- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Business Continuity Plan Basics
- Understanding BCPs
- Benefits of BCPs
- How to Create a BCP
- BCP & Impact Analysis
- BCP vs. Disaster Recovery Plan

Frequently Asked Questions
- Business Continuity Plan FAQs
The Bottom Line
What is a business continuity plan (bcp), and how does it work.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/wk_headshot_aug_2018_02__william_kenton-5bfc261446e0fb005118afc9.jpg)
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
What Is a Business Continuity Plan (BCP)?
A business continuity plan (BCP) is a system of prevention and recovery from potential threats to a company. The plan ensures that personnel and assets are protected and are able to function quickly in the event of a disaster.
Key Takeaways
- Business continuity plans (BCPs) are prevention and recovery systems for potential threats, such as natural disasters or cyber-attacks.
- BCP is designed to protect personnel and assets and make sure they can function quickly when disaster strikes.
- BCPs should be tested to ensure there are no weaknesses, which can be identified and corrected.
Understanding Business Continuity Plans (BCPs)
BCP involves defining any and all risks that can affect the company's operations, making it an important part of the organization's risk management strategy. Risks may include natural disasters—fire, flood, or weather-related events—and cyber-attacks . Once the risks are identified, the plan should also include:
- Determining how those risks will affect operations
- Implementing safeguards and procedures to mitigate the risks
- Testing procedures to ensure they work
- Reviewing the process to make sure that it is up to date
BCPs are an important part of any business. Threats and disruptions mean a loss of revenue and higher costs, which leads to a drop in profitability. And businesses can't rely on insurance alone because it doesn't cover all the costs and the customers who move to the competition. It is generally conceived in advance and involves input from key stakeholders and personnel.
Business impact analysis, recovery, organization, and training are all steps corporations need to follow when creating a Business Continuity Plan.
Benefits of a Business Continuity Plan
Businesses are prone to a host of disasters that vary in degree from minor to catastrophic. Business continuity planning is typically meant to help a company continue operating in the event of major disasters such as fires. BCPs are different from a disaster recovery plan, which focuses on the recovery of a company's information technology system after a crisis.
Consider a finance company based in a major city. It may put a BCP in place by taking steps including backing up its computer and client files offsite. If something were to happen to the company's corporate office, its satellite offices would still have access to important information.
An important point to note is that BCP may not be as effective if a large portion of the population is affected, as in the case of a disease outbreak. Nonetheless, BCPs can improve risk management—preventing disruptions from spreading. They can also help mitigate downtime of networks or technology, saving the company money.
How To Create a Business Continuity Plan
There are several steps many companies must follow to develop a solid BCP. They include:
- Business Impact Analysis : Here, the business will identify functions and related resources that are time-sensitive. (More on this below.)
- Recovery : In this portion, the business must identify and implement steps to recover critical business functions.
- Organization : A continuity team must be created. This team will devise a plan to manage the disruption.
- Training : The continuity team must be trained and tested. Members of the team should also complete exercises that go over the plan and strategies.
Companies may also find it useful to come up with a checklist that includes key details such as emergency contact information, a list of resources the continuity team may need, where backup data and other required information are housed or stored, and other important personnel.
Along with testing the continuity team, the company should also test the BCP itself. It should be tested several times to ensure it can be applied to many different risk scenarios . This will help identify any weaknesses in the plan which can then be corrected.
In order for a business continuity plan to be successful, all employees—even those who aren't on the continuity team—must be aware of the plan.
Business Continuity Impact Analysis
An important part of developing a BCP is a business continuity impact analysis. It identifies the effects of disruption of business functions and processes. It also uses the information to make decisions about recovery priorities and strategies.
FEMA provides an operational and financial impact worksheet to help run a business continuity analysis. The worksheet should be completed by business function and process managers who are well acquainted with the business. These worksheets will summarize the following:
- The impacts—both financial and operational—that stem from the loss of individual business functions and process
- Identifying when the loss of a function or process would result in the identified business impacts
Completing the analysis can help companies identify and prioritize the processes that have the most impact on the business's financial and operational functions. The point at which they must be recovered is generally known as the “recovery time objective.”
Business Continuity Plan vs. Disaster Recovery Plan
BCPs and disaster recovery plans are similar in nature, the latter focuses on technology and information technology (IT) infrastructure. BCPs are more encompassing—focusing on the entire organization, such as customer service and supply chain.
BCPs focus on reducing overall costs or losses, while disaster recovery plans look only at technology downtimes and related costs. Disaster recovery plans tend to involve only IT personnel—which create and manage the policy. However, BCPs tend to have more personnel trained on the potential processes.
Why Is Business Continuity Plan (BCP) Important?
Businesses are prone to a host of disasters that vary in degree from minor to catastrophic and business continuity plans (BCPs) are an important part of any business. BCP is typically meant to help a company continue operating in the event of threats and disruptions. This could result in a loss of revenue and higher costs, which leads to a drop in profitability. And businesses can't rely on insurance alone because it doesn't cover all the costs and the customers who move to the competition.
What Should a Business Continuity Plan (BCP) Include?
Business continuity plans involve identifying any and all risks that can affect the company's operations. The plan should also determine how those risks will affect operations and implement safeguards and procedures to mitigate the risks. There should also be testing procedures to ensure these safeguards and procedures work. Finally, there should be a review process to make sure that the plan is up to date.
What Is Business Continuity Impact Analysis?
An important part of developing a BCP is a business continuity impact analysis which identifies the effects of disruption of business functions and processes. It also uses the information to make decisions about recovery priorities and strategies.
FEMA provides an operational and financial impact worksheet to help run a business continuity analysis.
These worksheets summarize the impacts—both financial and operational—that stem from the loss of individual business functions and processes. They also identify when the loss of a function or process would result in the identified business impacts.
Business continuity plans (BCPs) are created to help speed up the recovery of an organization filling a threat or disaster. The plan puts in place mechanisms and functions to allow personnel and assets to minimize company downtime. BCPs cover all organizational risks should a disaster happen, such as flood or fire.
Federal Emergency Management Agency. " Business Process Analysis and Business Impact Analysis User Guide ." Pages 15 - 17.
Ready. “ IT Disaster Recovery Plan .”
Federal Emergency Management Agency. " Business Process Analysis and Business Impact Analysis User Guide ." Pages 15-17.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/BusinessPlanMeeting-570270145f9b5861953a6732.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
- ERM Solution
- Compliance Solution
- Operational Resilience Management Solution
- IT Risk Management (ITRM) Solution For Regulated Industries
- Audit Solution
- Procurement Solution
- The Quantivate Platform
- Enterprise Risk Management
- Business Continuity
- Vendor Management
- Compliance Management
- IT Risk Management
- Internal Audit
- Issue Management
- Complaint Management
- Policy & Document Management
- Consulting for GRC Success
- ERM Services
- Vendor Due Diligence
- Contract Review
- Business Continuity Services
- Credit Unions
- Financial Services
- Mortgage Banking
- Resource Center
- Webinars & Events
- About Quantivate
- Request a Demo
Business Continuity Glossary: 40+ Important Terms for Your Continuity & Recovery Planning
- October 17, 2018
Business continuity planning is an essential part of protecting your organization — but preparing for the unexpected can be complicated, and there’s a lot to consider. Make sure you’re covering all your bases with this glossary of important terminology you need to know.
→ Get a copy of this business continuity glossary in PDF format. ←
Business Continuity Terminology
Activation:.
The implementation of business continuity capabilities, procedures, activities, and plans in response to an emergency or disaster declaration; the execution of the recovery plan
1) Notification that a disaster may occur (a standby for possible activation of the continuity plan);
2) Notification that an interruption may occur due to planned events (such as a system upgrade) or expected events (such as a hurricane warning), when preparation or relocation begins before the incident
Alternate Site / Location:
A location other than the normal facility that is used to process data and/or conduct critical business processes in the event that access to the primary facility is denied or the facility is damaged
Authentication:
The verification of the identity of an individual, system, machine, or any other unique entity
Authorization:
The process of allowing access to specific areas of a system based on the role and needs of the user
Business Continuity Plan (BCP):
The plan used by an organization or business unit to respond to a disaster or disruption of operations; includes a predetermined set of procedures and documentation that defines the resources, actions, tasks, data, and processing priorities required to manage business continuity and restoration processes in the event of an incident
Business Continuity Planning:
Advance planning and preparations to minimize loss and ensure recovery of the organization’s critical business functions in the event of an unexpected incident, disaster, or other interruption; includes establishing strategies, determining procedures, and arranging for necessary recovery resources
Business Continuity Plan Owner:
The individual responsible for the overall continuity of a business unit, organization, or specific technology components within their department who acts as a liaison with other teams and outside service providers; this person ensures that the plan is effective, comprehensive, and sufficient to meet the organization’s recovery objectives
Business Impact Analysis (BIA):
The process of identifying the potential impact of uncontrolled, non-specific events on an organization’s business processes; measurements are derived from analyzing impact types over time for a particular business unit
A document that identifies who is responsible for contacting management, employees, customers, vendors, and other key contacts in the event of an emergency, disaster, or severe outage situation
Methods that preserve the integrity of important information, meet operational or financial targets, and/or communicate management policies
A time period or continuing condition initiated by an event or incident that precludes the use of normal processes or procedures; demands focused attention from management to prevent unacceptable / catastrophic or undesirable losses
Crisis Management Plan:
Provides the overall policies, procedures, and guidance for responding to an event that poses substantive risk to the organization; used to organize, evaluate, and control significant events that impact normal operations, focusing on managing departments and their resources during a disruption
Crisis Management Team:
The group responsible for maintaining, validating, and coordinating the recovery or recovery support processes for all business units and technology
Criticality Levels:
Rankings used to determine process restoration (e.g., mission critical, critical, important, etc.)
Dependency:
1) Any resource needed to perform a process (may include applications, vendors, skills, locations, other processes, etc.);
2) The relationship between resources
An unanticipated event or interruption that impacts an organization’s critical business functions and/or technology environment
Disaster Declaration:
The formal notification process that takes place after determining that it is not feasible to recover normal operations at a primary business site within an acceptable time period
Disaster Recovery Plan:
The compilation of technological strategies and actions that minimize both the impact of business interruptions and the effort to recover and fully resume business processes; generally focuses on technology recovery and restoration
Governance:
Processes and structures implemented to communicate, manage, and monitor organizational activities
A readily available recovery facility and associated resources; typically staffed and maintained 24 hours a day, seven days a week
The influence and effect of a risk
Any unplanned event with the potential to disrupt critical business processes
Key Control:
A primary control that is essential for a business process; typically takes place during the process it applies to
Likelihood:
The probability of a risk occurring
Manual Workaround:
An alternate method for completing a process without the resource in question
Maturity Methodology or Exercise Program:
An annual internal review process to maintain the quality of the business continuity plan; includes exercising, editing, and revising plan documents, attachments, and call lists and forms to maintain the plan in a perpetual state of readiness
Mitigation Actions:
The necessary steps, or action items, to reduce the likelihood and/or impact of a potential risk
An epidemic or infectious disease that can have a worldwide impact
1) The principle elements of essential business functions within work groups or business units;
2) A set of tasks completed by business continuity plan owners within a department
Activities performed to enable the timely re-initiation of business processes
Recovery Point (RP):
The actual maximum amount of data that could be lost with current backup and recovery options
Recovery Point Objective (RPO):
The acceptable level of data loss exposure following an unplanned event; the maximum amount of data you can afford to lose or recreate
Recovery Time (RT):
The actual amount of time it will take for a service or technology to be recovered
Recovery Time Objective (RTO):
The acceptable duration of time following an unplanned event until a critical business function has been restored; the maximum allowable time a service or technology can be unavailable
A person, place, or thing that provides service to your business or department
A potential event or action that would have an adverse effect on the organization
Risk Assessment:
The prioritization of potential business disruptions based on the impact and likelihood of occurrence; includes an analysis of threats based on the impact to the organization, its customers, and financial markets
Salvage & Restoration:
The process of reclaiming work in progress, refurbishing computer hardware, or recovering office facilities, equipment, or vital records following a disaster
Salvage Requirements:
A list that documents essential items at a business location that should be retrieved in the event that the building is intact and reentry is allowed
Secondary Control:
An important control that typically takes place after the process it applies to (i.e., reporting or ongoing monitoring)
Solutions Gap :
The difference between the amount of time a business unit needs to restore a resource and the actual time it will take for restoration (RTO vs. RT and RPO vs. RP)
Strategic Management Team:
Provides strategic direction and support for the crisis management team (CMT) when requested or required by events beyond the CMT’s purview
Tertiary Control:
A non-essential control that can still be applied effectively to a business process
Vital Records :
Any information resources (e.g., paperwork, computer files) essential to the conduct of business
Walkthrough Exercise:
A training and evaluation event created to guide continuity and recovery processes for the organization; typically occurs at least annually as part of the maturity methodology program and includes a post-exercise review
Can you trust your business continuity plan to get you through a crisis?
Learn how you can take the guesswork out of business continuity and disaster recovery planning with the help of Quantivate’s all-in-one Business Continuity Management Software and consulting services .
Stay up to date with the latest news, compliance alerts, and thought leadership for the financial services industry:
More topics.
- Risk Management
- Regulatory Compliance
- Cybersecurity
- Integration
- Third-Party Risk
- AML Compliance
- Third-Party Risk Management
- Information Security
What Is A Business Continuity Plan? [+ Template & Examples]
Published: December 30, 2022
When a business crisis occurs, the last thing you want to do is panic.

The second-to-last thing you want to do is be unprepared. Crises typically arise without warning. While you shouldn't start every day expecting the worst, you should be relatively prepared for anything to happen.
A business crisis can cost your company a lot of money and ruin your reputation if you don't have a business continuity plan in place. Customers aren't very forgiving, especially when a crisis is influenced by accidents within the company or other preventable mistakes. If you want your company to be able to maintain its business continuity in the face of a crisis, then you'll need to come up with this type of plan to uphold its essential functions.

In this post, we'll explain what a business continuity plan is, give examples of scenarios that would require a business continuity plan, and provide a template that you can use to create a well-rounded program for your business.
Table of Contents:
What is a business continuity plan?
- Business Continuity Types
- Business Continuity vs Disaster Recovery
Business Continuity Plan Template
How to write a business continuity plan.
- Business Continuity Examples
A business continuity plan outlines directions and procedures that your company will follow when faced with a crisis. These plans include business procedures, names of assets and partners, human resource functions, and other helpful information that can help maintain your brand's relationships with relevant stakeholders. The goal of a business continuity plan is to handle anything from minor disruptions to full-blown threats.
For example, one crisis that your business may have to respond to is a severe snowstorm. Your team may be wondering, "If a snowstorm disrupted our supply chain, how would we resume business?" Planning contingencies ahead of time for situations like these can help your business stay afloat when you're faced with an unavoidable crisis.
When you think about business continuity in terms of the essential functions your business requires to operate, you can begin to mitigate and plan for specific risks within those functions.
.png)
Crisis Communication and Management Kit
Manage, plan for, and communicate during your corporate crises with these crisis management plan templates.
- Free Crisis Management Plan Template
- 12 Crisis Communication Templates
- Post-Crisis Performance Grading Template
- Additional Crisis Best Management Practices
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Business Continuity Planning
Business continuity planning is the process of creating a plan to address a crisis. When writing out a business continuity plan, it's important to consider the variety of crises that could potentially affect the company and prepare a resolution for each.
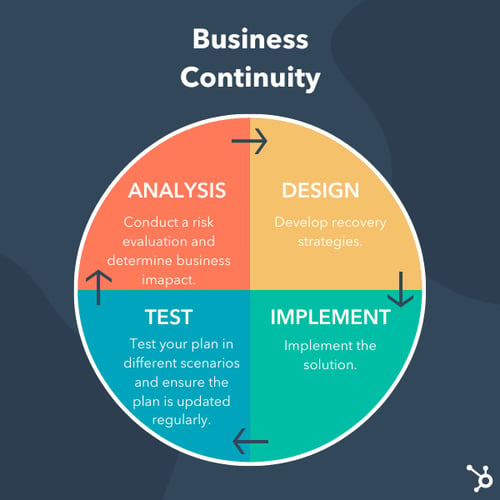
Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
How to Navigate Customer Service During a Business Closure

10 Crisis Communication Plan Examples (and How to Write Your Own)

I Tried 7 Crisis Management Software to See if They’re Worth It (Results & Recommendations)

20 Crisis Management Quotes Every PR Team Should Live By
![business continuity plan terms Social Media Crisis Management: Your Complete Guide [Free Template]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/social-media-crisis-management_11.webp)
Social Media Crisis Management: Your Complete Guide [Free Template]
![business continuity plan terms De-Escalation Techniques: 19 Best Ways to De-Escalate [Top Tips + Data]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/de-escalation-techniques_2.webp)
De-Escalation Techniques: 19 Best Ways to De-Escalate [Top Tips + Data]

Situational Crisis Communication Theory and How It Helps a Business

What Southwest’s Travel Disruption Taught Us About Customer Service

Showcasing Your Crisis Management Skills on Your Resume
![business continuity plan terms What Is Contingency Planning? [+ Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/contingency-planning.jpg)
What Is Contingency Planning? [+ Examples]
Manage, plan for, and communicate during a corporate crisis.
Service Hub provides everything you need to delight and retain customers while supporting the success of your whole front office
- Advisera Home
- ISO in General
Partner Panel
ISO 22301 Documentation Toolkits
Iso 22301 training.
- Documentation Toolkits
- White Papers
- Templates & Tools
Where to Start
New ai tool.
- Live Consultations
- Consultant Directory
- For Consultants

Dejan Kosutic
- Get Started
Explanation of the most common business continuity terms

The pandemic has increased organizations’ interest in business continuity, as a way to protect themselves against disruption of their operations. However, in most cases, there is no time to wait for learning about business continuity processes, policies, procedures, and terms.
In this article, we offer help in understanding the difference between the most common business continuity terms, mainly based on the ISO 22301 glossary, the leading ISO standard for business continuity management.
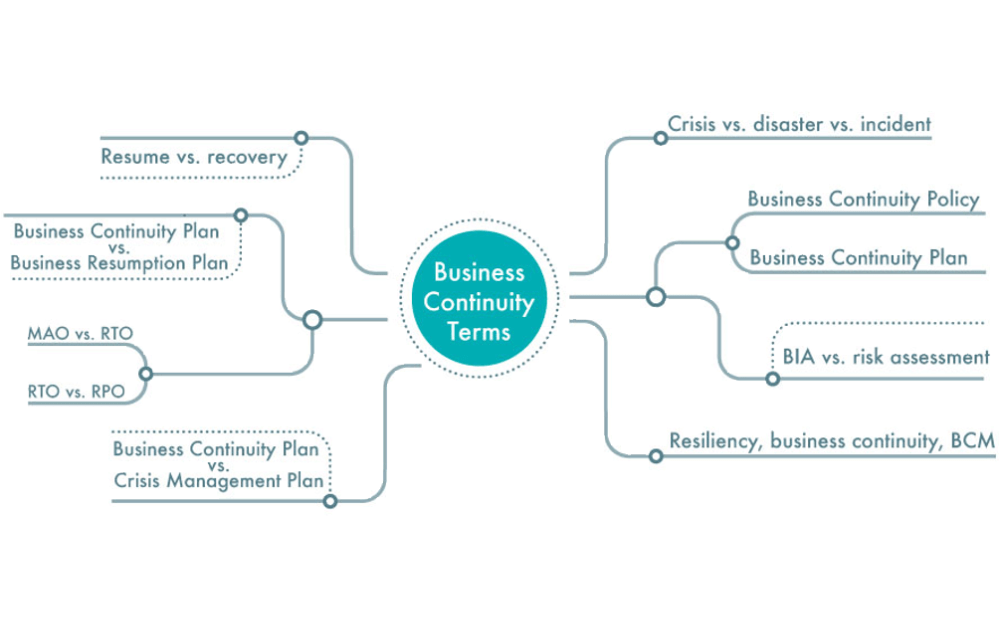
Resume vs. recovery
Resume refers to having operations working again with a smaller capacity and in a different environment (e.g., operations resumed in the alternative site), while recovery refers to having operations back to normal conditions (i.e., main site is operational again). Restore , or restoration , is also a term that can be used instead of recovery .
MAO vs. RTO
Think about the maximum time your business can afford to be down after a disaster (e.g., minutes, hours, days, etc.) – this is the Maximum Acceptable Outage (MAO) . Now, think about how fast after a disaster you want your business to resume operations – this is the Return Time Objective (RTO) . In recent days, the term MTPD (Maximum Tolerable Period of Disruption) is replacing the use of MAO (both terms have the same meaning).
The relationship between them is that RTO can be equal to or smaller than MAO , but never greater – an RTO greater than MAO does not make sense, because you would be resuming operations after the impact has become so big that doing business might lead to bankruptcy.
RTO vs. RPO
The Recovery Time Objective (RTO) is the time after a disaster in which business operation(s) must be resumed. For example, if the RTO is 2 hours, then it means you want to resume delivery of products or services, or execution of activities, within 2 hours.
The Recovery Point Objective (RPO) is the amount of data, measured in terms of time before the occurrence of a disruption, the business is willing to lose. For example, if the RPO is 1 hour, then it means you can afford the loss of the data stored/processed during the hour before the occurrence of a disruption.
Difference between crisis, disaster, and incident
- An incident is any situation that can result in a negative impact on normal operations.
- A crisis is an unstable situation that requires immediate attention and action.
- A disaster is a situation where losses are greater than the normal capacity of an organization to handle them.
Considering these definitions, an incident can lead to a crisis , which can lead to a disaster . An example of an incident that can lead to a crisis and a disaster would be a fire (without immediate attention and action, it can destroy assets and facilities that cannot be easily replaced). Other examples are a pandemic, an earthquake, or a riot.
Difference between resiliency, business continuity, and BCM
- Resiliency refers to the capacity to adapt to new situations.
- Business continuity refers to the capacity to continue to deliver products or services after a disruptive event.
- Business continuity management (BCM) refers to the general process to ensure business continuity.
Considering these definitions, business continuity management helps build business continuity , which covers one aspect of resiliency (please note that you can have new situations that an organization will need to adapt to that do not involve a disruptive event, like the enforcement of a new regulation).
BIA vs. risk assessment
The Business Impact Analysis (BIA) is the process by which you get to understand the impact of a disaster on your business processes and services over time. The risk assessment is the part of the risk management process by which you identify, analyze, and evaluate risks to which your organization is exposed, in order to prioritize the most relevant ones.
BIA and risk assessment are used together to help define business continuity and disaster recovery strategies and plans, and there is no specific sequence in which they need to be performed.
For further information, see Risk assessment vs. business impact analysis .
Business Continuity Policy vs. Business Continuity Plan
The Business Continuity Policy is a top management document that defines the high-level guidelines, objectives, and responsibilities for business continuity planning and management, while the Business Continuity Plan is an operational document to define the steps for immediate response, resumption, and recovering of business operations after a disaster.
For further information, see The purpose of Business continuity policy according to ISO 22301 .
Business Continuity Plan vs. Crisis Management Plan
A Business Continuity Plan (BCP) defines the activities to respond to a specific disruptive situation, as well as to resume and recover a service or process from the disruption.
Meanwhile, a Crisis Management Plan is a set of business-oriented activities (e.g., evaluation of business impacts, declaration of emergency/crisis/disaster, press communication, follow up of immediate response, resume and recovery activities, etc.) to be performed to ensure overall handling of critical situations that can negatively impact an organization. Crisis Management Plan is neither a term defined by ISO 22301, nor does it have a universal definition, because it has a wider application than only on disaster situations (e.g., on public relations crises, on financial crises, etc.), and may or may not be part of the Business Continuity Plan.
BCP (Business Continuity Plan) vs. BRP (Business Resumption Plan)
The Business Resumption Plan is a concept not present in ISO 22301, but widely used in other frameworks, like NIST 800-34, BS 25999-1, APS 232, NFPA 1600, COBIT, HB 292-2006, and PAS 77.
In these documents, the BRP refers to the actions needed to resume normal operations following the recovery of their critical processes, while a BCP is a concept covered in ISO 22301, and it represents a wider document, which covers not only the actions to resume operations, but also to respond to a disruptive event, and to recover and restore normal operations. Considering these definitions, the content of a BRP would be part of a BCP .
Related Products

ISO 27001 Premium Documentation Toolkit

ISO 27001 Lead Auditor Course
Related articles.
You may unsubscribe at any time. For more information, please see our privacy notice .
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Business Continuity Planning
Organize a business continuity team and compile a business continuity plan to manage a business disruption. Learn more about how to put together and test a business continuity plan with the videos below.
Business Continuity Plan Supporting Resources
- Business Continuity Plan Situation Manual
- Business Continuity Plan Test Exercise Planner Instructions
- Business Continuity Plan Test Facilitator and Evaluator Handbook
Business Continuity Training Videos
The Business Continuity Planning Suite is no longer supported or available for download.
Business Continuity Training Introduction
An overview of the concepts detailed within this training. Also, included is a humorous, short video that introduces viewers to the concept of business continuity planning and highlights the benefits of having a plan. Two men in an elevator experience a spectrum of disasters from a loss of power, to rain, fire, and a human threat. One man is prepared for each disaster and the other is not.
View on YouTube
Business Continuity Training Part 1: What is Business Continuity Planning?
An explanation of what business continuity planning means and what it entails to create a business continuity plan. This segment also incorporates an interview with a company that has successfully implemented a business continuity plan and includes a discussion about what business continuity planning means to them.
Business Continuity Training Part 2: Why is Business Continuity Planning Important?
An examination of the value a business continuity plan can bring to an organization. This segment also incorporates an interview with a company that has successfully implemented a business continuity plan and includes a discussion about how business continuity planning has been valuable to them.
Business Continuity Training Part 3: What's the Business Continuity Planning Process?
An overview of the business continuity planning process. This segment also incorporates an interview with a company about its process of successfully implementing a business continuity plan.
Business Continuity Training Part 3: Planning Process Step 1
The first of six steps addressed in this Business Continuity Training, which detail the process of building a business continuity plan. This step addresses how organizations should “prepare” to create a business continuity plan.
Business Continuity Training Part 3: Planning Process Step 2
The second of six steps addressed in this Business Continuity Training, which detail the process of building a business continuity plan. This step addresses how organizations should “define” their business continuity plan objectives.
Business Continuity Training Part 3: Planning Process Step 3
The third of six steps addressed in this Business Continuity Training, which detail the process of building a business continuity plan. This step addresses how organizations should “identify” and prioritize potential risks and impacts.
Business Continuity Training Part 3: Planning Process Step 4
The fourth of six steps addressed in this Business Continuity Training, which detail the process of building a business continuity plan. This step addresses how organizations should “develop” business continuity strategies.
Business Continuity Training Part 3: Planning Process Step 5
The fifth of six steps addressed in this Business Continuity Training, which detail the process of building a business continuity plan. This step addresses how organizations should define their “teams” and tasks.
Business Continuity Training Part 3: Planning Process Step 6
The sixth of six steps addressed in this Business Continuity Training, which detail the process of building a business continuity plan. This step addresses how organizations should “test” their business continuity plans. View on YouTube
Last Updated: 12/21/2023
Return to top
- Developing Your MVP
- Incident Management
- Needs Assessment Process
- Product Development From Ideation to Launch
- Visualizing Competitive Landscape
- Communication Plan
- Graphic Organizer Creator
- Fault Tree Software
- Bowman's Strategy Clock Template
- Decision Matrix Template
- Communities of Practice
- Goal Setting for 2024
- Meeting Templates
- Meetings Participation
- Microsoft Teams Brainstorming
- Retrospective Guide
- Skip Level Meetings
- Visual Documentation Guide
- Weekly Meetings
- Affinity Diagrams
- Business Plan Presentation
- Post-Mortem Meetings
- Team Building Activities
- WBS Templates
- Online Whiteboard Tool
- Communications Plan Template
- Idea Board Online
- Meeting Minutes Template
- Genograms in Social Work Practice
- How to Conduct a Genogram Interview
- How to Make a Genogram
- Genogram Questions
- Genograms in Client Counseling
- Understanding Ecomaps
- Visual Research Data Analysis Methods
- House of Quality Template
- Customer Problem Statement Template
- Competitive Analysis Template
- Creating Operations Manual
- Knowledge Base
- Folder Structure Diagram
- Online Checklist Maker
- Lean Canvas Template
- Instructional Design Examples
- Genogram Maker
- Work From Home Guide
- Strategic Planning
- Employee Engagement Action Plan
- Huddle Board
- One-on-One Meeting Template
- Story Map Graphic Organizers
- Introduction to Your Workspace
- Managing Workspaces and Folders
- Adding Text
- Collaborative Content Management
- Creating and Editing Tables
- Adding Notes
- Introduction to Diagramming
- Using Shapes
- Using Freehand Tool
- Adding Images to the Canvas
- Accessing the Contextual Toolbar
- Using Connectors
- Working with Tables
- Working with Templates
- Working with Frames
- Using Notes
- Access Controls
- Exporting a Workspace
- Real-Time Collaboration
- Notifications
- Meet Creately VIZ
- Unleashing the Power of Collaborative Brainstorming
- Uncovering the potential of Retros for all teams
- Collaborative Apps in Microsoft Teams
- Hiring a Great Fit for Your Team
- Project Management Made Easy
- Cross-Corporate Information Radiators
- Creately 4.0 - Product Walkthrough
- What's New
Understanding the Essentials of a Business Continuity Plan
In the face of unforeseen disruptions, a robust business continuity plan (BCP) is essential to preserve the trust of stakeholders. If you are able to seamlessly continue operations even in the face of sudden challenges, stakeholders are reassured of the company’s resilience and commitment to their interests.
In this blog post, we offer a comprehensive guide to business continuity planning, how it can benefit organizations and share key insights into Developing and Maintaining an Effective business continuity plan.
What is a Business Continuity Plan?
A business continuity plan (BCP) is an essential blueprint that outlines how a company will continue operating during an unplanned disruption in service. It’s more than just a reactive strategy; it’s a proactive measure to ensure that critical business functions can continue during and after a crisis. The purpose of a BCP is to provide a systematic approach to mitigate the potential impact of disruptions and maintain business operations at an acceptable predefined level.
The role of a BCP is crucial in maintaining operations during unforeseen events such as natural disasters, cyber-attacks, or any other incident that could interrupt business processes. By having a well-structured business continuity plan, organizations can:
- Minimize downtime and ensure that essential functions remain operational
- Protect the integrity of data and IT infrastructure
- Maintain customer service and preserve stakeholder trust
Why is a Business Continuity Plan Important
Immediate Response : A BCP ensures that there is a predefined action plan, minimizing downtime and demonstrating control over the situation.
Transparent Communication : Keeping stakeholders informed during a crisis promotes transparency and maintains confidence in the company’s management.
Inclusive Planning : Involve stakeholders in the business continuity plan development process. Their insights can enhance the plan’s effectiveness and ensure their needs are addressed.
Consistency in Service : By prioritizing critical operations, a BCP helps maintain the quality and consistency of services or products, which is important for customer retention.
The absence of a business continuity plan can lead to a domino effect of negative outcomes, including a tarnished reputation and the potential loss of future business. Stakeholders remember how a company responds in a crisis, and a well-executed BCP can be the difference between a temporary setback and a long-term impact on the company’s image and relationships.
Elements of a Business Continuity Plan
When exploring various business continuity plan examples, certain common elements emerge as critical for their effectiveness. These elements serve as the backbone for a robust BCP plan, ensuring that businesses can maintain operations and protect their reputation during unforeseen events. Here are some of the key components found in successful BCP examples:
Risk Assessment and Business Impact Analysis : Identifying potential threats and assessing their impact on business operations is a foundational step in any BCP plan.
Crisis Communication Plan : A clear communication strategy is essential to manage stakeholder expectations and maintain trust.
Recovery Strategies : Detailed procedures for restoring business functions and services post-disruption are indispensable.
Employee Training and Awareness : Ensuring staff are well-prepared and knowledgeable about the BCP plan is crucial for its successful implementation.
Case studies of successful BCP implementations often highlight how these elements are tailored to fit specific business models and industries. For instance, a financial institution may focus heavily on data security and regulatory compliance within their BCP, while a manufacturing business might prioritize supply chain alternatives and on-site safety protocols. Regular testing and adjustment of these plans are also a common thread, underscoring the importance of adaptability and continuous improvement in business continuity planning.
Business Continuity Plan Toolkit
- Ready to use
- Fully customizable template
- Get Started in seconds

Business Continuity vs. Disaster Recovery
It’s important to distinguish between a business continuity plan and a disaster recovery plan. While both are vital, a BCP is broader and focuses on the continuity of the entire business, whereas a disaster recovery plan is more technical and concentrates on the recovery of specific operations, such as IT services. Understanding these differences helps organizations allocate resources effectively and ensures comprehensive preparedness for any type of disruption. Understanding when to activate a business continuity plan (BCP) versus a disaster recovery plan is crucial for maintaining operational resilience.
To ensure a comprehensive crisis management strategy, consider the following integration points:
Pre-emptive Planning : Establish clear triggers for when each plan is activated. For instance, a BCP might be initiated in the face of a supply chain disruption, while disaster recovery would come into play during a data breach or server failure.
Unified Communication : Both plans should have a coordinated communication strategy to inform stakeholders and employees about the status and steps being taken.
Regular Testing : Conduct joint drills that test both the BCP and disaster recovery plans to identify any gaps or overlaps in procedures.
Continuous Improvement : Use insights from drills and actual incidents to refine both plans, ensuring they evolve with the changing business landscape and technological advancements.
By integrating both plans, organizations can navigate crises with agility and confidence, minimizing downtime and protecting their reputation. Tools like Creately, with features such as real-time collaboration and visual project management, can help create and maintain these critical plans, ensuring that all stakeholders are on the same page and ready to act when necessary.
Crisis Communication Strategies within Business Continuity Planning
A business continuity plan (BCP) is not just about responding to the crisis at hand, but also about how you communicate during the disruptions and the decisions you make. Here are some best practices to ensure your crisis communication and decision-making processes effective:
Clear Communication Channels : Establish predefined channels for internal and external communication. This ensures that messages are consistent and reach all stakeholders promptly.
Designated Spokespersons : Identify individuals who are authorized to speak on behalf of the company during a crisis. This helps maintain a unified voice and message.
Factual Updates : Provide regular, factual updates to keep stakeholders informed. Avoid speculation and commit to transparency.
Decision-Making Protocols : Implement decision-making protocols that are clear and allow for swift action. This includes having a chain of command and predefined criteria for making critical decisions.
Training and Simulations : Regularly train your crisis management team and conduct simulations to prepare for potential scenarios. This ensures that when a crisis does occur, your team is ready to act effectively.
By integrating these best practices into your BCP plan, you can maintain control during a crisis, make informed decisions, and communicate effectively with all parties involved. Remember, the goal is to protect your company’s operations, reputation, and stakeholder relationships during unexpected events.
Utilizing Business Continuity Plan Templates and Tools
When it comes to developing a robust business continuity plan (BCP), leveraging templates can offer a significant head start. These templates serve as a foundational framework that can be customized to align with the specific requirements of your business. Here’s why using BCP templates is advantageous:
Efficiency in Development : BCP templates provide a structured approach, ensuring that all critical elements are considered without starting from scratch. This saves valuable time and resources.
Consistency Across the Organization : Templates help maintain a uniform response strategy, which is crucial for coherent and coordinated action during a crisis.
Ease of Customization : While templates offer a general outline, they are designed to be adaptable. This means you can tailor them to reflect your business’s unique operational processes, risk profile, and recovery objectives.
Incorporating features like crisis response directions into your BCP template is essential. With Creately you can,
- Visualize these procedures on an infinite canvas, ensuring clarity and accessibility for all team members.
- Easily modify the plan as your business evolves, with the drag-and-drop functionality, making regular testing and adjustment a seamless process.
- Create a central repository of information by having docs, links and attachments in the notes panel of any shape in your diagram.
Key Insights for Developing and Maintaining an Effective Business Continuity Plan
A robust business continuity plan (BCP) is not a ‘set it and forget it’ document; it requires ongoing attention and refinement. Here’s why regular testing, updates, and staff training are non-negotiables in business continuity:
Financial Protection : By regularly testing your BCP, you can identify and rectify gaps that could otherwise lead to significant financial losses during a crisis. It’s not just about having a plan, but ensuring it works effectively when you need it most.
Reputational Safeguarding : Your company’s reputation is on the line when disaster strikes. A well-rehearsed BCP means your team can respond swiftly and competently, preserving stakeholder trust and customer loyalty.
Customization for Evolving Threats : The threat landscape is constantly changing. Regular BCP reviews allow you to tailor your plan to new types of risks, ensuring your business remains resilient against the unforeseen.
Empowered Employees : Training staff on the BCP turns theory into practice. When every team member knows their role in a crisis, response times improve, and confusion is minimized.
Remember, a BCP is a living document. It thrives on the feedback loop created by regular drills and updates, ensuring that when a crisis does occur, your business is prepared not just to survive, but to continue operations with minimal disruption.
Join over thousands of organizations that use Creately to brainstorm, plan, analyze, and execute their projects successfully.
More Related Articles

Hansani has a background in journalism and marketing communications. She loves reading and writing about tech innovations. She enjoys writing poetry, travelling and photography.
- Artificial Intelligence
- Generative AI
- Business Operations
- Cloud Computing
- Data Center
- Data Management
- Emerging Technology
- Enterprise Applications
- IT Leadership
- Digital Transformation
- IT Strategy
- IT Management
- Diversity and Inclusion
- IT Operations
- Project Management
- Software Development
- Vendors and Providers
- Enterprise Buyer’s Guides
- United States
- Middle East
- Italia (Italy)
- Netherlands
- United Kingdom
- New Zealand
- Data Analytics & AI
- Newsletters
- Foundry Careers
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Copyright Notice
- Member Preferences
- About AdChoices
- Your California Privacy Rights
Our Network
- Computerworld
- Network World
How to create an effective business continuity plan
A business continuity plan outlines procedures and instructions an organization must follow in the face of disaster, whether fire, flood, or cyberattack. here’s how to create a plan that gives your business the best chance of surviving such an event..

The tumultuous events of the past several years have impacted practically every business. And with the number of extreme weather events, cyberattacks, and geopolitical conflicts continuing to rise, business leaders are bracing for the possibility of increasingly more frequent impactful incidents their organizations will need to respond to.
According to PwC’s 2023 Global Crisis and Resilience Survey , 96% of 1,812 business leaders said their organizations had experienced disruption in the past two years and 76% said their most serious disruption had a medium to high impact on operations.
It’s little wonder then that 89% of executives list resilience as one of their most important strategic priorities.
Yet at the same time, only 70% of respondents said they were confident in their organization’s ability to respond to disruptions, with PwC noting that its research shows that too many organizations “are lacking the foundational elements of resilience they need to be successful.”
A solid business continuity plan is one of those foundational elements.
“Every business should have the mindset that they will face a disaster, and every business needs a plan to address the different potential scenarios,” says Goh Ser Yoong, head of compliance at Advance.AI and a member of the Emerging Trends Working Group at the professional governance association ISACA.
A business continuity plan gives the organization the best shot at successfully navigating a disaster by providing ready-made directions on who should do what tasks in what order to keep the business viable.
Without such as a plan, the organization will take longer than necessary to recover from an event or incident — or may never recover at all.
What is a business continuity plan?
A business continuity plan (BCP) is a strategic playbook created to help an organization maintain or quickly resume business functions in the face of disruption, whether that disruption is caused by a natural disaster, civic unrest, cyberattack, or any other threat to business operations.
A business continuity plan outlines the procedures and instructions that the organization must follow during such an event to minimize downtime, covering business processes, assets, human resources, business partners, and more.
A business continuity plan is not the same as a disaster recovery plan , which focuses on restoring IT infrastructure and operations after a crisis. Still, a disaster recovery plan is part of the overall strategy to ensure business continuity, and the business continuity plan should inform the action items detailed in an organization’s disaster recovery plan. The two are tightly coupled, which is why they often are considered together and abbreviated as BCDR.
Why business continuity planning matters
Whether you operate a small business or a large corporation, it’s vital to retain and increase your customer base. There’s no better test of your capability to do so than right after an adverse event.
Because restoring IT is critical for most companies, numerous disaster recovery solutions are available. You can rely on IT to implement those solutions. But what about the rest of your business functions? Your company’s future depends on your people and processes. Being able to handle any incident effectively can have a positive effect on your company’s reputation and market value, and it can increase customer confidence.
Moreover, there are increasing consumer and regulatory expectations for both enterprise security and continuity today. Consequently, organizations must prioritize continuity planning to prevent not only business losses, but financial, legal, reputational, and regulatory consequences.
For example, the risk of having an organization’s “license to operate” withdrawn by a regulator or having conditions applied (retrospectively or prospectively) can adversely affect market value and consumer confidence.
Building (and updating) a business continuity plan
Whether building the organization’s first business continuity plan or updating an existing one, the process involves multiple essential steps.
Assess business processes for criticality and vulnerability: Business continuity planning “starts with understanding what’s most important to the business,” says Joe Nocera, principle in the cyber risk and regulatory practice at PwC, a professional services firm.
So the first step in building your business continuity plan is assessing your business processes to determine which are the most critical; which are the most vulnerable and to what type of events; and what are the potential losses if those processes go down for a day, a few days, or a week.
“This step essentially determines what you are trying to protect and what you are trying to keep up for systems,” says Todd Renner, senior managing director in the cybersecurity practice at FTI Consulting.
This assessment is more demanding than ever before because of the complexity of today’s hybrid workplace, the modern IT environment, and the reliance on business partners and third-party providers to perform or support critical processes.
Given that complexity, Goh says a thorough assessment requires an inventory of not only key processes but also the supporting components — including the IT systems, networks, people, and outside vendors — as well as the risks to those components.
This is essentially a business impact analysis.
Determine your organization’s RTO and RPO: The next step in building a business continuity plan is determining the organization’s recovery time objective (RTO), which is the target amount of time between point of failure and the resumption of operations, and the recovery point objective (RPO), which is the maximum amount of data loss an organization can withstand.
Each organization has its own RTO and RPO based on the nature of its business, industry, regulatory requirements, and other operational factors. Moreover, different parts of a business can have different RTOs and RPOs, which executives need to establish, Nocera says.
“When you meet with individual aspects of the business, everyone says everything [they do] is important; no one wants to say their part of the business is less critical, but in reality you have to have those challenging conversations and determinations about what is actually critical to the business and to business continuity,” he adds.
Detail the steps, roles, and responsibilities for continuity: Once that is done, business leaders should use the RTO and the RPO, along with the business impact analysis, to determine the specific tasks that need to happen, by whom, and in what order to ensure business continuity.
“It’s taking the key components of your analysis and designing a plan that outlines roles and responsibilities, about who does what. It gets into the nitty-gritty on how you’re going to keep the company up and running,” Renner explains.
One common business continuity planning tool is a checklist that includes supplies and equipment, the location of data backups and backup sites, where the plan is available and who should have it, and contact information for emergency responders, key personnel, and backup site providers.
Although the list of possible scenarios that could impact business operations can seem extensive, Goh says business leaders don’t have to compile an exhaustive list of potential incidents. Rather, they should compile a list that includes likely incidents as well as representative ones so that they can create responses that have a higher likelihood of ensuring continuity even when faced with an unimagined disaster.
“So even if it’s an unexpected event, they can pull those building blocks from the plan and apply them to the unique crisis they’re facing,” Nocera says.
The importance of testing the business continuity plan
Devising a business continuity plan is not enough to ensure preparedness; testing and practicing are other critical components.
Renner says testing and practicing offer a few important benefits.
First, they show whether or how well a plan will work.
Testing and practicing help prepare all stakeholders for an actual incident, helping them build the muscle memory needed to respond as quickly and as confidently as possible during a crisis.
They also help identify gaps in the devised plan. As Renner says: “Every tabletop exercise that I’ve ever done has been an eye-opener for everyone involved.”
Additionally, they help identify where there may be misalignment of objectives. For example, executives may have deprioritized the importance of restoring certain IT systems only to realize during a drill that those are essential for supporting critical processes.
Types and timing of tests
Many organizations test a business continuity plan two to four times a year. Experts say the frequency of tests, as well as reviews and updates, depends on the organization itself — its industry, its speed of innovation and transformation, the amount of turnover of key personnel, the number of business processes, and so on.
Common tests include tabletop exercises , structured walk-throughs, and simulations. Test teams are usually composed of the recovery coordinator and members from each functional unit.
A tabletop exercise usually occurs in a conference room with the team poring over the plan, looking for gaps and ensuring that all business units are represented therein.
In a structured walk-through, each team member walks through his or her components of the plan in detail to identify weaknesses. Often, the team works through the test with a specific disaster in mind. Some organizations incorporate drills and disaster role-playing into the structured walk-through. Any weaknesses should be corrected and an updated plan distributed to all pertinent staff.
Some experts also advise a full emergency evacuation drill at least once a year.
Meanwhile, disaster simulation testing — which can be quite involved — should still be performed annually. For this test, create an environment that simulates an actual disaster, with all the equipment, supplies and personnel (including business partners and vendors) who would be needed. The purpose of a simulation is to determine whether the organization and its staff can carry out critical business functions during an actual event.
During each phase of business continuity plan testing, include some new employees on the test team. “Fresh eyes” might detect gaps or lapses of information that experienced team members could overlook.
Reviewing and updating the business continuity plan should likewise happen on an ongoing basis.
“It should be a living document. It shouldn’t be shelved. It shouldn’t be just a check-the-box exercise,” Renner says.
Otherwise, plans go stale and are of no use when needed.
Bring key personnel together at least annually to review the plan and discuss any areas that must be modified.
Prior to the review, solicit feedback from staff to incorporate into the plan. Ask all departments or business units to review the plan, including branch locations or other remote units.
Furthermore, a strong business continuity function calls for reviewing the organization’s response in the event of an actual event. This allows executives and their teams to identify what the organization did well and where it needs to improve.
How to ensure business continuity plan support, awareness
One way to ensure your plan is not successful is to adopt a casual attitude toward its importance. Every business continuity plan must be supported from the top down. That means senior management must be represented when creating and updating the plan; no one can delegate that responsibility to subordinates. In addition, the plan is likely to remain fresh and viable if senior management makes it a priority by dedicating time for adequate review and testing.
Management is also key to promoting user awareness. If employees don’t know about the plan, how will they be able to react appropriately when every minute counts?
Although plan distribution and training can be conducted by business unit managers or HR staff, have someone from the top kick off training and punctuate its significance. It’ll have a greater impact on all employees, giving the plan more credibility and urgency.
Related content
Is the power of people skills enough to keep gen ai in check, new us cio appointments, april 2024, canteen australia’s pursuit of a greater good through tech, seekr finds the ai computing power it needs in intel’s cloud, from our editors straight to your inbox, show me more, atos staves off bankruptcy, casts wider net for refinancing.

Inferencing holds the clues to AI puzzles

6 trends defining the enterprise IT market today

CIO Leadership Live Australia with Scott Andrews, Chief Operating Officer, Idea Science

Eaton CIO Katrina Redmond on optimizing AI and digital services


Tech layoffs continue, while AI prevents them from getting new jobs quickly

3 Leadership Tips: Adam Ennamli, Chief Risk Officer, General Bank of Canada

Sponsored Links
- Digital infrastructure plays a big role in business outcomes. Read this IDC report to learn more.
- IDC report: Life-cycle services can help align technology, operational, and business outcomes.
Advisory boards aren’t only for executives. Join the LogRocket Content Advisory Board today →

- Product Management
- Solve User-Reported Issues
- Find Issues Faster
- Optimize Conversion and Adoption
How to craft an effective business continuity plan

Let me take you back in time to the United Kingdom in the 1970s. Punk music was gaining popularity, and the Sex Pistols entered the punk rock scene with the force of a shooting star, capturing fans’ attention.

But as quickly as they arrived, they quickly left the scene. When they broke up in 1978 after a period of internal conflicts, legal troubles, and their frontman’s imprisonment, fans were left both shocked and surprised.
Just like the Sex Pistols, plenty of companies experience rapid growth and success, only to face unexpected challenges and internal conflicts that result in their downfall.
In this article, we’ll draw inspiration from the Sex Pistols’ turbulent journey to explore the concept of business continuity planning (BCP). We’ll look at what a BCP is, why you need one and delve into the strategies and contingency measures that can help you maintain your rhythm and continuity, even when faced with the inevitable storms that can disrupt your operations.
What is a business continuity plan?
A business continuity plan describes how you’ll continue your business when disaster hits. It is a structured strategy outlining how your organization will maintain essential functions when disaster strikes, to ensure minimal downtime and guarantee that operations continue.
Why do you need a BCP in place?
The BCP is crucial and revolves around ensuring your resilience and ability to continue operating in the face of unexpected disruptions, such as natural disasters, cyberattacks, or other emergencies.
Let’s look at it a bit closer, and understand some of the key reasons to have a BCP better:
Minimize downtime
Protect revenue and reputation, compliance and legal requirements, resource allocation, maintain customer service, employee safety.
A BCP helps you minimize downtime. It does this by providing a structured approach to quickly recover and resume your critical business functions.
Example: You’re a retail company with an extensive online presence. If your website experiences a cyberattack that takes it offline, a well-prepared BCP outlines the steps to take to mitigate the attack, get your website back up in no time, and allow you to continue serving your customers.
No one likes disruptions as they result in revenue loss and can damage your reputation. A BCP helps you protect against financial losses and keep customer trust.
Example: You’re the owner of a restaurant chain with multiple locations and one of your branches has a food safety crisis. A BCP can guide you in managing the crisis, ensuring food safety compliance, and communicating effectively with customers to maintain trust in the brand and other locations.
Some industries, like the financial, and pharma industries, have regulatory requirements that mandate businesses to have BCPs in place. Failure to do so has legal and financial consequences.
Example: You’re the owner of a FinTech company. You are required by regulators to have robust BCPs to ensure customer data security and financial system stability.
When a crisis hits you need the right resources to get you back up and running. A BCP helps allocate resources effectively during a crisis, ensuring that personnel, equipment, and materials are used efficiently to address the most critical needs.

Over 200k developers and product managers use LogRocket to create better digital experiences
Example: You’re a manufacturing company hit by a sudden supply chain disruption because the Suez Canal is blocked again. You use your BCP to allocate available resources to meet customer demands and minimize production delays.
When all hell breaks loose you want to make sure customer experience takes a minimum blow. A BCP outlines measures to maintain customer service and communication, so customers receive timely updates and support.
Example: You run an airline and there is a labor strike. Your BCP tells you how to manage customer inquiries, rebook affected passengers, and maintain a level of service.
Let’s not forget about the well-being of your employees. During a crisis, this is a top priority. A BCP includes procedures for evacuations, remote work arrangements, and employee support.
Example: There is a fire at your workplace. The BCP outlines evacuation routes, assembly points, and contact information for employees to report their safety status.
Business continuity planning: Steps for success
That’s a lot of reasons, right? Now that we addressed the necessity and urgency of having BCP, let’s look at 5 steps to creating a successful one:
- Analyze your company
- Assess the risk
- Create the procedures
- Get the word out
- Iterate and improve
1. Analyze your company
In this phase you conduct an analysis to identify critical activities, determine which activities must continue, which can be temporarily paused, and which can operate at a reduced capacity.
You then assess the financial impact of disruptions. This involves asking yourself the question, “How long can I operate without generating revenue and incurring recovery costs?”
As this step covers your whole company, it’s important to get key stakeholders involved from the beginning.
2. Assess the risk
Now you have a good overview of your critical processes and the impact of disruption. At this point, pivot your attention to the risks they face, how well you can handle when things don’t work as usual, and how long you can manage if things go wrong.
The goal here is to understand what could go wrong and find ways to avoid, reduce, or transfer them. This assessment will help you strengthen your preparedness and resilience.
More great articles from LogRocket:
- How to implement issue management to improve your product
- 8 ways to reduce cycle time and build a better product
- What is a PERT chart and how to make one
- Discover how to use behavioral analytics to create a great product experience
- Explore six tried and true product management frameworks you should know
- Advisory boards aren’t just for executives. Join LogRocket’s Content Advisory Board. You’ll help inform the type of content we create and get access to exclusive meetups, social accreditation, and swag.
Think about risks specific to your industry and location
It’s important to consider both internal (e.g. an IT system failure or employee shortage) and external threats (e.g. a natural disaster or supply chain disruption) to your critical business activities.
3. Create the procedures
Once you analyze and assess, you need to create procedures.
Develop detailed, step-by-step procedures to minimize risks to your organization’s people, operations, and assets. This can include changes to your operating model, such as using alternative suppliers or implementing remote work options.
4. Get the word out
A plan is just a plan and no one will know how to act if you don’t communicate.
This step is all about communication. Integrate the BCP into your operations, policies, and company culture, and train, test, and communicate with your employees.
And don’t forget that communication is not limited to your company only. Communicate with external stakeholders, customers, suppliers, and so forth.
5. Iterate and improve
Before implementing your BCP ensure its effectiveness.
Don’t worry there are plenty more options to test your BCP. Consider involving external stakeholders or vendors as it makes exercises more realistic. Frequently train those who are accountable for executing the BCP.
After experiencing a real incident or conducting a training exercise, update your plan to improve its ability to protect your business. Keep in mind that both your organization’s development and the circumstances you operate in change, so a regular review isn’t a luxury but a necessity.
How to structure your continuity plan
Now you have a high-level understanding, let’s look at how to structure your business continuity plan.
You can find a copy of the template I use here .
Make sure to include the following sections in your BCP:
Version history
Executive summary, functions and process prioritization, plan activation, governance and responsibilities, recovery plans, crisis communication plan, emergency location and contents, review and testing.
This section shows the revision history. It includes the version numbers of the changes made, by whom, when, and who approved the changes. The revision history allows anyone reading the BCP to understand how it has evolved over time.
The executive summary provides a brief summary of the key objectives, goals, scope, and applicability of the BCP.
This chapter outlines the critical functions and processes in scope of continuation in case of a disastrous event.
This section refers to the risk and business impact assessment outcome. Its aim is to set out what triggers the activation of the plan.
Governance and responsibilities talks about who has to act when the BCP is activated. It includes the members, a description of their responsibilities, contact details of the BCP team, and the chain of command during a crisis.
This section builds upon the business continuity strategies, specifically the one chosen when a disaster occurs. It describes the detailed recovery plans for each critical function, the procedures for restarting operations, resource allocation, and recovery time objectives (RTOs).
Here you cover the internal and external communication strategies. You also address employee awareness and training activities.
Now there is a good chance the disaster will require your crucial activities to temporarily continue at a different location. This section covers all details about the location and what needs to be available at the location.
The BCP is to be tested to reduce the risk of missing things or even worse failing. Here jot down the testing procedures and document results and lessons learned.
This section includes all appendices. Think about the following
- Supporting documents, such as contact lists, maps, and technical specifications
- References to external standards, guidelines, or regulations
- Training programs for BCP team members
- Review of insurance policies
- Financial reserves and funding for recovery efforts
- Procedures for keeping the BCP documentation up to date
Business continuity plan example
Earlier this year, the Koninklijke Nederlands Voetbal Bond (KNVB), which is the Royal Dutch Football Association, was hit by ransomware. The cyberattackers threatened to share personally identifiable information captured and the KNVB paid over one million euros to avoid this from happening.
What could have been done to mitigate the ransomware attack risk?
The Risk of the attack to succeed could have been mitigated with:
- Regular data backups
- Segmentation of networks
- Intrusion detection systems
How to ensure business continuity in case of ransomware?
In response to the ransomware incident, and to allow for continued business as usual as soon as possible, steps could include:
- Isolating affected systems
- Activating backups
- Notifying law enforcement
- Engaging with a cybersecurity incident response team
Key takeaways
A business continuity plan (BCP) is like a safety net for your business when things go haywire. It helps you keep going, avoiding downtime, revenue loss, and reputation hits. On top of that, it’s a legal must in certain industries.
To make a solid BCP, just follow five steps: figure out what’s crucial for your business, spot the risks, plan how to bounce back, make sure everyone knows the plan, and keep fine-tuning it.
Structurally, your BCP should have sections like history, a quick guide, what’s most important, when to activate it, who’s in charge, the nitty-gritty recovery plans, how communication is done, where to go in a crisis, how to test the BCP works, and some extra info.
Featured image source: IconScout
LogRocket generates product insights that lead to meaningful action
Get your teams on the same page — try LogRocket today.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- #collaboration and communication
- #project management

Stop guessing about your digital experience with LogRocket
Recent posts:.
Leader Spotlight: Improving product development through documentation, with Mark Francis
Mark Francis discusses the importance of stakeholders across all business groups embracing the need for documentation and transparency.

A guide to crafting your brand strategy
Brand strategy is one of the most underestimated forces that shapes the trajectory of your products and services.

Leader Spotlight: Helping turn Apple’s business around, with Steve Chazin
Steve Chazin, VP of Products at Alarm.com, shares how he was re-hired by Steve Jobs to help turn Apple around.

Leader Spotlight: Building a comprehensive migration plan, with Deepika Manglani
Deepika Manglani discusses major transitions she’s worked on at Tribune Publishing, including a divestiture and application migration plan.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
📈 How much does it cost to pay and manage global teams in 2024? Download our FREE guide here 🔗
Hire full-time talent anywhere with EOR
Easily manage and pay your contractors
Run payroll with or without a subsidiary
Global Benefits
Benefits & insurances for your workforce
Global Immigration
Relocation and visa made easy
Talent Acquisition
Find the best candidates for your team
- Discover More
Hire from $49, scalable & transparent
Data protection & Security
About Horizons
Our borderless team and our global purpose
Success Stories
How businesses accelarate hiring with Horizons
Partner Program
Become a partner and benefit from unique offerings
Global Hubs
Discover our international offices
Join our mission to shaping the New World of Work
Shape your strategy with key insights
Inside Horizons
A behind-the-scenes look at the best EOR
Help Center
Learn about the Horizons platform
Contact our support team
Global Payroll Calculator
Calculate employment cost
Employee Misclassification Calculator
Calculate employee misclassification risk
What is a Business Continuity Plan (BCP)? Purpose, Template & Examples
- Marie Laure Troadec Legal Counsel
- August 29, 2023
Key Takeaways
1. A business continuity plan is an essential risk management tool that helps organizations proactively prepare for unexpected disruptions and events, ensuring the continuity of critical operations.
2. By identifying and assessing potential risks and threats to their operations, businesses can develop appropriate response strategies to prevent or minimize disruption during challenging times.
3. Businesses should avoid certain pitfalls to successfully implement their business continuity plan. These include a lack of employee engagement, an over-reliance on technology, and a failure to test their plans.
4. By proactively addressing these areas, businesses can increase the chances of successful implementation and execution of their business continuity plans.
Ensuring business continuity is a topic high on the agenda for most businesses and one that has become increasingly paramount in light of recent events: Few things have focused attention on the need to have a contingency plan more than the COVID-19 pandemic. The potential disruption caused by a pandemic, or indeed any other unforeseen event, to a business’s operations can have significant financial, legal, and reputational ramifications that can be mitigated or even prevented if appropriate measures are put in place.
This article delves into the essential elements of a business continuity plan (BCP) and provides valuable guidance on avoiding common pitfalls to help your business implement and execute a robust plan that safeguards your operations.
What is a Business Continuity Plan?
A business continuity plan is a risk management strategy that a business implements to protect its operations in the face of an unexpected event or disruption such as a natural disaster, cyberattack, or technological failure. By anticipating and preparing for potential crises or unplanned eventualities, businesses can take preemptive measures to ensure they remain operational and maintain a sense of normalcy despite interruptions.
The business continuity planning process enables businesses to assess potential threats to their operations and identify vulnerabilities that could impact their ability to function effectively. Through the implementation of a business continuity plan, business leaders can swiftly respond to emergencies, minimizing any potential downtime and mitigating the negative effects on their operations. This proactive approach can help businesses navigate challenging situations with relative ease and resilience, ensuring minimal impact on their productivity and profits.
Main Elements of a Business Continuity Plan
A robust and effective business continuity plan will comprise the following key elements that facilitate business resilience and preparedness during uncertain times.
- Business impact analysis
- During this phase, a business will identify and assess potential risks and threats to their organization’s operations. A business impact analysis (BIA) assesses the potential consequences of disruptions in critical business functions. This allows businesses to prioritize resources, allocate budgets, and develop strategies to minimize downtime and facilitate recovery.
- Recovery strategies
- This step addresses the risks identified in the BIA by developing appropriate responses to prevent or minimize disruption. Recovery strategies outline the immediate actions required following an incident, those responsible for implementing them and coordinating the allocation of resources.
- Plan development
- The plan development phase involves developing the framework of the business continuity plan by establishing the relevant recovery teams, establishing communication channels, creating relocation plans, and gaining management buy-in.
- Testing and maintenance
- This phase involves training and testing the relevant teams and systems by conducting exercises to measure the effectiveness of the business continuity plan and identifying areas for improvement. Processes are also established for regularly reviewing and updating the business continuity plan to account for changes in technology, previous incidents, and evolving threats and risks.
Common Business Continuity Plan Pitfalls
To ensure the efficacy of their response during unexpected events or disruptions, organizations should be mindful of common mistakes encountered in the business continuity planning process.
An awareness of the following issues can help businesses avoid certain pitfalls which could hinder their efforts in this area:
1. Lack of employee engagement
The success of any business continuity plan hinges on an organization’s ability to execute it successfully as even the most comprehensive and detailed plan will fall flat if it is ineffective in real-world situations.
The successful execution of a business continuity plan goes beyond senior management. To ensure business continuity in times of trouble it is essential that those on the ground have also been briefed on contingency measures and are ready to step into action accordingly. Without adequate employee training and awareness, organizations run the risk of compromising critical business functions leading to further disruptions and losses.
By prioritizing employee engagement and involvement in the business continuity plan, organizations can strengthen and streamline their response efforts ensuring a robust and resilient response to potential disruptions, while fostering a culture of confidence and preparedness within their organization.
2. Overreliance on technology
While technological solutions play a crucial role and should be a feature of any robust business continuity plan, an overreliance on digital services and technical infrastructure can pose potential challenges for organizations.
Sole or heavy reliance on this area increases the risk of a single point of failure. This is especially pertinent at a time when cyberattacks and data breaches are prevalent creating vulnerabilities in a business’ technological systems, and thereby undermining the effectiveness of its business continuity plan. Unforeseen events such as natural disasters which can lead to infrastructure damage and power outages can also severely compromise an organization’s ability to function effectively during a crisis.
To counter these problems, organizations should incorporate a diverse range of technological and non-technological solutions into their business continuity plan, taking into account manual processes and alternatives that are not solely dependent on digital services. Data backup options should also be put in place to help businesses restore swift operations and minimize extended downtime.
3. Failure to test
Without proper testing, the effectiveness of a business continuity plan remains theoretical rather than proven in practice. Regular testing enables businesses to identify and address any gaps or limitations in their plan, avoiding the risk of critical business functions being left vulnerable in an actual crisis situation.
Through drills, real-life simulations, and tabletop exercises, organizations can learn from real-world incidents, gaining practical insight into the feasibility of their business continuity plans and identifying any areas that require improvement. Regular testing plays a crucial role in helping businesses to optimize their response strategies and ensure resilience and readiness in the face of difficult or unforeseen circumstances.
By proactively addressing and avoiding these common pitfalls, businesses can develop comprehensive business continuity plans that help to bolster their resilience, minimize disruptions, and ensure the continuity of their operations during challenging times.
BCP Template
The precise content of your BCP will depend on the nature of your business. However, below is a useful template for a typical business:
1. Introduction
- Purpose: Outline the purpose of the BCP.
- Scope: Specify which parts of the organization this BCP covers.
- Assumptions: State any assumptions made during the BCP’s creation.
2. Business Continuity Policy
Outline the company’s policy regarding business continuity. This can include the company’s commitment to employee safety, client service, data protection, etc.
3. Roles and Responsibilities
List the key personnel responsible for executing the BCP:
- Business Continuity Manager/Coordinator
- Crisis Communication Team
- Emergency Response Team
- IT Recovery Team
- Employee Assistance Team
4. Risk Assessment
Identify potential risks and threats:
- Natural disasters
- Technological failures
- Security breaches
5. Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
Identify the potential impacts of each threat:
- Financial impacts
- Reputational impacts
- Operational impacts
- Legal/Regulatory impacts
6. Business Continuity Strategies
Outline strategies for:
- Data backup and recovery
- Alternate work locations
- Communication protocols
- Supply chain management
7. Incident Response Plan
Details the immediate actions to be taken following an incident:
- Alert and notification procedures
- Evacuation procedures
- Safety checks
8. Recovery Plans
For each critical department/function, provide a detailed plan on how to resume operations:
- IT systems recovery
- Resumption of critical business functions
- Communication with stakeholders
9. Training and Testing
Outline how the plan will be tested and how often, as well as any training programs for employees:
- Tabletop exercises
- Full-scale drills
- Employee training sessions
10. Maintenance and Review
Describe how the plan will be kept current:
- Regularly scheduled reviews
- Updates following any changes in the business environment or operations
- Feedback loop from testing
11. Communication Protocols
Specify how communication will be maintained:
- Emergency contact lists
- Communication methods (phone, email, etc.)
- External communication (with media, stakeholders, etc.)
12. Appendices
- Resource lists
- Vendor contacts
- Floor plans
- Backup data locations
Business Continuity Plan Examples
If you are looking for some other examples of well-designed BCPs and BCP templates, check out the following:
- Durham County Council’s BCP
- Chisholm & Winch (UK Construction Company)
- Ready (US Government Disaster Response Resource).
Developing and implementing business continuity plans
Expertise in critical business functions such as compliance, HR management, and global payroll solutions ensures your business can confidently navigate through unexpected challenges or crises.
Contact us today to learn how we can support your business continuity efforts and provide the stability and peace of mind you need in an ever-changing world.
Hire and pay talents with Horizons in 180+ countries
Related posts
Horizons x hofy: seamlessly supply, manage, service your global teams’ devices, horizons berlin: an evening with hr leaders, horizons x safetywing: get insurance for nomads and remote teams, guide to marketing in china: advice, strategies, rules [2024].
- Marie Laure Troadec
- Oct 14, 2023
Hire Anywhere. Today.
Join 1,500+ companies already hiring with Horizons
Headquarters 71 Robinson Road #13-153 Singapore 068895 +65 3158 1382
Europe Skalitzer Str. 85/86 10997, Berlin +49 30 3119 9653
Americas 1700 S. Lamar Blvd Suite 338 Austin, Texas 78704 +1 (737) 265-6065
See more locations
Horizons © 2024 – Privacy Imprint & Terms Third-Party Processor GDPR Policy
Privacy Preference Centre
- Artificial Intelligence
- Generative AI
- Business Operations
- IT Leadership
- Application Security
- Business Continuity
- Cloud Security
- Critical Infrastructure
- Identity and Access Management
- Network Security
- Physical Security
- Risk Management
- Security Infrastructure
- Vulnerabilities
- Software Development
- Enterprise Buyer’s Guides
- United States
- United Kingdom
- Newsletters
- Foundry Careers
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Member Preferences
- About AdChoices
- E-commerce Links
- Your California Privacy Rights
Our Network
- Computerworld
- Network World

Business continuity and disaster recovery planning: The basics
Good business continuity plans will keep your company up and running through interruptions of any kind: power failures, it system crashes, natural disasters, pandemics and more..

Editor’s note: This article, originally published on March 27, 2014, has been updated to more accurately reflect recent trends.
Wildfires in California. A snowstorm in Texas. Windstorms across the Midwest. Floods in Hawaii. Hurricanes in Florida and Louisiana. Russian hackers and ransomware attacks. And let’s not forget the global pandemic.
If anyone still thinks that having a disaster recovery and business continuity plan isn’t a high priority, you haven’t been paying attention to recent events. As we begin to emerge from the COVID-19 pandemic, organizations are shifting to a new normal that will certainly be more remote, more digital and more cloud-based. Disaster recovery plans will have to evolve to keep up with these changing business conditions.
On top of that, business requirements for disaster recovery have changed dramatically. There was a time when it was acceptable for recovery time to be measured in days or hours. Now it’s minutes. In some cases, business units are demanding zero down time in the event of an unplanned outage.
Here are the basics of a state-of-the-art disaster recovery/business continuity (DR/BC) plan for 2021 and beyond. (Without getting too hung up on definitions, let’s say that disaster recovery is getting the IT infrastructure back up and running, while business continuity is a broader discipline that gets the business back up and functioning once the lights are back on.)
Integrate cybersecurity, intrusion detection/response, disaster recovery into a comprehensive data protection plan
For CISOs, the first goal of a disaster recovery plan is to avoid the disaster in the first place, which is becoming increasingly challenging. First, data is no longer safely tucked away in an on-premises data center. It’s distributed across on-premises environments, hyperscale clouds, the edge and SaaS applications. ESG Research Senior Analyst Christophe Bertrand points out that SaaS presents a serious data protection and recovery challenge because “now you have mission critical applications running as a service that you have no control over.”
Second, the pandemic drove millions of employees out of the secure confines of the corporate office to their home offices, where the Wi-Fi is less secure and where employees might be sharing sensitive data on collaboration applications.
Third, hackers took notice of these expanding attack vectors and launched a barrage of new and more targeted ransomware attacks. According to the Sophos State of Ransomware 2020 Report, hackers have moved from spray-and-pray desktop attacks to server-based attacks. “These are highly targeted, sophisticated attacks that take more effort to deploy. However, they are typically far more deadly due to the higher value of assets encrypted and can cripple organizations with multi-million dollar ransom requests,” according to the report .
In response to these changing conditions, CISOs should focus on beefing up endpoint security for remote workers, deploying VPNs and encryption, protecting data at rest no matter where it lives, and also making sure that collaboration tools don’t become a source of security vulnerabilities.
Conduct a business impact analysis (BIA)
Organizations need to conduct a thorough business impact analysis to identify and evaluate potential effects of disasters through the lenses of financial fallout, regulatory compliance, legal liability, and employee safety. Gartner estimates that 70% of organizations are making disaster recovery decisions without any business-aligned data points or based on an outdated BIA. “Without the fact base the BIA provides, teams can only guess at the appropriate level of DR and what risks are tolerable. This results in overspend or unmet expectations,” according to Gartner.
Remember, you don’t need to protect everything. Organizations that conduct these exercises are often surprised to discover servers that do nothing but run a routine back-end business process once a month, or even once a year.
Organizations need to prioritize applications by their criticality to the business, and to identify all the dependencies associated with a business process, particularly applications that may have been virtualized across multiple physical servers, might be running in containers in the cloud, or in serverless cloud environments.
Classify data
Along the same lines, you don’t need to protect all data, just the data that you need to keep the business running. You do need to go through the process of locating, identifying, and classifying data. Be sure to protect data that falls under regulatory requirements, customer data, patient data, credit card data, intellectual property, private communications, etc. The good news is that tools can automate data identification and classification.
Consider disaster recovery as a service (DRaaS)
DRaaS is an increasingly popular option for CISOs at small- to mid-sized organizations who want to cost-effectively improve IT resilience, meet compliance or regulatory requirements, and address resource deficiencies. The DRaaS market is expected to grow at a rate of 12% a year over the next five years, according to Mordor Intelligence . DRaaS services cover the full gamut of disaster recovery and business continuity, providing flexibility and agility to enterprises, according to the Mordor report.
Gartner adds that as the DRaaS market has matured and vendor offerings have become more industrialized, the size and scope of DRaaS implementations have increased significantly, compared with a few years ago.
Develop a solid communication plan
Simply getting servers back up and running is essentially meaningless unless everyone knows their roles and responsibilities. Do people have the appropriate cell phone numbers and email addresses to share information? Do the relevant stakeholders have a playbook that spells out how to respond to a crisis in terms of contacting law enforcement, outside legal teams, utility companies, key technology and supply chain partners, senior leadership, the broader employee base, external PR teams, etc.?
Depending on the nature of the disaster, networking groups might need to establish new lines of connectivity for remote workers and reconfigure traffic flows; maintenance teams might need to perform remote troubleshooting, security teams might need to re-set firewalls, change access policies, extend security protection to new devices or to cloud-based resources. The biggest problem in a disaster isn’t related to data backups, it’s not having the right people in place and understanding all the steps required for the business to recover, says Bertrand.
Automate testing
To test disaster preparedness, companies traditionally conduct tabletop exercises in which key players physically come together to play out DR scenarios. However, only one-third of organizations perceive the exercises as “highly effective,” according to a July study by Osterman Research in association with Immersive Labs, a company that develops human-readiness skills in cybersecurity. The research also found that organizations don’t perform tabletop exercises often enough to keep up with evolving threats and that these exercises cost an average of $30,000. During the pandemic, it’s fair to assume that tabletop exercises fell by the wayside.
Doug Matthews, vice-president of enterprise data protection at Veritas, says there’s a better way. New tools can automatically test backup and recovery procedures on an ongoing basis and identify potential issues that need to be addressed. Modern testing solutions are also able to use sandboxing technology to create safe environments in which companies can test the recoverability of applications without impacting production networks.
Create immutable data backups
Ransomware attackers are targeting backup repositories, particularly in the cloud. They are also targeting SaaS applications. In response, organizations should keep one copy of data that can’t be altered. “Be sure that you have an immutable copy of backup data that nobody can touch,” advises Matthews, who says companies should have three copies of data at all times, not just two.
Companies should also investigate isolated recovery environments, such as air gapping, in which one copy of the data lives in an environment not connected to the production environment.
Consider data re-use
“Business is the data and data is the business,” says Bertrand. Once organizations have a copy of their important data sitting in a safe backup environment, why not think about ways to reuse it to advance the company’s digital transformation efforts.
The idea is for organizations to “understand what you have, where it is, how to protect it, store it and optimize it.” Ultimately, Bertrand predicts that organizations will evolve an intelligent data strategy that encompasses regulatory compliance, disaster recovery/business continuity and data analytics.
Perform continuous updates
CISOs updating their DR/BC plans should take their cue from DevOps. It’s not about one-and-done, it’s about continuous improvement. DR planners need to be plugged into any changes at the company that might affect recoverability, including employees working from home permanently, stores or remote offices opening or closing, applications being replaced by SaaS, data moving to the edge, or DevOps moving to the cloud. Also, the technology is constantly improving, so be on the lookout for new tools that can help automate DR/BC processes. The plan should not be sitting on the shelf collecting dust. It should be updated on a regular basis.
Do long-term planning
In light of everything that has happened over the past 12 months, it’s a good time to shift thinking about DR/BC from reactive to proactive. Unfortunately, between public health emergencies, climate change and the increase in cyberattacks, disasters seem to be occurring more often and are certainly more devastating. DR/BC plans need to get ahead of the threats, not simply respond to them.
For example, if your company is in California, your DR/BC plan has to assume that there will be power outages from next season’s wildfires. Companies concerned about losing power when the next natural disaster hits might want to think about generating their own power from alternative sources.
A successful DR/BC plan requires that companies perform the basics, but it is also an opportunity for companies to find creative and innovative ways to keep the business running when disaster hits.
Related content
Boys’ club mentality still a barrier to women’s success in cybersecurity careers, gathid’s new access mapping tech promises affordable and streamlined iam, why global warnings about china’s cyber-espionage matter to cisos, researchers uncover evasion data exfiltration techniques that can be exploited in sharepoint, from our editors straight to your inbox.

Neal Weinberg is a freelance technology writer and editor. He can be reached at [email protected] .
More from this author
Best and worst data breach responses highlight the do’s and don’ts of ir, pci dss 4.0 is coming: how to prepare for the looming changes to credit card payment rules, 13 traits of a security-conscious board of directors, consumers are done with passwords, ready for more innovative authentication, most popular authors.

Show me more
Cohesity partners with intel to solve insider threat challenges.

Sysdig digs up a ransomware gang in stealth for over a decade

5 groups that support diversity in cybersecurity

CSO Executive Sessions: Geopolitical tensions in the South China Sea - why the private sector should care

CSO Executive Sessions: 2024 International Women's Day special

CSO Executive Sessions: Former convicted hacker Hieu Minh Ngo on blindspots in data protection

LockBit feud with law enforcement feels like a TV drama

Sponsored Links
- Tomorrow’s cybersecurity success starts with next-level innovation today. Join the discussion now to sharpen your focus on risk and resilience.
- IDC report: Life-cycle services can help align technology, operational, and business outcomes.
- Digital infrastructure plays a big role in business outcomes. Read this IDC report to learn more.
ISO 22301 Business Continuity Simplified: Fortify Your Business Against Disruption
By Andy Marker | June 22, 2020 (updated September 15, 2022)
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
In this article, you’ll find expert tips and implementation guides, and you'll learn how ISO 22301 can buffer your business against disasters.
Included on this page, you’ll find an International Standards Organization (ISO) 22301 audit checklist template , a simplified ISO 22301 cheat-sheet , and an ISO 22301 self-assessment checklist , as well as examples of ISO 22301 in action and an ISO 22301 quick-start guide .
What Is ISO 22301?
ISO 22301 is a global standard for business continuity planning requirements to help organizations protect themselves against disruptions. The most current version is 22301:2019, Security and resilience - Business continuity management systems - Requirements.
The requirements in ISO 22301 address disruptive incidents that can be natural or human-made, widespread or local, intentional or unintentional, such as a snowstorm, a broken water main, an epidemic, a data breach, or a phishing attack. Large or small, for- and nonprofit organizations alike can use ISO 22301.
The Business Manager’s Quick-Start Guide to ISO 22301
The ISO 22301 standard can provide benefits for your business continuity planning, even if your organization chooses not to pursue certification, or the review process that confirms your business continuity system meets all ISO 22301 requirements.
"Certification is nice, but not required,” says Mart Rovers of InterProm. “First, seek compliance. That way, you know that your business continuity management practices are in better shape." You can start to create a solid business continuity plan with just a few simple steps, which you can also download as this ISO 22301 Quick-Start Guide .
- Check If You Already Have Continuity Plans: Find out if your organization already has business continuity plans. Search through your document management system and ask management or long-time employees. Organizations sometimes create and quickly forget about resources, or store responses locally in an informal system. As Andrew Nichols of the Michigan Manufacturing Technology Center suggests, if your organization already implements other ISO standards, such as ISO 9001 or ISO 27000, you can leverage some of the common requirement elements for your 22301 plan.
- Identify Missing Components: Conduct a gap analysis of existing policies and processes to see what business continuity resources you need. According to Mart Rovers, one way to conduct a self-assessment is to copy into a spreadsheet each phrase of the ISO 22301 standard that contains the word "shall." Then, determine gaps between your company and the standard. "Use the standard as your guide to establishing a coherent set of practices to address business continuity management for your organization," says Rovers. You can also use Smartsheet's ISO 22301 Self-Assessment Checklist and ISO 22301 Simplified Cheatsheet for your gap analysis.
- Keep It Simple: Having binders full of perfectly formatted procedures won’t help in an emergency. Create easy-to-follow guidelines and checklists and, more importantly, build "muscle memory" in your employees through training and drills. That way, in a panic, people understand what to do without having to be told.
- Make Your Plan a Living Document: Ticking off items on an audit checklist doesn't mean you’re prepared. Frequently read, revise, and practice your plan to keep it relevant and to train new staff.

- Communicate Your Plan to Staff and Other Stakeholders: Even the most well-written plan is useless if the people who can benefit from it don't know about it. Inform everyone covered by the plan that it exists, including your supply chain and other outside stakeholders.
ISO 22301 Requirements
The ISO 22301 standard offers a framework for planning, testing, and monitoring a business continuity management system (BCMS). The ISO 22301 document contains 10 sections, which introduce the standard and definitions, as well as actionable requirements of the standard.
As with other ISO requirement documents, ISO 22301 describes only what organizations must do to reach minimum proficiency — it does not prescribe how to achieve these standards. Each organization must consider its distinct conditions and obligations to find the best way to follow the requirements.
Here is an overview of the clauses in ISO 22301 that impact an organization most:
- Clause 4, Context: Your organization must understand what it is, what it does, and what outputs and processes it must sustain. You must also determine who has a stake in the continuity of your operations — in other words, the interested parties. For example, customers have a stake in your organization continuing to function.
- Clause 5, Leadership: Few organizational initiatives thrive without the sustained support and championship of top management. Management must commit to a business continuity plan and make available any resources — human, financial, or otherwise — to ensure its success.
- Clause 6, Planning: To plan for sustainability, you must understand what disruptions could potentially occur and how these incidents affect the business — in other words, potential risks and their impact. Set measurable business continuity objectives to guarantee the minimum viable products or services, as well as compliance with any legal or regulatory requirements.
- Clause 7, Support: No program can advance without resources and support. Decide what personnel, roles, and teams you need for threat response and how you can best enhance their effectiveness. Create internal and external communication procedures for reference, and communicate the continuity plan to all necessary parties before and during a crisis. Establish a document management system for key continuity documents, such as procedures.
- Clause 8, Operation: Conduct your risk assessment and business impact analysis , and plan your disruption recovery approach. Implement the recovery plan with detailed procedures, and test it regularly to verify that it works. Make sure people can find the procedures (and other documents) they need, and revise your plan as necessary.
- Clause 9, Evaluation: Establish a process to regularly measure and assess your continuity policies and procedures and their execution. Review and revise your plan and documents to ensure they are effective and relevant
- Clause 10, Improvement: Seek continual improvement in all functional and operational areas, including through periodic management reviews. Improvements in day-to-day activities help bolster the organization in times of disruption. When processes veer from the standard or fail to conform with ISO and quality management standards, implement corrective action.
Key Definitions Related to ISO 22301
Some of the following key terms and concepts originate with ISO, some with ISO 22301, and some with business continuity and risk management:
- Context: The purpose and character of the organization and the environment in which it operates. This includes internal and external influences that shape the business continuity management system.
- Disruptive Incident: A disruptive incident is an event that stops or slows the everyday work of an organization. Examples of disruptive incidents include earthquakes, internet stoppages, broken fans in a data center, or food poisoning in a cafeteria.
- Interested Parties: Interested parties are stakeholders in the successful operation and outcomes of your business continuity plan. They can include customers, employees, suppliers, or regulatory officials.
- Leadership: In ISO 22301, leadership refers to top management or the person or people who run the organization and champion the business continuity effort.
- Maximum Acceptable Outage (MAO): The length of time an activity or process can be unavailable or ineffective before the health and survival of the organization are threatened.
- Minimum Business Continuity Objective (MBCO) : The lowest level of products or services that is acceptable for a business to offer during a disruption.
- Recovery Timeframe Objectives (RTO): This refers to the prioritization of key activities and the timing that makes those activities operational.
Benefits of ISO 22301 and Business Continuity Management System
If teams are already overwhelmed with their workload, they may not like to think about disasters. Furthermore, organizations might think that ISO standards include difficult jargon and that pursuing a continuity plan adds unnecessary work. However, management systems practitioners suggest that continuity preparations produce substantial gains.

“I think it's a truism that many organizations can benefit from the principles and some of the practices of resiliency and contingency planning,” says Andrew Nichols, Quality Program Manager at the Michigan Manufacturing Technology Center .
As an example of the benefits that risk analysis and preparation can yield, Nichols relates his experience of visiting a small northeastern town during a widespread winter power outage. The whole town was closed, with the exception of one restaurant that had a generator.
“They had a line of people out the door every mealtime because nowhere else was capable,” Nichols remembers. “Somebody had the foresight to think about the loss of power. And that organization cleaned up financially because they were able to provide what the customers needed.”
Consider these specific benefits to using ISO 22301 business continuity planning:
- Protect against and recover from disruptive incidents.
- Identify and control current and future threats.
- Improve your risk management planning efforts.
- Prevent large-scale damage.
- Become proactive in preventing problems and recovering from incidents, rather than reactive to damage and disruption.
- Reduce downtime and increase recovery time.
- Keep important activities running during disruption.
- Deliver quality products consistently.
- Provide dependable service.
- Prove you’re a reputable supplier.
- Prove your resilience to all stakeholders.
Experts also assert that ISO 22301 can be a simple and effective continuity tool. “All these ISO standards, they’re like hidden gems because of how fast they can get you up to speed without having to reinvent the wheel,” says Mart Rovers, President of IT consulting firm InterProm .

“I cannot emphasize enough how within reach this standard is. Anytime people hear the word ‘ISO,’ they think, ‘Oh, that's for large organizations. Oh, that's way too formal. It's too much. It's overkill.’ I understand where this is coming from because the word ‘standard’ itself is scary for many organizations. However, the size of organization really doesn't matter. The things you should be doing in ISO 22301, you can do at a smaller scale,” says Rovers.
Some also hesitate at the thought of certification. Both Nichols and Rovers stress that certification is not necessary for every enterprise. Although certification may be a condition of doing business for some companies, those who don’t need certification can still gain advantages from following ISO 22301.
In weighing the pros and cons of ISO certification, Rovers suggests buying a copy of ISO 22301 , and then copying and pasting each sentence that contains the word “shall” into a spreadsheet (these sentences represent the requirements you must follow). From the spreadsheet, consider whether full ISO adoption and certification are too complicated for your organization. Regardless of your decision, you can always use the spreadsheet to conduct a self-audit.
ISO 22301 in Action
The following image provides a small sample of the possible outcomes to business continuity management.
How a Management System Helps Business Continuity
For those familiar with other ISO standards, the management system component of ISO 22301 might be a new concept. Rovers describes management systems as follows:
“The best way to explain a management system is to imagine opening up an old watch. It has these spinning wheels, these gears. In the case of an ISO standard, you're looking at a number of requirements to put that watch together with all these spinning wheels. That watch is a coherent system. You take out one of those gears, and then the watch fails.
“A management system for continuity follows the same idea — every requirement that the standard asks for represents one of those gears. And every requirement serves a distinct purpose (otherwise, it would not be a requirement). If you don't meet a particular requirement, the watch, so to speak, may not function as it could or should. These ISO requirements are not just there to keep you busy.”
ISO 22301 and PDCA
Each segment of the PDCA (plan-do-check-act) cycle for continuous improvement corresponds to at least one ISO 22301 clause. Organizations can use ISO 22301 to test continuity procedures, review outcomes, and implement updates or fix problems in a continuous cycle that leads to an increasingly resilient business continuity system.
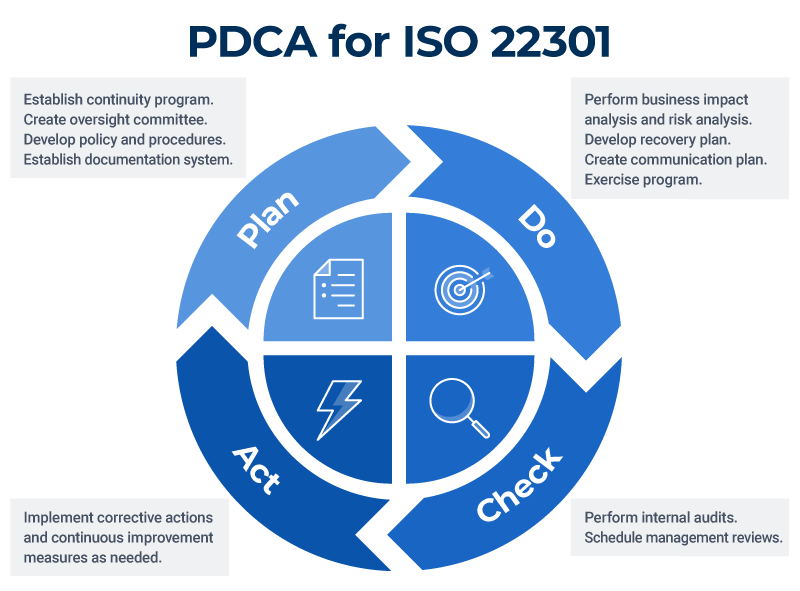
ISO 22301 and Maturity Models
A maturity model measures an organization’s ability to pursue continuous improvement in key areas. ISO 22301 does not have a maturity model.
As Rovers explains, “It was never the intent of ISO 22301 to be a maturity model. You either meet all the requirements of the standard, or you don’t. You could say that by not meeting the requirements of the standard, you’re not mature. Or better said, your business continuity management practices are not mature.”
BCM Lifecycle ISO 22301
The business continuity management (BCM) lifecycle represents industry best practices and some of the core requirements of ISO 22301. These practices offer a solid foundation for resilience, while offering flexibility to adapt to changes in the organization.
Guided by leadership, these are the key activities for the lifecycle:
- Conduct a business impact analysis and risk assessment.
- Establish a business continuity strategy.
- Establish and implement business continuity procedures.
- Exercise and test the procedures regularly before a disruption occurs.

ISO 22301 Audit Checklist Template (Excel)
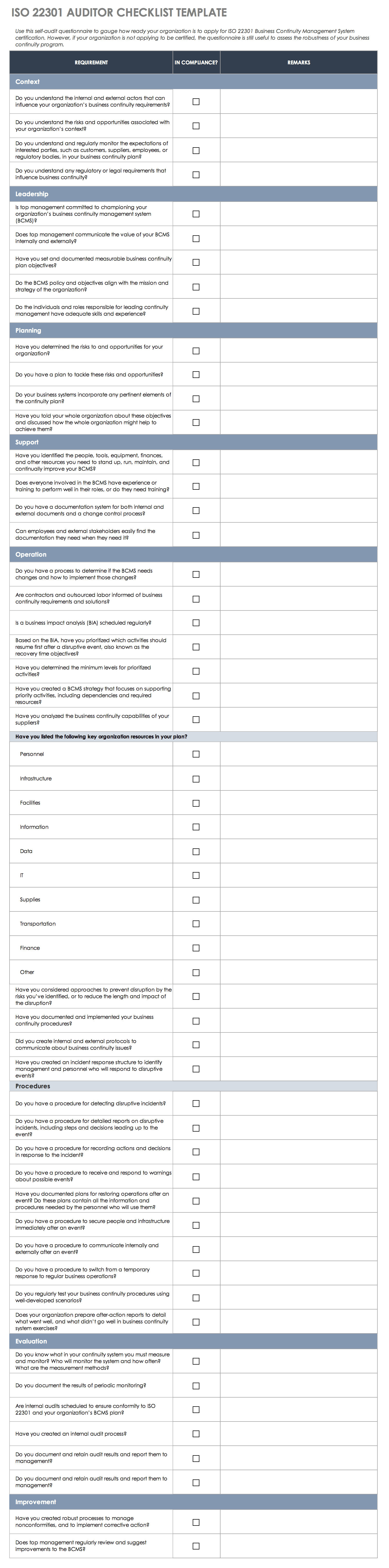
Use this detailed checklist to determine if your business continuity plan aligns with ISO 22301 standards. You can use the template whether you’re applying for certification or simply pursuing a continuity management plan.
Download ISO 22301 Audit Checklist Template
Excel | Smartsheet
ISO 22301 Self-Assessment Checklist
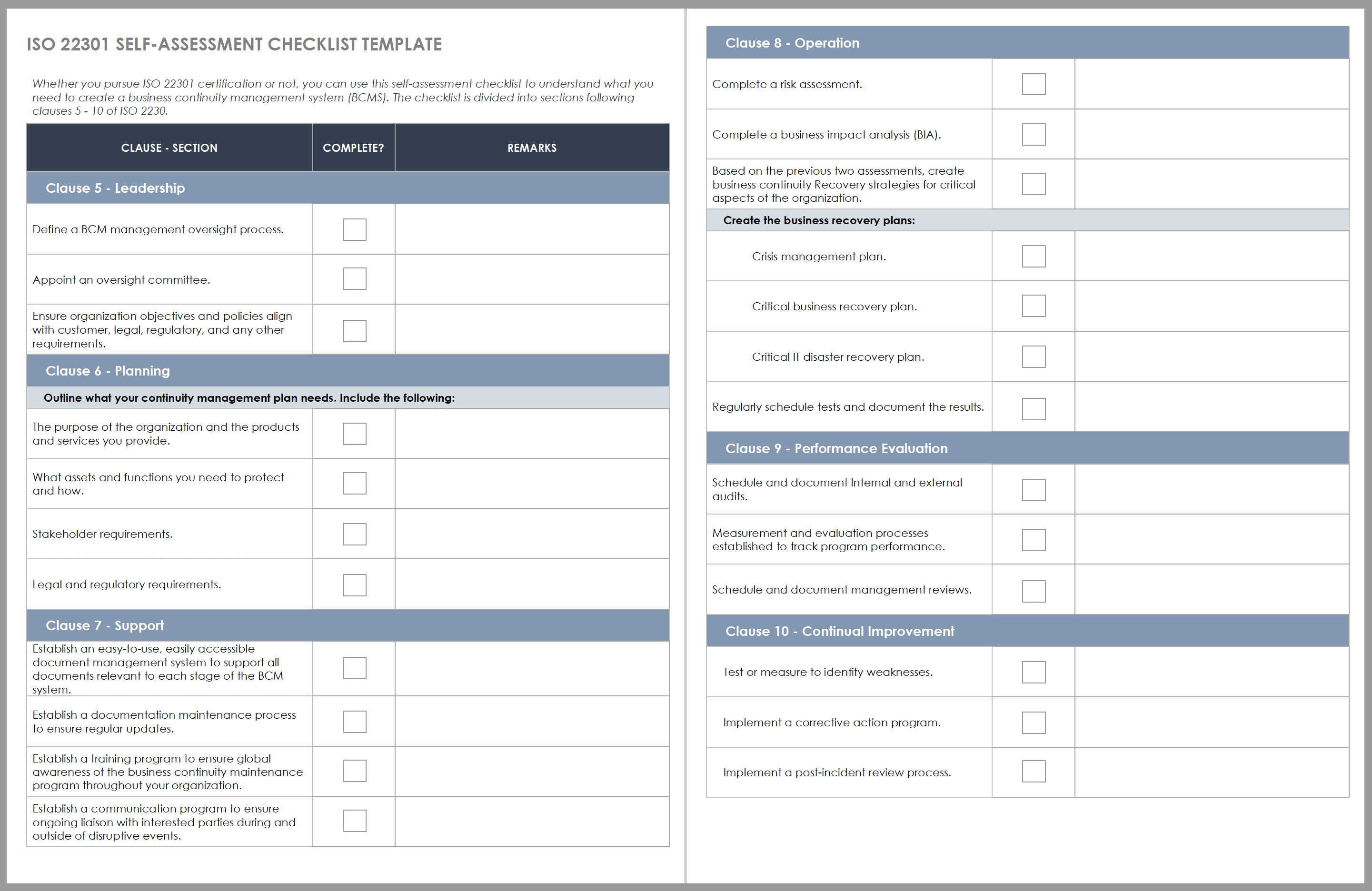
This self-assessment checklist is divided into sections that correspond to clauses in ISO 22301. Use it to confirm whether your business continuity system meets the requirements for leadership, planning, support, operation, performance evaluation, and continual improvement.
Download ISO 22301 Self-Assessment Checklist Template
Excel | Word | PDF
ISO 22301 Implementation Guide
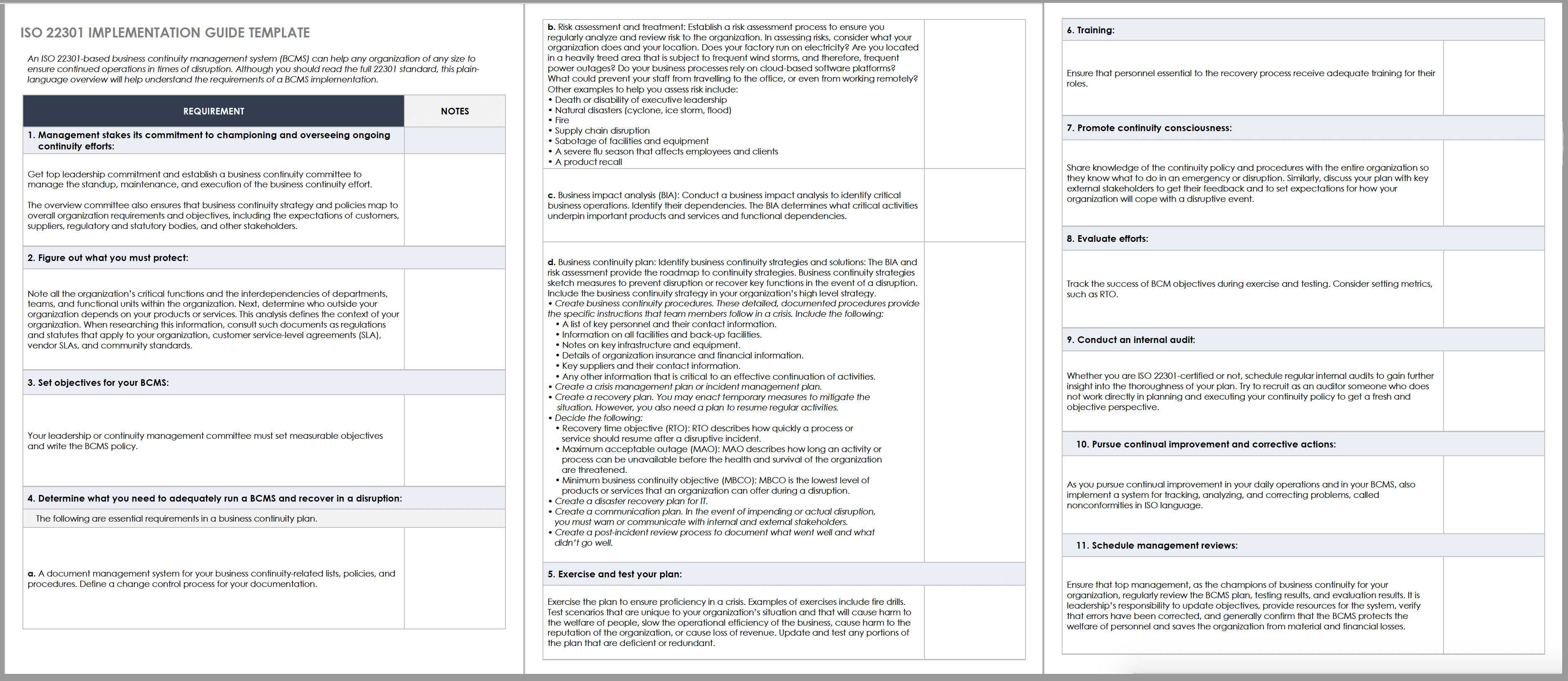
This guide states the essential information from ISO 22301 in plain English. For best results, read it with the full standard, which is currently available for free online to support the COVID-19 response.
Download ISO 22301 Implementation Guide Template
Excel | Word | PDF
ISO 22301 Simplified Cheat-Sheet
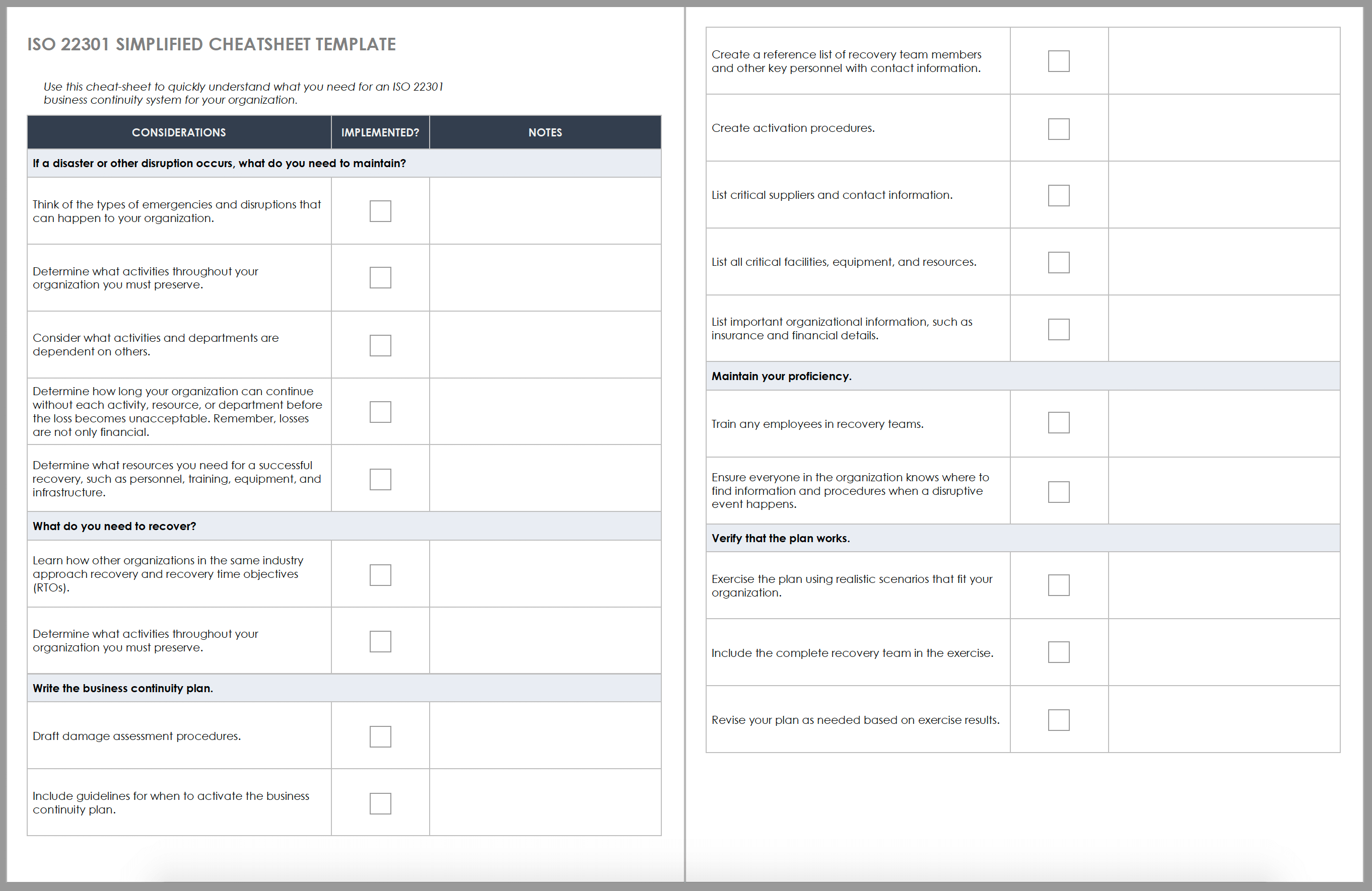
Use this simplified cheat-sheet to understand the basic elements of creating a business continuity plan. The template walks you through the process of determining critical aspects of your organization, writing the recovery plan, and exercising the plan to ensure proficiency.
Download ISO 22301 Simplified Cheat-Sheet Template
ISO 22301 Business Continuity Policy Template
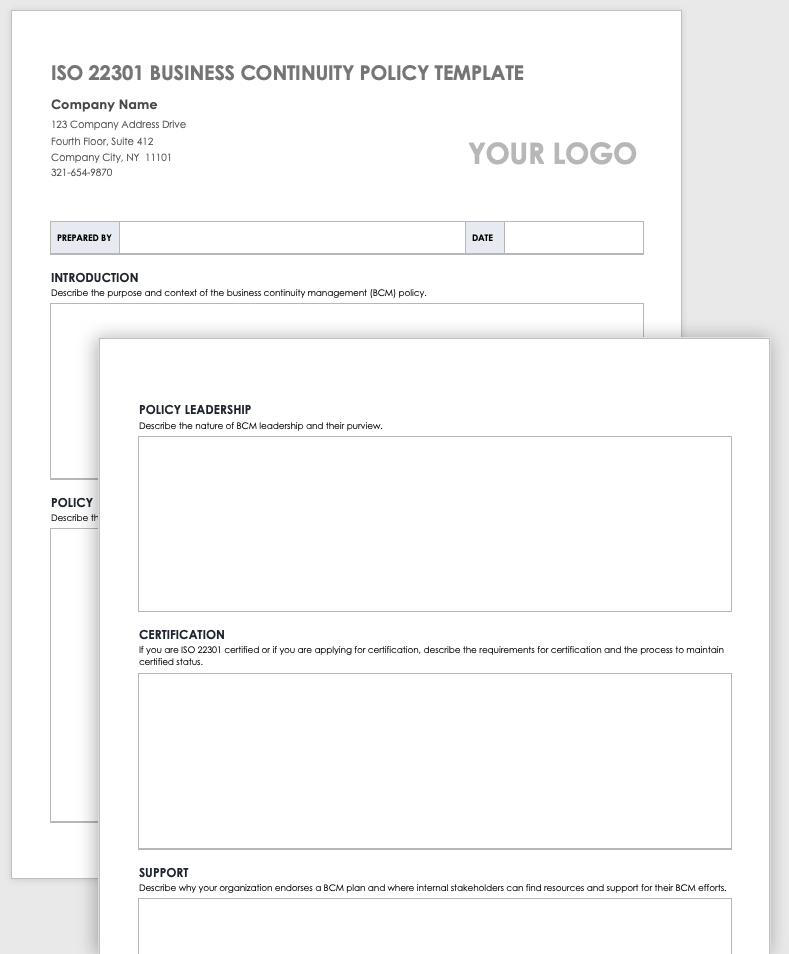
A business continuity policy describes the processes and procedures an organization needs in order to function well daily, including in times of disruption and crisis. This policy template includes space for BCMS objectives, a leadership description, a policy outline, and any certification details.
Download ISO 22301 Business Continuity Policy Template
ISO 22301 Business Continuity Template
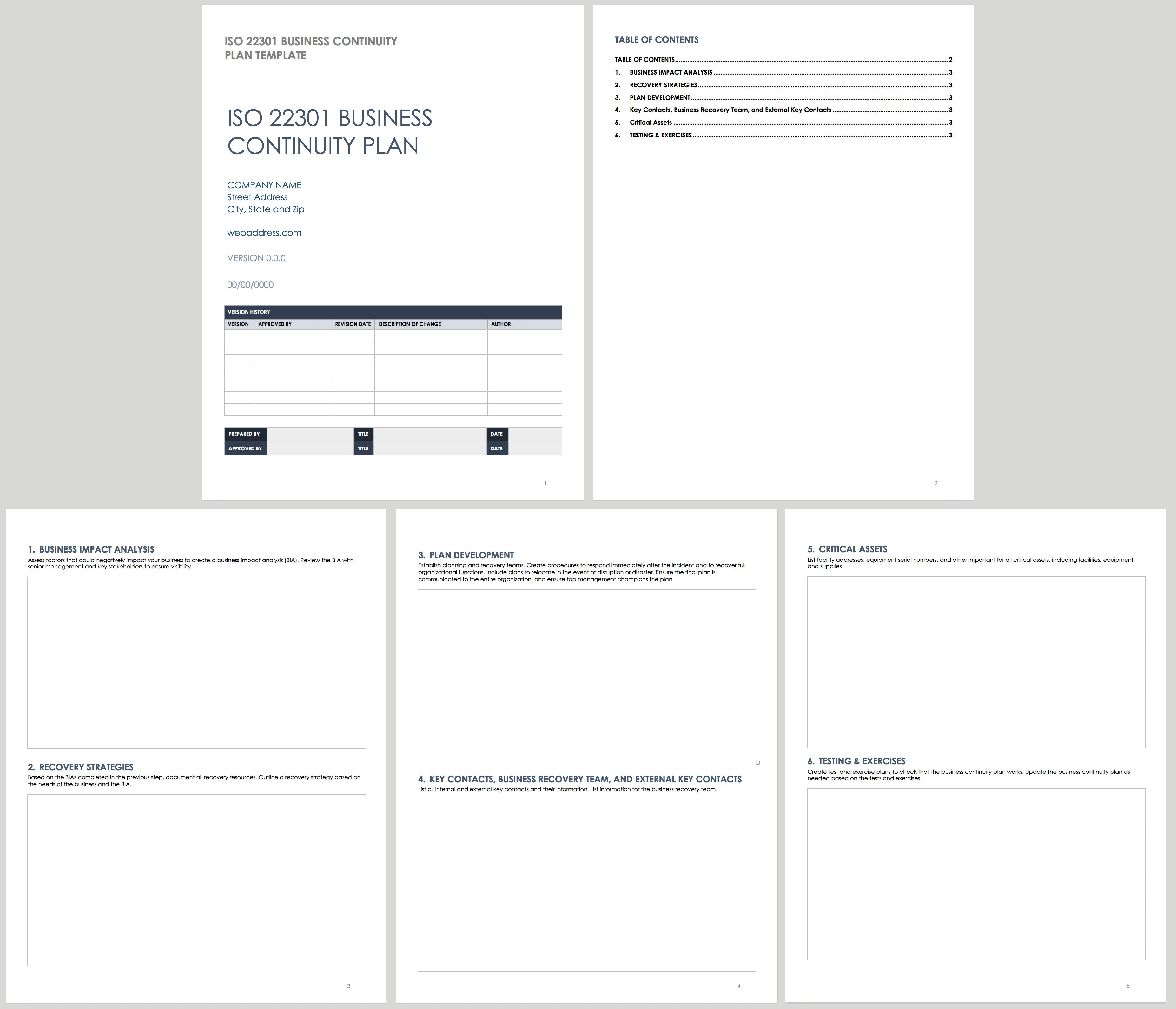
Use this template to create a business continuity plan. Describe the results of your risk analysis and business impact analysis, detail your disaster recovery and continuity procedures, and list key contacts and important assets.
Download ISO 22301 Business Continuity Template
Word | PDF
ISO 22301 Business Continuity Sample
The Community Nonprofit Center of New York made available this business continuity template to support the response to coronavirus. Find space to detail responses to minimal and critical emergencies, a risk matrix template, and lists for information about insurance, critical assets, and responses to disruptive events.
For other most useful free, downloadable business continuity plan (BCP) templates please read our "Free Business Continuity Plan Templates" article.
Disaster Recovery Plan Templates
After you perform a risk analysis and business impact analysis, consider writing a disaster recovery plan. Disaster recovery plan templates , available in different formats, provide an easy-to-use structure for documenting continuity plans. Download templates specialized for IT, payroll, small businesses, and more.
To learn about the difference between recovery plans and continuity plans, visit our "Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery: Their Differences and How They Work Together" article.
ISO 22301 Versus ISO 27301
ISO 27301 provides requirements that organizations use to ensure their information and communications technology (ICT) continuity, security, and readiness to survive a disruption. The standard is often staged with ISO 22301 because both are based on similar management system approaches.
The full name of this standard is ISO 27301 - Information Technology - Security Techniques . Originally published in 2011, it is soon to be revised.
“Both [ISO 27301 and ISO 22301] ask for top management involvement and commitment, both ask that you have the right resources, that you have documentation management, that you do performance evaluations, and that you make improvements,” explains Rovers.
They differ in the focus of the risk assessment: ISO 27001 addresses security, whereas ISO 22301 addresses business continuity. “Each area has different risks, but the approach to the risk management assessment and mitigation follows the same steps. There's enormous overlap.”
IT security continuity has significant relevance in the remote work environment. For example, while using your work laptop at home or signed into the work network, what happens when someone innocently plugs in a thumb drive that infects your laptop and corrupts the network? Both ISO 22301 and ISO 27001 work together to prevent such incidents and mitigate problems that occur.
For additional resources, visit " Free ISO 27001 Checklists and Templates ."
General Requirements Across Management System Standards
Some ISO requirements are commonly stated across the management system standards, which include ISO 22301; ISO 9001 , Quality Management; ISO 20000, IT Service Management; and ISO 27001, Information Security. Examples of common requirements include establishing objectives for the business continuity management system as appropriate to the organization, obtaining management’s commitment to supporting the system, implementing a documentation management system, conducting internal audits, and pursuing continual improvement. This functional overlap enables organizations to undertake combined audits for these standards.
Historical Foundations of ISO 22301
The concept of business continuity was borne out of the IT boom of the 1980s and 1990s. Public and private organizations realized the need to ensure continuity of service and key supplies and to mitigate the effects of disruptive events. The first formal standard reflecting these concerns was the United Kingdom’s British Standard (also known as BS) 25999, which introduced the management system concept to the business continuity discipline.
In 2012, the global standards body ISO released ISO 22301:2012 as the first international standard for business continuity. Based on the contributions and comments of continuity professionals from assorted industries in over 60 countries, ISO 22301 superseded BS 25999.
ISO’s consensus-based standards, such as 22301, cover practices and industries ranging from quality management, IT service, and food safety to environmental safety and information security. ISO standards aim to increase the quality and safety of many products and services, including most common household items, appliances, and cars. Although large enterprises and manufacturers usually follow ISO requirements and guidelines, organizations of all sizes and types can benefit from ISO principles.
For ISO 22301, the standard provides a consistent BCMS framework and a universal language among organizations for communicating about continuity and aligning processes.
When they get certified in ISO 22301 and other ISO standards, organizations can demonstrate to management, legislators, regulators, customers, and other stakeholders that they follow good practices. For ISO certification, organizations need third-party verification that they comply with all requirements of a standard.
“Certification shows you have some level of competence,” explains Rovers. “It shows you take the standard seriously. For organizations buying your goods or services, it can be a compelling reason to choose you.”
Guidance Documents for ISO 22301
For in-depth discussions of aspects of the 22301 standard, ISO offers a series of guidance documents. To those considering pursuing ISO 22301 certification, these documents provide additional insight:
- ISO 22313 - Security and resilience — Business continuity management systems — Guidance on the use of ISO 22301
- ISO 22316 - Security and resilience — Organizational resilience — Principles and attributes
- ISO 22317 - Societal security — Business continuity management systems — Guidelines for business impact analysis (BIA)
- ISO 22318 - Societal security — Business continuity management systems — Guidelines for supply chain continuity
- ISO 22330 - Security and resilience — Business continuity management systems — Guidelines for people aspects of business continuity
- ISO 22331 - Security and resilience — Business continuity management systems — Guidelines for business continuity strategy
What Is the Latest Version of ISO 22301?
The requirement document ISO 22301:2019, Security and resilience - Business continuity management systems - Requirements , was released on October 31, 2019. The update from the original 2012 version reflects changes in management system approaches and clarifies specifications around clause 8.
Build Powerful, Automated Business Processes and Workflows with Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Any articles, templates, or information provided by Smartsheet on the website are for reference only. While we strive to keep the information up to date and correct, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability, or availability with respect to the website or the information, articles, templates, or related graphics contained on the website. Any reliance you place on such information is therefore strictly at your own risk.
These templates are provided as samples only. These templates are in no way meant as legal or compliance advice. Users of these templates must determine what information is necessary and needed to accomplish their objectives.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.

Published: 21 December 2023 Contributors: Mesh Flinders, Ian Smalley
Business continuity disaster recovery (BCDR) refers to a process that helps organizations return to normal business operations if a disaster happens. While business continuity and disaster recovery are closely related, they describe two subtly different approaches to crisis management that businesses can take.
As data loss prevention and downtime become more expensive, many organizations are upping their investment in emergency management. In 2023, companies worldwide were set to spend USD 219 billion on cybersecurity, a 12% increase from the previous year according to a recent report by the International Data Corporation (link resides outside ibm.com).
What is a disaster recovery plan?
A disaster recovery plan (DRP) is a contingency plan for how an enterprise will recover from an unexpected event. DRPs help businesses manage different disaster scenarios, such as massive outages, natural disasters, ransomware and malware attacks, and many others.
What is a business continuity plan?
Like DRPs, business continuity plans (BCPs) play a critical role in disaster recovery and help organizations return to normal business functions when a disaster happens. Where a DRP focuses specifically on IT systems, business continuity management focuses more broadly on various aspects of preparedness.
Connect and integrate your systems to prepare your infrastructure for AI.
Register for the guide on DaaS
Most organizations divide BCDR planning into two separate processes: business continuity and disaster recovery. This approach is effective because while the two processes share many steps, there are also key differences in how organizations build, implement and test the plans.
The main difference is that BCPs are proactive, aiming to maintain operations before, during and right after a disaster. On the other hand, DRPs are reactive, focusing on how to respond and recover from an incident. This distinction should guide the creation of your BCDR strategy, with BCPs focusing on critical processes and roles, and DRPs on recovery actions post-incident.
Both processes depend heavily on two critical components: recovery time objective and recovery point objective.
Recovery time objective (RTO)
RTO refers to the amount of time it takes to restore business processes after an unplanned incident. Establishing a reasonable RTO is one of the first things businesses need do when they’re creating their DRP.
Recovery point objective (RPO)
Your business’ RPO is the amount of data it can afford to lose in a disaster and still recover. Since data protection is a core capability of many modern enterprises, some constantly copy data to a remote data center to ensure continuity in case of a massive breach. Others set an RPO of a few minutes—or even hours—for them to recover business data from a backup system, so they know they are able to recover from whatever they've lost during that time.
1. Conduct business impact analysis
To build an effective BCP, you first need to understand the various risks your organization faces. Business impact analysis (BIA) is vital in risk management and business resilience. BIA is the process of identifying and evaluating the potential impact of a disaster on normal operations. Strong BIA includes an overview of all potential existing threats and vulnerabilities—internal and external—and detailed plans for mitigation. The BIA must also identify the likelihood of an event occurring so the organization can prioritize accordingly.
2. Design responses
When your BIA is complete, the next step in building your BCP is planning effective responses to each of the threats you’ve identified. Different threats naturally require different disaster recovery strategies, so each of your responses should have a detailed plan for how the organization will spot a specific threat and address it.
3. Identify key roles and responsibilities
This step dictates how key members of your team responds when facing a crisis or disruptive event. It documents expectations for each team member and also the resources required for them to fulfill their roles. This part of the process is good to consider how individuals communicate when an incident occurs. Some threats shut down key networks—such as cellular or internet connectivity—so it’s important to have reliable fallback methods of communication.
4. Test and update your plan
To be actionable, you need to constantly practice and refine your BCDR plan. Constant testing and training of employees lead to a seamless deployment when an actual disaster strikes. Rehearse realistic scenarios like cyberattacks, fires, floods, human error, massive outages and other relevant threats so team members can build confidence in their roles and responsibilities.
Like BCPs, DRPs require BIA—the outlining of roles and responsibilities and constant testing and refinement. But because DRPs are more reactive in nature, there is more of a focus on risk analysis and data backup and recovery . Steps 2 and 3 of DRP development, analyzing risks and creating an asset inventory are not part of the BCP development process at all.
Here's a widely used five-step process for creating a DRP:
1. Conduct business impact analysis
Like in your BCP process, start by assessing each threat your company might face and what its ramifications might be. Consider how potential threats might impact daily operations, regular communication channels and worker safety. Other considerations for a strong BIA include loss of revenue, cost of downtime, cost of reputational repair (public relations), loss of customers and investors (short and long term) and any incurred penalties from compliance violations.
2. Analyze risks
DRPs typically require more careful risk assessment than BCPs since their role is to focus on recovery efforts from a potential disaster. During the risk analysis portion of planning, consider a risk’s likelihood and potential impact on your business.
3. Create an asset inventory
To create an effective DRP, you must know exactly what your enterprise owns, its purpose or function and its condition. Doing regular asset inventory helps identify hardware, software, IT infrastructure and anything else your organization might own that is crucial to your business operations. When you’ve identified your assets, you can group them into three categories: critical, important and unimportant.
- Critical: Only label assets as critical if your enterprise requires them for normal business operations.
- Important: Give this label to assets that you use at least once a day and that would have an impact on business operations (but not shut them down entirely) if they are disrupted.
- Unimportant: These are assets your business uses infrequently that are not essential for normal business operations.
4. Establish roles and responsibilities
Just like in your BCP development, you need to clearly outline responsibilities and ensure that team members have what they need to perform their required duties. Without this crucial step, no one knows how to act during a disaster. Here are some roles and responsibilities to consider when building your DRP:
- Incident reporter: Someone who maintains contact information for relevant parties and communicates with business leaders and stakeholders when disruptive events occur.
- DRP supervisor: The DRP supervisor ensures that team members perform their assigned tasks during an incident.
- Asset manager: Someone whose job it is to secure and protect critical assets when a disaster strikes.
- Third-party liaison: The person who coordinates with any third-party vendors or service providers you’ve hired as part of your DRP and updates stakeholders accordingly on how the DRP is going.
5. Test and refine
Like your BCP, your DRP requires constant practice and refinement to be effective. Practice it regularly and update it according to any meaningful changes that are necessary. For example, if your company acquires a new asset after you've formed your DRP, you’ll need to incorporate it into your plan to ensure it's protected going forward.
In terms of BCDR planning, every business is going to have its own unique set of needs. Here are a few examples of plans that are effective for companies of differing sizes and industries:
Crisis management plan
A crisis management plan, also known as an incident management plan, is a detailed plan for managing a specific incident. It provides detailed instructions on how your organization responds to a specific crisis, such as a power outage, cyberattack or natural disaster.
Communications plan
A communications plan outlines how your organization handles public relations (PR) in the event of a disaster. Business leaders typically coordinate with communications specialists to formulate communications plans that complement any crisis management activities needed to keep business operations going during an unplanned incident.
Data center recovery plan
A data center recovery plan focuses on the security of a data center facility and its ability to get back up and running after an unplanned incident. Some common threats to data storage include overstretched personnel that can result in human error, cyberattacks, power outages and difficulty following compliance requirements.
Network recovery plan
Network recovery plans help organizations recover from an interruption of network services, including internet access, cellular data, local area networks and wide area networks. Due to the critical role networked services play in business operations, network recovery plans must clearly outline the steps, roles and responsibilities needed to quickly and effectively restore services after a network compromise.
Virtualized recovery plan
A virtualized recovery plan relies on virtual machine (VM) instances that can be ready to operate within a couple of minutes of an interruption. Virtual machines are representations, or emulations, of physical computers that provide critical application recovery through high availability, or the ability of a system to operate continuously without failing.
BCDR planning helps organizations better understand the threats they face and better prepare to face them. Enterprises that don’t undertake BCDR planning face various risks, including data loss, downtime, financial penalties and reputational damage. Effective BCDR planning helps ensure business continuity and the prompt restoration of services after a business disruption. Here are some of the benefits companies with strong BCDR planning enjoy:
When an unplanned incident disrupts business as usual, it can cost hundreds of millions of dollars. Additionally, high-profile cyberattacks frequently attract unwanted attention in the press and can result in loss of confidence in both customers and investors. BCDR plans increase an organization’s ability get back up and running swiftly and smoothly after an unplanned incident.
According to IBM’s recent Cost of Data Breach Report , the average cost of a data breach in 2023 was USD 4.45 million, a 15% increase over the previous three years. Enterprises with strong BCDR can reduce those costs by helping maintain business continuity throughout an incident and speeding recovery afterward. Another opportunity for cost-savings with strong BCDR is in cyber insurance. Many insurers won’t insure organizations that haven't established a strong BCDR plan.
Data breaches incur hefty fines when private customer information is compromised. Businesses that operate in heavily regulated sectors like healthcare and personal finance face especially costly penalties. Since these penalties are often tied to the duration and severity of a breach, maintaining business continuity and shortening response and recovery lifecycles is critical to keeping financial penalties low.
Even a minor outage can put you at a competitive disadvantage. Protect your data with a cloud disaster recovery plan.
Employ a highly durable, scalable and security-rich destination for backing up your data.
Expand capacity and consolidate data center infrastructure onto an automated and centrally managed software-defined data center with IBM Cloud for VMware Solutions.
Many factors come into play when deciding whether to invest in and manage your on-premises disaster recovery (DR) solutions or use disaster recovery as a service (DRaaS) providers.
Backup and restore refers to technologies and practices for making periodic copies of data and applications to a separate, secondary device and then using those copies to recover the data and applications.
There are critical similarities and differences between disaster recovery and backup. These solutions can both help you solve your business' most important problems.
IBM has plans and processes in place globally that help sustain its business by assessing potential disasters. This paper provides an overview of the business continuity measures used by IBM to help prevent or reduce the impact of potential threats.
Zerto helps clients access robust disaster recovery and data protection capabilities while using the agility and flexibility of IBM Cloud for VMware solutions shared in a single-click deployment.
IBM's business continuity and resiliency engagement is designed to help you enable resumption of your business operations quickly and maintain the quality of your existing services in the event of an outage.
IBM Cloud Backup is a full-featured, agent-based backup and recovery system managed through a web interface. Back up data between IBM Cloud servers in one or more IBM Cloud global data centers.
Business Continuity Planning: Ensuring the Resilience of Your Organization
Let’s explore the intricacies of business continuity planning, from understanding its importance to implementing a robust strategy that safeguards your enterprise.
Published by Orgvue November 20, 2023
Home > Resources > article > Business Continuity Planning: Ensuring the Resilience of Your Organization
In an unpredictable world, the ability to sustain your business’s essential functions and operations, even in the face of disruptions, is paramount.

Business continuity planning is the framework that ensures your organization can weather storms, both literal and metaphorical.
What is Business Continuity Planning?
At its core, business continuity planning is the process of developing a proactive strategy to ensure an organization’s critical functions and operations can continue in the face of unforeseen disruptions.
It encompasses a range of activities, from risk assessment to the creation of detailed recovery plans, with the ultimate goal of minimizing downtime and ensuring the organization’s resilience.
The Importance of Business Continuity Planning
The importance of being prepared for various external and internal factors cannot be overstated. While many businesses have a standard business plan, not all of them consider the potential disruptions caused by natural calamities, economic downturns, or other unexpected events. Business continuity planning is the key to ensuring a company’s sustained operation, regardless of the challenges it may face.
Business continuity planning goes beyond the traditional business plan. While a business plan outlines goals and strategies for growth, a continuity plan focuses on how the organization will continue to function in the face of adversity. It involves identifying potential risks and developing strategies to mitigate and recover from them. Whether it’s a natural disaster, a cyberattack or an economic recession, having a well-thought-out strategic plan is essential for business survival.
One of the most significant threats to businesses is an economic downturn, such as a recession. During these challenging times, consumer spending often decreases, and businesses may face financial instability. A recession can have a ripple effect on companies of all sizes, causing decreased revenue, layoffs, and even closures.
For a detailed look at the impact of recessions on businesses, read how to prepare for a recession , which delves into strategies for navigating these challenging economic conditions.
Business strategy planning is not just about surviving during tough times; it’s also crucial for capitalizing on periods of growth. When businesses experience an upturn, they often need to scale rapidly to meet increased demand. Having a continuity plan in place allows for a smoother transition during periods of growth, ensuring that the infrastructure, resources and workforce can adapt effectively.
The financial consequences of not having a business continuity plan can be devastating. Without a plan in place, businesses are more vulnerable to unexpected disruptions, which can result in significant financial losses. These losses may come from increased downtime, lost revenue, legal liabilities, reputational damage and the costs associated with recovery efforts.
Considerations for Business Continuity Planning
Creating a robust business continuity plan is a complex task that involves a multitude of factors. Among these considerations, three key aspects stand out: cultural differences, limited resources and alignment with business objectives. A successful business strategy plan takes these factors into account to ensure that an organization can effectively respond to disruptions while maintaining its core values and strategic direction.
1. Cultural Differences
Cultural diversity is a significant consideration in business strategy planning, especially for multinational companies or organizations with a diverse workforce. Cultural differences can influence how employees perceive and respond to crises. When developing a business continuity plan, it is important to consider the following aspects:
- Communication Styles : Different cultures have varying communication norms and hierarchies. Understanding how employees from various cultural backgrounds communicate during a crisis can help in crafting effective crisis communication strategies.
- Decision-Making Processes : Some cultures prioritize consensus-driven decision-making, while others lean towards hierarchical authority. A business continuity plan should acknowledge these differences and provide flexibility in decision-making approaches during disruptions.
- Crisis Response Expectations : Cultural expectations can shape how employees expect the organization to respond to a crisis. Your business strategy plan should be sensitive to these expectations and ensure that response strategies align with cultural norms.
2. Limited Resources
For many businesses, resource constraints are a reality. When developing a business continuity plan, it’s crucial to consider the organization’s resource limitations, such as budget, personnel and technology. Here are some key considerations:
- Resource Allocation : Prioritize critical functions and allocate resources accordingly. Not all business processes are equally important, and a business continuity plan should identify and protect the most essential ones first.
- Efficiency and Scalability : Develop strategies that focus on efficiency and scalability. Efficient resource use is critical, and a business strategy plan should outline how to adapt to changing resource constraints during a crisis.
- Collaboration : Collaboration with external partners, such as suppliers, can be a resource-saving strategy. Establishing relationships with partners who can provide support during disruptions is a valuable aspect.
3. Business Objectives
A business continuity plan should align with the broader business objectives to ensure that it doesn’t hinder growth or innovation. Consider the following aspects:
- Market Expansion: If the organization’s objective is to expand into new markets, the business strategy plan should accommodate this goal. It should address the challenges and opportunities that come with market expansion, including regulatory compliance and logistical considerations.
- Relocation or Migration : If there are plans to relocate or migrate operations, the business continuity plan should include strategies for a seamless transition. This may involve considerations such as data migration, employee relocation and continuity of customer service.
- Competitive Landscape : Changes in the competitive landscape, such as the emergence of new competitors, can impact the organization’s continuity. The business strategy plan should be flexible enough to adapt to shifts in the competitive environment.
- The COVID-19 pandemic forced companies to adapt rapidly, with remote work becoming the norm for many, reshaping entire industries like healthcare and e-commerce.
- The global recession of 2008 had long-lasting effects on financial institutions and prompted regulatory changes that influenced business operations.
- The rise of the internet transformed countless businesses, from retail to media, and required adaptation to online platforms.
- Looking ahead, emerging technologies like artificial intelligence have the potential to disrupt industries in unprecedented ways, with automation and data-driven decision-making reshaping the future of work. These events emphasize the critical importance of adaptable and comprehensive business continuity planning to navigate the unpredictable landscape of our ever-evolving world.
Developing a Strategic Business Plan
A well structured business plan serves as a roadmap for your organization, guiding actions and decisions while enabling effective response to a dynamic business environment.
- Conduct a comprehensive assessment of the current state of the business.
- Review financial statements, market positioning and operational performance.
- Identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats.
- Evaluate the company’s internal resources and capabilities.
- Analyze micro-environment factors such as competitors, customers, suppliers and regulatory changes.
- Examine macro-environment factors like economic trends, technological advancements and political factors.
- Use tools like PESTEL analysis and Porter’s Five Forces to assess the external business environment.
- Clearly define short-term and long-term business objectives.
- Make objectives specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound (SMART).
- Align objectives with the company’s mission and vision.
- Identify key operational processes that drive business success.
- Evaluate the efficiency and effectiveness of these processes.
- Prioritize improvements in critical areas to align with strategic objectives.
- Plan for potential risks and uncertainties that could impact the business.
- Create contingency and crisis management strategies.
- Establish a risk management framework to mitigate and respond to unforeseen events.
- Implement key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress.
- Regularly review and revise the business plan based on changing market conditions.
- Adapt to emerging opportunities and challenges.
- Ensure that the strategic plan is communicated effectively throughout the organization.
- Secure buy-in and commitment from employees at all levels.
- Ensure that all team members understand their roles in achieving the plan’s objectives.
- Allocate resources, including finances and manpower, in alignment with the strategic priorities.
- Develop a budget that reflects the financial requirements of the plan.
- Monitor spending and adjust budgets as needed.
- Develop a timeline and action plan for the execution of the strategic initiatives.
- Assign responsibilities to specific teams or individuals.
- Regularly review progress and make adjustments to stay on track.
- Periodically evaluate the effectiveness of the strategic plan.
- Solicit feedback from employees, customers and stakeholders.
- Use feedback to make continuous improvements and refine the plan.
- Establish a system for measuring and reporting progress.
- Create dashboards or reports to communicate key metrics to stakeholders.
- Ensure that performance data aligns with the defined objectives.
- Incorporate sustainability and responsible growth practices into the plan.
- Address social and environmental impacts as part of corporate responsibility.
- Seek opportunities for sustainable growth and innovation.
- Develop scenarios that explore alternative future situations.
- Consider various outcomes and their implications on the business.
- Prepare for different scenarios to enhance adaptability.
- Leverage technology for data analytics, automation, and efficiency.
- Stay updated on emerging technologies that can support the strategic plan.
- Integrate technology solutions to enhance business processes.
Implementing a Business Continuity Plan

Importance of Training and Awareness:
- Awareness: Create awareness about the business continuity plan across the organization to foster a culture of preparedness. This includes educating employees on the potential risks and the importance of the plan.
Consistent Review of the Plan:
- Conduct post-incident reviews to assess the BCP’s performance after a real event and make necessary adjustments.
Address Cultural and Technological Issues:
- Technological Challenges: Recognize and mitigate technological hurdles that can hinder the plan’s execution, such as infrastructure limitations or cybersecurity threats. Ensure that IT systems are resilient and can support the plan.
Software Integration:
- Organizational design software like Orgvue can assist in visualizing and optimizing the organizational structure, enabling efficient allocation of resources and responsibilities during a disruption.
Business continuity planning is not merely a precaution but a strategic imperative for any organization. It provides a structured approach to safeguarding business operations in the face of unforeseen disruptions, thereby minimizing downtime and potential financial losses.
By fostering a culture of preparedness, training employees, regularly reviewing and adapting the plan, addressing cultural and technological issues, and leveraging software solutions like Orgvue for organizational design, businesses can ensure their resilience and adaptability in an ever-changing landscape.
For businesses with specific 1-5 year plans, the integration of business strategy planning is paramount. It aligns seamlessly with forward-looking strategies by fortifying the organization’s ability to execute those plans in the face of unexpected events.
By weaving business continuity considerations into your strategic framework, you not only protect your investments but also demonstrate your commitment to long-term success, customer trust and stakeholder confidence. The benefits of such foresight extend far beyond mitigating risk; they empower your business to thrive in an increasingly unpredictable world. Therefore, it is recommended that businesses of all sizes prioritize and integrate business continuity planning as an integral part of their strategic vision and ongoing operations.
Business Continuity Plan FAQs
● where does business continuity planning belong in an organization.
Depending on the organization’s culture, the department your business continuity plan falls under varies. IT is usually one of the most vital components of any business strategy plan, in which case it could belong under the IT department. Or, if financial impacts are your organization’s main concern, the finance department may need to run the plan.
● Who Is Responsible For the Business Continuity Plan?
The business continuity plan usually falls under the responsibility of a dedicated role or department, often led by a Business Continuity Manager, who reports to senior leadership. This individual or team is responsible for creating, implementing, and regularly updating the plan to ensure the organization’s resilience in the face of disruptions.
● Is Business Continuity Planning a Legal Requirement?
It is not always a legal requirement, but certain industries and jurisdictions may have regulations or standards that mandate organizations to have such plans in place to ensure operational resilience and preparedness for emergencies.
● What Role Can Business Continuity Planning Play In Recovering From an Incident?
It plays a crucial role in helping organizations recover from incidents by providing a structured framework to assess, respond to and mitigate the impact of disruptions, minimizing downtime and financial losses. It outlines clear procedures and responsibilities, ensuring that essential operations can resume swiftly and efficiently, thus safeguarding the organization’s reputation and maintaining stakeholder trust.
● When Should a Business Continuity Plan Be Activated?
A business continuity plan should be activated as a preventative measure in the event a disruptive incident occurs. Triggers may include natural disasters, cyberattacks, supply chain disruptions or any event that threatens the continuity of critical business functions.
Accelerate workforce transformation
Use Orgvue to streamline your organization.
Small Business Trends
What is a business continuity plan and can it benefit your business.

A big part of planning for small business success is a business continuity plan. This is the fallback position your business has when a natural disaster, power outage, or any one of a number of mishaps threatens your company’s ability to function.
Part of the initial planning for one of these important documents starts with understanding how vulnerable your small business might be if an emergency happens.
Here’s an insight from Mike Clayton, discussing the essentials of a Business Continuity Plan:
How to Get Started with a Business Continuity Plan

One of the first things that you will need to do is understand the natural disasters like floods and wildfires that can happen in your area. This is a good starting point so that you can tailor make a business continuity plan that reacts to any potential issues of this kind. Here’s a good starting point to better understand some of the risks.
Take Proactive Measure
Having one of these plans in place is a proactive measure. It is also motivational even if the disaster doesn’t strike because it shows your customers and shareholders as well as your employees that you are prepared.
Here’s some of the steps that you should work through with your small business to come up with a plan that will put everyone at ease.
Put an Emergency Team Together

Being ready for an emergency that can otherwise disrupt your business means having an emergency preparedness team in place. These are people that will be the foundation for how your business reacts and how operations will be able to continue.
Having this team in place means selecting some individuals or maybe a few managers who will be up to the task. They should have a thorough understanding of how your business works and these individuals all need to be reliable when it comes to decision-making.
If the whole idea was the brainchild of a committee in the first place, it’s a good idea to let them take charge although one person should lead the entire planning process.
Look at the Risks

Finding out where your company is vulnerable by looking at the risks and doing an assessment is the next step. One of the ways to approach this type of assessment is to take proactive steps for each disaster possibility.
In other words, it’s a good idea to be able to see any potential disruptions before they happen. There’s a National Weather Service that you can monitor and local services too. If you’re in a location where potential IT outages are an issue, assigning someone to monitor your network is a good idea.
If your business is near a body of water, making some flood preparations is a positive step.
Determine Essential Services
You’ll also need to be able to determine the essential services for your small business. Some of the things that your company does might need to satisfy regulatory requirements so they should be top priority. You might be in a business that makes goods or services that can impact the health and safety of your customers.
Your business may experience a disruption because of interruptions in power lines or communication. These are considered essential services because you need to keep them running so you will need to consider alternate sources like generators.
Indentify Major Customers

Even if your products and services don’t fit in those other categories, you’ll want to be able to earmark major customers that keep you afloat financially. Ticking off check marks next to your major clients so they are in the essential services category is a good idea.
Prepare an Action Plan
This is one of the foundations of your entire business continuity plan. It should start by describing the essential parts of your business that you identified in the previous step. Clearly mention the individuals in charge here.
It’s a good idea to have backups as well. This is the meat and potatoes of all planning that you’ve done. Everything needs to be covered here. This includes how you’re going to reallocate staff to keep things moving and what plans you have for using other sectors to keep the essential parts of your business up and running.
Any changes that you need to make with delivery models and business reporting are detailed here. An important part of any action plan lists contact information should you need to contract services including staffing and equipment.
Keep in mind you have a variety of software solutions that can help you by providing access to the cloud for disaster recovery.
Test and Train

Once you have a plan in place, you will need to test it and train the continuity team. By running through a few mock exercises, you see where the plan needs tweaking. It’s a good idea that you continue to test even when you get the plan to where you think it needs to be. Reviewing your plan quarterly is a good idea to stay on top of any changes that need to be implemented.
Table: Key Steps in Developing a Business Continuity Plan
This comparison table summarizes the key steps involved in developing a BCP from the previous list. It serves as a concise and informative reference for small business owners and entrepreneurs. The snapshot provides a quick overview, allowing small business owners to understand and compare different aspects of the planning process. It ensures you cover all essential areas to enhance your business’s resilience:
Reviewing and understanding each of these steps is essential for creating a robust and effective business continuity plan, capable of safeguarding your business against a range of potential disruptions.
Incorporating Technology and Digital Strategies into Your Business Continuity Plan
In today’s digital age, integrating technology and digital tools into your business continuity plan is a necessity. Why? For starters, this integration is paramount to enhancing resilience and operational continuity. These strategies not only ensure business stability during disruptions but also provide a competitive edge in rapidly changing scenarios.
Here are key aspects to consider:
- Leveraging Cloud Computing : Utilize cloud services to ensure data safety and accessibility. This approach enables remote work capabilities and maintains customer services during disasters.
- Utilizing Communication Tools : Implement digital communication tools to keep teams connected and operations running smoothly, especially in cases where physical office access is restricted.
- Implementing Cybersecurity Measures : Develop robust cybersecurity strategies to protect your business from increased risks during emergencies, such as phishing attacks or data breaches.
- Digital Training and Simulation : Use virtual training programs to prepare your team for various emergency scenarios, offering flexibility and ensuring everyone understands their role in the continuity plan.
- Automating Critical Processes : Automate essential operations to maintain continuity with minimal human intervention. This is particularly crucial for processes that are critical to business functioning.
- Data Analytics for Risk Assessment : Employ data analytics to predict potential threats and prepare accordingly. This proactive approach helps in refining the business continuity plan, making it more effective over time.
By incorporating these technological and digital strategies, your business continuity plan becomes more dynamic, adaptable, and equipped to handle the challenges of the modern business environment.
Find a Business Continuity Plan Template
Putting together a business continuity plan is easy if you can find a template and just fill in the blank spaces to tailor make it to suit your business. There are a series of excellent resources to help you with a small business plan including The National Fire Protection Association’s Standard on Continuity, Emergency and Crisis Management . Here’s another version you can download and customize for your small business.
Image: Depositphotos.com

You’ll need a business continuity plan along with a risk management plan so that you’ll know what to do in case disaster strikes.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
© Copyright 2003 - 2024, Small Business Trends LLC. All rights reserved. "Small Business Trends" is a registered trademark.
The Backbone of Resilient Organizations: Demystifying Business Continuity
What is business continuity.
No matter what business you’re in, unexpected disruptions can happen. Outages, natural disasters, supply chain failures, cyber incidents, equipment failures, and other physical and technical issues can all disrupt your ability to function and thrive.
To ensure your business is ready for unexpected events, you need to know what to do when things go wrong—and this is where business continuity comes in. Read on to learn more about business continuity, including disaster recovery, and what to include in your business continuity plan. Also, find out about business continuity management and business continuity solutions.
What is business continuity and why is it important?
Business continuity is an organization’s readiness to continue functioning during times of disruption. Business continuity is important because it reduces the potential impact of a disruption on customers, employees, and partners.
Having a business continuity plan (BCP)—which includes the analysis, technology, documentation, training, key team members, and procedures involved in resolving potential crisis situations—is vital for ensuring business continuity. A BCP includes goals focused on minimizing the potential impact of a crisis on a company’s financials and reputation—and maintaining industry, regional, and global compliance standards and regulations.
What’s the difference between business continuity and disaster recovery?
While business continuity and disaster recovery are often used interchangeably, they’re not the same thing.
Disaster recovery is a key part of a business continuity plan and is focused specifically on systems, data, and IT infrastructures. It includes technology, strategies, and processes for saving, restoring, and recovering data and protecting against cyber threats.
For a BCP to be successful in reducing downtime, mitigating risks, and remediating issues like data loss and corruption, disaster recovery measures are crucial. While both involve processes, people, and technology, business continuity offers a much wider scope to encompass the steps necessary for maintaining operations across every part of a business.
What should be included in a business continuity plan?
There are three components of a business continuity plan to consider:
- Resilience—developing business functions and infrastructures to be prepared for an unexpected situation.
- Recovery—setting up backup and recovery solutions for your applications, systems, and networks; determining what systems should be prioritized in the event of a disaster; and choosing a third-party vendor for additional help and resources if necessary.
- Contingency—creating steps for what to do if a disruption occurs. This includes setting up a chain of command with key people and defining their responsibilities when it comes to communication, technology, third-party contracting, and coordinating temporary spaces. Keep these in mind at every step in the planning process to help ensure your BCP covers the full scope of your business.
With these three key components in mind, take the following steps to start building your business continuity plan:
- Run a business impact analysis (BIA), which examines your current business functions, processes, and technology. An analysis will uncover potential vulnerabilities, risks, and threats you might encounter. Doing so helps identify areas of improvement and what to prioritize. After an analysis, you may consider making additional technology investments as well.
- Outline and assign responsibilities for who will delegate, act, and support in the event of a crisis. These individuals will execute any necessary steps, be points of contact, gather resources, and guide efforts to minimize downtime for affected business functions.
- Determine alternative forms of communication in case your standard means of communication are impacted by an outage or downtime.
- Prepare backup equipment in case of damage or outages to prevent business-critical functions from stopping.
- Understand and follow business continuity standards, which are legal and regulatory requirements determined for an industry. These are helpful when determining what steps you need to take in scenarios such as a breach or data loss. Creating a plan isn’t the last step—to make business continuity an important part of your organization, you also need business continuity management.
What is business continuity management?
Business continuity management includes the processes you put in place to set up and maintain your business continuity plan. It should include the following:
- Creating policies that define the scope, objectives, and principles of business continuity. These should always keep the customer in mind to ensure you’ve documented what business-critical functions may impact customers and who is involved in customer service communication in the event of an outage or disruption.
- Assembling business continuity teams throughout your organization who can communicate and enforce policies and procedures that are put in place. These employees will take part in ongoing reviews and tests to make sure everything and everyone is properly prepared for an incident.
- Supporting a culture of business continuity by educating your entire organization about risks, policies, and documentation available. Offering ongoing training is an important way to increase awareness and gather data to see if there are any gaps or areas in need of improvement.
- Maintaining up-to-date compliance standards and best practices to make sure your processes, workflows, and employees all work within the correct industry standards as they relate to data. If a business doesn’t keep up and an unexpected disruption occurs, there’s the risk of increased financial damages, legal costs, and fines.
Keeping track of all the continuously developing parts of a business continuity plan can be daunting for a growing organization. To reduce the time and effort involved, many businesses invest in business continuity solutions.
What kind of business continuity solutions should I consider?
The business continuity solutions you choose should be based on your organization’s needs. Depending on the industry you’re in, the size of your company, and your business-critical functions, you’ll find a range of software and resources available. These options include:
- Cloud-based storage solutions, which provide a secure, remote location to back up and run workflows and applications, as well as store data. If there’s a breach or error causing data loss, you can access what you need from the cloud.
- Backup and recovery tools for making copies of the data, applications, and systems within your IT infrastructure. If anything is deleted, corrupted, or shut down during a disruption, you can restore them and minimize downtime. These solutions offer different options for running backups, including automatically on a schedule, instantly, or as needed.
- Virtualization tools that replicate environments and workspaces. If there’s an outage or device issues, employees can still access their applications and run processes as normal, reducing downtime that may affect services.
- Contracts with third-party providers, such as disaster-recovery-as-a-service (DRaaS) and backup-as-a-service. Based on your agreement, a provider can run data backups, host your IT infrastructure, and offer support in the event of a disaster. These services are typically offered with a subscription or a pay-as-you-use model and include support from IT and cybersecurity experts.
- Unified communication tools to support collaboration across your entire organization. With one platform for connecting frontline workers, customer service agents, and other key members of your continuity teams, it’s easier to keep everyone up to date on disruptions and manage shifts and schedules to make sure the right people are available.
Business continuity should be a priority for any growing business looking to ensure the safety and security of their employees, technology, and data. To support the planning process, there are several solutions available to make business continuity planning easier. Though you can’t predict or prevent every disruption, with the right tools, a solid plan, and an educated team, business continuity can save you time, money, and resources across your organization.
Learn more • Developing your business continuity plan • Business continuity and disaster recovery
About the author

Get started with Microsoft 365
It’s the Office you know, plus the tools to help you work better together, so you can get more done—anytime, anywhere.
Business Insights and Ideas does not constitute professional tax or financial advice. You should contact your own tax or financial professional to discuss your situation..
- Skip to content
- Skip to search
- Skip to footer
What Is Business Continuity?

Business continuity is an organization's ability to maintain or quickly resume acceptable levels of product or service delivery following a short-term event that disrupts normal operations. Examples of disruptions range from natural disasters to power outages.
- Watch video (1:14)
- Business continuity
Contact Cisco
- Get a call from Sales
Call Sales:
- 1-800-553-6387
- US/CAN | 5am-5pm PT
- Product / Technical Support
- Training & Certification
Is business continuity the same as business resilience or disaster recovery?
Business continuity, disaster recovery, and business resilience are not the same, but they are related.
- Business continuity is a process-driven approach to maintaining operations in the event of an unplanned disruption such as a cyber attack or natural disaster. Business continuity planning covers the entire business—processes, assets, workers, and more. It isn't focused solely on IT infrastructure and business systems.
- Business resilience encompasses crisis management and business continuity. It requires a response to all types of risk that an organization may face. An organization that is business resilient is essentially in a constant state of "expecting the unexpected." It means continuously preparing to meet disruptions head-on, including events of extended duration that may affect more than one facility or region.
- Disaster recovery focuses specifically on how to restore an enterprise's IT infrastructure and business systems following a disruption. It is considered an element of business continuity. A business continuity plan (BCP) might contain several disaster recovery plans, for example.
What is a business continuity strategy?
A business continuity strategy is a summary of the mitigation, crisis, and recovery plans to be implemented after a disruption to resume normal operations. "Business continuity strategy" is often used interchangeably with "business continuity plan." Both consider the broader goals, legal and regulatory requirements, personnel, and even the business's clients and partners.
What does a business continuity plan mitigate?
A relevant and well-tested BCP can help ease the negative impacts of an unexpected business disruption in many ways.
- Financial impact: Disruptions to product supply chains and critical services to customers can directly affect sales and revenue. Downtime caused by unplanned disruptions can also result in higher costs for a business as it looks to repair operations and mitigate previously unidentified threats.
- Reputation and brand impact: Failure to resume operations quickly and supply customers with the products or services they expect can prompt customer defections and tarnish the brand. Damage to reputation can in turn cause investors and capital sources to pull back funding, exacerbating the financial impact of a business disruption.
- Regulatory impact: Customers and vendors are likely to complain when businesses fail to respond appropriately to disruptions, which may result in regulatory scrutiny or even censure. In highly-regulated industries, such as energy and financial services, business continuity planning is mandatory to ensure regulatory compliance.
Business continuity planning activities
A well-crafted and tested BCP can go a long way toward helping a business recover swiftly from a disruption. These are key steps a business may want to take.
Identifying critical business areas and functions
Business continuity planning begins with identifying an organization's key business areas and the critical functions within those areas. A business needs to determine and document the acceptable downtime for each area and function considered vital to operations. Then a plan to restore operations can be established, documented, and communicated.
Analyzing risks, threats, and potential impacts
Creating appropriate response scenarios requires knowing what disruptions the business could experience. An upfront analysis of risks and threats is necessary in order to prepare contingency responses to events. Organizations can also conduct a back-end analysis after an event to gather metrics and assess lessons learned. This information can drive improvements in how the business responds to disruptions.
Outlining and assigning responsibilities
A BCP details which personnel will be responsible for implementing specific aspects of the plan. It also identifies key decision-makers and a chain of command. The plan should include alternative options in case primary personnel are incapacitated or unavailable to respond to the disruption.
Defining and documenting alternatives
A business continuity plan should define and document alternative communication strategies in case telephone services or the internet are down. Enterprises should also have alternatives for mission-critical spaces such as data centers or manufacturing facilities in case buildings are damaged.
Assessing the need for critical backups
Essential equipment may be damaged or unavailable during a disruptive event. A business should consider whether it has access to backup equipment and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) during extended power outages. Business-critical data needs to be backed up regularly, and is mandatory in many regulated industries.
Testing, training, and communication
Business continuity plans need to be tested to ensure they will be effective. (Disaster recovery plans should be tested as well.) A best practice is to conduct a plan review at least quarterly with leadership and key team members who are responsible for executing the plan.
Many companies use role-playing sessions, simulations, and other types of exercises several times per year to test their BCPs. This approach helps to identify gaps, develop strategies for improvement, and determine if more resources are needed. Targeted staff training and communicating to the whole workforce the benefits of having a business continuity plan are also vital to its success.
Related products and solutions
- Cisco Webex Contact Center
- Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI)
- Cisco Intersight Workload Optimizer
- AppDynamics Application Performance Management
- ThousandEyes End User Monitoring
- ThousandEyes Endpoint Agents
You may also like…
- Cisco’s Business Resiliency Strategy
- Business Continuity Blogs
- Business Continuity Planning

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Glossary of Terms. Business Continuity (BC) Professional An experienced individual with responsibilities for practicing and/or managing business continuity. BCI Business Continuity Management Program(me) Ongoing management and governance process supported by Top Management and appropriately resourced to implement and maintain business continuity
Business Continuity Planning - BCP: The business continuity planning (BCP) is the creation of a strategy through the recognition of threats and risks facing a company, with an eye to ensure that ...
Business Continuity Plan Owner: The individual responsible for the overall continuity of a business unit, organization, or specific technology components within their department who acts as a liaison with other teams and outside service providers; this person ensures that the plan is effective, comprehensive, and sufficient to meet the organization's recovery objectives
1. Operational. Operational continuity means that the systems and processes your business relies on are able to continue functioning without disruption. As these processes are critical to business operations, it's important to have a plan in place in case disruption occurs so you can minimize the loss of revenue. 2.
A Business Continuity Plan (BCP) defines the activities to respond to a specific disruptive situation, as well as to resume and recover a service or process from the disruption. Meanwhile, a Crisis Management Plan is a set of business-oriented activities (e.g., evaluation of business impacts, declaration of emergency/crisis/disaster, press ...
Business continuity planning (BCP) refers to the work a company does to create a plan and system to deal with risks. Thorough planning seeks to prevent problems and ensure business processes continue during and after a crisis. Business continuity planning ensures that the company deals with disruptions quickly, and minimizes the impact on operations.
Business Continuity Training Part 3: Planning Process Step 2. The second of six steps addressed in this Business Continuity Training, which detail the process of building a business continuity plan. This step addresses how organizations should "define" their business continuity plan objectives. View on YouTube.
A business continuity plan (BCP) is a document that consists of the critical information an organization needs to continue operating during an unplanned event. The BCP states the essential functions of the business, identifies which systems and processes must be sustained, and details how to maintain them.
The absence of a business continuity plan can lead to a domino effect of negative outcomes, including a tarnished reputation and the potential loss of future business. Stakeholders remember how a company responds in a crisis, and a well-executed BCP can be the difference between a temporary setback and a long-term impact on the company's ...
A business continuity plan (BCP) is a strategic playbook created to help an organization maintain or quickly resume business functions in the face of disruption, whether that disruption is caused ...
Welcome to the Definitive Guide to Business Continuity Planning—the indispensable resource for developing your business continuity plan. This handbook can be used to guide you in developing a BC plan from start to finish, or as a tool to test and improve your existing plan, or for anything in between.
The Agility Glossary for Business Continuity is created by our subject matter experts to collect and store definitions for terms used in the business continuity industry. This page is regularly updated to promote a common set of universal terms and to create consistency throughout multiple resources. To keep a business running smoothly, you ...
Create the procedures. Get the word out. Iterate and improve. 1. Analyze your company. In this phase you conduct an analysis to identify critical activities, determine which activities must continue, which can be temporarily paused, and which can operate at a reduced capacity.
A business continuity plan is a risk management strategy that a business implements to protect its operations in the face of an unexpected event or disruption such as a natural disaster, cyberattack, or technological failure. By anticipating and preparing for potential crises or unplanned eventualities, businesses can take preemptive measures ...
Here are the basics of a state-of-the-art disaster recovery/business continuity (DR/BC) plan for 2021 and beyond. (Without getting too hung up on definitions, let's say that disaster recovery is ...
ISO 22301 Simplified Cheat-Sheet. Use this simplified cheat-sheet to understand the basic elements of creating a business continuity plan. The template walks you through the process of determining critical aspects of your organization, writing the recovery plan, and exercising the plan to ensure proficiency.
business continuity plan documented information (3.11) that guides an organization (3.21) to respond to a disruption (3.10) and resume, recover and restore the delivery of products and services (3.27) consistent with its business continuity (3.3) objectives (3.20)
What is a business continuity plan? Like DRPs, business continuity plans (BCPs) play a critical role in disaster recovery and help organizations return to normal business functions when a disaster happens. ... In terms of BCDR planning, every business is going to have its own unique set of needs. Here are a few examples of plans that are ...
A business continuity plan considers unpredictable events and potential threats, such as natural disasters, fires, disease outbreaks, pandemics, supply chain disruptions, cyber attacks and other external threats. A business continuity strategy is important for organizations of any size, but it might not be practical for any but the largest ...
Business continuity planning is the key to ensuring a company's sustained operation, regardless of the challenges it may face. Business continuity planning goes beyond the traditional business plan. While a business plan outlines goals and strategies for growth, a continuity plan focuses on how the organization will continue to function in ...
Business continuity planning (BCP) is a broad disaster recovery approach whereby enterprises plan for recovery of the entire business process. This includes a plan for workspaces, telephones, workstations, servers, applications, network connections and any other resources required in the business process.
3. Share on BizSugar. A big part of planning for small business success is a business continuity plan. This is the fallback position your business has when a natural disaster, power outage, or any one of a number of mishaps threatens your company's ability to function. Part of the initial planning for one of these important documents starts ...
Business continuity is an organization's readiness to continue functioning during times of disruption. Business continuity is important because it reduces the potential impact of a disruption on customers, employees, and partners. Having a business continuity plan (BCP)—which includes the analysis, technology, documentation, training, key ...
A business continuity strategy is a summary of the mitigation, crisis, and recovery plans to be implemented after a disruption to resume normal operations. "Business continuity strategy" is often used interchangeably with "business continuity plan." Both consider the broader goals, legal and regulatory requirements, personnel, and even the ...