- Scroll to top
- / Sign Up
- HOW WE HELP CLIENTS
- schedule your conversation

Strategic Planning Process Definition, Steps and Examples
Published: 03 January, 2024
Social Share:

Digital Strategy

Table of Contents
Organizations use Strategic Planning to gather all their stakeholders to evaluate the collection of current circumstances and decide upon their ongoing goals and benchmarks. They decide upon long-term objectives and establish a vision for the company’s future.
The efforts behind an organization’s Strategic Planning Processes are vital to its success, and yet, while many organizations acknowledge they need to do this kind of planning, they often don’t understand how to make it a reality. In this article, we explain the reasons behind Strategic Planning and how to make your Strategic Planning Process as powerful as possible.
What is a Strategic Plan
Strategic planning is a systematic process wherein the leaders of an organization articulate their vision for the future and delineate the goals and objectives that will guide the trajectory of the organization.
What is the Strategic Planning Process
Strategic planning is a process of defining an organization’s direction and making decisions on allocating its resources to pursue this direction . It involves creating a long-term plan that outlines the organization’s vision, mission, values, and objectives, as well as the strategies and tactics that will be used to achieve them.
Strategy is often misunderstood, which is surprising because fundamentally it’s a pretty basic concept. Strategy is a clearly expressed direction and a verified plan on how to get there. Your Strategic Planning Process formalizes the steps you’ll take to decide on your plan. The Strategic Planning Process facilitates using a Strategic Execution Framework that articulates where you’ll invest in innovation and where you can cut costs.
As far as business development planning is concerned, your Strategic Execution Framework is a vital tool for driving innovation, but first you must define the process you’ll undertake to determine how you and your team see the future of your organization. In this article, we discuss how to create your Strategic Plan and define its relationship to other concepts and documents that direct your business and its activities.

While it’s true that every business is different and must develop their own processes, we believe there are some process of strategic planning stepsthat benefit all organizations.
Below are our recommendations for the steps to take when undergoing your Strategic Planning Process, along with the questions we suggest you answer during each specific step.
Step One: Analyze your Business Environment
- Who are your competitors?
- What relevant market data do you have, and what do you still need?
- What technology has emerged that impacts your business model?
- How have customer expectations changed since your last Strategic Plan?
- What advantages do you have over competitors?
- Where is your company weaker compared to competitors?
- What predictable complications are on the horizon?
- Which unpredictable complications seem most likely or most potentially impactful?
Step Two: Set your Strategic Direction
- What is your overall Business Purpose ?
- How have your operations reflected your Purpose and Goals recently?
- How should your operations reflect your Purpose and Goals?
- Where do you see your business going in the next year?
- In two years? In three years?
- What are the metrics you’ll use to measure success?
- What are your make-or-break necessities?
Step Three: Set and develop Strategic Goals and Strategic Objectives
- Have you considered short-, mid-, and long-term business goals , and what are they?
- How do your Strategic Goals reflect your Mission Statement?
- How do your Strategic Goals reflect your company values and vision?
- What daily operations must be completed to work toward your Strategic Objectives?
- How will you communicate your Strategic Goals and Strategic Objectives?
- Who is responsible for reporting on success?
- How will strategic data be collected?
Related: Strategic Goals: Examples, Importance, Definitions and How to Set Them
Step Four: Drill down to Department-Level Objectives
- What are specific department concerns?
- How will your budget influence and be influenced by your Strategic Goals and Objectives?
- Which departments have resources that could be shared to better advantage?
- What roles do individual departments play in your overall Strategic Goals?
- What ongoing projects become a priority because of your new Strategic Goals?
- Are Departmental Objectives complementing each other and the overall Business Model?
Step Five: Manage and Analyze Performance
- Who is on the Strategic Planning team?
- Are tasks and job descriptions properly aligned to ensure the right work is getting completed?
- What is the schedule for the meeting for Strategic Planning?
- What are your metrics for measuring performance and success?
- Have you clearly articulated and shared KPIs?
- Who is responsible for gathering data?
- How will data be collected?
- How will data be reported?
- What’s at stake for strategy success or failure?
Step Six: Review and develop your Strategic Plan
- How should your Strategic Plan look on paper?
- What is your Strategy Execution Framework —how will you guarantee the Strategic Plan Team’s decisions are respected and executed?
- What is the review process?
- How often do you evaluate your Strategic Plan?
- How will you communicate your final Strategic Plan?
Strategic Planning Process Examples
1) apple strategic plan process.
- Vision and Mission: Apple’s strategic planning begins with a clear vision and mission. Apple’s vision is to create innovative products that inspire and enrich people’s lives.
- Environmental Analysis: Apple conducts thorough environmental analyses, considering technological trends, market demands, and competitive landscapes. This includes staying at the forefront of cutting-edge technologies.
- SWOT Analysis: Apple evaluates its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. For example, one of Apple’s strengths is its strong brand image, while a weakness might be dependence on a limited product line.
- Setting business Goals and Objectives: Apple sets specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals. This could include objectives like maintaining a certain market share, launching new products, or achieving specific financial targets.
- Strategies and Tactics: Apple develops strategies based on its goals. For instance, a strategic move might be expanding its ecosystem by integrating hardware, software, and services. Tactics could include aggressive marketing campaigns and product launches.
- Implementation and Execution: Apple’s strategic plans are meticulously executed. The launch of iconic products like the iPhone, iPad, and Mac series demonstrates effective implementation of their strategies.
- Monitoring and Adjusting: Apple constantly monitors its performance metrics, customer feedback, and market dynamics. If necessary, adjustments are made to the strategic plan to stay responsive to changing conditions.
2) Tesla Strategic Plan Process
- Vision and Mission: Tesla’s strategic planning revolves around its mission to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy. The vision includes producing electric vehicles and renewable energy solutions.
- Market Analysis: Tesla analyzes global markets for electric vehicles, renewable energy, and energy storage. This involves understanding regulatory environments, consumer behaviours, and technological advancements.
- Risk Assessment: Tesla conducts risk assessments related to manufacturing, supply chain, and market volatility. For instance, it considers risks associated with battery production and global economic conditions.
- Setting Bold Objectives: Tesla is known for setting ambitious objectives, such as achieving mass-market electric vehicle adoption and establishing a robust network of charging stations worldwide.
- Innovative Strategies: Tesla’s strategic planning involves innovation in technology and business models . For instance, the “Gigafactories” for mass production of batteries and the “Autopilot” feature in vehicles reflect innovative strategies.
- Agile Adaptation: Due to the rapidly changing automotive and energy sectors, Tesla maintains an agile approach. The company adapts its plans swiftly to capitalize on emerging opportunities, as seen in the expansion of its energy products.
- Continuous Improvement: Tesla places emphasis on continuous improvement. The iterative development of electric vehicle models, software updates, and advancements in battery technology showcase a commitment to refinement.
These examples demonstrate how strategic planning is a dynamic and integral part of the business processes of leading companies. They highlight the importance of a well-defined vision, rigorous analysis, adaptability, and innovation in the strategic planning process.
Tactical vs. Strategic Planning Process
An easy way to distinguish your company’s Tactical Planning from your Strategic Planning is to separate your wants from your HOWs.
In your Strategic Planning, you identify what you WANT for the company. These are big-picture dreams (achievable, but big ) that are your definition of success. In your Tactical Planning, you identify the HOW for reaching those dreams, including the smaller necessary steps.
Each kind of planning is vital for securing the organization’s future, but they require different sorts of attention and philosophy, and teams that are good at planning one way may not necessarily be good at the other kind of planning.
Strategic Planning vs. Your Business Purpose
Your Strategic Planning Process will of course be deeply connected to your Business Purpose .
We like to think of Business Purpose in broad terms, choosing especially to think of a business’s role in massive transformation. Embedded within a Business Purpose is the Business Plan that directs operations and how a company delivers value to its customers.
What is the relationship between your Strategic Planning and your Business Purpose? One feeds into the other. Your Business Purpose must point to a larger impact you’ll have on the people who purchase your goods and services, and your Strategic Planning takes into account how you’ll grow and expand that Purpose as you reach more customers more successfully.
Strategic Planning vs Business Planning
Strategic planning and business planning are two distinct processes that are often used interchangeably, but they have some key differences.
Strategic planning is a top-level process that focuses on determining the direction of an organization over the long term. It involves setting goals, determining the key resources and actions necessary to achieve those goals, and allocating those resources in a way that best serves the organization’s future. The outcome of strategic planning is typically a long-term strategic plan that outlines the organization’s vision, mission, values, and objectives.
Business planning , on the other hand, is a more tactical process that focuses on the implementation of specific initiatives and projects to support the organization’s long-term goals. Business plans typically outline the steps necessary to launch a new product, enter a new market, or achieve a specific objective. They may also include budgets, marketing plans, and other operational details.
In short, strategic planning is about setting the direction for an organization, while business planning is about implementing specific initiatives to support that direction. Both processes are important for the success of an organization and should be used in conjunction to ensure that resources are allocated effectively and that the organization is moving in the right direction.
Why is Strategic Planning Important?
Imagine this scenario: A warehouse full of goods sits, unsold and unmoved. A collection of brilliant people languishes at desks all day. Outside, the world spins and changes. It’s ready for what these people could do, can do, and yet nothing happens. Needs remain unmet. Progress is halted. Everyday life takes several backwards steps. This is what your business will look like without proper Strategic Planning.
Strategic Planning forces you to consider your Strategic Objectives and critically compare them to the resources you have available. As you continuously evaluate the circumstances of your business and your customers, your Strategic Plan evolves to match your goals and business capabilities.
The process involved pushes decision-makers to practice Strategic Thinking . It limits wasteful spending, especially when upper-level managers are willing to forgo pet projects in favor of operations with a broader use and appeal.
Strategic Planning is important because it directs your resources to efficiently meet your overall Business Goals. Without Strategic Planning, you are likely to waste resources, make conflicting decisions, or fail to grow your business to its greatest potential.
When Do You Create a Strategic Plan?
Most businesses find value in reviewing their Strategic Plan every three years. This allows enough time to pass that you can evaluate the success of previous plans, reflect on the achievement of your Strategic Goals, consider developments outside your organization that affect your business, and begin formulating new goals that will become the next version of your plans.
When businesses first begin, they often have too many fires burning at once. They remain focused on existing today rather than planning for tomorrow. Most entrepreneurs remember those stressful early days of starting their businesses and can understand why formalities like Strategic Plans can fall by the wayside. We believe if your business lasts longer than a year it’s important to develop a plan for the future. Think of Strategic Planning as a celebration of a first anniversary—a sign that you’re poised to continue moving forward for years to come.
However, Strategic Planning is not a one-off event that is over once the cookies are all gone and the room clears. Your Strategic Planning team should meet regularly to measure how effective the plans are at helping you reach your Strategic Goals. Ad hoc subcommittees can play a role in gathering evidence to ensure that your plans remain appropriate, especially if conditions change.
For example, we recommended a close review of Strategic Plans and Strategic Goals once the COVID-19 pandemic made it clear that business was going to be affected at least short- to mid-term. We continue to recommend teams regularly revisit their Strategic Plans with global circumstances in mind to recognize opportunities and prepare for challenges.
The Benefits of Strategic Planning
As we’ve mentioned, there are many benefits of Strategic Planning . Some of those benefits include:
- Shared sense of power and importance
- United direction
- Clear path and purpose for decision-making and operations
- Boosted operational effectiveness
- Responsible, efficient use of available resources
- Meaningful work done on a daily basis
- Tracking of progress
- Ability to adjust to changing circumstances
What is a business without Strategic Planning? In most cases, it’s not much, nor is it long for the world. While it’s possible to accidentally find success without much planning, most successful businesses are a result of careful thought mixed with the urge to pounce on the opportunity.
What prepares you to pounce?
Your Strategic Planning and the processes that make it possible.
The UNITE Business Model Framework: A Framework for Innovation Success

Examples and Types of Effective Functional Level Strategy for Business Support
A key objective of any business strategy is to improve operational efficiencies...

The Three Levels of Strategy: Corporate Strategy, Business Strategy, and Functional Strategy
Understanding the intricate levels of strategy is crucial for any organization aiming...
- FREE LIVE TRAINING
How To Overcome The 90% Failure Rate in Innovation
Learn the winning formula from over 80+ successful innovation projects
SAVE MY FREE SPOT NOW

Learn how to overcome the 90% failure rate in innovation from a master innovator & bestselling author!
Your e-mail address: * Your first name: *

One Last Step..
Help us better understand the UNITE community
Free guide to improve your innovation success rate*
Our 35-page comprehensive innovation guide covers the key areas why innovation fails. While it cannot cover all the solutions (that would take books to fill), it provides you with a convenient starting point for your analysis and provides further resources and links to the corresponding UNITE models, ultimately allowing you to work towards a doubling and tripling your chances of success.

Discover the largest library of innovation & transformation tools on the entire Internet!
LOG IN VIA E-MAIL
Forgot password?
New to Digital Leadership? Create your account

Get access to the UNITE Models now!
Discover the largest library of innovation & transformation tools on the internet!
First name *
Last name *
Professional E-mail *
Choose Your Password *
Confirm Your Password *
I want to be kept up-to-date and accept the privacy statement *
By signing up, you agree to receive news and accept the privacy statement (mandatory)
Already have an account? Log in
Verify your e-mail address now by entering the 6-digit code we’ve just sent to your inbox
Don't receive Code? Resend code
Country * Please Select Afghanistan Albania Algeria Andorra Angola Antigua and Barbuda Argentina Armenia Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belarus Belgium Belize Benin (Dahomey) Bolivia Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana Brazil Brunei Brunswick and Lüneburg Bhutan Bulgaria Burkina Faso (Upper Volta) Burundi Cabo Verde Cambodia Cameroon Canada Cayman Islands Central African Republic Central American Federation Chad Chile China Colombia Comoros Congo Free State Costa Rica Cote d’Ivoire (Ivory Coast) Croatia Cuba Cyprus Czechia Democratic Republic of the Congo Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic Ecuador Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Eswatini Ethiopia Fiji Finland France Gabon Gambia Georgia Germany Ghana Grand Duchy of Tuscany Greece Grenada Guatemala Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Holy See Honduras Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iran Iraq Ireland Israel Italy Jamaica Japan Jordan Kazakhstan Kenya Kiribati Korea Kosovo Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Laos Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Libya Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Marshall Islands Mauritania Mauritius Mexico Micronesia Moldova Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Morocco Mozambique Myanmar Namibia Nassau Nauru Nepal Netherlands New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria North Macedonia Norway Oman Pakistan Palau Panama Papal States Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Piedmont-Sardinia Poland Portugal Qatar Republic of Congo Republic of Korea (South Korea) Republic of the Congo Romania Russia Rwanda Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Samoa San Marino Sao Tome and Principe Saudi Arabia Schaumburg-Lippe Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Slovakia Slovenia Solomon Islands Somalia South Africa South Sudan Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Sweden Switzerland State of Palestine Syria Tajikistan Tanzania Thailand Timor-Leste Togo Tonga Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Tuvalu Uganda Ukraine United States United Arab Emirates United Kingdom Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Venezuela Vietnam Württemberg Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe Industry * Please Select Automotive, mobilty & transport Financial Services Chemical & agriculture Construction & Real Estate Consulting Education Energy Banking, insurance & FS FMCG Food Gov / Public Industry Health & lifestyle Logistics, Aero & Shipping Media & Entertainment Natural resources & mining Pharma & Biotech Retail & trade Tech & E-Commerce Telco Tourism design Information technology & services Management consulting Retail Pharmaceuticals International trade & development Professional training & coaching luxury goods & jewelry Automotive Insurance Mechanical or industrial engineering Company Size * XS - 1-10 S - 10-100 M - 100-1000 L - 1000-5000 XL - > 5000
Seniority * Please Select Junior Consultant Senior Consultant Manager Senior Manager Director VP SVP Partner CXO Board Member
Areas of interest * Innovation Digital Transformation Culture & Organization IT Strategy & Bus. Alignment Customer Experience
Editable UNITE models (PowerPoint) included
Most of our models and canvases are designed to be applied!
To help you personalize them to your exact business requirements, you can download fully editable versions of the UNITE models available (PowerPoint format)!
They are straightforward to work with, and you can directly incorporate them into your presentations as you need…thus saving countless hours of replication!
PS: did you know that you are also getting hi-res print-ready versions for your workshops?
Monthly live webinars
Each month we host our exclusive, invitation-only webinar series where one of our industry-leading experts updates our members on the latest news, progress and concepts around business strategy, innovation and digital transformation, as well as other related topics.
You will receive the book in PDF and EPUB formats, ideal for your computer, Kindle, Tablet or other eReading device.
Bi-weekly live group Q&A sessions
These sessions are your opportunity to bring any questions or challenges you’re facing and receive expert guidance on the spot.
Come and be a part of engaging discussions where your unique concerns are heard and addressed.
1x personal coaching session / month
If you are occasionally looking for a sparring partner or you need limited support, then this option will be ideal for you. Coaching sessions are 1-2 hours where we can discuss any challenge or opportunity you are currently facing.
If you need a few more hours outside of this provision, then these could be billed transparently.
Unlimited video call support! – it’s like always making the right decision!
We believe support shouldn’t be limited. Because we typically find that the occasional hour just doesn’t cut it – particularly if you and your team are in the midst of a large and complex project.
Your time with Stefan is therefore unlimited (fair usage applies) – in his function as coach and sparring partner. That does mean that you will still have to do the work – we cannot take that off you, unless you hire us as consultants. But you will get valuable strategic insight and direction to make sure you are always focusing your efforts where they will lead to the best results.
One personal coaching session / month + unlimited support via e-mail & WhatsApp
We believe support shouldn’t be limited. If you generally know what you are doing but want a sparring partner to frequently raise questions to, this is the perfect choice!
In addition to your monthly 1-1 live coaching sessions with Stefan, you will also get unlimited support from him via email and WhatsApp messaging (fair usage applies). This not only allows you to get valuable strategic direction in your calls, but also gives you instant access to expert help as you work through your plans each month.
The fact that support is text-based means that we can speed up our responses to you while keeping the overall cost of support down.
Welcome gift of our book “How to Create Innovation” (digital + physical editions)*
As a welcome gift, you will receive the both the digital and physical version of our book “How to Create Innovation”, which covers numerous relevant resources and provides additional deep dives into our UNITE models and concepts.
The print version will be shipped out to you on sign-up. The digital version will be emailed to you, and comes in PDF and EPUB formats, ideal for your computer, Kindle, Tablet or other eReading device.
1x major workshop or 2x smaller workshops / month
1x major or 2x smaller workshops based on the UNITE models.
- Topics covered: almost any challenge under the header of #strategy, #innovation or #transformation, leveraging the UNITE models.
- Hands-On Learning: solve your challenges while learning the practical application of the UNITE models and walk away with concrete plans and tools to take your next steps.
- Industry thought leadership: facilitated by Stefan, the founder of Digital Leadership and the main author of the UNITE models, ensuring top-tier guidance and knowledge sharing.
- Collaborative approach: engage in interactive sessions that foster collaboration, idea exchange, and real-time problem-solving among peers and industry leaders.
- Continuous Improvement: Regular workshops ensure ongoing development in your organization staying ahead of industry trends and customer needs.
Access all of our UNITE models, (incl. editable & print versions)
All of our Professional plans offer full access to the following:
- 6x UNITE model package downloads are included per month, if you need something in addition to these however, please let us know!
- Hi-res, print-ready versions you can use in your workshops
- Fully editable PowerPoint versions where applicable – personalize to your needs.
- Exclusive access to our vault of never-before-published strategic materials. We have much more to share – a lot of our concepts have never been published!
Exclusive access to our private UNITE community (upcoming)
We are currently in the process of launching our brand new community., we are designing our community to specifically help you:.
- Get answers to questions (“How do I …”)
- Share leading practices & knowledge
- Jointly develop new models
- Network amongst a highly qualified group of peers
Please, select the reason
Cancelling your plan will deactivate your plan after the current billing period ends. You will not be charged further, but also won’t be able to access [exclusive features/services].
- Cost-related issues
- Unsatisfied with the service
- Features I need are missing
- Switching to a different service
- Other (Please specify)
Book Your Initial Blueprint Session Now
Simply fill out the below form and book in a time for our initial session that works for you. This initial session is free, no strings attached, and is where we can discuss your Blueprint needs more in-depth before moving forward.

Stefan F. Dieffenbacher
Founder of digital leadership.

Adam D. Wisniewski
Partner for it strategy & business alignment.

Get in touch with Digital Leadership
Speak to our team today to find the best solution for your business to grow and scale.
We are here to support you across the entire lifecycle in all topics related to #digital, #innovation, #transformation and #marketing!

Stefan F. Dieffenbacher Founder of Digital Leadership
Contact Us!
Contact form, contact details, book a call.
Title, first name & last name * Email address * Phone number Please let us know how we can best support you! *
By clicking “Send”, I agree to Terms of Service and Privacy Policy.
Let’s have a conversation!
“Please be invited to reach out! We are happy to help and look forward to a first meeting!”
+41 (0) 44 562 42 24
Schedule Your Call With Our Team
Find a time on our calender that best suits you !

Founder and CEO of Digital Leadership
SCHEDULE YOUR INITIAL CALL
A Quick Survey!
What is the main challenge you're currently facing in your business?
You Want To Drive Change?
Let’s find the best solution for your business to grow and scale sustainably!
Let’s kick start it!
We will uncover your current business situation and goals and provide you with a bespoke solution that helps you drastically grow your business working with us.

Stefan F. Dieffenbacher, M.B.A.

Feedback about our consulting that we are proud of
Read the reviews and make sure that this is not a waste of time, but a super effective tool.

You want to drive change?
Schedule your free business assessment call with our founder.
On this call, we will uncover your current business situation and goals and talk about how to drive change and solve your need.
Choose the meeting type that applies to your needs and schedule a time to meet with someone from our team. We look forward to speaking with you soon!
Thanks, We’ve Received Your Updated Details

Schedule Your Free Business Assessment

Schedule Your Free Business Assessment Call With Adam D. Wisniewski
Welcome to our scheduling page.

Let’s Design your Customer Experience Blueprint !
In a uniquely designed 60 or 90 minute session* , we will …
- > identify where to start with near-certainty
- > define what approach it takes to create success in your organization
Based on the Blueprinting session, you will receive a tailored blueprint that aligns with your objectives, vision and goals, ensuring that your initiative is a success from start to finish.

In this session, you will be working together with Patrick Zimmermann, Associate Partner for Customer Experience

Let’s Design your Culture & Org-Change Blueprint !

In this session, you will be working together with Dr. Andreas Rein, Partner at Digital Leadership for Culture & Org Change
Let’s Design your Innovation Blueprint !

In this session, you will be working together with Sascha Martini, Partner at Digital Leadership for Innovation and Digital Transformation
Let’s Design your Transformation Blueprint !

In this session, you will be working together with Stefan F. Dieffenbacher, Founder of Digital Leadership Stefan is a global thought leader in the innovation space
Let’s Design your IT Strategy & Business Alignment Blueprint !

In this session, you will be working together with Adam D. Wisniewski, Partner for IT Strategy & Business Alignment

Patrick Zimmermann

Sascha Martini

Dr. Andreas Rein
Write a personalized review! Log in
Create Review

Strategic Planning Process: Why Is Strategic Planning Important for Organizations in 2024?

What to read next:
Playing chess without a strong opening is a guaranteed way to disadvantage yourself. Just like in chess, organizations without an adequate strategic planning process are unlikely to thrive and adapt long-term.
The strategic planning process is essential for aligning your organization on key priorities, goals, and initiatives, making it crucial for organizational success.
This article will empower you to craft and perfect your strategic planning process by exploring the following:
- What is strategic planning
- Why strategic planning is important for your business
- The seven steps of the strategic planning process
Strategic planning frameworks
- Best practices supporting the strategic planning process
By the end of this article, you’ll have the knowledge needed to perfect the key elements of strategic planning. Ready? Let’s begin.
What is strategic planning?
Strategic planning charts your business's course toward success. Using your organization’s vision, mission statement , and values — with internal and external information — each step of the strategic planning process helps you craft long-term objectives and attain your goals with strategic management.
The key elements of strategic planning includes a SWOT analysis, goal setting , stakeholder involvement, plus developing actionable strategies, approaches, and tactics aligned with primary objectives.
In short, the strategic planning process bridges the gap between your organization’s current and desired state, providing a clear and actionable framework that answers: Where are you now? Where do you want to be? How will you get there?
7 key elements of strategic planning
The following strategic planning components work together to create cohesive strategic plans for your business goals. Let’s take a close look at each of these:
- Vision : What your organization wants to achieve in the future, the long-term goal
- Mission : The driving force behind why your company exists, who it serves, and how it creates value
- Values : Fundamental beliefs guiding your company’s decision-making process
- Goals : Measurable objectives in alignment with your business mission, vision, and values
- Strategy : A long-term strategy map for achieving your objectives based on both internal and external factors
- Approach : How you execute strategy and achieve objectives using actions and initiatives
- Tactics : Granular short-term actions, programs, and activities
Why is the strategic planning process important?
Just as a chess player needs a gameplan to reach checkmate, a company needs a solid strategic plan to achieve its goals.
Without a strategic plan, your business will waste precious time, energy, and resources on endeavors that won’t get your company closer to where it needs to be.
Your ideal plan should cover all key strategic planning areas, while allowing you to stay present by measuring success and course-correcting or redefining the strategic direction when necessary. Ultimately, enabling your company to stay future-proof through the creation of an always-on strategy that reflects your company's mission and vision.
An always-on strategy involves continuous environmental scanning even after the strategic plan has been devised, ensuring readiness to adapt in response to quick, drastic changes in the environment.
Let’s dive deeper into the steps of the strategic planning process.
What are the 7 stages of the strategic planning process?
You understand the overall value of implementing a strategic planning process — now let’s put it in practice. Here's our 7-step approach to strategic planning that ensures everyone is on the same page:
- Clarify your vision, mission, and values
- Conduct an environmental scan
- Define strategic priorities
- Develop goals and metrics
- Derive a strategic plan
- Write and communicate your strategic plan
- Implement, monitor, and revise
1. Clarify your vision, mission, and values
The first step of the strategic planning process is understanding your organization’s core elements: vision, mission, and values. Clarifying these will align your strategic plan with your company’s definition of success. Once established, these are the foundation for the rest of the strategic planning process.
Questions to ask:
- What do we aspire to achieve in the long term?
- What is our purpose or ultimate goal?
- What do we do to fulfill our vision?
- What key activities or services do we provide?
- What are our organization's ethics?
- What qualities or behaviors do we expect from employees?
Read more: What is Mission vs. Vision

2. Conduct an environmental scan
Once everyone on the same page about vision, mission, and values, it's time to scan your internal and external environment. This involves a long-term SWOT analysis, evaluating your organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Internal factors
Internal strengths and weaknesses help you understand where your organization excels and what it could improve. Strengths and weaknesses awareness helps make more informed decisions with your capabilities and resource allocation in mind.
External factors
Externally, opportunities and threats in the market help you understand the power of your industry’s customers, suppliers, and competitors. Additionally, consider how broader forces like technology, culture, politics, and regulation may impact your organization.
- What are our organization's key strengths or competitive advantages?
- What areas or functions within our organization need improvement?
- What emerging trends or opportunities can we leverage?
- How do changes in technology, regulations, or consumer behavior impact us?
3. Define strategic priorities
Prioritization puts the “strategic” in strategic planning process. Your organization’s mission, vision, values, and environmental scan serve as a lens to identify top priorities. Limiting priorities ensures your organization intentionally allocates resources.
These categories can help you rank your strategic priorities:
- Critical : Urgent tasks whose failure to complete will have severe consequences — financial losses, reputation damage, or legal consequences
- Important : Significant tasks which support organizational achievements and require timely completion
- Desirable : Valuable tasks not essential in the short-term, but can contribute to long-term success and growth
- How do these priorities align with our mission, vision, and values?
- Which tasks need to be completed quickly to ensure effective progress towards our desired outcomes?
- What resources and capabilities do we need to pursue these priorities effectively?
4. Develop goals and metrics
Next, you establish goals and metrics to reflect your strategic priorities. Purpose-driven, long-term, actionable strategic planning goals should flow down through the organization, with lower-level goals contributing to higher-level ones.
One approach that can help you set and measure your aligned goals is objectives and key results (OKRs). OKRs consist of objectives, qualitative statements of what you want to achieve, and key results, 3-5 supporting metrics that track progress toward your objective.
OKRs ensure alignment at every level of the organization, with tracking and accountability built into the framework to keep everyone engaged. With ambitious, intentional goals, OKRs can help you drive the strategic plan forward.
- What metrics can we use to track progress toward each objective?
- How can we ensure that lower-level goals and metrics support and contribute to higher-level ones?
- How will we track and measure progress towards key results?
- How will we ensure accountability?
Get an in-depth look at OKRs with our Ultimate OKR Playbook

5. Derive a strategic plan
The next step of the strategic planning process gets down to the nitty-gritty “how” — developing a clear, practical strategic plan for bridging the gap between now and the future.
To do this, you’ll need to brainstorm short- and long-term approaches to achieving the goals you’ve set, answering a couple of key questions along the way. You must evaluate ideas based on factors like:
- Feasibility : How realistic and achievable is it?
- Impact : How conducive is it to goal attainment?
- Cost : Can we fund this approach, and is it worth the investment?
- Alignment : Does it support our mission, vision, and values?
From your approaches, you can devise a detailed action plan, which covers things like:
- Timelines : When will we take each step, and what are the deadlines?
- Milestones : What key achievements will ensure consistent progress?
- Resource requirements : What’s needed to achieve each step?
- Responsibilities : Who's accountable in each step?
- Risks and challenges : What can affect our ability to execute our plan? How will we address these?
With a detailed action plan like this, you can move from abstract goals to concrete steps, bringing you closer to achieving your strategic objectives.
6. Write and communicate your strategic plan
Writing and communicating your strategic plan involves everyone, ensuring each team is on the same page. Here’s a clear, concise structure you can use to cover the most important strategic planning components:
- Executive summary : Highlights and priorities in your strategic overview
- Introduction : Background on your strategic plan
- Connection : How your strategic plan aligns with your organization’s mission, vision, and values
- Environmental scan : An overview of your SWOT analysis findings
- Strategic priorities and goals : Informed short and long-term organizational goals
- Strategic approach : An overview of your tactical plan
- Resource needs : How you'll deploy technology, funding, and employees
- Risk and challenges : How you’ll mitigate the unknowns if and when they arise
- Implementation plan : A step-by-step resource deployment plan for achieving your strategy
- Monitoring and evaluation : How you’ll keep your plan heading in the right direction
- Conclusion : A summary of the strategic plan and everything it entails
- What information or context do stakeholders need to understand the strategic plan?
- How can we emphasize the connection between the strategic plan and the overall purpose and direction of the organization?
- What initiatives or strategies will we implement to drive progress?
- How will we mitigate or address risks?
- What are the specific steps and actions we need to take to implement the strategic plan?
- Any additional information or next steps we need to communicate?
7. Implement, monitor, and revise performance
Finally, it’s time to implement your strategic plan, making sure it's up to date, creating a persistent, always-on strategy that doesn't lag behind. As you get the ball rolling, keep a close eye on your timelines, milestones, and performance targets, and whether these align with your internal and external environment.
Internally, indicators like completions, issues, and delays provide visibility into your process. If any bottlenecks, inefficiencies, or misalignment arises, take corrective action promptly — adjust the plan, reallocate resources, or provide additional training to employees.
Externally, you should monitor changes such as customer preferences, competitive pressures, economic shifts , and regulatory changes. These impact the success of your strategic action plan and may require tweaks along the way.
Remember, implementing a strategic plan isn’t a one-time task — continual evaluation is essential for an always-on strategy. It involves extending beyond planning stages and contextualizing the strategy in real-time, allowing for swift adaptations to changing circumstances to ensure your plan remains relevant.
- Are there any bottlenecks, inefficiencies, or misalignments we need to address?
- Are we monitoring and analyzing external factors?
- Are we prepared to make necessary tweaks or adaptations along the way?
- Are we agile enough to promptly correct deviations from our strategic plan while maintaining an "always-on" strategy for continual adjustments?
You can use several frameworks to guide you through the strategic planning process. Some of the most influential ones include:
- Balanced scorecard (BSC) : Takes an overarching approach to strategic planning, covering financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth, aligning short-term operational tasks with long-term strategic goals.
- SWOT analysis : Highlights your business's internal strengths and weaknesses alongside external opportunities and threats to enable informed decisions about your strategic direction.
- OKRs : Structures goals as a set of measurable objectives and key results. They cascade down from top-level organizational objectives to lower-level team goals, ensuring alignment across the entire organization. Get an in-depth look at OKRs here .
- Scenario planning : Involves envisioning and planning for various possible future scenarios, allowing you to prepare for a range of potential outcomes. It's particularly useful in volatile environments rife with uncertainties.
- Porter's five forces : Evaluates the competitive forces within your industry — rivalry among existing competitors, bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, threat of new entrants, and threat of substitutes — to shape strategies that position the organization for success.

Common problems with strategic planning and how to overcome them
While strategic planning provides a roadmap for business success, it's not immune to challenges. Recognizing and addressing these is crucial for effective strategy implementation. Let's explore common issues encountered in strategic planning and strategies to overcome them.
Static nature
Traditional strategic planning models often follow a linear, annual, and inflexible process that doesn't accommodate quick changes in the business landscape. Strategies formulated this way may quickly become outdated in today's fast-paced environment.
To overcome the rigidity of traditional strategic planning, your organization should integrate continuous environmental scanning processes. This includes monitoring market changes, competitor actions, and technological advancements, ensuring real-time insights inform strategic decision-making. Additionally, adopting agile methodologies allows for iterative planning, breaking down strategies into smaller, manageable components reviewed and adjusted regularly, ensuring adaptability in today's fast-paced landscape.
Disconnect between strategic plan and execution
There's often a significant gap between the strategic objectives and their actual implementation, leading to misalignment, confusion, and inefficiency within the organization.
To bridge the gap, ensure accountability, alignment, and feedback-driven processes across the business. Linking team roles and responsibilities to lower-level objectives can fosters alignment and accountability, whereas aligning these with overarching strategic objectives ensure coherence in execution. To ensure goals are optimized on an ongoing basis, implement a feedback mechanism that continuously evaluates progress against goals, enabling regular adjustments based on market feedback and internal insights.
Lack of real-time insights
Traditional planning models rely on historical data and periodic reviews, which might not capture real-time changes or emerging trends accurately. This can result in misaligned strategies unsuitable for the current business landscape.
Leverage advanced analytics tools and AI-driven technologies. Invest in technologies that offer real-time tracking and reporting of key performance indicators, with dashboards and monitoring systems that provide up-to-date insights. These allow you to gather, process, and interpret real-time data for proactive decision-making that aligns with the current business landscape.
Failure to close the feedback loop
The absence of a feedback loop between strategy formulation, execution, and evaluation can impact learning and improvement. Companies might therefore struggle to refine their strategies based on real-time performance insights.
Establish a structured feedback loop encompassing strategy formulation, execution, and evaluation stages. Encourage employees to actively contribute insights on strategy execution, fostering a culture of continuous improvement and adaptation.
Best practices during the strategic planning process
Navigating strategic planning goes beyond overcoming challenges. A successful strategic plan requires you to embrace a set of guiding best practices, helping you navigate the development and implementation of your strategic planning process.
1. Keep the planning process flexible
With ever-changing business environments, a one-and-done approach to strategic planning is insufficient. Your strategic plan needs to be adaptable to ensure its relevancy and its ability to weather the effects of changing circumstances.
2. Pull together a diverse group of stakeholders
By including voices from across the organization, you can account for varying thoughts, perspectives, and experiences at each step of the strategic planning process, ensuring cross-functional alignment .
3. Document the process
Continuous documentation of the strategic management process is crucial in capturing and communicating the key elements of strategic planning. This keeps everyone on the same page and your strategic plan up-to-date and relevant.
4. Make data-driven decisions
Root your decisions in evidence and facts rather than assumptions or opinions. This cultivates accurate insights, improves prioritization, and reduces biased (flawed) decisions.
5. Align your company culture with the strategic plan
Your strategic plan can only be successful if everyone is on board with it — company culture supports what you’re trying to achieve. Behaviors, rules, and attitudes optimize the execution of your strategic plan.
6. Leverage AI
Using AI in strategic planning supports the development of an always-on strategy — amplifying strategic agility, conducting comprehensive environmental scans, and expediting planning phases. It can streamline operations, facilitate data-driven decision-making, and provide transparent insights into progress to drive accountability, engagement, and alignment with the strategic plan.
The strategic planning process in a nutshell
Careful strategy mapping is crucial for any organization looking to achieve its long-term goals while staying true to its mission, vision, and values. The seven steps in the strategic planning process outlined in this article provide a solid framework your organization can follow — from clarifying your organization’s purpose and developing a strategic plan, to implementing, monitoring, and revising performance. These steps will help your company meet goal measurements and create an always-on strategy that's rooted in the present.
It’s important to remember that strategic planning is not a one-time event. To stay effective and relevant, you must continuously monitor and adapt your strategy in response to changing circumstances. This ongoing process of improvement keeps your organization competitive and demonstrates your commitment to achieving your goals.
Quantive empowers modern organizations to turn their ambitions into reality through strategic agility. It's where strategy, teams, and data come together to drive effective decision-making, streamline execution, and maximize performance.
As your company navigates today’s competitive landscape, you need an Always-On Strategy to continuously bridge the gap between current and desired business outcomes. Quantive brings together the technology, expertise, and passion to transform your strategy from a static plan to a feedback-driven engine for growth.
Whether you’re a visionary start-up, a mid-market business looking to conquer, or a large enterprise facing disruption, Quantive keeps you ahead — every step of the way. For more information, visit www.quantive.com .
Additional resources
How top companies are closing the strategy execution gap, strategy execution in 4 steps: keys to successful strategy, 7 best practices for strategy execution, why your business needs strategy execution software, subscribe for our newsletter.
The Strategic Planning Process in 4 Steps
To guide you through the strategic planning process, we created this 4 step process you can use with your team. we’ll cover the basic definition of strategic planning, what core elements you should include, and actionable steps to build your strategic plan..
Free Strategic Planning Guide
What is Strategic Planning?
Strategic Planning is when a process where organizations define a bold vision and create a plan with objectives and goals to reach that future. A great strategic plan defines where your organization is going, how you’ll win, who must do what, and how you’ll review and adapt your strategy development.
A strategic plan or a business strategic plan should include the following:
- Your organization’s vision organization’s vision of the future.
- A clearly Articulated mission and values statement.
- A current state assessment that evaluates your competitive environment, new opportunities, and new threats.
- What strategic challenges you face.
- A growth strategy and outlined market share.
- Long-term strategic goals.
- An annual plan with SMART goals or OKRs to support your strategic goals.
- Clear measures, key performance indicators, and data analytics to measure progress.
- A clear strategic planning cycle, including how you’ll review, refresh, and recast your plan every quarter.

Overview of the Strategic Planning Process:
The strategic management process involves taking your organization on a journey from point A (where you are today) to point B (your vision of the future).
Part of that journey is the strategy built during strategic planning, and part of it is execution during the strategic management process. A good strategic plan dictates “how” you travel the selected road.
Effective execution ensures you are reviewing, refreshing, and recalibrating your strategy to reach your destination. The planning process should take no longer than 90 days. But, move at a pace that works best for you and your team and leverage this as a resource.
To kick this process off, we recommend 1-2 weeks (1-hour meeting with the Owner/CEO, Strategy Director, and Facilitator (if necessary) to discuss the information collected and direction for continued planning.)

Questions to Ask:
- Who is on your Planning Team? What senior leadership members and key stakeholders are included? Checkout these links you need help finding a strategic planning consultant , someone to facilitate strategic planning , or expert AI strategy consulting .
- Who will be the business process owner (Strategy Director) of planning in your organization?
- Fast forward 12 months from now, what do you want to see differently in your organization as a result of your strategic plan and implementation?
- Planning team members are informed of their roles and responsibilities.
- A strategic planning schedule is established.
- Existing planning information and secondary data collected.
Action Grid:

Step 1: Determine Organizational Readiness
Set up your plan for success – questions to ask:
- Are the conditions and criteria for successful planning in place at the current time? Can certain pitfalls be avoided?
- Is this the appropriate time for your organization to initiate a planning process? Yes or no? If no, where do you go from here?
Step 2: Develop Your Team & Schedule
Who is going to be on your planning team? You need to choose someone to oversee the strategy implementation (Chief Strategy Officer or Strategy Director) and strategic management of your plan? You need some of the key individuals and decision makers for this team. It should be a small group of approximately 12-15 people.
OnStrategy is the leader in strategic planning and performance management. Our cloud-based software and hands-on services closes the gap between strategy and execution. Learn more about OnStrategy here .
Step 3: Collect Current Data
All strategic plans are developed using the following information:
- The last strategic plan, even if it is not current
- Mission statement, vision statement, values statement
- Past or current Business plan
- Financial records for the last few years
- Marketing plan
- Other information, such as last year’s SWOT, sales figures and projections
Step 4: Review Collected Data
Review the data collected in the last action with your strategy director and facilitator.
- What trends do you see?
- Are there areas of obvious weakness or strengths?
- Have you been following a plan or have you just been going along with the market?
Conclusion: A successful strategic plan must be adaptable to changing conditions. Organizations benefit from having a flexible plan that can evolve, as assumptions and goals may need adjustments. Preparing to adapt or restart the planning process is crucial, so we recommend updating actions quarterly and refreshing your plan annually.

Strategic Planning Phase 1: Determine Your Strategic Position
Want more? Dive into the “ Evaluate Your Strategic Position ” How-To Guide.
Action Grid
Step 1: identify strategic issues.
Strategic issues are critical unknowns driving you to embark on a robust strategic planning process. These issues can be problems, opportunities, market shifts, or anything else that keeps you awake at night and begging for a solution or decision. The best strategic plans address your strategic issues head-on.
- How will we grow, stabilize, or retrench in order to sustain our organization into the future?
- How will we diversify our revenue to reduce our dependence on a major customer?
- What must we do to improve our cost structure and stay competitive?
- How and where must we innovate our products and services?
Step 2: Conduct an Environmental Scan
Conducting an environmental scan will help you understand your operating environment. An environmental scan is called a PEST analysis, an acronym for Political, Economic, Social, and Technological trends. Sometimes, it is helpful to include Ecological and Legal trends as well. All of these trends play a part in determining the overall business environment.
Step 3: Conduct a Competitive Analysis
The reason to do a competitive analysis is to assess the opportunities and threats that may occur from those organizations competing for the same business you are. You need to understand what your competitors are or aren’t offering your potential customers. Here are a few other key ways a competitive analysis fits into strategic planning:
- To help you assess whether your competitive advantage is really an advantage.
- To understand what your competitors’ current and future strategies are so you can plan accordingly.
- To provide information that will help you evaluate your strategic decisions against what your competitors may or may not be doing.
Learn more on how to conduct a competitive analysis here .
Step 4: Identify Opportunities and Threats
Opportunities are situations that exist but must be acted on if the business is to benefit from them.
What do you want to capitalize on?
- What new needs of customers could you meet?
- What are the economic trends that benefit you?
- What are the emerging political and social opportunities?
- What niches have your competitors missed?
Threats refer to external conditions or barriers preventing a company from reaching its objectives.
What do you need to mitigate? What external driving force do you need to anticipate?
Questions to Answer:
- What are the negative economic trends?
- What are the negative political and social trends?
- Where are competitors about to bite you?
- Where are you vulnerable?
Step 5: Identify Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths refer to what your company does well.
What do you want to build on?
- What do you do well (in sales, marketing, operations, management)?
- What are your core competencies?
- What differentiates you from your competitors?
- Why do your customers buy from you?
Weaknesses refer to any limitations a company faces in developing or implementing a strategy.
What do you need to shore up?
- Where do you lack resources?
- What can you do better?
- Where are you losing money?
- In what areas do your competitors have an edge?
Step 6: Customer Segments

Customer segmentation defines the different groups of people or organizations a company aims to reach or serve.
- What needs or wants define your ideal customer?
- What characteristics describe your typical customer?
- Can you sort your customers into different profiles using their needs, wants and characteristics?
- Can you reach this segment through clear communication channels?
Step 7: Develop Your SWOT
A SWOT analysis is a quick way of examining your organization by looking at the internal strengths and weaknesses in relation to the external opportunities and threats. Creating a SWOT analysis lets you see all the important factors affecting your organization together in one place.
It’s easy to read, easy to communicate, and easy to create. Take the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats you developed earlier, review, prioritize, and combine like terms. The SWOT analysis helps you ask and answer the following questions: “How do you….”
- Build on your strengths
- Shore up your weaknesses
- Capitalize on your opportunities
- Manage your threats

Strategic Planning Process Phase 2: Developing Strategy
Want More? Deep Dive Into the “Developing Your Strategy” How-To Guide.
Step 1: Develop Your Mission Statement
The mission statement describes an organization’s purpose or reason for existing.
What is our purpose? Why do we exist? What do we do?
- What are your organization’s goals? What does your organization intend to accomplish?
- Why do you work here? Why is it special to work here?
- What would happen if we were not here?
Outcome: A short, concise, concrete statement that clearly defines the scope of the organization.
Step 2: discover your values.
Your values statement clarifies what your organization stands for, believes in and the behaviors you expect to see as a result. Check our the post on great what are core values and examples of core values .
How will we behave?
- What are the key non-negotiables that are critical to the company’s success?
- What guiding principles are core to how we operate in this organization?
- What behaviors do you expect to see?
- If the circumstances changed and penalized us for holding this core value, would we still keep it?
Outcome: Short list of 5-7 core values.
Step 3: casting your vision statement.

A Vision Statement defines your desired future state and directs where we are going as an organization.
Where are we going?
- What will our organization look like 5–10 years from now?
- What does success look like?
- What are we aspiring to achieve?
- What mountain are you climbing and why?
Outcome: A picture of the future.
Step 4: identify your competitive advantages.

A competitive advantage is a characteristic of an organization that allows it to meet its customer’s need(s) better than its competition can. It’s important to consider your competitive advantages when creating your competitive strategy.
What are we best at?
- What are your unique strengths?
- What are you best at in your market?
- Do your customers still value what is being delivered? Ask them.
- How do your value propositions stack up in the marketplace?
Outcome: A list of 2 or 3 items that honestly express the organization’s foundation for winning.
Step 5: crafting your organization-wide strategies.

Your competitive strategy is the general methods you intend to use to reach your vision. Regardless of the level, a strategy answers the question “how.”
How will we succeed?
- Broad: market scope; a relatively wide market emphasis.
- Narrow: limited to only one or few segments in the market
- Does your competitive position focus on lowest total cost or product/service differentiation or both?
Outcome: Establish the general, umbrella methods you intend to use to reach your vision.

Phase 3: Strategic Plan Development
Want More? Deep Dive Into the “Build Your Plan” How-To Guide.
Strategic Planning Process Step 1: Use Your SWOT to Set Priorities
If your team wants to take the next step in the SWOT analysis, apply the TOWS Strategic Alternatives Matrix to your strategy map to help you think about the options you could pursue. To do this, match external opportunities and threats with your internal strengths and weaknesses, as illustrated in the matrix below:
TOWS Strategic Alternatives Matrix
Evaluate the options you’ve generated, and identify the ones that give the greatest benefit, and that best achieve the mission and vision of your organization. Add these to the other strategic options that you’re considering.
Step 2: Define Long-Term Strategic Objectives
Long-Term Strategic Objectives are long-term, broad, continuous statements that holistically address all areas of your organization. What must we focus on to achieve our vision? Check out examples of strategic objectives here. What are the “big rocks”?
Questions to ask:
- What are our shareholders or stakeholders expectations for our financial performance or social outcomes?
- To reach our outcomes, what value must we provide to our customers? What is our value proposition?
- To provide value, what process must we excel at to deliver our products and services?
- To drive our processes, what skills, capabilities and organizational structure must we have?
Outcome: Framework for your plan – no more than 6. You can use the balanced scorecard framework, OKRs, or whatever methodology works best for you. Just don’t exceed 6 long-term objectives.

Step 3: Setting Organization-Wide Goals and Measures

Once you have formulated your strategic objectives, you should translate them into goals and measures that can be communicated to your strategic planning team (team of business leaders and/or team members).
You want to set goals that convert the strategic objectives into specific performance targets. Effective strategic goals clearly state what, when, how, and who, and they are specifically measurable. They should address what you must do in the short term (think 1-3 years) to achieve your strategic objectives.
Organization-wide goals are annual statements that are SMART – specific, measurable, attainable, responsible, and time-bound. These are outcome statements expressing a result to achieve the desired outcomes expected in the organization.
What is most important right now to reach our long-term objectives?
Outcome: clear outcomes for the current year..

Step 4: Select KPIs

Key Performance Indicators (KPI) are the key measures that will have the most impact in moving your organization forward. We recommend you guide your organization with measures that matter. See examples of KPIs here.
How will we measure our success?
Outcome: 5-7 measures that help you keep the pulse on your performance. When selecting your Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), ask, “What are the key performance measures we need to track to monitor if we are achieving our goals?” These KPIs include the key goals you want to measure that will have the most impact on moving your organization forward.
Step 5: Cascade Your Strategies to Operations

To move from big ideas to action, creating action items and to-dos for short-term goals is crucial. This involves translating strategy from the organizational level to individuals. Functional area managers and contributors play a role in developing short-term goals to support the organization.
Before taking action, decide whether to create plans directly derived from the strategic plan or sync existing operational, business, or account plans with organizational goals. Avoid the pitfall of managing multiple sets of goals and actions, as this shifts from strategic planning to annual planning.
Questions to Ask
- How are we going to get there at a functional level?
- Who must do what by when to accomplish and drive the organizational goals?
- What strategic questions still remain and need to be solved?
Department/functional goals, actions, measures and targets for the next 12-24 months
Step 6: Cascading Goals to Departments and Team Members
Now in your Departments / Teams, you need to create goals to support the organization-wide goals. These goals should still be SMART and are generally (short-term) something to be done in the next 12-18 months. Finally, you should develop an action plan for each goal.
Keep the acronym SMART in mind again when setting action items, and make sure they include start and end dates and have someone assigned their responsibility. Since these action items support your previously established goals, it may be helpful to consider action items your immediate plans on the way to achieving your (short-term) goals. In other words, identify all the actions that need to occur in the next 90 days and continue this same process every 90 days until the goal is achieved.
Examples of Cascading Goals:

Phase 4: Executing Strategy and Managing Performance
Want more? Dive Into the “Managing Performance” How-To Guide.
Step 1: Strategic Plan Implementation Schedule
Implementation is the process that turns strategies and plans into actions in order to accomplish strategic objectives and goals.
How will we use the plan as a management tool?
- Communication Schedule: How and when will you roll-out your plan to your staff? How frequently will you send out updates?
- Process Leader: Who is your strategy director?
- Structure: What are the dates for your strategy reviews (we recommend at least quarterly)?
- System & Reports: What are you expecting each staff member to come prepared with to those strategy review sessions?
Outcome: Syncing your plan into the “rhythm of your business.”
Once your resources are in place, you can set your implementation schedule. Use the following steps as your base implementation plan:
- Establish your performance management and reward system.
- Set up monthly and quarterly strategy meetings with established reporting procedures.
- Set up annual strategic review dates including new assessments and a large group meeting for an annual plan review.
Now you’re ready to start plan roll-out. Below are sample implementation schedules, which double for a full strategic management process timeline.

Step 2: Tracking Goals & Actions
Monthly strategy meetings don’t need to take a lot of time – 30 to 60 minutes should suffice. But it is important that key team members report on their progress toward the goals they are responsible for – including reporting on metrics in the scorecard they have been assigned.
By using the measurements already established, it’s easy to make course corrections if necessary. You should also commit to reviewing your Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) during these regular meetings. Need help comparing strategic planning software ? Check out our guide.
Effective Strategic Planning: Your Bi-Annual Checklist

Never lose sight of the fact that strategic plans are guidelines, not rules. Every six months or so, you should evaluate your strategy execution and strategic plan implementation by asking these key questions:
- Will your goals be achieved within the time frame of the plan? If not, why?
- Should the deadlines be modified? (Before you modify deadlines, figure out why you’re behind schedule.)
- Are your goals and action items still realistic?
- Should the organization’s focus be changed to put more emphasis on achieving your goals?
- Should your goals be changed? (Be careful about making these changes – know why efforts aren’t achieving the goals before changing the goals.)
- What can be gathered from an adaptation to improve future planning activities?
Why Track Your Goals?
- Ownership: Having a stake and responsibility in the plan makes you feel part of it and leads you to drive your goals forward.
- Culture: Successful plans tie tracking and updating goals into organizational culture.
- Implementation: If you don’t review and update your strategic goals, they are just good intentions
- Accountability: Accountability and high visibility help drive change. This means that each measure, objective, data source and initiative must have an owner.
- Empowerment: Changing goals from In Progress to Complete just feels good!
Step 3: Review & Adapt
Guidelines for your strategy review.
The most important part of this meeting is a 70/30 review. 30% is about reviewing performance, and 70% should be spent on making decisions to move the company’s strategy forward in the next quarter.
The best strategic planners spend about 60-90 minutes in the sessions. Holding meetings helps focus your goals on accomplishing top priorities and accelerating the organization’s growth. Although the meeting structure is relatively simple, it does require a high degree of discipline.
Strategy Review Session Questions:
Strategic planning frequently asked questions, read our frequently asked questions about strategic planning to learn how to build a great strategic plan..
Strategic planning is when organizations define a bold vision and create a plan with objectives and goals to reach that future. A great strategic plan defines where your organization is going, how you’ll win, who must do what, and how you’ll review and adapt your strategy..
Your strategic plan needs to include an assessment of your current state, a SWOT analysis, mission, vision, values, competitive advantages, growth strategy, growth enablers, a 3-year roadmap, and annual plan with strategic goals, OKRs, and KPIs.
A strategic planning process should take no longer than 90 days to complete from start to finish! Any longer could fatigue your organization and team.
There are four overarching phases to the strategic planning process that include: determining position, developing your strategy, building your plan, and managing performance. Each phase plays a unique but distinctly crucial role in the strategic planning process.
Prior to starting your strategic plan, you must go through this pre-planning process to determine your organization’s readiness by following these steps:
Ask yourself these questions: Are the conditions and criteria for successful planning in place now? Can we foresee any pitfalls that we can avoid? Is there an appropriate time for our organization to initiate this process?
Develop your team and schedule. Who will oversee the implementation as Chief Strategy Officer or Director? Do we have at least 12-15 other key individuals on our team?
Research and Collect Current Data. Find the following resources that your organization may have used in the past to assist you with your new plan: last strategic plan, mission, vision, and values statement, business plan, financial records, marketing plan, SWOT, sales figures, or projections.
Finally, review the data with your strategy director and facilitator and ask these questions: What trends do we see? Any obvious strengths or weaknesses? Have we been following a plan or just going along with the market?
Join 60,000 other leaders engaged in transforming their organizations.
Subscribe to get the latest agile strategy best practices, free guides, case studies, and videos in your inbox every week..

Leading strategy? Join our FREE community.
Become a member of the chief strategy officer collaborative..
Free monthly sessions and exclusive content.
Do you want to 2x your impact.
The 5 steps of the strategic planning process
.jpg)
Starting a project without a strategy is like trying to bake a cake without a recipe — you might have all the ingredients you need, but without a plan for how to combine them, or a vision for what the finished product will look like, you’re likely to end up with a mess. This is especially true when working with a team — it’s crucial to have a shared plan that can serve as a map on the pathway to success.
Creating a strategic plan not only provides a useful document for the future, but also helps you define what you have right now, and think through and outline all of the steps and considerations you’ll need to succeed.
What is strategic planning?
While there is no single approach to creating a strategic plan, most approaches can be boiled down to five overarching steps:
- Define your vision
- Assess where you are
- Determine your priorities and objectives
- Define responsibilities
- Measure and evaluate results
Each step requires close collaboration as you build a shared vision, strategy for implementation, and system for understanding performance.
Related: Learn how to hold an effective strategic planning meeting
Why do I need a strategic plan?
Building a strategic plan is the best way to ensure that your whole team is on the same page, from the initial vision and the metrics for success to evaluating outcomes and adjusting (if necessary) for the future. Even if you’re an expert baker, working with a team to bake a cake means having a collaborative approach and clearly defined steps so that the result reflects the strategic goals you laid out at the beginning.
The benefits of strategic planning also permeate into the general efficiency and productivity of your organization as a whole. They include:
- Greater attention to potential biases or flaws, improving decision-making
- Clear direction and focus, motivating and engaging employees
- Better resource management, improving project outcomes
- Improved employee performance, increasing profitability
- Enhanced communication and collaboration, fostering team efficiency
Next, let’s dive into how to build and structure your strategic plan, complete with templates and assets to help you along the way.
Before you begin: Pick a brainstorming method
There are many brainstorming methods you can use to come up with, outline, and rank your priorities. When it comes to strategy planning, it’s important to get everyone’s thoughts and ideas out before committing to any one strategy. With the right facilitation , brainstorming helps make this process fair and transparent for everyone involved.
First, decide if you want to run a real-time rapid ideation session or a structured brainstorming . In a rapid ideation session, you encourage sharing half-baked or silly ideas, typically within a set time frame. The key is to just get out all your ideas quickly and then edit the best ones. Examples of rapid ideation methods include round robin , brainwriting , mind mapping , and crazy eights .
In a structured brainstorming session, you allow for more time to prepare and edit your thoughts before getting together to share and discuss those more polished ideas. This might involve brainstorming methods that entail unconventional ways of thinking, such as reverse brainstorming or rolestorming .
Using a platform like Mural, you can easily capture and organize your team’s ideas through sticky notes, diagrams, text, or even images and videos. These features allow you to build actionable next steps immediately (and in the same place) through color coding and tagging.
Whichever method you choose, the ideal outcome is that you avoid groupthink by giving everyone a voice and a say. Once you’ve reached a consensus on your top priorities, add specific objectives tied to each of those priorities.
Related: Brainstorming and ideation template
1. Define your vision
Whether it’s for your business as a whole, or a specific initiative, successful strategic planning involves alignment with a vision for success. You can think of it as a project-specific mission statement or a north star to guide employees toward fulfilling organizational goals.
To create a vision statement that explicitly states the ideal results of your project or company transformation, follow these four key steps:
- Engage and involve the entire team . Inclusivity like this helps bring diverse perspectives to the table.
- Align the vision with your core values and purpose . This will make it familiar and easy to follow through.
- Stay grounded . The vision should be ambitious enough to motivate and inspire yet grounded enough to be achievable and relevant.
- Think long-term flexibility . Consider future trends and how your vision can be flexible in the face of challenges or opportunities.
For example, say your vision is to revolutionize customer success by streamlining and optimizing your process for handling support tickets. It’s important to have a strategy map that allows stakeholders (like the support team, marketing team, and engineering team) to know the overall objective and understand the roles they will play in realizing the goals.
This can be done in real time or asynchronously , whether in person, hybrid, or remote. By leveraging a shared digital space , everyone has a voice in the process and room to add their thoughts, comments, and feedback.
Related: Vision board template
2. Assess where you are
The next step in creating a strategic plan is to conduct an assessment of where you stand in terms of your own initiatives, as well as the greater marketplace. Start by conducting a resource assessment. Figure out which financial, human, and/or technological resources you have available and if there are any limitations. You can do this using a SWOT analysis.
What is SWOT analysis?
SWOT analysis is an exercise where you define:
- Strengths: What are your unique strengths for this initiative or this product? In what ways are you a leader?
- Weaknesses: What weaknesses can you identify in your offering? How does your product compare to others in the marketplace?
- Opportunities: Are there areas for improvement that'd help differentiate your business?
- Threats: Beyond weaknesses, are there existing potential threats to your idea that could limit or prevent its success? How can those be anticipated?
For example, say you have an eco-friendly tech company and your vision is to launch a new service in the next year. Here’s what the SWOT analysis might look like:
- Strengths : Strong brand reputation, loyal customer base, and a talented team focused on innovation
- Weaknesses : Limited bandwidth to work on new projects, which might impact the scope of its strategy formulation
- Opportunities : How to leverage and experiment with existing customers when goal-setting
- Threats : Factors in the external environment out of its control, like the state of the economy and supply chain shortages
This SWOT analysis will guide the company in setting strategic objectives and formulating a robust plan to navigate the challenges it might face.
Related: SWOT analysis template
3. Determine your priorities and objectives
Once you've identified your organization’s mission and current standing, start a preliminary plan document that outlines your priorities and their corresponding objectives. Priorities and objectives should be set based on what is achievable with your available resources. The SMART framework is a great way to ensure you set effective goals . It looks like this:
- Specific: Set clear objectives, leaving no room for ambiguity about the desired outcomes.
- Measurable : Choose quantifiable criteria to make it easier to track progress.
- Achievable : Ensure it is realistic and attainable within the constraints of your resources and environment.
- Relevant : Develop objectives that are relevant to the direction your organization seeks to move.
- Time-bound : Set a clear timeline for achieving each objective to maintain a sense of urgency and focus.
For instance, going back to the eco-friendly tech company, the SMART goals might be:
- Specific : Target residential customers and small businesses to increase the sales of its solar-powered device line by 25%.
- Measurable : Track monthly sales and monitor customer feedback and reviews.
- Achievable : Allocate more resources to the marketing, sales, and customer service departments.
- Relevant : Supports the company's growth goals in a growing market of eco-conscious consumers.
- Time-bound : Conduct quarterly reviews and achieve this 25% increase in sales over the next 12 months.
With strategic objectives like this, you’ll be ready to put the work into action.
Related: Project kickoff template
4. Define tactics and responsibilities
In this stage, individuals or units within your team can get granular about how to achieve your goals and who'll be accountable for each step. For example, the senior leadership team might be in charge of assigning specific tasks to their team members, while human resources works on recruiting new talent.
It’s important to note that everyone’s responsibilities may shift over time as you launch and gather initial data about your project. For this reason, it’s key to define responsibilities with clear short-term metrics for success. This way, you can make sure that your plan is adaptable to changing circumstances.
One of the more common ways to define tactics and metrics is to use the OKR (Objectives and Key Results) method. By outlining your OKRs, you’ll know exactly what key performance indicators (KPIs) to track and have a framework for analyzing the results once you begin to accumulate relevant data.
For instance, if our eco-friendly tech company has a goal of increasing sales, one objective might be to expand market reach for its solar-powered products. The sales team lead would be in charge of developing an outreach strategy. The key result would be to successfully launch its products in two new regions by Q2. The KPI would be a 60% conversation rate in those targeted markets.
Related: OKR planning template
5. Manage, measure, and evaluate
Once your plan is set into motion, it’s important to actively manage (and measure) progress. Before launching your plan, settle on a management process that allows you to measure success or failure. In this way, everyone is aligned on progress and can come together to evaluate your strategy execution at regular intervals.
Determine the milestones at which you’ll come together and go over results — this can take place weekly, monthly, or quarterly, depending on the nature of the project.
One of the best ways to evaluate progress is through agile retrospectives (or retros) , which can be done in real time or asynchronously. During this process, gather and organize feedback about the key elements that played a role in your strategy.
Related: Retrospective radar template
Retrospectives are typically divided into three parts:
- What went well.
- What didn’t go well.
- New opportunities for improvement.
This structure is also sometimes called the “ rose, thorn, bud ” framework. By using this approach, team members can collectively brainstorm and categorize their feedback, making the next steps clear and actionable. Creating an action plan during a post-mortem meeting is a crucial step in ensuring that lessons learned from past projects or events are effectively translated into tangible improvements.
Another method for reviewing progress is the quarterly business review (QBR). Like the agile retrospective, it allows you to collect feedback and adjust accordingly. In the case of QBRs, however, we recommend dividing your feedback into four categories:
- Start (what new items should be launched?).
- Stop (what items need to be paused?).
- Continue (what is going well?).
- Change (what could be modified to perform better?).
Strategic planners know that planning activities continue even after a project is complete. There’s always room for improvement and an action plan waiting to be implemented. Using the above approaches, your team can make room for new ideas within the existing strategic framework in order to track better to your long-term goals.
Related: Quarterly business review template
Conclusions
The beauty of the strategic plan is that it can be applied from the campaign level all the way up to organizational vision. Using the strategic planning framework, you build buy-in , trust, and transparency by collaboratively creating a vision for success, and mapping out the steps together on the road to your goals.
Also, in so doing, you build in an ability to adapt effectively on the fly in response to data through measurement and evaluation, making your plan both flexible and resilient.
Related: 5 Tips for Holding Effective Post-mortems
Why Mural for strategic planning
Mural unlocks collaborative strategic planning through a shared digital space with an intuitive interface, a library of pre-fab templates, and methodologies based on design thinking principles.
Outline goals, identify key metrics, and track progress with a platform built for any enterprise.
Learn more about strategic planning with Mural.
About the authors

Bryan Kitch
Tagged Topics
Related blog posts
%20(2).jpg)
How to hold effective strategic planning meetings
%20(2).jpg)
Tactical vs. strategic planning: Why you need both
%20(2).jpg)
5 effective strategic planning models for your business
Related blog posts.
%20(3).jpg)
A guide to the Agile development lifecycle

Team collaboration software: A buyer’s guide

How to plan and organize a workshop
Essential Guide to the Strategic Planning Process
By Joe Weller | April 3, 2019 (updated March 26, 2024)
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
In this article, you’ll learn the basics of the strategic planning process and how a strategic plan guides you to achieving your organizational goals. Plus, find expert insight on getting the most out of your strategic planning.
Included on this page, you'll discover the importance of strategic planning , the steps of the strategic planning process , and the basic sections to include in your strategic plan .
What Is Strategic Planning?
Strategic planning is an organizational activity that aims to achieve a group’s goals. The process helps define a company’s objectives and investigates both internal and external happenings that might influence the organizational path. Strategic planning also helps identify adjustments that you might need to make to reach your goal. Strategic planning became popular in the 1960s because it helped companies set priorities and goals, strengthen operations, and establish agreement among managers about outcomes and results.
Strategic planning can occur over multiple years, and the process can vary in length, as can the final plan itself. Ideally, strategic planning should result in a document, a presentation, or a report that sets out a blueprint for the company’s progress.
By setting priorities, companies help ensure employees are working toward common and defined goals. It also aids in defining the direction an enterprise is heading, efficiently using resources to achieve the organization’s goals and objectives. Based on the plan, managers can make decisions or allocate the resources necessary to pursue the strategy and minimize risks.
Strategic planning strengthens operations by getting input from people with differing opinions and building a consensus about the company’s direction. Along with focusing energy and resources, the strategic planning process allows people to develop a sense of ownership in the product they create.

“Strategic planning is not really one thing. It is really a set of concepts, procedures, tools, techniques, and practices that have to be adapted to specific contexts and purposes,” says Professor John M. Bryson, McKnight Presidential Professor of Planning and Public Affairs at the Hubert H. Humphrey School of Public Affairs, University of Minnesota and author of Strategic Planning for Public and Nonprofit Organizations: A Guide to Strengthening and Sustaining Organizational Achievement . “Strategic planning is a prompt to foster strategic thinking, acting, and learning, and they all matter and they are all connected.”

What Strategic Planning Is Not
Strategic planning is not a to-do list for the short or long term — it is the basis of a business, its direction, and how it will get there.
“You have to think very strategically about strategic planning. It is more than just following steps,” Bryson explains. “You have to understand strategic planning is not some kind of magic solution to fixing issues. Don’t have unrealistic expectations.”
Strategic planning is also different from a business plan that focuses on a specific product, service, or program and short-term goals. Rather, strategic planning means looking at the big picture.
While they are related, it is important not to confuse strategic planning with strategic thinking, which is more about imagining and innovating in a way that helps a company. In contrast, strategic planning supports those thoughts and helps you figure out how to make them a reality.
Another part of strategic planning is tactical planning , which involves looking at short-term efforts to achieve longer-term goals.
Lastly, marketing plans are not the same as strategic plans. A marketing plan is more about introducing and delivering a service or product to the public instead of how to grow a business. For more about marketing plans and processes, read this article .
Strategic plans include information about finances, but they are different from financial planning , which involves different processes and people. Financial planning templates can help with that process.
Why Is Strategic Planning Important?
In today’s technological age, strategic plans provide businesses with a path forward. Strategic plans help companies thrive, not just survive — they provide a clear focus, which makes an organization more efficient and effective, thereby increasing productivity.

“You are not going to go very far if you don’t have a strategic plan. You need to be able to show where you are going,” says Stefan Hofmeyer, an experienced strategist and co-founder of Global PMI Partners . He lives in the startup-rich environment of northern California and says he often sees startups fail to get seed money because they do not have a strong plan for what they want to do and how they want to do it.
Getting team members on the same page (in both creating a strategic plan and executing the plan itself) can be beneficial for a company. Planners can find satisfaction in the process and unite around a common vision. In addition, you can build strong teams and bridge gaps between staff and management.
“You have to reach agreement about good ideas,” Bryson says. “A really good strategy has to meet a lot of criteria. It has to be technically workable, administratively feasible, politically acceptable, and legally, morally, and ethically defensible, and that is a pretty tough list.”
By discussing a company’s issues during the planning process, individuals can voice their opinions and provide information necessary to move the organization ahead — a form of problem solving as a group.
Strategic plans also provide a mechanism to measure success and progress toward goals, which keeps employees on the same page and helps them focus on the tasks at hand.
When Is the Time to Do Strategic Planning?
There is no perfect time to perform strategic planning. It depends entirely on the organization and the external environment that surrounds it. However, here are some suggestions about when to plan:
If your industry is changing rapidly
When an organization is launching
At the start of a new year or funding period
In preparation for a major new initiative
If regulations and laws in your industry are or will be changing
“It’s not like you do all of the thinking and planning, and then implement,” Bryson says. “A mistake people make is [believing] the thinking has to precede the acting and the learning.”
Even if you do not re-create the entire planning process often, it is important to periodically check your plan and make sure it is still working. If not, update it.
What Is the Strategic Planning Process?
Strategic planning is a process, and not an easy one. A key is to make sure you allow enough time to complete the process without rushing, but not take so much time that you lose momentum and focus. The process itself can be more important than the final document due to the information that comes out of the discussions with management, as well as lower-level workers.

“There is not one favorite or perfect planning process,” says Jim Stockmal, president of the Association for Strategic Planning (ASP). He explains that new techniques come out constantly, and consultants and experienced planners have their favorites. In an effort to standardize the practice and terms used in strategic planning, ASP has created two certification programs .
Level 1 is the Strategic Planning Professional (SPP) certification. It is designed for early- or mid-career planners who work in strategic planning. Level 2, the Strategic Management Professional (SMP) certification, is geared toward seasoned professionals or those who train others. Stockmal explains that ASP designed the certification programs to add structure to the otherwise amorphous profession.
The strategic planning process varies by the size of the organization and can be formal or informal, but there are constraints. For example, teams of all sizes and goals should build in many points along the way for feedback from key leaders — this helps the process stay on track.
Some elements of the process might have specific start and end points, while others are continuous. For example, there might not be one “aha” moment that suddenly makes things clear. Instead, a series of small moves could slowly shift the organization in the right direction.
“Don’t make it overly complex. Bring all of the stakeholders together for input and feedback,” Stockmal advises. “Always be doing a continuous environmental scan, and don’t be afraid to engage with stakeholders.”
Additionally, knowing your company culture is important. “You need to make it work for your organization,” he says.
There are many different ways to approach the strategic planning process. Below are three popular approaches:
Goals-Based Planning: This approach begins by looking at an organization’s mission and goals. From there, you work toward that mission, implement strategies necessary to achieve those goals, and assign roles and deadlines for reaching certain milestones.
Issues-Based Planning: In this approach, start by looking at issues the company is facing, then decide how to address them and what actions to take.
Organic Planning: This approach is more fluid and begins with defining mission and values, then outlining plans to achieve that vision while sticking to the values.
“The approach to strategic planning needs to be contingent upon the organization, its history, what it’s capable of doing, etc.,” Bryson explains. “There’s such a mistake to think there’s one approach.”
For more information on strategic planning, read about how to write a strategic plan and the different types of models you can use.
Who Participates in the Strategic Planning Process?
For work as crucial as strategic planning, it is necessary to get the right team together and include them from the beginning of the process. Try to include as many stakeholders as you can.
Below are suggestions on who to include:
Senior leadership
Strategic planners
Strategists
People who will be responsible for implementing the plan
People to identify gaps in the plan
Members of the board of directors
“There can be magic to strategic planning, but it’s not in any specific framework or anybody’s 10-step process,” Bryson explains. “The magic is getting key people together, getting them to focus on what’s important, and [getting] them to do something about it. That’s where the magic is.”
Hofmeyer recommends finding people within an organization who are not necessarily current leaders, but may be in the future. “Sometimes they just become obvious. Usually they show themselves to you, you don’t need to look for them. They’re motivated to participate,” he says. These future leaders are the ones who speak up at meetings or on other occasions, who put themselves out there even though it is not part of their job description.
At the beginning of the process, establish guidelines about who will be involved and what will be expected of them. Everyone involved must be willing to cooperate and collaborate. If there is a question about whether or not to include anyone, it is usually better to bring on extra people than to leave someone out, only to discover later they should have been a part of the process all along. Not everyone will be involved the entire time; people will come and go during different phases.
Often, an outside facilitator or consultant can be an asset to a strategic planning committee. It is sometimes difficult for managers and other employees to sit back and discuss what they need to accomplish as a company and how they need to do it without considering other factors. As objective observers, outside help can often offer insight that may escape insiders.
Hofmeyer says sometimes bosses have blinders on that keep them from seeing what is happening around them, which allows them to ignore potential conflicts. “People often have their own agendas of where they want to go, and if they are not aligned, it is difficult to build a strategic plan. An outsider perspective can really take you out of your bubble and tell you things you don’t necessarily want to hear [but should]. We get into a rhythm, and it’s really hard to step out of that, so bringing in outside people can help bring in new views and aspects of your business.”
An outside consultant can also help naysayers take the process more seriously because they know the company is investing money in the efforts, Hofmeyer adds.
No matter who is involved in the planning process, make sure at least one person serves as an administrator and documents all planning committee actions.
What Is in a Strategic Plan?
A strategic plan communicates goals and what it takes to achieve them. The plan sometimes begins with a high-level view, then becomes more specific. Since strategic plans are more guidebooks than rulebooks, they don’t have to be bureaucratic and rigid. There is no perfect plan; however, it needs to be realistic.
There are many sections in a strategic plan, and the length of the final document or presentation will vary. The names people use for the sections differ, but the general ideas behind them are similar: Simply make sure you and your team agree on the terms you will use and what each means.
One-Page Strategic Planning Template
“I’m a big fan of getting a strategy onto one sheet of paper. It’s a strategic plan in a nutshell, and it provides a clear line of sight,” Stockmal advises.
You can use the template below to consolidate all your strategic ideas into a succinct, one-page strategic plan. Doing so provides you with a high-level overview of your strategic initiatives that you can place on your website, distribute to stakeholders, and refer to internally. More extensive details about implementation, capacity, and other concerns can go into an expanded document.
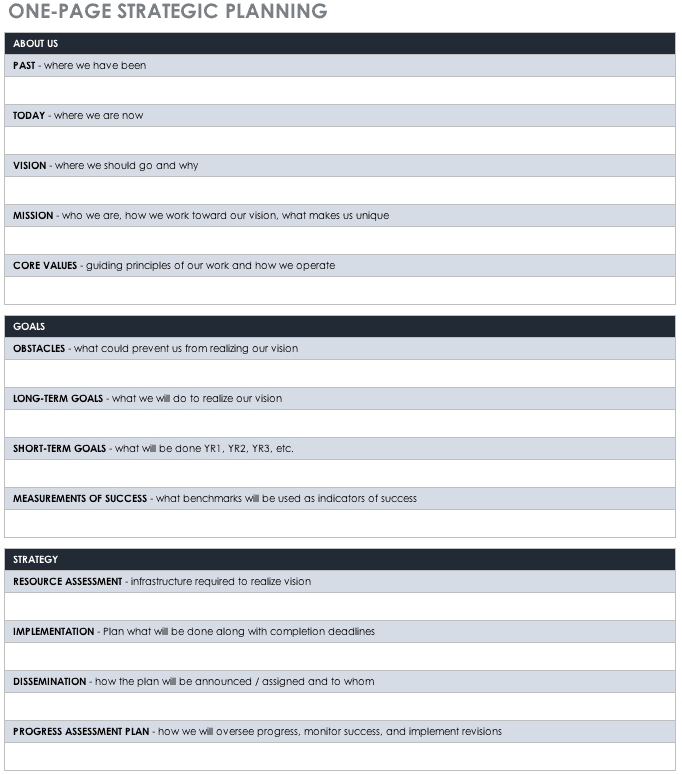
Download One-Page Strategic Planning Template Excel | Word | Smartsheet
The most important part of the strategic plan is the executive summary, which contains the highlights of the plan. Although it appears at the beginning of the plan, it should be written last, after you have done all your research.
Of writing the executive summary, Stockmal says, “I find it much easier to extract and cut and edit than to do it first.”
For help with creating executive summaries, see these templates .
Other parts of a strategic plan can include the following:
Description: A description of the company or organization.
Vision Statement: A bold or inspirational statement about where you want your company to be in the future.
Mission Statement: In this section, describe what you do today, your audience, and your approach as you work toward your vision.
Core Values: In this section, list the beliefs and behaviors that will enable you to achieve your mission and, eventually, your vision.
Goals: Provide a few statements of how you will achieve your vision over the long term.
Objectives: Each long-term goal should have a few one-year objectives that advance the plan. Make objectives SMART (specific, measurable, achievable, and time-based) to get the most out of them.
Budget and Operating Plans: Highlight resources you will need and how you will implement them.
Monitoring and Evaluation: In this section, describe how you will check your progress and determine when you achieve your goals.
One of the first steps in creating a strategic plan is to perform both an internal and external analysis of the company’s environment. Internally, look at your company’s strengths and weaknesses, as well as the personal values of those who will implement your plan (managers, executives, board members). Externally, examine threats and opportunities within the industry and any broad societal expectations that might exist.
You can perform a SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) analysis to sum up where you are currently and what you should focus on to help you achieve your future goals. Strengths shows you what you do well, weaknesses point out obstacles that could keep you from achieving your objectives, opportunities highlight where you can grow, and threats pinpoint external factors that could be obstacles in your way.
You can find more information about performing a SWOT analysis and free templates in this article . Another analysis technique, STEEPLE (social, technological, economic, environmental, political, legal, and ethical), often accompanies a SWOT analysis.
Basics of Strategic Planning
How you navigate the strategic planning process will vary. Several tools and techniques are available, and your choice depends on your company’s leadership, culture, environment, and size, as well as the expertise of the planners.
All include similar sections in the final plan, but the ways of driving those results differ. Some tools are goals-based, while others are issues- or scenario-based. Some rely on a more organic or rigid process.
Hofmeyer summarizes what goes into strategic planning:
Understand the stakeholders and involve them from the beginning.
Agree on a vision.
Hold successful meetings and sessions.
Summarize and present the plan to stakeholders.
Identify and check metrics.
Make periodic adjustments.
Items That Go into Strategic Planning
Strategic planning contains inputs, activities, outputs, and outcomes. Inputs and activities are elements that are internal to the company, while outputs and outcomes are external.
Remember, there are many different names for the sections of strategic plans. The key is to agree what terms you will use and define them for everyone involved.
Inputs are important because it is impossible to know where you are going until you know what is around you where you are now.
Companies need to gather data from a variety of sources to get a clear look at the competitive environment and the opportunities and risks within that environment. You can think of it like a competitive intelligence program.
Data should come from the following sources:
Interviews with executives
A review of documents about the competition or market that are publicly available
Primary research by visiting or observing competitors
Studies of your industry
The values of key stakeholders
This information often goes into writing an organization’s vision and mission statements.
Activities are the meetings and other communications that need to happen during the strategic planning process to help everyone understand the competition that surrounds the organization.
It is important both to understand the competitive environment and your company’s response to it. This is where everyone looks at and responds to the data gathered from the inputs.
The strategic planning process produces outputs. Outputs can be as basic as the strategic planning document itself. The documentation and communications that describe your organization’s strategy, as well as financial statements and budgets, can also be outputs.
The implementation of the strategic plan produces outcomes (distinct from outputs). The outcomes determine the success or failure of the strategic plan by measuring how close they are to the goals and vision you outline in your plan.
It is important to understand there will be unplanned and unintended outcomes, too. How you learn from and adapt to these changes influence the success of the strategic plan.
During the planning process, decide how you will measure both the successes and failures of different parts of the strategic plan.
Sharing, Evaluating, and Monitoring the Progress of a Strategic Plan
After companies go through a lengthy strategic planning process, it is important that the plan does not sit and collect dust. Share, evaluate, and monitor the plan to assess how you are doing and make any necessary updates.
“[Some] leaders think that once they have their strategy, it’s up to someone else to execute it. That’s a mistake I see,” Stockmal says.
The process begins with distributing and communicating the plan. Decide who will get a copy of the plan and how those people will tell others about it. Will you have a meeting to kick off the implementation? How will you specify who will do what and when? Clearly communicate the roles people will have.
“Before you communicate the plan [to everyone], you need to have the commitment of stakeholders,” Hofmeyer recommends. Have the stakeholders be a part of announcing the plan to everyone — this keeps them accountable because workers will associate them with the strategy. “That applies pressure to the stakeholders to actually do the work.”
Once the team begins implementation, it’s necessary to have benchmarks to help measure your successes against the plan’s objectives. Sometimes, having smaller action plans within the larger plan can help keep the work on track.
During the planning process, you should have decided how you will measure success. Now, figure out how and when you will document progress. Keep an eye out for gaps between the vision and its implementation — a big gap could be a sign that you are deviating from the plan.
Tools are available to assist with tracking performance of strategic plans, including several types of software. “For some organizations, a spreadsheet is enough, but you are going to manually enter the data, so someone needs to be responsible for that,” Stockmal recommends.
Remember: strategic plans are not written in stone. Some deviation will be necessary, and when it happens, it’s important to understand why it occurred and how the change might impact the company's vision and goals.
Deviation from the plan does not mean failure, reminds Hofmeyer. Instead, understanding what transpired is the key. “Things happen, [and] you should always be on the lookout for that. I’m a firm believer in continuous improvement,” he says. Explain to stakeholders why a change is taking place. “There’s always a sense of re-evaluation, but do it methodically.”
Build in a schedule to review and amend the plan as necessary; this can help keep companies on track.
What Is Strategic Management?
Strategic planning is part of strategic management, and it involves the activities that make the strategic plan a reality. Essentially, strategic management is getting from the starting point to the goal effectively and efficiently using the ongoing activities and processes that a company takes on in order to keep in line with its mission, vision, and strategic plan.
“[Strategic management] closes the gap between the plan and executing the strategy,” Stockmal of ASP says. Strategic management is part of a larger planning process that includes budgeting, forecasting, capital allocation, and more.
There is no right or wrong way to do strategic management — only guidelines. The basic phases are preparing for strategic planning, creating the strategic plan, and implementing that plan.
No matter how you manage your plan, it’s key to allow the strategic plan to evolve and grow as necessary, due to both the internal and external factors.
“We get caught up in all of the day-to-day issues,” Stockmal explains, adding that people do not often leave enough time for implementing the plan and making progress. That’s what strategic management implores: doing things that are in the plan and not letting the plan sit on a shelf.
Improve Strategic Planning with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.

How it works
Transform your enterprise with the scalable mindsets, skills, & behavior change that drive performance.
Explore how BetterUp connects to your core business systems.
We pair AI with the latest in human-centered coaching to drive powerful, lasting learning and behavior change.
Build leaders that accelerate team performance and engagement.
Unlock performance potential at scale with AI-powered curated growth journeys.
Build resilience, well-being and agility to drive performance across your entire enterprise.
Transform your business, starting with your sales leaders.
Unlock business impact from the top with executive coaching.
Foster a culture of inclusion and belonging.
Accelerate the performance and potential of your agencies and employees.
See how innovative organizations use BetterUp to build a thriving workforce.
Discover how BetterUp measurably impacts key business outcomes for organizations like yours.
A demo is the first step to transforming your business. Meet with us to develop a plan for attaining your goals.

- What is coaching?
Learn how 1:1 coaching works, who its for, and if it's right for you.
Accelerate your personal and professional growth with the expert guidance of a BetterUp Coach.
Types of Coaching
Navigate career transitions, accelerate your professional growth, and achieve your career goals with expert coaching.
Enhance your communication skills for better personal and professional relationships, with tailored coaching that focuses on your needs.
Find balance, resilience, and well-being in all areas of your life with holistic coaching designed to empower you.
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.

Research, expert insights, and resources to develop courageous leaders within your organization.
Best practices, research, and tools to fuel individual and business growth.
View on-demand BetterUp events and learn about upcoming live discussions.
The latest insights and ideas for building a high-performing workplace.
- BetterUp Briefing
The online magazine that helps you understand tomorrow's workforce trends, today.
Innovative research featured in peer-reviewed journals, press, and more.
Founded in 2022 to deepen the understanding of the intersection of well-being, purpose, and performance
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.
For Business
For Individuals
Strategic planning: Read this before it's that time again

Jump to section
What is strategic planning?
What is strategic plan management?
Benefits of robust strategic planning and management
10 steps in the strategic planning process.
Plans are worthless, but planning is everything. - Dwight D. Eisenhower
It’s that time again.
Every three to five years, most larger organizations periodically plan for the future. Many times strategic planning documents are shelved and forgotten until the next cycle begins. On the other hand, many smaller and newer organizations, propelled by urgency, may not devote the necessary time and energy to the strategic planning process.
Only 63% of businesses plan more than a year out. They fail to see that — contrary to Alice in Wonderland’s Cheshire cat — “any way” does not take you there.
For all organizations, a more rigorous annual planning process is critical for driving future success, profitability, value, and impact.
John Kotter, a former professor at Harvard Business School and noted expert on innovation says, “ Strategy should be viewed as a dynamic force that constantly seeks opportunities, identifies initiatives that will capitalize on them, and completes those initiatives swiftly and efficiently.”
There’s hardly a better case that can be made for dynamic planning than in the tech industry, where mergers and acquisitions are accelerating exponentially. Companies need to be nimble enough to navigate rapid change . In this case, planning should occur quarterly.
Strategic planning is an ongoing process by which an organization sets its forward course by bringing all of its stakeholders together to examine current realities and define its vision for the future.
It examines its strengths and weaknesses, resources available, and opportunities. Strategic planning seeks to anticipate future industry trends . During the process, the organization creates a vision, articulates its purpose, and sets strategic goals that are long-term and forward-focused.
Those strategic goals inform operational goals and incremental milestones that need to be reached. The operational plan has clear objectives and supporting initiatives tied to metrics to which everyone is accountable . The plan should be agile enough to allow for recalibrating when necessary and redistributing resources based on internal and external forces.
The output of the planning process is a document that is shared across the enterprise.
Strategic planning for individuals
Strategic planning isn’t just for companies. At BetterUp, strategic planning is one of the skills that we identify, track, and develop within the Whole Person Model . For individuals, strategic planning is the ability to think through ways to achieve desired outcomes. Just as strategic planning helps organizations realize their goals for the future, it helps individuals grow and achieve goals in a unified direction.
Working backward from the desired outcome, effective strategic planning consists of coming up with the steps we need to take today in order to get where we want to be tomorrow.
While no plan is infallible, people who develop this skill are good at checking to make sure that their actions are in alignment with the outcomes that they want to see in the future. Even when things don’t go according to plan, their long-term goals act as a “North star” to get them back on course. In addition, envisioning desired future states and figuring out how to turn them into reality enhances an individual’s sense of personal meaning and motivation.
Whether we’re talking about strategic planning for the company or the individual, strategic plans can go awry in a variety of ways including:
- Unrealistic goals and too many priorities
- Poor communication
- Using the wrong measures
- Lack of leadership
The extent to which that document is shelved until the next planning cycle or becomes a dynamic map of the future depends on the people responsible for overseeing the execution of the plan.

What is strategic plan management?
"Most people think of strategy as an event, but that’s not the way the world works," according to Harvard Business School Professor Clayton Christensen. "When we run into unanticipated opportunities and threats, we have to respond. Sometimes we respond successfully; sometimes we don’t. But most strategies develop through this process. More often than not, the strategy that leads to success emerges through a process that works 24/7 in almost every industry."
Strategic business management is the ongoing process by which an organization creates and sustains a successful roadmap that moves the company in the direction it needs to move, year after year, for long-term success. It spans from research and formulation to execution, evaluation, and adjustment. Given the pace of change, strategic management is more relevant and important than ever for assigning measurable goals and action steps
Many organizations fail because they don’t have the strategic management team at the table right from the beginning of the planning process. A strategic plan is only as good as its ability to be executed and sustained.
A strategic management initiative might be driven by an internal group — many companies have an internal strategy team — or an outside consulting firm. Ultimately company leaders need to own executing and sustaining the strategy.
Strategic management teams
In this Harvard Business Review article, Ron Carucci from consulting firm Navalent reports that 61% of executives in a 10-year longitudinal study felt they were not prepared for the strategic challenges they faced upon being appointed to senior leadership roles. Lack of commitment to the plan is also a contributing factor. In addition, leaders attending to quarterly targets, crisis management , and reconciling budgets often consider the execution of a long-term strategy a low priority.
A dedicated strategic management team works with those senior leaders and managers throughout the organization to communicate, coordinate and evaluate progress against goals. They tie strategic objectives to day-to-day operational metrics throughout the enterprise.
A good strategic management group can assist in creating a culture of empowerment and learning . It holds regular meetings with employees. It sets a clear agenda and expectations to make the strategic plan real and compelling to the organization through concrete objectives, results, and timelines.
Strategy development is a lot of work, but the benefits are lasting. After all, as the saying goes, "If you fail to plan, you plan to fail." Taking the time for review and planning activities has the following benefits:
- Organizations and people are set up to succeed
- Increased likelihood of staying on track
- Decreased likelihood of being distracted or derailed
- Progress through the plan is communicated throughout the organization
- Metrics facilitate course correction
- Budgets enterprise-wide are based on strategy
- Cross-organization alignment
- Robust employee performance and compensation plans
- Commitment to learning and training
- A robust strategic planning process gets everyone involved and invested in the organizations
- Employees inform management about what’s working or not working at the operational level
- Innovation is encouraged and rewarded
- Increased productivity
1. Define mission and vision
Begin by articulating the organization's vision for the future. Ask, "What would success look like in five years?" Create a mission statement describing organizational values and how you intend to reach the vision. What values inform and determine mission, vision, and purpose?
Purpose-driven strategic goals articulate the “why” of what the corporation is doing. It connects the vision statement to specific objectives, drawing a line between the larger goals and the work that teams and individuals do.
2. Conduct a comprehensive assessment
This stage includes identifying an organization’s strategic position.
Gathering data from internal and external environments and respective stakeholders takes place at this time. Involving employees and customers in the research.
The task is to gather market data through research. One of the most critical components of this stage is a comprehensive SWOT analysis that involves gathering people and bringing perspectives from all stakeholders to determine:
- W eaknesses
- O pportunities
Strengths and weaknesses — In this stage, planners identify the company’s assets that contribute to its current competitive advantage and/or the likelihood of a significant increase in the organization’s market share in the future. It should be an objective assessment rather than an inflated perspective of its strengths.
An accurate assessment of weaknesses requires looking outward at external forces that can reveal new opportunities as well as threats. Consider the massive shift in multiple industries whose strategy has been disrupted by the COVID-19 pandemic. While it was disastrous to the airline and restaurant industries’ business models , tech companies were able to seize the opportunity and address the demands of remote work.
Michael Porter’s book Competetive Strategy: Techniques for Analyzing Industries and Competitors claims that there are five forces at work in an industry that influence that industry’s ability to develop a competitive strategy. Since the book was published in 1979, organizations have turned to Porter’s theory to create their strategic framework.
Here are the 5 forces (and key questions) that determine the competitive strategy for most industries.
- Competitive rivalry : When considering the strengths of an organization’s competitors it’s important to ask: How do our products/services hold up to our competition? If the rivalry is intense, companies need to consider what capacity they have to gain leverage through price cuts or bold marketing strategies. If there is little competition, the organization has a substantial gain in the market.
- Supplier power: How might suppliers influence strategy? For example, what if suppliers raised their prices? To what extent would a company need a particular supplier for our product(s)? Is it possible to switch suppliers in a way that is more cost effective and efficient? The number of suppliers that exist will determine your ability to keep costs low.
- Buyer power: To what extent do buyers have the ability to shop around right into the hands of your competitors? How much power does your customer base have in determining price? A small number of well-informed buyers shifts the power in their direction while a large pool may give you the strategic advantage
- Threat of substitution: What is the threat of a company’s buyer substituting your services/products from the competition? What if the buyer figures out another way to access the services/products that it offers?
- Threat of new entry: How easy is it for newcomers to enter the organization’s market?

3. Forecast
Considering the factors above, determine the company’s value through financial forecasting . While almost certainly to become a moving target influenced by the five forces, a forecast can assign initial anticipated measurable results expected in the plan or ROI: profits/cost of investment.
4. Set the organizational direction of the business
The above research and assessment will help an organization to set goals and priorities. Too often an organization’s strategic plan is too broad and over-ambitious. Planners need to ask, ”What kind of impact are we seeking to have, and in what time frame?” They need to drill down to objectives that will have the most impact.
5. Create strategic objectives
This next phase of operational planning consists of creating strategic objectives and initiatives. Kaplan and Norton posit in their balanced scorecard methodology that there are four perspectives for consideration in identifying the conditions for success. They are interrelated and must be evaluated simultaneously.
- Financial : Such considerations as growing shareholder value, increasing revenue, managing cost, profitability, or financial stability inform strategic initiatives.
- Customer-satisfaction: Objectives can be determined by identifying targets related to one or some of the following: value for the cost, best service, increased market share, or providing customers with solutions.
- Internal processes such as operational processes and efficiencies, investment in innovation, investment in total quality and performance management , cost reduction, improvement of workplace safety, or streamlining processes.
- Learning and growth: Organizations must ask: Are initiatives in place in terms of human capital and learning and growth to sustain change? Objectives may include employee retention, productivity, building high-performing teams, or creating a pipeline for future leaders .
6. Align with key stakeholders
It’s a team effort. The success of the plan is in direct proportion to the organization’s commitment to inform and engage the entire workforce in strategy execution. People will only be committed to strategy implementation when they're connected to the organization's goals. With everyone pulling in the same direction, cross-functional decision-making becomes easier and more aligned.
7. Begin strategy mapping
A strategy map is a powerful tool for illustrating the cause-effect of those perspectives and connecting them to between 12 and 18 strategic objectives. Since most people are visual learners, the map provides an easy-to-understand diagram for everyone in the organization creating shared knowledge at all levels.
8. Determine strategic initiatives
Following the development of strategic objectives, strategic initiatives are determined. These are the actions the organization will take to reach those objectives. They may relate initiatives related to factors such as scope, budget, raising brand awareness, product development, and employee training.
9. Benchmark performance measures and analysis
Strategic initiatives inform SMART goals to which metrics are assigned to evaluate performance. These measures cascade from senior management to management to front-line workers. At this stage, the task is to create goals that are specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-based informing the operational plan.
Benchmarks are established against so that performance can be measures, and a time frame is created. Key performance indicators (KPI’s) are assigned based on organizational goals. These indicators align workers’ performance and productivity with long-term strategic objectives.
10. Performance evaluation
Assessment of whether the plan has been successful . It measures activities and progress toward objectives and allows for the creation of improved plans and objectives in order to improve overall performance .
Think of strategic planning as a circular process beginning and ending with evaluation. Adjust a plan as necessary. The pace at which review of the plan is necessary may be once a year for many organizations or quarterly for organizations in rapidly evolving industries.
Prioritizing the strategic planning process
The strategic planning meeting may have a reputation for being just another to-do, but it might be time to take a second look. With the right action plan and a little strategic thinking, you can reinvigorate your business environment and start planning for success.
It's that time to get excited about the future again.
Elevate your strategic planning
Discover how targeted coaching can enhance your strategic insight and execution across all levels of your organization.
Meredith Betz, M.S.Ed, M.S.O.D.
Meredith Betz is a Betterup Fellow Coach. As an organizational consultant and Executive Coach, Meredith's work focuses on leaders, teams, and the dynamics in the systems in which they live and work. She helps people become more influential and exhibit executive presence. Meredith is a certified Conscious Business Coach who helps leaders to exercise empathy and lead in a way that is consistent with their values. She gives them the tools to communicate and negotiate effectively with their stakeholders. Meredith recently co-wrote a memoir with a 103-year-old Estonian man who lived through the Nazi and Soviet occupations of Estonia in the 1940s. It was a profound experience. A seminal book for her is Man's Search for Meaning by Viktor Frankl, an Austrian Holocaust survivor and psychiatrist.
The only guide you’ll ever need for career planning
Contingency planning: 4 steps to prepare for the unexpected, 4 reasons why you can't afford to skip out on succession planning, strategic plan vs. work plan: what's the difference, declining capabilities in productivity and wellness signal a need for worker support, how to excel at life planning (a life planning template), making a career change at 30: 6 tips to embrace a new job, strategy versus tactics: planning and executing on your goals, what is an action plan how to become a real-life action hero, similar articles, everything you need to know about strategic leadership, what is strategic plan management and how does it benefit teams, 6 tactics to unlock operational excellence and drive performance, when you need to set the direction, swot analysis is a classic tool, how organizational effectiveness enhances how you work and grow, how to use strategic foresight to stay ahead of the curve, strategy vs. tactics: the difference is execution, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform Overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care™
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case Studies
- Why BetterUp?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Life Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Labs
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences
- Get started Get started for free
Figma design
Design and prototype in one place
Collaborate with a digital whiteboard
Translate designs into code
Get the desktop, mobile, and font installer apps
See the latest features and releases
- Prototyping
- Design systems
- Wireframing
- Online whiteboard
- Team meetings
- Strategic planning
- Brainstorming
- Diagramming
- Product development
- Web development
- Design handoff
- Product managers
Organizations
Config 2024
Register to attend in person or online — June 26–27

Creator fund
Build and sell what you love
User groups
Join a local Friends of Figma group
Learn best practices at virtual events
Customer stories
Read about leading product teams
Stories about bringing new ideas to life
Get started
- Developer docs
- Best practices
- Reports & insights
- Resource library
- Help center
What is strategic planning

Imagine you're ready to expand your thriving business to another market. Would you choose that market based on where you'd like to vacation, or just ask ChatGPT to decide for you? That wouldn’t be strategic, and it could backfire. The smart business move would be to assess risks, opportunities, regulations, competition, and the local business landscape—then use your analysis to plan your next move.
For businesses, strategic planning can make all the difference between expanding market share and closing up shop. Read on to find out how to excel at strategic planning.
What is strategic planning?
Whether your organization is a startup or established business charting the way forward, a strategic plan is a vital tool for success—and you can lead the charge. Strategic planning is the process of putting your best business theories to the test in the marketplace. Your strategic planning process starts with defining a mission/vision statement and setting key goals. To achieve those goals, you create a detailed plan, or strategy map .
Once you put that strategic plan into motion, you're no longer just reacting to market forces. You're proactive, blazing your own trail to your desired destination. There’s no better way to ensure that decisions are evidence-based, forward-looking, collaborative, and aligned with your entire organization’s long-term objectives.
Think of your business as an orchestra. No matter how skilled your musicians are, if they all play a different tune, you won't like what you hear. Wouldn’t you rather start out with sheet music and a brilliant conductor? An organization can make decisions without a strategic plan in place, just like an orchestra can play without a conductor. But when individuals or departments make decisions based on opinion, guesswork, or instinct, you can end up with disorganized, inefficient use of time and resources—and that’s not music to anyone’s ears.
How is strategic planning different from other plans?
Roger Martin, one of the world’s leading thinkers on strategy, cautions that “a plan is not a strategy.” A plan is comfortable because you control the levers, like time and costs. But strategic planning challenges you to put strategy to the test, making “an integrative set of choices that positions you on a playing field of your choice in a way that you win .”
Benefits of strategic planning
A strategic plan can be a competitive advantage. Harvard Business Review found that up to 67% of HR and IT departments have strategies of their own that don’t align with the larger corporate strategy. The bad news gets worse: 95% of employees don’t understand their organization’s strategy. Clear, effectively communicated strategic plans position organizations to outperform competitors struggling to articulate cohesive strategies to their employees.
With a strategic plan, you can help your organization to:
- Communicate priorities to employees at all levels
- Allocate resources appropriately to meet goals
- Track progress objectively
- Make clear decisions more efficiently
- Avoid mistakes caused by short-term thinking
3 strategic planning best practices
- Consider it a learning process. Creating strategic plans teaches teams to think more strategically, preparing decision-makers to make choices rationally under pressure.
- Make comprehensive plans. Research shows a thorough, comprehensive planning process yields strong results. Consider a variety of viewpoints and multiple options before setting your strategic objectives.
- Conduct regular updates. The most successful organizations are nimble, making wise strategic decisions in real time as circumstances change. Revisiting plans frequently with key decision-makers helps keep your strategy relevant and responsive.
Who belongs on strategic planning teams?
Strategic planning teams tackle key responsibilities: defining company mission/vision statements, setting goals, identifying opportunities, evaluating risks, and plotting a course to meet objectives. To achieve this ambitious agenda, your team should cover a broad spectrum of viewpoints and roles, including:
- VPs and C-suite executives who must be consulted, according to your RACI matrix
- Representatives from various departments, team leads, and department heads who are responsible or accountable for outcomes
- Other key stakeholders to keep informed, such as board members or investors
Not sure who your key stakeholders are? Check out the FigJam stakeholder analysis template to identify valuable collaborators right from the start, but make sure the group doesn’t get too big. Large groups can get bogged down in strategic planning discussions.
Strategic planning in 5 steps
Your organization's strategic planning process may take slightly different steps depending on its size and needs, but most organizations follow these five basic steps.
1. Define the organization's mission, vision, and values .
These elements of strategic planning inform all of your objectives and the overall direction of the business strategy from here on out. What does your organization intend to do? What does it stand for, and why?
2. Conduct a situational analysis.
SWOT analysis is a time-tested tool to assess the opportunities and risks your organization faces. Cover internal and external factors, including your resources, competition, and changes in the market.
3. Set goals and objectives .
Pinpoint what you want to achieve, then set realistic and achievable targets. You could focus on specific objectives (“reduce customer acquisition costs by 5% next quarter”) or address broader strategic goals (“increase customer satisfaction” ) . Articulate goals and objectives clearly , and define your measurements for success.
4. Develop and launch your action plan .
Outline the steps to take, and break down steps into tasks. Then decide who is responsible for each task, and when each task needs to be completed. With every decision, aim to minimize risk and maximize opportunity to achieve your goal.
To get your strategic plan on track for success, communicate the plan to everyone in the organization. You may want to launch your plan at an all-hands meeting, or break it up into meetings with separate departments.
5. Evaluate the results.
Establish a timeline of regular assessments to check plan progres. Assign responsibilities to monitor and assess outcomes, and make course corrections as needed.
Pro tips and tools for strategic planning
The strategic planning process involves gathering data, documents, and team input to define timelines with multiple steps and dependencies. Figma's makes this complex process easier with these collaborative strategic planning tools:
- Balanced scorecard. Organizations as diverse as Chrysler and the U.S. Army use the Balanced Scorecard to take performance to the next level. A Balanced Scorecard assigns weighted values to various options to remove bias from decision-making, guide plan implementation, and help you communicate your strategy clearly.
- SWOT analysis . Identify your company's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats with a SWOT analysis . This tool offers a comprehensive, objective overview of company resources and its internal and external working environment. You’ll draw on the data you collect during your SWOT analysis many times during your strategic planning process.
- KPI tracking dashboard. Key performance indicators (KPIs) quantify success measurements and establish the timeline for achieving specific financial, strategic, or operational milestones. A shared KPI dashboard template will get your KPI tracking system up and running fast, boosting visibility and collaboration.
- RACI matrix. Identify all the key stakeholders on your strategic plan and group them according to their level of involvement: R esponsible, A ccountable, C onsulted, and I nformed. Figma’s RACI template can get you started quickly.
- Gantt chart . To capture your strategic plan timeline and steps at a glance, try a Gantt chart . This bar chart highlights start dates, deadlines, resource allocations, assignments, and other key planning elements. Use a Gantt chart to sequence tasks and show your team exactly which steps need to be completed when.
Strategize for success with Figma
The keys to strategic planning are collaboration, effective teamwork, and comprehensive information-gathering—and Figma has you covered with online collaboration tools . Figma's easy, engaging strategic plan template gets your team started with tools for brainstorming, diagramming, and sharing data and feedback—all in one space.
Go to next section
Keep reading

Strategic planning process in 6 steps
Every business needs a great strategic plan to achieve their long term goals.
What is a strategy map
A strategy map is a visual representation of how a company can achieve their long-term goals and objectives.
Strategic vs. tactical planning
While strategic planning involves big-picture thinking, tactical planning covers the nitty-gritty of turning strategy into action.

5 steps of the strategic planning process
Lucid Content
Reading time: about 6 min
- Process improvement
Strategic planning process steps
- Determine your strategic position.
- Prioritize your objectives.
- Develop a strategic plan.
- Execute and manage your plan.
- Review and revise the plan.
Because so many businesses lack in these regards, you can get ahead of the game by using strategic planning. In this article, we will explain what the strategic planning process looks like and the steps involved.

What is the strategic planning process?
In the simplest terms, the strategic planning process is the method that organizations use to develop plans to achieve overall, long-term goals.
This process differs from the project planning process, which is used to scope and assign tasks for individual projects, or strategy mapping , which helps you determine your mission, vision, and goals.
The strategic planning process is broad—it helps you create a roadmap for which strategic objectives you should put effort into achieving and which initiatives would be less helpful to the business.
Before you begin the strategic planning process, it is important to review some steps to set you and your organization up for success.
1. Determine your strategic position
This preparation phase sets the foundation for all work going forward. You need to know where you are to determine where you need to go and how you will get there.
Involve the right stakeholders from the start, considering both internal and external sources. Identify key strategic issues by talking with executives at your company, pulling in customer insights, and collecting industry and market data. This will give you a clear picture of your position in the market and customer insight.
It can also be helpful to review—or create if you don’t have them already—your company’s mission and vision statements to give yourself and your team a clear image of what success looks like for your business. In addition, review your company’s core values to remind yourself about how your company plans to achieve these objectives.
To get started, use industry and market data, including customer insights and current/future demands, to identify the issues that need to be addressed. Document your organization's internal strengths and weaknesses, along with external opportunities (ways your organization can grow in order to fill needs that the market does not currently fill) and threats (your competition).
As a framework for your initial analysis, use a SWOT diagram. With input from executives, customers, and external market data, you can quickly categorize your findings as Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats (SWOT) to clarify your current position.

An alternative to a SWOT is PEST analysis. Standing for Political, Economic, Socio-cultural, and Technological, PEST is a strategic tool used to clarify threats and opportunities for your business.

As you synthesize this information, your unique strategic position in the market will become clear, and you can start solidifying a few key strategic objectives. Often, these objectives are set with a three- to five-year horizon in mind.

Use PEST analysis for additional help with strategic planning.
2. Prioritize your objectives
Once you have identified your current position in the market, it is time to determine objectives that will help you achieve your goals. Your objectives should align with your company mission and vision.
Prioritize your objectives by asking important questions such as:
- Which of these initiatives will have the greatest impact on achieving our company mission/vision and improving our position in the market?
- What types of impact are most important (e.g. customer acquisition vs. revenue)?
- How will the competition react?
- Which initiatives are most urgent?
- What will we need to do to accomplish our goals?
- How will we measure our progress and determine whether we achieved our goals?
Objectives should be distinct and measurable to help you reach your long-term strategic goals and initiatives outlined in step one. Potential objectives can be updating website content, improving email open rates, and generating new leads in the pipeline.
3. Develop a plan
Now it's time to create a strategic plan to reach your goals successfully. This step requires determining the tactics necessary to attain your objectives and designating a timeline and clearly communicating responsibilities.
Strategy mapping is an effective tool to visualize your entire plan. Working from the top-down, strategy maps make it simple to view business processes and identify gaps for improvement.

Truly strategic choices usually involve a trade-off in opportunity cost. For example, your company may decide not to put as much funding behind customer support, so that it can put more funding into creating an intuitive user experience.
Be prepared to use your values, mission statement, and established priorities to say “no” to initiatives that won’t enhance your long-term strategic position.
4. Execute and manage the plan
Once you have the plan, you’re ready to implement it. First, communicate the plan to the organization by sharing relevant documentation. Then, the actual work begins.
Turn your broader strategy into a concrete plan by mapping your processes. Use key performance indicator (KPI) dashboards to communicate team responsibilities clearly. This granular approach illustrates the completion process and ownership for each step of the way.
Set up regular reviews with individual contributors and their managers and determine check-in points to ensure you’re on track.
5. Review and revise the plan
The final stage of the plan—to review and revise—gives you an opportunity to reevaluate your priorities and course-correct based on past successes or failures.
On a quarterly basis, determine which KPIs your team has met and how you can continue to meet them, adapting your plan as necessary. On an annual basis, it’s important to reevaluate your priorities and strategic position to ensure that you stay on track for success in the long run.
Track your progress using balanced scorecards to comprehensively understand of your business's performance and execute strategic goals.

Over time you may find that your mission and vision need to change — an annual evaluation is a good time to consider those changes, prepare a new plan, and implement again.

Achieve your goals and monitor your progress with balanced scorecards.
Master the strategic planning process steps
As you continue to implement the strategic planning process, repeating each step regularly, you will start to make measurable progress toward achieving your company’s vision.
Instead of constantly putting out fires, reacting to the competition, or focusing on the latest hot-button initiative, you’ll be able to maintain a long-term perspective and make decisions that will keep you on the path to success for years to come.

Use a strategy map to turn your organization's mission and vision into actionable objectives.
About Lucidchart
Lucidchart, a cloud-based intelligent diagramming application, is a core component of Lucid Software's Visual Collaboration Suite. This intuitive, cloud-based solution empowers teams to collaborate in real-time to build flowcharts, mockups, UML diagrams, customer journey maps, and more. Lucidchart propels teams forward to build the future faster. Lucid is proud to serve top businesses around the world, including customers such as Google, GE, and NBC Universal, and 99% of the Fortune 500. Lucid partners with industry leaders, including Google, Atlassian, and Microsoft. Since its founding, Lucid has received numerous awards for its products, business, and workplace culture. For more information, visit lucidchart.com.
Related articles
How to use kaizen methodology to improve business processes.
The Kaizen methodology is an easy way to engage employees and develop a culture of continuous improvement. It strives to eliminate silos, egos, and waste and instead aims for efficient and standardized processes. See why you should use Kaizen and how you can get started.
Implement the strategic planning process to make measurable progress toward achieving your company’s vision and make decisions that will keep you on the path to success for years to come.
Bring your bright ideas to life.
or continue with
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading Change and Organizational Renewal
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
How to Set Strategic Planning Goals

- 29 Oct 2020
In an ever-changing business world, it’s imperative to have strategic goals and a plan to guide organizational efforts. Yet, crafting strategic goals can be a daunting task. How do you decide which goals are vital to your company? Which ones are actionable and measurable? Which goals to prioritize?
To help you answer these questions, here’s a breakdown of what strategic planning is, what characterizes strategic goals, and how to select organizational goals to pursue.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is Strategic Planning?
Strategic planning is the ongoing organizational process of using available knowledge to document a business's intended direction. This process is used to prioritize efforts, effectively allocate resources, align shareholders and employees, and ensure organizational goals are backed by data and sound reasoning.
Research in the Harvard Business Review cautions against getting locked into your strategic plan and forgetting that strategy involves inherent risk and discomfort. A good strategic plan evolves and shifts as opportunities and threats arise.
“Most people think of strategy as an event, but that’s not the way the world works,” says Harvard Business School Professor Clayton Christensen in the online course Disruptive Strategy . “When we run into unanticipated opportunities and threats, we have to respond. Sometimes we respond successfully; sometimes we don’t. But most strategies develop through this process. More often than not, the strategy that leads to success emerges through a process that’s at work 24/7 in almost every industry."
Related: 5 Tips for Formulating a Successful Strategy
4 Characteristics of Strategic Goals
To craft a strategic plan for your organization, you first need to determine the goals you’re trying to reach. Strategic goals are an organization’s measurable objectives that are indicative of its long-term vision.
Here are four characteristics of strategic goals to keep in mind when setting them for your organization.

1. Purpose-Driven
The starting point for crafting strategic goals is asking yourself what your company’s purpose and values are . What are you striving for, and why is it important to set these objectives? Let the answers to these questions guide the development of your organization’s strategic goals.
“You don’t have to leave your values at the door when you come to work,” says HBS Professor Rebecca Henderson in the online course Sustainable Business Strategy .
Henderson, whose work focuses on reimagining capitalism for a just and sustainable world, also explains that leading with purpose can drive business performance.
“Adopting a purpose will not hurt your performance if you do it authentically and well,” Henderson says in a lecture streamed via Facebook Live . “If you’re able to link your purpose to the strategic vision of the company in a way that really gets people aligned and facing in the right direction, then you have the possibility of outperforming your competitors.”
Related: 5 Examples of Successful Sustainability Initiatives
2. Long-Term and Forward-Focused
While strategic goals are the long-term objectives of your organization, operational goals are the daily milestones that need to be reached to achieve them. When setting strategic goals, think of your company’s values and long-term vision, and ensure you’re not confusing strategic and operational goals.
For instance, your organization’s goal could be to create a new marketing strategy; however, this is an operational goal in service of a long-term vision. The strategic goal, in this case, could be breaking into a new market segment, to which the creation of a new marketing strategy would contribute.
Keep a forward-focused vision to ensure you’re setting challenging objectives that can have a lasting impact on your organization.
3. Actionable
Strong strategic goals are not only long-term and forward-focused—they’re actionable. If there aren’t operational goals that your team can complete to reach the strategic goal, your organization is better off spending time and resources elsewhere.
When formulating strategic goals, think about the operational goals that fall under them. Do they make up an action plan your team can take to achieve your organization’s objective? If so, the goal could be a worthwhile endeavor for your business.
4. Measurable
When crafting strategic goals, it’s important to define how progress and success will be measured.
According to the online course Strategy Execution , an effective tool you can use to create measurable goals is a balanced scorecard —a tool to help you track and measure non-financial variables.
“The balanced scorecard combines the traditional financial perspective with additional perspectives that focus on customers, internal business processes, and learning and development,” says HBS Professor Robert Simons in the online course Strategy Execution . “These additional perspectives help businesses measure all the activities essential to creating value.”
The four perspectives are:
- Internal business processes
- Learning and growth

The most important element of a balanced scorecard is its alignment with your business strategy.
“Ask yourself,” Simons says, “‘If I picked up a scorecard and examined the measures on it, could I infer what the business's strategy was? If you've designed measures well, the answer should be yes.”
Related: A Manager’s Guide to Successful Strategy Implementation
Strategic Goal Examples
Whatever your business goals and objectives , they must have all four of the characteristics listed above.
For instance, the goal “become a household name” is valid but vague. Consider the intended timeframe to reach this goal and how you’ll operationally define “a household name.” The method of obtaining data must also be taken into account.
An appropriate revision to the original goal could be: “Increase brand recognition by 80 percent among surveyed Americans by 2030.” By setting a more specific goal, you can better equip your organization to reach it and ensure that employees and shareholders have a clear definition of success and how it will be measured.
If your organization is focused on becoming more sustainable and eco-conscious, you may need to assess your strategic goals. For example, you may have a goal of becoming a carbon neutral company, but without defining a realistic timeline and baseline for this initiative, the probability of failure is much higher.
A stronger goal might be: “Implement a comprehensive carbon neutrality strategy by 2030.” From there, you can determine the operational goals that will make this strategic goal possible.
No matter what goal you choose to pursue, it’s important to avoid those that lack clarity, detail, specific targets or timeframes, or clear parameters for success. Without these specific elements in place, you’ll have a difficult time making your goals actionable and measurable.
Prioritizing Strategic Goals
Once you’ve identified several strategic goals, determine which are worth pursuing. This can be a lengthy process, especially if other decision-makers have differing priorities and opinions.
To set the stage, ensure everyone is aware of the purpose behind each strategic goal. This calls back to Henderson’s point that employees’ alignment on purpose can set your organization up to outperform its competitors.
Calculate Anticipated ROI
Next, calculate the estimated return on investment (ROI) of the operational goals tied to each strategic objective. For example, if the strategic goal is “reach carbon-neutral status by 2030,” you need to break that down into actionable sub-tasks—such as “determine how much CO2 our company produces each year” and “craft a marketing and public relations strategy”—and calculate the expected cost and return for each.

The ROI formula is typically written as:
ROI = (Net Profit / Cost of Investment) x 100
In project management, the formula uses slightly different terms:
ROI = [(Financial Value - Project Cost) / Project Cost] x 100
An estimate can be a valuable piece of information when deciding which goals to pursue. Although not all strategic goals need to yield a high return on investment, it’s in your best interest to calculate each objective's anticipated ROI so you can compare them.
Consider Current Events
Finally, when deciding which strategic goal to prioritize, the importance of the present moment can’t be overlooked. What’s happening in the world that could impact the timeliness of each goal?
For example, the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic and the ever-intensifying climate change crisis have impacted many organizations’ strategic goals in 2020. Often, the goals that are timely and pressing are those that earn priority.

Learn to Plan Strategic Goals
As you set and prioritize strategic goals, remember that your strategy should always be evolving. As circumstances and challenges shift, so must your organizational strategy.
If you lead with purpose, a measurable and actionable vision, and an awareness of current events, you can set strategic goals worth striving for.
Do you want to learn more about strategic planning? Explore our online strategy courses and download our free flowchart to determine which is right for you and your goals.
This post was updated on November 16, 2023. It was originally published on October 29, 2020.

About the Author
- Product overview
- All features
- App integrations
CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana Intelligence
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Marketing strategic planning
- Request tracking
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- View all uses arrow-right icon
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- What's new Learn about the latest and greatest from Asana
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Support Need help? Contact the Asana support team
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- Business strategy |
- 7 strategic planning models, plus 8 fra ...
7 strategic planning models, plus 8 frameworks to help you get started
Strategic planning is vital in defining where your business is going in the next three to five years. With the right strategic planning models and frameworks, you can uncover opportunities, identify risks, and create a strategic plan to fuel your organization’s success. We list the most popular models and frameworks and explain how you can combine them to create a strategic plan that fits your business.
A strategic plan is a great tool to help you hit your business goals . But sometimes, this tool needs to be updated to reflect new business priorities or changing market conditions. If you decide to use a model that already exists, you can benefit from a roadmap that’s already created. The model you choose can improve your knowledge of what works best in your organization, uncover unknown strengths and weaknesses, or help you find out how you can outpace your competitors.
In this article, we cover the most common strategic planning models and frameworks and explain when to use which one. Plus, get tips on how to apply them and which models and frameworks work well together.
Strategic planning models vs. frameworks
First off: This is not a one-or-nothing scenario. You can use as many or as few strategic planning models and frameworks as you like.
When your organization undergoes a strategic planning phase, you should first pick a model or two that you want to apply. This will provide you with a basic outline of the steps to take during the strategic planning process.
![strategic planning process in an organization [Inline illustration] Strategic planning models vs. frameworks (Infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/89236d14-1abf-4f49-8b91-4187147f1c63/inline-business-strategy-strategic-planning-models-1-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
During that process, think of strategic planning frameworks as the tools in your toolbox. Many models suggest starting with a SWOT analysis or defining your vision and mission statements first. Depending on your goals, though, you may want to apply several different frameworks throughout the strategic planning process.
For example, if you’re applying a scenario-based strategic plan, you could start with a SWOT and PEST(LE) analysis to get a better overview of your current standing. If one of the weaknesses you identify has to do with your manufacturing process, you could apply the theory of constraints to improve bottlenecks and mitigate risks.
Now that you know the difference between the two, learn more about the seven strategic planning models, as well as the eight most commonly used frameworks that go along with them.
![strategic planning process in an organization [Inline illustration] The seven strategic planning models (Infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/23048ae4-8a18-4b9b-ad9e-33b0fc5d04ee/inline-business-strategy-strategic-planning-models-2-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
1. Basic model
The basic strategic planning model is ideal for establishing your company’s vision, mission, business objectives, and values. This model helps you outline the specific steps you need to take to reach your goals, monitor progress to keep everyone on target, and address issues as they arise.
If it’s your first strategic planning session, the basic model is the way to go. Later on, you can embellish it with other models to adjust or rewrite your business strategy as needed. Let’s take a look at what kinds of businesses can benefit from this strategic planning model and how to apply it.
Small businesses or organizations
Companies with little to no strategic planning experience
Organizations with few resources
Write your mission statement. Gather your planning team and have a brainstorming session. The more ideas you can collect early in this step, the more fun and rewarding the analysis phase will feel.
Identify your organization’s goals . Setting clear business goals will increase your team’s performance and positively impact their motivation.
Outline strategies that will help you reach your goals. Ask yourself what steps you have to take in order to reach these goals and break them down into long-term, mid-term, and short-term goals .
Create action plans to implement each of the strategies above. Action plans will keep teams motivated and your organization on target.
Monitor and revise the plan as you go . As with any strategic plan, it’s important to closely monitor if your company is implementing it successfully and how you can adjust it for a better outcome.
2. Issue-based model
Also called goal-based planning model, this is essentially an extension of the basic strategic planning model. It’s a bit more dynamic and very popular for companies that want to create a more comprehensive plan.
Organizations with basic strategic planning experience
Businesses that are looking for a more comprehensive plan
Conduct a SWOT analysis . Assess your organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats with a SWOT analysis to get a better overview of what your strategic plan should focus on. We’ll give into how to conduct a SWOT analysis when we get into the strategic planning frameworks below.
Identify and prioritize major issues and/or goals. Based on your SWOT analysis, identify and prioritize what your strategic plan should focus on this time around.
Develop your main strategies that address these issues and/or goals. Aim to develop one overarching strategy that addresses your highest-priority goal and/or issue to keep this process as simple as possible.
Update or create a mission and vision statement . Make sure that your business’s statements align with your new or updated strategy. If you haven’t already, this is also a chance for you to define your organization’s values.
Create action plans. These will help you address your organization’s goals, resource needs, roles, and responsibilities.
Develop a yearly operational plan document. This model works best if your business repeats the strategic plan implementation process on an annual basis, so use a yearly operational plan to capture your goals, progress, and opportunities for next time.
Allocate resources for your year-one operational plan. Whether you need funding or dedicated team members to implement your first strategic plan, now is the time to allocate all the resources you’ll need.
Monitor and revise the strategic plan. Record your lessons learned in the operational plan so you can revisit and improve it for the next strategic planning phase.
The issue-based plan can repeat on an annual basis (or less often once you resolve the issues). It’s important to update the plan every time it’s in action to ensure it’s still doing the best it can for your organization.
You don’t have to repeat the full process every year—rather, focus on what’s a priority during this run.
3. Alignment model
This model is also called strategic alignment model (SAM) and is one of the most popular strategic planning models. It helps you align your business and IT strategies with your organization’s strategic goals.
You’ll have to consider four equally important, yet different perspectives when applying the alignment strategic planning model:
Strategy execution: The business strategy driving the model
Technology potential: The IT strategy supporting the business strategy
Competitive potential: Emerging IT capabilities that can create new products and services
Service level: Team members dedicated to creating the best IT system in the organization
Ideally, your strategy will check off all the criteria above—however, it’s more likely you’ll have to find a compromise.
Here’s how to create a strategic plan using the alignment model and what kinds of companies can benefit from it.
Organizations that need to fine-tune their strategies
Businesses that want to uncover issues that prevent them from aligning with their mission
Companies that want to reassess objectives or correct problem areas that prevent them from growing
Outline your organization’s mission, programs, resources, and where support is needed. Before you can improve your statements and approaches, you need to define what exactly they are.
Identify what internal processes are working and which ones aren’t. Pinpoint which processes are causing problems, creating bottlenecks , or could otherwise use improving. Then prioritize which internal processes will have the biggest positive impact on your business.
Identify solutions. Work with the respective teams when you’re creating a new strategy to benefit from their experience and perspective on the current situation.
Update your strategic plan with the solutions. Update your strategic plan and monitor if implementing it is setting your business up for improvement or growth. If not, you may have to return to the drawing board and update your strategic plan with new solutions.
4. Scenario model
The scenario model works great if you combine it with other models like the basic or issue-based model. This model is particularly helpful if you need to consider external factors as well. These can be government regulations, technical, or demographic changes that may impact your business.
Organizations trying to identify strategic issues and goals caused by external factors
Identify external factors that influence your organization. For example, you should consider demographic, regulation, or environmental factors.
Review the worst case scenario the above factors could have on your organization. If you know what the worst case scenario for your business looks like, it’ll be much easier to prepare for it. Besides, it’ll take some of the pressure and surprise out of the mix, should a scenario similar to the one you create actually occur.
Identify and discuss two additional hypothetical organizational scenarios. On top of your worst case scenario, you’ll also want to define the best case and average case scenarios. Keep in mind that the worst case scenario from the previous step can often provoke strong motivation to change your organization for the better. However, discussing the other two will allow you to focus on the positive—the opportunities your business may have ahead.
Identify and suggest potential strategies or solutions. Everyone on the team should now brainstorm different ways your business could potentially respond to each of the three scenarios. Discuss the proposed strategies as a team afterward.
Uncover common considerations or strategies for your organization. There’s a good chance that your teammates come up with similar solutions. Decide which ones you like best as a team or create a new one together.
Identify the most likely scenario and the most reasonable strategy. Finally, examine which of the three scenarios is most likely to occur in the next three to five years and how your business should respond to potential changes.
5. Self-organizing model
Also called the organic planning model, the self-organizing model is a bit different from the linear approaches of the other models. You’ll have to be very patient with this method.
This strategic planning model is all about focusing on the learning and growing process rather than achieving a specific goal. Since the organic model concentrates on continuous improvement , the process is never really over.
Large organizations that can afford to take their time
Businesses that prefer a more naturalistic, organic planning approach that revolves around common values, communication, and shared reflection
Companies that have a clear understanding of their vision
Define and communicate your organization’s cultural values . Your team can only think clearly and with solutions in mind when they have a clear understanding of your organization's values.
Communicate the planning group’s vision for the organization. Define and communicate the vision with everyone involved in the strategic planning process. This will align everyone’s ideas with your company’s vision.
Discuss what processes will help realize the organization’s vision on a regular basis. Meet every quarter to discuss strategies or tactics that will move your organization closer to realizing your vision.
6. Real-time model
This fluid model can help organizations that deal with rapid changes to their work environment. There are three levels of success in the real-time model:
Organizational: At the organizational level, you’re forming strategies in response to opportunities or trends.
Programmatic: At the programmatic level, you have to decide how to respond to specific outcomes or environmental changes.
Operational: On the operational level, you will study internal systems, policies, and people to develop a strategy for your company.
Figuring out your competitive advantage can be difficult, but this is absolutely crucial to ensure success. Whether it’s a unique asset or strength your organization has or an outstanding execution of services or programs—it’s important that you can set yourself apart from others in the industry to succeed.
Companies that need to react quickly to changing environments
Businesses that are seeking new tools to help them align with their organizational strategy
Define your mission and vision statement. If you ever feel stuck formulating your company’s mission or vision statement, take a look at those of others. Maybe Asana’s vision statement sparks some inspiration.
Research, understand, and learn from competitor strategy and market trends. Pick a handful of competitors in your industry and find out how they’ve created success for themselves. How did they handle setbacks or challenges? What kinds of challenges did they even encounter? Are these common scenarios in the market? Learn from your competitors by finding out as much as you can about them.
Study external environments. At this point, you can combine the real-time model with the scenario model to find solutions to threats and opportunities outside of your control.
Conduct a SWOT analysis of your internal processes, systems, and resources. Besides the external factors your team has to consider, it’s also important to look at your company’s internal environment and how well you’re prepared for different scenarios.
Develop a strategy. Discuss the results of your SWOT analysis to develop a business strategy that builds toward organizational, programmatic, and operational success.
Rinse and repeat. Monitor how well the new strategy is working for your organization and repeat the planning process as needed to ensure you’re on top or, perhaps, ahead of the game.
7. Inspirational model
This last strategic planning model is perfect to inspire and energize your team as they work toward your organization’s goals. It’s also a great way to introduce or reconnect your employees to your business strategy after a merger or acquisition.
Businesses with a dynamic and inspired start-up culture
Organizations looking for inspiration to reinvigorate the creative process
Companies looking for quick solutions and strategy shifts
Gather your team to discuss an inspirational vision for your organization. The more people you can gather for this process, the more input you will receive.
Brainstorm big, hairy audacious goals and ideas. Encouraging your team not to hold back with ideas that may seem ridiculous will do two things: for one, it will mitigate the fear of contributing bad ideas. But more importantly, it may lead to a genius idea or suggestion that your team wouldn’t have thought of if they felt like they had to think inside of the box.
Assess your organization’s resources. Find out if your company has the resources to implement your new ideas. If they don’t, you’ll have to either adjust your strategy or allocate more resources.
Develop a strategy balancing your resources and brainstorming ideas. Far-fetched ideas can grow into amazing opportunities but they can also bear great risk. Make sure to balance ideas with your strategic direction.
Now, let’s dive into the most commonly used strategic frameworks.
8. SWOT analysis framework
One of the most popular strategic planning frameworks is the SWOT analysis . A SWOT analysis is a great first step in identifying areas of opportunity and risk—which can help you create a strategic plan that accounts for growth and prepares for threats.
SWOT stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Here’s an example:
![strategic planning process in an organization [Inline illustration] SWOT analysis (Example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/cfab4ed2-46d1-4636-b801-14b3d86c8367/inline-project-management-SWOT-analysis-4-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
9. OKRs framework
A big part of strategic planning is setting goals for your company. That’s where OKRs come into play.
OKRs stand for objective and key results—this goal-setting framework helps your organization set and achieve goals. It provides a somewhat holistic approach that you can use to connect your team’s work to your organization’s big-picture goals. When team members understand how their individual work contributes to the organization’s success, they tend to be more motivated and produce better results
10. Balanced scorecard (BSC) framework
The balanced scorecard is a popular strategic framework for businesses that want to take a more holistic approach rather than just focus on their financial performance. It was designed by David Norton and Robert Kaplan in the 1990s, it’s used by companies around the globe to:
Communicate goals
Align their team’s daily work with their company’s strategy
Prioritize products, services, and projects
Monitor their progress toward their strategic goals
Your balanced scorecard will outline four main business perspectives:
Customers or clients , meaning their value, satisfaction, and/or retention
Financial , meaning your effectiveness in using resources and your financial performance
Internal process , meaning your business’s quality and efficiency
Organizational capacity , meaning your organizational culture, infrastructure and technology, and human resources
With the help of a strategy map, you can visualize and communicate how your company is creating value. A strategy map is a simple graphic that shows cause-and-effect connections between strategic objectives.
The balanced scorecard framework is an amazing tool to use from outlining your mission, vision, and values all the way to implementing your strategic plan .
You can use an integration like Lucidchart to create strategy maps for your business in Asana.
11. Porter’s Five Forces framework
If you’re using the real-time strategic planning model, Porter’s Five Forces are a great framework to apply. You can use it to find out what your product’s or service’s competitive advantage is before entering the market.
Developed by Michael E. Porter , the framework outlines five forces you have to be aware of and monitor:
![strategic planning process in an organization [Inline illustration] Porter’s Five Forces framework (Infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/d63265bc-23e2-4ce6-9b91-b3da5a756619/inline-business-strategy-strategic-planning-models-3-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Threat of new industry entrants: Any new entry into the market results in increased pressure on prices and costs.
Competition in the industry: The more competitors that exist, the more difficult it will be for you to create value in the market with your product or service.
Bargaining power of suppliers: Suppliers can wield more power if there are less alternatives for buyers or it’s expensive, time consuming, or difficult to switch to a different supplier.
Bargaining power of buyers: Buyers can wield more power if the same product or service is available elsewhere with little to no difference in quality.
Threat of substitutes: If another company already covers the market’s needs, you’ll have to create a better product or service or make it available for a lower price at the same quality in order to compete.
Remember, industry structures aren’t static. The more dynamic your strategic plan is, the better you’ll be able to compete in a market.
12. VRIO framework
The VRIO framework is another strategic planning tool designed to help you evaluate your competitive advantage. VRIO stands for value, rarity, imitability, and organization.
It’s a resource-based theory developed by Jay Barney. With this framework, you can study your firmed resources and find out whether or not your company can transform them into sustained competitive advantages.
Firmed resources can be tangible (e.g., cash, tools, inventory, etc.) or intangible (e.g., copyrights, trademarks, organizational culture, etc.). Whether these resources will actually help your business once you enter the market depends on four qualities:
Valuable : Will this resource either increase your revenue or decrease your costs and thereby create value for your business?
Rare : Are the resources you’re using rare or can others use your resources as well and therefore easily provide the same product or service?
Inimitable : Are your resources either inimitable or non-substitutable? In other words, how unique and complex are your resources?
Organizational: Are you organized enough to use your resources in a way that captures their value, rarity, and inimitability?
It’s important that your resources check all the boxes above so you can ensure that you have sustained competitive advantage over others in the industry.
13. Theory of Constraints (TOC) framework
If the reason you’re currently in a strategic planning process is because you’re trying to mitigate risks or uncover issues that could hurt your business—this framework should be in your toolkit.
The theory of constraints (TOC) is a problem-solving framework that can help you identify limiting factors or bottlenecks preventing your organization from hitting OKRs or KPIs .
Whether it’s a policy, market, or recourse constraint—you can apply the theory of constraints to solve potential problems, respond to issues, and empower your team to improve their work with the resources they have.
14. PEST/PESTLE analysis framework
The idea of the PEST analysis is similar to that of the SWOT analysis except that you’re focusing on external factors and solutions. It’s a great framework to combine with the scenario-based strategic planning model as it helps you define external factors connected to your business’s success.
PEST stands for political, economic, sociological, and technological factors. Depending on your business model, you may want to expand this framework to include legal and environmental factors as well (PESTLE). These are the most common factors you can include in a PESTLE analysis:
Political: Taxes, trade tariffs, conflicts
Economic: Interest and inflation rate, economic growth patterns, unemployment rate
Social: Demographics, education, media, health
Technological: Communication, information technology, research and development, patents
Legal: Regulatory bodies, environmental regulations, consumer protection
Environmental: Climate, geographical location, environmental offsets
15. Hoshin Kanri framework
Hoshin Kanri is a great tool to communicate and implement strategic goals. It’s a planning system that involves the entire organization in the strategic planning process. The term is Japanese and stands for “compass management” and is also known as policy management.
This strategic planning framework is a top-down approach that starts with your leadership team defining long-term goals which are then aligned and communicated with every team member in the company.
You should hold regular meetings to monitor progress and update the timeline to ensure that every teammate’s contributions are aligned with the overarching company goals.
Stick to your strategic goals
Whether you’re a small business just starting out or a nonprofit organization with decades of experience, strategic planning is a crucial step in your journey to success.
If you’re looking for a tool that can help you and your team define, organize, and implement your strategic goals, Asana is here to help. Our goal-setting software allows you to connect all of your team members in one place, visualize progress, and stay on target.
Related resources

Write better AI prompts: A 4-sentence framework

How to find alignment on AI

What is content marketing? A complete guide
Grant management: A nonprofit’s guide
How to improve strategic planning
In conference rooms everywhere, corporate planners are in the midst of the annual strategic-planning process. For the better part of a year, they collect financial and operational data, make forecasts, and prepare lengthy presentations with the CEO and other senior managers about the future direction of the business. But at the end of this expensive and time-consuming process, many participants say they are frustrated by its lack of impact on either their own actions or the strategic direction of the company.
This sense of disappointment was captured in a recent McKinsey Quarterly survey of nearly 800 executives: just 45 percent of the respondents said they were satisfied with the strategic-planning process. 1 1. “ Improving strategic planning: A McKinsey Survey ,” The McKinsey Quarterly , Web exclusive, September 2006. The survey, conducted in late July and early August 2006, received 796 responses from a panel of executives from around the world. All panelists have mostly financial or strategic responsibilities and work in a wide range of industries for organizations with revenues of at least $500 million. Moreover, only 23 percent indicated that major strategic decisions were made within its confines. Given these results, managers might well be tempted to jettison the planning process altogether.
But for those working in the overwhelming majority of corporations, the annual planning process plays an essential role. In addition to formulating at least some elements of a company’s strategy, the process results in a budget, which establishes the resource allocation map for the coming 12 to 18 months; sets financial and operating targets, often used to determine compensation metrics and to provide guidance for financial markets; and aligns the management team on its strategic priorities. The operative question for chief executives is how to make the planning process more effective—not whether it is the sole mechanism used to design strategy. CEOs know that strategy is often formulated through ad hoc meetings or brand reviews, or as a result of decisions about mergers and acquisitions.
Our research shows that formal strategic-planning processes play an important role in improving overall satisfaction with strategy development. That role can be seen in the responses of the 79 percent of managers who claimed that the formal planning process played a significant role in developing strategies and were satisfied with the approach of their companies, compared with only 21 percent of the respondents who felt that the process did not play a significant role. Looked at another way, 51 percent of the respondents whose companies had no formal process were dissatisfied with their approach to the development of strategy, against only 20 percent of those at companies with a formal process.
So what can managers do to improve the process? There are many ways to conduct strategic planning, but determining the ideal method goes beyond the scope of this article. Instead we offer, from our research, five emergent ideas that executives can employ immediately to make existing processes run better. The changes we discuss here (such as a focus on important strategic issues or a connection to core-management processes) are the elements most linked with the satisfaction of employees and their perceptions of the significance of the process. These steps cannot guarantee that the right strategic decisions will be made or that strategy will be better executed, but by enhancing the planning process—and thus increasing satisfaction with the development of strategy—they will improve the odds for success.
Start with the issues
Ask CEOs what they think strategic planning should involve and they will talk about anticipating big challenges and spotting important trends. At many companies, however, this noble purpose has taken a backseat to rigid, data-driven processes dominated by the production of budgets and financial forecasts. If the calendar-based process is to play a more valuable role in a company’s overall strategy efforts, it must complement budgeting with a focus on strategic issues. In our experience, the first liberating change managers can make to improve the quality of the planning process is to begin it by deliberately and thoughtfully identifying and discussing the strategic issues that will have the greatest impact on future business performance.
Granted, an approach based on issues will not necessarily yield better strategic results. The music business, for instance, has discussed the threat posed by digital-file sharing for years without finding an effective way of dealing with the problem. But as a first step, identifying the key issues will ensure that management does not waste time and energy on less important topics.
We found a variety of practical ways in which companies can impose a fresh strategic perspective. For instance, the CEO of one large health care company asks the leaders of each business unit to imagine how a set of specific economic, social, and business trends will affect their businesses, as well as ways to capture the opportunities—or counter the threats—that these trends pose. Only after such an analysis and discussion do the leaders settle into the more typical planning exercises of financial forecasting and identifying strategic initiatives.
One consumer goods organization takes a more directed approach. The CEO, supported by the corporate-strategy function, compiles a list of three to six priorities for the coming year. Distributed to the managers responsible for functions, geographies, and brands, the list then becomes the basis for an offsite strategy-alignment meeting, where managers debate the implications of the priorities for their particular organizations. The corporate-strategy function summarizes the results, adds appropriate corporate targets, and shares them with the organization in the form of a strategy memo, which serves as the basis for more detailed strategic planning at the division and business-unit levels.
A packaged-goods company offers an even more tailored example. Every December the corporate senior-management team produces a list of ten strategic questions tailored to each of the three business units. The leaders of these businesses have six months to explore and debate the questions internally and to come up with answers. In June each unit convenes with the senior-management team in a one-day meeting to discuss proposed actions and reach decisions.
Some companies prefer to use a bottom-up rather than top-down process. We recently worked with a sales company to design a strategic-planning process that begins with in-depth interviews (involving all of the senior managers and selected corporate and business executives) to generate a list of the most important strategic issues facing the company. The senior-management team prioritizes the list and assigns managers to explore each issue and report back in four to six weeks. Such an approach can be especially valuable in companies where internal consensus building is an imperative.
Bring together the right people
An issues-based approach won’t do much good unless the most relevant people are involved in the debate. We found that survey respondents who were satisfied with the strategic-planning process rated it highly on dimensions such as including the most knowledgeable and influential participants, stimulating and challenging the participants’ thinking, and having honest, open discussions about difficult issues. In contrast, 27 percent of the dissatisfied respondents reported that their company’s strategic planning had not a single one of these virtues. Such results suggest that too many companies focus on the data-gathering and packaging elements of strategic planning and neglect the crucial interactive components.
Strategic conversations will have little impact if they involve only strategic planners from both the business unit and the corporate levels. One of our core beliefs is that those who carry out strategy should also develop it. The key strategy conversation should take place among corporate decision makers, business unit leaders, and people with expertise essential to the discussion. In addition to leading the corporate review, the CEO, aided by members of the executive team, should as a rule lead the strategy review for business units as well. The head of a business unit, supported by four to six people, should direct the discussion from its side of the table (see sidebar, "Things to ask in any business unit review").
Things to ask in any business unit review
Are major trends and changes in your business unit’s environment affecting your strategic plan? Specifically, what potential developments in customer demand, technology, or the regulatory environment could have enough impact on the industry to change the entire plan?
How and why is this plan different from last year’s?
What were your forecasts for market growth, sales, and profitability last year, two years ago, and three years ago? How right or wrong were they? What did the business unit learn from those experiences?
What would it take to double your business unit’s growth rate and profits? Where will growth come from: expansion or gains in market share?
If your business unit plans to take market share from competitors, how will it do so, and how will they respond? Are you counting on a strategic advantage or superior execution?
What are your business unit’s distinctive competitive strengths, and how does the plan build on them?
How different is the strategy from those of competitors, and why? Is that a good or a bad thing?
Beyond the immediate planning cycle, what are the key issues, risks, and opportunities that we should discuss today?
What would a private-equity owner do with this business?
How will the business unit monitor the execution of this strategy?
One pharmaceutical company invites business unit leaders to take part in the strategy reviews of their peers in other units. This approach can help build a better understanding of the entire company and, especially, of the issues that span business units. The risk is that such interactions might constrain the honesty and vigor of the dialogue and put executives at the focus of the discussion on the defensive.
Corporate senior-management teams can dedicate only a few hours or at most a few days to a business unit under review. So team members should spend this time in challenging yet collaborative discussions with business unit leaders rather than trying to absorb many facts during the review itself. To provide some context for the discussion, best-practice companies disseminate important operational and financial information to the corporate review team well in advance of such sessions. This reading material should also tee up the most important issues facing the business and outline the proposed strategy, ensuring that the review team is prepared with well-thought-out questions. In our experience, the right 10 pages provide ample fuel to fire a vigorous discussion, but more than 25 pages will likely douse the level of energy or engagement in the room.
Adapt planning cycles to the needs of each business
Managers are justifiably concerned about the resources and time required to implement an issues-based strategic-planning approach. One easy—yet rarely adopted—solution is to free business units from the need to conduct this rigorous process every single year. In all but the most volatile, high-velocity industries, it is hard to imagine that a major strategic redirection will be necessary every planning cycle. In fact, forcing businesses to undertake this exercise annually is distracting and may even be detrimental. Managers need to focus on executing the last plan’s major initiatives, many of which can take 18 to 36 months to implement fully.
Some companies alternate the business units that undergo the complete strategic-planning process (as opposed to abbreviated annual updates of the existing plan). One media company, for example, requires individual business units to undertake strategic planning only every two or three years. This cadence enables the corporate senior-management team and its strategy group to devote more energy to the business units that are “at bat.” More important, it frees the corporate-strategy group to work directly with the senior team on critical issues that affect the entire company—issues such as developing an integrated digitization strategy and addressing unforeseen changes in the fast-moving digital-media landscape.
Other companies use trigger mechanisms to decide which business units will undergo a full strategic-planning exercise in a given year. One industrial company assigns each business unit a color-coded grade—green, yellow, or red—based on the unit’s success in executing the existing strategic plan. “Code red,” for example, would slate a business unit for a strategy review. Although many of the metrics that determine the grade are financial, some may be operational to provide a more complete assessment of the unit’s performance.
Freeing business units from participating in the strategic-planning process every year raises a caveat, however. When important changes in the external environment occur, senior managers must be able to engage with business units that are not under review and make major strategic decisions on an ad hoc basis. For instance, a major merger in any industry would prompt competitors in it to revisit their strategies. Indeed, one advantage of a tailored planning cycle is that it builds slack into the strategic-review system, enabling management to address unforeseen but pressing strategic issues as they arise.
Implement a strategic-performance-management system
In the end, many companies fail to execute the chosen strategy. More than a quarter of our survey respondents said that their companies had plans but no execution path. Forty-five percent reported that planning processes failed to track the execution of strategic initiatives. All this suggests that putting in place a system to measure and monitor their progress can greatly enhance the impact of the planning process.
Most companies believe that their existing control systems and performance-management processes (including budgets and operating reviews) are the sole way to monitor progress on strategy. As a result, managers attempt to translate the decisions made during the planning process into budget targets or other financial goals. Although this practice is sensible and necessary, it is not enough. We estimate that a significant portion of the strategic decisions we recommend to companies can’t be tracked solely through financial targets. A company undertaking a major strategic initiative to enhance its innovation and product-development capabilities, for example, should measure a variety of input metrics, such as the quality of available talent and the number of ideas and projects at each stage in development, in addition to pure output metrics such as revenues from new-product sales. One information technology company, for instance, carefully tracks the number and skill levels of people posted to important strategic projects.
Strategic-performance-management systems, which should assign accountability for initiatives and make their progress more transparent, can take many forms. One industrial corporation tracks major strategic initiatives that will have the greatest impact, across a portfolio of a dozen businesses, on its financial and strategic goals. Transparency is achieved through regular reviews and the use of financial as well as nonfinancial metrics. The corporate-strategy team assumes responsibility for reviews (chaired by the CEO and involving the relevant business-unit leaders) that use an array of milestones and metrics to assess the top ten initiatives. One to expand operations in China and India, for example, would entail regular reviews of interim metrics such as the quality and number of local employees recruited and the pace at which alliances are formed with channel partners or suppliers. Each business unit, in turn, is accountable for adopting the same performance-management approach for its own, lower-tier top-ten list of initiatives.
When designed well, strategic-performance-management systems can give an early warning of problems with strategic initiatives, whereas financial targets alone at best provide lagging indicators. An effective system enables management to step in and correct, redirect, or even abandon an initiative that is failing to perform as expected. The strategy of a pharmaceutical company that embarked on a major expansion of its sales force to drive revenue growth, for example, presupposed that rapid growth in the number of sales representatives would lead to a corresponding increase in revenues. The company also recognized, however, that expansion was in turn contingent on several factors, including the ability to recruit and train the right people. It therefore put in place a regular review of the key strategic metrics against its actual performance to alert managers to any emerging problems.
Integrate human-resources systems into the strategic plan
Simply monitoring the execution of strategic initiatives is not sufficient: their successful implementation also depends on how managers are evaluated and compensated. Yet only 36 percent of the executives we surveyed said that their companies’ strategic-planning processes were integrated with HR processes. One way to create a more valuable strategic-planning process would be to tie the evaluation and compensation of managers to the progress of new initiatives.
Although the development of strategy is ostensibly a long-term endeavor, companies traditionally emphasize short-term, purely financial targets—such as annual revenue growth or improved margins—as the sole metrics to gauge the performance of managers and employees. This approach is gradually changing. Deferred-compensation models for boards, CEOs, and some senior managers are now widely used. What’s more, several companies have added longer-term performance targets to complement the short-term ones. A major pharmaceutical company, for example, recently revamped its managerial-compensation structure to include a basket of short-term financial and operating targets as well as longer-term, innovation-based growth targets.
Although these changes help persuade managers to adopt both short- and long-term approaches to the development of strategy, they don’t address the need to link evaluation and compensation to specific strategic initiatives. One way of doing so is to craft a mix of performance targets that more appropriately reflect a company’s strategy. For example, one North American services business that launched strategic initiatives to improve its customer retention and increase sales also adjusted the evaluation and compensation targets for its managers. Rather than measuring senior managers only by revenue and margin targets, as it had done before, it tied 20 percent of their compensation to achieving its retention and cross-selling goals. By introducing metrics for these specific initiatives and linking their success closely to bonus packages, the company motivated managers to make the strategy succeed.
An advantage of this approach is that it motivates managers to flag any problems early in the implementation of a strategic initiative (which determines the size of bonuses) so that the company can solve them. Otherwise, managers all too often sweep the debris of a failing strategy under the operating rug until the spring-cleaning ritual of next year’s annual planning process.
Some business leaders have found ways to give strategic planning a more valuable role in the formulation as well as the execution of strategy. Companies that emulate their methods might find satisfaction instead of frustration at the end of the annual process.
Renée Dye is a consultant in McKinsey’s Atlanta office, and Olivier Sibony is a director in the Paris office.
This article was first published in the Autumn 2007 issue of McKinsey on Finance . Visit McKinsey’s corporate finance site to view the full issue.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Distortions and deceptions in strategic decisions
Tired of strategic planning.
The Skyline G Blog: New ideas and perspectives focused on results
What is Strategic Planning? The Key Components, Process & Role Leaders Play in Ensuring a Strategy's Success
by Thuy Sindell, PhD. and Milo Sindell, MS.
Strategic planning is a process that is essential for companies to ensure successful and sustainable growth.
An intelligent and actionable strategic plan is a vital part of competing within the marketplace. It directs businesses to take meaningful action to help them reach their organization’s goals by mapping out a clear direction, creating measurable goals, and allocating resources to pursue these specific objectives.
What is Strategic Planning?
A strategic plan is an essential process and strategy execution document for any company looking to make the most of its resources and reach long-term organizational goals.
This vital and continually evolving document outlines a clear direction, sets objectives that must be achieved, and provides an actionable roadmap for success; it also helps organizations stand out from competitors by allowing them to differentiate themselves in the marketplace with their unique approach.
A well-crafted strategic plan will help companies stay focused on their mission while making decisions based on core values guiding them toward achieving desired results by ensuring everyone is moving in the same direction.

What are the Key Components of a Strategic Plan?
Several key components make up a well-developed strategic plan. These key components include:
A Mission Statement
An organization’s mission statement states the company’s purpose and the reasons why it exists. Although you might be already clear on the mission, reiterating your mission statement and connection to the plan acts as a foundation for the strategic plan and your strategy.
A Vision Statement
The company vision is the bigger objective that the company aspires to achieve. This may be as broad as making the world a better place through your product or service or ridding bathrooms of mildew. Whatever your vision, it should be connected to your strategic plan
Aligning the company mission and vision statements is the first crucial step to strategic planning.
SWOT Analysis
An overall evaluation of the company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Knowing these points will help you leverage your resources, shore up gaps, and realistically plan your path and the potential risks. Your SWOT analysis will help ensure that your strategic plan is based upon reality and play an important part in your strategic management process.
Goals & Objectives
Goals and objectives need specific, measurable, achievable, and time-bound targets the company wants to achieve. Ensure your goals are achievable, measurable, and can be clearly communicated as part of your strategic planning. High-level company objectives should cascade and align with the objectives of various divisions and teams. The Strategic plans of each division and team should map directly to broader company goals and methods.
The specific courses of action that the company will take to achieve its measurable goals and specific strategic issues.
Action Plans
Detailed project plans outlining the specific steps that will be taken to implement the strategies.
Resource Allocation
The allocation of financial, human, and other resources to implement the action plans.
Evaluation and Control
Evaluation and control are based on measures and systems to monitor the company’s progress toward achieving its organization’s goals, objectives, and financial plan and to make adjustments as necessary.

Who is Responsible for Creating a Strategic Plan?
In general, creating a strategic plan is the responsibility of the company’s top management team - the CEO, CFO, other executives, etc.
However, though the top management will do the strategic thinking, it’s essential for key members throughout the entire organization to be involved in the strategic planning process as different departments, employees, and human resources will have valuable insights and perspectives to contribute to the strategy formation. Also, when various constituents are a part of and the planning process a sense of ownership and commitment to the strategic plan’s success is reinforced.
It’s also common for companies to seek input from external stakeholders, customers, suppliers, and industry experts as part of the strategic planning process. As part of your planning process make sure to identify any critical stakeholders outside of your company.
What Makes the Strategic Planning Process Effective?
Below are some key factors that contribute to the overall effectiveness of a successful strategic plan and the strategic planning process. Understanding these points will help make your strategic planning process more effective:
The plan needs to be clear & concise, with specific strategic goals & objectives that are easy for everyone to understand. Senior leadership plays a critical role in ensuring that each objective is clear and how objectives will be achieved is understood.
The strategic plan needs to take the company’s resources & capabilities into account, and the goals need to be realistic & achievable based on the market data.
The plan needs to be flexible enough to allow for adjustments to be made in response to changes in the external environment after deployment.
The plan must be aligned with the company’s mission, vision & values and should support the organization’s overall direction in terms of business plan and annual budgets.
Easily Communicated
The plan needs to be communicated effectively to all stakeholders & investors, including employees & customers.
The plan needs clear & actionable steps and a timeline for implementation. It must be followed consistently to ensure progress toward business goals like increasing sales and maximizing profit.
The plan needs to measure & evaluate progress, collect feedback, and be reviewed and updated regularly to ensure continuous progress toward company goals and that the plan remains relevant and practical and targets logical key performance indicators.
An effective strategic plan identifies potential factors that might derail the plan and, at a minimum, provides high-level alternatives should the plan become derailed.

When Do Strategic Plans Fail?
Listed below are a few potential reasons why strategic planning might fail. Understanding why strategic plans fail will help create more effective strategic planning outcomes:
Lacks Clarity
Plans need to be clear and specific. If not, it may be difficult to understand and challenging to implement. When a strategic plan is ambitious it is tough for people to feel connected and motivated to take action.
Lack of Realistic Options and Objectives
Plans need to be realistic. If the plan cannot really be achieved, it’ll be difficult to implement and lead to frustration, disappointment, and potential failure.
Lack of Flexibility
The plan needs to be flexible; if it’s not is not flexible and doesn’t allow for adjustments in response to changes in the environment (internal and external) or from evaluation or measurement, it may become irrelevant or ineffective.
Lack of Alignment
The plan needs to be aligned with the company’s mission, vision, and values; if not consistent with the organization’s overall direction, it can quickly become out of sync with its underlying purpose and be ineffective in helping to reach desired goals.
Lack of Understanding
The plan needs to be communicated effectively to all key stakeholders and take feedback from all stakeholders; otherwise, it may be misunderstood or, worse - ignored or seen as not valuable.
Lack Actionable Steps
The strategic plan needs to be implemented swiftly and consistently; if the action steps are not clear or too hard to implement, they may not be implemented effectively.
Lack of Measurable Outcomes
The strategic plan needs to be reviewed and updated regularly, and its performance evaluated after implementation; otherwise, it may become ineffective or outdated, therefore ineffective at achieving desired outcomes.
External Factors
Changes in the external environment can have a huge effect. Changes like shifts in the economy or customer preferences, if not accounted for, can seriously impact the effectiveness of a once brilliant strategic plan.
However, as in life and business, things change, and every business must be able to adapt quickly to changing circumstances. This is why an effective plan includes contingencies.

What is a Company Leader’s Role in Ensuring the Strategic Plan is Implemented Successfully?
Strategic management.
Company leaders are responsible for ensuring that the strategic plan is implemented successfully.
Some specific ways business leaders can ensure the plan is implemented properly are:
Clearly Communicate the Plan
Business leaders need to communicate the strategic plan effectively to all key stakeholders, including employees, customers, and investors. Any questions need to be answered and clarified, so everyone is aligned. The strategic plan should be shared in a way that you (the leader) demonstrate ownership and enthusiasm and can share with your team how each role is vital to achieving the plan’s objectives.
Providing Resources
Leaders need to ensure that resources, such as funding, personnel, and technology, are available to everyone needed in order to implement the plan successfully.
Setting Expectations
Leaders need to set clear expectations for implementing the plan and hold the designated employees accountable for meeting those expectations. Clear and achievable timelines need to be established and committed to by each stakeholder.
Leading by Example
Leaders need to model the behaviors and values outlined in the plan and encourage others to do the same.
Providing Support
Leaders need to provide support and guidance to employees as they work through problems toward achieving the strategic goals and objectives of the plan.
Monitoring Progress
Leaders need to monitor the progress towards achieving the goals and objectives outlined in the plan and make adjustments in the operational plans as they see fit, as needed.
Celebrating Successes
Leaders need to recognize and celebrate wins along the way to help keep morale high and encourage continued progress toward the ultimate goals.

What’s the Role of Each Individual Employee in Implementing & Supporting the Strategic Plans Success?
Employees are the driving force and critical in implementing and supporting the strategic plan’s success. Your employees will be the eyes and ears of how the strategic plan works. This is why it is vital for leaders to create a business environment where there is open communication and all types of information can be shared and reviewed in relation to its impact on the long- term strategy. Leaders must foster an open environment where questions can be asked and bad and good news shared. Leaders can help employees play their part by ensuring employees are supported and are clear on their ability to do the following:
Understand the Plan
Employees need to understand the strategic plan, how it aligns with the company’s mission, the steps to take, and most importantly, the goals.
Aligning Work and Job Goals with the Plan
Leaders, managers, and employees need to align their work with the strategic plan and prioritize tasks that support achieving the plan’s goals & strategic objectives.
Manage Implementation
Employees must consistently follow through on their assigned tasks and responsibilities to implement the plans, steps, and processes.
Provide Feedback
During the initial review of the organization’s current status, employees must provide feedback and suggestions to improve the plan. During its implementation, employees need to provide feedback based on performance and potentially adjust the plan if needed for better performance and goals.
Communicate Laterally and Up
Employees need to communicate with coworkers to ensure everyone is working towards the same goals & objectives and, most importantly, employees need to communicate to their manager on how their contribution is proceeding.
Seek Support and Guidance
Employees need to seek support and guidance from leaders if they need help implementing any steps of the plan or achieving goals.

Do Some Companies Believe that Strategic Planning is a Waste of Time?
Sure. It’s possible some companies may view strategic planning as a waste of time. This could be due to a variety of reasons: resources required upfront, lack of understanding of the benefits of strategic planning, a lack of buy-in from senior management, or a lack of resources to dedicate to the process.
However, for massively successful companies, strategic planning is recognized as an invaluable tool to help organizations achieve their long-term goals and be outstanding in a competitive marketplace.
Strategic planning can also help companies be more agile and adapt to changes in the external environment. For these reasons, it’s generally recommended that companies engage in strategic planning and review results on a regular basis.
What Makes a Great Strategy?
What makes a great competitive strategy? Several characteristics are often considered to be key elements of great strategy execution:
A great strategy is clear & easy to understand, with specific goals & strategic objectives that are well-defined.
A great strategy is a focused strategy. A great strategy is focused on a specific area of the business and doesn’t try to do too many things at once.
A great strategy is aligned with the company’s overall mission, vision for the future, and values, supporting the organization’s overall direction.
Flexibility
A great strategy is flexible and allows for adjustments to be made in response to results and changes in the external environment.
A great strategy is realistic & achievable, taking into account the company’s resources & capabilities and what can actually get done.
Differentiation
The great strategy sets the company apart from its competitors in the marketplace and helps it to differentiate itself from competitors to customers.
A great strategy can be executed effectively, with clear action steps, a timeline for implementation, and who is responsible for each action step.
Evaluation & Feedback
The great strategy includes measures for evaluating progress and collecting feedback, and it needs to be reviewed regularly & potentially updated to ensure it remains relevant & effective.
When is a Great Strategy Not Enough to Ensure Company Success?
While a great strategy can certainly be a key factor in a company’s success, it’s not the only factor needed to be successful. There are a number of other internal and external factors that can impact a company’s success, including:
Even the best strategy will not be a successful strategy if executed poorly.
A company needs resources, period. Resources like funding, personnel, and technology, are essential to implement strategy effectively.
Changes in external factors are equally important as the internal environment. For example, economic shifts or customer preferences can impact a company’s success.
Competition
A company’s success can also be impacted by its competitors’ actions and even competitors’ reactions to strategy implementation.
Market Demand
A company’s success will depend partly on the market demand for its products or services. Demand should absolutely be a part of the strategy formulation.
A company’s success will highly depend on the quality of its products or services and its ability for its products to meet customer needs.
The senior leadership of a company can play a key role in its success, or failure, as they set the vision & direction of the organization.
How Does Company Leadership Play a Critical Part in a Company’s Strategic Success?
Without involved leadership, a strategic plan will more than likely fail. A company’s leadership plays a critical role in strategic success in several ways:
Setting the Direction
A company’s leadership is responsible for setting the organization’s vision and direction and creating a strategic management plan that aligns with that direction.
A company’s Leadership is responsible for ensuring that the necessary resources, such as funding, personnel, and technology, are available to implement the strategic plan.
Communicating the Plan
A company’s leadership communicates the strategic management plan effectively and consistently to all stakeholders, including employees, customers, and investors.
A company’s leadership needs to model the behaviors and values aligned with the plan and encourage others to do the same.
A company’s leadership needs to provide support & guidance to employees as they work towards achieving the goals and objectives of the strategic plan. This will help in employee retention and strategic success.
A company’s leadership needs to monitor progress toward achieving the goals & objectives of the plan and make necessary adjustments as needed.
A company’s leadership needs to recognize and celebrate successes along the way to help keep team morale high and encourage continued progress to achieve goals.
How Can Companies Prepare & Support their Leaders to Implement & Ensure Strategic Planning Success?
There are many ways in which companies can prepare and support their leaders to implement and ensure the success of their strategic planning initiative.
Provide Proper Training
Companies need to provide training & strategy development opportunities to help their leaders acquire the knowledge and skills they need to implement & support the strategic vision effectively.
Encourage Open Communication
Companies need to foster an environment of open, clear communication and encourage leaders to seek input & feedback from their teams within the strategic framework - even when the strategy map is not positive.
Align Leadership with Company Values
Companies must ensure that their leadership’s values align with the company’s values and culture and that their leaders are committed to the mission and vision of the organization.
Encourage Collaboration
Companies need to encourage collaboration & cross-functional teamwork as a part of project management to ensure that all departments work towards the same goals & objectives.
Provide Resources
As part of the strategic planning process, companies need to ensure their leadership has the necessary resources, such as funding, personnel, & technology, to implement the strategic plan effectively for the entire duration.
Establish Clear Expectations
Companies must set clear expectations for how strategic planning should be activated and implemented and hold leadership accountable for meeting expectations as per the strategic plan document.
Monitor Progress
Company leaders need to monitor the progress toward achieving the goals and objectives of the strategic plan and provide their support and guidance as needed. Strategic planning is essential for business success, and the key to achieving successful results lies in the hands of leadership. For leaders to ensure a strategy’s success, they must become strategic planners and the details of the business’s strategic plan must be organized and understood by each person responsible.
Leaders and managers need to communicate the strategic plan through consistent discussions that foster collaborative decision-making. Responsibilities for the planning process and success also extend beyond the leader and onto each individual employee to help realize the steps of an effective strategic plan. Companies must set clear strategic objectives that align with their mission and strategic goals while preparing business leaders to carry out those plans. When done correctly, with careful attention paid to all levels of the organization, successful strategic planning can lead a company in the right direction toward long-term sustainability and future opportunities.
Having a clear strategic plan is one of those obvious items that every company should have in place yet many companies don’t.
Although the effort of investing the time and resources into creating a strategic planning template can be demanding, the value and impact of your investment can return a healthy multiple.
Once your mission and vision statements and strategic plan are in place they become a touchstone to focus your business, align teams, and what makes your way of navigating your market and competition unique.
We hope that this resource provides a road map and helps facilitate the development of your strategic plan if you don’t have one yet. For those that do have strategic plans, we hope this resource helps act as a checklist to fortify the strategy development you’ve already created.
What is Leadership? A Guide To The Core Elements of Great Leadership & Behaviors That Make an Effective Leader
Business Goal Setting: How to Improve Team Performance & Morale
- Thriving Together: The Intersection of Organizational Culture and Employee Well-being
- What is executive coaching? The definition, benefits, process & why even good leaders need coaching
- Emotional intelligence in leadership: what it is & why it's Important
- Imposter syndrome: definition, types, symptoms, causes & strategies
- Self awareness in leadership: the x factor in team performance
- Effective decision-making: skills, process & strategies to improve as a leader
- 360 feedback assessment: what it is, who its for & how to implement at your organization
- Leadership transition: plan, process, challenges & best practices
- Mastering the CEO transition: How to craft an ironclad CEO succession plan & seamlessly transition a new CEO
- Toxic Leadership & Toxic Employees: How to Fix a Toxic Workplace
Let's explore how we can help you achieve your goals

Strategic Management & Strategic Planning Process
Strategic management process is a method by which managers conceive of and implement a strategy that can lead to a sustainable competitive advantage. [1 ]
Strategic planning process is a systematic or emerged way of performing strategic planning in the organization through initial assessment, thorough analysis, strategy formulation, its implementation and evaluation.
What is strategic planning process?
The process of strategic management lists what steps the managers should take to create a complete strategy and how to implement that strategy successfully in the company. It might comprise from 7 to nearly 30 steps [4] and tends to be more formal in well-established organizations.
The ways that strategies are created and realized differ. Thus, there are many different models of the process. The models vary between companies depending upon:
- Organization’s culture.
- Leadership style.
- The experience the firm has in creating successful strategies.
All the examples of the process in this article represent top-down approach and belong to the ‘design school’.
Components of strategic planning process
There are many components of the process which are spread throughout strategic planning stages. Most often, the strategic planning process has 4 common phases: strategic analysis, strategy formulation, implementation and monitoring (David [5] , Johnson, Scholes & Whittington [6] , Rothaermel [1] , Thompson and Martin [2] ). For clearer understanding, this article represents 5 stages of strategic planning process:
Initial Assessment
Situation analysis.
- Strategy Formulation
- Strategy Implementation
Strategy Monitoring
Components: Vision statement & Mission statement Tools used: Creating a Vision and Mission statements.
The starting point of the process is initial assessment of the firm. At this phase managers must clearly identify the company’s vision and mission statements.
Business’ vision answers the question: What does an organization want to become? Without visualizing the company’s future, managers wouldn’t know where they want to go and what they have to achieve. Vision is the ultimate goal for the firm and the direction for its employees.
In addition, mission describes company’s business. It informs organization’s stakeholders about the products, customers, markets, values, concern for public image and employees of the organization (David, p. 93) [5] . Thorough mission statement acts as guidance for managers in making appropriate (Rothaermel, p. 34) [1] daily decisions.
Components: Internal environment analysis, External environment analysis and Competitor analysis Tools used: PEST , SWOT , Core Competencies, Critical Success Factors, Unique Selling Proposition, Porter’s 5 Forces , Competitor Profile Matrix , External Factor Evaluation Matrix , Internal Factor Evaluation Matrix, Benchmarking , Financial Ratios, Scenarios Forecasting, Market Segmentation, Value Chain Analysis , VRIO Framework
When the company identifies its vision and mission it must assess its current situation in the market. This includes evaluating an organization’s external and internal environments and analyzing its competitors.
During an external environment analysis managers look into the key external forces: macro & micro environments and competition. PEST or PESTEL frameworks represent all the macro environment factors that influence the organization in the global environment. Micro environment affects the company in its industry. It is analyzed using Porter’s 5 Forces Framework.
Competition is another uncontrollable external force that influences the company. A good example of this was when Apple released its IPod and shook the mp3 players industry, including its leading performer Sony. Firms assess their competitors using competitors profile matrix and benchmarking to evaluate their strengths, weaknesses and level of performance.
Internal analysis includes the assessment of the company’s resources, core competencies and activities. An organization holds both tangible resources: capital, land, equipment, and intangible resources: culture, brand equity, knowledge, patents, copyrights and trademarks (Rothaermel, p. 90) [1] . A firm’s core competencies may be superior skills in customer relationship or efficient supply chain management. When analyzing the company’s activities managers look into the value chain and the whole production process.
As a result, situation analysis identifies strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats for the organization and reveals a clear picture of company’s situation in the market.
Components: Objectives, Business level, Corporate level and Global Strategy Selection Tools used: Scenario Planning, SPACE Matrix, Boston Consulting Group Matrix , GE-McKinsey Matrix, Porter’s Generic Strategies, Bowman’s Strategy Clock, Porter’s Diamond, Game Theory, QSP Matrix.
Successful situation analysis is followed by creation of long-term objectives. Long-term objectives indicate goals that could improve the company’s competitive position in the long run. They act as directions for specific strategy selection. In an organization, strategies are chosen at 3 different levels:
- Business level strategy. This type of strategy is used when strategic business units (SBU), divisions or small and medium enterprises select strategies for only one product that is sold in only one market. The example of business level strategy is well illustrated by Royal Enfield firms. They sell their Bullet motorcycle (one product) in United Kingdom and India (different markets) but focus on different market segments and sell at very different prices (different strategies). Firms may select between Porter’s 3 generic strategies: cost leadership, differentiation and focus strategies. Alternatively strategies from Bowman’s strategy clock may be chosen (Johnson, Scholes, & Whittington, p. 224 [6] ).
- Corporate level strategy. At this level, executives at top parent companies choose which products to sell, which market to enter and whether to acquire a competitor or merge with it. They select between integration, intensive, diversification and defensive strategies.
- Global/International strategy. The main questions to answer: Which new markets to develop and how to enter them? How far to diversify? (Thompson and Martin, p. 557 [2] , Johnson, Scholes, & Whittington, p. 294 [6] )
Managers may choose between many strategic alternatives. That depends on a company’s objectives, results of situation analysis and the level for which the strategy is selected.
Components: Annual Objectives, Policies, Resource Allocation, Change Management, Organizational chart, Linking Performance and Reward Tools used: Policies, Motivation, Resistance management, Leadership, Stakeholder Impact Analysis, Changing organizational structure, Performance management
Even the best strategic plans must be implemented and only well executed strategies create competitive advantage for a company.
At this stage managerial skills are more important than using analysis. Communication in strategy implementation is essential as new strategies must get support all over organization for effective implementation. The example of the strategy implementation that is used here is taken from David’s book, chapter 7 on implementation [5] . It consists of the following 6 steps:
- Setting annual objectives;
- Revising policies to meet the objectives;
- Allocating resources to strategically important areas;
- Changing organizational structure to meet new strategy;
- Managing resistance to change;
- Introducing new reward system for performance results if needed.
The first point in strategy implementation is setting annual objectives for the company’s functional areas. These smaller objectives are specifically designed to achieve financial, marketing, operations, human resources and other functional goals. To meet these goals managers revise existing policies and introduce new ones which act as the directions for successful objectives implementation.
The other very important part of strategy implementation is changing an organizational chart. For example, a product diversification strategy may require new SBU to be incorporated into the existing organizational chart. Or market development strategy may require an additional division to be added to the company. Every new strategy changes the organizational structure and requires reallocation of resources. It also redistributes responsibilities and powers between managers. Managers may be moved from one functional area to another or asked to manage a new team. This creates resistance to change, which has to be managed in an appropriate way or it could ruin excellent strategy implementation.
Components: Internal and External Factors Review, Measuring Company’s Performance Tools used: Strategy Evaluation Framework, Balanced Scorecard, Benchmarking
Implementation must be monitored to be successful. Due to constantly changing external and internal conditions managers must continuously review both environments as new strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats may arise. If new circumstances affect the company, managers must take corrective actions as soon as possible.
Usually, tactics rather than strategies are changed to meet the new conditions, unless firms are faced with such severe external changes as the 2007 credit crunch.
Measuring performance is another important activity in strategy monitoring. Performance has to be measurable and comparable. Managers have to compare their actual results with estimated results and see if they are successful in achieving their objectives. If objectives are not met managers should:
- Change the reward system.
- Introduce new or revise existing policies.
The key element in strategy monitoring is to get the relevant and timely information on changing environment and the company’s performance and if necessary take corrective actions.
Different models of the process
There is no universal model of the strategic management process. The one, which was described in this article, is just one more version of so many models that are established by other authors. In this section we will illustrate and comment on 3 more well-known frameworks presented by recognized scholars in the strategic management field. More about these models can be found in the authors’ books.
Source: David (p. 46)
- Strategy Evaluation
- Develop vision and mission
- External environment analysis
- Internal environment analysis
- Establish long-term objectives
- Generate, evaluate and choose strategies
- Implement strategies
- Measure and evaluate performance
- Indicates all the major steps that have to be met during the process.
- Illustrates that the process is a continuous activity.
- Arrows show the two way process. This means that companies may sometimes go a step or two back in the process rather than having to complete the process and start it all over from the beginning. For example , if in the implementation stage the company finds out that the strategy it chose is not viable, it can simply go back to the strategy selection point instead of continuing to the monitoring stage and starting the process from the beginning.
- Represents only strategy formulation stage and does separate situation analysis from strategy selection stages.
- Confuses strategy evaluation with strategy monitoring stage.
Source: Rothaermel (p. 20)
- Formulation
- Implementation
- Initial analysis
- External and internal analysis
- Business or corporate strategy formulation
- Shows that the process is a continuous activity.
- Separates initial analysis (in this articles it’s called initial assessment) from internal/external analysis.
- Emphasizes the main focus of strategic management: “Gain and sustain competitive advantage”.
- Does not include strategy monitoring stage.
- Arrows indicate only one way process. For example , after the strategy formulation the process continues to the implementation stage while this is not always the truth. Companies may go back and reassess their environments if some conditions had changed.
Source: Thompson and Martin (p.36)
- Where are we?
- Where are we going?
- How are we getting there?
- How are we doing?
- Situation appraisal: review of corporate objectives
- Situation assessment
- Clarification of objectives
- Corporate and competitive strategies
- Strategic decisions
- Monitor progress
- The model is supplemented by 4 fundamental strategic management questions.
- Arrows indicate only one way process.
Limitations
It is rare that the company will be able to follow the process from the first to the last step. Producing a quality strategic plan requires time , during which many external and even internal conditions may change. This results in the flawed strategic plan which has to be revised, hence requiring even more time to finish.
On the other hand, when implementing the strategic plan, the actual results do not meet the requirements of the strategic plan so the plan has to be altered or better methods for the implementation have to be discovered. This means that some parts of strategic management process have to be done simultaneously, which makes the whole process more complex .
- Rothaermel, F. T. (2012). Strategic Management: Concepts and Cases. McGraw-Hill/Irwin, p. 20, 32-45, 90
- Thompson, J. and Martin, F. (2010). Strategic Management: Awareness & Change. 6th ed. Cengage Learning EMEA, p. 34, 557, 790
- Clark, D. N. (1997). Strategic management tool usage: a comparative study. Strategic Change Vol. 6, pp. 417-427
- David, F.R. (2009). Strategic Management: Concepts and Cases. 12th ed. FT Prentice Hall, p. 36-37, 45-47, 93
- Johnson, G, Scholes, K. Whittington, R. (2008). Exploring Corporate Strategy. 8th ed. FT Prentice Hall, p. 11-13, 224, 294
- Virtual Strategist (2012). Overview of the Strategic Planning Process (VIDEO). Available at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sU3FLxnDv_A
- Strategic Management & Strategic Planning
- Total Quality Management
- Supplier Relationship Management (SRM)
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A strategic plan is a tool to define where your organization wants to go and what actions you need to take to achieve those goals. Strategic planning is the process of creating a plan in order to hit your strategic objectives. Strategic management includes the strategic planning process, but also goes beyond it. In addition to planning how you ...
The outcome of strategic planning is typically a long-term strategic plan that outlines the organization's vision, mission, values, and objectives. Business planning, on the other hand, is a more tactical process that focuses on the implementation of specific initiatives and projects to support the organization's long-term goals.
Write and communicate your strategic plan. Implement, monitor, and revise. 1. Clarify your vision, mission, and values. The first step of the strategic planning process is understanding your organization's core elements: vision, mission, and values. Clarifying these will align your strategic plan with your company's definition of success.
Estimated Duration. Determine organizational readiness. Owner/CEO, Strategy Director. Readiness assessment. Establish your planning team and schedule. Owner/CEO, Strategy Leader. Kick-Off Meeting: 1 hr. Collect and review information to help make the upcoming strategic decisions. Planning Team and Executive Team.
Determine your priorities and objectives. Define responsibilities. Measure and evaluate results. Each step requires close collaboration as you build a shared vision, strategy for implementation, and system for understanding performance. Related: Learn how to hold an effective strategic planning meeting.
Strategic planning is an organization's process of defining its direction and long-term goals, creating specific plans to achieve them, implementing those plans, and evaluating the results. On one hand, that definition makes strategy planning sound like a Business 101 concept—define your goals and a plan to achieve them.
The strategic planning process varies by the size of the organization and can be formal or informal, but there are constraints. For example, teams of all sizes and goals should build in many points along the way for feedback from key leaders — this helps the process stay on track.
Strategic planning is the process through which enterprises, functions and business units identify the roadmap of initiatives and portfolio of investments that will be required in the medium term to achieve long-term strategic objectives. ... The organization's mission articulates its reasons for being, and the vision lays out where the ...
Strategic planning seeks to anticipate future industry trends . During the process, the organization creates a vision, articulates its purpose, and sets strategic goals that are long-term and forward-focused. Those strategic goals inform operational goals and incremental milestones that need to be reached.
What is strategic planning? Whether your organization is a startup or established business charting the way forward, a strategic plan is a vital tool for success—and you can lead the charge. Strategic planning is the process of putting your best business theories to the test in the marketplace. Your strategic planning process starts with ...
Strategic planning process steps. Determine your strategic position. Prioritize your objectives. Develop a strategic plan. Execute and manage your plan. Review and revise the plan. Every business should have a strategic plan—but the number of businesses that try to operate without a defined plan (or at least a clearly communicated one) might ...
Strategic planning is the ongoing organizational process of using available knowledge to document a business's intended direction. This process is used to prioritize efforts, effectively allocate resources, align shareholders and employees on the organization's goals, and ensure those goals are backed by data and sound reasoning. It's ...
What Is Strategic Planning? Strategic planning is the ongoing organizational process of using available knowledge to document a business's intended direction. This process is used to prioritize efforts, effectively allocate resources, align shareholders and employees, and ensure organizational goals are backed by data and sound reasoning.
Strategic planning is defined as a pivotal organizational endeavor, meticulously charting the mission, goals, and objectives over a strategic timeframe, typically spanning 2-5 years. This comprehensive roadmap takes into meticulous consideration the current organizational landscape, navigating through the intricacies of prevailing legislation ...
The strategic planning process requires considerable thought and planning on the part of a company's upper-level management. Before settling on a plan of action and then determining how to strategically implement it, executives may consider many possible options. ... The purpose of this is to help identify the organization's strengths and ...
1. Basic model. The basic strategic planning model is ideal for establishing your company's vision, mission, business objectives, and values. This model helps you outline the specific steps you need to take to reach your goals, monitor progress to keep everyone on target, and address issues as they arise.
00:00. Audio. How to improve strategic planning. This sense of disappointment was captured in a recent McKinsey Quarterly survey of nearly 800 executives: just 45 percent of the respondents said they were satisfied with the strategic-planning process. 1 Moreover, only 23 percent indicated that major strategic decisions were made within its ...
Consider the following seven steps to help you create effective, actionable plans: 1. Understand the need for a strategic plan. The first and perhaps most important step of the planning process is understanding that there's a need for a plan. In terms of management, this means that you need to be aware of the industry environment in which the ...
strategic planning, disciplined effort to produce decisions and actions that shape and guide an organization's purpose and activities, particularly with regard to the future.Strategic planning is a fundamental component of organizational management and decision making in public, private, and nonprofit organizations. It is a structured approach to establishing an organization's direction ...
As part of the strategic planning process, companies need to ensure their leadership has the necessary resources, such as funding, personnel, & technology, to implement the strategic plan effectively for the entire duration. ... with careful attention paid to all levels of the organization, successful strategic planning can lead a company in ...
Strategic management process is a method by which managers conceive of and implement a strategy that can lead to a sustainable competitive advantage. [1] Strategic planning process is a systematic or emerged way of performing strategic planning in the organization through initial assessment, thorough analysis, strategy formulation, its ...
Strategic planning is an organization's process of defining its strategy or direction, and making decisions on allocating its resources to attain strategic goals.. Furthermore, it may also extend to control mechanisms for guiding the implementation of the strategy. Strategic planning became prominent in corporations during the 1960s and remains an important aspect of strategic management.
Strategic planning is a process in which organizational leaders determine their vision for the future as well as identify their goals and objectives for the organization. The process also includes establishing the sequence in which those goals should fall so that the organization is enabled to reach its stated vision .