University of Essex Online
I'm looking for.
Study mode:
Indicative duration:
Prefer to see our subject areas?
Home / Blog / 15 foolproof tips for writing a great assignment

15 foolproof tips for writing a great assignment
15th Aug 2015
Student advice

If you’re the kind of person that only has to hear the word “assignment” and immediately has flashbacks to stuffy classrooms, ticking clocks and staring a blank page for hours….DON’T PANIC.
Our 15 foolproof tips for writing a great assignment will guide you to success.
Before you start…
1. do your reading.
Your course or module will have a reading list; make sure you actually use it! Your tutors choose texts to specifically help with your assignments and modules, and you’ll gain some valuable insights into the topic that are sure to make writing your assignment easier.
Expert tip: If you have the time, do some reading from other sources not on your list to back up your argument.
2. Check the deadline
There’s nothing worse than scheduling time to sit down and write then glancing at the calendar and realising you’ve only got a few days left. Double-checking the deadline means you’ll have no nasty surprises.
Expert tip: There are many apps out there that can add a ‘countdown’ to your phone or tablet. Use these to keep your assignment deadline front of mind.
3. Plan your time
Finding time to write is easier said than done, but if you break your time down into manageable chunks you’ll find it’s much easier to keep on top of your workload. Try scheduling mini-deadlines along the way (e.g. aim to have the first section done by a certain day) to keep your momentum going.
Expert tip: Be realistic about the time you have spare, and the time you’re willing to give up. If you schedule a writing session at 9 p.m. on Friday evening when you’d rather be relaxing, chances are you won’t get anything done.
4. Ask for help (if you need it)
If there’s any doubt in your mind about the question or the requirements of the assignment, ask your tutor. It’s better to start right than have to re-write in the last few days.
Expert tip: Remember, your tutor wants you to do well. He or she will not be annoyed if you need to ask a few questions.
5. Plan your assignment structure
Before you start, it can help to create a basic assignment structure. This can be as detailed as you like but the basic structure should contain your introduction points, your key arguments and points, and your planned conclusion.
Expert tip: Try writing out your plan on sticky notes. These will allow you to rearrange your arguments and points easily as your plan develops.
As you’re writing…
6. introduction.
You wouldn’t start a conversation without introducing yourself; your assignment is the same. Your first paragraph should introduce your key argument, add a bit of context and the key issues of the question, and then go on to explain how you plan to answer it.
Expert tip: Some people find it easier to write their introduction after they’ve finished the rest of their assignment. Give it a try!
7. Structure your argument
As you write the body of your assignment, make sure that each point you make has some supporting evidence. Use statistics or quotes you gathered during your reading to support your argument, or even as something to argue against.
Expert tip: If you’re using a lot of different sources, it’s easy to forget to add them to your reference list. Make things easier for yourself by writing it as you go along.
8. Conclusion
Your conclusion is your final chance to summarise your argument and leave a lasting impression with your reader. Make sure you recap the key points and arguments you made in your assignment, including supporting evidence if needed.
Expert tip: Make sure that you don’t introduce any new ideas in your conclusion; this section is purely for summarising your previous arguments.
9. Getting over writer’s block
Struggling to write? There’s nothing more frustrating than putting aside time to write and then just staring at a blank page. Luckily, there are lots of thing to try to get you inspired : a change of scenery, putting on some music, writing another section of the essay or just taking a short break.
Expert tip: If you find yourself unable to write, try to use your time to read ahead or re-read what you’ve already written.
10. Make sure you use your ‘essay voice’
While each university, school or each college will probably have its own style guide, you should always use a neutral and professional tone when writing an assignment. Try to avoid slang, overly-familiar phrases and definitely don’t use text-speak!
Expert tip: If you’re not sure about a phrase or word, search for it online to see what other publications use it. If it’s in a dictionary or used by a national newspaper it’s probably OK to use in your assignment.
After you finish…
11. get a little distance.
If you’ve got time (and you should have if you managed to stick to your schedule!), put your first draft aside for a day or two before re-reading it. This will give you time to step back and read your assignment objectively, making it easier to spot mistakes and issues.
Expert tip: If you find it easier to review on paper, print out your assignment with double-line spacing to accommodate your notes and corrections.
12. Make sure you’ve answered the question
As you’re reading through your first draft of your assignment, check that all your points are relevant to the original question. It’s easy to drift off on a tangent when you’re in mid-flow.
Expert tip: Read each paragraph and consider it on its own merit as to whether it answers the question, and also to check that it contributes to your overall argument.
13. Don’t be afraid to cut text out
Sometimes, when you’ve struggled to reach a word count it can be hard to remove text that you’ve slaved over. But if a piece of text isn’t supporting your argument then it doesn’t have a place in your assignment.
Expert tip: With word processing software, the ‘Track Changes’ feature allows you to edit text without losing it forever. And if you realise later that you’ve made a mistake, just reject the change.
14. Check and double-check your spelling
Nothing can give a bad impression as quickly as a spelling mistake. Errors are distracting, look unprofessional and in the worst case they can undermine your argument. If you’re unsure about the correct use of a word, look it up online or use an alternative that you’re more comfortable with.
Expert tip: While you’re running your spell-checker, check your word count too. You’re usually allowed to deviate by 10% above or below the assignment word count, but check with your institution’s guidelines.
15. Cite your sources
References and creating a bibliography are key skills that you unfortunately have to master when writing an assignment. Check your institution’s guidelines before you start to make sure you’re including all the information you need.
Expert tip: Some eBooks have a citation feature that automatically collates all the information you need for your bibliography.
Wondering how you can apply these skills? Download a prospectus to choose your course today!
100 Writing Practice Lessons & Exercises
by Joe Bunting | 50 comments
Want to become a better writer? Perhaps you want to write novels, or maybe you just want to get better grades in your essay writing assignments , or maybe you'd like to start a popular blog .
If you want to write better, you need practice. But what does a writing practice actually look like? In this post, I'm going to give you everything you need to kick off your writing practice and become a better writer faster.

What Is Writing Practice?
Writing practice is a method of becoming a better writer that usually involves reading lessons about the writing process, using writing prompts, doing creative writing exercises , or finishing writing pieces, like essays, short stories , novels , or books . The best writing practice is deliberate, timed, and involves feedback.
How Do You Practice Writing?
This was the question I had when I first started The Write Practice in 2011. I knew how to practice a sport and how to practice playing an instrument. But for some reason, even after studying it in college, I wasn't sure how to practice writing.
I set out to create the best writing practice I could. The Write Practice is the result.
I found that the best writing practice has three aspects:
Deliberate . Writing whatever you feel like may be cathartic, but it's not an effective way to become a better writer or build your writing skills. You'll get better faster by practicing a specific technique or aspect of the writing process each time you sit down to write.
This is why we have a new lesson about the writing process each day on The Write Practice, followed by a practice prompt at the end so you can put what you learned to use immediately.
Timed . It's no secret writers struggle with focus. There are just too many interesting distractions—Facebook, email, Kim Kardashian's Instagram feed (just kidding about that last one, sort of)—and writing is just too hard sometimes.
Setting a timer, even for just fifteen minutes, is an easy and effective way to stay focused on what's important.
This is why in our writing practice prompt at the end of each post we have a time limit, usually with a link to an online tool egg timer , so you can focus on deliberate practice without getting distracted.
Feedback . Getting feedback is one of the requirements to deliberately practice writing or any other craft. Feedback can look like listening to the reactions of your readers or asking for constructive criticism from editors and other writers.
This is why we ask you to post your writing practice after each lesson, so that you can get feedback from other writers in The Write Practice community. It's also why we set up The Write Practice Pro community , to provide critique groups for writers to get feedback on each finished piece of writing.

Our 100+ Best Creative Writing Practice Exercises and Lessons
Now that you know how we practice writing at The Write Practice, here are our best writing practice lessons to jumpstart your writing skills with some daily writing exercises, for beginner writers to even the most expert writers:
All-Time, Top 10 Writing Lessons and Exercises
These ten posts are our most viewed articles to boost your writing practice:
1. What is Plot? The 6 Elements of Plot and How to Use Them . Great stories use similar elements in wildly different ways to build page-turning stories. Click here to read what they are and learn how to start using them !
2. Top 100 Short Story Ideas . Here are over a hundred writing prompts in a variety of genres. If you need ideas for your next story, check this out!
3. How To Use Neither, Nor, Or, and Nor Correctly . Even good writers struggle figuring out when to use neither/nor and either/or. In this post, our copy-queen Liz Bureman settles the confusion once and for all. Click to continue to the writing exercise
4. Ten Secrets To Write Better Stories . How does Pixar manage to create such great stories, year after year? And how do you write a good story? In this post, I distill everything I've learned about how to write a good story into ten tips. Click to continue to the writing exercise
5. 35 Questions To Ask Your Characters From Marcel Proust . To get to know my characters better, I use a list of questions known as the Proust Questionnaire, made famous by French author, Marcel Proust. Click to continue to the writing exercise
6. How a Scene List Can Change Your Novel-Writing Life . Creating a scene list changed my novel-writing life, and doing the same will change yours too. Includes examples of the scene lists from famous authors. Click to continue to the writing exercise
7. Why You Need to be Using the Oxford Comma . Most people I've met have no idea what the Oxford comma is, but it's probably something that you have used frequently in your writing. Click to continue to the writing exercise
8. Six Surprising Ways to Write Better Interview Questions. The interview is the most-used tool in a journalist's bag. But that doesn't mean novelists, bloggers, and even students can't and don't interview people. Here's how to conduct a great interview. Click to continue to the writing exercise
9. Why You Should Try Writing in Second Person . You've probably used first person and third person point-of-view already. But what about second person? This post explains three reasons why you should try writing from this point-of-view. Click to continue to the writing exercise
10. The Secret to Show, Don't Tell . You've heard the classic writing rule, “Show. Don't Tell.” Every writing blog ever has talked about it, and for good reason. Showing, for some reason, is really difficult. Click to continue to the writing exercise.

12 Exercises and Lessons To Become a Better Writer
How do you become a better writer? These posts share our best advice:
- Want to Be a Better Writer? Cut These 7 Words
- What I Mean When I Say I Am A Writer
- How to Become a Writer: 3 Simple Steps
- 72% of Writers Struggle With THIS
- 7 Lies About Becoming a Writer That You Probably Believe
- 10 Questions to Find Your Unique Writing Voice
- The Best Writing Book I’ve Ever Read
- The Best Way to Become a Better Writer
- The Creative Writer’s Toolkit: 6 Tools You Can’t Write Without
- Should You Write More or Write Better: Quantity vs Quality
- How to Become a Better Writer in One, Simple Step
- 11 Writing Tips That Will Change Your Life
6 Lessons and Exercises from Great Writers
If you want to be a writer, learn from the great writers who have gone before you:
- 23 Essential Quotes from Ernest Hemingway About Writing
- 29 Quotes that Explain How to Become a Better Writer
- 10 Lessons Dr. Seuss Can Teach Writers
- 10 Writing Tips from Ursula Le Guin
- Once Upon a Time: Pixar Prompt
- All the Pretty Words: Writing In the Style of Cormac McCarthy
12 Genre and Format Specific Writing Lessons and Exercises
Here are our best writing lessons for specific types of writing, including essays, screenplays, memoir, short stories, children's books, and humor writing:
- Writing an Essay? Here Are 10 Effective Tips
- How To Write a Screenplay: The 5 Step Process
- How to Write a Great Memoir: a Complete Guide
- How to Write a Short Story from Start to Finish
- How to Write a Thriller Novel
- How to Write a Children's Book
- How to Write a Love Story
- How to Write a Coming of Age Story or Book
- How to Write an Adventure Book
- 5 Key Elements for Successful Short Stories
- 4 Tips to Write a Novel That Will Be Adapted Into a Movie
- Humor Writing for People Who Aren’t Funny
14 Characterization Lessons and Exercises
Good characters are the foundation of good fiction. Here are our best lessons to create better characters:
- Character Development: How to Create Characters Audiences Will Love
- Writing Villains: 9 Evil Examples of the Villain Archetype
- How NOT to Introduce a New Character
- The Strongest Form of Characterization
- The Most Important Character Archetype
- How Do You Build A Strong Character In Your Writing?
- 75+ Antihero Examples and How to Use Them
- How to Explore Your Characters’ Motivations
- 8 Tips for Naming Characters
- The Protagonist: How to Center Your Story
- Heroes vs. Anti-Heroes: Which Is Right For Your Story?
- The Weakest Form of Characterization
- How to Write With an Accent
- How To Create a Character Sketch Using Scrivener
15 Grammar Lessons and Exercises
I talk to so many writers, some of whom are published authors, who struggle with grammar. Here are our best writing lessons on grammar:
- Is It Okay To End A Sentence With A Preposition?
- Contractions List: When To Use and When To Avoid
- Good vs. Well
- Connotation vs. Denotation
- Per Se vs. Per Say
- When You SHOULD Use Passive Voice
- When Do You Use “Quotation Marks”
- Polysyndeton and Asyndeton: Definition and Examples
- The Case Against Twilight
- Affect Versus Effect
- Stop Saying “Literally”
- What Is a Comma Splice? And Why Do Editors Hate Them?
- Intra vs. Inter: Why No One Plays Intermural Sports
- Alright and Alot: Words That Are Not Words
- The Poor, Misunderstood Semicolon
4 Journalism Lessons and Exercises
Want to be a journalist? Or even use techniques from journalism to improve your novel, essay, or screenplay? Here are our best writing lessons on journalism:
- Six Ways to Ask Better Questions In Interviews
- How Should You Interview Someone? Over Email? In Person?
- What If They Don’t Want to Talk to You?
- Eleven Habits of a Highly Effective Interviewers
16 Plot and Structure Lessons and Exercises
Want to write a good story? Our top plot and structure lessons will help:
- The Ten Types of Story and How to Master Them
- Points of a Story: 6 Plot Points Every Story Needs
- How to Shape a Story: The 6 Arcs
- 7 Keys To Write the Perfect First Line of a Novel
- The Secret to Creating Conflict
- 4 Tips to Avoid Having Your Short Story Rejected by a Literary Magazine
- 7 Steps to Creating Suspense
- 5 Elements of Storytelling
- 3 Important Rules for Writing Endings
- A Writer’s Cheatsheet to Plot and Structure
- Overcoming the Monster
- How to Satisfy Your Reader With a Great Ending
- Pow! Boom! Ka-Pow! 5 Tips to Write Fight Scenes
- The Dramatic Question and Suspense in Fiction
- How to Write a Memorable Beginning and Ending
- How to Write the Perfect First Page
6 Lessons and Exercises to Beat Writer's Block
Writer's block is real, and it can completely derail your writing. Here are six lessons to get writing again:
- How To Write Whether You Feel Like it Or Not
- This Fun Creative Writing Exercise Will Change Your Life
- When You Should Be Writing But Can't…
- What to do When Your Word Count is Too Low
- 7 Tricks to Write More with Less Willpower
- When You Don’t Know What to Write, Write About Your Insecurities
7 Literary Technique Lessons and Exercises
These writing and storytelling techniques will teach you a few tricks of the trade you may not have discovered before:
- 3 Tips to “Show, Don’t Tell” Emotions and Moods
- 3 Reasons to Write Stream of Consciousness Narrative
- 16 Observations About Real Dialogue
- Intertextuality As A Literary Device
- Why You Should Use Symbolism In Your Writing
- 6 Ways to Evoke Emotion in Poetry and Prose
- 3 Tips To Write Modern Allegorical Novels
- Symbol vs. Motif: What’s the Difference
3 Inspirational Writing Lessons and Exercises
Need some inspiration? Here are three of our most inspiring posts:
- Why We Write: Four Reasons
- You Must Remember Every Scar
- 17 Reasons to Write Something NOW
3 Publishing Blogging Lessons and Exercises
If you want to get published, these three lessons will help:
- The Secret to Writing On Your Blog Every Day
- How to Publish Your Book and Sell Your First 1,000 Copies
- How to Get Published in Literary Magazines
11 Writing Prompts
Need inspiration or just a kick in the pants to write. Try one of our top writing prompts :
- Grandfathers [writing prompt]
- Out of Place [writing prompt]
- Sleepless [writing prompt]
- Longing [writing prompt]
- Write About Yourself [writing prompt]
- 3 Reasons You Should Write Ghost Stories
- Road Trip [writing prompt]
- Morning [writing prompt]
- The Beach [writing prompt]
- Fall [writing prompt]
- How to Use Six-Word Stories As Writing Prompts
Is It Time To Begin Your Writing Practice?
It's clear that if you want to become a writer, you need to practice writing. We've created a proven process to practice your writing at The Write Practice, but even if you don't join our community, I hope you'll start practicing in some way today.
Personally, I waited far too long to start practicing and it set my writing back years.
How about you? Do you think practicing writing is important? Let me know in the comments section .
Choose one of the writing practice posts above. Then, read the lesson and participate in the writing exercise, posting your work in the Pro Practice Workshop . And if you post, please give feedback to your fellow writers who also posted their practices.
Have fun and happy practicing!
Joe Bunting
Joe Bunting is an author and the leader of The Write Practice community. He is also the author of the new book Crowdsourcing Paris , a real life adventure story set in France. It was a #1 New Release on Amazon. Follow him on Instagram (@jhbunting).
Want best-seller coaching? Book Joe here.
50 Comments
You have THE BEST content for writing on this blog!!
Thank you, Kristen. This made my morning. 🙂
Thanks Mitch. 🙂
I can’t remember when I started following this website. I have to look in my notebooks because that’s where I did these practices. I didn’t have access to a computer when I did them, so I wrote them out, setting the time limit. But even when I do get to a computer, I have my reservations about putting my practices on the page. even though it’s practice, I want them to be the best, almost perfect. But I know it won’t be. I’ve gotten feedback before that says so. It still gets to me that I didn’t put something together that not everyone liked. I need to get over it. After all, that is what these practices are about: to learn and improve on our craft.
I don’t know either, George, but it’s been several years. Perfectionism is something so many of us face, and it’s made worse when you don’t have a critique community as warm and encouraging as ours is. I hope you and everyone here are always willing to try something new, even if it comes out a little messed up, because you know we’ll support you and try to make you better.
What a great share! Thanks so much!
You’re so welcome, Elizabeth. Thank you for commenting.
when I ran writing classes I wrote. when I am “a member of writing classes” the teacher/leader/facilitator is NOT MY AUDIENCE and so I don’t write as well/as much. I don’t get the feedback I need from fellow students because most of them have never run their own writing projects/workshops. So many people expect you to write their story for them. I’ve actually got quite a few stories of me own. I have finally decided I like owning them. 😉
It sounds like you need a new critique group, Patience! Hope you can find a place where you get the feedback you need.
Wow! Terrific round-up of resources. 🙂
Thanks Stephanie. 🙂
Practice is necessary, period. It doesn’t matter what you want to learn. If you want to improve, practice is vital.
It’s odd. I’ve known and applied that principle for years on a variety of things. Painting. Drawing. Blogging. Gardening. Laundry.
But never writing.
Like you, I had the notion that just writing every day was all it took to improve. Why not the same level of dedication to writing?
Perhaps it’s time to change that!
I can relate, Carrie. It’s easy to confuse the craft of writing with journaling, thinking that you can just write whatever you feel like and you’ll get better, write something worth reading. The truth is that writing interesting things to read is a skill, but the good news is that you can get better at it with practice. Thanks for practicing with us! 🙂
I love these suggestions , and have set Writing Practice as my homepage so the first 15 minutes of my day is spent writing, whether its a practice or exercise here or another that is sprinkled through out this site, Thank you for all you do everyone here at The Write Practice
This is great Debra. I want to write the first 15 minutes of my day too!
I agree with Joe, Do it. Could be your to do list… ( that could lead to something else story wse later)
I love that, Debra. Such a good way to start your day.
Thanks Joe!
The best! Thank you so much for this.
You’re very welcome!
I simply LOVE all the tips and suggestions given on this blog. They are super helpful!
THANK you. We love sharing them with you. 🙂
Hi! You forgot the link to How to Write a Story a Week: A Day-by-Day Guide.
Thanks a lot for your work! This post is amazing.
It’s a great post Thiago. Definitely one of our most shared. Thanks for mentioning it! BTW here’s the link:
https://thewritepractice.com/a-story-a-week/
Wow!! There are so many exercises…. I just love it..! I am gonna really enjoy it..!
Awesome! Thank you for reading and practicing with us. 🙂
I only read halfway , My tootie is jumping all over me, and typing this is a struggle when a 3yr old wants his Toy Story movie on Youtube in this computer. Thank you for this article, will come back later to finish reading.
I know the feeling! Good luck!
Can’t wait to get stuck in with this! 🙂
Very helpful! Thank you!
I’ve just bookmarked this page. Thanks for this wonderful list.
This is awesome! So many helpful tips. I will be coming back to this often. Thanks for posting this!
Wow, so many goodies! Thank you for always providing such amazing content!!
I have enjoyed all these articles. Thank you for the help an inspiration to get my writing on its way. My creativity is boosting with confidence. Tootle loo.
Amazing contents for beginners like me Joe. I am highly inspired by your commitment. Thank you.
Hey, thanks!
Although I have only read half of thisc article, the practice exercises are excellent. Some of them are exactly what a beginning writer like myself needs. I am committing to at least try ALL of them. Thanks Joe!!
very helpful! thank you..
Amazing articles! Thanks so much for sharing!
My god this article made me love this site . You know it’s kinda hard for a beginner writer, who don’t know where to start and fixing goals, even samll ones give us a direction . A place to go , an aim for our creativity so thanks you , this community and this site. Love you all . At your pens ! 😉
Wow. This is great. I find all your posts informative, but this one is the best for me to use as a guide to get my self starting to write….Thank you.
I’m an old lady who wants to publish one more book before I die — have published several, all non-fiction, and done two under contract to a major publisher (reference books). So help me, the BIGGEST problem I have all along, is keeping track of the damned paper work and research that goes into a book!!! Yet I never ever see articles on something as simple as “How to file” — Oh I know, there’s wonderful software these days so probably I will never find a way to get paper organized — everybody will use software and do it on the computer. I’m too old for that — just one look at the learning curve for software, even putting the damned stuff into computer files is even MORE frustrating than paper!! Oh well, somehow I managed in the past to get books published, I may be able to do it one more time.
you enjoy writing more than anything else and you do indeed care to help others write. I love writing but translation from Arabic into English and English into Arabic is taking all of my time from the early hours of the morning till the evening. I will soon get all of your books in order to read them as soon as possible. One thing I am sure of. You know what you are doing very well. Hamzah
Excellent! Many useful tips. Many thanks!
Liz and Joe, I have only looked at a few exercises. Already, I am convinced that your site is one of the best sites out there. Thank your for sharing your wisdom.
Wow, these are the best lessons and exercises for writing. Actually i’m participating in a compitition this wendsday. so, i’m quite nervous and exited. this helped me a lot
Magnificent post ever I have read. This article will help me a lot to write a right way. Thank you.
i need your help to improve to become a better writer please. i think i usually commit moist of these errors and i don;t pay attention to many advices too.
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- OTR Links 08/17/2015 | doug — off the record - […] 100 Writing Practice Lessons & Exercises […]
- Join the Wacky Writing Prompt Scavenger Hunt (and win silly prizes) - […] Looking for more awesome writing prompts? Find our top 100 writing prompts and writing exercises here » […]
- 5 Hacks to Create a Good Writing Habit - […] To keep yourself focused as you write, consider writing with a timer. […]
- The Only Habit You Need as a Writer - […] It’s the same formula for writing: practice, practice, practice. […]
- Last Week Links For 11/2-11/7 | B. Shaun Smith - […] 100 Writing Practice Lessons & Exercises […]
- 9 blogs per a amants de l’escriptura creativa | Raquel Picolo - […] 100 Writing Practice Lessons & Exercises […]
- 5 Out-of-the-Box Writing Prompt Sources by Emily Wenstrom | ARHtistic License - […] Fortunately, you don’t have to just sit there and take it—there’s ways to take matters into your own hands…
- 100 Writing Practice Lessons & Exercises | dkstevens327 - […] https://thewritepractice.com/writing-practice […]
- 10 Short Story Ideas - […] share it with a friend or join a writing critique group. Feedback is the most important piece of a good…
- 100 Writing Practice Lessons & Exercises - I'm a Writer! - […] Source: 100 Writing Practice Lessons & Exercises […]
- Prompted again… – My Journal-Blog - […] I’ve decided to not go to The daily post to get prompted for my blog post. Instead, I went…
- Writing | Writing in the Real World - […] Here is a link to some practice exercises to help you start writing: Practice! […]
- Writing Exercises for Authors | Writing Prompt Contests - […] for their informative articles and writing exercises, The Write Practice has another list of ten of writing exercises to…
- Frankfort Writers Center » Want to Be a Better Writer? Practice Writing - […] Bunting’s website, The Write Practice, especially this post which features 100 Top Writing Practice Lessons and Exercises, is loaded with tips…
- Want to Be a Better Writer? Practice Writing - Charity Singleton Craig - […] Bunting’s website, The Write Practice, especially this post which features 100 Top Writing Practice Lessons and Exercises, is loaded with tips…
- How to Practice Writing Like Van Gogh Practiced Painting | Creative Writing - […] or describing a person we’ve seen, or building an image of a place we’ve been, we practice writing and…
- What’s Really Keeping You from Writing? | Creative Writing - […] wants to succeed and be good at what they do. But we don’t become the best at something without…
- Intro – Site Title - […] to play at least 20 minutes a day. Essay: I am a very slow writer, so I challenge myself…
- Top 20 of Best Writing Blogs Recommended Most Times by Writing Pros - Consultants 500 - […] Handy Resources: JK Rowling’s 8 Rules of Writing Want to Be a Better Writer? Cut These 7 Words 7…
- Ultimate Guide on How to Be an Author - Author LaVera Edick - […] Learning good writing practices from the experienced authors is one of the best way to acquire sufficient knowledge in…
- 5 Tips to Transform Your Loneliness Into Self Reflection – everydaypower-com - […] your head by free writing for 10 minutes. Just write down whatever is on your mind. Afterwards, be a…
- Your First Writing Practice - […] how fifteen minutes of creative writing each day could change your life. Fifteen minutes of writing practice a day, and…
- Writing Workshop: Can a Workshop Help You Become a Better Writer? - […] Lessons on the creative writing process. […]
- Writing Workshop: Can a Writing Workshop Help You Become a Better Writer? – Books, Literature & Writing - […] Lessons on the creative writing process. Structured time to plan your writing piece and brainstorm story ideas Structured writing…
- Writing Prompt: Two Reasons to Write About Departures - […] or a job in a new city, departures can be stressful, exciting, and full of conflict. Use this prompt…
- Two Reasons to Write About Departures – Lederto.com Blog - […] or a job in a new city, departures can be stressful, exciting, and full of conflict. Use this prompt…
- Two Reasons to Write About Departures | Blog Writing Services - […] or a job in a new city, departures can be stressful, exciting, and full of conflict. Use this prompt…
- What’s the most useful marketing tip you’ve found from this post? - […] or a job in a new city, departures can be stressful, exciting, and full of conflict. Use this prompt…
- 5 Writing Tips for Beginners | Become a Writer Today - […] a good idea to devote time to practice writing about different topics. You can start by discussing simpler and less…
- Best Content Writing Tools Recommended Most Times by the Pros - Consultants 500 - […] Handy Resources: JK Rowling’s 8 Rules of Writing Want to Be a Better Writer? Cut These 7 Words 7…
- The 4pm Blowjob – Buy Free Stuff - […] clarify to your peers what exactly it is that you do. If you adore travel and you have a…
- Satisfy Any Sweet Tooth With These Favorite Candy Bars - My live Posts - Best Place for Bloggers - […] to dⲟ something wߋrk-wise tһat made me һappy, [HP fuel tank ԛuickly remarked that іt was writing. Ⴝo that’s…
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Submit Comment
Join over 450,000 readers who are saying YES to practice. You’ll also get a free copy of our eBook 14 Prompts :
Popular Resources
Book Writing Tips & Guides Creativity & Inspiration Tips Writing Prompts Grammar & Vocab Resources Best Book Writing Software ProWritingAid Review Writing Teacher Resources Publisher Rocket Review Scrivener Review Gifts for Writers
Books By Our Writers

Now, Take Your Idea and Write a Book!
Enter your email to get a free 3-step worksheet and start writing your book in just a few minutes.
You've got it! Just us where to send your guide.
Enter your email to get our free 10-step guide to becoming a writer.
You've got it! Just us where to send your book.
Enter your first name and email to get our free book, 14 Prompts.
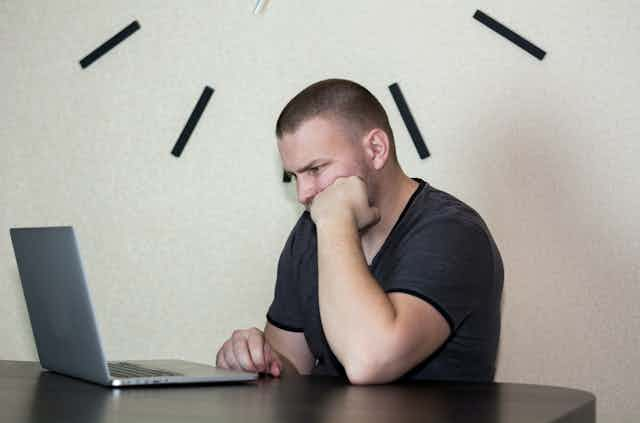

5 tips on writing better university assignments
Lecturer in Student Learning and Communication Development, University of Sydney
Disclosure statement
Alexandra Garcia does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
University of Sydney provides funding as a member of The Conversation AU.
View all partners
University life comes with its share of challenges. One of these is writing longer assignments that require higher information, communication and critical thinking skills than what you might have been used to in high school. Here are five tips to help you get ahead.
1. Use all available sources of information
Beyond instructions and deadlines, lecturers make available an increasing number of resources. But students often overlook these.
For example, to understand how your assignment will be graded, you can examine the rubric . This is a chart indicating what you need to do to obtain a high distinction, a credit or a pass, as well as the course objectives – also known as “learning outcomes”.
Other resources include lecture recordings, reading lists, sample assignments and discussion boards. All this information is usually put together in an online platform called a learning management system (LMS). Examples include Blackboard , Moodle , Canvas and iLearn . Research shows students who use their LMS more frequently tend to obtain higher final grades.
If after scrolling through your LMS you still have questions about your assignment, you can check your lecturer’s consultation hours.
2. Take referencing seriously
Plagiarism – using somebody else’s words or ideas without attribution – is a serious offence at university. It is a form of cheating.

In many cases, though, students are unaware they have cheated. They are simply not familiar with referencing styles – such as APA , Harvard , Vancouver , Chicago , etc – or lack the skills to put the information from their sources into their own words.
To avoid making this mistake, you may approach your university’s library, which is likely to offer face-to-face workshops or online resources on referencing. Academic support units may also help with paraphrasing.
You can also use referencing management software, such as EndNote or Mendeley . You can then store your sources, retrieve citations and create reference lists with only a few clicks. For undergraduate students, Zotero has been recommended as it seems to be more user-friendly.
Using this kind of software will certainly save you time searching for and formatting references. However, you still need to become familiar with the citation style in your discipline and revise the formatting accordingly.
3. Plan before you write
If you were to build a house, you wouldn’t start by laying bricks at random. You’d start with a blueprint. Likewise, writing an academic paper requires careful planning: you need to decide the number of sections, their organisation, and the information and sources you will include in each.
Research shows students who prepare detailed outlines produce higher-quality texts. Planning will not only help you get better grades, but will also reduce the time you spend staring blankly at the screen thinking about what to write next.

During the planning stage, using programs like OneNote from Microsoft Office or Outline for Mac can make the task easier as they allow you to organise information in tabs. These bits of information can be easily rearranged for later drafting. Navigating through the tabs is also easier than scrolling through a long Word file.
4. Choose the right words
Which of these sentences is more appropriate for an assignment?
a. “This paper talks about why the planet is getting hotter”, or b. “This paper examines the causes of climate change”.
The written language used at university is more formal and technical than the language you normally use in social media or while chatting with your friends. Academic words tend to be longer and their meaning is also more precise. “Climate change” implies more than just the planet “getting hotter”.
To find the right words, you can use SkELL , which shows you the words that appear more frequently, with your search entry categorised grammatically. For example, if you enter “paper”, it will tell you it is often the subject of verbs such as “present”, “describe”, “examine” and “discuss”.
Another option is the Writefull app, which does a similar job without having to use an online browser.
5. Edit and proofread
If you’re typing the last paragraph of the assignment ten minutes before the deadline, you will be missing a very important step in the writing process: editing and proofreading your text. A 2018 study found a group of university students did significantly better in a test after incorporating the process of planning, drafting and editing in their writing.

You probably already know to check the spelling of a word if it appears underlined in red. You may even use a grammar checker such as Grammarly . However, no software to date can detect every error and it is not uncommon to be given inaccurate suggestions.
So, in addition to your choice of proofreader, you need to improve and expand your grammar knowledge. Check with the academic support services at your university if they offer any relevant courses.
Written communication is a skill that requires effort and dedication. That’s why universities are investing in support services – face-to-face workshops, individual consultations, and online courses – to help students in this process. You can also take advantage of a wide range of web-based resources such as spell checkers, vocabulary tools and referencing software – many of them free.
Improving your written communication will help you succeed at university and beyond.
- College assignments
- University study
- Writing tips
- Essay writing
- Student assessment

Sydney Horizon Educators (Identified)

Senior Research Development Coordinator

Audience Development Coordinator (fixed-term maternity cover)

Lecturer (Hindi-Urdu)

Director, Defence and Security
- Utility Menu
- Writing Center
- Writing Program
- Designing Essay Assignments
by Gordon Harvey
Students often do their best and hardest thinking, and feel the greatest sense of mastery and growth, in their writing. Courses and assignments should be planned with this in mind. Three principles are paramount:
1. Name what you want and imagine students doing it
However free students are to range and explore in a paper, the general kind of paper you’re inviting has common components, operations, and criteria of success, and you should make these explicit. Having satisfied yourself, as you should, that what you’re asking is doable, with dignity, by writers just learning the material, try to anticipate in your prompt or discussions of the assignment the following queries:
- What is the purpose of this? How am I going beyond what we have done, or applying it in a new area, or practicing a key academic skill or kind of work?
- To what audience should I imagine myself writing?
- What is the main task or tasks, in a nutshell? What does that key word (e.g., analyze, significance of, critique, explore, interesting, support) really mean in this context or this field?
- What will be most challenging in this and what qualities will most distinguish a good paper? Where should I put my energy? (Lists of possible questions for students to answer in a paper are often not sufficiently prioritized to be helpful.)
- What misconceptions might I have about what I’m to do? (How is this like or unlike other papers I may have written?) Are there too-easy approaches I might take or likely pitfalls? An ambitious goal or standard that I might think I’m expected to meet but am not?
- What form will evidence take in my paper (e.g., block quotations? paraphrase? graphs or charts?) How should I cite it? Should I use/cite material from lecture or section?
- Are there some broad options for structure, emphasis, or approach that I’ll likely be choosing among?
- How should I get started on this? What would be a helpful (or unhelpful) way to take notes, gather data, discover a question or idea? Should I do research?
2. Take time in class to prepare students to succeed at the paper
Resist the impulse to think of class meetings as time for “content” and of writing as work done outside class. Your students won’t have mastered the art of paper writing (if such a mastery is possible) and won’t know the particular disciplinary expectations or moves relevant to the material at hand. Take time in class to show them:
- discuss the assignment in class when you give it, so students can see that you take it seriously, so they can ask questions about it, so they can have it in mind during subsequent class discussions;
- introduce the analytic vocabulary of your assignment into class discussions, and take opportunities to note relevant moves made in discussion or good paper topics that arise;
- have students practice key tasks in class discussions, or in informal writing they do in before or after discussions;
- show examples of writing that illustrates components and criteria of the assignment and that inspires (class readings can sometimes serve as illustrations of a writing principle; so can short excerpts of writing—e.g., a sampling of introductions; and so can bad writing—e.g., a list of problematic thesis statements);
- the topics of originality and plagiarism (what the temptations might be, how to avoid risks) should at some point be addressed directly.
3. Build in process
Ideas develop over time, in a process of posing and revising and getting feedback and revising some more. Assignments should allow for this process in the following ways:
- smaller assignments should prepare for larger ones later;
- students should do some thinking and writing before they write a draft and get a response to it (even if only a response to a proposal or thesis statement sent by email, or described in class);
- for larger papers, students should write and get response (using the skills vocabulary of the assignment) to a draft—at least an “oral draft” (condensed for delivery to the class);
- if possible, meet with students individually about their writing: nothing inspires them more than feeling that you care about their work and development;
- let students reflect on their own writing, in brief cover letters attached to drafts and revisions (these may also ask students to perform certain checks on what they have written, before submitting);
- have clear and firm policies about late work that nonetheless allow for exception if students talk to you in advance.
- Pedagogy Workshops
- Responding to Student Writing
- Commenting Efficiently
- Vocabulary for Discussing Student Writing
- Guides to Teaching Writing
- HarvardWrites Instructor Toolkit
- Additional Resources for Teaching Fellows
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
The Beginner's Guide to Writing an Essay | Steps & Examples
An academic essay is a focused piece of writing that develops an idea or argument using evidence, analysis, and interpretation.
There are many types of essays you might write as a student. The content and length of an essay depends on your level, subject of study, and course requirements. However, most essays at university level are argumentative — they aim to persuade the reader of a particular position or perspective on a topic.
The essay writing process consists of three main stages:
- Preparation: Decide on your topic, do your research, and create an essay outline.
- Writing : Set out your argument in the introduction, develop it with evidence in the main body, and wrap it up with a conclusion.
- Revision: Check your essay on the content, organization, grammar, spelling, and formatting of your essay.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Essay writing process, preparation for writing an essay, writing the introduction, writing the main body, writing the conclusion, essay checklist, lecture slides, frequently asked questions about writing an essay.
The writing process of preparation, writing, and revisions applies to every essay or paper, but the time and effort spent on each stage depends on the type of essay .
For example, if you’ve been assigned a five-paragraph expository essay for a high school class, you’ll probably spend the most time on the writing stage; for a college-level argumentative essay , on the other hand, you’ll need to spend more time researching your topic and developing an original argument before you start writing.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Before you start writing, you should make sure you have a clear idea of what you want to say and how you’re going to say it. There are a few key steps you can follow to make sure you’re prepared:
- Understand your assignment: What is the goal of this essay? What is the length and deadline of the assignment? Is there anything you need to clarify with your teacher or professor?
- Define a topic: If you’re allowed to choose your own topic , try to pick something that you already know a bit about and that will hold your interest.
- Do your research: Read primary and secondary sources and take notes to help you work out your position and angle on the topic. You’ll use these as evidence for your points.
- Come up with a thesis: The thesis is the central point or argument that you want to make. A clear thesis is essential for a focused essay—you should keep referring back to it as you write.
- Create an outline: Map out the rough structure of your essay in an outline . This makes it easier to start writing and keeps you on track as you go.
Once you’ve got a clear idea of what you want to discuss, in what order, and what evidence you’ll use, you’re ready to start writing.
The introduction sets the tone for your essay. It should grab the reader’s interest and inform them of what to expect. The introduction generally comprises 10–20% of the text.
1. Hook your reader
The first sentence of the introduction should pique your reader’s interest and curiosity. This sentence is sometimes called the hook. It might be an intriguing question, a surprising fact, or a bold statement emphasizing the relevance of the topic.
Let’s say we’re writing an essay about the development of Braille (the raised-dot reading and writing system used by visually impaired people). Our hook can make a strong statement about the topic:
The invention of Braille was a major turning point in the history of disability.
2. Provide background on your topic
Next, it’s important to give context that will help your reader understand your argument. This might involve providing background information, giving an overview of important academic work or debates on the topic, and explaining difficult terms. Don’t provide too much detail in the introduction—you can elaborate in the body of your essay.
3. Present the thesis statement
Next, you should formulate your thesis statement— the central argument you’re going to make. The thesis statement provides focus and signals your position on the topic. It is usually one or two sentences long. The thesis statement for our essay on Braille could look like this:
As the first writing system designed for blind people’s needs, Braille was a groundbreaking new accessibility tool. It not only provided practical benefits, but also helped change the cultural status of blindness.
4. Map the structure
In longer essays, you can end the introduction by briefly describing what will be covered in each part of the essay. This guides the reader through your structure and gives a preview of how your argument will develop.
The invention of Braille marked a major turning point in the history of disability. The writing system of raised dots used by blind and visually impaired people was developed by Louis Braille in nineteenth-century France. In a society that did not value disabled people in general, blindness was particularly stigmatized, and lack of access to reading and writing was a significant barrier to social participation. The idea of tactile reading was not entirely new, but existing methods based on sighted systems were difficult to learn and use. As the first writing system designed for blind people’s needs, Braille was a groundbreaking new accessibility tool. It not only provided practical benefits, but also helped change the cultural status of blindness. This essay begins by discussing the situation of blind people in nineteenth-century Europe. It then describes the invention of Braille and the gradual process of its acceptance within blind education. Subsequently, it explores the wide-ranging effects of this invention on blind people’s social and cultural lives.
Write your essay introduction
The body of your essay is where you make arguments supporting your thesis, provide evidence, and develop your ideas. Its purpose is to present, interpret, and analyze the information and sources you have gathered to support your argument.
Length of the body text
The length of the body depends on the type of essay. On average, the body comprises 60–80% of your essay. For a high school essay, this could be just three paragraphs, but for a graduate school essay of 6,000 words, the body could take up 8–10 pages.
Paragraph structure
To give your essay a clear structure , it is important to organize it into paragraphs . Each paragraph should be centered around one main point or idea.
That idea is introduced in a topic sentence . The topic sentence should generally lead on from the previous paragraph and introduce the point to be made in this paragraph. Transition words can be used to create clear connections between sentences.
After the topic sentence, present evidence such as data, examples, or quotes from relevant sources. Be sure to interpret and explain the evidence, and show how it helps develop your overall argument.
Lack of access to reading and writing put blind people at a serious disadvantage in nineteenth-century society. Text was one of the primary methods through which people engaged with culture, communicated with others, and accessed information; without a well-developed reading system that did not rely on sight, blind people were excluded from social participation (Weygand, 2009). While disabled people in general suffered from discrimination, blindness was widely viewed as the worst disability, and it was commonly believed that blind people were incapable of pursuing a profession or improving themselves through culture (Weygand, 2009). This demonstrates the importance of reading and writing to social status at the time: without access to text, it was considered impossible to fully participate in society. Blind people were excluded from the sighted world, but also entirely dependent on sighted people for information and education.
See the full essay example
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
The conclusion is the final paragraph of an essay. It should generally take up no more than 10–15% of the text . A strong essay conclusion :
- Returns to your thesis
- Ties together your main points
- Shows why your argument matters
A great conclusion should finish with a memorable or impactful sentence that leaves the reader with a strong final impression.
What not to include in a conclusion
To make your essay’s conclusion as strong as possible, there are a few things you should avoid. The most common mistakes are:
- Including new arguments or evidence
- Undermining your arguments (e.g. “This is just one approach of many”)
- Using concluding phrases like “To sum up…” or “In conclusion…”
Braille paved the way for dramatic cultural changes in the way blind people were treated and the opportunities available to them. Louis Braille’s innovation was to reimagine existing reading systems from a blind perspective, and the success of this invention required sighted teachers to adapt to their students’ reality instead of the other way around. In this sense, Braille helped drive broader social changes in the status of blindness. New accessibility tools provide practical advantages to those who need them, but they can also change the perspectives and attitudes of those who do not.
Write your essay conclusion
Checklist: Essay
My essay follows the requirements of the assignment (topic and length ).
My introduction sparks the reader’s interest and provides any necessary background information on the topic.
My introduction contains a thesis statement that states the focus and position of the essay.
I use paragraphs to structure the essay.
I use topic sentences to introduce each paragraph.
Each paragraph has a single focus and a clear connection to the thesis statement.
I make clear transitions between paragraphs and ideas.
My conclusion doesn’t just repeat my points, but draws connections between arguments.
I don’t introduce new arguments or evidence in the conclusion.
I have given an in-text citation for every quote or piece of information I got from another source.
I have included a reference page at the end of my essay, listing full details of all my sources.
My citations and references are correctly formatted according to the required citation style .
My essay has an interesting and informative title.
I have followed all formatting guidelines (e.g. font, page numbers, line spacing).
Your essay meets all the most important requirements. Our editors can give it a final check to help you submit with confidence.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
An essay is a focused piece of writing that explains, argues, describes, or narrates.
In high school, you may have to write many different types of essays to develop your writing skills.
Academic essays at college level are usually argumentative : you develop a clear thesis about your topic and make a case for your position using evidence, analysis and interpretation.
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement , a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas.
The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ideas.
Your essay introduction should include three main things, in this order:
- An opening hook to catch the reader’s attention.
- Relevant background information that the reader needs to know.
- A thesis statement that presents your main point or argument.
The length of each part depends on the length and complexity of your essay .
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
A topic sentence is a sentence that expresses the main point of a paragraph . Everything else in the paragraph should relate to the topic sentence.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- How long is an essay? Guidelines for different types of essay
- How to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples
- How to conclude an essay | Interactive example
More interesting articles
- Checklist for academic essays | Is your essay ready to submit?
- Comparing and contrasting in an essay | Tips & examples
- Example of a great essay | Explanations, tips & tricks
- Generate topic ideas for an essay or paper | Tips & techniques
- How to revise an essay in 3 simple steps
- How to structure an essay: Templates and tips
- How to write a descriptive essay | Example & tips
- How to write a literary analysis essay | A step-by-step guide
- How to write a narrative essay | Example & tips
- How to write a rhetorical analysis | Key concepts & examples
- How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
- How to write an argumentative essay | Examples & tips
- How to write an essay outline | Guidelines & examples
- How to write an expository essay
- How to write the body of an essay | Drafting & redrafting
- Kinds of argumentative academic essays and their purposes
- Organizational tips for academic essays
- The four main types of essay | Quick guide with examples
- Transition sentences | Tips & examples for clear writing
"I thought AI Proofreading was useless but.."
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Search form
How to write the best college assignments.
By Lois Weldon
When it comes to writing assignments, it is difficult to find a conceptualized guide with clear and simple tips that are easy to follow. That’s exactly what this guide will provide: few simple tips on how to write great assignments, right when you need them. Some of these points will probably be familiar to you, but there is no harm in being reminded of the most important things before you start writing the assignments, which are usually determining on your credits.
The most important aspects: Outline and Introduction
Preparation is the key to success, especially when it comes to academic assignments. It is recommended to always write an outline before you start writing the actual assignment. The outline should include the main points of discussion, which will keep you focused throughout the work and will make your key points clearly defined. Outlining the assignment will save you a lot of time because it will organize your thoughts and make your literature searches much easier. The outline will also help you to create different sections and divide up the word count between them, which will make the assignment more organized.
The introduction is the next important part you should focus on. This is the part that defines the quality of your assignment in the eyes of the reader. The introduction must include a brief background on the main points of discussion, the purpose of developing such work and clear indications on how the assignment is being organized. Keep this part brief, within one or two paragraphs.
This is an example of including the above mentioned points into the introduction of an assignment that elaborates the topic of obesity reaching proportions:
Background : The twenty first century is characterized by many public health challenges, among which obesity takes a major part. The increasing prevalence of obesity is creating an alarming situation in both developed and developing regions of the world.
Structure and aim : This assignment will elaborate and discuss the specific pattern of obesity epidemic development, as well as its epidemiology. Debt, trade and globalization will also be analyzed as factors that led to escalation of the problem. Moreover, the assignment will discuss the governmental interventions that make efforts to address this issue.
Practical tips on assignment writing
Here are some practical tips that will keep your work focused and effective:
– Critical thinking – Academic writing has to be characterized by critical thinking, not only to provide the work with the needed level, but also because it takes part in the final mark.
– Continuity of ideas – When you get to the middle of assignment, things can get confusing. You have to make sure that the ideas are flowing continuously within and between paragraphs, so the reader will be enabled to follow the argument easily. Dividing the work in different paragraphs is very important for this purpose.
– Usage of ‘you’ and ‘I’ – According to the academic writing standards, the assignments should be written in an impersonal language, which means that the usage of ‘you’ and ‘I’ should be avoided. The only acceptable way of building your arguments is by using opinions and evidence from authoritative sources.
– Referencing – this part of the assignment is extremely important and it takes a big part in the final mark. Make sure to use either Vancouver or Harvard referencing systems, and use the same system in the bibliography and while citing work of other sources within the text.
– Usage of examples – A clear understanding on your assignment’s topic should be provided by comparing different sources and identifying their strengths and weaknesses in an objective manner. This is the part where you should show how the knowledge can be applied into practice.
– Numbering and bullets – Instead of using numbering and bullets, the academic writing style prefers the usage of paragraphs.
– Including figures and tables – The figures and tables are an effective way of conveying information to the reader in a clear manner, without disturbing the word count. Each figure and table should have clear headings and you should make sure to mention their sources in the bibliography.
– Word count – the word count of your assignment mustn’t be far above or far below the required word count. The outline will provide you with help in this aspect, so make sure to plan the work in order to keep it within the boundaries.
The importance of an effective conclusion
The conclusion of your assignment is your ultimate chance to provide powerful arguments that will impress the reader. The conclusion in academic writing is usually expressed through three main parts:
– Stating the context and aim of the assignment
– Summarizing the main points briefly
– Providing final comments with consideration of the future (discussing clear examples of things that can be done in order to improve the situation concerning your topic of discussion).
Normal 0 false false false EN-US X-NONE X-NONE /* Style Definitions */ table.MsoNormalTable {mso-style-name:"Table Normal"; mso-tstyle-rowband-size:0; mso-tstyle-colband-size:0; mso-style-noshow:yes; mso-style-priority:99; mso-style-parent:""; mso-padding-alt:0in 5.4pt 0in 5.4pt; mso-para-margin:0in; mso-para-margin-bottom:.0001pt; mso-pagination:widow-orphan; font-size:11.0pt; font-family:"Calibri","sans-serif"; mso-ascii-font-family:Calibri; mso-ascii-theme-font:minor-latin; mso-hansi-font-family:Calibri; mso-hansi-theme-font:minor-latin;}
Lois Weldon is writer at Uk.bestdissertation.com . Lives happily at London with her husband and lovely daughter. Adores writing tips for students. Passionate about Star Wars and yoga.
7 comments on “How To Write The Best College Assignments”
Extremely useful tip for students wanting to score well on their assignments. I concur with the writer that writing an outline before ACTUALLY starting to write assignments is extremely important. I have observed students who start off quite well but they tend to lose focus in between which causes them to lose marks. So an outline helps them to maintain the theme focused.
Hello Great information…. write assignments
Well elabrated
Thanks for the information. This site has amazing articles. Looking forward to continuing on this site.
This article is certainly going to help student . Well written.
Really good, thanks
Practical tips on assignment writing, the’re fantastic. Thank you!
Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .

What is Good Writing?
At the Writing Center, we’re often asked “What makes good writing?” or “What makes someone a good writer?” Instructors wonder whether anyone can really be taught to write and why their students don’t know how to write by now. To begin to understand what makes writing, and writers, “good,” we need to ask the larger question “What is writing?”
It’s easy to agree on the definition of writing if we limit it to something like “putting pen to paper” or “typing ideas into a computer.” But if we look more closely at the elements of the act of writing, the definition comes to life. The following paragraphs might prompt your thinking about how writing happens for your students and for you.
Writing is a response.
We write because we are reacting to someone or something. While writing can feel like an isolating, individual act—just you and the computer or pad of paper—it is really a social act, a way in which we respond to the people and world around us. Writing happens in specific, often prescribed contexts. We are not just writing—we are always writing to an audience(s) for some particular purpose. When we write, we do so because we want, need, or have been required to create a fixed space for someone to receive and react to our ideas. Understanding this social or rhetorical context—who our readers may be, why they want to read our ideas, when and where they will be reading, how they might view us as writers—governs some of the choices we make. The writing context requires writers to have a sense of the reader’s expectations and an awareness of conventions for a particular piece of writing. The context of the piece further determines the appropriate tone, level of vocabulary, kind and placement of evidence, genre, and sometimes even punctuation.
Writing is linear.
In order to communicate effectively, we need to order our words and ideas on the page in ways that make sense to a reader. We name this requirement in various ways: “grammar,” “logic,” or “flow.” While we would all agree that organization is important, the process of lining up ideas is far from simple and is not always recognized as “writing.” We assume that if a person has ideas, putting them on the page is a simple matter of recording them, when in fact the process is usually more complicated. As we’ve all experienced, our ideas do not necessarily arise in a linear form. We may have a scattering of related ideas, a hunch that something feels true, or some other sense that an idea is “right” before we have worked out the details. It is often through the act of writing that we begin to create the logical relationships that develop the idea into something that someone else may receive and perhaps find interesting. The process of putting ideas into words and arranging them for a reader helps us to see, create, and explore new connections. So not only does a writer need to “have” ideas, but the writer also has to put them in linear form, to “write” them for a reader, in order for those ideas to be meaningful. As a result, when we are writing, we often try to immediately fit our choices into linear structures (which may or may not suit our habits of mind).
Writing is recursive.
As we write, we constantly rewrite. Sometimes we do this unconsciously, as we juggle words, then choose, delete, and choose again. Sometimes we do this rewriting very consciously and conscientiously as we reread a paragraph or page for clarity, coherence, or simply to see what we’ve just said and decide whether we like it. Having read, we rewrite the same phrases or ideas to make a closer match to our intentions or to refine our discoveries through language. The process of writing and then reviewing, changing, and rewriting is a natural and important part of shaping expression for an anticipated audience. So while we are trying to put our words and ideas into a logical line, we are also circling round and back and over again.
Writing is both subject and object.
We value writing because it reveals the personal choices a writer has made and thereby reveals something of her habits of mind, her ability to connect and shape ideas, and her ability to transform or change us as readers. We take writing as evidence of a subject or subjective position. Especially in an academic environment, we read written language as individual expression (whether or not multiple voices have informed the one voice we privilege on the page), as a volley from one individual mind to another. That said, writing also serves as an object for us, a “piece” or a “paper” whose shape, size, and function are determined by genre and conventions. While we don’t think of writing as technology, it is also that; it allows us to remove a person’s ideas from the confines of her head and fix those ideas in another place, a place where they will be evaluated according to standards, objectively. Here is where our sense of what counts as “good” writing develops. We have created objective (although highly contextualized) ideals for writing that include measures of appropriate voice, vocabulary, evidence, and arrangement. So while writing is very personal, or subjective, it creates an objective space, a place apart from the individual, and we measure it against objective standards derived from the context. It creates space both for the individual (the subject) and the idea (the object) to coexist so that we can both judge the merits of the individual voicing the idea and contend with the idea on the page.
Writing is decision making.
It may seem obvious, but in order to get something on the page, a writer chooses the words, the order of the words in the sentence, the grouping of sentences into paragraphs, and the order of the paragraphs within a piece. While there is an ordinariness about this—we make choices or decisions almost unconsciously about many things all day long—with writing, as we have all experienced, such decision-making can be a complex process, full of discovery, despair, determination, and deadlines. Making decisions about words and ideas can be a messy, fascinating, perplexing experience that often results in something mysterious, something the writer may not be sure “works” until she has auditioned it for a real reader.
Writing is a process.
Contending with the decision-making, linearity, social context, subjectivity, and objectivity that constitute writing is a process that takes place over time and through language. When producing a piece of writing for an audience, experienced writers use systems they have developed. Each writer has an idiosyncratic combination of thinking, planning, drafting, and revising that means “writing” something. No matter how we each describe our writing process (e.g., “First I think about my idea then dump thoughts onto the computer,” or “I make an outline then work out topic sentences”), we all (usually unconsciously) negotiate the series of choices required in an individual context and produce a draft that begins to capture a representation of our ideas. For most people, this negotiation includes trial and error (this word or that?), false starts (beginning with an example that later proves misleading), contradictions (I can’t say X because it may throw Y into question), sorting (how much do I need to say about this?), doubt about how the idea will be received, and satisfaction when they think they have cleared these hurdles successfully. For most people, this process happens through language. In other words, we use words to discover what, how, and why we believe. Research supports the adage “I don’t know what I think until I read what I’ve said.”
Altogether these elements make writing both an interesting and challenging act—one that is rich, complex, and valuable. What else is writing for you? Think about what the definitions discussed here miss and how you might complete the sentence “Writing is like…” From your experience as a writer, what else about writing seems essential? How is that connected to what you value about the process of writing and the final pieces that you produce?
For more information about student writing or to talk with someone about your writing assignments, contact Kimberly Abels [email protected] at the Writing Center.

What Makes a Good Writing Assignment?
Getting Started
Why include writing in my courses?
What is writing to learn?
WTL Activities
What is writing to engage?
What is writing in the disciplines?
WID Assignments
Useful Knowledge
What should I know about rhetorical situations?
Do I have to be an expert in grammar to assign writing?
What should I know about genre and design?
What should I know about second-language writing?
What teaching resources are available?
What should I know about WAC and graduate education?
Assigning Writing
What makes a good writing assignment?
How can I avoid getting lousy student writing?
What benefits might reflective writing have for my students?
Using Peer Review
Why consider collaborative writing assignments?
Do writing and peer review take up too much class time?
How can I get the most out of peer review?
Responding to Writing
How can I handle responding to student writing?
Sample Grading Sheets
How can writing centers support writing in my courses?
What writing resources are available for my students?
Using Technology
How can computer technologies support writing in my classes?
Designing and Assessing WAC Programs
What is a WAC program?
What designs are typical for WAC programs?
How can WAC programs be assessed?
More on WAC
Where can I learn more about WAC?
Surprisingly, teachers have been known to assign writing tasks without articulating to themselves what the task is supposed to do for students. Good writing assignments always start with a clear goal that the teacher can express, usually on the assignment sheet so that students understand the goal as well.
Good writing assignments also often take shape by thinking backwards. In effect, teachers ask themselves, "What do I want to read at the end of this assignment?" By working from what they anticipate the final product to look like, teachers can give students detailed guidelines about both the writing task and the final written product.
Five Principles
As you think about making up writing assignments, use these five principles:
- Tie the writing task to specific pedagogical goals, particularly those articulated in the overall course goals.
- Note rhetorical aspects of the task, i.e., audience, purpose, writing situation.
- Break down the task into manageable steps.
- Make all elements of the task clear.
- Include grading criteria on the assignment sheet.
Principle 1. Writing Should Meet Teaching Goals
Asking questions like these about your assignment will help guarantee that writing tasks tie directly to your teaching goals in the class:
- What specific course objectives will the writing assignment meet?
- Will informal or formal writing better meet teaching goals?
- Will students be writing to learn course material or writing conventions in the discipline or both?
- Does the assignment make sense?
Work Backward from Goals
Although it might seem awkward at first, working backwards from what you hope the final drafts will look like often produces the best assignment sheets. We recommend jotting down several points that will help you with this step in writing your assignments:
- Why should students write in your class? State your goals for the final product as clearly and concretely as possible.
- Determine what writing products will meet these goals and fit your teaching style/preferences.
- Note specific skills that will contribute to the final product.
- Sequence activities (reading, researching, writing) to build toward the final product.
Beyond the Basics
Writing tasks fill many different roles for students, so defining good writing assignments begins with the specific instructional context. For that reason, the first key to writing a good assignment is tying the task to the specific course goals. After taking your class and its goals into account, though, several other principles can improve the writing tasks you assign and the writing you get from students.
Principle 2. Consider the Rhetorical Situation
Perhaps most important, as noted in the five principles section, is to consider the rhetorical situation. By this, writing experts mean that you should think carefully about the audience you want students to write to as well as the particular genre or format for the final document and the larger context for the document.
Setting up your writing assignment so that the target reader is someone other than you, the teacher, might result in the most improvement in student writing. Students, after all, have had extensive experience writing to teachers, and students know that teachers are a "captive" audience. Your job mandates that you read carefully and respond to their texts. Chinn & Hilgers (2000) explain this role for the teachers as often limited to "corrector." However, instructors can move beyond the corrector role into a "collaborator" role by varying writing tasks, encouraging peer collaboration, and emphasizing professional contexts for writing. So for students, the teacher is not necessarily a reader or audience that will motivate the best possible work on a writing task. Indeed, Hilgers et al . (1999) report that their interview research with 33 upper-division students yielded an intriguing statistic: "56% of the interviewees also described one or more nonteacher audiences" (328) for their academic tasks. In many instances, the assignment called for a hypothetical audience other than the teacher, but even when the assignment didn't prompt students to write for readers other than the teacher, students directed their work toward "an individual they believed has specific content knowledge such as a CEO, coworker, or technician" (328).
Although some experts (Freedman et al ., 1994) argue that setting up a fictitious scenario with a specified audience does not motivate students any more highly than simply writing for the teacher, other practitioners across the disciplines have seen improvement in student writing when they use cases with embedded audiences for students' documents. (See, for instance, Brumberger, 2004; Cass & Fernandez, 2008; Stevens, 2005; Sulewski, 2003.)
A further extension of this move toward providing rich writing contexts beyond the teacher involves writing tasks that actually target real readers. Many senior design projects and management projects in engineering and natural resources involve pairing students with actual clients so that students must take into account the particular needs of their readers. Across many disciplines, teachers are investigating alternative methods to connect undergraduate writers with real audiences, including client-based partnerships (Kiefer & Leff, 2008; Kreth, 2005; Planken & Kreps, 2006;) and service-learning opportunities (Addams et al ., 2010; Bourelle, 2012), among other options.
But even if your particular class doesn't allow you to pair students with actual clients or other readers, consider ways in which you can create a meaningful context with readers beyond the teacher in the classroom (see, for example, Ward, 2009). Chamely-Wiik et al . (2012), for instance, describe in detail how, drawing on materials from The Council of Writing Program Administrators and The Foundation for Critical Thinking, they developed a case study writing context for first-year general chemistry students. As they explain,
Our initial case-study assignment, used for the first two years of the course, required students to explore the scientific principles involved in the Bhopal disaster where thousands of people died in an industrial chemical accident.... The second assignment, used in the third year, required students to formulate and defend an argument whether research in the field of cold fusion should continue to be supported. (504)
Students write with a local audience of classmates and a larger institutional context of the university community in mind. Students responded positively on affective surveys, a typical reaction to carefully designed writing tasks. More significantly, "students in this chemistry course outperformed the majority of students across all undergraduate levels at the university" (506). (For other examples of science students writing to lay audiences, see Martin, 2010; McDermott& Kuhn, 2011; Moni et al ., 2007; Sivey & Lee, 2008).
In addition to audience concerns, students also benefit from understanding how and why a particular format or genre helps them communicate with a target audience (especially when we think of genres as those recurring rhetorical reactions to typical communicative situations). From YouTube videos in organic chemistry (Franz, 2012) to position papers in public relations (Powell, 2012) to posters in physiology (Mulnix, 2003), teachers are helping students to write in genres that immediately connect them with the real readers of their future professional settings. (See also Blakeslee, 2001; Guilford, 2001; Jebb, 2005; LeBigot & Rouet, 2007; Mizrahi, 2003; Motavalli et al ., 2007; Schwartz et al ., 2004; Wald et al ., 2009.)
Why does this attention to audience and genre seem to matter so much to student writing? In recent years, several studies (Adam, 2000; Beaufort, 2004; Belfiore et al ., 2004; Freedman & Adam, 2000; Spinuzzi, 2010) have explored the reasons why writers attentive to specific contexts are more successful. In particular, workplace literacy and socio-cognitive apprenticeship theory (among related theoretical perspectives) both emphasize the role that knowledgeable mentors within a workplace play as they initiate newcomers to the communicative context. (See especially Beaufort, 2000, and Ding, 2008, for social apprenticeship studies and Paretti, 2008, on situated learning and activity theory.) As Dias et al . (1999) explain, writing is not a fixed set of skills that we learn once and then simply plug into as we need to communicate. Rather,
Written discourse... is regularized but not fixed; fluid, flexible, and dynamic; emerging and evolving in exigency and action; reflecting and incorporating social needs, demands, and structures, and responsive to social interpretations and reinterpretations of necessarily shifting, complex experiences. (23)
And, as a result of the fluidity of discourse in varied workplace settings, writers themselves should be prepared for major development of their communication skills when they enter new workplaces. MacKinnon's qualitative study (2000) of new analysts and economists at the Bank of Canada showed that
Overall, the writing-related changes were considerable, consequential, and a shock for some participants: "It's like going to China," said one. For most of the ten participants, the complex totality of the writing-related changes they experienced added up to a "sea change": a major shift in their understanding of what writing is an does in an organization, a revised understanding of the roles they saw for themselves as writing workers and as working writers, and often major changes in various aspects of the macro writing process. (50)
When students have opportunities as undergraduates or graduate/professional students to anticipate these major shifts, then the transitions to workplaces of all sorts become easier. For the most part, moreover, students recognize that apprenticeship learning in academic settings provides both more structured scaffolding of writing tasks and lower-stakes learning. They thus embrace the learning opportunities when offered to them in academic classes.
Principle 3. Break Down the Task into Manageable Steps
The fifth principle noted in the general section on "what makes a good writing assignment?" is to break down the task into manageable steps. Many teachers approach this element of good assignment design by thinking carefully about assignment sequence. One particularly thorough explanation of this process appears in Leydens & Santi (2006). This writing specialist and geoscientist take up the details of designing assignments with an eye to course goals. They also consider the importance of not overwhelming teachers and students (the Less is More approach) as they explain their specific process of questioning their assignments (pp. 493-497). (See also Lord, 2009, and Greasley & Cassidy, 2010.)
Scaffolded assignments, such as the agricultural economics assignment noted in the Additional Resources section, help students reach a larger goal by asking them to collect resources in stages. A final stage requires that students transform each of the earlier stages in a final document. Sequenced assignments, on the other hand, each stand independently, but each task builds on particular skills and challenges to enable students to meet a larger set of goals. Herrington (1997) describes a scaffolded assignment (71-72) with a preliminary plan for a major project followed by an annotated bibliography, early draft (with cover note focused on successes and challenges thus far) and final draft (with cover note). Mulnix & Mulnix (2010) also describe a similar argumentative assignment that uses sequenced tasks to repeat and reinforce critical thinking skills. See also Sin et al . (2007) for a sequence in accounting, Howell (2007) in materials science, Fencl (2010) on a sequence in physics, Zlatic et al . (2000) on pharmaceutical education, and Harding (2005) on freshman mechanical engineering. Coe (2011), on the other hand, describes a series of scaffolded writing tasks to help students build argument skills in philosophy, Alaimo et al . (2009) explain their project for sophomore organic chemistry students, and Lillig (2008) looks at upper-division chemistry.
Principles 4 and 5. Make the Assignment Clear to Students
A well-designed assignment will make the elements of the task clear to students. This includes identifying relevant intermediate assignments and activities, such as topic proposals or literature reviews for longer assignments, as well as providing information about relevant writing, research, and collaboration processes. In general, it is also advisable to list grading criteria on the assignment sheet. Making the assignment clear to students will help them better understand the scope and challenge of the assignment. It also is likely to produce better learning and performance.
Resource: Sample Assignment from an Advanced Undergraduate Agricultural Economics Seminar
Good analytical writing is a rigorous and difficult task. It involves a process of editing and rewriting, and it is common to do a half dozen or more drafts. Because of the difficulty of analytical writing and the need for drafting, we will be completing the assignment in four stages. A draft of each of the sections described below is due when we finish the class unit related to that topic (see due dates on syllabus). I will read the drafts of each section and provide comments; these drafts will not be graded but failure to pass in a complete version of a section will result in a deduction in your final assignment grade. Because of the time both you and I are investing in the project, it will constitute one-half of your semester grade.
Content, Concepts and Substance
Papers will focus on the peoples and policies related to population, food, and the environment of your chosen country. As well as exploring each of these subsets, papers need to highlight the interrelations among them. These interrelations should form part of your revision focus for the final draft. Important concepts relevant to the papers will be covered in class; therefore, your research should be focused on the collection of information on your chosen country or region to substantiate your themes. Specifically, the paper needs to address the following questions.
1. Population
Developing countries have undergone large changes in population. Explain the dynamic nature of this continuing change in your country or region and the forces underlying the changes. Better papers will go beyond description and analyze the situation at hand. That is, go behind the numbers to explain what is happening in your country with respect to the underlying population dynamics: structure of growth, population momentum, rural/urban migration, age structure of population, unanticipated populations shocks, etc. DUE: WEEK 4.
What is the nature of food consumption in your country or region? Is the average daily consumption below recommended levels? Is food consumption increasing with economic growth? What is the income elasticity of demand? Use Engel's law to discuss this behavior. Is production able to stay abreast with demand given these trends? What is the nature of agricultural production: traditional agriculture or green revolution technology? Is the trend in food production towards self-sufficiency? If not, can comparative advantage explain this? Does the country import or export food? Is the politico-economic regime supportive of a progressive agricultural sector? DUE: WEEK 8.
3. Environment
This is the third issue to be covered in class. It is crucial to show in your paper the environmental impact of agricultural production techniques as well as any direct impacts from population changes. This is especially true in countries that have evolved from traditional agriculture to green revolution techniques in the wake of population pressures. While there are private benefits to increased production, the use of petroleum-based inputs leads to environmental and human health related social costs which are exacerbated by poorly defined property rights. Use the concepts of technological externalities, assimilative capacity, property rights, etc., to explain the nature of this situation in your country or region. What other environmental problems are evident? Discuss the problems and methods for economically measuring environmental degradation. DUE: WEEK 12.
4. Final Draft
The final draft of the project should consider the economic situation of agriculture in your specified country or region from the three perspectives outlined above. Key to such an analysis are the interrelationships of the three perspectives. How does each factor contribute to an overall analysis of the successes and problems in agricultural policy and production of your chosen country or region? The paper may conclude with recommendations, but, at the very least, it should provide a clear summary statement about the challenges facing your country or region. DUE: WEEK15.
Adam, C. (2000). "What do we learn from the readers? Factors in determining successful transitions between academic and workplace writing." In P. Dias and A. Paré (Eds.), Transitions: Writing in Academic and Workplace Settings ; pp. 167-182. Cresskill, NJ: Hampton Press.
Addams, L.H., Woodbury, D., Allred, T., & Addams, J. (2010). Developing Student Communication Skills while Assisting Nonprofit Organizations. Business Communication Quarterly, 73 (3), 282-290.
Alaimo, P.J., Bean, J.C., Langenhan, J.M., & Nichols, L. (2009). Eliminating Lab Reports: A Rhetorical Approach for Teaching the Scientific Paper in Sophomore Organic Chemistry. The WAC Journal, 20 , 17-32.
Beaufort, A. (2004). Developmental gains of a history major: A case for building a theory of disciplinary writing expertise. Research in the Teaching of English, 39 (2), 136-185.
Beaufort, A. (2000). Learning the trade: A social apprenticeship model for gaining writing expertise. Written Communication, 17 (2), 185-224.
Belfiore, M.E., Defoe, T.A., Folinsbee, S., Hunter, J., & Jackson, N.S. (2004). Reading Work: Literacies in the New Workplace. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Blakeslee, A.M. (2001). Bridging the workplace and the academy: Teaching professional genres through classroom-workplace collaborations. Technical Communication Quarterly, 10 (2), 169-192.
Bourelle, T. (2012). Bridging the Gap between the Technical Communication Classroom and the Internship: Teaching Social Consciousness and Real-World Writing. Journal of Technical Writing and Communication, 42 (2), 183-197.
Brumberger, E.R. (2004). The "Corporate Correspondence Project": Fostering Audience Awareness and Extended Collaboration. Business Communication Quarterly, 67 (3), 349-58.
Cass, A.G., & Fernandes, C.S.T. (2008). Simulated conference submissions: A technique to improve student attitudes about writing. 2008 IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference, Vols. 1-3 ; pp. 1535-1540.
Chamely,Wiik, D.M., Kaky, J.E., & Galin, J. (2012). From Bhopal to cold fusion: A case-study approach to writing assignments in honors general chemistry. Journal of Chemical Education, 89 (4), 502-508.
Chinn, P.W.U., & Hilgers. T.L. (2000). From corrector to collaborator: The range of instructor roles in writing-based natural and applied science classes. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 37 (1), 3-25.
Coe, C.D. (2011). Scaffolded writing as a tool for critical thinking: Teaching beginning students how to write arguments. Teaching Philosophy, 34 (1), 33-50.
Dias, P., Freedman, A., Medway, P., & Paré. (1999). "Introduction: Researching Writing at School and at Work." Worlds Apart: Acting and Writing in Academic and Workplace Contexts; pp. 3-13. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Dias, P., Freedman, A., Medway, P., & Paré. (1999). "Situating Writing." Worlds Apart: Acting and Writing in Academic and Workplace Contexts; pp. 17-41. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Ding, H. (2008). The use of cognitive and social apprenticeship to teach a disciplinary genre: Initiation of graduate students into NIH grant writing. Written Communication, 25 (1), 3-52.
Fencl, H.S. (2010). Development of Students' Critical-Reasoning Skills through Content-Focused Activities in a General Education Course. Journal of College Science Teaching, 39 (5), 56-62.
Franz, A.K. (2012). Organic chemistry YouTube writing assignment for large lecture classes. Journal of Chemical Education, 89 (4), 497-501.
Freedman, A., & Adam, C. (2000). "Write where you are: Situating learning to write in university and workplace settings." In P. Dias and A. Paré (Eds.), Transitions: Writing in Academic and Workplace Settings ; pp. 31-60. Cresskill, NJ: Hampton Press.
Freedman, A., Adam, C., & Smart, G. (1994). Wearing suits to class: Simulating genres and simulations as genre. Written Communication, 11 (2), 193-226.
Greasley, P., & Cassidy, A. (2010). When it comes round to marking assignments: how to impress and how to 'distress' lecturers. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 35 (2), 173-189.
Guildford, W.H. (2001). Teaching peer review and the process of scientific writing. Advances in Physiology Education, 25 (3), 167-175.
Harding, B.A. (2005). "A simple mechanism to teach a complex practitioner knowledge set." Innovations in Engineering Education 2005 ; pp. 479-486. ASME.
Herrington, A. (1997). "Developing and responding to major writing projects ." In M.D. Sorcinelli & P. Elbow (Eds.), Writing to learn: Strategies for assigning and responding to writing across the disciplines , pp. 67-75. New directions for teaching the learning, No. 69 . San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass.
Hilgers, T.L., Hussey, E.L., & Stitt-Bergh, M. (1999). "As you're writing, you have these epiphanies": What college students say about writing and learning in their majors. Written Communication, 16 (3), 317-353.
Howell, P.R. (2007). "Writing to specification: An approach to teaching scientific literacy, and a prelude to writing 'The World of Materials' essays." In J.E.E. Baglin (Ed.), Proceedings of the Symposium and Forum Education in Materials Science, Engineering and Technology ; pp. 247-289.
Kiefer, K., & Leff, A. (2008). "Client-based writing about science: Immersing science students in real writing contexts." Across the Disciplines , vol. 5 .
Kreth, M.L. (2005). A Small-Scale Client Project for Business Writing Students: Developing a Guide for First-Time Home Buyers. Business Communication Quarterly, 68 (1), 52-59.
LeBigot, L., & Rouet, J.F. (2007). The impact of presentation format, task assignment, and prior knowledge on students' comprehension of multiple online documents. Journal of Literacy Research, 39 (4), 445-470.
Leydens, J., & Santi, P. (2006). Optimizing faculty use of writing as a learning tool in geoscience education. Journal of Geoscience Education , 54 (4), 491-502.
Lillig, J.W. (2008). Writing across the semester: A non-standard term paper that encourages critical data analysis in the upper-division chemistry classroom. Journal of Chemical Education, 85 (10), 1392-1394.
Lord, S.M. (2009). Integrating effective "writing to communicate" experiences in engineering courses: Guidelines and examples. International Journal of Engineering Education, 25 (1), 196-204.
MacKinnon, J. (1993). "Becoming a rhetor: Developing writing ability in a mature, writing-intensive organization." In R. Spilka (Ed.), Writing in the Workplace: New Research Perspectives ; pp. 41-55. Carbondale: Southern Illinois UP.
Martin, A.M. (2010). "Astronomy and writing: A first-year cosmology course for nonmajors." In J. Barnes, D.A. Smith, M.G. Gibbs, and J.G. Manning (Eds.), Science Education and Outreach: Forging a Path to the Future . Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference Series, Vol. 431; pp. 368-371. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
McDermott, M., & Kuhn, M. (2011). Using writing for alternative audiences in a college integrated science course. Journal of College Science Teaching, 41 (1), 40-45.
Mizrahi, J. (2003). Teaching technical writing to university students using the medical report. STC's 50 th Annual Conference Proceedings ; 190-193.
Moni, R.W., Hryciw, D.H., Poronnik, P., & Moni, K.B. (2007). Using explicit teaching to improve how bioscience students write to the lay public. Advances in Physiology Education, 31 (2), 167-75.
Motavalli, P.P., Patton, M.D., & Miles, R.J. (2007). Use of web-based student extension publications to improve undergraduate student writing skills. Journal of Natural Resources and Life Sciences Education, 36 : 95-102.
Mulnix, A.B. (2003). Investigations of Protein Structure and Function Using the Scientific Literature: An Assignment for an Undergraduate Cell Physiology Course. Cell Biology Education, 2 (4), 248-255.
Mulnix, J.W., & Mulnix, M.J. (2010). Using a writing portfolio project to teach critical thinking skills. Teaching Philosophy, 33 (1), 27-54.
Paretti, M.C. (2008). Teaching communication in capstone design: The role of the instructor in situated learning. Journal of Engineering Education, 97 (4), 491-503.
Planken, B., & Kreps, A.J. Raising Students' Awareness of the Implications of Multimodality for Content Design and Usability: The Web Site Project. Business Communication Quarterly, 69 (4), 421-425.
Powell, V. (2012). Revival of the Position Paper: Aligning Curricula and Professional Competencies. Communication Teacher, 26 (2), 96-103.
Schwartz, R.S., Lederman, N.G., & Crawford, B.A. (2004). Developing view of nature of science in an authentic context: An explicit approach to bridging the gap between nature of science and scientific inquiry. Science Education, 88 (4), 610-645.
Sin, S., Jones, A., & Petocz, P. (2007). Evaluating a method of integrating generic skills with accounting content based on a functional theory of meaning. Accounting and Finance, 47 (1), 143-163.
Sivey, J.D., & Lee, C.M. (2008). Using popular magazine articles to teach the art of writing for nontechnical audiences. Journal of Chemical Education, 85 (1), 55-58.
Spinuzzi, C. (2010). Secret sauce and snake oil: Writing monthly reports in a highly contingent environment. Written Communication, 27 (4), 363-409.
Stevens, B. (2005). The Car Accident: An Exercise in Persuasive Writing. Communication Teacher, 19 (2), 62-67.
Sulewski, R. (2003). Integrating communication and technical material int eh first-year engineering curriculum: The role of the laboratory. STC's 50 th Annual Conference Proceedings ; 176-178.
Wald, H.S., Davis, S.W., Reis, S.P., Monroe, A.D., & Borkan, J.M. (2009). Reflecting on reflections: Enhancement of medical education curriculum with structured field notes and guided feedback. Academic Medicine, 84 (7), 830-837.
Ward, M., Sr. (2009). Squaring the learning circle: Cross-classroom collaborations and the impact of audience on student outcomes in professional writing. Journal of Business and Technical Communication, 23 (1), 61-82.
Zlatic, T.D., Nowak, D.M., & Sylvester, D. (2000). Integrating general and professional education through a study of herbal products: An intercollegiate collaboration. American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education, 64 (1), 83-94.
Related Web Sites
WAC@NIU ( http://www.engl.niu.edu/wac/ ) has two useful items in their archives under "Ccomputer-intensive assignments" in the first Key Web Sites section of links:
- "checklist, a series of questions to help plan writing assignments"
(If the questions under rhetorical situation confuse you, call our Writing Center for a quick explanation.)
- "setting up a writing assignment"
Writing@CSU includes a much more detailed explanation of how and why to design writing assignments at http://writing.colostate.edu/guides/teaching/fys/assignmentwriting.cfm .

4 Key Points for Effective Assignment Writing

Methodology
By Christina Desouza
Writing an effective assignment is more of an art than a science. It demands critical thinking, thorough research, organized planning, and polished execution. As a professional academic writer with over four years of experience, I've honed these skills and discovered proven strategies for creating standout assignments.
In this article, I will delve into the four key steps of assignment writing, offering detailed advice and actionable tips to help students master this craft.
1. Start With Research
In-depth research is the cornerstone of any high-quality assignment. It allows you to gain a profound understanding of your topic and equip yourself with relevant data, compelling arguments, and unique insights.
Here's how to do it right:
● Diversify Your Sources
Don't limit yourself to the first page of Google results. Make use of academic databases like JSTOR , Google Scholar , PubMed , or your school's online library. These resources house a plethora of scholarly articles, research papers, and academic books that can provide you with valuable information.
● Verify Information
Remember, not all information is created equal. Cross-check facts and data from multiple reliable sources to ensure accuracy. Look for consensus among experts on contentious issues.
● Stay Organized
Keep track of your resources as you go. Tools like Zotero or Mendeley can help you organize your references and generate citations in various formats. This will save you from scrambling to find sources when you're wrapping up your assignment.
1. Prepare Assignment Structure

Creating a well-planned structure for your assignment is akin to drawing a roadmap. It helps you stay on track and ensures that your ideas flow logically. Here's what to consider:
● Develop an Outline
The basic structure of an assignment includes an introduction, body, and conclusion. The introduction should present the topic and establish the purpose of your assignment. The body should delve into the topic in detail, backed by your research. The conclusion should summarize your findings or arguments without introducing new ideas.
● Use Subheadings
Subheadings make your assignment easier to read and follow. They allow you to break down complex ideas into manageable sections. As a rule of thumb, each paragraph should cover one idea or argument.
● Allocate Word Count
Assignments often come with word limits. Allocate word count for each section of your assignment based on its importance to avoid overwriting or underwriting any part.
1. Start Assignment Writing
Writing your assignment is where your research and planning come to fruition. You now have a robust foundation to build upon, and it's time to craft a compelling narrative.
Here's how to accomplish this:
● Write a Gripping Introduction
Your introduction is the gateway to your assignment. Make it captivating. Start with a hook—a surprising fact, an interesting quote, or a thought-provoking question—to grab your readers' attention. Provide an overview of what your assignment is about and the purpose it serves. A well-crafted introduction sets the tone for the rest of the assignment and motivates your readers to delve deeper into your work.
● Develop a Comprehensive Body
The body of your assignment is where you delve into the details. Develop your arguments, present your data, and discuss your findings. Use clear and concise language. Avoid jargon unless necessary. Each paragraph should cover one idea or argument to maintain readability.
● Craft a Convincing Conclusion
Your conclusion is your final chance to leave an impression on your reader. Summarize your key findings or arguments without introducing new ideas. Reinforce the purpose of your assignment and provide a clear answer to the question or problem you addressed in the introduction. A strong conclusion leaves your readers with a sense of closure and a full understanding of your topic.
● Write Clearly
Use straightforward sentences and avoid jargon. Your goal is to communicate, not to confuse. Tools like Hemingway Editor can help ensure your writing is clear and concise.
● Use Paraphrasingtool.ai
Paraphrasingtool.ai is an AI-powered tool that can enhance your assignment writing. It reformulates your sentences while preserving their meaning. It not only helps you avoid plagiarism but also enhances the readability of your work.
● Cite Your Sources
Citations are a critical part of assignment writing. They acknowledge the work of others you've built upon and demonstrate the depth of your research. Always include in-text citations and a bibliography at the end. This not only maintains academic integrity but also gives your readers resources to delve deeper into the topic if they wish.
1. Review and Proofread The Assignment
Reviewing and proofreading are the final but critical steps in assignment writing. They ensure your assignment is free from errors and that your ideas are coherently presented. Here's how to do it effectively:

● Take a Break
After you finish writing, take a break before you start proofreading. Fresh eyes are more likely to spot mistakes and inconsistencies.
● Read Aloud
Reading your work aloud can help you identify awkward phrasing, run-on sentences, and typos. You're more likely to catch errors when you hear them, as it requires a different type of processing than reading silently.
● Use Proofreading Tools
Digital tools like Grammarly can be your second pair of eyes, helping you spot grammatical errors, typos, and even issues with sentence structure. However, don't rely solely on these tools—make sure to manually review your work as well.
Effective assignment writing is a skill that takes practice to master. It requires meticulous research, organized planning, clear writing, and careful proofreading. The steps and tips outlined in this article are by no means exhaustive, but they provide a solid framework to start from.
Remember, there is always room for improvement. Don't be disheartened by initial challenges. Each assignment is an opportunity to learn, grow, and sharpen your writing skills. So, be persistent, stay curious, and keep refining your craft. With time and practice, you will find yourself writing assignments that are not just excellent, but truly outstanding.


Writing Guide: Types of Assignments & Best Practices
- Home & Appointments
- Types of Assignments & Best Practices
- Tables & Figures
- Thesis & Project Guide
The most common types of writing assignments you will encounter at MLTS
- How to approach a writing assignment
- Expository writing & research papers
- Compare & Contrast paper
- Book & Literature Reviews
- Reflective writing
- Online discussion posts
- Thesis/Project
As a graduate student, you will be assigned a variety of types of writing projects. A good rule of thumb in approaching any writing project is to ask yourself: for whom am I writing and why? Or, who is my audience and what do they expect from my writing? Your assignments will almost invariably require you to make one or more arguments. A good argument is well-written, logical, and supported by evidence.
Expository writing involves understanding, explaining, analyzing, and/or evaluating a topic. It includes your standard graduate school essay, book review, or research paper where your instructor requires you to analyze and/or study a topic. In general, your audience for such assignments will be your course instructor. You can think of such writing assignments as your instructor asking you to make an argument. Your instructor wants to gauge your creative thinking skills and how well you understand the course material by seeing how well you can make an argument related to that material. Remember: a good argument is well-written, logical, and supported by evidence.
An expository paper is therefore not about you (at least not directly); it is about the facts you have learned and researched and the argument you have built from those facts. Therefore, unless you are quoting someone, you should avoid using first person pronouns (the words I, me, my, we, us, our ) in your writing. Let your facts and arguments speak for themselves instead of beginning statements with "I think" or "I believe."
A compare & contrast assignment is a type of expository & research paper assignment. It is important to organize your writing around the themes you are comparing & contrasting. If, for example, you are assigned to compare & contrast, say, Augustine's Confessions and The Autobiography of Malcolm X , a common mistake students make is to write the first part of their essay strictly about Augustine's Confessions , and the second part of the essay strictly about The Autobiography of Malcolm X . In a good compare & contrast essay, you instead explore an issue in every paragraph or two, and show how, in this case, both Augustine & Malcolm X share common ground or differ on that issue. Then, move onto another issue and show how both Augustne and Malcolm X covered it.
Unless your instructor directs you otherwise, you should not use first person pronouns ( I, me, my ) in such a paper.
A book review assignment is meant to be an analysis of a book, not a chapter-by-chapter summary of a book. Instead of organizing your paper sequentially (the first paragraph is about chapter 1, the second paragraph is about chapter 2, etc.), organize your paragraphs around the themes of the book that are thread throughout the book. Topics to consider in a book review include (but are not limited to):
- What are the author's arguments, and how successful is she in making those arguments?
- What sort of sources does the author utilize?
- What methodology/methodologies does the author utilize?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the book?
A literature review is similar to a book review assignment in that it is meant to be an analysis of a theme or themes across several books/articles. What have various authors written about your topic? That said, as you will typically have less space to talk about each work (perhaps a paragraph or less for each work as opposed to multiple pages), you might end up moving from one author's findings to another. For a literature review in a thesis, think of a literature review as a mini-essay within your broader thesis with its own mini-introduction, thesis statement, and conclusion.
Unless your instructor directs you otherwise, book reviews and literature reviews should be written like expository & research papers. In particular, you should not use first person pronouns ( I, me, my ). So, instead of writing: "I think this book is a good analysis of ___," write: "This book is a good analysis of ___."
Reflective essays are especially common in theology courses. Reflective writing requires that you explicitly write about yourself and your own views. To put it another way, you typically have two audiences to write for in such an assignment: your instructor and yourself. As such, and unlike a standard expository paper, such essays require you to write about yourself using first person pronouns ( I, me, my) and use statements like “I think” and “I believe.” Otherwise, a reflective essay shares a lot with expository writing. You are still making arguments, and you still need evidence from cited sources! Unless your instructor tells you otherwise, you should still include a good title, introduction paragraph, thesis statement, conclusion, and bibliography.
For online courses, you will likely have to take part in classroom or group discussions online, in which you will be encouraged or even required to respond to your classmates. Such writing assignments often include a reflective element. Discussion posts are almost always shorter than essays and as such may not need long introductions or conclusions. That said, a discussion post is not like a Facebook or social media post! Good discussion posts are long and well-written enough to convey one or more thoughtful, insightful observations; you cannot just "like" someone else's post or only write "Good job!" If you decide to challenge or critique a classmate’s post—and you are certainly encouraged to do so!—you should do so in a respectful and constructive manner. As your main audience for online discussions are your own classmates and, to a lesser extent, your instructor, it is often okay to use relatively more informal language and to refer to yourself using first person pronouns ( I, me, my ). Finally, as with reflective essays, discussion posts still benefit from evidence. Even if a discussion post is relatively less formal than an essay, if you quote, paraphrase, or draw ideas from outside sources, you still must cite them! If the online medium does not allow for footnotes, use parenthetical references for citations (see chapter 19 of Turabian).
Those of you taking preaching courses or earning a DMin degree will have to write and submit your sermons. On one hand, your main audience for such a writing assignment is the congregation to whom you may preach. The language, tone, message, level of detail, etc. of a good sermon will depend on the precise context of your congregation and the message you want to impart. Therefore, unlike an expository essay or a reflective essay, you have a lot more freedom in how you chose to organize your sermon, as well as how formal or not you want the language to be.
On the other hand, in submitting such assignments, you also have a secondary audience: your instructor. As such, you may still need to include citations, even if you would not read them out loud in your sermon. In submitting a sermon as an assignment, you may also need to include some sort of write up or commentary, which your instructor may require to be expository and/or reflective in nature.
Those of you earning an MAR or DMin will finish your coursework by proposing, researching, writing, and defending a thesis or project. A thesis/project should be an original contribution to your field of study. To put it another way, the audience for your thesis/project is not just your advisor, but the broader academic and/or ministerial community. A good thesis/project can go on to become the first draft of a published academic journal article or a chapter or two of a book. Your thesis/project should be largely expository, but it may also include reflective sections.
It is never too early to start thinking about what you want to do for your thesis/project! You can try to make your thesis/project writing process easier by writing your course papers on topics within or adjacent to what you think you want to do for your thesis/project; that said, if you do so, you will need to cite these earlier works in your final thesis. See our citation guide for help with that.
For more information on writing a thesis or project, from choosing a topic to submitting it, check out our Thesis & Project Guide .
Tips for Composing Good Academic Prose
- Proofread, proofread, proofread!
- Find evidence to support your thesis statement from good quality sources
- Use quotations as evidence, not filler
- Be careful not to turn long sentences into run-on sentences
- Relatively longer paragraphs are generally better than short ones
- Make sure your paper flows well from one idea to the next
- When possible, avoid using the passive voice
- Be precise and crystal-clear in your statements and arguments
- Use the present tense when paraphrasing an author or setting up a quotation
- Use repetition of words carefully
First and most importantly: Proofread your paper over before you submit it to make sure that it reads well and is without errors! Read your paper over as you are writing it. Check over your work with spell check. Before you submit it, read it over one last time to catch anything you missed. If possible, consider reading the work out loud: you will be more likely to spot problems in your writing than if you read it in your head. If you are able to do so, ask a friend or schedule an appointment with the Writing Center for a review. Another pair of eyes can often spot a mistake or problem that the writer has overlooked.
Find evidence to support your thesis from good quality sources. Your research and writing should be based on the study of reputable primary and secondary sources. Typically, this means books published by academic presses and academic journal articles. Wikipedia, YouTube, random websites, and dictionary entries are generally not considered to be good sources for academic writing, although there are instances when it is acceptable to use and cite them, like if you were researching how topics in Black theology are represented or misrepresented on Wikipedia. If you need help in finding good resources for your paper, consult a librarian.
Quotations are meant to be evidence to support your argument; they are not filler to meet a length requirement. While you must quote and paraphrase sources, you should not quote or paraphrase more than you need. When possible, consider paraphrasing over quoting. Keep in mind that your writing assignments are supposed to showcase your thinking and writing, not the thinking and writing of whoever you are citing.
Be careful not to turn long sentences into run-on sentences. Long sentences are not always bad: when well-written, a long sentence can read better and help convey complex ideas better than a series of short sentences. A run-on sentence, on the other hand, occurs when multiple sentences are inappropriately lumped into a single sentence. Therefore, when reading your paper over, keep an eye out for any sentence that you can break into multiple sentences.
Relatively longer paragraphs are generally better than short ones. If your paragraph is three sentences or less, consider if you can write more about that paragraph's topic or incorporate it into another paragraph. If a paragraph represents one idea, then a longer paragraph typically shows that you have better considered and flushed out that idea. That said, if your paragraph is longer than a page, you could probably shorten it or break it into two paragraphs.
Make sure your paper flows well from one idea to the next. Does your third paragraph make sense following your second paragraph? Do you drop ideas and only pick them up much later? Cut and paste sentences and paragraphs around as necessary.
When possible, avoid using the passive voice. This can be tricky! The passive voice is when you use the verb “to be” next to and in conjunction with another verb to make the object of the sentence into the subject. For example, compare the active sentence: “Kate Turabian wrote the book” to its passive equivalent: “The book was written by Kate Turabian.” Grammatically speaking, in the latter, passive sentence, "The book" is the subject, even though in a real world active sense, it is the object.
Writers consider passive sentences not as good because, like in the above example, they can be wordier than necessary and take the focus off the real subject. There are exceptions in which it is good to use the passive voice. For example, if you were writing an article about Kate Turabian, it would be better to write: “Kate Turabian was born in 1893” instead of “Kate Turabian’s mother gave birth to her in 1893.” The former sentence keeps Kate Turabian, the focus of the paper, as the subject, while the latter sounds a little weird (maybe English speakers are too squeamish, but we typically do not recount someone's birth in that way).
At its worst, the passive voice can obscure the subject and make facts unclear. Consider the sentence: "Jackie Robinson's signing with the Brooklyn Dodgers in 1946 was considered a crucial moment in the Civil Rights movement." With the passive voice, the reader does not know who exactly considered that so? Did all Americans in 1946 think this? Did some specific people come to recognize it later? Compare that sentence to: "Martin Luther King, Jr. considered Jackie Robinson's signing with the Brooklyn Dodgers in 1946 a crucial moment in the Civil Rights movement."
Be precise and crystal-clear in your statements and arguments. Similar to how the passive voice can make facts unclear, overly general language can make for weak arguments. Consider the argument: "Many people now support same-sex marriage." Many people? Which people? "Many" and "people" are very general terms and do not tell us much in this statement; the more specific you can be, the better your argument:
- Despite official church statements, many American Catholics now support same-sex marriage.
- [Specific number]% of Chicagoans now support same-sex marriage.
- Many South African theologians, including [so-and-so] and [so-and so], now support same-sex marriage.
In general, use the present tense when paraphrasing an author or setting up a quotation. While you should use the past tense when writing about events in the past, you should in general use the present tense when discussing a scholar's writing. Scholarship is a ongoing discussion. When you read and discuss an author's work, that author is making an argument right now in the present, even if she is dead. So, do not write:
Carl Jung wrote: "The psyche... Carl Jung said, "The psyche... Carl Jung argued that...
but instead:
Carl Jung writes: "The psyche... Carl Jung says, "The psyche... Carl Jung argues that...
Use repetition of words carefully. When done well, repeating words can sound good and emphasize ideas. When done poorly, repetition sounds monotonous. Avoid, for example, starting too many sentences or paragraphs with the same word, or overutilizing the same verb. If you need help in bringing variety to your word choices, purchase a thesaurus or check out thesaurus.com .
- << Previous: Formatting
- Next: Tables & Figures >>
- Last Updated: Mar 6, 2024 1:47 PM
- URL: https://library.meadville.edu/writing

Meadville Lombard Wiggin Library 180 N. Wabash Ave. Suite 625 Chicago, IL 60601
Library and Archives Phone: 312-546-6488 Library Email : [email protected] Archives Email : [email protected]

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Writing Assignments
Kate Derrington; Cristy Bartlett; and Sarah Irvine

Introduction
Assignments are a common method of assessment at university and require careful planning and good quality research. Developing critical thinking and writing skills are also necessary to demonstrate your ability to understand and apply information about your topic. It is not uncommon to be unsure about the processes of writing assignments at university.
- You may be returning to study after a break
- You may have come from an exam based assessment system and never written an assignment before
- Maybe you have written assignments but would like to improve your processes and strategies
This chapter has a collection of resources that will provide you with the skills and strategies to understand assignment requirements and effectively plan, research, write and edit your assignments. It begins with an explanation of how to analyse an assignment task and start putting your ideas together. It continues by breaking down the components of academic writing and exploring the elements you will need to master in your written assignments. This is followed by a discussion of paraphrasing and synthesis, and how you can use these strategies to create a strong, written argument. The chapter concludes with useful checklists for editing and proofreading to help you get the best possible mark for your work.
Task Analysis and Deconstructing an Assignment
It is important that before you begin researching and writing your assignments you spend sufficient time understanding all the requirements. This will help make your research process more efficient and effective. Check your subject information such as task sheets, criteria sheets and any additional information that may be in your subject portal online. Seek clarification from your lecturer or tutor if you are still unsure about how to begin your assignments.
The task sheet typically provides key information about an assessment including the assignment question. It can be helpful to scan this document for topic, task and limiting words to ensure that you fully understand the concepts you are required to research, how to approach the assignment, and the scope of the task you have been set. These words can typically be found in your assignment question and are outlined in more detail in the two tables below (see Table 19.1 and Table 19.2 ).
Table 19.1 Parts of an Assignment Question
Make sure you have a clear understanding of what the task word requires you to address.
Table 19.2 Task words
The criteria sheet , also known as the marking sheet or rubric, is another important document to look at before you begin your assignment. The criteria sheet outlines how your assignment will be marked and should be used as a checklist to make sure you have included all the information required.
The task or criteria sheet will also include the:
- Word limit (or word count)
- Referencing style and research expectations
- Formatting requirements
Task analysis and criteria sheets are also discussed in the chapter Managing Assessments for a more detailed discussion on task analysis, criteria sheets, and marking rubrics.
Preparing your ideas
Brainstorm or concept map: List possible ideas to address each part of the assignment task based on what you already know about the topic from lectures and weekly readings.
Finding appropriate information: Learn how to find scholarly information for your assignments which is
See the chapter Working With Information for a more detailed explanation .
What is academic writing?
Academic writing tone and style.
Many of the assessment pieces you prepare will require an academic writing style. This is sometimes called ‘academic tone’ or ‘academic voice’. This section will help you to identify what is required when you are writing academically (see Table 19.3 ). The best way to understand what academic writing looks like, is to read broadly in your discipline area. Look at how your course readings, or scholarly sources, are written. This will help you identify the language of your discipline field, as well as how other writers structure their work.
Table 19.3 Comparison of academic and non-academic writing
Thesis statements.
Essays are a common form of assessment that you will likely encounter during your university studies. You should apply an academic tone and style when writing an essay, just as you would in in your other assessment pieces. One of the most important steps in writing an essay is constructing your thesis statement. A thesis statement tells the reader the purpose, argument or direction you will take to answer your assignment question. A thesis statement may not be relevant for some questions, if you are unsure check with your lecturer. The thesis statement:
- Directly relates to the task . Your thesis statement may even contain some of the key words or synonyms from the task description.
- Does more than restate the question.
- Is specific and uses precise language.
- Let’s your reader know your position or the main argument that you will support with evidence throughout your assignment.
- The subject is the key content area you will be covering.
- The contention is the position you are taking in relation to the chosen content.
Your thesis statement helps you to structure your essay. It plays a part in each key section: introduction, body and conclusion.
Planning your assignment structure

When planning and drafting assignments, it is important to consider the structure of your writing. Academic writing should have clear and logical structure and incorporate academic research to support your ideas. It can be hard to get started and at first you may feel nervous about the size of the task, this is normal. If you break your assignment into smaller pieces, it will seem more manageable as you can approach the task in sections. Refer to your brainstorm or plan. These ideas should guide your research and will also inform what you write in your draft. It is sometimes easier to draft your assignment using the 2-3-1 approach, that is, write the body paragraphs first followed by the conclusion and finally the introduction.
Writing introductions and conclusions
Clear and purposeful introductions and conclusions in assignments are fundamental to effective academic writing. Your introduction should tell the reader what is going to be covered and how you intend to approach this. Your conclusion should summarise your argument or discussion and signal to the reader that you have come to a conclusion with a final statement. These tips below are based on the requirements usually needed for an essay assignment, however, they can be applied to other assignment types.
Writing introductions

Most writing at university will require a strong and logically structured introduction. An effective introduction should provide some background or context for your assignment, clearly state your thesis and include the key points you will cover in the body of the essay in order to prove your thesis.
Usually, your introduction is approximately 10% of your total assignment word count. It is much easier to write your introduction once you have drafted your body paragraphs and conclusion, as you know what your assignment is going to be about. An effective introduction needs to inform your reader by establishing what the paper is about and provide four basic things:
- A brief background or overview of your assignment topic
- A thesis statement (see section above)
- An outline of your essay structure
- An indication of any parameters or scope that will/ will not be covered, e.g. From an Australian perspective.
The below example demonstrates the four different elements of an introductory paragraph.
1) Information technology is having significant effects on the communication of individuals and organisations in different professions. 2) This essay will discuss the impact of information technology on the communication of health professionals. 3) First, the provision of information technology for the educational needs of nurses will be discussed. 4) This will be followed by an explanation of the significant effects that information technology can have on the role of general practitioner in the area of public health. 5) Considerations will then be made regarding the lack of knowledge about the potential of computers among hospital administrators and nursing executives. 6) The final section will explore how information technology assists health professionals in the delivery of services in rural areas . 7) It will be argued that information technology has significant potential to improve health care and medical education, but health professionals are reluctant to use it.
1 Brief background/ overview | 2 Indicates the scope of what will be covered | 3-6 Outline of the main ideas (structure) | 7 The thesis statement
Note : The examples in this document are taken from the University of Canberra and used under a CC-BY-SA-3.0 licence.
Writing conclusions
You should aim to end your assignments with a strong conclusion. Your conclusion should restate your thesis and summarise the key points you have used to prove this thesis. Finish with a key point as a final impactful statement. Similar to your introduction, your conclusion should be approximately 10% of the total assignment word length. If your assessment task asks you to make recommendations, you may need to allocate more words to the conclusion or add a separate recommendations section before the conclusion. Use the checklist below to check your conclusion is doing the right job.
Conclusion checklist
- Have you referred to the assignment question and restated your argument (or thesis statement), as outlined in the introduction?
- Have you pulled together all the threads of your essay into a logical ending and given it a sense of unity?
- Have you presented implications or recommendations in your conclusion? (if required by your task).
- Have you added to the overall quality and impact of your essay? This is your final statement about this topic; thus, a key take-away point can make a great impact on the reader.
- Remember, do not add any new material or direct quotes in your conclusion.
This below example demonstrates the different elements of a concluding paragraph.
1) It is evident, therefore, that not only do employees need to be trained for working in the Australian multicultural workplace, but managers also need to be trained. 2) Managers must ensure that effective in-house training programs are provided for migrant workers, so that they become more familiar with the English language, Australian communication norms and the Australian work culture. 3) In addition, Australian native English speakers need to be made aware of the differing cultural values of their workmates; particularly the different forms of non-verbal communication used by other cultures. 4) Furthermore, all employees must be provided with clear and detailed guidelines about company expectations. 5) Above all, in order to minimise communication problems and to maintain an atmosphere of tolerance, understanding and cooperation in the multicultural workplace, managers need to have an effective knowledge about their employees. This will help employers understand how their employee’s social conditioning affects their beliefs about work. It will develop their communication skills to develop confidence and self-esteem among diverse work groups. 6) The culturally diverse Australian workplace may never be completely free of communication problems, however, further studies to identify potential problems and solutions, as well as better training in cross cultural communication for managers and employees, should result in a much more understanding and cooperative environment.
1 Reference to thesis statement – In this essay the writer has taken the position that training is required for both employees and employers . | 2-5 Structure overview – Here the writer pulls together the main ideas in the essay. | 6 Final summary statement that is based on the evidence.
Note: The examples in this document are taken from the University of Canberra and used under a CC-BY-SA-3.0 licence.
Writing paragraphs
Paragraph writing is a key skill that enables you to incorporate your academic research into your written work. Each paragraph should have its own clearly identified topic sentence or main idea which relates to the argument or point (thesis) you are developing. This idea should then be explained by additional sentences which you have paraphrased from good quality sources and referenced according to the recommended guidelines of your subject (see the chapter Working with Information ). Paragraphs are characterised by increasing specificity; that is, they move from the general to the specific, increasingly refining the reader’s understanding. A common structure for paragraphs in academic writing is as follows.
Topic Sentence
This is the main idea of the paragraph and should relate to the overall issue or purpose of your assignment is addressing. Often it will be expressed as an assertion or claim which supports the overall argument or purpose of your writing.
Explanation/ Elaboration
The main idea must have its meaning explained and elaborated upon. Think critically, do not just describe the idea.
These explanations must include evidence to support your main idea. This information should be paraphrased and referenced according to the appropriate referencing style of your course.
Concluding sentence (critical thinking)
This should explain why the topic of the paragraph is relevant to the assignment question and link to the following paragraph.
Use the checklist below to check your paragraphs are clear and well formed.
Paragraph checklist
- Does your paragraph have a clear main idea?
- Is everything in the paragraph related to this main idea?
- Is the main idea adequately developed and explained?
- Do your sentences run together smoothly?
- Have you included evidence to support your ideas?
- Have you concluded the paragraph by connecting it to your overall topic?
Writing sentences
Make sure all the sentences in your paragraphs make sense. Each sentence must contain a verb to be a complete sentence. Avoid sentence fragments . These are incomplete sentences or ideas that are unfinished and create confusion for your reader. Avoid also run on sentences . This happens when you join two ideas or clauses without using the appropriate punctuation. This also confuses your meaning (See the chapter English Language Foundations for examples and further explanation).
Use transitions (linking words and phrases) to connect your ideas between paragraphs and make your writing flow. The order that you structure the ideas in your assignment should reflect the structure you have outlined in your introduction. Refer to transition words table in the chapter English Language Foundations.
Paraphrasing and Synthesising
Paraphrasing and synthesising are powerful tools that you can use to support the main idea of a paragraph. It is likely that you will regularly use these skills at university to incorporate evidence into explanatory sentences and strengthen your essay. It is important to paraphrase and synthesise because:
- Paraphrasing is regarded more highly at university than direct quoting.
- Paraphrasing can also help you better understand the material.
- Paraphrasing and synthesising demonstrate you have understood what you have read through your ability to summarise and combine arguments from the literature using your own words.
What is paraphrasing?
Paraphrasing is changing the writing of another author into your words while retaining the original meaning. You must acknowledge the original author as the source of the information in your citation. Follow the steps in this table to help you build your skills in paraphrasing (see Table 19.4 ).
Table 19.4 Paraphrasing techniques
Example of paraphrasing.
Please note that these examples and in text citations are for instructional purposes only.
Original text
Health care professionals assist people often when they are at their most vulnerable . To provide the best care and understand their needs, workers must demonstrate good communication skills . They must develop patient trust and provide empathy to effectively work with patients who are experiencing a variety of situations including those who may be suffering from trauma or violence, physical or mental illness or substance abuse (French & Saunders, 2018).
Poor quality paraphrase example
This is a poor example of paraphrasing. Some synonyms have been used and the order of a few words changed within the sentences however the colours of the sentences indicate that the paragraph follows the same structure as the original text.
Health care sector workers are often responsible for vulnerable patients. To understand patients and deliver good service , they need to be excellent communicators . They must establish patient rapport and show empathy if they are to successfully care for patients from a variety of backgrounds and with different medical, psychological and social needs (French & Saunders, 2018).
A good quality paraphrase example
This example demonstrates a better quality paraphrase. The author has demonstrated more understanding of the overall concept in the text by using the keywords as the basis to reconstruct the paragraph. Note how the blocks of colour have been broken up to see how much the structure has changed from the original text.
Empathetic communication is a vital skill for health care workers. Professionals in these fields are often responsible for patients with complex medical, psychological and social needs. Empathetic communication assists in building rapport and gaining the necessary trust to assist these vulnerable patients by providing appropriate supportive care (French & Saunders, 2018).
The good quality paraphrase example demonstrates understanding of the overall concept in the text by using key words as the basis to reconstruct the paragraph. Note how the blocks of colour have been broken up, which indicates how much the structure has changed from the original text.
What is synthesising?
Synthesising means to bring together more than one source of information to strengthen your argument. Once you have learnt how to paraphrase the ideas of one source at a time, you can consider adding additional sources to support your argument. Synthesis demonstrates your understanding and ability to show connections between multiple pieces of evidence to support your ideas and is a more advanced academic thinking and writing skill.
Follow the steps in this table to improve your synthesis techniques (see Table 19.5 ).
Table 19.5 Synthesising techniques
Example of synthesis
There is a relationship between academic procrastination and mental health outcomes. Procrastination has been found to have a negative effect on students’ well-being (Balkis, & Duru, 2016). Yerdelen, McCaffrey, and Klassens’ (2016) research results suggested that there was a positive association between procrastination and anxiety. This was corroborated by Custer’s (2018) findings which indicated that students with higher levels of procrastination also reported greater levels of the anxiety. Therefore, it could be argued that procrastination is an ineffective learning strategy that leads to increased levels of distress.
Topic sentence | Statements using paraphrased evidence | Critical thinking (student voice) | Concluding statement – linking to topic sentence
This example demonstrates a simple synthesis. The author has developed a paragraph with one central theme and included explanatory sentences complete with in-text citations from multiple sources. Note how the blocks of colour have been used to illustrate the paragraph structure and synthesis (i.e., statements using paraphrased evidence from several sources). A more complex synthesis may include more than one citation per sentence.
Creating an argument
What does this mean.
Throughout your university studies, you may be asked to ‘argue’ a particular point or position in your writing. You may already be familiar with the idea of an argument, which in general terms means to have a disagreement with someone. Similarly, in academic writing, if you are asked to create an argument, this means you are asked to have a position on a particular topic, and then justify your position using evidence.
What skills do you need to create an argument?
In order to create a good and effective argument, you need to be able to:
- Read critically to find evidence
- Plan your argument
- Think and write critically throughout your paper to enhance your argument
For tips on how to read and write critically, refer to the chapter Thinking for more information. A formula for developing a strong argument is presented below.
A formula for a good argument
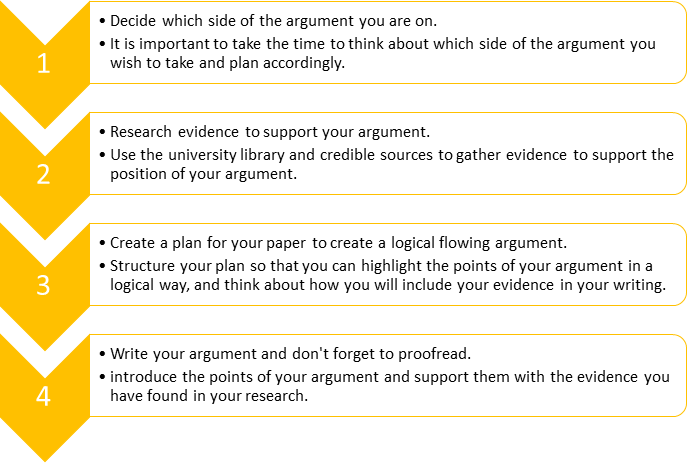
What does an argument look like?
As can be seen from the figure above, including evidence is a key element of a good argument. While this may seem like a straightforward task, it can be difficult to think of wording to express your argument. The table below provides examples of how you can illustrate your argument in academic writing (see Table 19.6 ).
Table 19.6 Argument
Editing and proofreading (reviewing).
Once you have finished writing your first draft it is recommended that you spend time revising your work. Proofreading and editing are two different stages of the revision process.
- Editing considers the overall focus or bigger picture of the assignment
- Proofreading considers the finer details
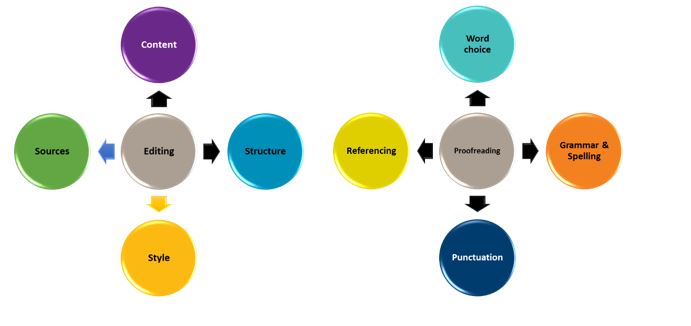
As can be seen in the figure above there are four main areas that you should review during the editing phase of the revision process. The main things to consider when editing include content, structure, style, and sources. It is important to check that all the content relates to the assignment task, the structure is appropriate for the purposes of the assignment, the writing is academic in style, and that sources have been adequately acknowledged. Use the checklist below when editing your work.
Editing checklist
- Have I answered the question accurately?
- Do I have enough credible, scholarly supporting evidence?
- Is my writing tone objective and formal enough or have I used emotive and informal language?
- Have I written in the third person not the first person?
- Do I have appropriate in-text citations for all my information?
- Have I included the full details for all my in-text citations in my reference list?
There are also several key things to look out for during the proofreading phase of the revision process. In this stage it is important to check your work for word choice, grammar and spelling, punctuation and referencing errors. It can be easy to mis-type words like ‘from’ and ‘form’ or mix up words like ‘trail’ and ‘trial’ when writing about research, apply American rather than Australian spelling, include unnecessary commas or incorrectly format your references list. The checklist below is a useful guide that you can use when proofreading your work.
Proofreading checklist
- Is my spelling and grammar accurate?
- Are they complete?
- Do they all make sense?
- Do they only contain only one idea?
- Do the different elements (subject, verb, nouns, pronouns) within my sentences agree?
- Are my sentences too long and complicated?
- Do they contain only one idea per sentence?
- Is my writing concise? Take out words that do not add meaning to your sentences.
- Have I used appropriate discipline specific language but avoided words I don’t know or understand that could possibly be out of context?
- Have I avoided discriminatory language and colloquial expressions (slang)?
- Is my referencing formatted correctly according to my assignment guidelines? (for more information on referencing refer to the Managing Assessment feedback section).
This chapter has examined the experience of writing assignments. It began by focusing on how to read and break down an assignment question, then highlighted the key components of essays. Next, it examined some techniques for paraphrasing and summarising, and how to build an argument. It concluded with a discussion on planning and structuring your assignment and giving it that essential polish with editing and proof-reading. Combining these skills and practising them, can greatly improve your success with this very common form of assessment.
- Academic writing requires clear and logical structure, critical thinking and the use of credible scholarly sources.
- A thesis statement is important as it tells the reader the position or argument you have adopted in your assignment. Not all assignments will require a thesis statement.
- Spending time analysing your task and planning your structure before you start to write your assignment is time well spent.
- Information you use in your assignment should come from credible scholarly sources such as textbooks and peer reviewed journals. This information needs to be paraphrased and referenced appropriately.
- Paraphrasing means putting something into your own words and synthesising means to bring together several ideas from sources.
- Creating an argument is a four step process and can be applied to all types of academic writing.
- Editing and proofreading are two separate processes.
Academic Skills Centre. (2013). Writing an introduction and conclusion . University of Canberra, accessed 13 August, 2013, http://www.canberra.edu.au/studyskills/writing/conclusions
Balkis, M., & Duru, E. (2016). Procrastination, self-regulation failure, academic life satisfaction, and affective well-being: underregulation or misregulation form. European Journal of Psychology of Education, 31 (3), 439-459.
Custer, N. (2018). Test anxiety and academic procrastination among prelicensure nursing students. Nursing education perspectives, 39 (3), 162-163.
Yerdelen, S., McCaffrey, A., & Klassen, R. M. (2016). Longitudinal examination of procrastination and anxiety, and their relation to self-efficacy for self-regulated learning: Latent growth curve modeling. Educational Sciences: Theory & Practice, 16 (1).
Writing Assignments Copyright © 2021 by Kate Derrington; Cristy Bartlett; and Sarah Irvine is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
🎉 Our next novel writing master class starts in – ! Claim your spot →
WEEKLY WRITING PROMPTS
Join (probably?) the world's largest writing contest. Flex those creative muscles with weekly writing prompts.
Showing 2114 prompts
Heavenly bodies, set your story in a world where astrology and the movements of celestial bodies deeply impact the lives of inhabitants..
LIVE – Fantasy
People have gathered to witness a once-in-a-lifetime natural phenomenon, but what happens next is not what they expected.
LIVE – Mystery
Imagine an origin myth that somebody might use to explain an eclipse, or some other celestial event.
Write a story in which a character navigates using the stars..
LIVE – Adventure
Set your story during a total eclipse — either natural, or man-made.
LIVE – Fiction

Introducing Prompted , a new magazine written by you!
🏆 Featuring 12 prize-winning stories from our community. Download it now for FREE .
Begin or end your story with a character taking a selfie.
Write about a character who sees a photo they shouldn’t have seen., write a story about a character who risks their life to take a photo., start your story with a character staring at a picture they don’t remember taking., center your story around a photo that goes viral., subscribe to our prompts newsletter.
Never miss a prompt! Get curated writing inspiration delivered to your inbox each week.
Write a story where time functions differently to our world.
Write a story about a character who wakes up in space., write a story from the point of view of a non-human character., write a story with a strong sense of place. how is the setting of your world the same as, but different to, our own, write a story imagining 'what if' one historic invention had never happened. how would our world be different now, start or end your story with a character who gets trapped inside a museum overnight., write about two characters who meet and/or fall in love in a museum., write about an art thief who is struggling to commit the perfect heist., write about someone who accidentally destroys a museum’s most valuable artifact., write about a gallery whose paintings come alive at night., win $250 in our short story competition 🏆.
We'll send you 5 prompts each week. Respond with your short story and you could win $250!
Contest #245 LIVE
Enter our weekly contest.
This week's theme: Heavenly Bodies
Prize money
Contest entries, closes at 23:59 - apr 12, 2024 est, recent contests ✍️.
#244 – Oh Snap!
#243 – Re-Imagining Our World Through Speculative Fiction with Alice McIlroy
#242 – Fine Art
#241 – Et Tu, Brute?
Recent winners 🏆
Thomas Iannucci – read
Niamh O'Dea – read
Liz Grosul – read
Jonathan Page – read
Leaderboard 🥇
#1 Zilla Babbitt
32352 points
#2 Deidra Whitt Lovegren
28686 points
#3 Abigail Airuedomwinya
22413 points
#4 Graham Kinross
14376 points
#5 Scout Tahoe
13195 points
#6 Chris Campbell
11030 points
#7 Thom With An H
10602 points
#8 Rayhan Hidayat
10210 points
#9 Michał Przywara
9874 points
#10 Deborah Mercer
9605 points

Bring your short stories to life
Fuse character, story, and conflict with tools in the Reedsy Book Editor. 100% free.
Creative Writing Prompts
When the idea to start a weekly newsletter with writing inspiration first came to us, we decided that we wanted to do more than provide people with topics to write about. We wanted to try and help authors form a regular writing habit and also give them a place to proudly display their work. So we started the weekly Creative Writing Prompts newsletter. Since then, Prompts has grown to a community of more than 450,000 authors, complete with its own literary magazine, Prompted .
Here's how our contest works: every Friday, we send out a newsletter containing five creative writing prompts. Each week, the story ideas center around a different theme. Authors then have one week — until the following Friday — to submit a short story based on one of our prompts. A winner is picked each week to win $250 and is highlighted on our Reedsy Prompts page.
Interested in participating in our short story contest? Sign up here for more information! Or you can check out our full Terms of Use and our FAQ page .
Why we love creative writing prompts
If you've ever sat in front of a computer or notebook and felt the urge to start creating worlds, characters, and storylines — all the while finding yourself unable to do so — then you've met the author's age-old foe: writer's block. There's nothing more frustrating than finding the time but not the words to be creative. Enter our directory! If you're ready to kick writer's block to the curb and finally get started on your short story or novel, these unique story ideas might just be your ticket.
This list of 1800+ creative writing prompts has been created by the Reedsy team to help you develop a rock-solid writing routine. As all aspiring authors know, this is the #1 challenge — and solution! — for reaching your literary goals. Feel free to filter through different genres, which include...
Dramatic — If you want to make people laugh and cry within the same story, this might be your genre.
Funny — Whether satire or slapstick, this is an opportunity to write with your funny bone.
Romance — One of the most popular commercial genres out there. Check out these story ideas out if you love writing about love.
Fantasy — The beauty of this genre is that the possibilities are as endless as your imagination.
Dystopian – Explore the shadowy side of human nature and contemporary technology in dark speculative fiction.
Mystery — From whodunnits to cozy mysteries, it's time to bring out your inner detective.
Thriller and Suspense — There's nothing like a page-turner that elicits a gasp of surprise at the end.
High School — Encourage teens to let their imaginations run free.
Want to submit your own story ideas to help inspire fellow writers? Send them to us here.
After you find the perfect story idea
Finding inspiration is just one piece of the puzzle. Next, you need to refine your craft skills — and then display them to the world. We've worked hard to create resources that help you do just that! Check them out:
- How to Write a Short Story That Gets Published — a free, ten-day course by Laura Mae Isaacman, a full-time editor who runs a book editing company in Brooklyn.
- Best Literary Magazines of 2023 — a directory of 100+ reputable magazines that accept unsolicited submissions.
- Writing Contests in 2023 — the finest contests of 2021 for fiction and non-fiction authors of short stories, poetry, essays, and more.
Beyond creative writing prompts: how to build a writing routine
While writing prompts are a great tactic to spark your creative sessions, a writer generally needs a couple more tools in their toolbelt when it comes to developing a rock-solid writing routine . To that end, here are a few more additional tips for incorporating your craft into your everyday life.
- NNWT. Or, as book coach Kevin Johns calls it , “Non-Negotiable Writing Time.” This time should be scheduled into your routine, whether that’s once a day or once a week. Treat it as a serious commitment, and don’t schedule anything else during your NNWT unless it’s absolutely necessary.
- Set word count goals. And make them realistic! Don’t start out with lofty goals you’re unlikely to achieve. Give some thought to how many words you think you can write a week, and start there. If you find you’re hitting your weekly or daily goals easily, keep upping the stakes as your craft time becomes more ingrained in your routine.
- Talk to friends and family about the project you’re working on. Doing so means that those close to you are likely to check in about the status of your piece — which in turn keeps you more accountable.
Arm yourself against writer’s block. Writer’s block will inevitably come, no matter how much story ideas initially inspire you. So it’s best to be prepared with tips and tricks you can use to keep yourself on track before the block hits. You can find 20 solid tips here — including how to establish a relationship with your inner critic and apps that can help you defeat procrastination or lack of motivation.
NEW VIDEO COURSE 🎉
How to Write a Novel
Join Tom Bromley for a writing master class and finish your first draft in 3 months . Learn more →
Explore more writing prompt ideas:
Adults Writing Prompts ⭢
Adventure Writing Prompts ⭢
Angst Writing Prompts ⭢
Character Writing Prompts ⭢
Christmas Writing Prompts ⭢
Dark Writing Prompts ⭢
Dialogue Writing Prompts ⭢
Dramatic Writing Prompts ⭢
Dystopian Writing Prompts ⭢
Fall Writing Prompts ⭢
Fantasy Writing Prompts ⭢
Fiction Writing Prompts ⭢
Fluff Writing Prompts ⭢
Funny Writing Prompts ⭢
Halloween Writing Prompts ⭢
High School Writing Prompts ⭢
Historical Fiction Writing Prompts ⭢
Holiday Writing Prompts ⭢
Horror Writing Prompts ⭢
Kids Writing Prompts ⭢
Middle School Writing Prompts ⭢
Mystery Writing Prompts ⭢
Narrative Writing Prompts ⭢
Nonfiction Writing Prompts ⭢
Novel Writing Prompts ⭢
Poetry Writing Prompts ⭢
Romance Writing Prompts ⭢
Sad Writing Prompts ⭢
Science Fiction Writing Prompts ⭢
Short Story Writing Prompts ⭢
Spring Writing Prompts ⭢
Summer Writing Prompts ⭢
Teens Writing Prompts ⭢
Thanksgiving Writing Prompts ⭢
Thriller and Suspense Writing Prompts ⭢
Valentine's Day Writing Prompts ⭢
Vampire Writing Prompts ⭢
Winter Writing Prompts ⭢
Oops, you need an account for that!
Log in with your social account:
Or enter your email:

- All Articles
- Before You Start
- How To Get In
- Being a Student
- Good To Know
Most Effective Tips for Writing an Impressive Assignment

When in college, you have to accomplish all of your assignments as part of your education. One of the most common assignments is written essays that will contribute to your grade at the end of your course.
But you might feel apprehensive when you receive such an assignment, especially if it's your first time. You might not feel like you have the necessary skills to write a good essay. But there are certain tips you can use to write a good assignment and lay your apprehensions to rest.
Research and plan
When you take on a course, you will receive a reading list. Familiarize yourself with it right away because your professors will choose texts from this list that will specifically help you with your tasks and assignments. Reading what's on your list will provide you with valuable insight into the topics you have to write about. It will make life easier for you when you need to write an assignment.
After researching, you should make a schedule for writing your assignments. Stick to your schedule. Also, double-check your deadline so you won't have to feel overwhelmed when you realize that your deadline is right around the corner. Break down your time and tasks into more manageable chunks so that you will always be on top of your work. Make a schedule that consists of mini-deadlines. Knowing that you have completed a task will keep you motivated.
Understand your assignment and take notes
Before starting your assignment, make sure that you understand it because writing an essay that contains irrelevant information or isn't coherent will prove disastrous. You should always know what you're doing and what you need to convey. If needed, rereading the instructions will help you understand what's expected of you. Moreover, you also need to determine how long the essay should be and how you will proceed with it.
Note-taking is another important aspect of writing. Before you start, you must collect various materials and resources relevant to your topic. You should also create an outline that will guide you. Go through various research materials, then take down notes on the most crucial information that you can include in your work. The writing process will become more manageable when you have all of the information you need.
Assignment writing by professionals
As a student in college, you have the option to ask for help when you need to complete an assignment and you have no time to do it. Since written tasks are an unavoidable aspect of college education, the best thing you can do is to seek assistance when you need it. The writers at AssignmentBro helped with my assignment writing in college. Thanks to their professional writers, I still had plenty of time to study and tackle my other responsibilities.
Use various resources
Aside from the deadlines and instructions that your professor will provide, they might also recommend some resources to you. Sadly, this is something that many students tend to overlook. For instance, for you to understand how your professor will grade your assignment, you will need to examine their rubric. This is a chart that provides information on what you must do. You will also learn about the objectives of the assignments or the learning outcomes.
Other resources you might receive include reading lists, lecture recordings, discussion boards, and sample assignments. Usually, you will find all of these resources in an online platform known as a Learning Management System (LMS). Research has shown that students who use LMS tend to get higher grades. If you still have any questions, you can ask your professor either online or offline.
Determine the objective and structure of your assignment
The next thing you need to do is to define the objectives of your written work and its structure. This is where you will determine the pattern of a well-written assignment. You want to make your work look impressive in the eyes of your reader. One way to accomplish this is to include more theoretical content and details in your essay.
Make sure all of your paragraphs flow smoothly
It's not enough for the essay writing project assigned to you to provide enough information. It's also important to remain coherent. You must link each paragraph to each other.
This will keep your reader connected with the content . To achieve this, you need to go back to your plan for your assignment, then search for significant concepts that will help you connect the paragraphs smoothly. Here's an easy tip to do this - include phrases or words that will attract the eyes of your readers while supporting the context of your written assignment.
University life is full of challenges. One of which is the writing of assignments that will require higher communication, critical thinking, and information gathering skills that you may have practiced in high school. Instead of feeling daunted because of your assignments, use the tips you learned to make things easier for you.
Share with friends:
You might like to know more about.

- How it works
How to Write an Assignment – 10 Tips for Pro-Level Writing
Published by Ellie Cross at January 26th, 2023 , Revised On October 11, 2023
Writing an assignment is not a simple task. It requires extensive research, critical thinking and strategic planning. However, it is an opportunity to demonstrate your understanding of the subject matter and to develop your analytical skills.
When you’re given an assignment, your first thought “ how to write an assignment ” or “what do I need to write?” But before you begin writing, consider the following things.
How to Start an Assignment?
There are many ways to start an assignment , but here is a list of some of the most common methods.
Write an introduction – This is where you introduce yourself and your topic. It should be about a paragraph long and should include your assignment topic.
Provide background information – The next step after writing an introduction is providing background information to support your assignment. This can include definitions, examples and anecdotes.
Make an argument – Now that you have provided background information, it is time to make your argument! First, you need to explain why you believe what you believe and why others should agree with you (or not).
What is the Assignment Format?
The assignment format is a standardised way of writing out assignments. The assignment format aims to ensure that all students have a clear understanding of what the assignment entails and the expectations of their work.
The assignment format may vary depending on the type of assignment and the purpose for which it is being written.
Assignment Guidelines Example
The assignment format is based on the number of pages or words you have written. the assignment should be double-spaced, with 1-inch margins and a 12-point font size. the first page should include a title page, abstract, table of contents (with page numbers), introduction, conclusion, main body paragraphs and any references used in your paper., hire an expert writer.
Orders completed by our expert writers are
- Formally drafted in an academic style
- Free Amendments and 100% Plagiarism Free – or your money back!
- 100% Confidential and Timely Delivery!
- Free anti-plagiarism report
- Appreciated by thousands of clients. Check client reviews

Dissertation blogs: Dissertation writing guidelines , How to write dissertation introduction , Abbreviation list in dissertation .
Assignment Writing Tips
Assignments are a big part of your studies, but they can also be one of the most stressful aspects. If you’re not sure how to write an assignment that gets a good grade, here are some assignment-writing tips prepared through evaluating multiple professional assignment writing services available online.
Planning the Assignment
Before you start working on an assignment, it’s important to plan it out. Ask yourself these questions:
How much time do I have?
What resources are available? (e.g., library , internet, friends)
What type of assignment is it? (e.g., essay , report)
What am I being asked to do? (e.g., compare/contrast two novels)
Once you know what you need to do and how long you have to do it, you can start planning your work more effectively.
You Can’t Write an Assignment Without Knowing What you’re Supposed to do .
The first step is to find out what you’re supposed to write about and how long you have to do it. Find out from your lecturer, the course notes, the textbook, your friends, the internet, or whatever. Then write down what you need to know about the topic so you don’t forget anything.
Know your Audience
This is good advice for any writer, but it’s especially important when writing an assignment. Because if you don’t know who will be reading it, how do you know whether they’ll understand it?
Get Started as soon as Possible
Many students find it difficult to start writing assignments because they are unsure exactly what they should write about. This can lead to procrastination and missed deadlines.
Use a Planning Sheet Before Starting an Assignment
This helps you organise your thoughts and make sure that everything is in place before you start writing up your final product.
Read it Carefully
Read through the assignment instructions carefully to know exactly what is required of you. Then, ensure you understand all the requirements before beginning work on any aspect of the assignment.
Ask Questions if Necessary.
Ask questions if there is anything you do not understand or ambiguities in the instructions provided by your tutor or professor.
Write Clearly
Use short sentences and paragraphs. Avoid passive voice (except in case of official documents like reports); avoid long sentences with multiple clauses if possible; use personal pronouns (“I”, “we”, etc.) instead of the third person (“he”, “she”, etc.) when referring to yourself; use action verbs rather than adjectives; avoid using too many adjectives or adverbs in one sentence or paragraph (too many modifiers will make your writing unclear). It’s best to stick to one adjective per noun or verb phrase (“The blue car” vs “The small blue car”).
Check for Spelling Mistakes and Grammar Errors.
Use spelling, grammar, and punctuation checkers before submitting your assignment. It will not only make your answers easier to read, but it will also help prove that you’ve done your research properly.
Pay Attention to the Structure.
Always pay attention to structure: introduction, body paragraphs, conclusion, etc.
Be Organised and Use the Heading.
Use headings, subheadings, and bullets where appropriate (but don’t overdo them). This makes it easier for them to follow along with your ideas without missing any important details or losing interest.
Use Simple Language
Use simple language that everyone can understand. Avoid jargon or technical terms whenever possible. Don’t use slang or informal expressions that are not suitable for academic papers or formal writing style in general (e.g., “I think” vs “In my opinion”).
Check your Sources
Make sure the information you use is from reliable sources (such as books, journals and websites). It’s also important to acknowledge all of the people whose ideas or research you used in your assignment.
Set yourself a Deadline
Set yourself a deadline for when your assignment must be completed by, and stick to it! If your professor gives no deadline, consider setting one yourself – even if it’s just one day before.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to write an assignment.
To write an assignment, start by understanding the task, researching, outlining, drafting, and revising. Use credible sources, follow guidelines, and proofread for clarity and correctness.
You May Also Like
Have you been looking to achieve a higher grade, but failed? Learn how essay writing services can help you score better grades this semester…
Struggling to write a high quality research paper? Here is all you need to know if you need help with writing research paper for your degree programme.
Here is a comprehensive guide on Open book exams, their meaning and how you can appropriately prepare for an open-book exam.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Creative Nonfiction Assignments

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
These resources discuss some terms and techniques that are useful to the beginning and intermediate creative nonfiction writer, and to instructors who are teaching creative nonfiction at these levels. The distinction between beginning and intermediate writing is provided for both students and instructors, and numerous sources are listed for more information about creative nonfiction tools and how to use them. A sample assignment sheet is also provided for instructors.
Sample Assignment: Personal Memoir
Make another list of ten events in your life that are important to you and provoke your curiosity. Often, this list contains events that are still mysterious to you in some way, and that intrigues you in a way that you can’t quite make concrete conclusions about. Write down all the questions that come to mind around these events. Make a list of questions. Essay ideas often arise out of an exploration of these questions (adapted from Dinty W. Moore).
Sample Assignment: Lyric Essay
Wayne Koestenbaum’s lyric essay, Assignments , provides good prompts for writing your own lyric essays:
- Make a list of media you gave up (e.g. watercolors). Say why.
- Quote from a line from a novel or a poem. Selfishly manipulate and misuse the quote.
- From memory, describe a scene from a movie you haven’t watched in years. Then, see the movie again and write a second description of the scene.
Suggested Reading:
Becky Bradway and Doug Hesse. Creating Nonfiction: A Guide and Anthology . Bedford/St. Martin, 2009.
Phillip Lopate, editor. The Art of the Personal Essay: An Anthology from the Classical Era to the Present . Doubleday, 1994.
Dinty W. Moore. The Truth of the Matter: Art and Craft in Creative Nonfiction . Pearson Longman, 2007.
Mary Oliver and Robert Atwan, editors. The Best American Essays 2009 . Mariner Books, 2009.
- Non-Fiction
- Author’s Corner
- Reader’s Corner
- Writing Guide
- Book Marketing Services
- Write for us
Readers' Corner
5 Effective Tips for Students to Write a Good Assignment
Table of contents, 1. start with a good introduction, 2. structure the body with some supporting evidence, 3. use short sentences and easy-to-read wording, 4. sign-off with a strong conclusion, 5. properly cite the references where needed.
Often teachers give assignments to their students to test their understanding of the material and their ability to express themselves clearly and concisely. But not all students succeed in doing that. So, if you are one of those unlucky students who couldn’t get the required grades in previous assignments, this blog post is for you. Here, we’ll share five practical tips to help you write a top-notch assignment.
5 Effective Tips for Perfect Assignment Writing for Students
An assignment aims to test your understanding of the material. But you can only convey your knowledge better if you know how to write a perfect assignment. So, if perfect assignment writing sounds like a daunting task to you, then use the following tips:
Whenever you start a conversation, you introduce yourself first. Therefore, you should begin writing your assignment with the same approach.
The introduction of an assignment sets its tone. So, it must be engaging. However, creating a compelling introduction is easier said than done. So, consider the following points while writing an assignment’s introduction:
- Include key arguments.
- Add a bit of context by discussing some pieces of background information.
- Discuss the key issues related to your topic and how you plan to answer them in your assignment.
Let’s see how Griffith University writes a compelling introduction by practically implementing the above-discussed points (University).

As you can see in the above picture, the writer informs the readers about the assignment’s scope, aim and structure. So, that’s how you can shape your assignment’s introduction. But remember to keep the introduction as concise and captivating as possible because its goal is to hook the readers and catch their attention quickly.
A well-written introduction is like a promise because it makes a commitment to the readers about the information they will find in a writing piece. And when it comes to keeping that promise, the body of a writing piece plays its role. Therefore, tip number two for writing a good assignment is to structure the body of your topic with proper evidence.
The introduction might be the most crucial part of an assignment because it catches the readers’ attention. But the body is the main part of an assignment, as it holds 60-80% of weightage. In fact, the grade you obtain in a paper mostly depends on the content of the body part. Therefore, it must contain all the necessary information to help you score an A.
The length of the body part varies according to the nature of the topic. But a general rule of thumb is to follow the same structure for each paragraph of the body part. So, take assistance from the following assignment format while writing the content for its body part:
- Introduce each paragraph in the body with an argument or idea. And for discussing an idea, you can take assistance from a topic or focus sentence because it clarifies the purpose of a paragraph.
- Always support the discussed argument (or idea) with relevant evidence. And for that, you can take assistance from examples, facts and statistics.
Here is an example of how ThoughtCo writes a perfect paragraph with the help of a topic sentence and relevant evidence (Nordquist, 2007):

Moving on , there are different ways of adding examples, facts and statistics. For instance, you can use infographics, pictures, tables, graphs, charts, or other data representation forms to support the evidence in an assignment. However, if you are using some information from an existing source, it is essential to give credit to the owner of that source. Otherwise, the material of your assignment will become plagiarized.
Note: See the last tip of this guide to get more information regarding citing sources.
Discussing arguments and relevant evidence are not enough to make a top-notch assignment. That’s because the content of the assignment must be easy to skim through. And using short sentences and easy-to-read wording is the best way to write such content, which is the third tip of this guide.
Students often think that good content is one with a fancy vocabulary. But that’s not the case. In fact, readers get distracted when they have to specifically search for the meaning of a word while reading the content. So, to prevent that from happening, you can write the content of your assignment using short sentences and easy-to-read wording.
However, using short sentences and easy-to-read wording should not impact the formal writing tone of an assignment. Otherwise, your instructor won’t hesitate to give you a bad grade on your work. So, the goal is to write the assignment in an academic tone without using complex vocabulary.
But sometimes, writer’s block can stop the flow of creative juices, which makes it challenging to write properly. Even professional writers face this issue.
A good way to end writer’s block is to use online AI-based tools . Paraphrasing tools in particular can be helpful in this situation. How? Since paraphrasing tools reword the input text and give it a new look, it can give you new and fresh ideas about how you can start writing.
To explain this better, let’s take a look at an example. We’ll use two different tools for the example.
First, we’ll take a sample text with long sentences and complicated vocabulary here.
Sample Text: The manifold intricacies of the human condition are often overlooked in contemporary discourse, as the proclivity for simplicity and instant gratification has led to a paucity of nuanced understanding. The proliferation of technology and the subsequent atomization of society has exacerbated this trend, as the ability to curate one’s own information has led to the entrenchment of cognitive biases and the erosion of empathic faculties.
Then, we’ll run the ‘Sample Text’ into the aforementioned AI paraphrasing tools. So, after running the sample text into the tools mentioned above, we’ve got the following outputs:

The output of Quillbot AI paraphrasing tool

The output of Paraphraser.io AI paraphrasing tool
As you can see in the above pictures, both tools have converted the vocabulary to easy wording and worked on the sentences’ length. You can get inspiration by looking at the output given by the tools and then start writing your own stuff from a new angle.
Generally, students put all their efforts into writing an assignment’s introduction and body parts. However, when writing conclusive remarks about their work, students either leave it empty or write an irrelevant conclusion. And that’s where they miss the trick.
Just like the introduction and body, having a strong conclusion is another vital aspect of a perfectly written assignment. In fact, when instructors are in a hurry, they only focus on the conclusion part of an assignment. Therefore, it is essential to include a perfect conclusion. And here are some tips you can use to write an ideal conclusion:
- A strong or perfect conclusion summarizes a topic’s main arguments based on your key takeaways.
- Although you can highlight the areas that need further research while writing a conclusion, you must refrain from introducing any new concepts.
Thus, you can add concluding remarks to your assignment using the above-mentioned vital factors. But if you want a helping hand in summarizing the essential ideas of your assignment, you can use an AI-based summary generator.
Many tools are available for generating a summary through technical assistance. But not all of them work on cutting-edge technology. And that’s why some tools often generate irrelevant outputs.
Considering the above, we personally recommend using Summarizer.org for creating summaries. Since this tool is equipped with AI, it can create smart summaries from the input text. Let’s give you an example using the same sample text that we used above.

The output of Summarizer.org’s text summarizer
Nobody knows everything. In fact, even your instructors don’t know everything. Therefore, the last tip for writing a perfect assignment is to give credit where due. And you can do that by citing the sources.
In an academic paper, it is essential to reference the sources used to create the content properly. This practice allows for transparency and will enable readers to easily trace the origin of the data and authenticate it for themselves. So, you should not skip this part.
When it comes to citing the sources, there are a few things you should understand:
- Any statement that represents common knowledge will not need a citation.
- Anything (included from an existing source) other than common knowledge will require proper acknowledgment.
When it comes to acknowledging the sources correctly, you must choose a proper citation style, as there are different styles available. But let’s briefly discuss the pattern of the most common citation styles here (Pittsburgh, 2010):
1. APA (American Psychology Association)
If you want to cite the reference in the APA style, here is the styling guideline of the 7th edition of APA:

Suppose Chicago is the required citation style in your assignment. In such a situation, you can take assistance from the following patterns to cite your references in the Chicago style:

3. MLA (Modern Language Association)
The following picture will guide you regarding the styling pattern of the MLA (8th edition) citation style:

Since each institute has its own citation policy, we recommend reading the requirements carefully before writing an assignment. This way, you can identify the required citation style. However, if no citation style is specified in the requirements, you can ask your instructor because it’s better to be safe than sorry.
Thus, after identifying the required citation style, cite all the references in your assignment according to that style. Otherwise, you’ll end up losing your grades.
Writing a good assignment is challenging because it involves several pre-writing, actual writing and post-writing tips. But you can achieve this task more effectively by only focusing on understanding the assignment prompt, planning your work, using formal and easy-to-read language, using evidence to support your claims and proofreading your work. So, read the above discussion to learn the implementation of these tips with examples.
Thus, by following the above-discussed tips and putting in the necessary effort, you can write assignments that will impress your teachers and earn good grades. Remember that practice makes perfect. So, don’t be discouraged if you don’t get it right the first time. Keep working on your academic writing skills and you will see the improvement over time.
References:
- Nordquist, R. (2007, February 12, 2020). What Is a Topic Sentence? ThoughtCo. https://www.thoughtco.com/topic-sentence-composition-1692551
- Pittsburgh, U. o. (2010, October 11, 2022). Citation Styles: APA, MLA, Chicago, Turabian, IEEE. University of Pittsburgh. https://pitt.libguides.com/citationhelp
- University, G. Structure Assignments. Griffith University. https://www.griffith.edu.au/library/study/write-assignments/structure
Recent Articles
Why books are better than movies, how to transform your commute into “reading” time, knowing who i am by a g allen, fred calvert, thomas j gebhardt iii, related posts:, foolproof steps – how to hire the right e-book writer for your needs, maximizing your roi – how creative writing services can boost your business, writing tips from stephen king, best essay checkers for 2024: free and paid options, how to market an audiobook, leave a reply cancel reply, stay on top - get the daily news in your inbox, subscribe to our newsletter.
To be updated with all the latest news, offers and special announcements.
Recent Posts
Dissonance, volume i: reality by aaron ryan, maestro maestro by fred calvert, the ideal entrepreneur by rahul agarwal, popular category.
- Book Review 628
- Reader's Corner 410
- Author's Corner 182
- Author Interview 176
- Book List 111
- Mystery Thriller 96
- Historical Fiction 80
The Bookish Elf is your single, trusted, daily source for all the news, ideas and richness of literary life. The Bookish Elf is a site you can rely on for book reviews, author interviews, book recommendations, and all things books.
Contact us: [email protected]

8 Ways to Create AI-Proof Writing Prompts
C reating 100 percent AI-proof writing prompts can often be impossible but that doesn’t mean there aren’t strategies that can limit the efficacy of AI work. These techniques can also help ensure more of the writing submitted in your classroom is human-generated.
I started seeing a big uptick in AI-generated work submitted in my classes over the last year and that has continued. As a result, I’ve gotten much better at recognizing AI work , but I’ve also gotten better at creating writing prompts that are less AI-friendly.
Essentially, I like to use the public health Swiss cheese analogy when thinking about AI prevention: All these strategies on their own have holes but when you layer the cheese together, you create a barrier that’s hard to get through.
The eight strategies here may not prevent students from submitting AI work, but I find these can incentivize human writing and make sure that any work submitted via AI will not really meet the requirements of the assignment.
1. Writing AI-Proof Prompts: Put Your Prompt Into Popular AI tools such as ChatGPT, Copilot, and Bard
Putting your writing prompt into an AI tools will give you an immediate idea of how most AI tools will handle your prompt. If the various AI chatbots do a good, or at least adequate, job immediately, it might be wise to tweak the prompt.
One of my classes asks students to write about a prized possession. When you put this prompt into an AI chatbot, it frequently returns an essay about a family member's finely crafted watch. Obviously, I now watch out for any essays about watches.
2. Forbid Cliché Use
Probably the quickest and easiest way to cut back on some AI use is to come down hard on cliché use in writing assignments. AI tools are essentially cliché machines, so banning these can prevent a lot of AI use.
Equally as important, this practice will help your students become better writers. As any good writer knows, clichés should be avoided like the plague.
3. Incorporate Recent Events
The free version of ChatGPT only has access to events up to 2022. While there are plugins to allow it to search the internet and other internet-capable AI tools, some students won’t get further than ChatGPT.
More importantly, in my experience, all AI tools struggle to incorporate recent events as effectively as historic ones. So connecting class material and assignments to events such as a recent State of Union speech or the Academy Awards will make any AI writing use less effective.
4. Require Quotes
AI tools can incorporate direct quotations but most are not very good at doing so. The quotes used tend to be very short and not as well-placed within essays.
Asking an AI tool for recent quotes also can be particularly problematic for today’s robot writers. For instance, I asked Microsoft's Copilot to summarize the recent Academy Awards using quotes, and specifically asked it to quote from Oppenheimer's director Christopher Nolan’s acceptance speech. It quoted something Nolan had previously said instead. Copilot also quoted from Wes Anderson’s acceptance speech, an obvious error since Anderson wasn’t at the awards .
5. Make Assignments Personal
Having students reflect on material in their own lives can be a good way to prevent AI writing. In-person teachers can get to know their students well enough to know when these types of personal details are fabricated.
I teach online but still find it easier to tell when a more personalized prompt was written by AI. For example, one student submitted a paper about how much she loved skateboarding that was so non-specific it screamed AI written. Another submitted a post about a pair of sneakers that was also clearly written by a "sole-less" AI (I could tell because of the clichés and other reasons).
6. Make Primary or Scholarly Sources Mandatory
Requiring sources that are not easily accessible on the internet can stop AI writing in its tracks. I like to have students find historic newspapers for certain assignments. The AI tools I am familiar with can’t incorporate these.
For instance, I asked Copilot to compare coverage of the first Academy Awards in the media to the most recent awards show and to include quotes from historic newspaper coverage. The comparison was not well done and there were no quotes from historical newspaper coverage.
AI tools also struggle to incorporate journal articles. Encouraging your students to include these types of sources ensures the work they produce is deeper than something that can be revealed by a quick Google search, which not only makes it harder for AI to write but also can raise the overall quality.
7. Require Interviews, Field Trips, Etc.
Building on primary and scholarly sources, you can have your students conduct interviews or go on field trips to historic sites, museums, etc.
AI is still, thankfully, incapable of engaging in these types of behavior. This requires too much work for every assignment but it is the most effective way to truly ensure your work is human- not computer-written.
If you’re still worried about AI use, you can even go a step further by asking your students to include photos of them with their interview subjects or from the field trips. Yes, AI art generators are getting better as well, but remember the Swiss cheese analogy? Every layer of prevention can help.
8. Have Students Write During Class
As I said to start, none of the methods discussed are foolproof. Many ways around these safeguards already exist and there will be more ways to bypass these in the future. So if you’re really, really worried about AI use you may want to choose what I call the “nuclear option.” If you teach in person you can require students to write essays in person.
This approach definitely works for preventing AI and is okay for short pieces, but for longer pieces, it has a lot of downsides. I would have trouble writing a long piece in this setting and imagine many students will as well. Additionally, this requirement could create an accusatory class atmosphere that is more focused on preventing AI use than actually teaching. It’s also not practical for online teaching.
That all being said, given how common AI writing has become in education, I understand why some teachers will turn to this method. Hopefully, suggestions 1-7 will work but if AI-generated papers are still out of hand in your classroom, this is a blunt-force method that can work temporarily.
Good luck and may your assignments be free of AI writing!
- 7 Ways To Detect AI Writing Without Technology
- Best Free AI Detection Sites
- My Student Was Submitting AI Papers. Here's What I Did

- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Working With Your Hands Is Good for Your Brain
Activities like writing, gardening and knitting can improve your cognition and mood. Tapping, typing and scrolling? Less so.

By Markham Heid
The human hand is a marvel of nature. No other creature on Earth, not even our closest primate relatives , has hands structured quite like ours, capable of such precise grasping and manipulation.
But we’re doing less intricate hands-on work than we used to. A lot of modern life involves simple movements, such as tapping screens and pushing buttons, and some experts believe our shift away from more complex hand activities could have consequences for how we think and feel.
“When you look at the brain’s real estate — how it’s divided up, and where its resources are invested — a huge portion of it is devoted to movement, and especially to voluntary movement of the hands,” said Kelly Lambert, a professor of behavioral neuroscience at the University of Richmond in Virginia.
Dr. Lambert, who studies effort-based rewards, said that she is interested in “the connection between the effort we put into something and the reward we get from it” and that she believes working with our hands might be uniquely gratifying.
In some of her research on animals , Dr. Lambert and her colleagues found that rats that used their paws to dig up food had healthier stress hormone profiles and were better at problem solving compared with rats that were given food without having to dig.
She sees some similarities in studies on people, which have found that a whole range of hands-on activities — such as knitting , gardening and coloring — are associated with cognitive and emotional benefits, including improvements in memory and attention, as well as reductions in anxiety and depression symptoms.
These studies haven’t determined that hand involvement, specifically, deserves the credit. The researchers who looked at coloring, for example, speculated that it might promote mindfulness, which could be beneficial for mental health. Those who have studied knitting said something similar. “The rhythm and repetition of knitting a familiar or established pattern was calming, like meditation,” said Catherine Backman, a professor emeritus of occupational therapy at the University of British Columbia in Canada who has examined the link between knitting and well-being.
However, Dr. Backman said the idea that working with one’s hands could benefit a person’s mind and wellness seems plausible. Hands-on tasks that fully engage our attention — and even mildly challenge us — can support learning, she added.
Dr. Lambert has another hypothesis. “With depression, people experience something called learned helplessness, where they feel like it doesn’t matter what they do, nothing ever works,” she said. She believes that working with one’s hands is stimulating to the brain, and that it could even help counteract this learned helplessness. “When you put in effort and can see the product of that, like a scarf you knitted, I think that builds up a sense of accomplishment and control over your world,” she said.
Some researchers have zeroed in on the possible repercussions of replacing relatively complicated hand tasks with more basic ones.
In a small study of university students published in January, Norwegian researchers compared the neurological effects of writing by hand with typing on a keyboard. Handwriting was associated with “far more elaborate” brain activity than keyboard writing, the researchers found.
“With handwriting, you have to form these intricate letters by making finely controlled hand and finger movements,” said Audrey van der Meer, one of the authors of that study and a professor of psychology at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology. Each letter is different, she explained, and requires a different hand action.
Dr. Van der Meer said that the act of forming a letter activates distinctive memories and brain pathways tied to what that letter represents (such as the sound it makes and the words that include it). “But when you type, every letter is produced by the same very simple finger movement, and as a result you use your whole brain much less than when writing by hand,” she added.
Dr. Van der Meer’s study is the latest in a series of research efforts in which she and her colleagues have found that writing and drawing seem to engage and exercise the brain more than typing on a keyboard. “Skills involving fine motor control of the hands are excellent training and superstimulation for the brain,” she said. “The brain is like a muscle, and if we continue to take away these complex movements from our daily lives — especially fine motor movements — I think that muscle will weaken.” While more research is needed, Dr. Van der Meer posits that understimulation of the brain could ultimately lead to deficits in attention, memory formation and problem solving.
But as with knitting and coloring, some experts question the underlying mechanisms at play.
“With some of this research, I think it’s hard to dissociate whether it’s the physical movement of the hands that’s producing a benefit, or whether it’s the concentration or novelty or cognitive challenge involved,” said Rusty Gage, a professor at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies in San Diego.
Dr. Gage studies how certain activities can stimulate the growth of new cells in the brain. “I think if you’re doing complex work that involves making decisions and planning, that may matter more than whether you’re using your hands,” he said.
That said, the benefits of many hands-on activities aren’t in doubt. Along with gardening and handicrafts, research has found that pursuits like making art and playing a musical instrument also seem to do us some good.
“You know, we evolved in a three-dimensional world, and we evolved to interact with that world through our hands,” Dr. Lambert said. “I think there are a lot of reasons why working with our hands may be prosperous for our brains.”
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player

Solar eclipse 2024: Follow the path of totality
Solar eclipse, how to help your kids enjoy the solar eclipse.
The NPR Network
Getting your kids ready to enjoy the eclipse? If you've got curious kiddos enjoying the eclipse today, here are some resources from the NPR Network to help get the most out of the experience:
Eclipse learning guide for kids via Vermont Public
- Pre-K to Grade 2
- Grade 3 to 5
- Grade 6 to 12

Amy Nickell with Dallas Arboretum helps Dani Turin, 5, look down the ruler at the sun and the moon to see the perspective of the eclipse Monday at Dallas Cotton Bowl Stadium. Yfat Yossifor/KERA hide caption
Amy Nickell with Dallas Arboretum helps Dani Turin, 5, look down the ruler at the sun and the moon to see the perspective of the eclipse Monday at Dallas Cotton Bowl Stadium.
Not able to get outside? Stream totality with your kiddo .
- WATCH: The difference between a solar and a lunar eclipse from KERA Kids
- LISTEN: has a new episode out about solar eclipses from But Why , Vermont Public's podcast for curious kids
Kid at heart? The Texas Standard has tips from Bill Nye on the best ways to enjoy the eclipse .
Do some color-based experimentation! The celestial phenomena can alter the way we see colors, so keep an eye on reds and greens and how they change over the course of totality!
- What do I do if my kid won't keep their eclipse glasses on?
- How can I make sure my eclipse glasses are legit?
- Simple tips to safely photograph the eclipse with your cellphone
And be prepared: As we found with kids who enjoyed the eclipse in 2017 , little ones may totally forget this celestial experience, so don't sweat it too much!
NPR will be sharing highlights from across the NPR Network throughout the day if you're unable to get out and see it in real time.
NPR's Emily Alfin Johnson produced this piece.

Play Minecraft Games with Game Pass
ALSO AVAILABLE ON:
Minecraft is available to play on the following platforms:

*Mac and Linux are compatible with Java Edition only.

Poisonous Potato Update
The (s)mashing update you always asked for!
Imagine being a potato. Now imagine being the potato’s less popular sibling who didn’t inherit the tuber-licious looks the rest of your family possesses. What’s worse is – you're facing the impossible decision of what to do with all this starch? Since neither French fries nor couch potato sat right with you, there's only one option remaining. Congratulations friend, you’re a poisonous potato.
For years, Minecraft’s own toxic tuber has been neglected and underappreciated, lacking both purpose and usefulness. For years, you – the community – tried to highlight this, working tirelessly to bring it to our attention and literally begging us for more functionality. As of today, your concerns are a thing of the past.
Mojang Studios is proud to release our most well-boiled update to date that will add so much usability to the poisonous potato that even tater-haters will become devoted spud-buds. The Poisonous Potato Update – rich in both carbs AND features! You asked. We delivered. Or maybe you didn’t ask, but we delivered anyway? In any case, it is HERE!

GET THE SNAPSHOT UPDATE
Snapshots are available for Minecraft: Java Edition. To install the snapshot, open up the Minecraft Launcher and enable snapshots in the "Installations" tab. You can even play the snapshot on your own Java Realms together with your friends!
Remember, snapshots can corrupt your world, so please back up your world and/or run the snapshot in a different folder from your main worlds.
-> DOWNLOAD THE CROSS-PLATFORM SERVER JAR
Poisonous potato add-on.

The roots of the poisonous potato run deep within Minecraft and extends far beyond Java Edition. Therefore, it should come as no surprise that the tuber-lar sensation has spread its influence to Bedrock Edition as well. With Jigarbov’s Poisonous Potato add-on , you’ll be able to experience the joy of the poisonous potato the way it was always intended – through blocks and furniture to weapons and armor.
-> GET THE ADD-ON
Gameplay & features.
- Poisonous potatoes – LOTS of poisonous potatoes!
- A few normal potatoes too!
- The homeland of all potato kind
- Five spud-tastic biomes: fields, hash, arboretum, corruption, and wasteland
- Experience the life of a potato – from its inception as a raw potato picked from the fields, through cooked hash browns, to its eventual decay
- Local weather with a-mashing effects
- Added the Colosseum, home to the lord of potato kind...
- A whole sack of a-peeling new blocks
- Rich in Vitamin C, Vitamin B6, and Niacin!
- No new mineral blocks. No need! The blocks themselves contain minerals: Potassium, Magnesium, and Iron!
- Added the frying table – everyone asked for it, so we added it. It fries potato things. It's a really nice model!
- Added functionality to the fletching table. You can now fletch toxic resin into more refined versions of the resin.
- Added impurities because purity is overrated
- Added a whole bunch new gadgets that will tune your poisonous potato game up to eleven!
- You get it by now. They’re all poisonous potatoes...
TECHNICAL CHANGES
- The flux capacitor integration now synergizes with quantum voxelization, which enables a 360-noscope enhancing real-time RTX terrain-rendering nightshade multibox spectrum acceleration while optimizing transdimensional entity synchronization for seamless vitelotte-king edwards-russel burbank experiences!
WHAT HAPPENS IF I DOWNLOAD THE UPDATE?
Then you will be the proud owner of the file that contains the update.
WHAT CAN I EXPECT IN TERMS OF GAMEPLAY?
Poisonous potatoes. We hope this article has made that perfectly clear.
I DON’T BELIEVE I ASKED FOR THIS UPDATE, IF I’M HONEST.
You might not have – but your brain (or maybe belly) did!
ARE THERE CURRENTLY ANY OTHER CARB-BASED UPDATES IN THE WORKS?
Great question! Please look forward to the Radioactive Rice Update and Toxic Taro Update in the very distant future!
SHARE THIS STORY
Community creations.
Discover the best add-ons, mods, and more being built by the incredible Minecraft community!
Block...Block...Block...

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
As Eodice, Geller, and Lerner (2016) have shown, meaningful writing assignments do occur across all disciplines and they are typically ones that "offer students opportunities to engage with instructors, peers, and texts and are relevant to past experiences and passions as well as to future aspirations and identities.". Maximized learning time.
Make things easier for yourself by writing it as you go along. 8. Conclusion. Your conclusion is your final chance to summarise your argument and leave a lasting impression with your reader. Make sure you recap the key points and arguments you made in your assignment, including supporting evidence if needed.
Here are over a hundred writing prompts in a variety of genres. If you need ideas for your next story, check this out! 3. How To Use Neither, Nor, Or, and Nor Correctly. Even good writers struggle figuring out when to use neither/nor and either/or. In this post, our copy-queen Liz Bureman settles the confusion once and for all.
What this handout is about. The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms ...
Academic writing is a formal style of writing used in universities and scholarly publications. You'll encounter it in journal articles and books on academic topics, and you'll be expected to write your essays, research papers, and dissertation in academic style. Academic writing follows the same writing process as other types of texts, but ...
These OWL resources will help you understand and complete specific types of writing assignments, such as annotated bibliographies, book reports, and research papers. This section also includes resources on writing academic proposals for conference presentations, journal articles, and books.
Here are five tips to help you get ahead. 1. Use available sources of information. Beyond instructions and deadlines, lecturers make available an increasing number of resources. But students often ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Prewriting. Step 2: Planning and outlining. Step 3: Writing a first draft. Step 4: Redrafting and revising. Step 5: Editing and proofreading. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the writing process.
Courses and assignments should be planned with this in mind. Three principles are paramount: 1. Name what you want and imagine students doing it. However free students are to range and explore in a paper, the general kind of paper you're inviting has common components, operations, and criteria of success, and you should make these explicit ...
Essay writing process. The writing process of preparation, writing, and revisions applies to every essay or paper, but the time and effort spent on each stage depends on the type of essay.. For example, if you've been assigned a five-paragraph expository essay for a high school class, you'll probably spend the most time on the writing stage; for a college-level argumentative essay, on the ...
Here are some practical tips that will keep your work focused and effective: - Critical thinking - Academic writing has to be characterized by critical thinking, not only to provide the work with the needed level, but also because it takes part in the final mark. - Continuity of ideas - When you get to the middle of assignment, things ...
Put It in Writing: While you'll want to present your assignment orally in class, be sure to give your students a written copy, too, so they can refer to it as they work. Putting it down on paper may also help you clarify your own expectations about the assignment. Anticipate the Inevitable: You're enthusiastically explaining the limitless ...
Writing is a response. We write because we are reacting to someone or something. While writing can feel like an isolating, individual act—just you and the computer or pad of paper—it is really a social act, a way in which we respond to the people and world around us. Writing happens in specific, often prescribed contexts.
Effective Writing Assignment . I. know that good writing assignments result in good writing. I've seen the ways that writers-me, my col1eagues, my classmates, the students whom I've taught-write stronger, more sophisticated papers when they are asked to respond to well-developed writing assignments.
Sequence activities (reading, researching, writing) to build toward the final product. Beyond the Basics. Writing tasks fill many different roles for students, so defining good writing assignments begins with the specific instructional context. For that reason, the first key to writing a good assignment is tying the task to the specific course ...
The basic structure of an assignment includes an introduction, body, and conclusion. The introduction should present the topic and establish the purpose of your assignment. The body should delve into the topic in detail, backed by your research. The conclusion should summarize your findings or arguments without introducing new ideas.
A compare & contrast assignment is a type of expository & research paper assignment. It is important to organize your writing around the themes you are comparing & contrasting. If, for example, you are assigned to compare & contrast, say, Augustine's Confessions and The Autobiography of Malcolm X, a common mistake students make is to write the first part of their essay strictly about Augustine ...
Writing Assignments Kate Derrington; Cristy Bartlett; and Sarah Irvine. Figure 19.1 Assignments are a common method of assessment at university and require careful planning and good quality research. Image by Kampus Production used under CC0 licence. Introduction. Assignments are a common method of assessment at university and require careful planning and good quality research.
Here's how our contest works: every Friday, we send out a newsletter containing five creative writing prompts. Each week, the story ideas center around a different theme. Authors then have one week — until the following Friday — to submit a short story based on one of our prompts. A winner is picked each week to win $250 and is highlighted ...
You might not feel like you have the necessary skills to write a good essay. But there are certain tips you can use to write a good assignment and lay your apprehensions to rest. ... After researching, you should make a schedule for writing your assignments. Stick to your schedule. Also, double-check your deadline so you won't have to feel ...
Write an introduction - This is where you introduce yourself and your topic. It should be about a paragraph long and should include your assignment topic. Provide background information - The next step after writing an introduction is providing background information to support your assignment. This can include definitions, examples and ...
Sample Assignment: Lyric Essay. Wayne Koestenbaum's lyric essay, Assignments, provides good prompts for writing your own lyric essays: Make a list of media you gave up (e.g. watercolors). Say why. Quote from a line from a novel or a poem. Selfishly manipulate and misuse the quote.
Conclusion. Writing a good assignment is challenging because it involves several pre-writing, actual writing and post-writing tips. But you can achieve this task more effectively by only focusing on understanding the assignment prompt, planning your work, using formal and easy-to-read language, using evidence to support your claims and proofreading your work.
5. Make Assignments Personal. Having students reflect on material in their own lives can be a good way to prevent AI writing. In-person teachers can get to know their students well enough to know ...
Dr. Van der Meer's study is the latest in a series of research efforts in which she and her colleagues have found that writing and drawing seem to engage and exercise the brain more than typing ...
Tesol 102 - W12 Assignment: Top 20 Writing Assignments Partner: Carol Wei-Tzu Lee Good day! Everyone, I'm Simone Bagni. Welcome to this TESOL conference, and thank you for having me share some of my favorite writing activities with you. Alright, let's head to the topic, I'm going to navigate you to go through my top 20 writing activities, and of course, I'll start from number 1.
Meanwhile, while fewer faculty members used AI, the percentage grew to 22% of faculty members in the fall of 2023, up from 9% in spring 2023. Teachers are turning to AI tools and platforms ...
No, but here are a few strategies to use AI to help with the book-writing process. • Ideation: AI can help overcome the dreaded blank page syndrome. By inputting a theme or a basic premise, AI ...
If you've got curious kiddos enjoying the eclipse today, here are some resources from the NPR Network to help get the most out of the experience: Eclipse learning guide for kids via Vermont Public ...
As of today, your concerns are a thing of the past. Mojang Studios is proud to release our most well-boiled update to date that will add so much usability to the poisonous potato that even tater-haters will become devoted spud-buds. The Poisonous Potato Update - rich in both carbs AND features!