Does Homework Really Help Students Learn?

A conversation with a Wheelock researcher, a BU student, and a fourth-grade teacher

“Quality homework is engaging and relevant to kids’ lives,” says Wheelock’s Janine Bempechat. “It gives them autonomy and engages them in the community and with their families. In some subjects, like math, worksheets can be very helpful. It has to do with the value of practicing over and over.” Photo by iStock/Glenn Cook Photography
Do your homework.
If only it were that simple.
Educators have debated the merits of homework since the late 19th century. In recent years, amid concerns of some parents and teachers that children are being stressed out by too much homework, things have only gotten more fraught.
“Homework is complicated,” says developmental psychologist Janine Bempechat, a Wheelock College of Education & Human Development clinical professor. The author of the essay “ The Case for (Quality) Homework—Why It Improves Learning and How Parents Can Help ” in the winter 2019 issue of Education Next , Bempechat has studied how the debate about homework is influencing teacher preparation, parent and student beliefs about learning, and school policies.
She worries especially about socioeconomically disadvantaged students from low-performing schools who, according to research by Bempechat and others, get little or no homework.
BU Today sat down with Bempechat and Erin Bruce (Wheelock’17,’18), a new fourth-grade teacher at a suburban Boston school, and future teacher freshman Emma Ardizzone (Wheelock) to talk about what quality homework looks like, how it can help children learn, and how schools can equip teachers to design it, evaluate it, and facilitate parents’ role in it.
BU Today: Parents and educators who are against homework in elementary school say there is no research definitively linking it to academic performance for kids in the early grades. You’ve said that they’re missing the point.
Bempechat : I think teachers assign homework in elementary school as a way to help kids develop skills they’ll need when they’re older—to begin to instill a sense of responsibility and to learn planning and organizational skills. That’s what I think is the greatest value of homework—in cultivating beliefs about learning and skills associated with academic success. If we greatly reduce or eliminate homework in elementary school, we deprive kids and parents of opportunities to instill these important learning habits and skills.
We do know that beginning in late middle school, and continuing through high school, there is a strong and positive correlation between homework completion and academic success.
That’s what I think is the greatest value of homework—in cultivating beliefs about learning and skills associated with academic success.
You talk about the importance of quality homework. What is that?
Quality homework is engaging and relevant to kids’ lives. It gives them autonomy and engages them in the community and with their families. In some subjects, like math, worksheets can be very helpful. It has to do with the value of practicing over and over.

What are your concerns about homework and low-income children?
The argument that some people make—that homework “punishes the poor” because lower-income parents may not be as well-equipped as affluent parents to help their children with homework—is very troubling to me. There are no parents who don’t care about their children’s learning. Parents don’t actually have to help with homework completion in order for kids to do well. They can help in other ways—by helping children organize a study space, providing snacks, being there as a support, helping children work in groups with siblings or friends.
Isn’t the discussion about getting rid of homework happening mostly in affluent communities?
Yes, and the stories we hear of kids being stressed out from too much homework—four or five hours of homework a night—are real. That’s problematic for physical and mental health and overall well-being. But the research shows that higher-income students get a lot more homework than lower-income kids.
Teachers may not have as high expectations for lower-income children. Schools should bear responsibility for providing supports for kids to be able to get their homework done—after-school clubs, community support, peer group support. It does kids a disservice when our expectations are lower for them.
The conversation around homework is to some extent a social class and social justice issue. If we eliminate homework for all children because affluent children have too much, we’re really doing a disservice to low-income children. They need the challenge, and every student can rise to the challenge with enough supports in place.
What did you learn by studying how education schools are preparing future teachers to handle homework?
My colleague, Margarita Jimenez-Silva, at the University of California, Davis, School of Education, and I interviewed faculty members at education schools, as well as supervising teachers, to find out how students are being prepared. And it seemed that they weren’t. There didn’t seem to be any readings on the research, or conversations on what high-quality homework is and how to design it.
Erin, what kind of training did you get in handling homework?
Bruce : I had phenomenal professors at Wheelock, but homework just didn’t come up. I did lots of student teaching. I’ve been in classrooms where the teachers didn’t assign any homework, and I’ve been in rooms where they assigned hours of homework a night. But I never even considered homework as something that was my decision. I just thought it was something I’d pull out of a book and it’d be done.
I started giving homework on the first night of school this year. My first assignment was to go home and draw a picture of the room where you do your homework. I want to know if it’s at a table and if there are chairs around it and if mom’s cooking dinner while you’re doing homework.
The second night I asked them to talk to a grown-up about how are you going to be able to get your homework done during the week. The kids really enjoyed it. There’s a running joke that I’m teaching life skills.
Friday nights, I read all my kids’ responses to me on their homework from the week and it’s wonderful. They pour their hearts out. It’s like we’re having a conversation on my couch Friday night.
It matters to know that the teacher cares about you and that what you think matters to the teacher. Homework is a vehicle to connect home and school…for parents to know teachers are welcoming to them and their families.
Bempechat : I can’t imagine that most new teachers would have the intuition Erin had in designing homework the way she did.
Ardizzone : Conversations with kids about homework, feeling you’re being listened to—that’s such a big part of wanting to do homework….I grew up in Westchester County. It was a pretty demanding school district. My junior year English teacher—I loved her—she would give us feedback, have meetings with all of us. She’d say, “If you have any questions, if you have anything you want to talk about, you can talk to me, here are my office hours.” It felt like she actually cared.
Bempechat : It matters to know that the teacher cares about you and that what you think matters to the teacher. Homework is a vehicle to connect home and school…for parents to know teachers are welcoming to them and their families.
Ardizzone : But can’t it lead to parents being overbearing and too involved in their children’s lives as students?
Bempechat : There’s good help and there’s bad help. The bad help is what you’re describing—when parents hover inappropriately, when they micromanage, when they see their children confused and struggling and tell them what to do.
Good help is when parents recognize there’s a struggle going on and instead ask informative questions: “Where do you think you went wrong?” They give hints, or pointers, rather than saying, “You missed this,” or “You didn’t read that.”
Bruce : I hope something comes of this. I hope BU or Wheelock can think of some way to make this a more pressing issue. As a first-year teacher, it was not something I even thought about on the first day of school—until a kid raised his hand and said, “Do we have homework?” It would have been wonderful if I’d had a plan from day one.
Explore Related Topics:
- Share this story
Senior Contributing Editor

Sara Rimer A journalist for more than three decades, Sara Rimer worked at the Miami Herald , Washington Post and, for 26 years, the New York Times , where she was the New England bureau chief, and a national reporter covering education, aging, immigration, and other social justice issues. Her stories on the death penalty’s inequities were nominated for a Pulitzer Prize and cited in the U.S. Supreme Court’s decision outlawing the execution of people with intellectual disabilities. Her journalism honors include Columbia University’s Meyer Berger award for in-depth human interest reporting. She holds a BA degree in American Studies from the University of Michigan. Profile
She can be reached at [email protected] .
Comments & Discussion
Boston University moderates comments to facilitate an informed, substantive, civil conversation. Abusive, profane, self-promotional, misleading, incoherent or off-topic comments will be rejected. Moderators are staffed during regular business hours (EST) and can only accept comments written in English. Statistics or facts must include a citation or a link to the citation.
There are 81 comments on Does Homework Really Help Students Learn?
Insightful! The values about homework in elementary schools are well aligned with my intuition as a parent.
when i finish my work i do my homework and i sometimes forget what to do because i did not get enough sleep
same omg it does not help me it is stressful and if I have it in more than one class I hate it.
Same I think my parent wants to help me but, she doesn’t care if I get bad grades so I just try my best and my grades are great.
I think that last question about Good help from parents is not know to all parents, we do as our parents did or how we best think it can be done, so maybe coaching parents or giving them resources on how to help with homework would be very beneficial for the parent on how to help and for the teacher to have consistency and improve homework results, and of course for the child. I do see how homework helps reaffirm the knowledge obtained in the classroom, I also have the ability to see progress and it is a time I share with my kids
The answer to the headline question is a no-brainer – a more pressing problem is why there is a difference in how students from different cultures succeed. Perfect example is the student population at BU – why is there a majority population of Asian students and only about 3% black students at BU? In fact at some universities there are law suits by Asians to stop discrimination and quotas against admitting Asian students because the real truth is that as a group they are demonstrating better qualifications for admittance, while at the same time there are quotas and reduced requirements for black students to boost their portion of the student population because as a group they do more poorly in meeting admissions standards – and it is not about the Benjamins. The real problem is that in our PC society no one has the gazuntas to explore this issue as it may reveal that all people are not created equal after all. Or is it just environmental cultural differences??????
I get you have a concern about the issue but that is not even what the point of this article is about. If you have an issue please take this to the site we have and only post your opinion about the actual topic
This is not at all what the article is talking about.
This literally has nothing to do with the article brought up. You should really take your opinions somewhere else before you speak about something that doesn’t make sense.
we have the same name
so they have the same name what of it?
lol you tell her
totally agree
What does that have to do with homework, that is not what the article talks about AT ALL.
Yes, I think homework plays an important role in the development of student life. Through homework, students have to face challenges on a daily basis and they try to solve them quickly.I am an intense online tutor at 24x7homeworkhelp and I give homework to my students at that level in which they handle it easily.
More than two-thirds of students said they used alcohol and drugs, primarily marijuana, to cope with stress.
You know what’s funny? I got this assignment to write an argument for homework about homework and this article was really helpful and understandable, and I also agree with this article’s point of view.
I also got the same task as you! I was looking for some good resources and I found this! I really found this article useful and easy to understand, just like you! ^^
i think that homework is the best thing that a child can have on the school because it help them with their thinking and memory.
I am a child myself and i think homework is a terrific pass time because i can’t play video games during the week. It also helps me set goals.
Homework is not harmful ,but it will if there is too much
I feel like, from a minors point of view that we shouldn’t get homework. Not only is the homework stressful, but it takes us away from relaxing and being social. For example, me and my friends was supposed to hang at the mall last week but we had to postpone it since we all had some sort of work to do. Our minds shouldn’t be focused on finishing an assignment that in realty, doesn’t matter. I completely understand that we should have homework. I have to write a paper on the unimportance of homework so thanks.
homework isn’t that bad
Are you a student? if not then i don’t really think you know how much and how severe todays homework really is
i am a student and i do not enjoy homework because i practice my sport 4 out of the five days we have school for 4 hours and that’s not even counting the commute time or the fact i still have to shower and eat dinner when i get home. its draining!
i totally agree with you. these people are such boomers
why just why
they do make a really good point, i think that there should be a limit though. hours and hours of homework can be really stressful, and the extra work isn’t making a difference to our learning, but i do believe homework should be optional and extra credit. that would make it for students to not have the leaning stress of a assignment and if you have a low grade you you can catch up.
Studies show that homework improves student achievement in terms of improved grades, test results, and the likelihood to attend college. Research published in the High School Journal indicates that students who spent between 31 and 90 minutes each day on homework “scored about 40 points higher on the SAT-Mathematics subtest than their peers, who reported spending no time on homework each day, on average.” On both standardized tests and grades, students in classes that were assigned homework outperformed 69% of students who didn’t have homework. A majority of studies on homework’s impact – 64% in one meta-study and 72% in another – showed that take home assignments were effective at improving academic achievement. Research by the Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) concluded that increased homework led to better GPAs and higher probability of college attendance for high school boys. In fact, boys who attended college did more than three hours of additional homework per week in high school.
So how are your measuring student achievement? That’s the real question. The argument that doing homework is simply a tool for teaching responsibility isn’t enough for me. We can teach responsibility in a number of ways. Also the poor argument that parents don’t need to help with homework, and that students can do it on their own, is wishful thinking at best. It completely ignores neurodiverse students. Students in poverty aren’t magically going to find a space to do homework, a friend’s or siblings to help them do it, and snacks to eat. I feel like the author of this piece has never set foot in a classroom of students.
THIS. This article is pathetic coming from a university. So intellectually dishonest, refusing to address the havoc of capitalism and poverty plays on academic success in life. How can they in one sentence use poor kids in an argument and never once address that poor children have access to damn near 0 of the resources affluent kids have? Draw me a picture and let’s talk about feelings lmao what a joke is that gonna put food in their belly so they can have the calories to burn in order to use their brain to study? What about quiet their 7 other siblings that they share a single bedroom with for hours? Is it gonna force the single mom to magically be at home and at work at the same time to cook food while you study and be there to throw an encouraging word?
Also the “parents don’t need to be a parent and be able to guide their kid at all academically they just need to exist in the next room” is wild. Its one thing if a parent straight up is not equipped but to say kids can just figured it out is…. wow coming from an educator What’s next the teacher doesn’t need to teach cause the kid can just follow the packet and figure it out?
Well then get a tutor right? Oh wait you are poor only affluent kids can afford a tutor for their hours of homework a day were they on average have none of the worries a poor child does. Does this address that poor children are more likely to also suffer abuse and mental illness? Like mentioned what about kids that can’t learn or comprehend the forced standardized way? Just let em fail? These children regularly are not in “special education”(some of those are a joke in their own and full of neglect and abuse) programs cause most aren’t even acknowledged as having disabilities or disorders.
But yes all and all those pesky poor kids just aren’t being worked hard enough lol pretty sure poor children’s existence just in childhood is more work, stress, and responsibility alone than an affluent child’s entire life cycle. Love they never once talked about the quality of education in the classroom being so bad between the poor and affluent it can qualify as segregation, just basically blamed poor people for being lazy, good job capitalism for failing us once again!
why the hell?
you should feel bad for saying this, this article can be helpful for people who has to write a essay about it
This is more of a political rant than it is about homework
I know a teacher who has told his students their homework is to find something they are interested in, pursue it and then come share what they learn. The student responses are quite compelling. One girl taught herself German so she could talk to her grandfather. One boy did a research project on Nelson Mandela because the teacher had mentioned him in class. Another boy, a both on the autism spectrum, fixed his family’s computer. The list goes on. This is fourth grade. I think students are highly motivated to learn, when we step aside and encourage them.
The whole point of homework is to give the students a chance to use the material that they have been presented with in class. If they never have the opportunity to use that information, and discover that it is actually useful, it will be in one ear and out the other. As a science teacher, it is critical that the students are challenged to use the material they have been presented with, which gives them the opportunity to actually think about it rather than regurgitate “facts”. Well designed homework forces the student to think conceptually, as opposed to regurgitation, which is never a pretty sight
Wonderful discussion. and yes, homework helps in learning and building skills in students.
not true it just causes kids to stress
Homework can be both beneficial and unuseful, if you will. There are students who are gifted in all subjects in school and ones with disabilities. Why should the students who are gifted get the lucky break, whereas the people who have disabilities suffer? The people who were born with this “gift” go through school with ease whereas people with disabilities struggle with the work given to them. I speak from experience because I am one of those students: the ones with disabilities. Homework doesn’t benefit “us”, it only tears us down and put us in an abyss of confusion and stress and hopelessness because we can’t learn as fast as others. Or we can’t handle the amount of work given whereas the gifted students go through it with ease. It just brings us down and makes us feel lost; because no mater what, it feels like we are destined to fail. It feels like we weren’t “cut out” for success.
homework does help
here is the thing though, if a child is shoved in the face with a whole ton of homework that isn’t really even considered homework it is assignments, it’s not helpful. the teacher should make homework more of a fun learning experience rather than something that is dreaded
This article was wonderful, I am going to ask my teachers about extra, or at all giving homework.
I agree. Especially when you have homework before an exam. Which is distasteful as you’ll need that time to study. It doesn’t make any sense, nor does us doing homework really matters as It’s just facts thrown at us.
Homework is too severe and is just too much for students, schools need to decrease the amount of homework. When teachers assign homework they forget that the students have other classes that give them the same amount of homework each day. Students need to work on social skills and life skills.
I disagree.
Beyond achievement, proponents of homework argue that it can have many other beneficial effects. They claim it can help students develop good study habits so they are ready to grow as their cognitive capacities mature. It can help students recognize that learning can occur at home as well as at school. Homework can foster independent learning and responsible character traits. And it can give parents an opportunity to see what’s going on at school and let them express positive attitudes toward achievement.
Homework is helpful because homework helps us by teaching us how to learn a specific topic.
As a student myself, I can say that I have almost never gotten the full 9 hours of recommended sleep time, because of homework. (Now I’m writing an essay on it in the middle of the night D=)
I am a 10 year old kid doing a report about “Is homework good or bad” for homework before i was going to do homework is bad but the sources from this site changed my mind!
Homeowkr is god for stusenrs
I agree with hunter because homework can be so stressful especially with this whole covid thing no one has time for homework and every one just wants to get back to there normal lives it is especially stressful when you go on a 2 week vaca 3 weeks into the new school year and and then less then a week after you come back from the vaca you are out for over a month because of covid and you have no way to get the assignment done and turned in
As great as homework is said to be in the is article, I feel like the viewpoint of the students was left out. Every where I go on the internet researching about this topic it almost always has interviews from teachers, professors, and the like. However isn’t that a little biased? Of course teachers are going to be for homework, they’re not the ones that have to stay up past midnight completing the homework from not just one class, but all of them. I just feel like this site is one-sided and you should include what the students of today think of spending four hours every night completing 6-8 classes worth of work.
Are we talking about homework or practice? Those are two very different things and can result in different outcomes.
Homework is a graded assignment. I do not know of research showing the benefits of graded assignments going home.
Practice; however, can be extremely beneficial, especially if there is some sort of feedback (not a grade but feedback). That feedback can come from the teacher, another student or even an automated grading program.
As a former band director, I assigned daily practice. I never once thought it would be appropriate for me to require the students to turn in a recording of their practice for me to grade. Instead, I had in-class assignments/assessments that were graded and directly related to the practice assigned.
I would really like to read articles on “homework” that truly distinguish between the two.
oof i feel bad good luck!
thank you guys for the artical because I have to finish an assingment. yes i did cite it but just thanks
thx for the article guys.
Homework is good
I think homework is helpful AND harmful. Sometimes u can’t get sleep bc of homework but it helps u practice for school too so idk.
I agree with this Article. And does anyone know when this was published. I would like to know.
It was published FEb 19, 2019.
Studies have shown that homework improved student achievement in terms of improved grades, test results, and the likelihood to attend college.
i think homework can help kids but at the same time not help kids
This article is so out of touch with majority of homes it would be laughable if it wasn’t so incredibly sad.
There is no value to homework all it does is add stress to already stressed homes. Parents or adults magically having the time or energy to shepherd kids through homework is dome sort of 1950’s fantasy.
What lala land do these teachers live in?
Homework gives noting to the kid
Homework is Bad
homework is bad.
why do kids even have homework?
Comments are closed.
Latest from Bostonia
American academy of arts & sciences welcomes five bu members, com’s newest journalism grad took her time, could boston be the next city to impose congestion pricing, alum has traveled the world to witness total solar eclipses, opening doors: rhonda harrison (eng’98,’04, grs’04), campus reacts and responds to israel-hamas war, reading list: what the pandemic revealed, remembering com’s david anable, cas’ john stone, “intellectual brilliance and brilliant kindness”, one good deed: christine kannler (cas’96, sph’00, camed’00), william fairfield warren society inducts new members, spreading art appreciation, restoring the “black angels” to medical history, in the kitchen with jacques pépin, feedback: readers weigh in on bu’s new president, com’s new expert on misinformation, and what’s really dividing the nation, the gifts of great teaching, sth’s walter fluker honored by roosevelt institute, alum’s debut book is a ramadan story for children, my big idea: covering construction sites with art, former terriers power new professional women’s hockey league.

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, how to do homework: 15 expert tips and tricks.
Coursework/GPA

Everyone struggles with homework sometimes, but if getting your homework done has become a chronic issue for you, then you may need a little extra help. That’s why we’ve written this article all about how to do homework. Once you’re finished reading it, you’ll know how to do homework (and have tons of new ways to motivate yourself to do homework)!
We’ve broken this article down into a few major sections. You’ll find:
- A diagnostic test to help you figure out why you’re struggling with homework
- A discussion of the four major homework problems students face, along with expert tips for addressing them
- A bonus section with tips for how to do homework fast
By the end of this article, you’ll be prepared to tackle whatever homework assignments your teachers throw at you .
So let’s get started!

How to Do Homework: Figure Out Your Struggles
Sometimes it feels like everything is standing between you and getting your homework done. But the truth is, most people only have one or two major roadblocks that are keeping them from getting their homework done well and on time.
The best way to figure out how to get motivated to do homework starts with pinpointing the issues that are affecting your ability to get your assignments done. That’s why we’ve developed a short quiz to help you identify the areas where you’re struggling.
Take the quiz below and record your answers on your phone or on a scrap piece of paper. Keep in mind there are no wrong answers!
1. You’ve just been assigned an essay in your English class that’s due at the end of the week. What’s the first thing you do?
A. Keep it in mind, even though you won’t start it until the day before it’s due B. Open up your planner. You’ve got to figure out when you’ll write your paper since you have band practice, a speech tournament, and your little sister’s dance recital this week, too. C. Groan out loud. Another essay? You could barely get yourself to write the last one! D. Start thinking about your essay topic, which makes you think about your art project that’s due the same day, which reminds you that your favorite artist might have just posted to Instagram...so you better check your feed right now.
2. Your mom asked you to pick up your room before she gets home from work. You’ve just gotten home from school. You decide you’ll tackle your chores:
A. Five minutes before your mom walks through the front door. As long as it gets done, who cares when you start? B. As soon as you get home from your shift at the local grocery store. C. After you give yourself a 15-minute pep talk about how you need to get to work. D. You won’t get it done. Between texts from your friends, trying to watch your favorite Netflix show, and playing with your dog, you just lost track of time!
3. You’ve signed up to wash dogs at the Humane Society to help earn money for your senior class trip. You:
A. Show up ten minutes late. You put off leaving your house until the last minute, then got stuck in unexpected traffic on the way to the shelter. B. Have to call and cancel at the last minute. You forgot you’d already agreed to babysit your cousin and bake cupcakes for tomorrow’s bake sale. C. Actually arrive fifteen minutes early with extra brushes and bandanas you picked up at the store. You’re passionate about animals, so you’re excited to help out! D. Show up on time, but only get three dogs washed. You couldn’t help it: you just kept getting distracted by how cute they were!
4. You have an hour of downtime, so you decide you’re going to watch an episode of The Great British Baking Show. You:
A. Scroll through your social media feeds for twenty minutes before hitting play, which means you’re not able to finish the whole episode. Ugh! You really wanted to see who was sent home! B. Watch fifteen minutes until you remember you’re supposed to pick up your sister from band practice before heading to your part-time job. No GBBO for you! C. You finish one episode, then decide to watch another even though you’ve got SAT studying to do. It’s just more fun to watch people make scones. D. Start the episode, but only catch bits and pieces of it because you’re reading Twitter, cleaning out your backpack, and eating a snack at the same time.
5. Your teacher asks you to stay after class because you’ve missed turning in two homework assignments in a row. When she asks you what’s wrong, you say:
A. You planned to do your assignments during lunch, but you ran out of time. You decided it would be better to turn in nothing at all than submit unfinished work. B. You really wanted to get the assignments done, but between your extracurriculars, family commitments, and your part-time job, your homework fell through the cracks. C. You have a hard time psyching yourself to tackle the assignments. You just can’t seem to find the motivation to work on them once you get home. D. You tried to do them, but you had a hard time focusing. By the time you realized you hadn’t gotten anything done, it was already time to turn them in.
Like we said earlier, there are no right or wrong answers to this quiz (though your results will be better if you answered as honestly as possible). Here’s how your answers break down:
- If your answers were mostly As, then your biggest struggle with doing homework is procrastination.
- If your answers were mostly Bs, then your biggest struggle with doing homework is time management.
- If your answers were mostly Cs, then your biggest struggle with doing homework is motivation.
- If your answers were mostly Ds, then your biggest struggle with doing homework is getting distracted.
Now that you’ve identified why you’re having a hard time getting your homework done, we can help you figure out how to fix it! Scroll down to find your core problem area to learn more about how you can start to address it.
And one more thing: you’re really struggling with homework, it’s a good idea to read through every section below. You may find some additional tips that will help make homework less intimidating.

How to Do Homework When You’re a Procrastinator
Merriam Webster defines “procrastinate” as “to put off intentionally and habitually.” In other words, procrastination is when you choose to do something at the last minute on a regular basis. If you’ve ever found yourself pulling an all-nighter, trying to finish an assignment between periods, or sprinting to turn in a paper minutes before a deadline, you’ve experienced the effects of procrastination.
If you’re a chronic procrastinator, you’re in good company. In fact, one study found that 70% to 95% of undergraduate students procrastinate when it comes to doing their homework. Unfortunately, procrastination can negatively impact your grades. Researchers have found that procrastination can lower your grade on an assignment by as much as five points ...which might not sound serious until you realize that can mean the difference between a B- and a C+.
Procrastination can also negatively affect your health by increasing your stress levels , which can lead to other health conditions like insomnia, a weakened immune system, and even heart conditions. Getting a handle on procrastination can not only improve your grades, it can make you feel better, too!
The big thing to understand about procrastination is that it’s not the result of laziness. Laziness is defined as being “disinclined to activity or exertion.” In other words, being lazy is all about doing nothing. But a s this Psychology Today article explains , procrastinators don’t put things off because they don’t want to work. Instead, procrastinators tend to postpone tasks they don’t want to do in favor of tasks that they perceive as either more important or more fun. Put another way, procrastinators want to do things...as long as it’s not their homework!
3 Tips f or Conquering Procrastination
Because putting off doing homework is a common problem, there are lots of good tactics for addressing procrastination. Keep reading for our three expert tips that will get your homework habits back on track in no time.
#1: Create a Reward System
Like we mentioned earlier, procrastination happens when you prioritize other activities over getting your homework done. Many times, this happens because homework...well, just isn’t enjoyable. But you can add some fun back into the process by rewarding yourself for getting your work done.
Here’s what we mean: let’s say you decide that every time you get your homework done before the day it’s due, you’ll give yourself a point. For every five points you earn, you’ll treat yourself to your favorite dessert: a chocolate cupcake! Now you have an extra (delicious!) incentive to motivate you to leave procrastination in the dust.
If you’re not into cupcakes, don’t worry. Your reward can be anything that motivates you . Maybe it’s hanging out with your best friend or an extra ten minutes of video game time. As long as you’re choosing something that makes homework worth doing, you’ll be successful.
#2: Have a Homework Accountability Partner
If you’re having trouble getting yourself to start your homework ahead of time, it may be a good idea to call in reinforcements . Find a friend or classmate you can trust and explain to them that you’re trying to change your homework habits. Ask them if they’d be willing to text you to make sure you’re doing your homework and check in with you once a week to see if you’re meeting your anti-procrastination goals.
Sharing your goals can make them feel more real, and an accountability partner can help hold you responsible for your decisions. For example, let’s say you’re tempted to put off your science lab write-up until the morning before it’s due. But you know that your accountability partner is going to text you about it tomorrow...and you don’t want to fess up that you haven’t started your assignment. A homework accountability partner can give you the extra support and incentive you need to keep your homework habits on track.
#3: Create Your Own Due Dates
If you’re a life-long procrastinator, you might find that changing the habit is harder than you expected. In that case, you might try using procrastination to your advantage! If you just can’t seem to stop doing your work at the last minute, try setting your own due dates for assignments that range from a day to a week before the assignment is actually due.
Here’s what we mean. Let’s say you have a math worksheet that’s been assigned on Tuesday and is due on Friday. In your planner, you can write down the due date as Thursday instead. You may still put off your homework assignment until the last minute...but in this case, the “last minute” is a day before the assignment’s real due date . This little hack can trick your procrastination-addicted brain into planning ahead!

If you feel like Kevin Hart in this meme, then our tips for doing homework when you're busy are for you.
How to Do Homework When You’re too Busy
If you’re aiming to go to a top-tier college , you’re going to have a full plate. Because college admissions is getting more competitive, it’s important that you’re maintaining your grades , studying hard for your standardized tests , and participating in extracurriculars so your application stands out. A packed schedule can get even more hectic once you add family obligations or a part-time job to the mix.
If you feel like you’re being pulled in a million directions at once, you’re not alone. Recent research has found that stress—and more severe stress-related conditions like anxiety and depression— are a major problem for high school students . In fact, one study from the American Psychological Association found that during the school year, students’ stress levels are higher than those of the adults around them.
For students, homework is a major contributor to their overall stress levels . Many high schoolers have multiple hours of homework every night , and figuring out how to fit it into an already-packed schedule can seem impossible.
3 Tips for Fitting Homework Into Your Busy Schedule
While it might feel like you have literally no time left in your schedule, there are still ways to make sure you’re able to get your homework done and meet your other commitments. Here are our expert homework tips for even the busiest of students.
#1: Make a Prioritized To-Do List
You probably already have a to-do list to keep yourself on track. The next step is to prioritize the items on your to-do list so you can see what items need your attention right away.
Here’s how it works: at the beginning of each day, sit down and make a list of all the items you need to get done before you go to bed. This includes your homework, but it should also take into account any practices, chores, events, or job shifts you may have. Once you get everything listed out, it’s time to prioritize them using the labels A, B, and C. Here’s what those labels mean:
- A Tasks : tasks that have to get done—like showing up at work or turning in an assignment—get an A.
- B Tasks : these are tasks that you would like to get done by the end of the day but aren’t as time sensitive. For example, studying for a test you have next week could be a B-level task. It’s still important, but it doesn’t have to be done right away.
- C Tasks: these are tasks that aren’t very important and/or have no real consequences if you don’t get them done immediately. For instance, if you’re hoping to clean out your closet but it’s not an assigned chore from your parents, you could label that to-do item with a C.
Prioritizing your to-do list helps you visualize which items need your immediate attention, and which items you can leave for later. A prioritized to-do list ensures that you’re spending your time efficiently and effectively, which helps you make room in your schedule for homework. So even though you might really want to start making decorations for Homecoming (a B task), you’ll know that finishing your reading log (an A task) is more important.
#2: Use a Planner With Time Labels
Your planner is probably packed with notes, events, and assignments already. (And if you’re not using a planner, it’s time to start!) But planners can do more for you than just remind you when an assignment is due. If you’re using a planner with time labels, it can help you visualize how you need to spend your day.
A planner with time labels breaks your day down into chunks, and you assign tasks to each chunk of time. For example, you can make a note of your class schedule with assignments, block out time to study, and make sure you know when you need to be at practice. Once you know which tasks take priority, you can add them to any empty spaces in your day.
Planning out how you spend your time not only helps you use it wisely, it can help you feel less overwhelmed, too . We’re big fans of planners that include a task list ( like this one ) or have room for notes ( like this one ).
#3: Set Reminders on Your Phone
If you need a little extra nudge to make sure you’re getting your homework done on time, it’s a good idea to set some reminders on your phone. You don’t need a fancy app, either. You can use your alarm app to have it go off at specific times throughout the day to remind you to do your homework. This works especially well if you have a set homework time scheduled. So if you’ve decided you’re doing homework at 6:00 pm, you can set an alarm to remind you to bust out your books and get to work.
If you use your phone as your planner, you may have the option to add alerts, emails, or notifications to scheduled events . Many calendar apps, including the one that comes with your phone, have built-in reminders that you can customize to meet your needs. So if you block off time to do your homework from 4:30 to 6:00 pm, you can set a reminder that will pop up on your phone when it’s time to get started.

This dog isn't judging your lack of motivation...but your teacher might. Keep reading for tips to help you motivate yourself to do your homework.
How to Do Homework When You’re Unmotivated
At first glance, it may seem like procrastination and being unmotivated are the same thing. After all, both of these issues usually result in you putting off your homework until the very last minute.
But there’s one key difference: many procrastinators are working, they’re just prioritizing work differently. They know they’re going to start their homework...they’re just going to do it later.
Conversely, people who are unmotivated to do homework just can’t find the willpower to tackle their assignments. Procrastinators know they’ll at least attempt the homework at the last minute, whereas people who are unmotivated struggle with convincing themselves to do it at a ll. For procrastinators, the stress comes from the inevitable time crunch. For unmotivated people, the stress comes from trying to convince themselves to do something they don’t want to do in the first place.
Here are some common reasons students are unmotivated in doing homework :
- Assignments are too easy, too hard, or seemingly pointless
- Students aren’t interested in (or passionate about) the subject matter
- Students are intimidated by the work and/or feels like they don’t understand the assignment
- Homework isn’t fun, and students would rather spend their time on things that they enjoy
To sum it up: people who lack motivation to do their homework are more likely to not do it at all, or to spend more time worrying about doing their homework than...well, actually doing it.
3 Tips for How to Get Motivated to Do Homework
The key to getting homework done when you’re unmotivated is to figure out what does motivate you, then apply those things to homework. It sounds tricky...but it’s pretty simple once you get the hang of it! Here are our three expert tips for motivating yourself to do your homework.
#1: Use Incremental Incentives
When you’re not motivated, it’s important to give yourself small rewards to stay focused on finishing the task at hand. The trick is to keep the incentives small and to reward yourself often. For example, maybe you’re reading a good book in your free time. For every ten minutes you spend on your homework, you get to read five pages of your book. Like we mentioned earlier, make sure you’re choosing a reward that works for you!
So why does this technique work? Using small rewards more often allows you to experience small wins for getting your work done. Every time you make it to one of your tiny reward points, you get to celebrate your success, which gives your brain a boost of dopamine . Dopamine helps you stay motivated and also creates a feeling of satisfaction when you complete your homework !
#2: Form a Homework Group
If you’re having trouble motivating yourself, it’s okay to turn to others for support. Creating a homework group can help with this. Bring together a group of your friends or classmates, and pick one time a week where you meet and work on homework together. You don’t have to be in the same class, or even taking the same subjects— the goal is to encourage one another to start (and finish!) your assignments.
Another added benefit of a homework group is that you can help one another if you’re struggling to understand the material covered in your classes. This is especially helpful if your lack of motivation comes from being intimidated by your assignments. Asking your friends for help may feel less scary than talking to your teacher...and once you get a handle on the material, your homework may become less frightening, too.
#3: Change Up Your Environment
If you find that you’re totally unmotivated, it may help if you find a new place to do your homework. For example, if you’ve been struggling to get your homework done at home, try spending an extra hour in the library after school instead. The change of scenery can limit your distractions and give you the energy you need to get your work done.
If you’re stuck doing homework at home, you can still use this tip. For instance, maybe you’ve always done your homework sitting on your bed. Try relocating somewhere else, like your kitchen table, for a few weeks. You may find that setting up a new “homework spot” in your house gives you a motivational lift and helps you get your work done.

Social media can be a huge problem when it comes to doing homework. We have advice for helping you unplug and regain focus.
How to Do Homework When You’re Easily Distracted
We live in an always-on world, and there are tons of things clamoring for our attention. From friends and family to pop culture and social media, it seems like there’s always something (or someone!) distracting us from the things we need to do.
The 24/7 world we live in has affected our ability to focus on tasks for prolonged periods of time. Research has shown that over the past decade, an average person’s attention span has gone from 12 seconds to eight seconds . And when we do lose focus, i t takes people a long time to get back on task . One study found that it can take as long as 23 minutes to get back to work once we’ve been distracte d. No wonder it can take hours to get your homework done!
3 Tips to Improve Your Focus
If you have a hard time focusing when you’re doing your homework, it’s a good idea to try and eliminate as many distractions as possible. Here are three expert tips for blocking out the noise so you can focus on getting your homework done.
#1: Create a Distraction-Free Environment
Pick a place where you’ll do your homework every day, and make it as distraction-free as possible. Try to find a location where there won’t be tons of noise, and limit your access to screens while you’re doing your homework. Put together a focus-oriented playlist (or choose one on your favorite streaming service), and put your headphones on while you work.
You may find that other people, like your friends and family, are your biggest distraction. If that’s the case, try setting up some homework boundaries. Let them know when you’ll be working on homework every day, and ask them if they’ll help you keep a quiet environment. They’ll be happy to lend a hand!
#2: Limit Your Access to Technology
We know, we know...this tip isn’t fun, but it does work. For homework that doesn’t require a computer, like handouts or worksheets, it’s best to put all your technology away . Turn off your television, put your phone and laptop in your backpack, and silence notifications on any wearable tech you may be sporting. If you listen to music while you work, that’s fine...but make sure you have a playlist set up so you’re not shuffling through songs once you get started on your homework.
If your homework requires your laptop or tablet, it can be harder to limit your access to distractions. But it’s not impossible! T here are apps you can download that will block certain websites while you’re working so that you’re not tempted to scroll through Twitter or check your Facebook feed. Silence notifications and text messages on your computer, and don’t open your email account unless you absolutely have to. And if you don’t need access to the internet to complete your assignments, turn off your WiFi. Cutting out the online chatter is a great way to make sure you’re getting your homework done.
#3: Set a Timer (the Pomodoro Technique)
Have you ever heard of the Pomodoro technique ? It’s a productivity hack that uses a timer to help you focus!
Here’s how it works: first, set a timer for 25 minutes. This is going to be your work time. During this 25 minutes, all you can do is work on whatever homework assignment you have in front of you. No email, no text messaging, no phone calls—just homework. When that timer goes off, you get to take a 5 minute break. Every time you go through one of these cycles, it’s called a “pomodoro.” For every four pomodoros you complete, you can take a longer break of 15 to 30 minutes.
The pomodoro technique works through a combination of boundary setting and rewards. First, it gives you a finite amount of time to focus, so you know that you only have to work really hard for 25 minutes. Once you’ve done that, you’re rewarded with a short break where you can do whatever you want. Additionally, tracking how many pomodoros you complete can help you see how long you’re really working on your homework. (Once you start using our focus tips, you may find it doesn’t take as long as you thought!)

Two Bonus Tips for How to Do Homework Fast
Even if you’re doing everything right, there will be times when you just need to get your homework done as fast as possible. (Why do teachers always have projects due in the same week? The world may never know.)
The problem with speeding through homework is that it’s easy to make mistakes. While turning in an assignment is always better than not submitting anything at all, you want to make sure that you’re not compromising quality for speed. Simply put, the goal is to get your homework done quickly and still make a good grade on the assignment!
Here are our two bonus tips for getting a decent grade on your homework assignments , even when you’re in a time crunch.
#1: Do the Easy Parts First
This is especially true if you’re working on a handout with multiple questions. Before you start working on the assignment, read through all the questions and problems. As you do, make a mark beside the questions you think are “easy” to answer .
Once you’ve finished going through the whole assignment, you can answer these questions first. Getting the easy questions out of the way as quickly as possible lets you spend more time on the trickier portions of your homework, which will maximize your assignment grade.
(Quick note: this is also a good strategy to use on timed assignments and tests, like the SAT and the ACT !)
#2: Pay Attention in Class
Homework gets a lot easier when you’re actively learning the material. Teachers aren’t giving you homework because they’re mean or trying to ruin your weekend... it’s because they want you to really understand the course material. Homework is designed to reinforce what you’re already learning in class so you’ll be ready to tackle harder concepts later.
When you pay attention in class, ask questions, and take good notes, you’re absorbing the information you’ll need to succeed on your homework assignments. (You’re stuck in class anyway, so you might as well make the most of it!) Not only will paying attention in class make your homework less confusing, it will also help it go much faster, too.

What’s Next?
If you’re looking to improve your productivity beyond homework, a good place to begin is with time management. After all, we only have so much time in a day...so it’s important to get the most out of it! To get you started, check out this list of the 12 best time management techniques that you can start using today.
You may have read this article because homework struggles have been affecting your GPA. Now that you’re on the path to homework success, it’s time to start being proactive about raising your grades. This article teaches you everything you need to know about raising your GPA so you can
Now you know how to get motivated to do homework...but what about your study habits? Studying is just as critical to getting good grades, and ultimately getting into a good college . We can teach you how to study bette r in high school. (We’ve also got tons of resources to help you study for your ACT and SAT exams , too!)
These recommendations are based solely on our knowledge and experience. If you purchase an item through one of our links, PrepScholar may receive a commission.

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
Does homework really work?
by: Leslie Crawford | Updated: December 12, 2023
Print article

You know the drill. It’s 10:15 p.m., and the cardboard-and-toothpick Golden Gate Bridge is collapsing. The pages of polynomials have been abandoned. The paper on the Battle of Waterloo seems to have frozen in time with Napoleon lingering eternally over his breakfast at Le Caillou. Then come the tears and tantrums — while we parents wonder, Does the gain merit all this pain? Is this just too much homework?
However the drama unfolds night after night, year after year, most parents hold on to the hope that homework (after soccer games, dinner, flute practice, and, oh yes, that childhood pastime of yore known as playing) advances their children academically.
But what does homework really do for kids? Is the forest’s worth of book reports and math and spelling sheets the average American student completes in their 12 years of primary schooling making a difference? Or is it just busywork?
Homework haterz
Whether or not homework helps, or even hurts, depends on who you ask. If you ask my 12-year-old son, Sam, he’ll say, “Homework doesn’t help anything. It makes kids stressed-out and tired and makes them hate school more.”
Nothing more than common kid bellyaching?
Maybe, but in the fractious field of homework studies, it’s worth noting that Sam’s sentiments nicely synopsize one side of the ivory tower debate. Books like The End of Homework , The Homework Myth , and The Case Against Homework the film Race to Nowhere , and the anguished parent essay “ My Daughter’s Homework is Killing Me ” make the case that homework, by taking away precious family time and putting kids under unneeded pressure, is an ineffective way to help children become better learners and thinkers.
One Canadian couple took their homework apostasy all the way to the Supreme Court of Canada. After arguing that there was no evidence that it improved academic performance, they won a ruling that exempted their two children from all homework.
So what’s the real relationship between homework and academic achievement?
How much is too much?
To answer this question, researchers have been doing their homework on homework, conducting and examining hundreds of studies. Chris Drew Ph.D., founder and editor at The Helpful Professor recently compiled multiple statistics revealing the folly of today’s after-school busy work. Does any of the data he listed below ring true for you?
• 45 percent of parents think homework is too easy for their child, primarily because it is geared to the lowest standard under the Common Core State Standards .
• 74 percent of students say homework is a source of stress , defined as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss, and stomach problems.
• Students in high-performing high schools spend an average of 3.1 hours a night on homework , even though 1 to 2 hours is the optimal duration, according to a peer-reviewed study .
Not included in the list above is the fact many kids have to abandon activities they love — like sports and clubs — because homework deprives them of the needed time to enjoy themselves with other pursuits.
Conversely, The Helpful Professor does list a few pros of homework, noting it teaches discipline and time management, and helps parents know what’s being taught in the class.
The oft-bandied rule on homework quantity — 10 minutes a night per grade (starting from between 10 to 20 minutes in first grade) — is listed on the National Education Association’s website and the National Parent Teacher Association’s website , but few schools follow this rule.
Do you think your child is doing excessive homework? Harris Cooper Ph.D., author of a meta-study on homework , recommends talking with the teacher. “Often there is a miscommunication about the goals of homework assignments,” he says. “What appears to be problematic for kids, why they are doing an assignment, can be cleared up with a conversation.” Also, Cooper suggests taking a careful look at how your child is doing the assignments. It may seem like they’re taking two hours, but maybe your child is wandering off frequently to get a snack or getting distracted.
Less is often more
If your child is dutifully doing their work but still burning the midnight oil, it’s worth intervening to make sure your child gets enough sleep. A 2012 study of 535 high school students found that proper sleep may be far more essential to brain and body development.
For elementary school-age children, Cooper’s research at Duke University shows there is no measurable academic advantage to homework. For middle-schoolers, Cooper found there is a direct correlation between homework and achievement if assignments last between one to two hours per night. After two hours, however, achievement doesn’t improve. For high schoolers, Cooper’s research suggests that two hours per night is optimal. If teens have more than two hours of homework a night, their academic success flatlines. But less is not better. The average high school student doing homework outperformed 69 percent of the students in a class with no homework.
Many schools are starting to act on this research. A Florida superintendent abolished homework in her 42,000 student district, replacing it with 20 minutes of nightly reading. She attributed her decision to “ solid research about what works best in improving academic achievement in students .”
More family time
A 2020 survey by Crayola Experience reports 82 percent of children complain they don’t have enough quality time with their parents. Homework deserves much of the blame. “Kids should have a chance to just be kids and do things they enjoy, particularly after spending six hours a day in school,” says Alfie Kohn, author of The Homework Myth . “It’s absurd to insist that children must be engaged in constructive activities right up until their heads hit the pillow.”
By far, the best replacement for homework — for both parents and children — is bonding, relaxing time together.
Homes Nearby
Homes for rent and sale near schools

How families of color can fight for fair discipline in school

Dealing with teacher bias

The most important school data families of color need to consider
Yes! Sign me up for updates relevant to my child's grade.
Please enter a valid email address
Thank you for signing up!
Server Issue: Please try again later. Sorry for the inconvenience

Homework: How to Effectively Build the Learning Bridge

How has the global health crisis impacted the place that homework has in student learning and the school-home connection? Homework holds its place as a school tradition, expected by students and their parents as part of the experience of growing and learning. While there is ongoing debate about homework’s effectiveness, it is traditionally seen as a tool that strengthens academics by providing learning practice at home. John Hattie’s meta-analysis of relevant research on educational practices found that the overall effects of homework on learning are positive, and that the positive effect is highest for junior high and high school students but generally neutral for elementary students. In addition, there is variability depending on the type of homework as well as student demographics (Hattie, 2008).
Schools implementing the Responsive Classroom approach, whether in person or virtually, use homework to effectively build a learning bridge between home and school. When homework is used as a tool to build social, emotional, and academic learning beyond the school day, it takes on a different look and purpose than just more work to do at home. The goal of Responsive Classroom schools is to design homework that meets the basic needs of significance and belonging for every student by strengthening relationships, differentiating what success looks like for each child, and supporting students’ social, emotional, and academic learning.
Focus on Relationships
Homework that impedes relationships— either teacher-to-student, teacher-toparent, or student-to-parent—can potentially damage the home-school partnership. When educators examine the amount, type, and expectations of homework, they often start with the impact of homework on academic achievement. But when schools look beyond academic achievement and also include relationships, they will often rethink the look and purpose of homework.
Effectively building this school-to-home connection starts by replacing homework that impedes relationships with homework that will enhance them. Examples for building these connections include ways for students to share about family traditions, cultural practices, and/or family adventures. Lauren Komanitsky, a special education teacher at Christa McAuliffe Middle School in Jackson, New Jersey, observes:
I’ve seen tremendous enthusiasm for homework and projects that involve family members and their family history. [Students] love to learn about ancestors, interesting facts and stories, and simply getting a deeper understanding of their background. It inspires pride in them and that’s important for their identity. Students also love to do surveys and interviews of their family members. I think anything designed to create good, meaningful conversation between students and their families is time well spent. Lauren Komanitsky (personal communication, February 7, 2021)
Schools that use homework to strengthen home-school relationships embed opportunities for students to develop belonging and significance. As students share the home connections with their classmates and teachers, the classroom community will develop a larger sense of belonging because students see connections among common experiences.
Build Success for Every Student
Classrooms are diverse communities. While teachers intentionally differentiate learning during the school day, providing homework that meets the individual and cultural needs of each student requires additional attention.
One strategy for success for every student is to provide choice. Komanitsky has seen this strategy work when she has had students reflect on what they need and then select homework to meet that need:
Having kids select specific problems from a group, select what part of an overall project they are choosing to focus on, etc. . . . helps with creating a sense of autonomy. When we can give kids a choice in their learning based on their own self-reflection, they learn what it feels like to be in control of the process and this leads to more success. Lauren Komanitsky (personal communication, February 7, 2021)
When homework is designed for success for each student, the bridge between home and school supports a higher level of success and engagement.
Include Practice of Social and Emotional Learning Skills
The first guiding principle of the Responsive Classroom approach states, “Teaching social and emotional skills is as important as teaching academic content.” Social and emotional learning (SEL) is embedded in academic learning throughout the school day. Teachers can create a bridge between home and school by suggesting opportunities for students to practice SEL skills at home and in their community. For example, parents can have their children practice speaking with confidence by having them “make a request, place an order, or thank customer service workers” (Wilson, 2014, p. 67).
In addition, homework may involve students having conversations with family members about their learning histories—the successes, struggles, and strategies t hey encountered when they were students at different levels. When family members share their learning histories, students discover the application of the SEL and academic competencies of perseverance, cooperation, and responsibility. As Komanitsky points out:
When we share how we overcame struggles in certain academic subjects, it encourages perseverance and resilience in our students. Having parents and kids discuss their personal strengths and weaknesses and how they compensate when necessary is also a really good conversation. Lauren Komanitsky (personal communication, February 7, 2021)
Homework that focuses on SEL competencies provides for the transfer of these vital skills to a variety of real-life situations, both at home and in the community.
When schools approach homework as an extension of the learning day and see it as a way to strengthen relationships—between teachers and parents, students and parents, and students and teachers—homework becomes a valuable part of the school experience for every child. Students’ needs for belonging and significance are met and strengthened when homework provides for individual success. And when educators view homework as a tool to strengthen academic, social, and emotional learning, it becomes a valuable piece of the learning puzzle for every student.

- Hattie, J. (2008). Visible learning: A synthesis of over 800 meta-analyses relating to achievement. Routledge.
- Wilson, M. B. (2014). The language of learning: Teaching students core thinking, listening, and speaking skills. Center for Responsive Schools, Inc
- Skip to Nav
- Skip to Main
- Skip to Footer

How to Create Effective Homework
Please try again
Based on a recent spate of articles on homework, it’s clear that the homework wars -- how much? how often? -- are still topic of big interest to both parents and teachers. Some teachers hate to give homework; others see it as a vital necessity. But according to some research presented by Annie Murphy Paul, the question isn’t how much, but whether the homework teachers do give actually advances learning.
“A recent study, published in the Economics of Education Review,” Paul wrote in “How Can We Make Homework Worthwhile?” , “reports that homework in science, English and history has ‘little to no impact’ on student test scores. (The authors did note a positive effect for math homework.) Enriching children’s classroom learning requires making homework not shorter or longer, but smarter.” Paul goes on to describe specific practices, like spaced repetition (in which information is presented and repeated spaced out over time), retrieval practice (testing or quizzing not for assessment, but to reinforce material learned), and cognitive disfluency (“desirable difficulties” used to make learning stick) -- all memory/retrieval techniques that may help homework move beyond busy work and advance real learning.
But to get those elements to work, said Fires in the Mind author and speaker Kathleen Cushman, students must be motivated to do their homework in the first place. One example Cushman gave was creating a project so interesting and involved, students naturally wanted to keep working on it after the bell rang. She pointed to a chapter in the book where she describes a particular motivation for some high school students she interviewed, under the heading “Homework We Actually Want to Do”:
“Christina and Nicholas both remembered a global studies unit on the French Revolution in which students acted out a courtroom trial of the king and queen. The project brought even routine homework assignments to life, they said.
“I was the queen. So of course I wanted to do my homework all the time, so I could know the facts of what happened and what didn’t happen, know what I wanted to say when someone tried to say I did this or that thing. I could say, ‘Oh no, I didn’t!’ - because I’d read my homework,” said Christina.
Christina was using a form of retrieval practice -- but because it was so much fun to be the queen, she only knew she wanted to stay in character. The queen had to study the information to get it right.
Another way teachers can take a good, hard look at homework practices, said Cushman, is to ask themselves a few vital questions: “Does this homework ask each student to practice something that the student hasn’t yet mastered? Does the student clearly see its purpose? When students are asked to repeat or rehearse something, does it require them to focus? Or can they do it without really paying attention?” If the homework meets these criteria, she said, then it falls into the desirable realm of “deliberate practice .”
Dan Bisaccio, former high school science teacher and now Director of Science Education at Brown University, said that after years of experience giving homework to high school students, he now “preaches” to his future teachers: “Homework should be practice and extensions of what happens in class and should not be ‘new learning,’” he said. “That is, students [shouldn’t be] having to teach themselves new content or skills.”
He said he agreed with Cushman that motivation is key, and tried to design homework that kept students interested. “Teachers need to clue into what motivates their students, giving them something that they really want to complete, and complete well.” One assignment Bisaccio used, called an “Experience Map,” asked students to create a map of their experiences after a field study or other important project - a technique employing both retrieval practice and the somewhat trickier interleaving, a “desirable difficulty” in which problems of different types are presented in one assignment, making students think harder to come up with solutions and answers.
“We ‘map’ mentally and physically each day. It helps to keep us orientated through our frenzied sun-up to sun-down daily experiences,” reads the assignment. Directions are to draw a field experience map, including -- with regard to the class -- where students have been, what they have done, new challenges, and insights. Special suggestions for drawing include “a place of danger, a favorite place, a place of power, a place with a secret.” Students are also called upon to map the places where they learned the most, where they were challenged the most, and where the funniest experience happened.
In addition, Bisaccio asked students to write what had challenged them most as a learner, what had stretched their limits most -- meant to be reflections just for students themselves, and asked to be kept on the back of the map. “What they wrote on the back was not shared with others,” he said. Once the assignment was completed, maps were posted to form a class atlas of what they had learned.
All the examples included here, however, are examples of homework in a traditional classroom. What about homework in a flipped classroom , where the lectures, usually videos, are the homework? A recent New York Times article on flipped classrooms may provide insight into flipping homework on its head, too: it quoted high school senior Luwayne Harris, saying, “Whenever I had a problem on the homework, I couldn’t do anything about it at home. Now if I have a problem with a video, I can just rewind and watch it over and over again.”
Is Homework Good for Kids? Here’s What the Research Says
A s kids return to school, debate is heating up once again over how they should spend their time after they leave the classroom for the day.
The no-homework policy of a second-grade teacher in Texas went viral last week , earning praise from parents across the country who lament the heavy workload often assigned to young students. Brandy Young told parents she would not formally assign any homework this year, asking students instead to eat dinner with their families, play outside and go to bed early.
But the question of how much work children should be doing outside of school remains controversial, and plenty of parents take issue with no-homework policies, worried their kids are losing a potential academic advantage. Here’s what you need to know:
For decades, the homework standard has been a “10-minute rule,” which recommends a daily maximum of 10 minutes of homework per grade level. Second graders, for example, should do about 20 minutes of homework each night. High school seniors should complete about two hours of homework each night. The National PTA and the National Education Association both support that guideline.
But some schools have begun to give their youngest students a break. A Massachusetts elementary school has announced a no-homework pilot program for the coming school year, lengthening the school day by two hours to provide more in-class instruction. “We really want kids to go home at 4 o’clock, tired. We want their brain to be tired,” Kelly Elementary School Principal Jackie Glasheen said in an interview with a local TV station . “We want them to enjoy their families. We want them to go to soccer practice or football practice, and we want them to go to bed. And that’s it.”
A New York City public elementary school implemented a similar policy last year, eliminating traditional homework assignments in favor of family time. The change was quickly met with outrage from some parents, though it earned support from other education leaders.
New solutions and approaches to homework differ by community, and these local debates are complicated by the fact that even education experts disagree about what’s best for kids.
The research
The most comprehensive research on homework to date comes from a 2006 meta-analysis by Duke University psychology professor Harris Cooper, who found evidence of a positive correlation between homework and student achievement, meaning students who did homework performed better in school. The correlation was stronger for older students—in seventh through 12th grade—than for those in younger grades, for whom there was a weak relationship between homework and performance.
Cooper’s analysis focused on how homework impacts academic achievement—test scores, for example. His report noted that homework is also thought to improve study habits, attitudes toward school, self-discipline, inquisitiveness and independent problem solving skills. On the other hand, some studies he examined showed that homework can cause physical and emotional fatigue, fuel negative attitudes about learning and limit leisure time for children. At the end of his analysis, Cooper recommended further study of such potential effects of homework.
Despite the weak correlation between homework and performance for young children, Cooper argues that a small amount of homework is useful for all students. Second-graders should not be doing two hours of homework each night, he said, but they also shouldn’t be doing no homework.
Not all education experts agree entirely with Cooper’s assessment.
Cathy Vatterott, an education professor at the University of Missouri-St. Louis, supports the “10-minute rule” as a maximum, but she thinks there is not sufficient proof that homework is helpful for students in elementary school.
“Correlation is not causation,” she said. “Does homework cause achievement, or do high achievers do more homework?”
Vatterott, the author of Rethinking Homework: Best Practices That Support Diverse Needs , thinks there should be more emphasis on improving the quality of homework tasks, and she supports efforts to eliminate homework for younger kids.
“I have no concerns about students not starting homework until fourth grade or fifth grade,” she said, noting that while the debate over homework will undoubtedly continue, she has noticed a trend toward limiting, if not eliminating, homework in elementary school.
The issue has been debated for decades. A TIME cover in 1999 read: “Too much homework! How it’s hurting our kids, and what parents should do about it.” The accompanying story noted that the launch of Sputnik in 1957 led to a push for better math and science education in the U.S. The ensuing pressure to be competitive on a global scale, plus the increasingly demanding college admissions process, fueled the practice of assigning homework.
“The complaints are cyclical, and we’re in the part of the cycle now where the concern is for too much,” Cooper said. “You can go back to the 1970s, when you’ll find there were concerns that there was too little, when we were concerned about our global competitiveness.”
Cooper acknowledged that some students really are bringing home too much homework, and their parents are right to be concerned.
“A good way to think about homework is the way you think about medications or dietary supplements,” he said. “If you take too little, they’ll have no effect. If you take too much, they can kill you. If you take the right amount, you’ll get better.”
More Must-Reads From TIME
- What Student Photojournalists Saw at the Campus Protests
- How Far Trump Would Go
- Why Maternity Care Is Underpaid
- Saving Seconds Is Better Than Hours
- Welcome to the Golden Age of Ryan Gosling
- Scientists Are Finding Out Just How Toxic Your Stuff Is
- The 100 Most Influential People of 2024
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Write to Katie Reilly at [email protected]
A community blog focused on educational excellence and equity
About the topic
Explore classroom guidance, techniques, and activities to help you meet the needs of ALL students.
most recent articles
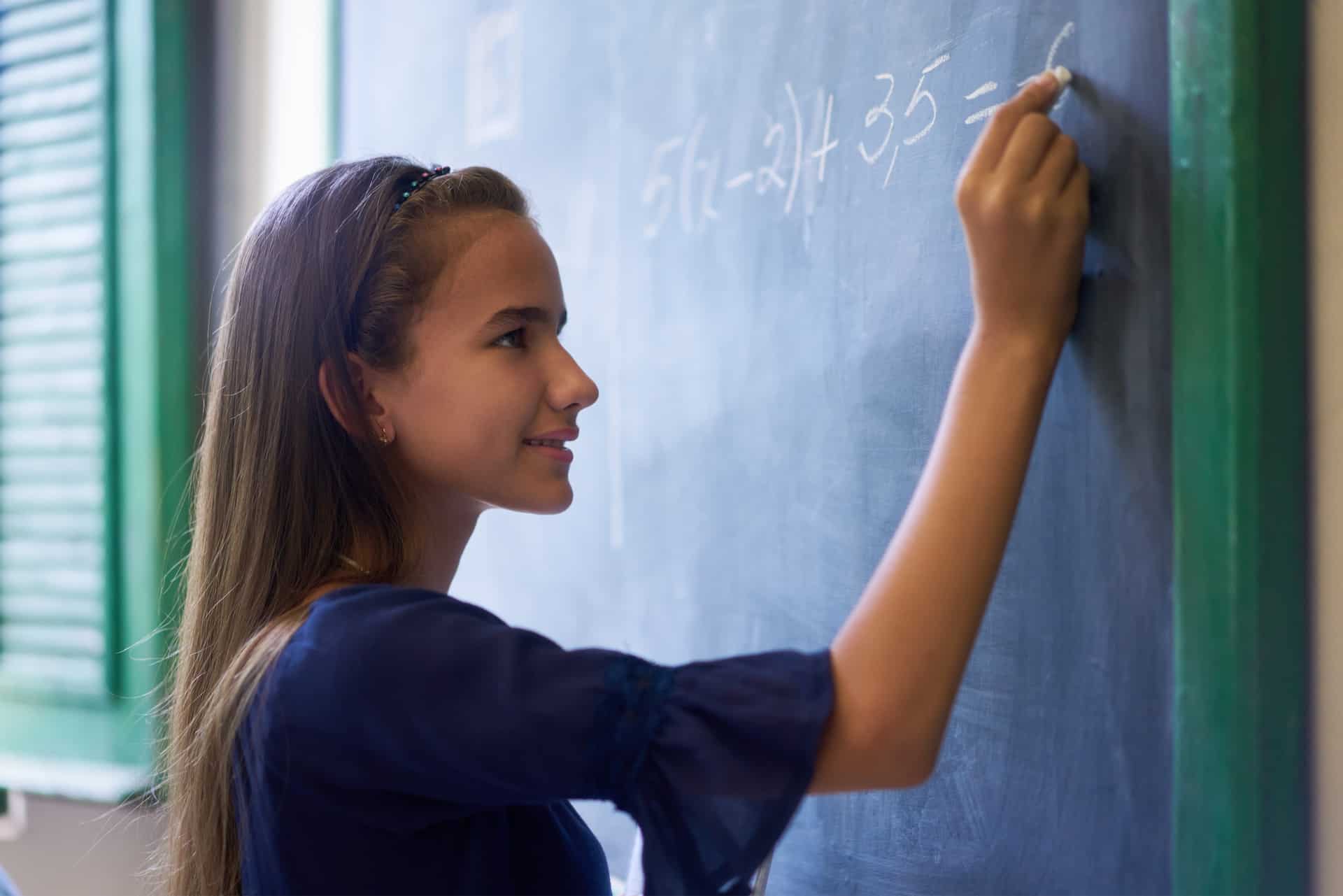
Shaking Up High School Math

Executive Functions and Literacy Skills in the Classroom


Connecting and Communicating With Families to Help Break Down Barriers to Learning
Discover new tools and materials to integrate into you instruction.

Culture, Community, and Collaboration
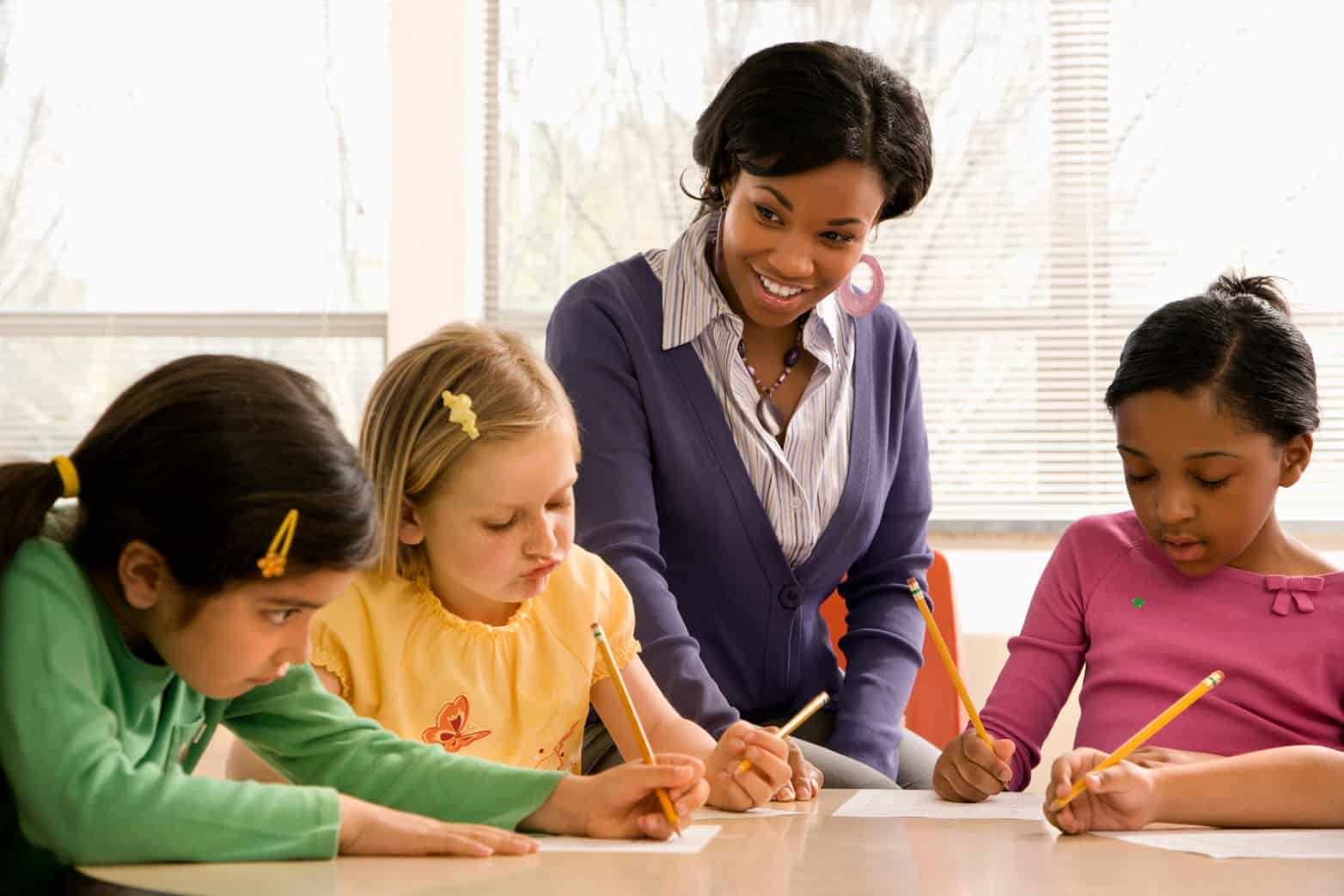

Vertical Progression of Math Strategies – Building Teacher Understanding

“Can I have this? Can I have that?”
Find instructions and recommendations on how to adapt your existing materials to better align to college- and career-ready standards.

To Teach the Truth

Helping Our Students See Themselves and the World Through the Books They Read in Our Classrooms
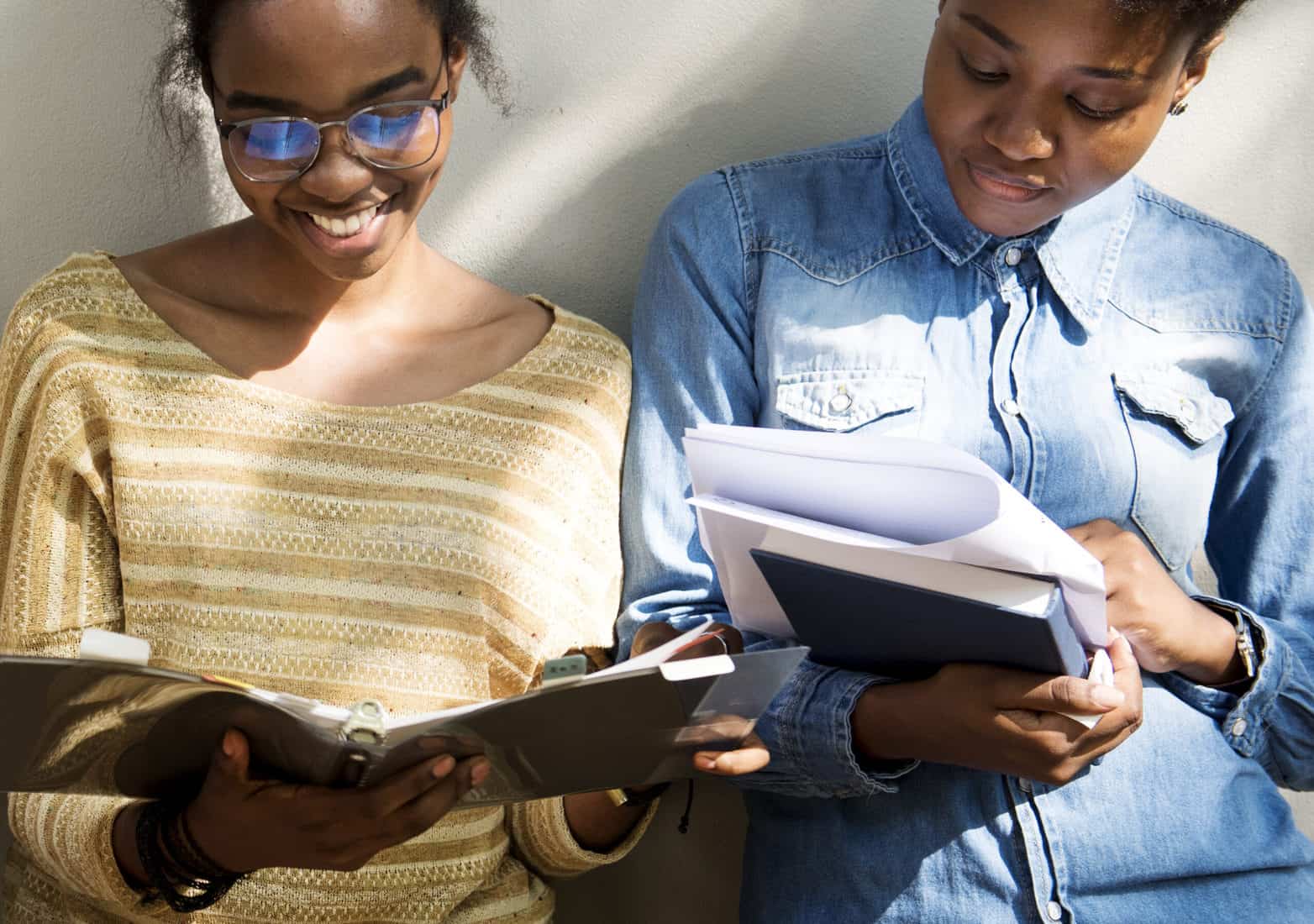

Textbooks: Who Needs Them?
Learn what it means for instructional materials and assessment to be aligned to college- and career-ready standards.

Let’s Not Make Power ELA/Literacy Standards and Talk About Why We Didn’t

What to Consider if You’re Adopting a New ELA/Literacy Curriculum

Not Your Mom’s Professional Development
Delve into new research and perspectives on instructional materials and practice.

Summer Reading Club 2023

Synergy between College and Career Readiness Standards-Aligned Instruction and Culturally Relevant Pedagogy

Children Should be Seen AND Heard
- Submissions Guidelines
- About the Blog
Designing Effective Homework
Best practices for creating homework that raises student achievement

Homework. It can be challenging…and not just for students. For teachers, designing homework can be a daunting task with lots of unanswered questions: How much should I assign? What type of content should I cover? Why aren’t students doing the work I assign? Homework can be a powerful opportunity to reinforce the Shifts in your instruction and promote standards-aligned learning, but how do we avoid the pitfalls that make key learning opportunities sources of stress and antipathy?
The nonprofit Instruction Partners recently set out to answer some of these questions, looking at what research says about what works when it comes to homework. You can view their original presentation here , but I’ve summarized some of the key findings you can put to use with your students immediately.
Does homework help?
Consistent homework completion has been shown to increase student achievement rates—but frequency matters. Students who are given homework regularly show greater gains than those who only receive homework sporadically. Researchers hypothesize that this is due to improved study skills and routines practiced through homework that allow students to perform better academically.
Average gains on unit tests for students who completed homework were six percentile points in grades 4–6, 12 percentile points in grades 7–9, and an impressive 24 percentile points in grades 10–12; so yes, homework (done well) does work. [i]
What should homework cover?
While there is little research about exactly what types of homework content lead to the biggest achievement gains, there are some general rules of thumb about how homework should change gradually over time.
In grades 1–5, homework should:
- Reinforce and allow students to practice skills learned in the classroom
- Help students develop good study habits and routines
- Foster positive feelings about school
In grades 6–12, homework should:
- Prepare students for engagement and discussion during the next lesson
- Allow students to apply their skills in new and more challenging ways
The most often-heard criticism of homework assignments is that they simply take too long. So how much homework should you assign in order to see results for students? Not surprisingly, it varies by grade. Assign 10-20 minutes of homework per night total, starting in first grade, and then add 10 minutes for each additional grade. [ii] Doing more can result in student stress, frustration, and disengagement, particularly in the early grades.
Why are some students not doing the homework?
There are any number of reasons why students may not complete homework, from lack of motivation to lack of content knowledge, but one issue to watch out for as a teacher is the impact of economic disparities on the ability to complete homework.
Multiple studies [iii] have shown that low-income students complete homework less often than students who come from wealthier families. This can lead to increased achievement gaps between students. Students from low-income families may face additional challenges when it comes to completing homework such as lack of access to the internet, lack of access to outside tutors or assistance, and additional jobs or family responsibilities.
While you can’t erase these challenges for your students, you can design homework that takes those issues into account by creating homework that can be done offline, independently, and in a reasonable timeframe. With those design principles in mind, you increase the opportunity for all your students to complete and benefit from the homework you assign.
The Big Picture
Perhaps most importantly, students benefit from receiving feedback from you, their teacher, on their assignments. Praise or rewards simply for homework completion have little effect on student achievement, but feedback that helps them improve or reinforces strong performance does. Consider keeping this mini-table handy as you design homework:
The act of assigning homework doesn’t automatically raise student achievement, so be a critical consumer of the homework products that come as part of your curriculum. If they assign too much (or too little!) work or reflect some of these common pitfalls, take action to make assignments that better serve your students.
[i] Cooper, H. (2007). The battle over homework (3rd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press.
[ii] Cooper, H. (1989a). Homework .White Plains, NY: Longman.
[iii] Horrigan, T. (2015). The numbers behind the broadband ‘homework gap’ http://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2015/04/20/the-numbers-behind-the-broadband-homework-gap/ and Miami Dade Public Schools. (2009). Literature Review: Homework. http://drs.dadeschools.net/LiteratureReviews/Homework.pdf
- ELA / Literacy
- Elementary School
- High School
- Mathematics
- Middle School
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
About the Author: Claire Rivero is the Digital Strategy Manager for Student Achievement Partners. Claire leads the organization’s communications and digital promotion work across various channels including email, Facebook, Twitter, and Pinterest, always seeking new ways to reach educators. She also manages Achieve the Core’s blog, Aligned. Prior to joining Student Achievement Partners, Claire worked in the Communications department for the American Red Cross and as a literacy instructor in a London pilot program. Claire holds bachelor’s degrees in English and Public Policy from Duke University and a master’s degree in Social Policy (with a concentration on Education Policy) from the London School of Economics and Political Science.
Stay In Touch
Like what you’re reading? Sign up to receive emails about new posts, free resources, and advice from educators.
- Our Mission

What’s the Right Amount of Homework?
Decades of research show that homework has some benefits, especially for students in middle and high school—but there are risks to assigning too much.
Many teachers and parents believe that homework helps students build study skills and review concepts learned in class. Others see homework as disruptive and unnecessary, leading to burnout and turning kids off to school. Decades of research show that the issue is more nuanced and complex than most people think: Homework is beneficial, but only to a degree. Students in high school gain the most, while younger kids benefit much less.
The National PTA and the National Education Association support the “ 10-minute homework guideline ”—a nightly 10 minutes of homework per grade level. But many teachers and parents are quick to point out that what matters is the quality of the homework assigned and how well it meets students’ needs, not the amount of time spent on it.
The guideline doesn’t account for students who may need to spend more—or less—time on assignments. In class, teachers can make adjustments to support struggling students, but at home, an assignment that takes one student 30 minutes to complete may take another twice as much time—often for reasons beyond their control. And homework can widen the achievement gap, putting students from low-income households and students with learning disabilities at a disadvantage.
However, the 10-minute guideline is useful in setting a limit: When kids spend too much time on homework, there are real consequences to consider.
Small Benefits for Elementary Students
As young children begin school, the focus should be on cultivating a love of learning, and assigning too much homework can undermine that goal. And young students often don’t have the study skills to benefit fully from homework, so it may be a poor use of time (Cooper, 1989 ; Cooper et al., 2006 ; Marzano & Pickering, 2007 ). A more effective activity may be nightly reading, especially if parents are involved. The benefits of reading are clear: If students aren’t proficient readers by the end of third grade, they’re less likely to succeed academically and graduate from high school (Fiester, 2013 ).
For second-grade teacher Jacqueline Fiorentino, the minor benefits of homework did not outweigh the potential drawback of turning young children against school at an early age, so she experimented with dropping mandatory homework. “Something surprising happened: They started doing more work at home,” Fiorentino writes . “This inspiring group of 8-year-olds used their newfound free time to explore subjects and topics of interest to them.” She encouraged her students to read at home and offered optional homework to extend classroom lessons and help them review material.
Moderate Benefits for Middle School Students
As students mature and develop the study skills necessary to delve deeply into a topic—and to retain what they learn—they also benefit more from homework. Nightly assignments can help prepare them for scholarly work, and research shows that homework can have moderate benefits for middle school students (Cooper et al., 2006 ). Recent research also shows that online math homework, which can be designed to adapt to students’ levels of understanding, can significantly boost test scores (Roschelle et al., 2016 ).
There are risks to assigning too much, however: A 2015 study found that when middle school students were assigned more than 90 to 100 minutes of daily homework, their math and science test scores began to decline (Fernández-Alonso, Suárez-Álvarez, & Muñiz, 2015 ). Crossing that upper limit can drain student motivation and focus. The researchers recommend that “homework should present a certain level of challenge or difficulty, without being so challenging that it discourages effort.” Teachers should avoid low-effort, repetitive assignments, and assign homework “with the aim of instilling work habits and promoting autonomous, self-directed learning.”
In other words, it’s the quality of homework that matters, not the quantity. Brian Sztabnik, a veteran middle and high school English teacher, suggests that teachers take a step back and ask themselves these five questions :
- How long will it take to complete?
- Have all learners been considered?
- Will an assignment encourage future success?
- Will an assignment place material in a context the classroom cannot?
- Does an assignment offer support when a teacher is not there?
More Benefits for High School Students, but Risks as Well
By the time they reach high school, students should be well on their way to becoming independent learners, so homework does provide a boost to learning at this age, as long as it isn’t overwhelming (Cooper et al., 2006 ; Marzano & Pickering, 2007 ). When students spend too much time on homework—more than two hours each night—it takes up valuable time to rest and spend time with family and friends. A 2013 study found that high school students can experience serious mental and physical health problems, from higher stress levels to sleep deprivation, when assigned too much homework (Galloway, Conner, & Pope, 2013 ).
Homework in high school should always relate to the lesson and be doable without any assistance, and feedback should be clear and explicit.
Teachers should also keep in mind that not all students have equal opportunities to finish their homework at home, so incomplete homework may not be a true reflection of their learning—it may be more a result of issues they face outside of school. They may be hindered by issues such as lack of a quiet space at home, resources such as a computer or broadband connectivity, or parental support (OECD, 2014 ). In such cases, giving low homework scores may be unfair.
Since the quantities of time discussed here are totals, teachers in middle and high school should be aware of how much homework other teachers are assigning. It may seem reasonable to assign 30 minutes of daily homework, but across six subjects, that’s three hours—far above a reasonable amount even for a high school senior. Psychologist Maurice Elias sees this as a common mistake: Individual teachers create homework policies that in aggregate can overwhelm students. He suggests that teachers work together to develop a school-wide homework policy and make it a key topic of back-to-school night and the first parent-teacher conferences of the school year.
Parents Play a Key Role
Homework can be a powerful tool to help parents become more involved in their child’s learning (Walker et al., 2004 ). It can provide insights into a child’s strengths and interests, and can also encourage conversations about a child’s life at school. If a parent has positive attitudes toward homework, their children are more likely to share those same values, promoting academic success.
But it’s also possible for parents to be overbearing, putting too much emphasis on test scores or grades, which can be disruptive for children (Madjar, Shklar, & Moshe, 2015 ). Parents should avoid being overly intrusive or controlling—students report feeling less motivated to learn when they don’t have enough space and autonomy to do their homework (Orkin, May, & Wolf, 2017 ; Patall, Cooper, & Robinson, 2008 ; Silinskas & Kikas, 2017 ). So while homework can encourage parents to be more involved with their kids, it’s important to not make it a source of conflict.
- Entrepreneurship
Best Practices for Completing Nursing Homework Efficiently
Homework serves as a critical component of nursing education, bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge acquired in lecture halls and the practical skills needed in clinical settings. Efficiently managing homework is not merely about achieving good grades; it is about nurturing a deep understanding of nursing principles that will underpin all future clinical decisions. However, many nursing students encounter challenges such as voluminous reading assignments, intricate medical concepts, and the daunting task of applying theoretical knowledge in practical assessments. Seeking nursing homework help can provide structured support and effective strategies to address these challenges, significantly enhancing a student’s learning experience and readiness for professional responsibilities.
Importance of Efficient Homework Practices in Nursing
Efficient homework execution is crucial in nursing, as it reinforces learned concepts and ensures students are well-prepared for clinical duties. By keeping up with homework, nursing students can avoid the buildup of unmanageable workloads, which often leads to stress and burnout. Efficient homework habits also cultivate a disciplined approach to learning and time management, which are essential traits for any healthcare professional. These practices not only prepare students for academic assessments but are also instrumental in building the confidence and competence required for handling the complexities of patient care.
Time Management Strategies
Mastering time management can dramatically improve a nursing student’s ability to handle homework effectively:
Recommended Reads
Wellness and self-care: nurturing mind, body, and soul for gorgeous hair, healthcare qui tam attorneys: what is it and how they can help, orthopedic mastery: unveiling the best surgeons in abu dhabi’s healthcare landscape, setting priorities.
Assessment Impact : Prioritize assignments that have a significant impact on your overall grade or are essential for upcoming clinical assessments.
Difficulty and Time : Assess tasks based on their difficulty and the estimated time to complete, starting with the most time-consuming or challenging.
Creating a Study Schedule
Weekly Breakdowns : Divide your workload by the week, then allocate specific days for different subjects or types of assignments, ensuring a balanced approach.
Flexibility : While consistency is key, adapt your schedule based on your most alert and productive times of the day for maximum efficiency.
Using Timers and Breaks
Regular Intervals : Implement regular intervals of focused study sessions followed by breaks to refresh your mind, which can help maintain a high level of concentration.
Restorative Breaks : Engage in activities that rejuvenate your mental energy during breaks, such as light exercise, meditation, or a short walk.
Understanding and Organizing Nursing Concepts
Effective organization of study materials is crucial for comprehending and retaining complex nursing information:
Effective Note-Taking
Active Listening and Annotation : Enhance traditional note-taking by actively listening during lectures and annotating reading materials with your thoughts or questions.
Review and Revise : Regularly review your notes to keep the information fresh and make revisions or summaries to reinforce your understanding.
Utilizing Concept Maps
Connection Building : Use concept maps to visually connect symptoms, treatments, and underlying conditions, which can help in understanding patient care pathways.
Group Study : Create and discuss concept maps in study groups to expose yourself to different perspectives and enhance collaborative learning.
Application of Theoretical Knowledge
Theoretical knowledge is more than just book learning; its application through practical scenarios is what truly prepares nursing students for real-world challenges:
Case Studies and Scenarios
Detailed Analysis : Engage deeply with each case study by identifying key problems, proposing possible interventions, and discussing potential outcomes.
Integration of Learning : Apply lessons learned from case studies to other aspects of your coursework to build a comprehensive understanding.
Peer Discussions and Study Groups
Diverse Perspectives : Leverage the varied experiences and backgrounds of your peers to enrich your own understanding of complex nursing issues.
Feedback and Support : Use these sessions as a platform to receive constructive feedback on your ideas and to offer support to others, fostering a supportive learning environment.
Tools and Resources for Nursing Students
Leveraging the right tools can significantly enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of homework completion:
Interactive Learning Platforms : Engage with platforms that offer interactive learning experiences, such as virtual dissections or patient simulations.
Academic Support Services : Make use of your institution’s academic support services, such as tutoring or writing centers, which can provide valuable guidance and assistance.
Grow Yourself to Grow Your Business and Life(Opens in a new browser tab)
Adopting and refining efficient homework practices is crucial for nursing students striving to excel both academically and professionally. These practices not only help manage the immediate challenges of nursing education but also instill lifelong skills that are essential in the fast-paced and demanding field of healthcare. By integrating effective time management, strategic learning techniques, and appropriate resources, nursing students can significantly enhance their educational outcomes and prepare thoroughly for their critical roles in patient care.
Eco-Friendly Energy Solutions: The Rise of Solar Panels
If you move goods, you may need storage containers.
Ahmed Raza with over three years in the SEO realm, has carved a niche as a specialist and contributing writer for prominent platforms. His adept insights and passion for digital trends have made him a respected voice in the optimization space.
Related Posts
Discussion about this post, recommended, the essential role of skip bins sunshine coast for food delivery businesses, quebec’s bill 96 is a linguistic culling of canada’s anglophones, the power of positive leadership | exploring its impact on effective leadership, why is orlando, florida the place to live.
- Construction
- Entertainment
- Home Improvement
- Renovations
- Uncategorized
© 2021 USA Wire
Navigate Site
- Join Council – Become a Contributor
- Join Council
More From Forbes
11 Barriers To Effective AI Adoption And How To Overcome Them
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
In today's digital era, artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a transformative force across diverse sectors. It promises not only heightened efficiencies and personalized customer experiences but also innovative solutions to longstanding challenges. However, despite its considerable potential, numerous organizations struggle to effectively adopt and integrate AI technologies. This article explores 11 prevalent obstacles that impede companies from harnessing AI's full power and offers practical strategies to overcome these hurdles, paving the way for successful implementation and integration.
1. Leadership Inertia
The shift towards AI-driven operations must start with a company's leadership. However, a significant barrier arises when executives display a reluctance to move away from traditional practices, often viewing digital innovation with skepticism. This inertia can stall an organization's digital transformation journey. To overcome this, it's essential for leaders to adopt a forward-thinking mindset. Exposure to successful AI implementations and interactions with peers who have embraced digital change can inspire reluctant leaders to reevaluate their stance and champion AI initiatives within their organizations.
2. Fear Of The Unknown
AI technology often represents a leap into the unknown, and this uncertainty can provoke fears—particularly regarding job displacement and organizational transformation. To address these concerns, it is crucial to foster an environment of transparency. Educating employees about how AI can augment human work rather than replace it and demonstrating AI's role in enhancing decision-making and operational efficiency can mitigate fears and build organizational confidence in AI technologies.
3. Lack Of Understanding Of AI's Potential
For many, AI remains a buzzword associated with futuristic applications rather than a practical tool available today. This disconnect impedes its adoption. Organizations can bridge this gap by facilitating workshops and seminars that highlight AI’s practical benefits and showcase real-world applications. Such initiatives help demystify AI and illustrate its value in solving everyday business problems, thus fostering a deeper appreciation and enthusiasm for its potential.
Samsung Issues Critical Update For Millions Of Galaxy Users
Steve bannon will go to jail as he loses appeal on contempt of congress charges, how can ukrainian drones keep dropping grenades into open tank hatches, 4. data availability and quality.
AI systems thrive on data, yet the availability and quality of this data can be limiting factors. Inaccurate or inaccessible data can undermine even the most advanced AI models. Establishing a comprehensive data governance strategy is vital. By implementing stringent data quality controls and investing in technologies that enhance data cleansing and enrichment, companies can provide their AI initiatives with the high-quality data needed to succeed.
5. Skills Shortage
The demand for AI skills frequently surpasses supply, putting companies at a competitive disadvantage. To combat this, organizations should consider developing targeted in-house training programs to cultivate their existing workforce while also forming partnerships with academic institutions. Additionally, outsourcing certain AI functions can provide access to the necessary skills in the short term, ensuring that AI projects do not stall due to a lack of internal expertise.
6. Integration Challenges With Legacy Systems
Integrating AI into outdated legacy systems can pose significant technical challenges. However, these can be navigated through the strategic use of APIs and middleware, which facilitate a smoother and more incremental integration process. This approach allows organizations to leverage the benefits of AI without the need for costly and disruptive overhauls of their IT infrastructure.
7. Ethical And Legal Considerations
AI presents a unique set of ethical and legal challenges, including concerns over privacy, data security, and decision-making biases. To navigate these issues, companies should establish and adhere to stringent AI ethics policies and ensure they are in compliance with all relevant laws and regulations. This proactive stance helps prevent potential legal and reputational risks associated with AI deployments.
The initial costs of AI adoption can be prohibitive, encompassing expenditures on technology, talent, and training. Adopting a phased investment approach can mitigate these costs. Starting with smaller-scale pilot projects allows a company to demonstrate AI's return on investment and strategically scale its expenditure based on proven benefits and acquired learnings.
9. Lack Of A Strategic Approach
Approaching AI without a coherent strategy is akin to navigating without a map. To effectively implement AI, organizations must develop a clear, strategic plan that aligns AI initiatives with broader business objectives. This strategy should include defined goals, performance metrics, and a framework for ongoing evaluation and adaptation.
10. Difficulty Scaling AI Initiatives
Scaling AI from pilot programs to broader organizational application remains a formidable challenge. To ensure scalability, standardizing AI tools and methodologies across the enterprise while allowing for customization to meet diverse departmental needs is crucial. This balanced approach facilitates wider adoption and maximizes the impact of AI technologies across the organization.
11. Lack of Innovation Culture
An organizational culture that is resistant to innovation can significantly impede AI initiatives. Cultivating a culture that values experimentation and tolerates failures is essential for fostering innovation and embracing the benefits of AI. This cultural shift can empower employees to take initiative and explore new ideas, thereby enhancing the organization's overall capacity for digital transformation.
By addressing these challenges with thoughtful strategies, companies can not only navigate the complex landscape of AI adoption but also position themselves as leaders in the AI-driven future. As AI continues to evolve, it's imperative for businesses to adapt and refine their strategies to harness its full potential. Let's not merely ride the wave of AI innovation—let's steer the ship towards a more intelligent and efficient future.
- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.
An official website of the United States Government
- Kreyòl ayisyen
- Search Toggle search Search Include Historical Content - Any - No Include Historical Content - Any - No Search
- Menu Toggle menu
- INFORMATION FOR…
- Individuals
- Business & Self Employed
- Charities and Nonprofits
- International Taxpayers
- Federal State and Local Governments
- Indian Tribal Governments
- Tax Exempt Bonds
- FILING FOR INDIVIDUALS
- How to File
- When to File
- Where to File
- Update Your Information
- Get Your Tax Record
- Apply for an Employer ID Number (EIN)
- Check Your Amended Return Status
- Get an Identity Protection PIN (IP PIN)
- File Your Taxes for Free
- Bank Account (Direct Pay)
- Payment Plan (Installment Agreement)
- Electronic Federal Tax Payment System (EFTPS)
- Your Online Account
- Tax Withholding Estimator
- Estimated Taxes
- Where's My Refund
- What to Expect
- Direct Deposit
- Reduced Refunds
- Amend Return
Credits & Deductions
- INFORMATION FOR...
- Businesses & Self-Employed
- Earned Income Credit (EITC)
- Child Tax Credit
- Clean Energy and Vehicle Credits
- Standard Deduction
- Retirement Plans
Forms & Instructions
- POPULAR FORMS & INSTRUCTIONS
- Form 1040 Instructions
- Form 4506-T
- POPULAR FOR TAX PROS
- Form 1040-X
- Circular 230
E-file Form 8300: Reporting of large cash transactions
More in news.
- Topics in the News
- News Releases
- Multimedia Center
- Tax Relief in Disaster Situations
- Inflation Reduction Act
- Taxpayer First Act
- Tax Scams/Consumer Alerts
- The Tax Gap
- Fact Sheets for Frequently Asked Questions
- IRS Tax Tips
- e-News Subscriptions
- IRS Guidance
- Media Contacts
- IRS Statements and Announcements
FS-2023-19, Aug. 2023
Who must file
Federal law requires a person to report cash transactions of more than $10,000 by filing Form 8300, Report of Cash Payments Over $10,000 Received in a Trade or Business . Although many cash transactions are legitimate, the information on the form can help law enforcement combat money laundering, tax evasion, drug dealing, terrorist financing and other criminal activities.
By law, a "person" is an individual, company, corporation, partnership, association, trust or estate. For example, dealers in jewelry, furniture, boats, aircraft or automobiles; pawnbrokers; attorneys; real estate brokers; insurance companies and travel agencies are among those who typically need to file Form 8300.
Tax-exempt organizations are also "persons" and may need to report certain transactions. A tax-exempt organization doesn't have to file Form 8300 for a charitable cash contribution. However, under a separate requirement, a donor often must obtain a written acknowledgement of the contribution from the organization. The organization must report noncharitable cash payments on Form 8300. For example, an exempt organization that receives more than $10,000 in cash for renting part of its building must report the transaction. See Publication 526, Charitable Contributions for details.
Effective Jan. 1, 2024, businesses must electronically file (e-file) Forms 8300 if they are required to e-file certain other information returns electronically, such as Forms 1099 series and Forms W-2. They must e-file Forms 8300 in a given calendar year if they are required to file at least 10 information returns of one or more types, other than Form 8300, beginning with the calendar year 2024. The number of Forms 8300 filed does not affect the information return threshold requirement.
For example, if a business files five Forms W-2 and five Forms 1099-INT in 2024, then they must e-file all information returns during the year, including any Forms 8300. But, if they file a total of less than 10 of one or more types of information returns other than Forms 8300, they do not have to e-file the information returns and are not required to e-file any Forms 8300. Although not required to e-file, a business may still choose to do so.
When to file
A person must file Form 8300 within 15 days after the date the person received the cash. If the person receives multiple payments toward a single transaction or two or more related transactions, and the total amount paid exceeds $10,000, the person should file Form 8300. Each time payments add up to more than $10,000, the person must file another Form 8300.
Examples of reporting situations
The following are examples of situations that demonstrate how certain large cash transactions require the filing of Form 8300.
- New or used automobile dealers – Each business must report cash receipts greater than $10,000 in single or related transactions. See Report of Cash Payments Over $10,000 Received in a Trade or Business - Motor Vehicle Dealership Q&As for more detailed information.
- Marijuana-related businesses – These businesses must report cash receipts greater than $10,000 in a single transaction or related transactions. See the frequently asked questions for more information about the marijuana industry .
Recordkeeping
A business must keep a copy of every Form 8300 it files, along with any supporting documentation and the required statement it sends to customers, for five years from the date filed.
Business should keep in mind that filing electronically will provide a confirmation email that the form was filed, but e-file confirmation emails do not meet the record keeping requirement. When e-filing, filers must save or print a copy or the form prior to finalizing the form submission. Businesses should associate the confirmation number with the saved copy.
More information:
- Publication 1544, Reporting Cash Payments of Over $10,000
- IRS Form 8300 Reference Guide
- Form 8300 and Reporting Cash Payments of Over $10,000

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Yes, and the stories we hear of kids being stressed out from too much homework—four or five hours of homework a night—are real. That's problematic for physical and mental health and overall well-being. But the research shows that higher-income students get a lot more homework than lower-income kids.
Less commonly, homework is assigned to extend student learning to different contexts or to integrate learning by applying multiple skills around a project. Little research exists on the effects of these different kinds of homework on student achievement, leaving policymakers with little evidence on which to base decisions (Cooper 1989; Foyle ...
How to Study Effectively: 12 Secrets For Success. Being properly organized and prepared for tests and exams can make all the difference to school performance. Effective studying starts with the right attitude—a positive outlook can shift studying from a punishment to an opportunity to learn. There is no one-size-fits-all approach when ...
Here's how it works: first, set a timer for 25 minutes. This is going to be your work time. During this 25 minutes, all you can do is work on whatever homework assignment you have in front of you. No email, no text messaging, no phone calls—just homework. When that timer goes off, you get to take a 5 minute break.
Designing Effective Homework To achieve a positive impact on student learning, homework assignments must be well-designed and carefully constructed. Some speci˛c research ˛nd-ings include: ˝ Homework is most e˚ective when it covers mate-rial already taught. However, giving an assignment on material that was taught the same day is not
After two hours, however, achievement doesn't improve. For high schoolers, Cooper's research suggests that two hours per night is optimal. If teens have more than two hours of homework a night, their academic success flatlines. But less is not better. The average high school student doing homework outperformed 69 percent of the students in ...
When homework is used as a tool to build social, emotional, and academic learning beyond the school day, it takes on a different look and purpose than just more work to do at home. The goal of Responsive Classroom schools is to design homework that meets the basic needs of significance and belonging for every student by strengthening ...
A schoolwide effort to reduce homework has led to a renewed focus on ensuring that all work assigned really aids students' learning. I used to pride myself on my high expectations, including my firm commitment to accountability for regular homework completion among my students. But the trauma of Covid-19 has prompted me to both reflect and adapt.
Enriching children's classroom learning requires making homework not shorter or longer, but smarter.". Paul goes on to describe specific practices, like spaced repetition (in which information is presented and repeated spaced out over time), retrieval practice (testing or quizzing not for assessment, but to reinforce material learned), and ...
Why Homework Should Be Balanced. Homework can boost learning, but doing too much can be detrimental. The National PTA and National Education Association support the "10-minute homework rule," which recommends 10 minutes of homework per grade level, per night (10 minutes for first grade, 20 minutes for second grade, and so on, up to two ...
Try creating a homework schedule and set a specific time and place for your child to get homework done. Use a timer to help your child stay on track and get a better sense of time. Learn about trouble with planning. The challenge: Studying effectively. Many kids need to be taught how to study effectively. But some may need concrete strategies.
Key Words: homework, learning, inclusive classrooms, special education, stu-dents with disabilities, supports, teachers, inclusion, parents, studying, home ... line the elements of effective homework, and provide practical suggestions for classroom applications. Increasing the effectiveness of homework is a multifaceted goal. Accom-
According to research findings, the answer is "yes." Try these three unusual-sounding but effective strategies: Spaced repetition. Typically a teacher presents an entire lesson, students take notes and complete class work, and then they do homework to reinforce learning. Once the lesson is over, the student may not need the information again ...
Strategies for practicing new learning include visualization, mnemonics, quick writes, and effective questioning. Finally, tips for homework completion are provided for both teachers and parents. It is important to make sure that all students understand the content that has been taught. Practice and homework are effective instructional ...
1. EFFECTIVE HOMEWORK PRACTICES. This issue of PRIMUS is the second of a two-part special issue on The Creation and Implementation of Effective Homework Assignments. Part 1 of the special issue focused on the creation of effective homework and featured papers that discussed elements of effective homework design and presented innovative homework systems targeting specific learning goals.
For decades, the homework standard has been a "10-minute rule," which recommends a daily maximum of 10 minutes of homework per grade level. Second graders, for example, should do about 20 ...
Reinforce and allow students to practice skills learned in the classroom. Help students develop good study habits and routines. Foster positive feelings about school. In grades 6-12, homework should: Reinforce and allow students to practice skills learned in the classroom. Prepare students for engagement and discussion during the next lesson.
As young children begin school, the focus should be on cultivating a love of learning, and assigning too much homework can undermine that goal. And young students often don't have the study skills to benefit fully from homework, so it may be a poor use of time (Cooper, 1989; Cooper et al., 2006; Marzano & Pickering, 2007). A more effective ...
Effective Practices for Homework. By: Kathy Ruhl, Charles Hughes. A review of the research on the effective use of homework for students with learning disabilities suggests that there are three big ideas for teachers to remember: (1) the best use of homework is to build proficiency in recently acquired skills or to maintain skills previously ...
Here are some strategies I've been using to support my pupils' independent and self-regulated study: 1) Design high-quality homework. I think carefully about how I can build pupils' knowledge and confidence through homework. Initially, I base homework on fact-recall to build confidence. e.g.
Pupils eligible for free school meals typically receive additional benefits from homework. However, surveys in England suggest that pupils from disadvantaged backgrounds are less likely to have a quiet working space, are less likely to have access to a device suitable for learning or a stable internet connection and may receive less parental support to complete homework and develop effective ...
The research cited by educators just doesn't seem to make sense. If a child wants to learn to play the violin, it's obvious she needs to practice at home between lessons (at least, it's ...
1. Plan Learning Episodes, not Lessons. Effective homework is a key feature of an overarching learning episode. In my early years in the profession, I would frequently spend extended periods ...
Mastering time management can dramatically improve a nursing student's ability to handle homework effectively: RecommendedReads. Wellness and Self-Care: Nurturing Mind, Body, and Soul for Gorgeous Hair ... Leveraging the right tools can significantly enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of homework completion: Interactive Learning ...
1. Leadership Inertia. The shift towards AI-driven operations must start with a company's leadership. However, a significant barrier arises when executives display a reluctance to move away from ...
Rule 281-15.1 - [Effective 5/22/2024] Definitions "Accredited nonpublic school" means a nonpublic school accredited pursuant to Iowa Code section 256.11. "Appropriately licensed and endorsed" or "appropriately licensed" means possession of current and valid licensure by the Iowa board of educational examiners to practice at a prescribed educational level in a specified content area.
FS-2023-19, Aug. 2023 — Federal law requires a person to report cash transactions of more than $10,000 by filing Form 8300, Report of Cash Payments Over $10,000 Received in a Trade or Business. Although many cash transactions are legitimate, the information on the form can help law enforcement combat money laundering, tax evasion, drug dealing, terrorist financing and other criminal activities.
Rule 281-41.309 - [Effective until 5/22/2024] Determining the existence of a specific learning disability (1) Required determinations. The group described in rule 281-41.306 (256B, 34CFR300 ) may determine that a child has a specific learning disability, as defined in subrule 41.50(10), after considering the following three factors: a. Lack of adequate achievement.
Read Rule 193E-17.10 - [Effective 5/22/2024] Standards for approval of distance learning courses, Iowa Admin. Code r. 193E-17.10, see flags on bad law, and search Casetext's comprehensive legal database