- Reference Manager
- Simple TEXT file

People also looked at
Review article, studies of teaching and learning english-speaking skills: a review and bibliometric analysis.

- School of Educational Studies, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Penang, Malaysia
This study conducted a comprehensive historical review and bibliometric analysis of the literature on English-speaking (ES) education and mapped the current state of the field, trends, and emerging topics, as well as identified gaps where further research is needed. We retrieved 361 sample documents on ES teaching and learning in Scopus (2010–2021) under certain conditions and analyzed the extracted data using Excel and VOSviewer 1.6.17 from the perspectives of the number of yearly publications, countries, authors, citation numbers, and keywords. The findings show that the number of publications on ES education increased from 2010 to 2021, but there was a lack of sustained engagement with this topic by researchers. Countries with an ESL or EFL context focused more on the subject of ES, although studies from native ES countries were more influential. The research topics showed a multidimensional trend, covering communicative skills, language knowledge, assessment, teaching or learning methods, ICT-related applications, and cognitive factors, of which ICT-related applications (such as flipped classrooms, blended learning, and e-learning) and cognitive factors (such as motivation, anxiety, and affect) were the areas of focus. Students in higher institutions, rather than children, became the main research subject of ES education over the period studied.
Introduction
A considerable amount of time and money has been invested in English language education (ELE) around the world, especially in countries where English is a Foreign (EFL) or Second Language (ESL). For example, ELE in East Asian countries such as China, South Korea, and Japan has been identified as a necessary skill, which has motivated the development of various approaches and policies ( Song, 2011 ; Hu and McKay, 2012 ). There have been at least three phases of English curriculum reforms by the Malaysian Ministry of Education directed toward improving students’ English proficiency and teachers’ professional development (TPD) ( Rashid et al., 2017 ; Kummin et al., 2020 ).
Despite unremitting efforts in many countries, ELE is still facing the problem of low average English skills. For example, students’ English skills in Turkey are not as good as expected ( Coskun, 2016 ; Özmen et al., 2016 ; Umunĉ and Raw, 2017 ). The survey by Wei and Su (2015) clearly showed that the subjects’ ES proficiency was generally low.
Many terms have been used to refer to the speaking aspects of the English language, e.g., “oral English,” “spoken English,” or “English speaking.” “English speaking” is the term used in this article. Speaking is different from writing, although both are productive skills, in that it is “transient, unplanned, context-dependent, oral/aural, and dynamic” ( Hughes, 2017 ). English-speaking (ES) has been treated as an indivisible language skill for learners in the language education fields of TESOL, EFL, and ESL.
How to improve ES ability, including teaching and learning approaches, influencing factors, and other related issues, have always been a focus of researchers. Thus, in view of the profound changes in society, politics, economics, and technologies, this article aims to give an overview of the current situation and trends regarding ES studies based on Scopus from 2010 to 2021. Moreover, it seeks to provide useful information for further ES teaching and learning research through visualized data analysis using VOSviewer 1.6.17 and Micro Excel.
Thus, the research questions (RQs) of this article are as follows:
RQ1. What is the bibliometric information regarding publications about ES teaching and learning in Scopus (2010–2021), including the number of yearly publications, authors, citations, country contributions, and keywords?
RQ2. What is the status of ES teaching and learning?
RQ3. What are the most influential authors in the field of ES teaching and learning?
RQ4. What are the trends in ES teaching and learning?
RQ5. What are the gaps in ES teaching and learning from the bibliometric information?
Materials and Methods
Bibliometric analysis refers to the cross-science of quantitative analysis of all carriers of knowledge by means of mathematics and statistics ( Broadus, 1987 ). The development of bibliometric software such as VOSviewer, Citespace, and Gephi, and the foundation of the big databases for academic documents such as Scopus, Web of Science, and Taylor and Francis make bibliometric analysis more feasible and practical ( Donthu et al., 2021 ). Meanwhile, according to Rogers et al. (2020) , the recommended minimum sample size for a bibliometric analysis is 200 entries.
Article Selection and Identification
Scopus was chosen as the database for this historical review and bibliometric analysis of ES education. This is because Scopus, as one of the world’s largest databases, covers a wide range of academic journals, conference proceedings, books, and other related publications with relatively high citation indexes and quality, much like the Web of Science ( Pham et al., 2018 ; Baas et al., 2020 ). Scopus is user-friendly in the sense that information can be conveniently retrieved through string retrieval. This study replicated the methodologies used by Lázaro (2022) and Kaya and Erbay (2020) . This article was conducted around RQs after the identification of some keywords as conditions for data mining.
Thus, 23,633 sample documents were first strictly extracted under the condition [TITLE-ABS-KEY (“English speaking” OR “English-speaking” OR “oral English” OR “spoken English”)] AND (“TESOL” OR “EFL” OR “ESL”). Then, the conditions of time span and document type were added for filtering from 2010 to 2021. Then, the articles, conference papers, reviews, book chapters, and books were chosen as the target document types. The detailed conditions can be seen in Table 1 .
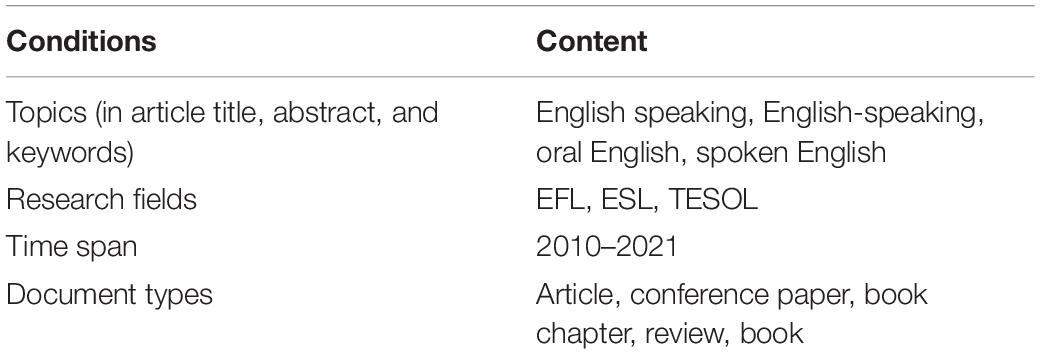
Table 1. Retrieval conditions.
Finally, 1,893 documents were obtained. These were exported in the form of an Excel document with citation information, bibliographic information, abstract and keywords, funding details, and other information.
After strict data cleaning through thematic analysis of the abstracts by three researchers for more than three times, 361 sample documents remained, which were classified into four types of documents: journal articles (256; 70.91%), conference papers (79; 21.88%), book chapters (16; 4.43%), and reviews (10; 2.77%), covering more than 10 subject areas, such as social sciences, computer sciences, medicine, engineering, and arts and humanities.
Research Framework and Instruments
In the data selection step, sample documents were screened for information about authors, titles, years, citations, author keywords, index keywords, publishers, document types, countries, and author affiliations from Scopus under strict conditions. The sample documents were then uploaded to Excel and VOSviewer 1.6.17 during the data-processing step. Excel and VOSviewer 1.6.17 were used to perform the visualized bibliometric analysis of the number of publications per year, contributions of authors and countries, and keywords ( Chen, 2016 ; Van Eck and Waltman, 2017 ). Finally, the current situation, developing trends, research gaps, and lessons we can learn about ES teaching were sorted. Thus, the research framework is divided into four main steps, as shown in Figure 1 .
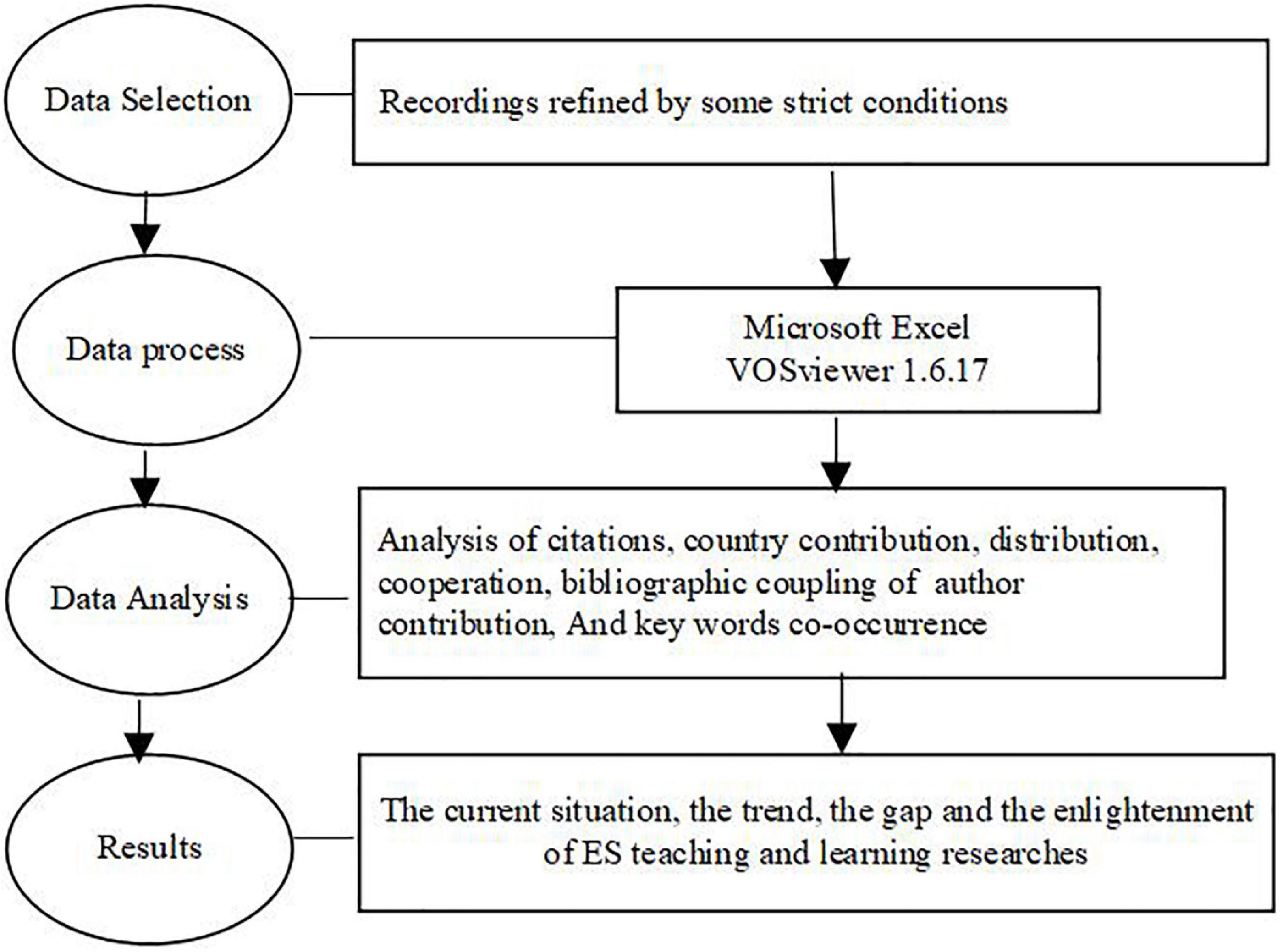
Figure 1. The conceptual framework.
Compared with studies on English writing and reading, studies on ES education are relatively very small in scale. Although only 361 sample documents conforming to the screening conditions were identified, it was still feasible to conduct a bibliometric analysis from the perspectives of the number of yearly publications, countries, authors, citations, and keywords.
Number of Publications by Year
According to the linear trend line in Figure 2 , the overall trend of the ES education literature in Scopus was on the rise from 2010 to 2021. The number of publications in 2021 was six times more than that in 2010, indicating that ES education was gradually beginning to be taken seriously by researchers.
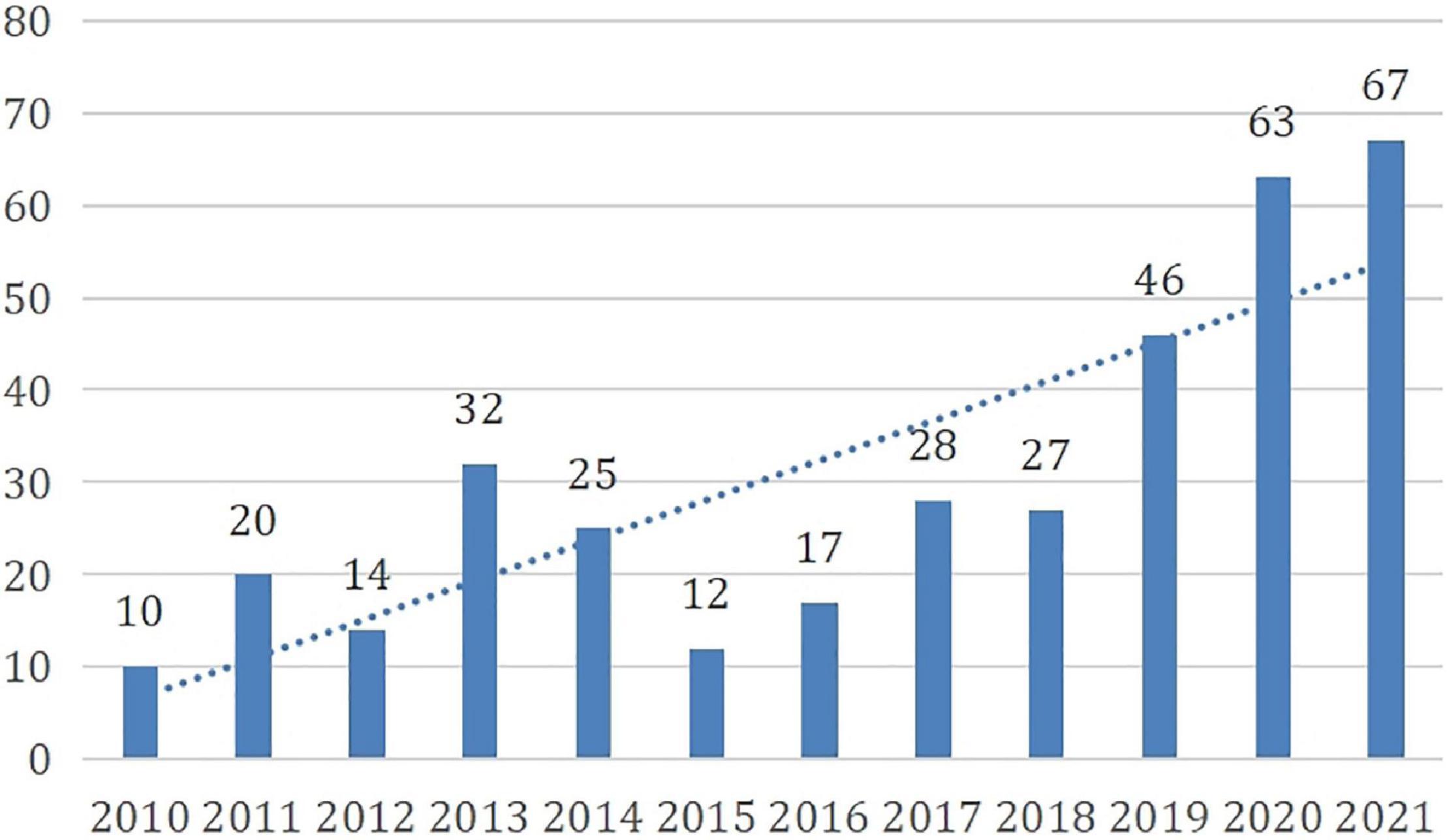
Figure 2. Yearly publications on English-speaking teaching and learning (2010–2021).
However, there were some tortuous changes. In 2010, only 10 studies were identified, but the percentage of the high citation index occupied 50%. From 2011 to 2018, the number of documents published in this area presented an up-and-down curve. The number of publications was slightly lower in 2012 than in 2021. This might be due to the decreased demand for ES education as a result of the economic downturn in many emerging economies such as China, South Korea, and Brazil ( Reid, 2013 ). Yearly publications in this field increased from 2012 to 2013, but decreased again from 2013 to 2015, which was again in line with the global economic situation ( Mau and Ulyukaev, 2015 ). In 2015, the number of publications was more or less the same as in 2010. The reasons for this might be that world trade reduced during the global crisis from 2014 to 2015 ( Baber, 2015 ; Xu and Carey, 2015 ) or that no new research directions were explored during that time. After 2015, there was a continuous increase until 2017. After a subtle decrease in 2018, there was a significant accumulation in the number of publications from 2018 to 2021, showing a new growth trend. Especially in 2020 and 2021, when the COVID-19 pandemic brought disaster to the whole world, publications on ES education increased, reflecting the increasing requirement for ES communication during this time of global cooperation ( Sun and Lan, 2021 ). The influence of the date on the extraction of the sample documents was not very great, as it was 12 December 2021.
Contributions and Collaborations by Country/Region
The 361 sample records extracted in Scopus from 2010 to 2021 were associated with around 40 countries, showing the global distribution of interest by country in ES education.
Figure 3 shows the top 20 countries/regions publishing articles in this field, and they were responsible for 344 ES education publications (2010–2021) (accounting for 95.29% of the total). The countries with big and bright circles were the ones with the large number of the publications. Apart from the 75 publications contributed by the United States, the United Kingdom, Australia, Canada, Spain, and New Zealand, the remaining 269 publications were published by 10 Asian countries, accounting for 74.52% of the total sample documents, which implied the huge demand for the improvement of the learners’ ES skills in those countries. Mainland China contributed 128 publications, accounting for 40.44% of the total, followed by the United States, with 38 documents, accounting for 10.53%.
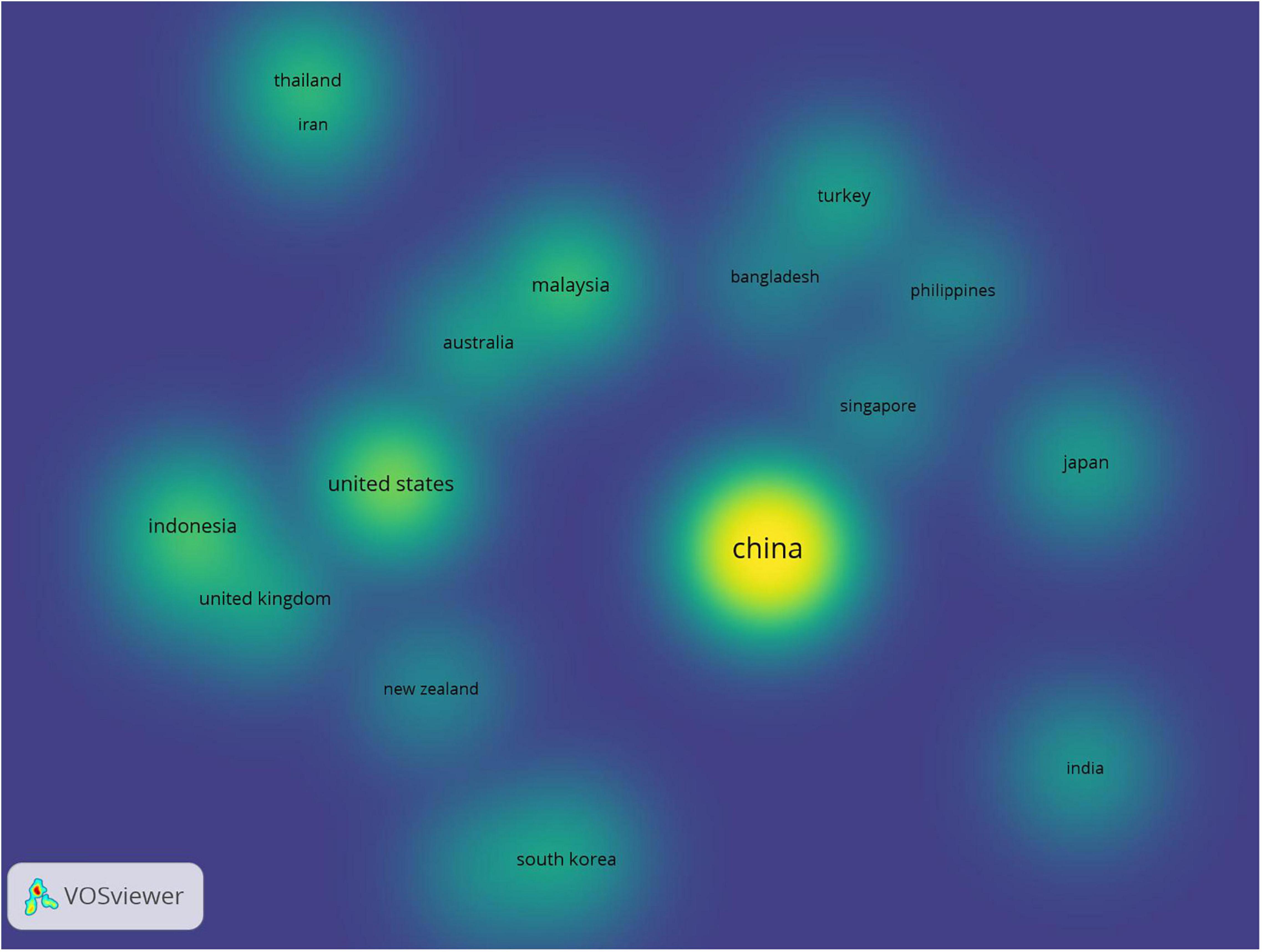
Figure 3. Density map of the top 10 countries.
Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand, countries in South-East Asia, occupied the third, fourth, and fifth positions, with 22, 22, and 18 publications, respectively. Thailand, Vietnam, the Philippines, and Bangladesh began to participate in country collaborations in recent years, in contrast to countries such as the United States, Australia, the United Kingdom, and Singapore where English is the native language or first language.
The citation network in Figure 4 shows only countries with more than five publications, which reflected the passive collaboration among the countries. As one of the native ES countries, home to many ELE approaches and English assessment tools such as TOFEL, the publications by the United States were cited 518 times (total link strength = 10). Meanwhile, the United Kingdom, home to IELTS, contributed 12 publications, which were cited 72 times (total link strength = 5). Malaysia, where ESL, contributed 22 publications, which were cited 90 times (total link strength = 17). Meanwhile, China, with an EFL context, ranked second with 128 publications, which were cited 395 times, and the total link strength achieved 24.
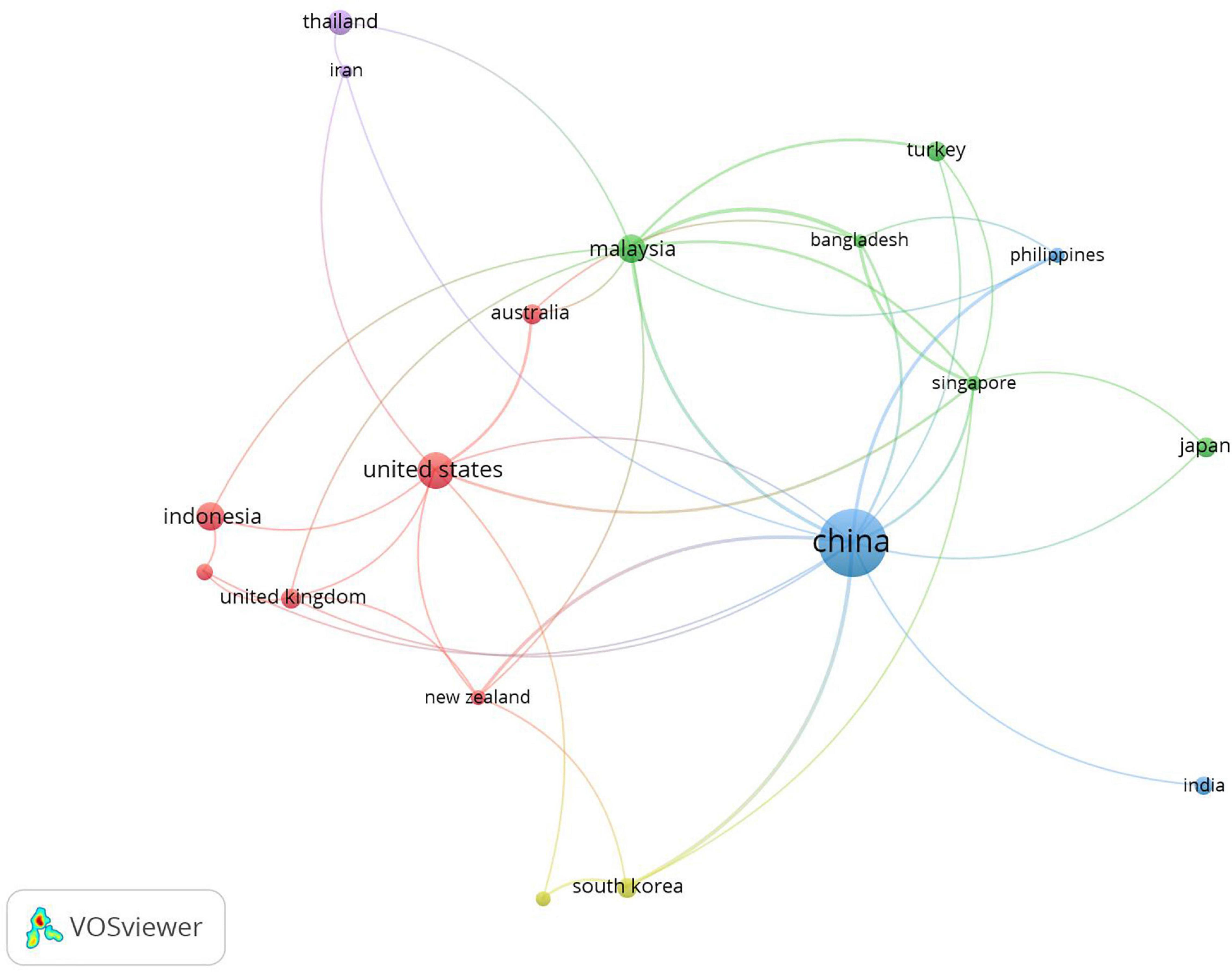
Figure 4. Country co-authorship in the field of English speaking teaching and learning.
The total citation number of the 361 sample publications was 1,828. Table 2 provides detailed information on the 15 countries that published the most cited articles. The publication and the corresponding citation rate of the United States, Australia, New Zealand, and Singapore showed huge contrasts, respectively, 12.92, 19.45, 19.5, and 13.83. The high citation rate may to a certain extent represent a high reference value, although it may also be influenced by some highly cited papers ( Schubert and Braun, 1986 ; Aksnes et al., 2012 ; Brika et al., 2021 ). Thus, it was concluded that the United States, Australia, New Zealand, and Singapore, where English was the official language, were the leading countries with high citation rates in the field of ES education studies. Similarly, native ES countries—the United Kingdom and Canada—showed relatively high citation rates of 5.83 and 6.14, respectively. Meanwhile, the citation rates of Asian countries such as China (4.73), Japan (6.35), South Korea (5.08), Vietnam (8.38), and Oman (6.75) indicated the progress and the relatively high reference value of publications on ES education studies in those countries. The non-ES European countries such as Spain received 4.57 in citation rates, which were much lower than those of the native ES countries.
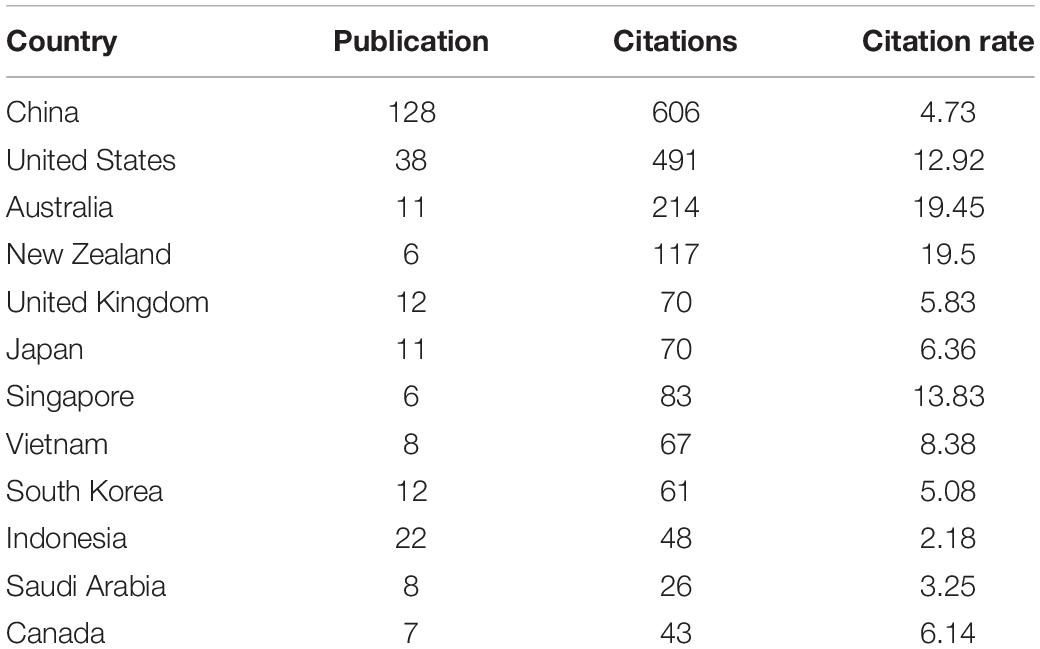
Table 2. Description of the 15 countries that published the most cited articles in the field of English-speaking (ES) education studies in Scopus (2010–2021).
Co-authorship among the countries is shown in Figure 5 , which is a presentation of active collaborations. The co-authorship links among Malaysia, India, China, and the United States were linear. However, the collaboration in the map showed a tendency toward a partial focus. For instance, the United States was the main collaborating country for Indonesia, South Korea, Japan, Thailand, Canada, Australia, and Singapore. While China collaborated mainly with the United Kingdom, the Philippines, Turkey, Vietnam, and New Zealand. Thus, there was a need for an omnidirectional and multi-angle collaboration among the countries for ES teaching and learning research across the world for further studies.
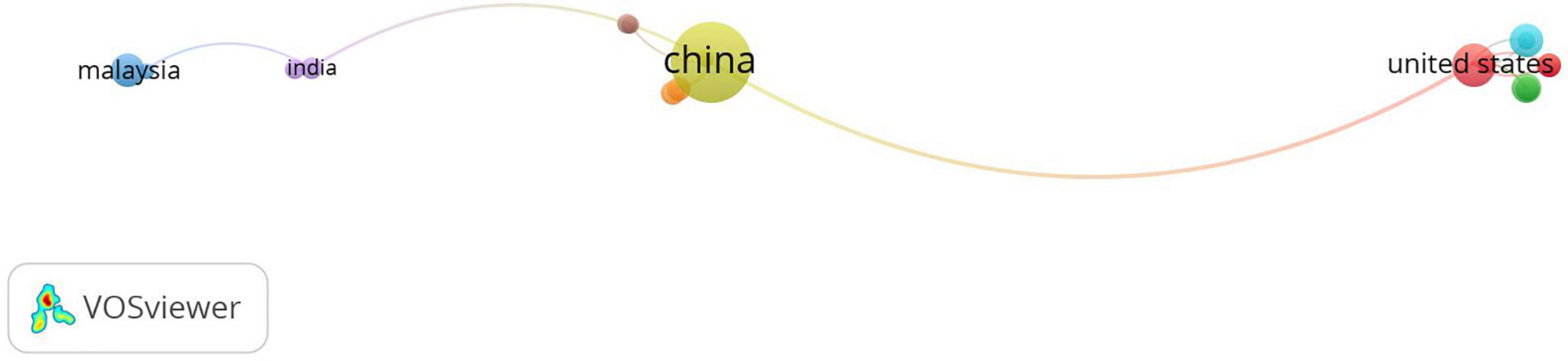
Figure 5. The map of the co-authorship among the countries on English-speaking teaching and learning.
Author Contributions
Table 3 shows general information about the citations for the 361 sample documents in Scopus (2010–2021). As can be seen in Table 4 , the topics of the top 10 most frequently cited articles were concerned with the assessment of ES proficiency and fluency, teachers’ influence, lexical acquisition, and the facilitation of mobile social networks. The total citation number was 1,828. On average, each document was cited 5.06 times. An experimental study by Kang et al. (2010) that proposed suprasegmental measurement for pronunciation assessment from the perspective of accent and equipment use was the most frequently cited article, which was cited 134 times. A qualitative study by Ma (2012) was cited 66 times, ranking second among the top 10 most frequently cited. It focused on ES teaching methods and investigated the advantages and disadvantages of native and non-native ES teachers in practice. The third most frequently cited article, which analyzed the academic lexical demands and academic word list coverage for ES communications by means of corpus, was cited 61 times ( Dang and Webb, 2014 ). Obviously, most of the top 10 most frequently cited articles were published before 2016, except for the experimental studies by Sun and Lan (2021) on the application of e-learning to develop young learners’ ES competence, implying the emergence of new research topics after 2016 in ES teaching and learning studies.

Table 3. General citations of English-speaking (ES) education publications in Scopus (2010–2021).

Table 4. Top 10 frequently cited authors on English-speaking (ES) education in Scopus (2010–2021).
The top 10 authors with more than three articles in order, were Ismail, K. (6), Abdullah, M. Y. (5), Hussin, S. (5), Liu, M. (5), Habil, H. (4), Chen, Z. (3), Hasan, M. K. (3), Hwang, G. J. (3), Rao, Z. (3), and Seraj, P. M. I. (4), and the co-authorship relationships can be seen in Figure 6 . Seraj, P. M. I published four articles (one in 2020 and three in 2021) focusing on the topic of a flipped classroom. The other author with four publications was Liu M., studying the problem of Chinese EFL students’ anxiety, respectively, in 2013, 2018, 2018, and 2021. Rao Z. made three publications on the issues of native and non-native English teachers in China in 2010, 2016, and 2020.
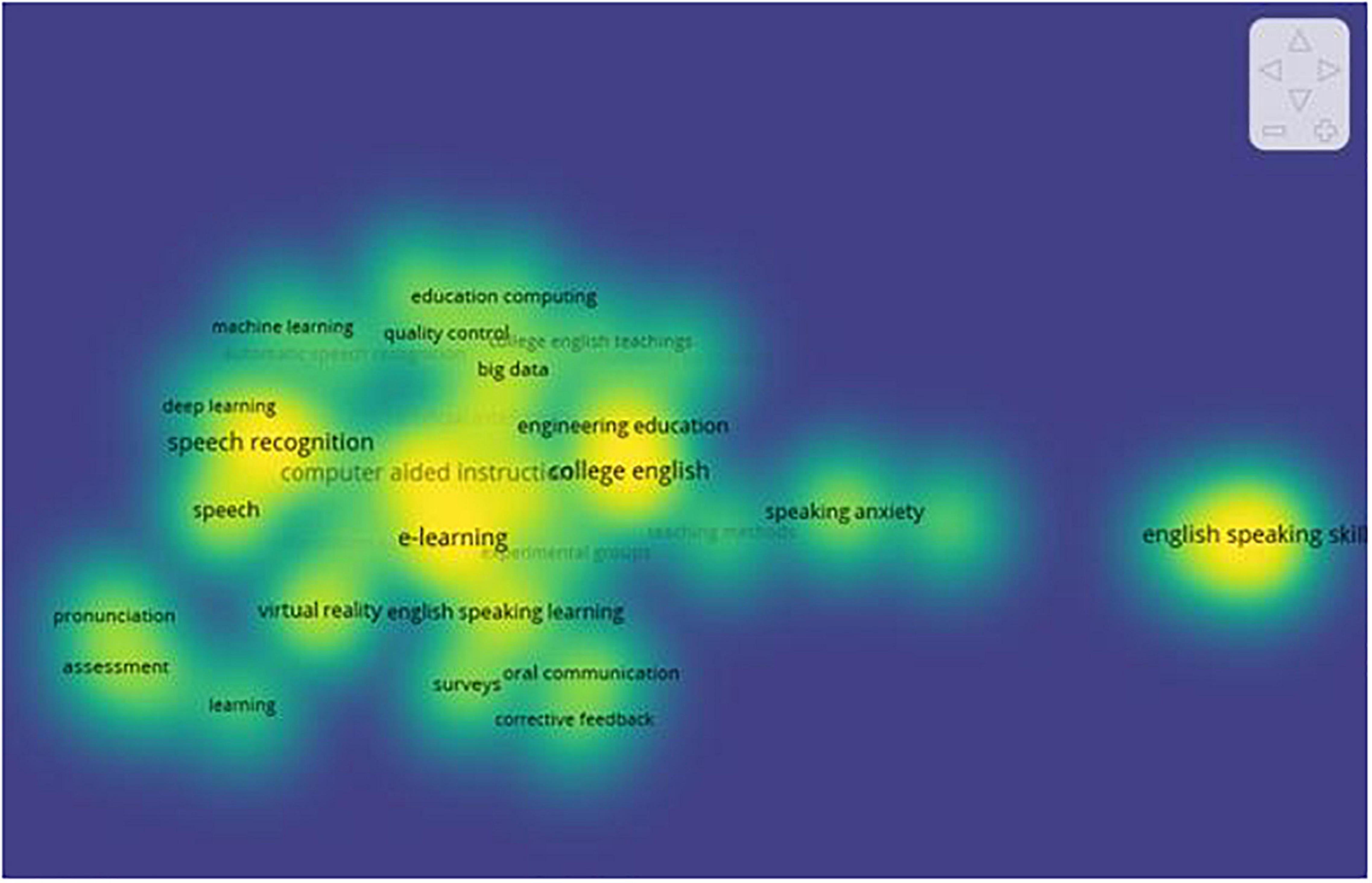
Figure 6. Density map of the key words.
Keyword Analysis
There were 1,049 keywords among the 361 sample documents, and only 49 keywords (2.88%) appeared more than five times after merging synonyms and deleting extraneous words. This indicates that the number of high-frequency keywords was relatively small, which reflects the relatively extensive content of ES research in the field of language education. Table 5 lists the top 10 keywords ordered by the frequency of occurrence apart from the retrieval words, among which the frequency of “ES skill” was the highest, accounting for 3.43%. The remaining keywords with a frequency greater than 10 were “speech recognition” (32), “College English” (26), “e-learning” (22), “computer-aided instruction” (19), “learning system” (14), “native-English speaking teachers” (13), anxiety (13), “oral communication” (12), “virtual reality” (11), and “artificial intelligence” (10). Obviously, the gap in frequency among keywords is not very large.

Table 5. The top 10 most frequently occurring keywords on English-speaking (ES) education in Scopus (2010–2021).
The bibliometric co-occurrence analysis of keywords provided a convenient way to assess the state of the research field and spot hot issues ( Chen, 2016 ; Mutira et al., 2021 ; Sun and Lan, 2021 ). Meanwhile, importantly, keyword co-occurrence analysis can reflect the viewpoints of core academic articles and may be beneficial for researchers trying to keep up with research trends in a certain area ( Li et al., 2016 ; Shoaib et al., 2021 ). Figure 6 shows the density of keywords that appeared more than 10 times; the brightness of the color represents the heat color of the keyword studied. The more studies, the brighter the color ( Van Eck and Waltman, 2020 ). The colors of the keywords “English speaking skill,” “college English,” “computer-aided learning instruction,” and “speech recognition” were brighter than others. The other keywords, such as “speaking anxiety” and “e-learning,” were also brighter. To some extent, these brighter keywords reflected the research hotspots in the field of ES education from 2010 to 2021 in Scopus.
Keyword cluster analysis reflected the topics to some extent ( Yang et al., 2017 ). After combining synonyms (e.g., oral English and spoken English; computer-aided learning and computer-aided instruction; and native and non-native ES teacher) and the deletion of non-sense words (e.g., human, priority journal, and education), the keywords except the retrieval terms “English speaking,” “oral English,” “English-speaking,” “spoken English,” “EFL,” “TESOL,” and “ESL” were categorized into seven clusters with three main topics, as seen in Figure 7 . The keywords with red color dealt with the application of ICT in ES education, including items such as artificial intelligence, automatic speech recognition, computer-aided instruction, correlation methods, deep learning, information science, learning system, machine learning, quality control, correlation methods, corrective feedback, ES learning, oral communication, etc. Cluster 2 dealt with the cognitive factors influencing students’ ES skills or performance, such as attitude, EFL, English speaking performance, ES skill, the flipped classroom, motivation, speaking anxiety, and teaching methods, of which flipped classroom as a teaching method had the highest frequency of occurrence. Clusters 3 and 4 dealt with the application of ICT in college ES education, covering topics such as e-learning, engineering education, English speaking, learning, virtual reality, big data, college English, and educational computing. Cluster 7 dealt with the assessment of pronunciation or others.
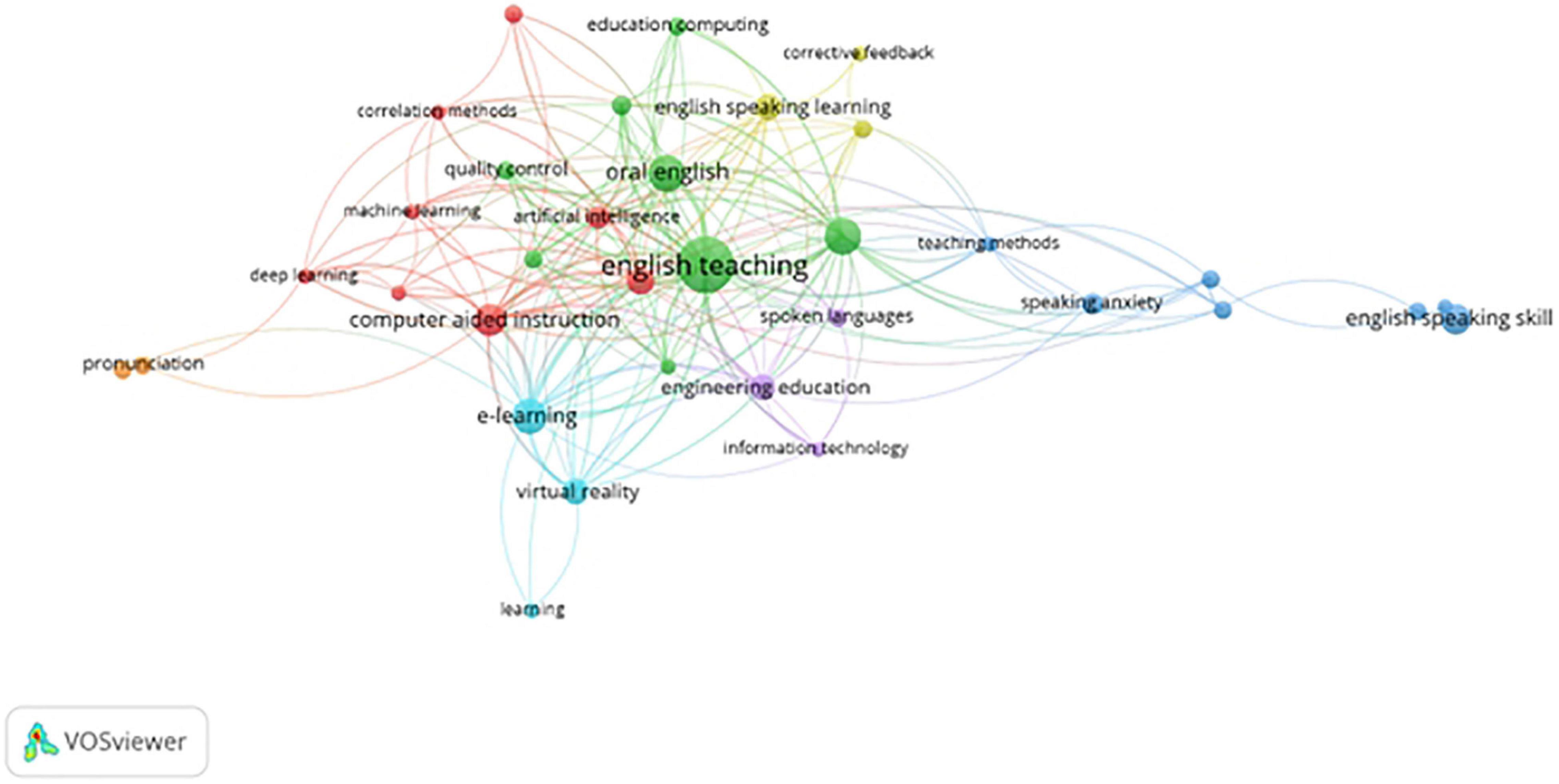
Figure 7. The network visualization map of co-occurrence of keywords.
Keyword Changes and the Enlightenment to Research Topics
Figure 8 reveals a change in the time distribution of topics. It was obvious that most of the light-colored nodes were close to the keyword “college English,” while there were only a few around the keywords “child,” “preschool,” and “adolescent” after 2016. This shows that college students had become the main subjects of ES education studies instead of young learners.
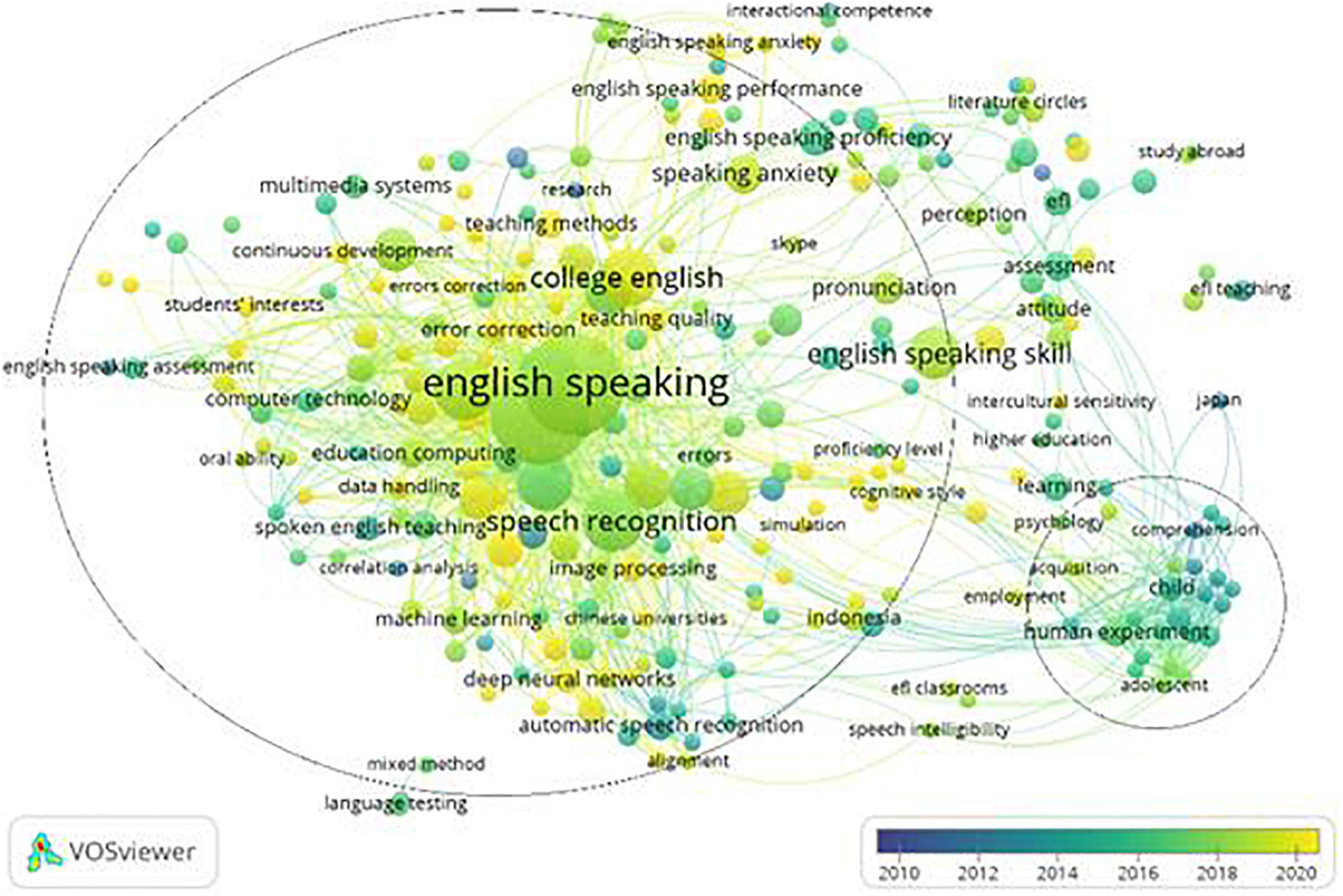
Figure 8. The overlay visualization map of keywords according to year.
Meanwhile, studies with keywords related to the application of ICT, such as “big data,” “artificial intelligence,” “flipped classroom,” “speech recognition system,” and “virtual reality” in ES education, were emerging as a focus of research. Academic ES also began to attract researchers’ attention. Some researchers started to consider the development of twenty first-century skills during ES education. In addition, light-colored nodes of the keywords concerning teaching and learning modes (“continuous development,” “teaching method,” “EMI,” “error correction,” etc.), cognitive factors (“students’ interests,” “anxiety,” “motivation,” etc.), language skills (“ES performance,” “communicative skills,” “accuracy,” “fluency,” etc.), and language knowledge (“pronunciation,” “grammar,” etc.) remained the focus of research.
Limitations
The interpretation of the review should be very cautious due to some limitations. First, bibliometric analysis is a literature review method based on big data technology rather than synthesized thematic analysis. The data were collected and analyzed through the software. Thus, the accuracy of this analysis method is highly dependent on that of the software. The second limitation refers to the database. Though Scopus has covered the majority of the publications on ES teaching and learning worldwide, there are still some publications that were not included in the research.
This historical review and bibliometric analysis sought to better understand the current state of the research field, trends, and emerging research topics on ES education from 2010 to 2021. The results show that there was an increasing trend in the number of publications in this area from 2010 to 2021 in Scopus, indicating that ES education studies remained a necessary research topic, although the research population was not large. Countries with an ESL or EFL context, such as China, Japan, South Korea, Malaysia, Indonesia, and Saudi Arabia, paid more attention to the development of learners’ ES abilities and contributed more to ES education studies. However, the citation analysis revealed that native ES countries such as the United States, Australia, New Zealand, the United Kingdom, and Canada, were the major authorities or origins of ES education studies, which can also be seen by author contributions. Country collaboration analysis showed that the United States, China, India, and Malaysia acted as hubs of contact, establishing overall relationships within the collaboration network. In addition, the analysis of author distribution and collaboration revealed that there were constantly new researchers entering this field, but the lack of authors focusing on ES education over the long term and sustained research was still a problem. Further exploration of keywords revealed that the hot research issues encompass communicative skills, language knowledge, assessment, teaching or learning methods, ICT-related applications, and cognitive factors. Rather than focusing on ES education for young and adolescent learners, researchers showed a preference for investigating ES education for college students, catering to the increasing requirements of oral international communication. Meanwhile, topics on ICT application, autonomous learning, academic ES ability, and twenty first-century learning skills are gradually becoming hot areas for the improvement of ES teaching and learning worldwide.
JW was the research designer and executor of this study, participated in and completed the data analysis, and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. RA and L-ML gave suggestions when necessary. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Acknowledgments
JW would like to express their gratitude to RA and L-ML who participated in this project.
Aksnes, D. W., Schneider, J. W., and Gunnarsson, M. (2012). Ranking national research systems by citation indicators: a comparative analysis using whole and fractionalized counting methods. J. Informetr. 6, 36–43. doi: 10.1016/j.joi.2011.08.002
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Baas, J., Schotten, M., Plume, A., Côté, G., and Karimi, R. (2020). Scopus as a curated, high-quality bibliometric data source for academic research in quantitative science studies. Quant. Sci. Stud. 1, 377–386. doi: 10.1162/qss_a_00019
Baber, G. (2015). “The European Union’s legislative response to the financial crisis: a perspective taken from 2015,” in Global Financial Crisis: Causes, Consequences and Impact on Economic Growth , 89–158.
Google Scholar
Brika, S. K. M., Algamdi, A., Chergui, K., Musa, A. A., and Zouaghi, R. (2021). Quality of higher education: a bibliometric review study. Front. Educ. 6:666087. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2021.666087
Broadus, R. N. (1987). Toward a definition of “bibliometrics”. Scientometrics 12, 373–379. doi: 10.1007/BF02016680
Chen, M.-L. (2016). Development of corpus-based studies in second/foreign language acquisition and pedagogy from 1990 to 2015: a bibliometric analysis. Engl. Teach. Learn. 40, 1–38. doi: 10.6330/ETL.2016.40.4.01
Chen, Z., Goh, C., and Chuen, M. (2011). Teaching oral English in higher education: challenges to EFL teachers. Teach. High. Educ. 16, 333–343. doi: 10.1080/09500782.2011.609281
Coskun, A. (2016). Causes of the ‘i can understand english, but i can’t speak’ syndrome in turkey. J. Engl. Lang. Teach. 6, 1–12. doi: 10.26634/jelt.6.3.8174
Dang, T. N. Y., and Webb, S. (2014). The lexical profile of academic spoken English. Eng. Specif. Purp. 33, 66–76. doi: 10.1016/j.esp.2013.08.001
Donthu, N., Kumar, S., Mukherjee, D., Pandey, N., and Lim, W. M. (2021). How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: an overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 133, 285–296. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.04.070
Ginther, A., Dimova, S., and Yang, R. (2010). Conceptual and empirical relationships between temporal measures of fluency and oral English proficiency with implications for automated scoring. Lang. Test. 27, 379–399. doi: 10.1177/0265532210364407
Hu, G., and McKay, S. L. (2012). English language education in East Asia: some recent developments. J. Multiling. Multicult. Dev. 33, 345–362. doi: 10.1080/01434632.2012.661434
Hughes, R. (2017). Teaching and Researching Speaking , 3rd Edn. New York, NY: Routledge.
Kang, O., Rubin, D., and Pickering, L. (2010). Suprasegmental measures of accentedness and judgments of language learner proficiency in oral English. Mod. Lang. J. 94, 554–566.
Kaya, M., and Erbay, E. (2020). Global trends of the research on COVID-19: a bibliometric analysis via VOSviewer. J. Ankara Health Sci. 9, 201–216.
Kummin, S., Surat, S., Amir, R., Maslawati, M., and Md Melor, Y. (2020). The effects of meta-discussion strategies toward low english proficiency students in oral english performance. Asia Pacific J. Educ. Educ. 35, 75–91. doi: 10.21315/apjee2020.35.1.5
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Lázaro, I. G. (2022). Integration and management of technologies through practicum experiences: a review in preservice teacher education (2010–2020). Contemp. Educ. Technol. 14:e352.
Li, H., An, H., Wang, Y., and Huang, J. (2016). Evolutionary features of academic articles co-keyword network and keywords co-occurrence network: based on two-mode affiliation network. Phys. A 450, 657–669. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2016.01.017
Ma, F., and Ping, L. (2012). Advantages and disadvantages of native- and nonnative-English-speaking teachers: student perceptions in Hong Kong. TESOL Q. 46, 280–305. doi: 10.1002/tesq.21
Mau, V., and Ulyukaev, A. (2015). Global crisis and challenges for Russian economic development. Russian J. Econ. 1, 4–29. doi: 10.1016/j.ruje.2015.05.003
Mutira, P., Meutia, Y. H., and Bastian, E. (2021). A bibliometrics analysis of management control system. Rev. Int. Geogr. Educ. Online 11, 2634–2649. doi: 10.48047/rigeo.11.05.160
Ojima, S. Matsuba-Kurita, H., Nakamura, N., Hoshino, T., and Hagiwara, H. (2011). Age and amount of exposure to a foreign language during childhood: behavioral and ERP data on the semantic comprehension of spoken English by Japanese children. Neurosci. Res. 70, 197–205. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2011.01.018
Oliver, R., Vanderford, S., and Grote, E. (2012). Evidence of English language proficiency and academic achievement of non-English-speaking background students. High. Educ. Res. Dev. 31, 541–555. doi: 10.1080/07294360.2011.653958
Özmen, K. S., Cephe, P. T., and Kınık, B. (2016). Trends in doctoral research on English language teaching in Turkey. Kuram Uygulamada Egitim Bilimleri 16, 1737–1759. doi: 10.12738/estp.2016.5.0069
Pham, X. L., Nguyen, T. H., and Chen, G. D. (2018). Research through the app store: understanding participant behavior on a mobile English learning app. J. Educ. Comput. Res. 56, 1076–1098. doi: 10.1177/0735633117727599
Rahimi, M., and Zhang, L. J. (2015). Exploring non-native English-speaking teachers’ cognitions about corrective feedback in teaching English oral communication. System 55, 111–122. doi: 10.1016/j.system.2015.09.006
Rashid, R. A. B., Abdul Rahman, S. B., and Yunus, K. (2017). Reforms in the policy of English language teaching in Malaysia. Policy Futures Educ. 15, 100–112. doi: 10.1177/1478210316679069
Reid, C. D. (2013). World economic outlook April 2013: hopes, realities, risks. Ref. Rev. 28, 23–24. doi: 10.1108/RR-02-2014-0042
Rogers, G., Szomszor, M., and Adams, J. (2020). Sample size in bibliometric analysis. Scientometrics 125, 777–794. doi: 10.1007/s11192-020-03647-7
Schubert, A., and Braun, T. (1986). Relative indicators and relational charts for comparative assessment of publication output and citation impact. Scientometrics 9, 281–291. doi: 10.1007/BF02017249
Shoaib, M., Ali, N., Anwar, B., Rasool, S., Mustafa, R. E., and Shi, Z. (2021). Research visualization on teaching, language, learning of English and higher education institutions from 2011 to 2020: bibliometric evidence. Libr. Philos. Pract. 2021, 1–27.
Song, J. J. (2011). English as an official language in South Korea: global English or social malady? Lang. Prob. Lang. Plan. 35, 35–55. doi: 10.1075/lplp.35.1.03son
Sun, X., Xie, B., and Zhu, R. (2021). “A review of oral english teaching methodologies in chinese colleges,” in Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Literature, Art and Human Development (ICLAHD 2021) , (Amsterdam: Atlantis Press), 368–372. doi: 10.2991/assehr.k.211120.069
Sun, Y., and Lan, G. (2021). Research trends in ‘trans-’ studies on writing: a bibliometric analysis. System 103, 1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.system.2021.102640
Umunĉ, H., and Raw, L. (2017). Reassessing english studies in turkey. Ariel 48, 137–145. doi: 10.1353/ari.2017.0005
Van Eck, N. J., and Waltman, L. (2017). Citation-based clustering of publications using CitNetExplorer and VOSviewer. Scientometrics 111, 1053–1070. doi: 10.1007/s11192-017-2300-7
Van Eck, N. J., and Waltman, L. (2020). VOSviewer Manual Version 1.6.16. Leiden: Univeristeit Leiden.
Wei, R., and Su, J. (2015). Surveying the English language across China. World Engl. 34, 175–189. doi: 10.1002/jid.3120
Xu, J., and Carey, R. (2015). Post-2015 Global governance of official development finance: harnessing the renaissance of public entrepreneurship. J. Int. Dev. 27, 856–880.
Yang, L., Sun, T., and Liu, Y. (2017). A bibliometric investigation of flipped classroom research during 2000–2015. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. 12, 178–186. doi: 10.3991/ijet.v12i06.7095
Keywords : English-speaking skills, bibliometric analysis, research trends, enlightenment, research state
Citation: Wang J, Abdullah R and Leong L-M (2022) Studies of Teaching and Learning English-Speaking Skills: A Review and Bibliometric Analysis. Front. Educ. 7:880990. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2022.880990
Received: 22 February 2022; Accepted: 01 June 2022; Published: 06 July 2022.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Abdullah and Leong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Rohaya Abdullah, [email protected]
- Search Menu
- Advance articles
- Editor's Choice
- Key Concepts
The View From Here
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Site
- Open Access
- Why Publish?
- About ELT Journal
- Editorial Board
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Journals Career Network
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Dispatch Dates
- Terms and Conditions
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic

Alessia Cogo
Reviews Editor
About the journal.
ELT Journal is a quarterly publication for all those involved in English Language Teaching (ELT), whether as a second, additional, or foreign language, or as an international Lingua Franca …
Highlights and features

Celebrating 75 Years of ELT Journal
2021 marks 75 years since the publication of the first issue of what is now known as ELT Journal . In celebration of this milestone, explore a selection of articles and content from the journal, including:
- ELT Journal editor Alessia Cogo's anniversary volume editorial
- Two landmark issues from the journal's history by A.S. Hornby and Richard Rossner
- Two articles from Richard Smith delving into ELT Journal 's origins and history
Explore now

Key Concepts in ELT
Explore this collection of articles looking at some of the central ideas in ELT. They are informed by current debate on aspects of theory and practice, and free to read online.

Editor’s Choice: Articles & Videos
Every issue the Editor of ELT Journal selects one paper for its high-quality and outstanding contribution to the ELT field. All articles are free to download and read, and short, introductory videos of authors discussing their Editor's Choice articles are also available.

The View from Here is a feature which reports on specific topics of interest or issues being dealt with in diverse ELT contexts across the globe.
Latest articles
Editor's choice, resources for authors and researchers.

Interested in submitting your research?
Read the Instructions for Authors and learn more about the ELT Journal submission process and requirements.

Make an impact with your work
Have you published an article? What should you do now? Read our top tips on promoting your work to reach a wider audience and ensure your work makes an impact.
Top Tips for Publishing in Linguistics Journals
Watch our top tips for publishing in Linguistics Journals video, featuring helpful advice from our Linguistics Journals editors.
Read ELT Journal

Personal subscriptions
Online-only personal subscriptions to ELT Journal start at just £25 / $47 / €37. Special rates are also available for print subscriptions.

Email alerts
Register to receive table of contents email alerts as soon as new issues of ELT Journal are published online.

Recommend to your library
Fill out our simple online form to recommend ELT Journal to your library.
Recommend now
Editor’s Choice – Author Videos
Freire’s problem-posing model: critical pedagogy and young learners
Nadine Nelson and Julian Chen discuss their article, ' Freire’s problem-posing model: critical pedagogy and young learners ' which has been selected as an Editor's Choice article for ELT Journal.
Explore all Editor’s Choice videos.
Engaging in pedagogical translanguaging in a Shanghai EFL high school
Xiaozhou (Emily) Zhou discusses her article, ' Engaging in pedagogical translanguaging in a Shanghai EFL high school class ' which has been selected as an Editor's Choice article for ELT Journal.
Learner-initiated exploratory practice: revisiting curiosity
From learners to users—errors, innovations, and universals
Elina Ranta discuss her article ‘ From learners to users—errors, innovations, and universals ' which was selected as an Editor's Choice article.
Explore all Editor's Choice videos
More from ELT Journal
Obituary: dr norman whitney.
In April 2022, our readers and colleagues around the world were saddened to hear of the death of Dr Norman Whitney. Learn more about his contributions to the journal and read tributes from his colleagues.
Read now
What’s the use of book reviews?
What are book reviews for? Who reads them, and why? What makes a good review?
Alessia Cogo, former Reviews Editor for ELT Journal , discusses answers to these questions in our blog post.
An editor's advice on writing for an academic journal
Do you want to write an article for an academic journal? Don’t know how to get started? Graham Hall, former editor of ELT Journal , offers his tips and insight on the process in this blog post, covering everything from writing to the peer review process.
Follow OUP ELT on social media
Subscribe to OUP ELT YouTube channel for information about latest releases, product demonstrations, author and teacher trainer interviews, and advice and tips to help improve your English language teaching.

ELT on Twitter
Follow us for news, info, articles, videos & tools to aid your ESL/EFL teaching.
OUP ELT blog
We’ll bring you resources you can use in your classrooms, hints and tips for teaching, insights into the lives of publishers and authors, and hopefully a few surprises you won’t find on any other publisher blogs.
Related Titles
- Recommend to Your Library
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 1477-4526
- Print ISSN 0951-0893
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
Impact of social media on learning English language during the COVID-19 pandemic
PSU Research Review
ISSN : 2399-1747
Article publication date: 21 January 2022
This research shows how social media has affected learning at present during the COVID-19 pandemic and how it has become the largest and most convenient area of communication. In the current scenario, it seems that social networking sites not only had a profound impact on our social structure and intra-social interaction, but also affected education in general and learning English language in particular. It has been proven that these various social media platforms have created a realm of digital environment in today's new-age learning. Social media platforms are social networking sites through which people interact and communicate with each other easily and conveniently. Undoubtedly and unquestionably, social networking has been proven to be a global phenomenon that has caused a vast paradigm shift in the world of Learning and education during the current pandemic. Therefore, the present study aims to reach the extent of the impact of the various social media platforms on learning English language during the COVID-19 pandemic from the students' point of view.
Design/methodology/approach
The study was conducted at the undergraduate level for English language learners. The sample comprised 166 undergraduate students at Najran University. A survey questionnaire was administered to find out the impact of various social media platforms and social networking sites on learning English language in the academic year of 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic and to highlight possible suggestions for improving future virtual language learning.
The findings of the study contributed to the area of online learning of English language during the COVID-19 pandemic. Final results confirmed that the utilization of social media has been significantly perceived to have positively impacted learning English language in terms of writing style, reading skills, listening and lexical variation, communication skills and grammar usage.
Practical implications
The findings of the study can serve as fundamental indicators to implement prompt pedagogical reformations, for which a number of pedagogical implications can be proposed. Another equally important pedagogical implication is to design and provide professional development and training sessions to both students and educators on the ultimate utilization of social media as instructional technologies in the context of English language teaching and learning.
Originality/value
This research provides insights in developing policies to assist with the integration and utilization of social media platforms as instructional technologies in the context of English language teaching and learning and how institutions can respond to the advent of advancing technology, especially during and after the COVID-19 era. A model to improve online English language learning process is recommended as a guideline for all educators offering online learning.
- Social media in education
- English language learning
- L2 learning style
- COVID-19 pandemic
Muftah, M. (2022), "Impact of social media on learning English language during the COVID-19 pandemic", PSU Research Review , Vol. ahead-of-print No. ahead-of-print. https://doi.org/10.1108/PRR-10-2021-0060
Emerald Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2022, Muneera Muftah
Published in PSU Research Review . Published by Emerald Publishing Limited. This article is published under the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY 4.0) licence. Anyone may reproduce, distribute, translate and create derivative works of this article (for both commercial and non-commercial purposes), subject to full attribution to the original publication and authors. The full terms of this licence may be seen at http://creativecommons.org/licences/by/4.0/legalcode
1. Introduction
Social media is constantly changing the way people live in different aspects. Nowadays, various social media platforms are affecting communication, information delivery, knowledge exchange, commerce, education and all different aspects of life ( Rieger and Christoph, 2018 ; Bhatti et al. , 2019 ; Amin et al. , 2020 ). With the vast spread of various social networking sites on the Internet, researchers from different fields have started to direct their attention and shed more light on the importance and impact of social media on different aspects of life including social as well as educational aspects.
To pursue their constant efforts and to look at those aspects as an area of concentration that needs to be investigated further, Language learning professionals and instructors specifically have attempted to investigate the effect of social media and social networking sites in second language acquisition and second/foreign language learning. In one of the researches, it was found out that the group who got learning, commitment and inspiration through social media sites has indicated higher results in an English proficiency test compared to the other one that got training on an eye-to-eye premise ( Wamba and Carter, 2016 ).
Up-to-date data available on Statista (2020) have indicated that there are about 3.96 billion social media users across the world. Social media networking sites range from microblogs such as Twitter and sites and applications such as Facebook, YouTube, Instagram, LinkedIn and Snapchat. Yet, these different platforms have influenced the individuals' social, educational and personal aspects of life.
In the area of education, a significant number of research studies have been conducted to estimate their effectiveness in different disciplines. Linguistically speaking, the influx of linguistic output on social media represents numerous opportunities for language learners to process language and obtain input, as young users of social media networks spend more than half of their days using and interacting on these networking sites using their language and communication skills ( Al Jahromi, 2020 ).
Consequently, online chats and discussions, whether oral or written, have replaced conventional face-to-face dialogues, leading to substantial changes in the users' daily language and language skills. The extensive use of smartphones, laptops, and tablets along with prosperous social media applications has perhaps availed rich linguistic input at the fingertips of their users and has contributed in the production of comprehensible L2 output ( Al Jahromi, 2020 ; Pikhart and Botezat, 2021 ).
Regardless of the inevitable impact of social media in individuals' lives everywhere, and taking into account that the students of today are insubordinate to old-fashioned instructing methods and learning techniques, there are not many studies that explore their effects in learning and education particularly in the English language context. Therefore, the present study aims to identify the impact of social media on learning English during the COVID-19 pandemic. To achieve this aim, the present work specifically seeks to address the following research questions.
In what way did social media platforms impact the learning of English Language during the COVID-19 pandemic?
In order to answer this question, the following sub-question was developed to direct the scope of the study: How do Saudi university students perceive the impacts of using social media platforms on their learning of English language during the COVID-19 pandemic with regard to (1) Positive and negative effect? (2) Number of social media platforms used? (3) Motives for using Social Media platforms? (4) Frequency and time spent in using Social Media? (5) Educational or communicative tools? (6) The Rate of using social media on Learning English Language? (7) Aspects of language Skills improved via social media? and (8) Social media effects on students' studies?
2. Literature review
The COVID-19 pandemic led to shocking and unpredicted experiences for Saudi university students. The precautionary measures followed during the pandemic have had a wide impact on the students' social and educational life aspects ( Alghamdi, 2021 ). Recently, we have seen a radical change in favor of distance learning due to the COVID-19 pandemics, therefore, it could be worthwhile to investigate the impact of social media in the foreign language context as they have been used much more now ( Pikhart and Botezat, 2021 ). The current COVID-19 situation makes us aware that the impact of social media will increase due to social distancing.
Social media platforms are omnipresent and the research into the use of them in foreign language learning has become immense ( Yurdagül and Öz, 2018 ; Artyushina and Sheypak, 2018 ; Ayers, 2020 ). Today, with 2.95 billion social network users worldwide, social media usage is increasingly attractive and accessible, especially among the younger generation ( Pikhart and Botezat, 2021 ). Social network sites have become the main means of communicating and a way to maintain a social life ( Li and Croucher, 2020 ).
Social Media refers to websites, blogs, chats, computer programs, i.e. any content-based form of e-communication that enables users to share information and expose ideas. While social networking sites for language learning represent the corpus of those social media channels and service, mainly designed for specific purposes, devoted to foreign language learning. Furthermore, it is also proposed that English might now be the first truly global language, being the dominant or official language in over 60 countries. The English language as stated is one of the most widely spoken languages in the world ( Akinwamide, 2012 ).
Roelofse (2013) argues that exposure to new literacies found in new technologies definitely impacts the way in which second/foreign language learners perceive the world. Likewise, the amount of contact with these social utilities certainly influences literacy practices by learners. New technologies do not merely alter the way people live, but it influences the way they think. Moreover, Davies (2012, p. 21) in Roelofse (2013) argues that “texts of the new technologies have mutated into complex hybrid systems that have made new demands on reading and writing, viewing, social exchange, and communication”.
Facebook is no exception in that the use of this social network site requires a multimodal approach of embedding and combining words and written texts from many sites. In the same sense, WhatsApp is perceived by the researchers as having the same contaminating effect on learners' writing skills. In this regard, social media is a “dialogue” and “means [of] engaging with people” ( Coons, 2012 , p. 44).
The body of literature reveals a significant number of studies in the area of the impact of social media on the linguistic output of non-native speakers of English. Chomsky (2014) has stated that our language is constantly, inevitably, and naturally changing, transforming and becoming more adaptive to its users due to the changes in our contemporaries. More particularly, the initiation and rapid development of social media networking sites as eminent activity has created a distinguishing language system necessary for practical communication ( Attila, 2017 ).
Baldwin (2012) suggests that social media can be both a friend and a foe for natural language processing. While he considers social media a cause for “spelling inconsistencies, the free-form adoption of new terms, and regular violations of English grammar norms,” he refers to the advantage of “lexical normalization” in the same linguistic setting. In this regard, Thurairaj et al. (2015) examined whether social media networks were “making or marring academic English” and whether infrequent online code-switching and inconsistent spelling affect non-native learners' language learning process. Their findings revealed that the discourse used on social media had not influenced the learners' English language proficiency due to their higher awareness of the deviations between their online informal meta-language and their formal academic language.
Furthermore, simplified online interactions help speakers produce meaningful exchanges whilst using the target language in useful manners ( Mutum and Wang, 2010 ). Another advantage of social media is the reduced communication anxiety. People often exchange and share information and construct new personal and linguistic identities on social media because of being at ease with revealing their preferred identities behind monitors as a result of the anonymity expedited in such situations ( Blattner and Fiori, 2011 ). Lowered anxiety in online settings coined with heightened motivation and self-confidence have been shown to provide L2 learners with anxiety-free zones that enable them to produce language spontaneously and creatively ( Al Jahrami, 2019 ).
Studies conducted by Slim and Hafedh (2019) , Thurairaj et al. (2015) have revealed that social media platforms such as Facebook and Twitter enhance students' overall language learning process. In connection with particular language skills, a significant number of studies have found that the use of social media enhances learners' grammatical complexity and vocabulary acquisition and learning ( Al Jahrami, 2019 ; Attila, 2017 ; Mills, 2011 ; Stevenson and Liu, 2010 ). Mason and Rennie (2008) notice that vocabulary acquisition on social media has become a phenomenon due to the employment of techniques such as coining and compounding to produce words such as Face + book, Snap + chat and Blog + sphere.
Another employed technique is sound imitation resulting in words such as Twitter which comes from the verb tweet, and Boo which reflects the sound of contempt. Similarly, social media have affected the forms of different words. For instance, the proper names of social media applications and websites have become verbs and adjectives (e.g. Google it, I'll Instagram this). Another technique is the change in the negative form of the verb like and the noun friend to become unlike and unfriend. Additionally, the semantic connotations of many words have undergone change on social media (e.g. wall on Facebook, spam, steam, etc.).
As to the writing skill, the fact that social media exchanges are more written than spoken in what is referred to as “text speak”. Attila (2017) argues that the use of logograms, abbreviations, acronyms and paralinguistic features (e.g. b4 = before, Gr8 = great) has made writing easier, faster and more liberated from the normal constraints of traditional writing. However, spelling can accordingly be negatively affected when frequently using logograms and abbreviations (e.g. 2 day = today).
Longitudinal studies have also indicated a significant improvement of oral proficiency with particular reference to speaking and listening ( Chen, 2013 ; Lin et al. , 2016 ). Lin et al. , however, have asserted caution that learners would need carefully planned instructional guidance and tailored activities in order to be able to use social media efficiently to enhance their language learning process.
Despite the positive effects of social media on language proficiency and language learning, many researchers are more concerned with the harmful effects these networking sites might have on L2 learners' interlanguage with particular reference to inconsistent spelling and violated grammatical rules ( Baldwin, 2012 ). Lin et al. (2016 , p. 143) claim that “language use on the Internet is often criticized as being less correct and less coherent than other forms of language use, and as having disrupted adjacency.” Effects of social media on Pakistani students' L2 learning process have also been reported in a study conducted by Tariq et al. (2012) . Similarly, Akram and Albalawi (2016) found Facebook to be a negative learning distraction for their Saudi students.
Amidst these incompatible claims, the present study aims to confirm the possible impact of social media platforms on learning English language during the Covid-19 Pandemic from the perspectives of undergraduate students in the Saudi context. The precautionary measures followed during the pandemic have led the Saudi government to abundantly utilize the World Wide Web and all its facets for different socioeconomic and educational purposes. It is not surprising, then, that social media platforms and social networking sites are heavily used by L2 learners. Consequently, the purpose of the current study is to evaluate the possible gains of the broad use of social media platforms on the learning of the English language during the pandemic and to view the perceptions of the learners in regard to these possible gains, which is a gap in the literature that the current study aims to fill.
3. Methodology
The purpose of the current study is to find out the impact of various social media platforms and social networking sites on learning English language in the academic year of 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic and to highlight possible suggestions for improving future virtual language learning.
3.1 Participants
The study was conducted at the undergraduate level for English language learners in the College of Languages and Translation–Najran University, KSA. It was performed after completing a full year of online education and teaching classes and during the final examinations in the second semester of 2020. The sample comprised 166 students: 66 male and 100 female students in all bachelor's degrees with English language majors. Students in the English department form the highest number of students with their ages ranging from below 20 years–23 years old. The participants are native speakers of Arabic. Their interaction outside the classroom is low. That's to say, most of them had very little interaction with native English speakers outside the classroom and in most cases no contact at all.
Most of the students do not have any prior experience with online learning. Requirement courses including Arabic, Religious Culture and other general courses were conducted online on the main campus before the recent crisis, and it was optional. However, the examinations were conducted on campus. The following Figure 1 displays the percentage of the participants.
3.2 Research instrument
The method chosen for this study is quantitative; a more in-depth method was designed to estimate the impact of various social media platforms on learning English language during the COVID-19 pandemic. The quantitative method was used to conduct more detailed studies of a smaller area using closed-questionnaires. This survey-based questionnaire consists of 10 multiple choice questions, which covered the study objectives. The questionnaire was administered to 166 English language learners. It consists of different parts; the first part is looking at students' demographic information, the second part includes a set of multiple-choice questions about learners' experiences with social media platforms (e.g. Facebook, WhatsApp, Twitter, Instagram, Google+, … etc.), and their effect on learning English during the COVID-19 pandemic, the number of Social Media platforms they use and have access to, the motives for using social media during the pandemic, the Frequently used Social Media platforms, the extent to which social media is used for educational and communication purposes, The rate of social media use on learning English language during the COVID-19 pandemic, time spent on social media platforms, language skills improved via social media use and finally the effect of social networking sites Students' Studies. The questionnaire was checked for validity and reliability fulfillment.
3.3 Data analysis procedures
In this study, a quantitative approach to data collection has been employed. A descriptive analysis method was applied to analyze the research by counting the answers for every question to get the percentages. A questionnaire was the tool that was used in order to collect data. The questionnaire consisted of ten questions. Thick description and reflective thinking are the two most important elements that have been used while analyzing and interpreting the data. The data were carefully read for possible categories relevant to the purpose of the study. Then, these reported statements were categorized based on the purpose to be achieved.
4. Results and interpretation
The results of the present study were structured based on the varying types and length of questions applied in the close-ended questionnaire. In the scheduled questionnaire, the researchers set certain questions to gain a wide range of answers and opinions regarding the impact of social media platforms on learning English language during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Figure 2 displays the results of the students who think that social media can affect learning English positively during the pandemic. The results indicate that the majority of the participants use social media as a language learning tool. Almost 86.75% of the students believe that social media can affect learning English positively, while 13.25% of them think that it has a negative effect on the language learning process.
As to the number of social media platforms that students have access to and can straightforwardly use, Figure 3 indicates that 25.91% of the total respondents use only one social networking site, 22.29% use two sites and 37.35% of them use three social networking sites. Yet, only 14.45% of the students use more than three social media platforms.
Concerning the reasons and the motives for using social media during the pandemic, Figure 4 below shows that 60.84% of the participants use social networking sites for the purpose of studying. Likewise, the results indicate that 19.27% of them use social networking sites for playing games, while the students who use these sites for making friends and chatting with friends are 28.31 and 31.74% respectively. The remaining 24.09% reported that they use social networking sites for other purposes.
Figure 5 below shows the most frequently used social media platforms. The data indicate that the most popular online networking site was WhatsApp, with the highest percentage of 72.89% of all university students stating that they use it on a typical day. Facebook is the second mostly-used platform, with 53.01% of the students using it daily. It is also reported that only 31.32% use Twitter, another 26.50 and 21.68% use Google+ and Instagram respectively. The least used social media platform was WeChat, with 3.61% of students using it daily. Moreover, 18.07% of the students prefer to use different other social media platforms and no one of them uses LinkedIn.
Similarly, Figure 6 below presents results related to the use of social media as a communication tool during the COVID-19 Pandemic. The results point out that 81.92% of the students prefer to use social media platforms for learning purposes. They believe that social media provide the facility to communicate among the students during the pandemic, i.e. to communicate with their teachers and classmates. On the other hand, 18.07% did not use social media for educational purposes, as they believe that social networking platforms did not support their studies. They believe that these platforms are supposed to make them feel more connected.
Figure 7 reflects the students' perception towards using social media as an educational tool and as a support for their studies in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic. Results point out that the majority of the students 84.94% are interested in using social media as an educational tool as it helps them to get more useful information and to interact with learning groups and other educational systems that make the learning process more convenient. However, only a few students, 15.06% mention that social media platforms did not support their own studies.
Results reported prove that the majority of the students are interested in using social media as an educational tool and that almost 51.20 and 18.08% of the students use social media to learn English language at higher rates “good” and “excellent” respectively. Moreover, it is also reported that only 21.09% of the students rate the use of social media on learning English language during the COVID-19 pandemic as “average”, another 7.23% rate it as “poor” and only 2.40% rate using social media in learning English as “very poor” (see Figure 8 ).
Concerning how much time do students actively spend on social networking sites, Figure 9 shows that 6.02% of the students do not spend a moment on social networking sites during a typical day, almost 21.08% of them spend 10–30 min a day. Most of the students 31.93% spend about one to two hours on social networking sites during their typical day, while 27.71% spend from 2 to 3 h of their time. It is also reported that 4.22% of the participants spend between 4 and 5 h on social networking sites, and only 9.04% of the participants spend more than 5 h on social networking sites daily.
Interactive social media channels to language learning enable students to develop communication and language skills. Regarding the different aspects of language skills the students improve via social media platforms, the results presented in Figure 10 below showed that 40.96% of the students improved their writing skill, 39.15% improved their reading skill, the third skill is listening and vocabulary with a ratio of 31.92%. In addition, their speaking skill was improved with a percentage of 31.32% and only 22.28% of learners improved their grammar.
The last question discusses the effect of social networking sites on students' studies. The results specified that social networking sites have seriously affected students' studies at a ratio of 24.09%, whereas 31.93% of the participants believe that social networking sites have slightly affected their performance and their language achievement.
On the other hand, 18.07% of the learners agreed that social networking sites have no impact on their studies. Moreover, 14.46% of them believed that such sites are seriously helping, while only 11.45% of the total number of students admitted that social networking sites can slightly help them on their studies. The extent to which social networking sites are affecting the learners' studies is presented in Figure 11 above.
5. Discussion and conclusion
The present work attempts to investigate the most important impacts of using social media for learning English language during the Covid-19 Pandemic. The challenges of the digital world are omnipresent, and different options have to be considered so that educators are able to use them to assist the learners.
Social media is no exception, as it can provide many opportunities in the foreign language learning process. The technological revolution today, like never before, can be obviously reflected in the L2 learners' wide experience, the independence in exploring digital resources and documents that represent powerful support in enhancing oral, written, listening and reading competence. In this sense, L2 learners do no longer depend directly and entirely on the teacher to improve their skills but on other resources such as Internet and technology ( Al Jahromi, 2020 ; Pikhart and Botezat, 2021 ; Slim and Hafedh, 2019 ; Thurairaj et al. , 2015 ).
In other words, social media along with social networking sites have become part of the learners' as well as educators' daily routines, in terms of communication, language experience, practice and exercise, news feed and knowledge sharing. The digital world has seemingly become their way of life inside and outside class settings and that is the reason behind examining their impact on L2 learners.
With the help of social media platforms, L2 learners can learn, read, write, advertise or communicate in a more efficient way. The main questions addressed referred to the impact of social media on learning English language during the Covid-19 pandemic and usage and the degree of facilitation and assistance of foreign language learning by social media, and the findings revealed that students were very positive and felt motivated by social media.
L2 learners do not have to rely on classes or handbooks to get their daily amount of knowledge. It can all be achieved from the social networking sites as indicated in question 2. At least, the learners can use three different types of social media platforms and formats to reach their educational goals and in some cases four types. The learners can follow or get information about their studeis from any part of the world. For instance, Twitter allows a user to get information which is more interactive in nature with the help of embed photo and video. Smartphones are an example of a handheld device through which learners can communicate and exchange information by using any social media platform which is allowed.
The world is getting closer every day and everyone, including L2 learners, needs to be connected. It is moving strongly and more towards “social media”. The information comes to users rather than users have to make effort to get the information. In terms of personal relationships too, social networking is connecting people. Social networking can also be very crucial in educational help. Education support groups can be created from which learners can get information as indicated in question 3 where 60.84% of L2 learners indicated that they use social media platforms for studying and for educational purposes while the rest of them use them for other purposes including chatting with friends, making friends, playing games and for other different purposes.
The kind of interaction a user wants from these social networks depends on the type of information the user is interested in. With reference to question 4, using different platforms depends on users' purposes, for the participants in the study aiming at enhancing proficiency in English language, WhatsApp can be used for chatting or sending many kinds of text-information, assignments or even creating groups for different courses. Facebook was not appealing due to its informal style, while the participants aiming at improving communicating skills found it useful for social and L2 identity construction. Google + can be used for academic purposes, it can greatly enhance the way people learn. Twitter and Instagram have also become popular and integral part of everyday communication. Other platforms such as YouTube, learners can watch videos to understand a topic better or look at photos which might help them to visualize a concept, after all, “a picture speaks a thousand words”. Brick (2011) reported it as the main positive aspect of using social networking sites, adding to it the real-time feedback. The immediate response and real-time conversation are also achieved through live sessions on Instagram or Facebook dedicated pages for L2 learners, such as the Instagram stories that offer quizzes focusing on idioms, phrasal verbs or other lexical related items or lives where learners are invited to write down words that they would like to learn the pronunciation.
The fact that technology including social media and the different networking sites should be part of the educational process is not questionable anymore, the way it finds its scope within it and how and to which extent should educators, as well as learners, use it, had better be delivered by a multidisciplinary methodological framework. Among the numerous potential advantages to using social media, L2 learners have perceived that it can be used as a good communication and educational tool (See Question 5 and 6). The opportunities provided by this medium are immense and many L2 learners are making use of this medium to better their practices. Social networks, unlike the common media, do not have a pattern as to how much information has to be conveyed and where to draw the line. Therefore, learners can obtain much information and better performance. Similar findings were found by Sitthirak (2012) , who acknowledged the attitudinal impact of social media on language from an educational perspective. Similarly, Mutum and Wang (2010) and Blattner and Fiori (2011) have declared that social media provides a smoother, more direct communication tool.
In other words, by maximizing the benefits of social networks, whether it be their role in delivering educational outcomes, or facilitating supportive relationships, identity formation, or a sense of belonging and resiliency, the direct contacts that occur in discussion groups, exercises, conversations, videos and other widgets on linguistic social networks cover various language registers. With the expanding demand of various social media platforms, the growing numbers of users in different parts of the world, it is fair to assume that it impacts second language acquisition, at least by the permanent flow of visuals and text that we access on a daily basis. In the broad context of globalization, all visuals improve not only linguistic skills, but they also build an international culture ( Pikhart and Botezat, 2021 ).
The current Covid-19 pandemic has posed some challenges, and like any emergency event, it has some inherent risks. Through increased social media literacy as an educational tool– ensuring all students can utilize these media to develop the skills and to critically understand, analyze and create content – these challenges can be overcome and risks mitigated in a way that ensures the many benefits for both learners and educators. The findings shown in questions 7 and 8 corresponded with the aforementioned ones related to L2 learners' views on the particular effects of social media on the enhancement of these language learning skills. Results have asserted that approximately 69.28% of the frequent users of social media platforms for learning purposes have rated them as excellent and good mediums to enhance language skills, especially during the Covid-19 pandemic. This is in line with Li (2017) study. Li argued that students' comfort with online class design, structure, level of interaction between students and faculty, the quality and amount of class content and overall experience with online class delivery impact the overall learning experience and determine the ultimate success or failure of online mode of education. Haque and Al-Salem (2019) have also found that social media is a good platform for students as it provides opportunities for learners to study foreign languages.
The intensity of using English-language social media content is positively and significantly related to students' perceptions of their ability to speak English including reading, writing, listening and speaking aspects. Hence, social media is needed to be learning media for learning English language as a Foreign Language ( Anwas et al. , 2020 ). Online socialization according to Slim and Hafedh (2019) seems to have positively affected the production of an acknowledged linguistic repertoire independent of age or gender.
With reference to the last question, results show positive perceptions of the respondents of the effects of using social media on their L2 writing (see Figure 11 ). In addition to improved English language learning, these effects included enhanced writing style, quality and quantity. Al Jahromi (2019) and Li (2017) have similarly found that online interactions on social media networks and online facets significantly develop L2 learners' writing accuracy and complexity. These findings could also be related in this regard to the influence of the projection of authorial and social presence and identity practices facilitated on social media due to the increased linguistic input and output on these platforms in comparison to the less-advantageous classroom settings ( Chen, 2013 ).
In addition, L2 learners who acknowledged the positive impact of social media on their English learning reported that their L2 Reading skills are also enhanced. This is due to the improvement of the L2 learners' vocabulary as well as listening skills. This is similar to the findings obtained by Mutum and Wang (2010) , Thurairaj et al. (2015) and Slim and Hafedh (2019) . However, online communication of students raises another important issue discussed by the great majority of authors, that of the nonacademic purposes of social media usage of students. Given that the majority of the students were using written-based social media networks such as WhatsApp, Twitter and Instagram, speaking, grammar and pronunciation skills were perceived as the least enhanced. However, Al Jahrami (2019) has claimed that language accuracy is concerned, extensive reading and writing online can enhance L2 learners' grammatical competence (see also Attila, 2017 ; Mills, 2011 ; Stevenson and Liu, 2010 ).
In sum, the research study investigated the impact of social media platforms on learning English language during the Covid-19 pandemic from undergraduate Saudi users' perspectives. The aforementioned findings suggest that Saudi L2 learners find social media platforms effective in enhancing their L2 proficiency, with particular reference to how positively they influence L2 writing, vocabulary learning and communication skills. They also reported that they use various social media platforms including WhatsApp, Facebook, Google+, Twitter, etc., and that they find social media as both educational and communicative tools. Based on these findings, it is safe to conclude that social media can be appreciably helpful in enhancing English language learning.
6. Research implications and recommendations
The findings of the study can serve as fundamental indicators to implement prompt pedagogical reformations, for which a number of pedagogical implications can be proposed. Social media can be implemented to make teaching more student-centered through the facilitation of interactive collaboration and exchange of information, resulting in an enhancement of syntactic and lexical complexity.
L2 teachers in particular need to use social media to aid their teaching strategies and amplify their material with interactive and innovative activities on social media such as online debates and group discussions. Another equally important pedagogical implication is to design and provide professional development and training sessions, workshops, seminars to both students and educators on the ultimate utilization of social media as instructional technologies in the context of English language teaching and learning.
Social media networks can be employed in this regard to provide authentic extensive reading tasks that can facilitate intentional and incidental vocabulary learning and writing complexity. Furthermore, awareness campaigns can be conducted by e-learning educationists to recognize the benefits of online learning and teaching and validate the acceptability of social media learning, mobile learning and mixed teaching via learning management systems.
For implementing the positive findings of different studies and for educational technology to be used effectively, educators must be ready for a paradigm shift: from traditional education to pedagogy enhanced by the new technology. Further research is needed into the current realism and prospects of the utilization of digital media in connection with the wellbeing of the learners, increased levels of depression and anxiety, and some other negative psychological, social and economic aspects of the use of social media. This paper is the starting point and should be an impetus for further research into the topic of utilization of social media, especially during and after the COVID-19 era.
To offer online learning, English language undergraduate students require assistance. The following model is recommended as a guideline for all educators offering online learning. The proposed model is demonstrated in Figure 12 .
Participants distribution
The effect of social media platforms on learning English
The use of social media
Motives for using social media platforms
Frequently used social media platforms
Use of social media platforms as a communication tool
Using social media platforms as an educational tool
The rate of social media use on learning English language during the COVID-19 pandemic
Time spent on social media platforms
Language skills improved via social media use
Social networking sites effects on students' studies
Procedure to improve online English language learning process
Akinwamide , T.K. ( 2012 ), “ The influence of process approach on English as second language students' performances in essay writing ”, ELT , Vol. 5 No. 3 , pp. 16 - 29 , doi: 10.5539/elt.v5n3p16 .
Akram , M.S. and Albalawi , W. ( 2016 ), “ Youths' social media adoption: theoretical model and empirical evidence ”, International Journal of Business and Management , Vol. 11 No. 2 , pp. 22 - 30 .
Al Jahrami , D. ( 2019 ), “ The impact of online discussions on the accuracy of the written output of Bahraini L2 university students ”, in Hidri , S. (Ed.), English Language Teaching Research in the Middle East and North Africa , Palgrave Macmillan , Cham , pp. 637 - 666 .
Al Jahromi , D. ( 2020 ), “ A quantitative study of the perceived impact of social media networks on Bahraini users' English language learning ”, Teaching English with Technology , Vol. 20 No. 4 , pp. 23 - 40 .
Alghamdi , A.A. ( 2021 ), “ Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the social and educational aspects of Saudi university students' lives ”, PLoS One , Vol. 16 No. 4 , doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0250026 .
Amin , B. , Rafiq , R. and Mehmood , N. ( 2020 ), “ The impact of social media in English language learning ”, Journal of Critical Reviews , Vol. 7 No. 10 , pp. 3126 - 3135 , doi: 10.31838/jcr.07.10.507 .
Anwas , E. , Sugiarti , Y. , Permatasari , A. , Warsihna , J. , Anas , Z. , Alhapip , L. , Siswanto , H. and Rivalina , R. ( 2020 ), “ Social media usage for enhancing English language skill ”, International Journal of Interactive Mobile Technologies , Vol. 7 No. 14 , pp. 41 - 56 .
Artyushina , G. and Sheypak , O.A. ( 2018 ), “ Mobile phones help develop listening skills ”, Informatics , Vol. 5 , p. 32 .
Attila , B. ( 2017 ), “ The effects of social media on the language: do social networks have damaging or constructing effects on language? ”, available at: http://midra.unimiskolc.hu/document/26612/22012.pdf .
Ayers , J. ( 2020 ), “ Competence literate but context lacking? Investigating the potential of study abroad programs to promote sustainability competence acquisition in students ”, Sustainability , Vol. 12 , p. 5389 .
Baldwin , T. ( 2012 ), “ Social media: friend or foe of natural language processing? ”, Paper presented in the 26th Pacific Asia Conference on Language, Information and Computation , pp. 58 - 59 , available at: https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/Y12-1005.pdf ( accessed 29 June 2019 ).
Bhatti , A. , Bano , T. and Rehman , S.-U. ( 2019 ), “ Social media and consumer satisfaction effect on consumer purchase intention with the moderating role of trust ”, International Journal of Business Management , Vol. 4 No. 2 , pp. 131 - 141 .
Blattner , G. and Fiori , M. ( 2011 ), “ Virtual social network communities: an investigation of language learners' development of sociopragmatic awareness and multiliteracy skills ”, CALICO Journal , Vol. 29 No. 1 , pp. 24 - 43 .
Brick , B. ( 2011 ), “ Social networking sites and language learning ”, International Journal of Virtual and Personal Learning Environments (IJVPLE) , Vol. 2 No. 3 , pp. 18 - 31 .
Chen , H.-I. ( 2013 ), “ Identity practices of multilingual writers in social networking spaces ”, Language Learning and Technology , Vol. 17 No. 2 , pp. 143 - 170 .
Chomsky , N. ( 2014 ), Aspects of the Theory of Syntax , The MIT Press , Cambridge, Massachusetts .
Coons , S. ( 2012 ), “ Communication through social media: its potential and pitfalls ”, Research Practitioner , Vol. 13 No. 2 , pp. 44 - 45 .
Haque , S. and Al-Salem , N. ( 2019 ), “ Social media in EFL context: attitudes of Saudi learners ”, Journal of Language Teaching and Research , Vol. 5 No. 10 , pp. 1029 - 1040 .
Li , V. ( 2017 ), “ Social media in English language teaching and learning ”, International Journal of Learning and Teaching , Vol. 3 No. 2 , pp. 148 - 153 .
Li , M. and Croucher , S. ( 2020 ), “ Effects of social media use on cultural adaptation ”, in Rings , G. and Rasinger , S. (Eds), The Cambridge Handbook of Intercultural Communication (Cambridge Handbooks in Language and Linguistics) , Cambridge University Press , Cambridge , pp. 504 - 520 . doi: 10.1017/9781108555067.037 .
Lin , C.-H. , Warschauer , M. and Blake , R. ( 2016 ), “ Language learning through social networks: perceptions and reality ”, Language Learning and Technology , Vol. 20 No. 1 , pp. 124 - 147 .
Mason , R. and Rennie , F. ( 2008 ), E-Learning and Social Networking Handbook: Resources for Higher Education , Routledge , Abingdon, Oxon .
Mills , N.A. ( 2011 ), “ Situated learning through social networking communities: the development of joint enterprise, mutual engagement, and a shared repertoire ”, CALICO Journal , Vol. 28 No. 2 , pp. 345 - 368 .
Mutum , D. and Wang , Q. ( 2010 ), “ Consumer generated advertising in blogs ”, in Burns , N.M. , Daugherty , T. and Eastin , M.S. (Eds), Handbook of Research on Digital Media and Advertising: User Generated Content Consumption 1 , IGI Global , Hershey, Pennsylvania , pp. 248 - 261 .
Pikhart , M. and Botezat , O. ( 2021 ), “ The impact of the use of social media on second language acquisition ”, Procedia Computer Science , Vol. 192 , pp. 1621 - 1628 .
Rieger , D. and Christoph , K. ( 2018 ), “ The daily dose of digital inspiration: a multi-method exploration of meaningful communication in social media ”, New Media and Society , Vol. 21 No. 1 , pp. 97 - 118 .
Roelofse , L. ( 2013 ), Investigating the Impact of Facebook-Speak on the Written Academic Work of Learners in a Western Cape High School , Department of General Linguistics, Faculty of Arts and Social Sciences, Stellenbosch University , available at: http://scholar.sun.ac.za ( accessed 10 May 2018 ).
Sitthirak , C. ( 2012 ), “ Social media for language teaching and learning ”, Thammasat Journal , Vol. 31 , pp. 1 - 25 .
Slim , H. and Hafedh , M. ( 2019 ), “ Social media impact on language learning for specific purposes: a study in English for business administration ”, Teaching English with Technology , Vol. 19 No. 1 , pp. 56 - 71 .
Statista ( 2020 ), “ Social media: statistics and facts ”, available at: https://www.statista.com/topics/1164/social-networks ( accessed 29 June 2019 ).
Stevenson , M.P. and Liu , M. ( 2010 ), “ Learning a language with Web 2.0: exploring the use of social networking features of foreign language learning websites ”, CALICO Journal , Vol. 27 No. 2 , pp. 233 - 259 .
Tariq , W. , Mehboob , M. , Khan , M.A. and Ullah , F. ( 2012 ), “ The impact of social media and social networks on education and students of Pakistan ”, International Journal of Computer Science Issues , Vol. 9 No. 4 , pp. 407 - 411 .
Thurairaj , S. , Hoon , E.P. , Roy , S.S. and Fong , P.K. ( 2015 ), “ Reflections of students' language usage in social networking sites: making or marring academic English ”, The Electronic Journal of E-Learning , Vol. 13 No. 4 , pp. 302 - 316 .
Wamba , S.F. and Carter , L. ( 2016 ), “ Social media tools adoption and use by SMES: an empirical study ”, Social Media and Networking: Concepts, Methodologies, Tools, and Applications , pp. 791 - 806 .
Yurdagül , C. and Öz , S. ( 2018 ), “ Attitude towards mobile learning in English language education ”, Education Sciences , Vol. 8 , p. 142 .
Further reading
Bhatti , A. ( 2018 ), “ Sales promotion and price discount effect on consumer purchase intention with the moderating role of social media in Pakistan ”, International Journal of Business Management , Vol. 3 No. 4 .
Habermas , J. ( 1979 ), “ What is universal pragmatics? ”, in McCarthy , T. (Ed.), Communication and the Evolution of Society , Beacon , Boston, Massachusetts , Vol. 2 No. 5 , pp. 1 - 68 .
Corresponding author
About the author.
Dr. Muneera Muftah is an Associate Professor in the Department of English at the Faculty of Arts, Thamar University, Yemen. She is currently working in the Department of English Language at the College of Languages and Translation, Najran University, KSA. She earned PhD in English Language Studies from Universiti Putra Malaysia, Malaysia. She teaches courses in linguistics, applied linguistics and translation. Her main research interests are in the areas of translation, syntactic and morphological mental representation and development, and vocabulary development in SLA, generative syntax and morphology, discourse studies and second language assessment.
Related articles
We’re listening — tell us what you think, something didn’t work….
Report bugs here
All feedback is valuable
Please share your general feedback
Join us on our journey
Platform update page.
Visit emeraldpublishing.com/platformupdate to discover the latest news and updates
Questions & More Information
Answers to the most commonly asked questions here
2M-NER: contrastive learning for multilingual and multimodal NER with language and modal fusion
- Published: 09 May 2024
Cite this article

- Dongsheng Wang 1 ,
- Xiaoqin Feng 2 ,
- Zeming Liu ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3691-8097 3 &
- Chuan Wang 4
Named entity recognition (NER) is a fundamental task in natural language processing that involves identifying and classifying entities in sentences into pre-defined types. It plays a crucial role in various research fields, including entity linking, question answering, and online product recommendation. Recent studies have shown that incorporating multilingual and multimodal datasets can enhance the effectiveness of NER. This is due to language transfer learning and the presence of shared implicit features across different modalities. However, the lack of a dataset that combines multilingualism and multimodality has hindered research exploring the combination of these two aspects, as multimodality can help NER in multiple languages simultaneously. In this paper, we aim to address a more challenging task: multilingual and multimodal named entity recognition (MMNER), considering its potential value and influence. Specifically, we construct a large-scale MMNER dataset with four languages (English, French, German and Spanish) and two modalities (text and image). To tackle this challenging MMNER task on the dataset, we introduce a new model called 2M-NER , which aligns the text and image representations using contrastive learning and integrates a multimodal collaboration module to effectively depict the interactions between the two modalities. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our model achieves the highest F1 score in multilingual and multimodal NER tasks compared to some comparative and representative baselines. Additionally, in a challenging analysis, we discovered that sentence-level alignment interferes a lot with NER models, indicating the higher level of difficulty in our dataset.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions

https://huggingface.co/datasets/flax-community/conceptual-12m-mbart-50-multilingual/tree/main
https://huggingface.co
https://spacy.io/
https://fanyi-api.baidu.com
An image named 17_06_4705.jpg with the words “image not found”.
https://huggingface.co/bert-base-multilingual-cased
https://nlp.johnsnowlabs.com/2020/01/22/glove_6B_300.html
https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet152-b121ed2d.pth
Cui H, Peng T, Xiao F, Han J, Han R, Liu L (2023) Incorporating anticipation embedding into reinforcement learning framework for multi-hop knowledge graph question answering. Inf Sci 619:745–761
Article Google Scholar
Du Y, Jin X, Yan R, Yan J (2023) Sentiment enhanced answer generation and information fusing for product-related question answering. Inf Sci 627:205–219
Li D, Li J, Li H, Niebles JC, Hoi SCH (2022) Align and prompt: video-and-language pre-training with entity prompts. In: CVPR. IEEE, pp 4943–4953
Yang J, Yin Y, Ma S, Yang L, Guo H, Huang H, et al (2023) HanoiT: enhancing context-aware translation via selective context. In: DASFAA (3). vol. 13945 of lecture notes in computer science. Springer, pp 471–486
Guerreiro NM, Voita E, Martins AFT (2023) Looking for a needle in a haystack: a comprehensive study of hallucinations in neural machine translation. In: EACL. association for computational linguistics, pp 1059–1075
Huang Z, Xu W, Yu K (2015) Bidirectional LSTM-CRF models for sequence tagging. CoRR arXiv:1508.01991
Ma X, Hovy EH (2016) End-to-end sequence labeling via Bi-directional LSTM-CNNs-CRF. In: ACL (1). the association for computer linguistics
Yu J, Jiang J, Yang L, Xia R (2020) Improving multimodal named entity recognition via entity span detection with unified multimodal transformer. In: ACL. association for computational linguistics, pp 3342–3352
Zhang D, Wei S, Li S, Wu H, Zhu Q, Zhou G (2021) Multi-modal graph fusion for named entity recognition with targeted visual guidance. In: AAAI. AAAI Press, pp 14347–14355
Li J, Chiu B, Feng S, Wang H (2022) Few-Shot named entity recognition via meta-learning. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 34(9):4245–4256
Agarwal O (2022) Towards robust named entity recognition via temporal domain adaptation and entity context understanding. In: AAAI. AAAI Press, pp 12866–12867
Shen Y, Wang X, Tan Z, Xu G, Xie P, Huang F et al (2022) Parallel instance query network for named entity recognition. In: ACL (1). association for computational linguistics, pp 947–961
Schmidt FD, Vulic I, Glavas G (2022) SLICER: sliced fine-tuning for low-resource cross-lingual transfer for named entity recognition. In: EMNLP. association for computational linguistics, pp 10775–10785
Zhang X, Yuan J, Li L, Liu J (2023) Reducing the ltion. In: WSDM. ACM, pp 958–966
Kulkarni M, Preotiuc-Pietro D, Radhakrishnan K, Winata G, Wu S, Xie L, et al (2023) Towards a unified multi-domain multilingual named entity recognition model. In: EACL. association for computational linguistics, pp 2202–2211
Zhang Y, Meng F, Chen Y, Xu J, Zhou J (2021) Target-oriented fine-tuning for zero-resource named entity recognition. In: ACL/IJCNLP (Findings). vol. ACL/IJCNLP 2021 of findings of ACL. association for computational linguistics, pp 1603–1615
Boros E, González-Gallardo C, Moreno JG, Doucet A (2022) L3i at SemEval-2022 task 11: straightforward additional context for multilingual named entity recognition. In: SemEval@NAACL. association for computational linguistics, pp 1630–1638
Zhang Q, Fu J, Liu X, Huang X (2018) Adaptive Co-attention network for named entity recognition in tweets. In: AAAI. AAAI Press, pp 5674–5681
Chen X, Zhang N, Li L, Deng S, Tan C, Xu C et al (2022) Hybrid transformer with multi-level fusion for multimodal knowledge graph completion. In: SIGIR. ACM, pp 904–915
Wang X, Gui M, Jiang Y, Jia Z, Bach N, Wang T et al (2022) ITA: Image-text alignments for multi-modal named entity recognition. In: NAACL-HLT. association for computational linguistics, pp 3176–3189
Sang EFTK (2002) Introduction to the CoNLL-2002 shared task: language-independent named entity recognition. In: CoNLL. ACL
Sang EFTK (2003) Meulder FD. Introduction to the CoNLL-2003 shared Task: language-independent named entity recognition. In: CoNLL. ACL, pp 142–147
Pan X, Zhang B, May J, Nothman J, Knight K, Ji H (2017) Cross-lingual name tagging and linking for 282 languages. In: ACL (1). association for computational linguistics, pp 1946–1958
Lu D, Neves L, Carvalho V, Zhang N, Ji H (2018) Visual attention model for name tagging in multimodal social media. In: ACL (1). Association for computational linguistics, pp 1990–1999
Sui D, Tian Z, Chen Y, Liu K, Zhao J (2021) A large-scale chinese multimodal ner dataset with speech clues. In: ACL/IJCNLP (1). association for computational linguistics, pp 2807–2818
Dosovitskiy A, Beyer L, Kolesnikov A, Weissenborn D, Zhai X, Unterthiner T et al (2021) An image is worth 16x16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale. In: ICLR. OpenReview.net
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: CVPR. IEEE computer society, pp 770–778
Sun E, Zhou D, Tian Y, Xu Z, Wang X (2024) Transformer-based few-shot object detection in traffic scenarios. Appl Intell 54(1):947–958
Lample G, Ballesteros M, Subramanian S, Kawakami K, Dyer C (2016) Neural architectures for named entity recognition. In: HLT-NAACL. the association for computational linguistics, pp 260–270
Devlin J, Chang M, Lee K, Toutanova K (2019) BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In: NAACL-HLT (1). association for computational linguistics, pp 4171–4186
Sen P, Aji AF, Saffari A (2022) Mintaka: a complex, natural, and multilingual dataset for End-to-End question answering. In: COLING. international committee on computational linguistics, pp 1604–1619
Perevalov A, Both A, Diefenbach D, Ngomo AN (2022) Can machine translation be a reasonable alternative for multilingual question answering systems over knowledge graphs. In: WWW. ACM, pp 977–986
Wang R, Zhang Z, Zhuang F, Gao D, Wei Y, He Q (2021) Adversarial domain adaptation for cross-lingual information retrieval with multilingual BERT. In: CIKM. ACM, pp 3498–3502
Sun S, Duh K (2020) CLIRMatrix: a massively large collection of bilingual and multilingual datasets for cross-lingual information retrieval. In: EMNLP (1). association for computational linguistics, pp 4160–4170
Bhartiya A, Badola K, Mausam (2022) DiS-ReX: a multilingual dataset for distantly supervised relation extraction. In: ACL (2). association for computational linguistics, pp 849–863
Rathore V, Badola K, Singla P, Mausam (2022) PARE: a simple and strong baseline for monolingual and multilingual distantly supervised relation extraction. In: ACL (2). association for computational linguistics, pp 340–354
Nothman J, Ringland N, Radford W, Murphy T, Curran JR (2013) Learning multilingual named entity recognition from Wikipedia. Artif Intell 194:151–175
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
Malmasi S, Fang A, Fetahu B, Kar S, Rokhlenko O (2022) MultiCoNER: a large-scale multilingual dataset for complex named entity recognition. In: COLING. international committee on computational linguistics, pp 3798–3809
Malmasi S, Fang A, Fetahu B, Kar S, Rokhlenko O (2022) SemEval-2022 task 11: multilingual complex named entity recognition (MultiCoNER). In: SemEval@NAACL. association for computational linguistics, pp 1412–1437
Emelyanov AA, Artemova E (2019) Multilingual named entity recognition using pretrained embeddings, attention mechanism and NCRF. In: BSNLP@ACL. association for computational linguistics, pp 94–99
Arkhipov MY, Trofimova M, Kuratov Y, Sorokin A (2019) Tuning multilingual transformers for language-specific named entity recognition. In: BSNLP@ACL. association for computational linguistics, pp 89–93
Winata GI, Lin Z, Fung P (2019) Learning multilingual meta-embeddings for code-switching named entity recognition. In: RepL4NLP@ACL. association for computational linguistics, pp 181–186
Wu Q, Lin Z, Wang G, Chen H, Karlsson BF, Huang B, et al (2020) Enhanced meta-learning for cross-lingual named entity recognition with minimal resources. In: AAAI. AAAI Press, pp 9274–9281
Moon S, Neves L, Carvalho V (2018) Multimodal named entity recognition for short social media posts. In: NAACL-HLT. association for computational linguistics, pp 852–860
Zhao F, Li C, Wu Z, Xing S, Dai X (2022) Learning from different text-image pairs: a relation-enhanced graph convolutional network for multimodal NER. In: ACM multimedia. ACM,pp 3983–3992
Sun L, Wang J, Zhang K, Su Y, Weng F (2021) RpBERT: A text-image relation propagation-based BERT model for multimodal NER. In: AAAI. AAAI Press, pp 13860–13868
Zheng C, Wu Z, Wang T, Cai Y, Li Q (2021) Object-aware multimodal named entity recognition in social media posts with adversarial learning. IEEE Trans Multim 23:2520–2532
Li X, Kong D (2023) SRIF-RCNN: Sparsely represented inputs fusion of different sensors for 3D object detection. Appl Intell 53(5):5532–5553
Google Scholar
Wu Z, Zheng C, Cai Y, Chen J, Leung H, Li Q (2020) Multimodal representation with embedded visual guiding objects for named entity recognition in social media posts. In: ACM Multimedia. ACM, pp 1038–1046
Liu Y, Gu J, Goyal N, Li X, Edunov S, Ghazvininejad M et al (2020) Multilingual denoising pre-training for neural machine translation. Trans Assoc Comput Linguistics 8:726–742
Cohen J (1960) A Coefficient of agreement for nominal scales. Educational and psychological measurement 20(1):37–46
Oskouei AG, Balafar MA, Motamed C (2023) RDEIC-LFW-DSS: ResNet-based deep embedded image clustering using local feature weighting and dynamic sample selection mechanism. Inf Sci. 646:119374
Chen T, Kornblith S, Norouzi M, Hinton GE (2020) A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations. In: ICML. vol 119 of Proceedings of machine learning research. PMLR, pp 1597–1607
He K, Fan H, Wu Y, Xie S, Girshick RB (2020) Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual representation learning. In: CVPR. computer vision foundation / IEEE, pp 9726–9735
Radford A, Kim JW, Hallacy C, Ramesh A, Goh G, Agarwal S et al (2021) Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In: ICML, vol 139 of proceedings of machine learning research. PMLR, pp 8748–8763
Download references
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key R &D Program of China (No. 2023YFF0725600) and Major Special Funds of the Changsha Scientific and Technological Project (Grant No. kh2202006).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
The Department of Science and Technology Teaching, China University of Political Science and Law, Beijing, 102249, China
Dongsheng Wang
Mobvoi AI Lab, Beijing, 100044, China
Xiaoqin Feng
School of Computer Science and Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing, 100191, China
Institute of Information Engineering, CAS, Beijing, 100085, China
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Zeming Liu .
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Wang, D., Feng, X., Liu, Z. et al. 2M-NER: contrastive learning for multilingual and multimodal NER with language and modal fusion. Appl Intell (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-05490-2
Download citation
Accepted : 20 April 2024
Published : 09 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-05490-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Multilingual NER
- Multimodal NER
- Contrastive learning
- Multimodal interaction
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learn about the challenges and solutions of English language learning from a research paper that examines the traditional and innovative modes of teaching.
Research on Language Learning Strategies In the field of learning strategy research, language learning strategies can be defined as "strategies that contribute to the development of the language system which the learner constructs and affect learning directly" (Rubin, 1987, p. 23).
Introduction. Technology has become increasingly prevalent in language education (Palacious Hidalgo, Citation 2020), as evident with dedicated subfields from computer-assisted language learning (CALL; Gillespie, Citation 2020), mobile-assisted language learning (MALL; Elaish et al., Citation 2019), to technology-enhanced language learning (TELL; Shadiev & Yang, Citation 2020).
beliefs about English language learning, English language learning strategies, and the relationship of them. Descriptive and correlational design, quantitative methods were applied in this research. The students' final English scores of the first year, BALLI, and SILL were used as the instruments.
Teachers' kn owledge on. these strategies will help language learners in overcoming the problems of their learning. process. This survey study aims t o describe students' profile of strategic ...
Six of the included studies are informed by language learning strategies research, focusing on reading skills (Karimi & Dastgoshadeh, ... The second is that we limited ourselves to studies on English language learning. The rationale for this was pragmatic; the vast majority of papers in learner autonomy are on English learning and of those that ...
Language learning strategies have been a research focus since the mid-1970s, as strategic language learning is a key to successfully acquiring a foreign language (Rubin, 1975). A number of definitions of LLS have emerged, with one of the most influential having proved to be that of Rebecca Oxford, who not only established a conceptualization ...
Our specific research question we focus on in this paper is the following: ... C., and Incecay, G. (2016). "New directions in language learning strategy research: engaging with the complexity of strategy use," in New Directions in ... Rao, Z. (2016). Language learning strategies and English proficiency: interpretations from information ...
This study conducted a comprehensive historical review and bibliometric analysis of the literature on English-speaking (ES) education and mapped the current state of the field, trends, and emerging topics, as well as identified gaps where further research is needed. We retrieved 361 sample documents on ES teaching and learning in Scopus (2010-2021) under certain conditions and analyzed the ...
Statistically, about 2.4 articles per year were published over the 100-year period. Quantitatively, the figure strongly implies that the field is under-researched and needs a greater. number of ...
OUP ELT blog. We'll bring you resources you can use in your classrooms, hints and tips for teaching, insights into the lives of publishers and authors, and hopefully a few surprises you won't find on any other publisher blogs. Publishes research for all those involved in English Language Teaching. Content links the everyday concerns of ...
Literature review. In the 1990s, learning strategies attracted the attention of researchers involved in studying the acquisition of a second language (Ellis, Citation 1994; McDonough, Citation 1999).Oxford (Citation 1990) proposed that a strategy system is composed of learning behaviors, and other scholars studied the learning strategies used in English learning (Huang & Naerssen, Citation ...
The specific processes, techniques, and actions that learners take to facilitate their language learning have been widely explored under the concept of language learning strategies (LLS); however, more exploration is needed about recent investigations in this area, as calls for new theorization of strategies research have emerged. This systematic literature review aimed at exploring the ...
Originality/value. This research provides insights in developing policies to assist with the integration and utilization of social media platforms as instructional technologies in the context of English language teaching and learning and how institutions can respond to the advent of advancing technology, especially during and after the COVID-19 era.
1. Introduction. There is a growing body of literature that recognizes the importance of quality education for learners who study in a language other than their native language (Estrella et al., 2018; Ludwig et al., 2019).As cultural, racial, ethnic, and linguistic diversification takes place globally, the number of students studying a second language different from their native language is ...
The Language Learning Journal (LLJ) is an academic, peer-reviewed journal, providing a forum for research and scholarly debate on current aspects of foreign and second language learning and teaching. Its international readership includes foreign and second language teachers and teacher educators, researchers in language education and language acquisition, and educational policy makers.
the author's position on the topic of the research. The paper involves 3 sections. Section 1 introduces language acquisition. Language learning will be presented in Section The 2. synergy between language acquisition and language learning is presented in Section 3. Finally, some concluding remarks are provided.
SUBMIT PAPER. Language Teaching Research is a peer-reviewed journal that publishes research within the area of second or foreign language teaching. Although articles are written in English, the journal welcomes studies dealing with the teaching of languages other than English as well. The journal is a venue for studies that demonstrate sound ...
The SCOPUS database records show that before December 31, 2020, the journal published 1974 full-length articles (including empirical studies, conceptual papers, review studies, and notes), 1 including 208 articles (10.5% of the full-length articles) on the learning and teaching of LOTEs (See Table 1).As can be seen in Fig. 1 and Table 1, the number of articles related to LOTE is on the rise ...
For decades, AI applications in education (AIEd) have shown how AI can contribute to education. However, a challenge remains: how AIEd, guided by educational knowledge, can be made to meet specific needs in education, specifically in supporting learners' autonomous learning. To address this challenge, we demonstrate the process of developing an AI-applied system that can assist learners in ...
least preferred language learning strategies and how a) task requirement; b) age; and c) length of time learning English, affect their use of language learning strategies. In doing so, 108 students were asked to answer 50-item questionnaire (SILL) developed by Oxford in the late 90's for students who are studying English as a second language.
Reading helps students apply English in their daily interactions. Reading might be very beneficial for learning, according to Hashim et al. (2018).Based on the interview excerpts with the pupils ...
This exploratory study examined older adults' English learning motivation in the Chinese context of English as a foreign language (EFL) by conducting a web-based survey (n = 510) and semi-structured interviews (n = 21). Results showed that (1) the selected sociobiographical variables influenced older adults' English learning motivation to ...
Named entity recognition (NER) is a fundamental task in natural language processing that involves identifying and classifying entities in sentences into pre-defined types. It plays a crucial role in various research fields, including entity linking, question answering, and online product recommendation. Recent studies have shown that incorporating multilingual and multimodal datasets can ...
the language of the int ernet. n estimated 565 million. people use the internet every da y, and an estimated 52. percent of the world's most visited websites are. displayed in the English ...
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue.
Chinese Language and Culture. Environmental Science. Psychology. Friday, May 10, 2024. European History. ... English Language and Composition. African American Studies. Physics C: Mechanics. Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism ... AP Seminar and AP Research students to submit performance tasks as final and their presentations to be scored by ...
R. Meganathan*. Abstract. English language education in India is vast and complex. Research, both in school and. higher education during the curr ent and last decades r eflects the felt realities ...