- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- What Is B2B?
- Understanding B2B

Special Considerations
- Examples of B2B Commerce
The Bottom Line
- Corporate Finance
Business-to-Business (B2B): What It Is and How It’s Used
James Chen, CMT is an expert trader, investment adviser, and global market strategist.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/photo__james_chen-5bfc26144cedfd0026c00af8.jpeg)
Ariel Courage is an experienced editor, researcher, and former fact-checker. She has performed editing and fact-checking work for several leading finance publications, including The Motley Fool and Passport to Wall Street.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/ArielCourage-50e270c152b046738d83fb7355117d67.jpg)
What Is Business-to-Business (B2B)?
Business-to-business (B2B), also called B-to-B, is a form of transaction between businesses such as a manufacturer and wholesaler or a wholesaler and a retailer. Business-to-business refers to commerce that's conducted between companies rather than companies and individual consumers.
Business-to-business stands in contrast to business-to-consumer (B2C) and business-to-government (B2G) transactions.
Key Takeaways
- Business-to-business (B2B) is a transaction or business conducted between one business and another, such as a wholesaler and retailer.
- B2B transactions tend to happen in the supply chain where one company will purchase raw materials from another to be used in the manufacturing process.
- B2B transactions are also commonplace for auto industry companies, as well as property management, housekeeping, and industrial cleanup companies.
- Meanwhile, business-to-consumer transactions (B2C) are those made between a company and individual consumers.
Lara Antal / Investopedia
Understanding Business-to-Business (B2B)
Business-to-business transactions are common in a typical supply chain because companies must typically purchase components and raw materials for use in their manufacturing processes. Finished products can then be sold to individuals via business-to-consumer transactions.
In the context of communication, business-to-business refers to methods by which employees from different companies can connect through outlets such as social media . This type of communication between the employees of two or more companies is called B2B communication.
B2B E-Commerce
Grand View Research has reported that the B2B e-commerce market was estimated at $18,665.5 billion in 2023 and that it's expected to grow at a rate of about 18.2% annually from 2024 through 2030. It attributes the growth to rapid technology improvements.
The Internet provides a robust environment in which businesses can find out about products and services and lay the groundwork for future business-to-business transactions.
Company websites allow interested parties to learn about a business's products and services and to initiate contact. Online product and supply exchange websites allow businesses to search for products and services and initiate procurement through e-procurement interfaces. Specialized online directories provide information about particular industries and companies and the products and services they provide. This also facilitates B2B transactions.
Successful business-to-business transactions require planning. They rely on a company’s account management personnel to establish business-client relationships. Business-to-business relationships must also be nurtured for successful transactions to take place, typically through professional interactions before sales.
Traditional marketing practices also help businesses connect with business clients. Trade publications aid in this effort, offering opportunities to advertise in print and online. A business’s presence at conferences and trade shows also builds awareness of its products and the services it provides to other businesses.
Examples of Business-to-Business (B2B) Commerce
Business-to-business transactions and large corporate accounts are commonplace for firms in manufacturing. Samsung is one of Apple's largest suppliers in the production of the iPhone. Apple also holds B2B relationships with firms like Intel, Panasonic, and semiconductor producer Micron Technology as of fiscal year 2022.
B2B transactions are also the backbone of the automobile industry. Many vehicle components are manufactured independently and auto manufacturers purchase these parts to assemble automobiles. Tires, batteries, electronics, hoses, and door locks are typically manufactured by various companies and sold directly to automobile manufacturers.
Service providers also engage in B2B transactions. Companies specializing in property management, housekeeping, and industrial cleanup often sell these services exclusively to other businesses rather than to individual consumers.
What Is the E-commerce Market?
E-commerce includes all transactions that are accomplished from start to finish on the Internet. Products and services are purchased online and payments for products and services are also transmitted electronically. But this doesn't mean that a company can't also engage in brick-and-mortar transactions with customers or clients.
What Are Some Common B2B Purchases?
A retailer who purchases merchandise from manufacturers for resale to consumers has engaged in a B2B purchase but the purchases don't necessarily have to be resold. They can include software that's used for business purposes or shared business or office spaces.
What Is a Business-to-Government (B2G) Transaction?
A B2G transaction involves selling information, services, or products to a government. These are generally E-commerce exchanges but they're not limited to online activity. They're typically entered into under contract. A business submits bids and the government selects one of those bids and takes it to contract.
B2B transactions usually occur between wholesalers and retailers. A wholesaler will sell products to a retailer and that retailer then places price tags on them and offers them to consumers for a profit. They can also involve a manufacturer purchasing necessary raw materials from a supplier to create a product that can eventually be sold to consumers. In any case, the cost generally trickles down to consumers.
Grand View Research. " Business-to-Business E-commerce Market Size Report, 2030 ."
Apple Inc. " Supplier List ."
Coursera. " What Is E-commerce? Types, Benefits, and More ."
The SMB Guide. " What Is Business to Business (B2B) ?"
Market Business News. " What Is B2G or Business-to-Government? Definition and Examples ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/btoc.asp-final-37a45954e5a846b8b1db4ac6a5e688e9.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
Sales CRM Terms
What is B2B (Business-to-Business)? (Explained With Examples)
Oct 11, 2023

In the world of commerce, businesses can take different forms and operate in various ways. One commonly used term is B2B, which stands for Business-to-Business. This article aims to explore and explain the concept of B2B, providing examples and insights into its definition, advantages, disadvantages, and real-world applications
1°) What is B2B (Business-to-Business)?
1.1 - definition of b2b (business-to-business).
At its core, B2B refers to transactions and interactions between two or more businesses. In this context, the products, services, or resources exchanged are specifically intended for business purposes rather than for individual consumption. B2B interactions can occur within the same industry or across different sectors, connecting businesses to facilitate growth, cooperation, and value creation.
When engaging in B2B transactions, businesses often establish relationships with suppliers, distributors, manufacturers, or service providers to meet their specific needs. These relationships are built on trust, reliability, and mutual benefit, allowing businesses to access the resources and expertise necessary for their operations.
For example, in the manufacturing industry, a company that specializes in producing automobile components may engage in B2B transactions with car manufacturers. The automobile manufacturer relies on the specialized components provided by the supplier to assemble their vehicles, while the supplier benefits from a consistent stream of orders and a stable customer base.
1.2 - Advantages of B2B (Business-to-Business)
The B2B model offers various advantages for participating businesses. Firstly, it enables economies of scale as businesses can buy or sell in larger quantities, leading to cost savings. By purchasing raw materials, components, or finished products in bulk, businesses can negotiate better prices and reduce their overall production costs.
Additionally, B2B relationships often foster long-term partnerships, promoting stability, trust, and mutual support. Businesses that engage in B2B transactions tend to develop strong connections with their partners, working together to achieve common goals. This collaboration can lead to shared knowledge, resources, and expertise, enhancing the overall competitiveness of both parties.
Furthermore, B2B transactions tend to be more predictable, with structured terms and conditions, facilitating effective planning and risk management. Businesses can rely on the consistency and reliability of their B2B partners, reducing uncertainties and ensuring a smoother workflow.
Moreover, B2B interactions often involve specialized products, services, or expertise, enabling businesses to tap into a wider range of resources and capabilities they may not possess internally. This access to external expertise enhances innovation and competitiveness, empowering businesses to meet evolving customer demands and market trends effectively.
1.3 - Disadvantages of B2B (Business-to-Business)
While B2B has its merits, there are also potential drawbacks to consider. One key challenge is the complexity that can arise from negotiating and managing business-to-business agreements. With multiple stakeholders and intricate contractual arrangements, ensuring alignment and fair terms can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Another area of concern is the potential for increased competition within the B2B landscape. As businesses leverage the expertise and resources of their partners, they may unintentionally facilitate the growth and competitiveness of their counterparts. This may result in potential conflicts of interest or the need for businesses to stay vigilant and continuously innovate to maintain their market position.
Furthermore, B2B transactions can also be affected by external factors such as economic fluctuations, changes in regulations, or shifts in market dynamics. Businesses engaged in B2B activities need to closely monitor these external factors and adapt their strategies accordingly to mitigate potential risks.
Despite these challenges, B2B remains a fundamental aspect of the business world, enabling collaboration, growth, and value creation. By understanding the advantages and disadvantages of B2B, businesses can make informed decisions and develop strategies that maximize their potential for success.
2°) Examples of B2B (Business-to-Business)
To better understand the practical application of B2B, let's explore a few examples across different contexts:
2.1 - Example in a Startup Context
In the startup ecosystem, B2B interactions are common. For instance, a technology startup might provide a software solution specifically tailored for other businesses to enhance their operational efficiency or customer experience.
Let's imagine a scenario where a startup develops a cutting-edge project management software. This software streamlines task allocation, facilitates communication among team members, and provides real-time progress updates. By offering their product to other businesses, the startup aims to establish mutually beneficial partnerships, while their B2B customers gain access to cutting-edge technology that improves their productivity and competitiveness.
2.2 - Example in a Consulting Context
Consulting firms often operate within the B2B realm. They provide specialized knowledge, strategic guidance, and advisory services to businesses seeking external expertise.
Consider a consulting firm that specializes in digital transformation strategies. They work closely with businesses to analyze their current digital infrastructure, identify areas for improvement, and develop comprehensive plans for digital integration. By engaging with a consulting firm, businesses can tap into the firm's industry insights and leverage their experience to gain a competitive edge. In this scenario, both parties mutually benefit, with the consulting firm offering their services while the business gains valuable insights and recommendations.
2.3 - Example in a Digital Marketing Agency Context
A digital marketing agency can demonstrate the B2B model by providing online marketing services to other companies.
Imagine a digital marketing agency that specializes in search engine optimization (SEO) and social media marketing. They work with businesses across various industries to develop tailored digital marketing strategies, optimize their online presence, and drive targeted traffic to their websites. Through this collaboration, the agency assists businesses in reaching their target audience more effectively, optimizing their digital presence, and achieving their marketing goals. The agency's expertise in various digital strategies and techniques benefits their B2B clients, ultimately driving business growth and success.
2.4 - Example with Analogies
To further illustrate the concept of B2B, we can draw analogies to everyday life. For example, think of a restaurant purchasing fresh ingredients from local farmers or a retailer sourcing products from manufacturers.
In the case of a restaurant, their B2B transactions involve procuring high-quality ingredients from local farmers. By establishing direct relationships with these suppliers, the restaurant ensures the freshness and quality of their dishes, while also supporting local agriculture.
Similarly, a retailer engages in B2B transactions when sourcing products from manufacturers. By partnering with reliable manufacturers, the retailer can offer a wide range of products to their customers, ensuring a diverse and appealing selection.
These examples highlight how businesses engage in B2B transactions to procure goods specifically intended for resale or use within their operations.
In conclusion, B2B (Business-to-Business) is a fundamental aspect of the business landscape, enabling intercompany transactions, partnerships, and value creation. By understanding the definition, advantages, and disadvantages of B2B, businesses can harness its potential to drive growth, innovation, and success. Through the examples provided, we can see how B2B manifests itself in real-world scenarios, empowering businesses to thrive in a collaborative and interconnected environment.
About the author

Arnaud Belinga

Close deals x2 faster with
Breakcold sales crm.
SEE PRICING
*No credit card required
Related Articles

What is the 80-20 rule? (Explained With Examples)

What is the ABCD Sales Method? (Explained With Examples)

What is an Accelerated Sales Cycle? (Explained With Examples)

What is Account-Based Marketing (ABM)? (Explained With Examples)

What is an Account Manager? (Explained With Examples)

What is Account Mapping? (Explained With Examples)

What is Account-Based Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Ad Targeting? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Addressable Market? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Adoption Curve? (Explained With Examples)

What is an AE (Account Executive)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Affiliate Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is AI in Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is an AI-Powered CRM? (Explained With Examples)

What is an Alternative Close? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Annual Contract Value? (ACV - Explained With Examples)

What are Appointments Set? (Explained With Examples)

What is an Assumptive Close? (Explained With Examples)

What is Automated Outreach? (Explained With Examples)

What is Average Revenue Per Account (ARPA)? (Explained With Examples)

What is B2G (Business-to-Government)? (Explained With Examples)

What is B2P (Business-to-Partner)? (Explained With Examples)

What is BANT (Budget, Authority, Need, Timing)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Behavioral Economics in Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Benchmark Data? (Explained With Examples)

What is Benefit Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What are Benefit Statements? (Explained With Examples)

What is Beyond the Obvious? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Bootstrapped Startup? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Bottom of the Funnel (BOFU)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Bounce Rate? (Explained With Examples)

What is Brand Awareness? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Break-Even Point? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Breakup Email? (Explained With Examples)

What is Business Development? (Explained With Examples)

What are Business Insights? (Explained With Examples)

What is Business Process Automation? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Buyer Persona? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Buyer's Journey? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Buying Cycle? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Buying Signal? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Buying Team? (Explained With Examples)

What is a C-Level Executive? (Explained With Examples)

What is Call Logging? (Explained With Examples)

What is Call Recording? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Call-to-Action (CTA)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Case Study Analysis? (Explained With Examples)

What is Challenger Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Chasing Lost Deals? (Explained With Examples)

What is Churn Prevention? (Explained With Examples)

What is Churn Rate? (Explained With Examples)

What is Click-Through Rate (CTR)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Client Acquisition? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Closing Ratio? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Ben Franklin Close? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cognitive Bias in Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cognitive Dissonance in Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cold Calling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cold Outreach? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Competitive Advantage? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Competitive Analysis? (Explained With Examples)

What is Competitive Positioning? (Explained With Examples)

What is Conceptual Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Consultative Closing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Consultative Negotiation? (Explained With Examples)

What is Consultative Prospecting? (Explained With Examples)

What is Consultative Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Content Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Content Syndication? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Conversion Funnel? (Explained With Examples)

What is Conversion Optimization? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Conversion Path? (Explained With Examples)

What is Conversion Rate? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cost-Per-Click (CPC)? (Explained With Examples)

What is a CRM (Customer Relationship Management)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cross-Cultural Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Cross-Sell Ratio? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cross-Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Customer-Centric Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Customer-Centric Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Customer Journey Mapping? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Customer Journey? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Customer Profiling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Customer Retention? (Explained With Examples)

What is Dark Social? (Explained With Examples)

What is Data Enrichment? (Explained With Examples)

What is Data Segmentation? (Explained With Examples)

What is Database Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What are Decision Criteria? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Decision Maker? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Decision-Making Unit (DMU)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Demand Generation? (Explained With Examples)

What is Digital Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Direct Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Discovery Call? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Discovery Meeting? (Explained With Examples)

What are Discovery Questions? (Explained With Examples)

What is Door-to-Door Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Drip Campaign? (Explained With Examples)

What is Dunning? (Explained With Examples)

What is an Early Adopter? (Explained With Examples)

What is Elevator Pitch? (Explained With Examples)

What is Email Hygiene? (Explained With Examples)

What is Email Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Emotional Intelligence Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Engagement Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Engagement Rate? (Explained With Examples)

What is Engagement Strategy? (Explained With Examples)

What is Feature-Benefit Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Field Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Follow-Up? (Explained With Examples)

What is Forecast Accuracy? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Funnel? (Explained With Examples)

What is Gamification in Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Gatekeeper Strategy? (Explained With Examples)

What is Gatekeeper? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Go-to Market Strategy? (Explained With Examples)

What is Growth Hacking? (Explained With Examples)

What is Growth Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Guerrilla Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is High-Ticket Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Holistic Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Ideal Customer Profile (ICP)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Inbound Lead Generation? (Explained With Examples)

What is an Inbound Lead? (Explained With Examples)

What is Inbound Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Inbound Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Influencer Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Inside Sales Representative? (Explained With Examples)

What is Inside Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Insight Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Key Account? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Key Performance Indicator (KPI)? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Landing Page? (Explained With Examples)

What is Lead Database? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Lead Enrichment? (Explained With Examples)

What is Lead Generation? (Explained With Examples)

What is Lead Nurturing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Lead Qualification? (Explained With Examples)

What is Lead Scoring? (Explained With Examples)

What are LinkedIn InMails? (Explained With Examples)

What is LinkedIn Sales Navigator? (Explained With Examples)

What is Lost Opportunity? (Explained With Examples)

What is Market Positioning? (Explained With Examples)

What is Market Research? (Explained With Examples)

What is Market Segmentation? (Explained With Examples)

What is MEDDIC? (Explained With Examples)

What is Middle Of The Funnel (MOFU)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Motivational Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is a MQL (Marketing Qualified Lead)? (Explained With Examples)

What is MRR Growth? (Explained With Examples)

What is MRR (Monthly Recurring Revenue)? (Explained With Examples)

What is N.E.A.T. Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Neil Rackham's Sales Tactics? (Explained With Examples)

What is Networking? (Explained With Examples)

What is NLP Sales Techniques? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Net Promotion Score? (NPS - Explained With Examples)

What is Objection Handling Framework? (Explained With Examples)

What is On-Hold Messaging? (Explained With Examples)

What is Onboarding in Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Online Advertising? (Explained With Examples)

What is Outbound Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Pain Points Analysis? (Explained With Examples)

What is Permission Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Personality-Based Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Persuasion Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Pipeline Management? (Explained With Examples)

What is Pipeline Velocity? (Explained With Examples)

What is Predictive Lead Scoring? (Explained With Examples)

What is Price Negotiation? (Explained With Examples)

What is Price Objection? (Explained With Examples)

What is Price Sensitivity? (Explained With Examples)

What is Problem-Solution Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Product Knowledge? (Explained With Examples)

What is Product-Led-Growth? (Explained With Examples)

What is Prospecting? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Qualified Lead? (Explained With Examples)

What is Question-Based Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Referral Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Relationship Building? (Explained With Examples)

What is Revenue Forecast? (Explained With Examples)

What is a ROI? (Explained With Examples)

What is Sales Automation? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Bonus Plan? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Champion? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Collateral? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Commission Structure Plan? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales CRM? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Cycle? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Demo? (Explained With Examples)

What is Sales Enablement? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Flywheel? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Funnel? (Explained With Examples)

What are Sales KPIs? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Meetup? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Pipeline? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Pitch? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Playbook? (Explained With Examples)
Try breakcold now, are you ready to accelerate your sales pipeline.
Join over +1000 agencies, startups & consultants closing deals with Breakcold Sales CRM
Get Started for free
Sales CRM Features
Sales CRM Software
Sales Pipeline
Sales Lead Tracking
CRM with social media integrations
Social Selling Software
Contact Management
CRM Unified Email LinkedIn Inbox
Breakcold works for many industries
CRM for Agencies
CRM for Startups
CRM for Consultants
CRM for Small Business
CRM for LinkedIn
CRM for Coaches
Sales CRM & Sales Pipeline Tutorials
The 8 Sales Pipeline Stages
The Best CRMs for Agencies
The Best CRMs for Consultants
The Best LinkedIn CRMs
How to close deals in 2024, not in 2010
CRM automation: from 0 to PRO in 5 minutes
LinkedIn Inbox Management
LinkedIn Account-Based Marketing (2024 Tutorial with video)
Tools & more
Sales Pipeline Templates
Alternatives
Integrations
CRM integration with LinkedIn
© 2024 Breakcold
Privacy Policy
Terms of Service

B2B Business Models: The Ultimate Guide
Are you thinking about starting a business but have difficulty understanding what exactly B2B business models are?
Well, you’re in luck because in this article, we provide a detailed guide that explains everything, from the concept of a B2B business model to the principles of its functioning, so you no longer feel intimidated or confused and can nail down as a pro.
What Is a B2B Business Model?
3 popular b2b business model types, b2b models that help establish connections with your trading partners, benefits of b2b business models, b2b e-commerce, final thoughts.
Let’s start with fundamentals and define what a B2B business model is.
In layman’s terms, a business model is a set of rules and processes that explain how a company is functioning and how it is making money. In other words, it’s a strategy that companies stick to in order not to deviate from their business goals.
Business models may look slightly different, but the core elements are typically the same and include the following information:
- A brief description of the product or service offered;
- Methods of interacting with clients and selling goods;
- Ways to penetrate new markets;
- Details about revenue streams.
When it comes to B2B business models, it’s important to note that, while they may share some core elements with B2C models, there are significant differences between the two. These differences mainly stem from the fact that the former target other businesses, while the latter are aimed at regular customers.
Of course, just like any other business model, B2B can be divided into several types, depending on the sector they operate in and their approach to doing business. Let’s discuss each of them in detail so you can understand how they differ and which of them would be the most beneficial for you.
- Customer-Centric Type
What defines a customer-centric B2B model is that it puts the needs and preferences of customers at the forefront of every business decision and is focused on continuous improvement. Thanks to this, businesses can offer more customized marketing campaigns and re-engage with their existing customers over and over again.
One example of a successful implementation of a customer-centric model is Amazon. From its inception in 1994, the company has placed a strong emphasis on their customers. This approach has played a significant role in its success, allowing the company to become the e-commerce giant we know today.
- Buyer Centric Type
Another type of B2B model is buyer centric. Under it, businesses put the buyer at the center of the sales process rather than the customer and focus on creating a personalized experience for them. Most often, it’s used by large companies that have a good flow of buyers and a high rate of purchases overall. Walmart is a case in point.
The company has created a portal for buyers and sellers where they can interact. It has set certain rules and standards that they must comply with, but the success of a sale depends entirely on the approach that sellers use to lure customers into buying.
- Intermediary Centric Type
The intermediary centric model is another popular type of B2B that is widely used by companies around the world. As the name suggests, it functions by providing a common platform for vendors and sellers, with businesses acting as intermediaries between the two parties and earning profits through commissions. To give you an example, take eBay.
All participants that go on the platform understand commission charges and agree to the terms before they can get started.
In addition to the aforementioned ones, there exist a few more categories of B2B models that can come in helpful when it comes to connecting with your trading partners. Here they are:
- Direct Model
Under it, companies connect with their trading partners directly to transfer electronic documents easily. They have an IT team that takes the authority for all of the tasks like document translation and technical support. As the number of partners increases, monitoring communications and resolving issues becomes a priority.
- Network B2B
This type of model was created to simplify the direct one. Instead of connecting with each partner directly, companies use a B2B Service Provider called a Value-Added Network (VAN). The VAN provides a single connection for companies to transfer documents using different protocols like AS2, SFTP, FTPS, FTP over VPN, and RosettaNet.
Trading partners, in turn, could also connect to the SP using the protocol that worked best for them.
A combination of the direct and network models is known as the hybrid B2B type. Businesses use it to connect directly with their high-volume trading partners through the Internet to save on transaction fees. At the same time, they still may use a SP to trade with their partners, allowing them to benefit from both models.
Finally, let’s talk about the Managed B2B model. It implies outsourcing the company’s entire B2B process to a third-party service provider, which effectively helps them save on resources, costs, and complexity involved.
The service provider receives documents directly from the company’s ERP system and handles tasks like mapping, technical support, and document tracking. Then they deliver the documents to trading partners via the agreed method that works best for both parties.
Now that we’ve covered all existing types of B2B models as well as their subdivisions, it’s time to take a closer look at their advantages compared to B2C. We may not be able to tell about all of them, but we’ll certainly go over the most important.
- B2B experiences greater stability . Businesses strive to build long-term relationships with their clients and partners, which allows them to build a loyal customer base;
- Higher accuracy in budget predictions . As companies have a more stable customer base, they can make more accurate predictions with regard to their future spending;
- A strong network of partners . Relationships between clients and partners are built on trust, which leads to more effective collaboration;
- The sales cycle is significantly shorter , which helps lower overall costs;
- It relies on factual data . This makes it easier for businesses to calculate sales and other important metrics while minimizing the risk of error.
The B2B model is not only advantageous for businesses but also for their clients. By using this model, clients can access the desired services or goods at a lower cost without the need to switch between multiple providers.
What’s more, they are guaranteed to get consistent quality and may also be eligible for additional loyalty discounts over time.
This guide would be incomplete without mentioning B2B E-Commerce, a model that has shown significant growth in the last few years as more companies understand its benefits.
B2B E-Commerce offers numerous benefits. First of all, it helps businesses attract more buyers by offering higher-quality products and services. It also increases brand awareness, which can result in higher sales volumes and profits.
Moreover, this model provides businesses with the means to monitor their performance, marketing campaigns, and inventory turnover, as well as analyze metrics such as ROE and adjust in time to align them with their end goals.
To wrap it up, choosing the right B2B business model is crucial for any company looking to succeed in today’s competitive landscape. Therefore, it’s important to understand the various types of models available and their benefits.
Hopefully, with the tips and explanations provided in our guide, you’ll decide on the right business model and create an effective strategy that drives growth, increases, and meets your customer needs.
Our Recommendations
- Best Small Business Loans for 2024
- Businessloans.com Review
- Biz2Credit Review
- SBG Funding Review
- Rapid Finance Review
- 26 Great Business Ideas for Entrepreneurs
- Startup Costs: How Much Cash Will You Need?
- How to Get a Bank Loan for Your Small Business
- Articles of Incorporation: What New Business Owners Should Know
- How to Choose the Best Legal Structure for Your Business
Small Business Resources
- Business Ideas
- Business Plans
- Startup Basics
- Startup Funding
- Franchising
- Success Stories
- Entrepreneurs
- The Best Credit Card Processors of 2024
- Clover Credit Card Processing Review
- Merchant One Review
- Stax Review
- How to Conduct a Market Analysis for Your Business
- Local Marketing Strategies for Success
- Tips for Hiring a Marketing Company
- Benefits of CRM Systems
- 10 Employee Recruitment Strategies for Success
- Sales & Marketing
- Social Media
- Best Business Phone Systems of 2024
- The Best PEOs of 2024
- RingCentral Review
- Nextiva Review
- Ooma Review
- Guide to Developing a Training Program for New Employees
- How Does 401(k) Matching Work for Employers?
- Why You Need to Create a Fantastic Workplace Culture
- 16 Cool Job Perks That Keep Employees Happy
- 7 Project Management Styles
- Women in Business
- Personal Growth
- Best Accounting Software and Invoice Generators of 2024
- Best Payroll Services for 2024
- Best POS Systems for 2024
- Best CRM Software of 2024
- Best Call Centers and Answering Services for Busineses for 2024
- Salesforce vs. HubSpot: Which CRM Is Right for Your Business?
- Rippling vs Gusto: An In-Depth Comparison
- RingCentral vs. Ooma Comparison
- Choosing a Business Phone System: A Buyer’s Guide
- Equipment Leasing: A Guide for Business Owners
- HR Solutions
- Financial Solutions
- Marketing Solutions
- Security Solutions
- Retail Solutions
- SMB Solutions
What Is B2B, and How Does It Differ From B2C and DTC?

Table of Contents
B2B is short for “business to business.” It’s a business model in which the companies involved create products and services for other businesses and organizations. B2B companies can include software as a service (SaaS) , marketing firms, and businesses that create and sell various supplies. B2B businesses have unique challenges, including cash flow management, and must continually innovate and maintain customer loyalty.
We’ll explore the B2B business model and how B2B businesses can maximize their profits and market share.
How do B2B business models work?
In the business-to-business model, businesses and organizations exchange goods and services. For example, one company may contract with another business to provide the raw materials needed to manufacture a product.
Another business may need to purchase products from another to stock their shelves, while other companies hire businesses to promote their products and services, insure their operations, design their logo, or write website content.
Consumers aren’t a direct factor in B2B transactions, but they’re a critical component of why B2B companies work together.
B2B isn’t the only business model involved in the supply chain. While B2B companies sell products and services to other private businesses, public-sector organizations, and charities, B2C (business-to-consumer) – or DTC (direct-to-consumer) – companies sell products and services directly to consumers.
Where do B2B companies sit in the supply chain?
If you want to understand where B2B companies factor into the supply chain, it’s essential to look at the three economic sectors: primary, secondary and tertiary.
- Primary market: The primary market is exclusively B2B. Primary-sector companies are responsible for extracting or producing raw materials – for example, farmers or oil and gas companies.
- Secondary market: The secondary market is almost exclusively B2B. Secondary-market companies manufacture and assemble products. They add value to the raw materials they buy from the primary market by turning them into something else. Think about manufacturers that turn oil into plastics or jewelers that cut and polish diamonds. Secondary-market assembling companies include car manufacturers and construction companies. Occasionally, secondary-market companies use the B2C model – for example, farmers who sell products in a market stall.
- Tertiary market: The tertiary market is a mixture of B2B and B2C models. Some tertiary-market companies deliver the goods or services businesses or consumers want. These businesses include plumbers, internet retailers, floor installers, supermarkets, commercial finance brokers, home improvement specialists, tutors and the hospitality sector.
What are some B2B tertiary market examples?
Some tertiary companies are B2B only. They provide goods and services other customer-facing tertiary companies need to do their jobs. Here are some examples:
- Plumbing supply companies sell plumbers the equipment they need.
- Point-of-sale (POS) providers sell POS systems to retailers.
- Commercial finance brokers need lenders to fund small business loans , equipment leasing packages and asset-based loans .
- Management and business consultants help companies survive and grow.
- Retailers need credit card processors to process payments from customers.
- Companies need advertising firms to help them achieve higher sales.
- Businesses need payroll providers and financial services companies to run payroll and streamline taxes.
- Businesses need lead-generation services to create revenue opportunities.
- Organizations need insurance providers to protect employees, customers and their own interests.
Challenges of running a B2B company
Perhaps the most significant challenge most B2B companies face is finding businesses to buy their goods and services. B2B marketplaces are much smaller than consumer-facing models. For example, a B2C clothing e-commerce website would have a broad audience of potential buyers.
However, businesses often spend more on purchasing than consumers and have much more generous budgets. So, while a B2B company may make fewer sales, it’s likely to see a much higher profit than a B2C company.
Here are some of the unique challenges B2B businesses face.
1. B2B businesses must continually innovate and maintain customer loyalty.
Innovation is a critical issue for many B2B companies, especially those that sell products and services with a monthly subscription model, such as SaaS packages and online accounting software .
B2B businesses must find new ways to constantly improve their products’ functionality and ease of use to improve their chances of increasing market share while maintaining customer loyalty. And their competitors are also in the same continual development cycle looking to create an even better product.
2. B2Bs must build a strong internet presence.
B2B companies must invest in a well-designed and consistently maintained business website so their customers can find them and easily navigate their offerings. Search engine optimization is critical for achieving a top ranking in Google, as is optimizing your website for mobile .
Your website content – including blogs, guides, product descriptions and whitepapers – should appeal to customers and prospects at the three stages of the sales funnel : the awareness, investigative and action stages.
- Awareness stage (top of the funnel): This stage is when a potential client realizes there are points of friction within their business or opportunities that they currently don’t have the personnel, technology or knowledge to pursue.
- Investigative stage (middle of the funnel): In this stage, a potential client is proactively looking for a solution, and they know there are multiple solutions and providers. During the investigative phase, clients consider different solutions and providers, often relying on website content to make decisions.
- Action stage (bottom of the funnel): After a prospect makes a shortlist of solutions and providers, they contact candidates to begin the sales discovery process.
3. B2B companies must manage cash flow and late payments.
Many B2B companies invoice clients on 30- or 60-day payment windows. For example, an invoice issued on Feb. 1 may not be paid until April 1. Even then, some clients don’t make timely payments, despite generous credit terms.
If your company issues many invoices, the effect of delayed payments may be mitigated by the regular arrival of money in your account. However, some manufacturing businesses may only issue a handful of substantial invoices a year, so being paid late puts the company’s future in jeopardy.
While business loans are available , consider invoice factoring if late payment is an issue for your company. Invoice factoring (sometimes called invoice discounting) means you sell your invoices to a finance company and receive 80% or more of the invoice value the following day. When the client makes a payment, you receive the remaining 20% minus factoring fees.
How B2B companies can boost market share
Running a B2B business presents many challenges, but there are ways to maximize revenues and market share.
1. Join supply and procurement exchanges.
Supply and procurement refer to a business purchasing the goods and supplies it needs to run profitably.
Cost-effective procurement is an ongoing challenge for many businesses. Within larger organizations, multiple departments and locations may have distinct budgets and agreements with various suppliers. This might mean one department pays $3 for a lightbulb while another pays $30.
Online supply and procurement sites provide pre-approved, pre-priced lists of goods and services to larger businesses and public sector organizations. If you register with one of these e-procurement sites, your company will immediately be visible to buyers and specifiers within some of the world’s largest companies.
2. Use keyword-targeted marketing.
B2B businesses prioritize high-quality websites and high-ranking search engine results. To maximize your website’s ranking potential, use targeted keywords that your competition may be overlooking.
For example, if you’re a broker competing for the term “business loan,” according to SEO marketing platform Ahrefs, your site would need 202 backlinks from third-party sites to have a chance of getting onto the first page of search results.
There are more than 640 associated “business loan” keywords that might work for you, such as “small business loan,” “business loan calculator,” and “startup business loan.” Try using effective terms with less competition to draw traffic to your site and build your site’s status with Google over time.
3. Try direct marketing campaigns.
To help your sales team generate leads , consider building or purchasing email lists of decision-makers in the types of companies you target.
CRM software can make email marketing campaigns and follow-up seamless. Stay in touch with decision-makers once a month so they become familiar with your company and how it’s helped other clients. Over time, you’ll create familiarity and trust, and these campaigns will start to generate strong, closeable, inbound leads.
4. Use lead-generation websites.
Although not suitable for every type of B2B company, lead-generation websites create detailed buyers’ guides on a wide range of business goods and services.
These sites let visitors get two or more quotes from suppliers and then sell these leads to fully qualified B2B companies. When a sales rep reaches out to these prospects, they already know the client’s budget, needs and timeframe.
Lead-generation sites offer two lead types: exclusive leads that only you receive, and shared leads that you and other companies have the chance to pitch.
B2B-specific sales and marketing
B2B marketing campaigns require careful planning, according to Brent Walker, senior vice president of marketing and analytics at PatientBond.
“B2B typically relies on its sales function and account management team to establish and strengthen customer-client relationships ,” he said. “Marketing may include advertising in trade journals, having a presence at conventions and trade conferences, digital marketing – an online presence, SEO, email outreach – and other traditional awareness efforts.”
The key to B2B marketing is demonstrating value to a business’s bottom line, increasing your likelihood of achieving a return on investment . If your solution makes business processes more cost-effective and efficient, promote these points. If your service increases traffic to a website or boosts conversion rates, highlight these benefits for added revenue.
The underlying motivation behind all business purchases is increasing profit. If you demonstrate how your product and service can boost your customers’ bottom line, you’ll likely get the opportunity to discuss it with a decision-maker.
Matt D’Angelo contributed to the writing and research in this article. Source interviews were conducted for a previous version of this article.

Building Better Businesses
Insights on business strategy and culture, right to your inbox. Part of the business.com network.
Business to Business (B2B) | Definition, Types, & Examples

While there are many types of businesses , the majority of the businesses out there depend on B2B suppliers and companies in order to function.
What are these B2B companies and why are they called B2B?
Well, let’s find out.
What is Business to Business (B2B)?
Business to Business (B2B or B to B) is the method of doing commerce where businesses trade and transact with other businesses rather than end customers. These businesses use the traded offering to step up their offering or to resell it to make profits.
This is in contrast to the businesses selling to customers. Take the example –
A company manufactures automotive parts say, brake pads and supplies them to an automotive manufacturer who builds the entire vehicle. This company is said to follow the B2B model. It is a business that serves another business.
Simple as that.
Any business model which creates value for other businesses to consume this value is said to have a Business to Business (B2B) model of operation (B2B model). Also, B2B is different from B2C business model as it focuses on creating value for businesses not end consumers.
B2C or Business to Consumer is the type of business model where the business serves the customer and unlike B2B, does not serve other businesses.
This brings us to –
The basic different types of B2B models.
Types of B2B Models
With B2B being a large and complex model, it can be classified into popular and mainstream types –
Product-based B2B Model
The product-based B2B model is a type of B2B model where the business sells physical products to other businesses. This business may act as a supplier and sell your customized products to various other businesses. Know that the business is servicing other enterprises and companies; not consumers or individuals.
An example of a product-based B2B company would be one that sells security hardware to businesses and institutions. Kisi is a great example of a B2B company providing other businesses with security hardware.

Also, product-based B2B companies can have a physical or online presence or both and it also helps to mention that the products are generally physical (in nature), hence requiring a much higher initial investment and overhead costs compared to other B2B types.
Service-based B2B Model
A company with a service-based B2B model functions exactly as the name suggests – it helps provide other businesses with services of its own.
A few examples of Service-based B2B businesses would be –
- Providing consultancy services
- Marketing Agencies
- Call management services
- Employee Training Services
- Providing translation services
Rioks is a great example of a service-based B2B company. It provides marketing consultancy services to other businesses to improve their marketing reach and strategies.

Service-based B2B companies are many and large since it is much simpler to scale up accordingly. Also, service-based B2B companies are easier to set up and run compared to product-based B2B businesses. While these service-based B2B companies could have an online or physical presence or both, it depends on the service that the company provides.
Software-based B2B Model
Software-based B2B companies can come under either “product” or “service” based B2B model. While the latter deals in providing services to other people, the former provides software solutions to them. This warrants a separate model for software since there are a lot of products and services provided as software-based tools to other businesses.
The software-based B2B model can be split primarily into –
“Product-focussed” software-based B2B model
“service-focussed” software-based b2b model (saas model).
Xero and Freshbooks are great examples of “product-focussed” software-based B2B companies in which they provide accounting and invoicing software to businesses respectively.

Salesforce is a great example of a “service-focussed” software-based B2B company. Salesforce provides Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and cloud services to other enterprises and companies.
The software-based solutions are usually membership or subscription-based and are the easiest to scale accordingly; since the software can be deployed or removed quite quickly and instantly as required.
While these are a few major and distinguishable types of B2B models, there are a lot of other types which are the hybrid mixes of the above few. But there is one other field that helps to be categorized separately – B2B-based ecommerce.
B2B Ecommerce
B2B ecommerce is the selling and buying of goods between businesses through the use of online marketplaces. Ecommerce is a major field of the B2B model and it works really works well, be it servicing customers or businesses. The B2B ecommerce field can be divided into three different sub-models. They are –
Supplier Centric Model
In supplier centric model, the ecommerce business acts as the supplier for other businesses. This is mostly due to there being more buyers and fewer sellers on the market. Under this model, the business tends to sell their products via their own or other platforms to various other businesses.
Cisco is a great example of supplier centric model – it owns its own marketplace through which it sells network equipment to other businesses.

Supplier centric model means that you tend to have control over the pricing and inventory of the products.
Buyer Centric Model
In the buyer-centric model, the ecommerce business is looking to procure products and has its own online marketplace – inviting suppliers (read: other businesses) to put up their products and quotations on it in order to compare and decide on the best accordingly.
Walmart is a great example when it comes to the buyer-centric model. Walmart has a global presence and purchases huge quantities in bulk most of the time. It also tends to procure its supplies from local suppliers rather than importing them from somewhere else.
This has led them to come up with standards and an online marketplace for suppliers to enter and bid to become the supplier for Walmart.
Intermediary Centric Model
In this model, the ecommerce business tends to act as the intermediary, helping connect the buyers and sellers. This is feasible in markets or sectors having a lot of sellers and buyers. The ecommerce business has a platform or marketplace helping connect and facilitate the transaction between businesses.
Alibaba , the Chinese-based e-commerce site is a great example. Unlike Amazon, it mainly focuses on serving businesses.

Alibaba is one of the big-name players in the e-commerce sector and it primarily focuses on promoting other businesses to trade and sell their products to other businesses via their online marketplace.
The advantages and disadvantages that the B2B model offers.
Advantages of B2B Model
A predictable and stable market.
The B2B market is filled with businesses catering to other businesses. This means that sales and purchases are based on rational decisions rather than based on impulse decisions. This allows for more predictability.
Also, a buyer in B2C may or may not be a repeat customer but in B2B the deals and contracts tend to last longer – at least a year or more with guaranteed pricing and terms negotiated between the two parties.
Better Customer Loyalty
Since the B2B deals and contracts tend to last for years most of the time, it leads to the formation of a much better evolution of supply chain management. It brings about a collaborative mindset in distribution channels and this helps contribute to high levels of customer loyalty.
This can loyalty can be achieved by providing consistent and reliable service since B2B deals tend to be both costly and time-consuming. As long as you remain dependable and consistent, B2B loyalty is a given.
A Trillion Dollar Industry
The B2B ecommerce sector was one of the fastest-growing industries of 2018 and in March 2019, it breached the trillion-dollar mark. This is in total only accounts for 13% of the entire B2B sales. This in itself is a great incentive to get into the B2B field, since this growth is expected to continue for the time being. The market is ripe with the potential for newer businesses to take advantage of the rising sales and demand for B2B solutions and products.
Disadvantages of B2B Model
Smaller customer pool.
Since the B2B market basically deals with businesses instead of individuals, it has fewer potential buyers and sellers at any given time. Unlike serving to the consumer market, selling niche or specialized products and services further limits your serviceable and potential clients.
Marketing Challenges
Marketing to other businesses is quite complex compared to marketing to regular consumers. While B2C businesses use social media and content marketing to bring in customers, B2B companies need to plan carefully before employing any of the marketing methods. Businesses tend to be more critical of the brand-image and status of the other business that they interact with. This means that B2B companies need to invest in quality staff in order to create polished and clear-cut marketing campaigns.
With the advantages and disadvantages of B2B businesses out of the way, let’s look at a few examples of B2B companies to get a better understanding.
B2B Companies Examples
As seen before, most companies, be it B2C or C2B or C2C or even B2B, all depend on basically at least one other company or business in order to function. This means that there are a lot of B2B companies serving other companies out there.
Here are five such examples of B2B businesses –
WeWork is basically a real estate-cum-software based company that helps provide workspaces for businesses and entrepreneurs.
WeWork is a great example of a B2B company since it is basically a business that sub-lets office space for other businesses.
Slack stands for ‘Searchable Log of All Conversation and Knowledge’ and is an online platform that acts as a chat room with added features to it – making it easier to share content and messages all from the same platform.
Slack is a business that provides a communication platform service for other businesses.
LinkedIn is part social media and part B2B company. The social media aspect is well known. But LinkedIn also acts as the hub for most businesses to keep themselves informed about the happenings of the business world.
LinkedIn helps inform other businesses about market issues and help get to know others in their fields digitally.
International Business Machine (IBM) is a global software and technology company that provides hardware, software and cloud-based services to other companies.
Though the company has dabbled in the consumer market, it’s primary operations always was in providing services for other companies making it one of the biggest and oldest B2B company in our list.
The B2B model is a fairly simple business model. It helps solve or provide services to other businesses while, at the same time, operating one on their own.
All the B2B companies that we listed above are all addressing pain points other businesses have and they have created a B2B business solution to help solve those pain points. And all it takes for you to start one is as simple as finding the market deficiencies at any time and help provide a solution to it.
Go On, Tell Us What You Think!
Did we miss something? Come on! Tell us what you think about our article on Business to Business (B2B) in the comments section.

Started out to become a developer but felt at home in the home of startups. The journey started from a single novel. Been an entrepreneur since schooling days. Interested in coding, reading and movies.
Related Posts:

B2B Meaning: What Is B2B & The B2B Model?

B2B, or business to business, is a vital sales method for many businesses. It is a growing and profitable market, too.
But it comes with its own unique requirements and set of tools for selling, marketing, and invoicing customers.
We'll walk you through the most important aspects of each and get you the information you need to make your B2B business grow.
What Is a B2B Company ?
A B2B business is a company that sells its products or services to another company. This is in contrast to the B2C model where they sell to individual consumers. These businesses include product manufacturers, wholesalers, distributors, retailers, and more.
B2B Business Model Pros and Cons
The B2B business model has both pros and cons for the business owner and their team.
- Larger orders. B2B sales are high and orders are made in bulk. This means revenue can be higher with fewer sales than B2C businesses.
- Increase conversion. Businesses convert better than individuals. This makes marketing efforts more successful and wastes less money attracting new customers.
- Streamlined structure. Communication between businesses happens regularly so sellers are more informed about their customers’ needs.
- Long buying cycle. B2B consumers take a long time to make purchasing decisions. Multiple stakeholders are involved and need a number of approvals to go forward.
- Limited market. B2B sellers have fewer potential customers and the ones they do have are very important. If even a single customer is unhappy, they can lose a lot of money.
- Difficulty forecasting. Both manufacturers and resellers can run into issues with demand forecasting since B2B has a shorter inventory cycle. This can in turn lead to overestimating demand and leave all parties with dead stock (see dead stock meaning ).
The B2B business model is a tried-and-true form of commerce. These businesses are continuing to grow at an exponential rate through the internet, much like their B2C counterparts.
B2B vs. B2C
While B2B companies provide services or products to other businesses, B2C, or "business-to-consumer," companies sell direct to consumer . They’re two separate business models that serve different types of customers.
B2B or B2C: Which Is Better?
Neither the B2B nor B2C business model is inherently better, they both have their own pros and cons. The model that best fits your business is determined by your goals, infrastructure, and industry.
Here are four of the biggest differences:
- Pricing. B2C businesses (see D2C meaning ) offer a single tier of pricing for all customers that are only affected by sales or discounts. B2B businesses usually offer multiple levels of discounted prices based on the quantities and frequency of orders.
- Customer service. B2C companies use customer support representatives to answer general questions and help with issues. B2C businesses use account managers who bring in new wholesale customers and regularly push sales and assist with account and order issues.
B2B vs B2C Buying
B2B and B2C consumers behave very differently and their buying processes reflect this.
Here are a few ways they differ:
- Buying cycle time. B2B consumers act more slowly and are better informed about their purchases. This is because their purchases are of a much larger quantity and their own business is greatly affected by their purchases. B2C consumers convert more quickly and are often less informed about product differences.
- Emotional investment. B2C consumers often make emotionally-driven purchasing decisions. They may be moved by advertising to associate your product with happiness, or they may be trying to alleviate some frustration. B2B consumers are much more calculating and driven by numbers.
- Parties involved. B2C consumers are individuals or a small group. They can easily communicate their wants and needs and are much easier to build a relationship with as a business. B2B consumers often involve multiple people and teams in their purchasing decisions. Rapport can still be built, but it will take longer and requires more investment.
Both models are capable of providing a business with a large volume of sales and push product. Once you determine the B2B model is best for your business, you need to learn how to make B2B sales.
Ready to unlock the full potential of kitting for your business? Discover the ins and outs of this efficient inventory management technique that can streamline your business operations, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction .
What Is B2B Sales ?
B2B sales is a sales model where products or services are sold from one business to another. It is contrasted to B2C sales where a business sells to individual customers.
Why Use B2B Sales?
B2B sales is a business model that can pay massive dividends. Though harder to make than B2C sales, the return is higher and results in establishing relationships with a much higher lifetime value.

Generating B2B Sales Leads
Generating qualified B2B sales leads is vital in growing your business and heading off competition. These leads can be acquired in many ways, from email marketing to cold calls. Pick the strategy that works best for your business and your bottom line.
The B2B Sales Process
The B2B sales process is a set of steps the sales team follows to convert prospects into customers. It's how your company operates to move leads through the sales funnel. This process is different for every company, but should be a rigid framework for all salespeople to follow.
A structured approach will minimize the number of mistakes and ensure salespeople are selling your products or services in the same manner.
The B2B Sales Methodology
A sales methodology is a set of rules that define how a business sells products or services to its customers. This is not the same as the sales process which is focused on the steps in the sales process. Sales methodologies are built around identifying customer needs, establishing the value your business brings, and then communicating both to your target customers.
Making B2B sales takes hard work and dedication, but can lead a business to make strong relationships and create sustainable growth. The best way to make sales leads is with a robust digital marketing strategy.

What Is B2B Marketing ?
B2B Marketing used to be done entirely through cold calls and lead buying, but has transformed in the technological era. Digital marketing is now the most common form of advertising and a powerful sales tool.
Content Marketing
B2B content marketing is using content to attract an audience, build brand awareness, collect leads, and drive sales. Successful B2B content is designed to be useful, informative, and professional. This content can be blog posts, whitepapers, webinars, and more.
B2B email marketing refers to pushing marketing campaigns to existing or prospective customers using email. Email marketing has the highest click-through and conversion rate of any channel and allows for a lot of personalization. It also has low startup costs and there are many services on the market that allow people with little experience to run campaigns.
Social Media
Social media is often one of the most difficult marketing tools for B2B companies to use. It can be hard to avoid being boring while promoting your product or service. The key is to focus on your audience's needs and wants. Then, tailor your social media marketing to match while still conveying the value you bring. Social media marketing is a major player in the DTC marketing world.
Marketing Strategies
A B2B marketing strategy is the overall plan a business uses to acquire customers. B2B marketing can be done in many ways to great effect, but there are a few strategies that most B2B businesses should adopt. They need to conduct thorough research, have a user-friendly website, and use paid and organic search engine optimization. These efforts will pay dividends and make the most of their marketing budget.
How To Promote in B2B
Promoting a B2B business can be difficult and requires looking into a variety of marketing channels. Focusing on a few free channels like content marketing, SEO, social media, and referrals are a good place to start. Organically building your marketing can take longer, but also gives you a solid base to work from with less risk.
B2B marketing takes more effort than its B2C counterpart but also has a much higher return. Marketing and sales are only worth investing in if you're able to handle B2B payments.
B2B Payments
B2B payments are transactions processed between two businesses for exchanged products or services. B2B payments tend to be for high sums and are often split across months or quarters.
Payment Systems
A B2B payment system is the software or program used to process payments. Many come with the ability to hold payments in escrow, check a customer's credit-worthiness, and have integrated reporting. The best, like BlueCart Payment Processing, include the ability to send automated payment reminders, process vendor payment s, report on on-time or late payments, collections, and more.

How Payments Work
B2B payments are either received at the point of sale or an invoice is sent to the buyer at a later date. Most B2B businesses send invoice templates monthly and require payment in 30 days. The method and terms of payment vary by business and relationship of the parties involved.
Card Payments
B2B card payments are when a buyer pays in full via a credit card. The buyer then has a variety of options in paying back their credit provider. This is one of the quickest and the second most popular methods of payment.
Check Payments
B2B check payments are the most common form of payment and can be either physical or electronic. These checks are endorsed by the buyer and deposited by the seller into their own bank account. Many banks now offer mobile apps that let you scan checks for quicker depositing.
Mobile Payments
B2B mobile commerce payments involve using a digital wallet on the buyer's phone to send a payment to the seller's phone. Many businesses fear it is not secure enough to conduct large B2B sales through it.
Electronic Payments
Electronic payments for B2B include many types of payments and make up the bulk of B2B transactions. Whether ACH, RTP, or even mobile payments, the convenience and security of electronic payments make them popular among B2B wholesale businesses.
The Future of B2B Payments
The future of B2B payments is through the cloud and online payment platforms like BlueCart Payment Processing. These tools continue to grow more secure every day and allow for immediate transmission of funds and access to historical data. It truly is the future of eCommerce growth .
They also allow small businesses to have access to robust financial tools and sell to a larger market with less risk. For wholesale food distributors, the BlueCart Digital Storefront is one of the best eCommerce platforms to increase revenue and reach new customers.
B2B eCommerce Platform
B2B eCommerce platforms are online services that allow B2B businesses to conduct business more easily. B2B headless eCommerce is conducted across many industries and by businesses of all sizes using a variety of platforms.
B2B eCommerce Platform Features
With so many options on the market, it's important to get the best platform for your business. Here are a few features to look for in a B2B eCommerce platform:
- Volume discounts. Look for a platform that lets you make discount tiers based on order quantity to automate the process, like BlueCart.
- Personalized offerings. This allows you to set different prices and feature different products for your customers. This may be by order level, geographic location, or any other qualifier. Many in the food industry use BlueCart specifically for this.
- Easy reordering. B2B customers like to order the same products multiple times. Making it easier to reorder these products will make your customers more satisfied and can lead to more purchases. BlueCart is great at this and even has “standing orders”, which are essentially automated recurring orders.
- Flexible payments. The more options for B2B payments available, the more likely your customers are to convert. Look for a platform that can accommodate a variety of payment options including checks, credit cards, electronic transfers, and invoicing. BlueCart offers these options and more.
B2B eCommerce Solutions
There are many eCommerce software solutions for B2B eCommerce companies to choose from. For food manufacturers, broadline distributors, and wholesalers, the best choice is BlueCart . This all-in-one platform is designed to streamline processes and make selling easy. It lets business owners monitor their product catalogs and sales, manage and fulfill incoming orders, and communicate with customers on the fly.
B2B eCommerce platforms are vital tools in growing your B2B business. Now that you know what to look for, you can find a platform that is robust, but cost-effective to help grow your business. B2B Marketplaces are another viable option for growing your business.
B2B Wholesale Marketplace
A wholesale marketplace is a B2B eCommerce platform that connects wholesale suppliers to wholesale buyers. These marketplaces are growing at an exponential rate and opening new channels of opportunity for small-to-midsize businesses. Most marketplaces also allow sellers to market, sell, invoice, and fulfill orders using a single platform. They're like a wholesale directory on steroids and help you learn how to find vendors and wholesale items to sell .
Most marketplaces also allow sellers to market, sell, invoice, and fulfill orders using a single platform.
The Basic B2B eMarketplaces
There are three basic types of eMarketplaces that each have their own services and structure.
The three types are:
- Supplier-oriented marketplace. This model is also called e-distribution and is noted for having many buyers and few suppliers. It is good for building goodwill and loyal customers. Cisco runs one of the largest of these and sells more than $1 billion worth of network products each year.
- Buyer-oriented marketplace. Also called e-procurement, this model has few buyers and many sellers. In this model sellers list competing products at different prices for buyers to bid on. GE's electronic bidding site, which goes by the name of GE TPN Post, is one of the biggest buyer-oriented marketplaces.
- Intermediary-oriented marketplace. This fast-growing marketplace is called an e-exchange and features many buyers and sellers. It is owned by a third party that connects buyers to sellers for a small fee. It is the ideal solution for small- and medium-sized businesses. BlueCart is a great example of this type of marketplace that connects thousands of wholesale food suppliers and buyers.
Best B2B Marketplace
The best B2B trade marketplace varies based on industry and a business's needs. The key is to find a site that offers the tools you need to make informed decisions. You also want to make sure the user base is large enough to connect you with the best buyers and sellers. Vertical marketplaces are a great place to start.
For food wholesalers and those in the restaurant industry, the best B2B online marketplace is BlueCart. It's an all-in-one solution that lets sellers have control over every aspect of their sales.
You, Me, and B2B
B2B businesses are a major part of the world economy and are responsible for billions of dollars of sales each year. Running a successful one requires understanding B2B sales and marketing funnels, ecommerce platforms, and payment systems. Using the information we've shared above, you should have the tools you need to make your business grow.
Once you have all that under your belt, make sure to invest in quality eCommerce packaging and a fast eCommerce shipping team to ensure your customers get their products safely and quickly.

B2B Business Model and How it works
Businesses are evolving. Unlike the past decade where businesses operated on brick and mortar stores, virtualization is the new norm. You do not need to have a physical shop to drive sales. All you require is a digital store where customers can access your products and place orders.
Despite all these changes, one thing remains constant. Every business needs a model that they use to achieve its objectives. As an entrepreneur, you must come up with a way of operating your venture. B2B or business-to-business is one of the model e-commerce businesses is to run their operations. If you do not know how this model works, you are on the right page.
In this article, we cover what B2B is as well as how it works and its pros and cons. Thus, keep reading on to learn more about this model.
What is B2B Business Model?
For many entrepreneurs, selling to consumers is their objective. You develop products that you offer to your consuming customers. However, this is not the only way to operate your business. B2B business model is where businesses sell to other businesses or simply called business to business. It is a situation where a business offers its products to another business instead of selling them directly to the consumers.
Here, businesses make products destined for use by other businesses. You sell what you make to another business that can either use it to generate other products or sell the same product to the final consumers. So, this model does not involve transactions between a business and consumers.
How Does B2B Work?
Typically, B2B business involves transactions between one company/business to another business. Your company makes products or services for consumption in another company. For instance, your company can be a supplier of raw materials to company B which produces a given product. Or else, you might be selling products to wholesalers and retailers in bulk for them to sell them to the consumers.
In this model, your targets are other businesses and not consumers. This means that you must reach out to other businesses and offer convincing reasons to consider your goods or services. Say for example you offer business solutions. You need to convince the business owners or decision makers why and how your solutions will enhance their operations.
In most cases, the B2B model involves the use of proposals and procurements. Businesses require suppliers and solution providers for proposals. The engagement is also on a long-term basis rather than a single purchase.
Example of B2B Business
B2B business model applies in every stage of the supply chain or value chain . When a manufacturer orders raw materials to make a product from another company, this relationship involves two businesses. Also, when you source products from a wholesaler or supplier to sell in your retail store, you are applying the B2B model. So, there are many examples of businesses applying this concept in their operations.
Apple is a good example of a company using the B2B concept. As you know, Apple is a renowned high-edge smartphone. In developing their iPhones, Apple sources chips from Samsung. Without Samsung, Apple can have challenges in manufacturing its iPhones. Also, Apple has other B2B connections with companies providing semiconductors and other materials for making smartphones such as Micron Technology and Intel.
Pros and cons of B2B Business Model
B2B model allows many businesses to operate and succeed in both physical and virtual arena. However, it is not perfect and has both pros and cons. Here they are:
Long-term engagement leading to customer loyalty
B2B model operates on long-term engagement. Both businesses agree to supply raw material or products/solutions for a given duration. This aspect enhances customer loyalty as the two have a mutual agreement. As the supplier, you have consistent sales as long as you retain the quality and dependability of your product and services. This aspect is hard to achieve in other models.
Easy to predict revenue
Since you have a long-term engagement, you can easily predict your revenue. You can determine with certainty the amount of revenue you’ll generate in a given period. With this, you can easily make conscious decisions and business plans. So, this model makes your business more secure as you will have customers for your products at any given time.
Short selling cycle
No doubt, selling to consumers can be a long process. The process involves a number of intermediaries. When you consider selling to consumers directly, you need a lot of time to clear your inventory. As you know, the longer the selling cycle or duration, the more expensive it becomes. You need to invest a huge amount in promoting your products and service when dealing with final consumers.
Unlike the business-to-consumer approach, the B2B model comes with a short-selling cycle. You sell your products or service to specific customers. You do not need to spend a lot of time money on marketing what you are offering. So, the short-selling cycle saves you money and time.
Limited customer pool
By concentrating on businesses as your customers, you reduce your pool. Having a small customer pool can affect your sales and expectations. The small target poses a lot of challenges to beginners in securing their first customers. For this reason, many B2B businesses do not last for long due to the hardship of driving sales.
Long decision-making period
Unlike selling to customers, dealing with businesses is a complex affair. Businesses have long decision-making processes that involve several parties. First, you need to send a proposal. The business can take several weeks or months to respond to your proposal and accept the deal. This approach can hurt your expectations especially when patience is not your virtue.
As an entrepreneur, you can consider using the B2B business model in your venture. The model will work effectively when what you offer is suitable for other businesses. Also, you can consider this concept if you want a short-selling cycle by selling your products in bulk to other businesses.
However, you need to be aware of the hurdles to expect in your operations. The businesses can take a longer duration to accept your proposal. Nonetheless, when your business gets some grips, you’ll enjoy massive sales and long-term relationships meaning consistent revenue generation.
Related Posts
Business model canvas: a great tools for an innovative business model design, walmart business model and how it makes money, dropshipping business model and how it works.


Business-to-Business Model (B2B): What It Is and How It Works

The business-to-business, often abbreviated to B2B, model is a fundamental business model to the economy as it facilitates the exchange of goods and services across industries. Businesses depend on other businesses in order to operate. Let’s take a look at what the business-to-business model is and the key advantages and disadvantages.
What is the Business-to-Business (B2B) Model?
A business-to-business company caters to the needs of other businesses. In this business model, a company will sell products or services to another company, instead of an individual buyer.
Most B2B interactions happen within the supply chain. This would include buying and selling between suppliers, manufacturers , wholesalers, distributors, and retailers. Before making it into the hands of individual buyers, products typically go through several B2B interactions. Instead of having to handle all of the steps it takes to produce an item, the business-to-business model allows companies to specialize in a specific part of the supply chain.
However, not all B2B interactions have to do with the supply chain. The key element of the B2B model is that the interactions are between two businesses. You can compare this model to the business-to-consumer (B2C) model .
Types of Business-to-Business Models
The B2B model can vary depending on what products or services the business specializes in. There are three main types of B2B business models.
Product-Based : When businesses need to purchase large quantities of items, they will go to a product-based B2B company. This type of B2B model sells physical products and supplies them to other companies. We can see this model most often in the construction or manufacturing industries. For example, when a lumber company sells wood to a company that builds residential housing.
Service-Based: A service-based B2B company will provide specific services to businesses, and place a lot of importance on customer service. They help to solve issues or challenges that businesses face. Some examples of services that a company would provide another company would be accounting, IT support, marketing, or recruitment services.
Software-Based: This type of B2B model is when a company provides software to other companies to use, most commonly to improve processes and become more efficient. These types of B2B companies usually also provide support and maintenance when a company is using their software. An example of this would be a software B2B that provides email automation tools in order to help streamline a company’s marketing messages.
Advantages of the Business-to-Business Model
Low marketing efforts.
Generally, B2B companies do not have to go all out for their marketing efforts. They are able to target a well-defined and specific audience which allows for more precise marketing efforts. Instead of casting a wide net, B2B companies can focus their resources on reaching the businesses most likely to need their products or services. This makes it easier to tailor their messaging and connect with potential clients.
Bulk Orders and Revenue
B2B transactions typically involve bulk ordering as companies have higher budgets and needs than individuals. These larger orders lead to a higher revenue per transaction. Instead of needing to sell items to multiple customers, they will sell a thousand of one item to one customer. Bulk ordering can help businesses to increase their profit margins.
Long-Term Clients
Long-term client relationships are more common within the B2B market. Because of the length of the sales cycle and the nature of the products and services being sold, B2B businesses and their clients often form stronger relationships. Once a customer is satisfied with the products or services they are more likely to continue their business relationship. A steady and loyal customer base can be a substantial asset to a B2B company.
Disadvantages of the Business-to-Business Model
Complex sales process.
Sales transactions between businesses can be more intricate than a sales transaction with an individual customer. There are often several decision-makers within a company that all need to provide their stamp of approval before a sale can be made. B2B salespeople often invest considerable time into building trust and understanding their clients’ needs. Sometimes purchases can take months to finalize.
Small Customer Base
Considering there are fewer companies than there are individuals in the world, B2B companies have a smaller pool of clients to work with. This limited customer base has its benefits but also means that customer loyalty is extremely important. Losing a key client can be more detrimental to a company, impacting its revenue and stability. Managing existing client relationships and continuing to diversify their client base are both important for B2B companies to mitigate these risks.
Cash Flow Management
B2B companies can sometimes find managing their cash flow to be challenging. Clients can often have different payment terms and schedules, with payment usually happening in 30 or 60-day increments. It can also be common for B2B clients to not always pay on time. This can get tricky to balance and can affect a company’s ability to manage operating costs as well as invest in their growth. B2B companies need to develop strategies such as effective invoicing and credit management to ensure a healthy cash flow and financial stability.
By focusing on serving the needs of other businesses, B2B companies enable the efficient exchange of products and services globally. It is a business model that provides a firm yet versatile framework within the supply chain. Whether providing physical products, services, or software, B2B companies are essential to modern commerce.
The Advantages and Disadvantages of Business-to-Consumer (B2C) Model
(B2C) Business-to-Consumer Model: Types and How it Works

Like this article? Get updates by email and get our eBook for FREE
GET PREMIUM CONTENT AND UPDATES FOR FREE !
Team Writer: Courtney Kovacs is a Texas based writer who enjoys writing about various topics such as entrepreneurship, travel, health and wellness, and faith.
Recent Posts

The Impact of AI on Software Development

5 Ways to Use Chat GPT for Marketing
Strategic approaches to enhance online visibility through ppc.

Understanding the Amazon Marketplace Ecosystem & Strategies for Amazon Sellers

6 Things I Wish I Knew Before Starting a Business
Related posts, popular posts.

21 Different Types of Business Models With Examples

100 Best Business Ideas that You Can Start this Year
5 types of target marketing strategies you should know, 10 successful entrepreneurs that failed at first.
Pingback: Business-to-Business Model (B2B): What It Is and How It Works – Austin Rotter
- Grow Your Business
- Leading Your Team
- Find Your Way
- Business Models
- Social Media
- Entrepreneurial Lifestyle
- Your Mindset
- Our Writing Team
- Get “The Fast Growing Startup” Ebook Free
- Advertise With StartUp Mindset
- The Part-Time Entrepreneur


Written by True Tamplin, BSc, CEPF®
Reviewed by subject matter experts.
Updated on March 27, 2023
Get Any Financial Question Answered
Table of contents, b2b vs b2c: an overview.
Business-to-Business (B2B) and Business-to-Consumer (B2C) are two different types of business models . These two terms describe a typical business relationship.
B2C is a business model in which a company sells a service or product directly to a consumer.
It is the alternative to the B2B model in which a company sells its products first to another business, who then sells the product at a retail store at a marked-up price.
In a B2B model, an entire organization could be involved in finalizing the purchase.
It can involve other departments such as, but is not limited to, a board of trustees, C-level executives, and finance. In the case of a B2C model, the customer is the sole decision maker.
What Is B2B?
B2B is a type of business transaction between two businesses. It targets other companies and involves selling products or services that will be used in the business operations of another company.
It can also target other organizations, such as government agencies and non-profit organizations. A B2B can occur between a manufacturer and wholesaler, wholesaler and retailer, or two companies that use the services or products of each other.
The B2B market encompasses everything from industrial suppliers to payroll processors to software developers.
For example, the automobile industry. A truck or car that ends up in a consumer's driveway contains dozens of parts and products that were purchased through different suppliers in a B2B transaction.
Typically, B2B transactions occur under three conditions:
- When a business is sourcing materials , like office supplies or automobile parts
- When a business is sourcing services , such as hiring an accounting firm to manage finances
- When a business is sourcing products to resell , like a dealership purchasing a car from the manufacturer to sell to a customer
In B2B business models, both businesses benefit from each other. The company selling the product or service gains revenue , while the company buying gets a product or service it needs to help run its business.
B2B companies exist in every industry, and some B2C companies generate B2B activities.
For instance, a pharmaceutical company sells medicines to consumers but also sells products and services to hospitals, clinics, and other pharmacies.
Examples of B2B
Some companies that apply the B2B model are the following:
Alibaba is an e-commerce platform that connects Chinese manufacturers and suppliers with international buyers. It is one of the largest B2B companies worldwide.
It sells its goods to 40 industries and serves over 18 million sellers and buyers in 240 countries and territories.
Mailchimp is a software company that provides marketing automation and email marketing services to businesses of all sizes.
It helps businesses send better mail and email marketing campaigns. They provide their services from small e-commerce shops to large online retailers—reach their audience, engage with them, and build their brand.
Slack is a cloud-based set of team collaboration tools and services. It offers one-on-one messaging, file sharing, searchable message archives, and integration with a variety of business software, making it a go-to B2B communication platform for businesses.
What Is B2C?
B2C is a type of business model where a company sells products or services to individual consumers.
B2C was described as commerce between traditional brick-and-mortar retailers and people who walk in to purchase the products or avail of the services.
However, today, B2C has evolved to include digital channels such as company websites, e-commerce platforms, and social media.
In the B2C business model, the company and the customer are the only two parties involved in the transaction.
The B2C market is broad and includes companies that offer physical goods such as clothing and electronics, as well as digital goods such as books, music, and apps.
There are five distinct models that B2C companies use to move their products in a digital space.
- Direct Sellers - This is one of the most common B2C business models that sell products directly to consumers. These include small online businesses as well as large retailers, like Microsoft and Apple, that sell exclusively in-house products.
- Online Intermediaries - They do not own the products that are sold on their site, but they put sellers directly in contact with the buyers and usually profit by taking a cut of the transaction. eBay and Etsy are examples of online intermediaries.
- Advertising-Based - It involves a company purchasing advertising space on a platform that receives large volumes of traffic, like Youtube or Reddit.
Targeted advertising used criteria such as internet searches, content viewed, and demographics to strategically place advertisements in front of a promising customer.
- Community-Based - It takes advantage of online, like-minded communities occurring on media platforms and beyond. Since many of these communities form around a shared interest or a physical location, companies can identify promising leads more easily.
Examples of this B2C model are Instagram, Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, and other online forums.
- Fee-Based - These B2C models require payment to access a company's content. Subscription services like Spotify, Hulu, and Lynda, are prime examples of this model.
Examples of B2C
Some companies that use the B2C business model are the following:
Netflix is a B2C company that offers its services to mass-market consumers. They offer access to various documentaries, television, and movies when consumers pay for monthly subscriptions.
It also has produced original content for viewers, which is an example of a B2C transaction.
H&M is a top B2C fashion company that sells various clothing to mass-market consumers worldwide.
They also market their other products, including beauty products and home decor, to consumers who will buy an item and perform the B2C transaction.
Uber is a ridesharing app that allows people to request a ride from drivers in their area. It is a convenient way to get around, especially in large cities where public transportation can be difficult to use.
Uber earns income by taking a percentage of each ride that is requested and completed. This is an example of a B2C transaction since Uber is selling a service directly to consumers.
Key Differences Between B2B and B2C
Let us look at the differences between B2B and B2C through the following key points:
In a B2B company, the end user is typically another business, whereas, in a B2C company, the end user is an individual consumer.
Product Pricing and Presentation
Businesses as end users are typically more price sensitive than individual consumers. In B2B, the sales process is more complex, and the decision-makers are usually looking for the best value for their company.
On the other hand, in B2C, consumers are generally less price sensitive and care more about product presentation.
For example, a business that sells chocolates to another business that is going to create something with the chocolate would not care so much about the packaging the chocolate arrives in.
Because of this, pricing will typically be lesser considering that the company does not have to spend extra on marketing or packaging.
Discounts will also be given for larger orders to incentivize businesses to buy in bulk.
On the other hand, a B2C company that sells chocolates to individuals would be more focused on product presentation because the product needs to look appealing on store shelves.
Usually, a higher price will be charged for this to make up for the extra marketing and packaging costs.
Customer Segmentation and Distribution
B2B businesses typically have a smaller customer base than B2C businesses.
They often sell their products or services to other businesses through direct sales or indirect sales channels such as distributors or resellers.
On the other hand, B2C businesses usually have a larger customer base and sell their products or services directly to consumers through channels such as brick-and-mortar stores, online stores, or catalogs.
B2B vs. B2C: Pros and Cons
There are both advantages and disadvantages to using a B2B and B2C business model. Some of the pros and cons of each are as follows:

Operational Costs
B2B businesses often have higher operational costs than B2C businesses.
B2B businesses need to establish systems and hire employees to manage customer relationships and develop and maintain their products and services.
This results in high set-up and maintenance costs. B2C businesses, on the other hand, can be run with a leaner staff and have lower set-up and maintenance costs.
B2B business models often have higher revenue potential because they sell their products or services in large-scale businesses.
They typically have more sales because other businesses often purchase in bulk in a single transaction.
B2C companies, on the other hand, tend to make smaller sales to individual customers in a single transaction and may attain limited sales growth.
Sales Cycle
Both B2B and B2C business models must learn about their target market and create a sales strategy.
However, the sales cycle for B2C business models is typically much shorter than the sales cycle for B2B business models because B2B consumers require rigorous decision-making in making purchases.
B2C consumers typically make emotionally-driven decisions when purchasing items.
B2B calculates the cost-benefit of a product or service before making a decision, while B2C looks at the immediate want or need.
Business Administration
B2B business models are often complex and require systematic business administration. They handle various business operations that must be carried out efficiently and effectively.
B2B companies also require a good understanding of their target market, product development, and pricing strategies. They also need to have systems in place to manage customer relationships.
B2C businesses, on the other hand, often have less formal business administration because they are typically smaller and have simpler operations.
Hybrid B2B B2C Business Model
A hybrid business model uses both B2B and B2C business models. In this type of business model, the company sells its products or services to both other businesses and individual consumers.
An example of a hybrid B2B B2C business model would be a company that manufactures and sells car parts. The company sells its car parts to both other businesses (B2B) and individual consumers (B2C).
Amazon is a real-life example of a company with a hybrid B2B B2C business model.
While it is best known for its B2C capacities, Amazon has a large B2B relationship as well. Its B2B channel, Amazon Business, supports small businesses by offering business-exclusive prices and discounts on millions of items.
The main advantage of a hybrid business model is that it allows the company to reach a larger market.
The company can sell its products or services to both businesses and consumers, which gives it a greater chance of making sales and generating revenue.
The flexibility of a hybrid business model is also an advantage, as the company can adjust its focus depending on the needs of the market.
The main disadvantage of a hybrid business model is that it can be more difficult to manage.
The company has to juggle two different types of customers (businesses and consumers) with potentially different needs.
The company also has to maintain two separate marketing campaigns (one for businesses and one for consumers). This can be costly and time-consuming.
The Bottom Line
Business-to-business or B2B refers to commercial transactions between two businesses, such as a manufacturer, a wholesaler, or a retailer.
Business-to-consumer or B2C refers to selling goods or services from businesses to individuals.
There are several key differences between B2B and B2C, including end users, product pricing and presentation, and customer segmentation and distribution.
The two models also have certain pros and cons in terms of operational costs, revenue potential, sales cycles, and business administration.
A hybrid business model uses both B2B and B2C business models. This business model has the advantage of being able to reach a wider range of customers.
By using both B2B and B2C models, businesses can target both businesses and consumers, which can help to increase sales and revenue.
B2B vs B2C FAQs
What is the difference between b2b and b2c.
B2B businesses are typically commercial transactions between two businesses, while B2C businesses sell goods or services from businesses to individuals.
Which is better between B2B and B2C?
There is no definitive answer as to whether B2B or B2C is better. It depends on the products and services being offered, the target market, and the business goals of the company.
What are the advantages of B2B over B2C?
The main advantage of B2B over B2C is the potential for higher revenue. This is because B2B companies sell larger quantities of products.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of B2B?
An advantage of B2B businesses is the potential for higher revenue because of bulk purchases by other businesses. Disadvantages of B2B businesses include the need for more formal business administration and a smaller target market.
What is B2B and B2C with examples?
Alibaba, Mailchimp, and Slack are all examples of B2B businesses. Apple, Uber, Etsy, and Nike are all examples of B2C businesses.

About the Author
True Tamplin, BSc, CEPF®
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide , a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University , where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon , Nasdaq and Forbes .
Related Topics
- B2C Marketing
- Business-to-Business (B2B)
- Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
Ask a Financial Professional Any Question
Meet top certified financial advisors near you, find advisor near you, our recommended advisors.

Taylor Kovar, CFP®
WHY WE RECOMMEND:
Fee-Only Financial Advisor Show explanation
Certified financial planner™, 3x investopedia top 100 advisor, author of the 5 money personalities & keynote speaker.
IDEAL CLIENTS:
Business Owners, Executives & Medical Professionals
Strategic Planning, Alternative Investments, Stock Options & Wealth Preservation

Claudia Valladares
Bilingual in english / spanish, founder of wisedollarmom.com, quoted in gobanking rates, yahoo finance & forbes.
Retirees, Immigrants & Sudden Wealth / Inheritance
Retirement Planning, Personal finance, Goals-based Planning & Community Impact
We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it.
Fact Checked
At Finance Strategists, we partner with financial experts to ensure the accuracy of our financial content.
Our team of reviewers are established professionals with decades of experience in areas of personal finance and hold many advanced degrees and certifications.
They regularly contribute to top tier financial publications, such as The Wall Street Journal, U.S. News & World Report, Reuters, Morning Star, Yahoo Finance, Bloomberg, Marketwatch, Investopedia, TheStreet.com, Motley Fool, CNBC, and many others.
This team of experts helps Finance Strategists maintain the highest level of accuracy and professionalism possible.
Why You Can Trust Finance Strategists
Finance Strategists is a leading financial education organization that connects people with financial professionals, priding itself on providing accurate and reliable financial information to millions of readers each year.
We follow strict ethical journalism practices, which includes presenting unbiased information and citing reliable, attributed resources.
Our goal is to deliver the most understandable and comprehensive explanations of financial topics using simple writing complemented by helpful graphics and animation videos.
Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications. Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others.
Our mission is to empower readers with the most factual and reliable financial information possible to help them make informed decisions for their individual needs.
How It Works
Step 1 of 3, ask any financial question.
Ask a question about your financial situation providing as much detail as possible. Your information is kept secure and not shared unless you specify.

Step 2 of 3
Our team will connect you with a vetted, trusted professional.
Someone on our team will connect you with a financial professional in our network holding the correct designation and expertise.

Step 3 of 3
Get your questions answered and book a free call if necessary.
A financial professional will offer guidance based on the information provided and offer a no-obligation call to better understand your situation.

Where Should We Send Your Answer?

Just a Few More Details
We need just a bit more info from you to direct your question to the right person.
Tell Us More About Yourself
Is there any other context you can provide.
Pro tip: Professionals are more likely to answer questions when background and context is given. The more details you provide, the faster and more thorough reply you'll receive.
What is your age?
Are you married, do you own your home.
- Owned outright
- Owned with a mortgage
Do you have any children under 18?
- Yes, 3 or more
What is the approximate value of your cash savings and other investments?
- $50k - $250k
- $250k - $1m
Pro tip: A portfolio often becomes more complicated when it has more investable assets. Please answer this question to help us connect you with the right professional.
Would you prefer to work with a financial professional remotely or in-person?
- I would prefer remote (video call, etc.)
- I would prefer in-person
- I don't mind, either are fine
What's your zip code?
- I'm not in the U.S.
Submit to get your question answered.
A financial professional will be in touch to help you shortly.

Part 1: Tell Us More About Yourself
Do you own a business, which activity is most important to you during retirement.
- Giving back / charity
- Spending time with family and friends
- Pursuing hobbies
Part 2: Your Current Nest Egg
Part 3: confidence going into retirement, how comfortable are you with investing.
- Very comfortable
- Somewhat comfortable
- Not comfortable at all
How confident are you in your long term financial plan?
- Very confident
- Somewhat confident
- Not confident / I don't have a plan
What is your risk tolerance?
How much are you saving for retirement each month.
- None currently
- Minimal: $50 - $200
- Steady Saver: $200 - $500
- Serious Planner: $500 - $1,000
- Aggressive Saver: $1,000+
How much will you need each month during retirement?
- Bare Necessities: $1,500 - $2,500
- Moderate Comfort: $2,500 - $3,500
- Comfortable Lifestyle: $3,500 - $5,500
- Affluent Living: $5,500 - $8,000
- Luxury Lifestyle: $8,000+
Part 4: Getting Your Retirement Ready
What is your current financial priority.
- Getting out of debt
- Growing my wealth
- Protecting my wealth
Do you already work with a financial advisor?
Which of these is most important for your financial advisor to have.
- Tax planning expertise
- Investment management expertise
- Estate planning expertise
- None of the above
Where should we send your answer?
Submit to get your retirement-readiness report., get in touch with, great the financial professional will get back to you soon., where should we send the downloadable file, great hit “submit” and an advisor will send you the guide shortly., create a free account and ask any financial question, learn at your own pace with our free courses.
Take self-paced courses to master the fundamentals of finance and connect with like-minded individuals.
Get Started
Hey, did we answer your financial question.
We want to make sure that all of our readers get their questions answered.
Great, Want to Test Your Knowledge of This Lesson?
Create an Account to Test Your Knowledge of This Topic and Thousands of Others.
Get Your Question Answered by a Financial Professional
Create a free account and submit your question. We'll make sure a financial professional gets back to you shortly.
To Ensure One Vote Per Person, Please Include the Following Info
Great thank you for voting..
The Ultimate Guide to B2B Marketing in 2023 [+ New Data]
Discover a variety of B2B marketing strategies you can use to reach and resonate with your business audience

THE ULTIMATE PRODUCT MARKETING GO-TO-MARKET KIT
Ensure that your whole team is aligned with four planning and internal enablement templates for your next product launch.

Updated: 05/04/23
Published: 05/04/23
Effective B2B marketing is difficult to get right. Between creative demands, budget limits, and channel decisions, marketers have a lot to juggle when developing their marketing strategy.
The biggest determinant of effective marketing, however, is your audience .
If you’re not properly targeting your buyer persona , your promotions and advertisements will likely fall on deaf ears. You might as well not be marketing at all.
![what is a b2b business model → Download Now: Free Product Marketing Kit [Free Templates]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/08b5e1f4-5d26-405b-b986-29c99bd0cb14.png)
Where target audiences vary the most, though, is between individual consumers and businesses . Some companies serve individual shoppers, while others cater to companies and organizations.
Marketing to businesses is very different from marketing to individual consumers. That’s why an entirely different marketing method — B2B marketing — exists, and that’s why we built this guide.
By the end of this article, you’ll have a better understanding of B2B marketing, the most effective B2B marketing strategies, and how you can tap into and convert your business audience. Plus, the trends you can expect in the B2B space in 2023, according to new research plus expert tips.
What is B2B Marketing?
B2b vs b2c marketing, b2b marketing strategies.
B2B Marketing Trends to Watch
B2B Marketing Examples
What is b2b.
B2B stands for “business-to-business,” which refers to a business model where businesses sell products and services to other companies as opposed to consumers.
If you’re a new marketer in the B2B space, or a small B2B business owner learning the ropes, B2B marketing can seem new and strange, but not to worry — you’ll soon learn it’s not so different from typical consumer marketing, and we’ll go over everything you need to know so you can create an effective B2B marketing strategy.
B2B (business-to-business) marketing refers to any marketing strategy or content that is geared towards a business or organization. Companies that sell products or services to other businesses or organizations (vs. consumers) typically use B2B marketing strategies.
The purpose of B2B marketing is to make other businesses familiar with your brand name, the value of your product or service, and convert them into customers.
HubSpot is an example of a company that engages in B2B marketing. HubSpot’s customers are other businesses, not individual consumers. Therefore, all of our marketing efforts can be classified as B2B.
HubSpot uses the information you provide to us to contact you about our relevant content, products, and services. HubSpot will share the information you provide to us with the following partners, who will use your information for similar purposes: Search Engine Journal, Litmus, Rock Content. You can unsubscribe from communications from HubSpot at any time. For more information, check out HubSpot's Privacy Policy . To unsubscribe from Search Engine Journal's communications, see Search Engine Journal's Privacy Policy . To unsubscribe from Litmus's communications, see Litmus's Privacy Policy . To unsubscribe from Rock Content's communications, see Rock Content's Privacy Policy .

The State of Marketing in 2024
HubSpot's Annual Inbound Marketing Trends Report
- Top Marketing Channels
- AI in Marketing
- Managing Privacy
- The Future of Marketing
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
B2B and B2C (business-to-consumer) marketing are very different. B2B and B2C marketing differ in their respective strategies and applications, as well as in their audiences and how they communicate with them .
B2B marketing targets the needs, interests, and challenges of individuals who are making purchases on behalf of, or for, their organization (rather than for themselves), thus making the organization the customer.
Here are a few examples of B2B companies:
A coworking space that leases office spaces to remote teams and freelancers (like Spaces )
An on-demand order fulfillment, warehousing, and screen printing service (like Printful )
A marketing software company that sells social media management tools, lead generation software, and other marketing tools to businesses and organizations (like HubSpot !)
B2C marketing targets the needs, interests, and challenges of individual consumers who are making purchases on behalf of, or for, themselves, thus making the individual the customer. Here are a few examples of B2C companies:
An e-commerce company that sells office supplies to remote or self-employed individuals (like Poppin )
A store that sells t-shirts and other clothing and accessories (like Target )
A music platform that sells streaming subscriptions (like Spotify )
Take a look at this chart comparing B2B and B2C customers.
As much as they differ, though, B2B and B2C also intersect in many ways. While Poppin sells office supplies to remote or self-employed individuals, they also design corporate office spaces and branded supplies.
On the flip side, Printful not only offers order fulfillment and warehousing to businesses; they also fill e-commerce printing orders for individuals.
As distinct as the B2B and B2C marketing audiences can be, B2B marketers can always learn from B2C campaigns , too.
As I said above, marketing depends on its audience. While B2B and B2C marketing vary, not every piece of B2B marketing material is alike, either.
In this section, we’ll talk about various B2B marketing strategies you can implement to reach your specific business audience. Some of these strategies are preparatory, such as identifying your audience, while others are ready to be executed, such as creating a B2B website. Let’s get started.
1. Understand the B2B buyer’s journey.
Before we dive into actual strategies you can implement, it’s important to understand the B2B buyer’s journey . This piece of information will help you create and implement marketing strategies that meet prospects at every stage of their purchase process.
Because of the higher price point of B2B products, B2B sales cycles tend to be a lot longer than B2C cycles. Nurturing these prospects via marketing takes a similarly long time, too, and you must use specific tactics at every stage to drive them toward a purchase decision or a demo request.
In other words: B2B marketing is not as easy as setting up ads on Instagram and hoping for clicks. (We wish! That can work, however, in conjunction with other strategies.)
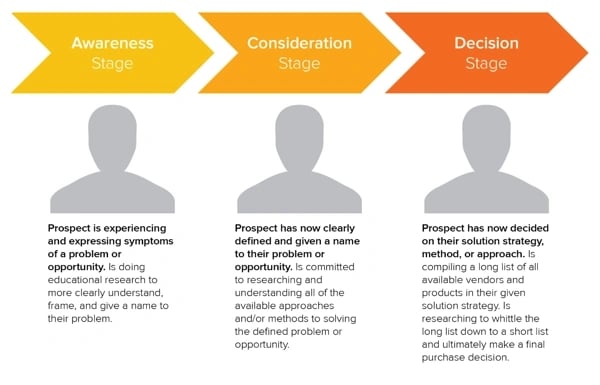
The B2B buyer’s journey is divided into three stages:
Awareness Stage: The prospect has become aware of a problem and begins educating themselves.
Consideration Stage: The prospect researches solutions for their new problem.
Decision Stage: The prospect is ready to make a purchase or formally begin a buying process.
After understanding the buyer’s journey, take this opportunity to create a customer journey map for your company — or, if you’re a new marketer at a B2B company, asking for one for reference.
A customer journey map is a customized version of the buyer’s journey that shows how your brand interacts with prospects during each phase. When you have that information, you can understand which marketing strategies, such as content marketing, will be most effective at each stage.
2. Identify your target market and target audience.
Now that you have a strong understanding of the buyer’s journey, it’s time to begin understanding who you’re marketing to specifically. Who is taking the buyer’s journey and purchasing your products? You get to decide — and it all begins by identifying who they are.
First up, define your target market . For B2B companies, we first recommend identifying your target companies with firmographic data such as:
- Company size, i.e small, medium, or enterprise
- Company region or location, i.e North America, South America, Africa, or specific countries and regions
- Company industry, i.e healthcare, fintech, or SaaS
- Number of employees
Then, define your target audience — that is, the specific human prospect who is looking for your brand’s products or services. Remember, you’re not marketing to other companies, you’re marketing to people who work at that company.
You can use demographic and psychographic data to identify individual prospects you’ll be marketing to. This may include their:
- Education level
This information will help you create buyer personas and customer profiles , which in turn will help you understand how they make purchase decisions and which marketing channels they’re more likely to use.
For instance, if you’re targeting an entry-level employee, ages 22-26, at a small business in North America, you can likely use social media to reach them effectively.
3. Choose your marketing mix (or the 4 Ps of marketing).
Now that you’re armed with your buyer’s firmographic, demographic, and psychographic information, it’s time to start building a B2B marketing strategy that’s tailored specifically to them. Start by defining your marketing mix, or the 4 Ps of marketing :
- Product: What product you sell
- Price: How much the product costs
- Place: Where the product is sold
- Promotion: Where customers will find out about the product
Defining your 4 Ps is an excellent precursor to creating a more extensive marketing strategy. It marries all of the information you’ve recently found about your potential customers with the information you already know about your own product.
That will empower you to create a more effective strategy than if you jumped right into tactics and execution.
Featured Resource: Marketing Mix Templates

Click here to download the templates for free .
4. Create a B2B marketing plan and a marketing strategy.
Once you’ve defined your marketing mix, you can dive in even more deeply by creating a marketing plan and a marketing strategy . A marketing strategy marries market conditions with your company’s goals, and a marketing plan provides an actionable roadmap with specific channels and metrics.
What’s most important is outlining your own company’s summary and target markets, then deciding where you’ll promote your company. The thing is, it’s all too easy to choose specific strategies, like social media marketing and content marketing, without a strategic approach. That can easily lead to overspending in the wrong areas.
To create a marketing plan and strategy, we recommend starting with a template.
Featured Resource: Free Marketing Plan Template

Click here to download HubSpot's free Marketing Plan Template.
Using this template, you’ll be able to compile all the information you need to choose the right B2B marketing channels for your company. You’ll be able to lay out your:
- Business Summary and Initiatives
- Target Market
- Market Strategy
- Marketing Channels
- Marketing Technology
In this list, we could have easily shared specific marketing tasks you can do, such as creating online content or publishing short videos. And while these things will likely be a worthy use of your time, it’s more important to spend your time strategizing to minimize marketing costs and increase your ROI .
Strategizing is the core of your B2B marketing strategy — not implementing specific tactics such as blogging or SEO. Those will come later once you have defined the big picture.
5. Cover all of your B2B marketing bases, such as launching a website.
It’s time to dive into the more tactical aspects of your B2B marketing strategy by ensuring all of your marketing bases are covered. But we don’t want to dive too deeply yet; this is about nailing down the basics. The “basics” will vary per industry; for instance, in a more traditional vertical, you might rely less on your website and more on industry events.
That said, you want to ensure your B2B company has covered most of the following things (click on each one for a checklist to run through):
- Launching a website
- Creating and maintaining your social media profiles
- Starting an email marketing newsletter
- Signing up for industry events and conferences
No matter which B2B industry you’re in, and regardless of your audience type and age, these things will likely benefit you. Later, we’ll cover specific types of B2B marketing that you can integrate under each of these strategies. But here’s a good introduction:
- Strategies for your website: Content marketing , blogging , SEO
- Strategies for your social media profiles: Social media marketing , paid social media , short form video marketing
- Strategies for your email marketing newsletter: Email marketing , lead nurturing
- Strategies for industry events and conferences: Event marketing , trade show marketing
6. Run a competitive analysis.
To choose your specific marketing strategies even more strategically, carry out a competitive analysis .
Scope out the market and see which businesses are marketing to your target audience. Learn what they’re currently doing — do they have a website? A presence on a specific social media platform, such as LinkedIn? Things to be on the lookout for when inspecting competitors are:
- Competitor product offerings
- Competitor sales tactics and results
- Competitor marketing content and social media presence
Featured Resource: 10 Competitive Analysis Templates
Download Now
Getting a general overview of these items can help you recognize your competitors’ strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats — otherwise known as a SWOT analysis . Once you understand where they stand, you can better compete with them and choose the best channels.
If none of your competitors are on Instagram, for instance, then Instagram marketing may not be a good strategy to pursue (or, at least, you should test it out first before investing too many resources in it).
7. Determine your brand positioning.
Next, define your brand positioning in the market. This statement is the who, when, why, and how of your brand identity — or the way your brand is perceived through the eyes of the customer.
This will help you cultivate a consistent brand image, regardless of the marketing channels and tactics you use.
Devise a brand positioning statement that your team and prospective customers can believe in, and you’ll be ready for the next step.
Featured Resource: Positioning Statement Templates

Download for Free Now
8. Explore marketing channels to use.
By now, you’ve likely run across the different types of marketing channels your competitors use successfully, and the channels they haven’t taken advantage of. You’ve also likely gotten an idea of what you want to do based on your big-picture strategizing so far.
With the previous steps completed, you’re ready to diversify your B2B marketing portfolio and reach the businesses you need to. Depending on your customer segments and competitor analysis, you can now explore channels, strategies, and tools to optimize your leads and customer funnels.
Next up, let’s look at the types of B2B marketing you can implement now that you’ve created your overall strategy.
Types of B2B Marketing
The following categories are B2B marketing channels bound to connect you to your target audience.
B2B Email Marketing
Email marketing is a tried and true method of reaching both individual consumers and business customers. Most B2B marketers use email — are you one of them? You should be. Emails lead to engagement, which turns subscribers into leads … and then customers.
Download our guide to optimizing email marketing for conversions and learn how to grow your email list, ensure deliverability, and increase engagement .
Unlike B2C customers who respond best to emotions and entertainment, B2B customers look for logic and positive ROI. Essentially, they’re asking themselves, How can your business help my business grow? Because of this, your email marketing must consistently resonate with your business customers and focus on things that matter to them — like time, money, and resources.
Email marketing is also a powerful vehicle for sharing your brand’s content. Many B2B companies use email newsletters as part of their content marketing program, and the B2B marketers we’ve spoken to say these newsletters are most critical to their content marketing success.
With the constant barrage of emails flooding our inboxes today, it’s more important than ever to create and send out effective marketing emails. To help you create emails that stand out, you can use HubSpot's AI Email Writer .
B2B Email Marketing Best Practices
Write enticing subject lines . Think about your email subject lines as a Netflix trailer — if you can’t hook your audience with a two-minute clip (or, in this case, a few dozen characters), don’t expect them to open and watch (or read) the whole thing. We recommend spending almost as much time on your email subject lines as you do on the emails themselves.
Stick to one call-to-action (CTA) per email . If you think the number of emails you receive is a lot, take a look at the CTAs in those emails … some are packed with two, three, and sometimes up to 10 different CTAs. Don’t make this mistake, which can leave your recipients’ heads spinning, asking “What should I click on first?” and ultimately clicking on nothing. With one CTA per email, you allow your audience to focus on your email content and ultimately one action … a welcome reprieve from today’s frequent decision-making and analysis paralysis.
Segment your email to reach the most relevant audience . Not every email you send will be appropriate for everyone on your list. Your subscribers may be at different stages of the buyer’s journey or be seeking different solutions. That’s where email list segmentation comes into play. Not only does this help you relate to your audience better, but it gives your emails that personal feel that says “Hey, I’m listening and I know what you’d like to see.” Consumers prefer email quality over quantity anytime.
Make sure your email designs are responsive . Most email users access their inbox on their phones, and emails that don’t show up correctly on mobile devices are often deleted. Ouch. Don’t let your email be one of those.
Don’t be afraid of the cold email . As uncomfortable as it is, the right email can convert new customers — like these cold sales email templates , which will help you get your leads’ attention.
👉🏼 HubSpot Tip : You can’t send marketing emails without any recipients — these people make up your lists. There are plenty of easy ways to grow your email list . Begin with opt-in forms on your website homepage, About page, and blog. Check out HubSpot’s Free Form Builder tool to get started.
B2B Digital Marketing
Every business, whether B2B or B2C, should have a digital presence — which is comprised of paid ads, search engine optimization, a website, and any other place your B2B company is active online. Let’s walk through a handful of tactics that can strengthen your B2B digital marketing strategy.
1. Define your target audience.
A strong B2B digital marketing strategy starts with defining your target audience, or buyer persona . This demographic and psychographic information will inform almost every other marketing activity thereafter, ensuring your content and digital material is absorbed by the right eyes and ears (and that no resources go to waste on your end).
2. Create your website.
Secondly, digital marketing can’t quite function without an informative, engaging website. Most buyers visit a website before making a purchase. Moreover, since the typical B2B sales cycle often involves many key players (such as gatekeepers, decision makers , and other folks who have to buy into a purchase), websites are easy, straightforward ways for influencers to share information about your product or service.
For inspiration on how the best B2B websites are built to impress, check out this video:
3. Optimize your digital presence.
Your website needs to be more than informative and engaging, though … it needs to be discoverable. You can do this with on-page SEO and technical SEO tactics. These include everything from image alt-text and meta descriptions (what your visitors can see) to structured data and site speed (what your visitors can’t see). Off-page SEO is also at play here, which refers to external linking strategies and social sharing — SEO tactics that take place off your website.
4. Run PPC campaigns.
Finally, round out your digital presence with pay-per-click (PPC) advertising , which allows you to get your content and brand in front of new audiences via search engines and other advertising platforms. I recommend maximizing your PPC investment by advertising more than your specific products or services — such as your brand personality, blog or social media content, or company tagline.
The best way to see an ROI from your paid ads is by 1) incorporating your buyer persona data and 2) boosting content that they can relate to. For example, it’s highly unlikely a brand new consumer who’s never heard of you is searching for your exact product.
They may be searching for a location-based solution or product feature. To reach the greatest number of potential customers, pay to target relevant categories within your brand vs. promoting your product or services.
B2B Content Marketing
We’ve talked about how B2B customers are focused on expertise, driven by logic, and desire to be educated. What better marketing tool to satisfy these priorities than B2B content marketing ?
Whereas a traditional PR marketing strategy interrupts a consumer’s day-to-day with promotional material, a content marketing strategy adds valuable information and informs the consumer — which is precisely what B2B customers are looking for. Not to mention that content marketing supports SEO efforts, which involves anticipating what your audience is searching for , helping them discover your website and content … and potentially converting them to customers.
It's important to note, content marketing is most effective when you align your content to various stages of the buyer's journey. As Jonathan Franchell, CEO and Founder of Ironpaper . points out: "Effective content in the awareness phase educates the buyer on their pain points."
"A frequent mistake B2B organizations make is educating the buyer on their own company, product, or service. The buyer isn't ready for that; they are just beginning to understand their problem."
Franchell adds, "Additionally, B2B companies should test content. Run a test on an incentive and vary the type of content - use a webinar, an ebook, or a video. Understand what format of content attracts the right types of buyers and measure it down to an individual human level."
Business decision makers prefer to get information from an article than an ad. Knowing this, I’d say you should be putting the same (if not more) resources into your content marketing than your traditional advertising strategy.
Because the B2B buyer’s journey is slightly different than the B2C buyer’s journey (which has shorter sales cycles and fewer decision makers involved), the content you create for your B2B content marketing strategy may vary more than the content you’ve seen as a consumer yourself, as illustrated in the below graphic.
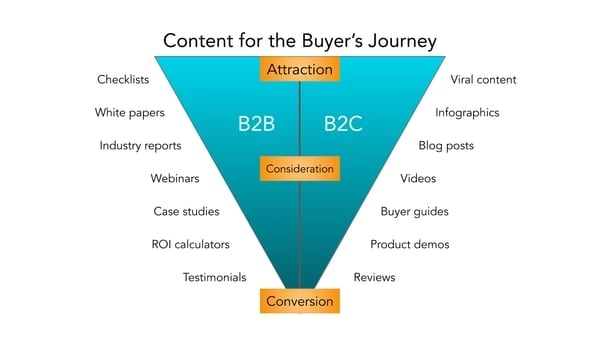
Before you start creating content, though, I recommend creating a business blog . (Don’t worry, growing your blog readership is easier than you think.) Your blog will house all the content you create and serve as a home base for readers to visit and subscribe to.
B2B Social Media Marketing
Believe it or not, B2B buyers and C-Suite executives can and do use social media when making a purchase. That’s right — social media marketing isn’t just for brands targeting individual consumers.
Many B2B companies struggle with social media marketing, though. It can be harder to use social media to connect with business customers, especially because (as we mentioned above) there’s typically a lengthier sales cycle and longer chain of command.
Honestly, B2B social media marketing might not be where you convert the greatest number of leads, and that’s OK. It likely comes into play near the beginning of your customers’ buyer’s journeys.
Social media is a powerful tool for building brand awareness, giving your company an online personality, and humanizing your business — all very powerful factors when it comes to marketing and connecting with potential customers. Like email marketing, social media is also a highly effective channel for sharing your content and enhancing your brand expertise, the latter of which we know B2B customers appreciate.
Overwhelmed by social media? Spend more time connecting with your followers with our time-saving suite of social tools.
While your social media accounts might not convert as frequently as your content or email marketing, they’re just as important. In this case, followers are just as valuable — you never know when they might convert to leads or customers.
👉🏼 HubSpot Tip : Content shared by employee advocates can generate more engagement than content shared by brands. So, involve your employees in your B2B social media marketing strategy. Encourage them to create their own social media channels and share about life at your company. Create a culture account ( like our @HubSpotLife Instagram ) to show what’s going on at work, not just what you’re selling. You never know — this might attract strong talent, too.
B2B Marketing Trends to Watch in 2023 [New Data]
HubSpot's Blog team conducted research to determine the challenges, opportunities, and initiatives that most B2B marketers are focusing on in 2023.
Let's dive in.
1. Generating leads and traffic is the top challenge for marketers.
Top of mind for everyone this coming year is generating more traffic. Marketers surveyed in our 2023 Industry Trends Report cited generating leads and traffic as the top challenge they face, followed by hiring talent and pivoting their marketing strategy to round out the top three answers.
With changes on the horizon and a potential recession looming, it's no surprise 17% of marketers are concerned with pivoting their marketing strategy. Throw in increased competition, and budget constraints and it's safe to say marketers have their work cut out for them in 2023.
2. Marketers anticipate struggling to keep up with trends in 2023.
Marketing trends move fast, so it’s not surprising that marketers we surveyed cited keeping up with trends as a top concern heading into 2023.
Facing increased competition, leveraging CRM systems, and having to pivot marketing strategy rounded out the top five concerns on the horizon for marketers.
3. Social media marketers report 'creating engaging content' will be their number one challenge in 2023.
22% of social media marketers marked "creating engaging content" as the number one challenge they believe they'll face in 2023.
With nearly all businesses utilizing social media vying for customer attention, competition is stiff. Businesses have had to evaluate what makes them stand out above the crowd and how they can better engage and target prospects. To make their best efforts shine, marketers have been utilizing a variety of formats, which we'll dive into next.
4. Marketers leverage video the most.
When it comes to marketing formats, video is the preferred choice with 50% of marketers making it their go-to option. Images came in a close second with 47% of marketers utilizing this format.
Video also provided the most ROI when compared to other formats like images, blog posts, podcasts, and case studies.
It’s popularity isn’t expected to wane anytime soon. Video is expected to grow among new users in 2023 with 1 in 3 planning to leverage this format next year.
5. Influencer marketing was the trend leveraged most this year.
As a result of the pandemic, we've seen an immense shift in how consumers' shop, with the majority now shopping online — and, in particular, purchasing products directly on social media .
It makes sense, then, that B2B marketers want to ensure their products or services are showing up on social channels with influencer partnerships.
Influencer marketing is projected to become a $13.8 billion dollar industry by the end of this year, and it's showing no signs of slowing down.
Most B2B marketers — 71% — planned on investing more in influencer marketing this year, and likely was a wise choice as this avenue will continue to grow in 2023.
However, you'll want to ensure you choose partnerships wisely. While it can be tempting to find influencers with massive audiences, many businesses have seen more success with micro-influencers, so be sure to do your research to determine which influencers have the most authentic connections with your desired audience.
6. Facebook leads in ROI, but other platforms are gaining popularity.
Our 2023 Trends Report found that not only was Facebook the most widely used marketing platform, but also provided marketers the most ROI . Out of the marketers surveyed, 18% stated they plan to invest in Facebook the most, followed by TikTok and YouTube tied with 16%.
While Facebook provides the most ROI, investment in other platforms is on the rise. YouTube is expected to see the most growth in 2023 with marketers with 91% of those using it planning to increase their investment.
Measuring ROI can be easier for some activities compared to others. For instance, it's easy enough to track a social media advertising campaign's ROI if you're tracking sales made from an ad placed on Facebook. Sales is a tangible outcome, and Facebook's Ad Manager enables you to easily track ROI from your efforts.
However, other activities can be more difficult to track. Analyzing which pieces of social or blog content resulted in sales, for instance, can be a more arduous and convoluted process.
To combat this challenge, take a look at How to Calculate ROI in Marketing [Free Excel Templates].
Additionally, consider A/B testing various marketing activities and tracking ROI to determine which platforms traditionally have the biggest ROI for your business. For instance, most marketers find the highest ROI from Facebook — but this could vary for your brand or business needs.
7. The number one goal for marketers in 2023 is increasing revenue.
Understanding your big-picture goals is imperative for creating an effective marketing strategy for 2023 — so it's likely helpful to know what other B2B marketers' plan to focus on next year. .
Looking ahead, B2B marketers’ top priority is to increase revenue and sales, knocking increasing brand awareness down to the third spot from last year.
Top marketing goals:
- Increase revenue
- Improve customer experience
- Increase brand awareness
- Increase engagement
- Improve brand loyalty
Roughly half of B2B marketers reported that 'increasing brand awareness' was their number one goal in 2022.
Brand awareness is critical for fostering trust, long-term loyalty, and brand equity. It makes sense, then, that so many marketers feel it's critical for long-term success.
Additionally, Chief Evangelist at Terminus Sangram Vajre says he predicts that data collection will become a major priority for brands.
As he puts it, "The quality of our campaigns and initiatives will increasingly rely on our CRM, CDP, and 3rd-party sources to help create stylized, targeted, and convertible marketing initiatives. And since CMOs are increasingly held to ROI numbers, we have to up our game."
To consider how you might manage your data in a more efficient, sustainable way, take a look at Everything You Need to Know About Data Management .
Additionally, if you're unsure how you can continue tracking your audience without using third-party cookies, read 7 Marketing Alternatives to Tracking Cookies .
8. This year marketers stopped leveraging podcasts and audio content, while others stopped implementing VR and AR.
As important as it is to learn what marketers plan to do , it's equally vital to learn what they plan not to do. This can help you identify your own guardrails, and ensure you're sticking to the most efficient marketing strategies, rather than wasting time and resources on all of them.
HubSpot's Blog Research found 25% of marketers plan to stop leveraging podcasts and audio content ; followed closely by 23% who plan to stop leveraging VR and AR .
This doesn't mean these activities are inefficient, but it does suggest that some survey respondents found the time, effort, and resources required for each of these efforts wasn't worth it. Ultimately, it depends on your audiences' preferences.
If your audience doesn't enjoy consuming business content on podcast or audio formats, then re-consider investing in these initiatives.
However, audio content isn't going anywhere — so if you haven't already, you might consider testing various audio formats in 2023 to see how they perform with your audience. If you're unsure how to get started, take a look at Everything You Need to Know About Starting a Podcast or Clubhouse vs. Podcasts: Which Should Marketers Use? [Data + Expert Tips] .
9. Philanthropy is best when it's genuine.
Carla Andre-Brown, a Content Marketer at Mailbird told me, "Brand-building activities will look to work with social and environmental causes in a format that is ongoing and builds recognition for both parties. Marketers will need to be especially mindful of the way they present their company, to avoid being accused of having poor intentions."
"For instance," Andre-Brown continues, "a company using the Pride theme each summer without having policies that protect LGBTQ2IA+ employees is called 'Rainbow washing'. To ensure this work is well-received and has an impact, marketers should listen to their communities' suggestions and look for sustainable changes that everyone can benefit from."
A B2B marketing approach that works for one business may not work for another, but that’s not to say we can’t learn something from the pros. Here are eight B2B marketing examples of businesses who did it right.
1. Social Media Marketing: Adobe
TikTok can seem like a difficult platform to stand out as a B2B brand, but some companies have managed to attract thousands — if not millions — of viewers to their videos through high-quality content and an understanding of the app.
Take software company Adobe, which has 262.3K followers and 2 million likes on its TikTok account .
When Adobe first joined the app, the company's second video got over 2 million views. The video asked its audience, Who is a creative TikToker we should know about?, which encouraged high audience engagement.
Adobe succeeds on the app because it creates engaging content specifically catered for TikTok's audience. All Adobe's videos are short, entertaining, and easily digestible.
Take the following example, which has over 370K views and highlights how user @emilesam used Adobe's After Effects edit to create a fighting sequence against himself.
@adobe May the force be with @emilesam in his #AfterEffects edit. ✨ #Adobe #foryoupage #fyp #foryoup ♬ original sound - Adobe
The brand does a good job highlighting its products in a fun, non-promotional way. Both consumers and businesses can see a clear connection between using Adobe's products and finding success on TikTok — which makes this a great example of B2B marketing.
2. Content Marketing: Shopify
Ecommerce company Shopify produces many different types of content resources, such as a blog, business courses, and community events. But one content avenue that helps the brand stand out is its podcast , aptly titled Shopify Masters: The ecommerce business and marketing podcast for ambitious entrepreneurs.
The podcast focuses on inspiration stories from entrepreneurs, and offers practical tips for starting an online business on Shopify. Episode topics range from "Disrupting the Soda Industry with a Healthy Spin" to "How Masks For Dogs Landed a Deal on Shark Tank".
Offering so much valuable, interesting content for free is a fantastic example of effective B2B marketing, which should always provide value before it tries to extract it.
3. Digital Marketing: Mailchimp
Mailchimp's homepage is easy to navigate, clean, and focuses entirely on its customers' pain points.
Consider, for instance, the first large text you see when you click on the page: "Get down to business and grow sales". The smaller text below it reads, "Engage your customers and boost your business with Mailchimp's advanced, yet easy-to-use marketing platform."
The language focuses on the customer, and how Mailchimp can help the customer reach their goal: To grow their businesses.
Additionally, the website offers a banner at the top of the page that enables customers to choose in which language they'd prefer to view the website. Even the company's Products navigation menu includes how the product can "Get Your Business Online" and "Market Your Business".
Ultimately, the company demonstrates how much they value each of their customers by tailoring each piece of content towards its customers' unique challenges.
4. Client Testimonials: Venngage
Venngage took its positive client testimonials and sprinkled them throughout its website. This social proof lets prospects know that you have a track record of reliability, and have delighted previous customers beyond expectation. Not only that, but sharing testimonials can have a big impact on potential consumers in the Consideration and Decision stages .
After all, 98% of consumers read online reviews for local businesses, which is up from 81% in 2019, so using client feedback is a great tool to attract new ones.

Image Source
5. B2B SEO: TravelPerk, Google
A B2B buyer spends 27% of the time in the purchase journey independently researching online, potentially using at least one search engine during the online research. It’s worth the time and money to invest in making sure other businesses can find you with ease.
TravelPerk displays a diverse range of paid search and SEO. An impressive SEO strategy is its use of topic clusters and sub-topics for reaching its target audience. TravelPerk ensures that search engine pages like “business travel expenses” have a paid ad leading to its website, or high-ranking blog content providing information travelers are looking for.
6. Inside Influence Marketing: IBM, Influencer and Employee Advocacy Program
IBM Systems business group has seen the growing importance of employee voice and the rise of employee influencers as a strategy in B2B marketing.
In the words of Ryan Bares , Global Social Programs Lead, he states, “In the B2B marketing world, we’ve all come to understand that buyers trust individual voices more than formal marketing and advertising messages, so finding ways to optimize influence internally is becoming a key area of focus.”

Leveraging employees in your company that have an affinity for the industry, vast knowledge of trending topics and your brand, could be key in building new relationships in the industry.
7. B2B Referral Program: Blackbaud, Blackbaud Champions
Blackbaud offers an incredible B2B referral program that incentivizes current customers to become product advocates — Blackbaud Champions. Champions are encouraged to share their insight into how the implementation process works, what it’s like to work with the team, and how Blackbaud solutions have helped you advance their mission.
“When you share your experiences and expertise and help us spread the word about our products and services, we’ll reward you with benefits only available to Champions. By providing your feedback, participating in activities like reference calls and case studies, and sharing educational content and events on social media, you’ll earn Reward Points in the Blackbaud Champions Hub which you can redeem from the Champions Rewards”
These points are what Champions strive to redeem, as they include incentives like discounts, complimentary passes, gift cards and VIP experiences, and more.

Referral programs are a great way to kindle customer loyalty and have advocates spread the word about your business through the network.
Invest in B2B Marketing and Reach Your Business Customers
Marketing isn’t effective unless you keep your audience in mind, and no other audience is as fickle and critical as business customers. Your marketing should communicate how your business can help theirs, and if it doesn’t, you can redirect your B2B marketing strategies to reach them.
Editor's note: This post was originally published in March 2021 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.

Don't forget to share this post!
Free planning and communication templates align your team for your next product launch.
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
The Businessman Post
B2B Business Models: Exploring Examples, Types & Strategies
Discover what B2B business models are and explore various examples, types, and the benefits they offer in the e-commerce industry. Learn how B2B models can revolutionize the way businesses operate.
In today’s dynamic business landscape, companies are constantly seeking innovative approaches to drive growth and achieve sustainable success.
One such approach is the adoption of B2B (business-to-business) business models, which have gained significant traction in various industries.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of B2B business models, explore examples, types, and their specific applications in e-commerce, and highlight the numerous benefits they offer to organizations.
Table of Contents
- What is B2B Business Models?
The foundation of B2B interactions
The key characteristics of B2B business models
- How B2B models differ from B2C models
B2B Business Models Examples
- Manufacturer-Distributor-Wholesaler model
- Platform-based model
- Subscription-based model
B2B Business Model Types
- Direct sales model
- Marketplace model
- Value-added reseller (VAR) model
B2B Business Model in E-commerce
Leveraging technology for seamless transactions
Enhancing supply chain management through B2B e-commerce
B2B e-commerce platforms and marketplaces
Benefits of B2B Business Model
Streamlined processes and increased efficiency
Expanded market reach and customer base
Improved customer relationships and loyalty
B2B Business Models : Explanation
B2B business models refer to the strategies and frameworks that govern transactions between two or more businesses. Unlike B2C (business-to-consumer) models where the focus is on catering to individual customers, B2B models primarily revolve around fulfilling the unique needs and requirements of other businesses. Let’s delve deeper into the key aspects of B2B business models:
At the core of B2B interactions lies the concept of exchanging goods, services, or information between organizations. These transactions can involve manufacturers, wholesalers, distributors, retailers, or even service providers. B2B models facilitate the flow of products or services throughout the supply chain, ensuring businesses have access to the resources they need to operate efficiently.
B2B business models possess certain characteristics that set them apart from other types of business models:
- Interdependence: B2B transactions are interdependent, relying on the collaboration and cooperation between businesses to meet their respective objectives.
- Long-term relationships: B2B relationships often foster long-term partnerships, as businesses aim to establish trust and reliability with their counterparts.
- Customization: B2B models emphasize tailoring products, services, or solutions to suit the unique requirements of business clients.
How B2B models differ from B2C models ?
While B2B and B2C models share similarities, they differ significantly in their focus and approach:
- Target audience: B2B models target businesses and organizations as their primary customers, whereas B2C models target individual consumers.
- Purchase volume: B2B transactions generally involve larger order volumes, given the business-to-business nature, while B2C transactions often consist of smaller quantities.
- Decision-making process: B2B purchases often require more complex decision-making processes involving multiple stakeholders, compared to B2C purchases, which are typically made by individual consumers.
Let’s explore a few prominent examples of B2B business models that illustrate the diverse approaches organizations can adopt to drive success:
1. Manufacturer-Distributor-Wholesaler model
This traditional B2B model involves manufacturers producing goods and relying on distributors and wholesalers to reach a wide network of retailers. Manufacturers focus on production, while distributors and wholesalers handle logistics and distribution, ensuring products are efficiently delivered to retailers and, ultimately, end customers.
2. Platform-based model
Platform-based B2B models leverage technology to create digital marketplaces where businesses can connect and trade products, services, or information. These platforms facilitate transactions, streamline communication, and provide a conducive environment for businesses to collaborate and grow collectively.
3. Subscription-based model
The subscription-based B2B model offers businesses access to a wide range of products or services for a recurring fee. This model provides convenience, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, allowing businesses to access the resources they need on-demand without large upfront investments.
B2B business models encompass various types, each catering to specific needs and preferences. Let’s explore some of the most common types:
1. Direct sales model
In the direct sales model, businesses engage in direct transactions with their clients, eliminating intermediaries. This approach allows organizations to have more control over the sales process, build stronger relationships with customers, and ensure better alignment with their specific requirements.
2. Marketplace model
Marketplace models provide a platform for multiple businesses to showcase and sell their products or services. These marketplaces act as intermediaries, connecting buyers and sellers, and fostering a competitive environment where businesses can reach a broader audience and expand their market reach.
3. Value-added reseller (VAR) model
The VAR model involves businesses purchasing products or services from manufacturers and adding value to them through customization, bundling, or integration with complementary offerings. Value-added resellers then sell the enhanced products or services to end customers, providing tailored solutions that meet specific business needs.
The rise of e-commerce has significantly impacted B2B transactions, revolutionizing the way businesses operate and interact. Here’s how B2B models have found their place in the realm of e-commerce:
B2B e-commerce leverages technology to streamline transactions between businesses. Through online platforms and portals, companies can browse catalogs, place orders, track shipments, and handle payments more efficiently, enhancing the overall purchasing experience.
B2B e-commerce enables organizations to optimize their supply chain management by automating processes and reducing manual intervention. This leads to improved inventory management, better demand forecasting, and enhanced collaboration between suppliers and buyers.
E-commerce platforms and marketplaces tailored for B2B transactions have emerged, offering businesses a dedicated space to engage in trade. These platforms provide secure environments, robust catalog management systems, and efficient order processing capabilities, enabling businesses to connect and conduct transactions seamlessly.
Implementing a B2B business model can yield numerous benefits for organizations. Let’s explore some of the key advantages:
B2B models often incorporate streamlined processes, optimized supply chain management, and automated transactions. This leads to increased efficiency, reduced operational costs, and improved productivity, allowing businesses to focus on core competencies and deliver exceptional value to their customers.
By adopting B2B models, businesses can expand their market reach beyond traditional boundaries. Collaboration with other businesses, strategic partnerships, and access to diverse networks enable organizations to tap into new
markets, target larger customer segments, and unlock new growth opportunities.
B2B models emphasize building strong relationships with business clients, fostering trust, and delivering exceptional customer experiences. By understanding and addressing specific business needs, organizations can cultivate loyalty, drive customer retention, and benefit from long-term partnerships that provide stability and consistent revenue streams.
What are the 4 types of B2B models?
There are several types of B2B (business-to-business) models that organizations can adopt to facilitate transactions between businesses. Four common types include:
- Direct Sales Model: In this model, businesses engage in direct transactions with their customers without intermediaries. This allows for greater control over the sales process and enables organizations to build stronger relationships with their clients.
- Marketplace Model: Marketplace models provide a digital platform where multiple businesses can connect and conduct transactions. These platforms act as intermediaries, connecting buyers and sellers, and often offer additional services such as payment processing and logistics support.
- Subscription Model: The subscription model involves businesses offering products or services to customers for a recurring fee. This allows businesses to provide ongoing value, build long-term relationships, and generate predictable revenue streams.
- Value-Added Reseller (VAR) Model: In the VAR model, businesses purchase products or services from manufacturers and enhance them by adding value through customization, bundling, or integration with complementary offerings. They then resell the enhanced products or services to end customers.
What are the 7 major B2B business models?
B2B business models vary depending on industry, market dynamics, and specific business objectives. While there are numerous models to consider, here are seven major B2B business models:
- Manufacturer-Distributor-Wholesaler Model: Manufacturers produce goods and rely on distributors and wholesalers to reach a wide network of retailers and end customers.
- Platform-Based Model: Platforms create digital marketplaces where businesses can connect and trade products, services, or information.
- Subscription-Based Model: Businesses offer access to a range of products or services for a recurring fee, providing convenience and flexibility to customers.
- Value-Added Reseller (VAR) Model: Businesses purchase products or services from manufacturers, add value through customization or bundling, and then sell the enhanced offerings to end customers.
- Direct Sales Model: Businesses engage in direct transactions with customers, eliminating intermediaries and allowing for more control over the sales process.
- Franchise Model: Businesses expand their operations by granting franchises to other businesses, allowing them to operate under an established brand and business model.
- Service Provider Model: Businesses offer specialized services to other businesses, catering to their specific needs and requirements.
Which B2B models should we use?
The choice of B2B models depends on various factors, including the nature of your business, target market, industry dynamics, and strategic goals. It’s essential to evaluate each model’s suitability based on your specific circumstances, such as product/service offering, customer preferences, and competitive landscape. Conducting market research, analyzing customer needs, and assessing your organization’s capabilities will help determine the most suitable B2B model for your business.
Is Alibaba a B2B model?
Yes, Alibaba is a well-known B2B model. Alibaba Group operates various online platforms, including Alibaba.com, which serves as a leading global wholesale marketplace connecting businesses. It enables businesses to trade products in bulk, find suppliers, and engage in B2B transactions across different industries.
Is Amazon a B2B?
While Amazon is primarily recognized as a leading B2C (business-to-consumer) e-commerce platform, it also operates a significant B2B segment called Amazon Business. Amazon Business offers a range of products and services tailored specifically for businesses, including bulk purchasing, business pricing, and streamlined procurement processes. It acts as a B2B model, connecting businesses with suppliers and facilitating transactions.
What is B2B delivery example?
B2B delivery refers to the transportation and distribution of goods and services from one business to another. It involves the efficient movement of products between suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, wholesalers, and retailers. An example of B2B delivery is the transportation of raw materials from a supplier to a manufacturing facility, where the materials are used to produce finished goods. Another example is the delivery of products from a wholesaler to a retailer’s store for sale to end customers. B2B delivery plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth flow of goods within the supply chain, enabling businesses to meet the demands of their customers efficiently.
What is B2B sales examples?
B2B sales, or business-to-business sales, involve the selling of products or services from one business to another. Here are a few examples of B2B sales:
- Software Solutions : A software company selling its software products or licenses to other businesses to enhance their operations, such as customer relationship management (CRM) software or project management tools.
- Manufacturing Equipment : A manufacturer selling machinery or equipment to other businesses involved in production processes, such as industrial machinery used in manufacturing plants.
- Consulting Services : A consulting firm offering specialized services, such as financial consulting, marketing strategy consulting, or IT consulting, to assist other businesses in improving their performance and achieving their objectives.
- Office Supplies : A supplier selling office supplies, stationery, and equipment to other businesses, ensuring they have the necessary tools to operate effectively.
- Wholesale Goods : A wholesaler selling bulk quantities of products, such as electronics, clothing, or food items, to retailers who then sell them to end customers.
What is B2B marketing strategy?
B2B marketing strategy refers to the plan and approach that businesses employ to promote their products or services to other businesses. Unlike B2C marketing, which targets individual consumers, B2B marketing focuses on building relationships, delivering value, and addressing the specific needs of business clients. Some key elements of a B2B marketing strategy include:
- Target Audience Identification : Clearly defining the target market and understanding the characteristics, pain points, and preferences of businesses within that market.
- Relationship Building : Establishing and nurturing relationships with key decision-makers and influencers in target businesses through personalized communication, networking, and providing tailored solutions.
- Content Marketing : Creating and distributing valuable and informative content, such as blog posts, whitepapers, case studies, and videos, to educate and engage potential B2B customers.
- Lead Generation : Implementing strategies to attract and convert leads into customers, utilizing tactics such as email marketing, search engine optimization (SEO), social media advertising, and industry-specific events.
- Thought Leadership : Positioning the business as an industry expert through thought leadership initiatives, including publishing authoritative content, participating in industry events as speakers, and engaging in relevant industry forums.
What are the 4 pillars of B2B marketing?
The four pillars of B2B marketing encompass key aspects that contribute to a successful B2B marketing strategy. These pillars are:
- Segmentation : Segmenting the target market based on relevant criteria such as industry, company size, location, and specific needs. This allows for more precise targeting and personalized marketing approaches.
- Targeting : Selecting specific segments or businesses within the market that align with the organization’s objectives and have a higher likelihood of becoming valuable customers.
- Positioning : Developing a unique value proposition and positioning the business as the preferred solution provider within the target market. Effective positioning highlights the organization’s strengths, expertise, and ability to address customer challenges.
- Messaging : Crafting compelling and persuasive messaging that resonates with the target audience. This includes clearly communicating the value and benefits of the products or services, addressing pain points, and differentiating from competitors.
By focusing on these pillars, businesses can develop a robust B2B marketing strategy that effectively reaches and engages their target audience, driving business growth and success.
Q: What are some key elements of successful B2B business models? A: Successful B2B business models often incorporate efficient supply chain management, robust technology infrastructure, effective communication channels, and a customer-centric approach.
Q: How can B2B models drive innovation and collaboration? A: B2B models encourage collaboration between businesses, facilitating knowledge-sharing, resource pooling, and joint innovation efforts that lead to the development of new products, services, or solutions.
Q: Can B2B business models be applied to service-oriented industries? A: Absolutely! B2B models are not limited to product-based industries. Service-oriented businesses can also adopt B2B models by catering to the unique needs of other businesses and providing tailored services.
Q: Are B2B e-commerce platforms secure for conducting transactions? A: B2B e-commerce platforms prioritize security and implement robust measures to protect sensitive data, ensuring secure transactions and maintaining confidentiality.
Q: How do B2B models contribute to sustainability and environmental responsibility? A: B2B models enable businesses to optimize their supply chains, reduce waste, and implement sustainable practices. By streamlining processes and reducing resource consumption, B2B models contribute to environmental responsibility.
Q: Can B2B business models be combined with B2C models? A: Yes, many businesses adopt hybrid models, combining B2B and B2C approaches to cater to both business and individual customers, providing them with a seamless and integrated experience.
B2B business models have emerged as a powerful strategy for businesses to navigate the complex and ever-evolving landscape of commerce. By focusing on meeting the unique needs of other businesses, B2B models foster collaboration, drive innovation, and unlock new avenues for growth. In the e-commerce realm, B2B models have transformed the way organizations conduct transactions, optimize supply chains, and enhance customer relationships. By embracing B2B business models, companies can position themselves for success, expand their market reach, and build long-lasting partnerships in the dynamic world of business.
Similar Posts
{cardekho business model} unlocking success in the automotive industry.
In the fast-paced world of online automotive platforms, Cardekho has emerged as a dominant player. With its innovative business model and customer-centric approach, Cardekho has revolutionized the way people buy and sell cars. In this article, we will delve into the various aspects of Cardekho’s business model, explore how they make money, examine their competition,…
Boat Business Model: Navigating Success in the Marine Industry
Introduction In today’s fast-paced world, businesses are constantly evolving and adapting to meet the needs of their consumers. One such industry that has experienced significant growth and innovation is the marine industry. Boat, a leading company in this sector, has revolutionized the way people engage with boating and water activities. This article explores the Boat…
Shaadi.com Business Model: Matchmaking Industry [Secrets]
Shaadi.com, a pioneer in the online matchmaking industry, has transformed the way people find their life partners. With its innovative business model and user-friendly platform, Shaadi.com has successfully created a global community of individuals seeking meaningful relationships. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of Shaadi.com, exploring its business model, revenue streams,…
{Explained} Cloud Kitchen Business Models & Strategies [Example]
Cloud kitchen business models have revolutionized the food industry, offering a cost-effective and flexible solution for entrepreneurs to enter the market. Also known as virtual kitchens, ghost kitchens, or dark kitchens, cloud kitchens operate solely for food delivery without any dine-in facilities. This article explores the various aspects of cloud kitchen business models, including examples,…
Indiamart Business Model: Revolutionizing B2B Commerce in India
SEO meta-description: Explore the comprehensive Indiamart Business Model, including how Indiamart makes money, its history, business model canvas, case study, competitors, and SWOT analysis. Discover the innovative approach that has made Indiamart a dominant player in the B2B marketplace in India. Introduction In the fast-paced world of e-commerce, Indiamart has emerged as a trailblazer, transforming…
Uber Business Model: Revolutionizing the Transportation Industry
Introduction In today’s fast-paced world, disruptive business models have reshaped various industries. One such example is Uber, a ride-hailing service that has revolutionized the transportation industry. This article explores the Uber business model, its disruptive nature, how Uber makes money, a brief history of the company, the Uber Business Model Canvas, a case study on…
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
The new B2B growth equation
After two years of nearly nonstop business disruption, B2B companies have finally flexed to meet their customers’ omnichannel expectations. Or so they think. McKinsey’s most recent global B2B Pulse reveals that B2B companies have reached equilibrium in their omnichannel capabilities—just in time for customers to disrupt that balance again.
Our research, which just surveyed close to 3,500 decision makers in 12 markets (and over 21,000 since 2016), found that what customers want from omnichannel is “more”—more channels, more convenience, and a more personalized experience. And if they don’t get what they’re looking for, they’ll take their business elsewhere.
The results are a wake-up call. B2B companies that assume they’ve cleared the omnichannel bar in sales and marketing will need to think again. Among the headlines:
- Omnichannel is a path to share growth. The more channels a sales organization deploys, the bigger the market share gains.
- There are no exceptions. All B2B customers prefer omnichannel, no matter their industry, country, size, or customer relationship stage.
- B2B loyalty is up for grabs. Customers are more willing than ever to switch suppliers to gain exceptional omnichannel experiences.
- Make your numbers. The new bar for omnichannel excellence is ten or more channels over three engagement modes (in-person, remote, and self-service), delivered 24/7.
- Master the five “must dos.” Customers are resoundingly clear on the five capabilities they most want from omnichannel—and they want all of them, from performance guarantees to real-time customer service.
But good news is buried in the more than 300,000 data points we’ve gathered in our latest B2B Pulse. If keeping up with customers’ omnichannel expectations has felt like a game of two steps forward, one step backward, B2B companies now have a once-in-a-generation opportunity to shift share meaningfully—through greater orchestration, integration, and personalization.
The great rebalancing: From channel spikes to omnichannel equilibrium
Customers have been clamoring for omnichannel sales for years, and our research shows that more B2B companies are getting the message. Gone are the pandemic-related swings that led some B2B companies to go all in on e-commerce or sharply revert to field sales after lockdowns ended. Instead, B2B companies are beginning to provide what customers have long wanted: the right balance across many channels.
And customers are responding. A major finding from our global B2B Pulse is that the “rule of thirds” has become entrenched. Given the choice of traditional (for example, in-person), remote (for example, video conference or phone) and self-service (for example, e-commerce) interactions, buyers globally have shown they want them all—and in equal measure throughout the purchasing journey (Exhibit 1).
We’ve made a commitment to our customers that they can interact with us any way they want—whether that’s via fax, calling a customer support representative, or trading online with us. Chris Breslin, president, Farnell Global and Avnet Digital
Rebalancing works: Omnichannel is more effective than traditional sales models alone
As more companies enable face-to-face, remote, and e-commerce interactions, satisfaction with the sales model has grown exponentially. More than 90 percent of B2B companies say their go-to-market model is just as or more effective than before the pandemic began. And 31 percent believe their model is “much more” effective at reaching and serving customers, compared with nine percent who said the same two years ago—a 3x difference (Exhibit 2).
From the sellers’ perspective, omnichannel is an “omni” opportunity that makes their work easier and enables greater sales growth. And suppliers say they are just as bullish prospecting in an omnichannel ecosystem as they are engaging with existing customers.
The power of true omnichannel is understanding all the channels our customers use, and how they want to use them, throughout their entire journey. If you don’t understand what that journey is, you can’t provide the right information at the right time. Victoria Morrissey, chief marketing officer, Ferguson Enterprises
Outliers prove the rule of thirds works
Break the rule of thirds, and customers won’t be the only unhappy ones; sellers will be too. Despite noting some improvement in go-to-market results over the past two years, respondents at B2B companies in France and Japan are far less likely than their peers in other markets to say they are pleased with their sales model performance. In fact, 14 percent of respondents from France say their models are now “less effective” than they were before the pandemic began (Exhibit 3). Notably, companies in both markets tend to lean more toward traditional sales models and to prefer in-person engagement.
There is no such thing as stasis: Omnichannel is now a ten-channel world
Five years ago, being omnichannel meant offering four or five channels. Now our data shows that customers want—and expect—to engage seamlessly across ten or more (Exhibit 4). And the businesses that have been quick to meet that demand have profited: 72 percent of B2B companies that sell via seven or more channels grew their market share (Exhibit 5).
As customers have transitioned from predominantly face-to-face meetings to interacting more virtually, we’ve adapted our engagement model. We are prioritizing more targeted virtual platforms to share scientific capabilities and build credibility around the work that we do, while optimizing continued opportunities for live engagement where possible. Gina Mullane, chief marketing officer, Charles River Laboratories
Many of the channels customers are clamoring for have digital roots, with video, chat, and e-commerce all seeing much greater customer adoption. For example, mobile apps first appeared on the list of most-used channels in 2019.
Mobile has been a huge enabler of these heightened expectations, largely replacing the customer service agent of the past. There shouldn’t be a limit to what types of transactions can be done on your phone. Tom House, chief technology officer, Noble
B2B companies that are eager to test and refine new capabilities, especially digital ones, should look for early-adopter markets. Customers in India, for example, now use an average of 11 channels when moving through their purchasing journey. And in Brazil, nearly one-third of B2B customers were using ten or more channels as far back as 2019.
The five new must-dos to retain customer loyalty
It’s not enough for B2B companies to meet this moment; they need to prepare for the next one: delivering consistent, exceptional experiences across the omnichannel ecosystem.
The majority of B2B customers globally say they will actively look for another supplier if five core needs are unmet when engaging with suppliers. Nearly 80 percent of B2B customers say that a performance guarantee is critical for brand loyalty, including a full refund if the product or service fails to reach the agreed-upon performance level. Other must-dos include showing product availability online, enabling purchases over any channel, providing real-time customer service, and offering a consistent experience as buyers toggle between channels (Exhibit 6). And B2B customers who want any one of these options are 80 percent to 90 percent likely to want the other four!
Our B2B Pulse also revealed areas that B2Bs should deemphasize. When asked to rate loyalty drivers, customers globally put rewards programs and 3-D/virtual product demos at the bottom of their list.
Next on the list: Marketplaces are the next gen for the next-gen leaders
Market-share leaders are investing in marketplaces while also improving the quality of their branded websites. Nearly three-quarters (72 percent) of companies that built their own marketplace experienced market-share growth over the past two years. Among those that did not build a marketplace, only 42 percent of companies saw share growth—a difference of 1.7x (Exhibit 7).
Branded sites behind paywalls are also a key focus: 57 percent of B2B decision makers say they are most comfortable making online transactions on a supplier website that is behind a paywall.

Busting the five biggest B2B e-commerce myths
To win in the new omnichannel world, orchestrate, integrate, and personalize.
Rather than continually catching up to their customers’ omnichannel demands, leading B2B companies can anticipate where that curve is headed and get there ahead of the pack, which will improve customer value and opportunity for market share growth. Here’s how.
1. Become journey orchestrators
B2B decision makers are omnichannel customers in both a macro and micro sense. They use multiple channels across the purchasing journey and within every buying stage of that journey (Exhibit 8). And while some buyers will gravitate toward one-on-one interactions for complex and high-value deals, many are comfortable using digital self-serve for major purchases.
To meet these expectations, sales professionals need to become “journey orchestrators,” guiding customers to the channels that, according to their buyer intelligence, are most helpful to specific audiences and purchasing stages. Also, suppliers may need to shift their online product mix and launch new pricing processes to streamline quoting and approvals for large-value purchases.
2. Integrate, integrate, integrate
Agility is the key, and a hybrid sales model is a natural enabler, since it is more than one channel by definition and integrated by design. Hybrid sellers come into their roles ready to serve customers the way they want to be served, seamlessly across channels, resulting in faster market-share growth, and less channel conflict (Exhibit 9, part 1). Roughly 40 percent of organizations added hybrid sellers to their ranks over the past two years, and this role is set to become the second most prominent B2B sales role over the next three years (Exhibit 9, part 2).
Being agile has elevated marketing’s ability to translate the sales message better. They’re closer to what the customer needs are and better equipped to create tools and materials that resonate with them. For IT, agility means we integrate seamlessly with marketing, sales and operations, with direct connections to customers, to create digital capabilities that bring together disparate data and create seamless experiences, regardless of the channel. Mark Mintz, chief information officer, Charles River Laboratories
3. Personalize everything
Tailored outreach needs to become the de facto way of engaging across all channels. Providing customers with intuitive interfaces, warm transitions across channels, and speed, transparency and expertise have become major market differentiators.
One of the biggest shifts we’ve seen in how customers interact with companies is how quickly the bar has been raised. There is greater demand to instantly know who they are, what they want, and how they can get the product/service they’re interested in. Tom House, chief technology officer, Noble
Customers don’t want to give up face-to-face visits altogether: 68 percent see those visits as a sign of how much a supplier values a relationship. But in-person is not a check-the-box path to personalization. Customers everywhere—including outlier markets France and Japan—describe suppliers as “too frantic” about trying to meet in person. Globally, 61 percent of buyers say they can get as much value from meeting suppliers over video conference as they can from in-person visits. And in China, India, and the United States, that number rises to a staggering 72 percent.
Tailoring interactions to markets of one requires deeper prowess with data and analytics. While that takes investment, the payoff can be significant. The more adept an organization becomes at personalization, the greater the share gains (Exhibit 10).
A one-size service offering doesn’t fit everything. We’ll use tools, like machine learning or AI, to mine our own data to help personalize offerings to the different types of customers we serve. For example, if a customer searches for something on our site, we can then serve up related content to them the next time they return. Chris Breslin, president, Farnell Global and Avnet Digital
Customers are willing to spend more remotely
One in five B2B decision makers are now willing to spend between $500,000 and $5 million on a single interaction on remote or self-service channels. That’s a leap from the 16 percent who said the same earlier in 2021 (Exhibit 11). In addition, seven percent of buyers are willing to complete transactions valued at more than $5 million fully online.
Comfort with spending big over digital channels is particularly robust in China and the United States, where close to eight in ten buyers say they’re willing to spend at least $50,000 through digital channels. And roughly 20 percent of customers in China, India, and the United States are open to spending $1 million or more on fully online or remote transactions.
Conversely, where the rule of thirds is weak or broken, buyers are less comfortable making big-ticket purchases online. Only about 36 percent of Japanese buyers and 44 percent of French buyers say they are willing to spend more than $50,000 through digital channels.
The message from our global B2B Pulse is resounding. To secure customer loyalty—and the potential of two-times-greater share gains—B2B companies must make omnichannel a cornerstone of their value proposition and selling model. Their profitable growth and competitive standing depend upon it.
Arun Arora is a senior partner in McKinsey’s Paris office; Liz Harrison is a partner in the Charlotte office and global leader of McKinsey’s B2B Pulse; Candace Lun Plotkin and Jennifer Stanley are partners in the Boston office; and Max Magni is a senior partner in the New Jersey office.
The authors would like to thank David Greenawalt, Kate Piwonski, and Danielle Taylor for contributions to this article.
Explore a career with us
Business to Business (B2B) – Definition, Types & Examples
Table of Contents
What is Business to Business?
Business to business or B2B is a business model when a company sells its products and services to another company’s customer for further processing and then reselling it. In simple words, one business sells its product/service to another business. The reason B2B is different from business to customer (B2C), where a business sells its product/service directly to the customer who consumer.
Characteristics of Business-to-Business
Multiple decision-makers.
Since business to business usually happens in the supply chain, where one company supplies products and services to the other company. That relationship among companies tends to last for years. Therefore, companies in B2B don’t make their decision in haste. They follow the standard protocol and proper documentation, visitation, evaluation, and inspection of products, negotiation, and contract signing.
When everyone agrees like visiting officer, evaluation and inspection officer, and the management checkmark their concerned lists, and then they sign the contract.
Longer Decision Cycle
As we know that there are multiple decision-makers are involved, and they have to perform their duties. Sometimes it takes months and years to close the deal.
Customer-Specific Discounts
Since the nature of the relationship between business to business is long term, and so many stakeholders are involved. Sometimes, only one full-time customer is sufficient for the companies. Companies want the B2B relationship to work for a longer time because it is good for both of them. Therefore, they give special discounts and rates to their business customers.
Conflict with Direct Sales Channels
When we talk about direct sales to the customers or B2C type, then it involves a lot of issues. The relation between the business and the customer is limited, short terms, and uncertain. If the customer doesn’t like the product, price, or color, then he would move on to the store. B2B relationship is free of such conflicts.
International Markets
B2B is not confined to the geographical borderlines. Companies are doing business globally, both in physically and digitally as well. Oil and gas is a very good example of it. How governments and companies work with one another.
Business to customer (B2C) is where businesses directly sell their products and services to the ultimate consumer. In B2B, businesses sell their product/service to the other business for further processing and then reselling.
The difference is that customers consume the product in the B2C, and they consume, add value, and resell the product/service in B2B.
Types of B2B Models
There are many types of business that uses the B2B model like human resource management, salary payroll, taxes, construction companies, research and developments, marketing, call center, advertisements, web development, and design. You can find other businesses that use the B2B eCommerce and what category of product or service they deal through the internet. Here are some of the following types of B2B;
Customer-Centric Model
The customer-centric model is where the company prefers to establish a long term profitable relationship with the customers even after the sale. The value of the customer remains the same; it doesn’t change after the transaction. When customers are the main focus of the business, then they would have a great influence over the branding and other operations of the company.
Amazon and Flipkart are the two major examples of e-commerce businesses, and they follow the customer-centric model. It took them years to develop reliable and trustworthy relations with their customers, and they are also loyal to their brand.
Buyer Centric Model
Buyer centric is a type of model where different companies set higher purchase prices for buyers. Then the marketers and sellers of different companies approach buyers with different offers and packages, that how their quotation would serve them better. In the end, the buyer would compare all the quotes and offers, and choose one of the offers most relevant to his budget.
Walmart is the best example of the buyer-centric model because it has a shopping mall across the world. Every branch of Walmart has different and multiple suppliers. However, different suppliers approach the company and bid, and the best bidder becomes the supplier of the company.
Intermediary Centric Model
Intermediary centric is a B2B type of model where buyers and sellers get together at a common shared platform to complete the transaction. It establishes a shared common platform to attract buyers and sellers. At every complete transaction, intermediary would get its share of the commission. Customers can’t check out all the products in the digital market. But this intermediary provided platform is a great place to check out all the products.
OLX and eBay are two major examples of such intermediary eCommerce platforms where buyer and seller meet, check out the product/service being offered. Earning of the platform is either through commission after a successful transaction or through advertisement.
The Direct Connection B2B Model
The direct connection is also a type of B2B model where the company is directly connected to all of the partners and stakeholders for sharing and transferring of all the electronic documents.
In simple words, a third-party IT organization is connected to your business, and it would manage all the business operations of your company like mapping, tech support, translation, and tracking of all the documents. Once your platform starts getting bigger, managing partners and stakeholders would become the top priority to manage their communication and resolve their issues.
Network B2B Model
Network B2B model is when your direct model has multiple problems and complexities, then the network jumps in and resolves it. This type of business model used to be functioning before the arrival of the internet. By using this model, you can create a single connection to the service providers to use the protocol like FTP over VPN, RosettaNet, FTPS, AS2, and SFTP.
Hybrid B2B Model
Hybrid B2B model is a combination of two models; direct connection and network B2B model. The purpose of this model is to save the transaction fee of a service provider, and the company would connect with the maximum transaction client. When you use this model, then your company would have the advantage of the service provider, and to work with many low volume trading partners.
Managed B2B Model
Managed B2B model is when your company outsource or hire an outside service provider to manage its entire B2B processes. The most obvious advantage of outsourcing is lower cost and simplicity. This model works only if the service provider of your company shares documents through the ERP (enterprise resource planning) system.
Managed B2B model would perform activities like translation, mapping, tech support, document tracking, and data center operations.
Advantages of Business to Business Model
Some of the advantages of the business to business model are given below;
Unlike business to customer (B2C) model where businesses and customers keep on their relations from one buyer or seller to the next buyer or seller. On the other hand, B2B (between buyer and seller) is a very stable relationship that goes for years.
Before signing any contract in the B2B model, buyers and sellers both go at a length to plan their budget, revenues, and rates. When both parties close the deal, then they rely on one another in terms of supplies and payments. Business to business supplier market is not big and limited parties are loyal to one another.
Fewer Expenses
In a business to business relationship, both parties spend a lot of time planning and working on the details. Therefore, it leaves no room for mistakes and errors. As a result, everything works out as plan without costing any extra expenses.
Easier Calculation
Most importantly, you can buy the product or service through online auction at a much lower price. Therefore, it becomes so easier for them to calculate the sales because the figures are based on the facts.
Disadvantages of Business to Business Model
Fewer customers.
In the B2B market, you won’t find a plethora of buyers and sellers just like you see it in the B2C market. Although the market is small with fewer buyers and sellers, but their orders are big.
Time Consuming
Since the orders of business to business clients are big, and their relations are of a long term in nature. But the process of finding and building with B2B clients is so lengthy that you can’t go and buy products and services just like in the B2C market.
Formalities
It also involves a lot of formalities like documentation, quotations, negotiations, and meetings. Sometimes, you have to bribe and make under the table deals in order to sign the contracts.
Examples of B2B E-commerce Companies
Alibaba is a Chinese world-leading e-commerce, retail, internet and technology company. It has supplying partners worldwide. Those suppliers are business companies, and Alibaba is also an e-commerce company. Therefore, it’s a perfect example of a B2B model.
Slack is a windows tool that brings multiple separate tools working and functioning at a singles platform. For communication, and sharing of files and documents, many B2B companies use slack.
Skype is an online tool and application which provides the service of free audio/video calls, text messaging, and file sharing. Many businesses use Skype for communication and file sharing.
WeWork is a world-leading co-work spacing company. Many businesses rent the workspaces of WeWork to run their daily business operations. WeWork is also a very good example of a B2B model.
After understanding the definition, types, characteristics, and advantages/disadvantages of business-to-business model. You must have got a clear idea that how it works and it differs from the business to the customer model.
If you want to start a business; B2C or B2B, both are good. Knowing their categories, types and their functionality would help you to make a better decision.
About The Author
Ahsan Ali Shaw

What is B2B or business-to-business? Definition and examples
B2B , which stands for business-to-business , is a way of doing commerce, specifically companies doing business with other companies. It refers to the exchange of products or services among companies. We can use this term to describe both traditional and online commerce. However, we more commonly use it for e-commerce.
E-commerce is a business model that focuses on doing business online , i.e., on the Internet. ‘E-commerce’ stands for ‘electronic commerce.’
The National Association of Sales Professionals has the following definition of the term :
“B2B is short for business-to-business. It refers to companies – or salespeople – who sell products chiefly to other businesses, rather than selling them to consumers.”
“B2B sales are often more complex than B2C (business to consumer) sales.”
It is important to remember that in its short form – B2B – the number ‘ 2 ‘ represents the word ‘ to ‘ in ‘business- to -business.’ Therefore, when you write the long form, don’t write it as ‘business- two -business.’ That is wrong!
B2B takes longer
When a company focuses on a B2B model, their marketing targets other companies. Therefore, the sales process may be longer and more intricate than a business-to-consumer model, i.e., B2C model .
It also takes much longer than in a C2C model. C2C stands for consumer-to-consumer .
To get a sale, the seller must usually deal with multiple departments within the target company.

Some companies sell both B2B and B2C, i.e., business-to-business and business-to-consumer. In this image, Avis is a car rental company, a business customer. The woman who just bought a car, on the other hand, is an individual consumer.
Decision-making process
The decision-making process is often more complicated when companies purchase something. Perhaps the idea to buy goes first, for example, from the sales agent to the sales manager.
The sales manager may subsequently have to get the OK from the financial or legal department. Perhaps one of the directors also has to sign if it is a large order.
Unlike other business models, such as B2C, i.e., business-to-consumer, in B2B, companies are often selling raw materials.
The seller may also be selling services or parts that the customers needs from manufacturers.
For example, a car manufacturer will depend on a parts company to complete the assembly of a car. It may also need to purchase the software to automatize the assembly process.
B2B e-commerce
B2B e-commerce has been increasing ever since the advent of the internet.
More companies are taking their business to online platforms. They are partly doing so because of the benefits and also because they have no choice.
E-commerce is no longer an option for most businesses; it is now a basic requirement if they want to survive.
B2B categories
The top categories of B2B commerce are:
Web development
More and more companies have decided to migrate to the digital world. Subsequently, more companies are looking for other businesses that specialize in web development, web design, SEO, and even AI-driven content personalization.
They are also looking for businesses that specialize in site building software and databases.
Supply and procurement exchanges
Companies pay to have access to a site or portal that has information on different supplies.
They also pay to have access to price listings, forums about a specific industry, and other features.
It’s now becoming more common for companies to use blockchain-backed supply chains to ensure transparency, security, and efficiency.
Cloud Services & Infrastructure
Modern B2B commerce heavily relies on cloud infrastructure providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform, which offer scalable solutions and heightened cybersecurity.
Intermediaries
These are sites that gather and provide specialized data on certain industries or commerce to companies.
Usually, this type of company acts as an intermediary between companies that provide the information and companies that get it.
A company can focus on just one model, or it can mix its strategy, i.e., B2C, B2G, etc. It all depends on the needs of the market and what it is selling. B2G means b usiness- to – g overnment .
B2B example
One example of a business that focuses on the B2B model is International Business Machines Corporation or IBM . The technology multinational giant offers a range of services to companies, such as cloud computing for enterprises.
With cloud computing , remote computers rather than the user’s hard drive store files and other data.
Organizations can add this service to their internal structure. They then have data available for their employees in real time 24/7.
IBM can also create an extranet service that the customer can access at all times.
It’s important to note that while IBM remains a stalwart in the B2B segment, there are also many other businesses, such as Salesforce with its CRM solutions or AWS with its range of cloud services.
Video – B2B Marketing Strategies
In the video embedded below, Gary Vaynerchuk, co-founder of the restaurant reservation software company Resy, shares some leading B2B marketing strategies:
B2B Marketing in the Age of AI & Automation
AI and automation have become increasingly important for B2B marketers. There are many ways that businesses can now leverage toolkits to create better marketing campaigns.
How do AI toolkits offer create better campaigns?
Put simply, we want our marketing campaigns to identify prospects who are worth our time and effort; those most likely to buy something. Modern AI toolkits can pinpoint prospects who are the most likely to buy through the use of predictive analysis, intent analysis, and lead scoring.
Businesses that adapt and make use of these advanced tools can gain a significant competitive edge – as long as the tools are properly used.
Share this:
- Renewable Energy
- Artificial Intelligence
- 3D Printing
- Financial Glossary
- Marketplaces
- In-person (POS)
- Advertising
- Connect domain
- Integrations
- Marketing channels
- Acquire customers
- Retain customers
- Business models
- Store customization
- Staff Accounts
- Ecwid Igniter
- Help Center
- Ecwid Academy
- Case studies
- Ecwid Insights
Set up an online store in minutes to sell on a website, social media, or marketplaces.
- What is B2B? Everything About Business to Business Model
The most common business models you’ve probably heard of are B2B, B2C, subscriptions, and on-demand. These business models are unique in their ways and serve different audiences.
This post will focus on the B2B definition and every facet of this business model. So, what does B2B mean? Keep reading to find out!
How to sell online Tips from e-commerce experts for small business owners and aspiring entrepreneurs. Subscribe Please enter a valid email address I consent to receive Ecwid Newsletter. I can unsubscribe anytime.
Business-to-Business (B2B) Meaning
B2B means business-to-business . It’s one form of a transaction or business model that occurs between two companies. The consumer is not involved in a B2B transaction.
Unlike consumer purchases, B2B transactions are more complicated than a simple purchase in an online store. They involve larger order quantities, negotiations, and the shipping and delivering large amounts of goods.
B2B companies keep many markets moving forward. Think about the last time you purchased an item from a major retailer. Regardless of what the product was, it likely came from a manufacturer who sold it to a supplier. This is a typical example of the B2B business model.
Even though the consumer is not involved in the B2B sale, it directly affects their shopping habits and what is made available to purchase in stores.
B2B Examples
If you find yourself Googling, “What is a B2B company?”Here are some common examples of B2B companies in various industries.
- Wholesalers and manufacturers of goods
- Wholesalers and retailers
- SaaS companies selling a service to companies
- Marketing agencies that help small businesses grow
- Payment processing companies sell their services to retailers
- Telecom service providers for businesses
Who do B2B Companies Sell To?
Business-to-business companies sell to a variety of companies and industries, including:
- Private businesses
- Wholesalers
- B2C companies
- Government groups and public entities
- Direct-to-consumer organizations
Defining B2B Sales
This section answers the question, ‘What is B2B sales?’. Let’s jump in!
In 2022 alone, B2B ecommerce revenue reached $2 trillion — the opportunities in this market are substantial.
Traditionally, B2B sales entail much higher transaction amounts, educated buyers (as they work for relevant companies), a lengthy approval process , and a much longer sales cycle.
Business-to-Business Service Challenges
Like any business model, B2B services have their own challenges and drawbacks specific to the market and customer base they’re serving. This includes:
Cash flow management
Customer loyalty, digital presence.
- Sales process
- Sales cycle
Working with other businesses means managing invoices, late payments, and various client payment windows. Some B2B companies bill in 30-day cycles, while others use 60 or 90-day invoice cycles.
Dealing with conflicts related to delayed client payments can be a significant deterrent for B2B companies. Without cash flow, purchasing inventory, paying bills, paying employees, and dealing with various business expenses is challenging.
Fostering customer loyalty takes time, energy, and consistency in any business model.
Since many B2B companies are subscription-based or offer a platform, customer loyalty is heavily influenced by the performance of these services. A business selling a platform must provide professional services, maintenance, and upgrades to ensure customer efficiency.
As B2B companies showcase their commitment to customer satisfaction , customer loyalty builds over time. Whether they’re selling a service, a platform, or products, improving the functionality and quality is mission-critical for customer retention.
Establishing a solid digital presence online is essential for B2B companies to market themselves and sell products or services.
From a captivating website to interactive social media platforms, existing online is no longer an option for businesses — it’s a requirement. If you want to compete in the space, you must participate in the digital revolution.
Any B2B company should maintain a website with information on their products or services so potential customers can find them. Using best practices in SEO (search engine optimization), businesses can increase their search engine ranking amongst their potential customers.
Did you know that 95% of B2B businesses utilize social media? They advertise products, interact with customers, and perform lead generation. This shows how valuable a digital marketing strategy is for B2B companies, regardless of their industry or market.
Organized sales process
The sales process can be long and unorganized for many B2B companies. When relying on multiple people within an organization to make a decision, the process is daunting.
B2B sales reps can combat this long sales process by doing their research to find companies who are genuinely in need of their service or solution. B2B buyers are about 57% into their decision-making process when they engage with a sales team about a product, service, or platform. This leaves quite a bit of opportunity to close the deal, but the sales team must be strategic with a tailored solution for the company’s unique pain points.
The sales process is best organized into the following strategic steps:
- Researching potential customers, competitor offerings, and market trends
- Prospecting leads for sales pitches, demos, and exploratory calls
- Assessing target customers to determine if your solution provides a fix
- Pitching your service or products in a tailored way
- Winning the sale
- Following up with add-ons and other features of the product
- Maintaining the relationship with the customer for referrals and additional business opportunities
How Does a B2B Transaction Work?
Three main types of B2B sales and transactions occur, including the following.
1. Supply chain sales
B2B companies sell supplies or equipment to other companies, like wholesalers or retailers. The purchase involves multiple stakeholders rather than a consumer purchasing one unit at a time.
The buying process may require more authorization, and multiple people are involved. Supply chain sales include medical or office supplies, equipment, clothing, and more.
2. Wholesale
Wholesale suppliers sell products like food and beverages to restaurants and stores at low prices. These companies turn around and sell the products directly to the consumer at a marked-up price.
3. Service/Platform sales
From platforms that send SMS messages to payroll software and task management, B2B platforms and services are abundant for various companies. These purchases involve several organizational people, including a Sales manager, CTO, and even the CEO.
B2B vs. B2C: Key Differences
Now that you know the B2B sales meaning, it’s time to explore the key differences between B2B and B2C.
The primary difference between B2B and B2C is the customer. Where B2B serves other businesses, B2C involves businesses selling directly to consumers.
B2C sales typically include lower prices (i.e., when you shop at a retailer like Target), and the buying decisions come strictly from the consumer. Some B2C examples include:
- Buying a custom t-shirt through an ecommerce store
- Purchasing a smartphone from a telecom provider like Verizon or AT&T
- Buying goods from a farmer’s market
There are endless examples of B2C interactions, but the big picture is simple. Any time you as an individual purchase goods or services directly from a store or company is considered B2C .
Other key differences between B2B and B2C include:
Salesperson involvement
With B2B sales, at least one (if not more) salesperson is involved in the process. Whether vetting new technology or researching a new product to add to your inventory, B2B requires more involvement on both sides.
B2C, on the other hand, doesn’t always require the help of a salesperson. You don’t need the influence of a salesperson when picking up groceries for the week. You may need help when shopping at a clothing store but already intend to buy, so a salesperson isn’t as necessary.
Transaction value
Some B2C purchases, like buying a home, a vehicle, or luxury goods like diamonds, have high transaction values. For the most part, the transaction value of consumer purchases is much lower when compared to B2B purchases.
Payment methods
In a B2C transaction , the consumer pays the business upfront to purchase goods. In a B2B transaction, the sales and payment processes are much more drawn out. Potential customers often use the product or service on a trial basis to test the features and decide whether or not it’s what their business is looking for.
Final Thoughts on B2B
Business-to-business transactions keep the economy moving and help many industries and markets thrive. Without B2B, many products and goods we’re accustomed to having would not exist or be accessible for the everyday consumer to buy.
For more information on B2B, including our highly coveted marketing strategies , explore the Ecwid ecommerce blog. We share tons of resources, relevant content, and How-To’s to ensure your business can thrive, no matter what you’re selling and where.
Upgrade your B2B business with an ecommerce solution that helps Learn more
- B2B Marketing Guide: Strategy, Goals, Tactics
- What is B2B Ecommerce? Platforms, Companies, Trends
- B2B Software: Choosing the Right Software for B2B
- B2B Websites: Best Practices with Examples
Sell online
With Ecwid Ecommerce, you can easily sell anywhere, to anyone — across the internet and around the world.
About the author
Max has been working in the ecommerce industry for the last six years helping brands to establish and level-up content marketing and SEO. Despite that, he has experience with entrepreneurship. He is a fiction writer in his free time.
Ecommerce that has your back
Your ecommerce dreams start here, more resources.
SELL ONLINE
- Sell Everywhere
- Sell on Website
- Sell on Social Media
- Sell on Instagram
- Sell on TikTok
- Sell on Facebook
- Sell on Google
- Sell on Marketplaces
- Sell on WhatsApp
- Sell on Pinterest
- Sell on Snapchat
- Sell on YouTube
- Sell on Mobile (ShopApp)
BUSINESS SOLUTIONS
- Dropshipping
- Local Business
- Restaurants
- Health and beauty
- Cross-border commerce
- Headless commerce
TECHNOLOGY SOLUTIONS
- Squarespace
- Expression engine
- Static websites
FOR INDIVIDUALS
- Photographers
- Influencers
- Songwriters
- Website builder
- Website templates
- Customization
- Ecwid reviews
- Compare Ecwid
- For developers
- Partner program
- API Documentation
- Status monitoring
- Instant Site
- Shipping labels
- Automated taxes
- Buy Now button
- Digital products
- Subscriptions
- Abandoned cart recovery
- Point-of-Sale
- Inventory management
- Staff management
- Store management app
- Ecommerce Academy
- Ecommerce stats
- Ecom glossary
- How to sell online
- Create an online store
- Products to sell
Latest blog
- A Local Gift Shop to Global Omnichannel Sales: Silver in the City's Growth Strategy (opens in new window)
- How Ecwid's Accessible Online Store Template Became a Hit (opens in new window)
- (opens in new window)
- Terms of Service
- Copyright Policy
Almost there. Enter your email and get

Salesforce is closed for new business in your area.
The B2B2C model — what it is and how it works

As a manufacturer, your organization’s success depends on expanding into new markets and increasing top-line revenue — day in and day out.
But in an age of evolving customer expectations, product and price advantages are no longer enough to deliver exceptional experiences. Meanwhile, with digital disruption at every front, established competitive advantages aren’t as secure as they once were.
Amid these changes, a robust business-to-business-to-consumer (B2B2C) model can help you restock your wholesalers and dealers faster, solve marketing budget headaches, and reduce operating costs — ultimately acquiring new customers in a sustainable, scalable way.
In this article, you’ll learn what B2B2C means, how it’s different from business models like B2B or B2C, and whether it might be right for your business.
What is B2B2C?
In the business-to-business-to-consumer (B2B2C) model, businesses sell products to retailers while gaining valuable data directly from the customers who purchase those goods. B2B2C businesses are present all around us, in our shelves and closets — from Mondelez, the maker of classic snack brands like Chips Ahoy, to Unilever, which manufactures diverse products like Dove and Hellmann’s.
Because manufacturers partner with a retailer, they can take advantage of a B2C business’s investment in customer experience and marketing, ultimately reaching new markets at scale with greater revenue opportunities.

The B2B2C model hinges on successful relationships to deliver exceptional customer experiences.
B2B vs. B2C vs. B2B2C
When it comes to ecommerce, know the differences between these business models to make the right choice for your organization.
B2B — business to business
In a B2B model, businesses sell to other businesses through a process that can include a combination of a sales force, channel partnerships, and ecommerce. Within this model, there are three common business categories.

B2C — business to consumer
Business to consumer is a business model where businesses sell directly to consumers. B2C businesses may manufacture the products themselves, like Nike or Apple. They can also buy products wholesale from different manufacturers and sell an assortment to consumers, in the case of a B2C brand like Macy’s or Dick’s Sporting Goods.
B2B2C — business to business to consumer
With B2B2C models, businesses partner with other companies to reach new customers. Manufacturers sell a consumer product to retailers, who in turn sell that product to consumers.
How does a B2B2C model work?
In a B2B2C relationship, the manufacturer benefits from direct access to customer data and additional brand recognition through the retailer. With these keys to growth, the manufacturer can accelerate their expansion and scale.
Let’s look at a simple, hypothetical scenario where a baseball bat is being sold through a B2B2C model:

Examples of B2B2C partnerships
Every B2B2C relationship can operate differently based on the business’s needs. Let’s look at some real-world examples of successful partnerships.

Protein bar company RXBAR gained enough early momentum with a B2B2C model to also take advantage of a direct-to-consumer (D2C) model where consumers can purchase directly from them through its B2C ecommerce site .
How it works: RXBAR sells wholesale to a range of businesses like Whole Foods and REI. Whether they’re grocery stores, fitness centers, or convenience stores, retailers purchase the product through RXBAR’s B2B ecommerce site , email, and phone.

A look at the RXBAR websites reflecting the different B2B (left) and B2C (right) models.

A leading manufacturer of gaming and consumer computers, ASUS also finds success with a B2B2C model, complemented by ecommerce capabilities where the company can offer D2C through its website.
How it works: ASUS relies on a network of resellers like Best Buy, Costco, and Walmart. In addition to traditional channels, ASUS offers ecommerce functionality for resellers to browse and purchase ASUS products to resell to its customers through ecommerce and brick-and-mortar stores.

Digital streaming and recording product manufacturer TiVo operates both a B2B2C and D2C business model, partnering with a variety of retailers that can offer national reach.
- How it works: TiVo sells its media streaming devices directly through its website and electronics retailers like Best Buy and QVC, which feature the product both in store and through ecommerce.

Tivo offers its products through its website (left) as well as resellers like Best Buy (right).
Channel partnerships vs. B2B2C
Comparing channel partnerships to B2B2C can be confusing because it’s a similar type of interaction where a manufacturer sells its products to a retailer. But in a channel partnership, the relationship stops after that transaction — the manufacturer doesn’t gain access to any customer data or insights.
A real-world example of B2B2C in action is when Office Depot sells a Swingline stapler. Office Depot purchases the staplers in bulk and sells them to its customers. While Office Depot manages the customer experience, Swingline isn’t responsible for any part of that relationship.
In some cases, channel partnerships can lead to a company relabeling the products it sells under a house brand instead of the original manufacturer. For instance, this would mean Office Depot rebrands the Swingline staplers under its own brand. Because consumers aren’t aware of the original manufacturer, Swingline loses out on an opportunity to build brand recognition.
When to consider B2B2C
Knowing when your business is ready for the B2B2C model is a pivotal moment in an organization. Here are two criteria to keep in mind:
High level of digital maturity
Operating a B2B2C business requires achieving a certain threshold of ecommerce capabilities. Digital maturity is essential for both delivering a seamless customer experience and increasing efficiency to reduce operational costs between the businesses.
While this may seem daunting for traditional B2B businesses, it’s technically simple to set up a B2B2C ecommerce strategy that allows retailers to buy directly from you online instead of traditional channels like electronic data interchange (EDI) or a sales force.
Non-competitive relationships
B2B2C works best when both businesses aren’t competing for the same goods or service offerings. It’s an ideal arrangement for manufacturers that want to let the retailer tackle the challenges of customer support and operations.
Perhaps the business wants to focus on product development and rely on the retailer’s marketing expertise to scale. Retail partners typically have access to bigger consumer markets, bringing opportunities like international expansion within closer reach.
Reimagine your business’s trajectory with B2B2C
With a strong understanding of the B2B2C model and its potential impact to change the course of your business, consider whether you have the right technology to take it there. The ecommerce platform you build your business on can drive scalable success. Make sure to investigate new technology purchases to find the features and functionality that matter most.
Ready to find an ecommerce platform to take your revenue to the next level? Check out 12 Things to Know When Choosing a B2B Ecommerce Platform , which teaches you how to make the best decision based on your business needs.
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/best-b2b-ecommerce-platforms
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/b2b-ecommerce-trends-and-how-to-win
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/ecommerce-business-models

Customer login
Tax Pro login
Business tips
The Power of Online Sales: Demystifying the Ecommerce Business Model
13 Minutes Read
Copy Article URL
Learn How to Start an Ecommerce Business and Drive Online Sales
Antonio Del Cueto, CPA
May 8, 2024

Have you ever wondered how the digital marketplace has transformed the traditional shopping experience and what it means for the future of buying and selling? In an era where clicking replaces queuing, and digital carts are filled from the comfort of our homes, how does this shift impact both consumers and businesses alike?
By 2027, the e-commerce market is expected to surpass $7.9 trillion , signaling a massive transformation in conducting transactions globally. In this article, you will explore the essence of ecommerce—its evolution, key components, and future trends. Discover how ecommerce reshapes industries worldwide and what it could mean for your shopping habits or business strategies.
Further reading: Ultimate Guide: How to Start an Ecommerce Business in 2024 for Beginners and Experts
Understanding ecommerce fundamentals, brief history and evolution of online sales.
Ecommerce's roots trace back to the 1960s with the advent of Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) to transfer documents. The real transformation began with the public introduction of the internet in the 1990s, propelling online shopping into the mainstream through pioneers like Amazon and eBay.
Today, ecommerce encompasses everything from mobile commerce to electronic funds transfers and beyond, making it easier than ever for consumers to buy and sell goods and services online.
Types of Ecommerce Models
Understanding different ecommerce business models is vital for anyone interested in participating in ecommerce, whether you’re looking to start selling today or plan to grow your business online. Here are the primary models:
- Business to Business (B2B Ecommerce): This type of ecommerce involves transactions between two businesses, like manufacturers selling to wholesalers. B2B ecommerce platforms offer substantial opportunities for businesses to expand by supplying products or services to other businesses.
- Business to Consumer (B2C Ecommerce): The most common model, B2C ecommerce, involves businesses selling goods and services directly to consumers through an online store. Major ecommerce companies like Amazon and Alibaba are leading examples, showcasing a wide range of products to customers worldwide.
- Consumer to Consumer (C2C): Platforms such as eBay and Craigslist exemplify the C2C model, where individuals can sell products and services to each other online. This type of ecommerce platform facilitates an online marketplace where users can engage in buying and selling of goods, often with the platform taking a small commission.
- Consumer to Business (C2B): In a twist on traditional business structures, the C2B model sees consumers offering products or services to businesses. This can include freelance work, digital products, or other services, often mediated through platforms that help businesses thrive by finding the right solutions for their needs.
Key Components of a Successful Ecommerce Business
Website and mobile app functionality.
In today's digital marketplace, the functionality of your ecommerce website and mobile app is integral. These platforms serve as the primary storefront for your online business, enabling customers to easily browse and purchase products or services.
For businesses that sell through both brick-and-mortar and online stores, ensuring a seamless integration and a consistent user experience across all platforms can significantly increase ecommerce sales.
Whether you operate a large enterprise ecommerce system or a small online store, the functionality of your site directly influences customer satisfaction and your revenue model.
Importance of User Experience and Design
The user experience (UX) of your ecommerce site is vital for retaining customers and encouraging repeat business. A successful ecommerce website must be not only functional but also inviting and easy to navigate. This includes thoughtful design elements that create an enjoyable online shopping experience.
Good ecommerce design goes beyond aesthetics, involving clear categorization of products, optimized search functionality, and responsive customer interaction points. Businesses vying in competitive markets will find that superior UX design can be a distinguishing factor that sets their ecommerce store apart from others.
Secure Payment Gateways and Data Security
Secure payment gateways are a backbone of successful ecommerce operations, ensuring that customers can safely and conveniently make purchases online. Integrating robust security measures into your ecommerce platform helps protect against fraud and builds trust with your buyers. This trust is integral, especially for businesses operating solely online without a physical presence.
Adhering to ecommerce revenue models and security standards like PCI DSS not only protects your business and customers but also supports your business as it grows. Data security isn't just about protecting financial information—it's about securing all customer data, which is essential as ecommerce allows a greater reach across various social media platforms and markets.
Advantages and Challenges of Ecommerce
Benefits of running an ecommerce business.
Ecommerce has fundamentally transformed how businesses showcase and sell products or services online, providing several compelling advantages:
- Broader Reach: Ecommerce enables businesses to extend their reach far beyond traditional boundaries. An online store that allows global access means that small- and medium-sized businesses can attract customers from all over the world, not just locally.
- Lower Operational Costs: Unlike brick-and-mortar locations, ecommerce stores can operate with significantly lower overhead. This reduction in costs enables businesses, especially startups and small enterprises, to allocate resources more efficiently and scale as the business grows.
- Increased Convenience: The convenience of ecommerce allows customers to make purchases 24/7, providing a seamless buying experience that traditional physical stores cannot match. This aspect is particularly appealing in today's fast-paced world where time is a premium.
- Data-Driven Customer Insights: Modern ecommerce platforms offer powerful analytics tools that help businesses understand customer preferences and behaviors. This data is invaluable for refining marketing strategies and enhancing product offerings, ultimately driving better sales performance.
Common Challenges Faced by Ecommerce Businesses
Despite the many benefits, ecommerce also presents unique challenges that can impact a business owner's ability to succeed:
- Logistics and Shipping: Effective management of logistics is key, particularly for businesses engaged in dropshipping or selling a wide variety of types of products. Challenges in this area can include managing inventory levels, optimizing shipping routes, and ensuring timely delivery—all vital to maintaining customer satisfaction.
- High Competition: The ecommerce space is crowded, with many ecommerce brands vying for consumer attention. Standing out requires innovative ecommerce marketing strategies and a commitment to building a strong brand identity.
- Customer Service: Delivering excellent customer service online is often more challenging than in a face-to-face setting. Ecommerce businesses need robust systems to handle customer inquiries and complaints efficiently, ensuring a positive customer experience.
- Security and Data Privacy: With the rise in cyber threats, securing an ecommerce site and protecting customer data are paramount. A breach can severely damage a brand's reputation and consumer trust.
- Adapting to Market Trends: Keeping up with ecommerce trends and statistics is essential for staying relevant. Whether it's adopting new technologies or responding to changes in consumer behavior, ecommerce businesses must be agile and proactive.
- Technical Challenges: Maintaining a smoothly functioning ecommerce website requires technical expertise. Issues like website downtime, slow loading times, and poor user interface design can deter potential sales and harm a business’s reputation.
Further reading: The Ultimate Guide: Understanding the Dropshipping Business Model
Future trends in ecommerce, predictions for the growth of ecommerce.
The ecommerce landscape continues to evolve, with significant growth expected in the coming years. As more consumers opt to shop online, the potential for businesses to expand their reach and increase sales of goods or services is substantial.
This growth is not just beneficial for large enterprises. Small business owners can also capitalize on the expanding digital marketplace. The scalability of ecommerce can serve as a pivotal sales model for businesses of all sizes.
Technological Advancements Impacting Ecommerce
Several emerging technologies are poised to dramatically influence how ecommerce takes place:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is reshaping ecommerce by personalizing the customer experience and optimizing business operations. From AI-driven recommendations to automated customer service, the integration of AI can help your business enhance efficiency and customer satisfaction.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): These technologies are revolutionizing the online shopping experience by allowing customers to visualize products in a highly interactive manner. Whether it’s trying on virtual outfits or placing furniture in your home via AR, these tools are adding a new dimension to ecommerce.
- Blockchain: Known for its security features, blockchain technology offers transparency and efficiency in transactions, which is increasingly important in ecommerce today. It ensures that the buying and selling of goods or services online are secure, fostering trust among consumers.
How Businesses Can Adapt to Future Changes in the Online Marketplace
Adapting to the fast-paced changes in ecommerce requires businesses to be agile and forward-thinking:
- Embrace Cutting-Edge Technologies: To remain competitive, businesses need an ecommerce guide to online technology integration that outlines how to effectively use AI, VR, AR, and blockchain. Understanding how ecommerce works with these technologies can provide a significant advantage.
- Optimize for Mobile and Beyond: Given the shift towards mobile commerce, ensuring your ecommerce site or app offers an exceptional mobile shopping experience is beneficial. This involves more than just responsive design. It means thinking mobile-first in every aspect of your digital strategy.
- Leverage Data for Customer Insights: Advanced data analytics are critical for understanding consumer behavior and personalizing the shopping experience. By analyzing data, ecommerce businesses can fine-tune their marketing strategies and product offerings to better meet the needs of their customers.
- Prioritize Customer-Centric Initiatives: Implementing customer-centric strategies, such as enhanced customer support and personalized user experiences, can differentiate your brand in a crowded market. Selling products to customers online offers unique opportunities to build relationships and loyalty through personalized interactions.
- Sustainability as a Core Value: In today’s market, sustainability is not just a trend but a business imperative. By adopting eco-friendly practices and promoting them on your ecommerce site, you can attract a growing demographic of environmentally conscious consumers.
Key Takeaways
- Seller's Realm : Ecommerce allows sellers to reach global markets, transcending geographical limitations.
- Exploring Benefits : Take time to explore the myriad benefits of ecommerce, from expanded customer reach to reduced overhead costs.
- Pros and Cons : Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of ecommerce is vital for informed decision-making in this type of business.
- Ecommerce Essentials : Key components of ecommerce include online storefronts , secure payment gateways, and efficient logistics systems.
- Branding Matters : In starting an ecommerce business, choosing a memorable business name is essential for building brand recognition and trust among customers.
How can Taxfyle help?
Finding an accountant to manage your bookkeeping and file taxes is a big decision. Luckily, you don't have to handle the search on your own.
At Taxfyle , we connect small businesses with licensed, experienced CPAs or EAs in the US. We handle the hard part of finding the right tax professional by matching you with a Pro who has the right experience to meet your unique needs and will manage your bookkeeping and file taxes for you.
Legal Disclaimer
Tickmark, Inc. and its affiliates do not provide legal, tax or accounting advice. The information provided on this website does not, and is not intended to, constitute legal, tax or accounting advice or recommendations. All information prepared on this site is for informational purposes only, and should not be relied on for legal, tax or accounting advice. You should consult your own legal, tax or accounting advisors before engaging in any transaction. The content on this website is provided “as is;” no representations are made that the content is error-free.

Was this post helpful?
Did you know business owners can spend over 100 hours filing taxes, it’s time to focus on what matters..
With Taxfyle, the work is done for you. You can connect with a licensed CPA or EA who can file your business tax returns. Get $30 off off today.
Want to put your taxes in an expert’s hands?
Taxes are best done by an expert. Here’s a $30 coupon to access to a licensed CPA or EA who can do all the work for you.
Is this article answering your questions?
Thanks for letting us know.
Whatever your questions are, Taxfyle’s got you covered. If you have any further questions, why not talk to a Pro? Get $30 off today.
Our apologies.
Taxes are incredibly complex, so we may not have been able to answer your question in the article. Fortunately, the Pros do have answers. Get $30 off a tax consultation with a licensed CPA or EA, and we’ll be sure to provide you with a robust, bespoke answer to whatever tax problems you may have.
Do you do your own bookkeeping?
There’s an easier way to do bookkeeping..
Taxfyle connects you to a licensed CPA or EA who can take time-consuming bookkeeping work off your hands. Get $30 off today.
Why not upgrade to a licensed, vetted Professional?
When you use Taxfyle, you’re guaranteed an affordable, licensed Professional. With a more secure, easy-to-use platform and an average Pro experience of 12 years, there’s no beating Taxfyle. Get $30 off today.
Are you filing your own taxes?
Do you know if you’re missing out on ways to reduce your tax liability.
Knowing the right forms and documents to claim each credit and deduction is daunting. Luckily, you can get $30 off your tax job.
Get $30 off your tax filing job today and access an affordable, licensed Tax Professional. With a more secure, easy-to-use platform and an average Pro experience of 12 years, there’s no beating Taxfyle.
How is your work-life balance?
Why not spend some of that free time with taxfyle.
When you’re a Pro, you’re able to pick up tax filing, consultation, and bookkeeping jobs on our platform while maintaining your flexibility.
Why not try something new?
Increase your desired income on your desired schedule by using Taxfyle’s platform to pick up tax filing, consultation, and bookkeeping jobs.
Is your firm falling behind during the busy season?
Need an extra hand.
With Taxfyle, your firm can access licensed CPAs and EAs who can prepare and review tax returns for your clients.
Perhaps it’s time to scale up.
We love to hear from firms that have made the busy season work for them–why not use this opportunity to scale up your business and take on more returns using Taxfyle’s network?

by this author
Share this article
Subscribe to taxfyle.
Sign up to hear Taxfye's latest tips.
By clicking subscribe, I agree to Taxfyle's Terms of Service , Privacy Policy , and am opting in to receive marketing emails.
Get our FREE Tax Guide for Individuals
Looking for something else? Check out our other guides here .
By clicking download, I agree to Taxfyle's Terms of Service , Privacy Policy , and am opting in to receive marketing emails.
File simpler.
File smarter., file with taxfyle..
2899 Grand Avenue, Coconut Grove, FL 33133
Copyright © 2024 Tickmark, Inc.

Grove Cookie Company Brings Business Logo Cookies to Your Employees and B2B Prospects
I n the fast-paced and often impersonal world of business, where competition is fierce and relationships are crucial, standing out and making genuine connections can be a formidable challenge. Based on this challenge, Grove Cookie Company is introducing a new twist to the traditional business prospecting game. By blending the world of SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) with a unique culinary approach, they're offering a groundbreaking way to foster relationships and enhance collaboration in the corporate arena.
SaaS platforms have revolutionized the way businesses operate, providing cloud-based applications for various needs, from email to sales communication, thereby eliminating the necessity for costly hardware updates and upfront equipment expenses. These platforms enable businesses to streamline operations, increase efficiency, and scale effectively in the digital age.
SaaS platforms are all around us. They help businesses connect to and use cloud-based apps, like email and sales communication, on the internet, and sometimes they do simple things like keeping track of leads or finances. By eliminating the need for equipment updates and upfront hardware costs, SaaS can help you manage many facets of running a business. However, Grove Cookie Company is taking it one step further with its CaaS approach, also known as “Cookie-as-a-service” 🍪.
Sounds delicious, right? This business approach is the latest tool you should consider adding to your toolbelt, as it capitalizes on the power of cookies to enhance your business relationships and follow up after a demo. Thank you for attending your webinar. Are you hosting an in-person event giveaway, or do you want to create a moment of delight? Cookies are the answer!
Grove’s B2B Custom Logo Cookies
Grove Cookie Company is innovating beyond digital solutions with its distinctive CaaS (Cookie-as-a-Service) model. This ingenious approach merges the practicality of SaaS with the personal touch of corporate gifting, offering company logo cookies, corporate logo cookies, and custom logo cookies. These aren't just ordinary cookies; they are bespoke creations that carry your brand's identity, crafted to make a lasting impression in the corporate landscape. With Grove, you can set up automated logo cookie gifts for your prospects, customers, and employees to receive on their life milestones (birthdays, anniversaries, baby showers, engagements/weddings, and more!)
Grove's CaaS model, businesses can send custom logo cookies as a sophisticated and flavorful gesture of appreciation, celebration, or partnership, providing a memorable experience that transcends the usual corporate gift. Whether it's marking a milestone, welcoming a new client, or showing gratitude to your team, these cookies serve as a tangible representation of your brand's creativity and commitment to building meaningful relationships.
What is New in Customized Cookies With Logos?
Grove Cookie Company is at the forefront of transforming this delightful concept into reality, providing an array of corporate cookies with logos that serve as both a treat and a testament to your company's dedication to fostering meaningful connections. These cookies are more than just a thank you; they're an innovative expression of appreciation and a way to make your company stand out in the minds and hearts of clients, partners, and employees alike.
Whether it's a gesture of gratitude, a follow-up to an event, or simply a way to sweeten your corporate communications, these company logo gifts for employees offer a unique blend of tasteful branding and personal touch, proving that sometimes, the way to enhance business relationships might just be through a batch of freshly baked, logo-adorned cookies.
The Creators of the Business Logo Cookies - CaaS Model
This female and veteran-owned business began with Marie Grayson, one of the founders, who worked from home during the pandemic. Wanting to find a hobby to fill the time between meetings, Marie picked up a mixer and cracked an egg in her townhome’s kitchen. While Marie and her husband, Grayson, may not be trained bakers, learning to perfect homemade goodies through trial and error, this brand has proven it is more than flavorful; it’s also innovative and successful.
Since its inception in January 2021, Grove Cookie Company has evolved from a humble home-based operation into a beacon of creativity and innovation within the corporate gifting world. Nestled in the suburbs of Portland, Oregon, the Hogards initially grappled with carving out their niche in a market teeming with traditional bakeries. Yet, it was their pivot to the B2B sector, spurred by a friendly financial advisor who still orders cookies every week for his beloved customers, that the Hogards were able to find a profitable niche in the B2B gifting space.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Business To Business - B To B: Business to business, also called B to B or B2B, is a type of transaction that exists between businesses, such as one involving a manufacturer and wholesaler, or a ...
Business-to-business (B2B) refers to the transactions that take place between two businesses. In other words, it is the exchange of products, services, or information between companies rather than between a company and a consumer. B2B transactions are typically larger and more complex than B2C transactions, and they involve multiple decision-makers and longer sales cycles.
1.2 - Advantages of B2B (Business-to-Business) The B2B model offers various advantages for participating businesses. Firstly, it enables economies of scale as businesses can buy or sell in larger quantities, leading to cost savings. By purchasing raw materials, components, or finished products in bulk, businesses can negotiate better prices and ...
What Is a B2B Business Model? Let's start with fundamentals and define what a B2B business model is. In layman's terms, a business model is a set of rules and processes that explain how a company is functioning and how it is making money. In other words, it's a strategy that companies stick to in order not to deviate from their business ...
B2B isn't the only business model involved in the supply chain. While B2B companies sell products and services to other private businesses, public-sector organizations, and charities, B2C ...
B2B (business-to-business): On the Internet, B2B (business-to-business), also known as e-biz , is the exchange of products, services or information (aka e-commerce ) between businesses, rather than between businesses and consumers.
The B2B model is a fairly simple business model. It helps solve or provide services to other businesses while, at the same time, operating one on their own. All the B2B companies that we listed above are all addressing pain points other businesses have and they have created a B2B business solution to help solve those pain points. And all it ...
Business-to-business (B2B) is a type of transaction that occurs between two businesses, such as a manufacturer and a wholesaler, or a wholesaler and a retailer. Business-to-business transactions usually involve goods and services that help one business to operate. Examples include raw materials for production, components for product assembly ...
What Is B2B Business? Business-to-business, or B2B, is a company that sells its products or services directly to another company. This is in contrast to the B2C model where they sell directly to individual consumers. B2B Business Model. The B2B business model features the exchange of products and services between two or more businesses.
The B2B business model has both pros and cons for the business owner and their team. Pros: Larger orders. B2B sales are high and orders are made in bulk. This means revenue can be higher with fewer sales than B2C businesses. Increase conversion. Businesses convert better than individuals.
Business-to-business (B2B or, in some countries, BtoB) is a situation where one business makes a commercial transaction with another. This typically occurs when: ... Business to business model Vertical B2B model. Vertical B2B is generally oriented to manufacturing or business. It can be divided into two directions: upstream and downstream.
Business-to-business (B2B) is a business model where a business sells or purchases products or services to and from another business. This type of relationship is common among manufacturers, wholesalers, distributors, and retailers that will resell the products or services.
B2B business model is where businesses sell to other businesses or simply called business to business. It is a situation where a business offers its products to another business instead of selling them directly to the consumers. Here, businesses make products destined for use by other businesses. You sell what you make to another business that ...
A business-to-business company caters to the needs of other businesses. In this business model, a company will sell products or services to another company, instead of an individual buyer. Most B2B interactions happen within the supply chain. This would include buying and selling between suppliers, manufacturers, wholesalers, distributors, and ...
An example of a hybrid B2B B2C business model would be a company that manufactures and sells car parts. The company sells its car parts to both other businesses (B2B) and individual consumers (B2C). Amazon is a real-life example of a company with a hybrid B2B B2C business model. While it is best known for its B2C capacities, Amazon has a large ...
B2B stands for "business-to-business," which refers to a business model where businesses sell products and services to other companies as opposed to consumers. ... Every business, whether B2B or B2C, should have a digital presence — which is comprised of paid ads, search engine optimization, a website, and any other place your B2B company ...
Subscription-based model. B2B Business Model Types. Direct sales model. Marketplace model. Value-added reseller (VAR) model. B2B Business Model in E-commerce. Leveraging technology for seamless transactions. Enhancing supply chain management through B2B e-commerce. B2B e-commerce platforms and marketplaces.
Outliers prove the rule of thirds works. Break the rule of thirds, and customers won't be the only unhappy ones; sellers will be too. Despite noting some improvement in go-to-market results over the past two years, respondents at B2B companies in France and Japan are far less likely than their peers in other markets to say they are pleased with their sales model performance.
Business to business or B2B is a business model when a company sells its products and services to another company's customer for further processing and then reselling it. In simple words, one business sells its product/service to another business. The reason B2B is different from business to customer (B2C), where a business sells its product ...
E-commerce is a business model that focuses on doing business online, i.e., on the Internet. 'E-commerce' stands for 'electronic commerce.' The National Association of Sales Professionals has the following definition of the term: "B2B is short for business-to-business.
B2B means business-to-business. It's one form of a transaction or business model that occurs between two companies. The consumer is not involved in a B2B transaction. Unlike consumer purchases, B2B transactions are more complicated than a simple purchase in an online store. They involve larger order quantities, negotiations, and the shipping ...
Business-to-business (or B2B) refers to selling products and services directly between two businesses. As a business model, B2B differs significantly from B2C, where businesses sell directly to consumers. B2B ecommerce involves transactions between a manufacturer and wholesaler, or a wholesaler and a retailer, through an online sales portal.
Thus, the B2B model works well for consulting, as it does in a number of other industries. John Mackey, former CEO of Whole Foods Market, an Amazon subsidiary, is a member of The Motley Fool's ...
B2B stands for 'business to business' while B2C is 'business to consumer'. B2B ecommerce utilises online platforms to sell products or services to other businesses. B2C e-commerce targets personal consumers. A company that sells office furniture, software, or paper to other businesses would be an example of a B2B company.
In a B2B model, businesses sell to other businesses through a process that can include a combination of a sales force, channel partnerships, and ecommerce. Within this model, there are three common business categories. B2C — business to consumer. Business to consumer is a business model where businesses sell directly to consumers.
B2B Software as a Service (SaaS) offers cloud-based solutions accessible through subscription services. This provides businesses a flexible and affordable alternative to traditional software licensing since B2B SaaS does not require huge initial costs. Consider a virtual toolbox that meets your company's requirements.
B2B ecommerce platforms offer substantial opportunities for businesses to expand by supplying products or services to other businesses. Business to Consumer (B2C Ecommerce): The most common model, B2C ecommerce, involves businesses selling goods and services directly to consumers through an online store. Major ecommerce companies like Amazon ...
Orla Murphy is co-founder of Seeblue, an ABM agency. She has over 20 years of B2B Marketing expertise across the tech sector. In the world of B2B marketing, the relationship between agencies and ...
Grove's B2B Custom Logo Cookies. Grove Cookie Company is innovating beyond digital solutions with its distinctive CaaS (Cookie-as-a-Service) model.