- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
- Research Papers

How to Write and Publish Your Research in a Journal
Last Updated: February 26, 2024 Fact Checked
Choosing a Journal
Writing the research paper, editing & revising your paper, submitting your paper, navigating the peer review process, research paper help.
This article was co-authored by Matthew Snipp, PhD and by wikiHow staff writer, Cheyenne Main . C. Matthew Snipp is the Burnet C. and Mildred Finley Wohlford Professor of Humanities and Sciences in the Department of Sociology at Stanford University. He is also the Director for the Institute for Research in the Social Science’s Secure Data Center. He has been a Research Fellow at the U.S. Bureau of the Census and a Fellow at the Center for Advanced Study in the Behavioral Sciences. He has published 3 books and over 70 articles and book chapters on demography, economic development, poverty and unemployment. He is also currently serving on the National Institute of Child Health and Development’s Population Science Subcommittee. He holds a Ph.D. in Sociology from the University of Wisconsin—Madison. There are 13 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 696,661 times.
Publishing a research paper in a peer-reviewed journal allows you to network with other scholars, get your name and work into circulation, and further refine your ideas and research. Before submitting your paper, make sure it reflects all the work you’ve done and have several people read over it and make comments. Keep reading to learn how you can choose a journal, prepare your work for publication, submit it, and revise it after you get a response back.
Things You Should Know
- Create a list of journals you’d like to publish your work in and choose one that best aligns with your topic and your desired audience.
- Prepare your manuscript using the journal’s requirements and ask at least 2 professors or supervisors to review your paper.
- Write a cover letter that “sells” your manuscript, says how your research adds to your field and explains why you chose the specific journal you’re submitting to.

- Ask your professors or supervisors for well-respected journals that they’ve had good experiences publishing with and that they read regularly.
- Many journals also only accept specific formats, so by choosing a journal before you start, you can write your article to their specifications and increase your chances of being accepted.
- If you’ve already written a paper you’d like to publish, consider whether your research directly relates to a hot topic or area of research in the journals you’re looking into.

- Review the journal’s peer review policies and submission process to see if you’re comfortable creating or adjusting your work according to their standards.
- Open-access journals can increase your readership because anyone can access them.

- Scientific research papers: Instead of a “thesis,” you might write a “research objective” instead. This is where you state the purpose of your research.
- “This paper explores how George Washington’s experiences as a young officer may have shaped his views during difficult circumstances as a commanding officer.”
- “This paper contends that George Washington’s experiences as a young officer on the 1750s Pennsylvania frontier directly impacted his relationship with his Continental Army troops during the harsh winter at Valley Forge.”

- Scientific research papers: Include a “materials and methods” section with the step-by-step process you followed and the materials you used. [5] X Research source
- Read other research papers in your field to see how they’re written. Their format, writing style, subject matter, and vocabulary can help guide your own paper. [6] X Research source

- If you’re writing about George Washington’s experiences as a young officer, you might emphasize how this research changes our perspective of the first president of the U.S.
- Link this section to your thesis or research objective.
- If you’re writing a paper about ADHD, you might discuss other applications for your research.

- Scientific research papers: You might include your research and/or analytical methods, your main findings or results, and the significance or implications of your research.
- Try to get as many people as you can to read over your abstract and provide feedback before you submit your paper to a journal.

- They might also provide templates to help you structure your manuscript according to their specific guidelines. [11] X Research source

- Not all journal reviewers will be experts on your specific topic, so a non-expert “outsider’s perspective” can be valuable.

- If you have a paper on the purification of wastewater with fungi, you might use both the words “fungi” and “mushrooms.”
- Use software like iThenticate, Turnitin, or PlagScan to check for similarities between the submitted article and published material available online. [15] X Research source

- Header: Address the editor who will be reviewing your manuscript by their name, include the date of submission, and the journal you are submitting to.
- First paragraph: Include the title of your manuscript, the type of paper it is (like review, research, or case study), and the research question you wanted to answer and why.
- Second paragraph: Explain what was done in your research, your main findings, and why they are significant to your field.
- Third paragraph: Explain why the journal’s readers would be interested in your work and why your results are important to your field.
- Conclusion: State the author(s) and any journal requirements that your work complies with (like ethical standards”).
- “We confirm that this manuscript has not been published elsewhere and is not under consideration by another journal.”
- “All authors have approved the manuscript and agree with its submission to [insert the name of the target journal].”

- Submit your article to only one journal at a time.
- When submitting online, use your university email account. This connects you with a scholarly institution, which can add credibility to your work.

- Accept: Only minor adjustments are needed, based on the provided feedback by the reviewers. A first submission will rarely be accepted without any changes needed.
- Revise and Resubmit: Changes are needed before publication can be considered, but the journal is still very interested in your work.
- Reject and Resubmit: Extensive revisions are needed. Your work may not be acceptable for this journal, but they might also accept it if significant changes are made.
- Reject: The paper isn’t and won’t be suitable for this publication, but that doesn’t mean it might not work for another journal.

- Try organizing the reviewer comments by how easy it is to address them. That way, you can break your revisions down into more manageable parts.
- If you disagree with a comment made by a reviewer, try to provide an evidence-based explanation when you resubmit your paper.

- If you’re resubmitting your paper to the same journal, include a point-by-point response paper that talks about how you addressed all of the reviewers’ comments in your revision. [22] X Research source
- If you’re not sure which journal to submit to next, you might be able to ask the journal editor which publications they recommend.

Expert Q&A
You might also like.

- If reviewers suspect that your submitted manuscript plagiarizes another work, they may refer to a Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE) flowchart to see how to move forward. [23] X Research source Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

- ↑ https://www.wiley.com/en-us/network/publishing/research-publishing/choosing-a-journal/6-steps-to-choosing-the-right-journal-for-your-research-infographic
- ↑ https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s13187-020-01751-z
- ↑ https://libguides.unomaha.edu/c.php?g=100510&p=651627
- ↑ http://www.canberra.edu.au/library/start-your-research/research_help/publishing-research
- ↑ https://writingcenter.fas.harvard.edu/conclusions
- ↑ https://writing.wisc.edu/handbook/assignments/writing-an-abstract-for-your-research-paper/
- ↑ https://www.springer.com/gp/authors-editors/book-authors-editors/your-publication-journey/manuscript-preparation
- ↑ https://apus.libanswers.com/writing/faq/2391
- ↑ https://academicguides.waldenu.edu/library/keyword/search-strategy
- ↑ https://ifis.libguides.com/journal-publishing-guide/submitting-your-paper
- ↑ https://www.springer.com/kr/authors-editors/authorandreviewertutorials/submitting-to-a-journal-and-peer-review/cover-letters/10285574
- ↑ http://www.apa.org/monitor/sep02/publish.aspx
- ↑ Matthew Snipp, PhD. Research Fellow, U.S. Bureau of the Census. Expert Interview. 26 March 2020.
About This Article

To publish a research paper, ask a colleague or professor to review your paper and give you feedback. Once you've revised your work, familiarize yourself with different academic journals so that you can choose the publication that best suits your paper. Make sure to look at the "Author's Guide" so you can format your paper according to the guidelines for that publication. Then, submit your paper and don't get discouraged if it is not accepted right away. You may need to revise your paper and try again. To learn about the different responses you might get from journals, see our reviewer's explanation below. Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
RAMDEV GOHIL
Oct 16, 2017
Did this article help you?
David Okandeji
Oct 23, 2019
Revati Joshi
Feb 13, 2017
Shahzad Khan
Jul 1, 2017
Apr 7, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
Editorial Manager, our manuscript submissions site will be unavailable between 12pm April 5, 2024 and 12pm April 8 2024 (Pacific Standard Time). We apologize for any inconvenience this may cause.
When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
Understanding the Publishing Process

What’s happening with my paper? The publication process explained
The path to publication can be unsettling when you’re unsure what’s happening with your paper. Learn about staple journal workflows to see the detailed steps required for ensuring a rigorous and ethical publication.
Your team has prepared the paper, written a cover letter and completed the submission form. From here, it can sometimes feel like a waiting game while the journal has your paper. It can be unclear exactly who is currently handling your paper as most individuals are only involved in a few steps of the overall process. Journals are responsible for overseeing the peer review, publication and archival process: editors, reviewers, technical editors, production staff and other internal staff all have their roles in ensuring submissions meet rigorous scientific and ethical reporting standards.
Read on for an inside look at how a conventional peer-reviewed journal helps authors transform their initial submission to a certified publication.
Note that the description below is based on the process at PLOS journals. It is likely that at other journals, various roles (e.g. technical editor) may in fact also be played by the editor, and some journals may not have journal staff at all, with all roles played by volunteer academics. As such, please consider the processes and waypoints, rather than who performs them, as the key information.

Internal Checks on New Submissions
Estimated time: 10 days.
When a journal first receives your submission, there are typically two separate checks to confirm that the paper is appropriate and ready for peer review:
- Technical check. Performed by a technical editor to ensure that the submission has been properly completed and is ready for further assessment. Blurry figures, missing ethical statements, and incomplete author affiliations are common issues that are addressed at this initial stage. Typically, there are three technical checks: upon initial submission, alongside the first decision letter, and upon acceptance.
- Editorial screening . Once a paper passes the first check, an editor with subject expertise assesses the paper and determines whether it is within the journal’s scope and if it could potentially meet the required publication criteria. While there may be requests for further information and minor edits from the author as needed, the paper will either be desk rejected by the editor or allowed to proceed to peer review.
Both editors at this point will additionally make notes for items to be followed-up on at later stages. The publication process involves finding a careful balance for when each check occurs. Early checks need to be thorough so that editors with relevant expertise can focus on the scientific content and more advanced reporting standards, but no one wants to be asked to reformat references only to have their paper desk rejected a few days later.
Peer Review
Estimated time: 1 month.
Depending on the journal’s editorial structure, the editor who performed the initial assessment may also oversee peer review or another editor with more specific expertise may be assigned. Regardless of the journal’s specific process, the various roles and responsibilities during peer review include:
When you have questions or are unsure who your manuscripts is currently with, reach out to the journal staff for help (eg. [email protected]). They will be your lifeline, connecting you to all the other contributors working to assess the manuscript.
Whether an editor needs a reminder that all reviews are complete or a reviewer has asked for an extension, the journal acts as a central hub of communication for those involved with the publication process. As editors and reviewers are used to hearing from journal staff about their duties, any messages you send to the journal can be forwarded to them with proper context and instructions on how to proceed appropriately. Additionally, journal staff will be able to inform you of any delays, such as reviewer availability during summer and holiday periods.
Revision Decision
Estimated time: 1 day.
Editors evaluate peer reviewer feedback and their own expert assessment of the manuscript to reach a decision. After your editor submits a decision on your manuscript, the journal may review it before formally processing the decision and sending it on to you.
A technical editor may scan the manuscript and the review comments to ensure that journal standards have been followed. At this stage, the technical editor will also add requests to ensure the paper, if published, will adhere to journal requirements for data sharing, copyright, ethical reporting and the like.
Performing the second technical check at this stage and adding the journal requirements to the decision letter ultimately saves time by allowing authors to resolve the journal’s queries while making revisions based on comments from the reviewers.
Revised Submission Received
Estimated time: 3 days.
Upon receiving your revised submission, a technical editor will assess the revisions to confirm that the requests from the journal have been properly addressed. Before the paper is returned to the editor for their consideration, the journal needs to be confident that the paper won’t have any issues related to the metadata and reporting standards that could prevent publication. The editor may contact you to resolve any serious issues, though minor items can wait until the paper is accepted.
Subsequent Peer Review
Estimated time: 2 weeks, highly variable.
When your resubmitted paper has passed the required checks, it’ll be assigned back to the same editor who handled it during the first round of peer review. At this point, your paper has gone through two sets of journal checks and one round of peer review. If all has gone well so far, the paper should feel quite solid both in terms of scientific content and proper reporting standards.
When the editor receives your revised paper, they are asked to check if all reviewer comments have been adequately addressed and if the paper now adheres to the journal’s publication criteria. Depending on the situation, some editors may feel confident making this decision based on their own expertise while others may re-invite the previous reviewers for their opinions.
Individual responsibilities are the same as the initial round of peer review, but it is generally expected that later stages of peer review proceed quicker unless new concerns have been introduced as part of the revision.
Preliminary Acceptance
Estimated time: 1 week.
Your editor is satisfied with the scientific quality of your work and has chosen to accept it in principle. Before it can proceed to production and typesetting, the journal office will perform it’s third and final technical check, requesting any formatting changes or additional details that may be required.
When fulfilling these final journal requests, double check the final files to confirm all information is correct. If you need to make changes beyond those specifically required in the decision letter, inform the journal and explain why you made the unrequested changes. Any change that could affect the scientific meaning of the work will need to be approved by the handling editor. While including your rationale for the changes will help avoid delays, if there are extensive changes made at this point the paper may need to go through another round of formal review.
Formal Acceptance and Publication
Estimated time: 2 weeks.
After a technical editor has confirmed that all requests from the provisional acceptance letter have been addressed, you will receive your formal acceptance letter. This letter indicates that your paper is being passed from the Editorial department to the production department—that all information has been editorially approved. The scientific content has been approved through peer review, and the journal’s publication requirements have been met.
Congratulations to you and your co-authors! Your article will be available as soon as the journal transforms the submission into a typeset, consistently structured scientific manuscript, ready to be read and cited by your peers.
The contents of the Peer Review Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
The contents of the Writing Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher…

Explore millions of high-quality primary sources and images from around the world, including artworks, maps, photographs, and more.
Explore migration issues through a variety of media types
- Part of The Streets are Talking: Public Forms of Creative Expression from Around the World
- Part of The Journal of Economic Perspectives, Vol. 34, No. 1 (Winter 2020)
- Part of Cato Institute (Aug. 3, 2021)
- Part of University of California Press
- Part of Open: Smithsonian National Museum of African American History & Culture
- Part of Indiana Journal of Global Legal Studies, Vol. 19, No. 1 (Winter 2012)
- Part of R Street Institute (Nov. 1, 2020)
- Part of Leuven University Press
- Part of UN Secretary-General Papers: Ban Ki-moon (2007-2016)
- Part of Perspectives on Terrorism, Vol. 12, No. 4 (August 2018)
- Part of Leveraging Lives: Serbia and Illegal Tunisian Migration to Europe, Carnegie Endowment for International Peace (Mar. 1, 2023)
- Part of UCL Press
Harness the power of visual materials—explore more than 3 million images now on JSTOR.
Enhance your scholarly research with underground newspapers, magazines, and journals.
Explore collections in the arts, sciences, and literature from the world’s leading museums, archives, and scholars.
How to Write and Publish a Research Paper for a Peer-Reviewed Journal
- Open access
- Published: 30 April 2020
- Volume 36 , pages 909–913, ( 2021 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article
- Clara Busse ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0178-1000 1 &
- Ella August ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5151-1036 1 , 2
265k Accesses
15 Citations
705 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Communicating research findings is an essential step in the research process. Often, peer-reviewed journals are the forum for such communication, yet many researchers are never taught how to write a publishable scientific paper. In this article, we explain the basic structure of a scientific paper and describe the information that should be included in each section. We also identify common pitfalls for each section and recommend strategies to avoid them. Further, we give advice about target journal selection and authorship. In the online resource 1 , we provide an example of a high-quality scientific paper, with annotations identifying the elements we describe in this article.
Similar content being viewed by others

Literature reviews as independent studies: guidelines for academic practice
Sascha Kraus, Matthias Breier, … João J. Ferreira

Plagiarism in research
Gert Helgesson & Stefan Eriksson
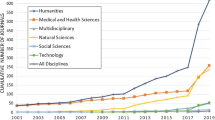
Open peer review: promoting transparency in open science
Dietmar Wolfram, Peiling Wang, … Hyoungjoo Park
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Writing a scientific paper is an important component of the research process, yet researchers often receive little formal training in scientific writing. This is especially true in low-resource settings. In this article, we explain why choosing a target journal is important, give advice about authorship, provide a basic structure for writing each section of a scientific paper, and describe common pitfalls and recommendations for each section. In the online resource 1 , we also include an annotated journal article that identifies the key elements and writing approaches that we detail here. Before you begin your research, make sure you have ethical clearance from all relevant ethical review boards.
Select a Target Journal Early in the Writing Process
We recommend that you select a “target journal” early in the writing process; a “target journal” is the journal to which you plan to submit your paper. Each journal has a set of core readers and you should tailor your writing to this readership. For example, if you plan to submit a manuscript about vaping during pregnancy to a pregnancy-focused journal, you will need to explain what vaping is because readers of this journal may not have a background in this topic. However, if you were to submit that same article to a tobacco journal, you would not need to provide as much background information about vaping.
Information about a journal’s core readership can be found on its website, usually in a section called “About this journal” or something similar. For example, the Journal of Cancer Education presents such information on the “Aims and Scope” page of its website, which can be found here: https://www.springer.com/journal/13187/aims-and-scope .
Peer reviewer guidelines from your target journal are an additional resource that can help you tailor your writing to the journal and provide additional advice about crafting an effective article [ 1 ]. These are not always available, but it is worth a quick web search to find out.
Identify Author Roles Early in the Process
Early in the writing process, identify authors, determine the order of authors, and discuss the responsibilities of each author. Standard author responsibilities have been identified by The International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) [ 2 ]. To set clear expectations about each team member’s responsibilities and prevent errors in communication, we also suggest outlining more detailed roles, such as who will draft each section of the manuscript, write the abstract, submit the paper electronically, serve as corresponding author, and write the cover letter. It is best to formalize this agreement in writing after discussing it, circulating the document to the author team for approval. We suggest creating a title page on which all authors are listed in the agreed-upon order. It may be necessary to adjust authorship roles and order during the development of the paper. If a new author order is agreed upon, be sure to update the title page in the manuscript draft.
In the case where multiple papers will result from a single study, authors should discuss who will author each paper. Additionally, authors should agree on a deadline for each paper and the lead author should take responsibility for producing an initial draft by this deadline.
Structure of the Introduction Section
The introduction section should be approximately three to five paragraphs in length. Look at examples from your target journal to decide the appropriate length. This section should include the elements shown in Fig. 1 . Begin with a general context, narrowing to the specific focus of the paper. Include five main elements: why your research is important, what is already known about the topic, the “gap” or what is not yet known about the topic, why it is important to learn the new information that your research adds, and the specific research aim(s) that your paper addresses. Your research aim should address the gap you identified. Be sure to add enough background information to enable readers to understand your study. Table 1 provides common introduction section pitfalls and recommendations for addressing them.

The main elements of the introduction section of an original research article. Often, the elements overlap
Methods Section
The purpose of the methods section is twofold: to explain how the study was done in enough detail to enable its replication and to provide enough contextual detail to enable readers to understand and interpret the results. In general, the essential elements of a methods section are the following: a description of the setting and participants, the study design and timing, the recruitment and sampling, the data collection process, the dataset, the dependent and independent variables, the covariates, the analytic approach for each research objective, and the ethical approval. The hallmark of an exemplary methods section is the justification of why each method was used. Table 2 provides common methods section pitfalls and recommendations for addressing them.
Results Section
The focus of the results section should be associations, or lack thereof, rather than statistical tests. Two considerations should guide your writing here. First, the results should present answers to each part of the research aim. Second, return to the methods section to ensure that the analysis and variables for each result have been explained.
Begin the results section by describing the number of participants in the final sample and details such as the number who were approached to participate, the proportion who were eligible and who enrolled, and the number of participants who dropped out. The next part of the results should describe the participant characteristics. After that, you may organize your results by the aim or by putting the most exciting results first. Do not forget to report your non-significant associations. These are still findings.
Tables and figures capture the reader’s attention and efficiently communicate your main findings [ 3 ]. Each table and figure should have a clear message and should complement, rather than repeat, the text. Tables and figures should communicate all salient details necessary for a reader to understand the findings without consulting the text. Include information on comparisons and tests, as well as information about the sample and timing of the study in the title, legend, or in a footnote. Note that figures are often more visually interesting than tables, so if it is feasible to make a figure, make a figure. To avoid confusing the reader, either avoid abbreviations in tables and figures, or define them in a footnote. Note that there should not be citations in the results section and you should not interpret results here. Table 3 provides common results section pitfalls and recommendations for addressing them.
Discussion Section
Opposite the introduction section, the discussion should take the form of a right-side-up triangle beginning with interpretation of your results and moving to general implications (Fig. 2 ). This section typically begins with a restatement of the main findings, which can usually be accomplished with a few carefully-crafted sentences.
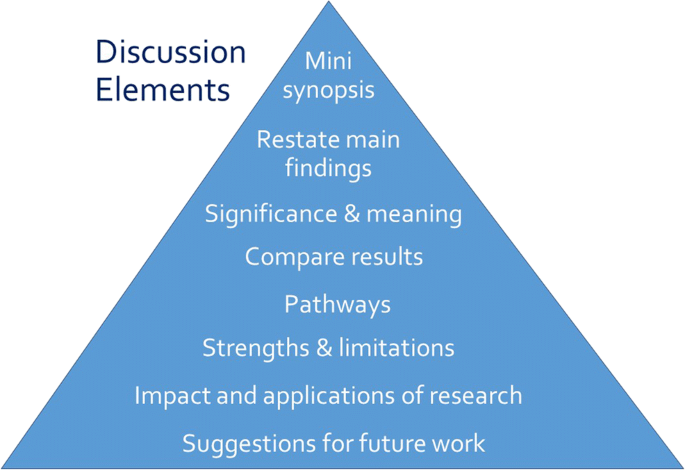
Major elements of the discussion section of an original research article. Often, the elements overlap
Next, interpret the meaning or explain the significance of your results, lifting the reader’s gaze from the study’s specific findings to more general applications. Then, compare these study findings with other research. Are these findings in agreement or disagreement with those from other studies? Does this study impart additional nuance to well-accepted theories? Situate your findings within the broader context of scientific literature, then explain the pathways or mechanisms that might give rise to, or explain, the results.
Journals vary in their approach to strengths and limitations sections: some are embedded paragraphs within the discussion section, while some mandate separate section headings. Keep in mind that every study has strengths and limitations. Candidly reporting yours helps readers to correctly interpret your research findings.
The next element of the discussion is a summary of the potential impacts and applications of the research. Should these results be used to optimally design an intervention? Does the work have implications for clinical protocols or public policy? These considerations will help the reader to further grasp the possible impacts of the presented work.
Finally, the discussion should conclude with specific suggestions for future work. Here, you have an opportunity to illuminate specific gaps in the literature that compel further study. Avoid the phrase “future research is necessary” because the recommendation is too general to be helpful to readers. Instead, provide substantive and specific recommendations for future studies. Table 4 provides common discussion section pitfalls and recommendations for addressing them.
Follow the Journal’s Author Guidelines
After you select a target journal, identify the journal’s author guidelines to guide the formatting of your manuscript and references. Author guidelines will often (but not always) include instructions for titles, cover letters, and other components of a manuscript submission. Read the guidelines carefully. If you do not follow the guidelines, your article will be sent back to you.
Finally, do not submit your paper to more than one journal at a time. Even if this is not explicitly stated in the author guidelines of your target journal, it is considered inappropriate and unprofessional.
Your title should invite readers to continue reading beyond the first page [ 4 , 5 ]. It should be informative and interesting. Consider describing the independent and dependent variables, the population and setting, the study design, the timing, and even the main result in your title. Because the focus of the paper can change as you write and revise, we recommend you wait until you have finished writing your paper before composing the title.
Be sure that the title is useful for potential readers searching for your topic. The keywords you select should complement those in your title to maximize the likelihood that a researcher will find your paper through a database search. Avoid using abbreviations in your title unless they are very well known, such as SNP, because it is more likely that someone will use a complete word rather than an abbreviation as a search term to help readers find your paper.
After you have written a complete draft, use the checklist (Fig. 3 ) below to guide your revisions and editing. Additional resources are available on writing the abstract and citing references [ 5 ]. When you feel that your work is ready, ask a trusted colleague or two to read the work and provide informal feedback. The box below provides a checklist that summarizes the key points offered in this article.

Checklist for manuscript quality
Data Availability
Michalek AM (2014) Down the rabbit hole…advice to reviewers. J Cancer Educ 29:4–5
Article Google Scholar
International Committee of Medical Journal Editors. Defining the role of authors and contributors: who is an author? http://www.icmje.org/recommendations/browse/roles-and-responsibilities/defining-the-role-of-authosrs-and-contributors.html . Accessed 15 January, 2020
Vetto JT (2014) Short and sweet: a short course on concise medical writing. J Cancer Educ 29(1):194–195
Brett M, Kording K (2017) Ten simple rules for structuring papers. PLoS ComputBiol. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005619
Lang TA (2017) Writing a better research article. J Public Health Emerg. https://doi.org/10.21037/jphe.2017.11.06
Download references
Acknowledgments
Ella August is grateful to the Sustainable Sciences Institute for mentoring her in training researchers on writing and publishing their research.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Maternal and Child Health, University of North Carolina Gillings School of Global Public Health, 135 Dauer Dr, 27599, Chapel Hill, NC, USA
Clara Busse & Ella August
Department of Epidemiology, University of Michigan School of Public Health, 1415 Washington Heights, Ann Arbor, MI, 48109-2029, USA
Ella August
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Ella August .
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interests.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
(PDF 362 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Busse, C., August, E. How to Write and Publish a Research Paper for a Peer-Reviewed Journal. J Canc Educ 36 , 909–913 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13187-020-01751-z
Download citation
Published : 30 April 2020
Issue Date : October 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s13187-020-01751-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Manuscripts
- Scientific writing
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research paper
- Research Paper Format | APA, MLA, & Chicago Templates
Research Paper Format | APA, MLA, & Chicago Templates
Published on November 19, 2022 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on January 20, 2023.
The formatting of a research paper is different depending on which style guide you’re following. In addition to citations , APA, MLA, and Chicago provide format guidelines for things like font choices, page layout, format of headings and the format of the reference page.
Scribbr offers free Microsoft Word templates for the most common formats. Simply download and get started on your paper.
APA | MLA | Chicago author-date | Chicago notes & bibliography
- Generate an automatic table of contents
- Generate a list of tables and figures
- Ensure consistent paragraph formatting
- Insert page numbering
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Formatting an apa paper, formatting an mla paper, formatting a chicago paper, frequently asked questions about research paper formatting.
The main guidelines for formatting a paper in APA Style are as follows:
- Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman or 11 pt Arial.
- Set 1 inch page margins.
- Apply double line spacing.
- If submitting for publication, insert a APA running head on every page.
- Indent every new paragraph ½ inch.
Watch the video below for a quick guide to setting up the format in Google Docs.
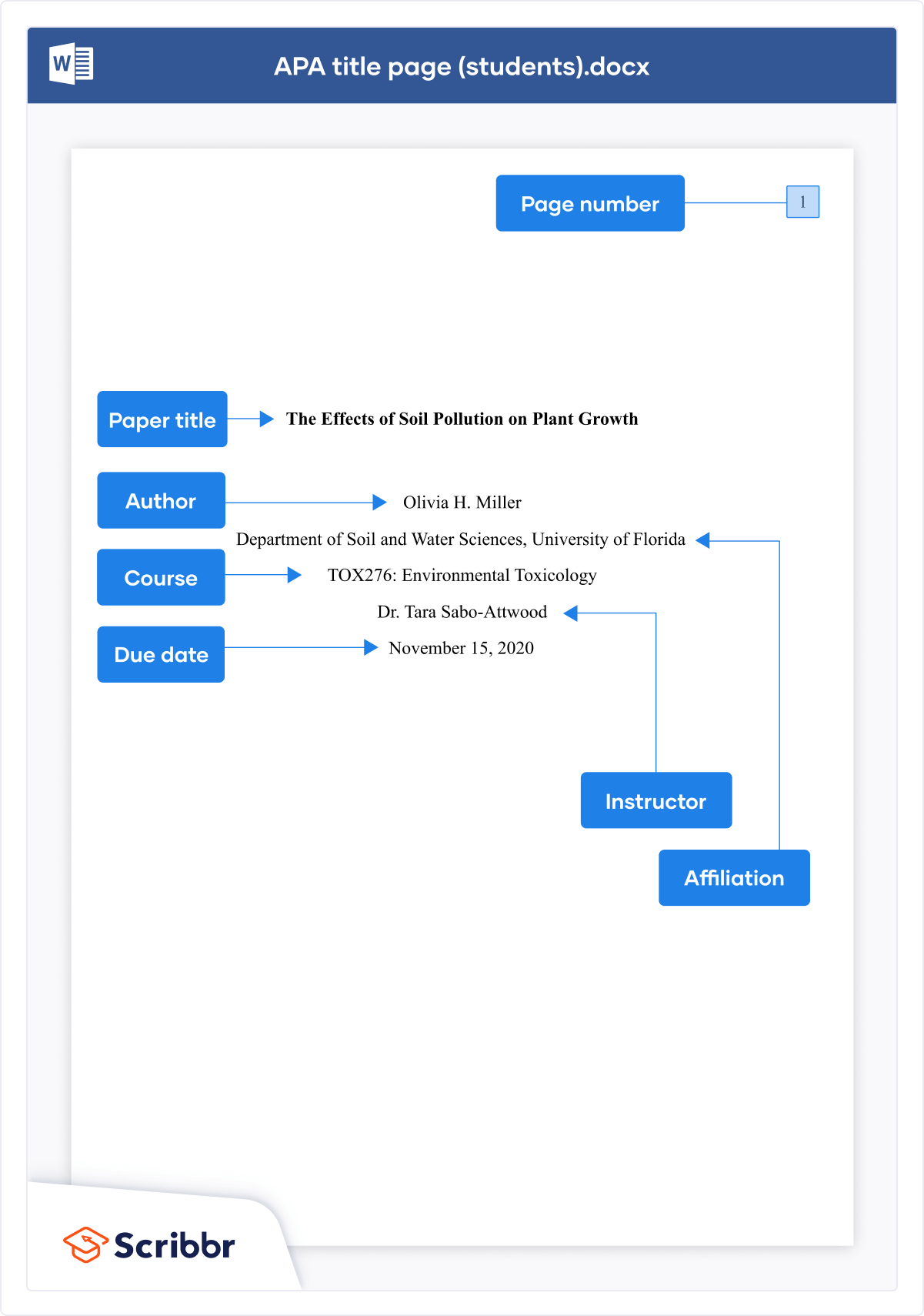
The image below shows how to format an APA Style title page for a student paper.
Running head
If you are submitting a paper for publication, APA requires you to include a running head on each page. The image below shows you how this should be formatted.
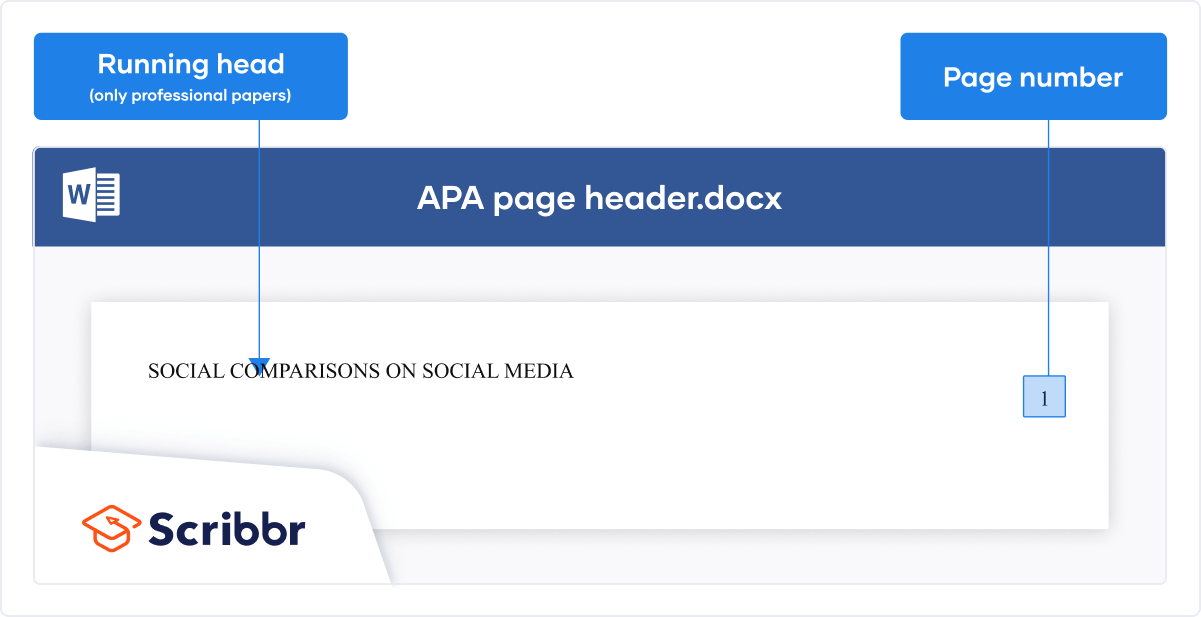
For student papers, no running head is required unless you have been instructed to include one.
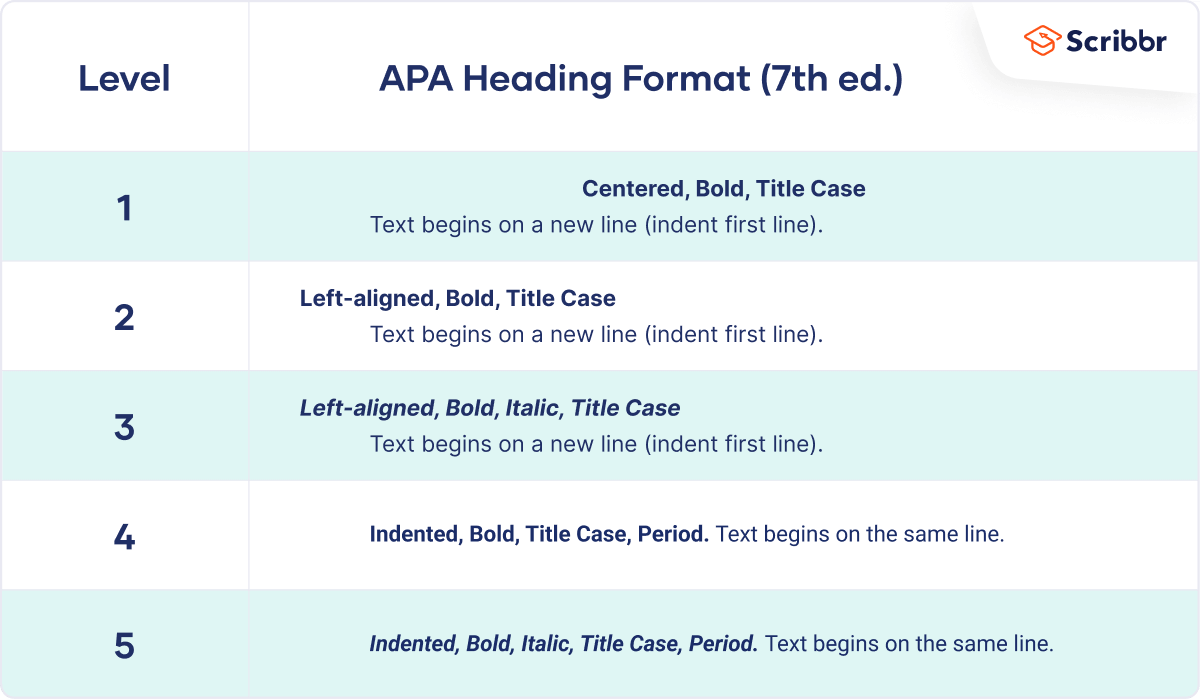
APA provides guidelines for formatting up to five levels of heading within your paper. Level 1 headings are the most general, level 5 the most specific.
Reference page
APA Style citation requires (author-date) APA in-text citations throughout the text and an APA Style reference page at the end. The image below shows how the reference page should be formatted.
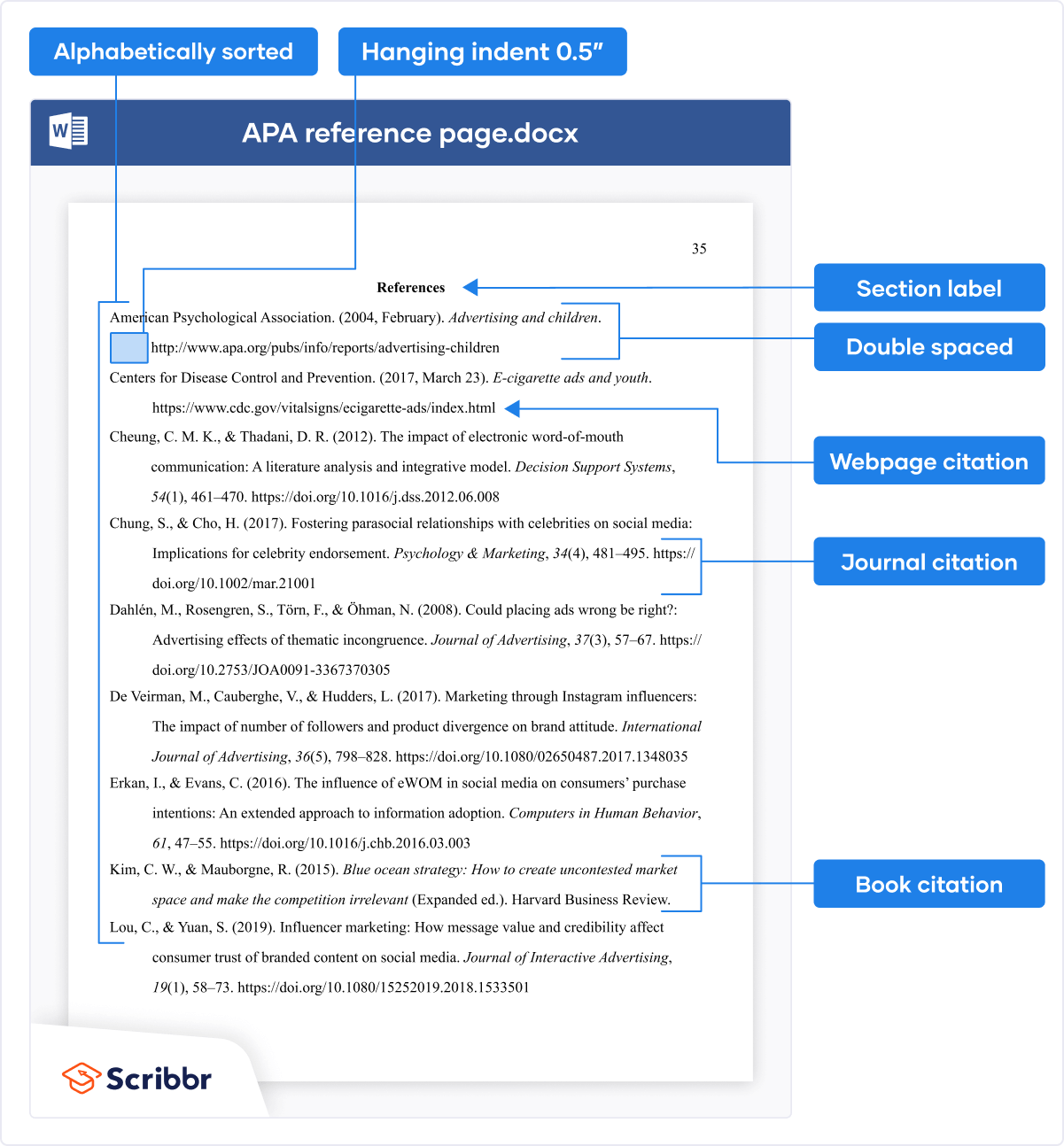
Note that the format of reference entries is different depending on the source type. You can easily create your citations and reference list using the free APA Citation Generator.
Generate APA citations for free
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
The main guidelines for writing an MLA style paper are as follows:
- Use an easily readable font like 12 pt Times New Roman.
- Use title case capitalization for headings .
Check out the video below to see how to set up the format in Google Docs.
On the first page of an MLA paper, a heading appears above your title, featuring some key information:
- Your full name
- Your instructor’s or supervisor’s name
- The course name or number
- The due date of the assignment
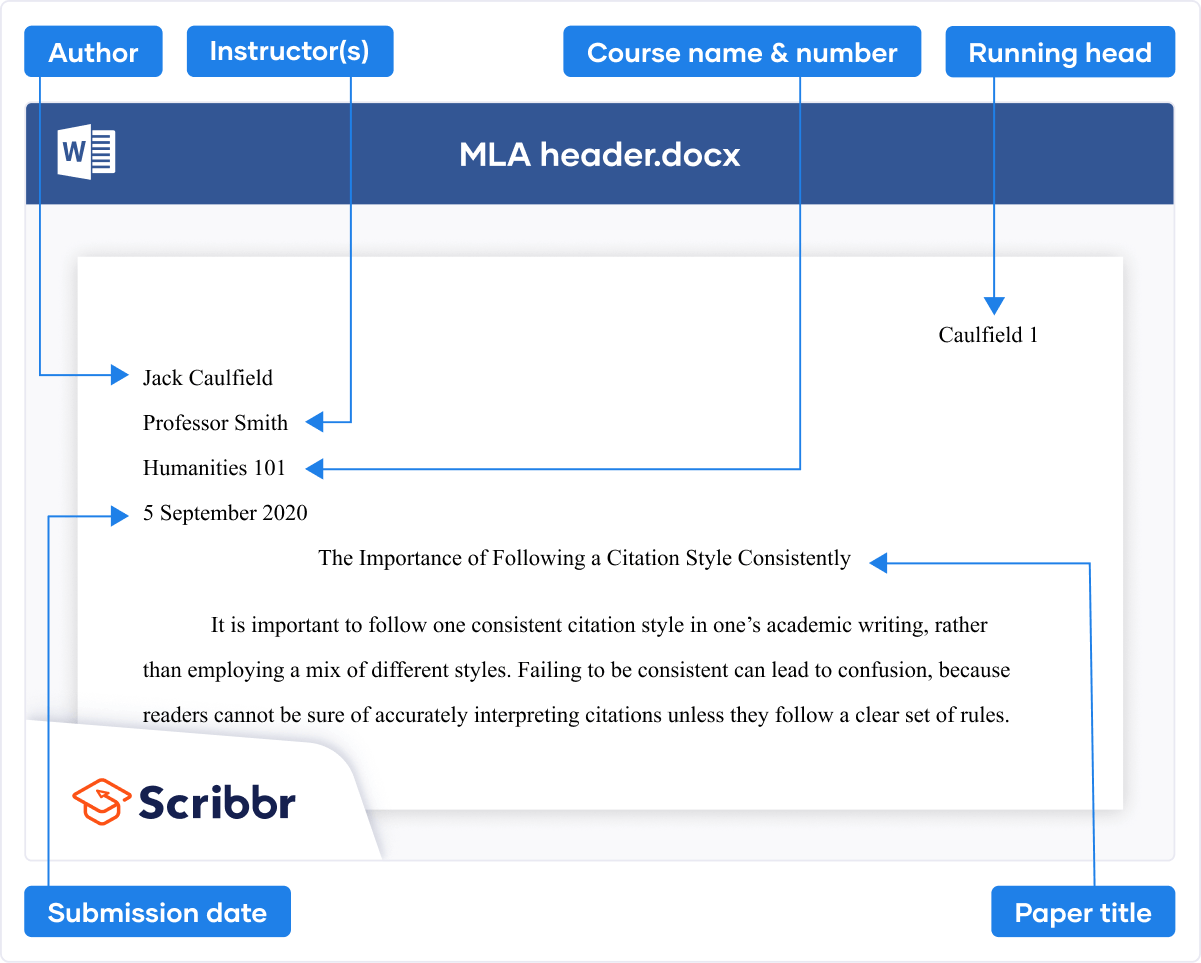
Page header
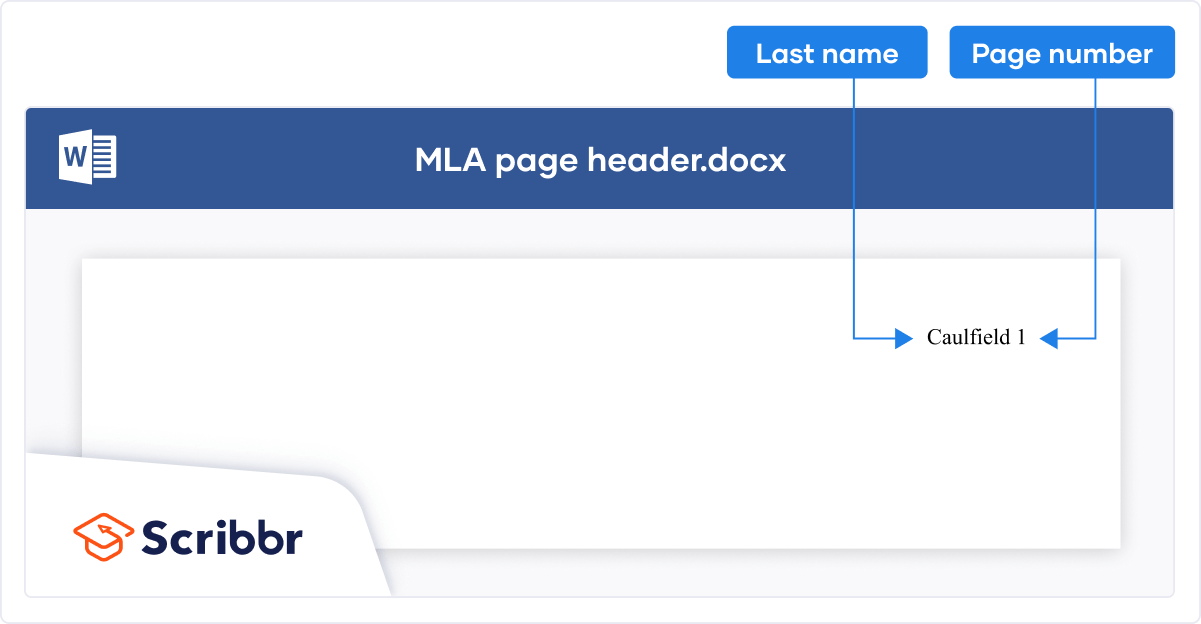
A header appears at the top of each page in your paper, including your surname and the page number.
Works Cited page
MLA in-text citations appear wherever you refer to a source in your text. The MLA Works Cited page appears at the end of your text, listing all the sources used. It is formatted as shown below.
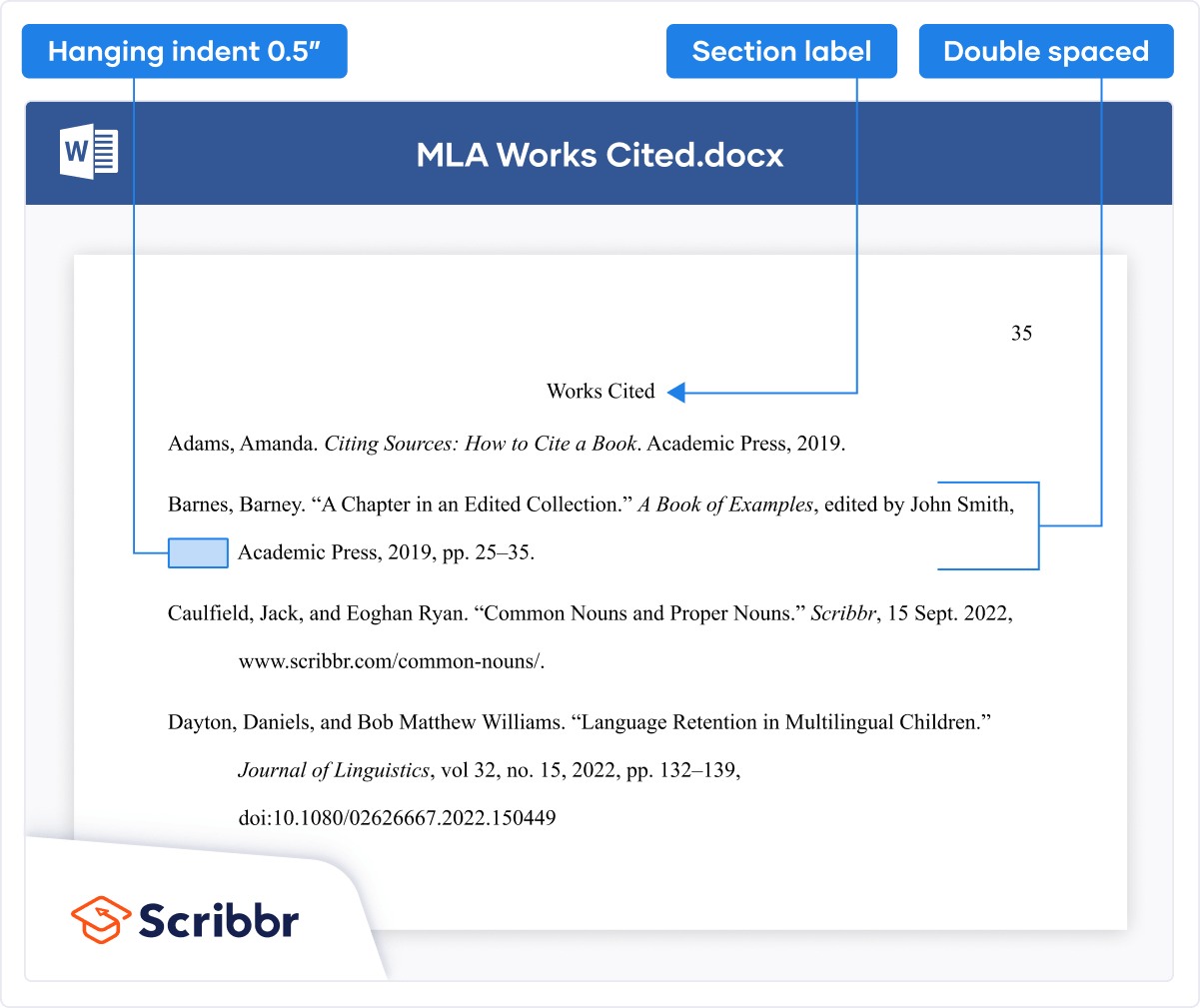
You can easily create your MLA citations and save your Works Cited list with the free MLA Citation Generator.
Generate MLA citations for free
The main guidelines for writing a paper in Chicago style (also known as Turabian style) are:
- Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman.
- Use 1 inch margins or larger.
- Place page numbers in the top right or bottom center.
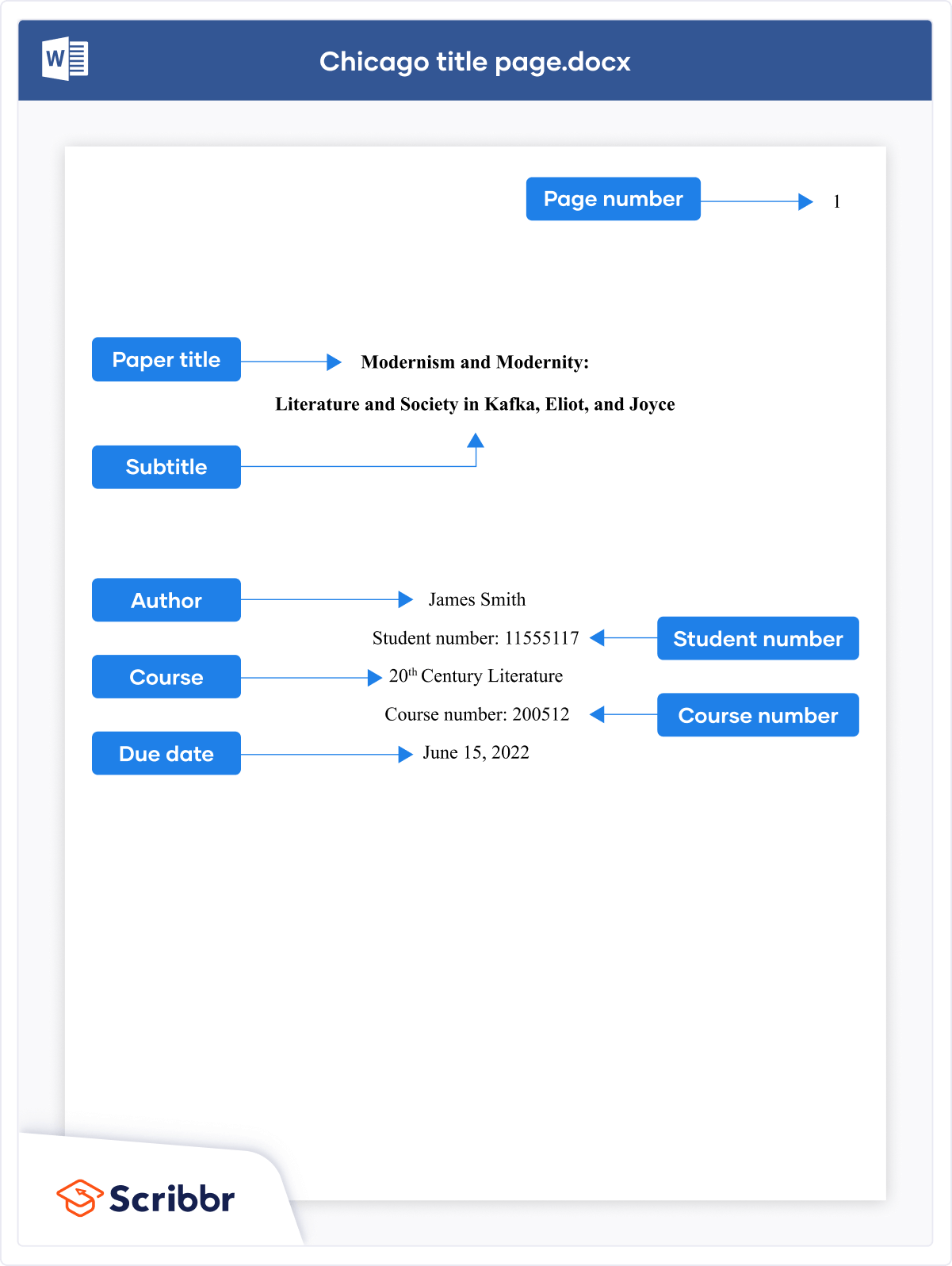
Chicago doesn’t require a title page , but if you want to include one, Turabian (based on Chicago) presents some guidelines. Lay out the title page as shown below.
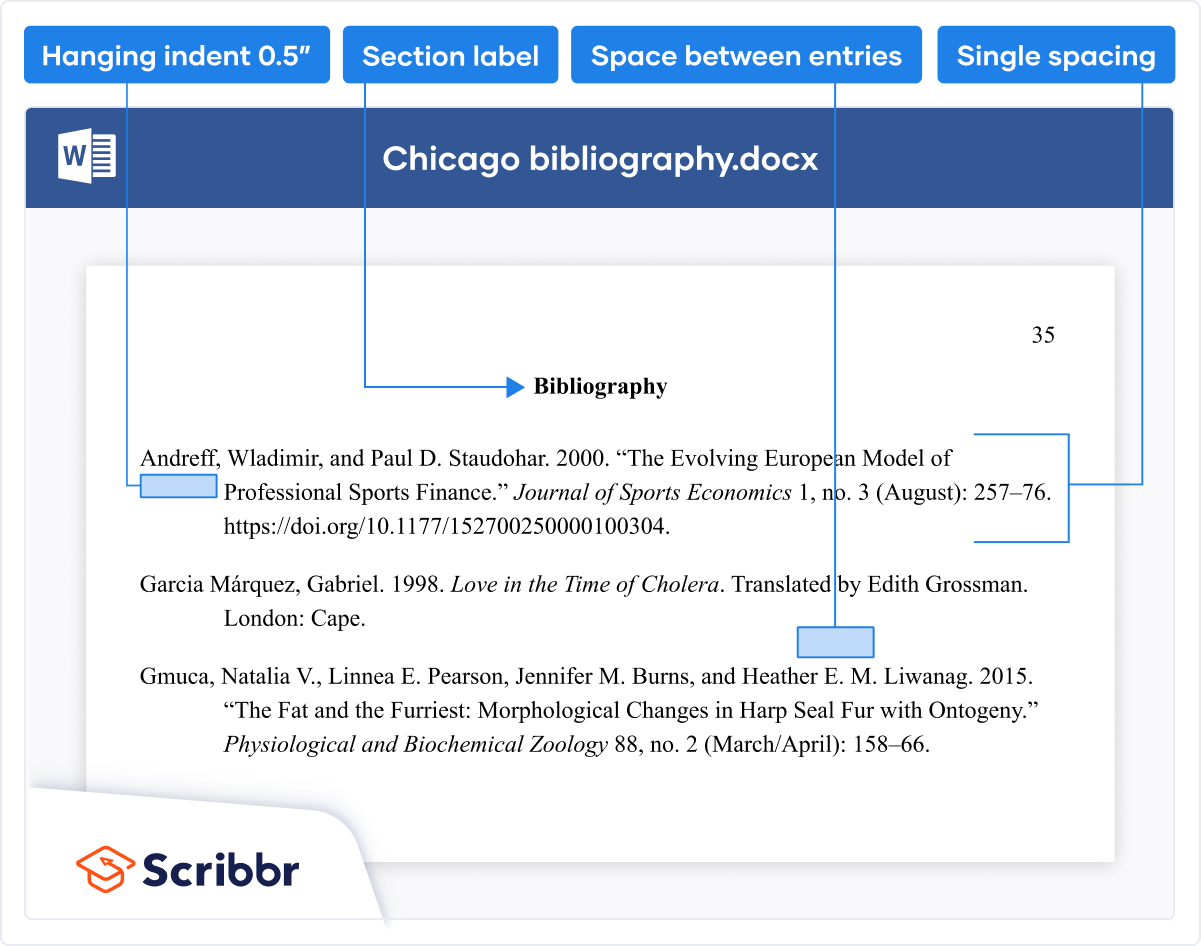
Bibliography or reference list
Chicago offers two citation styles : author-date citations plus a reference list, or footnote citations plus a bibliography. Choose one style or the other and use it consistently.
The reference list or bibliography appears at the end of the paper. Both styles present this page similarly in terms of formatting, as shown below.
To format a paper in APA Style , follow these guidelines:
- Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman or 11 pt Arial
- Set 1 inch page margins
- Apply double line spacing
- Include a title page
- If submitting for publication, insert a running head on every page
- Indent every new paragraph ½ inch
- Apply APA heading styles
- Cite your sources with APA in-text citations
- List all sources cited on a reference page at the end
The main guidelines for formatting a paper in MLA style are as follows:
- Use an easily readable font like 12 pt Times New Roman
- Include a four-line MLA heading on the first page
- Center the paper’s title
- Use title case capitalization for headings
- Cite your sources with MLA in-text citations
- List all sources cited on a Works Cited page at the end
The main guidelines for formatting a paper in Chicago style are to:
- Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman
- Use 1 inch margins or larger
- Place page numbers in the top right or bottom center
- Cite your sources with author-date citations or Chicago footnotes
- Include a bibliography or reference list
To automatically generate accurate Chicago references, you can use Scribbr’s free Chicago reference generator .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, January 20). Research Paper Format | APA, MLA, & Chicago Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved April 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-paper/research-paper-format/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, apa format for academic papers and essays, mla format for academic papers and essays, chicago style format for papers | requirements & examples, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Journals By Subject | Journals A - Z
Architecture / Design
Biomedicine, business and management, computer science, earth sciences, engineering, environment, life sciences, materials science, mathematics, medicine & public health, science, humanities and social sciences, multidisciplinary, social sciences.
Browse article collections by subject.
- Built Heritage
- Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology
- Future Business Journal
- International Journal of Corporate Social Responsibility
- Journal of Innovation and Entrepreneurship
- Journal of Shipping and Trade
- Schmalenbach Journal of Business Research
- Applied Biological Chemistry
- Bioresources and Bioprocessing
- Fashion and Textiles
- Journal of Analytical Science and Technology
- Journal of Umm Al-Qura University for Applied Sciences
- Applied Network Science
- Brain Informatics
- Cybersecurity
- Energy Informatics
- EPJ Data Science
- International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education
- Journal of Big Data
- Journal of Cloud Computing
- Visual Computing for Industry, Biomedicine, and Art
- International Journal of Implant Dentistry
- Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Progress in Orthodontics
- Earth, Planets and Space
- Geoscience Letters
- Geothermal Energy
- Progress in Earth and Planetary Science
- Swiss Journal of Geosciences
- Swiss Journal of Palaeontology
- Agricultural and Food Economics
- Financial Innovation
- Journal for Labour Market Research
- Journal of Economic Structures
- Marine Development
- Swiss Journal of Economics and Statistics
- Asian-Pacific Journal of Second and Foreign Language Education
- Disciplinary and Interdisciplinary Science Education Research
- Empirical Research in Vocational Education and Training
- International Journal of Child Care and Education Policy
- International Journal of STEM Education
- Language Testing in Asia
- Large-scale Assessments in Education
- Smart Learning Environments
- Sustainable Energy Research
- Advanced Modeling and Simulation in Engineering Sciences
- Advances in Aerodynamics
- Advances in Bridge Engineering
- AI Perspectives & Advances
- Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering
- EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing
- EURASIP Journal on Audio, Speech, and Music Processing
- EURASIP Journal on Image and Video Processing
- EURASIP Journal on Information Security
- EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking
- European Transport Research Review
- International Journal of Concrete Structures and Materials
- Journal of Electrical Systems and Information Technology
- Journal of Engineering and Applied Science
- Journal of Infrastructure Preservation and Resilience
- Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Engineering
- Journal of Umm Al-Qura University for Engineering and Architecture
- Micro and Nano Systems Letters
- Moore and More
- ROBOMECH Journal
- Satellite Navigation
- Ecological Processes
- Environmental Sciences Europe
- Environmental Systems Research
- Geoenvironmental Disasters
- City, Territory and Architecture
- European Journal of Futures Research
- Journal of International Humanitarian Action
- AMB Express
- Animal Cognition
- Botanical Studies
- Cell Regeneration
- Chemical and Biological Technologies in Agriculture
- Crop Health
- Egyptian Journal of Biological Pest Control
- Fire Ecology
- Horticulture Advances
- Journal of Wood Science
- Natural Products and Bioprospecting
- The Journal of Basic and Applied Zoology
- Applied Microscopy
- Collagen and Leather
- Functional Composite Materials
- Heritage Science
- Journal of Materials Science: Materials Theory
- Microplastics and Nanoplastics
- Nano Convergence
- Advances in Continuous and Discrete Models
- Boundary Value Problems
- Fixed Point Theory and Algorithms for Sciences and Engineering
- Journal of Inequalities and Applications
- Journal of Mathematics in Industry
- African Journal of Urology
- Annals of Intensive Care
- Beni-Suef University Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences
- Blood Research
- Bulletin of Faculty of Physical Therapy
- Clinical Phytoscience
- CVIR Endovascular Open peer review
- Egyptian Journal of Forensic Sciences
- Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics
- Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery
- Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine
- Egyptian Liver Journal
- Egyptian Pediatric Association Gazette
- Egyptian Rheumatology and Rehabilitation
- EJNMMI Physics
- EJNMMI Radiopharmacy and Chemistry
- EJNMMI Reports
- EJNMMI Research
- European Radiology Experimental
- Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences
- Insights into Imaging
- Intensive Care Medicine Experimental
- International Journal of Bipolar Disorders
- JA Clinical Reports
- Journal of Ophthalmic Inflammation and Infection
- Journal of Orthopaedics and Traumatology
- Journal of Patient-Reported Outcomes
- Journal of the Egyptian National Cancer Institute
- Journal of the Egyptian Public Health Association
- Middle East Current Psychiatry
- Middle East Fertility Society Journal
- Molecular and Cellular Pediatrics
- Sports Medicine - Open
- The Cardiothoracic Surgeon
- The Egyptian Heart Journal
- The Egyptian Journal of Bronchology
- The Egyptian Journal of Internal Medicine
- The Egyptian Journal of Neurology, Psychiatry and Neurosurgery
- The Egyptian Journal of Otolaryngology
- The Ultrasound Journal
- eLight Transparent peer review
- EPJ Quantum Technology
- EPJ Techniques and Instrumentation
- Surface Science and Technology
- Cognitive Research: Principles and Implications
- Psicologia: Reflexão e Crítica
- Bulletin of the National Research Centre
- Comparative Migration Studies
- International Journal of Anthropology and Ethnology
- The Journal of Chinese Sociology
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Paper
Definition:
Research Paper is a written document that presents the author’s original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue.
It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new knowledge or insights to a particular field of study, and to demonstrate the author’s understanding of the existing literature and theories related to the topic.

Structure of Research Paper
The structure of a research paper typically follows a standard format, consisting of several sections that convey specific information about the research study. The following is a detailed explanation of the structure of a research paper:
The title page contains the title of the paper, the name(s) of the author(s), and the affiliation(s) of the author(s). It also includes the date of submission and possibly, the name of the journal or conference where the paper is to be published.
The abstract is a brief summary of the research paper, typically ranging from 100 to 250 words. It should include the research question, the methods used, the key findings, and the implications of the results. The abstract should be written in a concise and clear manner to allow readers to quickly grasp the essence of the research.
Introduction
The introduction section of a research paper provides background information about the research problem, the research question, and the research objectives. It also outlines the significance of the research, the research gap that it aims to fill, and the approach taken to address the research question. Finally, the introduction section ends with a clear statement of the research hypothesis or research question.
Literature Review
The literature review section of a research paper provides an overview of the existing literature on the topic of study. It includes a critical analysis and synthesis of the literature, highlighting the key concepts, themes, and debates. The literature review should also demonstrate the research gap and how the current study seeks to address it.
The methods section of a research paper describes the research design, the sample selection, the data collection and analysis procedures, and the statistical methods used to analyze the data. This section should provide sufficient detail for other researchers to replicate the study.
The results section presents the findings of the research, using tables, graphs, and figures to illustrate the data. The findings should be presented in a clear and concise manner, with reference to the research question and hypothesis.
The discussion section of a research paper interprets the findings and discusses their implications for the research question, the literature review, and the field of study. It should also address the limitations of the study and suggest future research directions.
The conclusion section summarizes the main findings of the study, restates the research question and hypothesis, and provides a final reflection on the significance of the research.
The references section provides a list of all the sources cited in the paper, following a specific citation style such as APA, MLA or Chicago.
How to Write Research Paper
You can write Research Paper by the following guide:
- Choose a Topic: The first step is to select a topic that interests you and is relevant to your field of study. Brainstorm ideas and narrow down to a research question that is specific and researchable.
- Conduct a Literature Review: The literature review helps you identify the gap in the existing research and provides a basis for your research question. It also helps you to develop a theoretical framework and research hypothesis.
- Develop a Thesis Statement : The thesis statement is the main argument of your research paper. It should be clear, concise and specific to your research question.
- Plan your Research: Develop a research plan that outlines the methods, data sources, and data analysis procedures. This will help you to collect and analyze data effectively.
- Collect and Analyze Data: Collect data using various methods such as surveys, interviews, observations, or experiments. Analyze data using statistical tools or other qualitative methods.
- Organize your Paper : Organize your paper into sections such as Introduction, Literature Review, Methods, Results, Discussion, and Conclusion. Ensure that each section is coherent and follows a logical flow.
- Write your Paper : Start by writing the introduction, followed by the literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. Ensure that your writing is clear, concise, and follows the required formatting and citation styles.
- Edit and Proofread your Paper: Review your paper for grammar and spelling errors, and ensure that it is well-structured and easy to read. Ask someone else to review your paper to get feedback and suggestions for improvement.
- Cite your Sources: Ensure that you properly cite all sources used in your research paper. This is essential for giving credit to the original authors and avoiding plagiarism.
Research Paper Example
Note : The below example research paper is for illustrative purposes only and is not an actual research paper. Actual research papers may have different structures, contents, and formats depending on the field of study, research question, data collection and analysis methods, and other factors. Students should always consult with their professors or supervisors for specific guidelines and expectations for their research papers.
Research Paper Example sample for Students:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health among Young Adults
Abstract: This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults. A literature review was conducted to examine the existing research on the topic. A survey was then administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Introduction: Social media has become an integral part of modern life, particularly among young adults. While social media has many benefits, including increased communication and social connectivity, it has also been associated with negative outcomes, such as addiction, cyberbullying, and mental health problems. This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults.
Literature Review: The literature review highlights the existing research on the impact of social media use on mental health. The review shows that social media use is associated with depression, anxiety, stress, and other mental health problems. The review also identifies the factors that contribute to the negative impact of social media, including social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Methods : A survey was administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The survey included questions on social media use, mental health status (measured using the DASS-21), and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and regression analysis.
Results : The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Discussion : The study’s findings suggest that social media use has a negative impact on the mental health of young adults. The study highlights the need for interventions that address the factors contributing to the negative impact of social media, such as social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Conclusion : In conclusion, social media use has a significant impact on the mental health of young adults. The study’s findings underscore the need for interventions that promote healthy social media use and address the negative outcomes associated with social media use. Future research can explore the effectiveness of interventions aimed at reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health. Additionally, longitudinal studies can investigate the long-term effects of social media use on mental health.
Limitations : The study has some limitations, including the use of self-report measures and a cross-sectional design. The use of self-report measures may result in biased responses, and a cross-sectional design limits the ability to establish causality.
Implications: The study’s findings have implications for mental health professionals, educators, and policymakers. Mental health professionals can use the findings to develop interventions that address the negative impact of social media use on mental health. Educators can incorporate social media literacy into their curriculum to promote healthy social media use among young adults. Policymakers can use the findings to develop policies that protect young adults from the negative outcomes associated with social media use.
References :
- Twenge, J. M., & Campbell, W. K. (2019). Associations between screen time and lower psychological well-being among children and adolescents: Evidence from a population-based study. Preventive medicine reports, 15, 100918.
- Primack, B. A., Shensa, A., Escobar-Viera, C. G., Barrett, E. L., Sidani, J. E., Colditz, J. B., … & James, A. E. (2017). Use of multiple social media platforms and symptoms of depression and anxiety: A nationally-representative study among US young adults. Computers in Human Behavior, 69, 1-9.
- Van der Meer, T. G., & Verhoeven, J. W. (2017). Social media and its impact on academic performance of students. Journal of Information Technology Education: Research, 16, 383-398.
Appendix : The survey used in this study is provided below.
Social Media and Mental Health Survey
- How often do you use social media per day?
- Less than 30 minutes
- 30 minutes to 1 hour
- 1 to 2 hours
- 2 to 4 hours
- More than 4 hours
- Which social media platforms do you use?
- Others (Please specify)
- How often do you experience the following on social media?
- Social comparison (comparing yourself to others)
- Cyberbullying
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO)
- Have you ever experienced any of the following mental health problems in the past month?
- Do you think social media use has a positive or negative impact on your mental health?
- Very positive
- Somewhat positive
- Somewhat negative
- Very negative
- In your opinion, which factors contribute to the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Social comparison
- In your opinion, what interventions could be effective in reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Education on healthy social media use
- Counseling for mental health problems caused by social media
- Social media detox programs
- Regulation of social media use
Thank you for your participation!
Applications of Research Paper
Research papers have several applications in various fields, including:
- Advancing knowledge: Research papers contribute to the advancement of knowledge by generating new insights, theories, and findings that can inform future research and practice. They help to answer important questions, clarify existing knowledge, and identify areas that require further investigation.
- Informing policy: Research papers can inform policy decisions by providing evidence-based recommendations for policymakers. They can help to identify gaps in current policies, evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, and inform the development of new policies and regulations.
- Improving practice: Research papers can improve practice by providing evidence-based guidance for professionals in various fields, including medicine, education, business, and psychology. They can inform the development of best practices, guidelines, and standards of care that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- Educating students : Research papers are often used as teaching tools in universities and colleges to educate students about research methods, data analysis, and academic writing. They help students to develop critical thinking skills, research skills, and communication skills that are essential for success in many careers.
- Fostering collaboration: Research papers can foster collaboration among researchers, practitioners, and policymakers by providing a platform for sharing knowledge and ideas. They can facilitate interdisciplinary collaborations and partnerships that can lead to innovative solutions to complex problems.
When to Write Research Paper
Research papers are typically written when a person has completed a research project or when they have conducted a study and have obtained data or findings that they want to share with the academic or professional community. Research papers are usually written in academic settings, such as universities, but they can also be written in professional settings, such as research organizations, government agencies, or private companies.
Here are some common situations where a person might need to write a research paper:
- For academic purposes: Students in universities and colleges are often required to write research papers as part of their coursework, particularly in the social sciences, natural sciences, and humanities. Writing research papers helps students to develop research skills, critical thinking skills, and academic writing skills.
- For publication: Researchers often write research papers to publish their findings in academic journals or to present their work at academic conferences. Publishing research papers is an important way to disseminate research findings to the academic community and to establish oneself as an expert in a particular field.
- To inform policy or practice : Researchers may write research papers to inform policy decisions or to improve practice in various fields. Research findings can be used to inform the development of policies, guidelines, and best practices that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- To share new insights or ideas: Researchers may write research papers to share new insights or ideas with the academic or professional community. They may present new theories, propose new research methods, or challenge existing paradigms in their field.
Purpose of Research Paper
The purpose of a research paper is to present the results of a study or investigation in a clear, concise, and structured manner. Research papers are written to communicate new knowledge, ideas, or findings to a specific audience, such as researchers, scholars, practitioners, or policymakers. The primary purposes of a research paper are:
- To contribute to the body of knowledge : Research papers aim to add new knowledge or insights to a particular field or discipline. They do this by reporting the results of empirical studies, reviewing and synthesizing existing literature, proposing new theories, or providing new perspectives on a topic.
- To inform or persuade: Research papers are written to inform or persuade the reader about a particular issue, topic, or phenomenon. They present evidence and arguments to support their claims and seek to persuade the reader of the validity of their findings or recommendations.
- To advance the field: Research papers seek to advance the field or discipline by identifying gaps in knowledge, proposing new research questions or approaches, or challenging existing assumptions or paradigms. They aim to contribute to ongoing debates and discussions within a field and to stimulate further research and inquiry.
- To demonstrate research skills: Research papers demonstrate the author’s research skills, including their ability to design and conduct a study, collect and analyze data, and interpret and communicate findings. They also demonstrate the author’s ability to critically evaluate existing literature, synthesize information from multiple sources, and write in a clear and structured manner.
Characteristics of Research Paper
Research papers have several characteristics that distinguish them from other forms of academic or professional writing. Here are some common characteristics of research papers:
- Evidence-based: Research papers are based on empirical evidence, which is collected through rigorous research methods such as experiments, surveys, observations, or interviews. They rely on objective data and facts to support their claims and conclusions.
- Structured and organized: Research papers have a clear and logical structure, with sections such as introduction, literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. They are organized in a way that helps the reader to follow the argument and understand the findings.
- Formal and objective: Research papers are written in a formal and objective tone, with an emphasis on clarity, precision, and accuracy. They avoid subjective language or personal opinions and instead rely on objective data and analysis to support their arguments.
- Citations and references: Research papers include citations and references to acknowledge the sources of information and ideas used in the paper. They use a specific citation style, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago, to ensure consistency and accuracy.
- Peer-reviewed: Research papers are often peer-reviewed, which means they are evaluated by other experts in the field before they are published. Peer-review ensures that the research is of high quality, meets ethical standards, and contributes to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
- Objective and unbiased: Research papers strive to be objective and unbiased in their presentation of the findings. They avoid personal biases or preconceptions and instead rely on the data and analysis to draw conclusions.
Advantages of Research Paper
Research papers have many advantages, both for the individual researcher and for the broader academic and professional community. Here are some advantages of research papers:
- Contribution to knowledge: Research papers contribute to the body of knowledge in a particular field or discipline. They add new information, insights, and perspectives to existing literature and help advance the understanding of a particular phenomenon or issue.
- Opportunity for intellectual growth: Research papers provide an opportunity for intellectual growth for the researcher. They require critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity, which can help develop the researcher’s skills and knowledge.
- Career advancement: Research papers can help advance the researcher’s career by demonstrating their expertise and contributions to the field. They can also lead to new research opportunities, collaborations, and funding.
- Academic recognition: Research papers can lead to academic recognition in the form of awards, grants, or invitations to speak at conferences or events. They can also contribute to the researcher’s reputation and standing in the field.
- Impact on policy and practice: Research papers can have a significant impact on policy and practice. They can inform policy decisions, guide practice, and lead to changes in laws, regulations, or procedures.
- Advancement of society: Research papers can contribute to the advancement of society by addressing important issues, identifying solutions to problems, and promoting social justice and equality.
Limitations of Research Paper
Research papers also have some limitations that should be considered when interpreting their findings or implications. Here are some common limitations of research papers:
- Limited generalizability: Research findings may not be generalizable to other populations, settings, or contexts. Studies often use specific samples or conditions that may not reflect the broader population or real-world situations.
- Potential for bias : Research papers may be biased due to factors such as sample selection, measurement errors, or researcher biases. It is important to evaluate the quality of the research design and methods used to ensure that the findings are valid and reliable.
- Ethical concerns: Research papers may raise ethical concerns, such as the use of vulnerable populations or invasive procedures. Researchers must adhere to ethical guidelines and obtain informed consent from participants to ensure that the research is conducted in a responsible and respectful manner.
- Limitations of methodology: Research papers may be limited by the methodology used to collect and analyze data. For example, certain research methods may not capture the complexity or nuance of a particular phenomenon, or may not be appropriate for certain research questions.
- Publication bias: Research papers may be subject to publication bias, where positive or significant findings are more likely to be published than negative or non-significant findings. This can skew the overall findings of a particular area of research.
- Time and resource constraints: Research papers may be limited by time and resource constraints, which can affect the quality and scope of the research. Researchers may not have access to certain data or resources, or may be unable to conduct long-term studies due to practical limitations.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
Research articles
Reduction in limb-movement complexity at term-equivalent age is associated with motor developmental delay in very-preterm or very-low-birth-weight infants
- Myung Woo Park
- Hyung-Ik Shin
- Woo Hyung Lee
Visual outcomes and patient satisfaction after implantations of three types of presbyopia-correcting intraocular lenses that have undergone corneal refractive surgery
- Baoxian Zhuo
Optimal timing for the first cystoscopic follow-up using time-to-treatment initiation analysis of oncologic outcomes in primary non-muscle invasive bladder cancer
- Jeong-Soo Kim
- Jooyoung Lee
- Se Young Choi
Highly biomimetic spiking neuron using SiGe heterojunction bipolar transistors for energy-efficient neuromorphic systems
- Hyangwoo Kim
- Chang-Ki Baek
Numerical subgrid Bi-cubic methods of partial differential equations in image segmentation
- Dongyung Kim
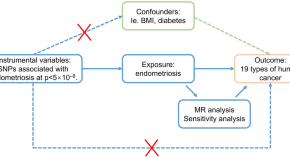
Genetically identification of endometriosis and cancers risk in women through a two-sample Mendelian randomization study
- Huaqing Yan
Effect of a novel mesh design and the sandblasting technique on the bond strength of computer-designed and three-dimension laser printed resin bonded bridges: an in vitro study
- Mariam Diab
- Mawia Karkoutly
- Jihad Abou Nassar
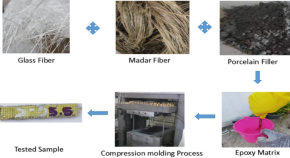
Fabrication of glass/madar fibers reinforced hybrid epoxy composite: a comprehensive study on the material stability
- Thandavamoorthy Raja
- D. Yuvarajan
- Nandagopal Kaliappan
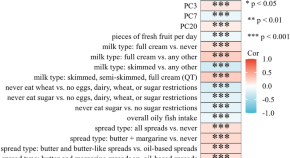
Genetic correlation and Mendelian randomization analyses support causal relationships between dietary habits and age at menarche
- Ruilong Guo
- Ruoyang Feng
- Chunyan Yin
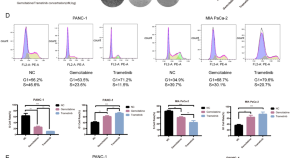
CDK4/6 inhibition sensitizes MEK inhibition by inhibiting cell cycle and proliferation in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- Zijian Zhou

Natural course of hemodynamically stable hemispheres contralateral to operated hemispheres in adult patients with ischemic moyamoya diseases
- Young Sill Kang
- Won-Sang Cho
- Jeong Eun Kim
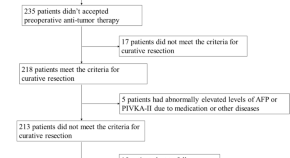
Diagnostic performance of PIVKA-II in identifying recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma following curative resection: a retrospective cohort study
- Wenfeng Zhu
- Weilong Wang
- Genshu Wang
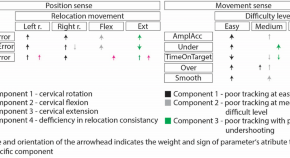
Cervicocephalic kinaesthesia reveals novel subgroups of motor control impairments in patients with neck pain
- Ziva Majcen Rosker
- Jernej Rosker
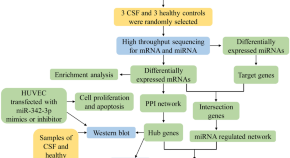
Differential gene expression and miRNA regulatory network in coronary slow flow
- Shifeng Xing
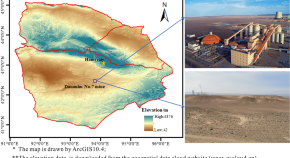
Overburden failure and water–sand mixture outburst conditions of weakly consolidated overlying strata in Dananhu No.7 coal mine
- Jingzhong Zhu
- Liangning Li
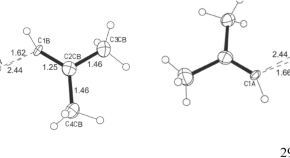
A new type of C + ⋯H δ− (C=) bond in adducts of vinyl carbocations with alkenes
- Evgenii S. Stoyanov
- Irina Yu. Bagryanskaya
- Irina V. Stoyanova

Calculation method of spherically expanding flame propagation radius to consider ignition electrode effects
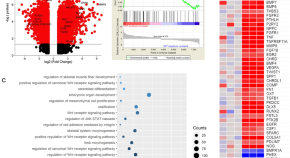
Ablation of Wnt signaling in bone marrow stromal cells overcomes microenvironment-mediated drug resistance in acute myeloid leukemia
- Hamenth Kumar Palani
- Saravanan Ganesan
- Vikram Mathews
A Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus secretome induces immunoregulatory transcriptional, functional and immunometabolic signatures in human THP-1 monocytes
- Michael P. Jeffrey
- Julia M. Green-Johnson
Microbe cultivation guidelines to optimize rhamnolipid applications
- Ilona E. Kłosowska-Chomiczewska
- Adam Macierzanka
- Christian Jungnickel
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Language selection
- Français fr
Call for papers: Generating stronger evidence to inform policy and practice: natural experiments on built environments, health behaviours and chronic diseases

HPCDP Journal Home

Submit a manuscript
- Information for authors
About HPCDP
- About the Journal
- Contact the Editors
- Past issues
Previous | Table of Contents | Next
https://doi.org/10.24095/hpcdp.44.4.05

Recommended Attribution
This call for papers in the HPCDP Journal is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
Guest editors: Dr. Stephanie Prince Ware (Public Health Agency of Canada), Dr. Gavin McCormack (University of Calgary)
HPCDP Journal Editors: Robert Geneau and Margaret de Groh (Public Health Agency of Canada)
Where we work, learn, play, eat and live has important implications for health. The built environment has been associated with the development of chronic disease, and with health behaviours often seen as critical pathways for this relationship. Footnote 1 Footnote 2 Built environments refer to components of the physical environment that are human-made or human-modified and include structures and buildings, recreation facilities, green spaces and parks, transportation systems and community design.
Natural experiments are interventions that occur without a researcher’s ability to manipulate the intervention or exposure to the intervention. Footnote 3 Footnote 4 Natural experiments offer the opportunity to evaluate the effects of “naturally occurring” interventions such as changes to the built environment (e.g. creation of a new bike path, park improvements, infrastructure changes to schools or workplaces, construction of a new recreation facility or grocery store) on health behaviours and chronic disease risk. Natural experiments are often more practical for investigating the health impacts of environmental interventions when compared to traditional experimental studies (e.g. randomized controlled trials). Compared to cross-sectional studies, natural experiments provide a means to generate rigorous evidence to better establish causality, as well as to understand the implementation of interventions in “real-world” scenarios.
This special issue answers the 2017 Canadian Public Health Officer annual report’s call to further evaluate the health impacts of community design features in Canada. Footnote 5 This special issue resonates with the expanding scholarly and policy-oriented interest in the utility of natural experiments as a critical tool in advancing the body of evidence and for informing interventions to improve public and population health. Footnote 6 Footnote 7 Specifically, the objective of this special issue on natural experiments is to provide timely evidence to further understand the effectiveness of built environment interventions on health behaviours and chronic disease prevention in a Canadian context.
Health Promotion and Chronic Disease Prevention in Canada: Research, Policy and Practice is seeking relevant topical research articles that present new findings or synthesize/review existing evidence on natural experiments of the built environment (or related policies) that influence health behaviours with implications for chronic disease prevention in Canada.
Relevant topic areas include, but are not limited to:
- Built environments, including community or neighbourhoods, workplaces, schools, transportation infrastructure, home environments, recreation environments, parks, playgrounds, green spaces, public open spaces, natural environments and seniors’ residences.
- All health-related behaviours, including physical activity, sedentary behaviour, sleep, food consumption, smoking and substance use.
- Chronic diseases and health-related outcomes, including body mass index, fitness, blood pressure, blood lipids, blood sugar, injuries, falls, mental health, stress, depression, anxiety, Alzheimer's disease, dementia, obesity, metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes and lung disease.
International submissions will be considered if they include Canadian data, results (e.g. as part of multi-country studies or global comparisons) and/or evidence-based discussion of implications for community or population health in Canada.
Consult the Journal’s website for information on article types and detailed submission guidelines for authors . Kindly refer to this call for papers in your cover letter.
All manuscripts should be submitted using the Journal’s ScholarOne Manuscripts online system. Pre-submission inquiries and questions about suitability or scope can be directed to [email protected] .
Submission deadline: November 30, 2024
Page details
This website uses cookies.
By clicking the "Accept" button or continuing to browse our site, you agree to first-party and session-only cookies being stored on your device to enhance site navigation and analyze site performance and traffic. For more information on our use of cookies, please see our Privacy Policy .
The 2024 AEJ Best Paper Awards Have Been Announced
- Announcement
- April 9, 2024
The 2024 AEJ Best Paper Awards have been announced. The papers selected are highlighted below.
AEJ: Applied Economics
In " Disability and Distress: The Effect of Disability Programs on Financial Outcomes ," authors Manasi Deshpande, Tal Gross, and Yalun Su estimated the impact of disability programs on financial distress. They find that US disability allowances decrease the likelihood of bankruptcy by 20 percent, foreclosure by 33 percent, and home sale by 15 percent. They argue that such significant declines in financial distress lend support to policies that reduce the waiting times between a disability application and the receipt of the benefits. ( AEJ: Applied Economics, Volume 13, No. 2, April 2021 )
AEJ: Economic Policy
In " The Labor Market for Teachers under Different Pay Schemes ," author Barbara Biasi examined the introduction of a flexible pay scheme for Wisconsin public school teachers, in which teachers are compensated according to performance rather than by seniority and education alone. Her findings show that districts adopting the new pay scheme were able to attract and retain better talent than those that did not, providing insight into what motivates teachers and highlighting inefficiencies produced by union-negotiated pay structures. ( AEJ: Economic Policy, Vol. 13, No. 3, August 2021 )
Read the Research Highlight here .
AEJ: Macroeconomics
In " The Transmission of Monetary Policy Shocks ," authors Silvia Miranda-Agrippino and Giovanni Ricco studied widely used instruments for the identification of monetary policy disturbances. They show how these instruments give rise to common empirical puzzles, and propose a new high-frequency instrument for monetary policy shocks that accounts for informational rigidities. Using this novel instrument, they find that monetary tightening is unequivocally contractionary. ( American Economic Journal: Macroeconomics Vol. 13 No. 3 July 2021 )
AEJ: Microeconomics
In " A Reputational Theory of Firm Dynamics ," authors Simon Board and Moritz Meyer-ter-Vehn investigated the incentives that companies have to maintain quality when consumers have limited information about the quality of their products or services. They model how consumers learn about such products via public breakthroughs. In their model, if firms fail to generate such breakthroughs, they will lose revenue and eventually exit. Their findings may have important implications for evaluating the impact of policy changes that affect businesses. ( American Economic Journal: Microeconomics Vol. 14 No. 2 May 2022 )
Journal of Materials Chemistry B
Tetramethylpyrazine-loaded electroconductive hydrogel promotes tissue repair after spinal cord injury by protecting the blood-spinal cord barrier and neuron.
Spinal cord injury (SCI) usually induces profound microvascular dysfunction. It disrupts the integrity of the blood-spinal cord barrier (BSCB), which could trigger a cascade of secondary pathological events that manifest as neuronal apoptosis and axonal demyelination. These events can further lead to irreversible neurological impairments. Thus, reducing the permeability of the BSCB and maintaining its substructural integrity is essential to promote neuronal survival following SCI. Tetramethylpyrazine (TMP) has emerged as a potential protective agent for treating BSCB after SCI. However, its therapeutic potential is hindered by challenges in the administration route and suboptimal bioavailability, leading to attenuated clinical outcomes. To address this challenge, traditional Chinese medicine, TMP, was used in this study to construct drug-loaded electroconductive hydrogel for synergistic treatment of SCI. Conductive hydrogel combined with TMP demonstrates good electrical and mechanical properties as well as superior biocompatibility. Further, it also facilitates sustained local release of TMP at the implantation site. Furthermore, TMP-loaded electroconductive hydrogel could suppress oxidative stress responses, thereby diminishing endothelial cell apoptosis and the breakdown of tight junction proteins. This concerted action repairs BSCB integrity. Concurrently, myelin-associated axonal and neuron is protected against death, which meaningfully restores neurological function post-spinal cord injury. Hence, these findings indicate that combining electroconductive hydrogel with TMP presents a promising avenue for potentiating drug efficacy and synergistic repair following SCI.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Journal of Materials Chemistry B HOT Papers
Supplementary files
- Supplementary information PDF (2504K)
- Supplementary information PDF (121K)
Article information
Download Citation
Permissions.
B. Deng, S. Jiang, G. Liu, X. Li, Y. Zhao, X. Fan, J. Ren, C. Ning, L. Xu, L. Ji and X. Mu, J. Mater. Chem. B , 2024, Accepted Manuscript , DOI: 10.1039/D3TB02160B
This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Unported Licence . You can use material from this article in other publications, without requesting further permission from the RSC, provided that the correct acknowledgement is given and it is not used for commercial purposes.
To request permission to reproduce material from this article in a commercial publication , please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page .
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party commercial publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page .
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content .
Social activity
Search articles by author.
This article has not yet been cited.
Advertisements
Debates about the nature and economic role of money are mostly informed by evidence from the 20th century, but money has existed for millennia. We argue that there are many lessons to be learned from monetary history that are relevant for current topics of policy relevance. The past acts as a source of evidence on how money works across different situations, helping to tease out features of money that do not depend on one time and place. A close reading of history also offers testing grounds for models of economic behavior and can thereby guide theories on how money is transmitted to the real economy.
Working papers are not edited, and all opinions and errors are the responsibility of the author(s). The views expressed do not necessarily reflect the views of the Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago or the Federal Reserve System.
- Download Entire Publication
Subscribe Now
Register to receive email alerts when new issues are published.
Related Topics
- Ahead: Another Year of Growth
- Review and Outlook: 1976-77 Business: Broad Improvement Continues
- Business Insights: Federal Spending Lags Expectations
- Government: A Year of Change and Surprise
- Region & Community
- Style Guide
Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago, 230 South LaSalle Street, Chicago, Illinois 60604-1413, USA. Tel. (312) 322-5322
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved.
Please review our Privacy Policy | Legal Notices

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
4. Track your paper. 5. Share and promote. 1. Find a journal. Find out the journals that could be best suited for publishing your research. For a comprehensive list of Elsevier journals check our Journal Catalog. You can also match your manuscript using the JournalFinder tool, then learn more about each journal.
Research paper publication is important for several reasons, both for individual researchers and for the scientific community as a whole. Here are some reasons why: Advancing scientific knowledge : Research papers provide a platform for researchers to present their findings and contribute to the body of knowledge in their field.
The first step in publishing a research paper should always be selecting the journal you want to publish in. Choosing your target journal before you start writing means you can tailor your work to build on research that's already been published in that journal. This can help editors to see how a paper adds to the 'conversation' in their ...
This article aims to provide an overview of the form, structure, and reporting standards for different types of papers, with a focus on writing for publication in peer-reviewed journals. It will also provide a summary of the different considerations to be made by authors selecting the right journals in which to publish their research, and offer ...
3. Submit your article according to the journal's submission guidelines. Go to the "author's guide" (or similar) on the journal's website to review its submission requirements. Once you are satisfied that your paper meets all of the guidelines, submit the paper through the appropriate channels.
The publication process explained. The path to publication can be unsettling when you're unsure what's happening with your paper. Learn about staple journal workflows to see the detailed steps required for ensuring a rigorous and ethical publication. Your team has prepared the paper, written a cover letter and completed the submission form.
Part of Indiana Journal of Global Legal Studies, Vol. 19, No. 1 (Winter 2012) Part of R Street Institute (Nov. 1, 2020) Part of Leuven University Press. Part of UN Secretary-General Papers: Ban Ki-moon (2007-2016) Part of Perspectives on Terrorism, Vol. 12, No. 4 (August 2018)
Communicating research findings is an essential step in the research process. Often, peer-reviewed journals are the forum for such communication, yet many researchers are never taught how to write a publishable scientific paper. In this article, we explain the basic structure of a scientific paper and describe the information that should be included in each section. We also identify common ...
A research paper is a piece of academic writing that provides analysis, interpretation, and argument based on in-depth independent research. Research papers are similar to academic essays, but they are usually longer and more detailed assignments, designed to assess not only your writing skills but also your skills in scholarly research ...
The main guidelines for formatting a paper in APA Style are as follows: Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman or 11 pt Arial. Set 1 inch page margins. Apply double line spacing. If submitting for publication, insert a APA running head on every page. Indent every new paragraph ½ inch.
Elsevier journals offer the latest peer-reviewed research papers on climate change, biodiversity, renewable energy and other topics addressing our planet's climate emergency. ... 2023 marked 200 years since Thomas Wakley founded The Lancet with the vision that it should be more than a medical journal. Over the past two centuries the journal ...
Asian-Pacific Journal of Second and Foreign Language Education. Disciplinary and Interdisciplinary Science Education Research. Empirical Research in Vocational Education and Training. International Journal of Child Care and Education Policy. International Journal of STEM Education. Language Testing in Asia.
Elsevier Journal Finder helps you find journals that could be best suited for publishing your scientific article. Journal Finder uses smart search technology and field-of-research specific vocabularies to match your paper's abstract to scientific journals.
For publication: Researchers often write research papers to publish their findings in academic journals or to present their work at academic conferences. Publishing research papers is an important way to disseminate research findings to the academic community and to establish oneself as an expert in a particular field.
Subscription and open access journals from Sage, the world's leading independent academic publisher.
Google Scholar provides a simple way to broadly search for scholarly literature. Search across a wide variety of disciplines and sources: articles, theses, books, abstracts and court opinions.
A comparison of two complete sets of human centromeres reveals that the centromeres show at least a 4.1-fold increase in single-nucleotide variation compared with their unique flanks, and up to 3 ...
Journal policies Calls for Papers Guide to referees Editor's Choice Journal highlights Publish with us. For authors ...
One of the largest and most authoritative collections of online journals, books, and research resources, covering life, health, social, and physical sciences.
Access 160+ million publications and connect with 25+ million researchers. Join for free and gain visibility by uploading your research.
Find the research you need | With 160+ million publications, 1+ million questions, and 25+ million researchers, this is where everyone can access science
Feature papers are submitted upon individual invitation or recommendation by the scientific editors and must receive positive feedback from the reviewers. ... Editors select a small number of articles recently published in the journal that they believe will be particularly interesting to readers, or important in the respective research area. ...
Kindly refer to this call for papers in your cover letter. All manuscripts should be submitted using the Journal's ScholarOne Manuscripts online system. Pre-submission inquiries and questions about suitability or scope can be directed to [email protected]. Submission deadline: November 30, 2024. References Footnote 1
The 2024 AEJ Best Paper Awards have been announced. The papers selected are highlighted below. AEJ: Applied Economics . In "Disability and Distress: The Effect of Disability Programs on Financial Outcomes," authors Manasi Deshpande, Tal Gross, and Yalun Su estimated the impact of disability programs on financial distress.They find that US disability allowances decrease the likelihood of ...
Spinal cord injury (SCI) usually induces profound microvascular dysfunction. It disrupts the integrity of the blood-spinal cord barrier (BSCB), which could trigger a cascade of secondary pathological events that manifest as neuronal apoptosis and axonal demyelination. These events can further lead to irrever Journal of Materials Chemistry B HOT Papers
Understanding Money Using Historical Evidence. Debates about the nature and economic role of money are mostly informed by evidence from the 20th century, but money has existed for millennia. We argue that there are many lessons to be learned from monetary history that are relevant for current topics of policy relevance.
This supplement includes five background papers and provides background information on various aspects of capacity development (CD) for the main Board paper, Review of the Fund's Capacity Development Strategy—Towards a More Flexible, Integrated, and Tailored Model. It is divided into five sections, each consisting of a different background paper.