Reference management. Clean and simple.

The top list of academic search engines
1. Google Scholar
4. science.gov, 5. semantic scholar, 6. baidu scholar, get the most out of academic search engines, frequently asked questions about academic search engines, related articles.
Academic search engines have become the number one resource to turn to in order to find research papers and other scholarly sources. While classic academic databases like Web of Science and Scopus are locked behind paywalls, Google Scholar and others can be accessed free of charge. In order to help you get your research done fast, we have compiled the top list of free academic search engines.
Google Scholar is the clear number one when it comes to academic search engines. It's the power of Google searches applied to research papers and patents. It not only lets you find research papers for all academic disciplines for free but also often provides links to full-text PDF files.
- Coverage: approx. 200 million articles
- Abstracts: only a snippet of the abstract is available
- Related articles: ✔
- References: ✔
- Cited by: ✔
- Links to full text: ✔
- Export formats: APA, MLA, Chicago, Harvard, Vancouver, RIS, BibTeX
BASE is hosted at Bielefeld University in Germany. That is also where its name stems from (Bielefeld Academic Search Engine).
- Coverage: approx. 136 million articles (contains duplicates)
- Abstracts: ✔
- Related articles: ✘
- References: ✘
- Cited by: ✘
- Export formats: RIS, BibTeX

CORE is an academic search engine dedicated to open-access research papers. For each search result, a link to the full-text PDF or full-text web page is provided.
- Coverage: approx. 136 million articles
- Links to full text: ✔ (all articles in CORE are open access)
- Export formats: BibTeX
Science.gov is a fantastic resource as it bundles and offers free access to search results from more than 15 U.S. federal agencies. There is no need anymore to query all those resources separately!
- Coverage: approx. 200 million articles and reports
- Links to full text: ✔ (available for some databases)
- Export formats: APA, MLA, RIS, BibTeX (available for some databases)
Semantic Scholar is the new kid on the block. Its mission is to provide more relevant and impactful search results using AI-powered algorithms that find hidden connections and links between research topics.
- Coverage: approx. 40 million articles
- Export formats: APA, MLA, Chicago, BibTeX

Although Baidu Scholar's interface is in Chinese, its index contains research papers in English as well as Chinese.
- Coverage: no detailed statistics available, approx. 100 million articles
- Abstracts: only snippets of the abstract are available
- Export formats: APA, MLA, RIS, BibTeX

RefSeek searches more than one billion documents from academic and organizational websites. Its clean interface makes it especially easy to use for students and new researchers.
- Coverage: no detailed statistics available, approx. 1 billion documents
- Abstracts: only snippets of the article are available
- Export formats: not available
Consider using a reference manager like Paperpile to save, organize, and cite your references. Paperpile integrates with Google Scholar and many popular databases, so you can save references and PDFs directly to your library using the Paperpile buttons:
Google Scholar is an academic search engine, and it is the clear number one when it comes to academic search engines. It's the power of Google searches applied to research papers and patents. It not only let's you find research papers for all academic disciplines for free, but also often provides links to full text PDF file.
Semantic Scholar is a free, AI-powered research tool for scientific literature developed at the Allen Institute for AI. Sematic Scholar was publicly released in 2015 and uses advances in natural language processing to provide summaries for scholarly papers.
BASE , as its name suggest is an academic search engine. It is hosted at Bielefeld University in Germany and that's where it name stems from (Bielefeld Academic Search Engine).
CORE is an academic search engine dedicated to open access research papers. For each search result a link to the full text PDF or full text web page is provided.
Science.gov is a fantastic resource as it bundles and offers free access to search results from more than 15 U.S. federal agencies. There is no need any more to query all those resources separately!
5 best search engines for students in 2022 besides Google
How often do you Google information? One of the best search engines in the world is indispensable to our daily lives, especially for university students swamped with course readings and assignments. A few keywords in the search bar — and voilà — the results link you to endless facts and suggestions on a particular topic.
Google might win the popular vote, but it’s far from the only resource on the internet for aspiring scholars. How you find sources for assignments matters just as much as the information you get. For that, there’s no better way to dive into your subject through search engines optimised for academic research — it’s part of developing your critical thinking skills while sharpening your eyes on fact-checking to spot fake news .
If you’re ready to up your searching game, make sure to bookmark this list for future references:
Where you get your information from matters just as much as the material. Using academic search engines eliminates questionable sources in your paper. Source: Philippe Lopez/AFP
Best search engines to use in academia
Worldcat.org.
If you’re familiar with Google Scholar or JSTOR, you might’ve encountered this nifty website through your university library. WorldCat.org prides itself on being the world’s largest network of library content and services.
You can use WorldCat.org through your student library account to unlock an endless treasure trove of knowledge. It works by directing you to collections of more than 10,000 libraries globally, including the prestigious Bodleian Library at the University of Oxford and The Library of Congress.
WorldCat.org grants you access to various formats in its catalogue, such as old VHS tapes and downloadable musical scores — all of which are primary sources that enhance your research quality considerably.
Semantic Scholar
Need a more precise and analytical method to interpret your sources? Semantic Scholar is your answer.
Powered by the Allen Institute for Artificial Intelligence (AI), this free search engine harnesses sophisticated AI and machine learning techniques to augment its discovery tools. It has a function that extracts meaning and connects the dots between papers, so it’s handy for data interpretation.
You can also say goodbye to confusion in navigating advanced search tools and wordy texts on the screen. Visually, it’s one of the best academic search engines with a user-friendly interface that uses a simple but vibrant design. The easy-to-follow tutorials are a plus to help you maximise your search on the website.
Would you like to plant a tree with every search? Ecosia ‘s unique philosophy lands it on our best search engines list: it’s a social business founded on the principle that everyone can combat climate change, even with a click.
Ecosia channels the ad revenue it makes to support reforestation projects that aim to neutralise carbon dioxide emissions. According to the website, it has planted over 154 million trees worldwide, from Mount Bamboutos in Cameroon to restoring Indonesian forests in former oil plantations.
Its green initiatives aside, Ecosia is ideal for students as it can be added as extensions to default browsers, with an app version for your mobile devices. Environmental sciences students can rejoice: its blog regularly updates the latest scoop in the eco world, so you’re always in the loop on current climate action news.
Ecosia uses revenue from ads to support reforestation projects worldwide, and can be easily added as an extension on your default browser. Source: Nipah Dennis/AFP
Open Knowledge Maps
Scientific journals don’t have to be dry and dull, and developers of this search engine astutely understand the power of visual learning. Instead of getting results in lines of text, it gives you a map with an overview of the 100 most relevant documents related to your search query. The algorithm then groups them together in circles based on the number of common words they have.
It’s one of the best search engines vetted by researchers from prestigious schools like ETH Zurich and Harvard University. The best part? There’s an automatic citation generator for each document you click on, saving you time when formatting your references correctly.
Open Knowledge Maps visualises your search queries by grouping scholarly articles together based on recurring words and phrases. Source: Open Knowledge Maps
COnnecting REpositories (CORE)
CORE is a not-for-profit service with the aim of becoming the world’s largest aggregator of open-access journals and peer-reviewed papers on the web. It has over 200 million scholarly articles gathered from 11,000 data providers, connecting you with multiple research repositories from universities across the world.
If you’re tired of pesky paywalls blocking access to papers you need, you can add the CORE Discovery extension to either Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, or Opera for free. This handy feature searches for an accessible copy elsewhere, so you don’t have to scramble for it on your own.
Popular stories
Pack your bags, there’s good reason to move to the most expensive countries to live in, earning a veterinary degree is harder than you think, just ask this singaporean student in rural australia, need reasons to study in the most educated countries in the world this isn’t the list for you, the most respected engineering degrees are what you’d expect them to be, here are 5 free alternatives to microsoft word, 5 websites to download free textbooks, 11 sites to download audiobooks for free.

28 Best Academic Search Engines That make your research easier
This post may contain affiliate links that allow us to earn a commission at no expense to you. Learn more

If you’re a researcher or scholar, you know that conducting effective online research is a critical part of your job. And if you’re like most people, you’re always on the lookout for new and better ways to do it.
I’m sure you are familiar with some research databases. But, top researchers keep an open mind and are always looking for inspiration in unexpected places.
This article aims to give you an edge over researchers that rely mainly on Google for their entire research process.
Our list of 28 academic search engines will start with the more familiar to less.
Table of Contents
#1. Google Scholar
Google Scholar is an academic search engine that indexes the full text or metadata of scholarly literature across an array of publishing formats and disciplines.
Great for academic research, you can use Google Scholar to find articles from academic journals, conference proceedings, theses, and dissertations. The results returned by Google Scholar are typically more relevant and reliable than those from regular search engines like Google.
Tip: You can restrict your results to peer-reviewed articles only by clicking on the “Scholarly”
- Scholarly results are typically more relevant and reliable than those from regular search engines like Google.
- You can restrict your results to peer-reviewed articles only by clicking on the “Scholarly” tab.
- Google Scholar database Coverage is extensive, with approx. 200 million articles indexed.
- Abstracts are available for most articles.
- Related articles are shown, as well as the number of times an article has been cited.
- Links to full text are available for many articles.
- Abstracts are only a snippet of the full article, so you might need to do additional searching to get the full information you need.
- Not all articles are available in full text.
Google Scholar is completely free.
#2. ERIC (Education Resources Information Center)
ERIC (short for educational resources information center) is a great academic search engine that focuses on education-related literature. It is sponsored by the U.S. Department of Education and produced by the Institute of Education Sciences.
ERIC indexes over a million articles, reports, conference papers, and other resources on all aspects of education from early childhood to higher education. So, search results are more relevant to Education on ERIC.
- Extensive coverage: ERIC indexes over a million articles, reports, and other resources on all aspects of education from early childhood to higher education.
- You can limit your results to peer-reviewed journals by clicking on the “Peer-Reviewed” tab.
- Great search engine for educators, as abstracts are available for most articles.
ERIC is a free online database of education-related literature.
You might also like:
- Best Plagiarism Checkers For Research Papers
- 30+ Essential Software For Researchers
- Best AI-Based Summary Generators
- 25 Best Schools For International Relations In The US
- GPTZero Review
#3. Wolfram Alpha

Wolfram Alpha is a “computational knowledge engine” that can answer factual questions posed in natural language. It can be a useful search tool.
Type in a question like “What is the square root of 64?” or “What is the boiling point of water?” and Wolfram Alpha will give you an answer.
Wolfram Alpha can also be used to find academic articles. Just type in your keywords and Wolfram Alpha will generate a list of academic articles that match your query.
Tip: You can restrict your results to peer-reviewed journals by clicking on the “Scholarly” tab.
- Can answer factual questions posed in natural language.
- Can be used to find academic articles.
- Results are ranked by relevance.
- Results can be overwhelming, so it’s important to narrow down your search criteria as much as possible.
- The experience feels a bit more structured but it could also be a bit restrictive
Wolfram Alpha offers a few pricing options, including a “Pro” subscription that gives you access to additional features, such as the ability to create custom reports. You can also purchase individual articles or download them for offline use.
Pro costs $5.49 and Pro Premium costs $9.99
#4. iSEEK Education
- 15 Best Websites To Download Research Papers For Free
- 15 Best Academic Research Trend Prediction Platforms
- Academic Tools
- 15 Best Academic Networking And Collaboration Platforms
iSEEK is a search engine targeting students, teachers, administrators, and caregiver. It’s designed to be safe with editor-reviewed content.
iSEEK Education also includes a “Cited by” feature which shows you how often an article has been cited by other researchers.
- Editor-reviewed content.
- “Cited by” feature shows how often an article has been cited by other researchers.
- Limited to academic content.
- Doesn’t have the breadth of coverage that some of the other academic search engines have.
iSEEK Education is free to use.
#5. BASE (Bielefeld Academic Search Engine)

BASE is hosted at Bielefeld University in Germany and that’s where it name stems from (Bielefeld Academic Search Engine).
Known as “one of the most comprehensive academic web search engines,” it contains over 100 million documents from 4,000 different sources.
Users can narrow their search using the advanced search option, so regardless of whether you need a book, a review, a lecture, a video or a thesis, BASE has what you need.
BASE indexes academic articles from a variety of disciplines, including the arts, humanities, social sciences, and natural sciences.
- One of the world’s most voluminous search engines,
- Indexes academic articles from a variety of disciplines, especially for academic web resources
- Includes an “Advanced Search” feature that lets you restrict your results to peer-reviewed journals.
- Doesn’t include abstracts for most articles.
- Doesn’t have related articles, references, cited by
BASE is free to use.
- 10 Best Reference Management Software for Research 2023
- 15 Best Academic Networking and Collaboration Platforms
- 30+ Essential Software for Researchers
- 15 Best Academic Blogging and Content Management
- 11 Best Academic Writing Tools For Researchers
CORE is an academic search engine that focuses on open access research papers. A link to the full text PDF or complete text web page is supplied for each search result. It’s academic search engine dedicated to open access research papers.
- Focused on open access research papers.
- Links to full text PDF or complete text web page are supplied for each search result.
- Export formats include BibTeX, Endnote, RefWorks, Zotero.
- Coverage is limited to open access research papers.
- No abstracts are available for most articles.
- No related articles, references, or cited by features.
CORE is free to use.
- Best Plagiarism Checkers for Research Papers in 2024
#7. Science.gov

Science.gov is a search engine developed and managed by the United States government. It includes results from a variety of scientific databases, including NASA, EPA, USGS, and NIST.
US students are more likely to have early exposure to this tool for scholarly research.
- Coverage from a variety of scientific databases (200 million articles and reports).
- Links to full text are available for some articles.
Science.gov is free to use.
- 15 Best Academic Journal Discovery Platforms
- Sci Hub Review
#8. Semantic Scholar

Semantic Scholar is a recent entrant to the field. Its goal is to provide more relevant and effective search results via artificial intelligence-powered methods that detect hidden relationships and connections between research topics.
- Powered by artificial intelligence, which enhances search results.
- Covers a large number of academic articles (approx. 40 million).
- Related articles, references, and cited by features are all included.
- Links to full text are available for most articles.
Semantic Scholar is free to use.
- 11 Best Academic Writing Tools For Researchers
- 10 Best Reference Management Software for Research
- 15 Best Academic Journal Discovery Platforms
#9. RefSeek
RefSeek searches more than five billion documents, including web pages, books, encyclopedias, journals, and newspapers.
This is one of the free search engines that feels like Yahoo with a massive directory. It could be good when you are just looking for research ideas from unexpected angles. It could lead you to some other database that you might not know such as the CIA The World Factbook, which is a great reference tool.
- Searches more than five billion documents.
- The Documents tab is very focused on research papers and easy to use.
- Results can be filtered by date, type of document, and language.
- Good source for free academic articles, open access journals, and technical reports.
- The navigation and user experience is very dated even to millenials…
- It requires more than 3 clicks to dig up interesting references (which is how it could lead to you something beyond the 1st page of Google)
- The top part of the results are ALL ads (well… it’s free to use)
RefSeek is free to use.
#10. ResearchGate

A mixture of social networking site + forum + content databases where researchers can build their profile, share research papers, and interact with one another.
Although it is not an academic search engine that goes outside of its site, ResearchGate ‘s library of works offers an excellent choice for any curious scholar.
There are more than 100 million publications available on the site from over 11 million researchers. It is possible to search by publication, data, and author, as well as to ask the researchers questions.
- A great place to find research papers and researchers.
- Can follow other researchers and get updates when they share new papers or make changes to their profile.
- The network effect can be helpful in finding people who have expertise in a particular topic.
- Interface is not as user friendly
- Can be overwhelming when trying to find relevant papers.
- Some papers are behind a paywall.
ResearchGate is free to use.
- 15 Best Academic Research Trend Prediction Platforms
- 25 Best Tools for Tracking Research Impact and Citations
#11. DataONE Search (formerly CiteULike)
A social networking site for academics who want to share and discover academic articles and papers.
- A great place to find academic papers that have been shared by other academics.
- Some papers are behind a paywall
CiteULike is free to use.
#12. DataElixir
DataElixir is deigned to help you find, understand and use data. It includes a curated list of the best open datasets, tools and resources for data science.
- Dedicated resource for finding open data sets, tools, and resources for data science.
- The website is easy to navigate.
- The content is updated regularly
- The resources are grouped by category.
- Not all of the resources are applicable to academic research.
- Some of the content is outdated.
DataElixir is free to use.
#13. LazyScholar – browser extension
LazyScholar is a free browser plugin that helps you discover free academic full texts, metrics, and instant citation and sharing links. Lazy Scholar is created Colby Vorland, a postdoctoral fellow at Indiana University.
- It can integrate with your library to find full texts even when you’re off-campus.
- Saves your history and provides an interface to find it.
- A pre-formed citation is availlable in over 900 citation styles.
- Can recommend you topics and scans new PubMed listings to suggest new papers
- Results can be a bit hit or miss
LazyScholar is free to use.
#14. CiteseerX – digital library from PenState

CiteseerX is a digital library stores and indexes research articles in Computer Science and related fields. The site has a robust search engine that allows you to filter results by date, author.
- Searches a large number of academic papers.
- Results can be filtered by date, author, and topic.
- The website is easy to use.
- You can create an account and save your searches for future reference.
CiteseerX is free to use.
- Surfer Review: Is It Worth It?
- 25 Best Tools For Tracking Research Impact And Citations
#15. The Lens – patents search
The Lens or the Patent Lens is an online patent and scholarly literature search facility, provided by Cambia, an Australia-based non-profit organization.
- Searches for a large number of academic papers.
The price range can be free for non-profit use to $5,000 for commercial enterprise.
#16. Fatcat – wiki for bibliographic catalog
Fatcat is an open bibliographic catalog of written works. The scope of works is somewhat flexible, with a focus on published research outputs like journal articles, pre-prints, and conference proceedings. Records are collaboratively editable, versioned, available in bulk form, and include URL-agnostic file-level metadata.
- Open source and collaborative
- You can be part of the community that is very focused on its mission
- The archival file-level metadata (verified digests and long-term copies) is a great feature.
- Could prove to be another rabbit hole
- People either love or hate the text-only interface
#17. Lexis Web – Legal database
Are you researching legal topics? You can turn to Lexis Web for any law-related questions you may have. The results are drawn from legal sites and can be filtered based on criteria such as news, blogs, government, and commercial. Additionally, users can filter results by jurisdiction, practice area, source and file format.
- Results are drawn from legal sites.
- Filters are available based on criteria such as news, blogs, government, and commercial.
- Users can filter results by jurisdiction, practice area, source and file format.
- Not all law-related questions will be answered by this search engine.
- Coverage is limited to legal sites only.
Lexis Web is free for up to three searches per day. After that, a subscription is required.
#18. Infotopia – part of the VLRC family
Infotopia touts itself as an “alternative to Google safe search.” Scholarly book results are curated by librarians, teachers, and other educational workers. Users can select from a range of topics such as art, health, and science and technology, and then see a list of resources pertaining to the topic.
Consequently, if you aren’t able to find what you are looking for within Infotopia’s pages, you will probably find it on one of its many suggested websites.
#19. Virtual Learning Resources Center

Virtual Learning Resources Center (VLRC) is an academic search engine that features thousands of academic sites chosen by educators and librarians worldwide. Using an index generated from a research portal, university, and library internet subject guides, students and instructors can find current, authoritative information for school.
- Thousands of academic information websites indexed by it. You will also be able to get more refined results with custom Google search, which will speed up your research.
- Many people consider VLRC as one of the best free search engines to start looking for research material.
- TeachThought rated the Virtual LRC #3 in it’s list of 100 Search Engines For Academic Research
- More relevant to education
- More relevant to students
Powered by Google Custom Search Engine (CSE), Jurn is a free online search engine for accessing and downloading free full-text scholarly papers. It was created by David Haden in a public open beta version in February 2009, initially for locating open access electronic journal articles in the arts and humanities.
After the indexing process was completed, a website containing additional public directories of web links to indexed publications was introduced in mid-2009. The Jurn search service and directory has been regularly modified and cleaned since then.
- A great resource for finding academic papers that are behind paywalls.
- The content is updated regularly.uren
Jurn is free to use.
#21. WorldWideScience
The Office of Scientific and Technical Information—a branch of the Office of Science within the U.S. Department of Energy—hosts the portal WorldWideScience , which has dubbed itself “The Global Science Gateway.”
Over 70 countries’ databases are used on the website. When a user enters a query, it contacts databases from all across the world and shows results in both English and translated journals and academic resources.
- Results can be filtered by language and type of resource
- Interface is easy to use
- Contains both academic journal articles and translated academic resources
- The website can be difficult to navigate.
WorldWideScience is free to use.
#22. Google Books
A user can browse thousands of books on Google Books, from popular titles to old titles, to find pages that include their search terms. You can look through pages, read online reviews, and find out where to buy a hard copy once you find the book you are interested in.
#23. DOAJ (Directory of Open Access Journals)
DOAJ is a free search engine for scientific and scholarly materials. It is a searchable database with over 8,000 peer-reviewed research papers organized by subject. It’s one of the most comprehensive libraries of scientific and scholarly resources, with over 8,000 journals available on a variety of themes.
#24. Baidu Scholar
Baidu Xueshu (Academic) is the Chinese version for Google Scholar. IDU Scholar indexes academic papers from a variety of disciplines in both Chinese and English.
- Articles are available in full text PDF.
- Covers a variety of academic disciplines.
- No abstracts are available for most articles, but summaries are provided for some.
- A great portal that takes you to different specialized research platform
- You need to be able to read Chinese to use the site
- Since 2021 there is a rise of focus on China and the Chinese Communist Party
Baidu Scholar is free to use.
#25. PubMed Central
PubMed is a free search engine that provides references and abstracts for medical, life sciences, and biomedical topics.
If you’re studying anything related to healthcare or science, this site is perfect. PublicMed Central is operated by the National Center for Biotechnology Information, a division of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. It contains more than 3 million full-text journal articles.
It’s similar to PubMed Health, which focuses on health-related research and includes abstracts and citations to over 26 million articles.
#26. MEDLINE®
MEDLINE® is a paid subscription database for life sciences and biomedicine that includes more than 28 million citations to journal articles. For finding reliable, carefully chosen health information, Medline Plus provides a powerful search tool and even a dictionary.
- A great database for life sciences and biomedicine.
- Contains more than 28 million references to journal articles.
- References can be filtered by date, type of document, and language.
- The database is expensive to access.
- Some people find it difficult to navigate and find what they are looking for.
MEDLINE is not free to use ( pricing information ).
Defunct Academic Search Engines
#27. microsoft academic .
Microsoft Academic
Microsoft Academic Search seemed to be a failure from the beginning. It ended in 2012, then re-launched in 2016 as Microsoft Academic. It provides the researcher with the opportunity to search academic publications,
Microsoft Academic used to be the second-largest academic search engine after Google Scholar. Microsoft Academic provides a wealth of data for free, but Microsoft has announced that it will shut Microsoft Academic down in by 2022.
#28. Scizzle
Designed to help researchers stay on top of the literature by setting up email alerts, based on key terms, for newspapers.
Unfortunately, academic search engines come and go. These are two that are no longer available.
Final Thoughts
There are many academic search engines that can help researchers and scholars find the information they need. This list provides a variety of options, starting with more familiar engines and moving on to less well-known ones.
Keeping an open mind and exploring different sources is essential for conducting effective online research. With so much information at our fingertips, it’s important to make sure we’re using the best tools available to us.
Tell us in the comment below which academic search engine have you not heard of? Which database do you think we should add? What database do your professional societies use? What are the most useful academic websites for research in your opinion?
There is more.
Check out our other articles on the Best Academic Tools Series for Research below.
- Learn how to get more done with these Academic Writing Tools
- Learn how to proofread your work with these Proofreading Tools
- Learn how to broaden your research landscape with these Academic Search Engines
- Learn how to manage multiple research projects with these Project Management Tools
- Learn how to run effective survey research with these Survey Tools for Research
- Learn how get more insights from important conversations and interviews with Transcription Tools
- Learn how to manage the ever-growing list of references with these Reference Management Software
- Learn how to double your productivity with literature reviews with these AI-Based Summary Generators
- Learn how to build and develop your audience with these Academic Social Network Sites
- Learn how to make sure your content is original and trustworthy with these Plagiarism Checkers
- Learn how to talk about your work effectively with these Science Communication Tools
10 thoughts on “28 Best Academic Search Engines That make your research easier”
Thank you so much Joannah..I have found this information useful to me as librarian in an academic library
You are welcome! We are happy to hear that!
Thank You Team, for providing a comprehensive list of academic search engines that can help make research easier for students and scholars. The variety of search engines included offers a range of options for finding scholarly articles, journals, and other academic resources. The article also provides a brief summary of each search engine’s features, which helps in determining which one is the best fit for a specific research topic. Overall, this article is a valuable resource for anyone looking for a quick and easy way to access a wealth of academic information.
Thank you for taking the time to share your feedback with us. We are delighted to hear that you found our list of academic search engines helpful in making research easier for students and scholars. We understand the importance of having a variety of options when it comes to finding scholarly articles, journals, and other academic resources, and we strive to provide a comprehensive list of resources to meet those needs.
We are glad that you found the brief summary of each search engine’s features helpful in determining which one is the best fit for a specific research topic. Our goal is to make it easy for our readers to access valuable academic information and we’re glad that we were able to achieve that for you.
We appreciate your support and thank you for your kind words. We will continue to provide valuable resources for students and researchers in the future. Please let us know if you have any further questions or suggestions.
No more questions Thank You
I cannot thank you enough!!! thanks alot 🙂
Typography animation is a technique that combines text and motion to create visually engaging and dynamic animations. It involves animating individual letters, words, or phrases in various ways to convey a message, evoke emotions, or enhance the visual impact of a design or video. – Typography Animation Techniques Tools and Online Software {43}
Hi Joannah! Here’s another one you may want to add! Expontum ( https://www.expontum.com/ ) – Helps researchers quickly find knowledge gaps and identify what research projects have been completed before. Thanks!
Expontum – Helps researchers quickly find knowledge gaps and identify what research projects have been completed before. Expontum is free, open access, and available to all globally with no paid versions of the site. Automated processes scan research article information 24/7 so this website is constantly updating. By looking at over 35 million research publications (240 million by the end of 2023), the site has 146 million tagged research subjects and 122 million tagged research attributes. Learn more about methodology and sources on the Expontum About Page ( https://www.expontum.com/about.php )
Hey Ryan, I clicked and checked your site and thought it was very relevant to our reader. Thank you for sharing. And, we will be reviewing your site soon.
Sounds good! Thanks, Joannah!
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
We maintain and update science journals and scientific metrics. Scientific metrics data are aggregated from publicly available sources. Please note that we do NOT publish research papers on this platform. We do NOT accept any manuscript.
2012-2024 © scijournal.org
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

Best Academic Search Engines [2024]

Table of Contents
Gone are the days when researchers used to spend hours in the library skimming through endless reference books and resources. Now, thanks to academic search engines — with just a few clicks, researchers can access an extensive amount of information at their fingertips.
However, not all search engines are designed to make the research discovery process easier. It varies from one search engine to another, few might not have updated their database to the latest articles, while others might still provide older articles as a result of your search keyword or topic, and so on. This way, half of the researcher’s time is consumed shortlisting the best academic search engines.
Therefore, to help you choose the best search engine for academic research, we’ve crafted this blog. In this article, we will explore the best academic search engines available and why they are essential for scholars, researchers, and students alike.
Introduction to Academic Search Engines
Academic search engines are online repositories or databases that host millions of research articles and allow users to find relevant scholarly articles, research publications, conference proceedings, and other academic resources. Unlike web search engines like Google or Bing, these platforms are specifically designed to provide accurate, reliable, and relevant academic content.
These search engines often have advanced features that help users filter their search results based on specific criteria. For example, SciSpace helps you filter the results based on author, publication date, PDF, open-access, and more. In addition, it also provides citation information, abstracts, and full-text access to research papers and other scholarly literature, making them invaluable tools for scholars and researchers.
Academic search engines play a crucial role in the research process by providing scholars with easy access to relevant and reliable information. They save researchers valuable time by eliminating the need to sift through irrelevant search results and provide them with free access to a focused pool of academic resources.
With their advanced features and comprehensive coverage, these academic databases empower researchers to stay at the forefront of their fields and contribute to the advancement of knowledge.
Benefits of using reliable academic search engines for research
When it comes to academic research, using reliable search engines is of utmost importance. The credibility and quality of the sources you rely on can significantly impact the results of your research findings and conclusions.
Here are the potential advantages of using a popular search engine!
1. Reliable scholarly source: By using an academic search engine, researchers can ensure that the information they find is from reputable sources. These academic databases typically index content from scholarly journals, universities, research institutions, and other reliable and cited sources. As a result, the risk of using incorrect or biased information, which is prevalent on the open web, is significantly reduced.
2. Increased exposure to enormous articles: With a reliable academic search engine, you can access a vast array of scholarly articles and research publications. These search engines have extensive academic databases that include articles from various disciplines, including science and social sciences, allowing researchers to explore a wide range of topics and find relevant studies to support their research.
3. Advanced search filters: Reliable academic search engines often provide advanced search features that enable researchers to refine their search queries and narrow down the results to find the most relevant and latest information. These features may include filters for publication date, author, journal, and citation count, among others. By utilizing these advanced search terms and options, researchers can save time and effort by quickly finding the most pertinent resources.
4. Access full-text journal articles: Another advantage of using search engine for academic research is the ability to access full-text scientific articles. Many academic search engines provide direct links to the full text of articles, either freely available or through institutional subscriptions. This ensures that researchers can read and analyze the complete article, rather than relying on abstracts or TL;DR summaries.
5. Additional tools support: The most reliable search engines for research like SciSpace offer additional tools and features to enhance the research workflow. These may include citation generators, reference management systems, and options to save and organize search results. These tools can greatly facilitate the organization and the citation analysis of sources, making the research process more efficient and systematic.
Best search engines for research
Now that we’ve understood the importance of using reliable search engines for academic research, let's explore some of the best academic literature search engines available:
1. SciSpace

SciSpace is considered the best academic search engine that hosts and provides free access to a comprehensive index of 300 million+ scholarly articles from various fields. It utilizes advanced algorithms to provide users with highly relevant search results. Its intuitive and user-friendly interface makes it ideal for both novice and experienced researchers to navigate millions of research papers with no mess around.
One of the standout features of SciSpace is its “ Trace feature ” which allows users to find relevant research papers based on the preferred criteria including citation counts, related publications, references, authors, and more. It helps you land on the right research paper based on your preferences or research needs.
SciSpace is the only search engine that not only helps you discover relevant scholarly scientific literature but also allows you to read a research paper using its AI research assistant, conduct a literature review, and generate accurate citations for your research publications. It is an all-in-one platform that accelerates your research workflow with its AI-powered tools. You can explore all of them here
2. Google Scholar

Google Scholar is undoubtedly one of the popular search engines. With its vast database of scholarly literature, Google Scholar allows users to search for articles, theses, books, and conference papers across multiple academic disciplines. Google Scholar helps users save their search queries and set up email alerts for new publications in their field of interest. This ensures that researchers stay up-to-date with the latest developments in their respective fields.
PubMed is a go-to academic search engine for those in the field of medicine and life sciences. Developed by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), PubMed provides access to a vast collection of medicine, biomedical, health sciences, or literature, including journals, clinical trials, and scientific articles. Its meticulously curated articles makes it a trusted resource for medical professionals, scientists, researchers, and students alike.

Scopus is a comprehensive database of science that covers a wide range of scholarly literature across multiple disciplines. It offers a vast collection of peer reviewed articles, including publications, conference papers, and patents. With its extensive coverage and powerful search capabilities, Scopus is a valuable tool for researchers looking to explore the latest developments in their respective fields.
JSTOR is a repository that provides access to a vast collection of academic journals, books, and primary sources. Its interdisciplinary approach makes it a valuable resource for researchers across various fields of study.
6. IEEE Xplore
IEEE Xplore is a premier academic search engine for those in the fields of engineering, computer science, and technology. It provides access to a vast collection of technical articles, conference papers, and standards published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE).
IEEE Xplore is a treasure trove of knowledge for researchers and engineers looking to stay at the forefront of technological advancements.
Criteria for choosing the best academic search engine
With so many free academic search engines to choose from, it can be challenging to determine which one is the best fit for your research needs. Here are some criteria to consider when selecting an academic search engine:
- Relevance: The search engine should provide highly relevant search results that are specific to your area of study.
- Database size: A larger database gives you access to a broader range of scientific literature.
- Advanced search capabilities: Look for search engines that offer advanced search filters, allowing you to refine your search based on specific criteria.
- User-friendly interface: A user-friendly interface makes it easier for researchers to navigate and retrieve the information they need efficiently.
- Accessibility: Consider the availability of full-text or PDF access to articles and the ease of obtaining the necessary permissions to cite or use the content.
In conclusion, academic search engines play a vital role in scholarly communication, facilitating efficient and reliable academic research. They provide scholars, researchers, and students with access to a vast array of scholarly articles, research papers, and other academic resources. By using the best academic search engines, researchers can ensure that their research is backed by evidence (accurate and trustworthy information).
While each search engine has its own unique features and strengths, the key is to choose the one that best aligns with your research needs and preferences. Remember to utilize advanced search filters, explore related articles and citations, and keep your research well-organized for maximum efficiency. As technology continues to advance, we can expect academic search engines to evolve and provide even more innovative solutions to the challenges faced in academic research.
So, embrace these powerful tools, explore the above-featured academic search engines, and let us know which tool you are clinging to!
Frequently Asked Questions
Google Scholar, SciSpace, PubMed, and JSTOR are widely used tools for academic research.
Academic search engineinvolves an in-depth examination of scholarly sources with a rigorous approach, while a Google search engine explores a wider range of web content, including non-academic sources, with varying levels of reliability.
They provide a comprehensive overview of existing research on diverse topics aiding researchers in conducting an efficient literature review without investing more time.
A few more good reads for you!
Elevate Your Writing Game With AI Grammar Checker Tools
How To Humanize AI Text In Scientific Articles
A Guide to Using AI Tools to Summarize Literature Reviews
AI for Essay Writing — Exploring Top 10 Essay Writers
Role of AI in Systematic Literature Review
You might also like

AI for Meta Analysis — A Comprehensive Guide

Cybersecurity in Higher Education: Safeguarding Students and Faculty Data

How To Write An Argumentative Essay

Table of Contents

- November 2, 2023
10 Educational Search Engines for Students: From Homework to High-Quality Resources
Educational Search Engines are specialised search engines for finding scholarly and academic information. Students need to cite reputable sources for their research papers or other academic assignments. Usual search engines are good for navigating the vast internet. However, it becomes difficult to find reputable sources such as research papers and clinical trials.
The article mentions the top 10 educational search engines for students, such as Google Scholar, Google Books, Microsoft Academic, WorldWideScience, Educational Resources Information Center (ERIC), Virtual Learning Resources Center (VLRC), ResearchGate, PubMed Central, Infotopia, and Science.gov.
1. Google Scholar
Google Scholar was created by Google to create a database of scholarly literature from the web. Students can find different scholarly literature, such as peer-reviewed papers, theses, books, research papers, clinical trials, and discoveries from many different academic institutions and organisations.
2. Google Books
Google Books was created by Google to browse the index containing thousands of books from various authors and publications. You can search books using the title, author, publication, and ISBN number. It stores information such as reviews, where to buy, sample pages, and entire book information for certain books.
3. Microsoft Academic
Microsoft Academic was created by Microsoft for storing over 120 million publications in its database and allowing students to search scientific papers, research, journals, and conferences.
4. WorldWideScience
WorldWideScience is managed by the U.S. Department of Energy. It searches databases from more than 70 countries for academic resources. You can search for both English and translated academic resources.
5. Educational Resources Information Center (ERIC)
The Educational Resources Information Center (ERIC) is managed by the U.S. Department of Education. ERIC has over 1.3 million bibliographic educational literature.
6. Virtual Learning Resources Center (VLRC)
Virtual Learning Resources Center (VLRC) is an online index of academic resources. It is an alternative to Google Scholar. The index stores the websites reviewed by librarians and teachers on topics such as Art, Social sciences, Social Issues, and History.
7. ResearchGate
ResearchGate is a social networking website for scientists and researchers. It has over 11 million researchers who share their work. The users can share research papers, do projects together, find experts in a particular field, and ask questions.
8. PubMed Central
PubMed Central (PMC) is a free and open-access digital library of academic articles, such as medical research, clinical trials, and analytical studies. These resources are published in biomedical and life sciences journals.
9. Infotopia
Infotopia is a free educational search engine optimized for students and teachers. It is based on Google searches and searches from websites reviewed by librarians and teachers. It covers various topics, such as Sci/Tech, Images, Games, Health, and mythology.
10. Science.gov
Science.gov is a free search engine that searches for information from 13 federal agencies, including the Department of Homeland Security, U.S. Geological Survey, Department of Transportation, Environmental Protection Agency, Government Publishing Office, National Aeronautics and Space Administration, and National Science Foundation. It has an index of over 2200 scientific websites and 70 scientific databases.
Final Words
Educational Search Engines for Students provide access to various academic resources to students, including research papers, medical studies, books, clinical trials, studies from scholars, and theses. The top 10 educational search engines include Google Scholar, Google Books, Microsoft Academic, Science.gov, PubMed Central, Researchgate, and others. Each search engine has its own index and database of academic resources and searches through them.
Utilizing the internet effectively for college students involves discerning credible sources, leveraging online tools for research, and fostering digital literacy to maximize learning opportunities and academic resources.

Emily Watson
Recent posts.

Scholarships for Working Moms in 2024

Associate Degree vs Bachelor’s Degree

11 Main Reasons Why Students Drop out of College

At Back2College, we’re firm believers that the pursuit of knowledge is an ageless odyssey.

We use cookies on our website to support technical features that enhance your user experience, and to help us improve our website. By continuing to use this website, you accept our privacy policy .
- Student Login
- No-Cost Professional Certificates
- COVID-19 Response
- Call Us: 888-549-6755
- 888-559-6763
- Search site Search our site Search Now Close
- Request Info
Skip to Content (Press Enter)
15 Educational Search Engines College Students Should Know About
By Anna Heinrich on 03/22/2017

After hours spent scrolling through Google and pulling up endless clickbait results, you’re frustrated with the internet. You have a paper to write, homework to do and things to learn—and this degree isn’t going to earn itself. You know you won’t get away with citing Wikipedia or Buzzfeed in your research paper. Even the big news engines aren’t scholarly enough. You need reputable sources for your homework, and you need them now.
With so many resources online, it’s hard to narrow it down and find ones that are not only reliable and useful, but also free for students. We’ve saved you the time and picked out our 15 best free search engines for research.
15 Scholarly search engines every student should bookmark
1. google scholar.
Google Scholar was created as a tool to congregate scholarly literature on the web. From one place, students have the ability to hunt for peer-reviewed papers, theses, books, abstracts and articles from academic publishers, professional societies, preprint repositories, universities and other scholarly organizations.
2. Google Books
Google Books allows web users to browse an index of thousands of books, from popular titles to old, to find pages that include your search terms. Once you find the book you are looking for, you can look through pages, find online reviews and learn where you can get a hard copy.
3. Microsoft Academic
Operated by the company that brings you Word, PowerPoint and Excel, Microsoft Academic is a reliable, comprehensive research tool. The search engine pulls content from over 120 million publications, including scientific papers, conferences and journals. You can search directly by topic, or you can search by an extensive list of fields of study. For example, if you’re interested in computer science, you can filter through topics such as artificial intelligence, computer security, data science, programming languages and more.
4. WorldWideScience
WorldWideScience , which refers to itself as “The Global Science Gateway,” is operated by the Office of Scientific and Technical Information—a branch of the Office of Science within the U.S. Department of Energy. The site utilizes databases from over 70 countries. When users type a query, it hits databases from all over the world and will display both English and translated results from related journals and academic resources.
5. Science.gov
Science.gov is operated and maintained by the Office of Science and Technical Information, the same department that collaborates on WorldWideScience.org. This search engine pulls from over 60 databases, over 2,200 websites and 200 million pages of journals, documents and scientific data. Search results can be filtered by author, date, topic and format (text or multimedia).
6. Wolfram Alpha
A self-described “computational knowledge engine,” Wolfram Alpha does not so much provide search results as it does search answers. Simply type in a topic or question you may be interested in, such as, “What is the function of the pancreas?” and the answer will show up without making you scroll through pages of results. This is especially handy for those in need of math help.
With its minimalist design, Refseek doesn’t look like much. However, the engine pulls from over one billion web pages, encyclopedias, journals and books. It is similar to Google in its functionality, except that it focuses more on scientific and academic results—meaning more results will come from .edu or .org sites, as well as online encyclopedias. It also has an option to search documents directly—providing easy access to PDFs of academic papers.
8. Educational Resources Information Center
Populated by the U.S. Department of Education, the Educational Resources Information Center (ERIC) is a great tool for academic research with more than 1.3 million bibliographic records of articles and online materials. ERIC provides access to an extensive body of education-related literature including journal articles, books, research syntheses, conference papers, technical reports, policy papers and more. With more than eight million searches each month, it’s no wonder why this search engine is a great web source for education.
9. Virtual Learning Resources Center
The Virtual Learning Resources Center (VLRC) is an online index hosting thousands of scholarly websites, all of which are selected by teachers and librarians from around the globe. The site provides students and teachers with current, valid information for school and university academic projects using an index gathered from research portals, universities and library internet subject guides recommended by teachers and librarians.
iSeek is a great search engine for students, teachers and administrators alike. Simply ask a question or enter search topics or tools, and iSeek will pull from scholastic sources to find exactly what you are looking for. The search engine is safe, intelligent and timesaving—and it draws from trusted resources from universities, government and established non-commercial sites.
11. ResearchGate
ResearchGate is a unique social networking site for scientists and researchers. Over 11 million researchers submit their work, which totals more than 100 million publications, on the site for anyone to access. You can search by publication, data and author, or you can even ask the researchers questions. Though it’s not a search engine that pulls from external sources, ResearchGate’s own collection of publications provides a hearty selection for any inquisitive scholar.
The Bielefeld Academic Search Engine (BASE) prides itself as being “one of the world’s most voluminous search engines especially for academic web resources.” Utilizing 4,000 sources, the site contains results from over 100 million documents. The advanced search option allows users to narrow their research—so whether you’re looking for a book, review, lecture, video or thesis, BASE can provide the specific format you need.
13. Infotopia
Infotopia describes itself as a “Google-alternative safe search engine.” The academic search engine pulls from results that have been curated by librarians, teachers and other educational workers. A unique search feature allows users to select a category, which ranges from art to health to science and technology, and then see a list of internal and external resources pertaining to the topic. So if you don’t find what you’re looking for within the pages of Infotopia, you will probably find it in one of its many suggested sites.
14. PubMed Central
This site is perfect for those studying anything related to healthcare or science. PubMed Central is operated by the National Center for Biotechnology Information, a division of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. The database contains more than 3 million full-text journal articles. It’s similar to PubMed Health , which is specifically for health-related research and studies, and includes citations and abstracts to more than 26 million articles.
15. Lexis Web
Researching legal topics? Lexis Web is your go-to for any law-related inquiries you may have. The results are drawn from legal sites, which can be filtered by criteria such as news, blog, government and commercial. Users can also filter results by jurisdiction, practice area, source and file format.
Start searching
Pulling up an Internet search might be second nature to you by now. But a little forethought into where you begin your hunt can make your life much easier. Save yourself the time wading through basic Google search results and utilize some of these tools to ensure your results will be up to par with academic standards.
As a student at Rasmussen University, you’ll have access to library resources and librarians to help you with your research or writing for any of our classes. Visit our student experience page to learn more about the support you’ll have at Rasmussen University.
EDITOR’S NOTE: This article was originally published in December 2009. It has since been updated to include information relevant to 2017.
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on Pinterest
- Share on LinkedIn
Request More Information
Talk with an admissions advisor today. Fill out the form to receive information about:
- Program Details and Applying for Classes
- Financial Aid and FAFSA (for those who qualify)
- Customized Support Services
- Detailed Program Plan
There are some errors in the form. Please correct the errors and submit again.
Please enter your first name.
Please enter your last name.
There is an error in email. Make sure your answer has:
- An "@" symbol
- A suffix such as ".com", ".edu", etc.
There is an error in phone number. Make sure your answer has:
- 10 digits with no dashes or spaces
- No country code (e.g. "1" for USA)
There is an error in ZIP code. Make sure your answer has only 5 digits.
Please choose a School of study.
Please choose a program.
Please choose a degree.
The program you have selected is not available in your ZIP code. Please select another program or contact an Admissions Advisor (877.530.9600) for help.
The program you have selected requires a nursing license. Please select another program or contact an Admissions Advisor (877.530.9600) for help.
Rasmussen University is not enrolling students in your state at this time.
By selecting "Submit," I authorize Rasmussen University to contact me by email, phone or text message at the number provided. There is no obligation to enroll. This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
About the author
Anna Heinrich
Anna is a Copywriter at Collegis Education who researches and writes student-focused content on behalf of Rasmussen University. She believes the power of the written word can help educate and assist students on their way to a rewarding education.

Posted in Student Success
- college student tips
- college student resources
- college life
Related Content

Brianna Flavin | 05.23.2023

Jordan Jantz | 08.01.2022

Kirsten Slyter | 05.30.2022

Carrie Mesrobian | 02.28.2022
This piece of ad content was created by Rasmussen University to support its educational programs. Rasmussen University may not prepare students for all positions featured within this content. Please visit www.rasmussen.edu/degrees for a list of programs offered. External links provided on rasmussen.edu are for reference only. Rasmussen University does not guarantee, approve, control, or specifically endorse the information or products available on websites linked to, and is not endorsed by website owners, authors and/or organizations referenced. Rasmussen University is accredited by the Higher Learning Commission, an institutional accreditation agency recognized by the U.S. Department of Education.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Working with sources
How to Find Sources | Scholarly Articles, Books, Etc.
Published on June 13, 2022 by Eoghan Ryan . Revised on May 31, 2023.
It’s important to know how to find relevant sources when writing a research paper , literature review , or systematic review .
The types of sources you need will depend on the stage you are at in the research process , but all sources that you use should be credible , up to date, and relevant to your research topic.
There are three main places to look for sources to use in your research:
Research databases
- Your institution’s library
- Other online resources
Table of contents
Library resources, other online sources, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about finding sources.
You can search for scholarly sources online using databases and search engines like Google Scholar . These provide a range of search functions that can help you to find the most relevant sources.
If you are searching for a specific article or book, include the title or the author’s name. Alternatively, if you’re just looking for sources related to your research problem , you can search using keywords. In this case, it’s important to have a clear understanding of the scope of your project and of the most relevant keywords.
Databases can be general (interdisciplinary) or subject-specific.
- You can use subject-specific databases to ensure that the results are relevant to your field.
- When using a general database or search engine, you can still filter results by selecting specific subjects or disciplines.
Example: JSTOR discipline search filter

Check the table below to find a database that’s relevant to your research.
Google Scholar
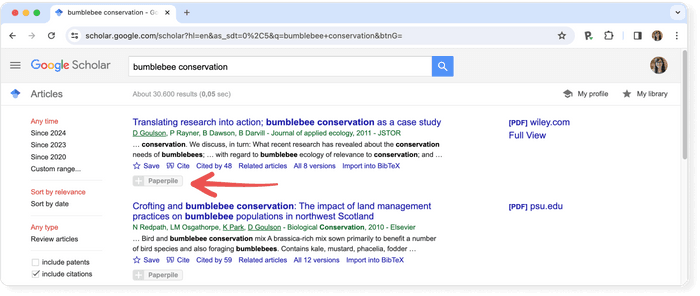
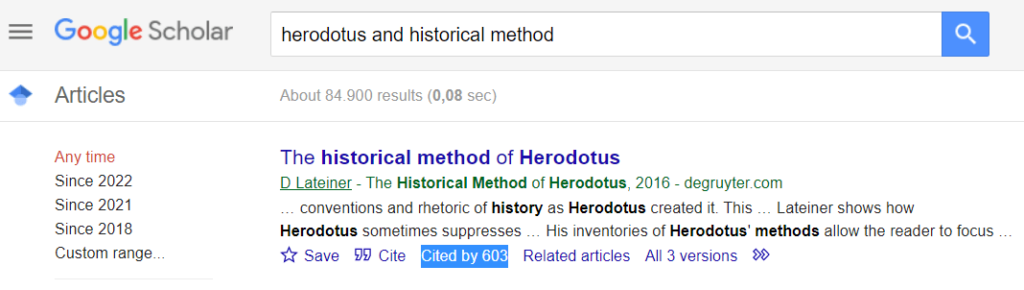
To get started, you might also try Google Scholar , an academic search engine that can help you find relevant books and articles. Its “Cited by” function lets you see the number of times a source has been cited. This can tell you something about a source’s credibility and importance to the field.
Example: Google Scholar “Cited by” function
Boolean operators
Boolean operators can also help to narrow or expand your search.
Boolean operators are words and symbols like AND , OR , and NOT that you can use to include or exclude keywords to refine your results. For example, a search for “Nietzsche NOT nihilism” will provide results that include the word “Nietzsche” but exclude results that contain the word “nihilism.”
Many databases and search engines have an advanced search function that allows you to refine results in a similar way without typing the Boolean operators manually.
Example: Project Muse advanced search

The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
You can find helpful print sources in your institution’s library. These include:
- Journal articles
- Encyclopedias
- Newspapers and magazines
Make sure that the sources you consult are appropriate to your research.
You can find these sources using your institution’s library database. This will allow you to explore the library’s catalog and to search relevant keywords. You can refine your results using Boolean operators .
Once you have found a relevant print source in the library:
- Consider what books are beside it. This can be a great way to find related sources, especially when you’ve found a secondary or tertiary source instead of a primary source .
- Consult the index and bibliography to find the bibliographic information of other relevant sources.
You can consult popular online sources to learn more about your topic. These include:
- Crowdsourced encyclopedias like Wikipedia
You can find these sources using search engines. To refine your search, use Boolean operators in combination with relevant keywords.
However, exercise caution when using online sources. Consider what kinds of sources are appropriate for your research and make sure the sites are credible .
Look for sites with trusted domain extensions:
- URLs that end with .edu are educational resources.
- URLs that end with .gov are government-related resources.
- DOIs often indicate that an article is published in a peer-reviewed , scientific article.
Other sites can still be used, but you should evaluate them carefully and consider alternatives.
If you want to know more about ChatGPT, AI tools , citation , and plagiarism , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- ChatGPT vs human editor
- ChatGPT citations
- Is ChatGPT trustworthy?
- Using ChatGPT for your studies
- What is ChatGPT?
- Chicago style
- Paraphrasing
Plagiarism
- Types of plagiarism
- Self-plagiarism
- Avoiding plagiarism
- Academic integrity
- Consequences of plagiarism
- Common knowledge
You can find sources online using databases and search engines like Google Scholar . Use Boolean operators or advanced search functions to narrow or expand your search.
For print sources, you can use your institution’s library database. This will allow you to explore the library’s catalog and to search relevant keywords.
It is important to find credible sources and use those that you can be sure are sufficiently scholarly .
- Consult your institute’s library to find out what books, journals, research databases, and other types of sources they provide access to.
- Look for books published by respected academic publishing houses and university presses, as these are typically considered trustworthy sources.
- Look for journals that use a peer review process. This means that experts in the field assess the quality and credibility of an article before it is published.
When searching for sources in databases, think of specific keywords that are relevant to your topic , and consider variations on them or synonyms that might be relevant.
Once you have a clear idea of your research parameters and key terms, choose a database that is relevant to your research (e.g., Medline, JSTOR, Project MUSE).
Find out if the database has a “subject search” option. This can help to refine your search. Use Boolean operators to combine your keywords, exclude specific search terms, and search exact phrases to find the most relevant sources.
There are many types of sources commonly used in research. These include:
You’ll likely use a variety of these sources throughout the research process , and the kinds of sources you use will depend on your research topic and goals.
Scholarly sources are written by experts in their field and are typically subjected to peer review . They are intended for a scholarly audience, include a full bibliography, and use scholarly or technical language. For these reasons, they are typically considered credible sources .
Popular sources like magazines and news articles are typically written by journalists. These types of sources usually don’t include a bibliography and are written for a popular, rather than academic, audience. They are not always reliable and may be written from a biased or uninformed perspective, but they can still be cited in some contexts.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Ryan, E. (2023, May 31). How to Find Sources | Scholarly Articles, Books, Etc.. Scribbr. Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/working-with-sources/finding-sources/
Is this article helpful?

Eoghan Ryan
Other students also liked, types of sources explained | examples & tips, primary vs. secondary sources | difference & examples, boolean operators | quick guide, examples & tips, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

- Board Members
- Management Team
- Become a Contributor
- Volunteer Opportunities
- Code of Ethical Practices
KNOWLEDGE NETWORK
- Search Engines List
- Suggested Reading Library
- Web Directories
- Research Papers
- Industry News

- Become a Member
- Associate Membership
- Certified Membership
- Membership Application
- Corporate Application

- CIRS Certification Program
- CIRS Certification Objectives
- CIRS Certification Benefits
- CIRS Certification Exam
- Maintain Your Certification

- Upcoming Events
- Live Classes
- Classes Schedule
- Webinars Schedules

- Latest Articles
- Internet Research
- Search Techniques
- Research Methods
- Business Research
- Search Engines
- Research & Tools
- Investigative Research
- Internet Search
- Work from Home
- Internet Ethics
- Internet Privacy
Top 9 Education Search Engines for Students

Research is the most critical step when writing an academic paper. It’s nearly impossible for students to impress and inspire the assessor with their academic paper if it’s not well-researched. It needs to contain authentic and genuine information for credibility, and that requires a credible source with authoritative reference materials.
Research is the foundation of successful academic work. However, navigating the vast sea of information can be a difficult task for students. Any student sooner or later wonders: "Who could help me write my research paper ?" and this is where professional research paper writing help services come in. These services offer a selection of educational materials and professional writers who carefully select and systematize information for you. By availing such services, students can be sure that their research papers are well-researched and delivered in the best possible way.
We both know that you can’t get away with citing WikiHow, Hubspot, or Wikipedia in your research paper. So what’s next? You need a list of search engines for students which will provide credible and authentic scholarly material for your use and reference – and for that, we’ve got you covered. Below is a list of the top 9 Education Search Engines for Students that you will find rich in authoritative, accurate, and credible information for your academic projects and assignments.
If for some reason you still can’t find what you’re looking for or you are overloaded with other research papers or essays and still want to provide high-quality work with credible resources, you may try a custom writing service like www.copycrafter.net/custom-writing . CopyCrafter company has qualified and experienced authors that will deliver high-quality custom essays or research papers on pretty much any subject area. And for now, you may try it yourself, with the help of the following resources:
List of Best 9 Education Search Engines
1. google scholar.
Google Scholar is a free, customized academic search engine designed specifically for students, tutors, researchers and anyone interested in academic materials. It’s the most popular research search engine for students and it lists academic resources across a wide range of sources. It allows students and researchers to find credible information, research papers and search journals, and save them in their personal library.
2. iSEEK- Education
iSeek is another widely used and one of the best search engines for students, educators, and scholars. It’s a reliable, smart, and safe tool for your academic research and paper writing. Since the search engine was specially designed with students, educators, and researchers in mind, you will be able to find credible and relevant resources that will ultimately save your time.
3. Microsoft Academic Research
4. content-writing.net :.
This is the latest technology that helps students with their content writing needs. Whether you need to write an essay, a report, a blog post, or any other type of content, content-writing.net can assist you with its AI technology. You can use content-writing.net to generate ideas, outlines, titles, summaries, and even full texts for your content. You can also use it to check your grammar, spelling, and plagiarism. It is a useful tool for students who want to improve their content writing skills and save time and effort.
5. ResearchGate
If you’re a science major, you will love ResearchGate. In fact, chances are you’ve already searched for certain academic topics in Google and ended up on the ResearchGate platform. It’s a networking site for students, researchers, and scientists and provides access to more than 100 million publications and over 15 million researchers. Other than accessing the information, the platform also lets you ask researchers questions.
6. Wolfram Alpha
Wolfram Alpha presents itself as a computational knowledge engine’ that provides results as answers. All you need is to type in the question or topic that you’re interested in like “What is the diameter of the observable universe?” and the answer will pop up. The best part is it doesn’t make you scroll through tens of pages of results. It doesn’t present search results as the other engines, but it’s great for students looking for quick, snappy answers to bits of questions as they go about their assignments and projects.

7. ScienceDirect
RefSeek employs a minimalistic design, which doesn’t look like much at first, but there is a lot going on in the background. It’s probably the most aggressive search engine for students as it pulls from more than 1 billion journals, research papers, books, encyclopedias, and web pages. It works more or less like Google, but it only focuses on or academic and scientific results without the distraction of paid links. So you can expect the most results from the .edu and .org sites.
9. Educational Resources Information Center (ERIC)
ERIC is a reliable and informative online digital library that is populated and maintained by the U.S. Department of Education. The platform provides academic and educational resources for educators, students, and researchers with over 1.3 million publications. Students can find materials such as books, research papers, journals, technical reports, policy papers, dissertations, conference papers, and so on. The platform receives over eight million searches per month, meaning it’s a reliable and authoritative source of academic and research information.
10. The Virtual Learning Resources Center (Virtual LRC)
Virtual LRC is a search engine for college students which allows students to search and explore educational websites with authoritative and high-quality information. The search engine indexes thousands of scholarly and academic information sites ensuring that you get the most refined and relevant results. The platforms and the results you get have been organized by researchers, library professionals, and teachers around the globe to ensure that students easily get resources for their projects and academic assignments.
The above-named directories and databases are among the most trusted and highly reputable search engines for students to find credible, authoritative, and reliable academic resources. They offer information and references on all subject areas including chemistry, biology, physics, business, social science, mathematics, computer and technology, and environmental science.
Live Classes Schedule
World's leading professional association of Internet Research Specialists - We deliver Knowledge, Education, Training, and Certification in the field of Professional Online Research. The AOFIRS is considered a major contributor in improving Web Search Skills and recognizes Online Research work as a full-time occupation for those that use the Internet as their primary source of information.
Get Exclusive Research Tips in Your Inbox
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- Advertising Opportunities
- Knowledge Network

- Richard G. Trefry Library
Q. Where can I find a good website to use for my assignment?

- Course-Specific
- Textbooks & Course Materials
- Tutoring & Classroom Help
- Writing & Citing
- 44 Articles & Journals
- 11 Capstone/Thesis/Dissertation Research
- 37 Databases
- 56 Information Literacy
- 9 Interlibrary Loan
- 9 Need help getting started?
- 22 Technical Help
Answered By: APUS Librarians Last Updated: Jun 13, 2023 Views: 27430
Remember that many open websites are not scholarly .
- Always double-check with your instructor to be sure that you are allowed to use websites for your assignment.
- Be sure that you know how to recognize a credible, authoritative website .
1. Take a few minutes to identify the best keywords . This may seem too simple a step to bother with, but it's a common stumbling block for many researchers.
- Narrow keywords often work best, especially when your searches are bringing you too many irrelevant sites.
- Sometimes, though, you'll need to broaden your search to find a more general (but related) website that you can then search within for your more specific topic .
2. Don't get stuck on Google (or any other single search engine). Here are the librarians' favorite web search spots:
- Use library's subject pages . Each pages includes a "websites" section, and each link was chosen by a librarian, so you can feel confident that they're trustworthy. (Note that you may need to click a website, then search within it for a page that fits your topic.)
- Browse the library's open access research guide. It compiles links to all of the best free scholarly and educational sites.
- Search Google smarter. Use the " advanced search " to limit your results to .edu, .gov or .org domains, which tend to be more authoritative than .com sites. Google Scholar is another fantastic place to do research (and you can set it up to show you links from our library !).
- Target government information by topic at USA.gov .
- Look for discipline-specific search engines. We all love Google, but you can find search engines that target education (like iSeek ) or science (like ScienceResearch.com ), just to name a couple. Try googling "business search engine" (substitute the discipline that pertains to your topic, if it isn't business) and explore the results.
- Seek out professional organizations or associations related to your research topic. For example, if your topic is related to online learning, search for online learning association or online learning organization . You should see several to choose from -- click one, then search within it for your more specific keywords.
- If you come across a Wikipedia article for your topic, take a look at its references (scroll down to the bottom). Wikipedia, by itself, is not a good source to cite in a college-level assignment, but its articles will often link you to better sites or pages.
Need help? Contact us!
- Share on Facebook
Was this helpful? Yes 73 No 98
Related Topics
- Information Literacy
Need personalized help? Librarians are available 365 days/nights per year! See our schedule.

Learn more about how librarians can help you succeed.

10 Best Educational Search Engines for Students in 2023
What is the best educational search engine?
There are many search engines out there, but not all of them are created equal.
On the other hand, when it comes to finding educational information, over 75% of students have been using search engines to find information since junior high school, this is according to research carried out by IOPSCIENCE.
So practically, when using these search engines, most of us already know that we want to make sure we are using a reliable and reputable search engine . So how do you find one?
To help you out.
In this article, I’ll provide you with a compendium of the 10 best educational search engines for students in 2023. These search engines are guaranteed to help you find the answers you’re seeking in the most expeditious manner.
These search engines will also engender an easy path to your academic goals.
Let’s begin.
1. Google Scholar
Google Scholar is without a doubt one of the best search engines for students in 2023.
Without a doubt, It gives you an impressive array of features to make your academic endeavors much easier.
With access to millions of scholarly publications, easy-to-use tools that allow you to filter results by date and citation counts, and advanced search functions, you’d surely love Google Scholar.
In addition, its vast collection of online resources like peer-reviewed articles and books allows you to quickly find what you need with just a few clicks.
On top of all this, Google Scholar provides free access to many scientific papers and journals. Providing invaluable assistance when researching topics or looking for answers.
Even though its process looks identical to Google, this targeted search engine gives you access to multiple relevant studies from reliable sources, unlike Google which gives you an intuitive design with results that you are never sure are accurate.
All in all, it’s clear why so many students use Google Scholar as their primary source for research; it’s incredibly fast, efficient, and comprehensive. So it’s understandable if you choose it as your jumping-off point.
2. Microsoft Academic
Microsoft Academic is an excellent alternative to Google Scholar for students.
It offers a range of features that make academic research easier and faster, such as the ability to quickly search millions of scholarly publications and online resources.
Additionally, Microsoft Academic’s advanced search functions allow you to filter results by date and citation count, making it easy to find exactly what you need with minimal effort.
Not only does Microsoft Academic have everything you need for successful research, but it also gives you free access to many scientific papers and journals – something which can be incredibly helpful when researching difficult topics or seeking out answers.
What makes Microsoft Academic stand out as one of the best search engines for educational research is its ability to utilize semantic search. This ensures that its algorithm uses the actual meaning of words and phrases instead of using only selected keywords.
On top of that, this search engine uses filters to help you search more specifically. The filter criteria used range from institutions, journals, authors, papers, topics, and more.
When all’s said and done, it’s no surprise why you would turn to Microsoft Academic as your go-to resource; its speed, efficiency, and breadth of content are truly remarkable.
3. ResearchGate
ResearchGate is often considered one of the best search engines for students in this digital era.
This is due to its comprehensive capabilities and wide range of features.
Not only can you quickly access millions of scholarly publications, but you can also utilize advanced search functions of over 130 million publications filtered to narrow down your results.
Additionally, this search engine also offers free access to many scientific papers and journals which makes it invaluable when seeking answers from experts.
Trusted by over 15 million researchers, ResearchGate gives you an unparalleled breadth of content and efficiency that’s hard to match.
ResearchGate was founded by two physicians and a computer scientist back in 2008 and stands as a beacon for student researchers everywhere. On top of that, its versatility makes it ideal for both novice and experienced users, allowing you to easily find what you need with minimal effort.
However, this search engine encourages you to connect with users that express interest in your similar field. With that mentioned, you should note that ResearchGate is currently dominated by users providing and seeking news and information on medicine and biology.
For these reasons, ResearchGate remains at the top of the list when considering reliable search engines for students.
4. Educational Resource Information Center
The Educational Resource Information Center (ERIC) is widely regarded as one of the premier search engines for students in 2023.
It gives you unique access to a vast array of educational resources, from academic journals and articles to dissertations, conference proceedings, and policy documents.
Moreover, it has an intuitive user interface that allows you to easily locate relevant content with powerful tools like keyword search, date filtering, and subject categories.
With advanced features such as document citation reference linking, ERIC takes its place at the head of the class when compared to other search engines for students.
The sheer breadth and depth of information make ERIC a valuable asset for educators and researchers alike, allowing you to quickly find the right material no matter how difficult or niche the topic may be.
It also boasts a massive database that contains more than 1 million bibliographic records like citations and abstracts. On top of that, this best search engine for students contains resources from peer-reviewed journals which dominate its digital collection.
As such, ERIC stands out as one of the most reliable search engines for students in 2023 due to its efficient capabilities and abundant resources.
5. Semantic Scholar
Semantic Scholar has emerged as one of the best search engines for educational research in 2023.
Undoubtedly, it stands out from the competition due to its advanced features, such as an AI-powered citation system and natural language processing tools that make finding relevant content faster than ever before.
Moreover, Semantic Scholar provides robust access to a large repository of high-quality academic resources papers, and technical reports from various disciplines.
With its intuitive interface and powerful semantic search capabilities, you can effortlessly locate accurate information with specific keyword searches or broader subject filters. Furthermore, Semantic Scholar also provides extensive visualization tools that enable you to quickly analyze data trends across multiple disciplines.
I love this search engine because, with its AI-driven algorithm, it retrieves information from over 180 million scientific papers which are then linked to give you accurate answers to your queries.
What’s more, you can get more information on a topic from their topic pages, where you can review key definitions while also discovering the latest trends in contrast to your specific subject.
All in all, this comprehensive search engine is sure to empower you to easily find the content you need for research projects and coursework.
6. Virtual Learning Resources Center
The Virtual Learning Resources Center (VLRC) has rapidly become one of the most formidable search engines for students in this era.
The primary focus of this innovative platform is to give you easy access to academic materials, including research papers, technical reports, and multimedia resources.
With VLRC’s advanced AI-driven tools and natural language processing capabilities, you can quickly identify relevant content from vast databases with just a few clicks. Additionally, the intuitive user interface gives you an enhanced experience even if you are a novice searcher.
This gives you an opportunity to refine your searches by specific keywords or broader subject categories.
Furthermore, with its comprehensive visualization tools, you can quickly analyze data across different disciplines which helps you make sound decisions.
While at it, I should also mention that Virtual Learning Resources Center is an online index, offers hosting to thousands of scholarly websites. And most of these websites are handpicked by librarians and teachers from all over the world.
As such, VLRC stands out amongst other student search engines for providing powerful features that make accessing learning resources a breeze. Its unparalleled accuracy and efficiency have enabled it to emerge as one of the premier virtual learning resource centers available today.
RefSeek is a cutting-edge search engine for students in 2023.
With its powerful AI algorithms and natural language processing capabilities, RefSeek allows you to easily access relevant content from massive databases with just a few clicks.
This exceptional platform stands out amongst other student search engines by providing an intuitive user interface that enables refining searches by specific keywords or broader subject categories.
In addition, RefSeek’s comprehensive visualization tools offer quick data analysis across various disciplines, while searching more than 500 million web pages and educational materials to help you make more informed decisions.
As such, this state-of-the-art search engine has become one of the most sought-after virtual learning resource centers among today’s student population, due to its unmatched accuracy and efficiency.
It is also important to note that all the results that this search engine offers are more focused on education, academics, and science.
Moreover, RefSeek boasts advanced features such as personalized recommendations, customized filters, and predictive analytics that make navigating educational materials easier than ever before.
Thus, it is no surprise why RefSeek is widely regarded as one of the best search engines for students. So if you are looking for educational-related topics, Refseek is your go-to search engine.
8. Wolfram Alpha
Are you a student searching for a powerful, reliable search engine in 2023?
Well, Wolfram Alpha is an exceptional choice.
And here’s why. With its unique combination of advanced AI algorithms and natural language processing capabilities, this best search engine for educational research has set the bar high when it comes to finding relevant content quickly and accurately.
But that’s not all, Wolfram Alpha’s comprehensive database includes educational materials from numerous disciplines. So you can have access to a vast array of information sources.
Furthermore, just like ReSeek, this versatile platform offers intuitive user interfaces tools such as personalized recommendations, customized filters, and predictive analytics that make navigating large volumes of data easier than ever before.
By utilizing these innovative features, as a student, you can uncover useful knowledge and insights with unprecedented ease.
On the other hand, Wolfram Alpha not only provides you with a definition for words but also assists you in understanding the intricate nuances of English grammar. On top of that, this tool serves as an interactive dictionary and can even translate words into other languages
Without a doubt, Wolfram Alpha is one of the most invaluable virtual learning resources available, today due to its groundbreaking technology and unparalleled accuracy..
9. WorldWideScience
WorldWideScience is a powerful and reliable search engine for students.
With its advanced AI algorithms and natural language processing capabilities, WorldWideScience is a reliable, smart, and safe tool for academic research and paper writing that is frequently employed by students, educators, and scholars.
It also provides superior accuracy when finding relevant content from any discipline.
On the other hand, it was specifically constructed with you- the student in mind, to make it easier for you to uncover accurate and pertinent material that will save time.
And this is possible because of its intuitive user interface that makes navigating large volumes of data easier. Additionally, WorldWideScience boasts comprehensive database coverage and extensive educational materials for student researchers to access.
To top it all off, WorldWideScience is the perfect search engine for all types of users. So if you are a student, teacher, or administrator, then this is the search engine that you have been looking for.
If you are looking to get the most out of your searches, WorldWideScience is undoubtedly one of the best search engines available today. Its cutting-edge technology makes it easy to uncover useful knowledge and insights quickly and efficiently.
Also, with its safety features, intelligence, and time-saving capabilities, it’s an excellent choice for all your search needs.
10. ScienceDirect
ScienceDirect is another best search engines for educational research in this digital era.
It utilizes sophisticated AI algorithms, and natural language processing capabilities, to deliver when finding relevant content from any discipline.
With an intuitive user interface, personalized recommendations, customizable filters, and easy navigation of large volumes of data, ScienceDirect gives you a unique experience if you are looking to get the most out of your research.
Undoubtedly, the sheer breadth and depth of its database coverage make it a go-to destination for student researchers.
Whether it’s news articles, journals, or reference materials—it’s all accessible through ScienceDirect with ease. Moreover, its expansive selection of educational materials is sure to appeal to learners of all ages and backgrounds.
From webinars, guides, tutorials, and other resources to self-guided video courses and more.
Ultimately, it’s the best search engine available today if you are a student looking for the utmost precision and convenience for finding information on virtually any topic imaginable.
What’s more, ScienceDirect is an unmatched combination of technology and friendly searches that offer useful knowledge and insights quickly and efficiently.
Plus, with continuously updated content and new features added every day, ScienceDirect guarantees that you’ll never run out of ideas or stop learning.
These 10 Best Educational Search Engines for Students in 2023 offer a variety of resources and capabilities that are sure to meet your needs as a student.
Semantic Scholar stands out as a leader with its cutting-edge AI algorithm, natural language processing, intuitive user interface, personalized recommendations, customizable filters, and comprehensive database coverage.
Without forgetting the sheer breadth and depth of what it offers are unparalleled and makes it an invaluable asset for looking to find reliable and relevant information quickly. With such an impressive range of educational materials, students from all walks of life can find something that suits their needs with these search engines.
With constantly updated content and new features added every day, these educational search engines ensure that you’ll never run out of useful knowledge or stop learning.
Did I forget any other useful educational search engine?
Please share in the comment section.
Related Posts

10 Best Search Engines for Business Class Flights in 2023

10 Best Search Engines for Booking Cheap Hotels in 2023

10 Best Search Engines for Finding a Job Online in 2023
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
for Education
- Google Classroom
- Google Workspace Admin
- Google Cloud
Easily distribute, analyze, and grade student work with Assignments for your LMS
Assignments is an application for your learning management system (LMS). It helps educators save time grading and guides students to turn in their best work with originality reports — all through the collaborative power of Google Workspace for Education.
- Get started
- Explore originality reports
Bring your favorite tools together within your LMS
Make Google Docs and Google Drive compatible with your LMS
Simplify assignment management with user-friendly Google Workspace productivity tools
Built with the latest Learning Tools Interoperability (LTI) standards for robust security and easy installation in your LMS
Save time distributing and grading classwork
Distribute personalized copies of Google Drive templates and worksheets to students
Grade consistently and transparently with rubrics integrated into student work
Add rich feedback faster using the customizable comment bank
Examine student work to ensure authenticity
Compare student work against hundreds of billions of web pages and over 40 million books with originality reports
Make student-to-student comparisons on your domain-owned repository of past submissions when you sign up for the Teaching and Learning Upgrade or Google Workspace for Education Plus
Allow students to scan their own work for recommended citations up to three times
Trust in high security standards
Protect student privacy — data is owned and managed solely by you and your students
Provide an ad-free experience for all your users
Compatible with LTI version 1.1 or higher and meets rigorous compliance standards
Product demos
Experience google workspace for education in action. explore premium features in detail via step-by-step demos to get a feel for how they work in the classroom..
“Assignments enable faculty to save time on the mundane parts of grading and...spend more time on providing more personalized and relevant feedback to students.” Benjamin Hommerding , Technology Innovationist, St. Norbert College
Classroom users get the best of Assignments built-in
Find all of the same features of Assignments in your existing Classroom environment
- Learn more about Classroom
Explore resources to get up and running
Discover helpful resources to get up to speed on using Assignments and find answers to commonly asked questions.
- Visit Help Center
Get a quick overview of Assignments to help Educators learn how they can use it in their classrooms.
- Download overview
Get started guide
Start using Assignments in your courses with this step-by-step guide for instructors.
- Download guide
Teacher Center Assignments resources
Find educator tools and resources to get started with Assignments.
- Visit Teacher Center
How to use Assignments within your LMS
Watch this brief video on how Educators can use Assignments.
- Watch video
Turn on Assignments in your LMS
Contact your institution’s administrator to turn on Assignments within your LMS.
- Admin setup
Explore a suite of tools for your classroom with Google Workspace for Education
You're now viewing content for a different region..
For content more relevant to your region, we suggest:
Sign up here for updates, insights, resources, and more.
- Do Not Sell My Personal Info
- ⋅
23 Great Search Engines You Can Use Instead Of Google
Are you looking for alternative search engines & chatbots to use? Here's an analysis of multiple options so you can try each one and see how it can improve your search experience.
For over two decades, Google has been the search engine that most people use for everyday searches, product research, and staying up to date on the latest news.
Because of this market dominance, Google has also been the main search engine of focus for SEO and marketing professionals.
However, following the introduction of ChatGPT and Bing Chat , Google founders Larry Page and Sergey Brin reportedly returned to take an active role in Google’s plans to add chatbot features to Google Search.
Shortly after that, around May of 2023, Google introduced the chatbot Bard and Search Generative Experience in Google Search. As of writing this article, Google SGE is available in Google Labs only, and may roll out this year.
The next few years in search engine development will certainly be interesting.
However, no matter what happens, there are still several alternative search engines that offer distinct advantages over Google, such as enhanced privacy, specialized content, unique algorithms, and tailored user experiences.
Here are 20 of the best alternative search engines you can try.
AI-Powered Search Engines
Where search engines include AI chatbots based on large language models, they become prone to errors and hallucinations .
Always verify critical information you get from AI-based search engines, such as medical, financial, legal, safety, etc., using authoritative sources.
[Editor’s note: Creating content using generative AI is subject to the implications of a number of unresolved legal proceedings , and you should avoid publishing generative AI outputs as your own content.]
1. Bing.com
As of December 2023, Microsoft Bing sites handled 7.1% of all search queries in the United States.
One could argue that Bing outperforms Google in certain respects.
For starters, Bing has a rewards program that allows one to accumulate points while searching. These points are redeemable at the Microsoft and Windows stores, which is a nice perk.
In my view, the Bing visual search API is superior to its rivals and much more intuitive.
Bing carries that same clean user experience to video, making it the go-to source for video searches without a YouTube bias.
On February 7, 2023 , Bing announced an all-new, AI-powered version of its search engine called “ Bing Chat ,” which is now called Copilot . The stated goal is to “deliver better search, more complete answers, a new chat experience, and the ability to generate content.”
According to Satya Nadella, chairman and CEO of Microsoft, there are 10 billion search queries a day, but approximately half of those go unanswered. Bing is looking to fill that void.
2. Perplexity.ai
Perplexity.ai , founded in 2022 , is an innovative alternative to Google that provides contextually rich answers and has 10 million monthly active users.
Unlike traditional search engines that primarily link to webpages, Perplexity.ai is a chatbot that directly answers questions by citing sources from which it fetches information, with an option to ask follow-up questions.
This feature allows users to delve deeper into their initial queries by asking subsequent, related questions. This interactive approach mimics a conversational style, making it easier for users to refine their search and get more precise answers.
This evolving, dialog-based search experience positions Perplexity.ai as a compelling choice for users seeking a more intuitive and responsive search tool. Below is the feedback from Tobi Lütke , the CEO of Shopify, on Perplexity.ai.
However, since it uses LLMs for answer extraction, it can hallucinate, leading to incorrect or misleading answers.
You.com is an AI-powered search engine founded by Richard Socher , a prominent natural language processing (NLP) researcher and former chief scientist of Salesforce.
The site operates in two modes: a personal mode and a private mode.
In personal mode, users can configure their source preferences. While in private mode, they enjoy a completely untraceable experience; no telemetry data is recorded.
The company also offers a Chrome extension , AI-powered image generation , and YouWrite , an AI writing assistant.
The open search platform encourages developers to build apps and contribute to a more open and collaborative internet.
A Revenue-Sharing Search Engine

Yep.com (by Ahrefs) promotes itself as being a search engine with a difference that emphasizes user privacy by not tracking users or selling their data.
It monitors the frequency of specific word searches and the popularity of certain links in terms of clicks. However, it doesn’t compile a personal profile for the purpose of targeted advertising.
It is designed to directly reward and compensate content creators by using a 90/10 revenue share business model.
This means that 90% of all advertising revenue goes directly to the creators of content, allowing them to earn money for their work.
In addition, this business model allows users to directly support their favorite content creators and ensures that content creators are fairly compensated.
A Copyright-Free Search Engine
5. openverse.
Openverse should be your first stop on the hunt for nearly any type of copyright-free content.
While Google provides a broader range of search results, Openverse stands out with its focus on a vast, searchable collection of open-source media, including images, audio, and videos.
This search engine is perfect if you need music for a video, an image for a blog post, or anything else without worrying about angry artists coming after you for ripping off their work.
Mainstream Search Engines
Mainstream search engines are the Google alternatives that have managed to maintain a modest market share over the past several years.
6. Yahoo.com
As of December 2023, Yahoo.com (Verizon Media) had a search market share of 2.37% in the US.
Yahoo’s strength is in diversification by offering services like email, news, finance, and more in addition to search.
Yahoo has been innovating and evolving for more than two decades.
It made a cryptic tweet on January 20 about making search cool again but did not take me up on my request to explain what that means.
Ecosia’s primary distinguishing feature is its commitment to using ad revenue for environmental purposes, specifically tree planting.
The company is a not-for-profit business and dedicates 100% of its profits to the planet, collaborating with local communities to plant and care for trees around the world.
It partners with Microsoft’s Bing to use its search index and web advertisement and offers a browser extension for quicker access to the search engine.
AOL Search is one of the first search engines on the Internet, with a market share of 0.08% in the US.
It relies on partnerships with Google and Bing for its search results.
Unlike Google’s broad focus, AOL leans towards curated content, prioritizing news, entertainment, and a mix of AOL-owned, syndicated, and external website results.
While AOL tracks user data to personalize its advertising, it’s generally considered less sophisticated compared to Google. Its targeting relies more on broad demographics and interests than the highly granular individual profiles Google often builds.
Privacy-Focused Search Engines
Privacy is an increasingly important issue among internet users.
Privacy-focused search engines prioritize users’ privacy, and their appeal is that they do not track users’ activities or collect personal data.
Some of the most popular include:
9. DuckDuckGo
As of December 2023, DuckDuckGo had a search market share of 1.77% in the United States.
DuckDuckGo is a search engine that could also fit into the mainstream category, but the primary “selling feature” is that it doesn’t collect or store any of your personal information .
Unlike Google, which collects extensive user data to personalize search results and advertisements, DuckDuckGo does not track or profile its users. This means that when you search on DuckDuckGo, your activity remains anonymous.
Because DuckDuckGo does not track search history or create user profiles, it does not offer filter options based on a user’s search history profile, and there are no persistent targeted ads.
That means you can run your searches in peace without having to worry about the boogeyman watching you through your computer screen.
DuckDuckGo is the perfect choice for those who wish to keep their browsing habits and personal information private.
DuckDuckGo Lite is the mobile version.
10. Startpage

Startpage is a search engine aggregation and does not crawl the web itself.
Instead, it utilizes a metasearch approach , fetching results from multiple search engines, including Google, Bing, DuckDuckGo, etc., and prioritizing links that appear in all.
It’s a great choice for those who prefer Google’s search results but aren’t keen on having their search history tracked and stored.
It also includes a URL generator, proxy service, and HTTPS support.
The URL generator is especially useful because it eliminates the need to collect cookies. Instead, it remembers your settings in a way that promotes privacy.
11. Swisscows

Swisscows is a unique option on this list, billing itself as a family-friendly semantic search engine.
It utilizes Bing for its web search capabilities but has also developed its own index for the German language edition.
It also prides itself on respecting users’ privacy, never collecting, storing, or tracking data.
It uses artificial intelligence to determine the context of a user’s query.
Over time, Swisscows promises to answer your questions with surprising accuracy.

According to its website, Gibiru features “Uncensored Private Search” with no retargeting and no selling of private data.
It claims its search results are sourced from a modified Google algorithm, so users are able to query the information they seek without worrying about Google’s tracking activities.
Gibiru earns commissions when users buy something or take action through its search results, aligning with its privacy-centric approach by not relying on personal data for advertising.

In 2023, Brave Search achieved full independence from other search engines like Bing. It now operates solely on its own index, a move that emphasizes user privacy and transparency in search results.
Brave Search has experienced rapid growth; as of January 2024, it had 24.57 million daily active users. This growth reflects the increasing popularity of privacy-focused search engines.
It features free video calls, offline playlists, and a customizable news feed.
Advanced security features like IPFS integration, Tor (Onion Routing), and a crypto wallet are also available.
Brave offers rewards for opting into privacy-preserving ads. It claims over 65 million people use its browser each month for a faster and safer web experience.
Knowledge-Based Search Engines
14. wiki.com.

Wiki.com pulls its results from thousands of wikis on the net.
It is the perfect search engine for those who appreciate community-led information, as found on sites like Wikipedia.
15. X (Formerly Twitter)
X is hard to beat as a real-time search engine.
It’s the perfect place to go for minute-by-minute updates in case of an emergency.
Google will catch up eventually, but nothing beats a tweet in the heat of the moment.
To make the most of it, check out our guide to X/Twitter Advanced Search .
16. SlideShare
SlideShare allows you to search for documented slideshow presentations.
You can also search for ebooks and PDFs, making it an excellent tool if you have a business presentation to prepare for.
SlideShare also allows you to save slides and even download the entire slideshow for use on your local computer.
17. Wayback Machine
Internet Archive, a.k.a. the Wayback Machine , is great for researching old websites, but it’s also so much more.
As the name implies, this search engine queries a massive collection of documented material, including millions of free videos, books, music, and software.
Essentially, the Internet Archive is a vast online library where you can access just about anything you could imagine.
Specialized Search Engines
Specialized search engines cater to particular needs, providing results based on specific criteria. For example:
18. WolframAlpha

WolframAlpha is a computational knowledge engine that allows you to compute answers to problems and search through expert-level data on a variety of subjects, from algebra to words and linguistics.
It also offers Pro features for individuals, students, and educators who need professional-grade computation and analysis of imported data.
Pricing starts at $5.49 per month.
19. LinkedIn
LinkedIn, recognized as a professional networking platform, is increasingly being utilized as a business-focused search engine which has 61 million searches a week.
LinkedIn ‘s search algorithm for organizations considers the uniqueness and specificity of an organization’s LinkedIn Page name, as generic names tend to yield broad, less relevant results.
For instance, an organization named “Innovative Tech Solutions” would likely rank higher than one named “Professional Technology Services” due to the uniqueness of the name.
However, overloading a profile with keywords can be counterproductive, as it might trigger spam detection algorithms and negatively impact search visibility.
The algorithm also factors in the number of Page followers, connections between the Page and the searcher, the activity level on the Page, and the ratio of relevant search terms in the organization’s name.
International Search Engines
International search engines cater to specific regions and provide results based on local language and culture.
Some popular international search engines include:
Baidu is the largest search engine in China and has a 66% market share there.
Like Google, it offers a broad range of services, including maps, music, videos, and an app store.
Baidu also has a mobile browser and mobile app.
Yandex is used by more than 69% of Russian internet users. It is also used in Belarus, Kazakhstan, Turkey, and Ukraine.
Yandex is an overall easy-to-use search engine .
As a bonus, it offers a suite of some pretty cool tools .
It had a data leak in January 2023, leaving many speculating about the relevance of what was revealed.

Sogou is a Chinese search engine that is growing in popularity and has a 5% market share in China.
Sogou Search is an interactive search engine supporting WeChat, article search, English search and translation, and more.
It prides itself on providing users with professional, accurate, and convenient search through self-developed artificial intelligence algorithms.

Naver is a popular search engine in South Korea with a 34% market share in the country. It offers a range of services, including blogs, news, music, and shopping.
It also has a mobile app for searching on the go.
Naver is a great option for those looking for a search engine tailored to the Korean market.
The Takeaway
Google may be the most popular choice in search engines, but it may not always be the best choice, depending on your needs and priorities.
Alternative search engines can offer a wide range of benefits, including a better search experience and higher levels of privacy.
Nonetheless, do yourself a favor and give some of these a try.
More Resources:
- How Search Engines Use Machine Learning: 9 Things We Know For Sure
- ChatGPT & Search? NeevaAI’s Real-Time AI Search Is Already Here [Podcast]
- How Search Engines Work
- Meet The 7 Most Popular Search Engines In The World
Featured Image: Dilok Klaisataporn/Shutterstock
How can I switch to an alternative search engine?
Switching to an alternative search engine is a relatively simple process. Simply change your default search engine in your web browser to the desired search engine.
How do private search engines make money?
Unlike mainstream search engines that may use extensive data for personalized ads, private search engines rely on search terms for contextual ads, affiliate links for purchases via their platform, and user donations for funding.
Looking for a Content Marketing Solution to Increase Traffic and Revenue? I’m the founder of Measurable SEO and former COO ...
Subscribe To Our Newsletter.
Conquer your day with daily search marketing news.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Searching with a Search Engine

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
This section covers finding information online. It includes information about search engines, Boolean operators, Web directories, and the invisible Web. It also includes an extensive, annotated links section.
A search engine is a device that sends out inquiries to sites on the Web and catalogs any Web site it encounters, without evaluating it. Methods of inquiry differ from search engine to search engine, so the results reported by each one will also differ. Search engines maintain an incredibly large number of sites in their archives, so you must limit your search terms in order to avoid becoming overwhelmed by an unmanageable number of responses.
Search engines are good for finding sources for well-defined topics. Typing in a general term such as "education" or "Shakespeare" will bring back far too many results, but by narrowing your topic, you can get the kind (and amount) of information that you need.
- Go to Google (a search engine)
- Type in a general term ("education")
- Add modifiers to further define and narrow your topic ("rural education Indiana")
- Be as specific as you can ("rural education Indiana elementary school")
- Submit your search.
Adjust your search based upon the number of responses you receive (if you get too few responses, submit a more general search; if you get too many, add more modifiers).
Learn how the search engine works
Read the instructions and FAQs located on the search engine to learn how that particular site works. Each search engine is slightly different, and a few minutes learning how to use the site properly will save you large amounts of time and prevent useless searching.
Each search engine has different advantages. Google is one of the largest search engines, followed closely by MSN and Yahoo . This means that these three search engines will search a larger portion of the Internet than other search engines. Lycos allows you to search by region, language, and date. Ask allows you to phrase your search terms in the form of a question. It is wise to search through multiple search engines to find the most available information.
Select your terms carefully
Using inexact terms or terms that are too general will cause you problems. If your terms are too broad or general, the search engine may not process them. Search engines are programmed with various lists of words the designers determined to be so general that a search would turn up hundreds of thousands of references. Check the search engine to see if it has a list of such stopwords . One stopword, for example, is "computers." Some search engines allow you to search stopwords with a specific code (for Google, entering a "+" before the word allows you to search for it).
If your early searches turn up too many references, try searching some relevant ones to find more specific or exact terms. You can start combining these specific terms with NOT (see the section on Boolean operators below) when you see which terms come up in references that are not relevant to your topic. In other words, keep refining your search as you learn more about the terms.
You can also try to make your terms more precise by checking the online catalog of a library. For example, check THOR+ , the Purdue University Library online catalog, and try their subject word search. Or try searching the term in the online databases in the library.
Most search engines now have "Advanced Search" features. These features allow you to use Boolean operators (below) as well as specify other details like date, language, or file type.
Know Boolean operators
Most search engines allow you to combine terms with words (referred to as Boolean operators) such as "and," "or," or "not." Knowing how to use these terms is very important for a successful search. Most search engines will allow you to apply the Boolean operators in an "advanced search" option.
AND is the most useful and most important term. It tells the search engine to find your first word AND your second word or term. AND can, however, cause problems, especially when you use it with phrases or two terms that are each broad in themselves or likely to appear together in other contexts.
For example, if you'd like information about the basketball team Chicago Bulls and type in "Chicago AND Bulls," you will get references to Chicago and to bulls. Since Chicago is the center of a large meat packing industry, many of the references will be about this since it is likely that "Chicago" and "bull" will appear in many of the references relating to the meat-packing industry.
Use OR when a key term may appear in two different ways.
For example, if you want information on sudden infant death syndrome, try "sudden infant death syndrome OR SIDS."
OR is not always a helpful term because you may find too many combinations with OR. For example, if you want information on the American economy and you type in "American OR economy," you will get thousands of references to documents containing the word "American" and thousands of unrelated ones with the word "economy."
NEAR is a term that can only be used on some search engines, and it can be very useful. It tells the search engine to find documents with both words but only when they appear near each other, usually within a few words.
For example, suppose you were looking for information on mobile homes, almost every site has a notice to "click here to return to the home page." Since "home" appears on so many sites, the search engine will report references to sites with the word "mobile" and "click here to return to the home page" since both terms appear on the page. Using NEAR would eliminate that problem.
NOT tells the search engine to find a reference that contains one term but not the other. This is useful when a term refers to multiple concepts.
For example, if you are working on an informative paper on eagles, you may encounter a host of Web sites that discuss the football team the Philadelphia Eagles, instead. To omit the football team from your search results, you could search for "eagles NOT Philadelphia."

Getting Started with Research at Shapiro Library
Ask a librarian.
Effective Search Techniques
When searching for materials in electronic resources and databases, it's a good idea to use effective searching techniques to get the most out of your time and efforts. You don't want to waste your time gathering a bunch of irrelevant information that you can't use in your paper. Use these search strategies to help you find useful information quickly and effectively. Find out more about these techniques on the following pages.
Keyword Searching
Use a keyword search to search all parts of a source for the words you enter in the search box. This type of searching uses "natural language" and is one you're probably already familiar with--you simply enter words or phrases into a search box that you think are relevant to your topic. Click on the "Keyword Searching" page for more information.
Boolean Searching
Boolean searching is a search technique which uses Boolean operators to help bring back search results faster and with more precision. The most common Boolean operators are AND , OR , and NOT . These are logic-based words that help search engines narrow down or broaden search results. Click on the "Boolean Searching" page for more information.
Subject Searching
Within a database or online catalog, subject searching allows you to search by categories, which are found in the subject field of an item record. Subject terms are pre-defined and used for all items within a database or source that relate to that term. Click on the "Subject Searching" page for more information.
Many databases allow users to limit their search results by certain criteria. These options are often located somewhere on the database search page or results list as drop down menus or check boxes. Some common and useful limiters include date of publication, material type, full text, and more. Click on the "Limiters" page for more information.
Phrase Searching
When you search for a phrase like corporate social responsibility the search engine will bring back any results that have those words in them. However, if you put quotation marks around the phrase, "corporate social responsibility", the search engine will only bring back results that have all those words, exactly in the order you have them. This can also be useful when you're searching for the title of a book or other resource. Click on the "Phrase Searching" page for more information.
Using References/Works Cited Lists
Another good search tip is to let one good book or article lead you to others. Scholarly publications almost always have bibliographies or lists of works cited. These are lists of the resources the author used to write the book or article you've found. Explore these! If the original source is useful to you, works used by the author may be valuable, too. Click on the "Using References/Works Cited Lists" page for more information.
- << Previous: Tips for Using Keyword Searching Effectively
- Next: Keyword Searching >>

hariantulis
depo 25 bonus 25
mndrmndr.com
bonusdeposit.net
https://www.greentourstanzania.com/wp-includes/customize/
https://temp1.novotest.biz/id/
https://sumberjo-blitar.desa.id/images
https://sumberjo-blitar.desa.id/data
depo 25 bonus 25 to 5x
https://www.greentourstanzania.com/wp-includes/js/product/
https://smpabbs.sch.id/gacor/100/
https://smpabbs.sch.id/gacor/bonus/
deposit 25 bonus 25
bonus new member 100
Search Engines
Search engines are the go-to sites when searching for products, services and ideas on the web. The results of the search engines are known as the search engine results pages or SERPs. Search engines are known to mine information on the web and deliver all these to the internet users based on the queries made.

How Search Engines Started It all started with the project managed by Tim Berners-Lee. Also an important project that defined the now popular internet technology is Archie. This was a project of students from McGill University in Montreal where all files on the FTP sites were downloaded and in the process created a database. The limitation of the program is that the contents were not indexed. In 1991, two new search engines were created, Jughead and Veronica. These two names for the search engines was a playful follow-up to the earlier Archie. There were a number of catalogues that were maintained during the summer of 1993 but officially, none were considered search engines just yet. The first primitive search engine was written by Oscar Nierstrasz of the University of Geneva. From 1993, a number of developments happened and some basic search engines were introduced. This was the time when early search engines and sites like Yahoo , AltaVista and NorthernLight were introduced. It was in 1996 when the focus on search engines became intensified. Nestcape offered to host a search engine on the site. But due to the popularity of the offer, five search engines were hosted in rotation. This started the frenzy online and boosted the stock of search engines.
Top Search Engines
By 2000, Google entered the industry. The search engine became prominent due to its Page Rank innovation where websites and resources online were ranked.
How Search Engines Work There are three important processes that are followed by all search engines online including the smaller ones like DogPile , AOL.com and Ask Jeeves . Search engines are known to crawl first the web, index what has been found and continue searching the web. Internet users will fist type in the query or the keyword and will hit ‘Enter’. Once done, the search engines will then check its indexed pages and find the most relevant searches. Websites like About.com , Go.com and iWon.com will be included in the searches.
Google is still the world’s biggest search engine. The search engine peaked in April 2010, in terms of market share. Other search engines that rival Google include Yahoo, Bing and Baidu.
There were come concerns regarding the process adopted by search engines. Though websites like Deja/Google , HotBot and DogPile will rank based on popularity, still there are some perceived biases when it comes to rankings of the results. There are even reports of manipulating the results of the search engines called Google bombing and will target and involve different websites including Vivisimo , NBCi and Mamma.com . Though there are some concerns about manipulation, still by default search engines make use of popularity and MetaCrawler . Customized research will be made available as well and will cover different websites including News Search Portal .
- Featured Site
- Airfare / Hotels / Car Rental
- Auction Sites
- Aviation
- Business Magazines
- Businesswire
- Computer Virus Alerts
- Cop Stuff
- Crossword Puzzles
- E-greeting Cards
- Entertainment
- Find Experts
- Gov't Directories
- Horoscopes
- Int'l Pages
- Internet Zines/News
- Local News Resources
- Major Locals
- Maps
- Money
- Network News
- News Magazine
- News Wires
- Newspapers
- Online Local Newspapers - U.S.
- Personal Health Site
- Photo Search
- Politics
- PR News Wire
- Radio Sites
- Reporter Beats
- Research
- Reverse Directories
- Search Engines
- See Hear News Now
- Send a Text
- Senior Citizen Web Sites
- Social Media
- Sports News
- Tabloids
- Time Wasters
- Time Zones
- Track Packages
- Travel Info
- TV Network Schedules
- TV News Sites
- TV Sweeps Date
- Weather
- White Pages
- Women's/men's Mags
- World Papers
- Yellow Pages
- Your Stuff
- CenturyLink
- Yahoo! Mail
- Sliding Block
- Word Search
- Free Weather
- Weather.com
- Accuweather
- Catholic Charities
- Feeding America
- Habitat for Humanity
- Salvation Army
- Wounded Warrior
- YMCA of the USA
- ALS Association
- Alzheimer Assoc.
- American Cancer
- American Diabetes
- Cystic Fibrosis
- Make A Wish
- National Kidney
- National MS
- National Wildlife
- Parkinson’s Found.
- Ronald McDonald
- World Wildlife
- Suggest Charity
- Google Maps
- Yellow Pages
- White Pages
- Reverse Phone
- Fodor’s Travel
Search Engine
Assignment written by Julie Zelenski
An introduction to search engines

Search engines are one of the most influential developments of the modern internet age and have completely revolutionized how users interact with the web. What was once an intractable jumble of data with no semblance of organization has become a treasure trove of useful information due to the magic of search. Armed with the power of Map and Set , you can recreate this phenomenal achievement yourself. Once completed, you will understand the core technology underpinning Spotlight, Google, and Bing, and have solid practice in the use of the classic ADTs Map and Set .
Want to see the power of search right now? Click 🔍 Search in the top-right of the page navigation bar and search for easter egg to see what lurks deep in the recesses of the course website…
In your search engine, each web page has a URL ("Uniform Resource Locator") that serves as its unique id and a string containing the body text of the page. You will first write functions that pre-process the body text and populate the data structure. Next you'll implement the function to search for pages matching a search query. Finally, you will write a console program that allows the user to enter many search queries and retrieve the matching web pages. Put all together, you will have built your own mini search engine!
Understanding the web page data
We have harvested the body text from the pages of our course website into a database file. The format of the database file is as follows:
- The first line of a pair is a page URL.
- The second line of a pair is the body text of that page, with all newlines removed (the entire text of the page in a single string).
- The first two lines in the file form the first pair. The third and fourth lines form another pair, the fifth and sixth another, and so on, with alternating lines of page URL and page content.
To view an example database, open the file tiny . txt or website . txt in the folder Other files / res of the starter project.
Using an inverted index for searching
To make our search efficient, we need to be thoughtful about how we structure and store the data. A poor choice in data structures would make search painfully slow, but clever use of our wonderful ADTs can avoid that fate. A search engine typically uses a nifty arrangement known as an inverted index .
An inverted index is akin to the typical index in the back of a book. If you look up the keyword "internet" in the index of the CS106B textbook , it lists two page numbers, 18 and 821. The word internet occurs on page number 18 and again on page number 821. Thus, an inverted index is a mapping from word to locations. You look up a keyword in an inverted index to find all the locations where that keyword occurs.
In contrast a forward index operates in the other direction. For our book example, the forward index would be a mapping from a location (page number) to all the words that occur on that page. To build an inverted index, you typically start with the data in the form of a forward index and then process to convert to the inverted form. Inverting the index takes time up front, but once complete, the inverted index supports extremely fast operations to find query matches.
On to the code!
Decomposition is one of your best tools for tackling a complex problem. We'll guide you along by breaking the problem down into a sequence of steps. Follow our steps to success!
All of the functions and tests for the search engine are to be implemented in the file search . cpp .
1) Write helper function cleanToken ()
Start by writing a helper function for this small but important string-processing task:
cleanToken takes in a string of characters that appears in the body text and returns a "cleaned" version of that token, ready to be stored in the index in its canonical form. The cleaned version trims off any leading or trailing punctuation and converts all letters to lowercase. cleanToken also checks to see if the token contains only non-letters, in which case it returns empty string to indicate this token is to be discarded.
More precisely, cleanToken ( str ) should:
- Treat as punctuation exactly and only those characters for which ispunct returns true.
- You may encounter a few oddball characters (curly quotes, bullets, and the like) that are not recognized as punctuation by ispunct . Do not make a special case of this; trim exactly according to ispunct .
- Hint: this check does not remove non-letters or modify the string, it just examines the characters to find if at least one is a letter
- Convert the token to lowercase . Standardizing on a canonical form allows search queries to operate case-insensitively.
The return value from cleanToken is the trimmed lowercase version, or empty string if the token is to be discarded.
Writing this function will be right up your alley after your great work on soundex last week. The specification of this function is a bit quirky, so pay close attention to the details and ask questions if anything is unclear.
Write comprehensive test cases to confirm that cleanToken works correctly in all situations before moving on! You will make heavy use of cleanToken when building the inverted index and if this helper mishandles tokens, it will throw off your results and lead to sad times. Covering all your bases now will take quite a few test cases, but we assure you that it is well worth your time. Remember to label your tests as STUDENT_TEST .
2) Write helper function gatherTokens ()
The helper function gatherTokens extracts the set of unique tokens from the body text.
The argument to gatherTokens is a string containing the body text from a single web page. The function returns a Set of the unique cleaned tokens that appear in the body text.
The function first tokenizes the body text — this means to separate the string into words using the space character as delimiter. Call the stringSplit function from the Stanford library for this task. Then call your cleanToken helper function on each token and store the cleaned tokens into a Set. No matter how many repeat occurrences of a given word are in the body text, repeatedly adding it to a set stores just the one copy, which makes this ADT ideal for gathering the unique tokens.
Time to test! Add test cases that confirm the output from gatherTokens , so you will later be able to call on this function with confidence that it does its job correctly.
3) Create inverted index in buildIndex ()
The function buildIndex reads the content from the database file and processes it into the form of an inverted index.
The first argument to buildIndex is the name of the database file of the web page data, the second argument is the Map to be populated with data for the inverted index. The return value of buildIndex is the number of documents processed from the database file.
Before starting to code, work through a small example on paper to ensure you understand the data structure you are trying to build. Open the res / tiny . txt database file in Qt and manually process the content to build the inverted index.
Q7 . Sketch the contents of the inverted index built from the res / tiny . txt database file.
When you are ready to start writing code, read the previous section Understanding the web page data to review the format of the database file. Look at the code we provided for readMazeFile in maze . cpp for an example of C++ code to open a file and read the contents into a Vector of lines. Feel free to reuse that code for buildIndex .
For each page, you will call gatherTokens to extract the set of unique tokens. For each token in the page, you record the match to the page's URL by adding to its entry in the inverted index. The index is of type Map < string , Set < string >> , this map associates each keyword with the set of the URLs where that word occurs. The function returns the count of web pages that were processed.
Our starter code contains some provided tests to get you started; add student tests of your own to ensure your coverage is comprehensive. Use a TIME_OPERATION test to confirm your function operates in reasonable time. Building the inverted index should generally not take more than 5 seconds.
4) Search using findQueryMatches ()
Next up is to implement the function:
The query string can either be a single search term or a compound sequence of multiple terms. A search term is a single word, and a sequence of search terms is multiple consecutive terms, each of which (besides the first one) may or may not be preceded by a modifier like + or - (see below for details). The same stringSplit function used to divide the body text into tokens will be used to divide the query sentence into search terms.
When finding the matches for a given query, follow these rules:
- For a single search term, result is all web pages that contain that term.
- A sequence of terms is handled as a compound query, where the matches from the individual terms are synthesized into one combined result.
- Hint: use Set operation unionWith
- Hint: use the Set operation intersect
- Hint: use the Set operation difference
- The same token cleaning applied to the body text is also applied to query terms. Call your helper cleanToken to process each search term to strip punctuation, convert to lowercase, and discard non-words before performing the search for matches.
Note that searching is case-insensitive , that is, a search for "binky" returns the same results as "Binky" or "BINKY". Be sure to consider what implications this has for how you create and search the index.
Here are some example queries and how they are interpreted
- matches all pages containing the term "quokka"
- means simple OR cheap
- matches pages that contain either "simple" or "cheap" or both
- means tasty AND healthy
- matches pages that contain both "tasty" and "healthy"
- means tasty WITHOUT mushrooms
- matches pages that contain "tasty" but do not contain "mushrooms"
- means tasty WITHOUT mushrooms OR simple AND cheap
- matches pages that match ((("tasty" without "mushrooms") or "simple") and "cheap")
There is no precedence for the operators, the query is simply processed from left to right . The matches for the first term are combined with matches for second, then combined with matches for third term and so on. In the last query shown above, the matches for tasty are first filtered to remove all pages containing mushrooms , then unioned with all matches for simple and lastly intersected with all matches for cheap .
You may assume that the query sentence is well-formed, which means:
- The query sentence is non-empty and contains at least one search term
- A modifier will not appear on its own as a search term
- A + or - character within a search term that is not the first character is not considered a modifier
- The first search term in the query sentence will never have a modifier
- You can assume that no search term will clean to the empty string (i.e. has at least one letter)
There is a lot of functionality to test in query processing, be sure you add an appropriate range of student tests to be sure you're catching all the cases.
5) Put it all together with searchEngine ()
Thus far, your amazing code has re-arranged a mass of unstructured text data into a highly-organized inverted index with instantaneous retrieval and fancy query-matching capability. Now take it over the finish line to build your own search engine!
The final function to implement is:
This function implements a console program that works as follows:
- It first constructs an inverted index from the contents of the database file.
- It prints how many web pages were processed to build the index and how many distinct words were found across all pages.
- It enters a loop that prompts the user to enter a query
- For each query entered by the user, it find the matching pages and prints the URLs.
- When the user enters the empty string ( "" ), this indicates they are done and the program finishes.
After you have completed this function, your program should behave as shown in the transcript shown below.
Example program run (executed by running searchEngine ( "res/website.txt" ) in main . cpp ):
Way to go, 👍 you're well on your way to becoming the next internet search pioneer!
- The res folder of the starter project includes two database files: tiny . txt is the small example used in the writeup and website . txt is the body text extracted from all of the pages in our course website (as of Oct 1). You can open these files in Qt Creator to view their contents. The project resource files are listed under Other files -> res . Your program can open a resource file by specifying the path as "res/myfilename" .
- Inverted Index on GeeksForGeeks
- Wikipedia article on Inverted Indexes
- Stanford Natural Processing Group on Tokenization
If you have completed the basic assignment requirements and and want to go further, we encourage you to try adding an extension! A non-exhaustive list of potential extensions is listed below:
- When you get the results from a Google search, they are ranked so that the more relevant results are first on the list. The current Google algorithm is a well-kept trade secret (though it was originally the Page Rank algorithm, named for its creator, then-Stanford graduate student Larry Page), but a simple approach is to give higher rank to pages with more occurrences of the search term. For this extension, you would need to re-think how you create your index to include the number of matches.
- The assignment does not allow a search for multi-word terms, such as section leader . Searching for phrases is not trivial, as you cannot simply keep a mapping of all possible phrases in the document. You could, however, keep track of where in each document a word is, and then use that information to determine if words in a phrase are next to each other in any particular document.
- The English language has many, many words that show up in text but are not particularly important for content, such as the , and , if , a , etc. These words are called Stop Words , and it would make your index smaller if you removed such stop words from the index. Here is more info about stop words .
- In the current design, if a user searches for section they won't find matches for sections , even though pages that mention either might be a relevant match. Stemming is the process of reducing words to their base form, so that (for example) both section and sections would become, simply, section in the index.
If you have other creative ideas for extensions, run them by the course staff, and we'd be happy to give you guidance!
The Federal Register
The daily journal of the united states government, request access.
Due to aggressive automated scraping of FederalRegister.gov and eCFR.gov, programmatic access to these sites is limited to access to our extensive developer APIs.
If you are human user receiving this message, we can add your IP address to a set of IPs that can access FederalRegister.gov & eCFR.gov; complete the CAPTCHA (bot test) below and click "Request Access". This process will be necessary for each IP address you wish to access the site from, requests are valid for approximately one quarter (three months) after which the process may need to be repeated.
An official website of the United States government.
If you want to request a wider IP range, first request access for your current IP, and then use the "Site Feedback" button found in the lower left-hand side to make the request.
Cold weather pay offered to incentivize assignments to North Dakota bases

WASHINGTON (KMOT) – Airmen from other parts of the country sometimes lament assignments in North Dakota due to the cold winters, but the Air Force is starting a new incentive program for servicemembers who have to “come North.”
The Air Force is rolling out a special cold weather duty pay for airmen and guardians assigned to bases where the temperature can drop below -20 degrees Fahrenheit.
This includes Minot Air Force Base, Grand Forks Air Force Base and Cavalier Space Station.
The idea is to help offset the costs of cold-weather items, such as gear, snow tires, engine block heaters and emergency kits for your car.
Pay will begin July 1, and the Air Force will announce specifics on pay amounts closer to the date.
Both North Dakota Senators John Hoeven and Kevin Cramer, along with Alaska Senators Lisa Murkowski and Dan Sullivan, recently sent a letter to the Secretary of the Air Force to implement the program.
Copyright 2024 KFYR. All rights reserved.

Bismarck resident wins six-figures in ND Powerball

Carson Wentz signs with Chiefs

Here’s why the LSU women were absent during the National Anthem

Beulah man arrested for multiple counts of theft
Latest news.

Budget Inn demolition

Minot High Cheer celebrates titles at winter competitions

City of Sawyer invites residents to form new committee

How truckers stay active while on the road

Mandan Middle School students have egg-cellent experiment results
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- March Madness
- AP Top 25 Poll
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
Gmail revolutionized email 20 years ago. People thought it was Google’s April Fools’ Day joke
Google co-founders Larry Page and Sergey Brin unveiled something no one would believe was possible on April Fool’s Day 20 years ago: Gmail, a free service boasting 1 gigabyte of storage. Gmail now has 1.8 billion active accounts worldwide. (AP Video: Terry Chea)
Paul Buchheit, the former Google engineer who created Gmail, works at the company’s offices in Mountain View, Calif., in Dec. 10, 1999. Buchheit was the 23rd employee hired at Google, a company that now employs more than 180,000 people. (April Buchheit via AP)
- Copy Link copied
FILE - An ad for Google’s Gmail appears on the side of a bus on Sept. 17, 2012, in Lagos, Nigeria. Google founders Larry Page and Sergey Brin unveiled Gmail 20 years ago on April Fool’s Day. (AP Photo/Sunday Alamba, File)
Former Google executive Marissa Mayer poses for a photo on Wednesday, March 27, 2024 in Menlo Park, Calif. Mayer helped design Gmail and other company products before later becoming Yahoo’s CEO. (AP Photo/Mike Liedtke)
FILE - Google co-founders Sergey Brin, left, and Larry Page pose at company headquarters Jan.15, 2004, in Mountain View, Calif. Page and Brin unveiled Gmail 20 years ago on April Fool’s Day. (AP Photo/Ben Margot, File)
SAN FRANCISCO (AP) — Google co-founders Larry Page and Sergey Brin loved pulling pranks, so much so they began rolling outlandish ideas every April Fools’ Day not long after starting their company more than a quarter century ago. One year, Google posted a job opening for a Copernicus research center on the moon. Another year, the company said it planned to roll out a “scratch and sniff” feature on its search engine.
The jokes were so consistently over-the-top that people learned to laugh them off as another example of Google mischief. And that’s why Page and Brin decided to unveil something no one would believe was possible 20 years ago on April Fools’ Day.
It was Gmail, a free service boasting 1 gigabyte of storage per account, an amount that sounds almost pedestrian in an age of one-terabyte iPhones. But it sounded like a preposterous amount of email capacity back then, enough to store about 13,500 emails before running out of space compared to just 30 to 60 emails in the then-leading webmail services run by Yahoo and Microsoft. That translated into 250 to 500 times more email storage space.
Besides the quantum leap in storage, Gmail also came equipped with Google’s search technology so users could quickly retrieve a tidbit from an old email, photo or other personal information stored on the service. It also automatically threaded together a string of communications about the same topic so everything flowed together as if it was a single conversation.
“The original pitch we put together was all about the three ‘S’s” — storage, search and speed,” said former Google executive Marissa Mayer, who helped design Gmail and other company products before later becoming Yahoo’s CEO.
It was such a mind-bending concept that shortly after The Associated Press published a story about Gmail late on the afternoon of April Fools’ 2004, readers began calling and emailing to inform the news agency it had been duped by Google’s pranksters.
“That was part of the charm, making a product that people won’t believe is real. It kind of changed people’s perceptions about the kinds of applications that were possible within a web browser,” former Google engineer Paul Buchheit recalled during a recent AP interview about his efforts to build Gmail.
It took three years to do as part of a project called “Caribou” — a reference to a running gag in the Dilbert comic strip. “There was something sort of absurd about the name Caribou, it just made make me laugh,” said Buchheit, the 23rd employee hired at a company that now employs more than 180,000 people.
The AP knew Google wasn’t joking about Gmail because an AP reporter had been abruptly asked to come down from San Francisco to the company’s Mountain View, California, headquarters to see something that would make the trip worthwhile.
After arriving at a still-developing corporate campus that would soon blossom into what became known as the “Googleplex,” the AP reporter was ushered into a small office where Page was wearing an impish grin while sitting in front of his laptop computer.
Page, then just 31 years old, proceeded to show off Gmail’s sleekly designed inbox and demonstrated how quickly it operated within Microsoft’s now-retired Explorer web browser. And he pointed out there was no delete button featured in the main control window because it wouldn’t be necessary, given Gmail had so much storage and could be so easily searched. “I think people are really going to like this,” Page predicted.
As with so many other things, Page was right. Gmail now has an estimated 1.8 billion active accounts — each one now offering 15 gigabytes of free storage bundled with Google Photos and Google Drive. Even though that’s 15 times more storage than Gmail initially offered, it’s still not enough for many users who rarely see the need to purge their accounts, just as Google hoped.
The digital hoarding of email, photos and other content is why Google, Apple and other companies now make money from selling additional storage capacity in their data centers. (In Google’s case, it charges anywhere from $30 annually for 200 gigabytes of storage to $250 annually for 5 terabytes of storage). Gmail’s existence is also why other free email services and the internal email accounts that employees use on their jobs offer far more storage than was fathomed 20 years ago.
“We were trying to shift the way people had been thinking because people were working in this model of storage scarcity for so long that deleting became a default action,” Buchheit said.
Gmail was a game changer in several other ways while becoming the first building block in the expansion of Google’s internet empire beyond its still-dominant search engine.
After Gmail came Google Maps and Google Docs with word processing and spreadsheet applications. Then came the acquisition of video site YouTube, followed by the introduction of the the Chrome browser and the Android operating system that powers most of the world’s smartphones. With Gmail’s explicitly stated intention to scan the content of emails to get a better understanding of users’ interests, Google also left little doubt that digital surveillance in pursuit of selling more ads would be part of its expanding ambitions.
Although it immediately generated a buzz, Gmail started out with a limited scope because Google initially only had enough computing capacity to support a small audience of users.
“When we launched, we only had 300 machines and they were really old machines that no one else wanted,” Buchheit said, with a chuckle. “We only had enough capacity for 10,000 users, which is a little absurd.”
But that scarcity created an air of exclusivity around Gmail that drove feverish demand for an elusive invitations to sign up. At one point, invitations to open a Gmail account were selling for $250 apiece on eBay. “It became a bit like a social currency, where people would go, ‘Hey, I got a Gmail invite, you want one?’” Buchheit said.
Although signing up for Gmail became increasingly easier as more of Google’s network of massive data centers came online, the company didn’t begin accepting all comers to the email service until it opened the floodgates as a Valentine’s Day present to the world in 2007.
A few weeks later on April Fools’ Day in 2007, Google would announce a new feature called “Gmail Paper” offering users the chance to have Google print out their email archive on “94% post-consumer organic soybean sputum " and then have it sent to them through the Postal Service. Google really was joking around that time.
Google reportedly considers paywall for enhanced AI-powered search capabilities
Maxwell Nelson, a seasoned journalist and content strategist, has contributed to industry-leading platforms, weaving complex narratives into insightful articles that resonate with a broad readership.
Google is exploring the idea of introducing “premium” features powered by generative AI to its search engine. This potential shift, as per The Financial Times , marks the first time Google would place AI-generated elements of its core search functionality behind a paywall, signaling a significant pivot from its traditional ad-supported model.
For nearly two decades, Google has dominated the search engine market, providing free access to information while generating revenue through advertisements. However, the advent of generative AI technologies , epitomized by the launch of OpenAI’s ChatGPT, has prompted Google to reconsider its strategy. ChatGPT’s ability to deliver concise, complete answers poses a direct challenge to the conventional search engine format, which relies on directing users to external websites, including those of advertisers.
Google’s response to this competitive pressure has been twofold. The company began testing an AI-powered search service that offers more detailed answers to user queries while maintaining the traditional model of presenting links and advertisements. This “Search Generative Experience” (SGE), still in an experimental phase, leverages AI to provide “AI-powered snapshots” of information, a process that demands significantly more computing resources than standard search responses.
The introduction of premium, AI-enhanced search features would be incorporated into Google’s existing subscription services, such as the Google One bundle, which already includes access to the Gemini AI assistant in Gmail and Docs. This approach would maintain the free availability of Google’s traditional search engine and advertisement display, thus preserving its primary revenue stream while offering enhanced services to those willing to pay.
Google’s deliberation over premium AI search features occurs in a broader context of technological evolution and market competition. Microsoft, through its partnership with OpenAI, has already integrated GPT-powered search capabilities and the chatbot Copilot into its Bing search engine. Despite these advancements, Bing’s market share remains significantly lower than Google’s, underscoring the challenge of transforming AI capabilities into market dominance.
About ReadWrite’s Editorial Process
The ReadWrite Editorial policy involves closely monitoring the tech industry for major developments, new product launches, AI breakthroughs, video game releases and other newsworthy events. Editors assign relevant stories to staff writers or freelance contributors with expertise in each particular topic area. Before publication, articles go through a rigorous round of editing for accuracy, clarity, and to ensure adherence to ReadWrite's style guidelines.
Maxwell Nelson Tech Journalist
Related news.

Apple explores frontier of personal robotics with innovative home devices

Amazon scraps ‘Just Walk Out’ to smart carts in Fresh stores

Apple’s new AI model ReALM ‘surpasses GPT-4’
Yahoo is buying Artifact, the AI news app from the Instagram co-founders
Most popular tech stories.
- It’s-a-sale – Five Mario Day bargains to pick up this weekend on Nintendo Switch
- This AI realized it was being tested
- GTA 6 – Release date, trailers, setting, and everything we know so far
- Apple reportedly testing AI-driven ad placements in App Store strategy
- EmuDeck adds new emulators – won’t remove Yuzu from your Steam Deck & ROG Ally
Latest News
Google is exploring the idea of introducing "premium" features powered by generative AI to its search engine. This potential shift, as per The Financial Times, marks the first time Google...
EU's draft cybersecurity certification eases path for US tech giants

Saber Interactive CEO Says KOTOR Remake Is 'Alive and Well'
Saber interactive ceo says kotor remake is ‘alive and well’.

Call of Duty Warzone – Season 3 Patch Notes highlights as things are really shaken up
Popular topics, get the biggest tech headlines of the day delivered to your inbox.
By signing up, you agree to our Terms and Privacy Policy. Unsubscribe anytime.
Explore the latest in tech with our Tech News. We cut through the noise for concise, relevant updates, keeping you informed about the rapidly evolving tech landscape with curated content that separates signal from noise.
Explore tech impact in In-Depth Stories. Narrative data journalism offers comprehensive analyses, revealing stories behind data. Understand industry trends for a deeper perspective on tech's intricate relationships with society.
Empower decisions with Expert Reviews, merging industry expertise and insightful analysis. Delve into tech intricacies, get the best deals, and stay ahead with our trustworthy guide to navigating the ever-changing tech market.
OpenAI previews voice generator, acknowledging election risks

Artificial intelligence startup OpenAI released a preview Friday of a digital voice generator that it said could produce natural-sounding speech based on a single 15-second audio sample.
The software is called Voice Engine. It’s the latest product to come out of the San Francisco startup that’s also behind the popular chatbot ChatGPT and the image generator DALL-E.
The company said in a blog post that it had tested Voice Engine in an array of possible uses, including reading assistance to children, language translation and voice restoration for cancer patients.
Some social media users reacted by highlighting possible misuses, including potential fraud assisted with unauthorized voice imitation, or deepfakes.
But OpenAI said it was holding off for now on a wider release of the software because of the potential for misuse, including during an election year. It said it first developed the product in late 2022 and had been using it behind the scenes in other products.
“We are taking a cautious and informed approach to a broader release due to the potential for synthetic voice misuse,” the company said in the unsigned post .
“We hope to start a dialogue on the responsible deployment of synthetic voices, and how society can adapt to these new capabilities,” it said. “Based on these conversations and the results of these small scale tests, we will make a more informed decision about whether and how to deploy this technology at scale.”
The 2024 election has already witnessed its first fake voice , which appeared in New Hampshire in a robocall in January imitating President Joe Biden. A Democratic operative later said he commissioned the fake voice using artificial intelligence and the help of a New Orleans street magician.
After that call, the Federal Communications Commission voted unanimously to ban unsolicited AI robocalls.
OpenAI acknowledged the political risks in its blog post.
“We recognize that generating speech that resembles people’s voices has serious risks, which are especially top of mind in an election year,” it said.
The company said it was “engaging with U.S. and international partners from across government, media, entertainment, education, civil society and beyond to ensure we are incorporating their feedback as we build.”
It said its usage policies prohibit impersonation without consent or legal right, and it said broad deployment should be accompanied by “voice authentication experiences” to verify that the original speaker knowingly added their voice to the service. It also called for a “no-go voice list” to prevent the creation of voices that are too similar to prominent figures.
But finding a way to detect and label AI-generated content has proven difficult for the tech industry. Proposed solutions such as “watermarking” have proven easy to remove or bypass .
Geoffrey Miller, an associate professor of psychology at the University of New Mexico, responded to OpenAI on the platform X asking what it would do about potential misuse by criminals.
“When millions of older adults are defrauded out of billions of dollars by these deepfake voices, will @OpenAI be ready for the tsunami of litigation that follows?” he asked . The company did not immediately reply to him.
David Ingram covers tech for NBC News.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Get 30 days free. 1. Google Scholar. Google Scholar is the clear number one when it comes to academic search engines. It's the power of Google searches applied to research papers and patents. It not only lets you find research papers for all academic disciplines for free but also often provides links to full-text PDF files.
Ecosia 's unique philosophy lands it on our best search engines list: it's a social business founded on the principle that everyone can combat climate change, even with a click. Ecosia channels the ad revenue it makes to support reforestation projects that aim to neutralise carbon dioxide emissions. According to the website, it has planted ...
A search engine for students that emphasizes high quality resources evaluated and approved by educators, librarians and research experts.
RefSeek - Academic Search Engine. Web. Documents. Type 2 or more characters for results. Learn about: Calculators, Fahrenheit. Browse the Reference Site Directory. Academic search engine for students and researchers. Locates relevant academic search results from web pages, books, encyclopedias, and journals.
ERIC (short for educational resources information center) is a great academic search engine that focuses on education-related literature. It is sponsored by the U.S. Department of Education and produced by the Institute of Education Sciences. ERIC indexes over a million articles, reports, conference papers, and other resources on all aspects of education from early childhood to higher education.
5. Bielefeld Academic Search Engine. Operated by the Bielefeld University Library, the Bielefeld Academic Search Engine (BASE) draws from over 7,000 sources to provide users access to over 150 million documents. Paid subscriptions provide the greatest value, but open access users can still look to the academic search engine for journals ...
You can explore all of them here. 2. Google Scholar. Google Scholar. Google Scholar is undoubtedly one of the popular search engines. With its vast database of scholarly literature, Google Scholar allows users to search for articles, theses, books, and conference papers across multiple academic disciplines.
Still, Google Books is a great first step to find sources that you can later look for at your campus library. 6. Science.gov. If you're looking for scientific research, Science.gov is a great option. The site provides full-text documents, scientific data, and other resources from federally funded research.
The top 10 educational search engines include Google Scholar, Google Books, Microsoft Academic, Science.gov, PubMed Central, Researchgate, and others. Each search engine has its own index and database of academic resources and searches through them. Utilizing the internet effectively for college students involves discerning credible sources ...
15 Educational Search Engines College Students Should Know About. By Anna Heinrich on 03/22/2017. This piece of ad content was created by Rasmussen University to support its educational programs. Rasmussen University may not prepare students for all positions featured within this content. Please visit for a list of programs offered.
Research databases. You can search for scholarly sources online using databases and search engines like Google Scholar. These provide a range of search functions that can help you to find the most relevant sources. If you are searching for a specific article or book, include the title or the author's name. Alternatively, if you're just ...
List of Best 9 Education Search Engines. 1. Google Scholar. Google Scholar is a free, customized academic search engine designed specifically for students, tutors, researchers and anyone interested in academic materials. It's the most popular research search engine for students and it lists academic resources across a wide range of sources.
2. Don't get stuck on Google (or any other single search engine). Here are the librarians' favorite web search spots: Use library's subject pages. Each pages includes a "websites" section, and each link was chosen by a librarian, so you can feel confident that they're trustworthy. (Note that you may need to click a website, then search within ...
1. Google Scholar. Google Scholar is without a doubt one of the best search engines for students in 2023. Without a doubt, It gives you an impressive array of features to make your academic endeavors much easier. With access to millions of scholarly publications, easy-to-use tools that allow you to filter results by date and citation counts ...
Bing is the most full-featured contender in this group, with new AI Bing Chat search and content generation, strong news, image, video, and map searching capabilities. Bing is known for superior ...
Easily distribute, analyze, and grade student work with Assignments for your LMS. Assignments is an application for your learning management system (LMS). It helps educators save time grading and guides students to turn in their best work with originality reports — all through the collaborative power of Google Workspace for Education.
Mainstream search engines are the Google alternatives that have managed to maintain a modest market share over the past several years. 6. Yahoo.com. Screenshot from Yahoo.com. As of December 2023 ...
A search engine is a device that sends out inquiries to sites on the Web and catalogs any Web site it encounters, without evaluating it. Methods of inquiry differ from search engine to search engine, so the results reported by each one will also differ. Search engines maintain an incredibly large number of sites in their archives, so you must ...
Boolean searching is a search technique which uses Boolean operators to help bring back search results faster and with more precision. The most common Boolean operators are AND, OR, and NOT. These are logic-based words that help search engines narrow down or broaden search results. Click on the "Boolean Searching" page for more information.
The results of the search engines are known as the search engine results pages or SERPs. Search engines are known to mine information on the web and deliver all these to the internet users based on the queries made. It all started with the project managed by Tim Berners-Lee. Also an important project that defined the now popular internet ...
For this part of the assignment, you will recreate this phenomenal technological development by using the Map and Set ADTs to build a document search engine that can find matching pages for a user's query with lighting-fast response time. This is a simplified version of the technology underpinning Spotlight, Google, Bing, and every other modern ...
A search engine typically uses a nifty arrangement known as an inverted index. An inverted index is akin to the typical index in the back of a book. If you look up the keyword "internet" in the index of the CS106B textbook, it lists two page numbers, 18 and 821. The word internet occurs on page number 18 and again on page number 821.
A search engine typically uses a nifty arrangement known as an inverted index. An inverted index is akin to the typical index in the back of a book. If you look up the keyword "internet" in the index of the CS106B textbook, it lists two page numbers, 18 and 821. The word internet occurs on page number 18 and again on page number 821.
Search, browse and learn about the Federal Register. Federal Register 2.0 is the unofficial daily publication for rules, proposed rules, and notices of Federal agencies and organizations, as well as executive orders and other presidential documents.
The idea is to help offset the costs of cold-weather items, such as gear, snow tires, engine block heaters and emergency kits for your car. Pay will begin July 1, and the Air Force will announce ...
People thought it was Google's April Fool's Day joke. Google co-founders Larry Page and Sergey Brin unveiled something no one would believe was possible on April Fool's Day 20 years ago: Gmail, a free service boasting 1 gigabyte of storage. Gmail now has 1.8 billion active accounts worldwide. (AP Video: Terry Chea) SAN FRANCISCO (AP ...
The Microsoft Advertising Platform is upgrading all existing image and feed campaigns on a manual cost-per-click (CPC) bid strategy to enhanced CPC from May 13. This upgrade process is expected to ...
Google is exploring the idea of introducing "premium" features powered by generative AI to its search engine. This potential shift, as per The Financial Times, marks the first time Google ...
March 29, 2024, 1:47 PM PDT. By David Ingram. Artificial intelligence startup OpenAI released a preview Friday of a digital voice generator that it said could produce natural-sounding speech based ...
Where the Nationals' Top 30 prospects are starting the season. With the Minor League season opening this week, here's where the Nationals' Top 30 prospects are projected to start: 1. Dylan Crews ( MLB No. 7 ), OF -- Harrisburg (Double-A) 2. James Wood ( MLB No. 14 ), OF -- Rochester (Triple-A) 3.