What is a Business Plan? Definition, Tips, and Templates
Published: June 07, 2023
In an era where more than 20% of small enterprises fail in their first year, having a clear, defined, and well-thought-out business plan is a crucial first step for setting up a business for long-term success.

Business plans are a required tool for all entrepreneurs, business owners, business acquirers, and even business school students. But … what exactly is a business plan?

In this post, we'll explain what a business plan is, the reasons why you'd need one, identify different types of business plans, and what you should include in yours.

What is a business plan?
A business plan is a documented strategy for a business that highlights its goals and its plans for achieving them. It outlines a company's go-to-market plan, financial projections, market research, business purpose, and mission statement. Key staff who are responsible for achieving the goals may also be included in the business plan along with a timeline.
The business plan is an undeniably critical component to getting any company off the ground. It's key to securing financing, documenting your business model, outlining your financial projections, and turning that nugget of a business idea into a reality.
What is a business plan used for?
The purpose of a business plan is three-fold: It summarizes the organization’s strategy in order to execute it long term, secures financing from investors, and helps forecast future business demands.
Business Plan Template [ Download Now ]

Working on your business plan? Try using our Business Plan Template . Pre-filled with the sections a great business plan needs, the template will give aspiring entrepreneurs a feel for what a business plan is, what should be in it, and how it can be used to establish and grow a business from the ground up.
Purposes of a Business Plan
Chances are, someone drafting a business plan will be doing so for one or more of the following reasons:
1. Securing financing from investors.
Since its contents revolve around how businesses succeed, break even, and turn a profit, a business plan is used as a tool for sourcing capital. This document is an entrepreneur's way of showing potential investors or lenders how their capital will be put to work and how it will help the business thrive.
All banks, investors, and venture capital firms will want to see a business plan before handing over their money, and investors typically expect a 10% ROI or more from the capital they invest in a business.
Therefore, these investors need to know if — and when — they'll be making their money back (and then some). Additionally, they'll want to read about the process and strategy for how the business will reach those financial goals, which is where the context provided by sales, marketing, and operations plans come into play.
2. Documenting a company's strategy and goals.
A business plan should leave no stone unturned.
Business plans can span dozens or even hundreds of pages, affording their drafters the opportunity to explain what a business' goals are and how the business will achieve them.
To show potential investors that they've addressed every question and thought through every possible scenario, entrepreneurs should thoroughly explain their marketing, sales, and operations strategies — from acquiring a physical location for the business to explaining a tactical approach for marketing penetration.
These explanations should ultimately lead to a business' break-even point supported by a sales forecast and financial projections, with the business plan writer being able to speak to the why behind anything outlined in the plan.
.webp)
Free Business Plan Template
The essential document for starting a business -- custom built for your needs.
- Outline your idea.
- Pitch to investors.
- Secure funding.
- Get to work!
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Free Business Plan [Template]
Fill out the form to access your free business plan., 3. legitimizing a business idea..
Everyone's got a great idea for a company — until they put pen to paper and realize that it's not exactly feasible.
A business plan is an aspiring entrepreneur's way to prove that a business idea is actually worth pursuing.
As entrepreneurs document their go-to-market process, capital needs, and expected return on investment, entrepreneurs likely come across a few hiccups that will make them second guess their strategies and metrics — and that's exactly what the business plan is for.
It ensures an entrepreneur's ducks are in a row before bringing their business idea to the world and reassures the readers that whoever wrote the plan is serious about the idea, having put hours into thinking of the business idea, fleshing out growth tactics, and calculating financial projections.
4. Getting an A in your business class.
Speaking from personal experience, there's a chance you're here to get business plan ideas for your Business 101 class project.
If that's the case, might we suggest checking out this post on How to Write a Business Plan — providing a section-by-section guide on creating your plan?
What does a business plan need to include?
- Business Plan Subtitle
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- The Business Opportunity
- Competitive Analysis
- Target Market
- Marketing Plan
- Financial Summary
- Funding Requirements
1. Business Plan Subtitle
Every great business plan starts with a captivating title and subtitle. You’ll want to make it clear that the document is, in fact, a business plan, but the subtitle can help tell the story of your business in just a short sentence.
2. Executive Summary
Although this is the last part of the business plan that you’ll write, it’s the first section (and maybe the only section) that stakeholders will read. The executive summary of a business plan sets the stage for the rest of the document. It includes your company’s mission or vision statement, value proposition, and long-term goals.
3. Company Description
This brief part of your business plan will detail your business name, years in operation, key offerings, and positioning statement. You might even add core values or a short history of the company. The company description’s role in a business plan is to introduce your business to the reader in a compelling and concise way.
4. The Business Opportunity
The business opportunity should convince investors that your organization meets the needs of the market in a way that no other company can. This section explains the specific problem your business solves within the marketplace and how it solves them. It will include your value proposition as well as some high-level information about your target market.

5. Competitive Analysis
Just about every industry has more than one player in the market. Even if your business owns the majority of the market share in your industry or your business concept is the first of its kind, you still have competition. In the competitive analysis section, you’ll take an objective look at the industry landscape to determine where your business fits. A SWOT analysis is an organized way to format this section.
6. Target Market
Who are the core customers of your business and why? The target market portion of your business plan outlines this in detail. The target market should explain the demographics, psychographics, behavioristics, and geographics of the ideal customer.
7. Marketing Plan
Marketing is expansive, and it’ll be tempting to cover every type of marketing possible, but a brief overview of how you’ll market your unique value proposition to your target audience, followed by a tactical plan will suffice.
Think broadly and narrow down from there: Will you focus on a slow-and-steady play where you make an upfront investment in organic customer acquisition? Or will you generate lots of quick customers using a pay-to-play advertising strategy? This kind of information should guide the marketing plan section of your business plan.
8. Financial Summary
Money doesn’t grow on trees and even the most digital, sustainable businesses have expenses. Outlining a financial summary of where your business is currently and where you’d like it to be in the future will substantiate this section. Consider including any monetary information that will give potential investors a glimpse into the financial health of your business. Assets, liabilities, expenses, debt, investments, revenue, and more are all useful adds here.
So, you’ve outlined some great goals, the business opportunity is valid, and the industry is ready for what you have to offer. Who’s responsible for turning all this high-level talk into results? The "team" section of your business plan answers that question by providing an overview of the roles responsible for each goal. Don’t worry if you don’t have every team member on board yet, knowing what roles to hire for is helpful as you seek funding from investors.
10. Funding Requirements
Remember that one of the goals of a business plan is to secure funding from investors, so you’ll need to include funding requirements you’d like them to fulfill. The amount your business needs, for what reasons, and for how long will meet the requirement for this section.
Types of Business Plans
- Startup Business Plan
- Feasibility Business Plan
- Internal Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Business Acquisition Plan
- Business Repositioning Plan
- Expansion or Growth Business Plan
There’s no one size fits all business plan as there are several types of businesses in the market today. From startups with just one founder to historic household names that need to stay competitive, every type of business needs a business plan that’s tailored to its needs. Below are a few of the most common types of business plans.
For even more examples, check out these sample business plans to help you write your own .
1. Startup Business Plan

As one of the most common types of business plans, a startup business plan is for new business ideas. This plan lays the foundation for the eventual success of a business.
The biggest challenge with the startup business plan is that it’s written completely from scratch. Startup business plans often reference existing industry data. They also explain unique business strategies and go-to-market plans.
Because startup business plans expand on an original idea, the contents will vary by the top priority goals.
For example, say a startup is looking for funding. If capital is a priority, this business plan might focus more on financial projections than marketing or company culture.
2. Feasibility Business Plan
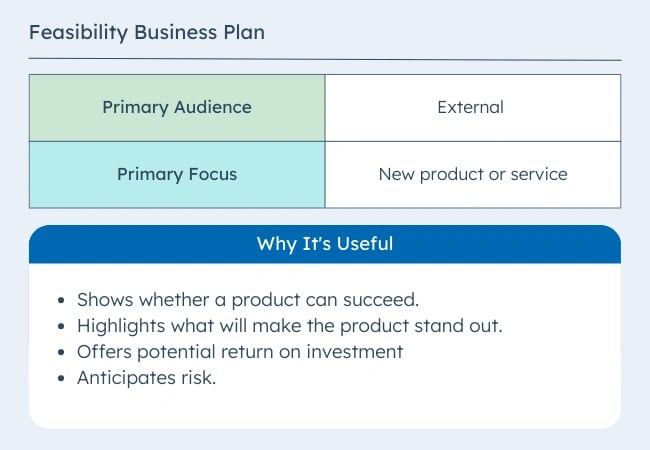
This type of business plan focuses on a single essential aspect of the business — the product or service. It may be part of a startup business plan or a standalone plan for an existing organization. This comprehensive plan may include:
- A detailed product description
- Market analysis
- Technology needs
- Production needs
- Financial sources
- Production operations
According to CBInsights research, 35% of startups fail because of a lack of market need. Another 10% fail because of mistimed products.
Some businesses will complete a feasibility study to explore ideas and narrow product plans to the best choice. They conduct these studies before completing the feasibility business plan. Then the feasibility plan centers on that one product or service.
3. Internal Business Plan

Internal business plans help leaders communicate company goals, strategy, and performance. This helps the business align and work toward objectives more effectively.
Besides the typical elements in a startup business plan, an internal business plan may also include:
- Department-specific budgets
- Target demographic analysis
- Market size and share of voice analysis
- Action plans
- Sustainability plans
Most external-facing business plans focus on raising capital and support for a business. But an internal business plan helps keep the business mission consistent in the face of change.
4. Strategic Business Plan

Strategic business plans focus on long-term objectives for your business. They usually cover the first three to five years of operations. This is different from the typical startup business plan which focuses on the first one to three years. The audience for this plan is also primarily internal stakeholders.
These types of business plans may include:
- Relevant data and analysis
- Assessments of company resources
- Vision and mission statements
It's important to remember that, while many businesses create a strategic plan before launching, some business owners just jump in. So, this business plan can add value by outlining how your business plans to reach specific goals. This type of planning can also help a business anticipate future challenges.
5. Business Acquisition Plan

Investors use business plans to acquire existing businesses, too — not just new businesses.
A business acquisition plan may include costs, schedules, or management requirements. This data will come from an acquisition strategy.
A business plan for an existing company will explain:
- How an acquisition will change its operating model
- What will stay the same under new ownership
- Why things will change or stay the same
- Acquisition planning documentation
- Timelines for acquisition
Additionally, the business plan should speak to the current state of the business and why it's up for sale.
For example, if someone is purchasing a failing business, the business plan should explain why the business is being purchased. It should also include:
- What the new owner will do to turn the business around
- Historic business metrics
- Sales projections after the acquisition
- Justification for those projections
6. Business Repositioning Plan
.webp?width=650&height=450&name=businessplan_6%20(1).webp)
When a business wants to avoid acquisition, reposition its brand, or try something new, CEOs or owners will develop a business repositioning plan.
This plan will:
- Acknowledge the current state of the company.
- State a vision for the future of the company.
- Explain why the business needs to reposition itself.
- Outline a process for how the company will adjust.
Companies planning for a business reposition often do so — proactively or retroactively — due to a shift in market trends and customer needs.
For example, shoe brand AllBirds plans to refocus its brand on core customers and shift its go-to-market strategy. These decisions are a reaction to lackluster sales following product changes and other missteps.
7. Expansion or Growth Business Plan
When your business is ready to expand, a growth business plan creates a useful structure for reaching specific targets.
For example, a successful business expanding into another location can use a growth business plan. This is because it may also mean the business needs to focus on a new target market or generate more capital.
This type of plan usually covers the next year or two of growth. It often references current sales, revenue, and successes. It may also include:
- SWOT analysis
- Growth opportunity studies
- Financial goals and plans
- Marketing plans
- Capability planning
These types of business plans will vary by business, but they can help businesses quickly rally around new priorities to drive growth.
Getting Started With Your Business Plan
At the end of the day, a business plan is simply an explanation of a business idea and why it will be successful. The more detail and thought you put into it, the more successful your plan — and the business it outlines — will be.
When writing your business plan, you’ll benefit from extensive research, feedback from your team or board of directors, and a solid template to organize your thoughts. If you need one of these, download HubSpot's Free Business Plan Template below to get started.
Editor's note: This post was originally published in August 2020 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

24 of My Favorite Sample Business Plans & Examples For Your Inspiration
![what are 3 types of business plans How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/executive-summary-example_5.webp)
How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]

Maximizing Your Social Media Strategy: The Top Aggregator Tools to Use

The Content Aggregator Guide for 2023
![what are 3 types of business plans 7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/gantt-chart-example.jpg)
7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]
![what are 3 types of business plans The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/flowchart%20templates.jpg)
The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]

16 Best Screen Recorders to Use for Collaboration

The 25 Best Google Chrome Extensions for SEO

Professional Invoice Design: 28 Samples & Templates to Inspire You
Customers’ Top HubSpot Integrations to Streamline Your Business in 2022
2 Essential Templates For Starting Your Business
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
BUSINESS STRATEGIES
7 types of business plans every entrepreneur should know
- Amanda Bellucco Chatham
- Aug 3, 2023

What’s the difference between a small business that achieves breakthrough growth and one that fizzles quickly after launch? Oftentimes, it’s having a solid business plan.
Business plans provide you with a roadmap that will take you from wantrepreneur to entrepreneur. It will guide nearly every decision you make, from the people you hire and the products or services you offer, to the look and feel of the business website you create.
But did you know that there are many different types of business plans? Some types are best for new businesses looking to attract funding. Others help to define the way your company will operate day-to-day. You can even create a plan that prepares your business for the unexpected.
Read on to learn the seven most common types of business plans and determine which one fits your immediate needs.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a written document that defines your company’s goals and explains how you will achieve them. Putting this information down on paper brings valuable benefits. It gives you insight into your competitors, helps you develop a unique value proposition and lets you set metrics that will guide you to profitability. It’s also a necessity to obtain funding through banks or investors.
Keep in mind that a business plan isn’t a one-and-done exercise. It’s a living document that you should update regularly as your company evolves. But which type of plan is right for your business?
7 common types of business plans
Startup business plan
Feasibility business plan
One-page business plan
What-if business plan
Growth business plan
Operations business plan
Strategic business plan

01. Startup business plan
The startup business plan is a comprehensive document that will set the foundation for your company’s success. It covers all aspects of a business, including a situation analysis, detailed financial information and a strategic marketing plan.
Startup plans serve two purposes: internally, they provide a step-by-step guide that you and your team can use to start a business and generate results on day one. Externally, they prove the validity of your business concept to banks and investors, whose capital you’ll likely need to make your entrepreneurial dreams a reality.
Elements of a startup business plan should include the following steps:
Executive summary : Write a brief synopsis of your company’s concept, potential audience, product or services, and the amount of funding required.
Company overview: Go into detail about your company’s location and its business goals. Be sure to include your company’s mission statement , which explains the “why” behind your business idea.
Products or services: Explain exactly what your business will offer to its customers. Include detailed descriptions and pricing.
Situation analysis: Use market research to explain the competitive landscape, key demographics and the current status of your industry.
Marketing plan: Discuss the strategies you’ll use to build awareness for your business and attract new customers or clients.
Management bios: Introduce the people who will lead your company. Include bios that detail their industry-specific background.
Financial projections: Be transparent about startup costs, cash flow projections and profit expectations.
Don’t be afraid to go into too much detail—a startup business plan can often run multiple pages long. Investors will expect and appreciate your thoroughness. However, if you have a hot new product idea and need to move fast, you can consider a lean business plan. It’s a popular type of business plan in the tech industry that focuses on creating a minimum viable product first, then scaling the business from there.
02. Feasibility business plan
Let’s say you started a boat rental company five years ago. You’ve steadily grown your business. Now, you want to explore expanding your inventory by renting out jet skis, kayaks and other water sports equipment. Will it be profitable? A feasibility business plan will let you know.
Often called a decision-making plan, a feasibility business plan will help you understand the viability of offering a new product or launching into a new market. These business plans are typically internal and focus on answering two questions: Does the market exist, and will you make a profit from it? You might use a feasibility plan externally, too, if you need funding to support your new product or service.
Because you don’t need to include high-level, strategic information about your company, your feasibility business plan will be much shorter and more focused than a startup business plan. Feasibility plans typically include:
A description of the new product or service you wish to launch
A market analysis using third-party data
The target market , or your ideal customer profile
Any additional technology or personnel needs required
Required capital or funding sources
Predicted return on investment
Standards to objectively measure feasibility
A conclusion that includes recommendations on whether or not to move forward
03. One-page business plan
Imagine you’re a software developer looking to launch a tech startup around an app that you created from scratch. You’ve already written a detailed business plan, but you’re not sure if your strategy is 100% right. How can you get feedback from potential partners, customers or friends without making them slog through all 32 pages of the complete plan?
That’s where a one-page business plan comes in handy. It compresses your full business plan into a brief summary. Think of it as a cross between a business plan and an elevator pitch—an ideal format if you’re still fine-tuning your business plan. It’s also a great way to test whether investors will embrace your company, its mission or its goals.
Ideally, a one-page business plan should give someone a snapshot of your company in just a few minutes. But while brevity is important, your plan should still hit all the high points from your startup business plan. To accomplish this, structure a one-page plan similar to an outline. Consider including:
A short situation analysis that shows the need for your product or service
Your unique value proposition
Your mission statement and vision statement
Your target market
Your management team
The funding you’ll need
Financial projections
Expected results
Because a one-page plan is primarily used to gather feedback, make sure the format you choose is easy to update. That way, you can keep it fresh for new audiences.
04. What-if business plan
Pretend that you’re an accountant who started their own financial consulting business. You’re rapidly signing clients and growing your business when, 18 months into your new venture, you’re given the opportunity to buy another established firm in a nearby town. Is it a risk worth taking?
The what-if business plan will help you find an answer. It’s perfect for entrepreneurs who are looking to take big risks, such as acquiring or merging with another company, testing a new pricing model or adding an influx of new staff.
A what-if plan is additionally a great way to test out a worst-case scenario. For example, if you’re in the restaurant business, you can create a plan that explores the potential business repercussions of a public health emergency (like the COVID-19 pandemic), and then develop strategies to mitigate its effects.
You can share your what-if plan internally to prepare your leadership team and staff. You can also share it externally with bankers and partners so that they know your business is built to withstand any hard times. Include in your plan:
A detailed description of the business risk or other scenario
The impact it will have on your business
Specific actions you’ll take in a worst-case scenario
Risk management strategies you’ll employ
05. Growth business plan
Let’s say you’re operating a hair salon (see how to create a hair salon business plan ). You see an opportunity to expand your business and make it a full-fledged beauty bar by adding skin care, massage and other sought-after services. By creating a growth business plan, you’ll have a blueprint that will take you from your current state to your future state.
Sometimes called an expansion plan, a growth business plan is something like a crystal ball. It will help you see one to two years into the future. Creating a growth plan lets you see how far—and how fast—you can scale your business. It lets you know what you’ll need to get there, whether it’s funding, materials, people or property.
The audience for your growth plan will depend on your expected sources of capital. If you’re funding your expansion from within, then the audience is internal. If you need to attract the attention of outside investors, then the audience is external.
Much like a startup plan, your growth business plan should be rather comprehensive, especially if the people reviewing it aren’t familiar with your company. Include items specific to your potential new venture, including:
A brief assessment of your business’s current state
Information about your management team
A thorough analysis of the growth opportunity you’re seeking
The target audience for your new venture
The current competitive landscape
Resources you’ll need to achieve growth
Detailed financial forecasts
A funding request
Specific action steps your company will take
A timeline for completing those action steps
Another helpful thing to include in a growth business plan is a SWOT analysis . SWOT stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. A SWOT analysis will help you evaluate your performance, and that of your competitors. Including this type of in-depth review will show your investors that you’re making an objective, data-driven decision to expand your business, helping to build confidence and trust.
06. Operations business plan
You’ve always had a knack for accessories and have chosen to start your own online jewelry store. Even better, you already have your eCommerce business plan written. Now, it’s time to create a plan for how your company will implement its business model on a day-to-day basis.
An operations business plan will help you do just that. This internal-focused document will explain how your leadership team and your employees will propel your company forward. It should include specific responsibilities for each department, such as human resources, finance and marketing.
When you sit down to write an operations plan, you should use your company’s overall goals as your guide. Then, consider how each area of your business will contribute to those goals. Be sure to include:
A high-level overview of your business and its goals
A clear layout of key employees, departments and reporting lines
Processes you’ll use (i.e., how you’ll source products and fulfill orders)
Facilities and equipment you’ll need to conduct business effectively
Departmental budgets required
Risk management strategies that will ensure business continuity
Compliance and legal considerations
Clear metrics for each department to achieve
Timelines to help you reach those metrics
A measurement process to keep your teams on track
07. Strategic business plan
Say you open a coffee shop, but you know that one store is just the start. Eventually, you want to open multiple locations throughout your region. A strategic business plan will serve as your guide, helping define your company’s direction and decision-making over the next three to five years.
You should use a strategic business plan to align all of your internal stakeholders and employees around your company’s mission, vision and future goals. Your strategic plan should be high-level enough to create a clear vision of future success, yet also detailed enough to ensure you reach your eventual destination.
Be sure to include:
An executive summary
A company overview
Your mission and vision statements
Market research
A SWOT analysis
Specific, measurable goals you wish to achieve
Strategies to meet those goals
Financial projections based on those goals
Timelines for goal attainment
Related Posts
What is a target market and how to define yours
21 powerful mission statement examples that stand out
Free business plan template for small businesses
Was this article helpful?
What is a Business Plan? Definition and Resources

9 min. read
Updated May 10, 2024
If you’ve ever jotted down a business idea on a napkin with a few tasks you need to accomplish, you’ve written a business plan — or at least the very basic components of one.
The origin of formal business plans is murky. But they certainly go back centuries. And when you consider that 20% of new businesses fail in year 1 , and half fail within 5 years, the importance of thorough planning and research should be clear.
But just what is a business plan? And what’s required to move from a series of ideas to a formal plan? Here we’ll answer that question and explain why you need one to be a successful business owner.
- What is a business plan?

A business plan lays out a strategic roadmap for any new or growing business.
Any entrepreneur with a great idea for a business needs to conduct market research , analyze their competitors , validate their idea by talking to potential customers, and define their unique value proposition .
The business plan captures that opportunity you see for your company: it describes your product or service and business model , and the target market you’ll serve.
It also includes details on how you’ll execute your plan: how you’ll price and market your solution and your financial projections .
Reasons for writing a business plan
If you’re asking yourself, ‘Do I really need to write a business plan?’ consider this fact:
Companies that commit to planning grow 30% faster than those that don’t.
Creating a business plan is crucial for businesses of any size or stage. It helps you develop a working business and avoid consequences that could stop you before you ever start.
If you plan to raise funds for your business through a traditional bank loan or SBA loan , none of them will want to move forward without seeing your business plan. Venture capital firms may or may not ask for one, but you’ll still need to do thorough planning to create a pitch that makes them want to invest.
But it’s more than just a means of getting your business funded . The plan is also your roadmap to identify and address potential risks.
It’s not a one-time document. Your business plan is a living guide to ensure your business stays on course.
Related: 14 of the top reasons why you need a business plan
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
What research shows about business plans
Numerous studies have established that planning improves business performance:
- 71% of fast-growing companies have business plans that include budgets, sales goals, and marketing and sales strategies.
- Companies that clearly define their value proposition are more successful than those that can’t.
- Companies or startups with a business plan are more likely to get funding than those without one.
- Starting the business planning process before investing in marketing reduces the likelihood of business failure.
The planning process significantly impacts business growth for existing companies and startups alike.
Read More: Research-backed reasons why writing a business plan matters
When should you write a business plan?
No two business plans are alike.
Yet there are similar questions for anyone considering writing a plan to answer. One basic but important question is when to start writing it.
A Harvard Business Review study found that the ideal time to write a business plan is between 6 and 12 months after deciding to start a business.
But the reality can be more nuanced – it depends on the stage a business is in, or the type of business plan being written.
Ideal times to write a business plan include:
- When you have an idea for a business
- When you’re starting a business
- When you’re preparing to buy (or sell)
- When you’re trying to get funding
- When business conditions change
- When you’re growing or scaling your business
Read More: The best times to write or update your business plan
How often should you update your business plan?
As is often the case, how often a business plan should be updated depends on your circumstances.
A business plan isn’t a homework assignment to complete and forget about. At the same time, no one wants to get so bogged down in the details that they lose sight of day-to-day goals.
But it should cover new opportunities and threats that a business owner surfaces, and incorporate feedback they get from customers. So it can’t be a static document.
Related Reading: 5 fundamental principles of business planning
For an entrepreneur at the ideation stage, writing and checking back on their business plan will help them determine if they can turn that idea into a profitable business .
And for owners of up-and-running businesses, updating the plan (or rewriting it) will help them respond to market shifts they wouldn’t be prepared for otherwise.
It also lets them compare their forecasts and budgets to actual financial results. This invaluable process surfaces where a business might be out-performing expectations and where weak performance may require a prompt strategy change.
The planning process is what uncovers those insights.
Related Reading: 10 prompts to help you write a business plan with AI
- How long should your business plan be?
Thinking about a business plan strictly in terms of page length can risk overlooking more important factors, like the level of detail or clarity in the plan.
Not all of the plan consists of writing – there are also financial tables, graphs, and product illustrations to include.
But there are a few general rules to consider about a plan’s length:
- Your business plan shouldn’t take more than 15 minutes to skim.
- Business plans for internal use (not for a bank loan or outside investment) can be as short as 5 to 10 pages.
A good practice is to write your business plan to match the expectations of your audience.
If you’re walking into a bank looking for a loan, your plan should match the formal, professional style that a loan officer would expect . But if you’re writing it for stakeholders on your own team—shorter and less formal (even just a few pages) could be the better way to go.
The length of your plan may also depend on the stage your business is in.
For instance, a startup plan won’t have nearly as much financial information to include as a plan written for an established company will.
Read More: How long should your business plan be?
What information is included in a business plan?
The contents of a plan business plan will vary depending on the industry the business is in.
After all, someone opening a new restaurant will have different customers, inventory needs, and marketing tactics to consider than someone bringing a new medical device to the market.
But there are some common elements that most business plans include:
- Executive summary: An overview of the business operation, strategy, and goals. The executive summary should be written last, despite being the first thing anyone will read.
- Products and services: A description of the solution that a business is bringing to the market, emphasizing how it solves the problem customers are facing.
- Market analysis: An examination of the demographic and psychographic attributes of likely customers, resulting in the profile of an ideal customer for the business.
- Competitive analysis: Documenting the competitors a business will face in the market, and their strengths and weaknesses relative to those competitors.
- Marketing and sales plan: Summarizing a business’s tactics to position their product or service favorably in the market, attract customers, and generate revenue.
- Operational plan: Detailing the requirements to run the business day-to-day, including staffing, equipment, inventory, and facility needs.
- Organization and management structure: A listing of the departments and position breakdown of the business, as well as descriptions of the backgrounds and qualifications of the leadership team.
- Key milestones: Laying out the key dates that a business is projected to reach certain milestones , such as revenue, break-even, or customer acquisition goals.
- Financial plan: Balance sheets, cash flow forecast , and sales and expense forecasts with forward-looking financial projections, listing assumptions and potential risks that could affect the accuracy of the plan.
- Appendix: All of the supporting information that doesn’t fit into specific sections of the business plan, such as data and charts.
Read More: Use this business plan outline to organize your plan
- Different types of business plans
A business plan isn’t a one-size-fits-all document. There are numerous ways to create an effective business plan that fits entrepreneurs’ or established business owners’ needs.
Here are a few of the most common types of business plans for small businesses:
- One-page plan : Outlining all of the most important information about a business into an adaptable one-page plan.
- Growth plan : An ongoing business management plan that ensures business tactics and strategies are aligned as a business scales up.
- Internal plan : A shorter version of a full business plan to be shared with internal stakeholders – ideal for established companies considering strategic shifts.
Business plan vs. operational plan vs. strategic plan
- What questions are you trying to answer?
- Are you trying to lay out a plan for the actual running of your business?
- Is your focus on how you will meet short or long-term goals?
Since your objective will ultimately inform your plan, you need to know what you’re trying to accomplish before you start writing.
While a business plan provides the foundation for a business, other types of plans support this guiding document.
An operational plan sets short-term goals for the business by laying out where it plans to focus energy and investments and when it plans to hit key milestones.
Then there is the strategic plan , which examines longer-range opportunities for the business, and how to meet those larger goals over time.
Read More: How to use a business plan for strategic development and operations
- Business plan vs. business model
If a business plan describes the tactics an entrepreneur will use to succeed in the market, then the business model represents how they will make money.
The difference may seem subtle, but it’s important.
Think of a business plan as the roadmap for how to exploit market opportunities and reach a state of sustainable growth. By contrast, the business model lays out how a business will operate and what it will look like once it has reached that growth phase.
Learn More: The differences between a business model and business plan
- Moving from idea to business plan
Now that you understand what a business plan is, the next step is to start writing your business plan .
The best way to start is by reviewing examples and downloading a business plan template. These resources will provide you with guidance and inspiration to help you write a plan.
We recommend starting with a simple one-page plan ; it streamlines the planning process and helps you organize your ideas. However, if one page doesn’t fit your needs, there are plenty of other great templates available that will put you well on your way to writing a useful business plan.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Tim Berry is the founder and chairman of Palo Alto Software , a co-founder of Borland International, and a recognized expert in business planning. He has an MBA from Stanford and degrees with honors from the University of Oregon and the University of Notre Dame. Today, Tim dedicates most of his time to blogging, teaching and evangelizing for business planning.

Table of Contents
- Reasons to write a business plan
- Business planning research
- When to write a business plan
- When to update a business plan
- Information to include
- Business vs. operational vs. strategic plans
Related Articles

13 Min. Read
How to Write an Online Fitness Business Plan

12 Min. Read
Free Amazon FBA Business Plan PDF [2024 Template + Sample Plan]

8 Min. Read
How to Format a Business Plan in 8 Simple Steps

6 Min. Read
How to Write Your Business Plan Cover Page + Template
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans for May 2024 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How To Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Write a Business Plan, Step by Step

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
What is a business plan?
1. write an executive summary, 2. describe your company, 3. state your business goals, 4. describe your products and services, 5. do your market research, 6. outline your marketing and sales plan, 7. perform a business financial analysis, 8. make financial projections, 9. summarize how your company operates, 10. add any additional information to an appendix, business plan tips and resources.
A business plan outlines your business’s financial goals and explains how you’ll achieve them over the next three to five years. Here’s a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan that will offer a strong, detailed road map for your business.

ZenBusiness
A business plan is a document that explains what your business does, how it makes money and who its customers are. Internally, writing a business plan should help you clarify your vision and organize your operations. Externally, you can share it with potential lenders and investors to show them you’re on the right track.
Business plans are living documents; it’s OK for them to change over time. Startups may update their business plans often as they figure out who their customers are and what products and services fit them best. Mature companies might only revisit their business plan every few years. Regardless of your business’s age, brush up this document before you apply for a business loan .
» Need help writing? Learn about the best business plan software .
This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your business offers and a broad summary of your financial growth plans.
Though the executive summary is the first thing your investors will read, it can be easier to write it last. That way, you can highlight information you’ve identified while writing other sections that go into more detail.
» MORE: How to write an executive summary in 6 steps
Next up is your company description. This should contain basic information like:
Your business’s registered name.
Address of your business location .
Names of key people in the business. Make sure to highlight unique skills or technical expertise among members of your team.
Your company description should also define your business structure — such as a sole proprietorship, partnership or corporation — and include the percent ownership that each owner has and the extent of each owner’s involvement in the company.
Lastly, write a little about the history of your company and the nature of your business now. This prepares the reader to learn about your goals in the next section.
» MORE: How to write a company overview for a business plan

The third part of a business plan is an objective statement. This section spells out what you’d like to accomplish, both in the near term and over the coming years.
If you’re looking for a business loan or outside investment, you can use this section to explain how the financing will help your business grow and how you plan to achieve those growth targets. The key is to provide a clear explanation of the opportunity your business presents to the lender.
For example, if your business is launching a second product line, you might explain how the loan will help your company launch that new product and how much you think sales will increase over the next three years as a result.
» MORE: How to write a successful business plan for a loan
In this section, go into detail about the products or services you offer or plan to offer.
You should include the following:
An explanation of how your product or service works.
The pricing model for your product or service.
The typical customers you serve.
Your supply chain and order fulfillment strategy.
You can also discuss current or pending trademarks and patents associated with your product or service.
Lenders and investors will want to know what sets your product apart from your competition. In your market analysis section , explain who your competitors are. Discuss what they do well, and point out what you can do better. If you’re serving a different or underserved market, explain that.
Here, you can address how you plan to persuade customers to buy your products or services, or how you will develop customer loyalty that will lead to repeat business.
Include details about your sales and distribution strategies, including the costs involved in selling each product .
» MORE: R e a d our complete guide to small business marketing
If you’re a startup, you may not have much information on your business financials yet. However, if you’re an existing business, you’ll want to include income or profit-and-loss statements, a balance sheet that lists your assets and debts, and a cash flow statement that shows how cash comes into and goes out of the company.
Accounting software may be able to generate these reports for you. It may also help you calculate metrics such as:
Net profit margin: the percentage of revenue you keep as net income.
Current ratio: the measurement of your liquidity and ability to repay debts.
Accounts receivable turnover ratio: a measurement of how frequently you collect on receivables per year.
This is a great place to include charts and graphs that make it easy for those reading your plan to understand the financial health of your business.
This is a critical part of your business plan if you’re seeking financing or investors. It outlines how your business will generate enough profit to repay the loan or how you will earn a decent return for investors.
Here, you’ll provide your business’s monthly or quarterly sales, expenses and profit estimates over at least a three-year period — with the future numbers assuming you’ve obtained a new loan.
Accuracy is key, so carefully analyze your past financial statements before giving projections. Your goals may be aggressive, but they should also be realistic.
NerdWallet’s picks for setting up your business finances:
The best business checking accounts .
The best business credit cards .
The best accounting software .
Before the end of your business plan, summarize how your business is structured and outline each team’s responsibilities. This will help your readers understand who performs each of the functions you’ve described above — making and selling your products or services — and how much each of those functions cost.
If any of your employees have exceptional skills, you may want to include their resumes to help explain the competitive advantage they give you.
Finally, attach any supporting information or additional materials that you couldn’t fit in elsewhere. That might include:
Licenses and permits.
Equipment leases.
Bank statements.
Details of your personal and business credit history, if you’re seeking financing.
If the appendix is long, you may want to consider adding a table of contents at the beginning of this section.
How much do you need?
with Fundera by NerdWallet
We’ll start with a brief questionnaire to better understand the unique needs of your business.
Once we uncover your personalized matches, our team will consult you on the process moving forward.
Here are some tips to write a detailed, convincing business plan:
Avoid over-optimism: If you’re applying for a business bank loan or professional investment, someone will be reading your business plan closely. Providing unreasonable sales estimates can hurt your chances of approval.
Proofread: Spelling, punctuation and grammatical errors can jump off the page and turn off lenders and prospective investors. If writing and editing aren't your strong suit, you may want to hire a professional business plan writer, copy editor or proofreader.
Use free resources: SCORE is a nonprofit association that offers a large network of volunteer business mentors and experts who can help you write or edit your business plan. The U.S. Small Business Administration’s Small Business Development Centers , which provide free business consulting and help with business plan development, can also be a resource.
On a similar note...
Find small-business financing
Compare multiple lenders that fit your business

- Top Courses
- Online Degrees
- Find your New Career
- Join for Free
Business Plan: What It Is + How to Write One
Discover what a business plan includes and how writing one can foster your business’s development.
![what are 3 types of business plans [Featured image] Woman showing a business plan to a man at a desk](https://d3njjcbhbojbot.cloudfront.net/api/utilities/v1/imageproxy/https://images.ctfassets.net/wp1lcwdav1p1/8jaIrEmfb9uCidnAGOr2F/c551eade2b440294787de7afd2acb369/GettyImages-1127726432__1_.jpg?w=1500&h=680&q=60&fit=fill&f=faces&fm=jpg&fl=progressive&auto=format%2Ccompress&dpr=1&w=1000)
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a written document that defines your business goals and the tactics to achieve those goals. A business plan typically explores the competitive landscape of an industry, analyzes a market and different customer segments within it, describes the products and services, lists business strategies for success, and outlines financial planning.
In your research into business plans, you may come across different formats, and you might be wondering which kind will work best for your purposes.
Let’s define two main types of business plans , the traditional business pla n and the lean start-up business plan . Both types can serve as the basis for developing a thriving business, as well as exploring a competitive market analysis, brand strategy , and content strategy in more depth. There are some significant differences to keep in mind [ 1 ]:
The traditional business plan is a long document that explores each component in depth. You can build a traditional business plan to secure funding from lenders or investors.
The lean start-up business plan focuses on the key elements of a business’s development and is shorter than the traditional format. If you don’t plan to seek funding, the lean start-up plan can serve mainly as a document for making business decisions and carrying out tasks.
Now that you have a clear business plan definition , continue reading to begin writing a detailed plan that will guide your journey as an entrepreneur.
How to write a business plan
In the sections below, you’ll build the following components of your business plan:
Executive summary
Business description
Products and services
Competitor analysis
Marketing plan and sales strategies
Brand strategy
Financial planning
Explore each section to bring fresh inspiration to the surface and reveal new possibilities for developing your business. You may choose to adapt the sections, skip over some, or go deeper into others, depending on which format you’re using. Consider your first draft a foundation for your efforts and one that you can revise, as needed, to account for changes in any area of your business.
Read more: What Is a Marketing Plan? And How to Create One
1. Executive summary
This is a short section that introduces the business plan as a whole to the people who will be reading it, including investors, lenders, or other members of your team. Start with a sentence or two about your business, your goals for developing it, and why it will be successful. If you are seeking funding, summarize the basics of the financial plan.
2. Business description
Use this section to provide detailed information about your company and how it will operate in the marketplace.
Mission statement: What drives your desire to start a business? What purpose are you serving? What do you hope to achieve for your business, the team, your customers?
Revenue streams: From what sources will your business generate revenue? Examples include product sales, service fees, subscriptions, rental fees, license fees, and more.
Leadership: Describe the leaders in your business, their roles and responsibilities, and your vision for building teams to perform various functions, such as graphic design, product development, or sales.
Legal structure: If you’ve incorporated your business or registered it with your state as a legal entity such as an S-corp or LLC, include the legal structure here and the rationale behind this choice.
3. Competitor analysis
This section will include an assessment of potential competitors, their offers, and marketing and sales efforts. For each competitor, explore the following:
Value proposition: What outcome or experience does this brand promise?
Products and services: How does each one solve customer pain points and fulfill desires? What are the price points?
Marketing: Which channels do competitors use to promote? What kind of content does this brand publish on these channels? What messaging does this brand use to communicate value to customers?
Sales: What sales process or buyer’s journey does this brand lead customers through?
Read more: What Is Competitor Analysis? And How to Conduct One
4. Products and services
Use this section to describe everything your business offers to its target market . For every product and service, list the following:
The value proposition or promise to customers, in terms of how they will experience it
How the product serves customers, addresses their pain points, satisfies their desires, and improves their lives
The features or outcomes that make the product better than those of competitors
Your price points and how these compare to competitors
5. Marketing plan and sales strategies
In this section, you’ll draw from thorough market research to describe your target market and how you will reach them.
Who are your ideal customers?
How can you describe this segment according to their demographics (age, ethnicity, income, location, etc.) and psychographics (beliefs, values, aspirations, lifestyle, etc.)?
What are their daily lives like?
What problems and challenges do they experience?
What words, phrases, ideas, and concepts do consumers in your target market use to describe these problems when posting on social media or engaging with your competitors?
What messaging will present your products as the best on the market? How will you differentiate messaging from competitors?
On what marketing channels will you position your products and services?
How will you design a customer journey that delivers a positive experience at every touchpoint and leads customers to a purchase decision?
Read more: Market Analysis: What It Is and How to Conduct One
6. Brand strategy
In this section, you will describe your business’s design, personality, values, voice, and other details that go into delivering a consistent brand experience.
What are the values that define your brand?
What visual elements give your brand a distinctive look and feel?
How will your marketing messaging reflect a distinctive brand voice, including the tone, diction, and sentence-level stylistic choices?
How will your brand look and sound throughout the customer journey?
Define your brand positioning statement. What will inspire your audience to choose your brand over others? What experiences and outcomes will your audience associate with your brand?
Read more: What Is a Brand Strategy? And How to Create One
7. Financial planning
In this section, you will explore your business’s financial future. If you are writing a traditional business plan to seek funding, this section is critical for demonstrating to lenders or investors that you have a strategy for turning your business ideas into profit. For a lean start-up business plan, this section can provide a useful exercise for planning how you will invest resources and generate revenue [ 2 ].
Use any past financials and other sections of this business plan, such as your price points or sales strategies, to begin your financial planning.
How many individual products or service packages do you plan to sell over a specific time period?
List your business expenses, such as subscribing to software or other services, hiring contractors or employees, purchasing physical supplies or equipment, etc.
What is your break-even point, or the amount you have to sell to cover all expenses?
Create a sales forecast for the next three to five years: (No. of units to sell X price for each unit) – (cost per unit X No. of units) = sales forecast
Quantify how much capital you have on hand.
When writing a traditional business plan to secure funding, you may choose to append supporting documents, such as licenses, permits, patents, letters of reference, resumes, product blueprints, brand guidelines, the industry awards you’ve received, and media mentions and appearances.
Business plan key takeaways and best practices
Remember: Creating a business plan is crucial when starting a business. You can use this document to guide your decisions and actions and even seek funding from lenders and investors.
Keep these best practices in mind:
Your business plan should evolve as your business grows. Return to it periodically, such as every quarter or year, to update individual sections or explore new directions your business can take.
Make sure everyone on your team has a copy of the business plan and welcome their input as they perform their roles.
Ask fellow entrepreneurs for feedback on your business plan and look for opportunities to strengthen it, from conducting more market and competitor research to implementing new strategies for success.
Start your business with Coursera
Ready to start your business? Watch this video on the lean approach from the Entrepreneurship Specialization :
Article sources
1. US Small Business Administration. “ Write Your Business Plan , https://www.sba.gov/business-guide/plan-your-business/write-your-business-plan." Accessed April 19, 2022.
2. Inc. " How to Write the Financial Section of a Business Plan , https://www.inc.com/guides/business-plan-financial-section.html." Accessed April 14, 2022.
Keep reading
Coursera staff.
Editorial Team
Coursera’s editorial team is comprised of highly experienced professional editors, writers, and fact...
This content has been made available for informational purposes only. Learners are advised to conduct additional research to ensure that courses and other credentials pursued meet their personal, professional, and financial goals.

- Customer Reviews
- Net 30 Account
- Wise Services
- Steps & Timeline
- Work at a Glance
- Market Research at a Glance
- Business Plan Writing Services
- Bank Business Plan
- Investor Business Plan
- Franchise Business Plan
- Cannabis Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Corporate Business Plan
- Merge and Acquisition Business Plan (M&A)
- Private Placement Memorandums (PPM)
- Sample Business Plans
- Professional Feasibility Study
- PowerPoint Presentations
- Pitch Deck Presentation Services
- Business Plan Printing
- Market Research
- L-1 Business Plan
- E-2 Business Plan
- EB-5 Business Plan
- EB-5 Regional Centers
- Immigration Attorneys
- Nonprofit Business Plan
- Exit Business Planning
- Business Planning
- Business Formation
- Business License
- Business Website
- Business Branding
- Business Bank Account
- Digital Marketing
- Business Funding Resources
- Small Business Loans
- Venture Capital
- Net 30 Apply

What is a business plan? Definition, Purpose, and Types
In the world of business, a well-thought-out plan is often the key to success. This plan, known as a business plan, is a comprehensive document that outlines a company’s goals, strategies , and financial projections. Whether you’re starting a new business or looking to expand an existing one, a business plan is an essential tool.
As a business plan writer and consultant , I’ve crafted over 15,000 plans for a diverse range of businesses. In this article, I’ll be sharing my wealth of experience about what a business plan is, its purpose, and the step-by-step process of creating one. By the end, you’ll have a thorough understanding of how to develop a robust business plan that can drive your business to success.
What is a business plan?
Purposes of a business plan, what are the essential components of a business plan, executive summary, business description or overview, product and price, competitive analysis, target market, marketing plan, financial plan, funding requirements, types of business plan, lean startup business plans, traditional business plans, how often should a business plan be reviewed and revised, what are the key elements of a lean startup business plan.
- What are some of the reasons why business plans don't succeed?
A business plan is a roadmap for your business. It outlines your goals, strategies, and how you plan to achieve them. It’s a living document that you can update as your business grows and changes.
Looking for someone to write a business plan?
Find professional business plan writers for your business success.
These are the following purpose of business plan:
- Attract investors and lenders: If you’re seeking funding for your business , a business plan is a must-have. Investors and lenders want to see that you have a clear plan for how you’ll use their money to grow your business and generate revenue.
- Get organized and stay on track: Writing a business plan forces you to think through all aspects of your business, from your target market to your marketing strategy. This can help you identify any potential challenges and opportunities early on, so you can develop a plan to address them.
- Make better decisions: A business plan can help you make better decisions about your business by providing you with a framework to evaluate different options. For example, if you’re considering launching a new product, your business plan can help you assess the potential market demand, costs, and profitability.

The executive summary is the most important part of your business plan, even though it’s the last one you’ll write. It’s the first section that potential investors or lenders will read, and it may be the only one they read. The executive summary sets the stage for the rest of the document by introducing your company’s mission or vision statement, value proposition, and long-term goals.
The business description section of your business plan should introduce your business to the reader in a compelling and concise way. It should include your business name, years in operation, key offerings, positioning statement, and core values (if applicable). You may also want to include a short history of your company.
In this section, the company should describe its products or services , including pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other relevant information could include production and manufacturing processes, patents, and proprietary technology.
Every industry has competitors, even if your business is the first of its kind or has the majority of the market share. In the competitive analysis section of your business plan, you’ll objectively assess the industry landscape to understand your business’s competitive position. A SWOT analysis is a structured way to organize this section.
Your target market section explains the core customers of your business and why they are your ideal customers. It should include demographic, psychographic, behavioral, and geographic information about your target market.
Marketing plan describes how the company will attract and retain customers, including any planned advertising and marketing campaigns . It also describes how the company will distribute its products or services to consumers.
After outlining your goals, validating your business opportunity, and assessing the industry landscape, the team section of your business plan identifies who will be responsible for achieving your goals. Even if you don’t have your full team in place yet, investors will be impressed by your clear understanding of the roles that need to be filled.
In the financial plan section,established businesses should provide financial statements , balance sheets , and other financial data. New businesses should provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years, and may also request funding.
Since one goal of a business plan is to secure funding from investors , you should include the amount of funding you need, why you need it, and how long you need it for.
- Tip: Use bullet points and numbered lists to make your plan easy to read and scannable.
Access specialized business plan writing service now!
Business plans can come in many different formats, but they are often divided into two main types: traditional and lean startup. The U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) says that the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
Lean startup business plans are short (as short as one page) and focus on the most important elements. They are easy to create, but companies may need to provide more information if requested by investors or lenders.
Traditional business plans are longer and more detailed than lean startup business plans, which makes them more time-consuming to create but more persuasive to potential investors. Lean startup business plans are shorter and less detailed, but companies should be prepared to provide more information if requested.
Need Guidance with Your Business Plan?
Access 14 free business plan samples!
A business plan should be reviewed and revised at least annually, or more often if the business is experiencing significant changes. This is because the business landscape is constantly changing, and your business plan needs to reflect those changes in order to remain relevant and effective.
Here are some specific situations in which you should review and revise your business plan:
- You have launched a new product or service line.
- You have entered a new market.
- You have experienced significant changes in your customer base or competitive landscape.
- You have made changes to your management team or organizational structure.
- You have raised new funding.
A lean startup business plan is a short and simple way for a company to explain its business, especially if it is new and does not have a lot of information yet. It can include sections on the company’s value proposition, major activities and advantages, resources, partnerships, customer segments, and revenue sources.
What are some of the reasons why business plans don't succeed?

- Unrealistic assumptions: Business plans are often based on assumptions about the market, the competition, and the company’s own capabilities. If these assumptions are unrealistic, the plan is doomed to fail.
- Lack of focus: A good business plan should be focused on a specific goal and how the company will achieve it. If the plan is too broad or tries to do too much, it is unlikely to be successful.
- Poor execution: Even the best business plan is useless if it is not executed properly. This means having the right team in place, the necessary resources, and the ability to adapt to changing circumstances.
- Unforeseen challenges: Every business faces challenges that could not be predicted or planned for. These challenges can be anything from a natural disaster to a new competitor to a change in government regulations.
What are the benefits of having a business plan?
- It helps you to clarify your business goals and strategies.
- It can help you to attract investors and lenders.
- It can serve as a roadmap for your business as it grows and changes.
- It can help you to make better business decisions.
How to write a business plan?
There are many different ways to write a business plan, but most follow the same basic structure. Here is a step-by-step guide:
- Executive summary.
- Company description.
- Management and organization description.
- Financial projections.
How to write a business plan step by step?
Start with an executive summary, then describe your business, analyze the market, outline your products or services, detail your marketing and sales strategies, introduce your team, and provide financial projections.
Why do I need a business plan for my startup?
A business plan helps define your startup’s direction, attract investors, secure funding, and make informed decisions crucial for success.
What are the key components of a business plan?
Key components include an executive summary, business description, market analysis, products or services, marketing and sales strategy, management and team, financial projections, and funding requirements.
Can a business plan help secure funding for my business?
Yes, a well-crafted business plan demonstrates your business’s viability, the use of investment, and potential returns, making it a valuable tool for attracting investors and lenders.
Quick Links

- Investor Business Plans
- M&A Business Plan
- Private Placement
- Feasibility Study
- Hire a Business Plan Writer
- Business Valuation Calculator
- Business Plan Examples
- Real Estate Business Plan
- Business Plan Template
- Business Plan Pricing Guide
- Business Plan Makeover
- SBA Loans, Bank Funding & Business Credit
- Finding & Qualifying for Business Grants
- Leadership for the New Manager
- Content Marketing for Beginners
- All About Crowdfunding
- EB-5 Regional Centers, A Step-By-Step Guide
- Logo Designer
- Landing Page
- PPC Advertising

- Business Entity
- Business Licensing
- Virtual Assistant
- Business Phone
- Business Address
- E-1 Visa Business Plan
- EB1-A Visa Business Plan
- EB1-C Visa Business Plan
- EB2-NIW Business Plan
- H1B Visa Business Plan
- O1 Visa Business Plan
- Business Brokers
- Merger & Acquisition Advisors
- Franchisors
Proud Sponsor of
- 1-800-496-1056

- (613) 800-0227

- +44 (1549) 409190

- +61 (2) 72510077


5 Types Of Business Plans (+ Customizable Templates)
Find the best form of business plan for your venture and learn to align your business plan model with a winning strategy. Grab a template to get started.
6 minute read

helped business professionals at:

Short answer
What are the main types of business plans?
5 main types of business plans:
Startup business plan
One-pager business plan
Operational business plan
Feasibility business plan
Growth business plan
Aligning your strategy with the wrong type of business plan leads to failure
Crafting a sharp business plan is non-negotiable if you want your project to lift off the ground.
Yet, many miss the mark by not adapting their strategy to the appropriate type of business plan. It's like trying to open a door with the wrong key, frustrating and futile. This oversight can lead to miscommunication, disinterest from crucial stakeholders, and missed growth opportunities.
Here's where I step in, offering you a master key to unlock the true potential of effective business planning.
You'll learn about the strategic value of tailoring your plan to fit specific needs, whether you're kickstarting a venture, seeking investment, or plotting growth. Let's go.
What makes a successful business plan?
Creating a business plan that stands out involves more than just outlining your business's operations. It's about highlighting how your business differentiates itself and thrives within its industry.
Drawing inspiration from expert advice on business planning, here's an overview of the key elements that make a business plan successful. 6 key elements of a winning business plan:
Precision and structure: It's sharp, structured, and zeroes in on the business's main goals and strategies without unnecessary fluff.
Grounded objectives and forecasts: It sets attainable objectives and includes grounded financial forecasts, informed by thorough market analysis and industry insights.
Flexibility: It remains adaptable, ready to evolve alongside the business and shifting market dynamics.
Audience-specific design: It's crafted with the target audience in mind, whether that's attracting investors, securing loans, or engaging customers, ensuring it resonates and meets their expectations.
Clear communication: It communicates the business idea, market potential, and growth trajectory clearly and persuasively.
Defined action plan: It provides a clear set of steps to be undertaken to reach the business's goals, making it practical and actionable.
Internal vs. external business plan
The difference between internal and external business plans is based on their intended audience.
INTERNAL BUSINESS PLAN
EXTERNAL BUSINESS PLAN
Internal business plan
Internal documents tailored for departments such as marketing or HR emphasize succinct insights about the company and a more focused financial outlook. These documents usually adopt a less formal tone.
Purpose: Align your team and streamline operations.
Key approach: Focus on strategy, flexibility, and clear metrics.
Tip: Regularly review and update the plan, and encourage team feedback.
External business plan
External documents reach out to those outside your immediate circle, such as investors or partners. They provide a thorough overview of your company, including detailed financials, and maintain a formal tone, typically aimed at securing funding or establishing partnerships.
Purpose: Impress and persuade investors or partners.
Key approach: Ensure clarity, and professionalism, and tailor content to your audience.
Tip: Understand your audience's priorities, and seek expert feedback before finalizing.
5 types of business plans to align your strategy with
Picking the right business plan is a big deal for founders, managers, and leaders. But let's be honest, diving into the sea of options can feel overwhelming.
Whether you're chasing funding, dreaming of expanding or looking to streamline your operations, I've got you covered.
I'm talking about seizing opportunities to not just meet your goals but to exceed them. Let's dive in and align your ambitions with the perfect plan.
1) Startup business plan
Audience: External stakeholders, including investors and financial institutions.
Depth: Comprehensive and detailed.
Purpose: To outline the steps for launching a new venture and securing funding.
The startup plan is your blueprint for launching a new venture.
It's packed with everything from a punchy executive summary that grabs you with the business concept to deep dives into market trends and who you're up against.
It lays out financial forecasts with precision, giving potential backers a crystal-clear picture of where you're headed in terms of profits and what you need to get there.
This plan isn't just about pulling in funds; it's your strategic playbook for carving out a successful path forward. For newbies on the entrepreneurial scene, it's nothing short of essential.
Here’s an example of a start-up business plan:
2) One-pager business plan
Audience: External parties, such as potential investors, partners, and vendors.
Depth: High-level and succinct.
Purpose: To quickly communicate the business's value proposition and growth potential.
The one-page plan condenses the core of a business strategy into a succinct and impactful document, crafted to immediately capture the attention of potential investors, partners, and vendors.
It showcases the unique value proposition, targets the market with effective strategies, and highlights financial insights and growth potential.
This streamlined plan turns out to be a game-changer for entrepreneurs looking to share their vision and strategy in a clear, easy-to-understand way.
It quickly gets the point across and sparks interest from potential stakeholders, encouraging them to dive deeper.
Here’s an example of a one-pager business plan:

3) Operational business plan
Audience: Internal management teams and department heads.
Depth: Detailed, focusing on day-to-day operations and short-term goals.
Purpose: To streamline internal processes and enhance operational efficiency.
The operational business plan is like the company's playbook, focusing on fine-tuning every single part of your operations.
It lays out the operational goals that sync up with your big-picture strategies, breaking down the exact tasks and processes you need to nail those targets.
You've got everything mapped out, from streamlining workflows to boosting efficiency, and even who's doing what to ensure you're all pulling in the same direction.
It also covers allocating resources, from budgets to materials, ensuring every department has what it needs.
Diving into the nitty-gritty of your day-to-day, this plan is key for spotting where you can do better, ramping up productivity, and hitting your short-term goals more smoothly.
Here’s an example of an operational business plan:
4) Growth business plan
Audience: Both internal stakeholders for strategic alignment and external parties for investment or partnership opportunities.
Depth: This can vary from lean to standard, depending on the audience.
Purpose: To provide a strategic framework for business expansion.
The growth plan feels like launching into a new adventure, much like a startup plan, but for your next big leap.
It's about charting a course for new markets, beefing up your product lines, or scaling operations to new heights.
This plan packs deep dives into the business, financial forecasts that map out your journey, and a rundown of the resources you'll need to expand.
It's a guiding light for businesses aiming for sustainable growth, laying out a clear path and milestones to hit along the way.
Whether it's guiding your team internally or dazzling potential investors, the growth plan pulls everyone together, focusing efforts on shared growth targets.
It's about making sure every stakeholder is in sync, marching towards the same ambitious goals.
Here’s an example of a growth business plan:
5) Feasibility business plan
Audience: Primarily internal, though it can be external if linked to funding requests.
Depth: Focused and streamlined.
Purpose: To assess the viability of a new product or service.
A feasibility plan, or feasibility study, acts as a litmus test for proposed business expansions or new product launches.
It delves into the practicality of the idea, examining market demand, technical requirements, and financial implications.
By focusing on specific growth opportunities and analyzing them against objective standards, this plan helps decision-makers within the organization determine whether to proceed with the venture.
It's a critical step in the planning process, ensuring resources are allocated to projects with the highest potential for success.
For ventures requiring external funding, a more detailed version of this plan may be necessary to convince investors of the project's feasibility.
If you want to learn more, check out our guides on business plan:
7 Key Components of a Precise Business Plan (2024)
How to Write a Business Plan (Examples & Templates)
How to Make a Killer Business Plan Presentation (+Templates)
Create a Business Plan One-Pager (+ Proven Templates)
Don’t let poor design sabotage your business plan
Designing a business plan presentation in today's digital age goes beyond mere text on a page, it's about crafting an engaging experience that captures and retains attention.
With the shift towards digital, the presentation of your plan is as crucial as its content.
5 crucial business plan design principles:
1) Transition from static to interactive
The era of static, text-heavy presentations is behind us. Modern business plans thrive on interactivity, incorporating elements like clickable links, dynamic charts, and embedded videos.
This approach not only enriches the reader's experience but also fosters a deeper engagement with the material, making your business plan far more compelling.
Here's what a static PPT looks like compared to an interactive deck:

Static PowerPoint

Interactive Storydoc
2) Implement scroll-based design
Ditch the cumbersome PDF format for a scroll-based design that mirrors the seamless experience of browsing a modern website.
This design choice is intuitive and aligns with our habitual online content consumption, making your business plan both accessible and enjoyable to navigate.
Here's an example of scroll-based design:

3) Prioritize mobile-friendliness
In a world where mobile devices dominate, ensuring your business plan looks great on any screen is non-negotiable.
Adopting responsive design guarantees that your plan is legible and appealing across all devices, from smartphones to desktops, ensuring your message resonates clearly with every reader.
4) Move to online documents
Forget about clunky Word docs or static PDFs. The future is online documents that allow for real-time updates, easy sharing, and collaboration.
They're not only convenient for you but also for your busy investors, offering access from anywhere, at any time.
For more information, check out our comparison of the best business plan document types .
5) Master visual storytelling
Leverage the power of visuals infographics, charts, and graphs to narrate your business's story.
Visuals can simplify complex information, making your key points more digestible and engaging than text alone could ever achieve.
Here's a great example of visual storytelling:

All forms of business plan templates to get you started
Just as a captivating presentation can transform the way your message is received, a well-crafted business plan is your gateway to turning your business vision into reality.
Why settle for a dry, uninspiring document when you can create a business plan that's a dynamic blueprint for success?
Consider your business plan as a journey for your readers — investors, partners, or internal team members — keeping them engaged from the executive summary to the final appendix.
These business plan templates serve as the perfect foundation for this journey.
I am a Marketing Specialist at Storydoc, I research, analyze and write on our core topics of business presentations, sales, and fundraising. I love talking to clients about their successes and failures so I can get a rounded understanding of their world.
Found this post useful?
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter.
Get notified as more awesome content goes live.
(No spam, no ads, opt-out whenever)
You've just joined an elite group of people that make the top performing 1% of sales and marketing collateral.

Make your best business plan to date
Stop losing opportunities to ineffective presentations. Your new amazing deck is one click away!

- Customer Reviews
- Extended Essays
- IB Internal Assessment
- Theory of Knowledge
- Literature Review
- Dissertations
- Essay Writing
- Research Writing
- Assignment Help
- Capstone Projects
- College Application
- Online Class
The 8 Types of Business Plans Explained
by Antony W
April 10, 2024

In this guide, we look at the different types of business plans and where they apply.
You can write a standard, lean, one-page, startup, strategic, feasibility, operational, or growth business plan depending on your needs.
Here’s an explanation for each:
1. Standard Business Plan
A standard business plan gives a detailed description of the operations of a business so stakeholders can understand the business well. A standard business plan features an executive summary , competitive analysis, SWOT analysis, and market summary.
The success of a standard business plan anchors on the information it provides. Therefore, focus on providing accurate information, so investors can have an easy time evaluating the risk and potential of the business before releasing funds.
A standard business plan should also include financial plan, problem analysis, and management objectives.
2. Lean Business Plan
A lean business plan is a condensed and straightforward document that highlights and summarizes the most important aspects of a business. Many entrepreneurs use this plan for efficient communication because it highlights only the most significant elements and milestones.
The necessary details to include in a lean business plan are operation strategies, financial projections, and the strategies necessary for business success in a rather competitive marketing landscape.
3. One-page Business Plan
A one-page business plan is more or less for direct to the point communication. It’s the best plan to use if you want to pitch investors and stakeholders who don’t have much time to read extensive documents.
The main benefit of a one-page business plan is that it presents only the most important information guaranteed to pique an audience’s attention. While the plan doesn’t have peripheral explanations, the information presented is enough to give a clear overview of the business.
A well-written one-page business plan summarizes the target market, operational requirements, objectives, forecasts, and products or services.
4. Startup Business Plan
A startup business plan states the requirements a business must meet to start operating in a specific market. It incorporates elements of lean and standard business plans, and its detailed sections are common when establishing new techniques likely to support the business’s overall operations.
A startup business plan has to address licensing, business permits, necessary equipment, and human resource management questions. And while the plan will vary based on the nature of business activities, comprehensive details are mandatory.
5. Strategic Business Plan
A strategic business plan describes the roadmap that a business leader intends to use to steer the enterprise in the right direction after overcoming different challenges and exploring opportunities.
You can only write a comprehensive strategic business plan after conducting an in-depth SWOT analysis and identifying the implementation processes necessary to put the business in the right direction.
The plan allows you to influence stakeholders to focus on specific aspects that eventually contribute to the overall success of the business.
6. Feasibility Business Plan
A feasibility plan allows a business to determine the existence of new markets and the potential benefits of investing in such markets.
To write a comprehensive feasibility plan, you have to understand the current business environment, evaluate opportunities, and consolidate funds to support the new ventures.
Keep in mind that your feasibility business plan may lead to recommendations that point out weaknesses and indicate ideas for growth after investments.
7. Operational Business Plan
An operational business plan is lean and focused on the implementation processes after goals are set and resources allocated to specific functions.
The specific sections of the plan will describe milestones, responsibilities, stakeholders, and goals.
Because an operational business plan focuses on internal processes, outsiders cannot contribute significantly to the business. However, they can participate in evaluation and tracking progress.
8. Growth Business Plan
Business growth is all about expansion. Therefore, you have to come up with a plan that identifies and integrate activities that facilitate expansion and drive the business to achieve specific milestone.
Your focus on growth requires accurate descriptions of long-term goals and the steps necessary to ignite the change you desire to see in your business.
The growth business plan integrates internal and external considerations to forecast, analyze, and secure resources for expansion. Incorporating What-if scenarios into the growth plan enables preparation for risky investments, ensuring readiness to address potential adverse outcomes.
What is a Business Plan?
We define a business plan as a document that describes a business’s goals and how it intends to achieve those goals. Business plans are for established enterprises and startups. A business plan is important because it documents an entity’s finance, marketing, and operational standpoint.
A comprehensive business plan acts as a powerful tool to attract investors, predict business demands in the future, and outline a long-term game plan for the business.
How Do I Write a Business Plan?
You can write a business plan by following the process we’ve outlined to get the task completed.
- Conduct in-depth business and market research to learn more about your audience.
- Have clear goals before you start writing.
- Go straight to the point.
- Keep your tone, voice, and style consistent and professional as you write.
What is the Best Business Plan Writing Service?
Help for Assessment is the best business plan writing service online. Our company has highly trained writers with years of academic and business experience. Therefore, paying for our service will definitely get you the best results.
Our business plan writing service takes you from a completely blank page to a comprehensive document in just 7 days. It doesn’t matter if you have a strict deadline to beat or a flexible deadline to meet. You can count on our team.
How Much Do You Charge to Write a Business Plan?
We charge $12.99 to $40 per page to write a business plan. The overall cost for a business plan depends on the number of pages ordered, number of charts requested, level of expertise required, number of slides, and urgency.
Help for Assessment offers up to 10% discount to new customers. Therefore, you can save money and benefit from our cost-effective writing if you’re on tight budget.
About the author
Antony W is a professional writer and coach at Help for Assessment. He spends countless hours every day researching and writing great content filled with expert advice on how to write engaging essays, research papers, and assignments.
- 400+ Sample Business Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Customer Success Stories
Business Plan Course
Strategic Planning Templates
E-books, Guides & More
Entrepreneurs & Small Business
Accelerators & Incubators
Business Consultants & Advisors
Educators & Business Schools
Students & Scholars
AI Business Plan Generator
Financial Forecasting
AI Assistance
Ai Pitch Deck Generator
Strategic Planning
See How Upmetrics Works →
- Sample Plans
Small Business Tools
The Different Types of Business Plans

Free Business Plan Template
Ayush Jalan
- December 14, 2023
A business plan is a blueprint for your business. No matter if you’re running a startup or a well-established company, every entrepreneur needs to create a business plan . It helps you have a clear idea of your goals, and objectives, the execution of your strategies, and tracking progress.
Business plans come in all shapes and sizes.
You can create a plan based on your unique requirements and goals. Often, businesses require different types of plans for different situations and to tackle different problems. Having just one standard business plan is not enough.
A meticulously crafted business plan will efficiently serve its intended purpose . In fact, business plans are categorized based on the type of audience, the scope of the plan, and the purpose and format of the plan.
Understanding the basics of each type will help you pick out the right one for your business requirements. In this article, you will learn the different types of business plans and when and where they are used.
Based on Audience

Business plans are broadly categorized into two types based on the type of audience. They are:
- 1. Internal business plans: As the name suggests, an internal business plan is solely for the people inside the company. These can be specific to certain departments such as marketing, HR, production, etc. Internal business plans focus primarily on the company’s goals, and the personnel and processes aimed to achieve them.
- 2. External business plans: On the contrary, external business plans are intended for people outside the company, such as investors, banks, partners, etc. These plans usually contain detailed information about the company’s background, finances, and overall operation of the business.
Based on the Scope

Similarly, business plans are classified into two types based on their size and the depth of information they encompass. They are:
1. Standard business plans
A standard business plan is a bulky document that contains every detail of the company. Most external plans slide into this category as they often need to be detailed for presentation to people outside the company.
A standard business plan contains these sections:
- Executive summary
- Company Overview
- Problem analysis
- Market analysis
- Customer analysis
- Competitive analysis
- SWOT analysis
- Marketing Plan
- Operations plan
- Management team
- Finances plan
- Supporting documentation
A standard plan is usually presented to banks and any potential investors as it provides a complete view of the company, and future financial projections , and helps attain funding. But oftentimes, drafting a traditional business plan can be a tedious task as it takes a lot of time and effort.
2. Lean business plans
A lean plan is a condensed version of the standard business plan. It includes the highlights of a standard business plan and summaries of all the sections. It is a compact document that emphasizes achieving milestones and tracking finances.
Drafting a lean business plan is easier, faster, and is considered to be more efficient compared to a standard plan. It is flexible and can be revised effortlessly as many times as needed, which provides room for adjusting milestones, and improvising.
A lean business plan is apt for situations where you are uncertain about the process of creating a business plan, and it can be the essential first draft for your business. Everything in a lean business plan should be concise and represented in bullet points or short texts.
These are the elements that a lean business plan focuses on:
Based on purpose and format.
Business plans are further classified based on their purpose and format into seven types, they are:
1. One-page business plans
A one-page business plan can be described as an outline of a lean business plan . It is also called a business pitch or a quick summary. It is sometimes used to present a quick overview of your business to your vendors, partners, and employees and as a summary to banks and investors.
This encapsulates all the essential parts of a business plan on a single page. This summarizes the target market, business offering, main milestones, and essential sales forecast.
2. Startup business plans
A startup business plan can be defined as a lean plan with elements of a standard plan included to seek investors. The primary purpose of a startup plan is to put forth the steps required to get a business up and running. Later on, it should also serve as a plan that will help score investment.
The steps of establishing a new company include acquiring licenses and permits, setting up an office or store, getting equipment, and hiring and managing employees. All of these should be included in the startup business plan.
A startup plan should include information about the company, its products, and services, a detailed analysis of the industry, market, competition, SWOT, the bios of management, their responsibilities and roles, complete financial details and analysis, and projections of the usage of funding.
3. Strategic business plans
A strategic business plan is a lean business plan that contains details of the strategies and their implementation to achieve the goals and objectives of a company. These are internal plans that will focus entirely on the strategies with almost no inclusion of finances.
Conduct SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) analysis to begin an effective strategic business plan. This will help you better understand the factors that play a role in the decision-making process of a business.
A SWOT analysis will help you decide the strategies that will best suit your company and accomplish the goals, utilizing the available resources. Every strategic plan should contain these five elements:
- Mission statement
- Vision statement
- Factors that determine success
- Strategies to achieve goals
- Implementation process
4. Feasibility business plans
You require a feasible plan in case the business is stepping into a new market or introducing a new product or service. It is more a decision-making plan than a business plan as it focuses on two primary concerns:
- Determining the existence of a market
- Determining the profits of the initiative
A feasibility plan is a quick analysis of the practicality of a business idea.
This type of business plan usually excludes all the other sections and solely focuses on the scope of the initiative, its profitability, analysis of the market and competition, and acquiring the funding for it.
It is mostly crafted for internal management and ends with recommendations on whether the decision of entering a new market or introducing a new product or service is viable or not.
5. Operational business plans
An operational plan is a type of lean plan that focuses on the implementation process, achieving milestones, project deadlines, and the responsibilities of management, departments, and employees. It also focuses on the funding required to accomplish the milestones.
This business plan is called an annual plan, as businesses often use it to plan and specify milestones and their implementation for the coming year.
Some of the key elements every operational plan should contain are:
- Objectives for the operations
- Activities required to achieve objectives
- Resources required
- Staffing requirements
- Deadlines for implementation
- Tracking progress
6. Growth business plans
Draft a growth business plan when a company looks to expand its business into new markets. It is essentially a startup plan for a new segment of your business. This is also known as an expansion plan as it focuses on the long-term goals of a business.
This business plan can be both external and internal.
An external growth plan includes complete financial details and a funding request. On the other hand, an internal one contains details of the forecast of sales and expenses of the upcoming venture.
7. What-if business plan
Use a what-if plan when a business is taking a risky decision and needs a plan if the outcome turns unfavorable. This plan is usually less formal unless a funding request is included.
It entails a contingency plan that considers the worst-case scenarios.
This plan provides a glimpse into the possible outcomes of taking that risky decision and its effects on the company. It makes sense when taking a major business decision, merging with another company, raising the prices of products, etc. These are all the different types of business plans from which you can hand-pick the best fit for your company.
A Plan for Every Priority
Planning is essential for every business, without one a business is not likely to sustain itself in the long run. Although daunting sometimes, choosing the right plan for your business requirement can help you achieve your goals faster and with smart use of resources.
Every situation needs a unique approach to tackle effectively. Fortunately, there’s a plan for every purpose to help your business stand the test of time. Feel free to pick one that suits your business the best. Make sure to update it regularly.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.
About the Author

Ayush is a writer with an academic background in business and marketing. Being a tech-enthusiast, he likes to keep a sharp eye on the latest tech gadgets and innovations. When he's not working, you can find him writing poetry, gaming, playing the ukulele, catching up with friends, and indulging in creative philosophies.
Related Articles

How to Write a Business Plan Complete Guide

Lean Business Planning: The Modern approach to Business Plan Writing
Business Plan Table of Contents
Reach your goals with accurate planning.
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Popular Templates

- Starting a business
The three types of business plans for most industries
Business plans are a crucial component in the success of any business, but different industries require different models. When deciding upon which plan is best for your company, you should consider what type of industry you’re in and your goals.
Three types of business plans
Wrapping up.
You should also understand that business plans can go by different names. Some have different names but are essentially the same thing, while others genuinely are different in terms of content. You might see operational plans, Lean plans, Strategic plans, internal plans, and more.
The truth is that the kind of business plan you should put together depends on the situation. Form follows function. The best business plans match the use for which they are intended. In the article below, we’ll list three different business plan models used by many companies today.
The following is a list of business plans used commonly in most industries today.
- What Uber’s resurrection teaches us about adversity as a startup
- Tips for starting a successful ice cream truck business
- Start your own business with these 5 devices
Startup plan
According to the Startup Genome Report , most startups fail. In many instances, that failure is due to a lack of market understanding, no clear vision, and little planning. A startup business plan is intended to provide a roadmap that can help entrepreneurs steer clear of the mistakes that lead to failure.
For example, a startup plan focuses on funding, market size analysis, team building strategy, or product development strategy. Indeed, these are all critical aspects for success when starting a business.
Additionally, a startup plan usually operates as the very first plan an entrepreneur develops to give to investors in order to gain funding and to show how the business intends to grow. If you’re just starting out, your plan should include the following elements and structure:
- Executive summary
- Overview of the company
- Management background
- What service or product the company provides
- Value proposition
- Strategic marketing plan
- Market evaluations
- Projected startup costs
- Cash flow projections and income and profit expectations
Inside the financial section, you should also explain your exit strategy and how you plan to use any money that you raise from investors.
Strategic plan
In general, you’ll use a strategic business plan for internal purposes only. It’s not a document that you’ll be showing to investors or anyone outside of your company. You’ll need to create a document that acts as a foundational plan for your whole organization in this plan.
Standard practices when creating this type of plan include assessing the strengths and weaknesses of your company. Therefore, using a SWOT analysis when putting the plan together is a smart move. SWOT is an acronym. It stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. It gives you and executives in your company a broad awareness of various factors that could impact your business.
Typically, a strategic plan will also include an outline with defined milestones and a path leading to specific company goals. There should also be a deadline to reach those goals. Remember that a strategic plan is different from just a business plan at the end of the day. A strategic business plan will focus on your company’s ultimate goals and how you’re going to get there.
Your strategic business plan ought to include the following elements and structure:
- Company mission statement
- Company vision
- Key factors for company success
- Strategies to meet goals
- Implementation deadline
Operations plan
This is a different type of business plan, but it’s still essential. An operations plan will outline the day-to-day resources and activities that are needed to run your company efficiently. It should take into account what needs to be done and when.
It can also help you anticipate any problems that may arise by anticipating common issues before they happen. This way, you’ll have time to come up with solutions or get in contact with someone who can help if anything goes wrong. You’ll want an operations plan so you’re prepared for things like slow periods where product orders might not meet expectations, or to know how many products need different types of maintenance during different times of the year because temperature changes affect them differently (think winter coats).
Your operations plan should include the following elements and structure:
- Organization objectives
- Activities required to complete objectives
- Resources needed for activities
- Staffing requirements
- Implementation deadlines
- Progress tracking processes
The different types of business plans are how companies present their long-term vision, management strategy, and goals for the future. The type of plan you put together is dependent on your industry – but as we’ve discussed, there are always a few core elements to all typical business plan models. These include an organization’s objectives, activities required to complete these objectives; resources needed for those activities; staff requirements (including skillsets); implementation deadlines & progress tracking processes.
Hopefully, this article has provided some new insight into how different business plans are used to produce and guide successful businesses.
Editors' Recommendations
- How to start your own landscaping business
- 5 successful businesses that launched during the pandemic and are thriving
- Here are some useful tools for a business owner
- 5 tools to start your beauty salon
- Products you need for your local salon
- Business plans

Everyone loves pizza, and so do you. That is why you want to do your local pizza bar that everyone will enjoy. You love to see the joy come across people's faces as you give them your homemade pizza. You also enjoy mixing drinks as part of your hobby, so have an idea of a bar and a pizza place where people can come to hang out with friends. You want to have a space that gives people happiness. You want to be the place where celebrations and events will be taken place. You want to enjoy having your place.
The items listed above will introduce a great start for your career. You get to share your delicious homemade pizza with your customers. You want to have a comfortable environment where you can introduce live music and cheer. Your business will continue to flourish with ease as not only a bar but a place where people can go with their friends, family, and their partners. You will be the place where the night is young with a lighted area where customers can sit outdoors. All you need is ideas, your recipe, and the supplies that you need to start your business.
Are you a person who just got a business degree? Do you want to start a business that helps others feel at home? You like to sell things that people need to make their homes clean and decorative. You know that homes reflect the owners' personality, and you want to give new homeowners the chance to decorate their new homes. To start helping others, you must decorate your building with home goods, knickknacks, and supplies. You know what customers are looking for and where they could get it, which is when your business comes in to give homeowners the supplies they need for their new home.
The items listed above are not only items you will sell but the items that you need to start your career off on the right track. You questioned how to start your business with an idea. The first idea is to organize and clean the building that will be the place for your business. You will also be selling items that homeowners need and that you will be using for your new business. You do not have to worry about starting your business blindly, some simple tasks and items will guide you to your journey to a successful career. You will be able to enjoy your first local business.
- Business Guides
You suddenly have a fun idea to show off your creative coffee and tea recipes. Why not start a coffee and tea shop? Coffee and tea shops are popular during modern times. People enjoy a nice cup of coffee or tea to start their day. You might even want to start with your food recipes and share them with the world. You do not have to worry about starting your coffee and tea business without any items. You can enjoy decorating and getting the items that you need to start your new business. You get to enjoy your wonderful coffee shop.
Your coffee and tea shop will start with a positive path to success. You get to choose and create your menu with the food you love to create. Your customers will enjoy your positive energy, and they will never want to leave. You will have that delicious scent of coffee and tea that your customers will not resist. You will host events such as poetry readings, musicians, and artists to promote your business. You will also help local artists succeed as they will help you succeed in your local business. You will enjoy your coffee shop and the career path that you have chosen.
- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Small Business Guide
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- For Subscribers
- Write for Entrepreneur
- Entrepreneur Store
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
The 4 Types of Business Plans Learn which of these four business plan formats best fits your needs.
By The Staff of Entrepreneur Media, Inc. • Dec 4, 2014
In their book Write Your Business Plan , the staff of Entrepreneur Media offer an in-depth understanding of what's essential to any business plan, what's appropriate for your venture, and what it takes to ensure success. In this edited excerpt, the authors describe four different types of plans you could write and what you'd use each one for.
Business plans can be divided roughly into four distinct types. There are very short plans, or miniplans, presentation plans or decks, working plans, and what-if plans. They each require very different amounts of labor and not always with proportionately different results. That is to say, a more elaborate plan isn't guaranteed to be superior to an abbreviated one. Success depends on various factors and whether the right plan is used in the right setting. For example, a new hire may not want to read the same, elaborate version of your plan that might be important to a potential investor.
The Miniplan
The miniplan is preferred by many recipients because they can read it or download it quickly to read later on their iPhone or tablet. You include most of the same ingredients that you would in a longer plan, but you cut to the highlights while telling the same story. For a small-business venture, it's typically all that you need. For a more complex business, you may need the longer version.
The Presentation Plan
The advent of PowerPoint presentations changed the way many, if not most, plans are presented. And while the plan is shorter than its predecessors, it's not necessarily easier to present. Many people lose sleep over an upcoming presentation, especially one that can play a vital role in the future of their business. But presenting your plan as a deck can be very powerful. Readers of a plan can't always capture your passion for the business nor can they ask questions when you finish. But in 20 minutes, you can cover all the key points and tell your story from concept and mission statement through financial forecasts.
Remember to keep your graphics uncluttered and to make comments to accentuate your ideas rather than simply reading what's in front of your audience.
While a presentation plan is concise, don't be fooled: It takes plenty of planning. The pertinent questions who, what, where, why, when and how all need to be answered.
The Working Plan
A working plan is a tool to be used to operate your business. It has to be long on detail but may be short on presentation. As with a miniplan, you can probably can afford a somewhat higher degree of candor and informality when preparing a working plan. In a plan you intend to present to a bank loan committee, you might describe a rival as "competing primarily on a price basis." In a working plan, your comment about the same competitor might be "When is Jones ever going to stop this insane price-cutting?"
A plan intended strictly for internal use may also omit some elements that you need not explain to yourself. Likewise, you probably don't need to include an appendix with resumes of key executives. Nor would a working plan especially benefit from product photos.
Internal policy considerations may guide the decision about whether to include or exclude certain information in a working plan. Many entrepreneurs are sensitive about employees knowing the precise salary the owner takes home from the business. To the extent such information can be left out of a working plan without compromising its utility, you can feel free to protect your privacy.
This document is like an old pair of khakis you wear to the office on Saturdays or that one ancient delivery truck that never seems to break down. It's there to be used, not admired.
The What-If Plan
When you face unusual circumstances, you need a variant on the working plan. For example, you might want to prepare a contingency plan when you're seeking bank financing. A contingency plan is a plan based on the worst-case scenario that you can imagine your business surviving—loss of market share, heavy price competition, defection of a key member of your management team. A contingency plan can soothe the fears of a banker or investor by demonstrating that you have indeed considered more than a rosy scenario.
Your business may be considering an acquisition, in which case a pro forma business plan (some call this a what-if plan) can help you understand what the acquisition is worth and how it might affect your core business. What if you raise prices, invest in staff training and reduce duplicative efforts? Such what-if planning doesn't have to be as formal as a presentation plan. Perhaps you want to mull over the chances of a major expansion. A what-if plan can help you spot the increased needs for space, equipment, personnel and other variables so you can make good decisions.
What sets these kinds of plans apart from the working and presentation plans is that they aren't necessarily describing how you'll run the business. They're essentially more like an addendum to your actual business plan. If you decide to acquire that competitor or grow dramatically, you'll want to incorporate some of the thinking already invested in these special purpose plans into your primary business plan.
Entrepreneur Staff
Want to be an Entrepreneur Leadership Network contributor? Apply now to join.
Editor's Pick Red Arrow
- This Mother and Daughter Were 'Kind of Fringe Weirdos' When They Started an Uncommon Business in Their Garage. Now They're in Major Retailers — and Victoria Beckham Is a Fan.
- Lock A Leadership Shortage Is Coming. Here's What Needs to Happen to Prevent It.
- Lock The Author of 'Million Dollar Weekend' Says This Is the Only Difference Between You and the Many 'Very, Very Dumb People' Making a Lot of Money
- What the NLRB Appeal of the Expanded Joint Employer Rule Judgment Means for Your Business
- Lock 12 Books That Self-Made Millionaires Swear By
- The Sweet Side Hustle She Started in an Old CVS Made $800,000 in One Year. Now She's Repeating the Success With Her Daughter — and They've Already Exceeded 8 Figures.
Most Popular Red Arrow
How small businesses can master a complex labor market.
Navigating today's labor market is a high-stakes game for small businesses as they compete to attract top talent. Here are a few strategies for small businesses to consider as they build and strengthen their teams.
Want to Start a Simple Business That Helps the Planet? After 'One Night's Worth of Research,' He Started an Eco-Friendly Gig And Now Makes $200K a Year
Environmentally-conscious laws are picking up steam across the country. When one went into effect in Zach Cavacas's home state, he saw a lucrative business opportunity. Chances are, a similar law is coming to your state, or is already there.
Drive Safe on Business Trips with This Car Display, Discounted to $90
Compatible with Apple CarPlay and Android Auto, this touchscreen display makes safer navigation easier.
63 Small Business Ideas to Start in 2024
We put together a list of the best, most profitable small business ideas for entrepreneurs to pursue in 2024.
Jack Dorsey Explains Bluesky Exit: 'Literally Repeating All the Mistakes We Made' at Twitter
Dorsey left the Bluesky board and deleted his account earlier this week.
McDonald's Is Responding to Sky-High Fast Food Prices By Rolling Out a Much Cheaper Value Meal: Report
The news comes as the chain looks to redirect back to customer "affordability."
Successfully copied link

1.905.717.3608
- Three Different Types Of Business Plans
by James Burgess | May 15, 2020 | Business Planning | 0 comments

Business Plans guide the management, owners, and investors as businesses start-up and grow. A business owner or prospective business owner composes a Business Plan to shed light on each aspect of his business, describing all the objectives that will anticipate and prepare it for its growth. Business owners create Business Plans to guide management and promote investment capital.

- Operational Business Plan
First is the Operational Business Plan. It is intended for internal use in an ongoing business. This is used mainly by the management, board of directors, and high-level advisors. Since this is used to focus and align the efforts of the managers in the company to achieve their business goals, it should be updated Quarterly
An Operational Business Plan is the master blueprint which ties your budget and department plans. Inside your operational plan are Company Direction, plans for Products or Services, Sales, Marketing, and Finance, and Administration. Being able to create a great operational plan is the foundation for running a viable business successfully.
- Summary Business Plan

You can also use a Summary Business Plan for inviting investors, small to moderate banks to offer you a loan, or to attract essential employees. A typical Summary Business Plan could run between 3-5 pages.
- Complete Business Plan
Lastly is a Complete Business Plan. Like a Summary Business Plan, this is also for external use. This is important if you are seeking a significant amount of funding – opposite with the previous business plan. You would want to show your readers the full picture of your business. A Complete Business Plan can be around 40 pages or more and invariably includes Financial Statement Projections for 3 to 5 years and Monthly Cash Flow projections over the same period. You also need to show in these projections why the funding is needed or how it will be used.
In this type of business plan, you need to explain your business ideas in detail to potential backers or investors, strategic partners or even potential buyers of your company, if you’re selling. This should clearly state the specific requests you’re making with your business plan and what your company can bring to the table.
The vast majority of Businesses will typically benefit massively from having the Operational Business Plan. The fear in creating such a Business Plan is the time required. The FOCUS Yourself; A 7-Module Business Planning Program referenced below under What’s Your Next Step is a templated Business Planning system thatmakes an OPerational Business Plan EASY & FAST and it so happens it’s FREE too.

WHAT’S THE NEXT STEP?

2. Use our FREE Business Planning Course, FOCUS Yourself; A 7 Module Business Plan Course . This is not a business plan template, it is a full Business Plan Course that provides Best Practice Business Planning insights PLUS enables you to create your Best Practice Business Plan on your own dedicated, password protected Workspace. Start your Business Plan NOW
3. Join our Business Planning Masterclass, How To Create An Annual Business Plan In JUST …28.7. Register for this Business Planning Masterclass HERE
4. Not sure why you need a Business Plan? Then REGISTER for a FREE Business Vision Quest. Call where you will talk business, your business, with international best-selling author James Burgess. Book that call right HERE
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Recent Posts
- How Does a Business Plan Template Work?
- Five Key Roles Of A Business Plan
- Advantages of a Business Plan
- The FUN 5-Steps In The Business Plan Journey
- Business Management (24)
- Business Planning (50)
- Business Plans (5)
- Business Selling (21)
- June 2020 (2)
- May 2020 (2)
- April 2020 (1)
- March 2020 (2)
- August 2019 (1)
- July 2019 (2)
- June 2019 (2)
- May 2019 (1)
- April 2019 (2)
- March 2018 (1)
- February 2018 (1)
- January 2018 (2)
- November 2017 (2)
- October 2017 (2)
- August 2017 (1)
- July 2017 (1)
- May 2017 (2)
- January 2017 (2)
- January 2016 (1)
- June 2015 (1)
- May 2015 (3)
- April 2015 (3)
- March 2015 (1)
- August 2014 (1)
- May 2014 (1)
- April 2014 (3)
- March 2014 (2)
- August 2013 (1)
- June 2013 (1)
- May 2013 (2)
- April 2013 (4)
- March 2013 (5)
- November 2012 (3)
- April 2012 (2)
- January 2012 (3)
- December 2011 (1)
- October 2011 (2)
- May 2011 (2)
- December 2010 (1)
- November 2010 (7)
- October 2010 (5)
- September 2010 (9)
- December 2009 (1)
17.3 Types of Plans
- Identify different types of plans and control systems employed by organizations.
From an activity perspective, organizations are relatively complex systems, as they are involved in numerous activities. Many of these activities require management’s attention from both a planning and controlling perspective. Managers therefore create different types of plans to guide operations and to monitor and control organizational activities. In this section, we introduce several commonly used plans. The major categories are hierarchical, frequency-of-use (repetitiveness), time-frame, organizational scope, and contingency. Table 17.1 provides a closer look at many types of plans that fall in each of these categories.
Hierarchical Plans
Organizations can be viewed as a three-layer cake, with its three levels of organizational needs. Each of the three levels—institutional, administrative, and technical core—is associated with a particular type of plan. As revealed in Table 17.1 , the three types of hierarchical plans are strategic, administrative, and operating (technical core). The three hierarchical plans are interdependent, as they support the fulfillment of the three organizational needs. In the organization’s hierarchy, the technical core plans day-to-day operations.
Strategic Plans
Strategic management is that part of the management process concerned with the overall integration of an organization’s internal divisions while simultaneously integrating the organization with its external environment. Strategic management formulates and implements tactics that try to match an organization as closely as possible to its task environment for the purpose of meeting its objectives.
Strategic plans address the organization’s institutional-level needs. Strategic plans outline a long-term vision for the organization. They specify the organization’s reason for being, its strategic objectives, and its operational strategies—the action statements that specify how the organization’s strategic goals are to be achieved.
Part of strategic planning involves creating the organization’s mission, a statement that specifies an organization’s reason for being and answers the question “What business(es) should we undertake?” The mission and the strategic plan are major guiding documents for activities that the organization pursues. Strategic plans have several defining characteristics: They are long-term and position an organization within its task environment; they are pervasive and cover many organizational activities; they integrate, guide, and control activities for the immediate and the long term; and they establish boundaries for managerial decision-making.
Operating plans provide direction and action statements for activities in the organization’s technical core. Administrative plans work to integrate institutional-level plans with the operating plans and tie together all of the plans created for the organization’s technical core.
Frequency-of-Use Plans
Another category of plans is frequency-of-use plans. Some plans are used repeatedly; others are used for a single purpose. Standing plans , such as rules, policies, and procedures, are designed to cover issues that managers face repeatedly. For example, managers may be concerned about tardiness, a problem that may occur often in the entire work force. These managers might decide to develop a standing policy to be implemented automatically each time an employee is late for work. The procedure invoked under such a standing plan is called a standard operating procedure (SOP).
Single-use plans are developed for unique situations or problems and are usually replaced after one use. Managers generally use three types of single-use plans: programs, projects, and budgets. See Table 17.1 for a brief description of standing and single-use plans.
Time-Frame Plans
The organization’s need to address the future is captured by its time-frame plans. This need to address the future through planning is reflected in short-, medium-, and long-range plans. Given the uniqueness of industries and the different time orientations of societies—study Hofstede’s differentiation of cultures around the world in terms of their orientation toward the future—the times captured by short, medium, and long range vary tremendously across organizations of the world. Konosuke Matsushita’s 250-year plan, which he developed for the company that bears his name, is not exactly typical of the long-range plans of U.S. companies!
Short-, medium-, and long-range plans differ in more ways than the time they cover. Typically, the further a plan projects into the future, the more uncertainty planners encounter. As a consequence, long-range plans are usually less specific than shorter-range plans. Also, long-range plans are usually less formal, less detailed, and more flexible than short-range plans in order to accommodate such uncertainty. Long-range plans also tend to be more directional in nature.
Organizational Scope Plans
Plans vary in scope. Some plans focus on an entire organization. For example, the president of the University of Minnesota advanced a plan to make the university one of the top five educational institutions in the United States. This strategic plan focuses on the entire institution. Other plans are narrower in scope and concentrate on a subset of organizational activities or operating units, such as the food services unit of the university. For further insight into organizational scope plans, see Table 17.1 .
Contingency Plans
Organizations often engage in contingency planning (also referred to as scenario or “what if” planning). You will recall that the planning process is based on certain premises about what is likely to happen in an organization’s environment. Contingency plans are created to deal with what might happen if these assumptions turn out to be wrong. Contingency planning is thus the development of alternative courses of action to be implemented if events disrupt a planned course of action. A contingency plan allows management to act immediately if an unplanned occurrence, such as a strike, boycott, natural disaster, or major economic shift, renders existing plans inoperable or inappropriate. For example, airlines develop contingency plans to deal with terrorism and air tragedies. Most contingency plans are never implemented, but when needed, they are of crucial importance.
Concept Check
- Define and describe the different types of plans defined in Table 17.1 and how organizations use them.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/principles-management/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: David S. Bright, Anastasia H. Cortes
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Principles of Management
- Publication date: Mar 20, 2019
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/principles-management/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/principles-management/pages/17-3-types-of-plans
© Jan 9, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

17.3: Types of Plans
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 15048

Learning Objectives
- Identify different types of plans and control systems employed by organizations.
From an activity perspective, organizations are relatively complex systems, as they are involved in numerous activities. Many of these activities require management’s attention from both a planning and controlling perspective. Managers therefore create different types of plans to guide operations and to monitor and control organizational activities. In this section, we introduce several commonly used plans. The major categories are hierarchical, frequency-of-use (repetitiveness), time-frame, organizational scope, and contingency. Table 17.1 provides a closer look at many types of plans that fall in each of these categories.
Hierarchical Plans
Organizations can be viewed as a three-layer cake, with its three levels of organizational needs. Each of the three levels—institutional, administrative, and technical core—is associated with a particular type of plan. As revealed in Table 17.1, the three types of hierarchical plans are strategic, administrative, and operating (technical core). The three hierarchical plans are interdependent, as they support the fulfillment of the three organizational needs. In the organization’s hierarchy, the technical core plans day-to-day operations.
Table 17.1 (Attribution: Copyright Rice University, OpenStax, under CC-BY 4.0 license)
Strategic Plans
Strategic management is that part of the management process concerned with the overall integration of an organization’s internal divisions while simultaneously integrating the organization with its external environment. Strategic management formulates and implements tactics that try to match an organization as closely as possible to its task environment for the purpose of meeting its objectives.
Strategic plans address the organization’s institutional-level needs. Strategic plans outline a long-term vision for the organization. They specify the organization’s reason for being, its strategic objectives, and its operational strategies—the action statements that specify how the organization’s strategic goals are to be achieved.
Part of strategic planning involves creating the organization’s mission, a statement that specifies an organization’s reason for being and answers the question “What business(es) should we undertake?” The mission and the strategic plan are major guiding documents for activities that the organization pursues. Strategic plans have several defining characteristics: They are long-term and position an organization within its task environment; they are pervasive and cover many organizational activities; they integrate, guide, and control activities for the immediate and the long term; and they establish boundaries for managerial decision-making.
Operating plans provide direction and action statements for activities in the organization’s technical core. Administrative plans work to integrate institutional-level plans with the operating plans and tie together all of the plans created for the organization’s technical core.
Frequency-of-Use Plans
Another category of plans is frequency-of-use plans. Some plans are used repeatedly; others are used for a single purpose. Standing plans, such as rules, policies, and procedures, are designed to cover issues that managers face repeatedly. For example, managers may be concerned about tardiness, a problem that may occur often in the entire workforce. These managers might decide to develop a standing policy to be implemented automatically each time an employee is late for work. The procedure invoked under such a standing plan is called a standard operating procedure (SOP).
Single-use plans are developed for unique situations or problems and are usually replaced after one use. Managers generally use three types of single-use plans: programs, projects, and budgets. See Table 17.1 for a brief description of standing and single-use plans.
Time-Frame Plans
The organization’s need to address the future is captured by its time-frame plans. This need to address the future through planning is reflected in short-, medium-, and long-range plans. Given the uniqueness of industries and the different time orientations of societies—study Hofstede’s differentiation of cultures around the world in terms of their orientation toward the future—the times captured by short, medium, and long-range vary tremendously across organizations of the world. Konosuke Matsushita’s 250-year plan, which he developed for the company that bears his name, is not exactly typical of the long-range plans of U.S. companies!
Short-, medium-, and long-range plans differ in more ways than the time they cover. Typically, the further a plan projects into the future, the more uncertainty planners encounter. As a consequence, long-range plans are usually less specific than shorter-range plans. Also, long-range plans are usually less formal, less detailed, and more flexible than short-range plans in order to accommodate such uncertainty. Long-range plans also tend to be more directional in nature.
Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): Digital clocks were installed on the Sapporo TV tower, which was donated by Matsushita Electric Industrial Company, a Japanese electronics manufacturer. This installation was suggested by the founder of the company, Konosuke Matsushita, who thought these digital clocks would draw great attention to the tower. Matsushita is revered as a management thought leader in Japan and favored long-term planning, including 250-year plans. (Credit: Arjan Richerter/ flickr/ Attribution 2.0 Generic (CC BY 2.0))
Organizational Scope Plans
Plans vary in scope. Some plans focus on an entire organization. For example, the president of the University of Minnesota advanced a plan to make the university one of the top five educational institutions in the United States. This strategic plan focuses on the entire institution. Other plans are narrower in scope and concentrate on a subset of organizational activities or operating units, such as the food services unit of the university. For further insight into organizational scope plans, see Table 17.1.
Contingency Plans
Organizations often engage in contingency planning (also referred to as scenario or “what if” planning). You will recall that the planning process is based on certain premises about what is likely to happen in an organization’s environment. Contingency plans are created to deal with what might happen if these assumptions turn out to be wrong. Contingency planning is thus the development of alternative courses of action to be implemented if events disrupt a planned course of action. A contingency plan allows management to act immediately if an unplanned occurrence, such as a strike, boycott, natural disaster, or major economic shift, renders existing plans inoperable or inappropriate. For example, airlines develop contingency plans to deal with terrorism and air tragedies. Most contingency plans are never implemented, but when needed, they are of crucial importance.
concept check
- Define and describe the different types of plans defined in Table 17.1 and how organizations use them.
- Integrations
- Sustainability & ESG
- How to Videos
- Developer Platform
- Zoom Ventures
- Zoom Merchandise Store
- Zoom Rooms Client
- Browser Extension
- Outlook Plug-in
- Lync Plug-in
- Android App
- Zoom Virtual Backgrounds
- 1.888.799.9666
- Contact Sales
- Plans & Pricing
- Request a Demo
- Webinars and Events
- Support Center
- Learning Center
- Zoom Community
- Accessibility
- Developer support
- Privacy, Security, Legal Policies, and Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement
- Bahasa Indonesia
- US Dollars $
Upcoming Meetings

What are the different types of Skype subscriptions and pay-as-you-go options?
Subscriptions are monthly calling plans that let you make unlimited or fixed-minute calls to landlines (and mobiles where applicable). A subscription is great if you make a lot of calls. All subscriptions are renewed automatically and offer a savings compared to our standard rates. You can cancel at any time. Need help troubleshooting a subscription? Skype Credit * is a pay-as-you-go option. Purchase some Skype Credit, and then call whoever you want at low rates . Skype Credit is a good option if you need to make a few calls and only want to pay for what you use.
A Skype Number is a phone number you pay for monthly. People can call you from their mobile or landline, and you answer the call in Skype. A Skype Number is a great option if you or your friends and family live in different countries, or plan to travel abroad and want an affordable way to keep in touch.
Can I have multiple Skype subscriptions?
Yes. You can purchase as many subscriptions as you like.
You can't add more minutes to your subscription by buying the same one again, but if you run out of minutes, you have a few options: you can buy a different subscription , upgrade to an unlimited subscription where available, or buy some Skype Credit to pay as you go until your existing subscription is automatically renewed.
If you have more than one subscription, Skype uses them in the following order:
By subscription type – unlimited subscriptions are used first, then limited ones.
By expiration date – subscriptions with the nearest expiration date are used first.
Note: When you upgrade to a new subscription, the previous one will be cancelled and replaced with the new one once you've used all the minutes or the expiration date has passed.
How is a subscription different from Skype Credit?
Subscriptions are 1, 3, or 12-month calling plans that let you make unlimited, or fixed-minute calls to landlines (and mobiles where applicable). A subscription is great if you make a lot of calls. Skype Credit allows you to pay as you go. Purchase some Skype Credit, and then call whoever you want at low rates. Skype Credit is a good option if you need to make a few calls and only want to pay for what you use each month. You can also use your Skype Credit to purchase other Skype features that aren’t free, like subscriptions and Skype Numbers .
Can I get a free Skype trial subscription?
Free trials are available in certain regions if you didn't have a subscription before. Only subscriptions below a certain price are available for free trials. If your region is unavailable, stay tuned. We are working on adding more. You can sign up for a free trial on the subscription page . Why are some subscriptions not available as free trial? Only Subscriptions below a certain price are available for free trials currently. Why am I not eligible for a free trial? Free trials are available only to new subscribers who didn't have a Skype Subscription before. Free trials are only available in certain regions. If your region is still unavailable, stay tuned. We are working on adding more.
* A fair usage policy applies to unlimited subscriptions and Skype Credit. Ready to learn more? Skype to Skype calls are free anywhere in the world How do I purchase Skype Credit? How do I cancel or change my Skype subscription?

Need more help?
Want more options.
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.

Microsoft 365 subscription benefits

Microsoft 365 training

Microsoft security

Accessibility center
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.

Ask the Microsoft Community

Microsoft Tech Community

Windows Insiders
Microsoft 365 Insiders
Was this information helpful?
Thank you for your feedback.
Money blog: 'Loud budgeting' - The money-saving trend that has nothing to do with giving up your daily coffee
Created accidentally by a comedian, "loud budgeting" is breaking down the taboo of speaking about money. Read this and the rest of our Weekend Money features, and leave a comment, and we'll be back with rolling personal finance and consumer news on Monday.
Saturday 11 May 2024 09:05, UK
Weekend Money
- 'Loud budgeting': The money-saving trend that has nothing to do with giving up your daily coffee
- What is most in-demand period property?
- £12m tea advert, downsizing, £320 tasting menus and job interview mistakes: What readers have said this week
- Free childcare applications about to open for new age band
- Where has huge week for UK economy left us?
Best of the week
- How to avoid a holiday data roaming charge (while still using the internet)
- Mortgage rates up again this week - here are the best deals on the market
- My daughter discovered undeclared £600 management fee after buying her flat - can we complain?
- Best of the Money blog - an archive
Ask a question or make a comment
By Jess Sharp , Money team
Money saving trends are constantly popping up on social media - but one in particular has been gaining huge amounts of attention.
Created accidentally by a comedian, loud budgeting is breaking down the taboo of speaking about money.
The idea is based on being firmer/more vocal about your financial boundaries in social situations and setting out what you are happy to spend your money on, instead of "Keeping up with the Joneses".
On TikTok alone, videos published under the hashtag #loudbudgeting have garnered more than 30 million views - and that figure is continuing to climb.
We spoke to Lukas Battle - the 26-year-old who unintentionally created the trend as part of a comedy sketch.
Based in New York, he came up with the term in a skit about the "quiet luxury" hype, which had spread online in 2023 inspired by shows like Succession.
The term was used for humble bragging about your wealth with expensive items that were subtle in their design - for example, Gwyneth Paltrow's £3,900 moss green wool coat from The Row, which she wore during her ski resort trial...
"I was never a big fan of the quiet luxury trend, so I just kind of switched the words and wrote 'loud budgeting is in'. I'm tired of spending money and I don't want to pretend to be rich," Lukas said.
"That's how it started and then the TikTok comments were just obsessed with that original idea."
This was the first time he mentioned it...
Lukas explained that it wasn't about "being poor" but about not being afraid of sharing your financial limits and "what's profitable for you personally".
"It's not 'skip a coffee a day and you'll become a millionaire'."
While talking money has been seen as rude or taboo, he said it's something his generation is more comfortable doing.
"I've seen more debate around the topic and I think people are really intrigued and attracted by the idea," he said.
"It's just focusing your spending and time on things you enjoy and cutting out the things you might feel pressured to spend your money on."
He has incorporated loud budgeting into his own life, telling his friends "it's free to go outside" and opting for cheaper dinner alternatives.
"Having the terminology and knowing it's a trend helps people understand it and there's no awkward conversation around it," he said.
The trend has been a big hit with so-called American "finfluencers", or "financial influencers", but people in the UK have started practising it as well.
Mia Westrap has taken up loud budgeting by embarking on a no-buy year and sharing her finances with her 11.3k TikTok followers.
Earning roughly £2,100 a month, she spends around £1,200 on essentials, like rent, petrol and car insurance, but limits what else she can purchase.
Clothes, fizzy drinks, beauty treatments, makeup, dinners out and train tickets are just some things on her "red list".
The 26-year-old PHD student first came across the idea back in 2017, but decided to take up the challenge this year after realising she was living "pay check to pay check".
She said her "biggest fear" in the beginning was that her friends wouldn't understand what she was doing, but she found loud budgeting helped.
"I'm still trying my best to just go along with what everyone wants to do but I just won't spend money while we do it and my friends don't mind that, we don't make a big deal out of it," she said.
So far, she has been able to save £1,700, and she said talking openly about her money has been "really helpful".
"There's no way I could have got this far if I wasn't baring my soul to the internet about the money I have spent. It has been a really motivating factor."
Financial expert John Webb said loud budgeting has the ability to help many "feel empowered" and create a "more realistic" relationship with money.
"This is helping to normalise having open and honest conversations about finances," the consumer affair manager at Experien said.
"It can also reduce the anxiety some might have by keeping their financial worries to themselves."
However, he warned it's important to be cautious and to take the reality of life into consideration.
"It could cause troubles within friendship groups if they're not on the same page as you or have different financial goals," he said.
"This challenge isn't meant to stop you from having fun, but it is designed to help people become more conscious and intentional when it comes to money, and reduce the stigma around talking about it."
Rightmove's keyword tool shows Victorian-era houses are the most commonly searched period properties, with people drawn to their ornate designs and features.
Georgian and Edwardian-style are second and third respectively, followed by Tudor properties. Regency ranked in fifth place.
Rightmove property expert Tim Bannister said: "Home hunters continue to be captivated by the character and charm of properties that we see in period dramas.
"Victorian homes remain particularly popular, characterised by their historic charm, solid construction, and spacious interiors. You'll often find Victorian houses in some of the most desirable locations which include convenient access to schools and transport links."
Throughout the week Money blog readers have shared their thoughts on the stories we've been covering, with the most correspondence coming in on...
- A hotly contested debate on the best brand of tea
- Downsizing homes
- The cost of Michelin-starred food
Job interview mistakes
On Wednesday we reported on a new £12m ad from PG Tips in response to it falling behind rivals such as Twinings, Yorkshire Tea and Tetley....
We had lots of comments like this...
How on earth was the PG Tips advert so expensive? I prefer Tetley tea, PG Tips is never strong enough flavour for me. Shellyleppard
The reason for the sales drop with PG Tips could be because they increased the price and reduced the quantity of bags from 240 to 180 - it's obvious. Royston
And then this question which we've tried to answer below...
Why have PG Tips changed from Pyramid shape tea bags, to a square? Sam
Last year PG Tips said it was changing to a square bag that left more room for leaves to infuse, as the bags wouldn't fold over themselves.
We reported on data showing how downsizing could save you money for retirement - more than £400,000, in some regions, by swapping four beds for two.
Some of our readers shared their experiences...
We are downsizing and moving South so it's costing us £100k extra for a smaller place, all money from retirement fund. AlanNorth
Interesting read about downsizing for retirement. We recently did this to have the means to retire early at 52. However, we bought a house in the south of France for the price of a flat in our town in West Sussex. Now living the dream! OliSarah
How much should we pay for food?
Executive chef at London's two-Michelin-starred Ikoyi, Jeremy Chan, raised eyebrows when he suggested to the Money blog that Britons don't pay enough for restaurant food.
Ikoyi, the 35th best restaurant in the world, charges £320 for its tasting menu.
"I don't think people pay enough money for food, I think we charge too little, [but] we want to always be accessible to as many people as possible, we're always trying our best to do that," he said, in a piece about his restaurant's tie up with Uber Eats...
We had this in...
Are they serious? That is two weeks' worth of food shopping for me, if the rich can afford this "tasting menu" then they need to be taxed even more by the government, it's just crazy! Steve T
If the rate of pay is proportionate to the vastly overpriced costs of the double Michelin star menu, I would gladly peel quail eggs for four-hour stints over continuing to be abused as a UK supply teacher. AndrewWard
Does this two-star Michelin star chef live in the real world? Who gives a toss if he stands and peels his quails eggs for four hours, and he can get the best turbot from the fishmonger fresh on a daily basis? It doesn't justify the outrageous price he is charging for his tasting menu. Topaztraveller
Chefs do make me laugh, a steak is just a steak, they don't make the meat! They just cook it like the rest of us, but we eat out because we can't be bothered cooking! StevieGrah
Finally, many of you reacted to this feature on common mistakes in job interviews...
Those 10 biggest mistakes people make in interviews is the dumbest thing I've ever read. They expect all that and they'll be offering a £25k a year job. Why wouldn't I want to know about benefits and basic sick pay? And also a limp handshake? How's that relevant to how you work? Jre90
Others brought their own tips...
Whenever I go for an interview I stick to three points: 1. Be yourself 2. Own the interview 3. Wear the clothes that match the job you are applying Kevin James Blakey
From Sunday, eligible working parents of children from nine-months-old in England will be able to register for access to up to 15 free hours of government-funded childcare per week.
This will then be granted from September.
Check if you're eligible here - or read on for our explainer on free childcare across the UK.
Three and four year olds
In England, all parents of children aged three and four in England can claim 15 hours of free childcare per week, for 1,140 hours (38 weeks) a year, at an approved provider.
This is a universal offer open to all.
It can be extended to 30 hours where both parents (or the sole parent) are in work, earn the weekly minimum equivalent of 16 hours at the national minimum or living wage, and have an income of less than £100,000 per year.
Two year olds
Previously, only parents in receipt of certain benefits were eligible for 15 hours of free childcare.
But, as of last month, this was extended to working parents.
This is not a universal offer, however.
A working parent must earn more than £8,670 but less than £100,000 per year. For couples, the rule applies to both parents.
Nine months old
In September, this same 15-hour offer will be extended to working parents of children aged from nine months. From 12 May, those whose children will be at least nine months old on 31 August can apply to received the 15 hours of care from September.
From September 2025
The final change to the childcare offer in England will be rolled out in September 2025, when eligible working parents of all children under the age of five will be able to claim 30 hours of free childcare a week.
In some areas of Wales, the Flying Start early years programme offers 12.5 hours of free childcare for 39 weeks, for eligible children aged two to three. The scheme is based on your postcode area, though it is currently being expanded.
All three and four-year-olds are entitled to free early education of 10 hours per week in approved settings during term time under the Welsh government's childcare offer.
Some children of this age are entitled to up to 30 hours per week of free early education and childcare over 48 weeks of the year. The hours can be split - but at least 10 need to be used on early education.
To qualify for this, each parent must earn less than £100,000 per year, be employed and earn at least the equivalent of working 16 hours a week at the national minimum wage, or be enrolled on an undergraduate, postgraduate or further education course that is at least 10 weeks in length.
All three and four-year-olds living in Scotland are entitled to at least 1,140 hours per year of free childcare, with no work or earnings requirements for parents.
This is usually taken as 30 hours per week over term time (38 weeks), though each provider will have their own approach.
Some households can claim free childcare for two-year-olds. To be eligible you have to be claiming certain benefits such as Income Support, Jobseeker's Allowance or Universal Credit, or have a child that is in the care of their local council or living with you under a guardianship order or kinship care order.
Northern Ireland
There is no scheme for free childcare in Northern Ireland. Some other limited support is available.
Working parents can access support from UK-wide schemes such as tax credits, Universal Credit, childcare vouchers and tax-free childcare.
Aside from this, all parents of children aged three or four can apply for at least 12.5 hours a week of funded pre-school education during term time. But over 90% of three-year-olds have a funded pre-school place - and of course this is different to childcare.
What other help could I be eligible for?
Tax-free childcare - Working parents in the UK can claim up to £500 every three months (up to £2,000 a year) for each of their children to help with childcare costs.
If the child is disabled, the amount goes up to £1,000 every three months (up to £4,000 a year).
To claim the benefit, parents will need to open a tax-free childcare account online. For every 80p paid into the account, the government will top it up by 20p.
The scheme is available until the September after the child turns 11.
Universal credit - Working families on universal credit can claim back up to 85% of their monthly childcare costs, as long as the care is paid for upfront. The most you can claim per month is £951 for one child or £1,630 for two or more children.
Tax credits - People claiming working tax credit can get up to 70% of what they pay for childcare if their costs are no more than £175 per week for one child or £300 per work for multiple children.
Two big economic moments dominated the news agenda in Money this week - interest rates and GDP.
As expected, the Bank of England held the base rate at 5.25% on Wednesday - but a shift in language was instructive about what may happen next.
Bank governor Andrew Bailey opened the door to a summer cut to 5%, telling reporters that an easing of rates at the next Monetary Policy Committee meeting on 20 June was neither ruled out nor a fait accompli.
More surprisingly, he suggested that rate cuts, when they start, could go deeper "than currently priced into market rates".
He refused to be drawn on what that path might look like - but markets had thought rates could bottom out at 4.5% or 4.75% this year, and potentially 3.5% or 4% next.
"To make sure that inflation stays around the 2% target - that inflation will neither be too high nor too low - it's likely that we will need to cut Bank rate over the coming quarters and make monetary policy somewhat less restrictive over the forecast period," Mr Bailey said.
You can read economics editor Ed Conway's analysis of the Bank's decision here ...
On Friday we discovered the UK is no longer in recession.
Gross domestic product (GDP) grew by 0.6% between January and March, the Office for National Statistics said.
This followed two consecutive quarters of the economy shrinking.
The data was more positive than anticipated.
"Britain is not just out of recession," wrote Conway. "It is out of recession with a bang."
The UK has seen its fastest growth since the tailend of the pandemic - and Conway picked out three other reasons for optimism.
1/ An economic growth rate of 0.6% is near enough to what economists used to call "trend growth". It's the kind of number that signifies the economy growing at more or less "normal" rates.
2/ 0.6% means the UK is, alongside Canada, the fastest-growing economy in the G7 (we've yet to hear from Japan, but economists expect its economy to contract in the first quarter).
3/ Third, it's not just gross domestic product that's up. So too is gross domestic product per head - the number you get when you divide our national income by every person in the country. After seven years without any growth, GDP per head rose by 0.4% in the first quarter.
GDP per head is a more accurate yardstick for the "feelgood factor", said Conway - perhaps meaning people will finally start to feel better off.
For more on where Friday's figures leaves us, listen to an Ian King Business Podcast special...
The Money blog is your place for consumer news, economic analysis and everything you need to know about the cost of living - bookmark news.sky.com/money .
It runs with live updates every weekday - while on Saturdays we scale back and offer you a selection of weekend reads.
Check them out this morning and we'll be back on Monday with rolling news and features.
The Money team is Emily Mee, Bhvishya Patel, Jess Sharp, Katie Williams, Brad Young and Ollie Cooper, with sub-editing by Isobel Souster. The blog is edited by Jimmy Rice.
If you've missed any of the features we've been running in Money this year, or want to check back on something you've previously seen in the blog, this archive of our most popular articles may help...
Loaves of bread have been recalled from shelves in Japan after they were found to contain the remains of a rat.
Production of the bread in Tokyo has been halted after parts of a "small animal" were found by at least two people.
Pasco Shikishima Corp, which produces the bread, said 104,000 packages have been recalled as it apologised and promised compensation.
A company representative told Sky News's US partner network, NBC News, that a "small black rat" was found in the bread. No customers were reported to have fallen ill as a result of ingesting the contaminated bread.
"We deeply apologise for the serious inconvenience and trouble this has caused to our customers, suppliers, and other concerned parties," the spokesman said.
Pasco added in a separate statement that "we will do our utmost to strengthen our quality controls so that this will never happen again. We ask for your understanding and your co-operation."
Japanese media reports said at least two people who bought the bread in the Gunma prefecture, north-west of Tokyo, complained to the company about finding a rodent in the bread.
Record levels of shoplifting appear to be declining as fewer shopkeepers reported thefts last year, new figures show.
A survey by the Office for National Statistics shows 26% of retailers experienced customer theft in 2023, down from a record high of 28% in 2022.
This comes despite a number of reports suggesting shoplifting is becoming more frequent.
A separate ONS finding , which used police crime data, showed reports of shoplifting were at their highest level in 20 years in 2023, with law enforcements logging 430,000 instances of the crime.
Let's get you up to speed on the biggest business news of the past 24 hours.
A privately owned used-car platform is circling Cazoo Group, its stricken US-listed rival, which is on the brink of administration.
Sky News has learnt that Motors.co.uk is a leading contender to acquire Cazoo's marketplace operation, which would include its brand and intellectual property assets.
The process to auction the used-car platform's constituent parts comes after it spent tens of millions of pounds on sponsorship deals in football, snooker and darts in a rapid attempt to gain market share.
The owner of British Airways has reported a sharp rise in profits amid soaring demand for trips and a fall in the cost of fuel.
International Airlines Group said its operating profit for the first three months of the year was €68m (£58.5m) - above expectations and up from €9m (£7.7m) during the same period in 2023.
The company, which also owns Aer Lingus, Iberia and Vueling, said earnings had soared thanks to strong demand, particularly over the Easter holidays.
The prospect of a strike across Tata Steel's UK operations has gained further traction after a key union secured support for industrial action.
Community, which has more than 3,000 members, said 85% voted in favour of fighting the India-owned company's plans for up to 2,800 job losses, the majority of them at the country's biggest steelworks in Port Talbot, South Wales.
Tata confirmed last month it was to press ahead with the closure of the blast furnaces at the plant, replacing them with electric arc furnaces to reduce emissions and costs.
In doing so, the company rejected an alternative plan put forward by the Community, GMB and Unite unions that, they said, would raise productivity and protect jobs across the supply chain.
Be the first to get Breaking News
Install the Sky News app for free

Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.
Introduction to HTH Worldwide Travel Insurance
- Plans Available
- How to Purchase and Manage Your Policy
HTH Worldwide Customer Service and Support Experience
Compare hth worldwide travel insurance.
- Why You Should Trust Us
HTH Worldwide Travel Insurance Review 2024
Affiliate links for the products on this page are from partners that compensate us (see our advertiser disclosure with our list of partners for more details). However, our opinions are our own. See how we rate insurance products to write unbiased product reviews.
No one likes to think about what could go wrong on vacation, but the truth is that anything can happen. That's why travel insurance is so important — it can help you recover from any unexpected emergencies that may occur while you're away from home.
If you're looking for a reputable travel insurance company, HTH Worldwide Travel Insurance is a great option. It's been in business for over 20 years and offers three different travel insurance plans. Whether you need basic coverage or more comprehensive protection, HTH Worldwide likely has a plan that will suit your needs.
- Check mark icon A check mark. It indicates a confirmation of your intended interaction. Three plans to choose from
- Check mark icon A check mark. It indicates a confirmation of your intended interaction. Reasonable premiums
- Check mark icon A check mark. It indicates a confirmation of your intended interaction. CFAR coverage available with some plans
- Check mark icon A check mark. It indicates a confirmation of your intended interaction. High medical emergency and evacuation coverage
- con icon Two crossed lines that form an 'X'. Special coverages for pets, sports equipment, etc not available
- con icon Two crossed lines that form an 'X'. Limited reviews with complaints about claims not being paid
- Trip cancellation of up to $5,000 with the Economy plan and up to $50,000 with the Preferred plan
- Cancel for any reason insurance and missed connection insurance available with the Preferred plan
- Baggage delay insurance starting after 24 or 12 hours depending on the plan
HTH Worldwide is a travel insurance company owned and operated by Worldwide Insurance Services, which also operates GeoBlue Travel Insurance . In fact, many of the policies listed on HTH Worldwide's website are actually provided by GeoBlue, specifically its travel medical insurance . While we'll talk about those policies here, you can find more details in our GeoBlue review .
HTH Worldwide's stand-alone products are its TripProtector trip cancellation policies. These offer comprehensive protection with relatively low premiums compared to many of its competitors. In fact, HTH Worldwide is among the companies included in our picks for the best cheap travel insurance .
That said, with the premiums you're paying, you'll encounter some concessions. For one, HTH Worldwide's coverage limits are far below that of many of the best travel insurance companies, particularly when it comes to trip cancellation limits, which start at $5,000 per person for its Economy plan.
Types of Policies Offered by HTH Worldwide
HTH Worldwide offers three primary plans: TripProtector Economy, Classic, and Preferred. Each plan has different coverage levels and features, so you can choose the one that best fits your needs. But they'll all cover (up to a specified amount) things like trip cancellation and interruption, emergency medical expenses, lost or delayed luggage, and more.
One important note, though, is that the TripProtector Economy plan is not available for trips where the per-person cost is greater than $5,000.
Below you'll find the per-person coverage limits of HTH Worldwide's three travel insurance plans:
These policies also include 24-hour emergency hotline service, an online database to search for doctors while you're traveling, a medical term translation database, and health and security news alerts.
Additional Coverage Options from HTH Worldwide
In addition to the three primary plans, HTH Worldwide also offers the following two plans, through GeoBlue, for travelers only looking for travel medical coverage:
- Single-trip option for travelers with primary health insurance: HTH Worldwide provides a short-term international medical plan for those who have other travel insurance but need travel medical coverage. It covers pre-existing conditions and medical evacuation costs, with maximum benefit amounts ranging from $50,000 to $1 million and deductibles from $0 to $500.
- Single-trip option for travelers without primary health insurance: This plan for travelers who don't have primary health insurance has maximum benefit amounts ranging from $50,000 to $1 million and deductibles ranging from $0 to $500. It covers pre-existing conditions for medical evacuation.
- Multi-trip option: This annual travel insurance plan is for people who are taking multiple sub-70-day trips within a 12-month period.
The following two plans listed on HTH Worldwide's website, also supplied by GeoBlue, are designed for people who live or work outside their home country:
- Xplorer plan: This plan is for individuals and families who intend to be outside their home country for more than three months per year.
- Navigator plan: This plan is specifically for students, faculty, mission, and maritime crews who will be outside of their home country for more than three months during the year.
Like other travel insurance providers, HTH Worldwide offers additional coverages that can be purchased along with the primary policy. These add-ons are only available for a Preferred plan, not an Economy or Classic plan.
The add-ons include:
- Cancel for any reason (CFAR): Will pay 75% of any prepaid trip expenses. You must purchase coverage within 21 days of your first trip deposit, and the trip must be canceled at least two days before your scheduled departure. This add-on is only available for TripProtector Preferred.
- Collision Damage Waiver (CDW): Coverage for your rental car in the event of damage due to crash, theft, vandalism, windstorm, fire, hail, flood, or any cause beyond your control. (Not available in NY, OR, or TX.)
HTH Worldwide Travel Insurance Cost
The premium you pay will depend on various factors, including the age of the travelers, destination, and total trip costs. The average cost of travel insurance is 4% to 8% of your travel costs.
After inputting some personal information, such as your age and state of residence, along with your trip details, like travel dates, destination, and trip costs, you'll get an instant quote for HTH Worldwide plans available for your trip. And from there, it's easy to compare each option based on your coverage needs and budget.
Now let's look at a few examples to estimate HTH Worldwide coverage costs.
As of 2024, a 23-year-old from Illinois taking a week-long, $3,000 budget trip to Italy would have the following travel insurance quotes:
- TripProtector Economy: $93.16
- TripProtector Classic: $115.56
- TripProtector Preferred: $156.20
Premiums for HTH Worldwide plans are between 3.1% and 5.2% of the trip's cost, well within the average cost of travel insurance.
HTH Worldwide provides the following quotes for a 30-year-old traveler from California heading to Japan for two weeks on a $4,000 trip:
- TripProtector Economy: $121.41
- TripProtector Classic: $149.43
- TripProtector Preferred: $200.75
Once again, premiums for HTH Worldwide plans are between 3% and 5% of the trip's cost, within and below the expected range of travel insurance costs.
A Texas family consisting of two 40-year-old parents with a 10-year-old and 4-year-old on a two-week trip to Australia for $20,000:
- TripProtector Economy: $610.74
- TripProtector Classic: $743.15
- TripProtector Preferred: $995.04
HTH Worldwide plans cost between 3% and 5% of the trip's cost, below and within the average cost of travel insurance.
A 65-year-old couple looking to escape New Jersey for Mexico for two weeks with a trip cost of $6,000 would have the following quotes:
- TripProtector Economy: $324.95
- TripProtector Classic: $389.12
- TripProtector Preferred: $474.12
Premiums for HTH Worldwide plans for older-age travelers are between 5.4% and 7.9%, which is well within the average cost for travel insurance. While it's certainly more expensive than coverage for younger travelers, it's on the lower end of what travel insurance companies often quote for older travelers.
How to Purchase and Manage a HTH Worldwide Policy
It's fast and simple to get a quote from HTH Worldwide. Visit its website and provide basic information about your trip. You'll receive an immediate quotation for the insurance plans available for your journey, so it's simple to compare each one. Make sure you have all of the following information on hand:
- Primary destination
- Age of traveler(s)
- Total trip cost
- Travel dates
- State of residence
If you're buying a trip cancellation policy, you'll be directed to the HTH Worldwide quote page, where you can choose one of three plans. If you're within the specified purchasing window, you'll also be able to add cancel for any reason coverage to the Preferred plan.
How to File a Claim with HTH Worldwide
For medical claims, you can contact HTH Worldwide by phone at 888-243-2358 or via email at [email protected]. For all other claims, you can call 866-655-3058.
You must notify HTH Worldwide of your claim within seven days of first experiencing the covered loss. You'll also need to provide proof of loss within 90 days after the loss. The company doesn't provide an expected window for response or payment in its terms, but said that a claim usually takes anywhere from 30-45 days to process in response to a review on SquareMouth.
You can find HTH Worldwide's claim forms here .
HTH Worldwide has relatively few customer reviews to speak of. It has an average of 4.24 stars out of five across just under 500 reviews on its SquareMouth page, which comprises the vast majority of online reviews. HTH Worldwide customer reviews were very complimentary about the purchasing experience, saying it was quick.
That said, customers also mentioned that HTH Worldwide is hard to reach for anything — purchasing, traveling, and claims. This can be especially concerning if you're trying to contact the 24/7 hotline while facing an emergency. That said, when customers were able to make contact, they had generally positive things to say about the experience.
One customer getting treated for a medical emergency was given a list of recommended hospitals in their area and HTH Worldwide's connection with GeoBlue meant that some hospitals were able to direct bill instead of the customer paying and getting reimbursed. This created some hoops the customer had to jump through, including obtaining a letter from HTH Worldwide. That said, the customer writes, "The whole thing took less than 30 minutes. With that letter in tow, I was able to be seen, treated and released without payment on my part."
Learn more about HTH Worldwide compares to some of the best travel insurance providers .
HTH Worldwide Travel Insurance vs. Allianz Travel Insurance
If you look at coverage with Allianz Travel Insurance , you'll see that you can select from 10 different insurance plans. Much like HTH Worldwide, Allianz Travel Insurance offers single-trip policies and options for those who plan to be outside the country for longer. And, like with all insurance, the different plans provide varying degrees of coverage.
Allianz Travel Insurance's most popular single-trip option is the OneTrip Prime plan, which offers:
- Trip cancellation coverage up to $100,000
- Trip interruption coverage up to $150,000
- Emergency medical coverage for $50,000
- Coverage for baggage loss, theft or damage up to $1,000
- Travel delay coverage up to $800
Compare that to HTH Worldwide's most popular TripProtector Preferred Plan and you'll see that HTH Worldwide's emergency medical coverage limit is substantially higher. But Allianz Travel Insurance's plan has better trip protection coverage limits. The right choice will depend on what coverages are most important to you and your personal situation.
Read our Allianz Travel Insurance review here.
HTH Worldwide Travel Insurance vs. Nationwide Travel Insurance
Amongst insurance providers, Nationwide Travel Insurance is one of the more familiar household names. Much like HTH Worldwide, Nationwide offers straightforward coverage with only two single-trip plans: the Essential Plan and the Prime Plan. Furthermore, Nationwide has designed policies specifically for those taking cruises or who travel frequently throughout the year.
To compare Nationwide and HTH Worldwide, we took a look at both companies' highest-tier plans.
Nationwide's Prime Plan includes coverage for trip cancellation up to $30,000, trip interruption coverage of 200% of the cost of the trip (with a maximum payout of $60,000), missed connection and itinerary change coverage each amounting to $500, per-day trip delay coverage of up to $250 for 6+ hour delays, and emergency medical evacuation with a limit of $1 million in payouts.
In comparison, HTH Worldwide's TripProtector Preferred plan offers trip cancellation coverage up to $50,000, trip interruption coverage 200% of the cost of the trip, coverage for a missed connection of up to $1,000, trip delay coverage up to $2,000, and emergency medical evacuation coverage of up to $1 million.
The two plans are quite similar in many regards. To determine which is best for you, you'll need to compare quotes based on your personal and trip-specific details.
Read our Nationwide Travel Insurance review here.
Compare HTH Worldwide vs. Credit Card Insurance
It's worthwhile to review the insurance coverage offered by your travel credit cards before you buy a separate travel insurance policy. Some essential coverages, like rental car insurance, might already be included with a card you have.
The coverage from your credit card may be enough if, for example, you don't have any non-refundable trip expenses and you're driving to your destination. Another scenario that could suffice is if your health insurance covers you while abroad, you're in decent health, and you aren't too concerned with potential medical costs while traveling.
It's essential to remember that credit card travel protection is usually secondary to the primary coverage you'd get with a travel insurance policy. This means you'll have to file a claim with the other applicable insurance before filing a claim with your credit card company.
Read our guide on the best credit cards with travel insurance here.
HTH Worldwide Travel Insurance FAQs
HTH Worldwide is known for its strong focus on medical coverage, providing comprehensive support during medical emergencies, including access to a wide network of hospitals and emergency medical assistance.
Yes, HTH Worldwide offers plans that cover travel to high-risk destinations, but it's important to review the specific terms and coverage limitations for such areas.
Pre-existing conditions are covered under HTH Worldwide's Classic and Preferred plans as long as you purchase your policy within 14 and 21 days of your initial trip deposit, respectively. HTH Worldwide TripProtector Economy does not cover pre-existing conditions.
HTH Worldwidepolicies max out at 90 days. If your trip exceeds this time frame, it's best to look elsewhere for travel insurance.
HTH Worldwide stands out for its comprehensive coverage at affordable prices.
Why You Should Trust Us: How We Reviewed HTH Worldwide Travel Insurance
In reviewing HTH Worldwide's travel insurance offerings, we considered things like different types of coverage available, claim limits, what expenses are included, available add-ons, and typical policy costs. We then compared them to similar plans from other top travel insurance companies.
The best policy for you is the one that offers the appropriate amount and type of coverage given your needs and budget. It should also be easy to use in case you ever need to make a claim.
You can read more about how Business Insider rates insurance products here.
Editorial Note: Any opinions, analyses, reviews, or recommendations expressed in this article are the author’s alone, and have not been reviewed, approved, or otherwise endorsed by any card issuer. Read our editorial standards .
Please note: While the offers mentioned above are accurate at the time of publication, they're subject to change at any time and may have changed, or may no longer be available.
**Enrollment required.

- Main content

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
7 Different Types of Business Plans Explained. Business plans go by many names: Strategic plans, traditional plans, operational plans, feasibility plans, internal plans, growth plans, and more. Different situations call for different types of plans. But what makes each type of plan unique?
In my experience, some of the more common types of plans include: Startup Plan. • Audience: External. • Depth: Standard. • Purpose: Development of a blueprint for building a successful ...
Below are a few of the most common types of business plans. For even more examples, check out these sample business plans to help you write your own. 1. Startup Business Plan. As one of the most common types of business plans, a startup business plan is for new business ideas. This plan lays the foundation for the eventual success of a business.
Seven types of business plans The following list of business plans are the most commonly used: Startup plan A startup plan is a business plan a new company gives to potential investors in the hopes of receiving startup funding. Startup plans operate as initial plans that businesses can adjust as needed as a company grows.
Operations business plan. Strategic business plan. 01. Startup business plan. The startup business plan is a comprehensive document that will set the foundation for your company's success. It covers all aspects of a business, including a situation analysis, detailed financial information and a strategic marketing plan.
Here are a few of the most common types of business plans for small businesses: One-page plan: Outlining all of the most important information about a business into an adaptable one-page plan. Growth plan: An ongoing business management plan that ensures business tactics and strategies are aligned as a business scales up.
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
Learn about the best business plan software. 1. Write an executive summary. This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your ...
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
A business plan is a written document that defines your business goals and the tactics to achieve those goals. A business plan typically explores the competitive landscape of an industry, analyzes a market and different customer segments within it, describes the products and services, lists business strategies for success, and outlines ...
This plan, known as a business plan, is a comprehensive document that outlines a company's goals, strategies, and financial projections. Whether you're starting a new business or looking to expand an existing one, a business plan is an essential tool. As a business plan writer and consultant, I've crafted over 15,000 plans for a diverse ...
5 types of business plans to align your strategy with. Picking the right business plan is a big deal for founders, managers, and leaders. ... 3) Operational business plan. Audience: Internal management teams and department heads. Depth: Detailed, focusing on day-to-day operations and short-term goals.
You can write a standard, lean, one-page, startup, strategic, feasibility, operational, or growth business plan depending on your needs. Here's an explanation for each: 1. Standard Business Plan. A standard business plan gives a detailed description of the operations of a business so stakeholders can understand the business well.
Based on Audience. Business plans are broadly categorized into two types based on the type of audience. They are: 1. Internal business plans: As the name suggests, an internal business plan is solely for the people inside the company. These can be specific to certain departments such as marketing, HR, production, etc. Internal business plans focus primarily on the company's goals, and the ...
Three types of business plans. Wrapping up. You should also understand that business plans can go by different names. Some have different names but are essentially the same thing, while others genuinely are different in terms of content. You might see operational plans, Lean plans, Strategic plans, internal plans, and more.
Business plans can be divided roughly into four distinct types. There are very short plans, or miniplans, presentation plans or decks, working plans, and what-if plans. They each require very ...
Inside your operational plan are Company Direction, plans for Products or Services, Sales, Marketing, and Finance, and Administration. Being able to create a great operational plan is the foundation for running a viable business successfully. Summary Business Plan. Second is a Summary Business Plan.
Business/divisional-level plans—focus on one of the organization's businesses (or divisions) and its competitive position. ... Managers generally use three types of single-use plans: programs, projects, and budgets. See Table 17.1 for a brief description of standing and single-use plans. Time-Frame Plans.
The organizational planning process includes five phases that, ideally, form a cycle. Strategic, tactical, operational, and contingency planning fall within these five stages. 1. Develop the strategic plan. Steps in this initial stage include: Review your mission, vision, and values.
Organizations can be viewed as a three-layer cake, with its three levels of organizational needs. Each of the three levels—institutional, administrative, and technical core—is associated with a particular type of plan. As revealed in Table 17.1, the three types of hierarchical plans are strategic, administrative, and operating (technical core).
A large percentage of entrepreneurs do not write business plans for their new ventures. There are three types of business plans. Summary business plan, full business plan, operational business plan. Most business plan writers interpret or make sense of a firm's historical and/ or pro financial statements through. Assumptions analysis.
Zoom is the leader in modern enterprise video communications, with an easy, reliable cloud platform for video and audio conferencing, chat, and webinars across mobile, desktop, and room systems. Zoom Rooms is the original software-based conference room solution used around the world in board, conference, huddle, and training rooms, as well as executive offices and classrooms. Founded in 2011 ...
Medicare.gov Care Compare is a new tool that helps you find and compare the quality of Medicare-approved providers near you. You can search for nursing homes, doctors, hospitals, hospice centers, and more. Learn how to use Care Compare and make informed decisions about your health care. Official Medicare site.
Business document from Arizona State University, 11 pages, PJM610 Project Planning, Execution and Closure Unit 3 Individual Project Noelle Marietta 2/25/2024 2 Contents Assignment Guidelines.3 Stakeholder Register.3 Stakeholder Analysis.4 Required Types of Communication.5 .5 Communications Plan Matrix (create a
Subscriptions are 1, 3, or 12-month calling plans that let you make unlimited, or fixed-minute calls to landlines (and mobiles where applicable). A subscription is great if you make a lot of calls. Skype Credit allows you to pay as you go. Purchase some Skype Credit, and then call whoever you want at low rates.
Community, which has more than 3,000 members, said 85% voted in favour of fighting the India-owned company's plans for up to 2,800 job losses, the majority of them at the country's biggest ...
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue.
But in many organizations, content still isn't treated as a coordinated business function. ... the three most popular content types/formats are short articles/posts (94%, up from 89% last year), videos (84%, up from 75% last year), and case studies/customer stories (78%, up from 67% last year). ... To explore budget plans for 2024, we asked ...
It's been in business for over 20 years and offers three different travel insurance plans. Whether you need basic coverage or more comprehensive protection, HTH Worldwide likely has a plan that ...