If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.

Want additional help with Algebra 2?

Unit 1: Polynomial arithmetic
Unit 2: complex numbers, unit 3: polynomial factorization, unit 4: polynomial division, unit 5: polynomial graphs, unit 6: rational exponents and radicals, unit 7: exponential models, unit 8: logarithms, unit 9: transformations of functions, unit 10: equations, unit 11: trigonometry, unit 12: modeling.

Algebra 2 Worksheets with answer keys
Enjoy these free printable math worksheets . Each one has model problems worked out step by step, practice problems, as well as challenge questions at the sheets end. Plus each one comes with an answer key.
- Absolute Value Equations
- Simplify Imaginary Numbers
- Adding and Subtracting Complex Numbers
- Multiplying Complex Numbers
- Dividing Complex Numbers
- Dividing Complex Number (advanced)
- End of Unit, Review Sheet
- Exponential Growth (no answer key on this one, sorry)
- Compound Interest Worksheet #1 (no logs)
- Compound Interest Worksheet (logarithms required)
- Simplify Rational Exponents
- Solve Equations with Rational Exponents
- Solve Equations with variables in Exponents
- Factor by Grouping
- 1 to 1 functions
- Evaluating Functions
- Composition of Functions
- Inverse Functions
- Operations with Functions
- Functions Review Worksheet
- Product Rule of Logarithms
- Power Rule of Logarithms
- Quotient Rule of Logarithms
- Logarithmic Equations Worksheet
- Dividing Polynomials Worksheet
- Solve Quadratic Equations by Factoring
- Solve Quadratic Equations by Completing the Square
- Quadratic formula Worksheet (real solutions)
- Quadratic Formula Worksheet (complex solutions)
- Quadratic Formula Worksheet (both real and complex solutions)
- Discriminant Worksheet
- Sum and Product of Roots
- Radical Equations
- Rationalizing the Denominator
- Simplify Rational Expressions Worksheet
- Dividing Rational Expressions
- Multiplying Rational Expressions
- Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions (with like denominators)
- Adding and Subtracting Ratioal Expressions with Unlike Denominators
- Mixed Review on Rational Expressions
Ultimate Math Solver (Free) Free Algebra Solver ... type anything in there!
Popular pages @ mathwarehouse.com.
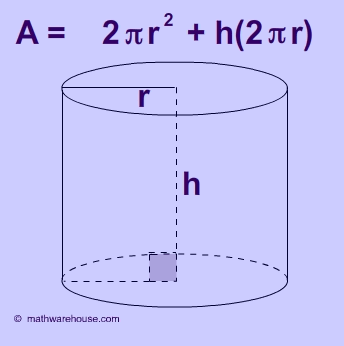
Algebra 2 Worksheets

MATH 1111 - College Algebra: 2.2 Intro to Functions
- 1.1 Sets and Set Operations
- 1.2 Linear Equations and Inequalities
- 1.3 Systems of Linear Equations
- 1.4 Polynomials; Operations with Polynomials
- 1.5 Factoring Polynomials
- 1.6 Quadratic Equations
- 1.7 Rational Expressions and Equations
- 1.8 Complex Numbers
- 2.1 Cartesian Coordinates/Relations
2.2 Intro to Functions
- 2.3 Operations with Functions
- 2.4 Graph of Functions
- 3.1 Linear Functions
- 3.2 Quadratic Functions and Quadratic Inequalities
- 4.1 Finding Zeros of Polynomial Functions
- 4.2 Graphing Polynomial Functions
- 4.3 Rational Functions
- 4.4 Rational Inequalities
- 5.1 Composition of Functions
- 5.2 Inverse Functions
- 5.3 Introduction to Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
At the end of this section students will be able to:
- Determine whether a relation is a function
- Find the domain and range of a function
- Evaluate functions
Required Reading
1.3 Introduction to Functions
Stitz-Zeager College Algebra - pages 43-47
1.4 Function Notation
Stitz-Zeager College Algebra - pages 55-59
Practice Exercises
Introduction to Functions
Stitz-Zeager College Algebra - pages 49-54
Answers to practice exercises can be found on pages 53-54.
Function Notation
Stitz-Zeager College Algebra - pages 63-65
Answers to practice exercises can be found on pages 69-74.
Supplemental Resources
Introduction to Functions (tutorial): West Texas A&M University Virtual Math Lab (College Algebra Tutorial 30)
Finding the Domain of a Function:
Evaluating Functions:
- << Previous: 2.1 Cartesian Coordinates/Relations
- Next: 2.3 Operations with Functions >>
- Last Updated: Apr 2, 2024 2:52 PM
- URL: https://libguides.gcsu.edu/math1111
Graphing Exponential Functions - Module 10.2
Model Exponential Growth and Decay - Module 10.3 (Part 1)
Model Exponential Growth and Decay - Module 10.3 (Part 2)
Circes - Module 12.1 (Part 1)
Circles - Module 12.1 (Part 2)
Parabolas - Module 12.2 (Part 1)
Parabolas - Module 12.2 (Part 2)
Parabolas - Module 12.2 (Part 3)
Parabolas - Module 12.2 (Part 4)
Parabolas - Module 12.2 (Part 5)
Solving Linear-Quadratic Systems Module 12.3 (Part 1)
Solving Linear-Quadratic Systems Module 12.3 (Part 2)
Review for Test on Mods 10, 11, and 12 (Part 1)
Review for Test on Mods 10, 11, and 12 (Part 2)
Review for Test on Mods 10, 11, and 12 (Part 3)
Proofs - Day 1
Proofs - Day 2
Proofs - Day 3
Understanding Polynomial Expressions - Module 4.1
Adding Polynomial Expressions - Module 4.2
Subtracting Polynomial Expressions - Module 4.3
Review on Module 4
Please Donate, if you're a regular!
The donate link is below. Thanks so much!!
Domain, Range, and End Behavior - Module 1.1 (Part 1)
Domain, Range, and End Behavior - Module 1.1 (Part 2)
Lesson Performance Task - Page 16
Characteristics of Function Graphs - Module 1.2
Graphing Calculator Exercise - Module 1.2
Inverse of Functions - Module 1.3
Review on Module 1 - Analyze Functions
Connecting Intercepts and Zeros - Module 7.1 (Part 1)
Connecting Intercepts and Linear Factors - Module 7.2 (Part 1)
The x-intercepts and Zeros of a Function - Module 7.2 (Part 2)
The Zero Product Property - Module 7.3
Review For Unit 3 Test (Part 1)
Review For Unit 3 Test (Part 2)
Rio Review for Unit 3 Test - 2019
Dilations - Module 16.1
Proving Figures Similar Using Transformations - Mod 16.2
Corresponding Parts of Similar Figures - Module 16.3
AA Similarity of Triangles - Module 16.4
Second Semester
Solving Quadratics by Taking Square Roots - Module 11.1 (Part 1)
The Imaginary Number " i " - Module 11.1 (Part 2)
Imaginary Solutions to Simple Quadratic Equations - Module 11.1 (Part 3)
Complex Numbers - Module 11.2
Finding Complex Solutions of Quadratic Equations - Module 11.3 (Part 1)
Applications with Complex Solutions - Module 11.3 (Part 2)
Understanding Rational Exponents and Radicals - Module 3.1 (Part 1)
Understanding Rational Exponents and Radicals - Module 3.1 (Part 2)
Simplifying Square Roots (Radicals) - Module 3.1 (Part 3)
Simplify Rational Exponents and Radicals - Module 3.2 (Part 1)
Simplify Rational Exponents and Radicals - Module 3.2 (Part 2)
More Simplifying Radicals - Module 3.2 (Part 4)
Properties of Exponents - Module 3.2 (Part 5)
Review For Test on Module 3
The Tangent Ratio - Module 18.1
Sine and Cosine Ratios - Module 18.2 (Part 1)
Sine and Cosine Ratios - Module 18.2 (Part 2)
Special Right Triangles - Module 18.3 (Part 1)
Special Right Triangles - Module 18.3 (Part 2)
Review 1 SOHCAHTOA Module 18 Test
Review 2 Special Right Triangles Module 18 Test
Review 3 SOHCAHTOA Word Problems Mod 18 Test
Review 4 for Module 18 Test
Understanding Quadratic Functions - Module 6.1 (Part 1)
Write Quadratic Functions From a Graph - Module 6.1 (Part 2)
Modeling with Quadratic Functions - Module 6.1 (Part 3)
Transforming Quadratic Functions - Module 6.2 (Part 1)
Vertex Form of a Quadratic Function - Module 6.2 (Part 2)
Interpret Vertex Form and Standard Form - Module 6.3
Review For Test on Module 6
Central and Inscribed Angles of a Circle - Module 19.1
Angles in Inscribed Quadrilaterals - Module 19.2
Review of Modules 19.1 and 19.2
Tangents and Circumscribed Angles - Module 19.3 (Pt. 1)
More Tangents and Circum. Angles - Module 19.3 (Part 2)
Segment Relationships in Circles - Module 19.4 (Part 1)
More Segments in Circles - Module 19.4 (Part 2)
Angle Relationships with Circles - Module 19.5 (Part 1)
More Angles with Circles - Module 19.5 (Part 2)
Review for Test on Circles - Module 19
Solving Equations by Taking Square Roots - Module 9.1
Solve Equations by Completing the Square - Module 9.2 (Part 1)
Solve Equations by Completing the Square - Module 9.2 (Part 2)
The Quadratic Formula - Module 9.3 (Part 1)
The Discriminant and Real-World Models - Module 9.3 (Part 2)
Choosing a Method for Solving Quadratic Equations - Module 9.4
Solving Nonlinear Systems - Module 9.5
Circumference and Area of Circles - Module 20.1
Arc Length and Radian Measure - Module 20.2
Sector Area - Module 20.3
Thanks for trying harder! :-)
Multiplying Polynomial with Monomials - Module 5.1
Multiplying Polynomial Expressions - Module 5.2 (Part 1)
Multiplying Polynomial Expressions - Module 5.2 (Part 2)
Special Products of Binomials - Module 5.3 (Part 1)
Special Products of Binomials - Module 5.3 (Part 2)
Review For Unit 2 Test on Modules 4 & 5
- Integrated Math 2
Greatest Common Factor (GCF) - Module 8.1 (Part 1)
Factoring x(squared) + (or -) bx + c - Module 8.1 (Part 2)
Factoring x(squared) + (or -) bx - c - Module 8.1 (Part 3)
Factoring ax(squared) + bx + c - Module 8.1 (Part 4)
More Factoring ax(squared) + bx + c - Module 8.1 (Part 5)
Factor By Grouping - Module 8.1 (Part 6)
Factor Difference of Squares & Perfect Square Tri's (Part 7)
Review of Factoring - Module 8.1 (Part 1)
Review of Factoring - Module 8.1 (Part 2)
Solving Equations by Factoring ax(squared) + bx + c = 0 - Mod 8.2
Special Factors to Solve Quadratic Equations - Module 8.3
Review of Module 8
First Semester
Online Math Class
Mr. Math Blog
- Second Grade Math
- Third Grade Math
- Fourth Grade Math
- Fifth Grade Math
- Sixth Grade Math
- Sixth Grade Math (CA)
- Seventh Grade Math (CA)
- Eighth Grade Math (CA)
- Independent Study
- Integrated Math 1
- Integrated Math 3
- PreCalculus
- AP Calculus
- AP Statistics
- AP Statistics Exam Prep
- Elementary Statistics
- ELM Practice
- Percents and Decimals
- Sixth Grade Math (Big Ideas)
Volume of Prisms and Cylinders - Module 21.1 (Part 1)
Volume of Prisms and Cylinders - Module 21.1 (Part 2)
Volume of Pyramids - Module 21.2
Volume of Cones - Module 21.3
Volume of Spheres - Module 21.4
Angles Formed by Intersecting Lines - Module 14.1
Proofs Numbers 13, 15, and 17 Pages 685-686
Transversals and Parallel Lines - Module 14.2
Proving Lines are Parallel - Module 14.3
Perpendicular Lines - Module 14.4
Triangle Proportionality Theorem - Module 17.1
Lesson Performance Task - Module 17.1
Using Proportional Relationships - Module 17.3
Similarity in Right Triangles - Module 17.4
Module 17 Review - Using Similar Triangles
Review For Final Worksheet - Part 1
Review For Final Worksheet - Part 2
Review For Final Worksheet - Part 3
Review For Final Worksheet - Part 4
Review For Final Worksheet - Part 5
Review For Final Worksheet - Part 6
Graphing Absolute Value Functions - Module 2.1
More Graphing Absolute Value Functions - Mod 2.1 (Part 2)
Modeling with Absolute Value Functions - Module 2.1 (Part 3)
Solving Absolute Value Equations - Module 2.2 (Part 1)
Solving Absolute Value Equations - Module 2.2 (Part 2)
Solving Absolute Value Inequalities - Module 2.3 (Part 1)
Solving Absolute Value Inequalities - Module 2.3 (Part 2)
Solving Compound Inequalities - Special Cases - Module 2.3
Applications with Absolute Value Inequalities - Mod 2.3 (Part 3)
Review for Test on Module 2 (Part 1)
Review for Test on Module 2 (Part 2)
Interior and Exterior Angles of Polygons - Module 15.1
Isosceles and Equilateral Triangles - Module 15.2
Inequalities in Triangles - Module 15.3
Perpendicular Bisectors of Triangles - Module 15.4
Angle Bisectors of Triangles - Module 15.5
Review of Modules 15.4 and 15.5
Five Ways Triangles are Congruent - Module 15.5 (b)
Properties of Parallelograms - Module 15.6
Proofs with Parallelograms - Module 15.6 (Part 2)
Rectangles, Rhombuses, and Squares - Module 15.7
Unit 6 Review for Test on Modules 14 & 15 (Part 1)
Unit 6 Review for Test on Modules 14 & 15 (Part 2)
Copyright 2013. All rights reserved.
2.1 The Rectangular Coordinate Systems and Graphs
x -intercept is ( 4 , 0 ) ; ( 4 , 0 ) ; y- intercept is ( 0 , 3 ) . ( 0 , 3 ) .
125 = 5 5 125 = 5 5
( − 5 , 5 2 ) ( − 5 , 5 2 )
2.2 Linear Equations in One Variable
x = −5 x = −5
x = −3 x = −3
x = 10 3 x = 10 3
x = 1 x = 1
x = − 7 17 . x = − 7 17 . Excluded values are x = − 1 2 x = − 1 2 and x = − 1 3 . x = − 1 3 .
x = 1 3 x = 1 3
m = − 2 3 m = − 2 3
y = 4 x −3 y = 4 x −3
x + 3 y = 2 x + 3 y = 2
Horizontal line: y = 2 y = 2
Parallel lines: equations are written in slope-intercept form.
y = 5 x + 3 y = 5 x + 3
2.3 Models and Applications
C = 2.5 x + 3 , 650 C = 2.5 x + 3 , 650
L = 37 L = 37 cm, W = 18 W = 18 cm

2.4 Complex Numbers
−24 = 0 + 2 i 6 −24 = 0 + 2 i 6
( 3 −4 i ) − ( 2 + 5 i ) = 1 −9 i ( 3 −4 i ) − ( 2 + 5 i ) = 1 −9 i
5 2 − i 5 2 − i
18 + i 18 + i
−3 −4 i −3 −4 i
2.5 Quadratic Equations
( x − 6 ) ( x + 1 ) = 0 ; x = 6 , x = − 1 ( x − 6 ) ( x + 1 ) = 0 ; x = 6 , x = − 1
( x −7 ) ( x + 3 ) = 0 , ( x −7 ) ( x + 3 ) = 0 , x = 7 , x = 7 , x = −3. x = −3.
( x + 5 ) ( x −5 ) = 0 , ( x + 5 ) ( x −5 ) = 0 , x = −5 , x = −5 , x = 5. x = 5.
( 3 x + 2 ) ( 4 x + 1 ) = 0 , ( 3 x + 2 ) ( 4 x + 1 ) = 0 , x = − 2 3 , x = − 2 3 , x = − 1 4 x = − 1 4
x = 0 , x = −10 , x = −1 x = 0 , x = −10 , x = −1
x = 4 ± 5 x = 4 ± 5
x = 3 ± 22 x = 3 ± 22
x = − 2 3 , x = − 2 3 , x = 1 3 x = 1 3
2.6 Other Types of Equations
{ −1 } { −1 }
0 , 0 , 1 2 , 1 2 , − 1 2 − 1 2
1 ; 1 ; extraneous solution − 2 9 − 2 9
−2 ; −2 ; extraneous solution −1 −1
−1 , −1 , 3 2 3 2
−3 , 3 , − i , i −3 , 3 , − i , i
2 , 12 2 , 12
−1 , −1 , 0 0 is not a solution.
2.7 Linear Inequalities and Absolute Value Inequalities
[ −3 , 5 ] [ −3 , 5 ]
( − ∞ , −2 ) ∪ [ 3 , ∞ ) ( − ∞ , −2 ) ∪ [ 3 , ∞ )
x < 1 x < 1
x ≥ −5 x ≥ −5
( 2 , ∞ ) ( 2 , ∞ )
[ − 3 14 , ∞ ) [ − 3 14 , ∞ )
6 < x ≤ 9 or ( 6 , 9 ] 6 < x ≤ 9 or ( 6 , 9 ]
( − 1 8 , 1 2 ) ( − 1 8 , 1 2 )
| x −2 | ≤ 3 | x −2 | ≤ 3
k ≤ 1 k ≤ 1 or k ≥ 7 ; k ≥ 7 ; in interval notation, this would be ( − ∞ , 1 ] ∪ [ 7 , ∞ ) . ( − ∞ , 1 ] ∪ [ 7 , ∞ ) .
2.1 Section Exercises
Answers may vary. Yes. It is possible for a point to be on the x -axis or on the y -axis and therefore is considered to NOT be in one of the quadrants.
The y -intercept is the point where the graph crosses the y -axis.
The x- intercept is ( 2 , 0 ) ( 2 , 0 ) and the y -intercept is ( 0 , 6 ) . ( 0 , 6 ) .
The x- intercept is ( 2 , 0 ) ( 2 , 0 ) and the y -intercept is ( 0 , −3 ) . ( 0 , −3 ) .
The x- intercept is ( 3 , 0 ) ( 3 , 0 ) and the y -intercept is ( 0 , 9 8 ) . ( 0 , 9 8 ) .
y = 4 − 2 x y = 4 − 2 x
y = 5 − 2 x 3 y = 5 − 2 x 3
y = 2 x − 4 5 y = 2 x − 4 5
d = 74 d = 74
d = 36 = 6 d = 36 = 6
d ≈ 62.97 d ≈ 62.97
( 3 , − 3 2 ) ( 3 , − 3 2 )
( 2 , −1 ) ( 2 , −1 )
( 0 , 0 ) ( 0 , 0 )
y = 0 y = 0
not collinear
A: ( −3 , 2 ) , B: ( 1 , 3 ) , C: ( 4 , 0 ) A: ( −3 , 2 ) , B: ( 1 , 3 ) , C: ( 4 , 0 )
d = 8.246 d = 8.246
d = 5 d = 5
( −3 , 4 ) ( −3 , 4 )
x = 0 y = −2 x = 0 y = −2
x = 0.75 y = 0 x = 0.75 y = 0
x = − 1.667 y = 0 x = − 1.667 y = 0
15 − 11.2 = 3.8 mi 15 − 11.2 = 3.8 mi shorter
6 .0 42 6 .0 42
Midpoint of each diagonal is the same point ( 2 , –2 ) ( 2 , –2 ) . Note this is a characteristic of rectangles, but not other quadrilaterals.
2.2 Section Exercises
It means they have the same slope.
The exponent of the x x variable is 1. It is called a first-degree equation.
If we insert either value into the equation, they make an expression in the equation undefined (zero in the denominator).
x = 2 x = 2
x = 2 7 x = 2 7
x = 6 x = 6
x = 3 x = 3
x = −14 x = −14
x ≠ −4 ; x ≠ −4 ; x = −3 x = −3
x ≠ 1 ; x ≠ 1 ; when we solve this we get x = 1 , x = 1 , which is excluded, therefore NO solution
x ≠ 0 ; x ≠ 0 ; x = − 5 2 x = − 5 2
y = − 4 5 x + 14 5 y = − 4 5 x + 14 5
y = − 3 4 x + 2 y = − 3 4 x + 2
y = 1 2 x + 5 2 y = 1 2 x + 5 2
y = −3 x − 5 y = −3 x − 5
y = 7 y = 7
y = −4 y = −4
8 x + 5 y = 7 8 x + 5 y = 7
Perpendicular
m = − 9 7 m = − 9 7
m = 3 2 m = 3 2
m 1 = − 1 3 , m 2 = 3 ; Perpendicular . m 1 = − 1 3 , m 2 = 3 ; Perpendicular .
y = 0.245 x − 45.662. y = 0.245 x − 45.662. Answers may vary. y min = −50 , y max = −40 y min = −50 , y max = −40
y = − 2.333 x + 6.667. y = − 2.333 x + 6.667. Answers may vary. y min = −10 , y max = 10 y min = −10 , y max = 10
y = − A B x + C B y = − A B x + C B
The slope for ( −1 , 1 ) to ( 0 , 4 ) is 3. The slope for ( −1 , 1 ) to ( 2 , 0 ) is − 1 3 . The slope for ( 2 , 0 ) to ( 3 , 3 ) is 3. The slope for ( 0 , 4 ) to ( 3 , 3 ) is − 1 3 . The slope for ( −1 , 1 ) to ( 0 , 4 ) is 3. The slope for ( −1 , 1 ) to ( 2 , 0 ) is − 1 3 . The slope for ( 2 , 0 ) to ( 3 , 3 ) is 3. The slope for ( 0 , 4 ) to ( 3 , 3 ) is − 1 3 .
Yes they are perpendicular.
2.3 Section Exercises
Answers may vary. Possible answers: We should define in words what our variable is representing. We should declare the variable. A heading.
2 , 000 − x 2 , 000 − x
v + 10 v + 10
Ann: 23 ; 23 ; Beth: 46 46
20 + 0.05 m 20 + 0.05 m
90 + 40 P 90 + 40 P
50 , 000 − x 50 , 000 − x
She traveled for 2 h at 20 mi/h, or 40 miles.
$5,000 at 8% and $15,000 at 12%
B = 100 + .05 x B = 100 + .05 x
R = 9 R = 9
r = 4 5 r = 4 5 or 0.8
W = P − 2 L 2 = 58 − 2 ( 15 ) 2 = 14 W = P − 2 L 2 = 58 − 2 ( 15 ) 2 = 14
f = p q p + q = 8 ( 13 ) 8 + 13 = 104 21 f = p q p + q = 8 ( 13 ) 8 + 13 = 104 21
m = − 5 4 m = − 5 4
h = 2 A b 1 + b 2 h = 2 A b 1 + b 2
length = 360 ft; width = 160 ft
A = 88 in . 2 A = 88 in . 2
h = V π r 2 h = V π r 2
r = V π h r = V π h
C = 12 π C = 12 π
2.4 Section Exercises
Add the real parts together and the imaginary parts together.
Possible answer: i i times i i equals -1, which is not imaginary.
−8 + 2 i −8 + 2 i
14 + 7 i 14 + 7 i
− 23 29 + 15 29 i − 23 29 + 15 29 i
8 − i 8 − i
−11 + 4 i −11 + 4 i
2 −5 i 2 −5 i
6 + 15 i 6 + 15 i
−16 + 32 i −16 + 32 i
−4 −7 i −4 −7 i
2 − 2 3 i 2 − 2 3 i
4 − 6 i 4 − 6 i
2 5 + 11 5 i 2 5 + 11 5 i
1 + i 3 1 + i 3
( 3 2 + 1 2 i ) 6 = −1 ( 3 2 + 1 2 i ) 6 = −1
5 −5 i 5 −5 i
9 2 − 9 2 i 9 2 − 9 2 i
2.5 Section Exercises
It is a second-degree equation (the highest variable exponent is 2).
We want to take advantage of the zero property of multiplication in the fact that if a ⋅ b = 0 a ⋅ b = 0 then it must follow that each factor separately offers a solution to the product being zero: a = 0 o r b = 0. a = 0 o r b = 0.
One, when no linear term is present (no x term), such as x 2 = 16. x 2 = 16. Two, when the equation is already in the form ( a x + b ) 2 = d . ( a x + b ) 2 = d .
x = 6 , x = 6 , x = 3 x = 3
x = − 5 2 , x = − 5 2 , x = − 1 3 x = − 1 3
x = 5 , x = 5 , x = −5 x = −5
x = − 3 2 , x = − 3 2 , x = 3 2 x = 3 2
x = −2 , 3 x = −2 , 3
x = 0 , x = 0 , x = − 3 7 x = − 3 7
x = −6 , x = −6 , x = 6 x = 6
x = 6 , x = 6 , x = −4 x = −4
x = 1 , x = 1 , x = −2 x = −2
x = −2 , x = −2 , x = 11 x = 11
z = 2 3 , z = 2 3 , z = − 1 2 z = − 1 2
x = 3 ± 17 4 x = 3 ± 17 4
One rational
Two real; rational
x = − 1 ± 17 2 x = − 1 ± 17 2
x = 5 ± 13 6 x = 5 ± 13 6
x = − 1 ± 17 8 x = − 1 ± 17 8
x ≈ 0.131 x ≈ 0.131 and x ≈ 2.535 x ≈ 2.535
x ≈ − 6.7 x ≈ − 6.7 and x ≈ 1.7 x ≈ 1.7
a x 2 + b x + c = 0 x 2 + b a x = − c a x 2 + b a x + b 2 4 a 2 = − c a + b 4 a 2 ( x + b 2 a ) 2 = b 2 − 4 a c 4 a 2 x + b 2 a = ± b 2 − 4 a c 4 a 2 x = − b ± b 2 − 4 a c 2 a a x 2 + b x + c = 0 x 2 + b a x = − c a x 2 + b a x + b 2 4 a 2 = − c a + b 4 a 2 ( x + b 2 a ) 2 = b 2 − 4 a c 4 a 2 x + b 2 a = ± b 2 − 4 a c 4 a 2 x = − b ± b 2 − 4 a c 2 a
x ( x + 10 ) = 119 ; x ( x + 10 ) = 119 ; 7 ft. and 17 ft.
maximum at x = 70 x = 70
The quadratic equation would be ( 100 x −0.5 x 2 ) − ( 60 x + 300 ) = 300. ( 100 x −0.5 x 2 ) − ( 60 x + 300 ) = 300. The two values of x x are 20 and 60.
2.6 Section Exercises
This is not a solution to the radical equation, it is a value obtained from squaring both sides and thus changing the signs of an equation which has caused it not to be a solution in the original equation.
He or she is probably trying to enter negative 9, but taking the square root of −9 −9 is not a real number. The negative sign is in front of this, so your friend should be taking the square root of 9, cubing it, and then putting the negative sign in front, resulting in −27. −27.
A rational exponent is a fraction: the denominator of the fraction is the root or index number and the numerator is the power to which it is raised.
x = 81 x = 81
x = 17 x = 17
x = 8 , x = 27 x = 8 , x = 27
x = −2 , 1 , −1 x = −2 , 1 , −1
y = 0 , 3 2 , − 3 2 y = 0 , 3 2 , − 3 2
m = 1 , −1 m = 1 , −1
x = 2 5 , ±3 i x = 2 5 , ±3 i
x = 32 x = 32
t = 44 3 t = 44 3
x = −2 x = −2
x = 4 , −4 3 x = 4 , −4 3
x = − 5 4 , 7 4 x = − 5 4 , 7 4
x = 3 , −2 x = 3 , −2
x = 1 , −1 , 3 , -3 x = 1 , −1 , 3 , -3
x = 2 , −2 x = 2 , −2
x = 1 , 5 x = 1 , 5
x ≥ 0 x ≥ 0
x = 4 , 6 , −6 , −8 x = 4 , 6 , −6 , −8
2.7 Section Exercises
When we divide both sides by a negative it changes the sign of both sides so the sense of the inequality sign changes.
( − ∞ , ∞ ) ( − ∞ , ∞ )
We start by finding the x -intercept, or where the function = 0. Once we have that point, which is ( 3 , 0 ) , ( 3 , 0 ) , we graph to the right the straight line graph y = x −3 , y = x −3 , and then when we draw it to the left we plot positive y values, taking the absolute value of them.
( − ∞ , 3 4 ] ( − ∞ , 3 4 ]
[ − 13 2 , ∞ ) [ − 13 2 , ∞ )
( − ∞ , 3 ) ( − ∞ , 3 )
( − ∞ , − 37 3 ] ( − ∞ , − 37 3 ]
All real numbers ( − ∞ , ∞ ) ( − ∞ , ∞ )
( − ∞ , − 10 3 ) ∪ ( 4 , ∞ ) ( − ∞ , − 10 3 ) ∪ ( 4 , ∞ )
( − ∞ , −4 ] ∪ [ 8 , + ∞ ) ( − ∞ , −4 ] ∪ [ 8 , + ∞ )
No solution
( −5 , 11 ) ( −5 , 11 )
[ 6 , 12 ] [ 6 , 12 ]
[ −10 , 12 ] [ −10 , 12 ]
x > − 6 and x > − 2 Take the intersection of two sets . x > − 2 , ( − 2 , + ∞ ) x > − 6 and x > − 2 Take the intersection of two sets . x > − 2 , ( − 2 , + ∞ )
x < − 3 or x ≥ 1 Take the union of the two sets . ( − ∞ , − 3 ) ∪ [ 1 , ∞ ) x < − 3 or x ≥ 1 Take the union of the two sets . ( − ∞ , − 3 ) ∪ [ 1 , ∞ )
( − ∞ , −1 ) ∪ ( 3 , ∞ ) ( − ∞ , −1 ) ∪ ( 3 , ∞ )
[ −11 , −3 ] [ −11 , −3 ]
It is never less than zero. No solution.
Where the blue line is above the orange line; point of intersection is x = − 3. x = − 3.
( − ∞ , −3 ) ( − ∞ , −3 )
Where the blue line is above the orange line; always. All real numbers.
( − ∞ , − ∞ ) ( − ∞ , − ∞ )
( −1 , 3 ) ( −1 , 3 )
( − ∞ , 4 ) ( − ∞ , 4 )
{ x | x < 6 } { x | x < 6 }
{ x | −3 ≤ x < 5 } { x | −3 ≤ x < 5 }
( −2 , 1 ] ( −2 , 1 ]
( − ∞ , 4 ] ( − ∞ , 4 ]
Where the blue is below the orange; always. All real numbers. ( − ∞ , + ∞ ) . ( − ∞ , + ∞ ) .
Where the blue is below the orange; ( 1 , 7 ) . ( 1 , 7 ) .
x = 2 , − 4 5 x = 2 , − 4 5
( −7 , 5 ] ( −7 , 5 ]
80 ≤ T ≤ 120 1 , 600 ≤ 20 T ≤ 2 , 400 80 ≤ T ≤ 120 1 , 600 ≤ 20 T ≤ 2 , 400
[ 1 , 600 , 2 , 400 ] [ 1 , 600 , 2 , 400 ]
Review Exercises
x -intercept: ( 3 , 0 ) ; ( 3 , 0 ) ; y -intercept: ( 0 , −4 ) ( 0 , −4 )
y = 5 3 x + 4 y = 5 3 x + 4
72 = 6 2 72 = 6 2
620.097 620.097
midpoint is ( 2 , 23 2 ) ( 2 , 23 2 )
x = 4 x = 4
x = 12 7 x = 12 7
y = 1 6 x + 4 3 y = 1 6 x + 4 3
y = 2 3 x + 6 y = 2 3 x + 6
females 17, males 56
x = − 3 4 ± i 47 4 x = − 3 4 ± i 47 4
horizontal component −2 ; −2 ; vertical component −1 −1
7 + 11 i 7 + 11 i
−16 − 30 i −16 − 30 i
−4 − i 10 −4 − i 10
x = 7 − 3 i x = 7 − 3 i
x = −1 , −5 x = −1 , −5
x = 0 , 9 7 x = 0 , 9 7
x = 10 , −2 x = 10 , −2
x = − 1 ± 5 4 x = − 1 ± 5 4
x = 2 5 , − 1 3 x = 2 5 , − 1 3
x = 5 ± 2 7 x = 5 ± 2 7
x = 0 , 256 x = 0 , 256
x = 0 , ± 2 x = 0 , ± 2
x = 11 2 , −17 2 x = 11 2 , −17 2
[ − 10 3 , 2 ] [ − 10 3 , 2 ]
( − 4 3 , 1 5 ) ( − 4 3 , 1 5 )
Where the blue is below the orange line; point of intersection is x = 3.5. x = 3.5.
( 3.5 , ∞ ) ( 3.5 , ∞ )
Practice Test
y = 3 2 x + 2 y = 3 2 x + 2
( 0 , −3 ) ( 0 , −3 ) ( 4 , 0 ) ( 4 , 0 )
( − ∞ , 9 ] ( − ∞ , 9 ]
x = −15 x = −15
x ≠ −4 , 2 ; x ≠ −4 , 2 ; x = − 5 2 , 1 x = − 5 2 , 1
x = 3 ± 3 2 x = 3 ± 3 2
( −4 , 1 ) ( −4 , 1 )
y = −5 9 x − 2 9 y = −5 9 x − 2 9
y = 5 2 x − 4 y = 5 2 x − 4
5 13 − 14 13 i 5 13 − 14 13 i
x = 2 , − 4 3 x = 2 , − 4 3
x = 1 2 ± 2 2 x = 1 2 ± 2 2
x = 1 2 , 2 , −2 x = 1 2 , 2 , −2
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/college-algebra/pages/1-introduction-to-prerequisites
- Authors: Jay Abramson
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: College Algebra
- Publication date: Feb 13, 2015
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/college-algebra/pages/1-introduction-to-prerequisites
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/college-algebra/pages/chapter-2
© Dec 8, 2021 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
Please ensure that your password is at least 8 characters and contains each of the following:
- a special character: @$#!%*?&
Finished Papers

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Our resource for Algebra 2, Volume 1 includes answers to chapter exercises, as well as detailed information to walk you through the process step by step. With Expert Solutions for thousands of practice problems, you can take the guesswork out of studying and move forward with confidence. Find step-by-step solutions and answers to Algebra 2 ...
Find step-by-step solutions and answers to Algebra 2 - 9780544385917, as well as thousands of textbooks so you can move forward with confidence. ... Module 2 Mixed Review. Page 75: Unit 1 Mixed Review. Exercise 1. Exercise 2. Exercise 3. Exercise 4. Exercise 5. ... Evaluate: Homework and Practice. Exercise 1. Exercise 2. Exercise 3. Exercise 4 ...
Evaluate Homework and Practice Module 1 Lesson 2 Answer Key - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free.
Section 15.1: Defining and Evaluating a Logarithmic Function. Section 15.2: Graphing Logarithmic Functions. Page 778: ... Our resource for Algebra 2, Volume 2 includes answers to chapter exercises, as well as detailed information to walk you through the process step by step. With Expert Solutions for thousands of practice problems, you can take ...
The Algebra 2 course, often taught in the 11th grade, covers Polynomials; Complex Numbers; Rational Exponents; Exponential and Logarithmic Functions; Trigonometric Functions; Transformations of Functions; Rational Functions; and continuing the work with Equations and Modeling from previous grades. Khan Academy's Algebra 2 course is built to deliver a comprehensive, illuminating, engaging, and ...
Multiplying Complex Numbers. Dividing Complex Numbers. Dividing Complex Number (advanced) End of Unit, Review Sheet. Exponential Growth (no answer key on this one, sorry) Compound Interest Worksheet #1 (no logs) Compound Interest Worksheet (logarithms required) Exponent Worksheets. Simplify Rational Exponents.
Sample spaces and The Counting Principle. Independent and dependent events. Mutualy exclusive events. Permutations. Combinations. Permutations vs combinations. Probability using permutations and combinations. Free Algebra 2 worksheets created with Infinite Algebra 2. Printable in convenient PDF format.
1.1 Self-Assessment. 7. Find the volume of the cone. Round your answer to the nearest tenth. 8. Determine which of the lines, if any, are parallel or perpendicular. Line a: 3 y − x = 2 Line b: y 3 x = 2 − Line c: 6 x 2 y 5 − + =.
A1 SpringBoard Algebra 2, Unit 1 Practice LeSSon 1-1 1. 65 5 15h 1 3 2.4 hours; the cost of renting a bike for 4 hours is $63. 3.$13; it costs $78 to rent the bike for 5 hours since 15(5) 1 3 5 78. This is $13 more than Aaron has, 78 2 65 5 13. 4. B 5. a.No; there are 5 quarter-hour segments from 7:00 p.m. to 8:15 p.m. Using the equation
Find step-by-step solutions and answers to Texas Algebra 2, Volume 2 - 9780544353947, as well as thousands of textbooks so you can move forward with confidence. ... Evaluate: Homework and Practice. Exercise 1. Exercise 2. Exercise 3. Exercise 4. Exercise 5. ... Module 10 Mixed Review. Page 563: Unit 4 Mixed Review. Exercise 1. Exercise 2 ...
2.2 Homework: "Find the equation of the lines below, in standard form."Pg 73 Problem Set: 11, 13. "Find the equation of the line, given the information" Problem #1 reads "Passes through (4, 7) and is parallel to x - y = -5" Pg 76 Problem Set: 1, 3, 6. "Find the equation of the line, give the information" Problem #5 reads "Passes thorugh (0, 6 ...
Algebra 2 Worksheets. Kuta Software. Open main menu. Products. Free Worksheets. Infinite Pre-AlgebraInfinite Algebra 1. Infinite Geometry. Infinite Algebra 2. Infinite Precalculus.
Introduction to Functions. Stitz-Zeager College Algebra - pages 49-54. Answers to practice exercises can be found on pages 53-54. Function Notation. Stitz-Zeager College Algebra - pages 63-65. Answers to practice exercises can be found on pages 69-74.
15.1 Defining & Evaluating a Logarithmic Function. 15.2 Graphing Logarithmic Functions. 16.1 Properties of Logarithms. 16.2 Solving Exponential Equations . Unit 7 - TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS. 17.1 Angles of Rotation and Radian Measure. 17.2 Defining & Evaluating Basic Trig Functions . 17.3 Using Pythagorean Identities . 18.1 The Sine and Cosine ...
Solve Equations by Completing the Square - Module 9.2 (Part 2) The Quadratic Formula - Module 9.3 (Part 1) The Discriminant and Real-World Models - Module 9.3 (Part 2) Choosing a Method for Solving Quadratic Equations - Module 9.4. Solving Nonlinear Systems - Module 9.5. Circumference and Area of Circles - Module 20.1.
Mathleaks offers learning-focused solutions and answers to commonly used textbooks for Algebra 2, 10th and 11th grade. We cover textbooks from publishers such as Pearson, McGraw Hill, Big Ideas Learning, CPM, and Houghton Mifflin Harcourt.
Introduction to Systems of Equations and Inequalities; 7.1 Systems of Linear Equations: Two Variables; 7.2 Systems of Linear Equations: Three Variables; 7.3 Systems of Nonlinear Equations and Inequalities: Two Variables; 7.4 Partial Fractions; 7.5 Matrices and Matrix Operations; 7.6 Solving Systems with Gaussian Elimination; 7.7 Solving Systems with Inverses; 7.8 Solving Systems with Cramer's Rule
Evaluate: Homework and Practice Solve the following absolute value equations by graphing. 4. — 2) 1+3—2 . Solve the absolute value equations. 13. 13x— 2—1 3 4 5 14. 6 ... 2—1 3) _ 3—2 —1 o o 2 3 2 4 3 5 4 6 5 10. 12. 512x+41—3— 6 . 18. A flock of geese is approaching a photographer, flying in
Our resource for Algebra 1: Homework Practice Workbook includes answers to chapter exercises, as well as detailed information to walk you through the process step by step. With Expert Solutions for thousands of practice problems, you can take the guesswork out of studying and move forward with confidence. Find step-by-step solutions and answers ...
Free math problem solver answers your algebra homework questions with step-by-step explanations. Mathway. Visit Mathway on the web. Start 7-day free trial on the app. Start 7-day free trial on the app. Download free on Amazon. Download free in Windows Store. get Go. Algebra. Basic Math. Pre-Algebra. Algebra. Trigonometry. Precalculus.
Evaluate Homework And Practice Module 5 Lesson 1 Algebra 2 - 4.8/5. ... Coursework, Term paper, Powerpoint Presentation, Research proposal, Case Study, Dissertation, Questions-Answers, Discussion Board Post, Dissertation chapter - Literature review, Thesis, Literature Review, Thesis/dissertation chapter, Book Review, Marketing Plan, Article ...
Now, with expert-verified solutions from Algebra 1, Volume 2 1st Edition, you'll learn how to solve your toughest homework problems. Our resource for Algebra 1, Volume 2 includes answers to chapter exercises, as well as detailed information to walk you through the process step by step. With Expert Solutions for thousands of practice problems ...