The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Nonprofit Business Plan
A business plan can be an invaluable tool for your nonprofit. Even a short business plan pushes you to do research, crystalize your purpose, and polish your messaging. This blog shares what it is and why you need it, ten steps to help you write one, and the dos and don’ts of creating a nonprofit business plan.
Nonprofit business plans are dead — or are they?
For many nonprofit organizations, business plans represent outdated and cumbersome documents that get created “just for the sake of it” or because donors demand it.
But these plans are vital to organizing your nonprofit and making your dreams a reality! Furthermore, without a nonprofit business plan, you’ll have a harder time obtaining loans and grants , attracting corporate donors, meeting qualified board members, and keeping your nonprofit on track.
Even excellent ideas can be totally useless if you cannot formulate, execute, and implement a strategic plan to make your idea work. In this article, we share exactly what your plan needs and provide a nonprofit business plan template to help you create one of your own.

What is a Nonprofit Business Plan?
A nonprofit business plan describes your nonprofit as it currently is and sets up a roadmap for the next three to five years. It also lays out your goals and plans for meeting your goals. Your nonprofit business plan is a living document that should be updated frequently to reflect your evolving goals and circumstances.
A business plan is the foundation of your organization — the who, what, when, where, and how you’re going to make a positive impact.
The best nonprofit business plans aren’t unnecessarily long. They include only as much information as necessary. They may be as short as seven pages long, one for each of the essential sections you will read about below and see in our template, or up to 30 pages long if your organization grows.
Why do we need a Nonprofit Business Plan?
Regardless of whether your nonprofit is small and barely making it or if your nonprofit has been successfully running for years, you need a nonprofit business plan. Why?
When you create a nonprofit business plan, you are effectively creating a blueprint for how your nonprofit will be run, who will be responsible for what, and how you plan to achieve your goals.
Your nonprofit organization also needs a business plan if you plan to secure support of any kind, be it monetary, in-kind , or even just support from volunteers. You need a business plan to convey your nonprofit’s purpose and goals.
It sometimes also happens that the board, or the administration under which a nonprofit operates, requires a nonprofit business plan.
To sum it all up, write a nonprofit business plan to:
- Layout your goals and establish milestones.
- Better understand your beneficiaries, partners, and other stakeholders.
- Assess the feasibility of your nonprofit and document your fundraising/financing model.
- Attract investment and prove that you’re serious about your nonprofit.
- Attract a board and volunteers.
- Position your nonprofit and get clear about your message.
- Force you to research and uncover new opportunities.
- Iron out all the kinks in your plan and hold yourself accountable.
Before starting your nonprofit business plan, it is important to consider the following:
- Who is your audience? E.g. If you are interested in fundraising, donors will be your audience. If you are interested in partnerships, potential partners will be your audience.
- What do you want their response to be? Depending on your target audience, you should focus on the key message you want them to receive to get the response that you want.
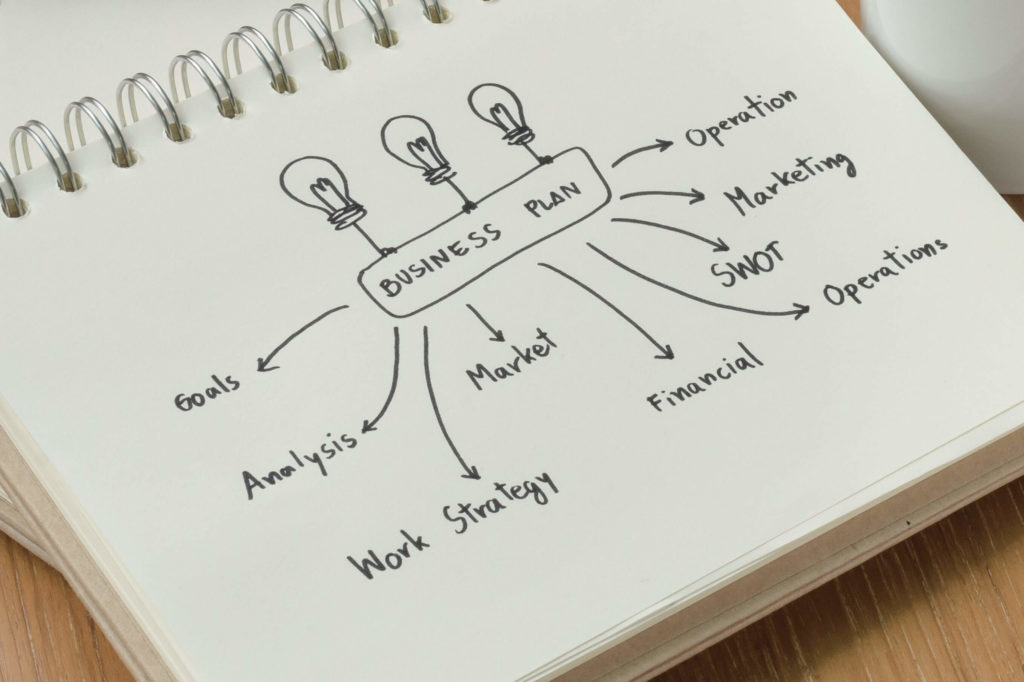
10-Step Guide on Writing a Business Plan for Nonprofits
Note: Steps 1, 2, and 3 are in preparation for writing your nonprofit business plan.
Step 1: Data Collection
Before even getting started with the writing, collect financial, operating, and other relevant data. If your nonprofit is already in operation, this should at the very least include financial statements detailing operating expense reports and a spreadsheet that indicates funding sources.
If your nonprofit is new, compile materials related to any secured funding sources and operational funding projections, including anticipated costs.
Step 2: Heart of the Matter
You are a nonprofit after all! Your nonprofit business plan should start with an articulation of the core values and your mission statement . Outline your vision, your guiding philosophy, and any other principles that provide the purpose behind the work. This will help you to refine and communicate your nonprofit message clearly.
Your nonprofit mission statement can also help establish your milestones, the problems your organization seeks to solve, who your organization serves, and its future goals.
Check out these great mission statement examples for some inspiration. For help writing your statement, download our free Mission & Vision Statements Worksheet .
Step 3: Outline
Create an outline of your nonprofit business plan. Write out everything you want your plan to include (e.g. sections such as marketing, fundraising, human resources, and budgets).
An outline helps you focus your attention. It gives you a roadmap from the start, through the middle, and to the end. Outlining actually helps us write more quickly and more effectively.
An outline will help you understand what you need to tell your audience, whether it’s in the right order, and whether the right amount of emphasis is placed on each topic.
Pro tip: Use our Nonprofit Business Plan Outline to help with this step! More on that later.
Step 4: Products, Programs, and Services
In this section, provide more information on exactly what your nonprofit organization does.
- What products, programs, or services do you provide?
- How does your nonprofit benefit the community?
- What need does your nonprofit meet and what are your plans for meeting that need?
E.g. The American Red Cross carries out its mission to prevent and relieve suffering with five key services: disaster relief, supporting America’s military families, lifesaving blood, health and safety services, and international service.
Don’t skimp out on program details, including the functions and beneficiaries. This is generally what most readers will care most about.
However, don’t overload the reader with technical jargon. Try to present some clear examples. Include photographs, brochures, and other promotional materials.
Step 5: Marketing Plan
A marketing plan is essential for a nonprofit to reach its goals. If your nonprofit is already in operation, describe in detail all current marketing activities: any outreach activities, campaigns, and other initiatives. Be specific about outcomes, activities, and costs.
If your nonprofit is new, outline projections based on specific data you gathered about your market.
This will frequently be your most detailed section because it spells out precisely how you intend to carry out your business plan.
- Describe your market. This includes your target audience, competitors, beneficiaries, donors, and potential partners.
- Include any market analyses and tests you’ve done.
- Outline your plan for reaching your beneficiaries.
- Outline your marketing activities, highlighting specific outcomes.
Step 6: Operational Plan
An operational plan describes how your nonprofit plans to deliver activities. In the operational plan, it is important to explain how you plan to maintain your operations and how you will evaluate the impact of your programs.
The operational plan should give an overview of the day-to-day operations of your organization such as the people and organizations you work with (e.g. partners and suppliers), any legal requirements that your organization needs to meet (e.g. if you distribute food, you’ll need appropriate licenses and certifications), any insurance you have or will need, etc.
In the operational plan, also include a section on the people or your team. Describe the people who are crucial to your organization and any staff changes you plan as part of your business plan.
Pro tip: If you have an organizational chart, you can include it in the appendix to help illustrate how your organization operates. Learn more about the six types of nonprofit organizational charts and see them in action in this free e-book .
Step 7: Impact Plan
For a nonprofit, an impact plan is as important as a financial plan. A nonprofit seeks to create social change and a social return on investment, not just a financial return on investment.
Your impact plan should be precise about how your nonprofit will achieve this step. It should include details on what change you’re seeking to make, how you’re going to make it, and how you’re going to measure it.
This section turns your purpose and motivation into concrete accomplishments your nonprofit wants to make and sets specific goals and objectives.
These define the real bottom line of your nonprofit, so they’re the key to unlocking support. Funders want to know for whom, in what way, and exactly how you’ll measure your impact.
Answer these in the impact plan section of your business plan:
- What goals are most meaningful to the people you serve or the cause you’re fighting for?
- How can you best achieve those goals through a series of specific objectives?
E.g. “Finding jobs for an additional 200 unemployed people in the coming year.”
Step 8: Financial Plan
This is one of the most important parts of your nonprofit business plan. Creating a financial plan will allow you to make sure that your nonprofit has its basic financial needs covered.
Every nonprofit needs a certain level of funding to stay operational, so it’s essential to make sure your organization will meet at least that threshold.
To craft your financial plan:
- Outline your nonprofit’s current and projected financial status.
- Include an income statement, balance sheet , cash flow statement, and financial projections.
- List any grants you’ve received, significant contributions, and in-kind support.
- Include your fundraising plan .
- Identify gaps in your funding, and how you will manage them.
- Plan for what will be done with a potential surplus.
- Include startup costs, if necessary.
If your nonprofit is already operational, use established accounting records to complete this section of the business plan.
Knowing the financial details of your organization is incredibly important in a world where the public demands transparency about where their donations are going.
Pro tip : Leverage startup accelerators dedicated to nonprofits that can help you with funding, sponsorship, networking, and much more.
Step 9: Executive Summary
Normally written last but placed first in your business plan, your nonprofit executive summary provides an introduction to your entire business plan. The first page should describe your non-profit’s mission and purpose, summarize your market analysis that proves an identifiable need, and explain how your non-profit will meet that need.
The Executive Summary is where you sell your nonprofit and its ideas. Here you need to describe your organization clearly and concisely.
Make sure to customize your executive summary depending on your audience (i.e. your executive summary page will look different if your main goal is to win a grant or hire a board member).
Step 10: Appendix
Include extra documents in the section that are pertinent to your nonprofit: organizational chart , current fiscal year budget, a list of the board of directors, your IRS status letter, balance sheets, and so forth.
The appendix contains helpful additional information that might not be suitable for the format of your business plan (i.e. it might unnecessarily make it less readable or more lengthy).

Do’s and Dont’s of Nonprofit Business Plans – Tips
- Write clearly, using simple and easy-to-understand language.
- Get to the point, support it with facts, and then move on.
- Include relevant graphs and program descriptions.
- Include an executive summary.
- Provide sufficient financial information.
- Customize your business plan to different audiences.
- Stay authentic and show enthusiasm.
- Make the business plan too long.
- Use too much technical jargon.
- Overload the plan with text.
- Rush the process of writing, but don’t drag it either.
- Gush about the cause without providing a clear understanding of how you will help the cause through your activities.
- Keep your formatting consistent.
- Use standard 1-inch margins.
- Use a reasonable font size for the body.
- For print, use a serif font like Times New Roman or Courier. For digital, use sans serifs like Verdana or Arial.
- Start a new page before each section.
- Don’t allow your plan to print and leave a single line on an otherwise blank page.
- Have several people read over the plan before it is printed to make sure it’s free of errors.
Nonprofit Business Plan Template
To help you get started we’ve created a nonprofit business plan outline. This business plan outline will work as a framework regardless of your nonprofit’s area of focus. With it, you’ll have a better idea of how to lay out your nonprofit business plan and what to include. We have also provided several questions and examples to help you create a detailed nonprofit business plan.
Download Your Free Outline

At Donorbox, we strive to make your nonprofit experience as productive as possible, whether through our donation software or through our advice and guides on the Nonprofit Blog . Find more free, downloadable resources in our Library .
Many nonprofits start with passion and enthusiasm but without a proper business plan. It’s a common misconception that just because an organization is labeled a “nonprofit,” it does not need to operate in any way like a business.
However, a nonprofit is a type of business, and many of the same rules that apply to a for-profit company also apply to a nonprofit organization.
As outlined above, your nonprofit business plan is a combination of your marketing plan , strategic plan, operational plan, impact plan, and financial plan. Remember, you don’t have to work from scratch. Be sure to use the nonprofit business plan outline we’ve provided to help create one of your own.
It’s important to note that your nonprofit should not be set in stone—it can and should change and evolve. It’s a living organism. While your vision, values, and mission will likely remain the same, your nonprofit business plan may need to be revised from time to time. Keep your audience in mind and adjust your plan as needed.
Finally, don’t let your plan gather dust on a shelf! Print it out, put up posters on your office walls, and read from it during your team meetings. Use all the research, data, and ideas you’ve gathered and put them into action!
If you want more help with nonprofit management tips and fundraising resources, visit our Nonprofit Blog . We also have dedicated articles for starting a nonprofit in different states in the U.S., including Texas , Minnesota , Oregon , Arizona , Illinois , and more.
Learn about our all-in-one online fundraising tool, Donorbox, and its simple-to-use features on the website here .

Raviraj heads the sales and marketing team at Donorbox. His growth-hacking abilities have helped Donorbox boost fundraising efforts for thousands of nonprofit organizations.
Join the fundraising movement!
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to receive the latest blogs, news, and more in your inbox.

- Insights & Analysis
- Nonprofit Jobs
Business Planning for Nonprofits
Business planning is a way of systematically answering questions such as, “What problem(s) are we trying to solve?” or “What are we trying to achieve?” and also, “Who will get us there, by when, and how much money and other resources will it take?”
The business planning process takes into account the nonprofit’s mission and vision, the role of the board, and external environmental factors, such as the climate for fundraising.

Ideally, the business planning process also critically examines basic assumptions about the nonprofit’s operating environment. What if the sources of income that exist today change in the future? Is the nonprofit too reliant on one foundation for revenue? What happens if there’s an economic downturn?
A business plan can help the nonprofit and its board be prepared for future risks. What is the likelihood that the planned activities will continue as usual, and that revenue will continue at current levels – and what is Plan B if they don't?
Narrative of a business plan
You can think of a business plan as a narrative or story explaining how the nonprofit will operate given its activities, its sources of revenue, its expenses, and the inevitable changes in its internal and external environments over time. Ideally, your plan will tell the story in a way that will make sense to someone not intimately familiar with the nonprofit’s operations.
According to Propel Nonprofits , business plans usually should have four components that identify revenue sources/mix; operations costs; program costs; and capital structure.
A business plan outlines the expected income sources to support the charitable nonprofit's activities. What types of revenue will the nonprofit rely on to keep its engine running – how much will be earned, how much from government grants or contracts, how much will be contributed? Within each of those broad categories, how much diversification exists, and should they be further diversified? Are there certain factors that need to be in place in order for today’s income streams to continue flowing?
The plan should address the everyday costs needed to operate the organization, as well as costs of specific programs and activities.
The plan may include details about the need for the organization's services (a needs assessment), the likelihood that certain funding will be available (a feasibility study), or changes to the organization's technology or staffing that will be needed in the future.
Another aspect of a business plan could be a "competitive analysis" describing what other entities may be providing similar services in the nonprofit's service and mission areas. What are their sources of revenue and staffing structures? How do their services and capacities differ from those of your nonprofit?
Finally, the business plan should name important assumptions, such as the organization's reserve policies. Do your nonprofit’s policies require it to have at least six months of operating cash on hand? Do you have different types of cash reserves that require different levels of board approval to release?
The idea is to identify the known, and take into consideration the unknown, realities of the nonprofit's operations, and propose how the nonprofit will continue to be financially healthy. If the underlying assumptions or current conditions change, then having a plan can be useful to help identify adjustments that must be made to respond to changes in the nonprofit's operating environment.
Basic format of a business plan
The format may vary depending on the audience. A business plan prepared for a bank to support a loan application may be different than a business plan that board members use as the basis for budgeting. Here is a typical outline of the format for a business plan:
- Table of contents
- Executive summary - Name the problem the nonprofit is trying to solve: its mission, and how it accomplishes its mission.
- People: overview of the nonprofit’s board, staffing, and volunteer structure and who makes what happen
- Market opportunities/competitive analysis
- Programs and services: overview of implementation
- Contingencies: what could change?
- Financial health: what is the current status, and what are the sources of revenue to operate programs and advance the mission over time?
- Assumptions and proposed changes: What needs to be in place for this nonprofit to continue on sound financial footing?
More About Business Planning
Budgeting for Nonprofits
Strategic Planning
Contact your state association of nonprofits for support and resources related to business planning, strategic planning, and other fundamentals of nonprofit leadership.
Additional Resources
- Components of transforming nonprofit business models (Propel Nonprofits)
- The matrix map: a powerful tool for nonprofit sustainability (Nonprofit Quarterly)
- The Nonprofit Business Plan: A Leader's Guide to Creating a Successful Business Model (David La Piana, Heather Gowdy, Lester Olmstead-Rose, and Brent Copen, Turner Publishing)
- Nonprofit Earned Income: Critical Business Model Considerations for Nonprofits (Nonprofit Financial Commons)
- Nonprofit Sustainability: Making Strategic Decisions for Financial Viability (Jan Masaoka, Steve Zimmerman, and Jeanne Bell)
Disclaimer: Information on this website is provided for informational purposes only and is neither intended to be nor should be construed as legal, accounting, tax, investment, or financial advice. Please consult a professional (attorney, accountant, tax advisor) for the latest and most accurate information. The National Council of Nonprofits makes no representations or warranties as to the accuracy or timeliness of the information contained herein.
Everything that you need to know to start your own business. From business ideas to researching the competition.
Practical and real-world advice on how to run your business — from managing employees to keeping the books
Our best expert advice on how to grow your business — from attracting new customers to keeping existing customers happy and having the capital to do it.
Entrepreneurs and industry leaders share their best advice on how to take your company to the next level.
- Business Ideas
- Human Resources
- Business Financing
- Growth Studio
- Ask the Board
Looking for your local chamber?
Interested in partnering with us?
Start » strategy, how to write a nonprofit business plan.
A nonprofit business plan ensures your organization’s fundraising and activities align with your core mission.

Every nonprofit needs a mission statement that demonstrates how the organization will support a social cause and provide a public benefit. A nonprofit business plan fleshes out this mission statement in greater detail. These plans include many of the same elements as a for-profit business plan, with a focus on fundraising, creating a board of directors, raising awareness, and staying compliant with IRS regulations. A nonprofit business plan can be instrumental in getting your organization off the ground successfully.
Start with your mission statement
The mission statement is foundational for your nonprofit organization. The IRS will review your mission statement in determining whether to grant you tax-exempt status. This statement also helps you recruit volunteers and staff, fundraise, and plan activities for the year.
[Read more: Writing a Mission Statement: A Step-by-Step Guide ]
Therefore, you should start your business plan with a clear mission statement in the executive summary. The executive summary can also cover, at a high level, the goals, vision, and unique strengths of your nonprofit organization. Keep this section brief, since you will be going into greater detail in later sections.
Identify a board of directors
Many business plans include a section identifying the people behind the operation: your key leaders, volunteers, and full-time employees. For nonprofits, it’s also important to identify your board of directors. The board of directors is ultimately responsible for hiring and managing the CEO of your nonprofit.
“Board members are the fiduciaries who steer the organization towards a sustainable future by adopting sound, ethical, and legal governance and financial management policies, as well as by making sure the nonprofit has adequate resources to advance its mission,” wrote the Council of Nonprofits.
As such, identify members of your board in your business plan to give potential donors confidence in the management of your nonprofit.
Be as realistic as possible about the impact you can make with the funding you hope to gain.
Describe your organization’s activities
In this section, provide more information about what your nonprofit does on a day-to-day basis. What products, training, education, or other services do you provide? What does your organization do to benefit the constituents identified in your mission statement? Here’s an example from the American Red Cross, courtesy of DonorBox :
“The American Red Cross carries out their mission to prevent and relieve suffering with five key services: disaster relief, supporting America’s military families, lifesaving blood, health and safety services, and international service.”
This section should be detailed and get into the operational weeds of how your business delivers on its mission statement. Explain the strategies your team will take to service clients, including outreach and marketing, inventory and equipment needs, a hiring plan, and other key elements.
Write a fundraising plan
This part is the most important element of your business plan. In addition to providing required financial statements (e.g., the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement), identify potential sources of funding for your nonprofit. These may include individual donors, corporate donors, grants, or in-kind support. If you are planning to host a fundraising event, put together a budget for that event and demonstrate the anticipated impact that event will have on your budget.
Create an impact plan
An impact plan ties everything together. It demonstrates how your fundraising and day-to-day activities will further your mission. For potential donors, it can make a very convincing case for why they should invest in your nonprofit.
“This section turns your purpose and motivation into concrete accomplishments your nonprofit wants to make and sets specific goals and objectives,” wrote DonorBox . “These define the real bottom line of your nonprofit, so they’re the key to unlocking support. Funders want to know for whom, in what way, and exactly how you’ll measure your impact.”
Be as realistic as possible about the impact you can make with the funding you hope to gain. Revisit your business plan as your organization grows to make sure the goals you’ve set both align with your mission and continue to be within reach.
[Read more: 8 Signs It's Time to Update Your Business Plan ]
CO— aims to bring you inspiration from leading respected experts. However, before making any business decision, you should consult a professional who can advise you based on your individual situation.
Applications are open for the CO—100! Now is your chance to join an exclusive group of outstanding small businesses. Share your story with us — apply today .
CO—is committed to helping you start, run and grow your small business. Learn more about the benefits of small business membership in the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, here .
Apply for the CO—100!
The CO—100 is an exclusive list of the 100 best and brightest small and mid-sized businesses in America. Enter today to share your story and get recognized.

Get recognized. Get rewarded. Get $25K.
Is your small business one of the best in America? Apply for our premier awards program for small businesses, the CO—100, today to get recognized and rewarded. One hundred businesses will be honored and one business will be awarded $25,000.
For more business strategies
How to build a b2b relationship with a large company, 6 tips for becoming a supplier to a big businesses, how to develop a qa process for your business.
By continuing on our website, you agree to our use of cookies for statistical and personalisation purposes. Know More
Welcome to CO—
Designed for business owners, CO— is a site that connects like minds and delivers actionable insights for next-level growth.
U.S. Chamber of Commerce 1615 H Street, NW Washington, DC 20062
Social links
Looking for local chamber, stay in touch.

How to Write a Business Plan For a Nonprofit Organization + Template

Creating a business plan is essential for any business, but it can be especially helpful for nonprofits. A nonprofit business plan allows you to set goals and track progress over time. It can also help you secure funding from investors or grant-making organizations.
A well-crafted business plan not only outlines your vision for the organization but also provides a step-by-step process of how you are going to accomplish it. In order to create an effective business plan, you must first understand the components that are essential to its success.
This article will provide an overview of the key elements that every nonprofit founder should include in their business plan.
Download the Ultimate Nonprofit Business Plan Template
What is a Nonprofit Business Plan?
A nonprofit business plan is a formal written document that describes your organization’s purpose, structure, and operations. It is used to communicate your vision to potential investors or donors and convince them to support your cause.
The business plan should include information about your target market, financial projections, and marketing strategy. It should also outline the organization’s mission statement and goals.
Why Write a Nonprofit Business Plan?
A nonprofit business plan is required if you want to secure funding from grant-making organizations or investors.
A well-crafted business plan will help you:
- Define your organization’s purpose and goals
- Articulate your vision for the future
- Develop a step-by-step plan to achieve your goals
- Secure funding from investors or donors
- Convince potential supporters to invest in your cause
Entrepreneurs can also use this as a roadmap when starting your new nonprofit organization, especially if you are inexperienced in starting a nonprofit.
Writing an Effective Nonprofit Business Plan
The key is to tailor your business plan to the specific needs of your nonprofit. Here’s a quick overview of what to include:
Executive Summary
Organization overview, products, programs, and services, industry analysis, customer analysis, marketing plan, operations plan, management team.
- Financial Plan
The executive summary of a nonprofit business plan is a one-to-two page overview of your entire business plan. It should summarize the main points, which will be presented in full in the rest of your business plan.
- Start with a one-line description of your nonprofit organization
- Provide a short summary of the key points of each section of your business plan.
- Organize your thoughts in a logical sequence that is easy for the reader to follow.
- Include information about your organization’s management team, industry analysis, competitive analysis, and financial forecast.
This section should include a brief history of your nonprofit organization. Include a short description of how and why you started it and provide a timeline of milestones the organization has achieved.
If you are just starting your nonprofit, you may not have a long history. Instead, you can include information about your professional experience in the industry and how and why you conceived your new nonprofit idea. If you have worked for a similar organization before or have been involved in a nonprofit before starting your own, mention this.
You will also include information about your chosen n onprofit business model and how it is different from other nonprofits in your target market.
This section is all about what your nonprofit organization offers. Include information about your programs, services, and any products you may sell.
Describe the products or services you offer and how they benefit your target market. Examples might include:
- A food bank that provides healthy meals to low-income families
- A job training program that helps unemployed adults find jobs
- An after-school program that helps kids stay out of gangs
- An adult literacy program that helps adults learn to read and write
Include information about your pricing strategy and any discounts or promotions you offer. Examples might include membership benefits, free shipping, or volume discounts.
If you offer more than one product or service, describe each one in detail. Include information about who uses each product or service and how it helps them achieve their goals.
If you offer any programs, describe them in detail. Include information about how often they are offered and the eligibility requirements for participants. For example, if you offer a job training program, you might include information about how often the program is offered, how long it lasts, and what kinds of jobs participants can expect to find after completing the program.
The industry or market analysis is an important component of a nonprofit business plan. Conduct thorough market research to determine industry trends, identify your potential customers, and the potential size of this market.
Questions to answer include:
- What part of the nonprofit industry are you targeting?
- Who are your competitors?
- How big is the market?
- What trends are happening in the industry right now?
You should also include information about your research methodology and sources of information, including company reports and expert opinions.
As an example, if you are starting a food bank, your industry analysis might include information about the number of people in your community who are considered “food insecure” (they don’t have regular access to enough nutritious food). You would also include information about other food banks in your area, how they are funded, and the services they offer.
For each of your competitors, you should include a brief description of their organization, their target market, and their competitive advantage. To do this, you should complete a SWOT analysis.
A SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis is a helpful tool to assess your nonprofit’s current position and identify areas where you can improve.
Some questions to consider when conducting a SWOT analysis include:
- Strengths : What does your nonprofit do well?
- Weaknesses : What areas could your nonprofit improve?
- Opportunities : What trends or changes in the industry could you take advantage of?
- Threats : What trends or changes in the industry could hurt your nonprofit’s chances of success?
After you have identified your nonprofit’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, you can develop strategies to improve your organization.
For example, if you are starting a food bank, your SWOT analysis might reveal that there is a need for more food banks in your community. You could use this information to develop a marketing strategy to reach potential donors who might be interested in supporting your organization.
If you are starting a job training program, your SWOT analysis might reveal that there is a need for more programs like yours in the community. You could use this information to develop a business plan and marketing strategy to reach potential participants who might be interested in enrolling in your program.
This section should include a list of your target audience(s) with demographic and psychographic profiles (e.g., age, gender, income level, profession, job titles, interests). You will need to provide a profile of each customer segment separately, including their needs and wants.
For example, if you are starting a job training program for unemployed adults, your target audience might be low-income adults between the ages of 18 and 35. Your customer analysis would include information about their needs (e.g., transportation, childcare, job readiness skills) and wants (e.g., good pay, flexible hours, benefits).
If you have more than one target audience, you will need to provide a separate customer analysis for each one.
You can include information about how your customers make the decision to buy your product or use your service. For example, if you are starting an after-school program, you might include information about how parents research and compare programs before making a decision.
You should also include information about your marketing strategy and how you plan to reach your target market. For example, if you are starting a food bank, you might include information about how you will promote the food bank to the community and how you will get the word out about your services.
Develop a strategy for targeting those customers who are most likely to use your program, as well as those that might be influenced to buy your products or nonprofit services with the right marketing.
This part of the business plan is where you determine how you are going to reach your target market. This section of your nonprofit business plan should include information about your marketing goals, strategies, and tactics.
- What are your marketing goals? Include information about what you hope to achieve with your marketing efforts, as well as when and how you will achieve it.
- What marketing strategies will you use? Include information about public relations, advertising, social media, and other marketing tactics you will use to reach your target market.
- What tactics will you use? Include information about specific actions you will take to execute your marketing strategy. For example, if you are using social media to reach your target market, include information about which platforms you will use and how often you will post.
Your marketing strategy should be clearly laid out, including the following 4 Ps.
- Product/Service : Make sure your product, service, and/or program offering is clearly defined and differentiated from your competitors, including the benefits of using your service.
- Price : How do you determine the price for your product, services, and/or programs? You should also include a pricing strategy that takes into account what your target market will be willing to pay and how much the competition within your market charges.
- Place : Where will your target market find you? What channels of distribution will you use to reach them?
- Promotion : How will you reach your target market? You can use social media or write a blog, create an email marketing campaign, post flyers, pay for advertising, launch a direct mail campaign, etc.
For example, if you are starting a job training program for unemployed adults, your marketing strategy might include partnering with local job centers and adult education programs to reach potential participants. You might also promote the program through local media outlets and community organizations.
Your marketing plan should also include a sales strategy, which includes information about how you will generate leads and convert them into customers.
You should also include information about your paid advertising budget, including an estimate of expenses and sales projections.
This part of your nonprofit business plan should include the following information:
- How will you deliver your products, services and/or programs to your target market? For example, if you are starting a food bank, you will need to develop a system for collecting and storing food donations, as well as distributing them to the community.
- How will your nonprofit be structured? For example, will you have paid staff or volunteers? How many employees will you need? What skills and experience will they need to have?
- What kind of facilities and equipment will you need to operate your nonprofit? For example, if you are starting a job training program, you will need space to hold classes, as well as computers and other office equipment.
- What are the day-to-day operations of your nonprofit? For example, if you are starting a food bank, you will need to develop a system for accepting and sorting food donations, as well as distributing them to the community.
- Who will be responsible for each task? For example, if you are starting a job training program, you will need to identify who will be responsible for recruiting participants, teaching classes, and placing graduates in jobs.
- What are your policies and procedures? You will want to establish policies related to everything from employee conduct to how you will handle donations.
- What infrastructure, equipment, and resources are needed to operate successfully? How can you meet those requirements within budget constraints?
The operations plan is the section of the business plan where you elaborate on the day-to-day execution of your nonprofit. This is where you really get into the nitty-gritty of how your organization will function on a day-to-day basis.
This section of your nonprofit business plan should include information about the individuals who will be running your organization.
- Who is on your team? Include biographies of your executive director, board of directors, and key staff members.
- What are their qualifications? Include information about their education, work experience, and skills.
- What are their roles and responsibilities? Include information about what each team member will be responsible for, as well as their decision-making authority.
- What is their experience in the nonprofit sector? Include information about their work with other nonprofits, as well as their volunteer experiences.
This section of your plan is important because it shows that you have a team of qualified individuals who are committed to the success of your nonprofit.
Nonprofit Financial Plan
This section of your nonprofit business plan should include the following information:
- Your budget. Include information about your income and expenses, as well as your fundraising goals.
- Your sources of funding. Include information about your grants, donations, and other sources of income.
- Use of funds. Include information about how you will use your income to support your programs and operations.
This section of your business plan is important because it shows that you have a clear understanding of your organization’s finances. It also shows that you have a plan for raising and managing your funds.
Now, include a complete and detailed financial plan. This is where you will need to break down your expenses and revenue projections for the first 5 years of operation. This includes the following financial statements:
Income Statement
Your income statement should include:
- Revenue : how will you generate revenue?
- Cost of Goods Sold : These are your direct costs associated with generating revenue. This includes labor costs, as well as the cost of any equipment and supplies used to deliver the product/service offering.
- Net Income (or loss) : Once expenses and revenue are totaled and deducted from each other, what is the net income or loss?
Sample Income Statement for a Startup Nonprofit Organization
| Revenues | $ 336,090 | $ 450,940 | $ 605,000 | $ 811,730 | $ 1,089,100 |
| $ 336,090 | $ 450,940 | $ 605,000 | $ 811,730 | $ 1,089,100 | |
| Direct Cost | |||||
| Direct Costs | $ 67,210 | $ 90,190 | $ 121,000 | $ 162,340 | $ 217,820 |
| $ 67,210 | $ 90,190 | $ 121,000 | $ 162,340 | $ 217,820 | |
| $ 268,880 | $ 360,750 | $ 484,000 | $ 649,390 | $ 871,280 | |
| Salaries | $ 96,000 | $ 99,840 | $ 105,371 | $ 110,639 | $ 116,171 |
| Marketing Expenses | $ 61,200 | $ 64,400 | $ 67,600 | $ 71,000 | $ 74,600 |
| Rent/Utility Expenses | $ 36,400 | $ 37,500 | $ 38,700 | $ 39,800 | $ 41,000 |
| Other Expenses | $ 9,200 | $ 9,200 | $ 9,200 | $ 9,400 | $ 9,500 |
| $ 202,800 | $ 210,940 | $ 220,871 | $ 230,839 | $ 241,271 | |
| EBITDA | $ 66,080 | $ 149,810 | $ 263,129 | $ 418,551 | $ 630,009 |
| Depreciation | $ 5,200 | $ 5,200 | $ 5,200 | $ 5,200 | $ 4,200 |
| EBIT | $ 60,880 | $ 144,610 | $ 257,929 | $ 413,351 | $ 625,809 |
| Interest Expense | $ 7,600 | $ 7,600 | $ 7,600 | $ 7,600 | $ 7,600 |
| $ 53,280 | $ 137,010 | $ 250,329 | $ 405,751 | $ 618,209 | |
| Taxable Income | $ 53,280 | $ 137,010 | $ 250,329 | $ 405,751 | $ 618,209 |
| Income Tax Expense | $ 18,700 | $ 47,900 | $ 87,600 | $ 142,000 | $ 216,400 |
| $ 34,580 | $ 89,110 | $ 162,729 | $ 263,751 | $ 401,809 | |
| 10% | 20% | 27% | 32% | 37% | |
Balance Sheet
Include a balance sheet that shows what you have in terms of assets, liabilities, and equity. Your balance sheet should include:
- Assets : All of the things you own (including cash).
- Liabilities : This is what you owe against your company’s assets, such as accounts payable or loans.
- Equity : The worth of your business after all liabilities and assets are totaled and deducted from each other.
Sample Balance Sheet for a Startup Nonprofit Organization
| Cash | $ 105,342 | $ 188,252 | $ 340,881 | $ 597,431 | $ 869,278 |
| Other Current Assets | $ 41,600 | $ 55,800 | $ 74,800 | $ 90,200 | $ 121,000 |
| Total Current Assets | $ 146,942 | $ 244,052 | $ 415,681 | $ 687,631 | $ 990,278 |
| Fixed Assets | $ 25,000 | $ 25,000 | $ 25,000 | $ 25,000 | $ 25,000 |
| Accum Depreciation | $ 5,200 | $ 10,400 | $ 15,600 | $ 20,800 | $ 25,000 |
| Net fixed assets | $ 19,800 | $ 14,600 | $ 9,400 | $ 4,200 | $ 0 |
| $ 166,742 | $ 258,652 | $ 425,081 | $ 691,831 | $ 990,278 | |
| Current Liabilities | $ 23,300 | $ 26,100 | $ 29,800 | $ 32,800 | $ 38,300 |
| Debt outstanding | $ 108,862 | $ 108,862 | $ 108,862 | $ 108,862 | $ 0 |
| $ 132,162 | $ 134,962 | $ 138,662 | $ 141,662 | $ 38,300 | |
| Share Capital | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ 0 |
| Retained earnings | $ 34,580 | $ 123,690 | $ 286,419 | $ 550,170 | $ 951,978 |
| $ 34,580 | $ 123,690 | $ 286,419 | $ 550,170 | $ 951,978 | |
| $ 166,742 | $ 258,652 | $ 425,081 | $ 691,831 | $ 990,278 | |
Cash Flow Statement
Include a cash flow statement showing how much cash comes in, how much cash goes out and a net cash flow for each year. The cash flow statement should include:
- Income : All of the revenue coming in from clients.
- Expenses : All of your monthly bills and expenses. Include operating, marketing and capital expenditures.
- Net Cash Flow : The difference between income and expenses for each month after they are totaled and deducted from each other. This number is the net cash flow for each month.
Using your total income and expenses, you can project an annual cash flow statement. Below is a sample of a projected cash flow statement for a startup nonprofit.
Sample Cash Flow Statement for a Startup Nonprofit Organization
| Net Income (Loss) | $ 34,580 | $ 89,110 | $ 162,729 | $ 263,751 | $ 401,809 |
| Change in Working Capital | $ (18,300) | $ (11,400) | $ (15,300) | $ (12,400) | $ (25,300) |
| Plus Depreciation | $ 5,200 | $ 5,200 | $ 5,200 | $ 5,200 | $ 4,200 |
| Net Cash Flow from Operations | $ 21,480 | $ 82,910 | $ 152,629 | $ 256,551 | $ 380,709 |
| Fixed Assets | $ (25,000) | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ 0 |
| Net Cash Flow from Investments | $ (25,000) | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ 0 |
| Cash from Equity | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ 0 |
| Cash from Debt financing | $ 108,862 | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ (108,862) |
| Net Cash Flow from Financing | $ 108,862 | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ (108,862) |
| Net Cash Flow | $ 105,342 | $ 82,910 | $ 152,629 | $ 256,551 | $ 271,847 |
| Cash at Beginning of Period | $ 0 | $ 105,342 | $ 188,252 | $ 340,881 | $ 597,431 |
| Cash at End of Period | $ 105,342 | $ 188,252 | $ 340,881 | $ 597,431 | $ 869,278 |
Fundraising Plan
This section of your nonprofit business plan should include information about your fundraising goals, strategies, and tactics.
- What are your fundraising goals? Include information about how much money you hope to raise, as well as when and how you will raise it.
- What fundraising strategies will you use? Include information about special events, direct mail campaigns, online giving, and grant writing.
- What fundraising tactics will you use? Include information about volunteer recruitment, donor cultivation, and stewardship.
Now include specific fundraising goals, strategies, and tactics. These could be annual or multi-year goals. Below are some examples:
Goal : To raise $50,000 in the next 12 months.
Strategy : Direct mail campaign
- Create a mailing list of potential donors
- Develop a direct mail piece
- Mail the direct mail piece to potential donors
Goal : To raise $100,000 in the next 24 months.
Strategy : Special event
- Identify potential special event sponsors
- Recruit volunteers to help with the event
- Plan and execute the special event
Goal : To raise $250,000 in the next 36 months.
Strategy : Grant writing
- Research potential grant opportunities
- Write and submit grant proposals
- Follow up on submitted grants
This section of your business plan is important because it shows that you have a clear understanding of your fundraising goals and how you will achieve them.
You will also want to include an appendix section which may include:
- Your complete financial projections
- A complete list of your nonprofit’s policies and procedures related to the rest of the business plan (marketing, operations, etc.)
- A list of your hard assets and equipment with purchase dates, prices paid and any other relevant information
- A list of your soft assets with purchase dates, prices paid and any other relevant information
- Biographies and/or resumes of the key members of your organization
- Your nonprofit’s bylaws
- Your nonprofit’s articles of incorporation
- Your nonprofit’s most recent IRS Form 990
- Any other relevant information that may be helpful in understanding your organization
Writing a good business plan gives you the advantage of being fully prepared to launch and grow your nonprofit organization. It not only outlines your vision but also provides a step-by-step process of how you are going to accomplish it. Sometimes it may be difficult to get started, but once you get the hang of it, writing a business plan becomes easier and will give you a sense of direction and clarity about your nonprofit organization.
Finish Your Nonprofit Business Plan in 1 Day!
Other helpful articles.
How to Write a Grant Proposal for Your Nonprofit Organization + Template & Examples
How To Create the Articles of Incorporation for Your Nonprofit Organization + Template
How to Develop a Nonprofit Communications Plan + Template
How to Write a Stand-Out Purpose Statement + Examples
Experience Convene Learn how Convene can give your boards a superior meeting experience. Enquire for a free demo with no cost or obligation.
Nonprofit Business Plan: A Comprehensive Guide
- by Jess Convocar on February 21, 2024
- last update on May 06, 2024
- Reading Time: 7 minutes

Like any other business, nonprofit organizations need careful, structured planning to ensure sustainable growth. This is possible by creating a business plan that not only serves as a roadmap but also helps in attracting donors and volunteers needed to bring the organization’s vision to fruition.
Crafting the perfect business plan involves many things, but the most important part is understanding what it should look like and how it can help the organization forward its mission. This guide simplifies the process, breaks down its unique components, and provides step-by-step instructions on how to write a nonprofit business plan.
What is a business plan for nonprofits?
A business plan for nonprofits is a strategic document that outlines a nonprofit organization’s goals and operational approach. While similar to for-profit business plans, the focus here is on achieving social impact rather than financial profit.
Projects implemented by nonprofit organizations typically revolve around fostering social welfare, advocacy, education, or humanitarian aid. For instance, a nonprofit working to address homelessness might outline projects such as providing shelter and meals, offering job training programs, and collaborating with local agencies to advocate for affordable housing policies.
A typical business plan for nonprofits includes:
- The nonprofit’s mission, which sets the foundation for the entire plan;
- Specific objectives,
- Fundraising strategies,
- Resource allocation,
- And how it plans to measure success in terms of societal or community benefit.
But one thing to note is that there is no one-size-fits-all plan. Every little detail incorporated into the plan must be tailored to the organization’s needs, where it currently stands, and how it can contribute to its primary purpose – guiding the nonprofit to success.
Why Your Nonprofit Needs a Business Plan
A good plan does not only help attract external support but also benefits the organization internally. Listed below are the key reasons why your nonprofit needs a business plan:
Clarity of Mission, Vision, and Strategic Direction
Running a nonprofit organization isn’t the easiest task, and there may be times when you question whether you’re truly making an impact. Having a business plan gives you a perspective of the progress you’ve made and provides a distinct path moving forward.
This clear-cut framework ensures that the mission, vision, and strategic direction remain focused, helping the nonprofit make informed decisions and navigate challenges with purpose.
Proper Resource Planning and Financial Management
Poor financial management can lead to many problems, especially in nonprofits. With a business plan, this can easily be taken care of.
Since nonprofit organizations rely on various external funds, there should be an emphasis on resource planning and management. This involves forecasting the organization’s needs, such as financial, human, and technological resources, and strategically allocating them to support the mission and vision. Doing so also demonstrates fiscal responsibility to donors and stakeholders.
Strategic Fundraising and Sustainability
One of the most common and effective ways nonprofits gain support is through fundraising activities. A business plan helps you develop a targeted fundraising strategy that aligns with the organization’s goals. Clearly outlining the fundraising objectives, target audiences, and specific tactics provides a roadmap for effective resource mobilization.
Additionally, a structured plan attracts and retains donors by instilling confidence in them about the tangible impact their contributions can make.
Risk Management
A business plan is vital for developing strategies to handle risks and potential challenges. This proactive approach helps minimize the impact of unforeseen events, like economic recessions or natural disasters, on the nonprofit’s operations.
A robust risk management strategy not only saves time and money but also improves decision-making, avoids surprises, and, most importantly, prevents harm to the people your nonprofit serves.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Because the business plan already lays out how the organization works, it’s easier to understand and adhere to nonprofit laws like tax exemption and revenue regulations.
Dealing with these things from the start helps prevent potential problems, maintains transparency, and builds trust with stakeholders. This allows you to focus on carrying out the mission without legal conflicts.
How to Create a Business Plan Strategy
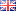
When gearing up to create a business plan for your nonprofit organization, it’s important to begin by thoroughly understanding the unique aspects of your mission. This solid foundation will guide you through the next steps of crafting a well-thought-out plan, which includes:
1. Create a strategy
Before anything else, you must identify your why .
Ask yourself what you want to happen. What does the organization stand for? Who does it serve? What do you hope for it to become?
If your long-term goal is to create a lasting impact and expand the community you serve, establish a strategy that mirrors your mission. Begin by assessing your organization’s current position, strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities. Based on your assessment, leverage the strengths and address weaknesses that may hinder progress.
Next, clearly define who your target audience is. Understand their specific needs and preferences to tailor your approach effectively.
Once the key factors have been determined and written down, it will serve as the starting point for the strategy.
2. Plan programs
The planning step is where you delve into the how. What are your plans to sustain and amplify the impact you aim to create?
Since you are not selling products or providing services to generate revenue, you’ll need to rely on fundraising events to support your cause. To do this effectively, create detailed program plans covering goals, activities, timelines, and expected outcomes. As always, ensure these plans align with your organization’s mission.
After establishing the programs, set up a monitoring system that tracks their effectiveness and evaluates them regularly. This helps you make informed changes as the nonprofit or the community’s needs evolve.
3. Ensure financial sustainability
Nonprofits receive financial support from various channels, such as individual donations, grants, sponsorships, and fundraising events. To ensure economic sustainability, building relationships with potential donors, individuals, institutions, and various funding sources is important to avoid relying too much on a single avenue.
In this sense, a well-thought-out budget is crucial for financial stability. Make sure to allocate resources carefully, considering program costs, administration expenses, and other needs. A clear and transparent budget not only aids in financial planning but also boosts trust with supporters.
4. Prioritize legal considerations
Even though dealing with changing rules might seem to lead to more paperwork than focusing on your mission, remember that compliance is as important as pursuing your organization’s goals. Some vital legal considerations include:
- Legal structure and registration
- Tax exemption (if applicable)
- Fundraising compliance
- Financial accountability
- Intellectual property (such as logos, trademarks, and copyrights)
- Data protection and privacy
Maintaining a good standing is crucial for obtaining licenses, securing grants and funding, protecting your organization’s reputation, and keeping the right to solicit support.
If you don’t have an in-house legal counsel, it’s a good idea to seek advice from experts who know nonprofit laws in your area when planning your business.
How to Write a Nonprofit Business Plan

Now that you’ve covered all the essential details, the next step is to create the business plan outline. There’s no strict format to follow, as it all depends on your organization’s specifics. However, make sure not to exclude these essential components when creating a nonprofit business plan:
1. Executive Summary
This part is a quick overview of the whole document. Since it’s the first thing people see in the business plan, it’s crucial to make it clear and interesting enough to grab their attention and encourage them to read the entire plan. Include the organization’s fundamentals – its history, objectives, and financing plans.
2. Organizational Overview
Provide a gist of who you are and who you serve. Here, express the organization’s mission, vision, and specific short-term and long-term goals.
3. Products, Programs, or Services Rendered
In this section, you must provide a detailed description of all the products and services mentioned in the executive summary. Highlight any unique aspects, such as innovative features and distinct advantages, that set you apart. State how instrumental these are to the success of your initiatives and how each one addresses the industry need.
4. Operational Plan
This is where you detail how your nonprofit will function on a day-to-day basis. Outline each team member’s daily, weekly, and monthly tasks, specifying responsibilities, timelines, and collaboration points to ensure a cohesive and efficient operation.
Additionally, spotlight any key processes, workflows, or systems necessary to achieve your mission.
5. Marketing Plan
The marketing plan should reflect the mission of the organization. Under this section, outline the strategies and channels to get your nonprofit out there. Include details about your target audience, methods for reaching them, and any promotional activities. This section may also cover partnerships, collaborations, and outreach efforts.
6. Financial Plan
The financial plan provides a comprehensive overview of your nonprofit’s financial health and projections. Include a budget, funding sources, and a breakdown of how funds will be allocated to support your operations and programs. This part is vital for demonstrating sustainability and helping make better-informed decisions.
7. Appendix
In the appendix, incorporate all the additional documents and information supporting the business plan’s main body. This may include resumes of key personnel, detailed financial statements, legal documents, or any other relevant materials.
Here’s a quick step-by-step guide on how to write a business plan:
- Start by outlining the executive summary providing a concise overview of the plan.
- Develop the organizational overview, which includes the mission and vision of the nonprofit.
- Conduct a SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats) analysis to identify and address internal and external factors.
- Clearly articulate short-term and long-term goals and objectives.
- Describe the programs and activities that will help achieve these goals.
- Develop a marketing and outreach strategy to engage the community and attract support.
- Create a detailed financial plan, including budgets, revenue streams, and financial projections.
- Outline the governance and management structure, including roles and responsibilities.
- Detail monitoring and evaluation processes to assess program effectiveness.
Nonprofit Business Plan Template
Once you have a clear grasp of your organizational goals and strategies, here’s a sample nonprofit business plan template to get you started:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Nonprofit Business Plan
Q: how often should a non-profit business plan be updated.
Although nonprofit plans usually set up a roadmap for at least three to five years, they should be regularly reviewed and updated to ensure they remain relevant and aligned with the organization’s purpose and changing external factors. For younger companies, an annual update with six monthly reviews may be sufficient, while more established nonprofits might opt for an annual review with quarterly check-ins.
Q: What role does evaluation play in a non-profit business plan?
Smaller nonprofits often conduct formal evaluations because their funders require it, but the benefits extend in both directions. Internally, evaluations help the organization assess its performance, impact, and effectiveness. In doing so, the nonprofit meets funder expectations and gains valuable insights for improvement, ensuring transparency and better alignment with its mission.
Q: How can a non-profit maintain adaptability in its strategies?
To stay adaptable, a nonprofit can follow three basic practices. First, keep the business plan up-to-date to align with the changing goals and environment. Second, stay on top of current industry trends to anticipate shifts in the landscape and prepare ahead of time. Lastly, revamp tools and approaches to ensure strategies remain innovative and effective.
Plan for Nonprofit Success with Convene

A well-crafted nonprofit business plan is crucial for success. To achieve this, cooperation is necessary within the internal teams and partners. However, communication can be a common roadblock, especially in a remote workplace.
This is where Convene comes into play.
Convene is a reliable board portal for nonprofits that facilitates effective planning through its interactive and secure features. Easily collaborate with everyone in the organization by leveraging Convene’s live meeting capabilities, such as annotations and digital sign-offs. Also, keep track of the updates and reports with its secure document management features.
Check out this page to learn more about Convene and how it can benefit your nonprofit organizations.
Related Articles

Board Portals for Nonprofits: A New Necessity?

A Definitive Guide to Effective Board Governance

Embracing Virtual Meetings for Nonprofits and Religious Institutions
Take your organization’s meetings to the next level.
Learn how Convene can give your boards a superior meeting experience. Enquire for a free demo with no cost or obligation.
- Apply for a Discount
- Sign Up for Free

How to write a nonprofit business plan: A comprehensive guide
Steps to write a nonprofit business plan.
- Start with research
- Define your mission and vision
- Outline your programs and services
- Determine your organizational structure
- Conduct a market analysis
- Craft your marketing strategy
- Develop financial projections
- Write and refine
Business plans aren’t only for startups and corporations; they’re equally crucial for nonprofit organizations. A well-drafted nonprofit business plan not only provides direction but also attracts donors and other stakeholders. In this article, we’ll delve into the hows and whys of writing a nonprofit business plan and walk you through the process step by step.
The purpose and importance of a nonprofit business plan
A business plan is like a roadmap. It charts the course, setting clear goals and detailing the strategies needed to reach your destination (e.g., business goals). Given the unique challenges nonprofits face — competing for funding, demonstrating impact, and managing resources efficiently — a business plan is indispensable for staying on track.
What is a nonprofit business plan?
A nonprofit business plan is a document that outlines an organization’s operational and financial objectives, and details the strategies and resources (both human and capital) required to achieve those objectives. It serves as an internal guide for the organization’s leadership and a tool for communicating with external stakeholders.
Why do nonprofits need a business plan?
At its core, a nonprofit organization thrives on clarity of purpose, and a business plan offers just that. It establishes a clear mission and vision, serving as a guiding light for every strategic decision and action.
Beyond this foundational benefit, a business plan fosters operational efficiency. Meticulously outlining processes and delineating roles and responsibilities ensures a streamlined workflow, preventing any overlaps or omissions that could hamper the organization’s effectiveness.
In a competitive landscape where nonprofits vie for funding, a well-articulated business plan attests to the organization’s seriousness, structure, and transparency. Donors and sponsors are more inclined to invest when they see a clear roadmap detailing how an organization will use their contributions.
Last, a business plan serves as a robust framework for performance evaluation. Setting benchmarks and expectations drives the organization toward its goals and creates a culture of accountability — ensuring that every stakeholder is aligned and contributing to the collective mission.
Key components of a nonprofit business plan
Like a blueprint, a business plan has several elements that are indispensable to its structure. But depending on your organization’s goals and purpose, there may be elements unique to you. Let’s consider the pillar elements of every plan:
- The executive summary provides an overview of the organization, including its mission, vision, goals, and achievements to date.
- An organization description details the history, structure, and values of the organization.
- A market analysis provides a detailed examination of the community or population the nonprofit serves as well as a description of their needs and the ways the organization meets them.
- The organizational structure outlines the roles and responsibilities of team members, the board of directors, and other key personnel.
- The services and programs section provides details on the services the organization provides or the programs it runs.
- The marketing plan explains how the organization will raise awareness about its work. It includes strategies for donor engagement, fundraising events, and promotional campaigns.
- The financial projections section provides an estimate of the organization’s financial outlook for the next three to five years. It includes expected income, expenses, and milestones to reach financial sustainability.
A step-by-step guide to writing a nonprofit business plan
Creating a nonprofit business plan can seem daunting, but it can be rewarding if you take the right approach. Follow this step-by-step guide to help you navigate the process:
- Start with research. Understand the needs of your target community. This knowledge forms the foundation of your business plan.
- Define your mission and vision. Clearly state what your organization aims to achieve and the change it wants to bring about.
- Outline your programs and services. Detail how you plan to achieve your mission. Break down your offerings, explaining the impact and benefit of each.
- Determine your organizational structure. Establish the hierarchy, roles, and responsibilities to help in operations and decision-making processes.
- Conduct a market analysis. Identify key trends in the nonprofit sector and analyze your competitors. Determine what sets you apart.
- Craft your marketing strategy. Consider how you’ll communicate your mission and raise funds. You might include events, online campaigns, and collaborations.
- Develop financial projections. While predicting donations is challenging, try to provide a realistic financial outlook. Base projections on past data, if available, or make educated guesses using your market analysis.
- Write and refine. Draft the business plan, integrating all the components. Use clear, concise language. Once your draft is complete, review and refine it for clarity and coherence. It’s a good idea to have another professional review it too, as they may see things that you’ve missed.
Tips and best practices
- Stay realistic. While optimism is great, your projections and plans should be grounded in reality.
- Engage stakeholders. Consult team members, board members, and even potential donors when drafting the plan.
- Regularly review and update. A business plan isn’t a static document. As your organization evolves, make sure your business plan does too.
- Use visuals. Graphs, charts, and infographics can make your plan more engaging and easier to understand.
How Jotform can help you create a nonprofit business plan
Crafting a nonprofit business plan requires meticulous organization and seamless data collection. As you dive into the process, Jotform can help you create customized forms that streamline various aspects of your planning.
Whether you’re gathering initial research and feedback, managing donor information, registering volunteers, or even tracking impact metrics, Jotform ensures that every piece of data is organized and accessible.
Jotform’s intuitive interface and templates make it easy to design forms tailored to your nonprofit’s specific needs. Use Jotform’s business plan templates to give yourself a head start. From soliciting feedback on a new program idea to managing donor relationships to reporting on the tangible impact of your efforts, Jotform simplifies the process. You can even use the business proposal template to collect grantor signatures.
Nonprofit organizations are eligible for a 50-percent discount on paid Jotform plans.
Photo by Monstera Production
Thank you for helping improve the Jotform Blog. 🎉
RECOMMENDED ARTICLES

How to Start A Nonprofit Organization

How to start an online petition

6 of the best credit card processing solutions for nonprofits

5 discount software tools for nonprofit organizations

DonorPerfect vs eTapestry: Comparing nonprofit CRM systems

DonorPerfect vs Raiser's Edge

How to accept nonprofit stock donations

How Jotform helps Women’s Wilderness promote women’s empowerment

The 10 best Blackbaud alternatives for nonprofits in 2024

How a Seattle Website Used Jotform to Raise $20,000 for Local Schools and Nonprofits

How to Create a Winning Donation Form

4 effective ways to boost your nonprofit’s finances

5 ways Jotform can facilitate your giving campaigns

The Importance of a Great Donate Button

6 tips to get your donation form in front of donors during COVID-19

15 best WordPress plug-ins for nonprofits

The United States of Charity The Generosity Index: Ranking the Most Charitable Places in the U.S.

Marketing automation for nonprofits

Year-end giving campaign ideas

Raiser’s Edge vs Salesforce: Which is best?

How to organize a 5K run
Reasons to Use Jotform as a PayPal Donate Button Alternative

Aplos vs QuickBooks: Navigating financial software choices

Reviewing WildApricot’s pricing: Which plan is best for you?

How to improve nonprofit grant management

Top 7 online donation tools to raise more money

WildApricot vs MemberPlanet: A detailed comparison

How to set up Venmo for nonprofit organizations

How to collect donations with Carrd

How to get people to donate money to you

How to set up an emergency rental assistance program in your community

Avoid making these costly donation form mistakes

Learn How MidTown Uses Jotform Nonprofit Forms
Top donation management software solutions

How to write a grant proposal for a nonprofit

Donor management: Nonprofit tips for retaining donors
Best way to collect donations online: Jotform

10+ marketing strategies and tools every nonprofit needs

Little Green Light vs Salesforce

10 of the best nonprofit event management software apps

How to start a scholarship fund

How to set up a GivingTuesday donation system using Jotform

Webinar: How to prepare for giving season with Jotform + Square

The best WordPress donation plug-ins
5 Ways Jotform Can Help Your Nonprofit

How to conduct prospect research for nonprofits

How does a nonprofit fill out a W-9 form?

Webinar: Maximum Impact: 5 ways to automate year-end giving
Top 25 nonprofit survey questions

9 table templates to help with your nonprofit

How a Nonprofit Supports Documentary Filmmaking with the Help of Jotform

How to use Jotform Tables to facilitate giving

Best 5 nonprofit websites of 2024

Top 5 membership management software solutions

Scaling up your operations: Unlocking growth with tech

How to find a Form 990 for a nonprofit

The essentials of Google Pay for nonprofits

Announcing a New Book on Maximizing Donations

Get a Nonprofit Discount With These Companies

The 14 best nonprofit CRM solutions for 2024

How to organize a potluck

How to write a powerful nonprofit mission statement

How First Tee Greater Detroit uses Jotform to empower youth through golf

How a Nonprofit Museum Uses Jotform

Use Jotform for Nonprofit Management

How to set up a relief fund
Send Comment :
Free Nonprofit Business Plan Templates
By Joe Weller | September 18, 2020
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
In this article, we’ve rounded up the most useful list of nonprofit business plan templates, all free to download in Word, PDF, and Excel formats.
Included on this page, you’ll find a one-page nonprofit business plan template , a fill-in-the-blank nonprofit business plan template , a startup nonprofit business planning timeline template , and more. Plus, we provide helpful tips for creating your nonprofit business plan .
Nonprofit Business Plan Template
Use this customizable nonprofit business plan template to organize your nonprofit organization’s mission and goals and convey them to stakeholders. This template includes space for information about your nonprofit’s background, objectives, management team, program offerings, market analysis, promotional activities, funding sources, fundraising methods, and much more.
Download Nonprofit Business Plan Template
One-Page Business Plan for Nonprofit Template
This one-page nonprofit business plan template has a simple and scannable design to outline the key details of your organization’s strategy. This template includes space to detail your mission, vision, and purpose statements, as well as the problems you aim to solve in your community, the people who benefit from your program offerings, your key marketing activities, your financial goals, and more.
Download One-Page Business Plan for Nonprofit Template
Excel | Word | PDF
For additional resources, including an example of a one-page business plan , visit “ One-Page Business Plan Templates with a Quick How-To Guide .”
Fill-In-the-Blank Nonprofit Business Plan Template
Use this fill-in-the-blank template as the basis for building a thorough business plan for a nonprofit organization. This template includes space to describe your organization’s background, purpose, and main objectives, as well as key personnel, program and service offerings, market analysis, promotional activities, fundraising methods, and more.
Download Fill-In-the-Blank Nonprofit Business Plan Template
For additional resources that cater to a wide variety of organizations, visit “ Free Fill-In-the-Blank Business Plan Templates .”
Startup Nonprofit Business Planning Template with Timeline
Use this business planning template to organize and schedule key activities for your business. Fill in the cells according to the due dates, and color-code the cells by phase, owner, or category to provide a visual timeline of progress.
Download Startup Nonprofit Business Planning Template with Timeline
Excel | Smartsheet
Nonprofit Business Plan Template for Youth Program
Use this template as a foundation for building a powerful and attractive nonprofit business plan for youth programs and services. This template has all the core components of a nonprofit business plan. It includes room to detail the organization’s background, management team key personnel, current and future youth program offerings, promotional activities, operations plan, financial statements, and much more.
Download Nonprofit Business Plan Template for Youth Program
Word | PDF | Google Doc
Sample Nonprofit Business Plan Outline Template
You can customize this sample nonprofit business plan outline to fit the specific needs of your organization. To ensure that you don’t miss any essential details, use this outline to help you prepare and organize the elements of your plan before filling in each section.
Download Sample Nonprofit Business Plan Outline Template
Nonprofit Startup Business Planning Checklist Template
Use this customizable business planning checklist as the basis for outlining the necessary steps to get your nonprofit organization up and running. You can customize this checklist to fit your individual needs. It includes essential steps, such as conducting a SWOT analysis , fulfilling the research requirements specific to your state, conducting a risk assessment , defining roles and responsibilities, creating a portal for board members, and other tasks to keep your plan on track.
Download Nonprofit Startup Business Planning Checklist Template
Tips to Create Your Nonprofit Business Plan
Your nonprofit business plan should provide your donors, volunteers, and other key stakeholders with a clear picture of your overarching mission and objectives. Below, we share our top tips for ensuring that your plan is attractive and thorough.
- Develop a Strategy First: You must aim before you fire if you want to be effective. In other words, develop a strategic plan for your nonprofit in order to provide your team with direction and a roadmap before you build your business plan.
- Save Time with a Template: No need to start from scratch when you can use a customizable nonprofit business plan template to get started. (Download one of the options above.)
- Start with What You Have: With the exception of completing the executive summary, which you must do last, you aren’t obligated to fill in each section of the plan in order. Use the information you have on hand to begin filling in the various parts of your business plan, then conduct additional research to fill in the gaps.
- Ensure Your Information Is Credible: Back up all the details in your plan with reputable sources that stakeholders can easily reference.
- Be Realistic: Use realistic assumptions and numbers in your financial statements and forecasts. Avoid the use of overly lofty or low-lying projections, so stakeholders feel more confident about your plan.
- Strive for Scannability: Keep each section clear and concise. Use bullet points where appropriate, and avoid large walls of text.
- Use Visuals: Add tables, charts, and other graphics to draw the eye and support key points in the plan.
- Be Consistent: Keep the voice and formatting (e.g., font style and size) consistent throughout the plan to maintain a sense of continuity.
- Stay True to Your Brand: Make sure that the tone, colors, and overall style of the business plan are a true reflection of your organization’s brand.
- Proofread Before Distribution: Prior to distributing the plan to stakeholders, have a colleague proofread the rough version to check for errors and ensure that the plan is polished.
- Don’t Set It and Forget It: You should treat your nonprofit business plan as a living document that you need to review and update on a regular basis — as objectives change and your organization grows.
- Use an Effective Collaboration Tool: Use an online tool to accomplish the following: collaborate with key personnel on all components of the business plan; enable version control for all documents; and keep resources in one accessible place.
Improve Your Nonprofit Business Planning Efforts with Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
Nonprofit Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Business Plan Outline
- Nonprofit Business Plan Home
- 1. Executive Summary
- 2. Company Overview
- 3. Industry Analysis
- 4. Customer Analysis
- 5. Competitive Analysis
- 6. Marketing Plan
- 7. Operations Plan
- 8. Management Team
- 9. Financial Plan
Nonprofit Business Plan
You’ve come to the right place to write a nonprofit business plan.
We have helped over 10,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create nonprofit business plans and many have used them to start or grow their nonprofit organizations.
Sample Business Plan for a Nonprofit Organization
Below are links to the essential sections of our sample nonprofit business plan template to help you with the business planning process for your organization:
- Executive Summary – The Executive Summary of your nonprofit business plan explains your overall strategic plan to achieve success as a nonprofit business. It will include your nonprofit mission statement, goals, and objectives. This section will also include information on your target market, competition, and marketing strategy.
- Company Overview – Also called the Organization Overview, you will include the mission statement and history of your nonprofit including the organization’s goals and any significant milestones achieved to date.
- Industry Analysis – Sometimes referred to as the Market Analysis, this section will provide an overview of the nonprofit industry, trends, and the competitive landscape.
- Customer Analysis – The Customer Analysis section details the demographics and psychographics of your target audience and how you plan to reach them.
- Competitive Analysis – In your Competitive Analysis, you will identify and describe the competition, both direct and indirect, including other nonprofits with the same mission. You will also include your strategic plan for competing in the market.
- Marketing Plan – The Marketing Plan will detail your products, programs and services, your overall marketing strategies and tactics, and how you will measure success. It should include information on your target market, positioning, branding, communications, and lead generation.
- Operations Plan – Your operational plan will outline your day-to-day operations as well as the specific objectives needed to achieve your long-term business goals and how you will measure success.
- Management Team – In the Management Team section of your business plan, you should include the organizational structure of your nonprofit business as well as bios of your executive team and each board member.
- Financial Plan – The Financial Plan is one of the most important sections of your nonprofit business plan. You will establish your financial goals and include financial statements such as the income statement, balance sheet and cash flow statement to show how your nonprofit will be sustainable. This section should also include your fundraising plan including potential donors, fundraising goals, and other funding sources for your organization.
Next Section: Executive Summary >
Nonprofit Business Plan FAQs
What is a nonprofit business plan.
A nonprofit business plan is a roadmap to start a nonprofit organization or as the organization grows. Among other things, it outlines your charitable concept, identifies your target customers, presents your marketing plan and details your financial projections. Your non profit business plan should be a living document that is updated frequently as your nonprofit grows.
You can easily complete your nonprofit business plan using our Nonprofit Business Plan Template here .
What Are the Main Types of Nonprofit Organizations?
There are many types of nonprofits, but each has a charitable mission to help an underserved segment of society. For example, there are nonprofits that serve the underserved youth, abused or abandoned animals, homeless, veterans and impoverished. There are also many nonprofits that support social awareness and global issues such as the environment, education and equality.
What Are the Main Sources of Revenue and Expenses for a Nonprofit Business?
The primary source of revenue for nonprofit organizations are monetary donations from sponsors, government grants and funding, and tax incentives through 501c3 designations.
The key expenses for a nonprofit business are staffing, supplies, rent, utilities, program costs and working capital to ensure the sustainability of the non profit. Proper business planning will help your nonprofit thrive financially.
This differs from a for profit business plan because you do not have to show profitability. Nonprofits focus away from profit and instead center on accountability.
How Do You Secure Funding For Your Nonprofit Organization?
Most nonprofit organizations are likely to receive funding from banks, grants, and donors. As the majority of the funding will come from government grants and funds, grant proposals will need to be compiled and proposed to the necessary funding organization.
A solid business plan is key to showing investors you are well-prepared to start your own business. A nonprofit business plan template is key to proper business planning and getting started quickly.
Where Can I Download a Nonprofit Business Plan PDF?
You can download our free nonprofit business plan template PDF . This nonprofit business plan outlines the key elements that should be used when drafting a business plan for a nonprofit organization.
Raise More & Grow Your Nonprofit.
The complete guide to writing a nonprofit business plan.
August 14, 2019
Leadership & Management
July 7, 2022
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Statistics from the National Center for Charitable Statistics (NCCS) show that there are over 1.5 million nonprofit organizations currently operating in the U.S. alone. Many of these organizations are hard at work helping people in need and addressing the great issues of our time. However, doing good work doesn’t necessarily translate into long-term success and financial stability. Other information has shown that around 12% of non-profits don’t make it past the 5-year mark, and this number expands to 17% at the 10-year mark.
12% of non-profits don’t make it past the 5-year mark and 17% at the 10-year mark
There are a variety of challenges behind these sobering statistics. In many cases, a nonprofit can be sunk before it starts due to a lack of a strong nonprofit business plan. Below is a complete guide to understanding why a nonprofit needs a business plan in place, and how to construct one, piece by piece.
The purpose of a nonprofit business plan
A business plan for a nonprofit is similar to that of a for-profit business plan, in that you want it to serve as a clear, complete roadmap for your organization. When your plan is complete, questions such as "what goals are we trying to accomplish?" or "what is the true purpose of our organization?" should be clear and simple to answer.

Your nonprofit business plan should provide answers to the following questions:
1. What activities do you plan to pursue in order to meet the organization’s high level goals?
2. What's your plan on getting revenue to fund these activities?
3. What are your operating costs and specifically how do these break down?
Note that there’s a difference between a business plan and a strategic plan, though there may be some overlap. A strategic plan is more conceptual, with different ideas you have in place to try and meet the organization’s greater vision (such as fighting homelessness or raising climate change awareness). A business plan serves as an action plan because it provides, in as much detail as possible, the specifics on how you’re going to execute your strategy.
More Reading
- What is the Difference Between a Business Plan and a Strategic Plan?
- Business Planning for Nonprofits
Creating a nonprofit business plan
With this in mind, it’s important to discuss the individual sections of a nonprofit business plan. Having a proper plan in a recognizable format is essential for a variety of reasons. On your business’s end, it makes sure that as many issues or questions you may encounter are addressed up front. For outside entities, such as potential volunteers or donors, it shows that their time and energy will be managed well and put to good use. So, how do you go from conceptual to concrete?
Step 1: Write a mission statement
Having a mission statement is essential for any company, but even more so for nonprofits. Your markers of success are not just how the organization performs financially, but the impact it makes for your cause.
One of the easiest ways to do this is by creating a mission statement. A strong mission statement clarifies why your organization exists and determines the direction of activities.

At the head of their ethics page , NPR has a mission statement that clearly and concisely explains why they exist. From this you learn:
- The key point of their mission: creating a more informed public that understands new ideas and cultures
- Their mechanism of executing that vision: providing and reporting news/info that meets top journalistic standards
- Other essential details: their partnership with their membership statement
You should aim for the same level of clarity and brevity in your own mission statement.
The goal of a mission statement isn’t just about being able to showcase things externally, but also giving your internal team something to realign them if they get off track.
For example, if you're considering a new program or services, you can always check the idea against the mission statement. Does it align with your higher level goal and what your organization is ultimately trying to achieve? A mission statement is a compass to guide your team and keep the organization aligned and focused.
Step 2: Collect the data
You can’t prepare for the future without some data from the past and present. This can range from financial data if you’re already in operation to secured funding if you’re getting ready to start.
Data related to operations and finances (such as revenue, expenses, taxes, etc.) is crucial for budgeting and organizational decisions.
You'll also want to collect data about your target donor. Who are they in terms of their income, demographics, location, etc. and what is the best way to reach them? Every business needs to market, and answering these demographic questions are crucial to targeting the right audience in a marketing campaign. You'll also need data about marketing costs collected from your fundraising, marketing, and CRM software and tools. This data can be extremely important for demonstrating the effectiveness of a given fundraising campaign or the organization as a whole.
Then there is data that nonprofits collect from third-party sources as to how to effectively address their cause, such as shared data from other nonprofits and data from governments.
By properly collecting and interpreting the above data, you can build your nonprofit to not only make an impact, but also ensure the organization is financially sustainable.
Step 3: Create an outline
Before you begin writing your plan, it’s important to have an outline of the sections of your plan. Just like an academic essay, it’s easier to make sure all the points are addressed by taking inventory of high level topics first. If you create an outline and find you don’t have all the materials you need to fill it, you may need to go back to the data collection stage.
Writing an outline gives you something simple to read that can easily be circulated to your team for input. Maybe some of your partners will want to emphasize an area that you missed or an area that needs more substance.
Having an outline makes it easier for you to create an organized, well-flowing piece. Each section needs to be clear on its own, but you also don’t want to be overly repetitive.
As a side-note, one area where a lot of business novices stall in terms of getting their plans off the ground is not knowing what format to choose or start with. The good news is there are a lot of resources available online for you to draw templates for from your plan, or just inspire one of your own.
Using a business plan template
You may want to use a template as a starting point for your business plan. The major benefit here is that a lot of the outlining work that we mentioned is already done for you. However, you may not want to follow the template word for word. A nonprofit business plan may require additional sections or parts that aren’t included in a conventional business plan template.
The best way to go about this is to try and focus less on copying the template, and more about copying the spirit of the template. For example, if you see a template that you like, you can keep the outline, but you may want to change the color scheme and font to better reflect your brand. And of course, all your text should be unique.
When it comes to adding a new section to a business plan template, for the most part, you can use your judgment. We will get into specific sections in a bit, but generally, you just want to pair your new section with the existing section that makes the most sense. For example, if your non-profit has retail sales as a part of a financial plan, you can include that along with the products, services and programs section.
- Free Nonprofit Sample Business Plans - Bplans
- Non-Profit Business Plan Template - Growthink
- Sample Nonprofit Business Plans - Bridgespan
- Nonprofit Business Plan Template - Slidebean
- 23+ Non Profit Business Plan Templates - Template.net
Nonprofit business plan sections
The exact content is going to vary based on the size, purpose, and nature of your nonprofit. However, there are certain sections that every business plan will need to have for investors, donors, and lenders to take you seriously. Generally, your outline will be built around the following main sections:
1. Executive summary
Many people write this last, even though it comes first in a business plan. This is because the executive summary is designed to be a general summary of the business plan as a whole. Naturally, it may be easier to write this after the rest of the business plan has been completed.
After reading your executive summary a person should ideally have a general idea of what the entire plan covers. Sometimes, a person may be interested in learning about your non-profit, but doesn’t have time to read a 20+ page document. In this case, the executive summary could be the difference between whether or not you land a major donor.
As a start, you want to cover the basic need your nonprofit services, why that need exists, and the way you plan to address that need. The goal here is to tell the story as clearly and and concisely as possible. If the person is sold and wants more details, they can read through the rest of your business plan.
2. Products/Services/Programs
This is the space where you can clarify exactly what your non-profit does. Think of it as explaining the way your nonprofit addresses that base need you laid out earlier. This can vary a lot based on what type of non-profit you’re running.

This page gives us some insight into the mechanisms Bucks County Historical Society uses to further their mission, which is “to educate and engage its many audiences in appreciating the past and to help people find stories and meanings relevant to their lives—both today and in the future.”
They accomplish this goal through putting together both permanent exhibits as well as regular events at their primary museum. However, in a non-profit business plan, you need to go further.
It’s important here not only to clearly explain who benefits from your services, but also the specific details how those services are provided. For example, saying you “help inner-city school children” isn’t specific enough. Are you providing education or material support? Your non-profit business plan readers need as much detail as possible using simple and clear language.
3. Marketing
For a non-profit to succeed, it needs to have a steady stream of both donors and volunteers. Marketing plays a key role here as it does in a conventional business. This section should outline who your target audience is, and what you’ve already done/plan on doing to reach this audience. How you explain this is going to vary based on what stage your non-profit is in. We’ll split this section to make it more clear.
Nonprofits not in operation
Obviously, it’s difficult to market an idea effectively if you’re not in operation, but you still need to have a marketing plan in place. People who want to support your non-profit need to understand your marketing plan to attract donors. You need to profile all the data you have about your target market and outline how you plan to reach this audience.
Nonprofits already in operation
Marketing plans differ greatly for nonprofits already in operation. If your nonprofit is off the ground, you want to include data about your target market as well, along with other key details. Describe all your current marketing efforts, from events to general outreach, to conventional types of marketing like advertisements and email plans. Specific details are important. By the end of this, the reader should know:
- What type of marketing methods your organization prefers
- Why you’ve chosen these methods
- The track record of success using these methods
- What the costs and ROI of a marketing campaign
4. Operations
This is designed to serve as the “how” of your Products/Services/Programs section.
For example, if your goal is to provide school supplies for inner-city schoolchildren, you’ll need to explain how you will procure the supplies and distribute them to kids in need. Again, detail is essential. A reader should be able to understand not only how your non-profit operates on a daily basis, but also how it executes any task in the rest of the plan.
If your marketing plan says that you hold community events monthly to drum up interest. Who is in charge of the event? How are they run? How much do they cost? What personnel or volunteers are needed for each event? Where are the venues?
This is also a good place to cover additional certifications or insurance that your non-profit needs in order to execute these operations, and your current progress towards obtaining them.
Your operations section should also have a space dedicated to your team. The reason for this is, just like any other business plan, is that the strength of an organization lies in the people running it.

For example, let’s look at this profile from The Nature Conservancy . The main points of the biography are to showcase Chief Development Officer Jim Asp’s work history as it is relevant to his job. You’ll want to do something similar in your business plan’s team section.
Equally important is making sure that you cover any staff changes that you plan to implement in the near future in your business plan. The reason for this is that investors/partners may not want to sign on assuming that one leadership team is in place, only for it to change when the business reaches a certain stage.
The sections we’ve been talking about would also be in a traditional for profit business plan. We start to deviate a bit at this point. The impact section is designed to outline the social change you plan to make with your organization, and how your choices factor into those goals.
Remember the thoughts that go into that mission statement we mentioned before? This is your chance to show how you plan to address that mission with your actions, and how you plan to track your progress.
Let’s revisit the idea of helping inner-city school children by providing school supplies. What exactly is the metric you’re going to use to determine your success? For-profit businesses can have their finances as their primary KPI, but it’s not that easy for non-profits. Let’s say that your mission is to provide 1,000 schoolchildren in an underserved school district supplies for their classes. Your impact plan could cover two metrics:
- How many supplies are distributed
- Secondary impact (improved grades, classwork completed, etc).
The primary goal of this section is to transform that vision into concrete, measurable goals and objectives. A great acronym to help you create these are S.M.A.R.T. goals which stands for: specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and timely.

Vitamin Angels does a good job of showing how their action supports the mission. Their goal of providing vitamins to mothers and children in developing countries has a concrete impact when we look at the numbers of how many children they service as well as how many countries they deliver to. As a non-profit business plan, it’s a good idea to include statistics like these to show exactly how close you are to your planned goals.
6. Finances
Every non-profit needs funding to operate, and this all-important section details exactly how you plan to cover these financial needs. Your business plan can be strong in every other section, but if your financial planning is flimsy, it’s going to prove difficult to gather believers to your cause.
It's important to paint a complete, positive picture of your fundraising plans and ambitions. Generally, this entails the following parts:
- Current financial status, such as current assets, cash on hand, liabilities
- Projections based off of your existing financial data and forms
- Key financial documents, such as a balance sheet, income statements, and cash flow sheet
- Any grants or major contributions received
- Your plan for fundraising (this may overlap with your marketing section which is okay)
- Potential issues and hurdles to your funding plan
- Your plans to address those issues
- How you'll utilize surplus donations
- Startup costs (if your non-profit is not established yet)
In general, if you see something else that isn’t accounted for here, it’s better to be safe than sorry, and put the relevant information in. It’s better to have too much information than too little when it comes to finances, especially since there is usually a clear preference for transparent business culture.
- How to Make a Five-Year Budget Plan for a Nonprofit
- Financial Transparency - National Council of Nonprofits
7. Appendix
Generally, this serves as a space to attach additional documents and elements that you may find useful for your business plan. This can include things like supplementary charts or a list of your board of directors.
This is also a good place to put text or technical information that you think may be relevant to your business plan, but might be long-winded or difficult to read. A lot of the flow and structure concerns you have for a plan don’t really apply with an appendix.
In summary, while a non-profit may have very different goals than your average business, the ways that they reach those goals do have a lot of similarities with for-profit businesses. The best way to ensure your success is to have a clear, concrete vision and path to different milestones along the way. A solid, in-depth business plan also gives you something to refer back to when you are struggling and not sure where to turn.
Alongside your business plan, you also want to use tools and resources that promote efficiency at all levels. For example, every non-profit needs a consistent stream of donations to survive, so consider using a program like GiveForms that creates simple, accessible forms for your donors to easily make donations. Accounting and budgeting for these in your plans can pay dividends later on.
Share this Article
Related articles, start fundraising today.
How to Write a Nonprofit Business Plan

Angelique O'Rourke
13 min. read
Updated May 10, 2024
Believe it or not, creating a business plan for a nonprofit organization is not that different from planning for a traditional business.
Nonprofits sometimes shy away from using the words “business planning,” preferring to use terms like “strategic plan” or “operating plan.” But, the fact is that preparing a plan for a for-profit business and a nonprofit organization are actually pretty similar processes. Both types of organizations need to create forecasts for revenue and plan how they’re going to spend the money they bring in. They also need to manage their cash and ensure that they can stay solvent to accomplish their goals.
In this guide, I’ll explain how to create a plan for your organization that will impress your board of directors, facilitate fundraising, and ensures that you deliver on your mission.
- Why does a nonprofit need a business plan?
Good business planning is about setting goals, getting everyone on the same page, tracking performance metrics, and improving over time. Even when your goal isn’t to increase profits, you still need to be able to run a fiscally healthy organization.
Business planning creates an opportunity to examine the heart of your mission , the financing you’ll need to bring that mission to fruition, and your plan to sustain your operations into the future.
Nonprofits are also responsible for meeting regularly with a board of directors and reporting on your organization’s finances is a critical part of that meeting. As part of your regular financial review with the board, you can compare your actual results to your financial forecast in your business plan. Are you meeting fundraising goals and keeping spending on track? Is the financial position of the organization where you wanted it to be?
In addition to internal use, a solid business plan can help you court major donors who will be interested in having a deeper understanding of how your organization works and your fiscal health and accountability. And you’ll definitely need a formal business plan if you intend to seek outside funding for capital expenses—it’s required by lenders.
Creating a business plan for your organization is a great way to get your management team or board to connect over your vision, goals, and trajectory. Even just going through the planning process with your colleagues will help you take a step back and get some high-level perspective .
- A nonprofit business plan outline
Keep in mind that developing a business plan is an ongoing process. It isn’t about just writing a physical document that is static, but a continually evolving strategy and action plan as your organization progresses over time. It’s essential that you run regular plan review meetings to track your progress against your plan. For most nonprofits, this will coincide with regular reports and meetings with the board of directors.
A nonprofit business plan will include many of the same sections of a standard business plan outline . If you’d like to start simple, you can download our free business plan template as a Word document, and adjust it according to the nonprofit plan outline below.
Executive summary
The executive summary of a nonprofit business plan is typically the first section of the plan to be read, but the last to be written. That’s because this section is a general overview of everything else in the business plan – the overall snapshot of what your vision is for the organization.
Write it as though you might share with a prospective donor, or someone unfamiliar with your organization: avoid internal jargon or acronyms, and write it so that someone who has never heard of you would understand what you’re doing.
Your executive summary should provide a very brief overview of your organization’s mission. It should describe who you serve, how you provide the services that you offer, and how you fundraise.
If you are putting together a plan to share with potential donors, you should include an overview of what you are asking for and how you intend to use the funds raised.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
Opportunity
Start this section of your nonprofit plan by describing the problem that you are solving for your clients or your community at large. Then say how your organization solves the problem.
A great way to present your opportunity is with a positioning statement . Here’s a formula you can use to define your positioning:
For [target market description] who [target market need], [this product] [how it meets the need]. Unlike [key competition], it [most important distinguishing feature].
And here’s an example of a positioning statement using the formula:
For children, ages five to 12 (target market) who are struggling with reading (their need), Tutors Changing Lives (your organization or program name) helps them get up to grade-level reading through a once a week class (your solution).
Unlike the school district’s general after-school homework lab (your state-funded competition), our program specifically helps children learn to read within six months (how you’re different).
Your organization is special or you wouldn’t spend so much time devoted to it. Layout some of the nuts and bolts about what makes it great in this opening section of your business plan. Your nonprofit probably changes lives, changes your community, or maybe even changes the world. Explain how it does this.
This is where you really go into detail about the programs you’re offering. You’ll want to describe how many people you serve and how you serve them.
Target audience
In a for-profit business plan, this section would be used to define your target market . For nonprofit organizations, it’s basically the same thing but framed as who you’re serving with your organization. Who benefits from your services?
Not all organizations have clients that they serve directly, so you might exclude this section if that’s the case. For example, an environmental preservation organization might have a goal of acquiring land to preserve natural habitats. The organization isn’t directly serving individual groups of people and is instead trying to benefit the environment as a whole.
Similar organizations
Everyone has competition —nonprofits, too. You’re competing with other nonprofits for donor attention and support, and you’re competing with other organizations serving your target population. Even if your program is the only one in your area providing a specific service, you still have competition.
Think about what your prospective clients were doing about their problem (the one your organization is solving) before you came on this scene. If you’re running an after-school tutoring organization, you might be competing with after school sports programs for clients. Even though your organizations have fundamentally different missions.
For many nonprofit organizations, competing for funding is an important issue. You’ll want to use this section of your plan to explain who donors would choose your organization instead of similar organizations for their donations.
Future services and programs
If you’re running a regional nonprofit, do you want to be national in five years? If you’re currently serving children ages two to four, do you want to expand to ages five to 12? Use this section to talk about your long-term goals.
Just like a traditional business, you’ll benefit by laying out a long-term plan. Not only does it help guide your nonprofit, but it also provides a roadmap for the board as well as potential investors.
Promotion and outreach strategies
In a for-profit business plan, this section would be about marketing and sales strategies. For nonprofits, you’re going to talk about how you’re going to reach your target client population.
You’ll probably do some combination of:
- Advertising: print and direct mail, television, radio, and so on.
- Public relations: press releases, activities to promote brand awareness, and so on.
- Digital marketing: website, email, blog, social media, and so on.
Similar to the “target audience” section above, you may remove this section if you don’t promote your organization to clients and others who use your services.
Costs and fees
Instead of including a pricing section, a nonprofit business plan should include a costs or fees section.
Talk about how your program is funded, and whether the costs your clients pay are the same for everyone, or based on income level, or something else. If your clients pay less for your service than it costs to run the program, how will you make up the difference?
If you don’t charge for your services and programs, you can state that here or remove this section.
Fundraising sources
Fundraising is critical for most nonprofit organizations. This portion of your business plan will detail who your key fundraising sources are.
Similar to understanding who your target audience for your services is, you’ll also want to know who your target market is for fundraising. Who are your supporters? What kind of person donates to your organization? Creating a “donor persona” could be a useful exercise to help you reflect on this subject and streamline your fundraising approach.
You’ll also want to define different tiers of prospective donors and how you plan on connecting with them. You’re probably going to include information about your annual giving program (usually lower-tier donors) and your major gifts program (folks who give larger amounts).
If you’re a private school, for example, you might think of your main target market as alumni who graduated during a certain year, at a certain income level. If you’re building a bequest program to build your endowment, your target market might be a specific population with interest in your cause who is at retirement age.
Do some research. The key here is not to report your target donors as everyone in a 3,000-mile radius with a wallet. The more specific you can be about your prospective donors —their demographics, income level, and interests, the more targeted (and less costly) your outreach can be.
Fundraising activities
How will you reach your donors with your message? Use this section of your business plan to explain how you will market your organization to potential donors and generate revenue.
You might use a combination of direct mail, advertising, and fundraising events. Detail the key activities and programs that you’ll use to reach your donors and raise money.
Strategic alliances and partnerships
Use this section to talk about how you’ll work with other organizations. Maybe you need to use a room in the local public library to run your program for the first year. Maybe your organization provides mental health counselors in local schools, so you partner with your school district.
In some instances, you might also be relying on public health programs like Medicaid to fund your program costs. Mention all those strategic partnerships here, especially if your program would have trouble existing without the partnership.
Milestones and metrics
Without milestones and metrics for your nonprofit, it will be more difficult to execute on your mission. Milestones and metrics are guideposts along the way that are indicators that your program is working and that your organization is healthy.
They might include elements of your fundraising goals—like monthly or quarterly donation goals, or it might be more about your participation metrics. Since most nonprofits working with foundations for grants do complex reporting on some of these, don’t feel like you have to re-write every single goal and metric for your organization here. Think about your bigger goals, and if you need to, include more information in your business plan’s appendix.
If you’re revisiting your plan on a monthly basis, and we recommend that you do, the items here might speak directly to the questions you know your board will ask in your monthly trustee meeting. The point is to avoid surprises by having eyes on your organization’s performance. Having these goals, and being able to change course if you’re not meeting them, will help your organization avoid falling into a budget deficit.
Key assumptions and risks
Your nonprofit exists to serve a particular population or cause. Before you designed your key programs or services, you probably did some research to validate that there’s a need for what you’re offering.
But you probably are also taking some calculated risks. In this section, talk about the unknowns for your organization. If you name them, you can address them.
For example, if you think there’s a need for a children’s literacy program, maybe you surveyed teachers or parents in your area to verify the need. But because you haven’t launched the program yet, one of your unknowns might be whether the kids will actually show up.
Management team and company
Who is going to be involved and what are their duties? What do these individuals bring to the table?
Include both the management team of the day-to-day aspects of your nonprofit as well as board members and mention those who may overlap between the two roles. Highlight their qualifications: titles, degrees, relevant past accomplishments, and designated responsibilities should be included in this section. It adds a personal touch to mention team members who are especially qualified because they’re close to the cause or have special first-hand experience with or knowledge of the population you’re serving.
There are probably some amazing, dedicated people with stellar qualifications on your team—this is the place to feature them (and don’t forget to include yourself!).
Financial plan
The financial plan is essential to any organization that’s seeking funding, but also incredibly useful internally to keep track of what you’ve done so far financially and where you’d like to see the organization go in the future.
The financial section of your business plan should include a long-term budget and cash flow statement with a three to five-year forecast. This will allow you to see that the organization has its basic financial needs covered. Any nonprofit has its standard level of funding required to stay operational, so it’s essential to make sure your organization will consistently maintain at least that much in the coffers.
From that point, it’s all about future planning: If you exceed your fundraising goals, what will be done with the surplus? What will you do if you don’t meet your fundraising goals? Are you accounting for appropriate amounts going to payroll and administrative costs over time? Thinking through a forecast of your financial plan over the next several years will help ensure that your organization is sustainable.
Money management skills are just as important in a nonprofit as they are in a for-profit business. Knowing the financial details of your organization is incredibly important in a world where the public is ranking the credibility of charities based on what percentage of donations makes it to the programs and services. As a nonprofit, people are interested in the details of how money is being dispersed within organizations, with this information often being posted online on sites like Charity Navigator, so the public can make informed decisions about donating.
Potential contributors will do their research—so make sure you do too. No matter who your donors are, they will want to know they can trust your organization with their money. A robust financial plan is a solid foundation for reference that your nonprofit is on the right track.
- Business planning is ongoing
It’s important to remember that a business plan doesn’t have to be set in stone. It acts as a roadmap, something that you can come back to as a guide, then revise and edit to suit your purpose at a given time.
I recommend that you review your financial plan once a month to see if your organization is on track, and then revise your plan as necessary .
Angelique is a skilled writer, editor, and social media specialist, as well as an actor and model with a demonstrated history of theater, film, commercial and print work.

Table of Contents
Related Articles

5 Min. Read
How to Write a Growth-Oriented Business Plan

7 Min. Read
8 Steps to Write a Useful Internal Business Plan

8 Min. Read
What Type of Business Plan Do You Need?

6 Min. Read
Differences Between Single-Use and Standing Plans Explained
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

How to Create a Nonprofit Business Plan
Could your organization use a nonprofit business plan ? The answer is yes . Although the nonprofit sector doesn’t always work like the for-profit world and you might not think of your nonprofit as a business, having a business plan can boost your growth and support.
The most important thing to remember is that your nonprofit needs to be unique so it stands out from other nonprofits. Secondly, you want to convey the value that those who engage with your organization or donate money will receive. This can be making them feel charitable but also more productive and engaged. Think about the value/emotion you are hoping to evoke and convey it through your business plan.
The following sections should be included in your nonprofit business plan:

Executive Summary
Organization overview.
- Products, Programs, and Services
Industry Analysis
Customer analysis, marketing plan, operations plan, management team, financial plan.
Let’s break each of these down.
Start your nonprofit business plan by clearly stating your organization’s mission and describing how it plans on reaching its goals. Include a concise description of what makes your organization stand out among competitors (e.g., “We are the only non-profit animal welfare organization in XYZ county” or “Our college student volunteers provide assistance at less than half the cost as our competitors”). Succinctly communicate why people should care about your organization so they will choose to support you. Include other pertinent information about your organization such as the bios of key staff members and the amount of funding you are looking to raise.
The purpose of the executive summary is to convey key information about your organization so readers can decide whether they are interested and willing to read the rest of your plan. Keep the executive summary to one to two pages in length. Create it after completing the other sections so you can simply summarize them. But make sure you do so in an exciting and compelling manner, so readers want to read and learn more about your organization.
This section should include a description of your organization’s overall structure, beginning with who founded it and how it is currently governed. Other important information to provide includes your the nonprofit is located, how many paid/unpaid staff members there are, what facilities are available for use by customers or employees, and what kind of support services are provided (e.g., IT, HR). Lastly, explain any accomplishments your organization has achieved to-date, as the best indicator of future success is past performance.
Products/Services/Programs
In this section, write about your nonprofit’s services or programs in detail. Document the programs you offer and how they function. Provide details, sketches, etc. to clearly communicate the offerings and value your organization provides. If applicable, consider including audience testimonials that express satisfaction with your nonprofit’s offerings.
For industry analysis, address some questions and provide information that supports your answers. Consider this: how big is the industry? For example, if you provide education to high school students, discuss the market size for public and private high school education.
Also answer the following questions:
- What trends are facing the industry (positive or negative)?
- What are some of the industry challenges facing organizations?
- How can your organization help people overcome those problems?
This section should begin with a definition of who the organization considers to be its primary target market (e.g., high school students, working moms, etc.). Based on this group’s needs and wants, prioritize which benefits/offerings from your services or programs are most important to them. This section should also include facts about your supporters’ key needs and pains or other information that might be helpful for your nonprofit’s fundraising efforts.
The marketing plan should discuss how the individuals you serve are likely to find out about your organization’s services and programs along with what promotional activities will be used to reach new audiences . Outline why each activity is beneficial for growing your nonprofit and which demographic it best targets. For strategies that have already been used, provide specific figures on results achieved.
Below are sample promotional activities that many nonprofit organizations use:
Public relations
Developing relationships with the media and utilizing earned media coverage helps with free public exposure. This in turn gets the word out about an organization’s mission. For example, you can create press releases related to new staff additions or upcoming events and share them with your media contacts.
Social media marketing
Social media sites allow organizations to stay connected with supporters and advocates at any time of day. There are different social media platforms that work for different organizations. For example, Twitter is a great way to have quick conversations with people about an issue. Facebook is a good place for sharing more in-depth content and articles on a particular subject area. LinkedIn is a platform where you can build your network of contacts and share information about your organization or topic area.
Blogs and Other Content
Producing great content for blogs or other channels can be an extremely effective way to bring people back to your site or area of social media where they are more likely to donate. A blog can allow you to have conversations with supporters and advocates, answer questions, give more information about your organization or cause, and talk about the issues in your community. In addition, the use of photos, videos, infographics, etc., is a great way to get information across in a compelling manner.
E-newsletters
Sending out an e-newsletter is a great way to engage your supporters. You can include links back to your website, send updates about your organization, share compelling videos or photos from recent events, etc. Just make sure your audience has opted in to hear from you and be sure you don’t spam their inboxes with constant updates every day.
Event marketing
Organizing special events around a particular subject area is a good way to inform the public about an issue or about your organization. Some examples of events are panel discussions about a subject, fundraising dinners, etc. Webinars have grown in popularity with nonprofits in recent years as well. With so many options for virtual, hybrid or in-person gatherings, you’ll be sure to find a way to boost your nonprofit’s audience and growth.
Newspaper/Magazine ads
Just because digital marketing has grown doesn’t mean that traditional media isn’t viable. Unfortunately, this can be one component of advertising that nonprofits often neglect due to lack of funds. Adding an ad to the back of a newspaper with some basic information about what you do, how people can get involved, and what you are looking for in terms of volunteers, donors, etc., is still a great way to spread the word.
PPC advertising
Don’t forget about pay-per-click advertising on search engines like Google. This makes it possible to drive traffic to your website based on specific keywords your target audience searches or pages they visit online. You can write compelling ads that allow you to get the word out about what your organization does.
This section should describe in detail how your nonprofit runs or plans to run its business day-to-day. Outline internal systems that will be used to track and monitor each product, service, or program offered by the organization (e.g., accounting software). Describe what kind of training employees may need to perform their duties effectively. Also include information about whether future hiring plans are scheduled. If so, mention whether all positions will need to be filled immediately or if some can be temporarily contracted out until permanent staff is hired. Finally, create a chart showing the milestones your organization hopes to achieve annually over the next five years.
Provide a list of important management team members within your organization. Make sure to include each person’s title, how long they have been working there, and what responsibilities are part of their role. For each person, include any previous experience they have as well as personal traits that would help them succeed in it. If there are no existing employees with enough business expertise to serve certain roles, list the qualifications the ideal candidate would possess instead.
In this section of your business plan, provide a detailed breakdown of how much funding you are seeking broken down by category (e.g., marketing, staffing, etc.). Provide information about how much revenue is expected from donors and customers compared to funds needed to cover operating costs such as salaries, advertising, and rent. If the organization already has an existing revenue stream, explain how new funding will be used to fund new operations.
The appendix is a good place for any additional information that you would like readers of your nonprofit business plan to have. This includes additional industry research and information on your products, services, or programs. It might also include testimonials from satisfied customers or profiles of board members. Or, it might include architectural designs of a new facility you hope to build.
In summary, a nonprofit business plan is a document that outlines your nonprofit organization’s goals and objectives. A well-written, comprehensive plan can help you attract funding from potential donors or investors. It will also provide clarity to stakeholders by giving them an understanding of your vision for the organization’s future growth.
*This spotlighted blog post is courtesy of Growthink

Dave Lavinsky
Nonprofit management, october 19, 2021, you may also enjoy.

Building AI Capacity in Nonprofits: Challenges and Opportunities
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a rapidly developing technology, and it can be difficult to...
Jun 27, 2024 | 5 Minute Read

[PODCAST] Finances Don’t Have To Be a Burden – Alexis Becker
Finances Don’t Have To Be a Burden - Alexis Becker How much time do you spend on your...
Jun 21, 2024 | 1 Minute Read

10 Benefits of Hosting a Hybrid Event for Nonprofits
Nonprofits are always looking for new ways to expand their reach, build donor relationships,...
Jun 20, 2024 | 7 Minute Read
Become a Member
Whether you’re with a large team or a solo entrepreneur looking to start the next great cause, we have a membership package that will help you grow your network and your cause.
How to write a nonprofit business plan
While a nonprofit business plan is similar to that of a for-profit company, it has a few important differences, including the need for a fundraising section.
Ready to start your business?

by Sandra Beckwith
Sandra Beckwith has been writing for traditional and online publications since she sold her first magazine article wh...
Read more...
Updated on: June 20, 2023 · 3 min read
Nonprofit business plan elements
Fundraising section is essential, keep it real.
While nonprofit organizations are purpose-driven rather than profit-driven, they have a great deal in common with their for-profit counterparts.
"We may be governed by a different part of the tax code and exempt from some—but not all—taxes, but we are businesses, too," says Rick Cohen, chief operating officer at the National Council of Nonprofits.
Like other types of businesses, successful nonprofits outline their goals and how they will achieve them in a written document known as a business plan.
A nonprofit's business plan is similar to that used by a for-profit entity but has key differences. Here's what you need to know about how to write a nonprofit business plan.

For-profit business plans detail what a company does, how it does it, who does it, and how it pays for it. A nonprofit business plan outlines that as well but approaches parts of the process differently.
The biggest difference is that nonprofit organizations focus on the problem they want to solve and how to fund programs and activities that help do that.
"Nonprofits have the added burden and opportunity of impact in their business plan," says Sara Gibson, co-founder and CEO of 20 Degrees, a consulting firm serving nonprofits. "The sector doesn't measure worth in profit—it is measured in lives and in change created. That has to be part of the plan."
Typical nonprofit business plans feature many of the following elements:
- Executive summary
- Mission and goals
- Community impact
- Products, services, and programs
- Organizational structure and staffing
- Market and competitive analysis
- Fundraising and development
- Financial plan
For-profit businesses might be funded initially by owners or outside investors, but the ultimate goal is usually self-sufficiency through sales. Many nonprofit organizations aren't structured or created to generate income to support their community services, so fundraising is key.
"It is critical for the sustainability of nonprofits that they are constantly being connected with grants and funders who will provide the financial resources needed for these nonprofits to continue offering quality and valuable assistance to the communities they serve," says Fernando Urbina, director of outreach for ImmigrationHelp.org.
Mikko Sperber, managing partner and founder of Fundamental Strategy, recommends taking on a for-profit business mindset when writing the fundraising section of the nonprofit business plan.
"If you build your plan to have a budget surplus at the end of your year, you then have the capital to reinvest in growing your organization and furthering your mission," he says.
The organization's communication and marketing strategy feeds fundraising goals, so be thoughtful about that piece when writing a nonprofit business plan.
"If no one knows who you are, then no one will be donating to your cause," says Mike McKnight, director of operations at Racing for Orphans with Down Syndrome.
When outlining your business plan, be realistic about fundraising and other revenue streams, then match your budget to your fundraising goal, not the other way around. "In worst-case scenarios, fundraising numbers are plugged into a budget after the programmatic expenses are figured to just offset them without a realistic plan," Sperber says.
Matching your budget to your fundraising goal is especially important because of the organization's impact on the community served, says Cohen, whose organization offers nonprofit business plan resources on its website.
"The worst thing a nonprofit can do is get to a place where people are counting on their services, but then need to close their doors, leaving those people in the lurch," he says.
To ensure your organization's business plan properly supports your mission, consider consulting with professionals such as nonprofit advisers and attorneys specializing in this sector.
Keep your nonprofit business plan handy, too. It's your organizational blueprint, but you'll also need to update it as circumstances or market conditions change.
You may also like

Why do I need to conduct a trademark search?
By knowing what other trademarks are out there, you will understand if there is room for the mark that you want to protect. It is better to find out early, so you can find a mark that will be easier to protect.
October 4, 2023 · 4min read

What is a power of attorney (POA)? A comprehensive guide
Setting up a power of attorney to make your decisions when you can't is a smart thing to do because you never know when you'll need help from someone you trust.
May 30, 2024 · 16min read

Write Your Nonprofit Business Plan in 9 Sections

Unfortunately, many founders or leaders skip creating one — which generally leads to fundraising frustrations and stalled services, among other problems.
Maybe they don’t know what a nonprofit business plan can do to help them.
Or perhaps it seems too daunting, and they don’t know where to start.
There’s also a common misconception out there that because your organization is labeled a “nonprofit” it doesn’t need to operate like a business. (That couldn’t be farther from the truth.)
Passion and enthusiasm can only get you so far. Without a guide or roadmap to get you where you want to go, you can spend a lot of time floundering.
After all, you can’t jump into your car and drive somewhere you’ve never been if you don’t have directions, can you?
So why do folks who are looking to start or grow a nonprofit not draft a business plan?
Why You Need a Nonprofit Business Plan
No matter where your nonprofit is in its growth or what you’re trying to accomplish, a plan will help you reach your goals faster than if you are trying to operate without one.
Your nonprofit business plan helps you figure out the direction for your nonprofit, the resources you need, and the shortest path to success.
For new nonprofits, it helps you see if you can actually gather the support that you hope you can. In short, you can determine before you begin if your idea for a nonprofit is feasible.
If your nonprofit is already up and running, a nonprofit business plan helps you decide if the funding and opportunities for growth exist for your new or young nonprofit.
Your organization doesn’t exist to make money. But a nonprofit business plan is necessary to attract major donors, foundations, Board members, and other potential partners.
You might need to apply for a business loan at some point, especially if you want to buy a building or set up a thrift store. Lenders will want to see your nonprofit business plan to get an idea of how well you’ve thought things through and to see what your revenue projections look like.
Regardless, your nonprofit needs a roadmap for the future so you can accomplish your goals and fulfill your mission.
So, let’s break it down and take a look at the pieces you’ll need to think through and include in your nonprofit’s business plan.
Getting Started With Your Nonprofit Business Plan

The most common question we get about business plans is “where do we start?”
I get it. It can be a little overwhelming, especially if you’re not naturally a planner.
Essentially, you start with the basics — your mission, vision, and goals.
Your nonprofit’s business plan will then expand on those, going into detail about what you’ll do and what it will cost.
A good plan answers a number of who, what, when, where questions like these:
- What problem is your nonprofit trying to solve?
- What are the exact goals you are trying to achieve?
- How will you measure success?
- How much will it cost?
- What resources do you have and what resources will you need?
- Who can help you achieve your goals?
Your Nonprofit Business Plan not only answers these questions in a format that’s easy to read and understand, but explains your organization and its processes clearly and factually.
What Should You Include in a Nonprofit Business Plan?
Your Nonprofit’s Business Plan should include only relevant information, including these 9 elements:
1. Executive Summary. The Executive Summary is the first thing that any potential partner or supporter will read, and it introduces the mission and purpose of your nonprofit.
It summarizes the identifiable needs you are committed to filling and explains how your nonprofit will meet those needs.
Unlike for-profit businesses, you are not just selling your potential partners on the numbers and inviting them to make a profit.
You are writing a compelling story about how you are helping change the world for the better.
Because this section of your nonprofit business plan is a summary of the facts contained throughout the whole document, it is often written last.
You can customize this section of your business plan depending on your purpose in sending it out. For example, the Executive Summary might have a very different focus if you are trying to recruit an expert in your service sector to the Board versus applying for a small business loan to open a gift shop.

For instance, if your nonprofit is a 501(c)(3), you will list that in this section. (There are other types of nonprofit organizations such as fraternal beneficiary organizations, or horticulture, labor, and agricultural organizations that are structured as nonprofits as well…so be clear here.). Or maybe your nonprofit is actually an NGO based in another country.
In this section, talk about whether you have employees or are all-volunteer. Do you have (or will have) a facility? Paint a picture of your organizational structure so the reader can understand quickly what your nonprofit looks like from an operational point of view.
If yours is an established organization, you can discuss how your nonprofit was started and the milestones you have reached. Listing previous successes and accomplishments in this section can be convincing for potential partners and reassure them that you will use their funding efficiently.
If your nonprofit is just getting started, explain your vision and why you are creating your organization. Focus on the problems you see and the practical ways you intend to alleviate those problems.
3. Products, Programs, and Services. This section provides detailed descriptions and documentation of how you meet needs in your community.
This is where you describe the need and who benefits from your programs. Talk about how lives are changed because of the work your nonprofit does.
Go into some detail to describe the number of people or animals who need you, the number you serve or intend to serve, and the remaining gap who need service.
For example, if you run a homeless shelter, you should mention the number of people who are homeless on any given night in your area. Talk about the number of beds you have, the number of beds you are planning to add in the coming year, and exactly what services you provide in addition to shelter.
If your shelter offers wrap-around services or plays a key role in connecting those you serve to other vital services, talk about those, too. Do your beneficiaries have access to medical care once a month? Does your organization provide a meal? Do you have volunteer tutors who can help students who are homeless with their work? Note who carries out your programs and services and whether you use mostly volunteers or whether you have paid staff in place.
This section will convince potential partners that you are making a difference in a concrete way.
Also, talk about any other nonprofits who are addressing the same need and how your services are/will be different. Donors don’t like duplication of services, and getting grants will be tough if you can’t articulate how your approach is unique.
4. Marketing Plan. Your marketing plan should describe the specific target audiences you want to reach for both programs and fundraising, key messages you’ll use, and which methods or vehicles you’ll use to reach the right people.
Describe whether you mostly advertise and market to a local community or whether your organization is national or worldwide in scope.
This section should include specific marketing strategies and associated costs, such as:
- Print and online marketing
- Email campaigns
- Social media
- Building, maintaining, and marketing your website
- Marketing or cause-related partnerships
- Fundraising or outreach events
If your nonprofit is already established, let your reader know what your marketing plan has been in the past, what has worked, and how you plan to expand it.

What do you and your staff do every day to run programs and provide services? Be specific. How much does a single unit of service cost per person? Who delivers the service? Where and how?
If you have a five-year plan for expanding operations, include that as well. Outline your ideas to move into new areas, new facilities, or new markets.
Note any expanded services. If you are planning on growing or expanding your services what would that mean in terms of operations? For instance, if you run a food bank and you are actively planning to double the number of people you feed in the next year, how will that affect operations? Will you need more refrigerated space? More trucks? More staff or volunteers? Will you expand hours? Be ready to share in the Financial section how this growth will impact your budget, both in revenue and expenses.
If you haven’t spent time making long-term plans, this is a good time to sit down with Board members and staff and think about it in detail! Decide if you’ll start the program or secure funding first (there’s a big difference!).
This section will show potential partners that you are professional, serious, and ready to act with whatever funding they can provide.
6. Evaluation Plan. This can be a separate section, or evaluation methods can be added to various other sections.
Evaluation is critical to determine your effectiveness as a nonprofit — and it’s particularly important for grants. How can you tell if a program is providing the benefit that you are promising? Potential donors and grantors will want to know how you will make sure that funds are used to their highest potential and that you are flexible enough to change if need be.
You should also talk about methods in place to evaluate various aspects of your nonprofit to make sure you’re getting a good return on investment for the time, energy, and resources you put into each area of operations.
For instance, you should monitor your marketing strategies to see what’s working to reach new people. Make sure someone is noting which social media posts are catching on. You should have a data collection system that helps evaluate which fundraising techniques bring in new donors and which techniques help you retain donors or take them to the next level.
You need to explain exactly how you will determine whether or not your beneficiaries are succeeding. For instance, how many of the students you tutor graduate high school? What is your mechanism for follow-up?
You can’t just tell people your idea is working. You need to have the data to prove it.
7. Management and Organizational Charts. In this section, explain the hierarchy of your organization and your expertise for doing the work ahead of you.
Who does what and what expertise do they have for doing it? Potential partners will feel more comfortable to know that the Director of Services for your women’s shelter has a PhD and 10 years of experience in social work.
They will also feel more comfortable knowing that you have all your bases covered in management and staff. This is a good place to outline your future staffing and management needs, including any reliance on volunteers.

Start by developing revenue projections, including anticipated sources of funding from donations, grants, etc. Your projections can’t just be guesses — they need to be based on something specific, whether it’s how much you raised last year, how much a similar organization raised last year, or on an expert’s recommendations. So, include a summary of your fundraising plan here to show how money will be raised.
In addition to revenue projections, also include a breakdown of anticipated expenses. How much of your funds go directly to those you serve? How much goes to your employees’ salaries? How much funding goes to facilities payments or upkeep? You should be very detailed in this section.
Don’t forget things like legal and accounting services, insurance, website upkeep, internet, phone bills, and utilities. If your nonprofit’s money goes into it, include it here.
Include future cash flow statements, income sheets, and balance sheets. You should let your potential partners know how you distribute these funds amongst your various programs and services. This is where your accounting practices can make or break you!
Writing out a detailed financial plan can be very revealing to you as well as to donors and foundations. It may help you identify gaps in your funding and how you plan to deal with them. It’s well worth the effort to gather this information. Not only will it make potential partners more comfortable, it will give you clarity as well!
9. Appendix. The appendix is where you should include extra information that might make the business plan too lengthy or complicated to read through.
You can include your current fiscal year budget , a list of your Board members and their bios, and other relevant documents. You can include any information that you feel is important but perhaps too detailed to include in the main body of your nonprofit business plan.
Tips for Your Nonprofit Business Plan
Use technical jargon or acronyms your reader might not be familiar with.
Make the document unreadably long. Instead, use the appendix for very long or dense documents.
Use only text. Break up the sections for easy reading, and use graphs and charts where you can.
Get so passionate about the cause you forget to tell your reader the nuts and bolts of your nonprofit.
Make the document easy to read. If it’s printed, print on reasonably heavy paper with at least a 12-pt. font.
Use reasonable margins. You want your reader to be able to easily read each page.
Divide the sections clearly with headers and white space.
Use color, graphs, and charts to draw the eye and keep the reader moving through the document.
Have someone, or even several someones, read and edit your nonprofit business plan. (Silly grammar errors and typos are not going to impress your reader with your professionalism.)
Update your audience and keep them excited.
The Bottom Line

Writing a nonprofit business plan is not the easiest thing in the world, but it’s definitely worth your while and gets your ideas down on paper. It may seem like a daunting task, but if you break it into sections and start gathering information, you will find that your business plan can help you find direction and the means to help fulfill your mission.
Share This Story, Choose Your Platform!
About the author: sandy rees.
Related Posts

What Should You Say to Get People to Donate?

The Ultimate List: Tools Every Small Nonprofit Needs to Be More Productive

Grab This Fundraising Plan Template for New Nonprofits

Nonprofit Taxes Made Easy: A Quick Guide for New Founders

How to Set Up Your Nonprofit Accounting System RIGHT So it Helps You Grow
I need help writing my non profit business plan
The resources listed in this article will help. Is there a specific place where you’re stuck?
Thank you so much for this! Is there a good sample you could point me to look at?
You might try googling “sample nonprofit business plan” and the type of nonprofit you have so you can find one that’s applicable to your work.
This information was informative, detailed and to the point without being too wordy. Thank you for your advice, it helped me a lot.
What is the average total page count for a business plan
It depends on how much detail you get into. Somewhere between 15 and 20 pages should give you plenty of direction.
Leave A Comment Cancel reply

How to Write a Nonprofit Business Plan in 12 Steps (+ Free Template!)
The first step in starting a nonprofit is figuring out how to bring your vision into reality. If there’s any tool that can really help you hit the ground running, it’s a nonprofit business plan!
With a plan in place, you not only have a clear direction for growth, but you can also access valuable funding opportunities.
Here, we’ll explore:
- Why a business plan is so important
- The components of a business plan
- How to write a business plan for a nonprofit specifically
We also have a few great examples, as well as a free nonprofit business plan template.
Let’s get planning!
What Is a Nonprofit Business Plan?
A nonprofit business plan is the roadmap to your organization’s future. It lays out where your nonprofit currently stands in terms of organizational structure, finances and programs. Most importantly, it highlights your goals and how you aim to achieve them!
These goals should be reachable within the next 3-5 years—and flexible! Your nonprofit business plan is a living document, and should be regularly updated as priorities shift. The point of your plan is to remind you and your supporters what your organization is all about.
This document can be as short as one page if you’re just starting out, or much longer as your organization grows. As long as you have all the core elements of a business plan (which we’ll get into below!), you’re golden.

Why Your Nonprofit Needs a Business Plan
While some people might argue that a nonprofit business plan isn’t strictly necessary, it’s well worth your time to make!
Here are 5 benefits of writing a business plan:
Secure funding and grants
Did you know that businesses with a plan are far more likely to get funding than those that don’t have a plan? It’s true!
When donors, investors, foundations, granting bodies and volunteers see you have a clear plan, they’re more likely to trust you with their time and money. Plus, as you achieve the goals laid out in your plan, that trust will only grow.
Solidify your mission
In order to sell your mission, you have to know what it is. That might sound simple, but when you have big dreams and ideas, it’s easy to get lost in all of the possibilities!
Writing your business plan pushes you to express your mission in the most straightforward way possible. As the years go on and new opportunities and ideas arise, your business plan will guide you back to your original mission.
From there, you can figure out if you’ve lost the plot—or if it’s time to change the mission itself!
Set goals and milestones
The first step in achieving your goals is knowing exactly what they are. By highlighting your goals for the next 3-5 years—and naming their key milestones!—you can consistently check if you’re on track.
Nonprofit work is tough, and there will be points along the way where you wonder if you’re actually making a difference. With a nonprofit business plan in place, you can actually see how much you’ve achieved over the years.
Attract a board and volunteers
Getting volunteers and filling nonprofit board positions is essential to building out your organization’s team. Like we said before, a business plan builds trust and shows that your organization is legitimate. In fact, some boards of directors actually require a business plan in order for an organization to run!
An unfortunate truth is that many volunteers get taken advantage of . With a business plan in place, you can show that you’re coming from a place of professionalism.
Research and find opportunities
Writing a business plan requires some research!
Along the way, you’ll likely dig into information like:
- Who your ideal donor might be
- Where to find potential partners
- What your competitors are up to
- Which mentorships or grants are available for your organization
- What is the best business model for a nonprofit like yours
With this information in place, not only will you have a better nonprofit business model created—you’ll also have a more stable organization!
Free Nonprofit Business Plan Template
If you’re feeling uncertain about building a business plan from scratch, we’ve got you covered!
Here is a quick and simple free nonprofit business plan template.
Basic Format and Parts of a Business Plan
Now that you know what a business plan can do for your organization, let’s talk about what it actually contains!
Here are some key elements of a business plan:
First of all, you want to make sure your business plan follows best practices for formatting. After all, it’ll be available to your team, donors, board of directors, funding bodies and more!
Your nonprofit business plan should:
- Be consistent formatted
- Have standard margins
- Use a good sized font
- Keep the document to-the-point
- Include a page break after each section
- Be proofread
Curious about what each section of the document should look like?
Here are the essential parts of a business plan:
- Executive Summary: This is your nonprofit’s story—it’ll include your goals, as well as your mission, vision and values.
- Products, programs and services: This is where you show exactly what it is you’re doing. Highlight the programs and services you offer, and how they will benefit your community.
- Operations: This section describes your team, partnerships and all activities and requirements your day-to-day operations will include.
- Marketing : Your marketing plan will cover your market, market analyses and specific plans for how you will carry out your business plan with the public.
- Finances: This section covers an overview of your financial operations. It will include documents like your financial projections, fundraising plan , grants and more
- Appendix: Any additional useful information will be attached here.
We’ll get into these sections in more detail below!
How to Write a Nonprofit Business Plan in 12 Steps
Feeling ready to put your plan into action? Here’s how to write a business plan for a nonprofit in 12 simple steps!
1. Research the market
Take a look at what’s going on in your corner of the nonprofit sector. After all, you’re not the first organization to write a business plan!
- How your competitors’ business plans are structured
- What your beneficiaries are asking for
- Potential partners you’d like to reach
- Your target donors
- What information granting bodies and loan providers require
All of this information will show you what parts of your business plan should be given extra care. Sending out donor surveys, contacting financial institutions and connecting with your beneficiaries are a few tips to get your research going.
If you’re just getting started out, this can help guide you in naming your nonprofit something relevant, eye-catching and unique!
2. Write to your audience
Your business plan will be available for a whole bunch of people, including:
- Granting bodies
- Loan providers
- Prospective and current board members
Each of these audiences will be coming from different backgrounds, and looking at your business plan for different reasons. If you keep your nonprofit business plan accessible (minimal acronyms and industry jargon), you’ll be more likely to reach everyone.
If you’d like, it’s always possible to create a one page business plan AND a more detailed one. Then, you can provide the one that feels most useful to each audience!
3. Write your mission statement
Your mission statement defines how your organization aims to make a difference in the world. In one sentence, lay out why your nonprofit exists.
Here are a few examples of nonprofit mission statements:
- Watts of Love is a global solar lighting nonprofit bringing people the power to raise themselves out of the darkness of poverty.
- CoachArt creates a transformative arts and athletics community for families impacted by childhood chronic illness.
- The Trevor Project fights to end suicide among lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, queer, and questioning young people.
In a single sentence, each of these nonprofits defines exactly what it is their organization is doing, and who their work reaches. Offering this information at a glance is how you immediately hook your readers!
4. Describe your nonprofit
Now that your mission is laid out, show a little bit more about who you are and how you aim to carry out your mission. Expanding your mission statement to include your vision and values is a great way to kick this off!
Use this section to highlight:
- Your ideal vision for your community
- The guiding philosophy and values of your organization
- The purpose you were established to achieve
Don’t worry too much about the specifics here—we’ll get into those below! This description is simply meant to demonstrate the heart of your organization.
5. Outline management and organization
When you put together your business plan, you’ll want to describe the structure of your organization in the Operations section.
This will include information like:
- Team members (staff, board of directors , etc.)
- The specific type of nonprofit you’re running
If you’re already established, make a section for how you got started! This includes your origin story, your growth and the impressive nonprofit talent you’ve brought on over the years.
6. Describe programs, products and services
This information will have its own section in your nonprofit business plan—and for good reason!
It gives readers vital information about how you operate, including:
- The specifics of the work you do
- How that work helps your beneficiaries
- The resources that support the work (partnerships, facilities, volunteers, etc!)
- If you have a membership base or a subscription business model
Above all, highlight what needs your nonprofit meets and how it plans to continue meeting those needs. Really get into the details here! Emphasize the work of each and every program, and if you’re already established, note the real impact you’ve made.
Try including pictures and graphic design elements so people can feel your impact even if they’re simply skimming.
7. Create an Executive Summary
Your Executive Summary will sit right at the top of your business plan—in many ways, it’s the shining star of the document! This section serves as a concise and compelling telling of your nonprofit’s story. If it can capture your readers’ attention, they’re more likely to read through the rest of the plan.
Your Executive Summary should include:
- Your mission, vision and values
- Your goals (and their timelines!)
- Your organization’s history
- Your primary programs, products and services
- Your financing plan
- How you intend on using your funding
This section will summarize the basics of everything else in your plan. While it comes first part of your plan, we suggest writing it last! That way, you’ll already have the information on hand.
You can also edit your Executive Summary depending on your audience. For example, if you’re sending your nonprofit business plan to a loan provider, you can really focus on where the money will be going. If you’re trying to recruit a new board member, you might want to highlight goals and impact, instead.
8. Write a marketing plan
Having a nonprofit marketing plan is essential to making sure your mission reaches people—and that’s especially true for your business plan.
If your nonprofit is already up and running, detail the work you’re currently doing, as well as the specific results you’ve seen so far. If you’re new, you’ll mostly be working with projections—so make sure your data is sound!
No matter what, your Marketing Plan section should market research such as:
- Beneficiary information
- Information on your target audience/donor base
- Information on your competitors
- Names of potential partners
Data is your friend here! Make note of market analyses and tests you’ve run. Be sure to also document any outreach and campaigns you’ve previously done, as well as your outcomes.
Finally, be sure to list all past and future marketing strategies you’re planning for. This can include promotion, advertising, online marketing plans and more.
9. Create a logistics and operations plan
The Operations section of your business plan will take the organizational information you’ve gathered so far and expand the details! Highlight what the day-to-day will look like for your nonprofit, and how your funds and resources will make it possible.
Be sure to make note of:
- The titles and responsibilities of your core team
- The partners and suppliers you work with
- Insurance you will need
- Necessary licenses or certifications you’ll maintain
- The cost of services and programs
This is the what and how of your business plan. Lean into those details, and show exactly how you’ll accomplish those goals you’ve been talking about!
10. Write an Impact Plan
Your Impact Plan is a deep dive into your organization’s goals. It grounds your dreams in reality, which brings both idealists and more practically-minded folks into your corner!
Where your Executive Summary lays out your ambitions on a broader level, this plan:
- Clarifies your goals in detail
- Highlights specific objectives and their timelines
- Breaks down how you will achieve them
- Shows how you will measure your success
Your Impact Plan will have quite a few goals in it, so be sure to emphasize which ones are the most impactful on your cause. After all, social impact is just as important as financial impact!
Speaking of…
11. Outline the Financial Plan
One of the main reasons people want to know how to write a nonprofit business plan is because of how essential it is to receiving funding. Loan providers, donors and granting bodies will want to see your numbers—and that’s where your Financial Plan comes in.
This plan should clearly lay out where your money is coming from and where it will go. If you’re just getting started, check out what similar nonprofits are doing in order to get realistic numbers. Even if you’re starting a nonprofit on a tight budget , every bit of financial information counts!
First, map out your projected (or actual) nonprofit revenue streams , such as:
- Expected membership contributions
- Significant donations
- In-kind support
- Fundraising plan
Then, do the same with your expenses:
- Startup costs
- Typical bills
- Web hosting
- Membership management software
- Subscription
- Costs of programs
If your nonprofit is already up and running, include your past accounting information. Otherwise, keep working with those grounded projections!
To make sure you have all of your information set, include documents like:
- Income statement
- Cash flow statement
- Balance sheet
This information comes together to show that your nonprofit can stay above water financially. Highlighting that you can comfortably cover your operational costs is essential. Plus, building this plan might help your team find funding gaps or opportunities!
12. Include an Appendix
Your appendix is for any extra pieces of useful information for your readers.
This could be documents such as:
- Academic papers about your beneficiaries
- Publications on your nonprofit’s previous success
- Board member bios
- Organizational flow chart
- Your IRS status letter
Make sure your additions contribute to your nonprofit’s story!
Examples of Business Plans for Nonprofits
Here are two great examples of nonprofit business plans. Notice how they’re different depending on the size of the organization!
Nonprofit Recording Co-op Business Plan
This sample nonprofit business plan shows what a basic plan could look like for a hobbyists’ co-op. If your nonprofit is on the smaller, more local side, this is a great reference!
What we like:
- Details on running a basic membership model
- Emphasis on what it means to specifically be a sustainable cooperative
- A list of early milestones, such as hitting their 100th member
- Clarification that all recordings will be legal
Nonprofit Youth Services Business Plan
This sample nonprofit business plan is for a much larger organization. Instead of focusing on the details of a membership model, it gets deeper into programs and services provided.
What we like
- The mission is broken down by values
- A detailed look at what each program provides
- A thorough sales plan
- Key assumptions are included for the financial plan
How to Create a Nonprofit Business Plan With Confidence
We hope this sheds some light on how creating a nonprofit business plan can help your organization moving forward! Remember: you know what you want for your organization. A business plan is simply a tool for making those dreams a reality.
Is a membership program part of your business plan? Check out WildApricot ’s award-winning membership management software!
With our 60-day free trial , you’ll have all the time you need to fall in love with what we have to offer.
Related Organizational Management Articles

30 Free Nonprofit Webinars for July 2024
Nonprofit Succession Planning: A Step-by-Step Guide

Strategic Planning for Nonprofits

The Membership Growth Report:
Benchmarks & insights for growing revenue and constituents.

Nonprofit Business Plan Template & Guide [Updated 2024]
Nonprofit business plan template.
Are you passionate about making a positive impact in your community? Are you part of a nonprofit organization or considering starting one? If so, you need a business plan and you’re in the right place to do that!
Below, we’ll guide you through the essential elements of a nonprofit business plan, sharing valuable insights and a user-friendly template to set you on the path to success.
- How to Write a Nonprofit Business Plan
Growthink’s nonprofit business plan template below is the result of 20+ years of research into the types of business plans that help nonprofit organizations (NPOs) to secure funding and achieve their goals.
Follow the links to each section of our non-profit business plan template:
- Executive Summary – The Executive Summary will provide a brief overview of each section of your nonprofit business plan including your mission statement, goals and objectives, key achievements, and financial highlights.
- Organization Overview – The Organization Overview which should include a description of your organization, its guiding philosophy, and the programs and services it provides.
- Products, Programs, and Services – In the Products, Programs and Services section, you will describe in detail the services or products your nonprofit provides to its target audience.
- Industry Analysis – The Industry Analysis section should provide an overview of the market in which your organization operates, including key trends, competitors, and potential opportunities for growth.
- Customer Analysis – The Customer Analysis section will identify the key customer segment(s) your NPO serves and then provide demographics and psychographic details about them.
- Marketing Plan – In the Marketing Plan section, you will outline how you plan to reach and engage with your target audience through various marketing and communication strategies.
- Operational Plan – The Operational Plan will include all the details of your day-to-day operations, including staffing, facilities, and any necessary equipment or technology.
- Management Team – The Management Team section will describe the organizational structure of your NPO, including key personnel, board members, and their roles and responsibilities.
- Financial Plan – The Financial Plan section will include a detailed budget, financial projections and analysis, as well as information on how your organization plans to generate revenue and manage expenses.
- Appendix – In the Appendix, you will include supporting documents and research for your business plan which may include the IRS status letter, financial statements, market research, and any additional information to support your organization’s financial goals and specific objectives.
NPO Planning Resources & FAQs
Below are answers to the most common questions asked by nonprofits:
Is there a nonprofit business plan template I can download?
Yes. If you’d like to quickly and easily complete your non-profit business plan, download our non-profit business plan template and complete your business plan and financial model in hours.
Where can I download a nonprofit business plan PDF?
You can download our free nonprofit business plan template PDF here . This is a sample nonprofit business plan template you can use in PDF format.
What Is a nonprofit business plan?
A non-profit business plan describes your organization as it currently exists (which could be just an idea) and presents a road map for the next three to five years. It lays out your goals, challenges, and plans for meeting your goals. Your business plan should be updated frequently, as it is not meant to be stagnant. It is particularly important to create/update your business plan annually to make sure your nonprofit remains on track towards successfully fulfilling its mission.
A nonprofit business plan template is a tool used to help your nonprofit business quickly develop a roadmap for your business.
Why do you need a business plan for your nonprofit?
A nonprofit business plan serves many purposes. Most importantly, it forces you to think through and perfect your nonprofit’s strategic plan, it provides a roadmap to follow to grow your nonprofit, and it provides financial and other information major donors and board members need to know before they invest in your organization. Business planning can be a challenge and business plan templates help make this task easier for your team.
What are the types of nonprofit organizations (NPOs)?
There are several types of nonprofits. These are categorized by section 500(c) by the IRS for tax exempt purposes. Listed below, are some of the frequently filed sections:
Corporations formed under Act of Congress. An example is Federal Credit Unions.
Holding corporations for tax exempt organizations. This group holds title to the property for the exempt group.
This is the most popular type of NPO. Examples include educational, literary, charitable, religious, public safety, international and national amateur sports competitions, organizations committed to the prevention of cruelty towards animals or children, etc. Organizations that fall into this category are either a private foundation or a public charity. Examples include Getty Foundation, Red Cross, Easter Seals, etc.
Examples include social welfare groups, civil leagues, employee associations, etc. This category promotes charity, community welfare and recreational/educational goals.
Horticultural, labor and agricultural organizations get classified under this section. These organizations are instructive or educational and work to improve products, working conditions and efficiency.
Examples include real estate boards, business leagues, etc. They work to ameliorate business conditions.
Recreation and social clubs that promote pleasure and activities fall into this category.
Fraternal beneficiary associations and societies belong to this section.
Voluntary Employees’ beneficiary associations which provide benefits, accidents and life payments to members are a part of this section.
When filling in your nonprofit business plan template, include the type of nonprofit business you intend to be.
What are the primary sources of funding for nonprofit business plans?
The primary funding sources for most nonprofit organizations are donors, grants and bank loans. Donors are individuals that provide capital to start and grow your nonprofit. Major donors, as the name implies, write large checks and are often instrumental in launching nonprofits. Grants are given by organizations and others to achieve specific goals and often nonprofits qualify for them. Business loans, particularly for asset purchases like buildings and equipment, are also typically used by nonprofits.
NPOs may also sell products or services, work with investors or develop their own investments. The expertise of the non-profit staff, members and board of directors will impact funding options for a nonprofit organization. The nonprofit’s mission, resources, goals and vision will all impact the funding sources a nonprofit business will place in it’s business plan as well.
How do you write a nonprofit business plan?
To most quickly write a nonprofit business plan, start with a template that lays out a nonprofit business plan outline. Answer the questions provided in the template and discuss them with your co-founders if applicable. A templated financial model will help you more easily complete your financial forecasts.
How do you start a nonprofit?
The key steps to starting a nonprofit are to choose the name of your organization, write your business plan and impact plan, incorporate your organization, apply for your IRS and state tax exemptions and get any required licenses and permits you need to operate.
How many nonprofit organizations are in the US?
According to the National Center for Charitable Statistics , there are approximately 1.54 million nonprofits registered in the United States (data pulled from registrations with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS)).
The nonprofit sector has annual expenses exceeding 2.46 trillion U.S dollars.
Does your action plan and fundraising plan belong in your plan?
Yes, both belong in your plan.
Include your action plan in the operations plan section.
Your fundraising plan goes in your financial plan section. Here you will discuss how much money you must raise and from whom you plan to solicit these funds, as well as outlines your fundraising events. It should clearly outline your fundraising goals and potential donors.
Where do you include your non profit mission in your plan?
Nonprofit mission statements, or a vision statement, are extremely important as it lays the foundation for and presents the vision of your nonprofit. You should clearly detail your nonprofit mission statement in both the executive summary and organizational overview of your nonprofit plan.
What do you include in a nonprofit’s financial projections?
Your financial projections must include an Income Statement, Balance Sheet and Cash Flow Statement. These statements within your business plan show how much money your organization will bring in from donors and customers/clients and how much your organization will spend.
The key purpose of your these projections is to ensure you have enough money to keep your organization operating. They also can be an important component of your nonprofit business plan template, as donors, your board of directors, and others may review to understand financial requirements of your nonprofit.
How do nonprofit owners get paid?
Nonprofits function like for-profit businesses in that they often have employees who receive salaries. As such, as the owner, founder and/or CEO of a nonprofit, you can give yourself a salary. Many nonprofit CEOs, particularly those running large health, finance and educational organizations earn millions of dollars each year.
How much does it cost to start a nonprofit business?
NPOs must complete Form 1023 with the IRS in order to get exemption status. The filing fee for this form is $600. If neither actual nor projected annual income for the organization exceeds $50,000, you can file form Form 1023-EZ which costs just $275.
In addition to the filing fee, there are other costs associated with starting a nonprofit organization based on the type of organization you are developing (for example, if you require buildings and equipment). Gathering information through the business planning process will help you accurately estimate costs for your nonprofit business plan template.
Where can I download a nonprofit business plan template doc?
You can download our free nonprofit business plan template DOC here . This is a nonprofit business plan template you can use in Microsoft DOC format.
Additional nonprofit resources
Below is a list of additional resources to help you get starting with your own nonprofit organization:
- How to Start a Non-Profit Organization
- Sample Nonprofit Business Plan
- Nonprofit Marketing Plan + Template
- How to Write a Mission Statement for Your Nonprofit Organization
- NonProfit Business Plan PDF
- National Council of Nonprofits
- Nonprofit Quarterly
- The Fundraising Authority
Helpful Video Tips for Nonprofit Business Plans
Below are tips to create select sections of your nonprofit business plan:
How to Write Your Nonprofit Business Plan’s Executive Summary
Writing the management team section of your nonprofit business plan, how to write the operations plan of your nonprofit business plan, writing the customer analysis section of your nonprofit business plan, finish your non profit business plan in 1 day.
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Nonprofit Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Click here to finish your Nonprofit business plan today.
NONPROFIT BUSINESS PLAN OUTLINE
- Nonprofit Business Plan Home
- 1. Executive Summary
- 2. Organization Overview
- 3. Products, Programs, and Services
- 4. Industry Analysis
- 5. Customer Analysis
- 6. Marketing Plan
- 7. Operations Plan
- 8. Management Team
- 9. Financial Plan
- 10. Appendix
- Nonprofit Business Plan Summary

Non-Profit Business Plan
A roadmap for the non-profit organization
What is a Non-Profit Business Plan?
A non-profit business plan is simply a roadmap for a non-profit organization , one which outlines the organization’s goals and objectives, and how it plans to attain them. A non-profit is a business entity that is started for any specified purpose other than making a profit. The most common reason for a non-profit organization is charity work.

Even though there are considerable differences between a profit and non-profit company, many of the same regulations apply. In fact, non-profit organizations need detailed and structured planning just like any other business. One of the core tasks of a non-profit startup entails developing a business plan.
This overview explains why non-profits should formulate business plans, and includes the required elements in such a plan.
Uses of a Non-Profit Business Plan
Owners of non-profit organizations need business plans for the following reasons:
- Persuading big donors or foundations to finance their projects
- Hiring board members who can help them in terms of getting a clearer idea of what they are committing themselves to
- Acting as a compass for the whole non-profit organization – to prevent key players from straying or going off the main course
- When applying for business loans , especially if the non-profit has plans to start a store, restaurant, gift shop, or other venture that can help fund its programs
One thing to keep in mind is that the business plan is not rigid. It should be created in such a way that it leaves room for adaptive changes. In this way, non-profit owners can adjust their plans as the organization grows.
Components of a Non-Profit Business Plan
A non-profit organization can use the business plan throughout its life, making changes to it whenever necessary. For a startup non-profit, the business plan can be quite brief as compared to that of a more mature non-profit. The plan may vary depending on the specific organization, however, there are a couple of things that should be included in every non-profit business plan.
1. Executive Summary
The executive summary is a brief breakdown of the contents outlined in the business plan. The trick here is to provide an interesting summary that will keep the reader engaged enough to go through the entire plan. Under this section, the non-profit owner can describe the organization’s mission , a short background of how and why it was started, and its unique strengths. He or she can also outline the non-profit’s products, services, and programs. Additionally, the owner needs to include the organization’s marketing and financial plans.
2. Organizational Structure
Under this section, the owner simply needs to explain how the non-profit is structured, starting from the board of directors and working down to executive staff. He or she should also highlight subsidiaries (if there are any), objectives, strategies on how to scale up, and a few trends in this particular non-profit area.
3. Products, Programs or Services Rendered
The products and services that were listed in the executive summary are now described in a more comprehensive way under this section. The individual should also incorporate unique features such as the delivery methods, sources of products, the benefits of the non-profit’s products and services, as well as future development plans. This section should also provide information relating to any copyrights or patents that the non-profit holds.
4. Marketing Plan
What is the target market or audience of the non-profit’s programs? How does the nonprofit intend to reach these people? What constituencies does the non-profit aim to serve? The marketing plan should provide detailed answers to these questions. For instance, the owner should outline the competitors of his non-profit, as well as other non-profits that may be potential collaborators.
5. Operational Plan
Under this section, the owner will be trying to answer questions such as: How does the nonprofit deliver its products or services? What is the location of its main facility? Does the nonprofit have any equipment or inventory needs? Essentially, the individual should explain the exact strategies he plans to use to maintain the operation. This section also covers the impact of the non-profit’s programs and services on clients and on the community at large.
6. Management and Organizational Team
This part covers the names and details of the staff in the management team. It also includes a list of board members and their respective areas of expertise. The easiest way to explain the non-profit’s management team is through the use of an organizational chart .
The chart outlines all the non-profit’s staff and the roles they play in the organization. Another thing to include in this section is the non-profit’s evaluation of its present and future staffing needs. Once the organization grows, it may need to hire several volunteers, an IT expert, accountants, and more.
7. Capitalization
Capitalization is another element that should not be left out in a non-profit’s business plan. This is the section where the owner lists all the non-profit’s outstanding loans, debts, bonds, and endowments. Endowments refer to government or private grants that the non-profit has received or applied for.
8. Appendix
In the appendix, the owner should incorporate the resumes of key staff, a list of the members of the board of directors, relevant charts and graphs, promotional materials, mission and vision statements, and an annual report if the non-profit is not a startup.
The Bottom Line
Non-profit organizations need to be managed effectively, just like any other enterprise. The best way to achieve this is by developing a business plan. A non-profit business plan serves as a roadmap or compass for the entire organization. Put simply, it outlines the non-profit’s goals and objectives, its organizational structure, marketing, financial, and operational plans, as well as the products or services rendered by the organization.
Related Readings
CFI offers the Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA)™ certification program for those looking to take their careers to the next level. To keep learning and advancing your career, the following CFI resources will be helpful:
- Business Life Cycle
- Evaluation Plan
- Project Finance
- Startup Valuation Metrics
- See all management & strategy resources
- Share this article

Create a free account to unlock this Template
Access and download collection of free Templates to help power your productivity and performance.
Already have an account? Log in
Supercharge your skills with Premium Templates
Take your learning and productivity to the next level with our Premium Templates.
Upgrading to a paid membership gives you access to our extensive collection of plug-and-play Templates designed to power your performance—as well as CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs.
Already have a Self-Study or Full-Immersion membership? Log in
Access Exclusive Templates
Gain unlimited access to more than 250 productivity Templates, CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs, hundreds of resources, expert reviews and support, the chance to work with real-world finance and research tools, and more.
Already have a Full-Immersion membership? Log in
Get started
- Project management
- CRM and Sales
- Work management
- Product development life cycle
- Comparisons
- Construction management
- monday.com updates
The best nonprofit business plan template
If you’re looking to start a new charity but don’t know where to start, a nonprofit business plan template can help. There are more than 1.5 million nonprofit organizations registered in the US. While it’s awesome that there are so many charitable orgs, unfortunately, many of them struggle to keep their doors open.
Like any other business, a nonprofit needs to prepare for the unexpected. Even without a global pandemic, strategic planning is crucial for a nonprofit to succeed.
In this article, we’ll look at why a business plan is important for nonprofit organizations and what details to include in your business plan. To get you started, our versatile nonprofit business plan template is ready for you to download to turn your nonprofit dreams into a reality.
Get the template
What is a nonprofit business plan template?
A nonprofit business plan template is not that different from a regular, profit-oriented business plan template. It can even focus on financial gain — as long as it specifies how to use that excess for the greater good.
A nonprofit business plan template includes fields that cover the foundational elements of a business plan, including:
- The overarching purpose of your nonprofit
- Its long and short-term goals
- An outline of how you’ll achieve these goals
The template also controls the general layout of the business plan, like recommended headings, sub-headings, and questions. But what’s the point? Let’s dive into the benefits a business plan template offers nonprofits.
Download Excel template
Why use a nonprofit business plan template?
To get your nonprofit business plans in motion, templates can:
Provide direction
If you’ve decided to start a nonprofit, you’re likely driven by passion and purpose. Although nonprofits are generally mission-driven, they’re still businesses. And that means you need to have a working business model. A template will give your ideas direction and encourage you to put your strategic thinking cap on.
Help you secure funding
One of the biggest reasons for writing a nonprofit business plan is to attract investment. After all, without enough funding , it’s nearly impossible to get your business off the ground. There’s simply no business without capital investment, and that’s even more true for nonprofits that rarely sell products.
Stakeholders and potential investors will need to assess the feasibility of your nonprofit business. You can encourage them to invest by presenting them with a well-written, well-thought-out business plan with all the necessary details — and a template lays the right foundation.
Facilitate clear messaging
One of the essential characteristics of any business plan — nonprofits included — is transparency around what you want to achieve and how you are going to achieve it. A nebulous statement with grandiose aspirations but no practical plan won’t inspire confidence.
Instead, you should create a clear and concise purpose statement that sums up your goals and planned action steps. A good template will help you maintain a strong purpose statement and use clear messaging throughout.
Of course, there are different types of nonprofit plan templates you can use, depending on the kind of business plan you want to draw up.
What are some examples of a nonprofit business plan template?
From summary nonprofit plans to all encompassing strategies, check out a few sample business plan templates for different nonprofit use cases.
Summary nonprofit business plan template
New nonprofit ventures in the early stages of development can use this business plan template. It’s created to put out feelers to see if investors are interested in your idea. For example, you may want to start an animal shelter in your community, but aren’t sure if it’s a viable option due to a lack of funds. You’d use a summary business plan template to gauge interest in your nonprofit.
Full nonprofit business plan template
In this scenario, you have already laid the foundations for your nonprofit. You’re now at a point where you need financing to get your nonprofit off the ground.
This template is much longer than a summary and includes all the sections of a nonprofit business plan including the:
Executive summary
- Nonprofit description
- Needs analysis
- Product/service
- Marketing strategy
- Management team & board
- Human resource needs
It also typically includes a variety of documents that back up your market research and financial situation.
Operational nonprofit business plan template
This type of business plan template is extremely detail-oriented and outlines your nonprofit’s daily operations. It acts as an in-depth guide for who does what, how they should do it, and when they should do it.
An operational nonprofit business plan is written for your internal team rather than external parties like investors or board members.
Convinced to give a business plan template a go? Lucky for you, our team has created the perfect option for nonprofits.
monday.com’s nonprofit business plan template
At monday.com, we understand that starting a nonprofit business can feel overwhelming — scrambling to line up investors, arranging fundraising events, filing federal forms, and more. Because we want you and your nonprofit to succeed, we’ve created a customizable template to get you started. It’s right inside our Work OS , a digital platform that helps you effectively manage every aspect of your work — from budgets and high-level plans to individual to-do lists.

Here’s what you can do on our template:
Access all your documents from one central location
Besides a business plan, starting a nonprofit requires a lot of other documentation. Supporting documents include a cash flow statement or a general financial statement, resumes of founders, and letters of support.
monday.com’s Work OS lets you store all these essential documents in one centralized location. That means you don’t need to open several tabs or run multiple programs to view your information. On monday.com, you can quickly and easily access documents and share them with potential investors and donors. Security features also help you control access to any board or document, only letting invited people or employees view or edit them. By keeping everything in one place, you save time on tracking down rogue files or statements and can focus on what really matters, such as running your nonprofit.
Turn your business plan into action
With monday.com’s nonprofit business plan template, you can seamlessly transform your plan into actionable tasks. After all, it’s going to take more than some sound strategic planning to bring your nonprofit to life.

Based on your business plan, you have the power to create interactive vision boards, calendars, timelines, cards, charts, and more. Because delegation is key, assign tasks to any of your team members from your main board. You can even set up notification automations so that everyone stays up to date with their responsibilities. Plus, to make sure the team stays on track, you can use the Progress Tracking Column that shows you the percent to completion of tasks based on the different status columns of your board.
Keep your finger on the pulse
From budgets to customer satisfaction, you need to maintain a high-level overview of your nonprofit’s key metrics.
monday.com keeps you well-informed on the status of your nonprofit’s progress, all on one platform. With customizable dashboards — for example, a real-time overview of donations received and projects completed — and visually appealing views, you can make confident decisions on how to take your nonprofit business forward.
Now that you have the template, let’s cover each section and how to fill it out correctly.
Essential sections of a nonprofit business plan template
So what exactly goes into a nonprofit business plan? Let’s take a look at the different sections you’ll find in most templates.
This is a concise summary of your business at the beginning of your plan. It should be both inspired and to the point. The executive summary is typically two pages long and dedicates about two sentences to each section of the plan.
Organization overview
This section gives some background on your company and summarizes the goal of your business. At the same time, it should touch on other important factors like your action plan for attracting potential external stakeholders. You can think of an organization overview as a mission statement and company description rolled into one.
Products, programs, and services
Any business exists to provide products, programs, and services — perhaps with a focus on the latter two for nonprofits. Your business plan should outline what you are bringing to your community. This will influence your target market , potential investors, and marketing strategies.
Marketing plan
An effective marketing strategy is the cornerstone of any successful business. Your marketing plan will identify your target audience and how you plan to reach them. It deals with pricing structures while also assessing customer engagement levels.
Operational plan
The operational plan describes the steps a company will take over a certain period. It focuses on the day-to-day aspects of the business, like what tasks need to be done and who is responsible for what. The operational section of a business plan works closely with strategic planning.
Competitive analysis
Even nonprofits face competition from other nonprofits with similar business profiles. A market analysis looks at the strengths and weaknesses of competing businesses and where you fit in. This section should include a strategy to overtake competitors in the market. There are many formats and templates you can use here, for example, a SWOT analysis .
Financial plan
Your financial plan should be a holistic image of your company’s financial status and financial goals. As well as your fundraising plan , make sure to include details like cash flow, investments, insurance, debt, and savings.
Before we wrap up, we’ll address some commonly asked questions about nonprofit business plan templates.
FAQs about nonprofit business plan templates
How do you write a business plan for a nonprofit.
The best way to write a nonprofit business plan is with a template so that you don’t leave anything out. Our template has all the sections ready for you to fill in, combined with features of a cutting-edge Work OS.
For some extra tips, take a look at our advice on how to write a business plan . We’ve detailed the various elements involved in business planning processes and how these should be structured.
How many pages should a nonprofit business plan be?
Business plans don’t have to be excessively long. Remember that concise communication is optimal. As a rule of thumb — and this will vary depending on the complexity and size of your business plan — a nonprofit business plan is typically between seven and thirty pages long.
What is a nonprofit business plan called?
A nonprofit business plan is called just that — a ‘nonprofit business plan.’ You may think that its nonprofit element makes it very different from a profit-oriented plan. But it is essentially the same type of document.
What is the best business structure for a nonprofit?
The consensus is that a corporation is the most appropriate and effective structure for a nonprofit business.
How do you start a nonprofit with no money?
Creating a business plan and approaching potential investors, aka donators, is the best way to start a nonprofit business if you don’t have the funds yourself.
Send this article to someone who’d like it.
How to Write a Business Plan: Your Step-by-Step Guide

So, you’ve got an idea and you want to start a business —great! Before you do anything else, like seek funding or build out a team, you'll need to know how to write a business plan. This plan will serve as the foundation of your company while also giving investors and future employees a clear idea of your purpose.
Below, Lauren Cobello, Founder and CEO of Leverage with Media PR , gives her best advice on how to make a business plan for your company.
Build your dream business with the help of a high-paying job—browse open jobs on The Muse »
What is a business plan, and when do you need one?
According to Cobello, a business plan is a document that contains the mission of the business and a brief overview of it, as well as the objectives, strategies, and financial plans of the founder. A business plan comes into play very early on in the process of starting a company—more or less before you do anything else.
“You should start a company with a business plan in mind—especially if you plan to get funding for the company,” Cobello says. “You’re going to need it.”
Whether that funding comes from a loan, an investor, or crowdsourcing, a business plan is imperative to secure the capital, says the U.S. Small Business Administration . Anyone who’s considering giving you money is going to want to review your business plan before doing so. That means before you head into any meeting, make sure you have physical copies of your business plan to share.
Different types of business plans
The four main types of business plans are:
Startup Business Plans
Internal business plans, strategic business plans, one-page business plans.
Let's break down each one:
If you're wondering how to write a business plan for a startup, Cobello has advice for you. Startup business plans are the most common type, she says, and they are a critical tool for new business ventures that want funding. A startup is defined as a company that’s in its first stages of operations, founded by an entrepreneur who has a product or service idea.
Most startups begin with very little money, so they need a strong business plan to convince family, friends, banks, and/or venture capitalists to invest in the new company.
Internal business plans “are for internal use only,” says Cobello. This kind of document is not public-facing, only company-facing, and it contains an outline of the company’s business strategy, financial goals and budgets, and performance data.
Internal business plans aren’t used to secure funding, but rather to set goals and get everyone working there tracking towards them.
As the name implies, strategic business plans are geared more towards strategy and they include an assessment of the current business landscape, notes Jérôme Côté, a Business Advisor at BDC Advisory Services .
Unlike a traditional business plan, Cobello adds, strategic plans include a SWOT analysis (which stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) and an in-depth action plan for the next six to 12 months. Strategic plans are action-based and take into account the state of the company and the industry in which it exists.
Although a typical business plan falls between 15 to 30 pages, some companies opt for the much shorter One-Page Business Plan. A one-page business plan is a simplified version of the larger business plan, and it focuses on the problem your product or service is solving, the solution (your product), and your business model (how you’ll make money).
A one-page plan is hyper-direct and easy to read, making it an effective tool for businesses of all sizes, at any stage.
How to create a business plan in 7 steps
Every business plan is different, and the steps you take to complete yours will depend on what type and format you choose. That said, if you need a place to start and appreciate a roadmap, here’s what Cobello recommends:
1. Conduct your research
Before writing your business plan, you’ll want to do a thorough investigation of what’s out there. Who will be the competitors for your product or service? Who is included in the target market? What industry trends are you capitalizing on, or rebuking? You want to figure out where you sit in the market and what your company’s value propositions are. What makes you different—and better?
2. Define your purpose for the business plan
The purpose of your business plan will determine which kind of plan you choose to create. Are you trying to drum up funding, or get the company employees focused on specific goals? (For the former, you’d want a startup business plan, while an internal plan would satisfy the latter.) Also, consider your audience. An investment firm that sees hundreds of potential business plans a day may prefer to see a one-pager upfront and, if they’re interested, a longer plan later.
3. Write your company description
Every business plan needs a company description—aka a summary of the company’s purpose, what they do/offer, and what makes it unique. Company descriptions should be clear and concise, avoiding the use of jargon, Cobello says. Ideally, descriptions should be a few paragraphs at most.
4. Explain and show how the company will make money
A business plan should be centered around the company’s goals, and it should clearly explain how the company will generate revenue. To do this, Cobello recommends using actual numbers and details, as opposed to just projections.
For instance, if the company is already making money, show how much and at what cost (e.g. what was the net profit). If it hasn’t generated revenue yet, outline the plan for how it will—including what the product/service will cost to produce and how much it will cost the consumer.
5. Outline your marketing strategy
How will you promote the business? Through what channels will you be promoting it? How are you going to reach and appeal to your target market? The more specific and thorough you can be with your plans here, the better, Cobello says.
6. Explain how you’ll spend your funding
What will you do with the money you raise? What are the first steps you plan to take? As a founder, you want to instill confidence in your investors and show them that the instant you receive their money, you’ll be taking smart actions that grow the company.
7. Include supporting documents
Creating a business plan is in some ways akin to building a legal case, but for your business. “You want to tell a story, and to be as thorough as possible, while keeping your plan succinct, clear, interesting, and visually appealing,” Cobello says. “Supporting documents could include financial projects, a competitive analysis of the market you’re entering into, and even any licenses, patents, or permits you’ve secured.”
A business plan is an individualized document—it’s ultimately up to you what information to include and what story you tell. But above all, Cobello says, your business plan should have a clear focus and goal in mind, because everything else will build off this cornerstone.
“Many people don’t realize how important business plans are for the health of their company,” she says. “Set aside time to make this a priority for your business, and make sure to keep it updated as you grow.”
Money blog: Bar charges holidaymakers £690 for two drinks; savers have a rare opportunity - but it might be the last hurrah
Welcome to the Money blog, your place for personal finance and consumer news and tips. Leave a comment on any of the stories we're covering below.
Thursday 4 July 2024 20:01, UK
- Barclaycard cutting minimum repayments - but it could cost you a lot of money
- Bar charges holidaymakers £690 for two drinks
- Great British mortgage divide - as people pay off all debt seven years earlier in some parts of country
- New record high for US stocks - as FTSE indexes also up
- M&S to launch clothing repair service
Essential reads
- Savings Guide: Savers have a rare opportunity - but it might be the last hurrah
- Cheap Eats : Two Michelin-starred chef reveals his favourites in Birmingham
- Women in Business : 'We don't get invited to golf' - The women who coordinated pregnancies to start virtual cancer care business and raised £5m
- Basically... What is income tax?
- Money Problem : 'I hired a car via EasyJet but they are directing my complaint to someone else - what can I do?'
- Best of the Money blog - an archive
Ask a question or make a comment
John Lewis is keeping its school uniform prices frozen for the fourth year running.
The department store chain also offers parents an online school uniform checklist to help prepare for the start of the new year.
It also offers a free shoe-fitting service, while some of its newer school uniform products released in the last three years have not seen a price rise.
John Lewis school uniform buyer Cydney Ball said: "Our customers trust us as the one-stop-shop for all things back to school."
Cineworld is drawing up plans to axe dozens of British cinemas as part of a radical restructuring that would also include extensive rent cuts.
Sky News has learned that the company, which until last year was listed on the London Stock Exchange, is considering closing about a quarter of its roughly-100 British multiplexes.
Cineworld also wants to renegotiate rent agreements at a further 50 sites, with the remaining 25 untouched by the restructuring.
Sources said the proposals were expected to be formally outlined to creditors including landlords in the coming weeks.
Read the full story here...
A safety charity has warned England fans against buying cheap electronics online amid a "blitz" of advertising.
Electrical Safety First is urging fans bombarded with ads for discounted goods "don't bring it home" in a new campaign to raise awareness of unregulated online marketplaces.
The charity have previously uncovered substandard and dangerous electrical products across major online marketplaces.
Examples of such include portable heaters posing a serious risk of electrocution, hair straighteners and hair dryers featuring illegal UK plugs and e-bike chargers that pose a fire risk.
"Football, and other global sporting events, are experiencing advertising blitzes by major online marketplaces across the globe, and at a time when millions of people are struggling with finances, we understand how appealing low-cost deals will be," said Electrical Safety First's chief executive Lesley Rudd.
"But it's important for fans to remember that they risk scoring an own goal if the deal they bag turns out to be a substandard or dangerous product.
"Substandard electronics can have serious consequences for your safety and an innocent purchase could put you and your family at risk."
The charity makes the following suggestions to consumers selecting electronics from online marketplaces:
- Pay attention to the plug - if a product is listed with a foreign plug and travel adaptor, do not buy it.
- Do not buy on price alone - not all bargains are worth it
- Make sure you do your homework if you decide to buy products below high street retail prices.
- Beware of a product with solely glowing reviews, especially if the reviewers are not verified.
- Make sure you know where the supplier is based - a "co.uk" URL doesn't guarantee the website is UK-based.
- If there is no address supplied, or there is just a PO Box, be wary; many dodgy electrical goods are manufactured overseas.
- Look for websites that allow you to pay safely – these have a padlock symbol in the address bar of the website you are visiting. If you cannot see it, do not enter your payment details.
Consumer spending on car purchases has risen three times faster than for public transport journeys, new figures show.
Around £57.4bn was spent in the UK on new and used cars in 2023, up 6% on five years earlier, according to AA analysis of Office for National Statistics data.
By comparison, consumer spending on public transport - including rail, buses, flights and taxis - was £60.9bn, representing a 2% increase on five years ago.
AA head of roads policy Jack Cousens claimed the figures highlight how vital motoring was for people in the UK, as well as the country's finances.
He said: "These latest ONS figures underline the UK's reliance on cars and the huge amounts of money they generate for the economy - not to mention VAT on that spending, and other tax.
"Cars are not just necessary but essential on so many levels. Even if a significant amount of car use was transformed into take-up of public transport, the impact on the economy and other income generation would be dramatic.
"Just think how much councils would lose if a high percentage of cars stopped turning up to their car parks or needing parking permits, and getting fined.
"The key question is whether what consumers spend on cars would translate into income for public transport and cover the cost of infrastructure investment to enable that.
"It seems that getting travelling consumers to fork out for their own transport and its maintenance, and then tax the heck out of them, is a pretty good deal for the public purse."
Running a car also accounted for a large chunk of the £78.6bn spent on what is described as the operation of personal transport, with spending on fuel and lubricants up 20% since 2018 to £41.7bn.
New car purchases down
But despite the fact more consumers are spending money on cars than on public transport, the number of purchases of new cars by private buyers has declined for nine months in a row, new figures show.
The Society of Motor Manufacturers and Traders (SMMT) said 67,625 new cars were registered by private consumers in June, down 15.3% from 79,798 during the same month last year.
Ian Plummer, commercial director at Auto Trader, said: "With average new car prices rising almost 40% over the last five years, it's clear cost is the culprit.
"Manufacturers are responding with discounts but they're failing to keep pace, which is forcing many buyers to opt for a used alternative.
"Whoever forms the next government needs to address electric car affordability and provide long-term stability for the market."
Environmental impact
Despite comments from the AA, the billions of pounds spent by consumers every year on cars is having a clear effect on UK roads - where overall traffic levels in 2023 were 2.2% higher than the previous year.
More cars on the roads means more air pollution, which is among the biggest environmental health risks facing people in the UK.
Burning petrol and diesel fuel creates harmful by products like nitrogen dioxide and carbon monoxide, while vehicles emit carbon dioxide, the most common human-caused greenhouse gas.
Even electric vehicles produce particulate matter from the friction between their tyres and the road.
Researchers from University College London estimated that 48,625 adults die prematurely each year in the UK due to particulate matter pollution.
Presently, 79% of the UK exceeds the World Health Organization's (WHO) annual mean guideline for safe fine particulate matter levels.
A Greek restaurant has faced criticism for its "rip off" prices.
Holidaymakers have been warned to stay away from DK Oyster on the popular holiday island of Mykonos, which has received swathes of bad reviews on Tripadvisor .
The restaurant, which describes itself as being an "oasis of ultimate luxury and extravagance", has an average star rating of two on the website - although, in the interests of balance, it has 4.8 on Google reviews.
Angry punters say they were lured into buying a drink at DK Oyster after being told the sunbeds were free, only for the prices for those drinks to be sky-high.
Among the latest to complain is Lori E, who said she returned home from her Greek holiday to see a charge of $876 (£690) for two drinks.
She wrote: "Total rip off! Make sure you get a receipt before leaving and check your credit card because they over charge.
"Was told beds were free to sit it if we order food or drink. No problem....ordered 2 drinks which we afterwards saw were 51 euros each.
"If that wasn't crazy enough we returned to the states and had a $876 charge on our account. FOR 2 DRINKS!!!"
The tourists are now trying to dispute the charge with their credit card company after never receiving a paper copy of a receipt.
Responding to the Tripadvisor review, DK Oyser said: "Our sunbeds come with minimum consumption, so we encourage all visitors to check the menus, before placing their orders.
"I would like to note that our menus are displayed on blackboards near the entrance, showing the prices of our food and drinks to keep our guests informed."
Other reviews claim DK Oyser charged them £253 for sea bass and £100 for a jumbo shrimp that "wasn't cooked properly".
DK Oyster has been contacted for comment.
Iceland is set to partner with parenting website Mumsnet to launch a range of children's products.
Mumsnet CEO Justine Roberts, and the brand's partnership director Sarah Murray-Muncila, met with members of Iceland's innovation team last week to work on the products.
According to The Grocer , the new products will hit the stores in early 2025.
"We've been working on something truly special in partnership with Iceland Foods," Mumsnet said.
"Big things are happening for little ones."
Iceland has launched several new collaborations in recent months, including exclusive products with brands such as Slimming World, MyProtein and boxer Tyson Fury's Furocity.
It's not just a big day in the UK with voters heading to the polls but also in the US with 4 July celebrations taking place.
And there's plenty to celebrate for those with a stake in US stocks.
Last night, there was another record high for the S&P 500 index that tracks the share price performance of the 500 largest companies listed on US stock exchanges.
The performance of companies on the tech firm-heavy New York-based NASDAQ too reached a new high.
It came as Elon Musk's Tesla saw its share price reaching a six-month high, along with the rise and rise of trillion-dollar AI microchip maker Nvidia.
Today and tomorrow will likely be quieter as the US markets close.
In the UK, both the Financial Times Stock Exchange (FTSE) 100 and 250 indexes are up - 0.76% in the list of 100 most valuable companies and 0.42% in the 101st to 250th most valued firms.
While the pound does by buy less euro than it did earlier this month, with £1 equal to €1.18 it's still buying more than during most of the last year.
Against the dollar, sterling has held the gains of the last few weeks and a pound will get you $1.2749.
There is no let up for motorists as the oil price is sticking around the two-month high mark. A barrel of the benchmark Brent crude oil costs $86.59.
As house prices continue to rise, so too does the age at which young people can expect to own their own home.
Unfortunately, even the ceiling of the term "young people" isn't far off from being challenged - with fresh research suggesting that the average age of a first-time buyer in the UK is 33 years and 8 months old, according to Mojo Mortgages .
In comparison, in 1960, the average first-time buyer was 23 years old, according to separate research by Keepmoat Homes.
Comparatively, however, the average age of a first-time buyer in 2014 was 32 years, 6 months old, according to the Office for National Statistics.
During the same period, the average price of a house in the UK rose from around £188,000 (January 2014) to £282,000 ( January this year).
Back to today's figures - and those in Wales are able to buy their homes the youngest, with the data suggesting the average first-time buyer there is 31 years old.
Naturally, the older you buy a home, the later in life you'll pay off a mortgage.
With an average mortgage length of 30 years, it seems the average UK first-time buyer isn't expected to be mortgage-free until they are 63 years and 8 months old.
And if you live in the capital, you'll surpass the current retirement age at 66 years, 8 months.
Here's a full breakdown of how old first-time buyers are, the average mortgage length and age they can expect to be mortgage-free by region...
A lot of people have had to renegotiate or extend their mortgages thanks to soaring interest rates in recent years - and the data from Mojo tells us a little about that too.
The study found extending your mortgage term by 10 years (to 35 years) will cost today's average first-time buyer an extra £110,640, which may impact later life planning and their pension.
Barclaycard is cutting the minimum amount its customers have to repay each month.
While the move may sound like good news on the surface, it could well mean you're in debt for longer and end up paying more interest.
At the moment, most Barclaycard customers have a minimum repayment of 3.75% of their balance, 2.5% of their balance plus interest, or £5.
But, from 22 July, that will change to the highest amount out of:
- 1% of their balance
- 1% of their balance plus interest
This means if you are currently only paying the minimum on your card, you'll likely repay less each month.
But, minimum amounts are designed to keep people in debt for as long as possible, and lowering them just makes this period even longer.
MoneySavingExpert says the change means it could now take a customer with a £1,000 debt an extra decade to pay it off, if they only pay the minimum amount.
On average, it says it will take 19 years and three months to clear and the interest will total £1,655.
Founder of MoneySavingExpert Martin Lewis says the change is "worryingly under the radar" and urged customers to check if their repayments are set to the minimum amount.
"Minimum repayments have always been credit card firms' secret weapon. Letting people repay little looks appealing – hence why Barclaycard says this is about 'flexibility'. Yet it takes flexibility to kick your own backside, and this will hurt some just as much," he said.
A Barclays spokesperson told Sky News: "We regularly review our products and from July, some Barclaycard customers will see changes to their minimum monthly payments, alongside adjustments to the APR.
"Customers will benefit from a reduction in their minimum monthly repayment and the vast majority have no change to APR, while some will receive a decrease.
"We have made these changes to increase flexibility for our customers and have been clear in our communications that paying more than the minimum can help customers clear their balance sooner and pay less interest."
Marks and Spencer is to launch a clothing repair service next month.
The retail giant has teamed up with clothing repair and alterations experts SOJO, which was founded in 2021 by Josephine Philips, to give clothes "another life".
From August, M&S customers will be able to book a bespoke repair service through a new online hub, "M&S Fixed by SOJO".
Repairs will start from £5 and be carried out by SOJO's in-house repair team.
The items will then be returned directly to the customer's doorstep within seven to 10 days.
Richard Price, managing director of clothing and home at M&S, said: "Through the launch of our repair service, we're making it even easier for customers to give their clothes another life, whether they are using our new repair service or long-standing clothes recycling scheme."
Be the first to get Breaking News
Install the Sky News app for free


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
10-Step Guide on Writing a Business Plan for Nonprofits. Note: Steps 1, 2, and 3 are in preparation for writing your nonprofit business plan. Step 1: Data Collection. Before even getting started with the writing, collect financial, operating, and other relevant data. If your nonprofit is already in operation, this should at the very least ...
Learn how to create a business plan for your nonprofit that answers key questions about your mission, vision, activities, revenue, expenses, and risks. Find resources, tips, and examples to guide you through the business planning process.
Avoid using jargon, acronyms, or any unfamiliar terms. Write for a general audience, and you'll be more likely to keep the reader engaged. 2. Outline your plan. Make a nonprofit business plan outline. Once you know what information will be put into the plan, you'll understand what data you need to source to write it.
Step 6: Fill in Your Nonprofit Business Plan Outline. Finally, you've made it to the last step in putting together your nonprofit business plan. By this point, you've answered just about every detail that goes into your plan—we just did it in a not-so-boring, roundabout way. Let's fill in the details.
Write a fundraising plan. This part is the most important element of your business plan. In addition to providing required financial statements (e.g., the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement), identify potential sources of funding for your nonprofit. These may include individual donors, corporate donors, grants, or in-kind ...
A nonprofit business plan is required if you want to secure funding from grant-making organizations or investors. A well-crafted business plan will help you: Define your organization's purpose and goals. Articulate your vision for the future. Develop a step-by-step plan to achieve your goals. Secure funding from investors or donors.
The first step in writing a nonprofit business plan is to conduct a feasibility study. This study will help to determine whether or not the nonprofit is viable and whether or not it has the potential to be successful. The feasibility study should include an assessment of the current market, an examination of the competition, and a review of the ...
A business plan for nonprofits is a strategic document that outlines a nonprofit organization's goals and operational approach. While similar to for-profit business plans, the focus here is on achieving social impact rather than financial profit. Projects implemented by nonprofit organizations typically revolve around fostering social welfare ...
A well-drafted nonprofit business plan not only provides direction but also attracts donors and other stakeholders. In this article, we'll delve into the hows and whys of writing a nonprofit business plan and walk you through the process step by step. The purpose and importance of a nonprofit business plan. A business plan is like a roadmap.
This template has all the core components of a nonprofit business plan. It includes room to detail the organization's background, management team key personnel, current and future youth program offerings, promotional activities, operations plan, financial statements, and much more. Download Nonprofit Business Plan Template for Youth Program.
Financial Plan - The Financial Plan is one of the most important sections of your nonprofit business plan. You will establish your financial goals and include financial statements such as the income statement, balance sheet and cash flow statement to show how your nonprofit will be sustainable. This section should also include your ...
Step 1: Write a mission statement. . Having a mission statement is essential for any company, but even more so for nonprofits. Your markers of success are not just how the organization performs financially, but the impact it makes for your cause. One of the easiest ways to do this is by creating a mission statement.
Executive summary. The executive summary of a nonprofit business plan is typically the first section of the plan to be read, but the last to be written. That's because this section is a general overview of everything else in the business plan - the overall snapshot of what your vision is for the organization. Write it as though you might ...
Executive Summary. Start your nonprofit business plan by clearly stating your organization's mission and describing how it plans on reaching its goals. Include a concise description of what makes your organization stand out among competitors (e.g., "We are the only non-profit animal welfare organization in XYZ county" or "Our college ...
That has to be part of the plan." Typical nonprofit business plans feature many of the following elements: Executive summary. Mission and goals. Community impact. Products, services, and programs. Organizational structure and staffing. Audiences. Market and competitive analysis.
If your nonprofit is already established, let your reader know what your marketing plan has been in the past, what has worked, and how you plan to expand it. 5. Operational Plan. This section should describe both day-to-day operations and long-term plans for operating your programs.
11. Outline the Financial Plan. One of the main reasons people want to know how to write a nonprofit business plan is because of how essential it is to receiving funding. Loan providers, donors and granting bodies will want to see your numbers—and that's where your Financial Plan comes in.
Growthink's nonprofit business plan template below is the result of 20+ years of research into the types of business plans that help nonprofit organizations (NPOs) to secure funding and achieve their goals. Follow the links to each section of our non-profit business plan template:
The plan may vary depending on the specific organization, however, there are a couple of things that should be included in every non-profit business plan. 1. Executive Summary. The executive summary is a brief breakdown of the contents outlined in the business plan. The trick here is to provide an interesting summary that will keep the reader ...
Step 2: Outline your plan. Make a nonprofit business plan outline that covers the main sections of your plan. These include: Executive summary: A brief overview of your nonprofit's mission, vision, goals, strategies, and financial summary. Learn more on business plan executive summary. Organization Overview: A description of your nonprofit ...
A nonprofit business plan template provides a strategic overview of your nonprofit. It's a breakdown of all higher-level information about your organization, such as the board of directors and your core mission. Use your nonprofit business plan template to give your staff, the board, potential donors, and government funding agencies an ...
Updated January 09, 2023. A non-profit business plan is a written roadmap for a non-profit organization. It serves to communicate the core purpose, funding needs, and action plan of the organization. Non-profit business plans typically describe in detail the organization's mission and values, administrative structure, staffing, industry analysis, revenue and donations, key milestones, and ...
A nonprofit business plan template includes fields that cover the foundational elements of a business plan, including: The overarching purpose of your nonprofit. Its long and short-term goals. An outline of how you'll achieve these goals. The template also controls the general layout of the business plan, like recommended headings, sub ...
Although a typical business plan falls between 15 to 30 pages, some companies opt for the much shorter One-Page Business Plan. A one-page business plan is a simplified version of the larger business plan, and it focuses on the problem your product or service is solving, the solution (your product), and your business model (how you'll make money).
The nonprofit Medicaid health plan is suing the state to make sure its plan is still an option for North Texas families. Skip to content. Thursday, July 4, 2024 Jul 4, 2024. 90° F Dallas, TX.
Women in Business: 'We don't get ... "We look forward to working with Savills to help us deliver on our plan for growth." 12:02:47. RAC says people who fail driving test should be charged more for ...