- 400+ Sample Business Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Customer Success Stories
Business Plan Course
Strategic Planning Templates
E-books, Guides & More
Entrepreneurs & Small Business
Accelerators & Incubators
Business Consultants & Advisors
Educators & Business Schools
Students & Scholars
AI Business Plan Generator
Financial Forecasting
AI Assistance
Ai Pitch Deck Generator
Strategic Planning
See How Upmetrics Works →
- Sample Plans
Small Business Tools

How to Write Competitive Analysis in a Business Plan (w/ Examples)

Free Competitive Analysis Kit
- Vinay Kevadia
- January 9, 2024
13 Min Read

Every business wants to outperform its competitors, but do you know the right approach to gather information and analyze your competitors?
That’s where competitive analysis steps in. It’s the tool that helps you know your competition’s pricing strategies, strengths, product details, marketing strategies, target audience, and more.
If you want to know more about competitor analysis, this guide is all you need. It spills all the details on how to conduct and write a competitor analysis in a business plan , with examples.
Let’s get started and first understand the meaning of competitive analysis.
What is Competitive Analysis?
A competitive analysis involves collecting information about what other businesses in your industry are doing with their products, sales, and marketing.
Businesses use this data to find out what they are good at, where they can do better, and what opportunities they might have. It is like checking out the competition to see how and where you can improve.
This kind of analysis helps you get a clear picture of the market, allowing you to make smart decisions to make your business stand out and do well in the industry.
After having a brief knowledge of what a competitive analysis is, let’s understand how to conduct it:
How to Conduct a Competitive Analysis?
- Identify your direct and indirect competitors
- Study the overall market space
- Prepare a competitive framework
- Take note of your competition’s strategies
- Perform a SWOT Analysis of your competitors
1. Identify Your Direct and Indirect Competitors
First things first — identify all your business competitors and list them. You can make the final list later, but right now jot down all the competitors including new competitors.
Explore your competitors using Google, social media platforms, or local markets. Then differentiate them into direct or indirect competitors. And then distinguish them into direct or indirect competitors.
Direct competitors
Businesses offering the same products or services, targeting a similar target market , are your direct competitors.
These competitors operate in the same industry and are often competing for the same market share.
Indirect competitors
On the other hand, indirect competitors are businesses that offer different products or services but cater to the same target customers.
While they may not offer identical solutions, they compete for the same customer budget or attention. Indirect competitors can pose a threat by providing alternatives that customers might consider instead of your offerings.
2. Study the Overall Market
Now that you know your business competitors, deep dive into the market research. The research should be a combination of both primary and secondary research methods.
Primary research
It means being involved in getting the information directly from customers or by buying the product itself. Some examples of primary market research methods include:
- Purchasing competitors’ products or services
- Conducting interviews with customers
- Administering online surveys to gather customer insights
Secondary research
The secondary research involves utilizing pre-existing gathered information from some relevant sources. Some of its examples include:
- Scrutinizing competitors’ websites
- Assessing the current economic landscape
- Identifying technological advancements
Have a good understanding of the market at this point before you proceed with the next step.
3. Prepare a Competitive Framework
Creating a competitive framework is like charting a strategic roadmap for your business in the competitive landscape. It includes defining your USPs, market positioning, and various strategies.
Establishing your competitive positioning clarifies where your business stands among competitors.
Plan how to make your product or service stand out by figuring out ways to make it different to stand out, whether it’s through new features, better quality, or excellent customer service.
Craft unique value propositions that resonate with your target audience, communicating the benefits of choosing your offerings. This framework serves as a compass for crucial business decisions, ensuring alignment with your strategic positioning.
By consistently referencing this framework, your business can effectively meet customer needs, fostering satisfaction and loyalty through tailored products, services, and interactions.
4. Take Note of Your Competition’s Strategies
By stepping into your competitors’ research, you will learn what strategies they use to market their products or services and how they engage with their customers.
This will motivate you to do something more for customers and give you an idea of what your consumers like.
Start by analyzing their marketing strategies, such as sales and marketing channels, promotional activities, and branding strategies. Understand how they position themselves in the market and what USPs they emphasize.
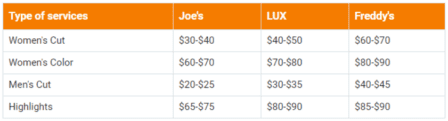
Evaluate their pricing strategies and offerings, and keep an eye on their distribution channel to better understand your competitors. For example, here are the pricing strategies of a barber shop and its competitors:
This information allows you to make informed decisions about your strategies, helping you identify opportunities for differentiation and improvement.
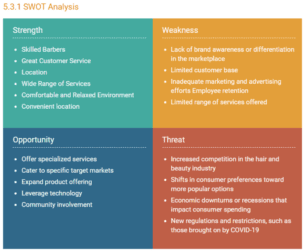
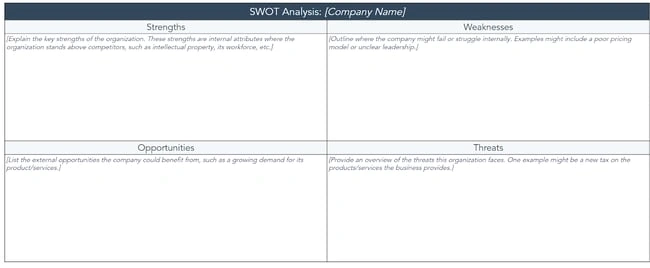
5. Perform a SWOT Analysis of Your Competitors
You would love to know the opportunities and threats of your business, right? To be prepared for it when the time comes.
Well, conducting a SWOT analysis is like the same, it is more about getting to know about your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. It also helps you understand your competitive edge in the market.
Whereas strengths and weaknesses focus on internal aspects of your company — opportunities and threats examine the external factors related to the industry and market.
Things to include in your SWOT analysis are:
It includes the positive features of your internal business operations. For example, it might include a strong brand, skilled workforce, innovative products/services, loyal customer base, etc.
It includes all the hindrances of your internal business operations. For example, it might include limited resources, outdated technology, weak brand recognition, inefficient processes, etc.
Opportunities
As the name says, it is all about the opportunities that will come your way in the near or far future. It is mainly about the external factors related to the market or industry trends.
For example, it might include emerging markets, technological advancements, changing consumer trends, profitable partnerships in the future, etc.
You should include any external factor that poses a challenge or any risk for your business in this section. For example, it might include intense competition, economic downturns, regulatory changes, or any advanced technology disruption.
These were the elements to help you conduct the competitive market analysis. Let us now go through how to write it in a business plan.

Want to Perform Competitive Analysis for your Business?
Discover your competition’s secrets effortlessly with our user-friendly and Free Competitor Analysis Generator!
How to Write Competitive Analysis in a Business Plan
1. determine who your readers are.
Know your audience first, because that will change the whole context of your competitor analysis business plan.
The competitive analysis section will vary depending on the intended audience is the team or investors.
Consider the following things about your audience before you start writing this section:
Internal competitor plan (employees or partners)
Objective: The internal competitor plan is to provide your team with an understanding of the competitive landscape.
Focus: The focus should be on the comparison of the strengths and weaknesses of competitors to boost strategic discussions within your team.
Use: It is to leverage the above information to develop strategies that highlight your strengths and address your weaknesses.
Competitor plan for funding (bank or investors)
Objective: Here, the objective is to reassure the potential and viability of your business to investors or lenders.
Focus: This section should focus on awareness and deep understanding of the competitive landscape to persuade the readers about the future of your business.
Use: It is to showcase your market position and the opportunities that are on the way to your business.
This differentiation is solely to ensure that the competitive analysis serves its purpose effectively based on the specific needs and expectations of the respective audience.
2. Describe Competitive Advantage
One of the most important things in the competitive analysis is to know your competitive advantage and gain insight into how you are a better option than competitors.
Your competitive analysis should pinpoint the competitive advantage based on the competitors’ product line or service and market segment, pricing, and other such situations. Some of the points you might include in this section are:
- Product/service differentiation in terms of quality or innovation
- Cost leadership or competitive pricing
- Brand reputation
- Customer service excellence
- Diverse and effective marketing strategy
3. Explain your strategies
Your competitor analysis section should not only highlight what opportunities or threats your business has. It should also mention that what will be the strategies to overcome those threats or capitalize on the opportunities.
It could be for taking a top-notch quality for your products or services, exploring the unexplored market segment, or having creative marketing strategies.
4. Know the pricing strategy
To understand the pricing strategy of your competitors, there are various aspects you need to have information about. It involves knowing their pricing model, evaluating their price points, and considering the additional costs, if any.
One way to understand this in a better way is to compare features and value offered at different price points and identify the gaps in competitors’ offerings.
Once you know the pricing structure of your competitors, compare it with yours and get to know the competitive advantage of your business from a pricing point of view.
Competitive analysis example
Need help writing the competitive analysis section of your business plan? Here’s the barbershop competitive analysis example to help you get started.
1. List of competitors
Direct & indirect competitors.
The following retailers are located within a 5-mile radius of J&S, thus providing either direct or indirect competition for customers:
Joe’s Beauty Salon
Joe’s Beauty Salon is the town’s most popular beauty salon and has been in business for 32 years. Joe’s offers a wide array of services that you would expect from a beauty salon.
Besides offering haircuts, Joe’s also offers nail services such as manicures and pedicures. In fact, over 60% of Joe’s revenue comes from services targeted at women outside of hair services. In addition, Joe’s does not offer its customers premium salon products.
For example, they only offer 2 types of regular hair gels and 4 types of shampoos. This puts Joe’s in direct competition with the local pharmacy and grocery stores that also carry these mainstream products. J&S, on the other hand, offers numerous options for exclusive products that are not yet available in West Palm Beach, Florida.
LUX CUTS has been in business for 5 years. LUX CUTS offers an extremely high-end hair service, with introductory prices of $120 per haircut.
However, LUX CUTS will primarily be targeting a different customer segment from J&S, focusing on households with an income in the top 10% of the city.
Furthermore, J&S offers many of the services and products that LUX CUTS offers, but at a fraction of the price, such as:
- Hairstyle suggestions & hair care consultation
- Hair extensions & coloring
- Premium hair products from industry leaders
Freddie’s Fast Hair Salon
Freddie’s Fast Hair Salon is located four stores down the road from J&S. Freddy’s has been in business for the past 3 years and enjoys great success, primarily due to its prime location.
Freddy’s business offers inexpensive haircuts and focuses on volume over quality. It also has a large customer base comprised of children between the ages of 5 to 13.
J&S has several advantages over Freddy’s Fast Hair Salon including:
- An entertainment-focused waiting room, with TVs and board games to make the wait for service more pleasurable. Especially great for parents who bring their children.
- A focus on service quality rather than speed alone to ensure repeat visits. J&S will spend on average 20 more minutes with its clients than Freddy’s.
While we expect that Freddy’s Fast Hair Salon will continue to thrive based on its location and customer relationships, we expect that more and more customers will frequent J&S based on the high-quality service it provides.
2. Competitive Pricing
John and Sons Barbing Salon will work towards ensuring that all our services are offered at highly competitive prices compared to what is obtainable in The United States of America.
We know the importance of gaining entrance into the market by lowering our pricing to attract all and sundry that is why we have consulted with experts and they have given us the best insights on how to do this and effectively gain more clients soon.
Our pricing system is going to be based on what is obtainable in the industry, we don’t intend to charge more (except for premium and customized services) and we don’t intend to charge less than our competitors are offering in West Palm Beach – Florida.
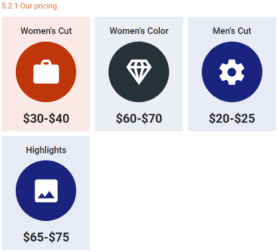
3. Our pricing
- Payment by cash
- Payment via Point of Sale (POS) Machine
- Payment via online bank transfer (online payment portal)
- Payment via Mobile money
- Check (only from loyal customers)
Given the above, we have chosen banking platforms that will help us achieve our payment plans without any itches.
4. Competitive advantage
5. SWOT analysis
Advantages of a Competitive Environment
Somewhere we all think, “What if we had no competition?” “What if we were the monopoly?” It would be great, right? Well, this is not the reality, and have to accept the competition sooner or later.
However, competition is healthy for businesses to thrive and survive, let’s see how:
1. It pushes you to innovation and improvement
In the competitive environment, a businessperson might get a new idea to bring innovation to the market to keep their products and services trending. This way innovation is promoted.
2. Competition validates your idea
Having a good idea becomes valid when others are developing similar products or services. A competitive market confirms that there is a market for your product and service. It also implies that the expenses of marketing and educating your target customers might likely decrease.
3. Efficiency and cost control
Businesses competing with each other get the motivation to operate efficiently to reduce costs and offer competitive prices. This thing for more sales benefits both businesses and customers.
4. Market responsiveness
A competitive environment forces businesses to be quick to adapt to market changes and customer demands. Companies need to adapt quickly to stay relevant and meet consumer preferences.
Competitive Analysis is critical, but don’t go overboard
Whether you are starting a new business or have an experience in the same field, gaining insight from your competitors will always be beneficial for your business.
Remember: Competitive analysis is essential for your business, but you can not assume all things positive on your side. Be realistic and practical while both conducting and writing this section.
Not only competitive analysis, but the whole business plan is necessary for any business to stay on the path. It will be your guide whenever your business is in any problem.
For assistance, you can visit our business plan writing guide . Additionally, we wish you all the luck in your competitive analysis journey.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is swot analysis a competitive analysis.
SWOT analysis is a component of a competitive analysis, not the whole competitive analysis. Competitive analysis covers a broad topic of analyzing competitors and knowing the competitive advantage.
What tools can i use for competitor analysis?
Executing a thorough competitor analysis requires the use of various tools to collect and analyze data. Here are some tools you can consider:
- Google Alerts
- Social media analytics
- Google Trends
- Google Analytics
- Competitors’ website
What are the 5 parts of a competitive analysis?
The main five components to keep in mind while having a competitor analysis are:
- Identifying the competitors
- Analyzing competitor’s strengths and weaknesses
- Assessing market share and trends
- Examining competitors’ strategies and market positioning
- Performing SWOT analysis
What is the difference between market analysis and competitive analysis?
Market analysis involves a comprehensive examination of the overall market dynamics, industry trends, and factors influencing a business’s operating environment.
On the other hand, competitive analysis narrows the focus to specific competitors within the market, delving into their strategies, strengths, weaknesses, and market positioning.
About the Author

Vinay Kevadiya
Vinay Kevadiya is the founder and CEO of Upmetrics, the #1 business planning software. His ultimate goal with Upmetrics is to revolutionize how entrepreneurs create, manage, and execute their business plans. He enjoys sharing his insights on business planning and other relevant topics through his articles and blog posts. Read more
Related Articles

How to Write a Customer Analysis Section for Your Business Plan
What is SWOT Analysis & How to Conduct it
How to Conduct a PESTLE Analysis Explained with Example
Reach your goals with accurate planning.
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Popular Templates

Competitive Analysis For Growth
Get our free competitor analysis kit to analyze competitors’ marketing, sales, and product strategies.
Join 50,000 entrepreneurs who have already downloaded these resources

How to Write a Competitive Analysis for Your Business Plan

11 min. read
Updated January 3, 2024
Do you know who your competitors are? If you do, have you taken the time to conduct a thorough competitor analysis?
Knowing your competitors, how they operate, and the necessary benchmarks you need to hit are crucial to positioning your business for success. Investors will also want to see an analysis of the competition in your business plan.
In this guide, we’ll explore the significance of competitive analysis and guide you through the essential steps to conduct and write your own.
You’ll learn how to identify and evaluate competitors to better understand the opportunities and threats to your business. And you’ll be given a four-step process to describe and visualize how your business fits within the competitive landscape.
- What is a competitive analysis?
A competitive analysis is the process of gathering information about your competitors and using it to identify their strengths and weaknesses. This information can then be used to develop strategies to improve your own business and gain a competitive advantage.
- How to conduct a competitive analysis
Before you start writing about the competition, you need to conduct your analysis. Here are the steps you need to take:
1. Identify your competitors
The first step in conducting a comprehensive competitive analysis is to identify your competitors.
Start by creating a list of both direct and indirect competitors within your industry or market segment. Direct competitors offer similar products or services, while indirect competitors solve the same problems your company does, but with different products or services.
Keep in mind that this list may change over time. It’s crucial to revisit it regularly to keep track of any new entrants or changes to your current competitors. For instance, a new competitor may enter the market, or an existing competitor may change their product offerings.
2. Analyze the market
Once you’ve identified your competitors, you need to study the overall market.
This includes the market size , growth rate, trends, and customer preferences. Be sure that you understand the key drivers of demand, demographic and psychographic profiles of your target audience , and any potential market gaps or opportunities.
Conducting a market analysis can require a significant amount of research and data collection. Luckily, if you’re writing a business plan you’ll follow this process to complete the market analysis section . So, doing this research has value for multiple parts of your plan.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
3. Create a competitive framework
You’ll need to establish criteria for comparing your business with competitors. You want the metrics and information you choose to provide answers to specific questions. (“Do we have the same customers?” “What features are offered?” “How many customers are being served?”)
Here are some common factors to consider including:
- Market share
- Product/service offerings or features
- Distribution channels
- Target markets
- Marketing strategies
- Customer service
4. Research your competitors
You can now begin gathering information about your competitors. Because you spent the time to explore the market and set up a comparison framework—your research will be far more focused and easier to complete.
There’s no perfect research process, so start by exploring sources such as competitor websites, social media, customer reviews, industry reports, press releases, and public financial statements. You may also want to conduct primary research by interviewing customers, suppliers, or industry experts.
You can check out our full guide on conducting market research for more specific steps.
5. Assess their strengths and weaknesses
Evaluate each competitor based on the criteria you’ve established in the competitive framework. Identify their key strengths (competitive advantages) and weaknesses (areas where they underperform).
6. Identify opportunities and threats
Based on the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors, identify opportunities (areas where you can outperform them) and threats (areas where they may outperform you) for your business.
You can check out our full guide to conducting a SWOT analysis for more specific questions that you should ask as part of each step.
- How to write your competitive analysis
Once you’ve done your research, it’s time to present your findings in your business plan. Here are the steps you need to take:
1. Determine who your audience is
Who you are writing a business plan for (investors, partners, employees, etc.) may require you to format your competitive analysis differently.
For an internal business plan you’ll use with your team, the competition section should help them better understand the competition. You and your team will use it to look at comparative strengths and weaknesses to help you develop strategies to gain a competitive advantage.
For fundraising, your plan will be shared with potential investors or as part of a bank loan. In this case, you’re describing the competition to reassure your target reader. You are showing awareness and a firm understanding of the competition, and are positioned to take advantage of opportunities while avoiding the pitfalls.
2. Describe your competitive position
You need to know how your business stacks up, based on the values it offers to your chosen target market. To run this comparison, you’ll be using the same criteria from the competitive framework you completed earlier. You need to identify your competitive advantages and weaknesses, and any areas where you can improve.
The goal is positioning (setting your business up against the background of other offerings), and making that position clear to the target market. Here are a few questions to ask yourself in order to define your competitive position:
- How are you going to take advantage of your distinctive differences, in your customers’ eyes?
- What are you doing better?
- How do you work toward strengths and away from weaknesses?
- What do you want the world to think and say about you and how you compare to others?
3. Visualize your competitive position
There are a few different ways to present your competitive framework in your business plan. The first is a “positioning map” and the second is a “competitive matrix”. Depending on your needs, you can use one or both of these to communicate the information that you gathered during your competitive analysis:
Positioning map
The positioning map plots two product or business benefits across a horizontal and vertical axis. The furthest points of each represent opposite extremes (Hot and cold for example) that intersect in the middle. With this simple chart, you can drop your own business and the competition into the zone that best represents the combination of both factors.
I often refer to marketing expert Philip Kohler’s simple strategic positioning map of breakfast, shown here. You can easily draw your own map with any two factors of competition to see how a market stacks up.

It’s quite common to see the price on one axis and some important qualitative factor on the other, with the assumption that there should be a rough relationship between price and quality.
Competitive matrix
It’s pretty common for most business plans to also include a competitive matrix. It shows how different competitors stack up according to the factors identified in your competitive framework.
How do you stack up against the others? Here’s what a typical competitive matrix looks like:

For the record, I’ve seen dozens of competitive matrices in plans and pitches. I’ve never seen a single one that didn’t show that this company does more of what the market wants than all others. So maybe that tells you something about credibility and how to increase it. Still, the ones I see are all in the context of seeking investment, so maybe that’s the nature of the game.
4. Explain your strategies for gaining a competitive edge
Your business plan should also explain the strategies your business will use to capitalize on the opportunities you’ve identified while mitigating any threats from competition. This may involve improving your product/service offerings, targeting underserved market segments, offering more attractive price points, focusing on better customer service, or developing innovative marketing strategies.
While you should cover these strategies in the competition section, this information should be expanded on further in other areas of your business plan.
For example, based on your competitive analysis you show that most competitors have the same feature set. As part of your strategy, you see a few obvious ways to better serve your target market with additional product features. This information should be referenced within your products and services section to back up your problem and solution statement.
- Why competition is a good thing
Business owners often wish that they had no competition. They think that with no competition, the entire market for their product or service will be theirs. That is simply not the case—especially for new startups that have truly innovative products and services. Here’s why:
Competition validates your idea
You know you have a good idea when other people are coming up with similar products or services. Competition validates the market and the fact that there are most likely customers for your new product. This also means that the costs of marketing and educating your market go down (see my next point).
Competition helps educate your target market
Being first-to-market can be a huge advantage. It also means that you will have to spend way more than the next player to educate customers about your new widget, your new solution to a problem, and your new approach to services.
This is especially true for businesses that are extremely innovative. These first-to-market businesses will be facing customers that didn’t know that there was a solution to their problem . These potential customers might not even know that they have a problem that can be solved in a better way.
If you’re a first-to-market company, you will have an uphill battle to educate consumers—an often expensive and time-consuming process. The 2nd-to-market will enjoy all the benefits of an educated marketplace without the large marketing expense.
Competition pushes you
Businesses that have little or no competition become stagnant. Customers have few alternatives to choose from, so there is no incentive to innovate. Constant competition ensures that your marketplace continues to evolve and that your product offering continues to evolve with it.
Competition forces focus & differentiation
Without competition, it’s easy to lose focus on your core business and your core customers and start expanding into areas that don’t serve your best customers. Competition forces you and your business to figure out how to be different than your competition while focusing on your customers. In the long term, competition will help you build a better business.
- What if there is no competition?
One mistake many new businesses make is thinking that just because nobody else is doing exactly what they’re doing, their business is a sure thing. If you’re struggling to find competitors, ask yourself these questions.
Is there a good reason why no one else is doing it?
The smart thing to do is ask yourself, “Why isn’t anyone else doing it?”
It’s possible that nobody’s selling cod-liver frozen yogurt in your area because there’s simply no market for it. Ask around, talk to people, and do your market research. If you determine that you’ve got customers out there, you’re in good shape.
But that still doesn’t mean there’s no competition.
How are customers getting their needs met?
There may not be another cod-liver frozen yogurt shop within 500 miles. But maybe an online distributor sells cod-liver oil to do-it-yourselfers who make their own fro-yo at home. Or maybe your potential customers are eating frozen salmon pops right now.
Are there any businesses that are indirect competitors?
Don’t think of competition as only other businesses that do exactly what you do. Think about what currently exists on the market that your product would displace.
It’s the difference between direct competition and indirect competition. When Henry Ford started successfully mass-producing automobiles in the U.S., he didn’t have other automakers to compete with. His competition was horse-and-buggy makers, bicycles, and railroads.
Do a competitive analysis, but don’t let it derail your planning
While it’s important that you know the competition, don’t get too caught up in the research.
If all you do is track your competition and do endless competitive analyses, you won’t be able to come up with original ideas. You will end up looking and acting just like your competition. Instead, make a habit of NOT visiting your competition’s website, NOT going into their store, and NOT calling their sales office.
Focus instead on how you can provide the best service possible and spend your time talking to your customers. Figure out how you can better serve the next person that walks in the door so that they become a lifetime customer, a reference, or a referral source.
If you focus too much on the competition, you will become a copycat. When that happens, it won’t matter to a customer if they walk into your store or the competition’s because you will both be the same.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Tim Berry is the founder and chairman of Palo Alto Software , a co-founder of Borland International, and a recognized expert in business planning. He has an MBA from Stanford and degrees with honors from the University of Oregon and the University of Notre Dame. Today, Tim dedicates most of his time to blogging, teaching and evangelizing for business planning.

Table of Contents
- Don't let competition derail planning
Related Articles

3 Min. Read
What to Include in Your Business Plan Appendix

24 Min. Read
The 10 AI Prompts You Need to Write a Business Plan

6 Min. Read
How to Write Your Business Plan Cover Page + Template

10 Min. Read
How to Write the Company Overview for a Business Plan
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
What is a Competitive Analysis — and How Do You Conduct One?
Published: April 24, 2024
Every time I work with a new brand, my first order of business is to conduct a competitive analysis.

A competitive analysis report helps me understand the brand’s position in the market, map competitors’ strengths/weaknesses, and discover growth opportunities.
![competitive analysis of a business plan Download Now: 10 Competitive Analysis Templates [Free Templates]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/b3ec18aa-f4b2-45e9-851f-6d359263e671.png)
In this article, I’ll break down the exact steps I follow to conduct competitor analysis and identify ways to one-up top brands in the market.
We’ll cover:
What is competitive analysis?
What is competitive market research, competitive analysis in marketing.
- How To Conduct Competitive Analysis in 5 Steps
How to Do a Competitive Analysis (the Extended Cut)
Competitive product analysis, competitive analysis example, competitive analysis templates.
- Competitive Analysis FAQs
Competitive analysis is the process of comparing your competitors against your brand to understand their core differentiators, strengths, and weaknesses. It’s an in-depth breakdown of each competitor’s market position, sales & marketing tactics, growth strategy, and other business-critical aspects to see what they’re doing right and find opportunities for your business.
Competitive analysis gives you a clearer picture of the market landscape to make informed decisions for your growth.
That said, you have to remember that competitive analysis is an opportunity to learn from others. It isn’t:
- Copying successful competitors to the T.
- Trying to undercut others’ pricing.
- A one-and-done exercise.
Let’s look at how this exercise can help your business before breaking down my 5-step competitive analysis framework.
4 Reasons to Perform Competitive Analysis
If you’re on the fence about investing time and effort in analyzing your competitors, know that it gives you a complete picture of the market and where you stand in it.
Here are four main reasons why I perform a competitive analysis exercise whenever working with a brand for the first time:
- Identify your differentiators. Think of competitor analysis as a chance to reflect on your own business and discover what sets you apart from the crowd. And if you’re only starting out, it helps you brainstorm the best opportunities to differentiate your business.
- Find competitors’ strengths. What are your competitors doing right to drive their growth? Analyzing the ins and outs of an industry leader will tell you what they did well to reach the top position in the market.
- Set benchmarks for success. A competitor analysis gives you a realistic idea of mapping your progress with success metrics. While every business has its own path to success, you can always look at a competitor’s trajectory to assess whether you’re on the right track.
- Get closer to your target audience. A good competitor analysis framework zooms in on your audience. It gives you a pulse of your customers by evaluating what they like, dislike, prefer, and complain about when reviewing competing brands.
The bottom line: Whether you’re starting a new business or revamping an existing one, a competitive analysis eliminates guesswork and gives you concrete information to build your business strategy.
.webp)
10 Free Competitive Analysis Templates
Track and analyze your competitors with these ten free planning templates.
- SWOT Analysis
- Battle Cards
- Feature Comparison
- Strategic Overview
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Competitive market research is a vital exercise that goes beyond merely comparing products or services. It involves an in-depth analysis of the market metrics that distinguish your offerings from those of your competitors.
A thorough market research doesn't just highlight these differences but leverages them, laying a solid foundation for a sales and marketing strategy that truly differentiates your business in a bustling market.
In the next section, we’ll explore the nuts and bolts of conducting a detailed competitive analysis tailored to your brand.
10 Competitive Analysis Templates
Fill out the form to access the templates., essential aspects to cover in competitive analysis research .
Before we walk through our step-by-step process for conducting competitor analysis, let’s look at the main aspects to include for every competitor:
- Overview. A summary of the company — where it’s located, target market, and target audience.
- Primary offering. A breakdown of what they sell and how they compare against your brand.
- Pricing strategy. A comparison of their pricing for different products with your pricing.
- Positioning. An analysis of their core messaging to see how they position themselves. Customer feedback: A curation of what customers have to say about the brand.
Now, it’s time to learn how to conduct a competitive analysis with an example to contextualize each step.
Every brand can benefit from regular competitor analysis. By performing a competitor analysis, you'll be able to:
- Identify gaps in the market.
- Develop new products and services.
- Uncover market trends.
- Market and sell more effectively.
As you can see, learning any of these four components will lead your brand down the path of achievement.
Next, let's dive into some steps you can take to conduct a comprehensive competitive analysis.
How to Conduct Competitive Analysis in 5 Quick Steps
As a content marketer, I’ve performed a competitive analysis for several brands to improve their messaging, plan their marketing strategy, and explore new channels. Here are the five steps I follow to analyze competitors.
1. Identify and categorize all competitors.
The first step is a simple yet strategic one. You have to identify all possible competitors in your industry, even the lesser-known ones. The goal here is to be aware of all the players in the market instead of arbitrarily choosing to ignore a few.
As you find more and more competitors, categorize them into these buckets:
- Direct competitors. These brands offer the same product/service as you to the same target audience. People will often compare you to these brands when making a buying decision. For example, Arcade and Storylane are direct competitors in the demo automation category.
- Indirect competitors. These businesses solve the same problem but with a different solution. They present opportunities for you to expand your offering. For example, Scribe and Whatfix solve the problem of documentation + internal training, but in different ways.
- Legacy competitors. These are established companies operating in your industry for several years. They have a solid reputation in the market and are a trusted name among customers. For example, Ahrefs is a legacy competitor in the SEO industry.
- Emerging competitors. These are new players in the market with an innovative business model and unique value propositions that pose a threat to existing brands. For example, ChatGPT came in as a disruptor in the conversational AI space and outperformed several brands.
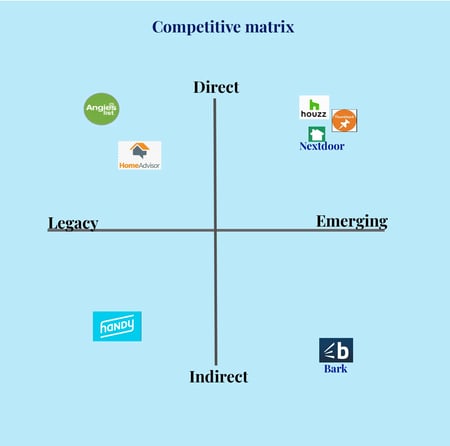
Here’s a competitive matrix classifying brands in the community and housing space:
Testing It Out
To help you understand each step clearly, we’ll use the example of Trello and create a competitor analysis report using these steps.
Here’s a table of the main competitors for Trello:
able of the main competitors for Trello:
2. Determine each competitor’s market position.
Once you know all your competitors, start analyzing their position in the market. This step will help you understand where you currently stand in terms of market share and customer satisfaction. It’ll also reveal the big guns in your industry — the leading competitors to prioritize in your analysis report.
Plus, visualizing the market landscape will tell you what’s missing in the current state. You can find gaps and opportunities for your brand to thrive even in a saturated market.
To map competitors’ market positions, create a graph with two factors: market presence (Y-axis) and customer satisfaction (X-axis). Then, place competitors in each of these quadrants:
- Niche. These are brands with a low market share but rank high on customer satisfaction. They’re likely targeting a specific segment of the audience and doing it well.
- Contenders. These brands rank low on customer satisfaction but have a good market presence. They might be new entrants with a strong sales and marketing strategy.
- Leaders. These brands own a big market share and have highly satisfied customers. They’re the dominant players with a solid reputation among your audience.
- High performers. These are another category of new entrants scoring high on customer satisfaction but with a low market share. They’re a good alternative for people not looking to buy from big brands.
This visualization will tell you exactly how crowded the market is. But it’ll also highlight ways to gain momentum and compete with existing brands.
Here’s a market landscape grid by G2 documenting all of Trello’s competitors in the project management space. For a leading brand like Trello, the goal would be to look at top brands in two quadrants: “Leaders” and “High Performers.”
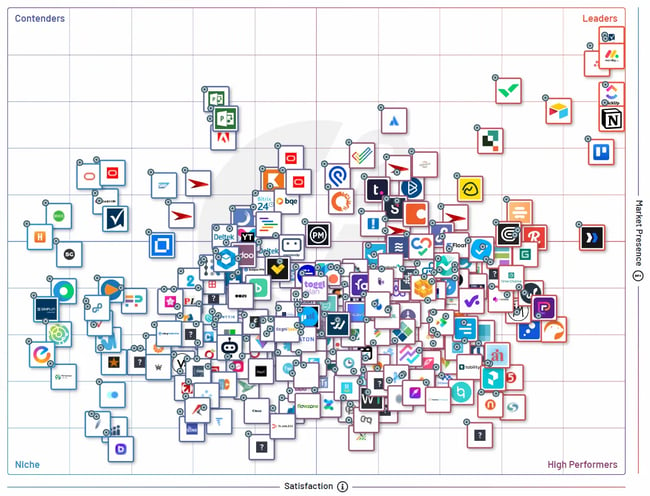
Image Source
3. Extensively benchmark key competitors.
Step 2 will narrow down your focus from dozens of competitors to the few most important ones to target. Now, it’s time to examine each competitor thoroughly and prepare a benchmarking report.
Remember that this exercise isn’t meant to find shortcomings in every competitor. You have to objectively determine both the good and bad aspects of each brand.
Here are the core factors to consider when benchmarking competitors:
- Quality. Assess the quality of products/services for each competitor. You can compare product features to see what’s giving them an edge over you. You can also evaluate customer reviews to understand what users have to say about the quality of their offering.
- Price. Document the price points for every competitor to understand their pricing tactics. You can also interview their customers to find the value for money from users’ perspectives.
- Customer service. Check how they deliver support — through chat, phone, email, knowledge base, and more. You can also find customer ratings on different third-party platforms.
- Brand reputation. You should also compare each competitor’s reputation in the market to understand how people perceive the brand. Look out for anything critical people say about specific competitors.
- Financial health. If possible, look for performance indicators to assess a brand's financial progress. You can find data on metrics like revenue growth and profit margins.
This benchmarking exercise will involve a combination of primary and secondary research. Invest enough time in this step to ensure that your competitive analysis is completely airtight.
Check out this example of a competitor benchmarking report for workforce intelligence tools:
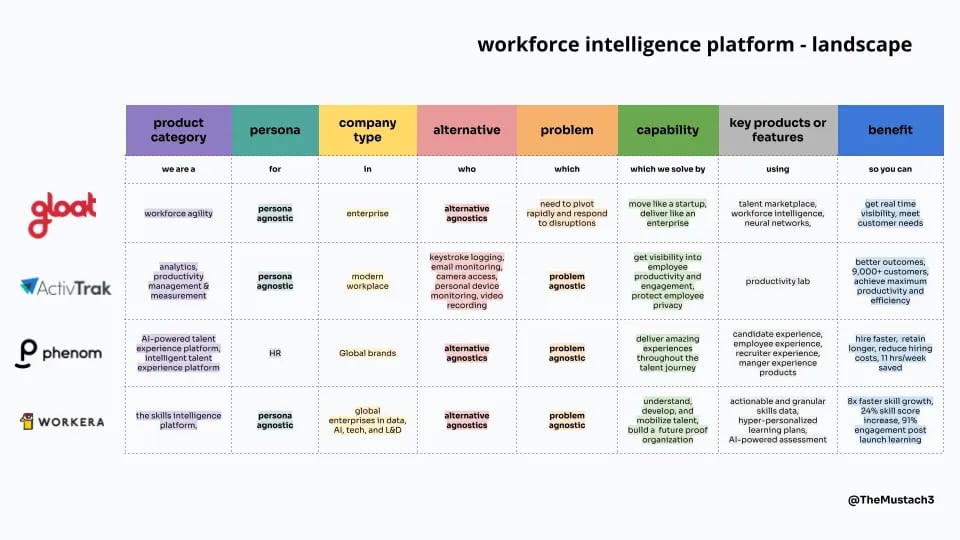
Here’s how I benchmarked Asana based on these criteria using the information I could find:
4. Deep dive into their marketing strategy.
While the first few steps will tell you what you can improve in your core product or service, you also need to find how competitors market their products.
You need to deep-dive into their marketing strategies to learn how they approach buyers. I analyze every marketing channel, then note my observations on how they speak to their audience and highlight their brand personality.
Here are a few key marketing channels to explore:
- Website. Analyze the website structure and copy to understand their positioning and brand voice.
- Email. Subscribe to emails to learn their cadence, copywriting style, content covered, and other aspects.
- Paid ads. Use tools like Ahrefs and Semrush to find if any competitor is running paid ads on search engines.
- Thought leadership. Follow a brand’s thought leadership efforts with content assets like podcasts, webinars, courses, and more.
- Digital PR. Explore whether a brand is investing in digital PR to build buzz around its business and analyze its strategy.
- Social media. See how actively brands use different social channels and what kind of content is working best for them.
- Partnerships. Analyze high-value partnerships to see if brands work closely with any companies and mutually benefit each other.
You can create a detailed document capturing every detail of a competitor’s marketing strategy. This will give you the right direction to plan your marketing efforts.
5. Perform a SWOT analysis.
The final step in a competitive analysis exercise is creating a SWOT analysis matrix for each company. This means you‘ll take note of your competitor’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Think of it as the final step to consolidate all your research and answer these questions:
- What is your competitor doing well?
- Where do they have an advantage over your brand?
- What is the weakest area for your competitor?
- Where does your brand have the advantage over your competitor?
- In what areas would you consider this competitor a threat?
- Are there opportunities in the market that your competitor has identified?
You can use tools like Miro to visualize this data. Once you visually present this data, you’ll get a clearer idea of where you can outgrow each competitor.
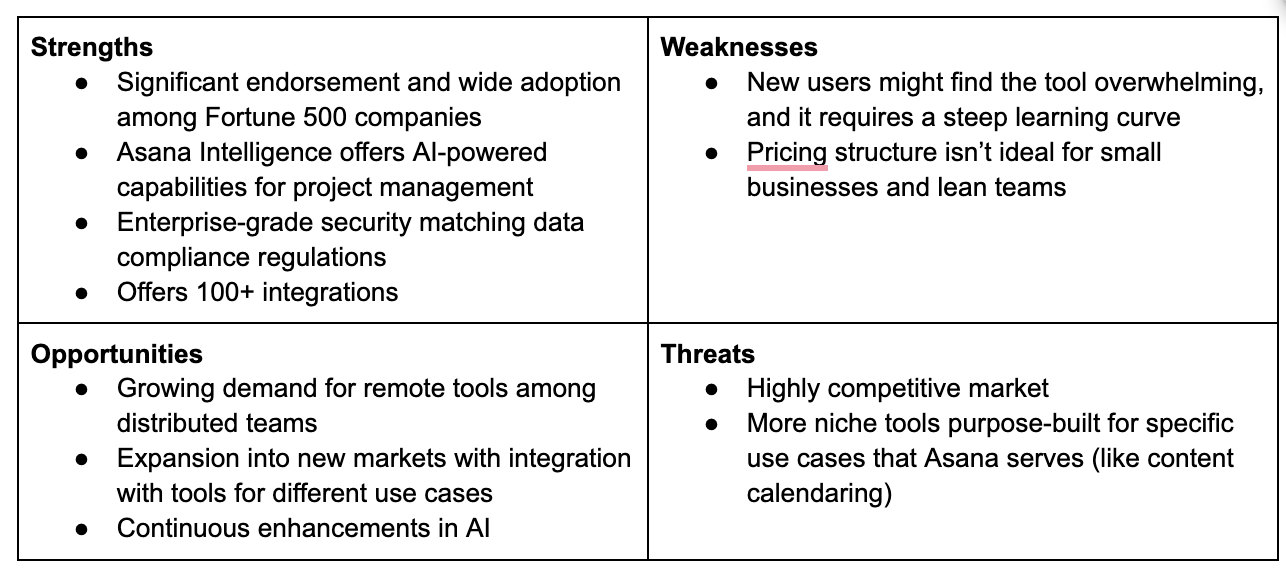
Here’s a SWOT analysis matrix I created for Asana as a competitor of Trello:
- Determine who your competitors are.
- Determine what products your competitors offer.
- Research your competitors' sales tactics and results.
- Take a look at your competitors' pricing, as well as any perks they offer.
- Ensure you're meeting competitive shipping costs.
- Analyze how your competitors market their products.
- Take note of your competition's content strategy.
- Learn what technology stack your competitors use.
- Analyze the level of engagement on your competitors' content.
- Observe how they promote marketing content.
- Look at their social media presence, strategies, and go-to platforms.
- Perform a SWOT Analysis to learn their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.

To run a complete and effective competitive analysis, use these ten templates, which range in purpose from sales to marketing to product strategy.
Featured Resource: 10 Competitive Analysis Templates
1. Assess your current product pricing.
The first step in any product analysis is to assess current pricing.
Nintendo offers three models of its Switch console: The smaller lite version is priced at $199, the standard version is $299, and the new OLED version is $349.
Sony, meanwhile, offers two versions of its PlayStation 5 console: The standard edition costs $499, and the digital version, which doesn’t include a disc drive, is $399.
2. Compare key features.
Next is a comparison of key features. In the case of our console example, this means comparing features like processing power, memory, and hard drive space.
3. Pinpoint differentiators.
With basic features compared, it’s time to dive deeper with differentiators. While a glance at the chart above seems to indicate that the PS5 is outperforming its competition, this data only tells part of the story.
Here’s why: The big selling point of the standard and OLED Switch models is that they can be played as either handheld consoles or docked with a base station connected to a TV. What’s more, this “switching” happens seamlessly, allowing players to play whenever, wherever.
The Playstation offering, meanwhile, has leaned into market-exclusive games that are only available on its system to help differentiate them from their competitors.
4. Identify market gaps.
The last step in a competitive product analysis is looking for gaps in the market that could help your company get ahead.
When it comes to the console market, one potential opportunity gaining traction is the delivery of games via cloud-based services rather than physical hardware.
Companies like Nvidia and Google have already made inroads in this space, and if they can overcome issues with bandwidth and latency, it could change the market at scale.
How do you stack up against the competition? Where are you similar, and what sets you apart? This is the goal of competitive analysis.
By understanding where your brand and competitors overlap and diverge, you’re better positioned to make strategic decisions that can help grow your brand.
Of course, it’s one thing to understand the benefits of competitive analysis, and it’s another to actually carry out an analysis that yields actionable results. Don’t worry — we’ve got you covered with a quick example.
Sony vs. Nintendo: Not all fun and games.
Let’s take a look at popular gaming system companies Sony and Nintendo.
Sony’s newest offering — the Playstation 5 — recently hit the market but has been plagued by supply shortages.
Nintendo’s Switch console, meanwhile, has been around for several years but remains a consistent seller, especially among teens and children.
This scenario is familiar for many companies on both sides of the coin; some have introduced new products designed to compete with established market leaders, while others are looking to ensure that reliable sales don’t fall.
Using some of the steps listed above, here’s a quick competitive analysis example.
In our example, it’s Sony vs Nintendo, but it’s also worth considering Microsoft’s Xbox, which occupies the same general market vertical.
This is critical for effective analysis; even if you’re focused on specific competitors and how they compare, it’s worth considering other similar market offerings.
PlayStation offers two PS5 versions, digital and standard, at different price points, while Nintendo offers three versions of its console.
Both companies also sell peripherals — for example, Sony sells virtual reality (VR) add-ons, while Nintendo sells gaming peripherals such as steering wheels, tennis rackets, and differing controller configurations.
When it comes to sales tactics and marketing, Sony and Nintendo have very different approaches.
In part thanks to the recent semiconductor shortage, Sony has driven up demand via scarcity — very low volumes of PS5 consoles remain available. Nintendo, meanwhile, has adopted a broader approach by targeting families as its primary customer base.
This effort is bolstered by the Switch Lite product line, which is smaller and less expensive, making it a popular choice for children.
The numbers tell the tale : Through September 2021, Nintendo sold 14.3 million consoles, while Sony sold 7.8 million.
Sony has the higher price point: Their standard PS5 sells for $499, while Nintendo’s most expensive offering comes in at $349. Both offer robust digital marketplaces and the ability to easily download new games or services.
Here, the key differentiators are flexibility and fidelity. The Switch is flexible — users can dock it with their television and play it like a standard console or pick it up and take it anywhere as a handheld gaming system.
The PS5, meanwhile, has superior graphics hardware and processing power for gamers who want the highest-fidelity experience.
5. Analyze how your competitors market their products.
If you compare the marketing efforts of Nintendo and Sony, the difference is immediately apparent: Sony’s ads feature realistic in-game footage and speak to the exclusive nature of their game titles.
The company has managed to secure deals with several high-profile game developers for exclusive access to new and existing IPs.
Nintendo, meanwhile, uses brightly lit ads showing happy families playing together or children using their smaller Switches while traveling.
6. Analyze the level of engagement on your competitor's content.
Engagement helps drive sales and encourage repeat purchases.
While there are several ways to measure engagement, social media is one of the most straightforward: In general, more followers equates to more engagement and greater market impact.
When it comes to our example, Sony enjoys a significant lead over Nintendo: While the official Playstation Facebook page has 38 million followers, Nintendo has just 5 million.
Competitive analysis is complex, especially when you’re assessing multiple companies and products simultaneously.
To help streamline the process, we’ve created 10 free templates that make it possible to see how you stack up against the competition — and what you can do to increase market share.
Let’s break down our SWOT analysis template. Here’s what it looks like:
Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

25 Tools & Resources for Conducting Market Research

Market Research: A How-To Guide and Template
![competitive analysis of a business plan SWOT Analysis: How To Do One [With Template & Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/marketingplan_20.webp)
SWOT Analysis: How To Do One [With Template & Examples]

TAM SAM SOM: What Do They Mean & How Do You Calculate Them?
![competitive analysis of a business plan How to Run a Competitor Analysis [Free Guide]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/Google%20Drive%20Integration/how%20to%20do%20a%20competitor%20analysis_122022.jpeg)
How to Run a Competitor Analysis [Free Guide]
![competitive analysis of a business plan 5 Challenges Marketers Face in Understanding Audiences [New Data + Market Researcher Tips]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/challenges%20marketers%20face%20in%20understanding%20the%20customer%20.png)
5 Challenges Marketers Face in Understanding Audiences [New Data + Market Researcher Tips]

Causal Research: The Complete Guide

Total Addressable Market (TAM): What It Is & How You Can Calculate It

What Is Market Share & How Do You Calculate It?
![competitive analysis of a business plan 3 Ways Data Privacy Changes Benefit Marketers [New Data]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/how-data-privacy-benefits-marketers_1.webp)
3 Ways Data Privacy Changes Benefit Marketers [New Data]
10 free templates to help you understand and beat the competition.
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
A Guide to Competitive Analysis: It’s Not Just about Competitors
By Joe Weller | April 16, 2018 (updated February 13, 2024)
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
If you were running a cross-country marathon, wouldn’t you want to know something of the terrain and expected weather conditions before you began? The same principle of preparation applies when starting and continuing a business. It’s not enough to focus on your own production and financial goals: You need to understand what’s happening around you, how others create goods or services, the economic forecast, changes in rules and regulations, and more. In other words, you need to conduct a competitive analysis. The thought of searching for and digesting the required information may seem overwhelming, but we make it easy.
In this article, we explain how to focus your analysis by first deciding what questions you want answered. Learn how to find current and potential competitors and how many of them you need to review. Then, we cover the specific aspects of your competitors that you need to consider as well as where to find more information about them. Marketing experts weigh in on how to maintain focus during analysis. We also offer free, downloadable competitive analysis templates to start you on your own information gathering and analysis.
What Is Competitor Analysis?
Competitor analysis (CA) is a process of identifying competitors and gauging their business and marketing strategies to understand both their strengths and weaknesses and those of your own business. Competitive analysis provides a higher-level perspective of the entire marketing landscape and competitive intelligence.

“Competitive analysis is the process of analyzing all collected information to derive some insight for reducing risk and making better decisions,” explains competitive intelligence expert and author Babette Bensoussan .
“It is about your broader competitive environment,” she says. “I always remind my clients that competitors make up only one element of a business’s competitive environment. Other elements include government, technology, buyers, and suppliers, to name a few that impact how well you can compete.”
What Is the Purpose of a Competitive Analysis?
Researching your competitive landscape is essential to business growth and survival, and helps you offer better products or services to customers. You should gain an understanding of how customers view your company, what you’re doing right, and what you’re doing wrong. Therefore, competitive analysis forms a crucial part of marketing plans to help you understand what differentiates your product or service. Particularly when applying for funding, competitive analysis provides valuable insight into business plans. However, competitive analysis offers much more:
- Branding possibilities
- Insight into how competitors design products and messages
- SEO possibilities
- CRO (conversion rate optimization)
- GTM strategies
- User experience (UX) advantages of your and others’ products and websites
- Gaps in the market
- New products and services to develop
- Market trends
According to a Conductor survey , 60 percent of marketers don’t feel proficient in competitive analysis. Many don’t practice it on a regular basis. Knowledge derived from these exercises is critical, and you need to assess competition regularly. Nevertheless, marketing departments often skip competitive analysis, which leaves them with a fragmentary understanding of the landscape and competitors. Being proactive can help you anticipate and prepare for competitor developments and provide you with the agility to take advantage of changes.
According to Bensoussan, “In today’s world of constant change and information overload (whether the information be real or fake), it is critical for any business person to understand the competitive landscape and the forces that impact the profitability and viability of a business.”
What Should Be Included in a Competitive Analysis?
In most cases, a competitive analysis contains a few basic sections, which may vary depending on the size and form of your company and the focus of your analysis:
- A list of your main competitors
- An overview or what you know about them
- Who their target customers are
- A list of their products or services
- What media they use to market their goods and services
- Their current and past marketing strategies
- Their value proposition and effectiveness
- An analysis of all of the strengths and weaknesses of your competition (and your own company)
- An overview of the strategies being used by the competition to achieve their objectives
- An overview of the market and projections for the future
How to Prepare for a Competitive Analysis
One of the crucial prerequisites for a successful competitive analysis is an open mind. Check your beliefs at the door — what you think about your company, your customers, or your competitors isn’t necessarily true. That can be a good thing.
In addition, it is vital to understand why you are conducting an analysis. What are your goals for the business? What are your goals for this analysis? “Always, always be very clear as to what the decision you will be making is all about,” advises Bensoussan. “If you are not clear about your decision, then you will never know if you have good competitive analysis or just some more information.”
She offers these two questions as examples of how different the impact of each answer can be: “Tell me who’s who in the [manufacturing] of zippers?” versus “Should I enter the zipper-manufacturing industry, and can I achieve a return on investment of, say, 15 percent in three years?”
“Which question would help you the most in delivering good quality CA? Which outcome do you think would provide the most value?” Bensoussan asks.
Companies often enlist the help of outside consulting firms dedicated to conducting competitive intelligence research. Guidance on competitive intelligence support, such as database information, software platforms for market program tracking, and more is available through the Society of Competitive Intelligence Professionals .
Competitor Analysis Frameworks
Over the decades, marketing gurus have developed or advocated several competitive analysis frameworks. Here are six well-known methods to consider.
- Porter’s Five Forces Model: First published in 1979 by Harvard Business School professor Michael Porter, the Five Forces model provides a view beyond competitors to factors in your industry landscape that may threaten or strengthen your position. The Five Forces include the following:
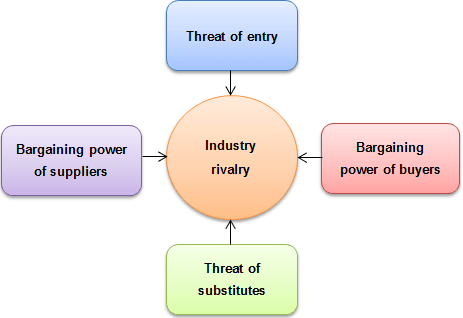
- Potential New Entrants: Consider how much money, time, and effort it would take for a company to displace you.
- Competitive Rivalry: Determine who your competitors are, who the closest competitors are, and their products, prices, and quality. Fewer rivals mean more opportunity for your unique qualities to shine; many rivals mean more competitors to steal your customers and potentially better deals to lead customers elsewhere.
- Suppliers: The more potential suppliers you have, the better for you. Consider how having fewer suppliers might impact your operation.
- Buyers: If you have many customers, you have the power. Otherwise, buyers can negotiate more advantageous deals elsewhere or find sources other than yours. Consider how you would treat that situation.
- Substitutes (or Complements): A competitor could create a product or model that replaces yours. On the other hand, a new product or service could also complement yours, which would create a symbiotic sales situation. Complements are sometimes considered the sixth force in the model.
Porter stressed the importance of not confusing these constants with temporary disruptions, such as technological innovations or government interventions in industry.
You can download the Five Forces model below to answer your own questions about an industry or business proposition.
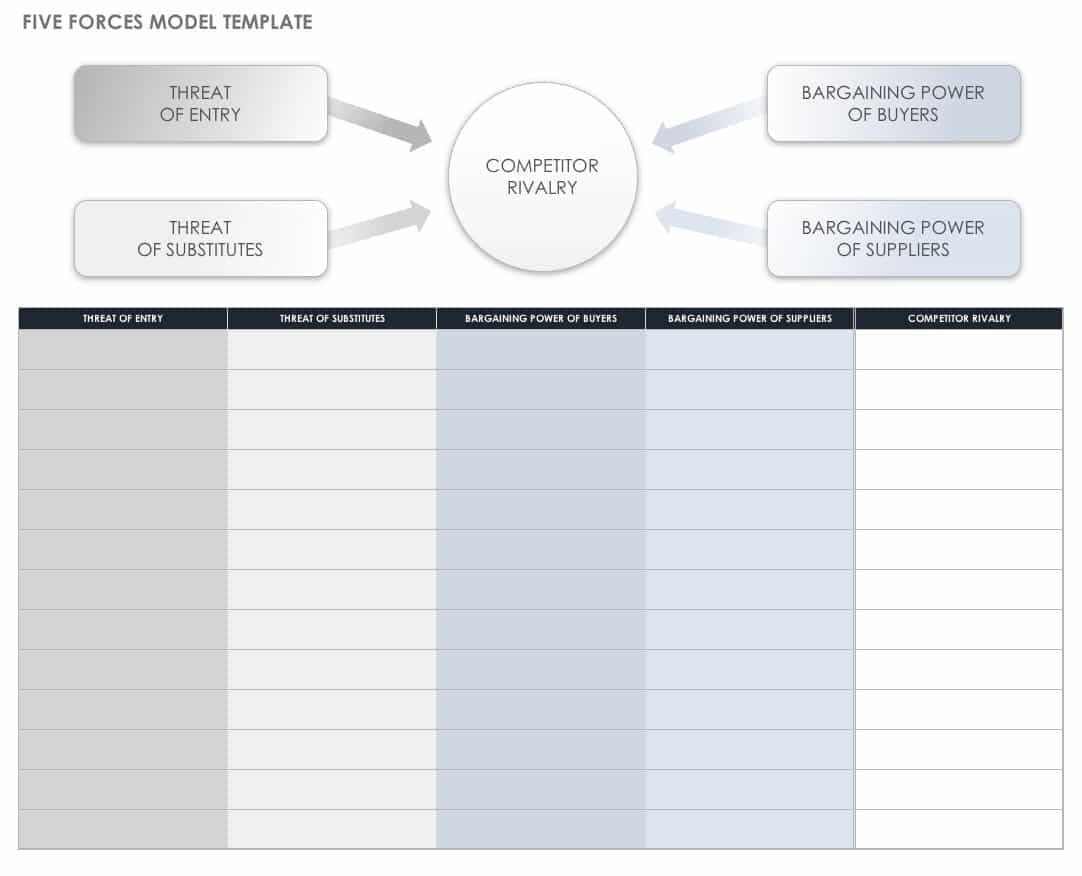
Download Five Forces Model
Excel | PDF
Industry Life Cycle Overview: Both industries and individual products have life cycles, which reflect the state of sales, whether robust or diminishing. Understand which stage of the life cycle your industry, company, or product is in to help target your marketing efforts. Product life cycles contain such stages as these:
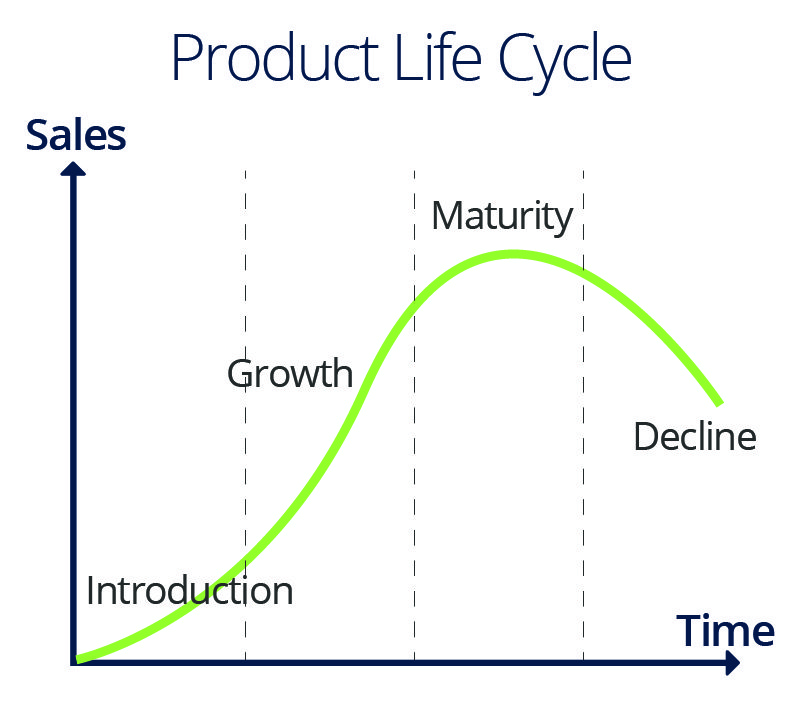
- Introduction: At the introductory stage, a new industry or product is not well known or proven. It is usually marketed to a few early adopters. Because resources focus on product development, testing, and refinement, few or no profits accrue. Marketing focuses on explaining the product, creating awareness around it, and establishing a niche.
- Growth: As awareness grows and the industry or product becomes established, profits may also grow. However, in the growth stage, rival products may also appear. Although improvements require funds, production efficiencies may also develop. Some products have only a short growth phase. For example, a particular fashion may last for only one season. Other products experience a long or extended growth phase, such as software products, which continue their usefulness through upgrades. During the growth stage, marketing centers on differentiating the product, so it stands out from competing products.
- Maturity: In the maturity stage of a product or industry, sales may expand, but at a less accelerated rate. Fewer competitors may dominate the market and may attempt to differentiate on quality or increase sales by touting low costs.
- Saturation: You reach the saturation stage when every customer who could buy the product already owns the product. A lack of innovation or competition from a superior product could result in saturation.
- Decline/Termination: Industries and products decline for several reasons. Innovations may overtake them and render them obsolete. Businesses and product lines may fail to upgrade and innovate. At the decline or termination stage, companies may fold, continue in a smaller market, or merge with larger, successful businesses.
Strategic Groups Analysis: You perform strategic groups analysis on companies within a business sector, such as automobiles, to see how they vie for their share of consumer expenditure. By dividing companies into strategic groups, you can understand how businesses of different sizes behave in the marketing landscape. Businesses within groups tend to be competitors, whereas businesses in other groups are related but not competitive. For example, running shoes and high-end women’s dress shoes are in different groups. Analyzing companies in this way can also reveal other significant information: direct competitors and their basis for competition; if and how a company can move to another group; and strategic problems and opportunities. Strategic groups are usually plotted on an x-y axis, where two highly relevant criteria form the axes. Here are some examples of criteria:
- Brand ownership
- Company size
- Capacity utilization
- Cost structure
- Geographical market segmentation
- Marketing activities
- Ownership structure
- Sales channels
- Product diversity
- Product quality
- R&D capability
- Vertical and horizontal integration
First, plot the companies where you think they belong on the graph. Now, with all companies plotted, create groupings. If you want, you can use larger or smaller circles to indicate market share. To gain greater insight, perform a Five Forces analysis on them, or consider the mobility barriers that prevent companies from shifting to other strategic groups.
SWOT: Perhaps one of the most commonly addressed marketing analyses is SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats). In essence, SWOT represents what competitors do and do not do well. As you look at SWOT for competitors, also consider it for your own products and services.
- Strengths: What do they do better than you? What are they known for? Is their pricing, inventory, convenience, and level of service better than yours?
- Weaknesses: How do they fall short of your company’s standards? Can you leverage their shortcomings to improve your standing with customers?
- Opportunities: What in your competitors’ landscape can you exploit to your advantage?
- Threats: What in your competitors’ landscape threatens their business position?
Note that strengths and weaknesses focus on internal characteristics, while opportunities and threats concern external forces. SWOT can be performed separately, but it may provide a useful frame for studying a business’ products and services, marketing, and sales.
Competitive Array: Competitive arrays, also known as competitive matrices , provide a way to quantify characteristics that may be unquantifiable. For example, if company A sells 500 widgets and company B sells 250, it’s clear which company sold more. But how do you quantify the attractiveness of online and print media or innovation? Creating the competitive array can be an individual or group exercise. To start, list your competitors across the top of your writing surface. In the left-most column, list important characteristics. Next, create a column for weighting the importance of each characteristic so that the sum of the characteristics totals one. The higher the weighting, the more important the characteristic (you may have a few characteristics with the same weight). Next, grade each competitor for each characteristic on a scale, such as from one to 10. Now, multiply the grade by the corresponding weight.
Competitive Value Proposition Analysis: The characteristics of a value proposition are exclusivity, clarity, and credibility. This method concerns how unique the product or service is, how clearly the product message is conveyed, and whether the message is credibly supported by evidence, such as testimonials, statistics, or test results. Because customers remember only a few key advantages of your product from your media promotion, the main value proposition must be correct and clear and mesh with your actual competitive advantage. To figure out how to differentiate your company, you must determine how competitors differentiate themselves from each other. POPs (points of parity), PODs (points of difference), and POIs (points of irrelevance) help you dissect value propositions.
- Points of Parity (POPs): These are elements of customer benefit that both you and your competitors offer.
- Points of Difference (PODs): These are features of customer benefit that you offer but competitors don’t. Keep in mind that not every point of difference is significant to consumers.
- Points of Irrelevance (POIs): These are characteristics that customers don’t care about.
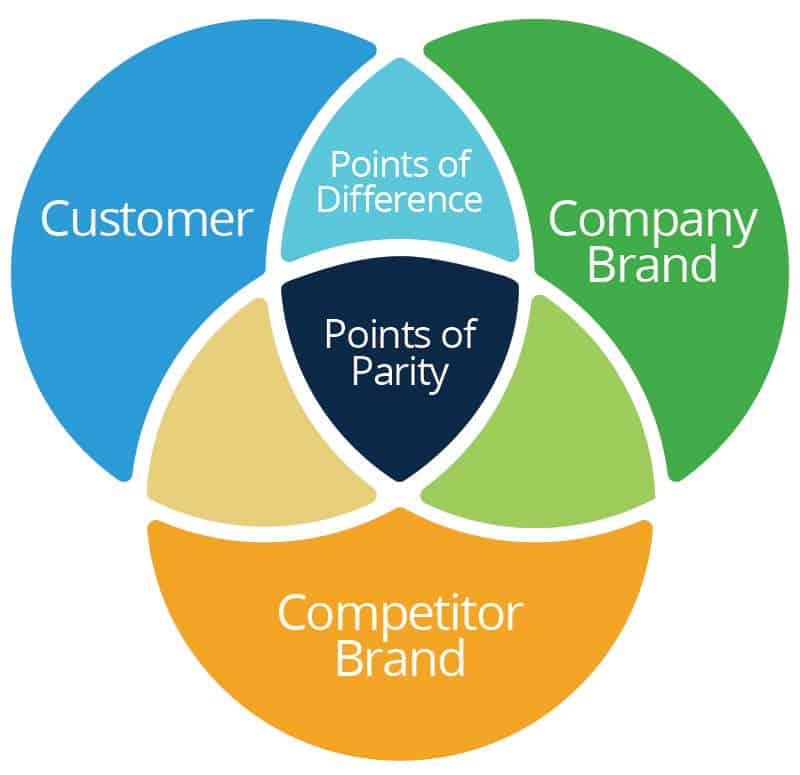
Your unique value proposition (differentiating characteristics) doesn’t need to appeal to every customer. Don’t make your value proposition too general. You can’t be all things to all customers, just as you can’t do what your competitors are doing.

Otherwise, there's no differentiation. You end up being like teenagers, everybody in the same jeans," says Sonia Schechter, Chief Marketing Officer of Marxent , a provider of virtual reality and augmented reality apps for furniture retailers. Therefore, target your message.
Discover your points of parity by using our POP template.
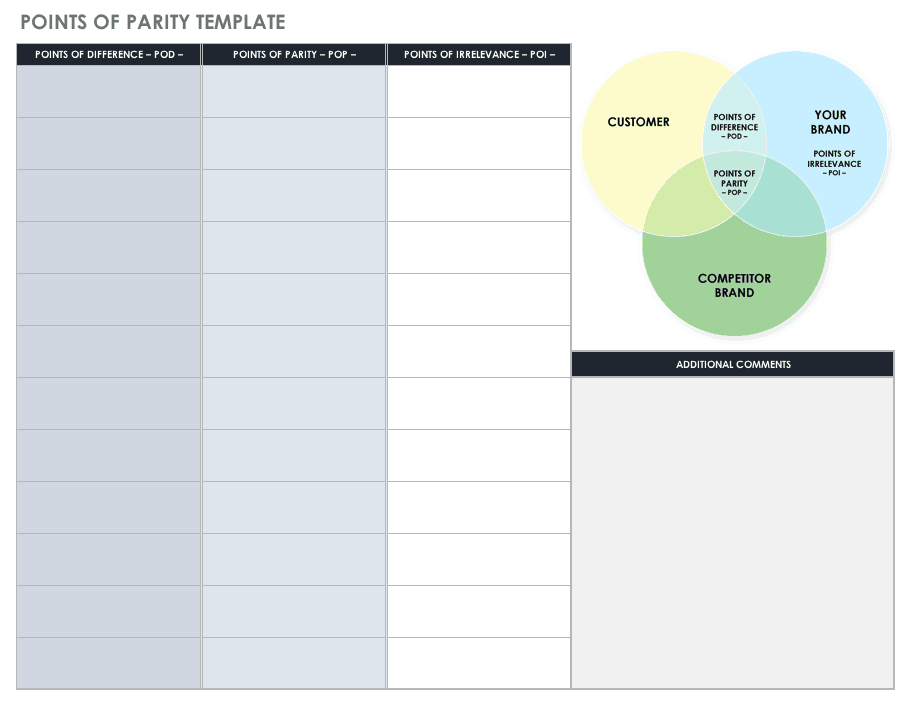
Download Points of Parity Template
Excel | Word | PDF
Who Are Your Competitors?
As a first step in competitive analysis, marketing guides typically suggest determining who your competitors are. Competitors can be divided into groups of direct competitors, indirect competitors, and future competitors.
- Direct Competitor: These are companies who sell a direct substitute for your product, operate in the same geographic area, and/or offer the same goods (such as groceries) to the same market. Ask who your customers would buy from if you weren’t in business.
- Indirect Competitor: These are companies in the same geographic area whose products occupy the same general, but not specific, category as your own (e.g., a general bakery versus a designer cake store). Indirect competition satisfies the customer’s need for a particular product or service, although that product or service may be different from yours. Similar products operating in different market segments do not represent direct competitors. For example, a high-end seafood restaurant doesn’t compete with a burger place.
- Future Competitor: Future competitors may currently be indirect competitors who change and expand solutions. In the bakery example, the general bakery could hire a high-end designer to compete with the specialty cake maker. Or, the designer cake store could branch out into breads and muffins.
It may be difficult at first to envision what types of organizations you need to analyze and whether you need to analyze all competitors.To identify competitors, ask yourself who your customers would buy from if your product did not exist. Perhaps even more important, consider who your customers think your competitors are. How many competitors you review depends: If only a few companies do what you do, analyze everyone. If you have many competitors, use Pareto analysis to focus on the critical 20 percent. Larger businesses may analyze the top 10, whereas a small business can focus on three. Disregard online competitors unless you plan to sell online.
Download Pareto Chart Template - Excel
How to Find Current Competitors
Some competitors may seem obvious, but sleuthing can reveal challengers you weren’t aware of.
- Google search for a product or service similar to yours. Consider the companies in paid ads and organic returns.
- Try SEMrush to check which domains are using which keywords.
- Ask your current customers who they would choose besides you.
- Check Alexa, Google Trends, or SimilarWeb for general estimates on the popularity of domain names and keywords.
- Review Dun & Bradstreet for new incorporations.
- Consult Derwent for new patent information.
- See who has booths at trade shows.
How to Find Potential Competitors
While you consider the current playing field, you must also keep your eye on what’s coming around the corner. These are the future new entrants in your niche. Consider who might start a business that would compete with yours. New competitors can be found in related markets, related technologies, or related products. Companies from other geographical areas with similar products may begin to sell in your area, and former employees or managers can start their own companies based on the themes of your business. In addition, consider the following conditions that may encourage competition:
- A company gains competitive advantage.
- Buyers are dissatisfied with suppliers.
- An unmet demand for goods exists.
- Few major barriers to entry exist.
- The industry offers high profit margins.
- The industry offers unrealized growth potential.
- Competitive rivalry is not intense.
It’s Not All about Competitors ( Competitive Doesn’t Always Mean Competitor )
Depending on what your product or service is and where it is in its life cycle, a competitor focus may not be optimal. For example, for emerging technologies, no true competitor may exist.
“Looking too closely at competition is a massive distraction,” Schechter notes. “If you’re selling a commodity or established product, such as a drugstore, which sells the same thing anywhere, you’d be looking at specific issues, like price, location, and assortment.”
Schecter says marketers themselves often don’t understand that what the competition is doing is not important: “Successful marketing is how you define yourself in the landscape. People don’t care about a feature-by-feature description, or even one feature. They buy the package. They like you. You’re different or you’re solving a particular problem. A new business must define and lay out the landscape for the customer.”
To succeed, understanding what customers want is key. “Marketers have nuanced detail, and customers don’t care about that detail,” Schechter continues. “But, you have to listen to their questions and engage in dialogue with them to gain real understanding,” she points out. She cites Apple’s promotion of the camera in the first iPhone as an example of marketers understanding what — out of thousands of potential functions — was important to consumers. “B2B marketing is the same. It’s about listening to customers, figuring out how they’re shopping, and trying to see through their eyes,” Schechter emphasizes.
“Obsessing over competition can get you off track. If you’re listening to customers, you’ll build the right product. But you don’t need to build your dreams on other people’s ideas,” she concludes.
Where to Find Information for a Competitive Analysis
Remember that every department of your business is a potential source for information, including the following areas:
- Sales: Questions for potential, current, and lost customers
- Research and Development: New patents
- Purchasing: Suppliers
- Marketing: Customers and other consumers
Once you’ve determined who your competitors are and what you want to learn about them and from them, you need to go information hunting:
- Visit offices or brick-and-mortar stores. What do they look like? Who’s there?
- Get financial and organizational information from public filings and from sources like Hoovers, Manta, and Dun & Bradstreet.
- Monitor PR Newswire for new developments and changes.
- Some marketing platforms may actually include information about your competitors.
Interviews and Research Surveys
Interviewing competitor customers and consumers who know little about your business is important to overcoming your preconceptions about the business landscape. You probably have specific questions in mind, but here are the basics:
- Why are you shopping for a solution?
- What were the main reasons you chose the company you did?
- Ranked from most important to least important, what are your five shopping criteria?
Media Scanning or Competitor Content Analysis
You can learn much about competitor products and messaging by scanning media. Media doesn’t just include online content (web pages, tweets, and Facebook posts) — it also includes such traditional marketing collateral as white papers, case studies, and data sheets. Moreover, consider reference materials, such as LexisNexis and Hoovers, and trade, business, or news publications for ads, news stories, and press releases. Media and content can reveal not only new products and new branding, but also new positioning and segmentation strategies, pricing, target markets, and promotion strategy.
What Information to Search for in Competitive Analysis
The approach to analysis depends on the questions requiring answers. To organize your analysis, divide it into three aspects: product or services, marketing, and sales. Each aspect contains its own questions and means of analysis.

Download Competitive Analysis Checklist
Products and Services
Your understanding of products and services must be thorough. Investigate the complete product or service line. Try to understand who your competitors’ customers are and what they need. Look at their pricing strategy and see if it differs for online and brick-and-mortar stores. Also, consider how they differentiate from their competitors.
Tracking competitor sales processes can involve more legwork. For public companies, SEC filings provide some financial information about growth or contraction, but, for private companies, information is less readily available. Information about sales channels may be easy to find through a look in the phone book or online. You can also gather details about the sale process by asking current customers why they chose your product over others. You can also acquire valuable information by following up even after you lose a sale in order to understand the customer’s thinking. What do their partner resales programs look like? What are their revenues versus sales volume?
Marketing Efforts in Competitive Analysis
What does the competitor marketing plan entail? How do competitors invest marketing efforts? What can you do even better? A variety of approaches can help you define competitor marketing strategy.
When you identify marketing assets, take a reasonable sample of items — no need to review all of them. Just remember to keep samples consistent among competitors. Also, when reviewing items, consider the quality of the collateral. It should appear professional, with no typos, and in the formal, professional, idiomatic voice. In addition, a solid library of resources, such as consistent blog posts, whitepapers, case studies, videos, webinars, and podcasts may point you to themes and leads you should follow.
E-Marketing Strategy Competitive Analysis
Few businesses today can function without a web presence that helps generate traffic and inquiries or purchases. Some statistics say that prospective buyers visit a website as many as nine times before purchasing and, depending on the product, visit multiple sites before purchasing. Forrester research after 2010 suggests potential customers visit three sites on average before buying. The more sites visited, the more money the customer intends to spend.
Therefore, understanding how your site compares to your nearest competitors can be helpful. To drive eyes to websites, online purveyors use search engine optimization (SEO) to employ the keywords most likely to garner high search ratings in Google (and other search engines). Marketers frequently also use SEM (search engine marketing) to promote a business or product by increasing visits to a website through paid keywords. Look at how saturated their content is with keywords and where they use keywords, whether in H1 and H2 tags, page titles, content, or links. Also, look at the difficulty level of their keywords.
Consider the usability of the steps in the sales funnel as well as the navigation. What do the landing pages say? Also, look at backlinks (i.e., links from other pages to your competitor’s page) to your web page. See how many backlinks exist — and from which pages — to understand if this is something you can improve for your website.
Structure is important, but quality content also matters. Online marketing collateral appears as blogs, white papers, ebooks, case studies or user stories, videos, webinars, podcasts, and more. But words and pictures themselves are not valuable if they don’t offer any unique information or concise approaches to existing knowledge. Check whether content is shared and which topics attract attention, or, conversely, what that content and those topics are linked to. What do readers comment on, if they do comment? Who else is sharing what your competitors are publishing?
Social Media
Certain social media platforms appeal to some audiences more than others. The channels a company favors can reveal clues to the demographics of their target market. Make note of what social media buttons they include on pages and where on the page they include them.
Software Tools for Understanding Online Competitors

Besides monitoring content, you can monitor the mechanics of competitor websites to glean more data about how marketing strategy and product offerings are changing. Software helps to automate these investigations for you. Following are some of the many products available:
- BuiltWith : See what platform was used to build a page.
- Ghostery : Find trackers on a website.
- SEMrush : Discover company rankings, organic keywords, AdWords, and analyses of backlinks.
- Versionista : Track web page and website changes, SEO changes, and more.
- Visualping : Monitor webpage updates.
- SpyFu : Find competitor keywords and AdWords, including AdWord and keyword variations and history.
- iSpionage : Track PPC and other keywords in competitor campaigns.
- SimilarWeb : Compare competitor websites to your own.
- Heatmaps: Use large amounts of data to provide a visual representation of how users interact with a website. Heatmaps can indicate where users click and look and for how long. Levels of intensity of activity are usually displayed through colors.
- Session Recording Tools: Record user browsing sessions. Session recording tools can yield a wealth of rich data, but raise some privacy concerns.
- Tag Management Systems: Advanced e-marketing implementations use tags to aid analysis and reporting. Tags are snippets of code that are usually added to the <head> tags of a web page.
Web Page User Testing for UX in Competitive Analysis
It’s essential to understand how consumers approach your website, especially for web-based products and marketing. Allow customers to test your site, and even view it yourself from a customer’s perspective, to help eliminate unnecessary steps and streamline your sales funnel. Doing so can also help to illuminate the opportunities for upsells and cross-sells.
Limiting the analysis to two or three competitors offers a manageable amount of insight into usability, which helps you avoid reviewer overload and confusion. For impartial results, don’t reveal to test participants which website is yours.
Ask test participants to enter words in Google or list the words and phrases they would use to find a certain product or service. Not only does this yield potentially fruitful keywords, it also indicates whether your site appears in search returns.
To get a sense of each participant’s impression, have them look at each website for five seconds and answer the following questions:
- What three words would you use to describe the site?
- What is it about? What products or services are offered and for whom?
- How does this website make you feel?
To understand their process, give participants a task to perform on each website. Ask them to answer the following questions:
- What was the worst thing about your visit to this website?
- What aspects of the experience could be improved?
- What did you like about the website?
- What other comments do you have?
- Which website did you like best and why?
How Much Data Do You Need in a Competitive Analysis?
It may seem overwhelming to sit down and search out your competitors’ business situations. That’s why setting a clear intention before you begin an analysis is so important. In addition, Babette Bensoussan advises that you don’t need to analyze everything:
“Over the years, I have learned that once you have 70 percent of the information required for your chosen analytical technique, you can proceed to the analysis,” she explains. “You never really need all the pieces of a jigsaw puzzle to tell you what the picture is. This same philosophy applies to analysis. More information may not yield better insights nor improve predictive accuracy.”
How Do I Write a Competitor Analysis Report?
The format of your analysis depends on individual choice and the audience. You may also choose to use one kind of format while you work through the analysis, and another when you present findings.
Take a sheet of paper. In the left-most column, write the names of your closest competitors. Across the top of the page, list the main attributes of each product, such as target market, price, size, method of distribution, extent of customer service, prospective buyers, and so on. Then, make a check or a note for each attribute the competitor fulfils. An additional column can contain information about service or product availability, the website, a toll-free phone number, and other general information.
A competitor profile helps you make a detailed record about each competitor, and also allows you to capture snapshots of a business over time. Consider listing some of the following information:
- Location of offices and factories
- Key personalities, history, and trends
- Ownership, organizational structure, and corporate governance
- Number of employees and skill sets
- Management and management style
- Compensation, benefits, and retention rates
- Plant capacity, utilization rate, age of plant, capital investment
- Product mix per plant and shipping logistics
- Products and services
- Depth of product line
- New products developed and success rate
- Research and development details
- Brands and brand loyalty and awareness
- Patents and licenses
- Quality control conformance
- Cash flow and liquidity
- Profit growth profile
- Method of growth (organic or acquisitive)
- Objectives, mission statement, growth plans, acquisitions
- Marketing strategies
- Segments served, market shares, customer base, growth rate, and customer loyalty
- Promotional mix, promotional budgets, advertising themes, ad agency used, online promotional strategy
- Distribution channels (direct and indirect) and exclusivity agreements
Here is a step-by-step process for writing a competitor analysis report:
- Write down your competitors.
- Write what you know about them already.
- Discover who their target customers are.
- Discover their pricing methods.
- Investigate their marketing strategy.
- Figure out their competitive advantage.
Download our competitive analysis landscape template to get ideas for gathering information and reporting analysis results.

Download Competitive Analysis Landscape Template
Excel | Word | PDF | Smartsheet
Competitive Analysis for Small Businesses
Small business can be competitive. Beyond meeting financial targets, you need to understand the competitive landscape (short of allowing it to distract you) and then target a niche market. Many of the same analyses that apply to large businesses also apply to small businesses. However, if this is your first business, or if you don’t have a marketing background, you may want to pay attention to a few aspects.
First, it is helpful to acknowledge how much or how little you know about your competitors by sketching a profile of your top two or three competitors. Next, try to learn all you can about your competition.
You can use the following template to perform a competitive analysis for your small business.
Download Small Business Competitive Analysis Template
Word | PDF
What Is a Competitive Analysis in a Business Plan?
Competitive analysis should play a key role in the preparation of a business plan. Particularly if you seek outside funding, your knowledge of the competitive landscape will show your understanding of your business and the market forces at play.
When starting a business, consider all the analysis questions described above, but pay particular attention to issues of growth and opportunity. Consider addressing the following circumstances:
- Whether current competitors target a specific niche or offer products to the mass market
- If, how, and why competitors are growing or reducing business
- How your company will be stronger than competitors and better able to exploit changes in the market landscape
- What you will offer customers that no one else does (your competitive advantage)
In the business plan, describe the competitive landscape as it relates to direct and indirect competitors and opportunities and risks, emphasizing your competitive advantage. This competitive analysis can form the basis for your first marketing plan.
Sharpen Your Competitive Analysis with Smartsheet for Marketing
The best marketing teams know the importance of effective campaign management, consistent creative operations, and powerful event logistics -- and Smartsheet helps you deliver on all three so you can be more effective and achieve more.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Improve your marketing efforts and deliver best-in-class campaigns.
Advisory boards aren’t only for executives. Join the LogRocket Content Advisory Board today →

- Product Management
- Solve User-Reported Issues
- Find Issues Faster
- Optimize Conversion and Adoption
What is competitive analysis? Template, examples, and how-to

In this comprehensive guide, we’ll define what a competitive analysis is, describe the benefits product teams stand to gain from conducting one, and walk through the steps of how to do a competitive analysis.

Through the tutorial, we’ll refer to examples to demonstrate how each step of a competitive analysis works in practice. We’ll also provide a list of customizable, free competitive analysis templates for you to use when completing these steps on your own.
Complete guide to competitive analysis
Picture this: you just came up with the next disruptive, game changing, AI-powered e-commerce marketplace. The objective is to connect buyers with sellers to fulfill their tailored and customized product needs.
You’re confident your product will take on Etsy and other big players in the market. You did some market and user research and have a good idea of your ideal customer and their (underserved) needs. Based on this data, you believe your marketplace can reach product-market fit quickly.
It’s now time for you to dust off your copy of Sun Tzu’s T he Art of War . Why is that, you ask?
The Art of War is an ancient Chinese military textbook that, although dated somewhere between ~500–400 B.C., is one of the most influential management books out there to this day. It provides great strategic and tactical advice. Moreover, it provides guidance to help you assess yourself and your competition to gain an advantage.
Maintaining a competitive advantage is the goal. Even if you have the best product in the world and you know there is a market for it, if you don’t understand your competition, you‘re bound to fail. That’s why you need to perform a competitive analysis.
As the band Rage Against the Machine would say, know your enemy .
What is competitive analysis?
Competitive analysis (sometimes called a competitor analysis or competition analysis) is exactly what it sounds like: a structured approach to identifying and analyzing your competitors. More concretely, it’s an assessment of your competition’s offerings, strategy, strengths, and weaknesses.
A competitive analysis helps you answer questions such as:
- Which other companies are providing a solution similar to ours?
- What are the ideal customer’s minimum expectations?
- What are they currently not getting from our product with regard to those expectations?
- What barriers do competitors in the market fce?
- What should we avoid introducing in our product?
- What price are customers willing to pay for our product?
- What value do we need to provide to make our product stand out in the market?
- What trends are happening and how might they change the playing field?
When conducted thoroughly and regularly, a competitive analysis provides you with tons of information that can be used to improve and optimize your product. The end result is a holistic overview of your competitor landscape.
Why do a competitive analysis?
Competitive analysis is a fundamental product management instrument. It helps PMs learn what works and what doesn’t when trying to acquire market share, identify market trends, and locate gaps in their product offering.
Competitive analysis exists to help you avoid making mistakes and empower you to beat competitors to the punch in the pursuit of product growth and success.
Knowing your competition will bring you great rewards. Conducting a competitive analysis will help you more effectively:
- Create benchmarks
- Identify opportunities to better serve customers
- Make strategic decisions
- Determine your pricing strategy
- Identify market gaps
- Determine distribution and marketing strategies
Typically, the first time you create a competitor analysis is when doing your market research. This helps you get an idea of the product-market fit , which will evolve along your journey.
As a product manager, your role is not to analyze how well your competitors are able to showcase themselves. It is your job to make the product what the customer needs it to be. Understanding your competitor’s capabilities, pricing, and product positioning helps you in this.
Keep in mind that your competitors will likely showcase themselves to appear better than they probably are. You’ll be able to acquire tons of information about them, but you should take that information with a pinch of salt.
How to do a competitive analysis
There is no a single way to do a competitive analysis. In general, a competitive analysis is made up of three fundamental components:
- A shortlist of competitors
- A competitor deep dive
- A holistic overview and strategy
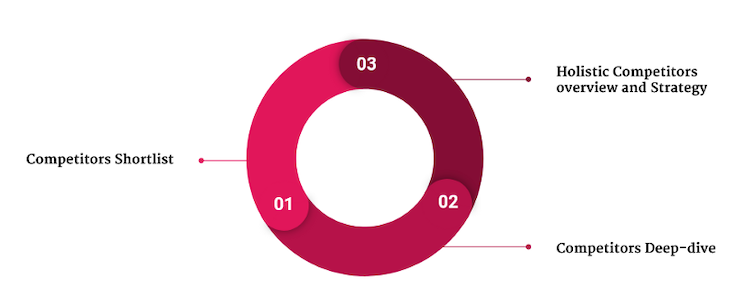
To demonstrate how to do a competitor analysis, we’ll refer back to the example outlined in the introduction.

Over 200k developers and product managers use LogRocket to create better digital experiences
Remember, in our example, we’re looking to disrupt the market with an AI-powered e-commerce marketplace app that helps buyers and sellers connect to fulfill highly customized orders. Let’s call our innovative new product AGORA.
1. Create a shortlist of your competitors
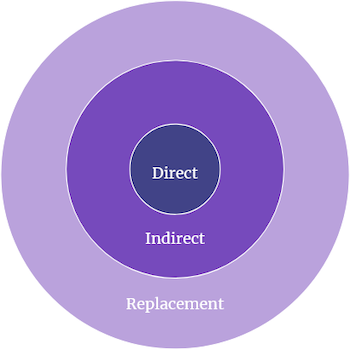
There are three types of competitors:
- Direct — Competitors that offer the same product and target the same ideal customer; you are battling direct competitors heads-on
- Indirect — Competitors that either offer a somewhat similar product or target the same ideal customer
- Replacement — Competitors that offer a different product but target the same ideal customer
For a competitive analysis, you need to identify at least your direct and indirect competitors. So how do you do that? By looking inward and researching obsessively .
Look inward
To figure out who your direct and indirect competitors are, you need to look inward first to understand your product positioning: who are you servicing and what is the offering you are providing?
You can answer these questions by doing a self-assessment using the product canvas . Originally introduced by Roman Pichler, the product canvas has since tbeen tweaked and refined.
In its core, the product canvas covers:
- The name of the product
- Objectives and key metrics for success
- The ideal customer
- A high-level overview of what’s required to meet the customer’s needs
- Just enough product details about short-term goals
For our example product, the competitive analysis might look something like this:
Research obsessively
A simple Google search using keywords from your self-assessment can get you pretty far. Other resources that can help you identify your competitors include tools such as Crunchbase, Similarweb, Statista, etc.
As the old saying goes, the customer knows best. If you don’t have many customers yet, review sites such G2, Capterra, Trustpilot, and Google Reviews can help you.
If you do have customers, go ask them. Most customers try and evaluate several products before deciding on the right product to buy. Nothing is stopping you from asking them which other brands they considered and why they ultimately chose yours.
Once you have established who your competitors are, you might find yourself in a market with many direct and indirect competitors. If that is the case, select about seven of the most relevant competitors to include in your competitor deep dive.
2. Do a deep dive on each competitor
From your a shortlist of competitors, choose about seven of your most important and dig up all the relevant information on each one.
The research conducted during the previous step will help you capture the most relevant information about your competitors for the following categories:
Company profile
Ideal customer profile, product information, market approach, swot analysis.
Start by creating a company profile for each of your competitors to gain a better understanding of who they are. Include the following information:
- Name — What is the name of your competitor?
- Founding date — When was the company founded? How long has it been in the market?
- Company size — How many employees does the company have? Are they equipped to service the market and innovate?
- Market share — The portion of the market controlled by the competitor’s product
- Revenue — The income the competitor generates from its product
- Reputation — What do customers think of your competitor’s product on a scale from one to five?
Let’s apply this framework to our AGORA competitive analysis example:
It’s important to understand who your competitors are serving and who is buying the product. This not only to reconfirm that the competitor is indeed a direct (or indirect) competitor, but also to understand what customers like and dislike about the competitor’s product.
The information you’re looking for includes:
- Ideal customer — Who is the competitor’s target customer and what defines them?
- Motivations — What does the customer enjoy about your competitor’s product?
- Frustrations — What does the customer hate about the product?
- Primary buyer — Who is the primary buyer of the product? Is it the as the ideal customer, or is it a different persona?
Let’s see what this would look like following our AGORA example. Below is an example ideal customer profile for Etsy. First, for the buyer:
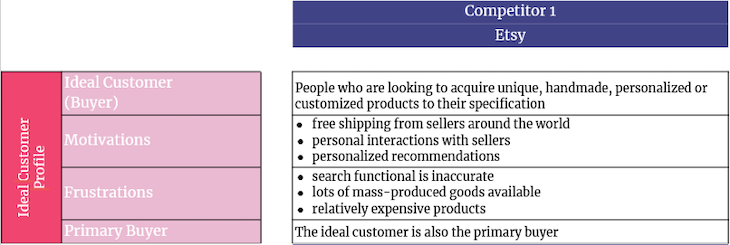
And the ideal customer profile for Etsy sellers:
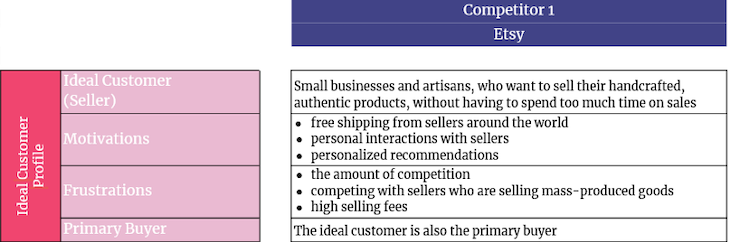
Not to be captain obvious, but you want to capture more details about the product your competitor is offering and its positioning.
The information we’re looking for at this step includes:
- The product — What is the tagline your competitor is using to market its product?
- Positioning — Based on the quality and price of the product, place the product into a one of several buckets. For example, Economy (low quality, low price), Skimming (low quality, high price), Penetration (high quality, low price), and Premium (high quality, high price)
- Product features — What are the key features being marketed and promoted?
Referring to our example AGORA app, the product information associated with Etsy on a competitor analysis might look as follows:
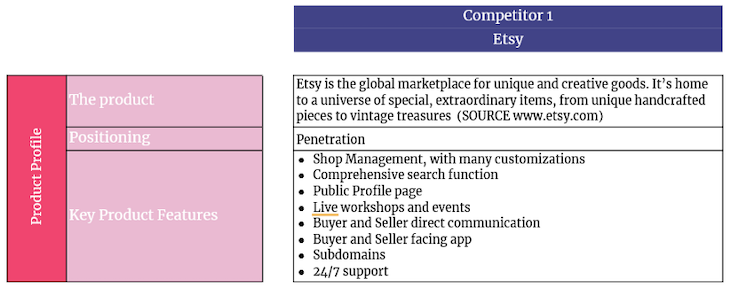
Next, seek to understand how your competitors are bringing the product to market .
List the following information:
- Pricing — What does the product costs? If there is a tiered pricing model, what does it look like?
- Distribution channels — Through which channels is your competitor selling the product?
- Marketing channels — Through which channels is the product being promoted?
In our AGORA competitor analysis example, this section would look something like:
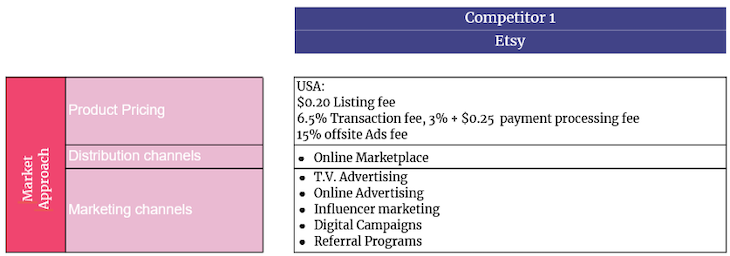
With all the information you’ve collected, you’ll find yourself in a good place to do a SWOT analysis . This is one of the most common and popular competitive analysis frameworks.
SWOT stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats:
- Strengths — What is going well for the competitor?
- Weaknesses — What is not going well? What obvious flaws are there?
- Opportunities — What could give your competitor an advantage?
- Threats — What might harm your competitor’s product?
For AGORA, our example competitive analysis might include a SWOT analysis that looks like this:
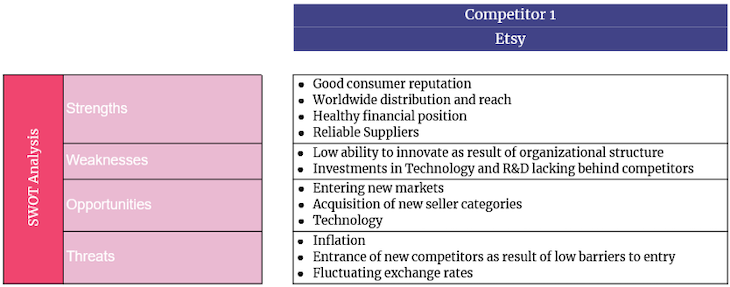
3. Develop a holistic overview and strategy
Now that you have a better view of your competitors, it’s time to determine how you want to approach them in the market: do you want to avoid your competitors or attack them?
Two extremely useful tools that can help you make this assessment are the competitive matrix and battle cards .
Competitive matrix
One way to operationalize the data you gathered during your competitive analysis is to plot out a four-quadrant competitive matrix.
Define key factors for the and x and y axes and plot yourself and your competition accordingly to see how you stack up. This approach is also known as perceptual mapping.
A competitive matrix for our example would look like this:
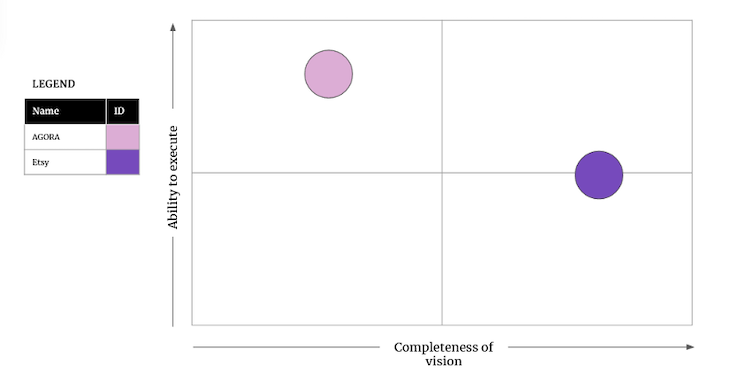
Battle cards
You can use the four-quadrant competitive matrix and competitor insights to create battle cards for each of your competitors.
Battle cards are a visual aid that help you compare your product against those of your competitors at a glance. It’s a quick and easy way to see how you stack up in key areas of performance and value. It’s also a neat way to help sales in their conversations with customers.
Here’s what you should include on each battle card:
- Company name — Name of your competitor
- Powers — What makes this competitor stand out from the rest?
- How we win — What should we do to gain a competitive advantage over this competitor?
- Why we lose — What is this competitor better at? What should we avoid so we don’t lose market share?
- Pricing — How much of a threat is the competitor’s product to our market share (low, medium, or high)?
- Strategy — Should we attack or avoid this competitor?
A battle card for our example competitive analysis might look as follows:
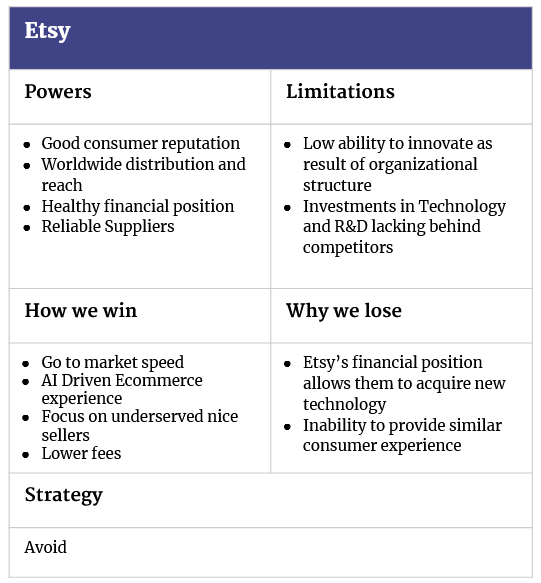
Alternative competitive analysis frameworks
If you‘ve followed the framework described above, you should have solid insight into your competitors, your product opportunities, and the best strategy to attack or avoid your competitors in the market.
If you want to dig deeper, you can follow up your competitive analysis by producing a Five Forces analysis and/or customer journey map .
The Five Forces model
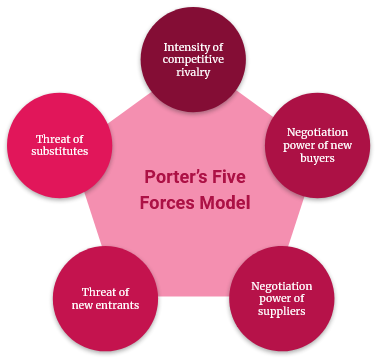
You still might want to consider gaining more insights into the competitive structure of the market you are in — in other words, gain a better understanding of how easy it is to either enter or be replaced by a competitor in the market.
A great framework to use for this type of competitor analysis is the Five Forces model , originally conceived by Michael Porter.
According to the Five Forces model, you can assess the market you are in by looking at:
- Intensity of competitive rivalry
- Negotiation power of new buyers
- Negotiation power of suppliers
- Threat of new entrants
- Threat of substitutes
Customer journey map
Instead of zooming out, you can also zoom in on the journey ideal customers make when interacting with the product itself, the distribution, or marketing channels.
On a journey map, your touchpoints are the customer, the activity performed, how the customer experiences the activities, and their expectations.
Free competitive analysis templates
A competitive analysis is a continuously updated document packed with information about your most important competitors to help you determine how to approach them in your target market.
The competitive analysis model described in this article consists of three steps that are designed to produce the insights you need to rule the market once and for all.
Below are free, customizable competitive analysis templates for each step of the process described in this article:
- Competitive analysis template
- Product canvas template
- Competitive matrix template
- Battle card template
- Customer journey map template
NOTE : To use and customize the competitive analysis templates above, after opening, select File > Make a copy from the main menu.
Featured image source: IconScout
LogRocket generates product insights that lead to meaningful action
Get your teams on the same page — try LogRocket today.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- #market analysis

Stop guessing about your digital experience with LogRocket
Recent posts:.

Exploring augmented products: Beyond the core offering
Augmented products leverage technology and additional services to provide enhanced functionality, convenience, and value to users.

A guide to acceptance test-driven development (ATDD)
ATDD is an agile methodology involving collaboration to define acceptance criteria before starting any development.


Leader Spotlight: Empowering teams via a shared vision, with Brian Peterson
Brian Peterson discusses how he creates empowered teams by establishing a shared vision across teams, organizations, and the company.

Implementing pilot projects: Purpose, process, and best practices
Instead of making an entire upfront investment, the pilot project aims to test something on a reduced scale to assess whether it works.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Plans
How to Write the Competitor Analysis Section of the Business Plan
Writing The Business Plan: Section 4
Susan Ward wrote about small businesses for The Balance for 18 years. She has run an IT consulting firm and designed and presented courses on how to promote small businesses.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/SusanWardLaptop2crop1-57aa62eb5f9b58974a12bac9.jpg)
The competitor analysis section can be the most difficult section to compile when writing a business plan because before you can analyze your competitors, you have to investigate them. Here's how to write the competitor analysis section of the business plan.
First, Find Out Who Your Competitors Are
If you're planning to start a small business that's going to operate locally, chances are you already know which businesses you're going to be competing with. But if not, you can easily find out by doing an internet search for local businesses, looking in the online or printed local phone book, or even driving around the target market area.
Your local business may also have non-local competitors that you need to be aware of.
If you're selling office supplies, for instance, you may also have to compete with big-box retailers within a driving distance of several hours and companies that offer office supplies online. You want to make sure that you identify all your possible competitors at this stage.
Then Find Out About Them
You need to know:
- what markets or market segments your competitors serve;
- what benefits your competitors offer;
- why customers buy from them;
- as much as possible about their products and/or services, pricing, and promotion.
Gathering Information for Your Competitor Analysis
A visit is still the most obvious starting point - either to the brick and mortar store or to the company's website. Go there, once or several times, and look around. Watch how customers are treated. Check out the prices.
You can also learn a fair bit about your competitors from talking to their customers and/or clients - if you know who they are. Other good "live" sources of information about competitors include a company's vendors or suppliers and a company's employees. They may or may not be willing to talk to you, but it's worth seeking them out and asking.
And watch for trade shows that your competitors may be attending. Businesses are there to disseminate information about and sell their products or services; attending and visiting their booths can be an excellent way to find out about your competition.
You'll also want to search for the publicly available information about your competitors. Online publications, newspapers, and magazines may all have information about the company you're investigating for your competitive analysis. Press releases may be particularly useful.
Once you've compiled the information about your competitors, you're ready to analyze it.
Analyzing the Competition
Just listing a bunch of information about your competition in the competitor analysis section of the business plan misses the point. It's the analysis of the information that's important.
Study the information you've gathered about each of your competitors and ask yourself this question: How are you going to compete with that company?
For many small businesses, the key to competing successfully is to identify a market niche where they can capture a specific target market whose needs are not being met.
- Is there a particular segment of the market that your competition has overlooked?
- Is there a service that customers or clients want that your competitor does not supply?
The goal of your competitor analysis is to identify and expand upon your competitive advantage - the benefits that your proposed business can offer the customer or client that your competition can't or won't supply.
Writing the Competitor Analysis Section
When you're writing the business plan, you'll write the competitor analysis section in the form of several paragraphs.
The first paragraph will outline the competitive environment, telling your readers who your proposed business's competitors are, how much of the market they control and any other relevant details about the competition.
The second and following paragraphs will detail your competitive advantage, explaining why and how your company will be able to compete with these competitors and establish yourself as a successful business.
Remember; you don't have to go into exhaustive detail here, but you do need to persuade the reader of your business plan that you are knowledgeable about the competition and that you have a clear, definitive plan that will enable your new business to successfully compete.
Our Recommendations
- Best Small Business Loans for 2024
- Businessloans.com Review
- Biz2Credit Review
- SBG Funding Review
- Rapid Finance Review
- 26 Great Business Ideas for Entrepreneurs
- Startup Costs: How Much Cash Will You Need?
- How to Get a Bank Loan for Your Small Business
- Articles of Incorporation: What New Business Owners Should Know
- How to Choose the Best Legal Structure for Your Business
Small Business Resources
- Business Ideas
- Business Plans
- Startup Basics
- Startup Funding
- Franchising
- Success Stories
- Entrepreneurs
- The Best Credit Card Processors of 2024
- Clover Credit Card Processing Review
- Merchant One Review
- Stax Review
- How to Conduct a Market Analysis for Your Business
- Local Marketing Strategies for Success
- Tips for Hiring a Marketing Company
- Benefits of CRM Systems
- 10 Employee Recruitment Strategies for Success
- Sales & Marketing
- Social Media
- Best Business Phone Systems of 2024
- The Best PEOs of 2024
- RingCentral Review
- Nextiva Review
- Ooma Review
- Guide to Developing a Training Program for New Employees
- How Does 401(k) Matching Work for Employers?
- Why You Need to Create a Fantastic Workplace Culture
- 16 Cool Job Perks That Keep Employees Happy
- 7 Project Management Styles
- Women in Business
- Personal Growth
- Best Accounting Software and Invoice Generators of 2024
- Best Payroll Services for 2024
- Best POS Systems for 2024
- Best CRM Software of 2024
- Best Call Centers and Answering Services for Busineses for 2024
- Salesforce vs. HubSpot: Which CRM Is Right for Your Business?
- Rippling vs Gusto: An In-Depth Comparison
- RingCentral vs. Ooma Comparison
- Choosing a Business Phone System: A Buyer’s Guide
- Equipment Leasing: A Guide for Business Owners
- HR Solutions
- Financial Solutions
- Marketing Solutions
- Security Solutions
- Retail Solutions
- SMB Solutions
How to Do a Competitive Analysis

Table of Contents
A competitive analysis is a tool you can use to discover where your business is doing well, where you need to improve and which trends you need to get ahead of. Complete a competitive analysis when your company isn’t moving forward as fast as you want or when competitors are securing orders from your ideal customers.
In this article, we’ll explain the concept of a competitive analysis and how to perform one for your business.
How to complete a competitive analysis
Josh Rovner, business consultant and bestselling author of Unbreak the System: Diagnosing and Curing the Ten Critical Flaws in Your Company (Lioncrest Publishing, 2020), shared with us nine steps for completing a competitive analysis.
1. Identify the products or services you want to evaluate.
For most analyses, they will be the products or services that generate the highest revenues or demonstrate the most significant potential for growth.
2. Seek direct competitors.
These companies compete for roughly the same market with comparable products or services. For example, accountants competing against other accountants.
3. Pinpoint indirect competitors.
These companies target the same market but with different products or services. For example, accountants competing against bookkeepers.
4. Examine replacement competitors.
These companies offer a different product or service, but address the same issue as your products or services (for example, apps that assist entrepreneurs).
5. Determine which parts of your competitors’ businesses are worth investigating.
These aspects could be pricing, distribution and delivery strategies, market share, new products or services coming to market, who their long-standing, highest-spending customers are, the quality of after-sales support, and which sales and marketing channels they use.
6. Research all identified competitors.
You may only find minimal accounting and operational records for most competitors, especially nonpublic companies. Other useful information – like target customers, product features, type of staff employed and price points – will be easier to find.
7. Document your research in a written analysis.
Make sure your document is substantive and actionable, but not so long that your staff won’t read it. Comparison charts and graphs are useful to help you and your team visualize your position in the market in relation to your competitors.
8. Identify areas to improve and execute the changes.
Could you improve the quality of your products or services by adding or amending a feature, lowering the price to be more affordable or improving after-sales support? Could you achieve a better ROI on your marketing budget by investing in a more capable CRM for better lead management ?
Rovner recommends including information about related trends in your market and region for a more complete picture of the entire competitive landscape. “Document what threats are out there that could have a negative impact on your business, and document the opportunities out there that you could take advantage of better than your competitors.”
9. Track your results.
Measure your sales with a profit and loss statement to determine if the changes were successful.
Competitive analysis explained
A competitive analysis – also known as a competitor analysis – is a way of evaluating how well your business and its products or services are performing compared to other companies selling similar products or services in your market.
“A competitor analysis focuses on identifying market participants positioned to encroach on your opportunity and isolates each participant’s operational strengths, substantive weaknesses, product offerings, market dominance, and missed opportunities,” said David Taffet, CEO of Petal.
Competitor analyses help you improve your business in these ways:
- Identify your strengths and weaknesses. When you know where you’re ahead of the competition, you can focus your marketing message to press home that advantage. When you know where you’re behind, you can better understand how you need to improve your products, services or after-sales to exceed your competitors.
- Understand the marketplace you operate in. You know who many of your competitors are but you won’t know all of them right off the bat and may not be aware of the latest entrants to the market . Identifying your primary competitors (as well as any upcoming threats), and how they differ from your business is key to beating them.
- Evaluate trends in your sector. Which new or improved product, service or feature are competitors offering to gain an advantage? Which trends have they seen that you haven’t yet? By examining the behaviors and actions of other companies in your marketplace, you can judge whether they’ve taken the right course and whether you should be going head-to-head with them. [Related content: Top E-Commerce Challenges Facing SMBs ]
- Plan future growth. Want to be the third-largest firm in your sector instead of the fourth? A competitive analysis gives you the information you need to get there, including how much more you need to sell, the demographics to market and any skill gaps your organization has.
Factors your competitor analysis should include
Colin Schacherbauer, executive marketing assistant at Investor Deal Room, recommended the following 10 components for an effective competitor analysis.
Feature matrix
Find all the features that each direct competitor’s product or service has. Keep this information in a competitor insight spreadsheet to visualize how companies stack up against one another.
Market share percentage
Evaluating the marketplace by percentage helps identify the main competitors in your area. Don’t exclude larger competitors entirely, as they have much to teach you about how to succeed in your industry. Instead, practice the 80/20 rule: Keep an eye on 80% direct competitors (companies with similarly sized market shares) and 20% top competitors.
Pinpoint how much your competitors charge and where they fall on the quantity versus quality spectrum.
What type of marketing plan does each competitor employ? Look at competitors’ websites, their social media strategy, the type of events they sponsor, their SEO strategies, their taglines and current marketing campaigns. [Follow these tips to create a great business marketing plan .]
Differentiators
What makes your competitors unique and what do they advertise as their best qualities? How is that different from your company?
Identify what your competitors are doing well and what works for them. Do reviews indicate they have a superior product? Do they have high brand awareness? Can you test a competitor’s products yourself to see where they are performing better?
Identify what each competitor could be doing better to give you a competitive advantage. Do they have a weak social media strategy? Do they lack an online store? Is their website outdated?
Look at where your competitors are located and the regions they service. Are they brick-and-mortar companies or is the bulk of their business performed online?
Evaluate your competitors’ objectives, employee satisfaction and company culture . Are they the type of business that advertises the year it was established or are they recent startups? Read employee reviews for further insight into competitors’ culture. [Learn the best ways to improve your company culture .]
Customer reviews
Analyze your competitors’ customer reviews, both positive reviews and negative ones. In a 5-star system, look at 5-star, 3-star and 1-star reviews. Three-star reviews are often the most honest.
Benefits of carrying out a competitive analysis
In an era of digital innovation , no business can remain preserved in time and expect to survive. Companies can disappear overnight if they don’t pay attention to new trends. A clear example of this is Blockbuster’s catastrophic error of initially dismissing Netflix’s services. Today, Netflix is a juggernaut, while Blockbuster is virtually extinct.
Even if your sector is not susceptible to this type of seismic change, it’s worth knowing what drives your clients’ decision-making processes. By keeping a regular eye on your marketplace through a competitive analysis, you’ll also be aware of these trends:
- Changes to competitors’ existing products or services that make them more attractive
- New complementary products or services from your contenders that you could also offer or alter
- The threat posed by new market entrants or transformative products
“In some cases, you may find that you are at a competitive disadvantage, in which case you may need to make a change in order to maintain your sales volumes,” Rovner said. “In other cases, you may notice that you have an advantage that could enable you to make a change that increases your sales or profit.”
How often you should perform a competitive analysis
Regular competitive analysis is key. You may want to do the analysis once a year on a large scale and quarterly on a smaller scale.
“Too many businesses do a competitor analysis early on and then neglect it once their brand is established,” Schacherbauer added. “Industries are constantly changing, and each time a new company enters your space, they are doing a competitor analysis on you. It’s important to continually evaluate your competitors.”
Analyzing your business regularly against your competitors will reveal opportunities to improve your products, better serve your target customers and increase levels of profitability. You may also want to consider using another model – like Porter’s Five Forces – to further analyze the competition.
“Understanding one’s competitors allows one to distinguish oneself from the competition, focus on the underserved market opportunities, determine the services to offer, identify the best practices to employ and isolate the worst practices and rotten players,” Taffet said.
How competitive analyses help small businesses
Your successful business today won’t necessarily be a successful tomorrow if you don’t keep an eye on the competition. By employing a competitive analysis, you can evaluate the current marketplace and where you stand compared to your competitors. With that knowledge, you can make adjustments to set your company up for continued success.
Skye Schooley contributed to the writing and reporting in this article. Source interviews were conducted for a previous version of this article.

Building Better Businesses
Insights on business strategy and culture, right to your inbox. Part of the business.com network.
%20(1).png)
How to Write a Competitor Analysis for a Business Plan (with AI in 2023)

Competitor analysis is a critical component of any business plan. It helps you understand the landscape of your industry, identify opportunities for growth and differentiation, and craft strategies that take advantage of your competitors' weaknesses.
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to conduct a comprehensive competitor analysis, including how to leverage AI tools like Bizway to make the process more efficient and effective.
Step-by-Step Guide to Performing a Competitor Analysis
1. identify your competitors.
Understanding your competitive landscape begins with pinpointing who your direct and indirect competitors are.
Points to Consider
- Direct Competitors : Those who offer similar products/services in the same market.
- Indirect Competitors : Businesses targeting your customer base with different offerings.
- Utilize market research and customer feedback to list competitors.
- Identify geographical considerations - local, regional, or global competitors.
2. Analyze Their Products/Services
A thorough examination of competitors’ offerings unveils potential areas for differentiation and enhancement in your product/service line.
- Feature comparisons.
- Pricing structures.
- Unique Selling Propositions (USPs).
- Adopt a customer-centric approach to understand how consumers perceive competitors’ offerings.
- Identify gaps in their product/service lines that you could explore.
3. Assess Their Marketing Strategy
Understanding competitors’ marketing approaches aids in crafting a superior, data-driven marketing strategy.
- Target audience.
- Key messages and value propositions.
- Channel effectiveness and presence.
- Use social listening tools to gauge their social media effectiveness.
- Analyze the SEO performance of competitors’ websites.
4. Examine Their Sales Strategy
Investigating sales channels and tactics employed by competitors reveals market penetration strategies and potential areas for diversification.
- Distribution channels.
- Pricing and sales tactics.
- Customer relationship management.
- Secret shop to observe sales tactics and customer experiences.
- Review customer feedback on their purchasing experience.
5. Analyze Their Strengths and Weaknesses
Identifying what competitors excel in and fall short on enables strategic decision-making in exploiting market opportunities.
- Operational efficiency.
- Customer service quality.
- Brand reputation and loyalty.
- Conduct a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) for each competitor.
- Leverage customer reviews and testimonials to gauge reputation.
Using AI for Competitor Analysis
Automated data collection.
AI automates the harvesting of data from myriad sources, ensuring robust research while saving time.
- Use AI tools to scrape and aggregate data from competitors' websites, social media, and customer review platforms.
- Ensure the data is categorized and stored systematically for easy analysis.
Real-Time Updates
AI provides a competitive edge by monitoring and reporting real-time updates on competitor activities.
- Set up AI monitoring for specific competitor activity: product launches, PR releases, or marketing campaigns.
- Ensure to leverage real-time data to inform swift strategic adjustments.
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics via AI deciphers patterns and anticipates future competitor moves, positioning your business proactively.
- Leverage AI to analyze historical data for predicting future trends.
- Utilize these insights to anticipate and formulate preemptive strategies.
Using Bizway for Competitor Analysis and Business Planning
One such AI tool that can revolutionize your competitor analysis process is Bizway . Bizway is an AI-powered business planning and research app that can help you research your competitors and write your entire competitor analysis with just a few clicks. Moreover, Bizway can assist you in writing your entire business plan, saving you time and providing you with expert-level planning documents.
With Bizway, you can automate the process of generating clear, concise planning docs across all areas of business, from an SEO Content Plan to User Onboarding Plan. It also helps fill knowledge gaps in areas of business you're not well-versed in.
So, whether you're a solopreneur, a small business owner, or an aspiring entrepreneur still in school, Bizway is the AI assistant you need to take your business planning to the next level.
Gerrard + Bizway AI Assistant
Start automating your business growth, today⚡
Create your first AI assistant & project in minutes.⚡
.png)
Bizway is brought to you by Landmark Labs Ltd.
©2024 Bizway Labs
Mastering Competitive Analysis in Business Plan
6 minutes read
In an ever-competitive business world where agility and innovation reign supreme, understanding the landscape in which your business operates is more than a mere advantage - it's a necessity. Thriving in today's dynamic environment demands a keen understanding not just of your business, but of the ecosystem within which it co-exists. This requires comprehensive awareness of who your competitors are, what they're doing, and how they're doing it. And this is precisely where competitor analysis comes into play.
In this article, you’ll know what competitive analysis is, why it is important and how to perform the analysis in a better way. Let’s dive in.
What Is Competitor Analysis
Competitor analysis is a strategic business practice that involves evaluating and understanding the strengths and weaknesses of competitors in the same industry or market. The primary goal is to gain insights into the competitive landscape, identify opportunities, and make informed decisions to improve your own business performance.
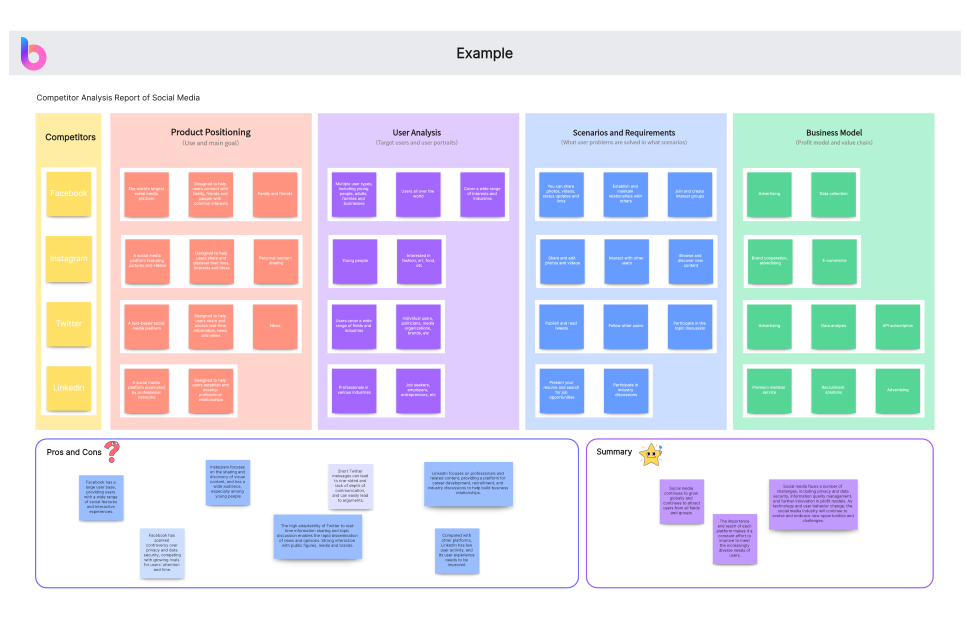
Key Aspects of Competitor Analysis in Business Plan
Competitor analysis is an essential part of any business plan, providing key insights that drive decision making and strategic planning. Understanding your competition can position your business favorably within the market and give you a competitive edge. This part highlights the critical aspects of competitor analysis you should focus on for effective business planning.
- Identification of Competitors: Recognizing who your competitors are is the first step. This includes both direct competitors offering similar products or services and indirect competitors who may fulfill the same need in a different way.
- SWOT Analysis: Assessing the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT) of your competitors helps in understanding their internal capabilities and external challenges. This analysis aids in developing strategies to capitalize on weaknesses and counteract threats.
- Market Share and Positioning: Understanding the market share of your competitors and their positioning in the market relative to yours provides valuable insights. It helps identify areas where you can differentiate your products or services.
- Product and Service Offerings: Analyzing the features, quality, and pricing of your competitors' offerings helps you benchmark your own products or services. It can also reveal areas for improvement or innovation.
- Marketing and Branding Strategies: Evaluating the marketing and branding strategies of competitors provides insights into how they are reaching and engaging with their target audience. This information can be valuable for refining your own marketing approach.
- Customer Reviews and Feedback: Examining customer reviews and feedback for your competitors' products or services can highlight areas where they excel or fall short. This information can guide your efforts to meet or exceed customer expectations.
- Technological Advancements: Keeping track of technological advancements adopted by competitors can inform your own technology strategy. It ensures that you stay competitive in terms of innovation.
- Financial Performance: Analyzing the financial health of your competitors can provide an understanding of their stability and growth potential. This information is crucial for strategic planning.
Overall, competitor analysis is an ongoing process that helps businesses stay informed about industry trends, anticipate changes, and make well-informed decisions to maintain or improve their competitive position.
Why Is Competitive Analysis Important in Business Plan
Conducting a competitor analysis is not just about observing and replicating what others are doing. It's about leveraging this knowledge to formulate a unique and superior strategy that distinguishes your business from the rest. The importance of competitive analysis in a business plan can be seen in the following points:
- Identify Market Gaps: Through competitor analysis, we can identify unmet needs in the market or gaps in competitors' offerings that can be leveraged as potential business opportunities.
- Inform Decision Making: By understanding what strategies are working for competitors and why, we can make more informed decisions about our own strategic direction.
- Predict Competitor Moves: A detailed understanding of competitors can help predict their future actions based on their past behavior. This allows businesses to proactively devise counter-strategies.
- Benchmark Performance: Comparing key performance indicators (KPIs) against industry competitors helps determine how well your business is doing and where improvements can be made.
- Reduce Risks: By regularly analyzing competitors, businesses can detect threats early and take preventive measures to reduce potential risks.
Competitor analysis is a critical component of any business strategy. It's not just about keeping tabs on competitors but using this knowledge as a strategic tool for growth and improvement.
How to Conduct a Great Competitive Analysis in Business Plan
The ability to stay ahead of the competition is vital in the ever-changing business landscape. Boardmix understands that importance and has made it a mission to equip businesses with the right tools to navigate this competitive environment. In this part, you will be led through a step-by-step process on how to conduct a great competitive analysis for your business plan.

Phase 1: Identifying Competitors
Every great competitive analysis starts with identifying your competitors. They can be direct (companies that offer the same products or services as yours) or indirect (companies that offer different products or services that serve the same purpose). With Boardmix's in-depth AI analysis tools, you can easily identify these competitors. Start with a list of 4-10 primary competitors in your market segment and then narrow down to those that directly impact your business.
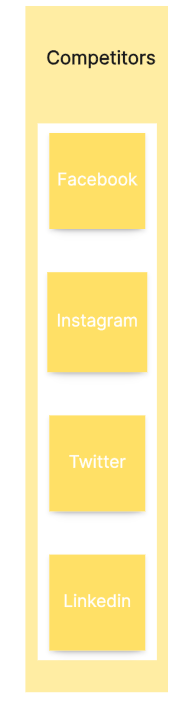
Phase 2: Analyzing Competitor Products and Services
Once you've identified your competitors, it's time to scrutinize their products or services. Are there features that stand out? Are they priced higher or lower? What is their perceived value among customers? Boardmix provdies a feature can help streamline this process by offering a side-by-side comparison of your products and services with those of your competitors.
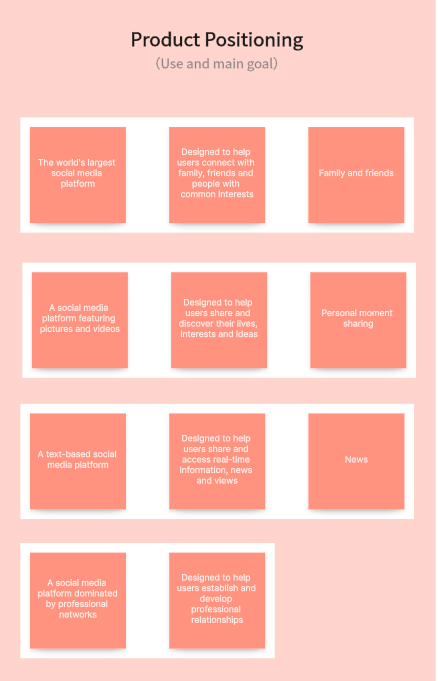
Phase 3: Assessing Competitors' Sales and Marketing Strategies
Understanding your competitors' sales and marketing strategies can provide crucial insights into their target audience, key messages, pricing strategy, and distribution channels. Leverage Boardmix's AI and infinite canvas capabilities to gather information about competitors' advertising, public relations, content marketing, SEO strategies, and more.

Phase 4: Examining Competitors’ Strengths and Weaknesses
This step involves analyzing each competitor's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats a SWOT analysis. Their strengths might be superior customer service, unique technology, or robust distribution networks. Weaknesses could be high prices or outdated offerings. Boardmix’s SWOT analysis tool can make this step seamless, helping you uncover potential areas where you can outshine your competition.
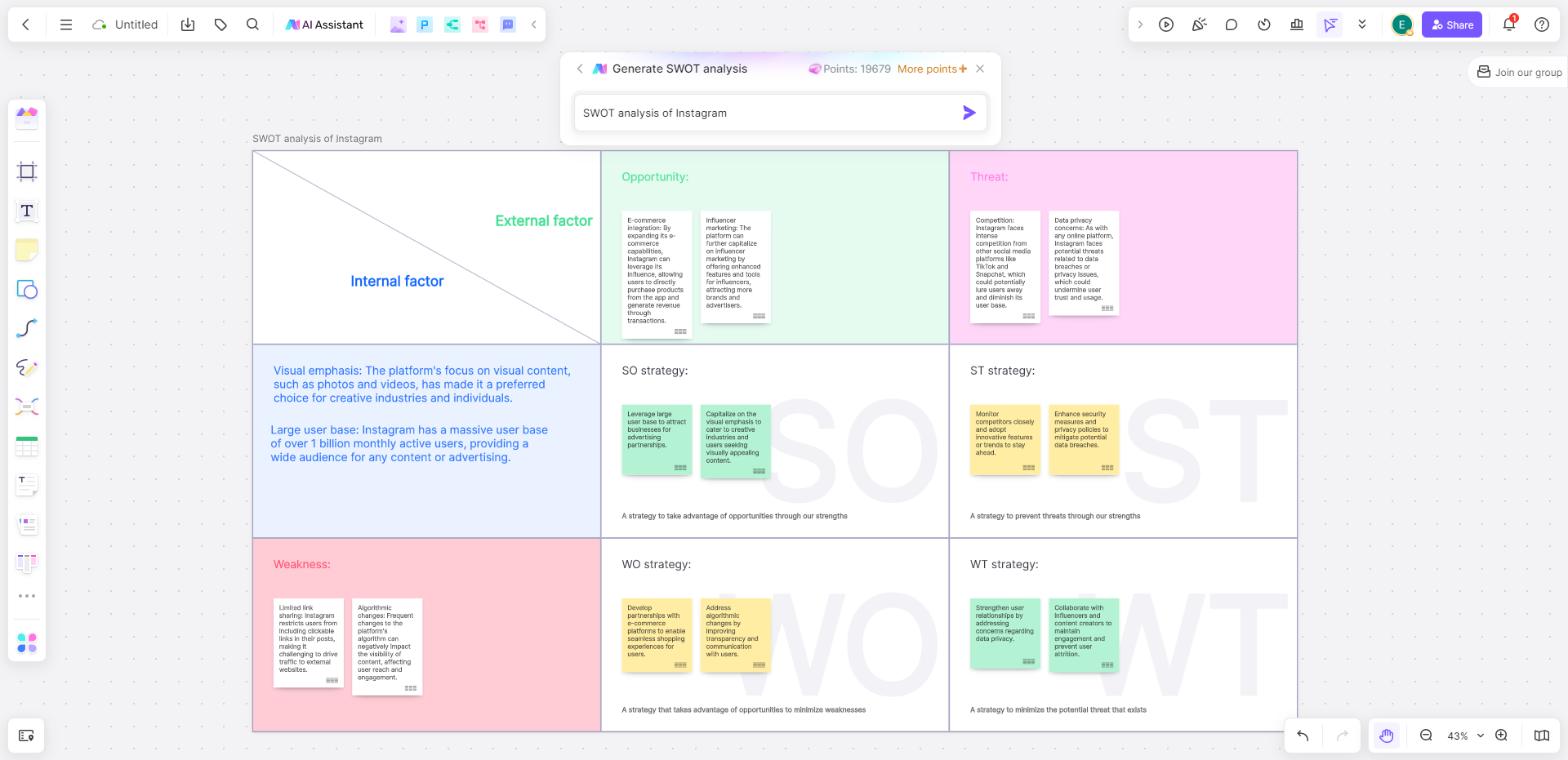
Phase 5: Studying Competitors' Market Positioning
How do your competitors position themselves in the market? Boardmix can help answer this by providing insights into competitors' branding strategy, unique selling propositions (USPs), and value proposition. Such an understanding will help you identify gaps you could fill to differentiate yourself in the market.
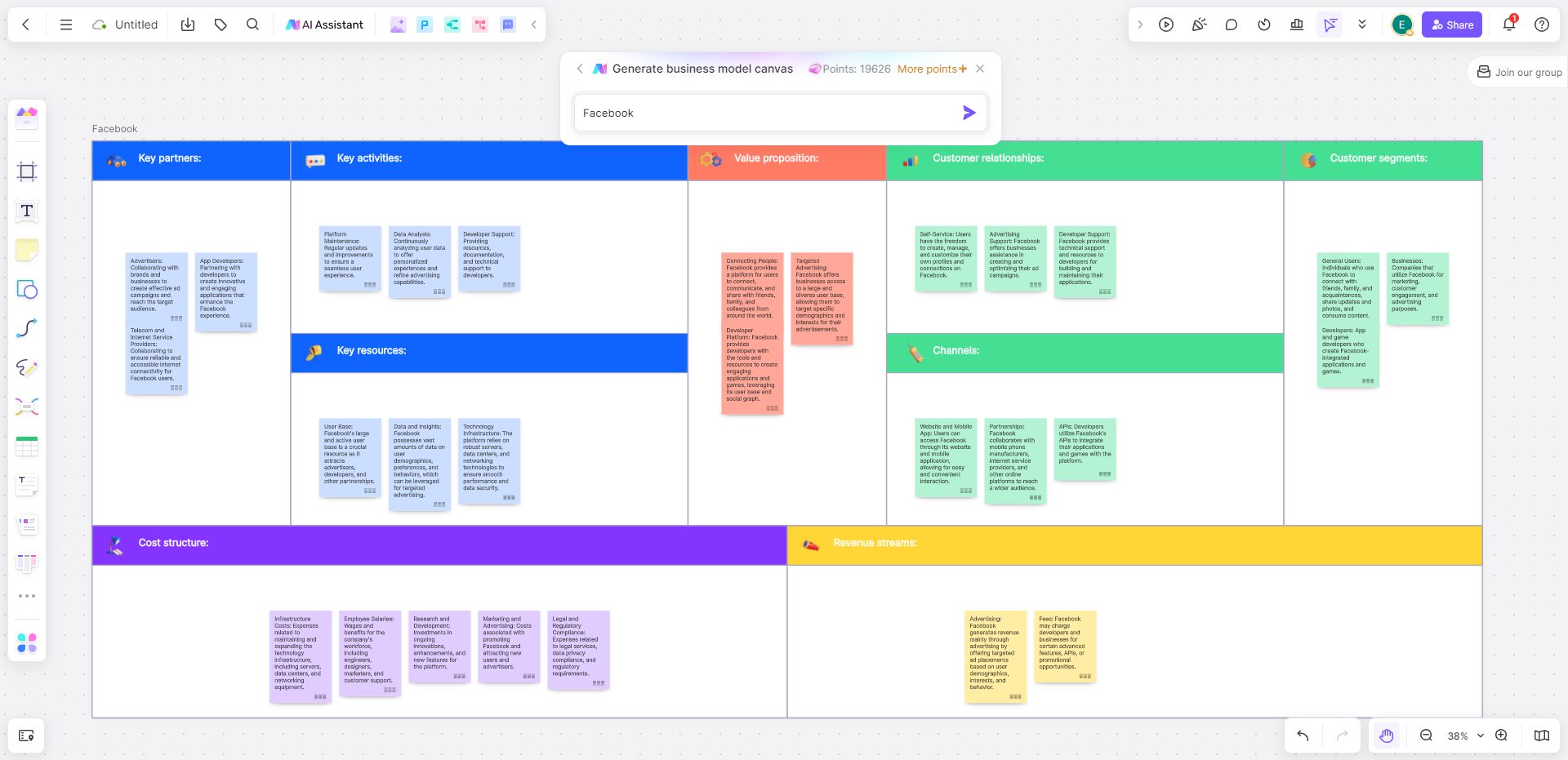
Phase 6: Ongoing Monitoring of Competitors
Competitive analysis should be an ongoing process due to ever-evolving markets and strategies. That's why Boardmix offers regular updates about changes in the competitive landscape so that you can adapt your strategies accordingly.
In conclusion, competitive analysis is pivotal in staying ahead of the game in business. It informs strategic decisions, helps exploit competitors' weaknesses, identifies market gaps, and creates unique value propositions. With Boardmix by your side, conducting a competitive analysis is made effortless and intuitive, ensuring your business carves out a unique and competitive space in the market.
Join Boardmix to collaborate with your team.
Harnessing Force Field Analysis for Effective Decision Making
DFD for Hospital Management System: A Comprehensive Guide
Mastering Project Timeline: Best Practices Revealed
We earn commissions if you shop through the links below. Read more
How to Write the Competitive Analysis for Your Business Plan
Back to Business Plans
Written by: Carolyn Young
Carolyn Young is a business writer who focuses on entrepreneurial concepts and the business formation. She has over 25 years of experience in business roles, and has authored several entrepreneurship textbooks.
Edited by: David Lepeska
David has been writing and learning about business, finance and globalization for a quarter-century, starting with a small New York consulting firm in the 1990s.
Published on February 19, 2023 Updated on December 12, 2023

Starting a business usually involves countless tasks, and one of the most important early hurdles is writing a business plan . Many entrepreneurs who aren’t looking for funding think they can skip this step, but that’s never a good idea.
A crucial element of the business plan is the competitive analysis, mainly because only by understanding your competition will your company be able to beat them.
Fortunately for you, this handy guide lays out all you need to know to whip up an excellent competitive analysis that’s sure to give you a serious advantage.
- What is a Competitive Analysis?
A competitive analysis describes your competitors and their products or services and identifies their strengths and weaknesses and competitive advantages. Writing the analysis involves detailed research and an examination of your competitors, their strategies, and their customers.
The goal is to identify how your business can gain a competitive advantage, usually by capitalizing on competitors’ weaknesses or beating them in a particular area, such as price or customer service.
A competitive advantage is critical to the success of your business, and something investors tend to focus on, so be sure to do your homework to determine yours.
- Steps to Write a Competitive Analysis
Writing a competitive analysis involves several steps.
1. Identify your top competitors
First, identify 5-10 competitors. They can be direct or indirect competitors. Direct competitors sell the same or similar products, while indirect competitors sell different products that solve the same problem. Burger King is McDonald’s direct competitor, for instance, while Chipotle is an indirect competitor.
A good competitive analysis begins with a brief overview of each competitor.
2. Research your competitors
Next, research those competitors to find out more about what they offer, how they offer it, and to whom. You can get this info on the company’s websites, social media, marketing, and any news and financial reporting.
Their marketing should help you to identify their value proposition and their target market . It may help to study their marketing through the eyes of a consumer.
What need do they fill? Who would find their marketing appealing? Where do they advertise? If their ads appear on TikTok, they’re looking to attract a younger market.
Read customer reviews to learn more about what they’re doing right, and more importantly, areas in which they fall short. You might even want to buy some of your competitors’ products, which would certainly help you with the next section of the plan.
3. Compare products
Now it’s time to thoroughly compare your competitors’ products to your own, examining the features and uses, as well as pricing, quality, and market placement.
This should show you how your product stacks up and give you ideas about how to improve it, perhaps with new features or added options.
4. Identify competitor strengths and weaknesses
By now you should be able to identify the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors. What do they do well? Where do they fall short? In your competitor summaries, list the strengths and weaknesses of each.
5. Identify competitor competitive advantages
At this point you should know each competitor’s competitive advantage. What is their key differentiator? How does their product stand out? A competitive advantage is usually one of the following:
- Customer service
- Brand awareness
- Technology
- Convenience
- Rapid innovation
- Unique features
- High quality
- Corporate social responsibility
- Empathetic marketing
- Eco-friendliness
- Employee expertise
6. Determine your competitive advantage
Now we get to the whole point the competitive analysis – figuring out where your business can gain an advantage. What does your company offer that they don’t? What can you do better than they do? Review the above list of competitive advantages – does any of them jump out to you?
It could be something your business already does or has, or something you need to implement to gain an edge. Either way, it’s critical that you identify at least one differentiator that’s likely to persuade customers to choose your business.
- Structure Your Competitive Analysis
As previously mentioned, your competitive analysis should be structured as a series of summaries about each competitor and how your company compares. It might help to create a chart or table to illustrate your main points and findings.
Each summary should mention the key product features as well as strengths, weaknesses, and competitive advantage. Conclude the plan by explaining your competitive advantage, as well as how you will leverage it and sustain it.
Sounds like a lot of work, right? And this is just one part of your business plan!
A great deal of effort and research goes into a good competitive analysis, which highlights the complexity, and the importance, of writing a business plan. It’s a lot of work, but also a fantastic learning opportunity that will help develop informed strategies that shape your business.
Even if you’re not seeking funding, take the time to write a solid business plan and be sure to dig into the competitive analysis. After all, finding and embracing your business’ competitive advantage is likely to be one of the keys to your success.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Featured resources.
Crafting the Perfect Business Plan: A Deep Dive with Upmetrics’ Vinay Kevadiya
Carolyn Young
Published on October 13, 2023
In the first segment of our conversation with Vinay Kevadiya, the visionary behind Upmetrics, we explored the platform’s origins and itsunique ...

LivePlan Software Review
Published on September 15, 2023
When you’re starting a business, a business plan is essential whether you’re going to obtain financing or not. Creating a business plan helpsyou ...

What to Include in Your Business Plan Appendix?
Published on September 13, 2023
Launching a business involves countless tasks, and one of the crucial early hurdles is writing a business plan. Many entrepreneurs who aren’tlooki ...
No thanks, I don't want to stay up to date on industry trends and news.

- Customer Reviews
- Net 30 Account
- Wise Services
- Steps & Timeline
- Work at a Glance
- Market Research at a Glance
- Business Plan Writing Services
- Bank Business Plan
- Investor Business Plan
- Franchise Business Plan
- Cannabis Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Corporate Business Plan
- Merge and Acquisition Business Plan (M&A)
- Private Placement Memorandums (PPM)
- Sample Business Plans
- Professional Feasibility Study
- PowerPoint Presentations
- Pitch Deck Presentation Services
- Business Plan Printing
- Market Research
- L-1 Business Plan
- E-2 Business Plan
- EB-5 Business Plan
- EB-5 Regional Centers
- Immigration Attorneys
- Nonprofit Business Plan
- Exit Business Planning
- Business Planning
- Business Formation
- Business License
- Business Website
- Business Branding
- Business Bank Account
- Digital Marketing
- Business Funding Resources
- Small Business Loans
- Venture Capital
- Net 30 Apply

Competitive Analysis for Business Plan
The Competitive Analysis section of your business plan provides an overview of the competition in your market. This section should help readers understand the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors and how your business will differentiate itself.
Why Competitive Analysis is Important in Business Plan?
The Competitive Analysis is important because it helps you understand your competitors and to develop strategies to differentiate your business and gain market share.
What to Include in Competitive Analysis
Before we jump in to the next section. You can download free business plan examples written by our professionals to see how we have written the competitive analysis in business plan. Here are some key components to include in your Competitive Analysis,
Competitor Overview:
Identify your main competitors including direct and indirect competitors, describe their products or services, market position, and target customers.
Direct & Indirect Competitors Example
Direct competitors:
- Pepsi and Coca-Cola are direct competitors in the soft drink industry.
- Nike and Adidas are direct competitors in the athletic shoe market.
- Apple and Samsung are direct competitors in the smartphone market.
Indirect competitors:
- A fine dining restaurant may have indirect competition from fast food chains.
- A high-end spa may have indirect competition from at-home spa products.
- A movie theater may have indirect competition from streaming services like Netflix.
Competitive Advantage:
Identify the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors and explain how your business will differentiate itself. This includes your unique value proposition, pricing strategy, and marketing approach.
Market Share:
Estimate the market share of each competitor and explain how you will gain market share. This includes your sales strategy, customer acquisition tactics, and promotional efforts.
Barriers to Entry:
Identify the barriers to entry in your industry, such as high capital costs, regulatory requirements, or proprietary technology. Explain how your business will overcome these barriers and establish a competitive advantage.
SWOT Analysis:
The SWOT Analysis component of the Competitive Analysis assesses the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats facing the business in relation to its competitors. This analysis should include an evaluation of the business’s internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as an analysis of external factors such as market trends, regulatory changes, and competition.
Risk Analysis:
The Risk Analysis component of the Competitive Analysis identifies potential risks and challenges that may impact the business’s ability to achieve its marketing goals. This includes an evaluation of financial risks, such as changes in market conditions or unexpected expenses, as well as non-financial risks such as reputational damage, supply chain disruptions, or legal and regulatory risks.
Miles stones
The milestones section in the competitive analysis of your business plan outlines the major goals and achievements that your business hopes to reach over a specific period.
The milestones section should include a clear timeline with specific, measurable objectives that will allow the business to track its progress towards achieving its goals. Some examples of milestones could include:
- Opening a new store or location
- Launching a new product or service
- Reaching a specific sales target
- Hiring key staff members or building out a team
- Implementing new technology or systems
- Obtaining regulatory approval or certification
Overall, the milestones section provides a roadmap for the business’s success, helping to ensure that it stays on track and achieves its objectives.
BUSINESS PLAN TEMPLATE OUTLINE
- Business Plan Template
- 1. Cover Page
- 2. Executive Summary
- 3. Company Overview
- 4. Market Analysis
- 5. Competitive Analysis
- 6. Marketing Plan
- 7. Operations Plan
- 8. Management Team
- 9. Financial Plan
- 10. Appendix
- Business Plan Summary
Quick Links

- Investor Business Plans
- M&A Business Plan
- Private Placement
- Feasibility Study
- Hire a Business Plan Writer
- Business Valuation Calculator
- Business Plan Examples
- Real Estate Business Plan
- Business Plan Pricing Guide
- Business Plan Makeover
- SBA Loans, Bank Funding & Business Credit
- Finding & Qualifying for Business Grants
- Leadership for the New Manager
- Content Marketing for Beginners
- All About Crowdfunding
- EB-5 Regional Centers, A Step-By-Step Guide
- Logo Designer
- Landing Page
- PPC Advertising

- Business Entity
- Business Licensing
- Virtual Assistant
- Business Phone
- Business Address
- E-1 Visa Business Plan
- EB1-A Visa Business Plan
- EB1-C Visa Business Plan
- EB2-NIW Business Plan
- H1B Visa Business Plan
- O1 Visa Business Plan
- Business Brokers
- Merger & Acquisition Advisors
- Franchisors
Proud Sponsor of
- 1-800-496-1056

- (613) 800-0227

- +44 (1549) 409190

- +61 (2) 72510077

If you still have questions or prefer to get help directly from an agent, please submit a request. We’ll get back to you as soon as possible.
Please fill out the contact form below and we will reply as soon as possible.
- Business Management & Operations
- Strategy, Entrepreneurship, & Innovation
Business Plan - Competitive Analysis
What is the Competitive Analysis Section of the Business Plan
Written by Jason Gordon
Updated at April 21st, 2024
- Marketing, Advertising, Sales & PR Principles of Marketing Sales Advertising Public Relations SEO, Social Media, Direct Marketing
- Accounting, Taxation, and Reporting Managerial & Financial Accounting & Reporting Business Taxation
- Professionalism & Career Development
- Law, Transactions, & Risk Management Government, Legal System, Administrative Law, & Constitutional Law Legal Disputes - Civil & Criminal Law Agency Law HR, Employment, Labor, & Discrimination Business Entities, Corporate Governance & Ownership Business Transactions, Antitrust, & Securities Law Real Estate, Personal, & Intellectual Property Commercial Law: Contract, Payments, Security Interests, & Bankruptcy Consumer Protection Insurance & Risk Management Immigration Law Environmental Protection Law Inheritance, Estates, and Trusts
- Business Management & Operations Operations, Project, & Supply Chain Management Strategy, Entrepreneurship, & Innovation Business Ethics & Social Responsibility Global Business, International Law & Relations Business Communications & Negotiation Management, Leadership, & Organizational Behavior
- Economics, Finance, & Analytics Economic Analysis & Monetary Policy Research, Quantitative Analysis, & Decision Science Investments, Trading, and Financial Markets Banking, Lending, and Credit Industry Business Finance, Personal Finance, and Valuation Principles
What is the competitive analysis portion of my business plan?
Barriers to entry, competitors, and how you will beat them. In this section, you are trying to identify all of the aspects of the market that could keep you out. Many business plans simply identify the competitors and products that will compete with their intended products/services; however, this is only one-half of the story. If there are a certain number of competitors or competitive product/services, why is that?
There has to be some factor that keeps others producer/providers from entering the market. These are commonly known as "barriers to entry". In the market analysis, you made the determination that the market is sufficiently big that you could be successful by grabbing even a conservative percentage. So, now:
- Tell why others aren't entering the market;
- Tell why you will be able to enter the market;
- List those who are going to attempt to keep you from taking their market share or will try to take your market share;
- List how you will be successful in taking their share, making the pie bigger, or fighting off their attempts.
If there is market potential, why are others NOT in this awesome market?
What are your barriers to entry? Assuming that you are not yet in the market, what is it going to take to get there? This will generally be the same explanation as to why others are not in the market. Remember, the chances are not good that you are the first person or business to come up with an idea for a product or service. There has to be something that is keeping others out. This may not be obvious at first, but identifying these early will allow you to make adjustments to meet these hurdles. Identify the barriers to entry and explain how they may affect your business or industry. Common barriers to entry include:
Funding or Capital Concerns
How much capital is required upfront? Will it require some level of revolving capital needs? Where are you going to get this capital?
Legal Barriers (Licensing, Regulatory approval)
Is there a required state or federal license? Does the product or service require inspection and approval by a state or federal regulatory agency? Is the business subject to some state or federal regulation that is subject to change? (ex. Labor laws, foreign embargos, etc.)
Costs of Production
Is there a cost of production that is inhibitive in starting out?(Ex.Many older companies avoid the high cost of production due to production methods established when costs were lower.)
Cost of Sales and Marketing
Suppose you have the perfect product. How are you going to let people know about it? (Remember, the Apple operating system was superior that of Microsoft in the early days of each company. Nonetheless, Microsoft dominated the market with a largelyinferior product.) Can you market and pitch sales sufficiently to create customer awareness and drive sales of your product. Often you will have to market far more than the established brands in order to convert existing customers to your product.
Logistical Concerns
How are you going get your raw material or other supplies for conducting business. How are you going to deliver your goods or services to your customers? Will it involve outsourcing or international shipping? Will this require strategic presence or distribution centers in various locations? All of these go into logistical concerns. Basically, you need to brainstorm of how every aspect of the business that requires the movement of product or material from one place to another will take place. Much of this information can be gleaned from competitors or businesses with similar business models. Understanding the logistical concerns will allow you to estimate costs and budgeting. Further, you may uncover a logistical aspect that supplies a competitive advantage to another business or, potentially, your planned business.
Required Skills and Knowledge
Who are you going to need to involve in order to carry out your business? It's a common mistake for the entrepreneur to believe that he or she can carry on too many of the actual business functions. If you haven't realized, you will be preoccupied with countless tasks and will not be able to carry on many of the tasks that you now assume will be your responsibility. You need to have an understanding of what you don't know have the time or ability to do. Again, look to competitors or similar businesses to determine the skills or market knowledge necessary to carry on your planned business operations.
Employee Concerns
Employee concerns are countless and daunting. There is no way to project for the types of employee troubles that you may face in starting your business. Types of employee issues include: hiring, training, employee benefits (healthcare, retirement), union negotiations, lawsuits (discrimination or hostile environment), and firing. The employee concerns for which you can plan include hiring, training, and employee benefits. All of these issues can entail considerable costs that were not previously anticipated. Planning and buying insurance for unplanned legal events can help to minimize these issues.
Intellectual Property
How are you going to protect your process or product? Does your product or service involve or potentially infringe on the intellectual property rights of others? Generally, the only way to protect your intellectual property is through patent, trademark, copyright, or trade secret. Some businesses develop around a product or service with the idea that they can start up under the radar of competitors and then grow quickly before competitors can catch up. This is commonly referred to as, "running faster" than the competition. In general, this is a last resort strategy as outrunning a competitor with superior funding is very difficult. Start by looking at the nature of your product or service and try to determine the best way to protect or establish defendable ownership or intellectual property rights.
Every business is going to pay taxes on the identifiable profit. The question is how much tax you will have to pay. Are there any tax advantages that exist for carrying on your business? Importantly, what tax advantages are your competitors employing that allow them to carry on business in an otherwise unprofitable venture. For example, there may be economic development or energy savings associated with your business venture. Another example is the effect or choosing a particular business entity above another. If you are going to need to use Net Operating Losses from the current year to offset personal income tax then an LLC may be a better option than an S-Corporation. Again, a percentage of tax savings can make a considerable difference in the profit margin or overall profitability of your business.
Strong Competitors
How strong are the competitors? What tactics are they likely to employ to defeat your product or service or to keep you from stealing market share? A large, well-capitalized competitor may be able to engage in a price war that you cannot withstand. This will require both primary and secondary research of your actual and potential competitors. (This concept is developed further below.)
Now, address each of the above-listed competitive barriers and explain how you will deal with the current situation, the situation that will arise along your projected growth path, and any contingent changes in these factors that could affect these businesses.
Competitive Analysis - Who Will You Have to Compete within This Market Space?
Who will be your competitors? Here you should prepare an exhaustive list of the players who will compete against you in your immediately relevant and prospective markets.
- List each competitor's name, location, and give a brief profile of their product or service.
- Create sub-categories and groupings for the competitors who are your most direct competitors.
- Classify the extent to why the subcategorized competitors are the greatest threat. (You will list aspects such as location, percentage of the market held - customer base, type of product or service lines, competitive or innovative nature of the firm, etc.)
- Expand on the secondary or indirect competitors. (Give an explanation of why you believe their product or service is a competitor to yours. This could explain how their product or service is a substitute product. Explain the situation in which these secondary or indirect competitors would be the greatest threat to your projected business, e.g., if they offer an inferior good (product or service) then a downturn in the economy may drive customers away from your more economically elastic product.
- Explain how your product or service is superior (or competitively advantaged) against each competitor's product service. The most difficult part of this component is identifying all of the characteristics that customers covet in the product or service, such as: design, speed, ease of use, dependability, price, customer service, etc. It may be useful to use a table listing the attributes of the products side-by-side. This allows for quick assessment by third-parties, as well as provides a framework for you to conceptualize the market position of your product or service. You can create multiple tables comparing your product or service to each category or individual competitor. You will need to compile the lists of competitive factors for that competitor or competitor's product. Note: These individual tables may not fit within the body of the business plan. You can always append or attach them to the end of the business plan.
Developing a Competitive Analysis section requires a great deal of research and knowledge about other businesses' products or services; however, the most difficult portion is assessing your product or service strength and weaknesses. In developing this section it is important to as honest and objective as possible in analyzing your value proposition. It may be useful to enlist third parties who are unbiased or unrelated to your business to provide their opinion on your product. This will help avoid the cognitive bias that nearly all entrepreneurs have when assessing the competitive strengths of their own product or service. Remember, even if you can explain away any fears or negative perceptions that customers have about your product, the customer's input is extremely valuable. You will not be there to explain away these fears or concerns at the point in which the customer learns of the product. These will be the perception issues that you have to address in marketing your product or service.
Related Topics
- Business Plan, Part 1 (Outline Overview)
- Business Plan, Part 2 (The Executive Summary)
- What is a Mission Statement?
- What is a Values Statement?
- Setting Company Goals
- Business Plan, Part 4 (Market Analysis)
- Business Plan, Part 5 (Competitive Analysis)
- Business Plan, Part 6 (Marketing Plan)
- Business Plan, Part 7 (Operations)
- Business Plan, Part 8 (Management and Organization)
- Business Plan, Part 9 (Financial Projections)
- Business Plan, Part 10 (Appendices)
- Business Plan , (Final Modifications)
Related Articles
- Aggregator Model - Explained
- PESTEL Factors - External Analysis
- Commoditize (Product) - Explained

500+ business plans and financial models
Competitive Analysis for an Optician (Example)
- May 9, 2024
- Business Plan , Competitive Analysis

A competitive analysis is not just a tool for gauging the position of your optician in the market and its key competitors; it’s also a fundamental component of your business plan.
This analysis helps in identifying your optician’s unique selling points, essential for differentiating your business in a competitive market.
In addition, the competitive analysis is integral in laying a solid foundation for your business plan. By examining various operational aspects of your competitors, you gain valuable information that ensures your business plan is robust, informed, and tailored to succeed in the current market environment.

Optician Business Plan

Fully editable 30+ slides Powerpoint presentation business plan template.
Download an expert-built 30+ slides Powerpoint business plan template
Identifying Your Competitors in the Optician Industry
The first step in conducting a competitive analysis is to identify who your competitors are. Start by listing local optician shops and larger optical chains that offer similar services such as eye exams, prescription glasses, and contact lenses. Also, consider online eyewear retailers as indirect competitors, as they can significantly impact customer choices.
Use digital tools like Google Maps to locate nearby competitors geographically. Websites like Yelp and Google Reviews provide customer feedback and ratings, offering insights into your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses . For example, if reviews frequently highlight the exceptional customer service and wide variety of styles at “Visionary Optics,” these are significant competitive strengths.
Optician Competitors’ Strategies
Exploring the strategies of your competitors involves several aspects:
- Product Range: Examine the variety of eyewear and related products offered. If “Trendy Eyes” is popular for its stylish and affordable eyewear collections, it indicates a market trend towards fashion-forward, budget-friendly options.
- Service Quality : Consider the level of service, including the thoroughness of eye exams, the expertise of the staff, and aftercare services. An optician like “Precision Optics” known for its meticulous eye care services might attract customers who prioritize health over cost.
- Pricing Strategy : Assess how your pricing compares with that of your competitors. Are your products and services priced on par with “Economy Vision,” or do they match the premium offerings at “Luxury Lenses”?
- Marketing Tactics: Review how competitors promote their products and services. Do they use aggressive online marketing strategies , or do they rely more on traditional advertising and community engagement?
- Customer Experience: Evaluate the shopping experience they offer, such as “Family Eye Care” which might be recognized for a family-friendly environment and patient-centric service.
- Operational Efficiency: Observe if competitors are utilizing technology to enhance service efficiency, like “FastFrame Optics” with its quick glasses fitting services.
What’s Your Optician’s Value Proposition?
Consider what sets your optician business apart. Maybe you offer exclusive designer frames that are not available elsewhere in your area, or perhaps you provide a comprehensive eye care plan that includes detailed diagnostics and follow-up care.
Identify market gaps through customer feedback and industry trends. For instance, the growing interest in advanced lens technology and customizable frames could be a significant opportunity if not widely offered by competitors.
Consider your location: An optician in a bustling shopping district might focus on trendy and high-end products to attract fashion-conscious shoppers, while one in a residential area might emphasize family-friendly services and affordability.
How To Summarize It All In Your Business Plan?
Competitors’ strategies and market positioning can be superposed with your own optician’s value proposition by laying out on a page (or a presentation slide) the main differentiating factors. These factors will show investors and banks:
- How each competitor is positioned in the market
- How your optician compares vs. competitors (what’s your value proposition )
In a competitive analysis, various parameters are used to compare and contrast your optician with its competitors. The parameters listed below are examples of what you might include in your analysis.
They are not exhaustive but serve as a guide to help you understand key aspects to consider. Each parameter provides insights into different facets of the competitive landscape, helping to paint a comprehensive picture of where your optician stands.
The location of an optician influences customer accessibility and demographic appeal. For instance, an optician in a shopping mall may attract more walk-in clients due to high foot traffic, whereas one in a medical complex might draw patients referred by healthcare professionals. The strategic location also impacts marketing and operational logistics.
Range of Eyewear Offered
This factor highlights the diversity of products available at your optician shop compared to others. Offering a wide range of eyewear, including designer frames, affordable options, and specialty lenses, can cater to a broader clientele. This sets your business apart if competitors have a limited selection.
Free Eye Exam?
Offering free eye exams can be a significant differentiator. This service not only attracts customers who are cost-conscious but also introduces them to your product range and additional services. It positions your business as customer-centric and value-oriented, especially if this is not a common practice among competitors.
Specialty Services
Specialty services such as contact lens fitting, pediatric eye care, or vision therapy can distinguish your optician business in a competitive market. These services cater to specific customer needs that might not be addressed by all competitors, thereby tapping into niche markets.
Number of Opticians
The availability of multiple opticians can improve service efficiency and customer satisfaction. It indicates your business’s capacity to handle a high volume of customers and provide personalized attention, reducing wait times and improving the overall customer experience.
Business Hours
Extended or flexible business hours, including weekends or evenings, cater to working professionals and busy families, providing convenience and accessibility that might not be offered by all competitors.
Whether your optician business is part of a franchise can affect brand recognition and consumer trust. Franchises often benefit from national marketing and a standardized service model, which can be an advantage or a limitation when compared to independent opticians who may offer more personalized services.
Online Reviews
Online reviews are a powerful indicator of reputation and customer satisfaction. High ratings can enhance credibility and attract new customers. Monitoring and responding to reviews also demonstrate customer service commitment.
Prescription Services
Offering comprehensive prescription services, including fast processing of prescription lenses and partnerships with reputable labs, ensures product quality and customer satisfaction. This is particularly important in the optician industry, where precision and reliability are key.
Additional Factors to Consider
- Marketing Strategies : Analyzing how competitors market their services provides insights into effective promotional tactics and channels.
- Customer Service: The level of customer service, such as staff responsiveness and friendliness, can highlight areas for your business to excel.
- Brand Presence: The strength of online and offline presence, including social media activity and community engagement, influences brand perception.
- Product Innovation: Staying updated on new technologies and trends in eyecare and eyewear can inspire innovation and maintain competitive advantage.
- Supplier Relationships: Information on suppliers and partnerships can reveal insights into product quality and cost efficiency, influencing your pricing strategy and product offerings.
Privacy Overview
Home Blog Business Value Chain Analysis: A Guide for Presenters
Value Chain Analysis: A Guide for Presenters
Successful businesses add value every time they sell something. Adding value means customers get what they want and are happy with their purchase, and the business owners earn revenue. Companies that give their customers more value make more profit than those that do not.
Therefore, understanding a business’s value chain is important for finding out how much value is added. This article highlights what a value chain is and why it matters. It will further guide you with a case study on how you can analyze yours to help your business keep more of the value it creates from sales.
Table of Contents
What is a Value Chain?
Elements of the value chain, advantages of value chain analysis in business, what is the difference between supply chain and value chain, how to create a value chain analysis, recommended ppt templates for value chain analysis presentations, final words.
Value chain refers to all the business processes that make a product or provide a service. This chain includes everything from coming up with ideas to selling the final product. Michael Porter introduced it to help the company break down its tasks into activities and focus on where it can be better than its competition [1] . These activities either make the product worth more to customers or cost less to produce.
Porter’s value chain is not just about what a company does. It is also about the other companies it works with, like suppliers and distributors. You can imagine it as a series of steps. Each step adds something meaningful to the final product or service.
Analyzing the value chain is like focusing closely on each stage to identify opportunities for improvement. By looking closely at each part of the process, businesses can find ways to make things more efficient [2] . This saves money and helps become more competitive in the market.
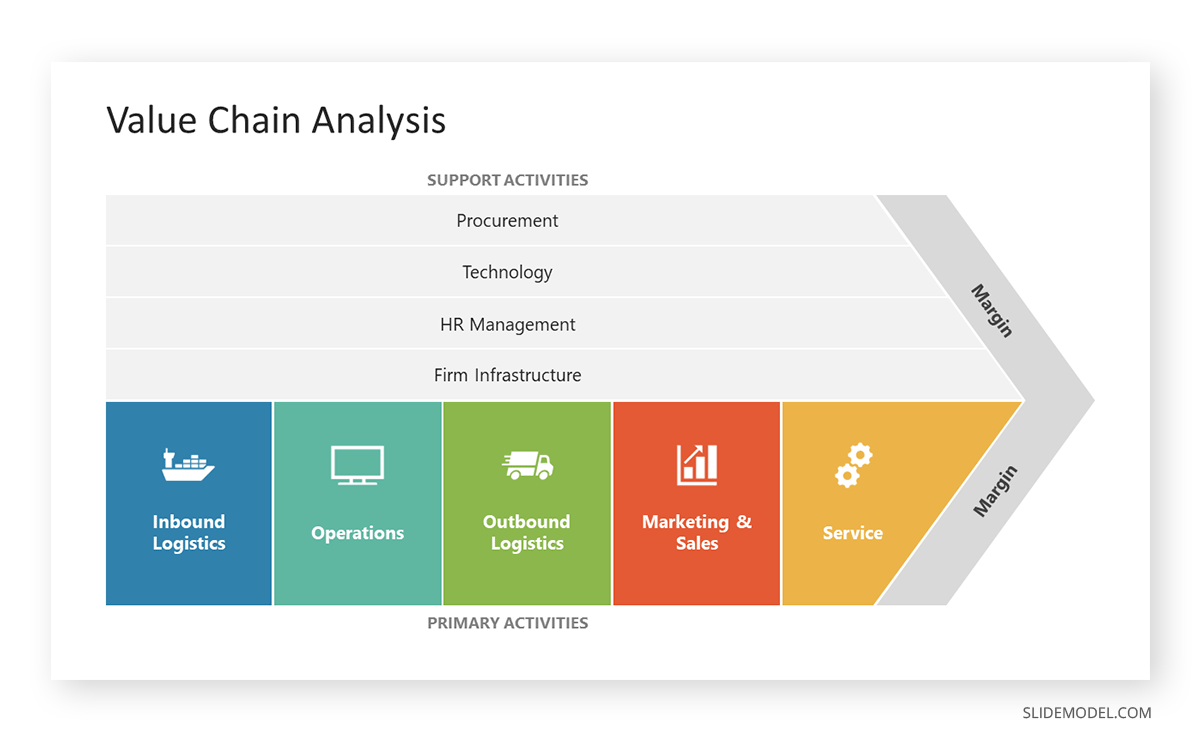
Activities of the value chain are divided into two categories.
Primary Activities
Inbound logistics.
It involves all the activities related to logistics. We are all aware that logistics in a business is all about receiving, storing, and distributing inputs required for the production process [4] . We will perform tasks such as sourcing raw materials, handling inventory, and managing suppliers.
These activities directly convert inputs into finished products or services. This stage includes the manufacturing, assembly, packaging, and testing processes.
Outbound Logistics
Once the products or services are ready, outbound logistics focuses on efficiently getting them to the customers. This includes order fulfillment, warehousing, transportation, and delivery.
Marketing and Sales
This section covers all activities related to promoting and selling products or services to customers. It includes market research, advertising, sales strategies, pricing, and distribution channels.
After-sales service is crucial for maintaining customer satisfaction and loyalty. This includes installation, repair, maintenance, customer support, and warranties.
Secondary Activities
Procurement.
It is sourcing and purchasing raw materials, equipment, and other resources required for production. Effective procurement practices can help to improve the quality, cost-effectiveness, and reliability of the inputs.
Technology Development
Innovation and technological advancements also improve efficiency and competitiveness. This includes research and development (R&D), technology acquisition, and innovation processes.
Human Resource Management
People are the driving force behind every business. Human resource management encompasses recruitment, training, performance management, and employee relations to ensure a skilled and motivated workforce.
Infrastructure
Infrastructure refers to the organizational support systems and facilities required to support the value-adding activities. This includes IT systems, communication networks, facilities management, and other administrative functions.
Value Chain Analysis helps businesses make intelligent decisions and improve their actions [5] . For example, companies can use it to find where they’re wasting time or money and fix those areas. It also allows businesses to understand their unique value from competitors in the same industry. Plus, it’s beneficial for ensuring everything runs smoothly in their supply chain, so they always have what they need and when needed.
The supply chain and the value chain are related but have different jobs. The value chain mainly focuses on the activities within a single company. It adds value at each stage of a product’s journey, from creation to customer satisfaction. This includes production, marketing, and customer support [3] . On the other hand, the supply chain has a broader scope. It involves acquiring materials from suppliers, manufacturing goods, and delivering them to customers. It coordinates with various partners to ensure smooth operations and minimize costs [3] . At the same time, the value chain focuses on value creation. Thus, the supply chain is more about efficiently moving goods and minimizing production and transportation costs.
NB: This case study simplifies the Value Chain Analysis process for easier concept understanding. Due to the depth required for this kind of study, value chain analysis is performed at large-scale organizations as a tool.
Step 1: Identify Value Chain Activities
First, you separate the business operations into primary and support activities. Primary activities directly relate to creating and delivering a product or service. Conversely, support activities assist and enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of primary activities.
Café Delight maps out all its activities, from sourcing ingredients to delivering the final cup of coffee. Its focus on high-quality ingredients and exceptional customer service are critical to its brand identity.
Primary Activities for Café Delight include
Inbound Logistics : Procuring coffee beans, milk, and bakery items.
Operations : Brewing coffee and preparing food.
Outbound Logistics : Serving customers in-store or delivering orders.
Marketing & Sales : Promotional campaigns and loyalty programs.
Service : Customer service and after-sales feedback handling.
Support Activities might involve
Procurement : Sourcing high-quality ingredients.
Technology Development : Implementing order management systems.
Human Resource Management : Training baristas and staff.
Infrastructure : Managing cafes and administrative tasks.
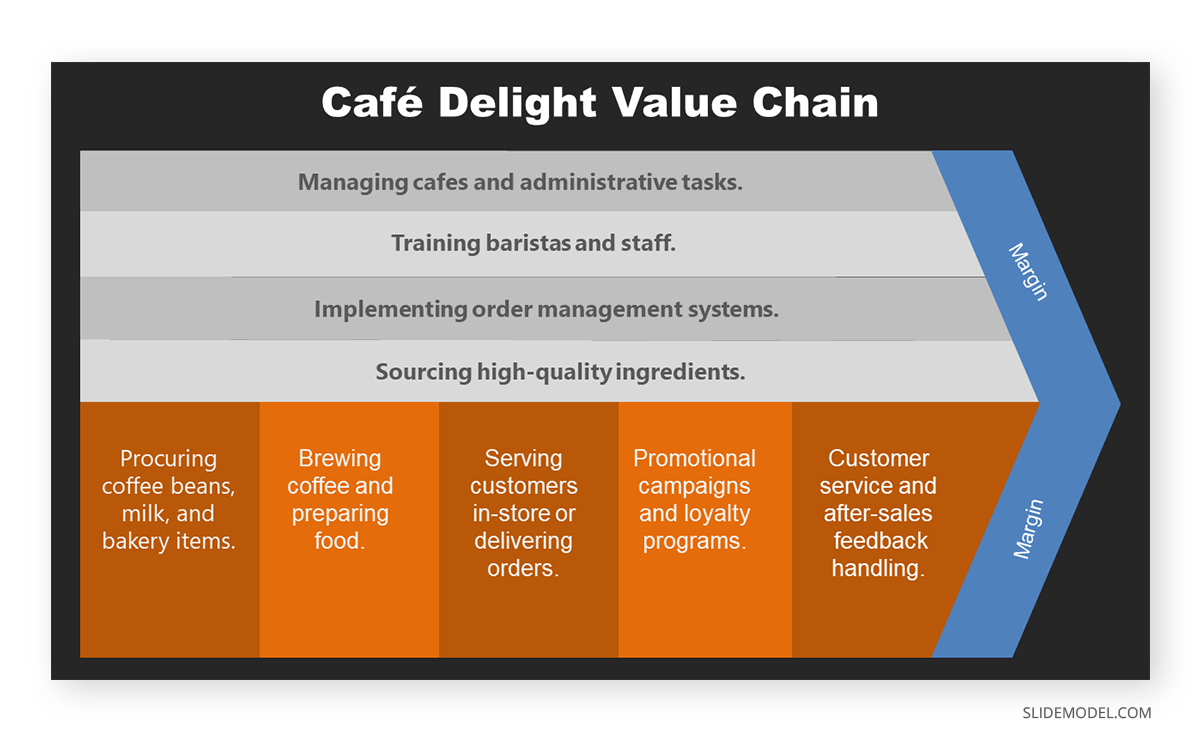
Step 2: Determine Activities’ Values and Costs
Here, you evaluate each identified activity to understand its cost structure and the value it adds to the final product or service. This involves assessing how each activity contributes to customer satisfaction and competitive advantage and pinpointing where costs are incurred.
In this crucial step, the focus shifts to analyzing the utility or value of each activity within Café Delight’s operations. It is identifying areas where costs can be reduced to enhance profitability. Let’s break down this step further.
Value Analysis
- Café Delight’s team conducts a thorough examination of its operations. It focuses on functions that directly impact customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. For instance, they identify that the primary function of serving quality coffee promptly to customers significantly enhances satisfaction.
- Café Delight offers a variety of specialty coffee blends sourced from exotic locations, priced at $4.50 per cup. Customers highly value the unique flavors and quality of the coffee.
- Secondary functions, such as the ambiance and customer service, are also evaluated for their contribution to customer experience and loyalty.
- Additionally, the café provides a cozy and inviting ambiance, with comfortable seating areas and aesthetically pleasing décor. This ambiance enhances the overall customer experience and encourages repeat visits.
Cost Analysis
- The team also examines the costs associated with each function, including procurement, labor, and operational expenses. For example, they find that high-quality coffee beans and skilled baristas contribute to higher procurement and labor costs.
- Additionally, they identify areas where costs could be reduced without compromising quality, such as optimizing inventory management or streamlining operational processes.
- Procuring high-quality coffee beans from international suppliers incurs significant costs for Café Delight, averaging $25 per pound. However, the café justifies this expense by offering premium coffee blends with higher prices and customer loyalty.
- Skilled baristas are essential to maintaining the café’s reputation for exceptional coffee. With an average hourly wage of $18 per barista and a team of 10 working 40-hour weeks, labor costs constitute a substantial portion of the expenses of Café Delight.
By conducting a thorough value and cost analysis, Café Delight also identifies areas for cost optimization without compromising its commitment to quality and customer satisfaction. For instance:
- The café explores alternative suppliers or bulk purchasing options to negotiate better prices for high-quality ingredients, such as coffee beans and bakery items.
- It implements efficient labor scheduling practices and training programs to maximize productivity and minimize labor costs while maintaining service excellence.
Step 3: Identify Competitive Advantage Opportunities
Here, it analyzes the information from the first two steps to uncover opportunities for gaining a competitive advantage. This could be through cost leadership (making activities more efficient to reduce costs) or differentiation (making products or services unique to enhance value).
For Café Delight, potential competitive advantages could include:
Product Innovation and Differentiation
Café Delight can make its menu more interesting by adding new coffee blends. They can even create unique blends for different times of the year. They will introduce exclusive limited-edition blends or seasonal flavors. This keeps customers excited and coming back for more.
Operational Excellence and Efficiency
While maintaining a commitment to quality, Café Delight can improve its operations to streamline processes, reduce costs, and enhance overall efficiency. It will implement technology solutions, such as inventory management software and automated brewing systems, to enhance workflow and minimize waste, which will help it save money and time.
Customer-Centric Service Excellence
Café Delight sets itself apart by providing top-notch customer experiences. This helps build customer loyalty and generates positive word-of-mouth recommendations. Prioritizing employee training programs that offer individualized and attentive service is crucial. They can significantly impact their staff by preparing to predict customer preferences, handle problems effectively, and establish meaningful connections.
Brand Storytelling and Community Engagement
Café Delight can tell customers where their coffee comes from and why it’s unique. They will engage in storytelling through social media, blog content, and in-store experiences, highlighting the journey from bean to cup and the impact of supporting local farmers. This makes customers feel good about coming to Café Delight.
If you are short on time and need to make a quick presentation, we recommend you use a value chain analysis template. Using PowerPoint templates from SlideModel or similar platforms can significantly enhance the clarity and impact of your presentation. Choosing a template that visually aligns with the depth and complexity of your analysis is very important. At the same time, creating a presentation from scratch can be time-consuming as well. Therefore, SlideModel Templates provide a structured starting point. These templates allow you to focus on customizing content rather than designing slides from the start.
1. Value Chain Analysis PowerPoint Template
You can present a value chain analysis sample in either an all-in-one format or slide-by-slide using this creative value chain PPT template. The diagram is featured in full format on the first slide, whereas the second slide attends to the primary activities and the third to the secondary activities. Get creative and customize this best PPT template for professional-looking presentation slides.
Use This Template
2. Competitive Analysis Slide Deck for PowerPoint & Google Slides

A slide deck intended for any kind of competitor analysis we need to create. Featuring 21 slides, we can perform an industry analysis, discover competitors, perform a competitor segmentation study, analyze competitor’s review data, create a SWOT analysis and more.
3. Key Diagram in 5 Steps
This key-inspired diagram slide makes it easy to express 5-step processes. It highlights each phase in a 5-step process, building the idea of the key components of any kind of process.
4. Value Chain Diagram Slide Deck for PowerPoint & Google Slides
Optimize operations management and any kind of logistics presentation by using our value chain model slide deck. 3 different diagram layouts in light and dark themes. Check them out!
5. Cost Reduction Plan PPT Template
As we’ve seen in our case study, this Cost Reduction PPT template helps us illustrate the different tactics driven out from the value chain analysis and cost analysis. Make your presentations more effective by summarizing your cost reduction plan with this versatile PPT template in light and dark themes.
6. Gradient Value Chain Framework Primary Activities
You can edit this 5 Steps Gradient PowerPoint Model and describe the 5 main activities of the Value Chain Framework. If your presentation requires to introduce the audience to the model, before getting deeper into the findings, it is recommended to explain the structure before, and set the context of the value chain analysis. Using impacting diagrams will help the audience engage, and remember the concepts you will use later.
7. Comparison Slide Value Chain Analysis Pros & Cons
For larger-format presentations, users can introduce the pros & cons of a value chain analysis with this colorful PPT template. Just add the information in the placeholder text areas and articulate your speech to discuss each one of the points.
Value chain analysis is crucial for businesses to improve efficiency, maximize value, and gain an edge over competitors. By carefully examining primary and support activities, along with costs and values, organizations can identify areas for improvement and innovation. This helps streamline operations, make products and services stand out, and focus on customer needs. Overall, value chain analysis empowers businesses to boost performance, foster innovation, and achieve sustainable growth in a competitive market.
[1] The Value Chain – Institute for Strategy and Competitiveness. Harvard Business School. https://www.isc.hbs.edu/strategy/business-strategy/Pages/the-value-chain.aspx
[2] What is a value chain analysis? 3 steps: HBS Online (2020) Business Insights Blog . https://online.hbs.edu/blog/post/what-is-value-chain-analysis
[3] https://ecampusontario.pressbooks.pub/globalvaluechain/chapter/1-4-learning-objective-3/
[4] https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Value-Chain-Analysis-A-Primary-Activities-Inbound-Logistics-the-company-receives_fig2_341070011
[5] https://www.aicpa-cima.com/resources/article/value-chain-analysis
[6] What Is A Value Chain Analysis? 3 Steps https://online.hbs.edu/blog/post/what-is-value-chain-analysis

Like this article? Please share
Business Planning, Value Filed under Business
Related Articles

Filed under Business • February 2nd, 2024
Business Plan Presentations: A Guide
Learn all that’s required to produce a high-quality business plan presentation in this guide. Suggested templates and examples are included.

Filed under Business • September 8th, 2023
Best Workplan Templates to Organize your Tasks
Create Professional Work Plan Presentations with our suggested Work Plan Templates.

Filed under Business • September 6th, 2023
A Comprehensive Guide to Strategic Planning for Success
Every organization has grand goals on their business agenda. However, there is a long way between formulating those goals and seeing the results of their successful accomplishment. A lot of things can happen in-between, the project can get side-tracked, the timeline may change and new threats may emerge. To get a better sense of what needs to be accomplished and how? Most managers regularly engage in strategic planning.
Leave a Reply

Butcher Shop Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky

Butcher Shop Business Plan
Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 1,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans to start and grow their butcher shops. On this page, we will first give you some background information with regards to the importance of business planning. We will then go through a butcher shop business plan template step-by-step so you can create your plan today.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here >
What is a Butcher Shop Business Plan?
A business plan provides a snapshot of your butcher shop as it stands today, and lays out your growth plan for the next five years. It explains your business goals and your strategy for reaching them. It also includes market research to support your plans.
Why You Need a Business Plan for a Butcher Shop
If you’re looking to start a butcher shop, or grow your existing butcher business, you need a business plan. A business plan will help you raise funding, if needed, and plan out the growth of your butcher shop in order to improve your chances of success. Your business plan is a living document that should be updated annually as your company grows and changes.
Sources of Funding for Butcher shops
With regards to funding, the main sources of funding for a butcher shop are personal savings, credit cards, bank loans and angel investors. With regards to bank loans, banks will want to review your business plan and gain confidence that you will be able to repay your loan and interest. To acquire this confidence, you will not only want to confirm that your financials are reasonable, but they will also want to see a professional plan. Such a plan will give them the confidence that you can successfully and professionally operate a business. Personal savings and bank loans are the most common funding paths for social media marketing businesses.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
How to write a business plan for a butcher shop.
Below we detail what should be included with each section of your business plan for a butcher shop.
Executive Summary
Your executive summary provides an introduction to your business plan, but it is normally the last section you write because it provides a summary of each key section of your plan.
The goal of your Executive Summary is to quickly engage the reader. Explain to them the type of meat shop you are operating and the status. For example, are you a startup, do you have a butcher shop that you would like to grow, or are you operating a chain of independent butcher shops?
Next, provide an overview of each of the subsequent sections of your plan. For example, give a brief overview of the meat industry. Discuss the type of butcher shop you are operating. Detail your direct competitors. Give an overview of your target market. Provide a snapshot of your marketing plan. Identify the key members of your team. And offer an overview of your financial plan.
Company Analysis
In your company analysis, you will detail the type of butcher shop you are operating.
For example, you might operate one of the following types of butcher businesses:
- Deli Butcher Shop : this type of meat shop specializes in cutting deli meats in small quantities for single or family size servings.
- Specialty Butcher Shop: this type of meat shop focuses on cutting specific meats such as wild game animals; their clients are usually hunters or fishermen.
- Abattoir Butcher: this type of meat shop specializes in cutting meats in wholesale sizes at abattoir/slaughterhouse.
In addition to explaining the type of butcher business you will operate, the Company Analysis section of your business plan needs to provide background on the business.
Include answers to question such as:
- When and why did you start the business?
- What milestones have you achieved to date? Milestones could include the number of customers served, number of positive reviews, total weight of fresh meat cuts, etc.
- Your legal structure. Are you incorporated as an S-Corp? An LLC? A sole proprietorship? Explain your legal structure here.
Industry Analysis
In your industry analysis, you need to provide an overview of the meat industry.
While this may seem unnecessary, it serves multiple purposes.
First, researching the meat industry educates you. It helps you understand the market in which you are operating.
Secondly, market research can improve your strategy, particularly if your research identifies market trends.
The third reason for market research is to prove to readers that you are an expert in your industry. By conducting the research and presenting it in your plan, you achieve just that.
The following questions should be answered in the industry analysis section of your meat shop business plan:
- How big is the meat and poultry industry (in dollars)?
- Is the market declining or increasing?
- Who are the key competitors in the market?
- Who are the key suppliers in the market?
- What trends are affecting the industry?
- What is the industry’s growth forecast over the next 5 – 10 years?
- What is the relevant market size? That is, how big is the potential market for your butcher shop? You can extrapolate such a figure by assessing the size of the market in the entire country and then applying that figure to your local population.
Customer Analysis
The customer analysis section must detail the customers you serve and/or expect to serve.
The following are examples of customer segments: individuals, families, deli shops, grocery stores, restaurants and fast food suppliers.
As you can imagine, the customer segment(s) you choose will have a great impact on the type of business you operate. Clearly, a family would respond to different marketing promotions than fast food supplier, for example.
Try to break out your target market in terms of their demographic and psychographic profiles. With regards to demographics, include a discussion of the ages, genders, locations and income levels of the customers you seek to serve. Because most butcher shops primarily serve customers living in their same city or town, such demographic information is easy to find on government websites.
Psychographic profiles explain the wants and needs of your target customers. The more you can understand and define these needs, the better you will do in attracting and retaining your customers.
Finish Your Butcher Shop Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Competitive Analysis
Your competitive analysis should identify the indirect and direct competitors your business faces and then focus on the latter.
Direct competitors are other butcher shops.
Indirect competitors are other options that customers have to purchase from that aren’t direct competitors. This includes delis, supermarkets and grocery stores.
With regards to direct competition, you want to describe the other butcher shops with which you compete. Most likely, your direct competitors will be house flippers located very close to your location.
For each such competitor, provide an overview of their businesses and document their strengths and weaknesses. Unless you once worked at your competitors’ businesses, it will be impossible to know everything about them. But you should be able to find out key things about them such as:
- What types of customers do they serve?
- What types of meats do they specialize in?
- What is their pricing (premium, low, etc.)?
- What are they good at?
- What are their weaknesses?
With regards to the last two questions, think about your answers from the customers’ perspective. And don’t be afraid to ask your competitors’ customers what they like most and least about them.
The final part of your competitive analysis section is to document your areas of competitive advantage. For example:
- Will you provide a wider variety of meat options?
- Will you provide special discounts or perks for new or returning customers?
- Will you provide the highest quality meat?
- Will you offer better pricing?
Think about ways you will outperform your competition and document them in this section of your plan.
Marketing Plan
Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P’s: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. Your marketing plan should include the following:
Product : In the product section, you should reiterate the type of meat shop that you documented in your Company Analysis. Then, detail the specific meat products you will be offering. For example, will other food options such as side dishes?
Price : Document the prices you will offer and how they compare to your competitors. Essentially in the product and price sub-sections of your marketing plan, you are presenting the services you offer and their prices.
Place : Place refers to the location of your business. Document your location and mention how the location will impact your success. For example, is your business located in a busy retail district, or a highly trafficked area? Discuss how your location might be the ideal location for your customers.
Promotions: The final part of your marketing plan is the promotions section. Here you will document how you will drive customers to your location(s). The following are some promotional methods you might consider:
- Advertising in local papers and magazines
- Reaching out to local websites
- Social media marketing
- Local radio advertising
Operations Plan
While the earlier sections of your meat shop business plan explained your goals, your operations plan describes how you will meet them. Your operations plan should have two distinct sections as follows.
Everyday short-term processes include all of the tasks involved in running your butcher shop, including cutting meats, tracking inventory, and completing orders and sales for customers.
Long-term goals are the milestones you hope to achieve. These could include the dates when you expect to have X number of customers, or when you hope to reach $X in revenue. It could also be when you expect to expand your business to a new city.
Management Team
To demonstrate your butcher shop’s ability to succeed, a strong management team is essential. Highlight your key players’ backgrounds, emphasizing those skills and experiences that prove their ability to grow a company.
Ideally you and/or your team members have direct experience in food service management. If so, highlight this experience and expertise. But also highlight any experience that you think will help your business succeed.
If your team is lacking, consider assembling an advisory board. An advisory board would include 2 to 8 individuals who would act like mentors to your business. They would help answer questions and provide strategic guidance. If needed, look for advisory board members with experience in overseeing supermarkets or grocery stores or successfully running their own business.
Financial Plan
Your financial plan should include your 5-year financial statement broken out both monthly or quarterly for the first year and then annually. Your financial statements include your income statement, balance sheet and cash flow statements.
Income Statement : an income statement is more commonly called a Profit and Loss statement or P&L. It shows your revenues and then subtracts your costs to show whether you turned a profit or not.
In developing your income statement, you need to devise assumptions. For example, will you only cut meats in small portions or in large quantities for other businesses such as a supermarket? And will sales grow by 2% or 10% per year? As you can imagine, your choice of assumptions will greatly impact the financial forecasts for your business. As much as possible, conduct research to try to root your assumptions in reality.
Balance Sheets : Balance sheets show your assets and liabilities. While balance sheets can include much information, try to simplify them to the key items you need to know about. For instance, if you spend $50,000 on building out your meat shop, this will not give you immediate profits. Rather it is an asset that will hopefully help you generate profits for years to come. Likewise, if a bank writes you a check for $50,000, you don’t need to pay it back immediately. Rather, that is a liability you will pay back over time.
Cash Flow Statement : Your cash flow statement will help determine how much money you need to start or grow your business, and make sure you never run out of money. What most entrepreneurs and business owners don’t realize is that you can turn a profit but run out of money and go bankrupt.
In developing your Income Statement and Balance Sheets be sure to include several of the key costs needed in starting or growing a meat shop:
- Location build-out including design fees, construction, etc.
- Cost of equipment and supplies
- Payroll or salaries paid to staff
- Business insurance
- Taxes and permits
- Legal expenses
Attach your full financial projections in the appendix of your plan along with any supporting documents that make your plan more compelling. For example, you might include your office location lease or blueprints for your shop.
Putting together your own business plan for your butcher shop is a worthwhile endeavor. If you follow the template above, by the time you are done, you will have an expert business plan (download it to PDF to show banks and investors). You will really understand the meat and poultry industry, your competition, and your customers. You will have developed a marketing plan and will really understand what it takes to launch and grow a successful butcher shop.
Butcher Shop Business Plan FAQs
What is the easiest way to complete my butcher shop business plan.
Growthink's Ultimate Business Plan Template allows you to quickly and easily complete your Butcher Shop Business Plan.
What is the Goal of a Business Plan's Executive Summary?
The goal of your Executive Summary is to quickly engage the reader. Explain to them the type of butcher shop you are operating and the status; for example, are you a startup, do you have a butcher shop that you would like to grow, or are you operating a chain of butcher shops?
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your Butcher Shop business plan?
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success. Click here to see how Growthink’s professional business plan consulting services can create your business plan for you.
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Perform a SWOT Analysis of your competitors. 1. Identify Your Direct and Indirect Competitors. First things first — identify all your business competitors and list them. You can make the final list later, but right now jot down all the competitors including new competitors.
Here are the steps you need to take: 1. Identify your competitors. The first step in conducting a comprehensive competitive analysis is to identify your competitors. Start by creating a list of both direct and indirect competitors within your industry or market segment. Direct competitors offer similar products or services, while indirect ...
You decide to conduct a market analysis for your business. To do so, you would: Step 1: Use Google to compile a list of your competitors. Steps 2, 3, and 4: Use your competitors' websites, as well as SEO analysis tools like Ahrefs, to deep-dive into the service offerings and marketing strategies of each company.
As a content marketer, I've performed a competitive analysis for several brands to improve their messaging, plan their marketing strategy, and explore new channels. Here are the five steps I follow to analyze competitors. 1. Identify and categorize all competitors. The first step is a simple yet strategic one.
The Competitive Analysis section of your business plan is devoted to analyzing your competition--both your current competition and potential competitors who might enter your market. Every business ...
Competitive analysis is a type of market research. It's the process of evaluating and understanding the strengths and weaknesses of competitors in your market. It involves gathering and analyzing data on competitors' products, pricing, marketing strategies, distribution channels, and customer base. Doing a competitive analysis helps you ...
Competitor analysis (CA) is a process of identifying competitors and gauging their business and marketing strategies to understand both their strengths and weaknesses and those of your own business. Competitive analysis provides a higher-level perspective of the entire marketing landscape and competitive intelligence.
Competitive analysis exists to help you avoid making mistakes and empower you to beat competitors to the punch in the pursuit of product growth and success. Knowing your competition will bring you great rewards. Conducting a competitive analysis will help you more effectively: Create benchmarks.
Writing the Competitor Analysis Section. When you're writing the business plan, you'll write the competitor analysis section in the form of several paragraphs. The first paragraph will outline the competitive environment, telling your readers who your proposed business's competitors are, how much of the market they control and any other ...
A competitor analysis, also called competitive analysis and competition analysis, is the process of examining similar brands in your industry to gain insight into their offerings, branding, sales, and marketing approaches. Knowing your competitors in business analysis is important if you're a business owner, marketer, start-up founder, or ...
2. Determine Products and Services That Your Competition Offers. To conduct a comprehensive competitor analysis, choose five to 10 competitors with similar product or service offerings and business models. Select a mix of direct and indirect competitors to understand how new markets may affect your company.
The steps to developing the competitive analysis section of your business plan include: Identify your competition. Select the appropriate competitors to analyze. Determine your competitive advantage. 1. Identify Your Competition. To start, you must align your definition of competition with that of investors. Investors define competition as to ...
Step 6: Document Your Research. In this last step, compile all your research in written format. Create an action plan that includes a tactical list of steps to take. This way, you can discuss and prioritize steps to take with your team. Aim to be concise as you create this competitor analysis document.
A competitive analysis - also known as a competitor analysis - is a way of evaluating how well your business and its products or services are performing compared to other companies selling ...
Competitor analysis is a critical component of any business plan. It helps you understand the landscape of your industry, identify opportunities for growth and differentiation, and craft strategies that take advantage of your competitors' weaknesses. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to conduct a comprehensive competitor analysis, including ...
The importance of competitive analysis in a business plan can be seen in the following points: Identify Market Gaps: Through competitor analysis, we can identify unmet needs in the market or gaps in competitors' offerings that can be leveraged as potential business opportunities. Inform Decision Making: By understanding what strategies are ...
Steps to Write a Competitive Analysis. Writing a competitive analysis involves several steps. 1. Identify your top competitors. First, identify 5-10 competitors. They can be direct or indirect competitors. Direct competitors sell the same or similar products, while indirect competitors sell different products that solve the same problem.
Understanding the competitive landscape is crucial for any business plan. A competitive analysis framework helps you scrutinize your competitors' strengths and weaknesses, anticipate market shifts ...
The SWOT Analysis component of the Competitive Analysis assesses the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats facing the business in relation to its competitors. This analysis should include an evaluation of the business's internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as an analysis of external factors such as market trends, regulatory ...
Conclusion. Developing a Competitive Analysis section requires a great deal of research and knowledge about other businesses' products or services; however, the most difficult portion is assessing your product or service strength and weaknesses. In developing this section it is important to as honest and objective as possible in analyzing your ...
In this video, Paul Borosky, MBA., and owner of Quality Business Plan, reviews important information that should be included in a competitor analysis section...
Competitor analysis. Look at how your competitors market themselves, how much they charge, and who they are targeting. ... Focus on writing a business plan that's most likely to secure funding. 3 ...
A competitive analysis is not just a tool for gauging the position of your optician in the market and its key competitors; it's also a fundamental component of your business plan.. This analysis helps in identifying your optician's unique selling points, essential for differentiating your business in a competitive market.
As a conclusion of the value and cost analysis, we can construct a cost reduction plan for the business. Step 3: Identify Competitive Advantage Opportunities. Here, it analyzes the information from the first two steps to uncover opportunities for gaining a competitive advantage.
In addition to explaining the type of butcher business you will operate, the Company Analysis section of your business plan needs to provide background on the business. ... Competitive Analysis. Your competitive analysis should identify the indirect and direct competitors your business faces and then focus on the latter.