the following lines (address, netmask, gateway, and dns-nameservers):
Users can replace the values with your own:

Save and close the file by pressing Ctrl+O and then Ctrl+X.
Note : Users can find the network interface using the “ nmcli connection show ” command by following the “ Device Name ” column.
IMPORTANT : Users ensure the default gateway is the same as the assigned IP address (for NAT or Bridged Network). Otherwise, look for “ iface ens33 inet dhcp ” and change the word “ dhcp ” to “ static ” by following the above configuration.
Step 3: Restart Networking Service
Finally, restart the networking service using the “ systemctl ” command or reboot the system for the changes to take effect:

Step 4: Verify Set up IP Address
To check the static IP address on the running system, use the “ ip ” command with “ a ” utility:

Finally, the static IP address has been set up using the “/ etc/network/interfaces ” file on Debian 12.
Note : Each method has independent settings/configurations to set up a static IP address on the Debian system.
Method 2: Set Up a Static IP Address on Debian 12 Using the nmcli
The nmcli is a part of the “ NetworkManager ” package that allows users to manage network connections from the terminal. This tool specifies the IP address, prefix, gateway, and DNS server associated with the device.
To set up a static IP address on Debian 12 using nmcli, follow these steps:
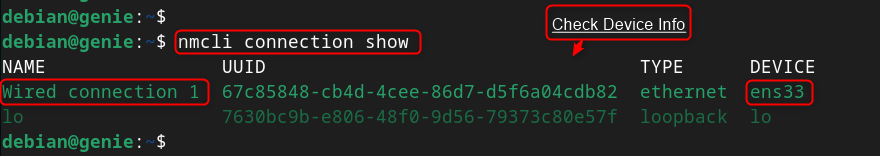
Step 1: List Network Connections
To list all the available network connections on the system, use “ nmcli ” command with “ connection show ”. It prints the network connections along with the connection name, UUID, connection type and device name:
Step 2: Configure Network Connection
To configure the ethernet connection “ ens33 ”, use the “ Wired connection 1 ” in the below instructions:
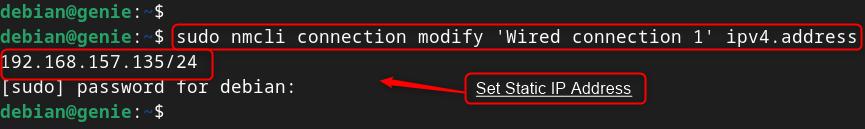
Now, configure/modify connection settings. Such as IP address
- Assign/Set Static IP Address
- Set Default Gateway

- Modify Configuration from Automatic to Static

- Set the DNS IP (Google DNS Server)

- Activate/Enable the Connection
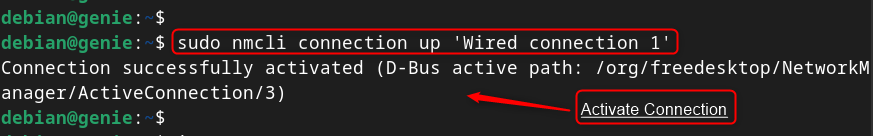
Note : To deactivate the connection, replace the “ down ” utility with the “ up ” utility in the above command.
Verify Static IP Address
Tip: Add or Delete Network Connection
Restart the NetworkManager service by typing sudo systemctl restart NetworkManager or reboot your system for the changes to take effect:
Finally, the static IP address has been set up on Debian 12 using nmcli command line tool.
Method 3: Set Up a Static IP Address on Debian 12 Using the nmtui
The nmtui is another part of the “ NetworkManager ” package that allows you to manage the network connections from a text-based user interface (TUI).
To set up a static IP address on Debian 12 using nmtui, follow these steps:
Step 1: Launch nmtui Interface
First, type “ nmtui ” command to launch the interface, use the arrow keys, and Enter key to navigate through the menus and options
Step 2: Edit a Connection
Select “ Edit a connection ” option and press Enter:
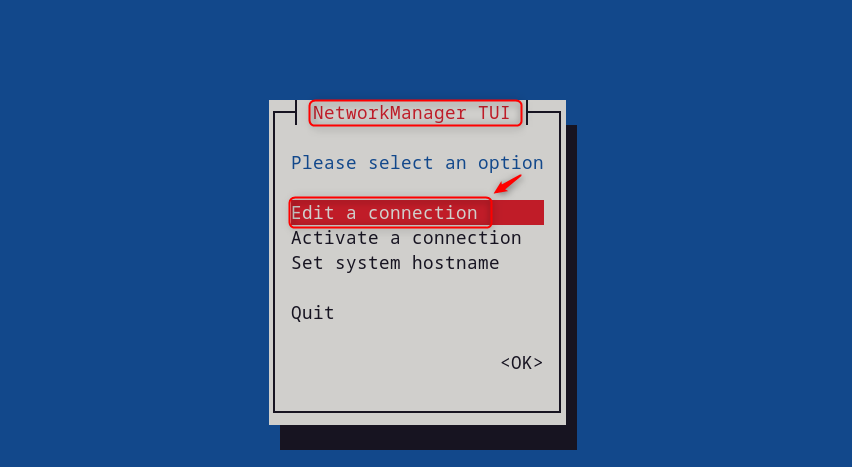
Select the connection (e.g., “ Wired connection 1 ”) that users want to configure and press Enter:

It navigates to the “ Edit a connection ” interface. At there,
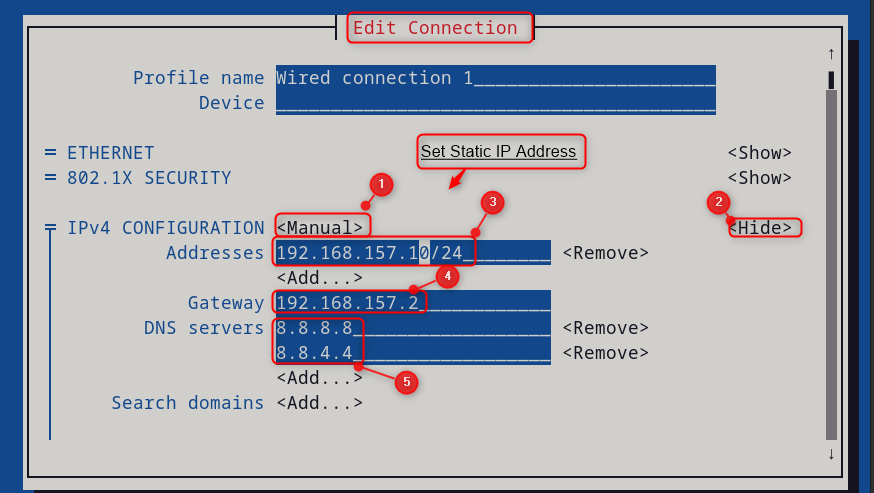
- Select “ IPv4 CONFIGURATION ” and press Enter. Pick “ Manual ” from the list and hit the “ Enter ” button.
- Select “ Show ” to add or edit the IPv4 addresses of the connection.
- Enter the static IP address (192.168.157.10), gateway(192.168.157.2) and DNS servers (8.8.8.8 8.8.4.4) of the connection that users want to assign to the connection.
Scroll down, and hit the “ OK ” button to save the address and return to the previous menu:
Step 3: Restart the NetworkManager Services

Then, press the “ Activate/Deactivate ” for the changes to take effect. Finally, back, and then “ Quit ” to exit the interface:
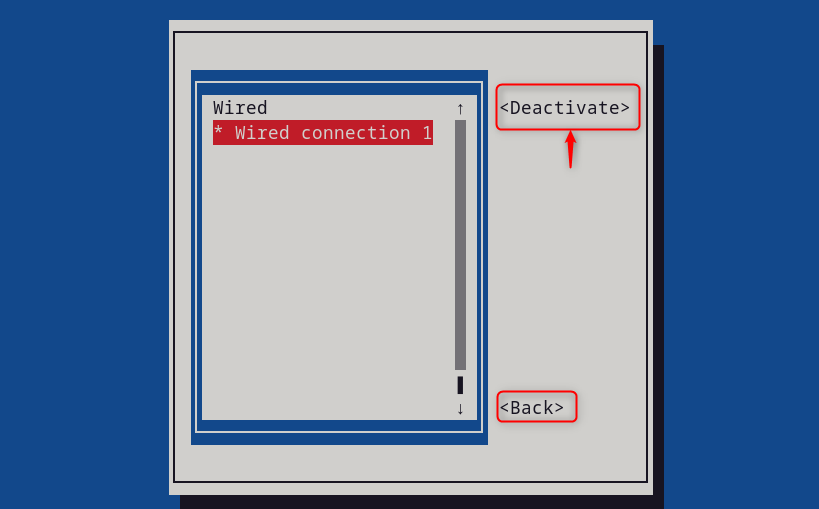
Step 4: Verify Static IP Address
Now, users can verify the Static IP address using the “ ip ” command with the “ a ” utility:
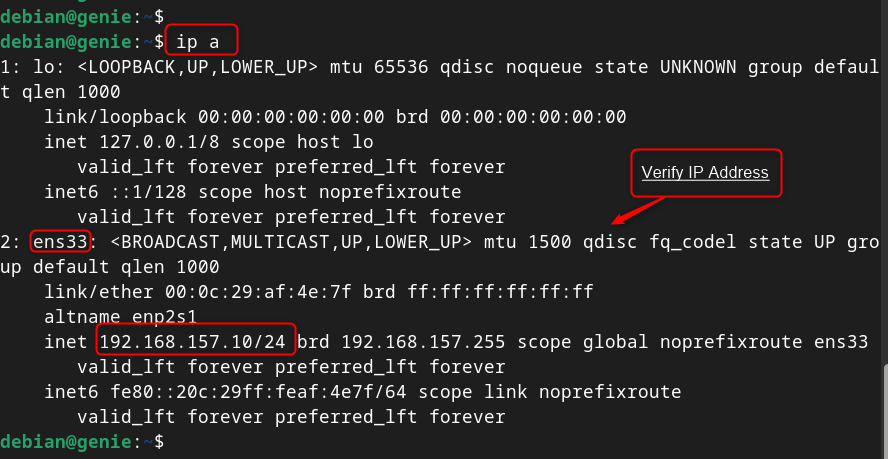
This section has set up/configured the static IP address on Debian 12 using nmtui tool.
Method 4: Set Up a Static IP Address on Debian 12 Using NetworkManager
The GUI method is an easy-to-implement method for static IP address configuration. To set up a static IP address using the graphical interface. Here are the steps:
Step 1: Click on the Network Icon
Click on the network icon on the top right corner of the screen and select “Wired Settings

Step 2: Access the Network Interface
In the “ Wired ” tab, hit the gear icon under the network interface for configuration:

Step 3: Edit Network Information
In the “ IPv4 ” tab, switch the method from “ Automatic (DHCP) ” to “ Manual ”. After that, enter the IP address (192.168.157.135), subnet mask (255.255.255.0), gateway (192.168.157.135) and DNS servers (8.8.4.4, 8.8.8.8). Finally, click on “ Apply ” to save the changes:

Note : If a user found any issue, check the Gateway that remains the same as in the previous configuration located in the “ Details ” tab.
Step 4: Restart Network Interface
Now, restart the network interface via toggle button for the changes to take effect:
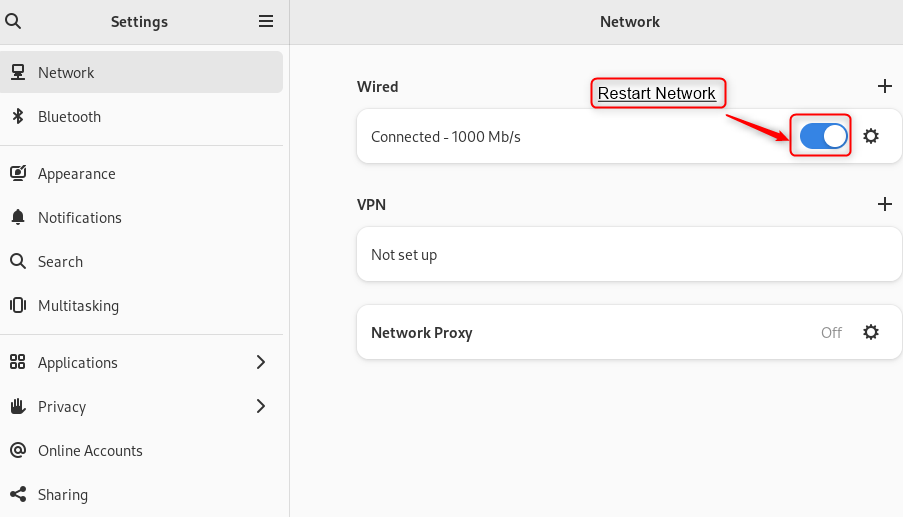
Step 5: Verification
User can verify the static ip address on settings by navigating to the “ Detail ” tab:
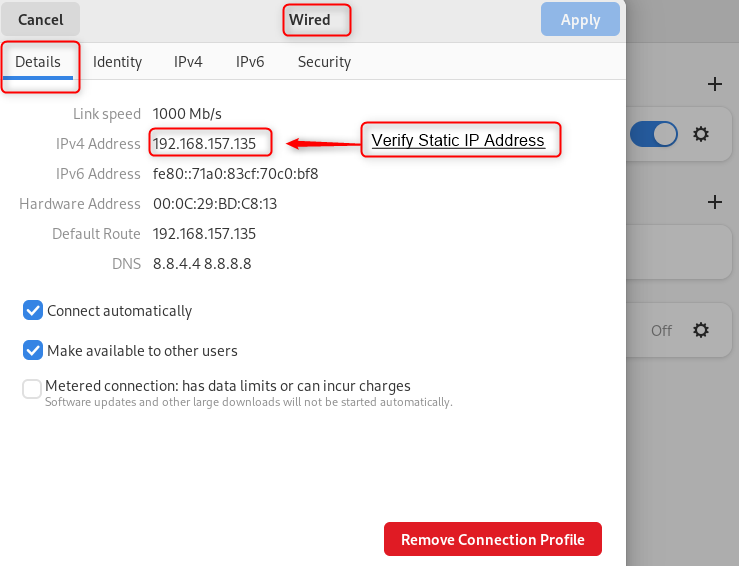
In this way, a static IP address has been set up on Debian 12 using the GUI.
Setting up a static IP address on Debian 12 is a simple and useful task that can improve your network security and stability. To set up a static IP address on Debian 12, use the “ /etc/network/interfaces ” file, the “ nmcli ” tool, and the “ nmtui ” interface.
Alternatively, use the “ NetworkManager ” graphical tool and configure the IPv4 settings for your connection. The easiest method is to use the “ NetworkManager ” tool to static IP addresses on Debian 12.
This guide has explained all possible ways to set up a static IP address on Debian 12.


- RecentChanges
- HelpContents
NetworkConfiguration
- Attachments
3 ways to configure the network
Starting and stopping interfaces, reinitialize new network setup, network interface names, using dhcp to automatically configure the interface, configuring the interface manually, setting the speed and duplex, bringing up an interface without an ip address, the resolv.conf configuration file, the resolvconf program, dns configuration for networkmanager, using systemd-resolved for dns resolution, dhcp client configuration, bridging without switching, manual config, network init script config, bridges and vlans, caveats when using bridging and vlan, network config, bonding with active backup, /etc/network/interfaces, how to set the mtu (max transfer unit / packet size) with vlans over a bonded interface, legacy method, iproute2 method.
- The interfaces configuration file at /etc/network/interfaces (this page): for basic or simple configurations (e.g. workstation)
Setting up an Ethernet Interface
Upgrading and network interface names.
- Identify the interface in question (it will often be eth0). Adjust the remainder of these instructions accordingly.
- Reboot the machine to make sure it comes up correctly, and be prepared to intervene manually (e.g. Ctrl-Alt-Del and then boot into single-user mode from GRUB or LILO) if things don't work.
Defining the (DNS) Nameservers
- DHCP clients
- Choose a connection (from the Wired or Wireless tab) and click Edit.
- Click on the IPv4 Settings tab
- Choose 'Automatic (DHCP) addresses only' instead of just 'Automatic (DHCP)'.
- Enter the DNS servers in the “DNS servers” field, separated by spaces (e.g. 208.67.222.222 for OpenDNS).
- Click “Apply.”
Enabling systemd-resolved
Checking the status and flushing the cache in systemd-resolved, managing systemd-resolved settings, setting additional dns servers, setting additional search domains, howto use vlan (dot1q, 802.1q, trunk) (etch, lenny), howto create fault tolerant bonding with vlan (etch - stretch).

Multiple IP addresses on one Interface
NetworkConfiguration ( last modified 2023-07-18 11:37:31 )
- Debian privacy policy , Wiki team , bugs and config .
- Powered by MoinMoin and Python , with hosting provided by Metropolitan Area Network Darmstadt .
How to Assign Static IP Address on Debian 12
In this blog post, we will show you how to assign static ip address on Debian 12.
In the world of Linux, Debian remains one of the most popular distributions, known for its stability and versatility. One essential aspect of managing a Linux system is configuring network settings. Whether you’re setting up a server or just want a consistent IP address for your desktop, assigning a static IP address on Debian 12 can be a crucial task.
Table of Contents
Prerequisites
- Pre-Installed Debian 12
- Sudo User with admin rights
There are different methods through we can assign static ip address on Debian 12.
Method1: Assign Static IP Address on Debian 12 Using GUI
Login to your Debian Desktop environment, From Activity –> Search Settings –> Choose Network
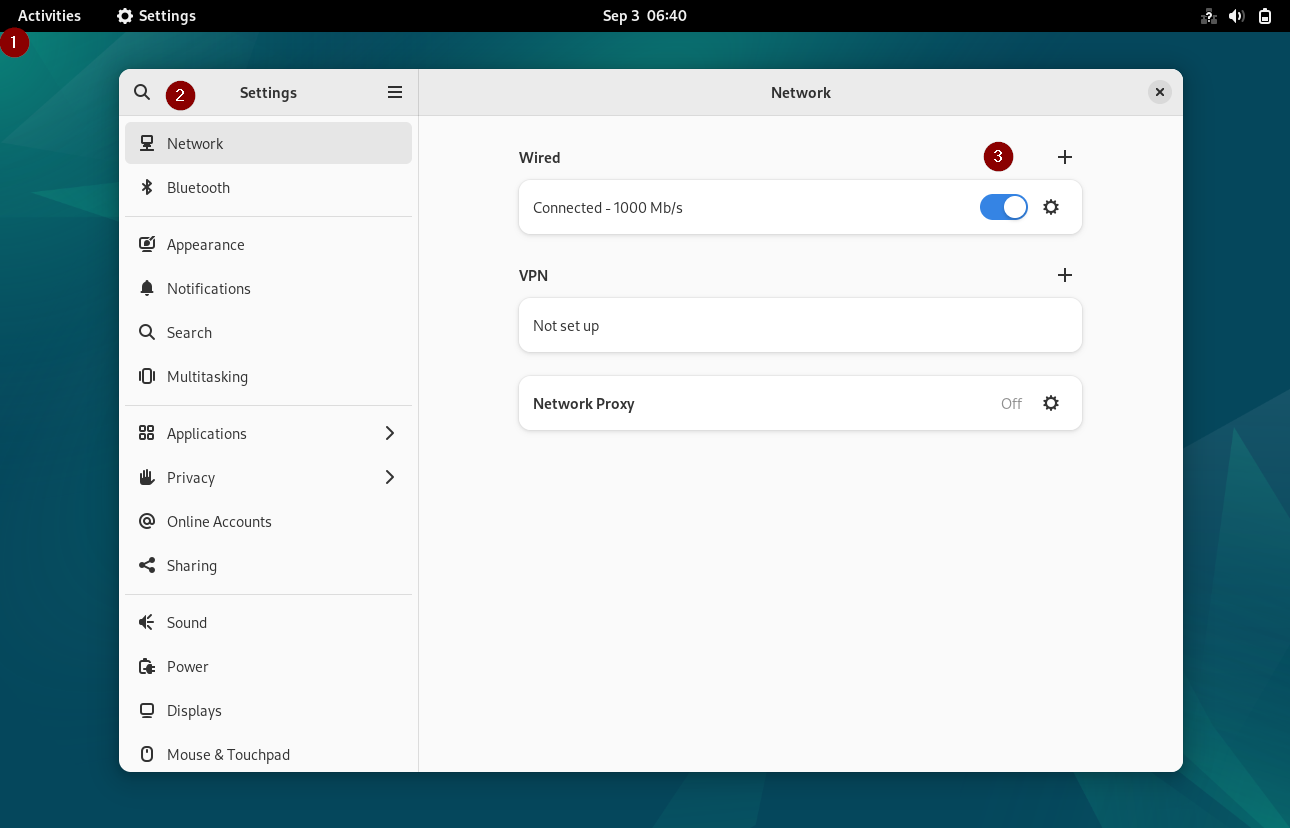
Click on Wired Settings and then we will get the following window,
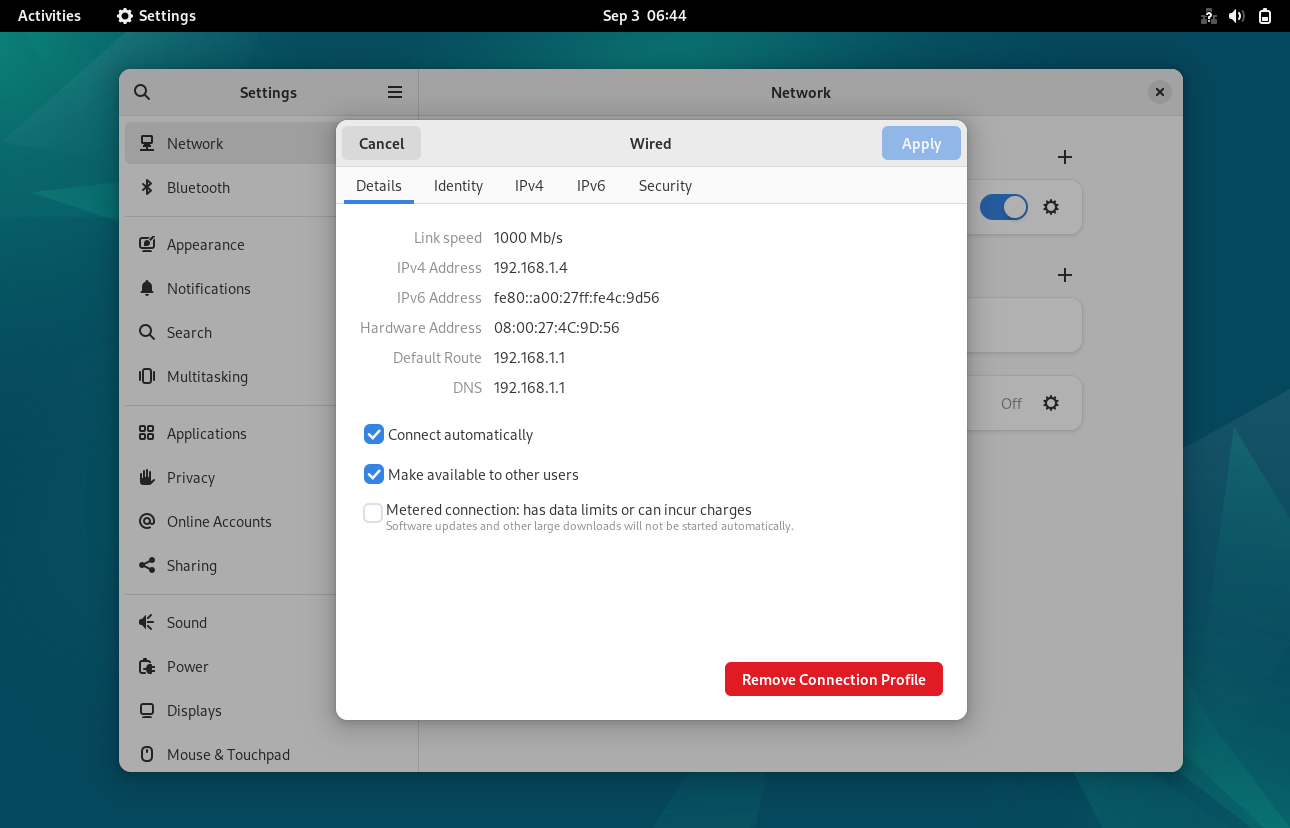
Note: To disable IPv6, go to IPv6 tab and choose ‘ Disable ’ option
Click on IPv4 Tab
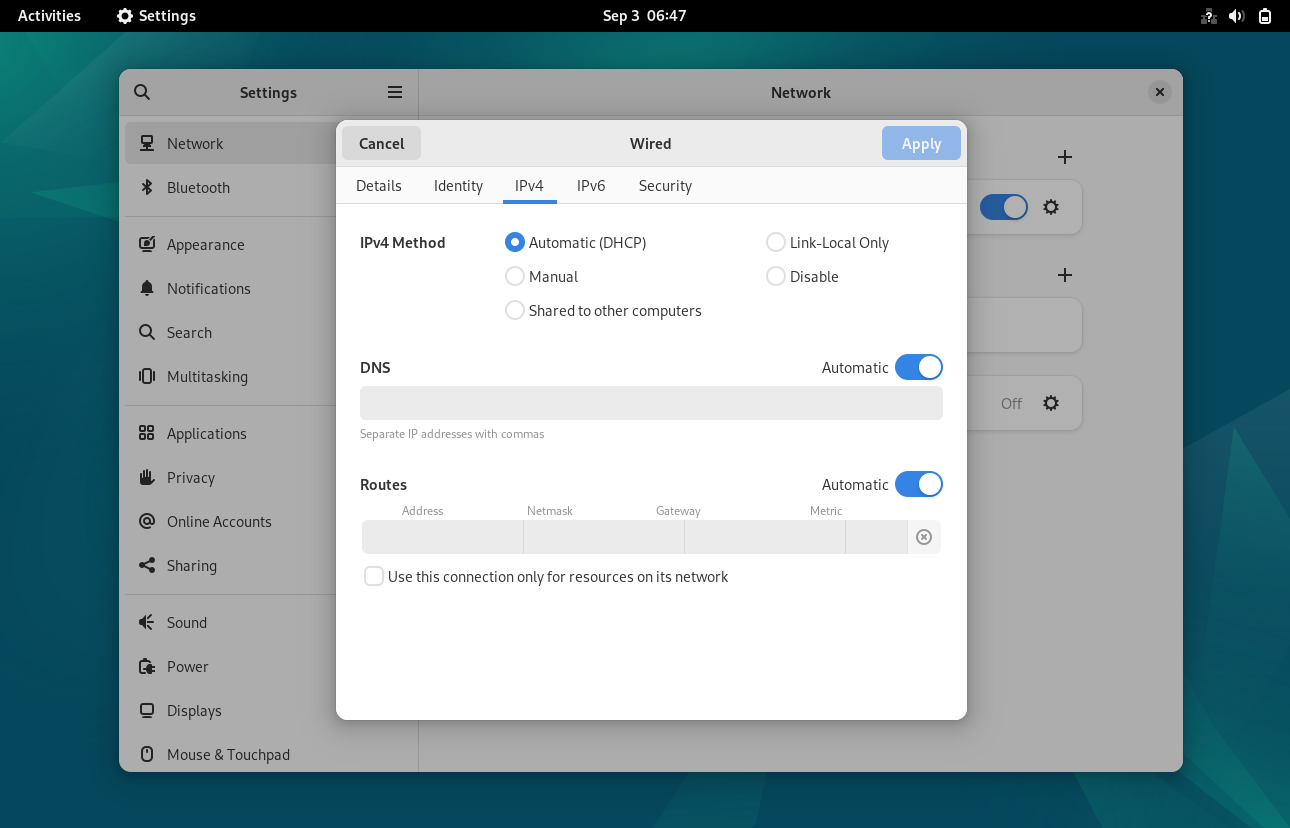
Above window shows that Automatic DHCP is enabled, so to Assign Static IP choose ‘ Manual’ and then specify the IP details like IP address, netmask, gateway and dns server IP.
Important Note: To Specify the dns server IP first disable the automatic dns IP by toggling it.
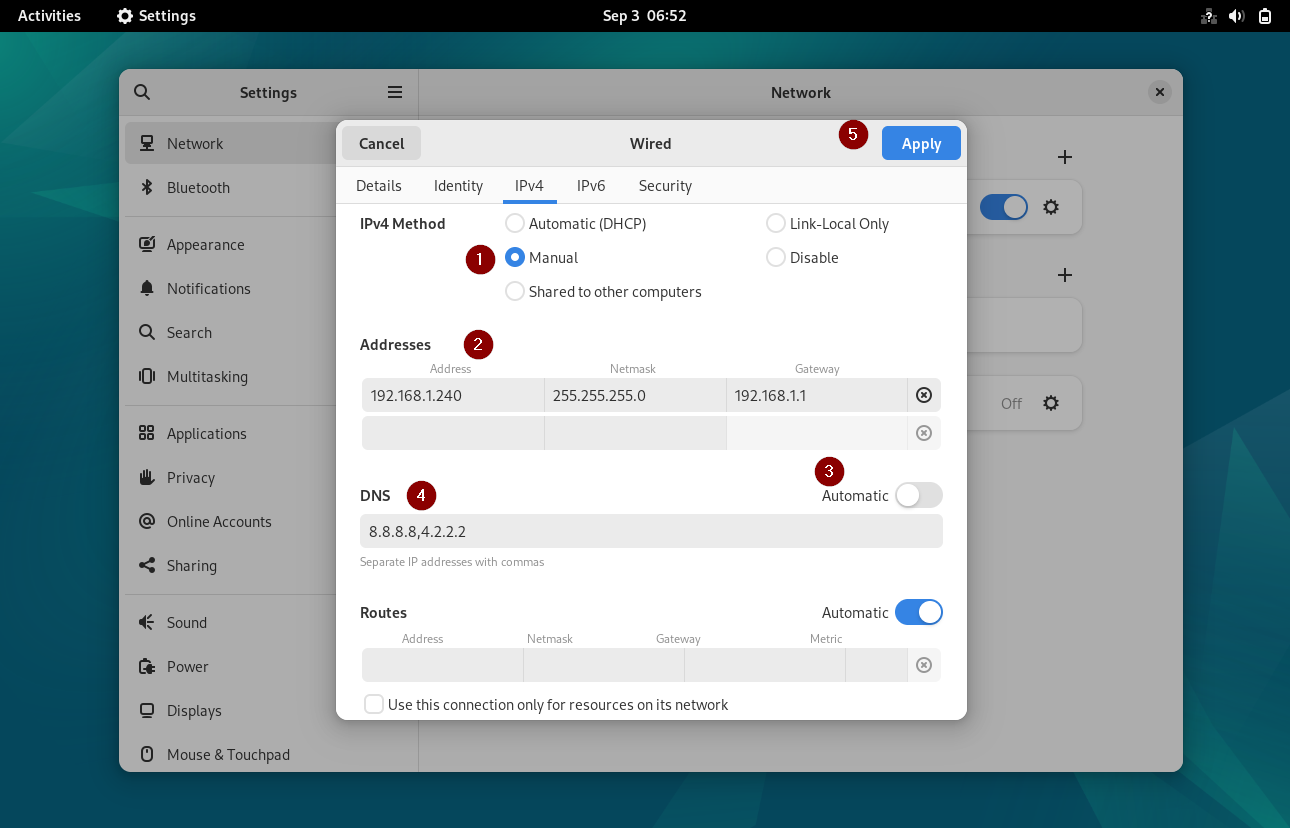
Click on Apply to save the changes.
Now, disable and enable the interface by toggling it so that new IP address is mapped to the Interface.
Now again click on wired settings to verify whether the new static ip address is assigned or not.
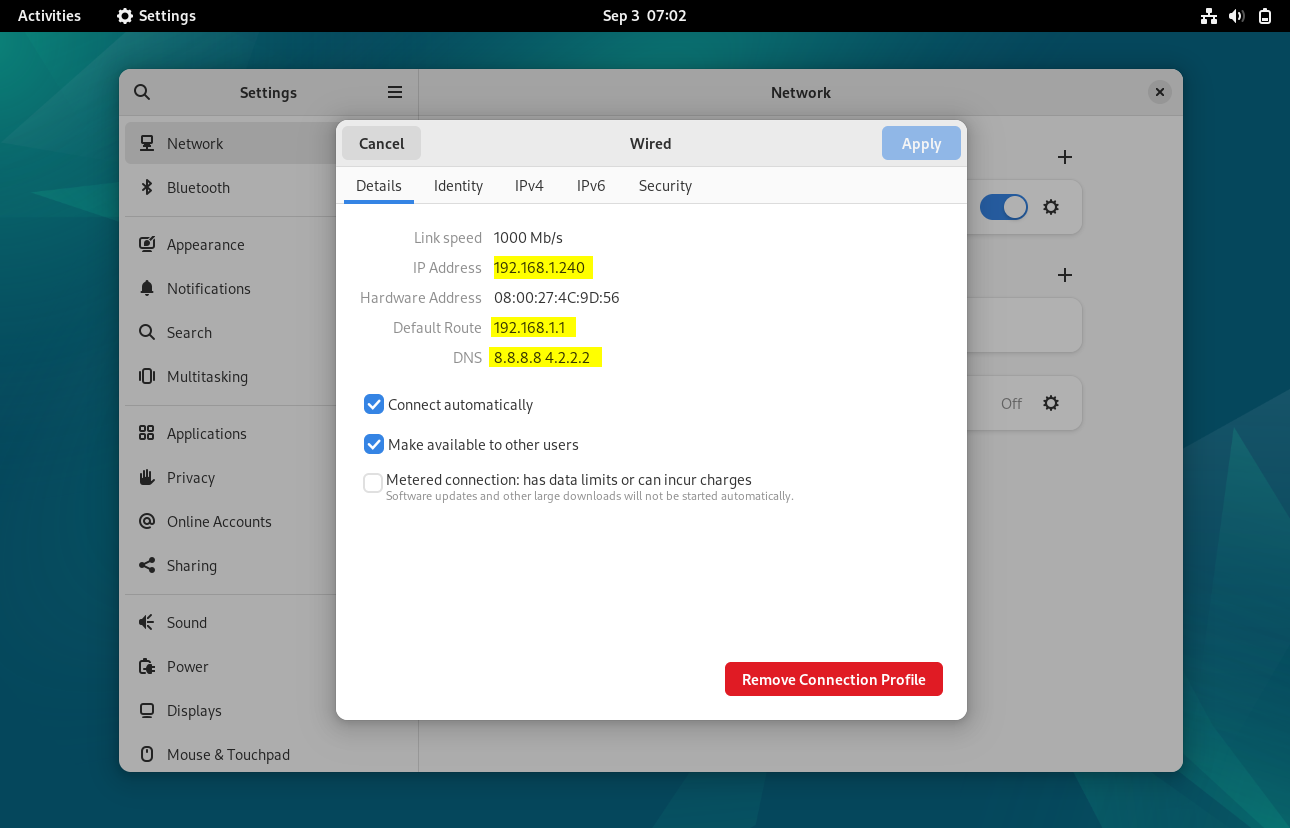
Perfect, above confirms that new static IP address is assigned successfully.
Method2: Assign Static IP Address on Debian 12 From Command Line
Open the terminal, check your current network configuration. You can do this by running the following ip command ,
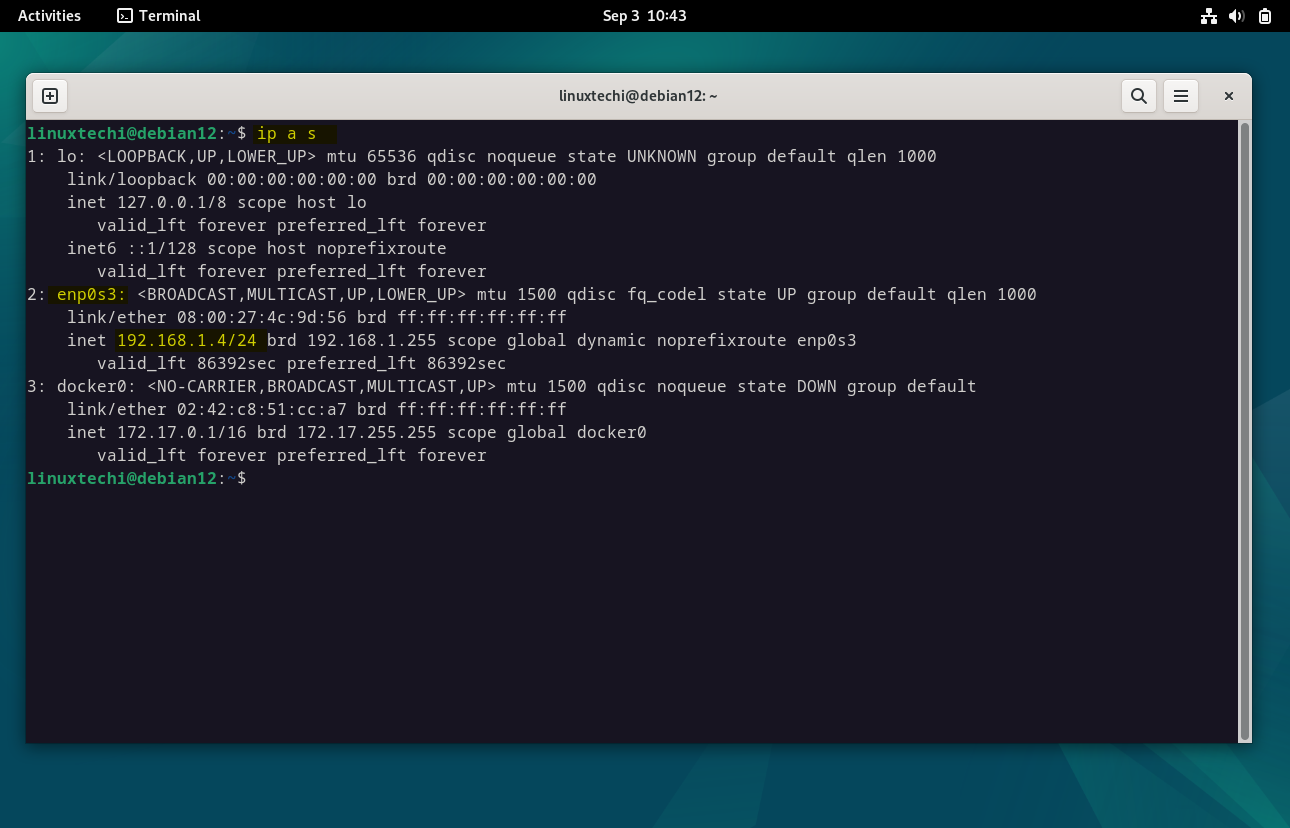
This will display a list of network interfaces on your system. Note down the name of the interface you want to assign a static IP address to (typically, it’s ‘ enp0s3 ‘ for Ethernet).
Next, run nmcli command to get connection name,
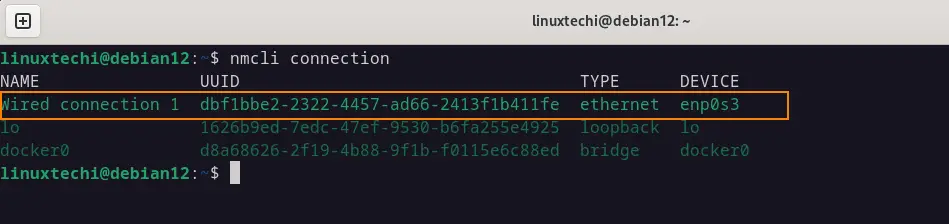
Once we get the connection name, run below nmcli command to assign static ipv4 address,
$ nmcli con mod ‘connection-name’ ipv4.address <IP-Address>
Set the gateway by running below
Change Configuration from DHCP to Manual , so that IP will be static and persistent, run
Set the DNS server IP by running below command,
Disable and enable the connection so that above changes come into the effect.
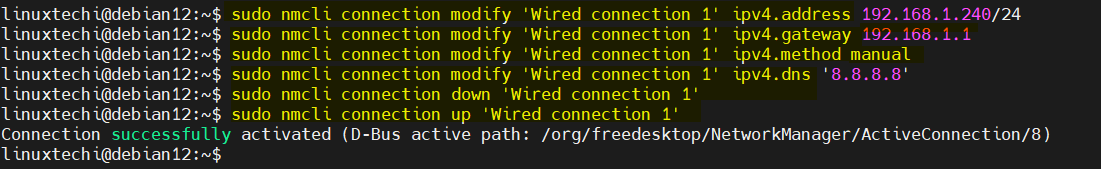
Now run IP Command to check IP address,
Output of above commands would look like below:
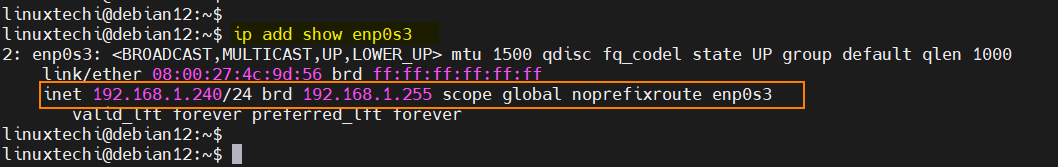
Perfect, above output confirms that static IP address has been assigned successfully on enp0s3 interface.
Assign Static IP Address on Minimal Installed Debian 12
Whenever we install minimal Debian 12 then we will have only the CLI console and don’t have any nmcli utility. So, to assin static ip address we must edit the file ‘ /etc/network/interfaces ’.
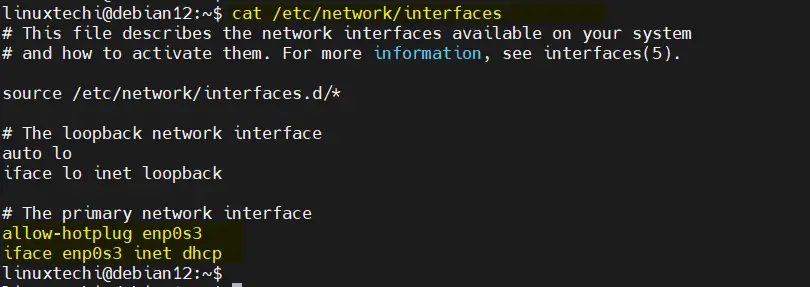
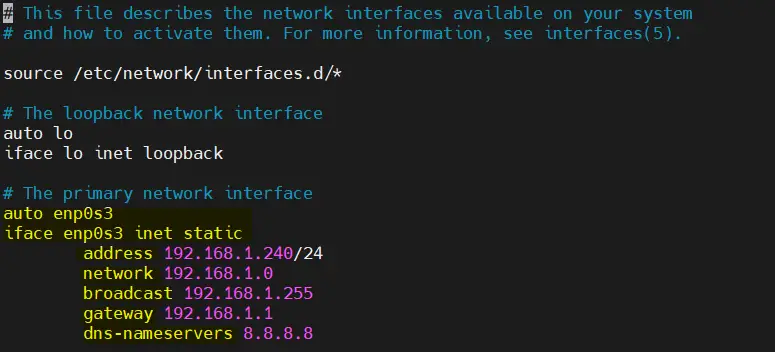
Edit the file and set the static IP address as shown below,
Replace the line ‘ allow-htplug enp0s3 ’ with ‘ auto enp0s3 ‘ and change dhcp parameter to static . Below is my sample file, change interface name and ip details as per your environment.
save & close the file.
To make above changes into the effect the restart the network service
Now, run ip command to verify the ip address,
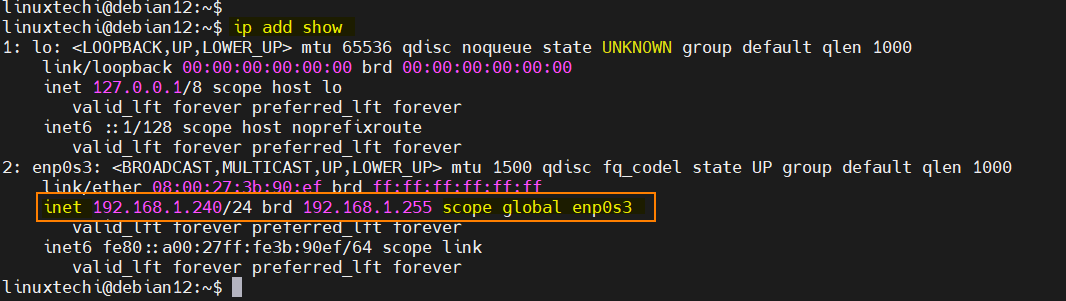
That’s all from this post. Please do share your feedback and queries in below comments section.
Assigning a static IP address on Debian 12 is a straightforward process that can greatly benefit your network stability and ease of access. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can ensure that your Debian 12 system always has a consistent IP address, making it easier to manage and access your resources. Whether you’re configuring a server or just prefer having a stable address for your desktop, Debian 12 provides a user-friendly environment for all your networking needs.
Also Read : How to Install Kubernetes Cluster on Debian 12 | 11
2 thoughts on “How to Assign Static IP Address on Debian 12”
Nice Guide. Appreciate it.
In case someone has used “sudo raspi-config” > Advanced Options > Network Interface Names > Would you like to enable predictable network interface names ?
pi@pi-san-rasp:~ $ sudo nmcli connection modify Wired\ connection\ 1 ipv4.addresses 192.168.1.10/24 pi@pi-san-rasp:~ $ sudo nmcli connection modify Wired\ connection\ 1 ipv4.gateway 192.168.1.1 pi@pi-san-rasp:~ $ sudo nmcli connection modify Wired\ connection\ 1 ipv4.method manual pi@pi-san-rasp:~ $ sudo nmcli connection modify Wired\ connection\ 1 ipv4.dns ‘8.8.8.8’ pi@pi-san-rasp:~ $ sudo reboot
Excellent, thanks.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply

@2023 - All Right Reserved.
How to set up a static IP address on Debian 11

W hen installing any operating system, it is always set to receive network configuration from the DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server. That includes IP address, routing, subnet, Gateway address, DNS information, and other network configurations. While that is always ok and enough to give you access to the internet, there are situations where a static IP address would be much more preferred. The main challenge with using the DHCP to assign IP addresses is that the IP is dynamic and might change.
To better understand the difference between Static and dynamic examples, let’s use a simple example. You have WiFi at your house, but you decide to go to a coffee shop with your laptop and use the internet there. When you come back to your home, there is a high probability that the DHCP will assign you a different IP address.
Why use a static IP
Some of the advantages of using a static IP include;
- It’s much easier to set up and manage DNS
- Reliable hosting services: Let’s say you are hosting a web server, game server, email server, or file server. Using a static IP will make it easier for clients to find you on a local network.
- Reliable Remote access: A static IP address would be more reliable if you connect to your system via SSH or a VPN.
- Reliable communication: Static Ip addressing ake it easier to configure VoIP (Voice Over Internet Protocol) and any other Video or Voice communication over IP.
- Reliable geo-location services: With static IPs, you will get much more accurate geo-location services than a dynamic IP. For example, if you want to know the weather status in your location, you are sure you won’t get weather information from another city.
Setting up a static IP on Debian 11
This post will guide you on setting up a static IP on Debian 11. There are two main methods that we can utilize.
- Set up static IP via the Terminal
- Set up static IP from the GUI
We will look at both methods. Let’s get started.
(Method 1) Set up static IP via the terminal
Before configuring our static IP address, we need to know the network interfaces we are connected to. There are several commands that we can use to achieve that. One of the most popular commands to list network interfaces on Linux is the ifconfig command. Unfortunately, this command is now deprecated and doesn’t come pre-installed on most systems.
The other command to list network interfaces is the IP command. Execute the command below on your Terminal.
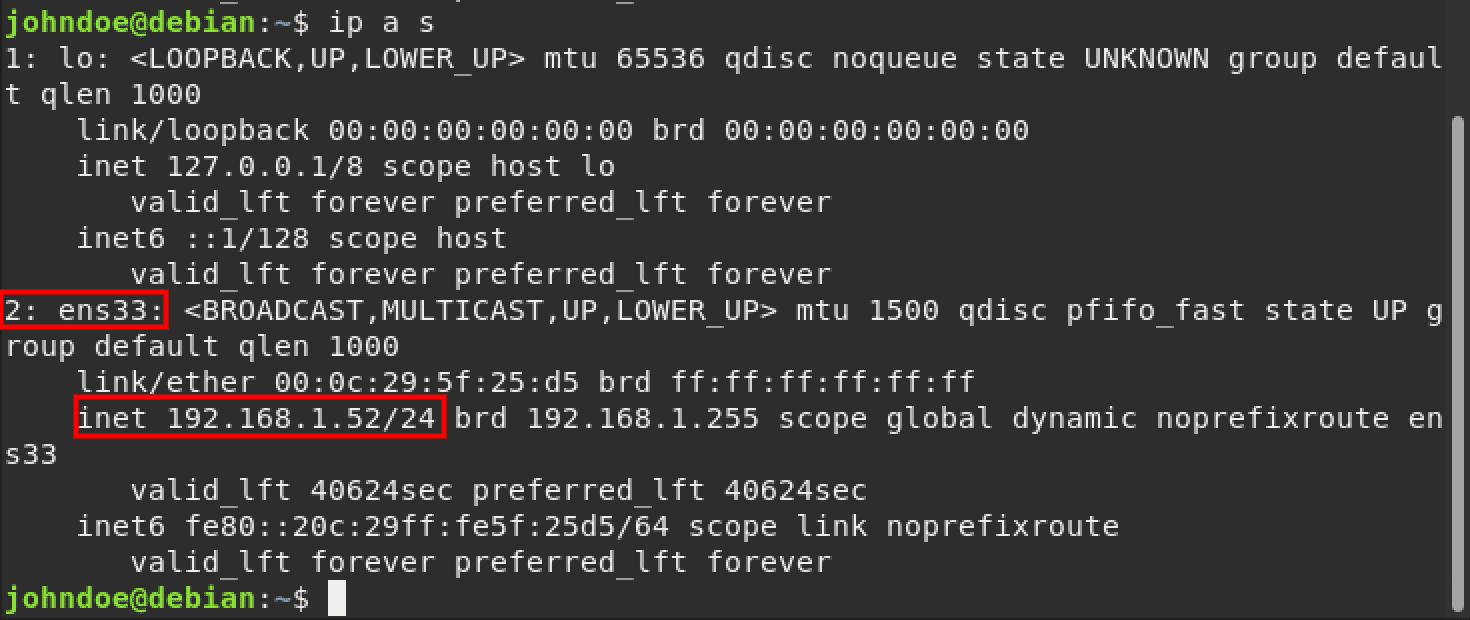
List network interfaces
From the image above, you can see we are connected to the network interface ens33 and the currently assigned IP address is 192.168.1.52 .
With that information, we can now set our static IP address. Execute the command below to open the /etc/network/interfaces configuration file with nano editor.
If you have not done any configurations before, the file will look as shown below.
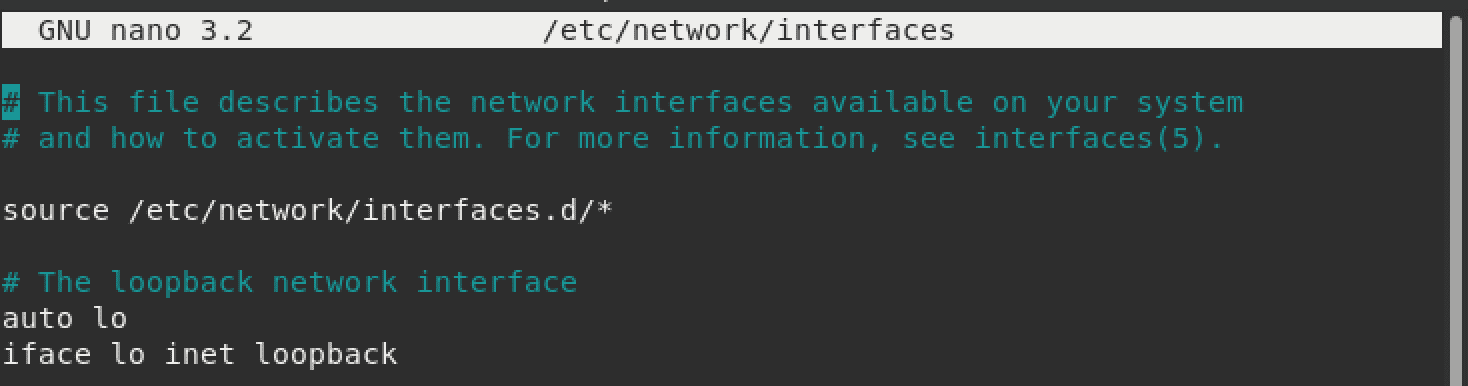
configure interfaces
To set a static IP, add lines below at the end of the file.
Now let’s go through the line above:
- auto ens33 : Here, we specify that we want to use the ens33 network interface.
- iface ens33 inet static : This line specifies that we want to set a static IP address for our network interface.
- address : Here, we set the static IP address that we want to assign to our network interface.
- netmask : Here, enter the subnet mask
- gateway : Here, type the gateway address. If you are unsure, use the IP route command to list the gateway address.
- dns-nameservers : Enter your name servers here. For this post, we will use the default Google name servers.

Static IP configuration
Save the file (Ctrl + S) and Exit (Ctrl + X) when done.
To apply the configurations, we will need to restart the networking service. Execute the command below.
That’s it! You have successfully set a static IP address for your Debian 11 system. Now, when you reboot your system or travel and come back and connect to your WiFi network, the IP address will not change dynamically.
(Method 2) Set up static IP from the GUI
If you are not a command-line person, GNOME (the default Desktop Environment for the Debian system) has provided you with a simple and intuitive interface to configure a static IP address.
First, launch the Settings app from the applications menu and select the ‘Network’ option from the left-hand side panel.
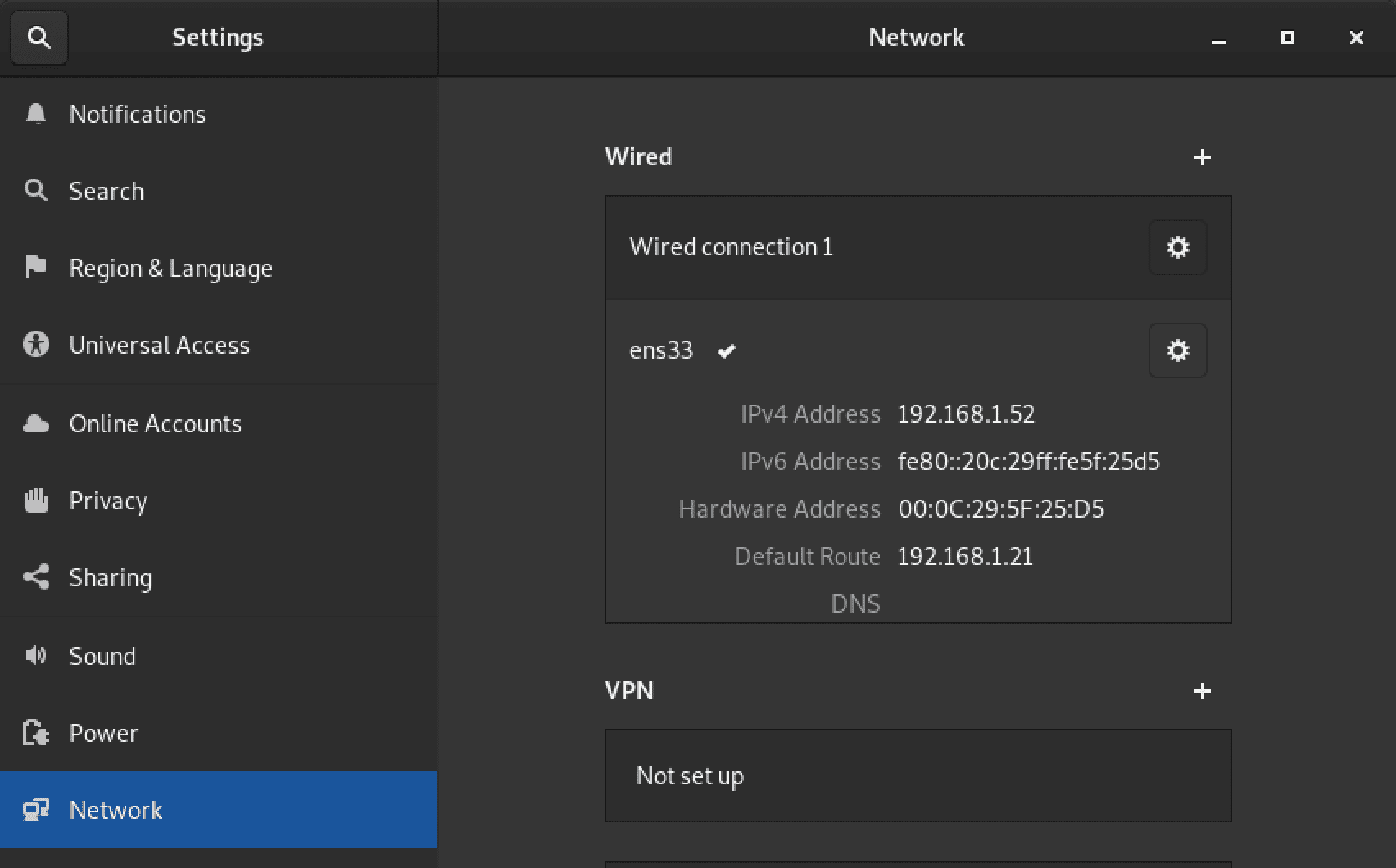
Network Settings
You can see the network interface you are connected to and the necessary network information from this screen. In our case, we are connected to the ens33 network interface.
To set a static IP address, click on the Settings icon (gear icon) next to the network interface you want to set the static IP address.
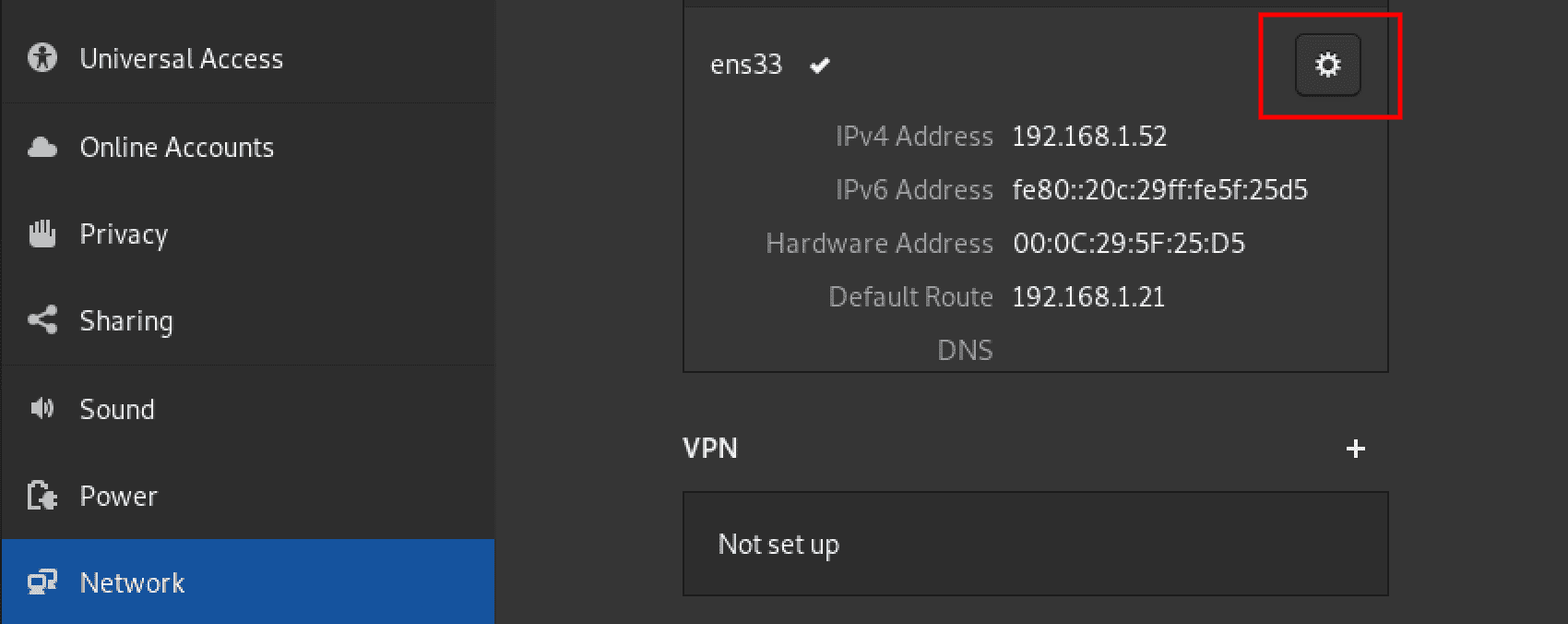
Network interface settings
That will open a configuration window where you can perform several network settings. Select the IPv4 tab and in the IPv4 method section, enable the “manual” radio button. A section will appear below where you must fill in the IP address, subnet mask, and Gateway address.
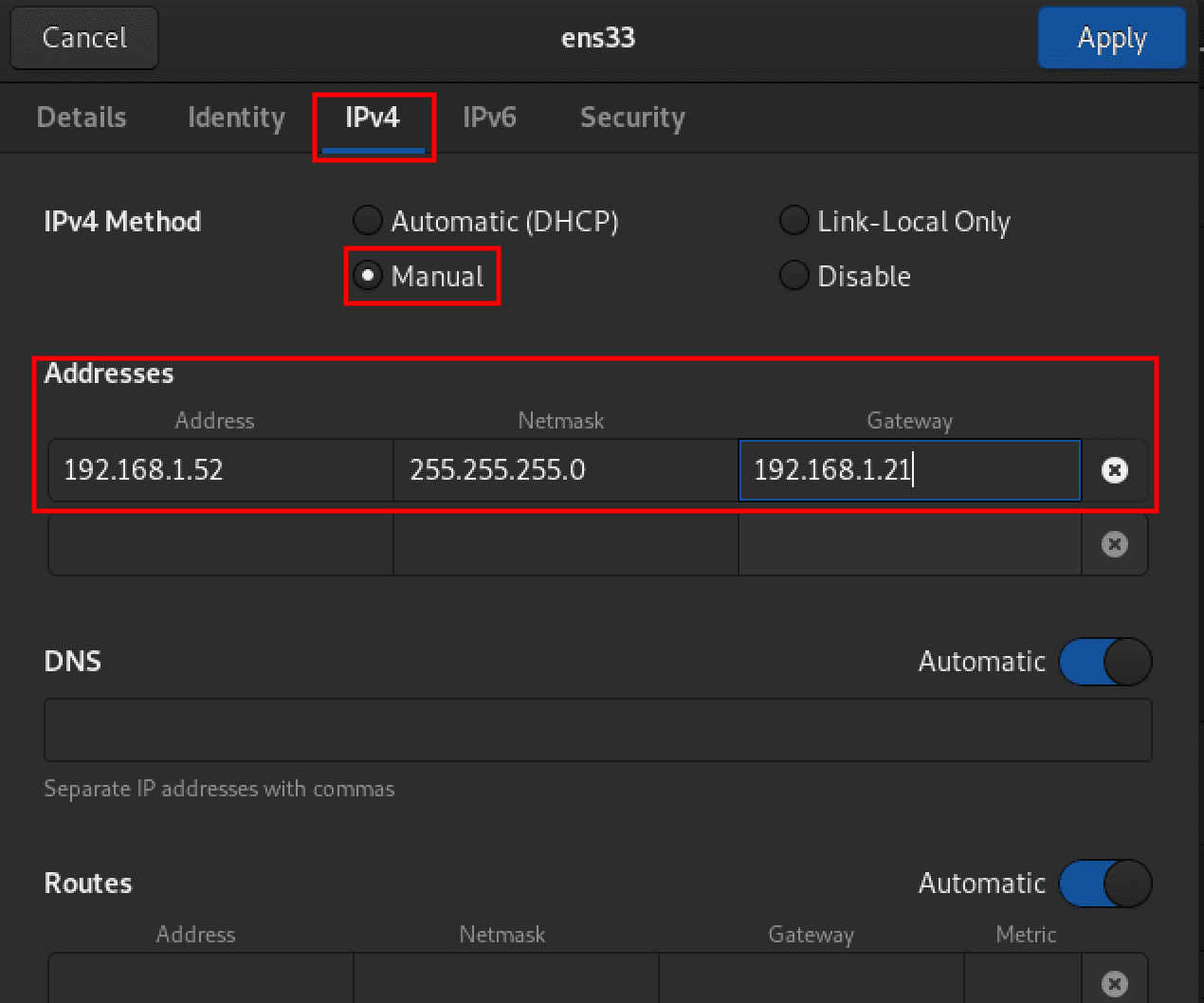
Network configurations
Leave the DNS and Routes set as automatic. But if you still want to use your DNS settings and Routes, click on the button next to the ‘Automatic’ tag to enable ‘manual’ mode.
Click the ‘Apply’ button at the top to save the new configurations. To confirm that your static IP address was set successfully, click on the Settings icon next to the network interface and check the ‘details’ section.
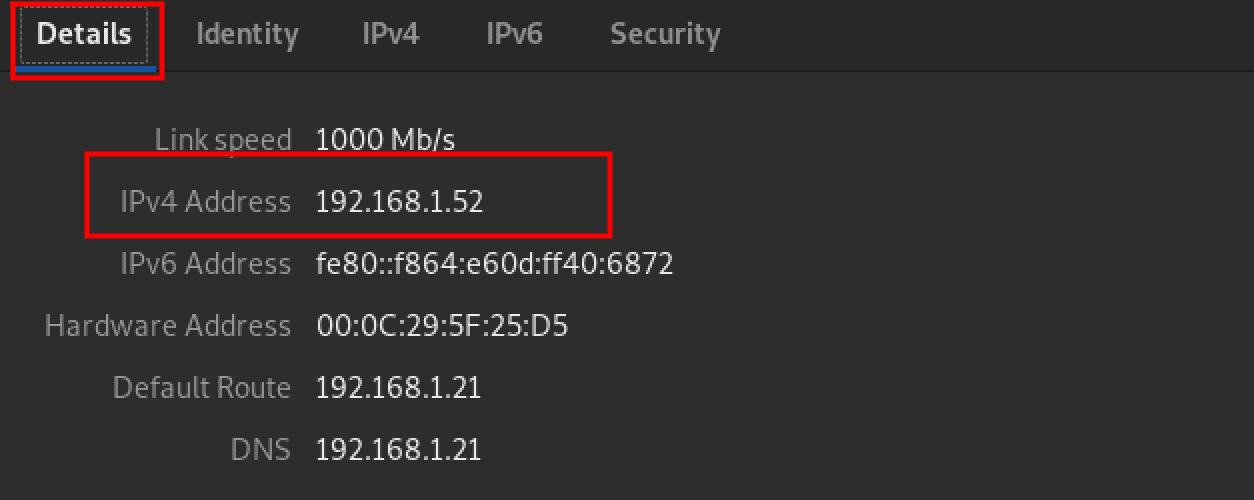
Confirm configurations
That’s it! You have successfully enabled a static IP address from the Graphical User Interface.
This post has given you a step-by-step guide on setting up a static IP address on the Debian 11. We have looked at two methods – setting a static IP via the command line and setting a static IP from the Graphical User Interface. We have also looked at the advantages of using a static IP address and the various scenarios best if you used a static IP. We hope you found this article helpful. If you have any queries or comments, please don’t hesitate to leave a comment below.
You may also like
A ultimate guide to setting up a vsftpd..., your complete guide to installing python on debian, fixing ‘repository does not have a release file’..., fix: ‘unable to locate package’ error in ubuntu..., how to install missing perl modules on debian, how to set up wireguard server on debian.
Thanks. On Raspberry Pi this can be done by adding: ip=192.168.x.xxx to a file in the boot directory that you name: cmdline.txt Are you aware of any similar method that can do this on Debian?
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
ENHANCE YOUR LINUX EXPERIENCE.
FOSS Linux is a leading resource for Linux enthusiasts and professionals alike. With a focus on providing the best Linux tutorials, open-source apps, news, and reviews written by team of expert authors. FOSS Linux is the go-to source for all things Linux.
Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced user, FOSS Linux has something for everyone.
MORE FROM US
- Ubuntu (311)
- Downloads (257)
- Learn Linux (256)
- Beginner's Guide (178)
- Terminal Tuts (168)
- Featured (124)
- Server (99)
- Linux Mint (98)
- Fedora (93)
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
A PART OF VIBRANT LEAF MEDIA COMPANY.
“Linux” is the registered trademark by Linus Torvalds in the U.S. and other countries.
- Beginner’s Guide
- Terminal Tuts
- Learn Linux
TechRepublic
Account information.

Share with Your Friends
How to set a static IP address on Debian server
Your email has been sent
Debian is one of the most reliable operating systems on the planet. Its slower release cycle means each iteration gets plenty of attention before each release. And Debian isn’t just for desktops. In fact, Debian has been deployed as a server for years.
The one thing many new admins might find with deploying Debian as a server is that setting an IP address isn’t exactly as intuitive as other distributions. RHEL-based Linux distributions have the nmtui ncurses tools for configuring network connections, and Ubuntu-based distributions have netplan. With Debian, setting a static IP address is a bit more old-school, so I’m going to show you how it’s done.
SEE: 40+ open source and Linux terms you need to know (TechRepublic Premium)
What you need to setup an IP address in a Debian server
To set the IP address on Debian server, you’ll need a running instance of the OS and either a user with sudo privileges or access to the root user account. I’ll show you first how to give a standard user sudo privileges.
How to give a standard user sudo privileges in a Debian server
Let’s create a new user first. I’ll demonstrate by creating the user olivia (you can name the user whatever you like). To do that, log into Debian server as the root user and issue the command:
adduser olivia
Once you’ve added the new user, add that user to the sudo group with:
sudo usermod -aG sudo olivia
Exit from the root user and log in with the new user account.
How to set a static IP address in a Debian server
The first thing you must do is locate the name of your network device. For that, issue the command:
ip -c link show
You should at least see two devices, lo (for loopback) and another named device (such as enp0s3).
Next, let’s back up the current network configuration file with the command:
sudo cp /etc/network/interfaces ~/
Open the configuration file for editing with the command:
sudo nano /etc/network/interfaces
If you find nano isn’t installed, add it with the command:
sudo apt-get install nano -y
With the interfaces file open for editing, you should see a DHCP configuration that looks like this:
# The primary network interface
allow-hotplug enp0s3
iface enp0s3 inet dhcp
Comment that block out so it looks like this:
# allow-hotplug enp0s3
# iface enp0s3 inet dhcp
Now, we can add the necessary configuration for a static IP address. Let’s configure enp0s3 to use the address 192.168.1.97, with a gateway of 192.168.1.1, and a DNS nameserver of 1.1.1.1. That configuration will look like this:
auto enp0s3
iface enp0s3 inet static
address 192.168.1.97
netmask 255.255.255.0
gateway 192.168.1.1
dns-domain example.com
dns-nameservers 1.1.1.1
Make sure to edit the above configuration to match your network scheme. Save and close the file.
Finally, restart the networking service with the command:
sudo systemctl restart networking
Make sure the networking configuration is correct, by issuing the command:
You should see the static IP address you configured. You’re good to go.
And that’s all there is to configure a static IP address in Debian server. Of course, if you installed your instance of Debian server with a desktop environment, you could simply use the GUI tool for this process. But for those who prefer to keep their servers sans GUI, this is the way to go.
Subscribe to TechRepublic’s How To Make Tech Work on YouTube for all the latest tech advice for business pros from Jack Wallen.
Subscribe to the Developer Insider Newsletter
From the hottest programming languages to commentary on the Linux OS, get the developer and open source news and tips you need to know. Delivered Tuesdays and Thursdays
- How to become a developer: A cheat sheet
- How-to guide for Linux administrators (free PDF)
- Linux 101: What tech pros need to know
- Linux, Android, and more open source tech coverage
Create a TechRepublic Account
Get the web's best business technology news, tutorials, reviews, trends, and analysis—in your inbox. Let's start with the basics.
* - indicates required fields
Sign in to TechRepublic
Lost your password? Request a new password
Reset Password
Please enter your email adress. You will receive an email message with instructions on how to reset your password.
Check your email for a password reset link. If you didn't receive an email don't forgot to check your spam folder, otherwise contact support .
Welcome. Tell us a little bit about you.
This will help us provide you with customized content.
Want to receive more TechRepublic news?
You're all set.
Thanks for signing up! Keep an eye out for a confirmation email from our team. To ensure any newsletters you subscribed to hit your inbox, make sure to add [email protected] to your contacts list.

- The Debian Administrator's Handbook
8.2. Configuring the Network
BACK TO BASICS Essential network concepts (Ethernet, IP address, subnet, broadcast)
NOTE NetworkManager
8.2.1. Ethernet Interface
Example 8.1. DHCP configuration
IN PRACTICE Names of network interfaces
Example 8.2. Static configuration
NOTE Multiple addresses
8.2.2. Wireless Interface
8.2.2.1. installing the required firmwares, 8.2.2.2. wireless specific entries in /etc/network/interfaces.
Example 8.3. DHCP configuration for a wireless interface
HISTORY WEP encryption
8.2.3. Connecting with PPP through a PSTN Modem
8.2.4. connecting through an adsl modem, 8.2.4.1. modems supporting pppoe.
TIP Starting ppp at boot
8.2.4.2. Modems Supporting PPTP
8.2.4.3. modems supporting dhcp.
BACK TO BASICS Crossover cable for a direct Ethernet connection
8.2.5. Automatic Network Configuration for Roaming Users
- Prev Chapter 8. Basic Configuration: Network, Accounts...
- Next 8.3. Setting the Hostname and Configuring the Nam...
How to Configure Static IP Address on Debian 12
To configure a static IP address on Debian 12, you can follow these steps:
Step 1 : Open a terminal window.
Step 2 : Open the network configuration file for editing using a text editor like nano or vi. In this example, we'll use nano:
Step 3 : Locate the network interface you want to configure with a static IP address. It is usually named "eth0" for Ethernet connections or "wlan0" for wireless connections. You might have a different interface name depending on your setup.
Step 4 : Replace the existing configuration with the following lines:
Replace <interface_name> with the actual name of your network interface, <desired_ip_address> with the IP address you want to assign to your Debian machine, <netmask_address> with the subnet mask, and <default_gateway_address> with the IP address of your router or gateway.
For example, the configuration for a static IP address of "192.168.1.100" with a subnet mask of "255.255.255.0" and a default gateway of "192.168.1.1" on the "eth0" interface would look like this:
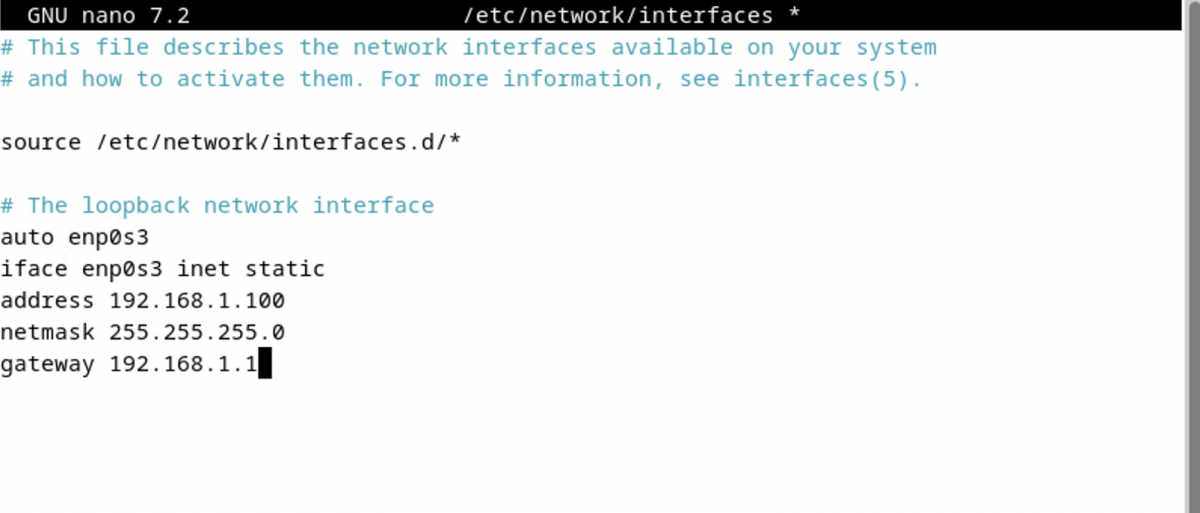
Step 5 : Save the changes by pressing Ctrl+O, then exit the text editor by pressing Ctrl+X.
Step 6 : Restart the networking service to apply the new configuration:
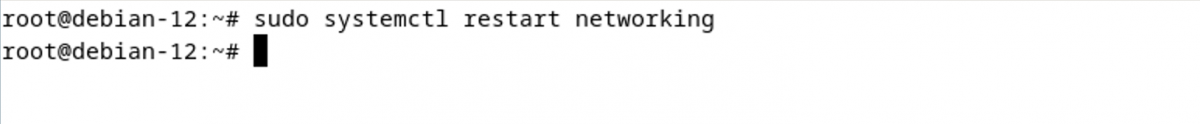
Note: If you are using NetworkManager instead of the traditional networking service, you can restart it using the following command:
Step 7 : Verify the changes by running the following command:
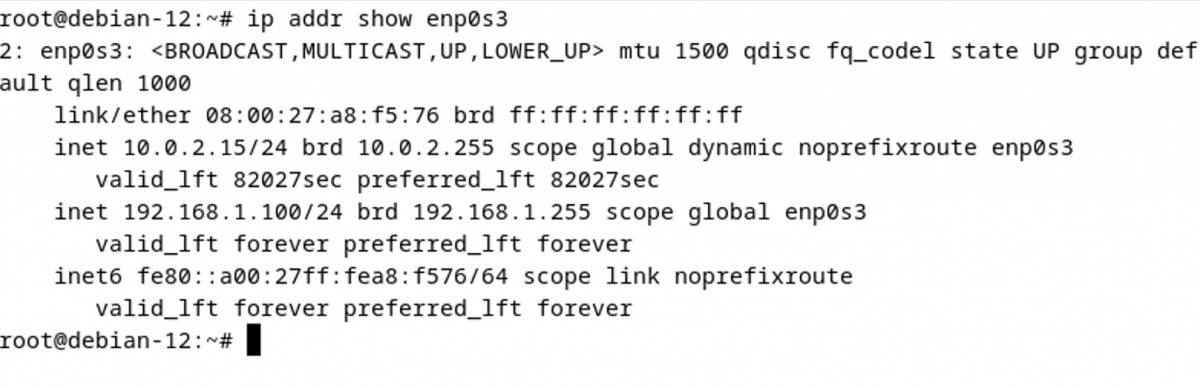
Replace <interface_name> with the actual name of your network interface. You should see the configured static IP address in the output.
That's it! You have successfully configured a static IP address on Debian 12.
Recommended

How to Configure Debian 9 Network Settings

This tutorial will walk you through configuring your network setting for Debian 9 Stretch. I will show you how to set static address and dynamic address for IPv4 and IPv6.
GNOME Desktop
The default desktop environment for Debian 9 Stretch is GNOME 3. We will focus on this environment,
IPv4 Static Address
Ipv6 static address.
For more advanced users and those running a GUI-less server, the following instructions will aid you.
All configuration can be found under /etc/network. You may either define all of your interfaces in a single file or place them in individual files under /etc/network/interfaces.d.
Understanding Network Interface Names
Most recent distributions have switched over to predictable naming. Prior to this an interfaces name was derived from the order it was discovered; the first interface would be named eth0, the second eth1, and so on. The problem with this approach is eth0 wasn’t always the same slot, making troubleshooting difficult.
I cover this topic in much more detail in Understanding Predictive Interface Naming in Linux. For most, the naming convention would be the following:
For example, an Ethernet interface – the most common – found on bus 0 and slot 3 of your motherboard would be named:
- Open the network interface configuration file into a text editor, such as VI.
- Add the following lines. auto enp0s3 iface enp0s3 inet static address 192.168.1.20 netmask 255.255.255.0 gateway 192.167.1.1
- Save your changes and exit the text editor.
- Bring the interface down. ifdown enp0s3
- Bring the interface back up. ifup enp0s3
- Verify your network settings have been applied. ip a
- Add the following lines. auto enp0s3 iface enp0s3 inet dhcp
- Add the following lines. auto enp0s3 iface enp0s3 inet6 static address fd9f:2685:51fa:2e4e:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx netmask 64 gateway fd9f:2685:51fa:2e4e:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx
- Add the following lines. auto enp0s3 iface enp0s3 inet6 auto
No related posts found

How-tos and tutorials for sys admins
How to Set a Static IP on Debian 11

On a DHCP network, your Linux system will usually receive an IP address automatically from the DHCP server which, in most cases, is the router. The IP configuration will usually comprise the IPv4 address, the netmask, gateway, and the DNS settings. This is usually convenient for desktop or client PCs which only need to access the internet or network resources.
However, the case is different when you want to set up a server. In this case, you would need to configure a static IP to make the server always available via the same IP address. With DHCP, the IP address is bound to change once the lease time is over leading to the unavailability of the server.
In this guide, we will take you through a walk-through of how to set a static IP on Debian 11. We will demonstrate how you can configure a static IP on both the desktop GUI and server instances.
Prerequisites
As you set sail, ensure that you have an instance of Debian 11 server installed and set up. In addition, ensure that you have configured a sudo user.
There are two ways of configuring a static IP on Debian. You can achieve this using GUI or on command-line.
Configure Static IP Address using the Graphical User Interface ( GUI )
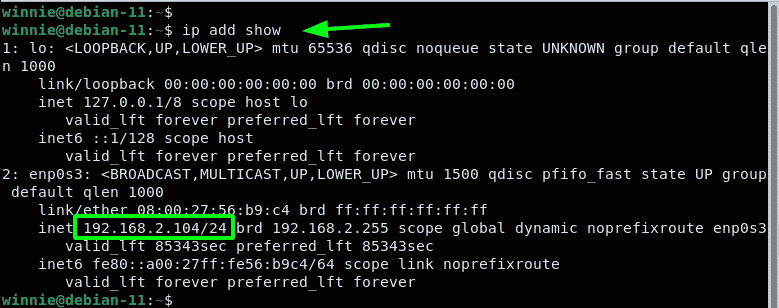
If you are running a Debian 11 desktop instance, log in using your username and password. Before we configure the static IP, first confirm the IP address assigned to your system. In our case, we have a Debian PC with an IP address of 192.168.2.104 in a DHCP network.
You can verify this using the command shown.
In our system, enp0s3 interface is the active link that is assigned the IP address. This may be something else in your case.
To get started with setting the static IP, click on ‘Activities ’ on the left far corner. Search for and click on the ‘ Settings ’ icon.
On the ‘Settings’ page, select the ‘ Network ’ tab. Next, head over to the ‘Wired’ section and click on the small gear wheel as indicated.
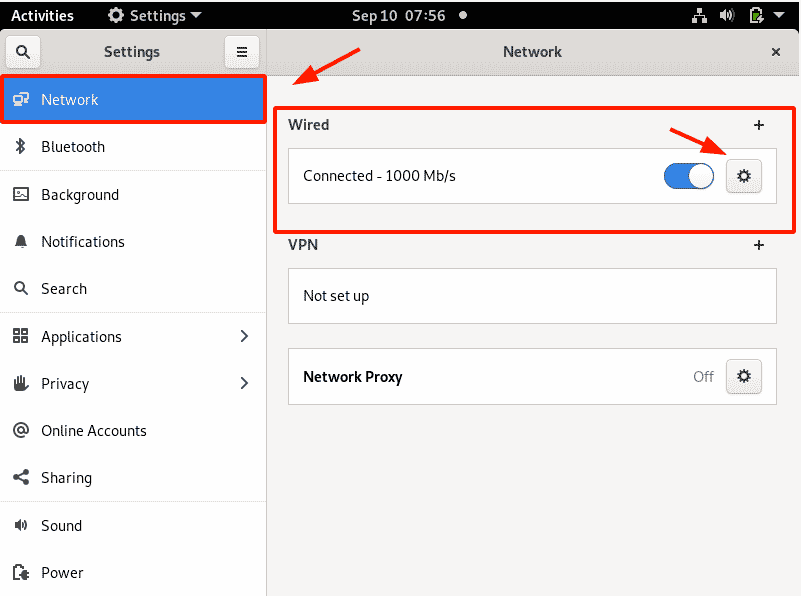
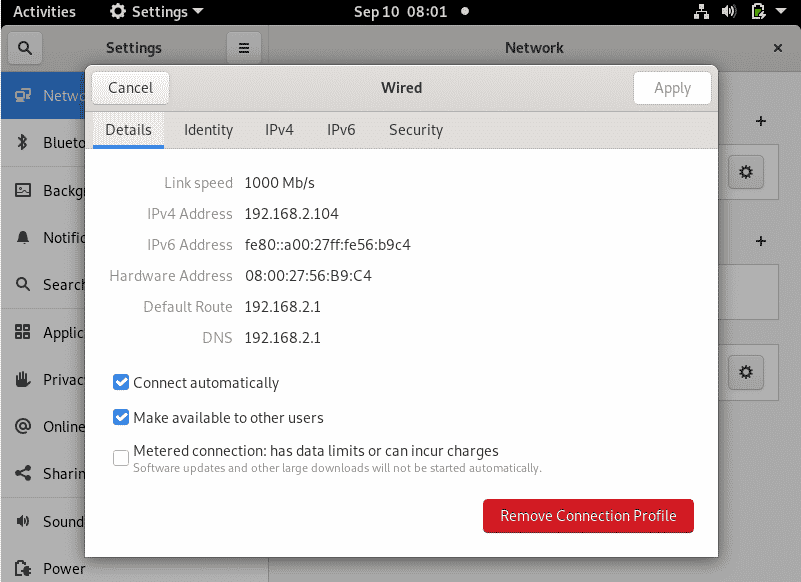
This displays the current IP address configuration as shown. As we confirmed earlier, our current IP address is 192.168.2.104. This has been dynamically allocated to the active interface using the DHCP service.
We are going to override the DHCP settings and manually set a static IP which will persist even upon a reboot.
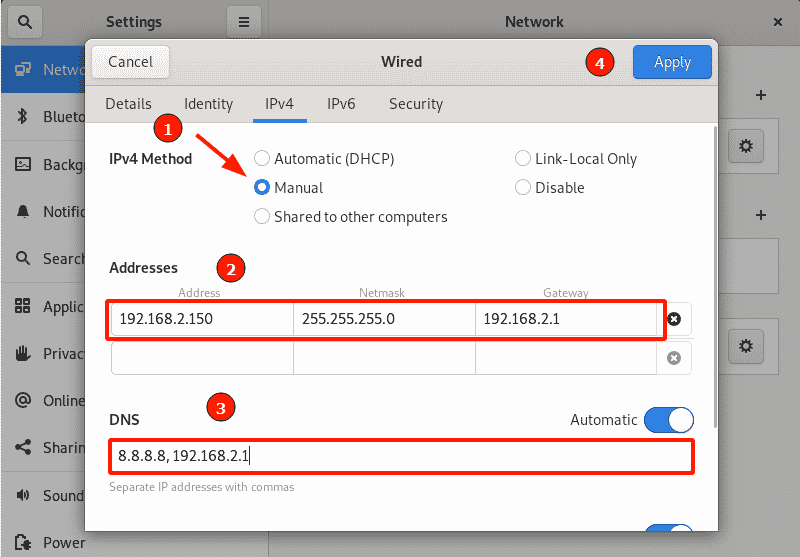
Click the IPv4 tab. Switch from ‘ Automatic ’ to ‘Manual ’ in the IPv4 method section. Thereafter, specify your desired IP address, netmask, and default gateway. Be sure to also provide the preferred DNS settings.
To apply the changes made, click the ‘ Apply’ button.
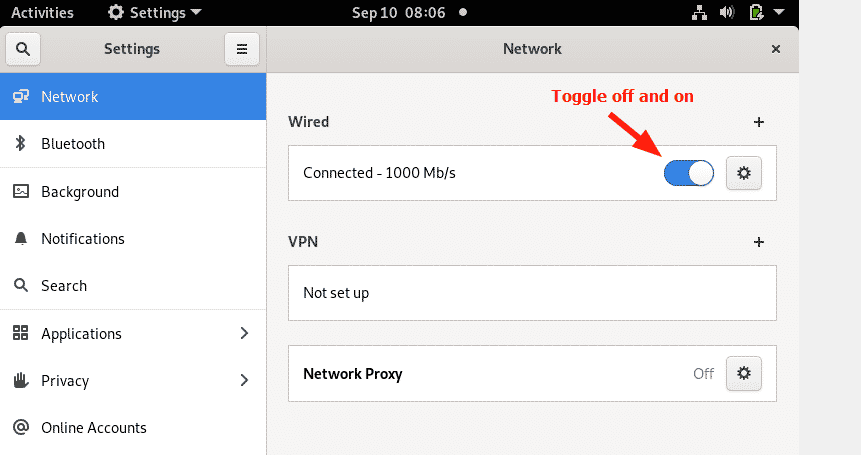
You need to restart the networking daemon or service for the Debian system to implement the new static IP settings. So, turn the toggle button off and then on.
Click on the gear icon once more to verify that the static IP settings have been applied.

On the terminal, verify that the network interface has acquired the newly configured IP address:
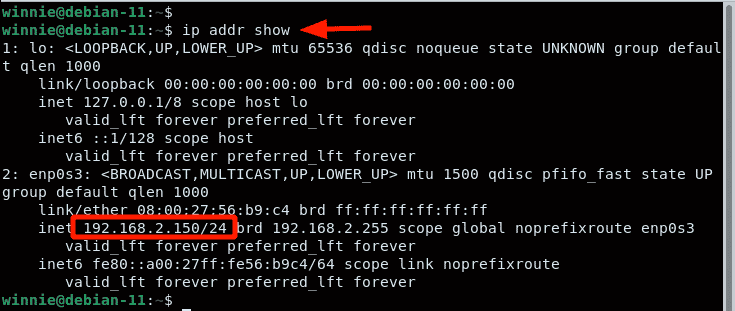
The output is a confirmation that the system was successfully configured using a static IP. Let’s now shift gears and explore setting a static IP on the command line.
Configure Static IP Address using the terminal
If you are running a headless server, or are connecting to a remote server via SSH, the only option available is to configure the static IP on the command line.
The network configuration settings are stored in the /etc/network/interfaces file. Have a peek at the file as follows. Feel free to use Nano editor if you don’t have vim installed.
By default, only the loopback settings are specified.
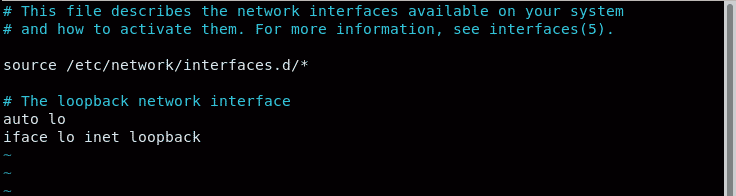
We are going to specify the IP settings for our active network interface. But before making any changes, make a backup of the configuration file.
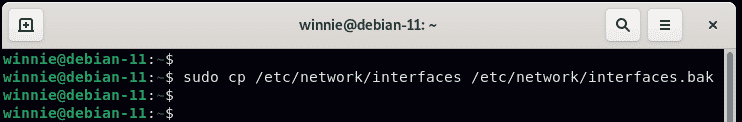
Specify the IP settings as provided. Ensure to make your settings in accordance with your network subnet.
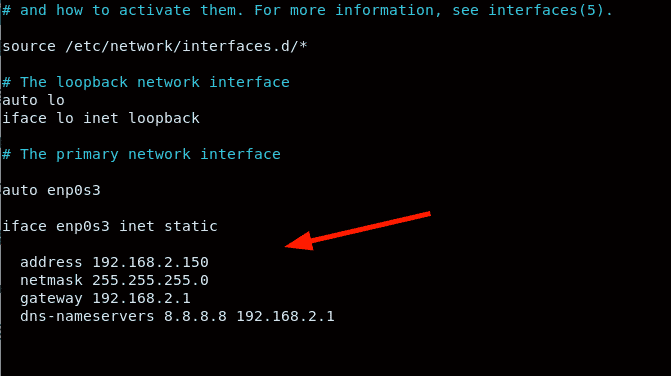
To apply the changes, restart the networking service.
This will disconnect you from the server if you are connected via SSH. Reconnect using the newly set static IP address.
We have outlined two methods of assigning a static IP on your Debian 11 PC – using GUI and the terminal. The former is the easier option when working on a Debian desktop and the latter comes in handy when configuring a remote server via an SSH client.

Karim Buzdar holds a degree in telecommunication engineering and holds several sysadmin certifications including CCNA RS, SCP, and ACE. As an IT engineer and technical author, he writes for various websites.
- ← How to Install VirtualBox Guest Additions on Debian 11
- How to Allow Remote Connections to MySQL →
Similar Posts

htop Tool in Linux

How to Configure NFS Client and Server on Linux

Configuring a Static IP Address on Debian 12

Note: Before making any changes, ensure that you have administrative privileges to modify network settings on your Debian system.
Identifying the Network Interface
The first step in configuring a static IP is to identify the network interface you wish to configure. You can list all available network interfaces using the command:
Look for the interface you want to configure, often named eth0 , ens33 , or similar.
Editing the Network Configuration File
Debian 12 uses the netplan utility for network configuration. Find the relevant YAML configuration file in the /etc/netplan/ directory. It is usually named 01-netcfg.yaml , 50-cloud-init.yaml , or similar. Edit this file using your preferred text editor:
Replace the contents with the following configuration, adjusting the addresses , gateway4 , and nameservers values to fit your network:
Important: Be sure to replace your_interface_name_here with the actual interface name you identified earlier.
Applying the Configuration
After saving your changes to the configuration file, apply them with the following netplan command:
If you encounter any errors, check the syntax of your YAML file; YAML is sensitive to indentation and formatting.

Testing the Configuration
Once you've applied your new static IP configuration, test the network connectivity:
If you receive a response, your network configuration is successful.
Troubleshooting
If you do not have network connectivity after applying the settings, double-check your configuration file for any errors. Additionally, ensure that your static IP does not conflict with other devices on your network.
For more complex network setups or troubleshooting assistance, consider the option to hire a remote DevOps engineer who can provide expert guidance and support.
Configuring a static IP address on Debian 12 is straightforward once you understand the steps involved. By following this guide, developers can ensure reliable network configurations for their systems, enabling more stable development and deployment environments.
If you're interested in enhancing this article or becoming a contributing author, we'd love to hear from you.
Please contact Sasha at [email protected] to discuss the opportunity further or to inquire about adding a direct link to your resource. We welcome your collaboration and contributions!
Maximize Your Team's Potential with Expert Remote Developers in Databases and DevOps with PostGIS Skills
Optimize Your Team with Expert Remote Developers Specializing in Databases, DevOps, and Heroku
Maximize Your Team's Potential with Remote Database and DevOps Experts Skilled in SSH Server

Newsletter Subscribe
Enter your email address below and subscribe to our newsletter

How to Set up Static IP Address on Debian 11/10
- Published on May 7, 2022
- Updated on May 30, 2022
- In Linux , Tips
- Read Time 4 mins
Share your love

Generally, when you install any Operating System, DHCP will assign a dynamic IP address. But there are some cases where you are required to assign a static IP address such as if you are using your system as a Server or granting someone remote access to your System.
In all of those cases, you will need a static IP because things such as servers should not be changing their IP addresses frequently. So let’s start the process of setting up a static IP on Debian
Table of Contents
Setting up Static IP Address on Debian 11/10
We will show you two different methods, one is Terminal based and another is GUI based by which you can change your dynamic IP address to a static IP Address. We will start will the Terminal-based method.
Method 1 – Setting up Static IP Address Using Terminal in Debian 11
If you are a little familiar with Terminal, you can easily perform given tasks and for your ease of use, we have also included screenshots of each step.
Let’s available networks in the Debian system
We will use IP which is the main command and often used to show us what are the currently available Network interfaces in our system. We are also going to use the link command which is a subcommand used with IP to make changes in Network interfaces
ip link
This has shown us the active Network interface which is enpos3 and we will change enpos3 from dynamic to static IP.

Credits: Linuxhint
Now, we will have to make some changes to our Network configuration file which is located at /etc/network/interfaces. We are using nano as a Text Editor because it is easy compared to vim, but you can use any preferred Text Editor. Use the following commands:
sudo nano /etc/network/interfaces
You will be asked to enter your password. Enter your password and you will be prompted to a completely new window. It is a nano text editor by which we are going to make changes to our file.

Now, we will have to enter our preferred choices related to which static address you want, your netmask, dns-nameserver. We have mentioned our preferred choice. You can tweak them according to your choice.
auto enp0s3
iface enp0s3 inet static
address 192.168.2.2
netmask 255.255.255.0
gateway 192.168.2.2
dns-nameservers 8.8.4.4 8.8.8.8
As you can see in the second line, we have mentioned that our Network Interface enp0s3 will be static. Insert these configurations at the end of our configuration. It will look like this:

To save the changes which we have made, press Ctrl + O. To quit from nano press Ctrl + X.
To make things work as our desired configuration, we are required to restart our Network Manager. Use the following commands to restart your Network Manager.
sudo systemctl restart NetworkManager.service

To verify whether the required changes have been made or not, use the following command:
ip a

As you can see, we have successfully configured the static IP address for our Network Interface enp0s3 at 192.168.2.2.
Method 2: Setting up Static IP Address Using GUI in Debian 11
If you do have a desktop environment instilled, you can use this method (In my case I’ve unofficial GNOME 40).
Open your App menu and search for settings. Click on the first result.

If you are using a standard version of GNOME, unlike me you will find your wireless network in the Networks menu. My wireless device is listed under WI-FI.
Click on the small gear button that is placed next to your Network’s name.

Now, click on IPv4. Then select the manual option.

Enter your required configuration in Address, Netmask, and Gateway. After that, click on Apply button.

Now, open the Details section. You will be able to see the changes we made recently.

Frequently asked questions related to IP Address
How do i find a static ip address in linux.
There is no predefined command which shows you whether you have dynamic or static IP. But there is one way, you have to note down your current IP and then Restart your machine. If it changes its IP, then it is assigned by DHCP, and if not then it is static.
Is static IP safe?
A static IP address is considered more vulnerable than a dynamic because it doesn’t change. It makes it easy for hackers to track you and gain access by continuously attacking your network.
Related Posts:
- Shutdown Debian
- How to Install Wine on Debian
Closing Thoughts
You may get higher speeds by setting up static IP on Debian and it is bundled with some risk too. But there are some use cases when you are required to use static IP, ignoring some vulnerabilities it has which you can handle by the Cyber security expert.
Sagar Sharma
Sagar always uses Linux to its core and loves to write the technical side of system administration! While he's not writing for GeniusGeeks, you can find him writing for core linux blogs like IT'SFOSS.com and LinuxHandBook.com
Newsletter Updates
Related posts.

How to Remove (Delete) Directory in Linux
- May 6, 2024

How to Install Node.js and npm on Ubuntu 22.04
- April 25, 2024

Beginner’s Guide to Bash while Loops
- April 22, 2024
Stay informed and not overwhelmed, subscribe now!
How to Set Static IP Address on Debian 12
Debian 12 Bookworm is the latest stable version of the Debian system that was introduced on 13 July 2023. Like other Linux operating systems, Debian 12 gets an IP address once you connect the system to the Internet. However, by default, the IP address on the Debian system is dynamic and keeps changing every time you go online. This can be annoying, especially for the servers, games, or devices you control remotely. To solve this issue, there is a trick to get a static IP address that will provide you with a reliable IP address, easy access to machines and remote control of the devices from anywhere.
In this guide, you will find:
How to Set Static IP Address on Debian 12 from Terminal
How to set static ip address on debian 12 from gui.
You can set static IP address on Debian 12 from:
You can set static IP address on Debian 12 from terminal through:
- Interfaces File
- nmcli Command Line Utility
How to Set Static IP Address on Debian 12 from Terminal Through an Interfaces File
By default, Debian 12 includes an interfaces file in the network directory that you can use to configure your network. You can open this file and add your network details to change your network settings on your system.
To set static IP address on Debian 12 from terminal through interfaces file , you can use the following steps:
Step 1: Check Current IP Address is Static or Dynamic
Before moving towards setting the static IP address on Debian 12, you should check whether the current IP address of your system is static or dynamic, for that, use:
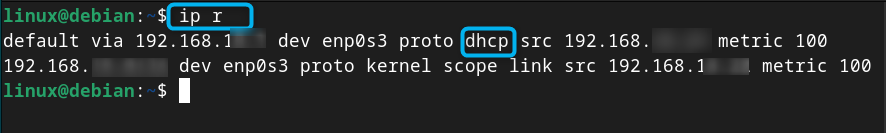
The presence of dhcp in the above command’s output ensures that the IP address of the system is dynamic.
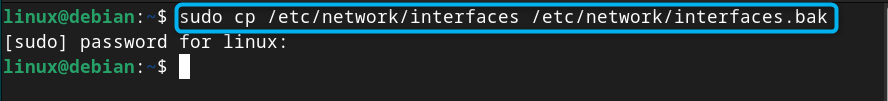
Step 2: Create a Backup of Interfaces File
It is better to create a backup of your network interfaces file through the below-given command since it will help you revert the changes back to the default one in case of an error:
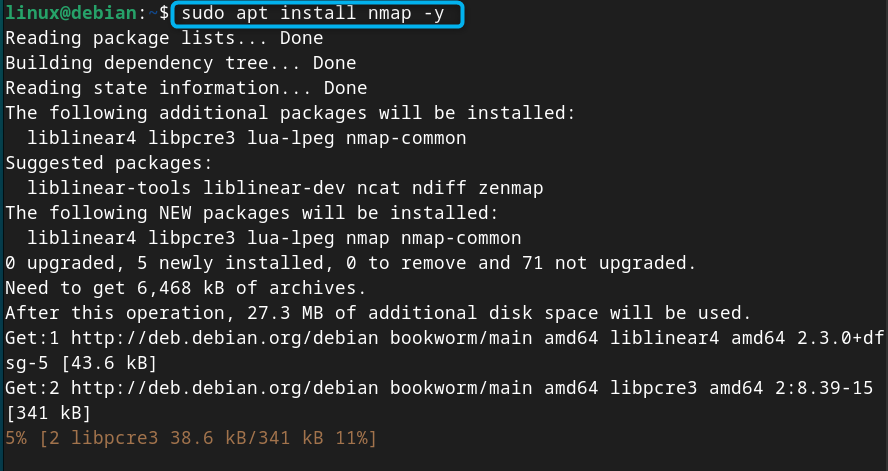
Step 3: Install nmap on Debian 12
You can also install nmap on your Debian system that will help you in retrieving the list of IP addresses that you can use on your system. It is useful for the beginners who are not sure which IP address they have to use.
You can install nmap on Debian 12 from the following command:
Step 4: Check List of IP Address on Debian 12
Now to check the list of IP addresses on Debian 12, you can use the nmap command followed by your network subnet which is 192.168.18.* in my case:
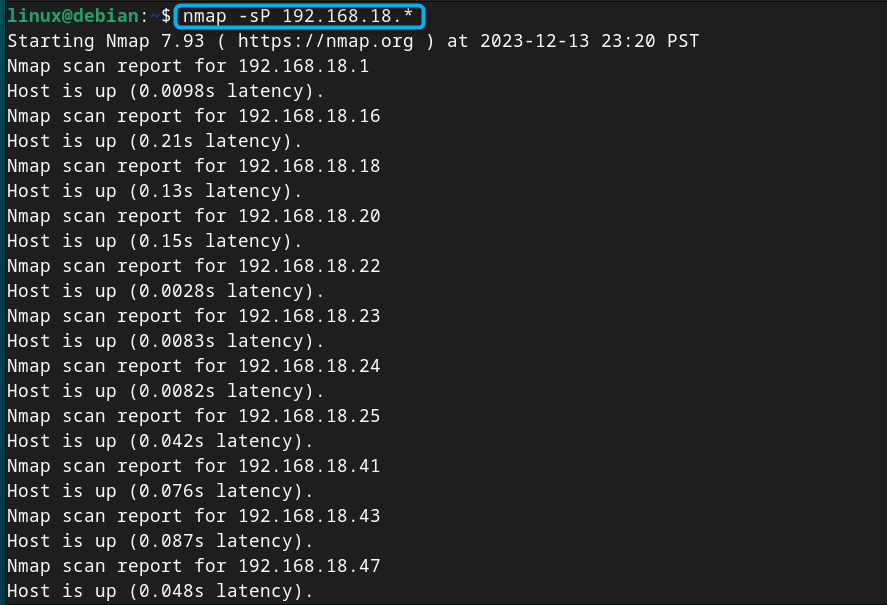
From the above list, you can pick any IP address as your static IP address on Debian.
Step 5: Add Network Interface Details
Now open the network interfaces file on Debian using the following command:
Add the following lines by replacing the IP address and default gateway according to your choice, and keeping the netmask and dns-nameservers same:
iface enp0s3 inet static
address 192.168.18.111 # Enter your desired static IP address
netmask 255.255.255.0 # Subnet mask
gateway 192.168.18.111 # Default gateway
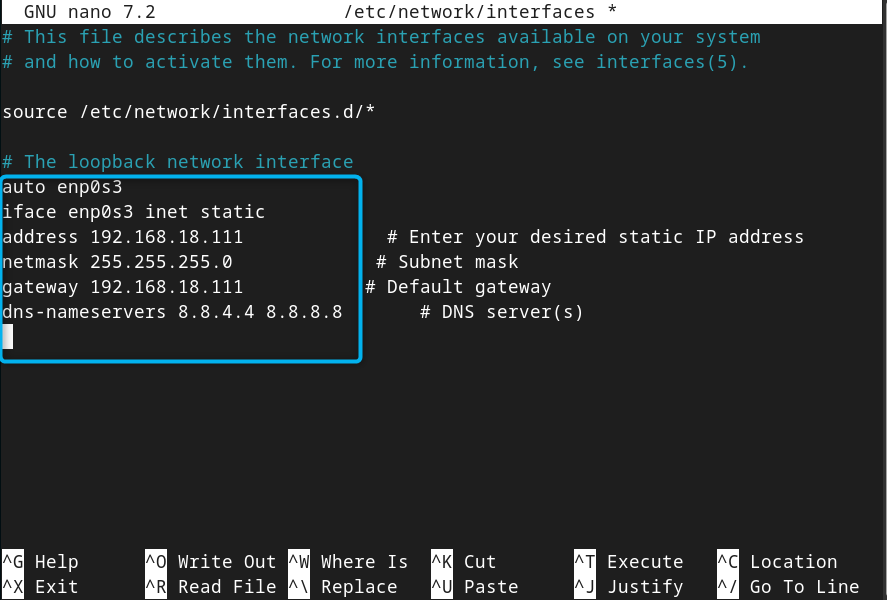
Then save this file using CTRL+X , add Y and press Enter .
Note: We keep the default gateway same as the IP address because our device is directly connected to another network without a router and a NAT device. You can change it to any value, but the first three subnets should remain the same. Further, if you have different IP address, you should set different netmask for each IP address so that they may be able to communicate.
You can also check your device name using:
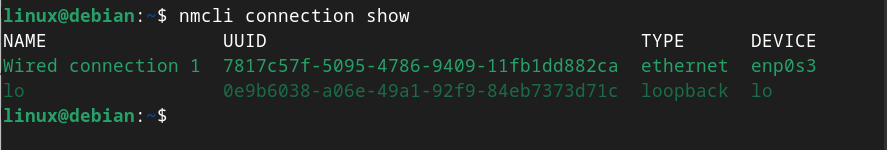
Step 6: Restart Network Manager Service on Debian 12
After adding the network settings, restart the network manager service on Debian 12 using the following command:
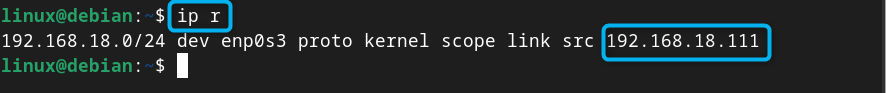
Step 7: Confirm Current IP Address is Static
After reloading the changes, you can confirm whether the current assign IP address is static on Debian, this can be done from the following command:
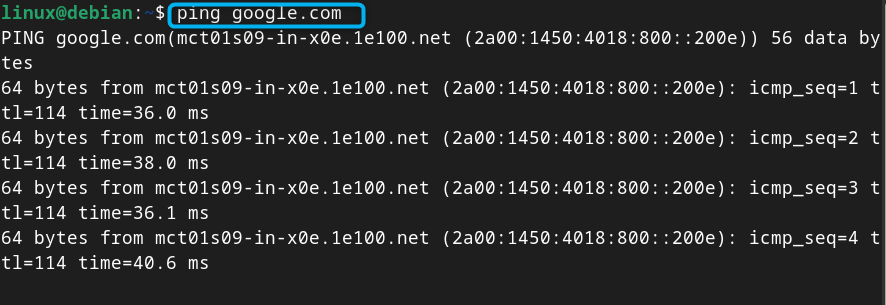
Step 8: Check Internet Connectivity on Debian
To check Internet is accessible on your device after the changes, you can use the ping command:
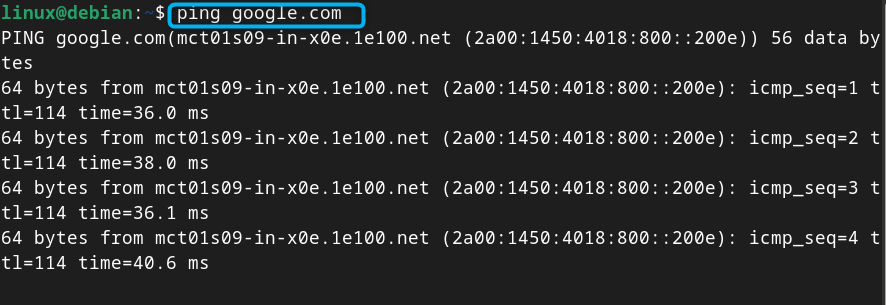
How to Set Static IP Address on Debian 12 from Terminal Through nmcli Command Line Utility
nmcli is a network manager command line utility preinstalled on Linux systems including Debian 12. You can use this utility and set the static IP address on your Debian system using the following steps:
Step 1: Check the Device
Before using the nmcli command for setting up static IP address on Debian 12, you should use the below-given command to check the device name on your system:
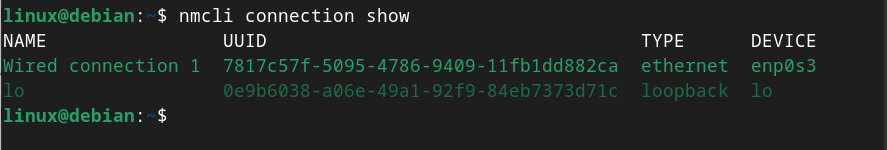
Step 2: Create a Static Connection on Debian 12
Now, you can use the following command with the connection name and device to create a static connection on Debian 12:
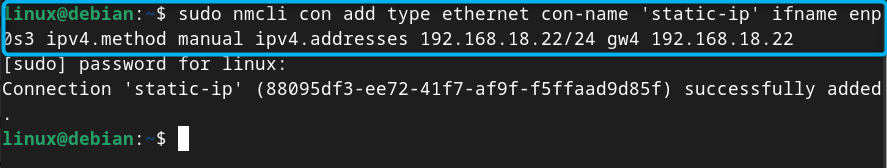
Note: Don’t forget to replace the device name enp0s3 , IP address and default gateway as they could be different in your case.
Step 3: Add DNS IP to Static IP Connection
You should also add DNS IP to your static IP connection on Debian 12. It allows the device to resolve domain name and connect to the Internet, this can be done from the following command:
Step 4: Activate the Static IP Connection
After creating the static IP connection, use the following command to activate it on Debian:
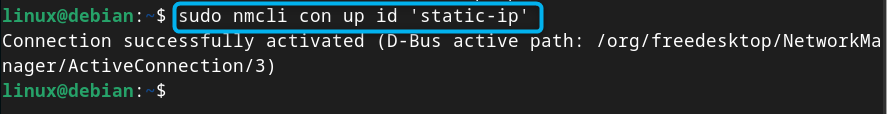
Step 5: Confirm Current IP Address is Static
You can then use the following command to confirm the IP you set on Debian through nmcli method is static, this can be done using:
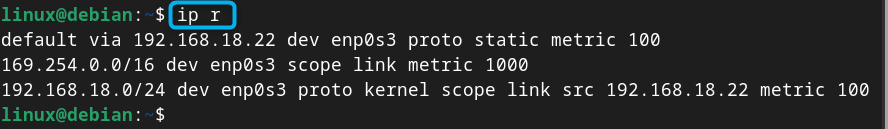
Note: Don’t forget to use the ping command to check the Internet connectivity on Debian:
How to Delete Connection on Debian 12 from Terminal Through nmcli Command Line Utility
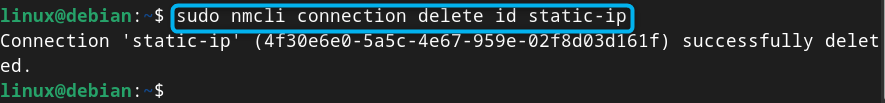
If you have configured your static IP connection in a wrong way, you can simply delete the connection from the nmcli command with the connection name :
You can also open the Network settings from the GUI on Debian 12 and set static IP address , this can be done using the following steps:
Step 1: Open Settings on Debian 12
First, open Settings on Debian by selecting the Ethernet icon and clicking the Settings icon:
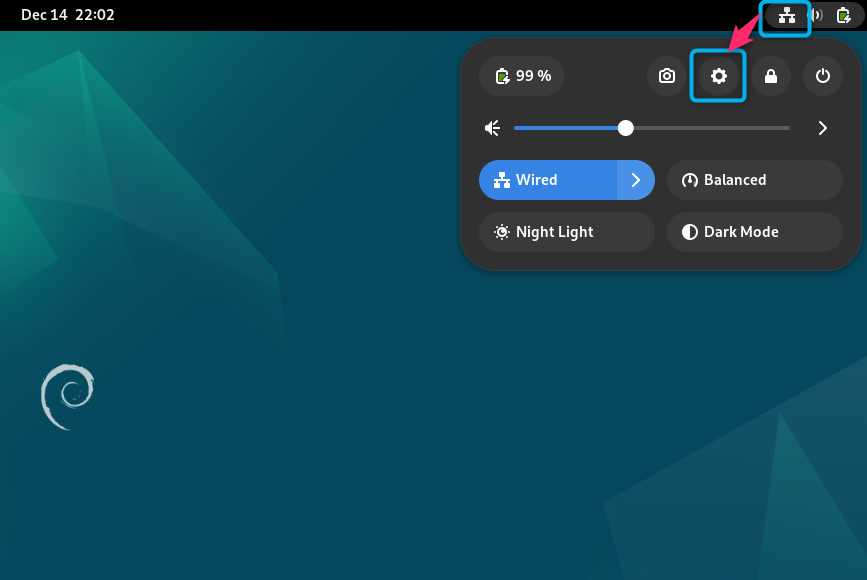
Note: You can also open Settings on Debian 12 from the application search menu.
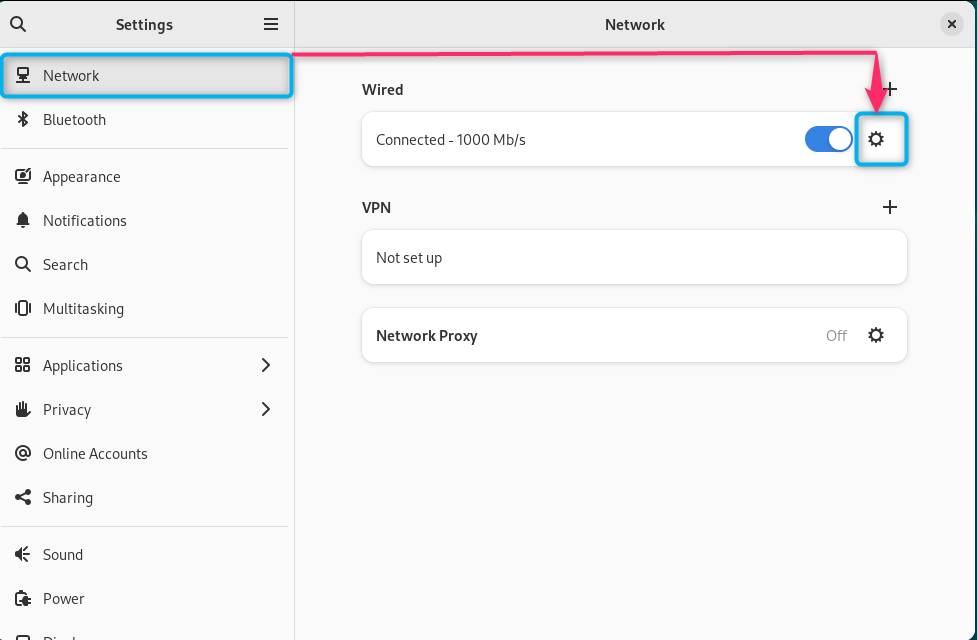
Step 2: Open Network Settings on Debian 12
Click on the Settings icon for Wired network:
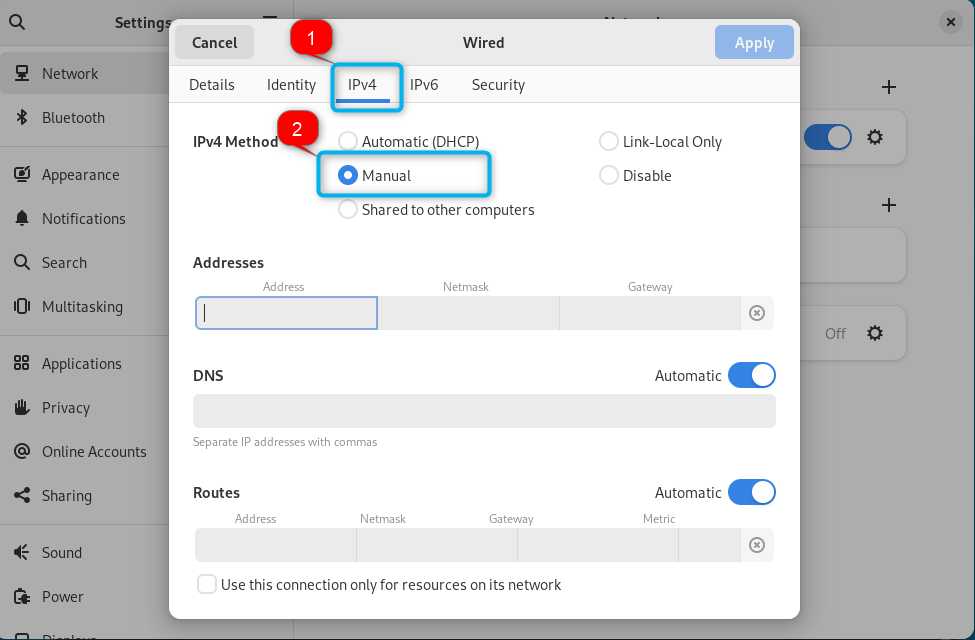
Step 3: Enable Manual Settings
Now, navigate to IPv4 tab and enable the manual settings by check boxing the Manual option:
Step 4: Set Static IP Address on Debian
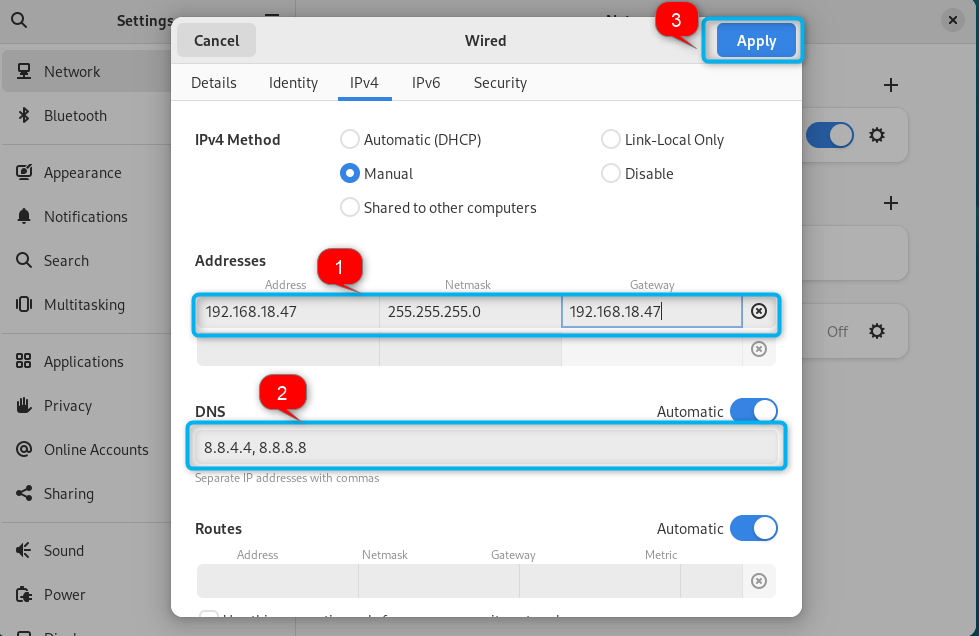
You can now fill in the boxes according to your choice, like adding the static IP address in the Address box, Netmask, gateway and default DNS. Once done, choose the Apply button to make changes to the network configuration:
Step 5: Reload the Network
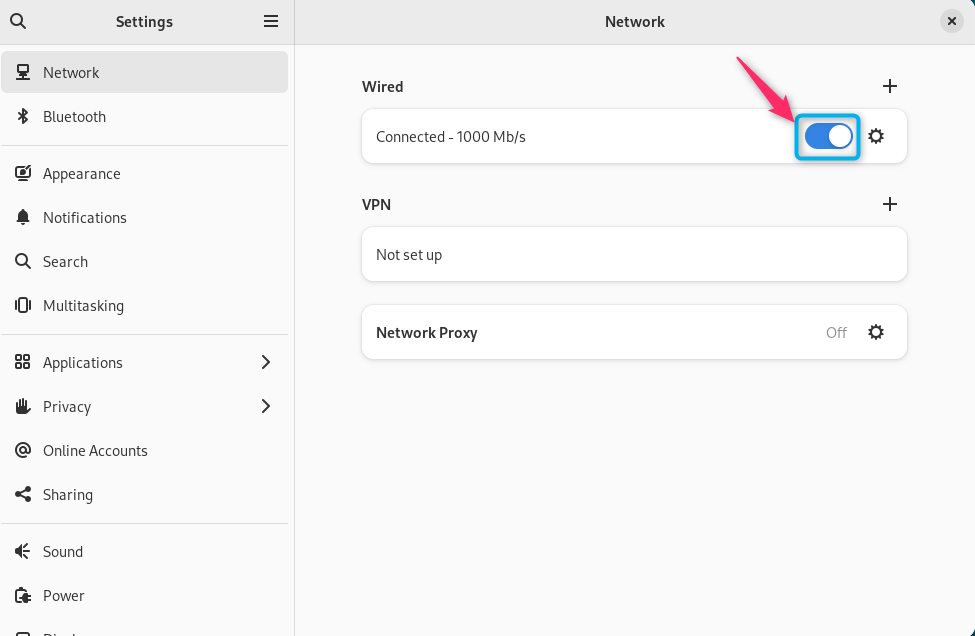
You should reload the network by using the toggle button. To do this, move towards the left to first disable the connection and then move it in the right direction to enable it again:
Step 6: Verify the Connection
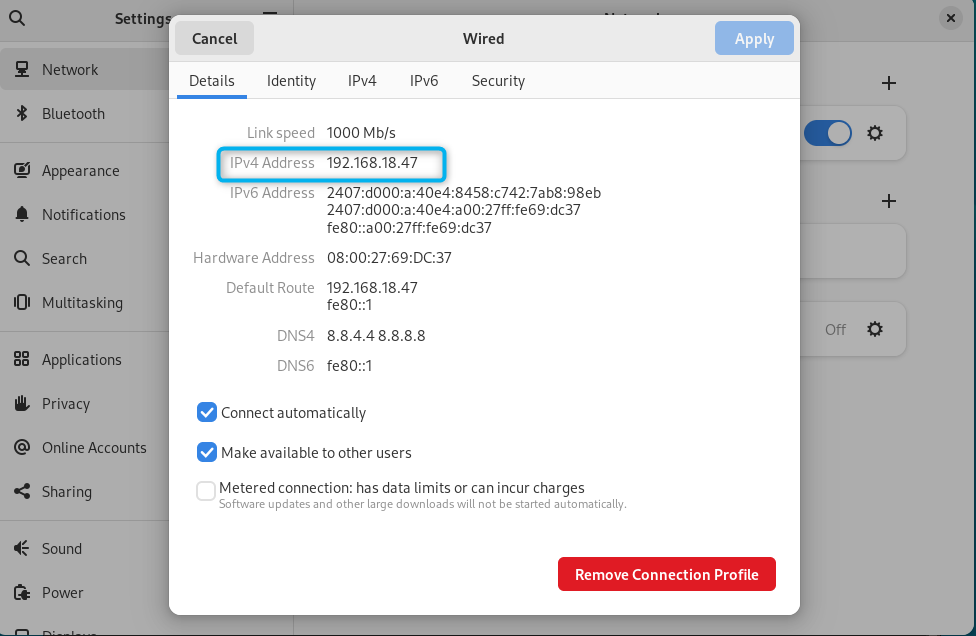
You can verify whether the IP address is successfully changed on Debian by going into the network settings again:
Note: Again, don’t forget to use the ping command to check the Internet connectivity:
You can also remove the connection any time by using the Remove Connection Profile button.
Setting a static IP address on Debian 12 is a useful task that can be done either from terminal or GUI. If you are using a terminal, you can set a static IP address on Debian from an interfaces file or using the nmcli command line utility. From the GUI, you can set a static IP address by the system Settings in the Network section. The complete step-by-step guide for both methods (terminal and GUI) is discussed in the above sections of this guide. Performing these methods will help you set a permanent IP address for your Debian system.

Related posts:
- How to Change Hostname in Debian 12
- Using GDM Settings to Customize Login Screen in GNOME
- How to Find the IP Address of a Docker Container?
Source: linuxhint.com
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.

How to Set Static IP in Debian?
Assigning a static IP address to your Debian system grants you greater control over its network behavior.
This can be crucial for tasks like network administration, server management, or simply ensuring consistent network connectivity for specific devices.
While DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is convenient for most everyday use cases, static IPs offer a layer of stability and predictability.
Table of Contents
Understanding Static IP Process
Before diving in, it’s essential to grasp the concept of a static IP. Unlike DHCP, which dynamically assigns an IP address to your device upon connection, a static IP remains constant.
This means you manually configure your system with a specific IP address, subnet mask, and gateway, ensuring it retains the same network identity throughout.
Prerequisites
Administrative privileges: You’ll need either root access or sudo privileges to modify network configurations.
Network information: Gather the following details about your network:
Desired static IP address: Choose an IP address within your network’s valid range, avoiding conflicts with existing devices.
Subnet mask: Typically, it’s 255.255.255.0 for most home networks. Consult your network administrator if unsure.
Gateway address: This is the IP address of your network router.
Steps to Set Static IP in Debian
Using the following steps, you can configure static IP on Debian 10/11.
1. Identify your network interface
Use the following command to list your network interfaces:
Typically, the wired connection is named eth0, and wireless is wlan0.
2. Edit the network configuration file
Open the /etc/network/interfaces file with a text editor like nano:
3. Locate the relevant interface block
Look for the section corresponding to your network interface (e.g., eth0 ). It should contain lines like:
4. Configure static IP settings
Replace the dhcp keyword with static and add the following lines under the interface block, replacing placeholders with your actual information:
For example:
5. Save and close the file
Press Ctrl+O to save and Ctrl+X to exit the editor.
6. Restart the networking service
Apply the changes with:
7. Verification Process
Once you’ve completed these steps, verify your new static IP configuration by running:
The output should display your assigned static IP address.
Additional Considerations
Conflicting configurations: Ensure your static IP doesn’t clash with existing devices on your network.
Network changes: If your network configuration changes (e.g., router replacement), you might need to adjust the static IP settings accordingly.
Alternative tools: Network management tools might offer graphical interfaces for configuring static IPs, but editing the /etc/network/interfaces file remains a common and reliable approach.
By following these steps, you can effectively assign a static IP address to your Debian system, granting you more control over its network behavior.
Remember, understanding your network configuration and exercising caution are crucial when making manual network changes.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Change the hostname of your AL2 instance
When you launch an instance into a private VPC, Amazon EC2 assigns a guest OS hostname. The type of hostname that Amazon EC2 assigns depends on your subnet settings. For more information about EC2 hostnames, see Amazon EC2 instance hostname types in the Amazon EC2 User Guide for Linux Instances .
A typical Amazon EC2 private DNS name for an EC2 instance configured to use IP-based naming with an IPv4 address looks something like this: ip-12-34-56-78.us-west-2.compute.internal , where the name consists of the internal domain, the service (in this case, compute ), the region, and a form of the private IPv4 address. Part of this hostname is displayed at the shell prompt when you log into your instance (for example, ip-12-34-56-78 ). Each time you stop and restart your Amazon EC2 instance (unless you are using an Elastic IP address), the public IPv4 address changes, and so does your public DNS name, system hostname, and shell prompt.
This information applies to Amazon Linux. For information about other distributions, see their specific documentation.
Change the system hostname
If you have a public DNS name registered for the IP address of your instance (such as webserver.mydomain.com ), you can set the system hostname so your instance identifies itself as a part of that domain. This also changes the shell prompt so that it displays the first portion of this name instead of the hostname supplied by AWS (for example, ip-12-34-56-78 ). If you do not have a public DNS name registered, you can still change the hostname, but the process is a little different.
In order for your hostname update to persist, you must verify that the preserve_hostname cloud-init setting is set to true . You can run the following command to edit or add this setting:
If the preserve_hostname setting is not listed, add the following line of text to the end of the file:
To change the system hostname to a public DNS name
Follow this procedure if you already have a public DNS name registered.
For AL2: Use the hostnamectl command to set your hostname to reflect the fully qualified domain name (such as webserver.mydomain.com ).
For Amazon Linux AMI: On your instance, open the /etc/sysconfig/network configuration file in your favorite text editor and change the HOSTNAME entry to reflect the fully qualified domain name (such as webserver.mydomain.com ).
Reboot the instance to pick up the new hostname.
Alternatively, you can reboot using the Amazon EC2 console (on the Instances page, select the instance and choose Instance state , Reboot instance ).
Log into your instance and verify that the hostname has been updated. Your prompt should show the new hostname (up to the first ".") and the hostname command should show the fully-qualified domain name.
To change the system hostname without a public DNS name
For AL2: Use the hostnamectl command to set your hostname to reflect the desired system hostname (such as webserver ).
For Amazon Linux AMI: On your instance, open the /etc/sysconfig/network configuration file in your favorite text editor and change the HOSTNAME entry to reflect the desired system hostname (such as webserver ).
Open the /etc/hosts file in your favorite text editor and change the entry beginning with 127.0.0.1 to match the example below, substituting your own hostname.
You can also implement more programmatic solutions, such as specifying user data to configure your instance. If your instance is part of an Auto Scaling group, you can use lifecycle hooks to define user data. For more information, see Run commands on your Linux instance at launch and Lifecycle hook for instance launch in the AWS CloudFormation User Guide .
Change the shell prompt without affecting the hostname
If you do not want to modify the hostname for your instance, but you would like to have a more useful system name (such as webserver ) displayed than the private name supplied by AWS (for example, ip-12-34-56-78 ), you can edit the shell prompt configuration files to display your system nickname instead of the hostname.
To change the shell prompt to a host nickname
Create a file in /etc/profile.d that sets the environment variable called NICKNAME to the value you want in the shell prompt. For example, to set the system nickname to webserver , run the following command.
Open the /etc/bashrc (Red Hat) or /etc/bash.bashrc (Debian/Ubuntu) file in your favorite text editor (such as vim or nano ). You need to use sudo with the editor command because /etc/bashrc and /etc/bash.bashrc are owned by root .
Edit the file and change the shell prompt variable ( PS1 ) to display your nickname instead of the hostname. Find the following line that sets the shell prompt in /etc/bashrc or /etc/bash.bashrc (several surrounding lines are shown below for context; look for the line that starts with [ "$PS1" ):
Change the \h (the symbol for hostname ) in that line to the value of the NICKNAME variable.
(Optional) To set the title on shell windows to the new nickname, complete the following steps.
Create a file named /etc/sysconfig/bash-prompt-xterm .
Make the file executable using the following command.
Open the /etc/sysconfig/bash-prompt-xterm file in your favorite text editor (such as vim or nano ). You need to use sudo with the editor command because /etc/sysconfig/bash-prompt-xterm is owned by root .
Add the following line to the file.
Log out and then log back in to pick up the new nickname value.
Change the hostname on other Linux distributions
The procedures on this page are intended for use with Amazon Linux only. For more information about other Linux distributions, see their specific documentation and the following articles:
How do I assign a static hostname to a private Amazon EC2 instance running RHEL 7 or Centos 7?

To use the Amazon Web Services Documentation, Javascript must be enabled. Please refer to your browser's Help pages for instructions.
Thanks for letting us know we're doing a good job!
If you've got a moment, please tell us what we did right so we can do more of it.
Thanks for letting us know this page needs work. We're sorry we let you down.
If you've got a moment, please tell us how we can make the documentation better.

COMMENTS
Save and close the file when using vim/vi text editor.. Restart networking service on Debian Linux to switch from DHCP to static IP config. Warning: Do not run the following over ssh based session as you will disconnect.. Use the systemctl command as follows: $ sudo systemctl restart networking.service Make sure service restarted without any errors. Hence, type the following command: $ sudo ...
How to install missing ifconfig command on Debian Linux; AMD Radeon Ubuntu 20.04 Driver Installation; Ubuntu Static IP configuration; How to use bash array in a shell script; Linux IP forwarding - How to Disable/Enable; How to install Tweak Tool on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS Focal Fossa Linux; How to enable/disable firewall on Ubuntu 18.04 Bionic ...
To set up a static IP address on Debian 12 using nmtui, follow these steps: Step 1: Launch nmtui Interface. First, type " nmtui " command to launch the interface, use the arrow keys, and Enter key to navigate through the menus and options. Step 2: Edit a Connection. Select " Edit a connection " option and press Enter:
3 ways to configure the network. Setting up an Ethernet Interface. Starting and Stopping Interfaces. Reinitialize new network setup. Network Interface Names. Using DHCP to automatically configure the interface. Configuring the interface manually. Setting the speed and duplex. Bringing up an interface without an IP address.
Method2: Assign Static IP Address on Debian 12 From Command Line. Open the terminal, check your current network configuration. You can do this by running the following ip command, $ ip add show. This will display a list of network interfaces on your system. Note down the name of the interface you want to assign a static IP address to (typically ...
Verify your network settings are applied correctly. For Debian 10 and Debian 9, you can use the ip a command. For Debian 8 you would use the ifconfig command. Setting a DHCP Address. A DHCP address is configured as shown in the example below. Unlike the the static IP address it's a one-liner, as we do not need to set an address or gateway.
The graphical user interface method is to understand, simply open the " Settings " of the Debian 12: Click on " Network " and then choose the " gear icon " for the network connection: Now click on " IPv4 ", then change the address to your own choice, and finally click on the " Apply " button: The static IP address will be ...
6.3K. W hen installing any operating system, it is always set to receive network configuration from the DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server. That includes IP address, routing, subnet, Gateway address, DNS information, and other network configurations. While that is always ok and enough to give you access to the internet, there are situations where a static IP address would be ...
Use the menu to select Manual instead. Enter IP on Debian 10. Below that, there's a blank table of addresses. Press the Add button next to it to set up a new static address. A new row will open up on the table. Enter your desired IP address in the Address cell and the IP of your router in the Gateway.
How to set a static IP address in a Debian server. The first thing you must do is locate the name of your network device. For that, issue the command: ip -c link show. You should at least see two ...
Setting A Static IP In Debian LXD Containers. For whatever reason, Debian configures their networking differently than normal in LXD containers. I make use of LXD containers in my homelab all the time - running various services as well as for setting up test environments and demos.
An IP address is a number used to identify a network interface on a computer on a local network or the Internet. In the currently most widespread version of IP (IPv4), this number is encoded in 32 bits, and is usually represented as 4 numbers separated by periods (e.g. 192.168..1), each number being between 0 and 255 (inclusive, which corresponds to 8 bits of data).
To configure a static IP address on Debian: Open the network settings. Locate the option to set a static IP address. Enter the desired IP address, subnet mask, and gateway. Save the changes and apply the new configuration. Setting Subnet Mask and Gateway. In addition to configuring the static IP address, it is important to set the subnet mask ...
To configure a static IP address on Debian 12, you can follow these steps: Step 1 : Open a terminal window. Step 2 : Open the network configuration file for editing using a text editor like nano or vi. In this example, we'll use nano: sudo nano /etc/network/ int erfaces. Step 3 : Locate the network interface you want to configure with a static ...
It requires a DHCP server running in the network. In the static IP assignment, we manually assign the IP address, routing gateway, and DNS resolvers. Static IP assignment gives to more control on assigning an IP address and setting the DNS resolvers. In this tutorial, we will learn how to assign static IP address on Debian 10 "Buster" server.
Open the network interface configuration file into a text editor, such as VI. Add the following lines. auto enp0s3. iface enp0s3 inet static. address 192.168.1.20. netmask 255.255.255.. gateway 192.167.1.1. Save your changes and exit the text editor. Bring the interface down.
Adding to that, most managers have a GUI, terminal user interface (TUI), or at least a flexible CLI. Unlike ip, settings from network management tools can persist between reboots. Now, we move to the most persistent, albeit in part, distribution-specific solutions. 5. Static IP on Debian Distributions
To get started with setting the static IP, click on 'Activities ' on the left far corner. Search for and click on the ' Settings ' icon. On the 'Settings' page, select the ' Network ' tab. Next, head over to the 'Wired' section and click on the small gear wheel as indicated.
The new IP address has been set to Debian 12 successfully using the nmcli command. Method 5: Change IP Address Using GUI. The last method to change the IP address on Debian 12 is by using the Graphical User Interface. For this method, click on the "Wired" on the top of the screen and click on the "Wired Settings" as shown:
Identifying the Network Interface. The first step in configuring a static IP is to identify the network interface you wish to configure. You can list all available network interfaces using the command: ip addr show. Look for the interface you want to configure, often named eth0, ens33, or similar.
Click on the small gear button that is placed next to your Network's name. Now, click on IPv4. Then select the manual option. Enter your required configuration in Address, Netmask, and Gateway. After that, click on Apply button. Now, open the Details section. You will be able to see the changes we made recently.
Step 1: Check Current IP Address is Static or Dynamic. Before moving towards setting the static IP address on Debian 12, you should check whether the current IP address of your system is static or dynamic, for that, use: ip r. The presence of dhcp in the above command's output ensures that the IP address of the system is dynamic.
Steps to Set Static IP in Debian. Using the following steps, you can configure static IP on Debian 10/11. 1. Identify your network interface. Use the following command to list your network interfaces: Typically, the wired connection is named eth0, and wireless is wlan0. 2. Edit the network configuration file.
Change the system hostname. If you have a public DNS name registered for the IP address of your instance (such as webserver.mydomain.com), you can set the system hostname so your instance identifies itself as a part of that domain.This also changes the shell prompt so that it displays the first portion of this name instead of the hostname supplied by AWS (for example, ip-12-34-56-78).